Laboratory Analysis Improves Crankshaft Design
|
|
|
- Octavia O’Brien’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1972 Laboratory Analysis Improves Crankshaft Design L. L. Faulkner Ohio State University J. F. Hamilton Purdue University Follow this and additional works at: Faulkner, L. L. and Hamilton, J. F., "Laboratory Analysis Improves Crankshaft Design" (1972). International Compressor Engineering Conference. Paper This document has been made available through Purdue e-pubs, a service of the Purdue University Libraries. Please contact epubs@purdue.edu for additional information. Complete proceedings may be acquired in print and on CD-ROM directly from the Ray W. Herrick Laboratories at Herrick/Events/orderlit.html
2 LABORATORY ANALYSIS IMPROVES CRANKSHAFT DESIGN LYnn L. Faulkner, Assistant Professor, Dept. of Mech. Engr., The Ohio state University, Columbus, Ohio. James F. Hamilton, Professor of Mechanical Engineering, The Ray W. Herrick Laboratories, Purdue University, Lafayette, Indiana ABSTRACT This paper describes an experimental method of investigating stress concentrations in crankshafts of small reciprocating compressors, the object being to determine operating stresses for selection of materials, shapes of fillets, and geometry of oil holes and grooves. The procedure consisted of determining dynamic operating forces and, by means of experimental stress analysis techniques, stress values were obtained using an equivalent static measurement. An analytical method of calculating the operating stress due to an oil hole in the shaft was developed using results from the experimental stress analysis. With consideration of the oiling system and machining operations, the optimum relocation of the oil hole in a region of lower nominal stress was determined using the mathematical model. INTRODUCTION It is not uncommon to extend mechanical devices to operating conditions beyond which the original design was intended. The result, in many cases, is the occurrence of component failures which previously were not encountered. A design re-analysis is usually necessary which in most cases is more elaborate than the original design of the component, but with the techniques presently available a more useful and optimal design can be achieved. This particular investigation was undertaken to improve the design of a crankshaft from a single cylinder, hermetically-sealed refrigeration compressor. Because of the enclosed construction and the operating requirements, the methods of measuring forces during operation were not available a few decades ago and consequently the original designs were developed using broad guidelines and building a number of proto~ypes. When performance requirements necessitated increased loads, failures began to occur. Figure 1 shows the particular piston-slider-crank mechanism of interest, which is commonly referred to as a "ScotchYoke", and a typical failure. The hole visible at the broken section is part of the shaft oiling system and is easily seen to be a stress concentration area. This work was sponsored by the White Corporation, Gibson Refrigerator Division, Greenville, Michigan. DETERMINATION OF FORCES Before any analytical or experimental investigation of the crankshaft stresses could be made, it was necessary to have some understanding of the forces acting on the crankshaft during compressor operation. It was considered necessary to determine independently: 1. Pressure forces acting on the piston during the compressor cycle. 2. Inertia forces due to reciprocating motion of the piston and connecting mechanism. 3. Frictional forces of the slider-crank mechanism. To determine the pressure forces acting on the piston during the cyclic operation, a crystal pressure transducer was mounted in the cylinder wall with a small opening to the clearance volume. A contact was attached to the crankshaft which completed an electrical circuit once every cycle and produced a signal as an indication of the top dead center position. Instrumentation cables were passed through the hermetic shell by means of seals which enabled the shell to be replaced and operated under normal R-12 pressure and temperature conditions. While operating the compressor at normal conditions, the pressure signal from the transducer was amplified and displayed on an oscilloscope along with the reference timing pulse as shown in Figure 2. The upper trace represents the reference pulse. Notice that since the contact had finite area the response was not a sharp peak. When the compressor was assembled the contact was adjusted so that the midpoint of the trace, which is easily distinguishable, represents the top dead center position. The sweep rate of the oscilloscope was known as well as the speed of the compressor and thus by reference to the top dead center position, the pressures in the cylinder were known in relation to the angular rotation of the crankshaft. The pressure force component was plotted as a function of crank angle in Figure 3. The forces were obtained from a dynamic analysis of the system. Figure 4 is a schematic of the piston- 28
3 slider-crank mechanism with appropriate forces. The reciprocating inertia component, F2, can be determined from = mass x acceleration = Mew2 cos wt where m = mass of piston + slider + pin e = eccentricity of the crankshaft w = rotational speed of the compressor t = time The vertical component of the counterweight inertia (1) (2) was subtracted as a component fore~ It was necessary to include forces in this manner because the yoke was not completely balanced by the counterweight. As written, the relation for F2 can be related directly to the crank angle, 8, with the top dead center position as reference. Using appropriate values for the above quantities, the inertia force was found to be = - 2).2 cos e lbs {)) This component was also plotted in Figure ). When determining friction forces there is usually same question concerning what coefficients of friction to use because of the dependence on surface finish, lubricant, temperature, and "run-in" of the bearing. In this application it was assumed that friction coefficients in the range of,1 to,5 would be appropriate for the sliding contact between the piston and slider. The maximum normal force acting on the slider surface is obtained from the maximum value of pressure and inertia forces which occurs at a crank angle of -4 degrees as indicated in Figure ), As shown in Figure 4, the friction force, f, at the piston-slider interface is always in the horizontal direction and the sum of the pressure and major inertia force is always in the vertical direction. The friction force was obtained by multiplying the normal force component, which in this case is the sum of the