Zelenchukskaya region, Karachai-Cherkesia, Russia H.FALCKE, R.OSTERBART, M.SCH OLLER AND G.WEIGELT
|
|
|
- Conrad Flowers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SPECKLE MASKING IMAGING OF THE SPECTROSCOPIC BINARIES GLIESE AND 41 DRACONIS I.BALEGA AND Y.BALEGA Special Astrophysical Observatory Zelenchukskaya region, Karachai-Cherkesia, Russia AND H.FALCKE, R.OSTERBART, M.SCH OLLER AND G.WEIGELT Max-Planck-Institut fur Radioastronomie Auf dem Hugel 69, Bonn, Germany 1. Introduction Despite a history of micrometric observations dating back more than 150 years, and many decades of astrometric and interferometric study of lowmass main sequence binary stars in the solar neighborhood, their masses and luminosities are known with much lower accuracies than for massive (1:5 M=M 10) stars of early spectral types. The latest "conservative" list of 45 binaries with normal components, whose masses and radii are measured with an error 2%, includes only 3 objects of spectral type G, one pair of the type M, and no K-type binaries (Andersen, 1991). Only 3 systems from this list are within 50 pc from the Sun. This is explained by the observation selection eect which connes the list of stars with fundamental masses and luminosities to double-lined eclipsing binaries. The HIPPAR- COS astrometric mission will not change the situation signicantly because its parallax errors will be too high to satisfy the 2% accuracy criterion even for stars within 25 pc from the Sun. Therefore, we decided to focus our attention on spectroscopic pairs recently discovered by cross-correlation spectroscopy. For nearby solar-type stars the most extensive surveys of radial velocities have been done by Duquennoy and Mayor (1991) and Tokovinin (1988). From Tokovinin's list, a few spectroscopic binaries with fast orbital motion were rst resolved by speckle interferometric observations at the 6-
2 2 I.BALEGA ET AL. m telescope of the Special Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) in Zelenchuk. All of them are interesting new candidates for precise mass determination. Here we present the rst results for two binaries included in our observational program in 1993: the nearby (=49 mas), 7.7 magnitude, K2 dwarf star Gliese and the F7V star 41 Dra. The 41 Dra binary is a member of the hierarchical quadruple system ADS 11061AB=40/41 Dra. Both 40 and 41 Dra pairs are SB2 (Tokovinin, 1995). For Gl and 41 Dra we present diraction-limited images obtained by the speckle-masking method. The images allow us to determine not only the geometry of the binaries, but also their exact maginitudes. The 41 Dra system could become one of the most interesting multiples for overall study by means of dierent methods. 2. Observations and image reconstructions Gl and 41 Dra were rst resolved at the 6-m telescope in 1993 using the SAO speckle camera (Balega et al., 1994). Speckle interferograms were recorded through 605/24 nm and 667/20 nm interference lters with 20 ms exposure time under seeing. Later, the measurements were continued using the Max-Planck-Institut fur Radioastronomie speckle camera (Baier and Weigelt, 1983) which provides higher dynamic range and better astrometric accuracy. The new detector of this camera is a Thompson pixels CCD optically coupled to a 3-stage electrostatic image intensier. The new data were collected through a 656/30 nm red lter, with the magnication 40 corresponding to an image scale of 4.97 mas/pixel. In addition, in 1996 we recorded 41 Dra speckle images in the K-band (lter 2191/411 nm) with a pixels NICMOS-3 camera. For infrared observations the exposure time of the speckle interferograms was 150 ms, and the scale in the image plane was 33.2 mas/pixel. A system of Digital Signal Processors was used for real-time speckle-masking computations, so we could see the evolution of the restored image during observing. Simultaneously, the data were recorded on Exabyte streamers for future detailed analysis. Diraction-limited images in the visible and in the infrared were reconstructed from speckle interferograms by the speckle-masking method (Weigelt,1977; Lohmann et al., 1983). The following processing steps were applied to the speckle data: 1. Subtraction of the detector average dark current and division by the ateld for each speckle interferogram; 2. Calculation of the average power spectrum of all speckle data; 3. Subtraction of detector noise bias terms from the average power spectrum; 4. Calculation of the average bispectrum of all speckle interferograms; 5. Subtraction of detector noise bias terms from the average bispectrum;
3 SPECKLE IMAGING OF GL AND 41 DRA 3 6. Compensation of the speckle interferometry transfer function in the bias-compensated average power spectrum to obtain the Fourier modulus; 7. Retrieval of Fourier phase from the bias-compensated average bispectrum; 8. Reconstruction of the diraction-limited image from the object modulus and phase. The object Fourier phase was reconstructed from the bias-compensated average bispectrum using the phase recursion method (Lohmann et al., 1983). The bispectrum of each frame consisted of 31: elements (maximum length of bispectrum vectors: u=50 px, v =95 px = diraction cut-o frequency). For correct recursive phase reconstruction each bispectrum element was weighted with its SNR. 3. Results During the observations of Gl in 1993 we suspected the existence of three components in the system at the following position angles and separations: AB = 107, AB = 186 mas; AC = 134, AC = 45 mas. The contrast of the secondary peaks in the correlation was rather low because of the large magnitude dierence between the stars in Gl TABLE 1. Interferometric measurements of Gl and 41 Dra Binary Date Filter 4m mas =4, nm Gl 150.2AB / / Gl 150.2AC(?) / Dra / / / / /30 { / The bispectrum image reconstruction of Gl 150.2AB through the red 656/30 nm lter is shown in Fig.1a. The measurements of the geometry and magnitude dierence are reported in Table 1. No evidence for the third star was found in The upper limit for the separation of suspected companion is about 10 ms for an equal brightness pair. Orbital motion of
4 4 I.BALEGA ET AL. such a close secondary would cause radial velocity variations with a period of 1 yr and an amplitude of 10 km/s. Such variations have never been reported for Gl 150.2, so we conclude that the suspected triple structure of the system is spurious. A year after the rst resolution, the angular distance a b Figure 1. (a) Diraction-limited 656/30 nm image of spectroscopic binary Gl 150.2AB reconstructed by the speckle masking method from 1600 speckle interferograms. (b) Image reconstruction of 41 Dra from 533 infrared speckle interferograms recorded through a 2129/411 nm lter. The scale and orientation are identical in both images: each panel covers 0:7 00 0:7 00, north is up and east is to the left. in Gl 150.2AB system increased by 63 mas thus conrming the identity of spectroscopic and interferometric pairs. From the estimated magnitude difference 4m = 2:49 we obtain for the second star m R = 10:3. The absolute magnitude for the main K2V star must be close to MV =6.4 (Allen, 1973), corresponding to m? M =1.4 and ph =52 mas. The absolute magnitude for the secondary is then M V =8.9 and its spectral type is M0V. Estimation of the masses of the A and B components are 0.7M and 0.5M respectively, and their orbital period is 10 yrs. In the following years, speckle measurements combined with radial velocity data and HIPPARCOS parallaxes will provide high precision masses and luminosities for Gl 150.2AB. Speckle measurements of 41 Dra are given in Table 1. In , 40 days after the periastron passage, the weaker star of the binary was observed in the NW direction at =25 mas - the separation equal to the diraction limit of the 6-m telescope at 650 nm. In Fig.1b it is shown one of the speckle masking images of 41 Dra, recorded through the 2191/411 nm lter where the diraction limit of the telescope is 75 mas.
