The 2 Icecube PeV events [A. ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
|
|
|
- Adam Bryan Haynes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The 2 Icecube PeV events [A. Schuhkraft@NOW2012 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
2 The 2 Icecube PeV events [A. Schuhkraft@NOW2012 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
3 The 2 Icecube PeV events [A. Schuhkraft@NOW2012 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
4 The 2 Icecube PeV events [A. Schuhkraft@NOW2012 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
5 The 2 Icecube PeV events [A. Schuhkraft@NOW2012 ] Comments: event rate of cosmogenic neutrinos in PeV range is 0 event rate due to Glashow resonance is 0 energies 1.1 PeV and 1.3 PeV below Glashow resonance unlikely cosmogenic, rather diffuse extragalactic flux Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
6 Acceleration in a Monte Carlo framework Bell s microscopic picture: random walk + advection flow x(t + t) = x(t) + l 0 + v 2 tϑ(r sh r)e r Bohm diffusion: step size l0 = R L energy gain, if shock is crossed ξ = 4 3c (v 2 v 1 ) = v sh /c stop, if t > tmax or r > r esc Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
7 Acceleration in a Monte Carlo framework Bell s microscopic picture: random walk + advection flow x(t + t) = x(t) + l 0 + v 2 tϑ(r sh r)e r Bohm diffusion: step size l0 = R L energy gain, if shock is crossed ξ = 4 3c (v 2 v 1 ) = v sh /c stop, if t > tmax or r > r esc Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
8 Acceleration in a Monte Carlo framework Bell s microscopic picture: random walk + advection flow x(t + t) = x(t) + l 0 + v 2 tϑ(r sh r)e r Bohm diffusion: step size l0 = R L energy gain, if shock is crossed ξ = 4 3c (v 2 v 1 ) = v sh /c stop, if t > tmax or r > r esc Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
9 Acceleration in a Monte Carlo framework Bell s microscopic picture: random walk + advection flow x(t + t) = x(t) + l 0 + v 2 tϑ(r sh r)e r Bohm diffusion: step size l0 = R L energy gain, if shock is crossed ξ = 4 3c (v 2 v 1 ) = v sh /c stop, if t > tmax or r > r esc easy to include: time-dependence of vsh,b,... interactions: production of multi-particle states using e.g. QGSJET Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
10 Time-dependent framework: Proton flux [MK, Ostapchenko, Tomàs 10, 11 ] 1 model 1 model 2 E 2 F p 10-1 up down total E (ev) Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
11 Time-dependent framework: Antiproton ratio F - p / F p+p A B A+B E (ev) Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
12 Time-dependent framework: Antiproton ratio F - p / F p+p A B A+B E (ev) component A: p produced in acceleration zone; component B: p produced downstream Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
13 Time-dependent framework: Antiproton ratio F - p / F p+p A B A+B E (ev) component A: p produced in acceleration zone; component B: p produced downstream A is flatter: dn/de(a) E 1 but dn/de(a + B) E 2 Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
14 Antimatter ratios from SNRs [MK, Ostapchenko, Tomàs 10, 11 ] F x - / F x+x e + /(e + +e - ) model 1 model 2 p/(p+p) E (ev) Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
15 (Hadronic) Photons and neutrinos from Tycho: p 2 J(p) [TeV m -2 s -1 ] gammas neutrinos E [ev] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
16 (Hadronic) Photons and neutrinos from Tycho: p 2 J(p) [TeV m -2 s -1 ] gammas neutrinos E [ev] SNR produce neutrinos with energies up to PeV I γ (E) I ν (E) Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
17 Tycho observations by VERITAS Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
18 CR diffusion close to source, E = 10PeV, t = 2000yr S Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
19 CR diffusion close to source, E = 10PeV, t = 7000yr S Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
20 CR diffusion close to source, E = 10PeV, t = 500yr S Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
21 Filamentary CR diffusion close to source: [Giacinti, MK, Semikoz 12 ] Explanation: CRs scatter on modes with kr L 1 fast modes with kr L 1: irrelevant slow modes with kr L 1: act as regular, uniform field B 0 propagation along B 0 is faster than perpendicular Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
22 Filamentary CR diffusion close to source: [Giacinti, MK, Semikoz 12 ] Explanation: CRs scatter on modes with kr L 1 fast modes with kr L 1: irrelevant slow modes with kr L 1: act as regular, uniform field B 0 propagation along B 0 is faster than perpendicular Why not seen earlier in simulations? too large scales, l l max, considered anisotropy vanishes averaging over field realizations anisotropy vanishes for random start positions Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
23 E = 100 TeV 1 PeV 10 PeV t = 500 yr 2000 yr 7000 yr S S S S S S S S S 0 Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
24 Calculation of diffusion tensor: inject N particles at x = 0 in one single realization b Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
25 Calculation of diffusion tensor: inject N particles at x = 0 in one single realization b calculate D (b) ij = 1 N N a=1 x (a) i x (a) j 2t Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
26 Calculation of diffusion tensor: inject N particles at x = 0 in one single realization b calculate D (b) ij = 1 N N a=1 x (a) i x (a) j 2t diagonalizes D (b) ij, determine eigenvalues d(b) i Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
27 Calculation of diffusion tensor: inject N particles at x = 0 in one single realization b calculate D (b) ij = 1 N N a=1 x (a) i x (a) j 2t diagonalizes D (b) ij, determine eigenvalues d(b) i average the ordered eigenvalues, d (b) 1 < d (b) 2 < d (b) 3, over the M realizations, d i = 1 M d (b) i M b=1 Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
28 Eigenvalues of D ij = x i x j /(2t) for E = ev D(1PeV) (cm 2 /s) 1e+29 1e+28 d 3 d 2 d 1D Time (kyr) Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
29 Eigenvalues of D ij = x i x j /(2t) for E = ev D(1PeV) (cm 2 /s) 1e+29 1e+28 d 3 d 2 d 1D Time (kyr) asymptotic value is 4 smaller than Galprop value Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
30 Transition time to standard diffusion: 1e+30 1e+30 1e+30 D(10PeV) (cm 2 /s) 1e+29 1e+29 1e+28 (b) d 1e+28 3 (b) d 2 (b) d 1 1e+27 1e+27 D (b) Time (kyr) Time (kyr) D(1PeV) (cm 2 /s) D(100TeV) (cm 2 /s) 1e+29 1e+28 1e Time (kyr) t 10 4 yrs (l max /150 pc) β (E/1 PeV) γ with β 2 and γ = for Kolmogorov turbulence and B rms = 4µG. Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
31 Comparison CR density vs. photon flux irregular gamma-ray halos as tracker of CR density Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
32 Average intensity I(E) of Galactic CRs precise measurements by PAMELA, soon AMS-02 Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
33 Average intensity I(E) of Galactic CRs precise measurements by PAMELA, soon AMS-02 local measurements I(x, E) may deviate from average: solar wind local sources Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
34 Average intensity I(E) of Galactic CRs precise measurements by PAMELA, soon AMS-02 local measurements I(x, E) may deviate from average: solar wind local sources reconstruct I(E) using gamma-rays from molecular clouds, dn γ de γ Emax E γ de dn CR de dσ pp γ (E, E γ ) de γ Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
35 Average intensity I(E) of Galactic CRs precise measurements by PAMELA, soon AMS-02 local measurements I(x, E) may deviate from average: solar wind local sources reconstruct I(E) using gamma-rays from molecular clouds, dn γ de γ Emax E γ de dn CR de dσ pp γ (E, E γ ) de γ ill-posed problem, fit instead physically motivated trial functions (broken) power-laws Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
36 Neronov, Semikoz and Taylor 2012: single power-law I(T) T α does not reproduce 2 GeV break of I γ Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
37 Neronov, Semikoz and Taylor 2012: single power-law I(T) T α does not reproduce 2 GeV break of I γ best-fit: broken power-law in T, breaks at 10 and 200 GeV Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
38 Neronov, Semikoz and Taylor 2012: single power-law I(T) T α does not reproduce 2 GeV break of I γ best-fit: broken power-law in T, breaks at 10 and 200 GeV physical explanation? 200 GeV: end of solar modulation 10 GeV: change in D(E) [Blasi, Amato, Serpico 12 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
39 How good are photon FF? QGSJET vs. SIBYLL [MK, Ostapchenko 12 ] π -1 x E dσ/dx F (mb) p + p π 0 at 400 GeV/c π -1 x E dσ/dx F (mb) 10 1 p + p η at 400 GeV/c x F x F Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