pressure and inertia forces, by a coefficient is usually small for well oiled bearings. It was shown by an order of magnitude procedure that the friction force could be neglected without introducing significant errors. The frictional forces at the piston-cylinder interface were also neglected. The total force acting on the crankshaft at the piston end was taken as the sum of the pressure and inertia forces as indicated in Figure ). DEI'ERMINING STRESSES where MY I crx,cry x and y components of stress ~xy shearing stress at radius r M = bending moment Y distance from the neutral axis T torque r radius J = polar moment of inertia I area moment of inertia From the geometry of the crankshaft and from the observed failures it was clear that the maximum ( 6) stress occurred at the oil hole when the piston was in the top dead center region. In this position the pressure forces are near the maximum values as indicated in Figure 3. When the pressure forces become small the oil hole location was such that it was in a region near the neutral axis and therefore the stress was small both at the oil hole and at other positions on the shaft because the load is reduced. It was evident that the stress at oil hole location as the oil hole rotates through 36 was of primary concern in the failure of the crankshaft. From the geometry of the crankshaft the tensile and shearing stresses were obtained from equation 6. The following expressions were obtained for the stresses at the surface of the circular section at the oil hole location as the section rotated with the crankshaft. where cr 17.1F(8) sin (9 - IS I) X ~xy = F(8) (7) F(8) = total force from Figure ) 8 crank angle from top dead center Note that equation 7 is for a solid section and the influence of the oil hole has not been accounted for. The 8 term is included because as the shaft rotates the oil hole changes location in relation to the bending axis. When e ; 9 the oil hole would be located on the bending axis and be in a region of zero stress. For a solid shaft the maximum stress at a particular location is called the principal stress and is a combination of the normal and shearing stresses given by: For a simply supported and loaded solid shaft the tensile and shearing stresses are given by 281
4 2 + +,. 2 xy ( 8) Noting that the maximum values of total force occur for values of 9 of 4 degrees or less, it is easily verified that o- 1 will be in error by less than one percent if the shear stress is neglected. The principal stress of a solid cylindrical shaft without a stress concentration is represented by the relation, o- 1 = 17.1 F(9) sin (9 -I 9 I ) (9) The accuracy of this relation was verified experimentally and will be discussed in the next section. In order to obtain the maximum stress which will occm for a section with a stress concentration it is desirable to determine a stress concentration factor, Kt, defined as maximum stress nominal stress and then crmax = Kt crl Published values for ~ are available for shafts (1) (11) with holes but usually are obtained under idealized conditions: In this particular application the hole was near the fillet and the method of loading was not pure bending as is the case for most published values of shafts with holes. To obtain more accurate stress values, a value for the stress concentration factor for this particular condition was determined experimentally. To allow the shaft to be coated with a strain indicating material and to provide support and loading the compressor casting was machined and a fixture was designed to bolt to the cylinder to allow force to be applied to the piston. A photograph of the test fixture is shown in Figure 5. The load was applied by turning the bolt against a crystal load cell which transmitted the force to the piston and to the crankshaft. The intent was to determine a stress concentration experimentally by applying a dynamically equivalent static load. Several castings were similarly modified to allow experimental values to be obtained for several crank positions. To determine the accuracy of the experimental method a shaft without a stress concentration in the fo~ of the oil hole was coated with birefringent material and loaded statically with a force obtained from Figure 3, for various 9 values. This experimental value was compared with the value obtained from equation 9. The experimental method gave stress values which differed from the calculated by 6 percent for a solid crankshaft without an oil hole. Kt' was established as being equal to 3.6 and the maximum principal stress at the oil hole was found from equation 11 to be o-max = 61 F(6) sin (9 - I e I ) To allow for oil hole locations other than the existing location a factor ~ was introduced as follows: crmax 61 F(9) sin (9 - le! ~ j) (12) (13) The value of ~ then corresponds to the position of the oil hole when the crankshaft is in the e = position. OIL HOLE LOCATION Equation 13 above, along with the plot of force versus crank angle, allows numerical calculations to be made for stress values as functions of crank angle and load for any desired circumferential position of the oil hole. Several proposed oil hole relocations were considered and the stress values as a function of crank angle are shown plotted in Figure 6. From these curves a new oil hole location was selected with consideration for the oil pumpage requirements, and the machining operations required. The hole could not be located where it would interfere with the bearing lubrication and existing manufacturing equipment and methods also limited some proposed positions. The optimal location was selected at 7gD45' leading angle from the existing oil hole position. A number of crankshafts were then machined with the new oil hole location, as shown in Figure 7, and were coated with birefringement material and tested using the static loading fixture as shown in Figure 5. The results of these tests are shown plotted with the dashed line on Figure 6. GONSLUSIONS A dynamically equivalent static investigation is an adequate representation of crankshaft loading and the~tress values did confirm that the original oil hole position had stress values above the endurance limit. Although the stress values in Figure 6 may not be exact due to the order of magnitude analysis on the forces, the percentage decrease in stress can be used directly because identical testing conditions were used. In this particular case an acceptable solution was found from a rather simple static analysis and the amount of improvement could be established with some confidence within the limits established by the bearing lubrication and existing manufacturing methods. Having established the validity of the experimental method, shafts with oil holes were coated and tested to determine the maximum stresses at the oil hole. A value for the stress concentration factor, 282