5 SPECKLE IMAGING OF GL AND 41 DRA 5 As was recently shown by Tokovinin (1995), all four components of 40/41 Dra = ADS 11061AB system have very similar spectral types and masses. The wide pair ADS 11061Aab shows the highest eccentricity among known spectroscopic binaries. By combining P,T,e elements from the spectroscopic orbit with our 6 speckle measurements in dierent lters, we can dene the parameters of the visual orbit. This was done with the help of the Monet method (1979) giving us the following: P = 3:4147, T = 1994:5988, e = , a 00 =70 mas, i =50, =358,! =130. The corresponding ellipse of the relative motion is shown in Fig.2. From the known values for (M Aa +M Ab ) sin 3 i = 1:100M and K Ab =K Aa =1.07 (Tokovinin, 1995), we can now estimate the masses of the Aa and Ab components: M Aa = 1:26M, M Ab = 1:18M. Taking into account the bolometric correction for an F7V star, the dynamic parallax of the system is dyn =21 mas, which is in agreement with the published trigonometric parallax (Turon et al., 1992). It is interesting to note that exactly the same parallax has been reported during this Workshop for the wide system ADS 10061AB by A.Kiselev, as a result of astrometric measurements at the Pulkovo observatory. Figure 2. The relative interferometric orbit for 41 Dra=ADS 11061Aab. Speckle measurements with the 6-m telescope are connected to their predicted positions on the orbit.
6 6 I.BALEGA ET AL. Close to the periastron passage the two components of 41 Dra are separated by only 1{2 mas, or 5{10 stellar radii. Short-term tidal frictions near the periastron could cause the evolution of orbit eccentricity, period, and semi-major axis. The quadruple system ADS 11061AB as a whole is therefore a critical test object for the verication of theories of multiple stars origin and evolution. 4. Conclusion We obtained the rst diraction-limited images of the nearby spectroscopic binaries Gl and 41 Dra. For 41 Dra, speckle observations were made both at visible wavelengths and in the K-band. This pair with K2V and M0V components shows orbital motion with a period of about 10 years. Because of a signicant magnitude dierence between the two stars of Gl 150.2, it can be observed only as SB1. For this system, precise parallaxes and new speckle measurements at dierent wavelengths can improve our knowledge about the physical characteristics of the components. The pair 41 Dra is a rare case of a relatively short-period SB2 with an eccentricity close to 1, and it is at the same time a member of a quadruple system. The preliminary combined spectroscopic-interferometric orbit is derived for 41 Dra, yielding the masses 1:22M and 1:18M for its F7V and F9V component. The dynamic parallax of the system is dyn = 21 mas. All the astrometric and photometric measurements for the two stars were made with the speckle-masking method. The use of Digital Signal Processors for bispectrum computations allows diraction-limited image reconstruction in real time. For binary star application, the speckle-masking method has signicant advantages. It provides diraction-limited image with high photometric and astrometric accuracy from 400 nm to the infrared. References Allen, C.W. Astrophysical Quantities. Univ. of London. Atlone Press, 1973 Andersen, J. (1991) Astron. Astropys. Rev. 3, 91 Balega, I.I. et al. (1994) Astron. Astrophys. Suppl.Ser. 105, 503 Baier, G. and Weigelt, G. (1983) Astron. Astrophys. 121, 137 Duquennoy A. and Mayor M. (1991) Astron. Astrophys. 248, 485 Hofmann, K.-H. and Weigelt, G. (1986) Astron. Astrophys. 167, L15 Lohmann, A.W. et al. (1983) Appl. Optics 22, 4028 Monet, D.G. (1979) Astrophys. J. 234, 275 Tokovinin, A.A. (1988) Astrophysics 28, 173 Tokovinin, A.A. (1995) Astronomy Lett. 21, 286 Turon, C. et al. (1992) The HIPPARCOS Input Catalogue, ESA SP-1136, 4 Weigelt, G. (1977) Opt. Commun. 21, 55
7 5. Discussion SPECKLE IMAGING OF GL AND 41 DRA 7 H.A.McAlister: Have you compared your magnitude dierences with lunar occultation observations? What is the accuracy of 4m measurements using the speckle-masking method? Y.Balega: No, we do not have lunar occultation binaries in our program list. The mean error of 4m measurement is 0.05{0.1 magnitude. The high quality of speckle-masking reconstructions was conrmed by HST observations of star clusters and other objects, for example, Carinae, R136, NGC 3603 whose images were published years before the launch of the HST. H.Zinnecker: (The question of Zinnecker about the comparison of speckle interferometry and adaptive optics was answered during the Workshop { see special forms).
Interferometric orbits of new Hipparcos binaries
 Interferometric orbits of new Hipparcos binaries I.I. Balega 1, Y.Y. Balega 2, K.-H. Hofmann 3, E.V. Malogolovets 4, D. Schertl 5, Z.U. Shkhagosheva 6 and G. Weigelt 7 1 Special Astrophysical Observatory,
Interferometric orbits of new Hipparcos binaries I.I. Balega 1, Y.Y. Balega 2, K.-H. Hofmann 3, E.V. Malogolovets 4, D. Schertl 5, Z.U. Shkhagosheva 6 and G. Weigelt 7 1 Special Astrophysical Observatory,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 3 Sep 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 3 Sep 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 3 Sep 2008](/thumbs/88/116499119.jpg) Astrophysical Bulletin, vol. 63, No.3, 2008, pp.278-289 September 3, 2008 Translated from Astrofizicheskij Byulleten, vol.63, No.3, 2008, pp. 298-310 Speckle Interferometry of Metal-Poor Stars in the Solar
Astrophysical Bulletin, vol. 63, No.3, 2008, pp.278-289 September 3, 2008 Translated from Astrofizicheskij Byulleten, vol.63, No.3, 2008, pp. 298-310 Speckle Interferometry of Metal-Poor Stars in the Solar
Binary star speckle measurements during from the SAO 6-m and 1-m telescopes in Zelenchuk
 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS DECEMBER II 1999, PAGE 287 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 140, 287 292 (1999) Binary star speckle measurements during 1992-1997 from the SAO 6-m and 1-m telescopes
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS DECEMBER II 1999, PAGE 287 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 140, 287 292 (1999) Binary star speckle measurements during 1992-1997 from the SAO 6-m and 1-m telescopes
Searching for Other Worlds
 Searching for Other Worlds Lecture 32 1 In-Class Question What is the Greenhouse effect? a) Optical light from the Sun is reflected into space while infrared light passes through the atmosphere and heats
Searching for Other Worlds Lecture 32 1 In-Class Question What is the Greenhouse effect? a) Optical light from the Sun is reflected into space while infrared light passes through the atmosphere and heats
Speckle Interferometry
 Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 43, 229 236, (2014) Speckle Interferometry R. Köhler Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie, Königstuhl 17, 69117 Heidelberg, Germany, (E-mail: koehler@mpia.de) Received:
Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 43, 229 236, (2014) Speckle Interferometry R. Köhler Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie, Königstuhl 17, 69117 Heidelberg, Germany, (E-mail: koehler@mpia.de) Received:
arxiv:astro-ph/ v3 24 Apr 2007
 Astrophysical Bulletin, vol. 62, No.2, 2007, pp. 111-116 July 6, 2018 Translated from Astrofizicheskij Byulleten, vol.62, No.2, 2007, pp. 124-130 Nearby low-mass triple system GJ 795 E. V. Malogolovets,
Astrophysical Bulletin, vol. 62, No.2, 2007, pp. 111-116 July 6, 2018 Translated from Astrofizicheskij Byulleten, vol.62, No.2, 2007, pp. 124-130 Nearby low-mass triple system GJ 795 E. V. Malogolovets,
A Survey of Stellar Families Multiplicity of Solar-type Stars
 A Survey of Stellar Families Multiplicity of Solar-type Stars Advisor: Dr. Hal McAlister GSU Committee members: Dr. Doug Gies GSU Deepak Raghavan Ph.D. Dissertation Talk March 17, 2009 Dr. Todd Henry GSU