40 How good are photon FF? QGSJET, SIBYLL, Kamae E γ dσ/de γ (mb) 10 2 p + p γ at 50 GeV p + p γ at 5 TeV p + p γ at 500 TeV x E x E x E Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
41 How good are Fragmentation Functions? there are differences: we recommend Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
42 How good are Fragmentation Functions? there are differences: we recommend Kamae FF used by NST works well up 50 GeV Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
43 How good are Fragmentation Functions? there are differences: we recommend Kamae FF used by NST works well up 50 GeV in integrated results spectral differences washed out E γ 2 dn γ /de γ (rel. units) E γ (GeV) Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
44 How good are Fragmentation Functions? there are differences: we recommend Kamae FF used by NST works well up 50 GeV in integrated results spectral differences washed out E γ 2 dn γ /de γ (rel. units) E γ (GeV) Kamae FF not reason for bump Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
45 Gammas from CR power-laws in T vs. p E_kin-spectrum p_lab-spectrum E_lab-spectrum e-05 1e Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
46 Gammas from CR power-laws in T vs. p E_kin-spectrum p_lab-spectrum E_lab-spectrum e-05 1e most of the bump comes from power-law in T DSA predicts power-law in p [Bell 77 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
47 Gammas from CR power-laws in T vs. p E 2 Flux [GeV/cm 2 s] 1e E [GeV] red: I p 2.85 (our FF) blue: I p 2.85, break to I p 1 at 3 GeV (our FF) Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
48 Gammas from CR power-laws in T vs. p E 2 Flux [GeV/cm 2 s] 1e E [GeV] red: I p 2.85 (our FF) blue: I p 2.85, break to I p 1 at 3 GeV (our FF) explanation: break in D(E) around 3 GeV as suggested by radio data caused by CR damping standard solar modulation Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
49 Summary Intensity I(p) of sea CRs important for CR physics, DM searches. determination via GMC requires additional input controversial solutions minimal: power-law in I(p) supports DSA, consistent with standard solar modulations, break 3 GeV Anisotropic diffusion on scales l < l max leads to irregular CR and gamma halos Icecube events: consistency between diffuse νµ and cosmogenic analysis unlikely cosmogenic, rather diffuse extragalactic flux; galactic possible? Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
50 Summary Intensity I(p) of sea CRs important for CR physics, DM searches. determination via GMC requires additional input controversial solutions minimal: power-law in I(p) supports DSA, consistent with standard solar modulations, break 3 GeV Anisotropic diffusion on scales l < l max leads to irregular CR and gamma halos Icecube events: consistency between diffuse νµ and cosmogenic analysis unlikely cosmogenic, rather diffuse extragalactic flux; galactic possible? Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
51 Summary Intensity I(p) of sea CRs important for CR physics, DM searches. determination via GMC requires additional input controversial solutions minimal: power-law in I(p) supports DSA, consistent with standard solar modulations, break 3 GeV Anisotropic diffusion on scales l < l max leads to irregular CR and gamma halos Icecube events: consistency between diffuse νµ and cosmogenic analysis unlikely cosmogenic, rather diffuse extragalactic flux; galactic possible? Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
Antimatter from Supernova Remnants
 Antimatter from Supernova Remnants Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim with S. Ostapchenko, R. Tomàs - PAMELA anomaly )) )+ φ(e + ) / (φ(e + 0.4 0.3 0.2 Positron fraction φ(e 0.1 0.02 Muller & Tang 1987
Antimatter from Supernova Remnants Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim with S. Ostapchenko, R. Tomàs - PAMELA anomaly )) )+ φ(e + ) / (φ(e + 0.4 0.3 0.2 Positron fraction φ(e 0.1 0.02 Muller & Tang 1987
The Escape Model. Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim. with G.Giacinti, O.Kalashev, A.Nernov, V.Savchenko, D.Semikoz
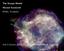 The Escape Model Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] with G.Giacinti, O.Kalashev, A.Nernov, V.Savchenko, D.Semikoz Introduction Outline Outline of the talk 1 Introduction Results on Composition 2 Escape
The Escape Model Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] with G.Giacinti, O.Kalashev, A.Nernov, V.Savchenko, D.Semikoz Introduction Outline Outline of the talk 1 Introduction Results on Composition 2 Escape
Charged Cosmic Rays and Neutrinos
 Charged Cosmic Rays and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline of the talk 1 Introduction talk by F. Halzen 2 SNRs as Galactic CR sources 3 Extragalactic CRs transition anisotropies
Charged Cosmic Rays and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline of the talk 1 Introduction talk by F. Halzen 2 SNRs as Galactic CR sources 3 Extragalactic CRs transition anisotropies
Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos
 Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline Plan of the lectures: Cosmic rays Galactic cosmic rays Basic observations Acceleration Supernova remnants Problems
Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline Plan of the lectures: Cosmic rays Galactic cosmic rays Basic observations Acceleration Supernova remnants Problems
Antimatter spectra from a time-dependent modeling of supernova remnants
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Antimatter spectra from a time-dependent modeling of supernova remnants To cite this article: M Kachelrieß et al 2010 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 259 012092 View the article
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Antimatter spectra from a time-dependent modeling of supernova remnants To cite this article: M Kachelrieß et al 2010 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 259 012092 View the article
TeV Cosmic Ray Anisotropies at Various Angular Scales
 TeV Cosmic Ray Anisotropies at Various Angular Scales Gwenael Giacinti University of Oxford, Clarendon Laboratory Based on : GG & G.Sigl GG, M.Kachelriess, D.Semikoz Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 071101(2012)
TeV Cosmic Ray Anisotropies at Various Angular Scales Gwenael Giacinti University of Oxford, Clarendon Laboratory Based on : GG & G.Sigl GG, M.Kachelriess, D.Semikoz Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 071101(2012)
Propagation of TeV PeV Cosmic Rays in the Galactic Magnetic Field
 Propagation of TeV PeV Cosmic Rays in the Galactic Magnetic Field Gwenael Giacinti Clarendon Laboratory, University of Oxford In collaboration with : GG & G.Sigl / Based on : Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 071101(2012)
Propagation of TeV PeV Cosmic Rays in the Galactic Magnetic Field Gwenael Giacinti Clarendon Laboratory, University of Oxford In collaboration with : GG & G.Sigl / Based on : Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 071101(2012)
TeV gamma-rays from UHECR sources 22 radio log10(e /ev ) 16 photon horizon γγ e + e CMB 14 IR kpc 10kpc 100kpc M pc Virgo 10M pc 100M pc G
 Gamma-rays from CR sources Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] TeV gamma-rays from UHECR sources 22 radio 20 18 log10(e /ev ) 16 photon horizon γγ e + e CMB 14 IR 12 10 kpc 10kpc 100kpc M pc Virgo 10M
Gamma-rays from CR sources Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] TeV gamma-rays from UHECR sources 22 radio 20 18 log10(e /ev ) 16 photon horizon γγ e + e CMB 14 IR 12 10 kpc 10kpc 100kpc M pc Virgo 10M
Diffusive shock acceleration with regular electric fields
 Diffusive shock acceleration with regular electric fields V.N.Zirakashvili Pushkov Institute of Terrestrial Magnetism, Ionosphere and Radiowave Propagation, Russian Academy of Sciences (IZMIRAN), 142190
Diffusive shock acceleration with regular electric fields V.N.Zirakashvili Pushkov Institute of Terrestrial Magnetism, Ionosphere and Radiowave Propagation, Russian Academy of Sciences (IZMIRAN), 142190
Galactic Neutrinos. Michael Kachelrieß. NTNU, Trondheim
 Galactic Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline of the talk 1 Introduction Observations Cascade limit and implications 2 Neutrinos from the Galactic CR sea Galactic plane
Galactic Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline of the talk 1 Introduction Observations Cascade limit and implications 2 Neutrinos from the Galactic CR sea Galactic plane
Multi-Messenger Astonomy with Cen A?