5 REFERENCES 1. Ially, James W. and Riley, William F., "Experimental Stress Analysis", McGraw-Hill, Faries, Virgil M., "~sign of Machine Elements", The McMillan Company, Hetenyi, M., "Handbook of Experimental stress Analysis", John Wiley and Sons, Lee, George H., "An Introduction to Experimental Stress Analysis", John Wiley and Sons, Peterson, R. W., "Stress Concentration Thlsign Factors", John Wiley and Sons, Ul z :::l a. w (.) a: LL ISO TOTAL FORCE ( F l PRESSURE COMPONENT <F 1 l INERTIA COMPONENT <f2 l CRANK ANGLE (DEGREES l Figure 3. Forces versus crank angle. PISTON Figure l. Scotch Yoke mechanism and a typical failure. SLIDER ~ PRESSURE FORCE INERTIA FORCE F TOTAL FORCE e ECCENTRICITY OF CRANKSHAFT 9 CRANK ANGLE R,R,R REACTION FORCES f' FRICTION FORCES Figure 2. Pressure signal and top dead center reference. Figure 4. Piston-slider-crank mechanism. 283
6 Figure 5. Static loading fixture with coated shaft exposed. Figure 7. Comparison of original and redesigned crankshafts. nz ORIGINAL OIL HOLE LOCATI~N ORIGINAL LOCATION a=o (/) (/) t:: LIJ :::?! a::......j (/)...J ~ LIJ (.) z <{ a:: u :::::> z a:: z a.. w.5 SHAFT WITHOUT HOLE CRANK ANGLE, LO = EXPERIMENTAL VALUES Figure 6. Naximum principal stress v~rsus for various hole locations. crank angle 284
Shape Optimization of Oldham Coupling in Scroll Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 24 Shape Optimization of Oldham Coupling in Scroll Compressor In Hwe Koo LG Electronics
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 24 Shape Optimization of Oldham Coupling in Scroll Compressor In Hwe Koo LG Electronics
Investigation Of The Parameters Affecting Crankshaft And Rotor Interference Fit
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 Investigation Of The Parameters Affecting Crankshaft And Rotor Interference Fit Naz?m
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 Investigation Of The Parameters Affecting Crankshaft And Rotor Interference Fit Naz?m
Measuring Friction Losses Using Accelerometer
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1994 Measuring Friction Losses Using Accelerometer W. Oh GoldStar Company H. Lee GoldStar
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1994 Measuring Friction Losses Using Accelerometer W. Oh GoldStar Company H. Lee GoldStar
Dynamics of the Swash Plate Mechanism
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs nternational Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1984 Dynamics of the Swash Plate Mechanism J. F. Below D. A. Miloslavich Follow this and
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs nternational Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1984 Dynamics of the Swash Plate Mechanism J. F. Below D. A. Miloslavich Follow this and
Study on Flow Characteristics of Oil Viscosity Pump for Refrigerant Compressors
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Study on Flow Characteristics of Oil Viscosity Pump for Refrigerant Compressors Kiyoshi
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Study on Flow Characteristics of Oil Viscosity Pump for Refrigerant Compressors Kiyoshi
Lubrication Analysis on the Profile of Slider in Reciprocating Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1996 Lubrication Analysis on the Profile of Slider in Reciprocating Compressor D. H. Kim
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1996 Lubrication Analysis on the Profile of Slider in Reciprocating Compressor D. H. Kim
Stress Analysis of a Compressor Vane-Spring
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1994 Stress Analysis of a Compressor Vane-Spring K. T. Ooi Nanyang Technological University
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1994 Stress Analysis of a Compressor Vane-Spring K. T. Ooi Nanyang Technological University
Charts for the Dynamic Properties of Counterweights
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1976 Charts for the Dynamic Properties of Counterweights T. C. Scott G. L. Davis Follow
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1976 Charts for the Dynamic Properties of Counterweights T. C. Scott G. L. Davis Follow
Vibro-Acoustic Modelling of Hermetic Reciprocating Compressors
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 Vibro-Acoustic Modelling of Hermetic Reciprocating Compressors L. Gavric CETIM Follow
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 Vibro-Acoustic Modelling of Hermetic Reciprocating Compressors L. Gavric CETIM Follow
Structure Design of a Scroll Compressor Using CAE Analysis
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Structure Design of a Scroll Compressor Using CAE Analysis Byung-Kil Yoo LG Electronics
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Structure Design of a Scroll Compressor Using CAE Analysis Byung-Kil Yoo LG Electronics
New Design Approach for a Scroll Compressor Anti-Rotation Mechanism
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 New Design Approach for a Scroll Compressor Anti-Rotation Mechanism S. Otake Sanden
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 New Design Approach for a Scroll Compressor Anti-Rotation Mechanism S. Otake Sanden
Variable Speed Tri-Rotor Screw Compression Technology
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Variable Speed Tri-Rotor Screw Compression Technology John S. Jacobs United Technologies
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Variable Speed Tri-Rotor Screw Compression Technology John S. Jacobs United Technologies
Dynamics of Compliance Mechanisms Scroll Compressors, Part II: Radial Compliance
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1990 Dynamics of Compliance Mechanisms Scroll Compressors, Part II: Radial Compliance J.
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1990 Dynamics of Compliance Mechanisms Scroll Compressors, Part II: Radial Compliance J.
Frictional Characteristics of Thrust Bearing in Scroll Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2004 Frictional Characteristics of Thrust Bearing in Scroll Compressor Hajime Sato Mitsubishi
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2004 Frictional Characteristics of Thrust Bearing in Scroll Compressor Hajime Sato Mitsubishi
Simple Modeling and Modal Analysis of Reciprocating Compressor Crankshaft System
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2010 Simple Modeling and Modal Analysis of Reciprocating Compressor Crankshaft System Binyan
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2010 Simple Modeling and Modal Analysis of Reciprocating Compressor Crankshaft System Binyan
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each.
 GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
Design and Friction Analysis of the Revolving Vane Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Design and Friction Analysis of the Revolving Vane Compressor Y. L. Teh Nanyang Technological
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Design and Friction Analysis of the Revolving Vane Compressor Y. L. Teh Nanyang Technological
A Study on High Efficiency Wing-Vane Compressor - Part.2: Lubrication Characteristic of The Partial Arc Guide Bearing -
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 016 A Study on High Efficiency Wing-Vane Compressor - Part.: Lubrication Characteristic
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 016 A Study on High Efficiency Wing-Vane Compressor - Part.: Lubrication Characteristic
Characteristics of CO2 Transcritical Expansion Process
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1 Characteristics of CO Transcritical Expansion Process Mitsuhiro Fukuta tmmfuku@ipc.shizuoka.ac.jp
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1 Characteristics of CO Transcritical Expansion Process Mitsuhiro Fukuta tmmfuku@ipc.shizuoka.ac.jp
Acceleration of the Apex Seals in a Wankel Rotary Compressor Including Manufacturing Process Variation in Location of the Seals
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs nternational Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2000 Acceleration of the Apex Seals in a Wankel Rotary Compressor ncluding Manufacturing
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs nternational Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2000 Acceleration of the Apex Seals in a Wankel Rotary Compressor ncluding Manufacturing
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECTS OF TORSIONAL EXCITATION OF VARIABLE INERTIA EFFECTS IN A MULTI-CYLINDER RECIPROCATING ENGINE
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 6, Issue 8, Aug 2015, pp. 59-69, Article ID: IJMET_06_08_006 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtypeijmet&vtype=6&itype=8
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 6, Issue 8, Aug 2015, pp. 59-69, Article ID: IJMET_06_08_006 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtypeijmet&vtype=6&itype=8
Dynamic Analysis of a Rotor-Journal Bearing System of Rotary Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 6 Dynamic Analysis of a Rotor-Journal Bearing System of Rotary Compressor Fei Xie Xi an
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 6 Dynamic Analysis of a Rotor-Journal Bearing System of Rotary Compressor Fei Xie Xi an
CHAPTER 6 FRICTION AND WEAR ANALYSIS FOR BUSHING
 CHAPTER 6 FRICTION AND WEAR ANALYSIS FOR BUSHING 6.1 TEST RIG SETUP FOR THE FRICTION AND WEAR ANALYSIS Knowing the frictional coefficient is important for the determination of wear loss and power loss
CHAPTER 6 FRICTION AND WEAR ANALYSIS FOR BUSHING 6.1 TEST RIG SETUP FOR THE FRICTION AND WEAR ANALYSIS Knowing the frictional coefficient is important for the determination of wear loss and power loss
Compressor Roller Bearing Dynamics Analysis
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1980 Compressor Roller Bearing Dynamics Analysis C.T. R. Slayton E. M. Hall Follow this
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1980 Compressor Roller Bearing Dynamics Analysis C.T. R. Slayton E. M. Hall Follow this
Criteria for the Design of Pressure Transducer Adapter Systems
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1972 Criteria for the Design of Pressure Transducer Adapter Systems J. P. Elson Bradley
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1972 Criteria for the Design of Pressure Transducer Adapter Systems J. P. Elson Bradley
Sound Radiation Of Cast Iron
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2002 Sound Radiation Of Cast Iron N. I. Dreiman Tecumseh Products Company Follow this and
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2002 Sound Radiation Of Cast Iron N. I. Dreiman Tecumseh Products Company Follow this and
Three-Crankshaft-Driven Scroll Compressor
 Purdue Universit Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 26 Three-Crankshaft-Driven Scroll Compressor Pierre Ginies Danfoss Commercial Compressor
Purdue Universit Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 26 Three-Crankshaft-Driven Scroll Compressor Pierre Ginies Danfoss Commercial Compressor
Scroll Compressor with no Tipping Moment
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 Scroll Compressor with no Tipping Moment J. R. Williams J. T. Hill G. M. Fields Follow
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 Scroll Compressor with no Tipping Moment J. R. Williams J. T. Hill G. M. Fields Follow
Energy and Exergy Analyses of the Scroll Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1994 Energy and Exergy Analyses of the Scroll Compressor T. C. Wagner R. L. DeBlois D. L.
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1994 Energy and Exergy Analyses of the Scroll Compressor T. C. Wagner R. L. DeBlois D. L.