A Survey of Stellar Families Multiplicity of Solar-type Stars Advisor: Dr. Hal McAlister GSU Committee members: Dr. Doug Gies GSU Deepak Raghavan Ph.D. Dissertation Talk March 17, 2009 Dr. Todd Henry GSU
Today in Astronomy 328: binary stars
 Today in Astronomy 38: binary stars Binary-star systems. Direct measurements of stellar mass and radius in eclipsing binary-star systems. At right: two young binary star systems in the Taurus star-forming
Today in Astronomy 38: binary stars Binary-star systems. Direct measurements of stellar mass and radius in eclipsing binary-star systems. At right: two young binary star systems in the Taurus star-forming
Classical Methods for Determining Stellar Masses, Temperatures, and Radii
 Classical Methods for Determining Stellar Masses, Temperatures, and Radii Willie Torres Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics 2010 Sagan Exoplanet Summer Workshop 1 Outline Basic properties of stars
Classical Methods for Determining Stellar Masses, Temperatures, and Radii Willie Torres Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics 2010 Sagan Exoplanet Summer Workshop 1 Outline Basic properties of stars
Fundamental (Sub)stellar Parameters: Masses and Radii. PHY 688, Lecture 10
 Fundamental (Sub)stellar Parameters: Masses and Radii PHY 688, Lecture 10 Outline Review of previous lecture brown dwarf effective temperatures finding cool brown dwarfs current problem: what are the coolest
Fundamental (Sub)stellar Parameters: Masses and Radii PHY 688, Lecture 10 Outline Review of previous lecture brown dwarf effective temperatures finding cool brown dwarfs current problem: what are the coolest
Lecture 12: Distances to stars. Astronomy 111
 Lecture 12: Distances to stars Astronomy 111 Why are distances important? Distances are necessary for estimating: Total energy released by an object (Luminosity) Masses of objects from orbital motions
Lecture 12: Distances to stars Astronomy 111 Why are distances important? Distances are necessary for estimating: Total energy released by an object (Luminosity) Masses of objects from orbital motions
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Department. Problem Set 6
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Department Astronomy 8.282J 12.402J March 17, 2006 Problem Set 6 Due: Friday, March 24 (in lecture) Reading:
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Department Astronomy 8.282J 12.402J March 17, 2006 Problem Set 6 Due: Friday, March 24 (in lecture) Reading:
Using Speckle Interferometry to Resolve Binary Stars
 Spectroscopically and Spatially Resolving the Components of Close Binary Stars ASP Conference Series, Vol. 318, 2004 R. W. Hilditch, H. Hensberge, and K. Pavlovski (eds.) Using Speckle Interferometry to
Spectroscopically and Spatially Resolving the Components of Close Binary Stars ASP Conference Series, Vol. 318, 2004 R. W. Hilditch, H. Hensberge, and K. Pavlovski (eds.) Using Speckle Interferometry to
Lecture 16 The Measuring the Stars 3/26/2018
 Lecture 16 The Measuring the Stars 3/26/2018 Test 2 Results D C B A Questions that I thought were unfair: 13, 18, 25, 76, 77, 80 Curved from 85 to 79 Measuring stars How far away are they? How bright are
Lecture 16 The Measuring the Stars 3/26/2018 Test 2 Results D C B A Questions that I thought were unfair: 13, 18, 25, 76, 77, 80 Curved from 85 to 79 Measuring stars How far away are they? How bright are
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 3 Jan 2018
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 3 Jan 2018 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 3 Jan 2018](/thumbs/75/71936557.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 7 (2018) Printed 8 January 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Spectroscopic orbits of nearby solar-type dwarfs. II. arxiv:1712.06389v2 [astro-ph.sr] 3 Jan 2018 N. A. Gorynya
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 7 (2018) Printed 8 January 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Spectroscopic orbits of nearby solar-type dwarfs. II. arxiv:1712.06389v2 [astro-ph.sr] 3 Jan 2018 N. A. Gorynya
Extrasolar Planets. Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects
 Extrasolar Planets Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects Methods of detection Methods of detection Methods of detection Pulsar timing Planetary motion around pulsar
Extrasolar Planets Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects Methods of detection Methods of detection Methods of detection Pulsar timing Planetary motion around pulsar
Multiple systems as a source of false positives in exo-planet detections
 Multiple systems as a source of false positives in exo-planet detections Andrei Tokovinin ( (NOAO/CTIO) Jean-Louis Halbwachs (Observatoire de Strasbourg) Astrometric companion to Zeta Aqr-A imaged at SOAR
Multiple systems as a source of false positives in exo-planet detections Andrei Tokovinin ( (NOAO/CTIO) Jean-Louis Halbwachs (Observatoire de Strasbourg) Astrometric companion to Zeta Aqr-A imaged at SOAR
Astronomy 421. Lecture 8: Binary stars
 Astronomy 421 Lecture 8: Binary stars 1 Key concepts: Binary types How to use binaries to determine stellar parameters The mass-luminosity relation 2 Binary stars So far, we ve looked at the basic physics
Astronomy 421 Lecture 8: Binary stars 1 Key concepts: Binary types How to use binaries to determine stellar parameters The mass-luminosity relation 2 Binary stars So far, we ve looked at the basic physics
Research Note An old nearby quadruple system Gliese 225.2
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. gl2252 July 26, 2005 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) Research Note An old nearby quadruple system Gliese 225.2 A. Tokovinin 1, O. Kiyaeva 2, M. Sterzik 3,
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. gl2252 July 26, 2005 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) Research Note An old nearby quadruple system Gliese 225.2 A. Tokovinin 1, O. Kiyaeva 2, M. Sterzik 3,
INTERNATIONAL ASTRONOMICAL UNION COMMISSION 26 (DOUBLE STARS) INFORMATION CIRCULAR No. 173 (FEBRUARY 2011) NEW ORBITS
 INTERNATIONAL ASTRONOMICAL UNION COMMISSION 26 (DOUBLE STARS) INFORMATION CIRCULAR No. 173 (FEBRUARY 2011) NEW ORBITS ADS Name P T e Ω(2000) 2011 Author(s) α2000δ n a i ω Last ob. 2012 - FIN 333 33 y 31
INTERNATIONAL ASTRONOMICAL UNION COMMISSION 26 (DOUBLE STARS) INFORMATION CIRCULAR No. 173 (FEBRUARY 2011) NEW ORBITS ADS Name P T e Ω(2000) 2011 Author(s) α2000δ n a i ω Last ob. 2012 - FIN 333 33 y 31
Spectroscopic orbits of 10 nearby solar-type dwarfs
 doi:10.1093/mnras/stu743 Spectroscopic orbits of 10 nearby solar-type dwarfs N. A. Gorynya 1,2 and A. Tokovinin 3 1 Institute of Astronomy of Russian Academy of Science, 48 Pyatnitskaya Str, 109017 Moscow,
doi:10.1093/mnras/stu743 Spectroscopic orbits of 10 nearby solar-type dwarfs N. A. Gorynya 1,2 and A. Tokovinin 3 1 Institute of Astronomy of Russian Academy of Science, 48 Pyatnitskaya Str, 109017 Moscow,
468 Six dierent tests were used to detect variables, with dierent sensitivities to light-curve features. The mathematical expression for the limiting
 467 PHOTOMETRIC ARIABILITY IN THE HR-DIAGRAM L. Eyer, M. Grenon Geneva Observatory, CH-129 Sauverny, Switzerland ABSTRACT The Hipparcos satellite has detected systematically variable stars when the amplitudes
467 PHOTOMETRIC ARIABILITY IN THE HR-DIAGRAM L. Eyer, M. Grenon Geneva Observatory, CH-129 Sauverny, Switzerland ABSTRACT The Hipparcos satellite has detected systematically variable stars when the amplitudes
Hubble Science Briefing: 25 Years of Seeing Stars with the Hubble Space Telescope. March 5, 2015 Dr. Rachel Osten Dr. Alex Fullerton Dr.