 Multi-Messenger Astonomy with Cen A? Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Outline of the talk 1 Introduction 2 Dawn of charged particle astronomy? Expectations vs. Auger data Effects of cluster fields
Multi-Messenger Astonomy with Cen A? Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Outline of the talk 1 Introduction 2 Dawn of charged particle astronomy? Expectations vs. Auger data Effects of cluster fields
Astroparticle Physics. Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim
 Astroparticle Physics Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Plan of the lectures: Today: High energy astrophysics Cosmic rays Observations Acceleration, possible sources High energy photons and neutrinos
Astroparticle Physics Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Plan of the lectures: Today: High energy astrophysics Cosmic rays Observations Acceleration, possible sources High energy photons and neutrinos
CRs THE THREE OF CR ISSUE! B amplifica2on mechanisms. Diffusion Mechanisms. Sources. Theory vs data. Oversimplifica8on of the Nature
 THE THREE OF CR ISSUE! ACCELERATION CRs TRANSPORT Sources B amplifica2on mechanisms Evidences Diffusion Mechanisms Contribu2ons Theory vs data Oversimplifica8on of the Nature Not accurate systema8cs SNAPSHOT!
THE THREE OF CR ISSUE! ACCELERATION CRs TRANSPORT Sources B amplifica2on mechanisms Evidences Diffusion Mechanisms Contribu2ons Theory vs data Oversimplifica8on of the Nature Not accurate systema8cs SNAPSHOT!
Seeing the moon shadow in CRs
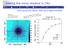 Seeing the moon shadow in CRs and using the Earth field as a spectrometer Tibet III Amenomori et al. arxiv:0810.3757 see also ARGO-YBJ results Bartoli et. al, arxiv:1107.4887 Milargo: 100% coverage r owe
Seeing the moon shadow in CRs and using the Earth field as a spectrometer Tibet III Amenomori et al. arxiv:0810.3757 see also ARGO-YBJ results Bartoli et. al, arxiv:1107.4887 Milargo: 100% coverage r owe
News from High-Energy Cosmic Rays and Neutrinos. Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim
 News from High-Energy Cosmic Rays and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline of the talk 1 Introduction Is progress slow? Results on Composition γ s and ν s as CR secondaries
News from High-Energy Cosmic Rays and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline of the talk 1 Introduction Is progress slow? Results on Composition γ s and ν s as CR secondaries
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 24 Jul 2012
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 24 Jul 2012 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 24 Jul 2012](/thumbs/87/95449334.jpg) Deriving the cosmic ray spectrum from gamma-ray observations M. Kachelrieß and S. Ostapchenko,2 Institutt for fysikk, NTNU, Trondheim, Norway and 2 D. V. Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics, Moscow
Deriving the cosmic ray spectrum from gamma-ray observations M. Kachelrieß and S. Ostapchenko,2 Institutt for fysikk, NTNU, Trondheim, Norway and 2 D. V. Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics, Moscow
Gamma rays from supernova remnants in clumpy environments.! Stefano Gabici APC, Paris
 Gamma rays from supernova remnants in clumpy environments!! Stefano Gabici APC, Paris Overview of the talk Galactic cosmic rays Gamma rays from supernova remnants Hadronic or leptonic? The role of gas
Gamma rays from supernova remnants in clumpy environments!! Stefano Gabici APC, Paris Overview of the talk Galactic cosmic rays Gamma rays from supernova remnants Hadronic or leptonic? The role of gas
Topics. 1. Towards a unified picture of CRs production and propagation: 2. AMS-02 good candidates for Dark Matter space search
 Nicolò Masi Bologna University and INFN - 31 May 2016 Topics 1. Towards a unified picture of CRs production and propagation: Astrophysical uncertainties with GALPROP Local Interstellar Spectra: AMS-02
Nicolò Masi Bologna University and INFN - 31 May 2016 Topics 1. Towards a unified picture of CRs production and propagation: Astrophysical uncertainties with GALPROP Local Interstellar Spectra: AMS-02
Cosmic Accelerators. 2. Pulsars, Black Holes and Shock Waves. Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford
 Cosmic Accelerators 2. Pulsars, Black Holes and Shock Waves Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford Particle Acceleration Unipolar Induction Stochastic Acceleration V ~ Ω Φ I ~ V / Z 0 Z 0 ~100Ω P ~ V I ~ V 2 /Z
Cosmic Accelerators 2. Pulsars, Black Holes and Shock Waves Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford Particle Acceleration Unipolar Induction Stochastic Acceleration V ~ Ω Φ I ~ V / Z 0 Z 0 ~100Ω P ~ V I ~ V 2 /Z
Cosmic Ray Astronomy. Qingling Ni
 Cosmic Ray Astronomy Qingling Ni What is Cosmic Ray? Mainly charged particles: protons (hydrogen nuclei)+helium nuclei+heavier nuclei What s the origin of them? What happened during their propagation?
Cosmic Ray Astronomy Qingling Ni What is Cosmic Ray? Mainly charged particles: protons (hydrogen nuclei)+helium nuclei+heavier nuclei What s the origin of them? What happened during their propagation?
Dark Matter in the Universe
 Dark Matter in the Universe NTNU Trondheim [] Experimental anomalies: WMAP haze: synchrotron radiation from the GC Experimental anomalies: WMAP haze: synchrotron radiation from the GC Integral: positron
Dark Matter in the Universe NTNU Trondheim [] Experimental anomalies: WMAP haze: synchrotron radiation from the GC Experimental anomalies: WMAP haze: synchrotron radiation from the GC Integral: positron
Supernova Remnants and Cosmic. Rays
 Stars: Their Life and Afterlife Supernova Remnants and Cosmic 68 th Rays Brian Humensky Series, Compton Lecture #5 November 8, 2008 th Series, Compton Lecture #5 Outline Evolution of Supernova Remnants
Stars: Their Life and Afterlife Supernova Remnants and Cosmic 68 th Rays Brian Humensky Series, Compton Lecture #5 November 8, 2008 th Series, Compton Lecture #5 Outline Evolution of Supernova Remnants
Subir Sarkar
 Trinity 2016 Oxford ² The universe observed ² Relativistic world models ² Reconstructing the thermal history ² Big bang nucleosynthesis ² Dark matter: astrophysical observations ² Dark matter: relic particles
Trinity 2016 Oxford ² The universe observed ² Relativistic world models ² Reconstructing the thermal history ² Big bang nucleosynthesis ² Dark matter: astrophysical observations ² Dark matter: relic particles
² The universe observed ² Relativistic world models ² Reconstructing the thermal history ² Big bang nucleosynthesis ² Dark matter: astrophysical
 ² The universe observed ² Relativistic world models ² Reconstructing the thermal history ² Big bang nucleosynthesis ² Dark matter: astrophysical observations ² Dark matter: relic particles ² Dark matter:
² The universe observed ² Relativistic world models ² Reconstructing the thermal history ² Big bang nucleosynthesis ² Dark matter: astrophysical observations ² Dark matter: relic particles ² Dark matter:
Particle Acceleration at Supernova Remnants and Supernovae
 Particle Acceleration at Supernova Remnants and Supernovae Gwenael Giacinti 1 & Tony Bell 2 1 MPIK, Heidelberg 2 Clarendon Laboratory, University of Oxford Giacinti & Bell, MNRAS 449, 3693 (2015); Bell,
Particle Acceleration at Supernova Remnants and Supernovae Gwenael Giacinti 1 & Tony Bell 2 1 MPIK, Heidelberg 2 Clarendon Laboratory, University of Oxford Giacinti & Bell, MNRAS 449, 3693 (2015); Bell,
The role of ionization in the shock acceleration theory
 The role of ionization in the shock acceleration theory Giovanni Morlino INAF - L.go E. Fermi 5, Firenze, Italy E-mail: morlino@arcetri.astro.it We study the acceleration of heavy nuclei at SNR shocks
The role of ionization in the shock acceleration theory Giovanni Morlino INAF - L.go E. Fermi 5, Firenze, Italy E-mail: morlino@arcetri.astro.it We study the acceleration of heavy nuclei at SNR shocks
Lower bound on the extragalactic magnetic field
 Lower bound on the extragalactic magnetic field Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Dolag, MK, Ostapchenko, Tomàs 10 Neronov, Semikoz, MK, Ostapchenko, Elyiv 10 Introduction Mean free path of photons
Lower bound on the extragalactic magnetic field Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Dolag, MK, Ostapchenko, Tomàs 10 Neronov, Semikoz, MK, Ostapchenko, Elyiv 10 Introduction Mean free path of photons
Difficulties of Star-forming Galaxies as the Source of IceCube Neutrinos. Takahiro Sudoh (UTokyo)
 Difficulties of Star-forming Galaxies as the Source of IceCube Neutrinos Takahiro Sudoh (UTokyo) IceCube Neutrino Astrophysical TeV - PeV neutrinos Isotropic arrival direction extragalactic origin? No
Difficulties of Star-forming Galaxies as the Source of IceCube Neutrinos Takahiro Sudoh (UTokyo) IceCube Neutrino Astrophysical TeV - PeV neutrinos Isotropic arrival direction extragalactic origin? No
High energy radiation from molecular clouds (illuminated by a supernova remnant
 High energy radiation from molecular clouds (illuminated by a supernova remnant A. Marcowith (L.P.T.A. Montpellier) collaboration with S. Gabici (D.I.A.S.) 1 Outlook Introduction: Scientific interests.