A Study on Contact Force Between Wraps of Scroll Compressor for CO2 Refrigerant
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1 A Study on Contact Force Beteen Wraps of Scroll Compressor for CO Refrigerant Akira Hiata
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1 A Study on Contact Force Beteen Wraps of Scroll Compressor for CO Refrigerant Akira Hiata
Gradient-Based Estimation of Air Flow and Geometry Configurations in a Building Using Fluid Dynamic Adjoint Equations
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International High Performance Buildings Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Gradient-Based Estimation of Air Flow and Geometry Configurations in a Building
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International High Performance Buildings Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Gradient-Based Estimation of Air Flow and Geometry Configurations in a Building
Numerical Prediction of the Radiated Noise of Hermetic Compressors Under the Simultaneous Presence of Different Noise Sources
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 Numerical Prediction of the Radiated Noise of Hermetic Compressors Under the Simultaneous
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 Numerical Prediction of the Radiated Noise of Hermetic Compressors Under the Simultaneous
ENT345 Mechanical Components Design
 1) LOAD AND STRESS ANALYSIS i. Principle stress ii. The maximum shear stress iii. The endurance strength of shaft. 1) Problem 3-71 A countershaft carrying two-v belt pulleys is shown in the figure. Pulley
1) LOAD AND STRESS ANALYSIS i. Principle stress ii. The maximum shear stress iii. The endurance strength of shaft. 1) Problem 3-71 A countershaft carrying two-v belt pulleys is shown in the figure. Pulley
DESIGN & STATIC STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF CRANKSHAFT FOR HIGH PRESSURE PLUNGER PUMP
 DESIGN & STATIC STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF CRANKSHAFT FOR HIGH PRESSURE PLUNGER PUMP Kiran A. Raut 1 and Sachin S. Mestry 2 1 M.E Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Finolex Academy of Management
DESIGN & STATIC STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF CRANKSHAFT FOR HIGH PRESSURE PLUNGER PUMP Kiran A. Raut 1 and Sachin S. Mestry 2 1 M.E Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Finolex Academy of Management
Members Subjected to Combined Loads
 Members Subjected to Combined Loads Combined Bending & Twisting : In some applications the shaft are simultaneously subjected to bending moment M and Torque T.The Bending moment comes on the shaft due
Members Subjected to Combined Loads Combined Bending & Twisting : In some applications the shaft are simultaneously subjected to bending moment M and Torque T.The Bending moment comes on the shaft due
An Experimental Study of Lubrication in Thrust Slide-Bearings of Scroll Compressors - Effect of Thickness and Inside Form of Thrust Plate -
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2012 An Experimental Study of Lubrication in Thrust Slide-Bearings of Scroll Compressors
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2012 An Experimental Study of Lubrication in Thrust Slide-Bearings of Scroll Compressors
Tuesday, February 11, Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE
 1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL 4.1 INTRODUCTION 4.2 DYNAMICALLY EQUIVALENT SYSTEM. Structure. Objectives. 4.1 Introduction
 UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4. Dynamically Equivalent System 4.3 Turning Moment Diagram 4.3.1 Turning Moment Diagram of a Single Cylinder 4-storke IC Engine 4.3. Turning Moment
UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4. Dynamically Equivalent System 4.3 Turning Moment Diagram 4.3.1 Turning Moment Diagram of a Single Cylinder 4-storke IC Engine 4.3. Turning Moment
Analysis of Scroll Thrust Bearing
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 006 Analysis of Scroll Thrust Bearing Masao Akei Emerson Climate Technologies/Copeland Corporation
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 006 Analysis of Scroll Thrust Bearing Masao Akei Emerson Climate Technologies/Copeland Corporation
A Numerical Friction Loss Analysis of the Journal Bearings in a Hermetic Reciprocating Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 216 A Numerical Friction Loss Analysis of the Journal Bearings in a Hermetic Reciprocating
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 216 A Numerical Friction Loss Analysis of the Journal Bearings in a Hermetic Reciprocating
Parametric Study of Shaft Subjected To Pure Bending
 Page167 Parametric Study of Shaft Subjected To Pure Bending Amar Kumar Patel*, Akash Kumar Patel**, Prajnasu Biswal***, & Satya Narayan Tripathy**** *Mechanical Department, Gandhi Institute of Engineering
Page167 Parametric Study of Shaft Subjected To Pure Bending Amar Kumar Patel*, Akash Kumar Patel**, Prajnasu Biswal***, & Satya Narayan Tripathy**** *Mechanical Department, Gandhi Institute of Engineering
Simulation Of Compressors With The Help Of An Engineering Equation Solver
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 00 Simulation Of Compressors With The Help Of An Engineering Equation Solver J. Lebrun University
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 00 Simulation Of Compressors With The Help Of An Engineering Equation Solver J. Lebrun University
(48) CHAPTER 3: TORSION
 (48) CHAPTER 3: TORSION Introduction: In this chapter structural members and machine parts that are in torsion will be considered. More specifically, you will analyze the stresses and strains in members
(48) CHAPTER 3: TORSION Introduction: In this chapter structural members and machine parts that are in torsion will be considered. More specifically, you will analyze the stresses and strains in members
The Mechanical Analysis of a Scroll Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1992 The Mechanical Analysis of a Scroll Compressor Y. Yu Xi an Jiaotong University; P.
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1992 The Mechanical Analysis of a Scroll Compressor Y. Yu Xi an Jiaotong University; P.
Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis. Lecture Slides
 Lecture Slides Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2015 by McGraw Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner.
Lecture Slides Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2015 by McGraw Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner.