 Hubble Science Briefing: 25 Years of Seeing Stars with the Hubble Space Telescope March 5, 2015 Dr. Rachel Osten Dr. Alex Fullerton Dr. Jay Anderson Hubble s Insight into the Lives of Stars Comes From:
Hubble Science Briefing: 25 Years of Seeing Stars with the Hubble Space Telescope March 5, 2015 Dr. Rachel Osten Dr. Alex Fullerton Dr. Jay Anderson Hubble s Insight into the Lives of Stars Comes From:
Dynamics of Multiple Stars: Observations
 Massive Stars in Interacting Binaries ASP Conference Series, Vol. 367, 2007 N. St-Louis & A.F.J. Moffat Dynamics of Multiple Stars: Observations A. Tokovinin Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory, Casilla
Massive Stars in Interacting Binaries ASP Conference Series, Vol. 367, 2007 N. St-Louis & A.F.J. Moffat Dynamics of Multiple Stars: Observations A. Tokovinin Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory, Casilla
MASS DETERMINATIONS OF POPULATION II BINARY STARS
 MASS DETERMINATIONS OF POPULATION II BINARY STARS Kathryn E. Williamson Department of Physics and Astronomy, The University of Georgia, Athens, GA 30602-2451 James N. Heasley Institute for Astronomy, University
MASS DETERMINATIONS OF POPULATION II BINARY STARS Kathryn E. Williamson Department of Physics and Astronomy, The University of Georgia, Athens, GA 30602-2451 James N. Heasley Institute for Astronomy, University
First results of the optical speckle interferometry with the 3.5-m telescope at Calar Alto (Spain): Measurements and orbits of visual binaries
 First results of the optical speckle interferometry with the 3.5-m telescope at Calar Alto (Spain): Measurements and orbits of visual binaries Docobo, J.A., Tamazian, V.S., Andrade, M., Ling, J.F., Balega,
First results of the optical speckle interferometry with the 3.5-m telescope at Calar Alto (Spain): Measurements and orbits of visual binaries Docobo, J.A., Tamazian, V.S., Andrade, M., Ling, J.F., Balega,
Exoplanets Direct imaging. Direct method of exoplanet detection. Direct imaging: observational challenges
 Black body flux (in units 10-26 W m -2 Hz -1 ) of some Solar System bodies as seen from 10 pc. A putative hot Jupiter is also shown. The planets have two peaks in their spectra. The short-wavelength peak
Black body flux (in units 10-26 W m -2 Hz -1 ) of some Solar System bodies as seen from 10 pc. A putative hot Jupiter is also shown. The planets have two peaks in their spectra. The short-wavelength peak
ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes Section III
 ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes Section III Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser East Tennessee State University Edition 4.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of the instructor and students
ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes Section III Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser East Tennessee State University Edition 4.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of the instructor and students
258 of the Hipparcos Catalogue (ESA 1997). What follows is an overview of these data as pertaining to this project. The Hipparcos split-mirror telesco
 257 USING HIPPARCOS TRANSIT DATA FOR APERTURE SYNTHESIS IMAGING Carl Fredrik Quist, Lennart Lindegren, Staan Soderhjelm Lund Observatory, Box 43, SE-221 00 Lund, Sweden ABSTRACT The ESA Hipparcos astrometry
257 USING HIPPARCOS TRANSIT DATA FOR APERTURE SYNTHESIS IMAGING Carl Fredrik Quist, Lennart Lindegren, Staan Soderhjelm Lund Observatory, Box 43, SE-221 00 Lund, Sweden ABSTRACT The ESA Hipparcos astrometry
SPECKLE MEASUREMENTS AND DIFFERENTIAL PHOTOMETRY OF VISUAL BINARIES WITH THE 6 METER TELESCOPE OF THE SPECIAL ASTROPHYSICAL OBSERVATORY
 The Astronomical Journal, 132:994 998, 2006 September # 2006. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. SPECKLE MEASUREMENTS AND DIFFERENTIAL PHOTOMETRY OF VISUAL BINARIES
The Astronomical Journal, 132:994 998, 2006 September # 2006. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. SPECKLE MEASUREMENTS AND DIFFERENTIAL PHOTOMETRY OF VISUAL BINARIES
ASTRONOMICAL SPECKLE INTERFEROMETRY. Review lecture by Y.Balega from the Special Astrophysical Observatory, Zelentchuk, Russia (preliminary version)
 NATO ADVANCED STUDY INSTITUTE on OPTICS IN ASTROPHYSICS ASTRONOMICAL SPECKLE INTERFEROMETRY Review lecture by Y.Balega from the Special Astrophysical Observatory, Zelentchuk, Russia (preliminary version)
NATO ADVANCED STUDY INSTITUTE on OPTICS IN ASTROPHYSICS ASTRONOMICAL SPECKLE INTERFEROMETRY Review lecture by Y.Balega from the Special Astrophysical Observatory, Zelentchuk, Russia (preliminary version)
Astrometric Detection of Exoplanets
 Astrometric Detection of Exoplanets Angles & Coordinates: 1 full circle = 360 degrees 1 degree = 60 arcminutes 1 arcminute = 60 arcseconds ~ 1 inch @ 100 yards (2.908 cm at 100 meters) 1 milliarcsec (mas)
Astrometric Detection of Exoplanets Angles & Coordinates: 1 full circle = 360 degrees 1 degree = 60 arcminutes 1 arcminute = 60 arcseconds ~ 1 inch @ 100 yards (2.908 cm at 100 meters) 1 milliarcsec (mas)
489 THE METALLICITY DISTRIBUTION OF LATE-TYPE DWARFS AND THE HIPPARCOS HR DIAGRAM M. Haywood, J. Palasi, A. Gomez, L. Meillon DASGAL, URA 335 du CNRS
 489 THE METALLICITY DISTRIBUTION OF LATE-TYPE DWARFS AND THE HIPPARCOS HR DIAGRAM M. Haywood, J. Palasi, A. Gomez, L. Meillon DASGAL, URA 335 du CNRS Observatoire de Paris - Meudon, France ABSTRACT The
489 THE METALLICITY DISTRIBUTION OF LATE-TYPE DWARFS AND THE HIPPARCOS HR DIAGRAM M. Haywood, J. Palasi, A. Gomez, L. Meillon DASGAL, URA 335 du CNRS Observatoire de Paris - Meudon, France ABSTRACT The
Observed Properties of Stars - 2 ASTR 2110 Sarazin
 Observed Properties of Stars - 2 ASTR 2110 Sarazin Properties Location Distance Speed Radial velocity Proper motion Luminosity, Flux Magnitudes Magnitudes Stellar Colors Stellar Colors Stellar Colors Stars
Observed Properties of Stars - 2 ASTR 2110 Sarazin Properties Location Distance Speed Radial velocity Proper motion Luminosity, Flux Magnitudes Magnitudes Stellar Colors Stellar Colors Stellar Colors Stars
Astronomy 113. Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D.
 Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. The Nature of Stars 8-2 Parallax For nearby stars - measure distances with parallax July 1 AU d p A A A January ³ d = 1/p (arcsec) [pc] ³ 1pc when p=1arcsec; 1pc=206,265AU=3
Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. The Nature of Stars 8-2 Parallax For nearby stars - measure distances with parallax July 1 AU d p A A A January ³ d = 1/p (arcsec) [pc] ³ 1pc when p=1arcsec; 1pc=206,265AU=3
A quasi-time-dependent radiative transfer model of OH arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 22 Jun 2005
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 2135 February 2, 28 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) A quasi-time-dependent radiative transfer model of OH14.9+2.4 arxiv:astro-ph/52269v2 22 Jun 25 D. Riechers
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 2135 February 2, 28 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) A quasi-time-dependent radiative transfer model of OH14.9+2.4 arxiv:astro-ph/52269v2 22 Jun 25 D. Riechers
Infrared Imaging of Capella with the IOTA Interferometer
 Infrared Imaging of Capella with the IOTA Interferometer Stefan Kraus ab and F. Peter Schloerb a a Department of Astronomy, University of Massachusetts, Amherst MA 01003 b Max-Planck Insitut für Radioastronomie
Infrared Imaging of Capella with the IOTA Interferometer Stefan Kraus ab and F. Peter Schloerb a a Department of Astronomy, University of Massachusetts, Amherst MA 01003 b Max-Planck Insitut für Radioastronomie
Speckle Interferometric Observation of WDS
 Page 172 Stephen White 1, Paige Benson 1, Sepehr Ardebilianfard 1, Gezal Bahmani 1, Alexander Beltzer Sweeney 1, Irena Stojimirovic 1, Richard Harshaw 2, Grady Boyce 3, Pat Boyce 3 1. San Diego Mesa College
Page 172 Stephen White 1, Paige Benson 1, Sepehr Ardebilianfard 1, Gezal Bahmani 1, Alexander Beltzer Sweeney 1, Irena Stojimirovic 1, Richard Harshaw 2, Grady Boyce 3, Pat Boyce 3 1. San Diego Mesa College
Exoplanets Direct imaging. Direct method of exoplanet detection. Direct imaging: observational challenges
 Black body flux (in units 10-26 W m -2 Hz -1 ) of some Solar System bodies as seen from 10 pc. A putative hot Jupiter is also shown. The planets have two peaks in their spectra. The short-wavelength peak
Black body flux (in units 10-26 W m -2 Hz -1 ) of some Solar System bodies as seen from 10 pc. A putative hot Jupiter is also shown. The planets have two peaks in their spectra. The short-wavelength peak
Characterizing Stars
 Characterizing Stars 1 Guiding Questions 1. How far away are the stars? 2. What evidence do astronomers have that the Sun is a typical star? 3. What is meant by a first-magnitude or second magnitude star?