High energy radiation from molecular clouds (illuminated by a supernova remnant A. Marcowith (L.P.T.A. Montpellier) collaboration with S. Gabici (D.I.A.S.) 1 Outlook Introduction: Scientific interests.
Gamma-ray and neutrino diffuse emissions of the Galaxy above the TeV
 Gamma-ray and neutrino diffuse emissions of the Galaxy above the TeV (with spatial dependent CR transport) D. Grasso (INFN, Pisa) with D. Gaggero, A. Marinelli, A. Urbano, M. Valli IceCube recent results
Gamma-ray and neutrino diffuse emissions of the Galaxy above the TeV (with spatial dependent CR transport) D. Grasso (INFN, Pisa) with D. Gaggero, A. Marinelli, A. Urbano, M. Valli IceCube recent results
UHECRs sources and the Auger data
 UHECRs sources and the Auger data M. Kachelrieß Institutt for fysikk, NTNU Trondheim, Norway I review the evidence for a correlation of the arrival directions of UHECRs observed by the Pierre Auger Observatory
UHECRs sources and the Auger data M. Kachelrieß Institutt for fysikk, NTNU Trondheim, Norway I review the evidence for a correlation of the arrival directions of UHECRs observed by the Pierre Auger Observatory
a cosmic- ray propagation and gamma-ray code
 GALPROP: a cosmic- ray propagation and gamma-ray code A. Strong, MPE Garching Tools for SUSY, Annecy, June 28 2006 The basis: cosmic-ray production & propagation in the Galaxy intergalactic space HALO
GALPROP: a cosmic- ray propagation and gamma-ray code A. Strong, MPE Garching Tools for SUSY, Annecy, June 28 2006 The basis: cosmic-ray production & propagation in the Galaxy intergalactic space HALO
99 Years from Discovery : What is our current picture on Cosmic Rays? #6 How cosmic rays travel to Earth? Presented by Nahee Park
 99 Years from Discovery : What is our current picture on Cosmic Rays? #6 How cosmic rays travel to Earth? Presented by Nahee Park #5 How do Cosmic Rays gain their energy? I. Acceleration mechanism of CR
99 Years from Discovery : What is our current picture on Cosmic Rays? #6 How cosmic rays travel to Earth? Presented by Nahee Park #5 How do Cosmic Rays gain their energy? I. Acceleration mechanism of CR
The Galactic diffuse gamma ray emission in the energy range 30 TeV 3 PeV
 The Galactic diffuse gamma ray emission in the energy range 30 TeV 3 PeV Mount Rainier by Will Christiansen Silvia Vernetto & Paolo Lipari 35th ICRC 12-20 July 2017 - Busan - South Korea Gamma ray astronomy
The Galactic diffuse gamma ray emission in the energy range 30 TeV 3 PeV Mount Rainier by Will Christiansen Silvia Vernetto & Paolo Lipari 35th ICRC 12-20 July 2017 - Busan - South Korea Gamma ray astronomy
Gamma ray emission from supernova remnant/molecular cloud associations
 Gamma ray emission from supernova remnant/molecular cloud associations Stefano Gabici APC, Paris stefano.gabici@apc.univ-paris7.fr The Origin of galactic Cosmic Rays Facts: the spectrum is (ALMOST) a single
Gamma ray emission from supernova remnant/molecular cloud associations Stefano Gabici APC, Paris stefano.gabici@apc.univ-paris7.fr The Origin of galactic Cosmic Rays Facts: the spectrum is (ALMOST) a single
Kathrin Egberts Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg for the H.E.S.S. Collaboration
 Kathrin Egberts Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg for the H.E.S.S. Collaboration Outline The H.E.S.S. Experiment The H.E.S.S. Electron Measurement Gamma-Ray Background Hadronic Background
Kathrin Egberts Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg for the H.E.S.S. Collaboration Outline The H.E.S.S. Experiment The H.E.S.S. Electron Measurement Gamma-Ray Background Hadronic Background
Particle Acceleration in the Universe
 Particle Acceleration in the Universe Hiroyasu Tajima Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology on behalf of SLAC GLAST team June 7, 2006 SLAC DOE HEP Program
Particle Acceleration in the Universe Hiroyasu Tajima Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology on behalf of SLAC GLAST team June 7, 2006 SLAC DOE HEP Program
Revue sur le rayonnement cosmique
 Revue sur le rayonnement cosmique Vladimir Ptuskin IZMIRAN Galactic wind termination shock GRB N cr ~ 10-10 cm -3 - total number density w cr ~ 1.5 ev/cm 3 - energy density E max ~ 3x10 20 ev - max. detected
Revue sur le rayonnement cosmique Vladimir Ptuskin IZMIRAN Galactic wind termination shock GRB N cr ~ 10-10 cm -3 - total number density w cr ~ 1.5 ev/cm 3 - energy density E max ~ 3x10 20 ev - max. detected
Questions 1pc = 3 ly = km
 Cosmic Rays Historical hints Primary Cosmic Rays: - Cosmic Ray Energy Spectrum - Composition - Origin and Propagation - The knee region and the ankle Secondary CRs: -shower development - interactions Detection:
Cosmic Rays Historical hints Primary Cosmic Rays: - Cosmic Ray Energy Spectrum - Composition - Origin and Propagation - The knee region and the ankle Secondary CRs: -shower development - interactions Detection:
Cosmic ray escape from supernova remnants
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 82, 760 c SAIt 2011 Memorie della Cosmic ray escape from supernova remnants Stefano Gabici Astroparticule et Cosmologie (APC), CNRS, Université Paris 7 Denis Diderot, Paris, France, e-mail:
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 82, 760 c SAIt 2011 Memorie della Cosmic ray escape from supernova remnants Stefano Gabici Astroparticule et Cosmologie (APC), CNRS, Université Paris 7 Denis Diderot, Paris, France, e-mail:
High and low energy puzzles in the AMS-02 positron fraction results
 High and low energy puzzles in the AMS-02 positron fraction results Dario Grasso (INFN, Pisa) D. Gaggero (SISSA), L.Maccione (MPI, Munich), C. Evoli(DESY), G. Di Bernardo (Göteborg) AMS-02 positron fraction
High and low energy puzzles in the AMS-02 positron fraction results Dario Grasso (INFN, Pisa) D. Gaggero (SISSA), L.Maccione (MPI, Munich), C. Evoli(DESY), G. Di Bernardo (Göteborg) AMS-02 positron fraction
Cosmic Ray Transport (in the Galaxy) Luke Drury. Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies Institiúid Ard-Léinn Bhaile Átha Cliath
 Cosmic Ray Transport (in the Galaxy) Luke Drury Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies Institiúid Ard-Léinn Bhaile Átha Cliath 1 A few disclaimers and preliminary remarks! Not my main field of research
Cosmic Ray Transport (in the Galaxy) Luke Drury Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies Institiúid Ard-Léinn Bhaile Átha Cliath 1 A few disclaimers and preliminary remarks! Not my main field of research
Recent Results from the KASCADE-Grande Data Analysis
 Recent Results from the KASCADE-Grande Data Analysis Donghwa Kang for the KASCADE-Grande Collaboration Karlsruhe Institute of Technology 20 th ISVHECRI 21 25 May 2018, Nagoya, Japan Status & Prospect KASCADE