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
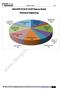 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
Dynamics of Machinery
 1 Preamble Dynamics of Machinery Relation between motion and forces causing is a fascinating subject. This study is a generally referred as dynamic. Modern Engineering aims at analysing and predicting
1 Preamble Dynamics of Machinery Relation between motion and forces causing is a fascinating subject. This study is a generally referred as dynamic. Modern Engineering aims at analysing and predicting
Oil Retention and Pressure Drop of R134a, R1234yf and R410A with POE 100 in Suction Lines
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2012 Oil Retention and Pressure Drop of R134a, R1234yf and R410A with POE 100
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2012 Oil Retention and Pressure Drop of R134a, R1234yf and R410A with POE 100
Sound Radiation of Structural Metals at Normal and Elevated Temperatures
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 Sound Radiation of Structural Metals at Normal and Elevated Temperatures N. Dreiman
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 Sound Radiation of Structural Metals at Normal and Elevated Temperatures N. Dreiman
Contents. Chapter 1 Introduction Chapter 2 Unacceptable Cam Curves Chapter 3 Double-Dwell Cam Curves... 27
 Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 1.0 Cam-Follower Systems... 1 1.1 Fundamentals... 1 1.2 Terminology... 4 Type of Follower Motion... 4 Type of Joint Closure... 4 Type of Follower... 5 Type of Cam...
Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 1.0 Cam-Follower Systems... 1 1.1 Fundamentals... 1 1.2 Terminology... 4 Type of Follower Motion... 4 Type of Joint Closure... 4 Type of Follower... 5 Type of Cam...
Investigation of Axial Compliance Mechanism in Scroll Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1996 Investigation of Axial Compliance Mechanism in Scroll Compressor J. Lee S. Kim S. Lee
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1996 Investigation of Axial Compliance Mechanism in Scroll Compressor J. Lee S. Kim S. Lee
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 General ptitude G Set-8 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The chairman requested the aggrieved shareholders to him. () bare with () bore with (C) bear with (D) bare Q.2 Identify the correct spelling out
General ptitude G Set-8 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The chairman requested the aggrieved shareholders to him. () bare with () bore with (C) bear with (D) bare Q.2 Identify the correct spelling out
Downloaded from Downloaded from / 1
 PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY III SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2002 LEVEL : B. E. (Civil) SUBJECT: BEG256CI, Strength of Material Full Marks: 80 TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32 Candidates are required to give their
PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY III SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2002 LEVEL : B. E. (Civil) SUBJECT: BEG256CI, Strength of Material Full Marks: 80 TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32 Candidates are required to give their
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS. Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola
 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola Mechanics of materials branch of mechanics that studies the internal effects of stress and strain in a solid body. stress is associated with the
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola Mechanics of materials branch of mechanics that studies the internal effects of stress and strain in a solid body. stress is associated with the
Dynamical Analysis of Scroll Compressor with the Compliant Crank Mechanism
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1994 Dynamical Analysis of Scroll Compressor with the Compliant Crank Mechanism J. Zhu Xi'an
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1994 Dynamical Analysis of Scroll Compressor with the Compliant Crank Mechanism J. Zhu Xi'an
Dynamic Modeling and Measurements on a Reciprocating Hermetic Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs nternational Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1996 Dynamic Modeling and Measurements on a Reciprocating Hermetic Compressor H. Erol stanbul
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs nternational Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1996 Dynamic Modeling and Measurements on a Reciprocating Hermetic Compressor H. Erol stanbul
API 11E - Specification for Pumping Units
 API 11E - Specification for Pumping Units 5 Beam Pump Structure Requirements 5.1 General Requirements for beam pump structures are specified in the following sections. Only loads imposed on the structure
API 11E - Specification for Pumping Units 5 Beam Pump Structure Requirements 5.1 General Requirements for beam pump structures are specified in the following sections. Only loads imposed on the structure
Optimal Muffler Design
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1974 Optimal Muffler Design E. Sandgren Purdue University K. M. Ragsdell Purdue University
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1974 Optimal Muffler Design E. Sandgren Purdue University K. M. Ragsdell Purdue University
First Law Analysis of a Compressar Using a Computer Simulation Model
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs nternational Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1982 First Law Analysis of a Compressar Using a Computer Simulation Model S. Lee R. Singh
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs nternational Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1982 First Law Analysis of a Compressar Using a Computer Simulation Model S. Lee R. Singh
A Study on the Reduction of Torque Variation in Scroll Compressors
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor ngineering Conference School of Mechanical ngineering 1996 A Study on the Reduction of Torque Variation in Scroll Compressors H. J. Kim University
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor ngineering Conference School of Mechanical ngineering 1996 A Study on the Reduction of Torque Variation in Scroll Compressors H. J. Kim University
Design of Phase-Angled Balance Weights for an Inverter Driven Scroll Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 Design of Phase-Angled Balance Weights for an Inverter Driven Scroll Compressor H.
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 Design of Phase-Angled Balance Weights for an Inverter Driven Scroll Compressor H.
Motion of the Sprung Mass and Housing of a Reciprocating Hermetic Compressor during Starting and Stopping
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2 Motion of the Sprung Mass and Housing of a Reciprocating Hermetic Compressor during Starting
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2 Motion of the Sprung Mass and Housing of a Reciprocating Hermetic Compressor during Starting
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5
 COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
ScienceDirect. Finite element analysis and optimization of flexure bearing for linear motor compressor
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 67 (2015 ) 379 385 25th International Cryogenic Engineering Conference and the International Cryogenic Materials Conference in 2014,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 67 (2015 ) 379 385 25th International Cryogenic Engineering Conference and the International Cryogenic Materials Conference in 2014,
IDE 110 Mechanics of Materials Spring 2006 Final Examination FOR GRADING ONLY
 Spring 2006 Final Examination STUDENT S NAME (please print) STUDENT S SIGNATURE STUDENT NUMBER IDE 110 CLASS SECTION INSTRUCTOR S NAME Do not turn this page until instructed to start. Write your name on
Spring 2006 Final Examination STUDENT S NAME (please print) STUDENT S SIGNATURE STUDENT NUMBER IDE 110 CLASS SECTION INSTRUCTOR S NAME Do not turn this page until instructed to start. Write your name on
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Fifth SI Edition CHAPTER 3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf David F. Mazurek Torsion Lecture Notes:
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Fifth SI Edition CHAPTER 3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf David F. Mazurek Torsion Lecture Notes:
Three-Dimension Numerical Simulation of Discharge Flow in a Scroll Air Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 24 Three-Dimension Numerical Simulation of Discharge Flow in a Scroll Air Compressor Jian
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 24 Three-Dimension Numerical Simulation of Discharge Flow in a Scroll Air Compressor Jian
Effective Flow And Force Areas Of Discharge Valve In A Rotary Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 Effective Flow And Force Areas Of Discharge Valve In A Rotary Compressor Qin Tan Xi'an
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 Effective Flow And Force Areas Of Discharge Valve In A Rotary Compressor Qin Tan Xi'an
The principle of the flywheel is found before the many centuries ago in spindle and the potter's wheel.