Characterizing Stars 1 Guiding Questions 1. How far away are the stars? 2. What evidence do astronomers have that the Sun is a typical star? 3. What is meant by a first-magnitude or second magnitude star?
Characterizing Stars. Guiding Questions. Parallax. Careful measurements of the parallaxes of stars reveal their distances
 Guiding Questions Characterizing Stars 1. How far away are the stars? 2. What evidence do astronomers have that the Sun is a typical star? 3. What is meant by a first-magnitude or second magnitude star?
Guiding Questions Characterizing Stars 1. How far away are the stars? 2. What evidence do astronomers have that the Sun is a typical star? 3. What is meant by a first-magnitude or second magnitude star?
ECLIPSING BINARIES: THE ROYAL ROAD. John Southworth (Keele University)
 ECLIPSING BINARIES: THE ROYAL ROAD John Southworth (Keele University) Astrometric binaries: distant friends? William Herschel (1802) christened the term binary star Félix Savary (in 1827) established the
ECLIPSING BINARIES: THE ROYAL ROAD John Southworth (Keele University) Astrometric binaries: distant friends? William Herschel (1802) christened the term binary star Félix Savary (in 1827) established the
Relativity and Astrophysics Lecture 15 Terry Herter. RR Lyrae Variables Cepheids Variables Period-Luminosity Relation. A Stellar Properties 2
 Stellar Properties Relativity and Astrophysics Lecture 15 Terry Herter Outline Spectroscopic Parallax Masses of Stars Periodic Variable Stars RR Lyrae Variables Cepheids Variables Period-Luminosity Relation
Stellar Properties Relativity and Astrophysics Lecture 15 Terry Herter Outline Spectroscopic Parallax Masses of Stars Periodic Variable Stars RR Lyrae Variables Cepheids Variables Period-Luminosity Relation
Astr 5465 Feb. 6, 2018 Today s Topics
 Astr 5465 Feb. 6, 2018 Today s Topics Stars: Binary Stars Determination of Stellar Properties via Binary Stars Classification of Binary Stars Visual Binaries Both stars visible Only one star visible Spectroscopic
Astr 5465 Feb. 6, 2018 Today s Topics Stars: Binary Stars Determination of Stellar Properties via Binary Stars Classification of Binary Stars Visual Binaries Both stars visible Only one star visible Spectroscopic
The HR Diagram. L f 2 L d2 N obj V d 3 N obj L3/2. Most (>90%) stars lie
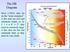 The HR Diagram Most (>90%) stars lie on the main sequence. A few stars are cool and extremely bright, so, by L = 4 π R 2 σ T 4, they must be extremely large. A few stars are hot, but extremely faint, so
The HR Diagram Most (>90%) stars lie on the main sequence. A few stars are cool and extremely bright, so, by L = 4 π R 2 σ T 4, they must be extremely large. A few stars are hot, but extremely faint, so
Chapter 8: The Family of Stars
 Chapter 8: The Family of Stars Motivation We already know how to determine a star s surface temperature chemical composition surface density In this chapter, we will learn how we can determine its distance
Chapter 8: The Family of Stars Motivation We already know how to determine a star s surface temperature chemical composition surface density In this chapter, we will learn how we can determine its distance
Astr 2320 Tues. March 7, 2017 Today s Topics
 Astr 2320 Tues. March 7, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 13: Stars: Binary Stars Determination of Stellar Properties vi Binary Stars Classification of Binary Stars Visual Binaries Both stars visible Only one
Astr 2320 Tues. March 7, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 13: Stars: Binary Stars Determination of Stellar Properties vi Binary Stars Classification of Binary Stars Visual Binaries Both stars visible Only one
Lecture 9: Speckle Interferometry. Full-Aperture Interferometry. Labeyrie Technique. Knox-Thompson Technique. Bispectrum Technique
 Lecture 9: Speckle Interferometry Outline 1 Full-Aperture Interferometry 2 Labeyrie Technique 3 Knox-Thompson Technique 4 Bispectrum Technique 5 Differential Speckle Imaging 6 Phase-Diverse Speckle Imaging
Lecture 9: Speckle Interferometry Outline 1 Full-Aperture Interferometry 2 Labeyrie Technique 3 Knox-Thompson Technique 4 Bispectrum Technique 5 Differential Speckle Imaging 6 Phase-Diverse Speckle Imaging
Near -IR interferometry:
 Near -IR interferometry: spectrally dispersed JHK-band IOTA / GI2T interferograms, advantages of NIR, and aims Gerd Weigelt Max-Planck Institute for Radioastronomy, Bonn Plan Interferometry with spectrally
Near -IR interferometry: spectrally dispersed JHK-band IOTA / GI2T interferograms, advantages of NIR, and aims Gerd Weigelt Max-Planck Institute for Radioastronomy, Bonn Plan Interferometry with spectrally
Eclipsing binary stars
 SEMINAR - 4. LETNIK Eclipsing binary stars Author: Daša Rozmus Mentor: dr. Tomaž Zwitter Ljubljana, November 2010 Abstract Observations indicate that the majority of stars have a companion, thus that stars
SEMINAR - 4. LETNIK Eclipsing binary stars Author: Daša Rozmus Mentor: dr. Tomaž Zwitter Ljubljana, November 2010 Abstract Observations indicate that the majority of stars have a companion, thus that stars
Lecture 2. The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Blackbody Radiation and Stellar Mass Determination. Glatzmaier and Krumholz 2 Prialnik 1.