Recent Results from the KASCADE-Grande Data Analysis Donghwa Kang for the KASCADE-Grande Collaboration Karlsruhe Institute of Technology 20 th ISVHECRI 21 25 May 2018, Nagoya, Japan Status & Prospect KASCADE
Evidence of Stochastic Acceleration of Secondary. Antiprotons by Supernova Remnants! Ilias Cholis, 08/09/2017
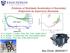 C [ ] -4 Evidence of Stochastic Acceleration of Secondary 2.2 1.0 2.0 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 C k p p Φ /Φ ratio fit Antiprotons by Supernova Remnants! 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0-6 - 1 k [ GV ] -1 AMS-02 PAMELA Fermi
C [ ] -4 Evidence of Stochastic Acceleration of Secondary 2.2 1.0 2.0 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 C k p p Φ /Φ ratio fit Antiprotons by Supernova Remnants! 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0-6 - 1 k [ GV ] -1 AMS-02 PAMELA Fermi
COSMIC RAY ACCELERATION
 COSMIC RAY ACCELERATION LECTURE 2: ADVANCED TOPICS P. BLASI INAF/OSSERVATORIO ASTROFISICO DI ARCETRI & GRAN SASSO SCIENCE INSTITUTE, CENTER FOR ADVANCED STUDIES SPSAS-HighAstro, 29-30 May 2917, Sao Paulo,
COSMIC RAY ACCELERATION LECTURE 2: ADVANCED TOPICS P. BLASI INAF/OSSERVATORIO ASTROFISICO DI ARCETRI & GRAN SASSO SCIENCE INSTITUTE, CENTER FOR ADVANCED STUDIES SPSAS-HighAstro, 29-30 May 2917, Sao Paulo,
Accelera'on of cosmic rays and gamma ray emission from supernova remnants in the Galaxy
 Accelera'on of cosmic rays and gamma ray emission from supernova remnants in the Galaxy P. Cristofari h9p:// arxiv.org/pdf/13022150v1.pdf S. Gabici, R. Terrier, S. Casanova, E. Parizot The local cosmic
Accelera'on of cosmic rays and gamma ray emission from supernova remnants in the Galaxy P. Cristofari h9p:// arxiv.org/pdf/13022150v1.pdf S. Gabici, R. Terrier, S. Casanova, E. Parizot The local cosmic
Neutrino Oscillations and Astroparticle Physics (5) John Carr Centre de Physique des Particules de Marseille (IN2P3/CNRS) Pisa, 10 May 2002
 Neutrino Oscillations and Astroparticle Physics (5) John Carr Centre de Physique des Particules de Marseille (IN2P3/CNRS) Pisa, 10 May 2002 n High Energy Astronomy Multi-Messanger Astronomy Cosmic Rays
Neutrino Oscillations and Astroparticle Physics (5) John Carr Centre de Physique des Particules de Marseille (IN2P3/CNRS) Pisa, 10 May 2002 n High Energy Astronomy Multi-Messanger Astronomy Cosmic Rays
Search for diffuse cosmic neutrino fluxes with the ANTARES detector
 Search for diffuse cosmic neutrino fluxes with the ANTARES detector Vladimir Kulikovskiy The ANTARES Collaboration 1 Overview ANTARES description Full sky searches Special region searches Fermi bubbles
Search for diffuse cosmic neutrino fluxes with the ANTARES detector Vladimir Kulikovskiy The ANTARES Collaboration 1 Overview ANTARES description Full sky searches Special region searches Fermi bubbles
Ultra- high energy cosmic rays
 Ultra- high energy cosmic rays Tiina Suomijärvi Institut de Physique Nucléaire Université Paris Sud, Orsay, IN2P3/CNRS, France Atélier CTA, IAP, Paris, 30-31 June 2014 Outline Pierre Auger Observatory:
Ultra- high energy cosmic rays Tiina Suomijärvi Institut de Physique Nucléaire Université Paris Sud, Orsay, IN2P3/CNRS, France Atélier CTA, IAP, Paris, 30-31 June 2014 Outline Pierre Auger Observatory:
Cosmic ray electrons from here and there (the Galactic scale)
 Cosmic ray electrons from here and there (the Galactic scale) Julien Lavalle Department of Theoretical Physics Torino University and INFN Outline: (i) local electrons (ii) comments on synchrotron [based
Cosmic ray electrons from here and there (the Galactic scale) Julien Lavalle Department of Theoretical Physics Torino University and INFN Outline: (i) local electrons (ii) comments on synchrotron [based
PeV Neutrinos from Star-forming Regions. Hajime Takami KEK, JSPS Fellow
 PeV Neutrinos from Star-forming Regions Hajime Takami KEK, JSPS Fellow Outline 0. Basic requirements for PeV neutrinos. Review on cosmogenic neutrinos for the PeV neutrinos. PeV neutrinos from Star-forming
PeV Neutrinos from Star-forming Regions Hajime Takami KEK, JSPS Fellow Outline 0. Basic requirements for PeV neutrinos. Review on cosmogenic neutrinos for the PeV neutrinos. PeV neutrinos from Star-forming
Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Rays propagation II
 Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Rays propagation II The March 6th lecture discussed the energy loss processes of protons, nuclei and gamma rays in interactions with the microwave background. Today I will give
Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Rays propagation II The March 6th lecture discussed the energy loss processes of protons, nuclei and gamma rays in interactions with the microwave background. Today I will give
Cosmic Pevatrons in the Galaxy
 Cosmic Pevatrons in the Galaxy Jonathan Arons UC Berkeley Cosmic Rays Acceleration in Supernova Remnants Pulsar Wind Nebulae Cosmic rays Cronin, 1999, RMP, 71, S165 J(E) = AE! p, p " 2.7,1GeV < E
Cosmic Pevatrons in the Galaxy Jonathan Arons UC Berkeley Cosmic Rays Acceleration in Supernova Remnants Pulsar Wind Nebulae Cosmic rays Cronin, 1999, RMP, 71, S165 J(E) = AE! p, p " 2.7,1GeV < E
Neutrino Flavor Ratios Modified by Cosmic Ray Secondary- acceleration
 Neutrino Flavor Ratios Modified by Cosmic Ray Secondary- acceleration ref.) NK & Ioka 2015, PRD accepted (arxiv:1504.03417) Norita Kawanaka (Univ. of Tokyo) Kunihito Ioka (KEK/Sokendai) TeV Particle Astrophysics
Neutrino Flavor Ratios Modified by Cosmic Ray Secondary- acceleration ref.) NK & Ioka 2015, PRD accepted (arxiv:1504.03417) Norita Kawanaka (Univ. of Tokyo) Kunihito Ioka (KEK/Sokendai) TeV Particle Astrophysics
Blazars as the Astrophysical Counterparts of the IceCube Neutrinos
 Blazars as the Astrophysical Counterparts of the IceCube Neutrinos Maria Petropoulou Department of Physics & Astronomy, Purdue University, West Lafayette, USA Einstein Fellows Symposium Harvard-Smithsonian
Blazars as the Astrophysical Counterparts of the IceCube Neutrinos Maria Petropoulou Department of Physics & Astronomy, Purdue University, West Lafayette, USA Einstein Fellows Symposium Harvard-Smithsonian
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays I
 Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays I John Linsley (PRL 10 (1963) 146) reports on the detection in Vulcano Ranch of an air shower of energy above 1020 ev. Problem: the microwave background radiation is discovered
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays I John Linsley (PRL 10 (1963) 146) reports on the detection in Vulcano Ranch of an air shower of energy above 1020 ev. Problem: the microwave background radiation is discovered
Status KASCADE-Grande. April 2007 Aspen workshop on cosmic ray physics Andreas Haungs 1
 Status KASCADE-Grande April 2007 Aspen workshop on cosmic ray physics Andreas Haungs 1 Cosmic Rays around the knee(s) Astrophysical questions for this energy range: (1 st ) knee Knee position Composition