 TOM Fly Wheel Mechanical Engineering Department The principle of the flywheel is found before the many centuries ago in spindle and the potter's wheel. A heavy-rimmed rotating wheel used to minimize variations
TOM Fly Wheel Mechanical Engineering Department The principle of the flywheel is found before the many centuries ago in spindle and the potter's wheel. A heavy-rimmed rotating wheel used to minimize variations
Sound Reduction Of Rotary Compressor Using Topology Optimization
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2002 Sound Reduction Of Rotary Compressor Using Topology Optimization S. Wang Kwangju Institute
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2002 Sound Reduction Of Rotary Compressor Using Topology Optimization S. Wang Kwangju Institute
SOLUTION (17.3) Known: A simply supported steel shaft is connected to an electric motor with a flexible coupling.
 SOLUTION (17.3) Known: A simply supported steel shaft is connected to an electric motor with a flexible coupling. Find: Determine the value of the critical speed of rotation for the shaft. Schematic and
SOLUTION (17.3) Known: A simply supported steel shaft is connected to an electric motor with a flexible coupling. Find: Determine the value of the critical speed of rotation for the shaft. Schematic and
Samantha Ramirez, MSE. Stress. The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. F 2
 Samantha Ramirez, MSE Stress The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. Δ ΔA Δ z Δ 1 2 ΔA Δ x Δ y ΔA is an infinitesimal size area with a uniform force
Samantha Ramirez, MSE Stress The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. Δ ΔA Δ z Δ 1 2 ΔA Δ x Δ y ΔA is an infinitesimal size area with a uniform force
Friction Power in Sliding Vane Type Rotary Compressors
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1996 Friction Power in Sliding Vane Type Rotary Compressors D. Aradau University Dunarea
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1996 Friction Power in Sliding Vane Type Rotary Compressors D. Aradau University Dunarea
Indirect Measurement of Random Force Spectra on Fractional Horse Power Reciprocating Compressor Shell
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 Indirect Measurement of Random Force Spectra on Fractional Horse Power Reciprocating
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 Indirect Measurement of Random Force Spectra on Fractional Horse Power Reciprocating
Co-Orbiting Scroll Design and Operational Characteristics
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs nternational Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1994 Co-Orbiting Scroll Design and Operational Characteristics J. W. Bush Carlyle Compressor
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs nternational Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1994 Co-Orbiting Scroll Design and Operational Characteristics J. W. Bush Carlyle Compressor
: APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE
 COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
Identification Number
 Identification Number The specification of Micro Linear Way LWL is specified by the identification number, which consists of a model code, a size, a part code, a preload symbol, a classification symbol,
Identification Number The specification of Micro Linear Way LWL is specified by the identification number, which consists of a model code, a size, a part code, a preload symbol, a classification symbol,
A Thermal Elastohydrodynamic Lubricated Thrust Bearing Contact Model
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 A Thermal Elastohydrodynamic Lubricated Thrust Bearing Contact Model G. Xu Tecumseh
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 A Thermal Elastohydrodynamic Lubricated Thrust Bearing Contact Model G. Xu Tecumseh
UNIT 2 KINEMATICS OF LINKAGE MECHANISMS
 UNIT 2 KINEMATICS OF LINKAGE MECHANISMS ABSOLUTE AND RELATIVE VELOCITY An absolute velocity is the velocity of a point measured from a fixed point (normally the ground or anything rigidly attached to the
UNIT 2 KINEMATICS OF LINKAGE MECHANISMS ABSOLUTE AND RELATIVE VELOCITY An absolute velocity is the velocity of a point measured from a fixed point (normally the ground or anything rigidly attached to the
Heat Transfer From the Evaporator Outlet to the Charge of Thermostatic Expansion Valves
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Heat Transfer From the Evaporator Outlet to the Charge of Thermostatic
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Heat Transfer From the Evaporator Outlet to the Charge of Thermostatic
Module 2 Stresses in machine elements. Version 2 ME, IIT Kharagpur
 Module Stresses in machine elements Lesson Compound stresses in machine parts Instructional Objectives t the end of this lesson, the student should be able to understand Elements of force system at a beam
Module Stresses in machine elements Lesson Compound stresses in machine parts Instructional Objectives t the end of this lesson, the student should be able to understand Elements of force system at a beam
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy
 Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
Simulation of An Innovative Rotary Compressor With Variable Speed Displacers
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 004 Simulation of An Innovative Rotary Compressor With Variable Speed Displacers A. R. Barreto
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 004 Simulation of An Innovative Rotary Compressor With Variable Speed Displacers A. R. Barreto
Design of Compressor Suspension Systems Using Modal Analysis
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs nternational Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 984 Design of Compressor Suspension Systems Using Modal Analysis N. Gupta R. J. Bernhard