 Lecture The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Blackbody Radiation and Stellar Mass Determination Andromeda and Milky Way collide in 4 billion years. Approaching us at 3 km/s (Doppler shift) HST astrometry plus
Lecture The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Blackbody Radiation and Stellar Mass Determination Andromeda and Milky Way collide in 4 billion years. Approaching us at 3 km/s (Doppler shift) HST astrometry plus
Measuring Radial Velocities of Low Mass Eclipsing Binaries
 Measuring Radial Velocities of Low Mass Eclipsing Binaries Rebecca Rattray, Leslie Hebb, Keivan G. Stassun College of Arts and Science, Vanderbilt University Due to the complex nature of the spectra of
Measuring Radial Velocities of Low Mass Eclipsing Binaries Rebecca Rattray, Leslie Hebb, Keivan G. Stassun College of Arts and Science, Vanderbilt University Due to the complex nature of the spectra of
The Binary System VV Cephei Eclipse Campaign 2017/2019 OHP-Meeting July 2017
 The Binary System VV Cephei Eclipse Campaign 2017/2019 OHP-Meeting July 2017 Ernst Pollmann International Working Group Active Spectroscopy in Astronomy http://astrospectroscopy.de 3 One of the best known
The Binary System VV Cephei Eclipse Campaign 2017/2019 OHP-Meeting July 2017 Ernst Pollmann International Working Group Active Spectroscopy in Astronomy http://astrospectroscopy.de 3 One of the best known
CCD astrometry and UBV photometry of visual binaries
 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS JUNE I 1998, PAGE 299 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 130, 299 304 (1998) CCD astrometry and UBV photometry of visual binaries II. Visual double stars with mainly
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS JUNE I 1998, PAGE 299 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 130, 299 304 (1998) CCD astrometry and UBV photometry of visual binaries II. Visual double stars with mainly
Exploring the giant planet - brown dwarf connection with astrometry. Johannes Sahlmann ESA Research Fellow at ESAC
 Exploring the giant planet - brown dwarf connection with astrometry ESA Research Fellow at ESAC Who s Who, Paris - 2 July 215 IS MASS A GOOD DEMOGRAPHIC INDICATOR? 2MASSWJ127334 393254 first image of a
Exploring the giant planet - brown dwarf connection with astrometry ESA Research Fellow at ESAC Who s Who, Paris - 2 July 215 IS MASS A GOOD DEMOGRAPHIC INDICATOR? 2MASSWJ127334 393254 first image of a
Intro to Astrophysics
 Intro to Astrophysics Dr. Bill Pezzaglia 1 III. Introduction To Astrophysics A. Distances to Stars B. Binary Stars C. HR Diagrams 2 Updated: Nov 2007 A. Stellar Distances 1. Method of Parallax 2. Absolute
Intro to Astrophysics Dr. Bill Pezzaglia 1 III. Introduction To Astrophysics A. Distances to Stars B. Binary Stars C. HR Diagrams 2 Updated: Nov 2007 A. Stellar Distances 1. Method of Parallax 2. Absolute
OBSERVATIONS OF THE BINARY STAR 61 Cyg ON THE 26 INCH REFRACTOR AT THE PULKOVO OBSERVATORY
 Astrophysics, Vol. 49, No. 3, 26 OBSERVATIONS OF THE BINAR STAR 61 Cyg ON THE 26 INCH REFRACTOR AT THE PULKOVO OBSERVATOR D. L. Gorshanov, N. A. Shakht, and A. A. Kisselev UDC: 524.38 Results from an analysis
Astrophysics, Vol. 49, No. 3, 26 OBSERVATIONS OF THE BINAR STAR 61 Cyg ON THE 26 INCH REFRACTOR AT THE PULKOVO OBSERVATOR D. L. Gorshanov, N. A. Shakht, and A. A. Kisselev UDC: 524.38 Results from an analysis
CHARA/NPOI 2013 Science & Technology Review MIRC Observations of the O-star Triple Sigma Orionis
 MIRC Observations of the O-star Triple Sigma Orionis Gail Schaefer Doug Gies John Monnier Nils Turner New Title: Do NPOI and CHARA Orbits Agree?... stay tuned... Sigma Orionis Image credit: Peter Wienerroither
MIRC Observations of the O-star Triple Sigma Orionis Gail Schaefer Doug Gies John Monnier Nils Turner New Title: Do NPOI and CHARA Orbits Agree?... stay tuned... Sigma Orionis Image credit: Peter Wienerroither
Fundamental (Sub)stellar Parameters: Surface Gravity. PHY 688, Lecture 11
 Fundamental (Sub)stellar Parameters: Surface Gravity PHY 688, Lecture 11 Outline Review of previous lecture binary stars and brown dwarfs (sub)stellar dynamical masses and radii Surface gravity stars,
Fundamental (Sub)stellar Parameters: Surface Gravity PHY 688, Lecture 11 Outline Review of previous lecture binary stars and brown dwarfs (sub)stellar dynamical masses and radii Surface gravity stars,
ECLIPSING AND SPECTROSCOPIC BINARY STARS
 FINAL YEAR SEMINAR, OLD PROGRAM ECLIPSING AND SPECTROSCOPIC BINARY STARS Author: Franci Gorjup Mentor: Prof. dr. Tomaž Zwitter Ljubljana, December 2013 Abstract: First, we will see, what kind of binary
FINAL YEAR SEMINAR, OLD PROGRAM ECLIPSING AND SPECTROSCOPIC BINARY STARS Author: Franci Gorjup Mentor: Prof. dr. Tomaž Zwitter Ljubljana, December 2013 Abstract: First, we will see, what kind of binary
Searching for transiting giant extrasolar planets. Department of Physics University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto
 Searching for transiting giant extrasolar planets Department of Physics University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto Cosmology in the 20 th th century Rapid progress of cosmology since 1980 s existence of dark matter
Searching for transiting giant extrasolar planets Department of Physics University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto Cosmology in the 20 th th century Rapid progress of cosmology since 1980 s existence of dark matter
Lecture 2. The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Blackbody Radiation and Stellar Mass Determination. Glatzmaier and Krumholz 2 Prialnik 1.
 Lecture 2 The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Blackbody Radiation and Stellar Mass Determination Glatzmaier and Krumholz 2 Prialnik 1.4 Pols 1 Andromeda and Milky Way collide in 4 billion years. Approaching
Lecture 2 The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Blackbody Radiation and Stellar Mass Determination Glatzmaier and Krumholz 2 Prialnik 1.4 Pols 1 Andromeda and Milky Way collide in 4 billion years. Approaching
Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative.
 Chapter 6 Distances 6.1 Preliminaries Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative. Absolute distance measurements involve objects possibly unique
Chapter 6 Distances 6.1 Preliminaries Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative. Absolute distance measurements involve objects possibly unique
First Orbital Solution and Evolutionary State for the Newly Discovered Eclipsing Binaries USNO-B and GSC
 First Orbital Solution and Evolutionary State for the Newly Discovered Eclipsing Binaries USNO-B1.0 1091-0130715 and GSC-03449-0680 M. M. Elkhateeb 1, 2, M. I. Nouh 1, 2 and R. H. Nelson 1 Astronomy Department,
First Orbital Solution and Evolutionary State for the Newly Discovered Eclipsing Binaries USNO-B1.0 1091-0130715 and GSC-03449-0680 M. M. Elkhateeb 1, 2, M. I. Nouh 1, 2 and R. H. Nelson 1 Astronomy Department,
Stars: basic observations
 Stars: basic observations Basic properties of stars we would like to know in order to compare theory against observations: Stellar mass M Stellar radius R Surface temperature - effective temperature T
Stars: basic observations Basic properties of stars we would like to know in order to compare theory against observations: Stellar mass M Stellar radius R Surface temperature - effective temperature T
TrES Exoplanets and False Positives: Finding the Needle in the Haystack
 Transiting Extrasolar Planets Workshop ASP Conference Series, Vol. 366, 2007 C. Afonso, D. Weldrake and Th. Henning TrES Exoplanets and False Positives: Finding the Needle in the Haystack F. T. O Donovan
Transiting Extrasolar Planets Workshop ASP Conference Series, Vol. 366, 2007 C. Afonso, D. Weldrake and Th. Henning TrES Exoplanets and False Positives: Finding the Needle in the Haystack F. T. O Donovan
Chapter 10 Measuring the Stars
 Chapter 10 Measuring the Stars Some of the topics included in this chapter Stellar parallax Distance to the stars Stellar motion Luminosity and apparent brightness of stars The magnitude scale Stellar
Chapter 10 Measuring the Stars Some of the topics included in this chapter Stellar parallax Distance to the stars Stellar motion Luminosity and apparent brightness of stars The magnitude scale Stellar
A search for binary stars using speckle interferometry
 Rochester Institute of Technology RIT Scholar Works Theses Thesis/Dissertation Collections 2000 A search for binary stars using speckle interferometry Matthew Hoffmann Follow this and additional works