Status KASCADE-Grande April 2007 Aspen workshop on cosmic ray physics Andreas Haungs 1 Cosmic Rays around the knee(s) Astrophysical questions for this energy range: (1 st ) knee Knee position Composition
Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants
 1 Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants with VERITAS Tülün Ergin (U. of Massachusetts Amherst, MA) on behalf of the VERITAS Collaboration (http://veritas.sao.arizona.edu) 2 Contents Supernova Remnants
1 Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants with VERITAS Tülün Ergin (U. of Massachusetts Amherst, MA) on behalf of the VERITAS Collaboration (http://veritas.sao.arizona.edu) 2 Contents Supernova Remnants
Neutrino Flavor Ratios as a Probe of Cosmic Ray Accelerators( 予定 ) Norita Kawanaka (UTokyo) Kunihito Ioka (KEK, Sokendai)
 Neutrino Flavor Ratios as a Probe of Cosmic Ray Accelerators( 予定 ) Norita Kawanaka (UTokyo) Kunihito Ioka (KEK, Sokendai) Introduction High Energy Neutrinos are produced in Cosmic Ray Accelerators (GRBs,
Neutrino Flavor Ratios as a Probe of Cosmic Ray Accelerators( 予定 ) Norita Kawanaka (UTokyo) Kunihito Ioka (KEK, Sokendai) Introduction High Energy Neutrinos are produced in Cosmic Ray Accelerators (GRBs,
High-energy cosmic rays
 High-energy cosmic rays And their acceleration Tom Gaisser 1 Outline Sources and acceleration mechanism End of the galactic cosmic-ray spectrum Transition to extra-galactic population Key questions Tom
High-energy cosmic rays And their acceleration Tom Gaisser 1 Outline Sources and acceleration mechanism End of the galactic cosmic-ray spectrum Transition to extra-galactic population Key questions Tom
MULTIMESSENGER APPROACH:Using the Different Messengers
 MULTIMESSENGER APPROACH:Using the Different Messengers PROTONS p NUCLEI (A,Z) NEUTRINOS νµ PHOTONS LECTURE PLAN: 1) COSMIC RAYS- proton interactions with photons, composition, nuclei interactions with
MULTIMESSENGER APPROACH:Using the Different Messengers PROTONS p NUCLEI (A,Z) NEUTRINOS νµ PHOTONS LECTURE PLAN: 1) COSMIC RAYS- proton interactions with photons, composition, nuclei interactions with
New results from the AMS experiment on the International Space Station. Henning Gast RWTH Aachen
 New results from the AMS experiment on the International Space Station Henning Gast RWTH Aachen 1 Questions to AMS-02: Are there galaxies made of anti-matter in the Universe? What is the nature of Dark
New results from the AMS experiment on the International Space Station Henning Gast RWTH Aachen 1 Questions to AMS-02: Are there galaxies made of anti-matter in the Universe? What is the nature of Dark
High energy neutrino signals from NS-NS mergers
 High energy neutrino signals from NS-NS mergers He Gao 高鹤 University of Nevada Las Vegas Collaborators: Bing Zhang, Xue-Feng Wu & Zi-Gao Dai 2013-05-08 Multi-Messenger Workshop @ KIAA EM signals for a
High energy neutrino signals from NS-NS mergers He Gao 高鹤 University of Nevada Las Vegas Collaborators: Bing Zhang, Xue-Feng Wu & Zi-Gao Dai 2013-05-08 Multi-Messenger Workshop @ KIAA EM signals for a
On (shock. shock) acceleration. Martin Lemoine. Institut d Astrophysique d. CNRS, Université Pierre & Marie Curie
 On (shock ( shock) acceleration of ultrahigh energy cosmic rays Martin Lemoine Institut d Astrophysique d de Paris CNRS, Université Pierre & Marie Curie 1 Acceleration Hillas criterion log 10 (B/1 G) 15
On (shock ( shock) acceleration of ultrahigh energy cosmic rays Martin Lemoine Institut d Astrophysique d de Paris CNRS, Université Pierre & Marie Curie 1 Acceleration Hillas criterion log 10 (B/1 G) 15
Cosmic Ray acceleration at radio supernovae: perspectives for the Cerenkov Telescope Array
 Cosmic Ray acceleration at radio supernovae: perspectives for the Cerenkov Telescope Array A.MARCOWITH ( LABORATOIRE UNIVERS ET PARTICULES DE MONTPELLIER, FRANCE) & M.RENAUD, V.TATISCHEFF, V.DWARKADAS
Cosmic Ray acceleration at radio supernovae: perspectives for the Cerenkov Telescope Array A.MARCOWITH ( LABORATOIRE UNIVERS ET PARTICULES DE MONTPELLIER, FRANCE) & M.RENAUD, V.TATISCHEFF, V.DWARKADAS
Remnants and Pulsar Wind
 High Energy Supernova Remnants and Pulsar Wind Nebulae F. Giordano Dipartimento Interateneo di Fisica and INFN Sez. Bari For the Fermi-LAT Collaboration Scineghe 2010 The Afterlife of a star IC443 Crab
High Energy Supernova Remnants and Pulsar Wind Nebulae F. Giordano Dipartimento Interateneo di Fisica and INFN Sez. Bari For the Fermi-LAT Collaboration Scineghe 2010 The Afterlife of a star IC443 Crab
Production of Secondary Cosmic Rays in Supernova Remnants
 Production of Secondary Cosmic Rays in Supernova Remnants E. G. Berezhko, Yu. G. Shafer Institute of Cosmophysical Research and Aeronomy, 31 Lenin Ave., 677891 Yakutsk, Russia E-mail: ksenofon@ikfia.sbras.ru
Production of Secondary Cosmic Rays in Supernova Remnants E. G. Berezhko, Yu. G. Shafer Institute of Cosmophysical Research and Aeronomy, 31 Lenin Ave., 677891 Yakutsk, Russia E-mail: ksenofon@ikfia.sbras.ru
Review of direct measurements of cosmic rays. Sources of Galactic cosmic rays APC, Paris - December 7-9, 2016
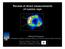 Review of direct measurements of cosmic rays Sources of Galactic cosmic rays APC, Paris - December 7-9, 2016 CR astrophуsics main problems Sources? - Accelerators? The basic paradigm of CR acceleration
Review of direct measurements of cosmic rays Sources of Galactic cosmic rays APC, Paris - December 7-9, 2016 CR astrophуsics main problems Sources? - Accelerators? The basic paradigm of CR acceleration
Constraining primordial magnetic fields with observations
 Constraining primordial magnetic fields with observations Kerstin Kunze (University of Salamanca and IUFFyM) KK PRD 83 (2011) 023006; PRD 85 (2012) 083004; PRD 87 (2013) 103005; PRD 89 (2014) 103016, arxiv:1703.03650
Constraining primordial magnetic fields with observations Kerstin Kunze (University of Salamanca and IUFFyM) KK PRD 83 (2011) 023006; PRD 85 (2012) 083004; PRD 87 (2013) 103005; PRD 89 (2014) 103016, arxiv:1703.03650
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 3 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 3 Jan 2019 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 3 Jan 2019](/thumbs/93/111951917.jpg) EPJ Web of Conferences will be set by the publisher DOI: will be set by the publisher c Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2019 arxiv:1901.00223v2 [astro-ph.he] 3 Jan 2019 Towards an anagraphical
EPJ Web of Conferences will be set by the publisher DOI: will be set by the publisher c Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2019 arxiv:1901.00223v2 [astro-ph.he] 3 Jan 2019 Towards an anagraphical
Strong collisionless shocks are important sources of TeV particles. Evidence for TeV ions is less direct but very strong.