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs nternational Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 984 Design of Compressor Suspension Systems Using Modal Analysis N. Gupta R. J. Bernhard
Mixed Lubrication Analysis of Vane Sliding Surface in Rotary Compressor Mechanisms
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 4 Mixed Lubrication Analysis of Vane Sliding Surface in Rotary Compressor Mechanisms Yasutaka
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 4 Mixed Lubrication Analysis of Vane Sliding Surface in Rotary Compressor Mechanisms Yasutaka
1 MR SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 2013
 SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
Rating Equations for Positive Displacement Compressors with Auxiliary Suction Ports
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 Rating Equations for Positive Displacement Compressors with Auxiliary Suction Ports
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 Rating Equations for Positive Displacement Compressors with Auxiliary Suction Ports
A Comparison of Thermal Deformation of Scroll Profiles inside Oil-free Scroll Vacuum Pump and Compressor via CAE/CFD Analysis
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2018 A Comparison of Thermal Deformation of Scroll Profiles inside Oil-free Scroll Vacuum
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2018 A Comparison of Thermal Deformation of Scroll Profiles inside Oil-free Scroll Vacuum
Nonlinear Vibration Analysis of Reed Valves
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2000 Nonlinear Vibration Analysis of Reed Valves H. C. Sheu Industrial Technology Research
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2000 Nonlinear Vibration Analysis of Reed Valves H. C. Sheu Industrial Technology Research
A Co-Rotating Scroll Compressor for Positive Displacement and Centrifugal Dual-Mode Operations
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1994 A Co-Rotating Scroll Compressor for Positive Displacement and Centrifugal Dual-Mode
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1994 A Co-Rotating Scroll Compressor for Positive Displacement and Centrifugal Dual-Mode
Optimal Performance Development of High- Pressure Type Ammonia Scroll Compressors for Maximum Efficiency
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2008 Optimal Performance Development of High- Pressure Type Ammonia Scroll Compressors for
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2008 Optimal Performance Development of High- Pressure Type Ammonia Scroll Compressors for
Lubrication Mechanism at Thrust Slide-Bearing of Scroll Compressors (Experimental Study)
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2004 Lubrication Mechanism at Thrust Slide-Bearing of Scroll Compressors (Experimental Study)
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2004 Lubrication Mechanism at Thrust Slide-Bearing of Scroll Compressors (Experimental Study)
A Calibration Procedure for Compressor Simulation Models using Evolutionary Algorithm
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 A Calibration Procedure for Compressor Simulation Models using Evolutionary Algorithm
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 A Calibration Procedure for Compressor Simulation Models using Evolutionary Algorithm
Key words: Polymeric Composite Bearing, Clearance, FEM
 A study on the effect of the clearance on the contact stresses and kinematics of polymeric composite journal bearings under reciprocating sliding conditions Abstract The effect of the clearance on the
A study on the effect of the clearance on the contact stresses and kinematics of polymeric composite journal bearings under reciprocating sliding conditions Abstract The effect of the clearance on the
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
Two-Phase Refrigerant Distribution in a Micro- Channel Manifold
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 6 Two-Phase Refrigerant Distribution in a Micro- Channel Manifold Chad D. Bowers
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 6 Two-Phase Refrigerant Distribution in a Micro- Channel Manifold Chad D. Bowers
Lubrication Tests to Support Optimal Performance Design Guidelines for Thrust Slide-Bearings in Scroll Compressors
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 26 Lubrication Tests to Support Optimal Performance Design Guidelines for Thrust Slide-Bearings
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 26 Lubrication Tests to Support Optimal Performance Design Guidelines for Thrust Slide-Bearings
10/23/2015. Chapter 7. Velocity in Mechanisms. (Relative Velocity Method) Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, Ph.D., PE
 Chapter 7 Velocity in Mechanisms (Relative Velocity Method) 1 2 7.2. Relative Velocity of Two Bodies Moving in Straight Lines 3 7.3. Motion of a Link Velocity of any point on a link wrt another point on
Chapter 7 Velocity in Mechanisms (Relative Velocity Method) 1 2 7.2. Relative Velocity of Two Bodies Moving in Straight Lines 3 7.3. Motion of a Link Velocity of any point on a link wrt another point on
Problem d d d B C E D. 0.8d. Additional lecturebook examples 29 ME 323
 Problem 9.1 Two beam segments, AC and CD, are connected together at C by a frictionless pin. Segment CD is cantilevered from a rigid support at D, and segment AC has a roller support at A. a) Determine
Problem 9.1 Two beam segments, AC and CD, are connected together at C by a frictionless pin. Segment CD is cantilevered from a rigid support at D, and segment AC has a roller support at A. a) Determine
Matlab Sheet 2. Arrays
 Matlab Sheet 2 Arrays 1. a. Create the vector x having 50 logarithmically spaced values starting at 10 and ending at 1000. b. Create the vector x having 20 logarithmically spaced values starting at 10
Matlab Sheet 2 Arrays 1. a. Create the vector x having 50 logarithmically spaced values starting at 10 and ending at 1000. b. Create the vector x having 20 logarithmically spaced values starting at 10