Rochester Institute of Technology RIT Scholar Works Theses Thesis/Dissertation Collections 2000 A search for binary stars using speckle interferometry Matthew Hoffmann Follow this and additional works
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 2 Mar 2005
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Ha281 February 2, 2008 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) A planet-sized transiting star around OGLE-TR-122 Accurate mass and radius near the Hydrogen-burning
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Ha281 February 2, 2008 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) A planet-sized transiting star around OGLE-TR-122 Accurate mass and radius near the Hydrogen-burning
Properties of Stars. For such huge objects, stars have comparatively simple properties when seen from a long way off
 Properties of Stars For such huge objects, stars have comparatively simple properties when seen from a long way off apparent magnitude distance and direction in space luminosity - absolute magnitude temperature
Properties of Stars For such huge objects, stars have comparatively simple properties when seen from a long way off apparent magnitude distance and direction in space luminosity - absolute magnitude temperature
THE OBSERVATION AND ANALYSIS OF STELLAR PHOTOSPHERES
 THE OBSERVATION AND ANALYSIS OF STELLAR PHOTOSPHERES DAVID F. GRAY University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface to the first edition Preface to the
THE OBSERVATION AND ANALYSIS OF STELLAR PHOTOSPHERES DAVID F. GRAY University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface to the first edition Preface to the
OGLE-TR-56. Guillermo Torres, Maciej Konacki, Dimitar D. Sasselov and Saurabh Jha INTRODUCTION
 OGLE-TR-56 Guillermo Torres, Maciej Konacki, Dimitar D. Sasselov and Saurabh Jha Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Caltech, Department of Geological and Planetary Sciences University of California
OGLE-TR-56 Guillermo Torres, Maciej Konacki, Dimitar D. Sasselov and Saurabh Jha Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Caltech, Department of Geological and Planetary Sciences University of California
Using Gravity to Measure the Mass of a Star
 STScI Newsletter Vol. 34 Issue 02 Using Gravity to Measure the Mass of a Star Abstract Kailash C. Sahu, ksahu[at]stsci.edu In a reprise of the famous 1919 solar eclipse experiment that confirmed Einstein's
STScI Newsletter Vol. 34 Issue 02 Using Gravity to Measure the Mass of a Star Abstract Kailash C. Sahu, ksahu[at]stsci.edu In a reprise of the famous 1919 solar eclipse experiment that confirmed Einstein's
Eclipsing Binary Star studies: Present and future
 Eclipsing Binary Star studies: Present and future P. G. iarchos Department of Astrophysics, Astronomy and Mechanics, ational and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Greece Abstract The importance of Eclipsing
Eclipsing Binary Star studies: Present and future P. G. iarchos Department of Astrophysics, Astronomy and Mechanics, ational and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Greece Abstract The importance of Eclipsing
Characterization of the exoplanet host stars. Exoplanets Properties of the host stars. Characterization of the exoplanet host stars
 Characterization of the exoplanet host stars Exoplanets Properties of the host stars Properties of the host stars of exoplanets are derived from a combination of astrometric, photometric, and spectroscopic
Characterization of the exoplanet host stars Exoplanets Properties of the host stars Properties of the host stars of exoplanets are derived from a combination of astrometric, photometric, and spectroscopic
Discovery of a deep, low mass ratio overcontact binary GSC
 Research in Astron. Astrophys. 2014 Vol. X No. XX, 000 000 http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics Discovery of a deep, low mass ratio overcontact
Research in Astron. Astrophys. 2014 Vol. X No. XX, 000 000 http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics Discovery of a deep, low mass ratio overcontact
How to Understand Stars Chapter 17 How do stars differ? Is the Sun typical? Location in space. Gaia. How parallax relates to distance
 How to Understand Stars Chapter 7 How do stars differ? Is the Sun typical? Image of Orion illustrates: The huge number of stars Colors Interstellar gas Location in space Two dimensions are easy measure
How to Understand Stars Chapter 7 How do stars differ? Is the Sun typical? Image of Orion illustrates: The huge number of stars Colors Interstellar gas Location in space Two dimensions are easy measure
Terrestrial Planet (and Life) Finder. AST 309 part 2: Extraterrestrial Life
 Terrestrial Planet (and Life) Finder AST 309 part 2: Extraterrestrial Life The Drake Equation: N = N * f pl n hab f L f C f T L/T Stars? Planets? Habitable Origin Complex Intelligence, Lifetime planets?
Terrestrial Planet (and Life) Finder AST 309 part 2: Extraterrestrial Life The Drake Equation: N = N * f pl n hab f L f C f T L/T Stars? Planets? Habitable Origin Complex Intelligence, Lifetime planets?
Observed Properties of Stars - 2 ASTR 2120 Sarazin
 Observed Properties of Stars - 2 ASTR 2120 Sarazin Properties Location Distance Speed Radial velocity Proper motion Luminosity, Flux Magnitudes Magnitudes Hipparchus 1) Classified stars by brightness,
Observed Properties of Stars - 2 ASTR 2120 Sarazin Properties Location Distance Speed Radial velocity Proper motion Luminosity, Flux Magnitudes Magnitudes Hipparchus 1) Classified stars by brightness,
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 17. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 17 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 17 Measuring the Stars Units of Chapter 17 17.1 The Solar Neighborhood 17.2 Luminosity and Apparent Brightness 17.3 Stellar
Lecture Outlines Chapter 17 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 17 Measuring the Stars Units of Chapter 17 17.1 The Solar Neighborhood 17.2 Luminosity and Apparent Brightness 17.3 Stellar
Physical and geometrical parameters of CVBS XI: Cou 1511 (HIP 12552)
 Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics PAPER Physical and geometrical parameters of CVBS XI: Cou 1511 (HIP 12552) Recent citations - Stellar parameters of the two binary systems: HIP 14075 and HIP 14230
Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics PAPER Physical and geometrical parameters of CVBS XI: Cou 1511 (HIP 12552) Recent citations - Stellar parameters of the two binary systems: HIP 14075 and HIP 14230
Today in Astronomy 142: observations of stars
 Today in Astronomy 142: observations of stars What do we know about individual stars?! Determination of stellar luminosity from measured flux and distance Magnitudes! Determination of stellar surface temperature
Today in Astronomy 142: observations of stars What do we know about individual stars?! Determination of stellar luminosity from measured flux and distance Magnitudes! Determination of stellar surface temperature
CCD astrometry and instrumental V photometry of visual double stars,
 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS MAY I 1999, PAGE 525 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 136, 525 529 (1999) CCD astrometry and instrumental V photometry of visual double stars, V. Differential measurements
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS MAY I 1999, PAGE 525 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 136, 525 529 (1999) CCD astrometry and instrumental V photometry of visual double stars, V. Differential measurements
Binary Stars. Jean-Louis Halbwachs Strasbourg Observatory. Summary
 Binary Stars Jean-Louis Halbwachs Strasbourg Observatory Summary 1. The double star zoo : visual binaries (wide and orbital), astrometric b., spectroscopic b., eclipsing b.. General description and physical
Binary Stars Jean-Louis Halbwachs Strasbourg Observatory Summary 1. The double star zoo : visual binaries (wide and orbital), astrometric b., spectroscopic b., eclipsing b.. General description and physical
The Gaia Mission. Coryn Bailer-Jones Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg, Germany. ISYA 2016, Tehran
 The Gaia Mission Coryn Bailer-Jones Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg, Germany ISYA 2016, Tehran What Gaia should ultimately achieve high accuracy positions, parallaxes, proper motions e.g.
The Gaia Mission Coryn Bailer-Jones Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg, Germany ISYA 2016, Tehran What Gaia should ultimately achieve high accuracy positions, parallaxes, proper motions e.g.