 Collisionless Shocks in 12 minutes or less Don Ellison, North Carolina State Univ. Andrei Bykov, Ioffe Institute, St. Petersburg Don Warren, RIKEN, Tokyo Strong collisionless shocks are important sources
Collisionless Shocks in 12 minutes or less Don Ellison, North Carolina State Univ. Andrei Bykov, Ioffe Institute, St. Petersburg Don Warren, RIKEN, Tokyo Strong collisionless shocks are important sources
PHY326/426 Dark Matter and the Universe. Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev F9b, Tel.:
 PHY326/426 Dark Matter and the Universe Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev F9b, Tel.: 0114 2224531 v.kudryavtsev@sheffield.ac.uk Indirect searches for dark matter WIMPs Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev Dark Matter and the Universe
PHY326/426 Dark Matter and the Universe Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev F9b, Tel.: 0114 2224531 v.kudryavtsev@sheffield.ac.uk Indirect searches for dark matter WIMPs Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev Dark Matter and the Universe
Cosmic ray studies at the Yakutsk EAS array: energy spectrum and mass composition
 Cosmic ray studies at the Yakutsk EAS array: energy spectrum and mass composition S. P. Knurenko 1 and A. Sabourov 2 1 s.p.knurenko@ikfia.ysn.ru, 2 tema@ikfia.ysn.ru Yu. G. Shafer Institute of cosmophysical
Cosmic ray studies at the Yakutsk EAS array: energy spectrum and mass composition S. P. Knurenko 1 and A. Sabourov 2 1 s.p.knurenko@ikfia.ysn.ru, 2 tema@ikfia.ysn.ru Yu. G. Shafer Institute of cosmophysical
1939 Baade&Zwicky 1949 Fermi 1977 (Krymski; Axford; Bell; Blandford & Ostriker
 46 1939 Baade&Zwicky 1949 Fermi 1977 (Krymski; Axford; Bell; Blandford & Ostriker From Aharonian et al. 2011 From Letessier-Sevon & Stanev 2011 Fermi 2-year sky map Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. knee ankle (b)
46 1939 Baade&Zwicky 1949 Fermi 1977 (Krymski; Axford; Bell; Blandford & Ostriker From Aharonian et al. 2011 From Letessier-Sevon & Stanev 2011 Fermi 2-year sky map Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. knee ankle (b)
A New View of the High-Energy γ-ray Sky with the Fermi Telescope
 A New View of the High-Energy γ-ray Sky with the Fermi Telescope Aurelien Bouvier KIPAC/SLAC, Stanford University On behalf of the Fermi collaboration SNOWPAC, 2010 The Fermi observatory Launch: June 11
A New View of the High-Energy γ-ray Sky with the Fermi Telescope Aurelien Bouvier KIPAC/SLAC, Stanford University On behalf of the Fermi collaboration SNOWPAC, 2010 The Fermi observatory Launch: June 11
Spatial Profile of the Emission from Pulsar Wind Nebulae with steady-state 1D Modeling
 Spatial Profile of the Emission from Pulsar Wind Nebulae with steady-state 1D Modeling Wataru Ishizaki ( Department of Physics, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo ) Abstract The pulsar
Spatial Profile of the Emission from Pulsar Wind Nebulae with steady-state 1D Modeling Wataru Ishizaki ( Department of Physics, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo ) Abstract The pulsar
Astrophysical issues in the cosmic ray e spectra: Have we seen dark matter annihilation?
 Astrophysical issues +/ in the cosmic ray e spectra: Have we seen dark matter annihilation? Julien Lavalle Department of Theoretical Physics University of Torino and INFN Collab: Torino: R. Lineros, F.
Astrophysical issues +/ in the cosmic ray e spectra: Have we seen dark matter annihilation? Julien Lavalle Department of Theoretical Physics University of Torino and INFN Collab: Torino: R. Lineros, F.
A few grams of matter in a bright world
 A few grams of matter in a bright world Benjamin Rouillé d Orfeuil (LAL) Fellow Collaborators: D. Allard, C. Lachaud & E. Parizot (APC) A. V. Olinto (University of Chicago) February 12 th 2013 LAL All
A few grams of matter in a bright world Benjamin Rouillé d Orfeuil (LAL) Fellow Collaborators: D. Allard, C. Lachaud & E. Parizot (APC) A. V. Olinto (University of Chicago) February 12 th 2013 LAL All
On the GCR/EGCR transition and UHECR origin
 UHECR 2014 13 15 October 2014 / Springdale (Utah; USA) On the GCR/EGCR transition and UHECR origin Etienne Parizot 1, Noémie Globus 2 & Denis Allard 1 1. APC Université Paris Diderot France 2. Tel Aviv
UHECR 2014 13 15 October 2014 / Springdale (Utah; USA) On the GCR/EGCR transition and UHECR origin Etienne Parizot 1, Noémie Globus 2 & Denis Allard 1 1. APC Université Paris Diderot France 2. Tel Aviv
Latest results and perspectives of the KASCADE-Grande EAS facility
 Latest results and perspectives of the KASCADE-Grande EAS facility 29/6-2/7/2010, Nantes, France Andreas Haungs 1 Motivation KASCADE-Grande Knee EeV PeV g-eg? Radio?! KASCADE 10 15-10 17 ev: Origin of
Latest results and perspectives of the KASCADE-Grande EAS facility 29/6-2/7/2010, Nantes, France Andreas Haungs 1 Motivation KASCADE-Grande Knee EeV PeV g-eg? Radio?! KASCADE 10 15-10 17 ev: Origin of
Galactic Sources with Milagro and HAWC. Jordan Goodman for the HAWC and Milagro Collaborations
 Galactic Sources with Milagro and HAWC Jordan Goodman for the HAWC and Milagro Collaborations Snowpack 2010 Milagro and HAWC Milagro was a first generation wide-field gamma-ray telescope: Proposed in 1990
Galactic Sources with Milagro and HAWC Jordan Goodman for the HAWC and Milagro Collaborations Snowpack 2010 Milagro and HAWC Milagro was a first generation wide-field gamma-ray telescope: Proposed in 1990
The air-shower experiment KASCADE-Grande
 The air-shower experiment KASCADE-Grande Andreas Haungs KASCADE-Grande 1 Cosmic Rays around the knee(s) galactic origin of CR EeV PeV Knee 2 nd Knee? Ralph Engel, 2004 KASCADE 1995-2009 -Grande 2003-2009
The air-shower experiment KASCADE-Grande Andreas Haungs KASCADE-Grande 1 Cosmic Rays around the knee(s) galactic origin of CR EeV PeV Knee 2 nd Knee? Ralph Engel, 2004 KASCADE 1995-2009 -Grande 2003-2009
IceCube. francis halzen. why would you want to build a a kilometer scale neutrino detector? IceCube: a cubic kilometer detector
 IceCube francis halzen why would you want to build a a kilometer scale neutrino detector? IceCube: a cubic kilometer detector the discovery (and confirmation) of cosmic neutrinos from discovery to astronomy
IceCube francis halzen why would you want to build a a kilometer scale neutrino detector? IceCube: a cubic kilometer detector the discovery (and confirmation) of cosmic neutrinos from discovery to astronomy
Hadronic Interaction Studies with ARGO-YBJ
 Hadronic Interaction Studies with ARGO-YBJ Ivan De Mitri University of Salento and Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare Lecce, Italy On behalf of the ARGO-YBJ Collaboration Hadron-Hadron & Cosmic Ray
Hadronic Interaction Studies with ARGO-YBJ Ivan De Mitri University of Salento and Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare Lecce, Italy On behalf of the ARGO-YBJ Collaboration Hadron-Hadron & Cosmic Ray
> News < AMS-02 will be launched onboard the Shuttle Endeavour On May 2nd 2:33 P.M. from NASA Kennedy space center!