Stellar distances and velocities. ASTR320 Wednesday January 24, 2018
 Stellar distances and velocities ASTR320 Wednesday January 24, 2018 Special public talk this week: Mike Brown, Pluto Killer Wednesday at 7:30pm in MPHY204 Why are stellar distances important? Distances
Stellar distances and velocities ASTR320 Wednesday January 24, 2018 Special public talk this week: Mike Brown, Pluto Killer Wednesday at 7:30pm in MPHY204 Why are stellar distances important? Distances
Indirect Methods: gravitational perturbation of the stellar motion. Exoplanets Doppler method
 Indirect Methods: gravitational perturbation of the stellar motion Exoplanets The reflex motion of the star is proportional to M p /M * This introduces an observational bias that favours the detection
Indirect Methods: gravitational perturbation of the stellar motion Exoplanets The reflex motion of the star is proportional to M p /M * This introduces an observational bias that favours the detection
Extrasolar Transiting Planets: Detection and False Positive Rejection
 4 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Extrasolar Transiting Planets: Detection and False Positive Rejection Willie Torres Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Young Planetary Systems Workshop
4 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Extrasolar Transiting Planets: Detection and False Positive Rejection Willie Torres Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Young Planetary Systems Workshop
HD Transits HST/STIS First Transiting Exo-Planet. Exoplanet Discovery Methods. Paper Due Tue, Feb 23. (4) Transits. Transits.
 Paper Due Tue, Feb 23 Exoplanet Discovery Methods (1) Direct imaging (2) Astrometry position (3) Radial velocity velocity Seager & Mallen-Ornelas 2003 ApJ 585, 1038. "A Unique Solution of Planet and Star
Paper Due Tue, Feb 23 Exoplanet Discovery Methods (1) Direct imaging (2) Astrometry position (3) Radial velocity velocity Seager & Mallen-Ornelas 2003 ApJ 585, 1038. "A Unique Solution of Planet and Star
Light Curve Analysis of GSC and GSC
 Light Curve Analysis of GSC 2750-0054 and GSC 03208-02644 M. M. Elkhateeb,2 and M. I. Nouh,2 E-mail: abdo_nouh@hotmail.com Physics Department, College of Science, Northern Border University, Arar, Saudi
Light Curve Analysis of GSC 2750-0054 and GSC 03208-02644 M. M. Elkhateeb,2 and M. I. Nouh,2 E-mail: abdo_nouh@hotmail.com Physics Department, College of Science, Northern Border University, Arar, Saudi
(a) B-V 6 V. (b) B-V
 721 TOWARDS AN IMPROVED MODEL OF THE GALAXY Johan Holmberg 1, Chris Flynn 2, Lennart Lindegren 1 1 Lund Observatory, Box 43, SE-22100 Lund, Sweden 2 Tuorla Observatory, Vaisalantie 20, FI-21500 Piikkio,
721 TOWARDS AN IMPROVED MODEL OF THE GALAXY Johan Holmberg 1, Chris Flynn 2, Lennart Lindegren 1 1 Lund Observatory, Box 43, SE-22100 Lund, Sweden 2 Tuorla Observatory, Vaisalantie 20, FI-21500 Piikkio,
Techniques for direct imaging of exoplanets
 Techniques for direct imaging of exoplanets Aglaé Kellerer Institute for Astronomy, Hawaii 1. Where lies the challenge? 2. Contrasts required for ground observations? 3. Push the contrast limit Recycle!
Techniques for direct imaging of exoplanets Aglaé Kellerer Institute for Astronomy, Hawaii 1. Where lies the challenge? 2. Contrasts required for ground observations? 3. Push the contrast limit Recycle!
So What is Speckle Interferometry Good For, Anyway?
 So What is Speckle Interferometry Good For, Anyway? Bill Hartkopf Brian Mason 8/16/2005 1 So What is Speckle An older (but not the oldest!), much simpler form of interferometry than you ve been hearing
So What is Speckle Interferometry Good For, Anyway? Bill Hartkopf Brian Mason 8/16/2005 1 So What is Speckle An older (but not the oldest!), much simpler form of interferometry than you ve been hearing
676 come of one century of ground-based parallax work. Since then only very few additions entered our data base. It contains 1973 nearby systems (alto
 675 THE IMPACT OF HIPPARCOS ON THE CATALOGUE OF NEARBY STARS: THE STELLAR LUMINOSITY FUNCTION AND LOCAL KINEMATICS H. Jahrei, R. Wielen Astronomisches Rechen-Institut, Monchhofstrae 12 { 14, D{69120 Heidelberg,
675 THE IMPACT OF HIPPARCOS ON THE CATALOGUE OF NEARBY STARS: THE STELLAR LUMINOSITY FUNCTION AND LOCAL KINEMATICS H. Jahrei, R. Wielen Astronomisches Rechen-Institut, Monchhofstrae 12 { 14, D{69120 Heidelberg,
7. BINARY STARS (ZG: 12; CO: 7, 17)
 7. BINARY STARS (ZG: 12; CO: 7, 17) most stars are members of binary systems or multiple systems (triples, quadruples, quintuplets,...) orbital period distribution: P orb = 11 min to 10 6 yr the majority
7. BINARY STARS (ZG: 12; CO: 7, 17) most stars are members of binary systems or multiple systems (triples, quadruples, quintuplets,...) orbital period distribution: P orb = 11 min to 10 6 yr the majority
Radio timing observations of the pulsar by Kaspi et al. (1994) have
 TIMING OBSERVATIONS OF THE SMC BINARY PSR J0045?7319 V. M. KASPI IPAC/Caltech/Jet Propulsion Laboratory Pasadena, CA, USA 91125 R. N. MANCHESTER AND M. BAILES ATNF/CSIRO Epping, Australia AND J. F. BELL
TIMING OBSERVATIONS OF THE SMC BINARY PSR J0045?7319 V. M. KASPI IPAC/Caltech/Jet Propulsion Laboratory Pasadena, CA, USA 91125 R. N. MANCHESTER AND M. BAILES ATNF/CSIRO Epping, Australia AND J. F. BELL
 251 BINARY STAR MASSES FROM HIPPARCOS S. Soderhjelm 1, L. Lindegren 1, M.A.C. Perryman 2 1 Lund Observatory, Box 43, SE-221 00 Lund, Sweden 2 Astrophysics Division, ESTEC, 2200AG Noordwijk, The Netherlands
251 BINARY STAR MASSES FROM HIPPARCOS S. Soderhjelm 1, L. Lindegren 1, M.A.C. Perryman 2 1 Lund Observatory, Box 43, SE-221 00 Lund, Sweden 2 Astrophysics Division, ESTEC, 2200AG Noordwijk, The Netherlands
Structure & Evolution of Stars 1
 Structure and Evolution of Stars Lecture 2: Observational Properties Distance measurement Space velocities Apparent magnitudes and colours Absolute magnitudes and luminosities Blackbodies and temperatures
Structure and Evolution of Stars Lecture 2: Observational Properties Distance measurement Space velocities Apparent magnitudes and colours Absolute magnitudes and luminosities Blackbodies and temperatures
Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol. 2 (2002), No. 5, 474{480 Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics Ghost Images in Schmidt CCD Photometry Bin Yan
 Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol. 2 (2002), No. 5, 474{480 Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics Ghost Images in Schmidt CCD Photometry Bin Yang 1 2?, Jin Zhu 1 and Yu-Ying Song 2 3 1 National Astronomical
Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol. 2 (2002), No. 5, 474{480 Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics Ghost Images in Schmidt CCD Photometry Bin Yang 1 2?, Jin Zhu 1 and Yu-Ying Song 2 3 1 National Astronomical
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 20 Apr 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 20 Apr 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 20 Apr 2012](/thumbs/94/121771759.jpg) Physical Parameters of the Visually Close Binary Systems Hip70973 and Hip72479 Mashhoor Al-Wardat A,B A Physics Department, Yarmouk University, P.O.B. 566 Irbid, 21163 Jordan B Department of Physics, Al-Hussein
Physical Parameters of the Visually Close Binary Systems Hip70973 and Hip72479 Mashhoor Al-Wardat A,B A Physics Department, Yarmouk University, P.O.B. 566 Irbid, 21163 Jordan B Department of Physics, Al-Hussein