 > News < Anti-matter, dark matter measurement By measuring the cosmic rays (Mainly electron, positron, proton, anti-proton and light nuclei) AMS-02 will be launched onboard the Shuttle Endeavour On May
> News < Anti-matter, dark matter measurement By measuring the cosmic rays (Mainly electron, positron, proton, anti-proton and light nuclei) AMS-02 will be launched onboard the Shuttle Endeavour On May
magnetic reconnection as the cause of cosmic ray excess from the heliospheric tail
 magnetic reconnection as the cause of cosmic ray excess from the heliospheric tail Paolo Desiati 1,2 & Alexander Lazarian 2 1 IceCube Research Center 2 Department of Astronomy University of Wisconsin -
magnetic reconnection as the cause of cosmic ray excess from the heliospheric tail Paolo Desiati 1,2 & Alexander Lazarian 2 1 IceCube Research Center 2 Department of Astronomy University of Wisconsin -
Confinement of CR in Dark Matter relic clumps
 Confinement of CR in Dark Matter relic clumps University Karlsruhe and SINP Moscow State University W.de Boer University Karlsruhe 1 Dark Matter in Universe and the Galaxy Strong evidences for DM existence:
Confinement of CR in Dark Matter relic clumps University Karlsruhe and SINP Moscow State University W.de Boer University Karlsruhe 1 Dark Matter in Universe and the Galaxy Strong evidences for DM existence:
Astroparticle Physics with IceCube
 Astroparticle Physics with IceCube Nick van Eijndhoven nickve.nl@gmail.com http://w3.iihe.ac.be f or the IceCube collaboration Vrije Universiteit Brussel - IIHE(ULB-VUB) Pleinlaan 2, B-1050 Brussel, Belgium
Astroparticle Physics with IceCube Nick van Eijndhoven nickve.nl@gmail.com http://w3.iihe.ac.be f or the IceCube collaboration Vrije Universiteit Brussel - IIHE(ULB-VUB) Pleinlaan 2, B-1050 Brussel, Belgium
Cosmic rays and relativistic shock acceleration
 Cosmic rays and relativistic shock acceleration Thank you Athina Meli ECAP Erlangen Center for Astroparticle Physics Friedrich-Alexander Universität Erlangen-Nüremberg Outline Cosmic ray spectrum (non)
Cosmic rays and relativistic shock acceleration Thank you Athina Meli ECAP Erlangen Center for Astroparticle Physics Friedrich-Alexander Universität Erlangen-Nüremberg Outline Cosmic ray spectrum (non)
Effect of the Regular Galactic Magnetic Field on the Propagation of Galactic Cosmic Rays in the Galaxy
 Effect of the Regular Galactic Magnetic Field on the Propagation of Galactic Cosmic Rays in the Galaxy Department of Electrical and Electronic Systems Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Ibaraki
Effect of the Regular Galactic Magnetic Field on the Propagation of Galactic Cosmic Rays in the Galaxy Department of Electrical and Electronic Systems Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Ibaraki
Exploring the Ends of the Rainbow: Cosmic Rays in Star-Forming Galaxies
 Exploring the Ends of the Rainbow: Cosmic Rays in Star-Forming Galaxies Brian Lacki With Todd Thompson, Eliot Quataert, Eli Waxman, Abraham Loeb 21 September 2010 The Cosmic SED Nonthermal Thermal Nonthermal
Exploring the Ends of the Rainbow: Cosmic Rays in Star-Forming Galaxies Brian Lacki With Todd Thompson, Eliot Quataert, Eli Waxman, Abraham Loeb 21 September 2010 The Cosmic SED Nonthermal Thermal Nonthermal
W.R. Webber. New Mexico State University, Astronomy Department, Las Cruces, NM 88003, USA
 A Galactic Cosmic Ray Electron Spectrum at Energies from 2 MeV to 2 TeV That Fits Voyager 5-60 MeV Data at Low Energies and PAMELA and AMS-2 Data at 10 GeV Using an Electron Source Spectrum ~E -2.25 A
A Galactic Cosmic Ray Electron Spectrum at Energies from 2 MeV to 2 TeV That Fits Voyager 5-60 MeV Data at Low Energies and PAMELA and AMS-2 Data at 10 GeV Using an Electron Source Spectrum ~E -2.25 A
Supernovae in stellar clusters as CR pevatrons. Collaborators: D.C.Ellison, P.E.Gladilin, S.M. Osipov
 Supernovae in stellar clusters as CR pevatrons Collaborators: D.C.Ellison, P.E.Gladilin, S.M. Osipov Gamma Ray Spectral Energy Distribu6on: Starburst galaxies Ackermann + 12 A&ARv v.22, p.54, 2014 S.Ohm,
Supernovae in stellar clusters as CR pevatrons Collaborators: D.C.Ellison, P.E.Gladilin, S.M. Osipov Gamma Ray Spectral Energy Distribu6on: Starburst galaxies Ackermann + 12 A&ARv v.22, p.54, 2014 S.Ohm,
A Multimessenger Neutrino Point Source Search with IceCube
 A Multimessenger Neutrino Point Source Search with IceCube Mădălina Chera FLC Group Meeting 04.10.2010 Mădălina Chera Overview 1 Introduction to UHE Cosmic Rays and Neutrino Astrophysics; 2 Motivation
A Multimessenger Neutrino Point Source Search with IceCube Mădălina Chera FLC Group Meeting 04.10.2010 Mădălina Chera Overview 1 Introduction to UHE Cosmic Rays and Neutrino Astrophysics; 2 Motivation
Extremely High Energy Neutrinos
 Extremely High Energy Neutrinos A. Ringwald http://www.desy.de/ ringwald DESY 6 th National Astroparticle Physics Symposium February 3, 2006, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam, Netherlands Extremely high energy
Extremely High Energy Neutrinos A. Ringwald http://www.desy.de/ ringwald DESY 6 th National Astroparticle Physics Symposium February 3, 2006, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam, Netherlands Extremely high energy
Proton/Helium spectral anomaly and other signatures of diffusive shock acceleration/propagation in/from SNR
 Proton/Helium spectral anomaly and other signatures of diffusive shock acceleration/propagation in/from SNR M. Malkov CASS/UCSD Collaborators: P. Diamond, R. Sagdeev 1 Supernova Remnant Shocks- Cosmic
Proton/Helium spectral anomaly and other signatures of diffusive shock acceleration/propagation in/from SNR M. Malkov CASS/UCSD Collaborators: P. Diamond, R. Sagdeev 1 Supernova Remnant Shocks- Cosmic
Magnetic Fields in Supernova Remnants and Pulsar Wind Nebulae: Deductions from X ray (and gamma ray) Observations
 Magnetic Fields in Supernova Remnants and Pulsar Wind Nebulae: Deductions from X ray (and gamma ray) Observations Stephen Reynolds (NC State U) 1. Introduction 2. Determining B in SNRs SED modeling Thin
Magnetic Fields in Supernova Remnants and Pulsar Wind Nebulae: Deductions from X ray (and gamma ray) Observations Stephen Reynolds (NC State U) 1. Introduction 2. Determining B in SNRs SED modeling Thin
EXCESS OF VHE COSMIC RAYS IN THE CENTRAL 100 PC OF THE MILKY WAY. Léa Jouvin, A. Lemière and R. Terrier
 1 EXCESS OF VHE COSMIC RAYS IN THE CENTRAL 100 PC OF THE MILKY WAY Léa Jouvin, A. Lemière and R. Terrier 2 Excess of VHE cosmic rays (CRs) γ-ray count map Matter traced by CS 150 pc After subtracting the
1 EXCESS OF VHE COSMIC RAYS IN THE CENTRAL 100 PC OF THE MILKY WAY Léa Jouvin, A. Lemière and R. Terrier 2 Excess of VHE cosmic rays (CRs) γ-ray count map Matter traced by CS 150 pc After subtracting the
Secondary particles generated in propagation neutrinos gamma rays
 th INT, Seattle, 20 Feb 2008 Ultra High Energy Extragalactic Cosmic Rays: Propagation Todor Stanev Bartol Research Institute Dept Physics and Astronomy University of Delaware Energy loss processes protons
th INT, Seattle, 20 Feb 2008 Ultra High Energy Extragalactic Cosmic Rays: Propagation Todor Stanev Bartol Research Institute Dept Physics and Astronomy University of Delaware Energy loss processes protons
Charged-particle and gamma-ray astronomy: deciphering charged messages from the world s most powerful
 Charged-particle and gamma-ray astronomy: deciphering charged messages from the world s most powerful Charged-particle astronomy coming of age How it is done The sources The signals What we have learned
Charged-particle and gamma-ray astronomy: deciphering charged messages from the world s most powerful Charged-particle astronomy coming of age How it is done The sources The signals What we have learned
