Giuseppe Bianchi, Ilenia Tinnirello
|
|
|
- Scott Caldwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Powe units - ecibel Decibel (B): logaithmic unit of intensity use to inicate powe lost o gaine between two signals Name afte Alexane Gaham Bell. ( ) log P P 1 /
3 Decibels - Bm» Not much use by us 1BW30Bm µ! " # " $ #! % & % & & % %
4 Quick evaluations!"#"$ %$"& ' ( ) * # $ ) ' ( * '&()*(+,) ++)*++ )++
5 Computation with B -$ +, - Es. 33 Bm.$ +, - Es. Bm ". * /, +, - 0,,, 1 * / Es. 43 B attenuation by facto 0.000
6 Attenuation moel fo LOS /"$ - ), - * 0 3" 0 "., ) /, 4 3, *,.$& 5 ), * 3 ), *, 6 * / 3, /,, 7 - P ( ) ( istance between sene an eceive)
7 fee space moel ieal antennas 0 8, 9 -, * 9,, - 3*, $1 / : 33 * / P P ( ) A e a λ 4π ( ) P a P t 4π ( ) A e
8 fee space moel eal antennas ' ; P a ( ) G P t 4π t ' ; P ( ) P ( ) G A a e PG t t λ G 4π 4π
9 Fiis Fee-Space Moel summaizing all pevious consieations PG t tgλ Gt G c P ( ) P t (4π ) L L 4πf P t tansmitte powe (W o mw) G t tansmitte antenna gain G tansmitte antenna gain (imensionless) λ c/f RF wavelength (m) c spee of light (3x 8 m/s) f RF fequency (Hz) P ( ) 0 log [ Bm] P [ Bm] λ 0log t + log (4π ) 0 log G t + log > 0 P t G t Equivalent Isotopic Raiate Powe (EIRP) L othe system losses (hawae) L >1 (imensionless) istance between tansmitte an eceive (m) log G L +
10 Example nomalize fequency [MHz] spee of light [Km lamba (m) 0, gain Tx 1 Gain Rx 1 Loss 1 Ptx [W] 5 istance (Km) Px W Px Bm 00 8,80E-08-40,55 400,0E-08-46, ,77E-09-50, 800 5,50E-09-5, ,5E-09-54,54 0,44E-09-56, ,79E-09-57, ,37E-09-58, ,09E-09-59, ,80E- -60, ,7E- -61, ,11E- -6, ,0E- -6, ,49E- -63, ,91E- -64, ,44E- -64, ,04E- -65, ,71E- -65, ,44E- -66, ,0E- -66, ,99E- -67, ,8E- -67, ,66E- -67, ,53E- -68, ,41E- -68,5-30,00-40,00-50,00-60,00-70,00 eceive powe (B istance (m)
11 Path Loss (popagation loss) positive value in B PL( ) [ B ] log 0 log 0 log 0 log P t L 4 log π P Gt G λ Gt G λ log 0log L 4π Gt G + 0 log f log 0log L Gt G + 0 log f log L c 4π
12 Fee space loss same as path loss, but pat ue to attenuation in fee space only (in B) L fee ( ) λ 4 π L fee ( ) [ B] λ c/ f 0log 0log 4 π 4π 0log + 0log f
13 Refeence istance 0$$ * * * - 3 < P ( )( Bm) o P ( ) P ( o ) o log P ( o ) + 0log P ( o)( Bm) + 0 log o 3"1 $1) 3"*#" ",,, ) <, - <, * -1 + &++*+++
14 Example P ( + ++% 0 )( Bm) 30 + log +++ Gt G Pt ( Bm) + log + 0log L log 34,5Bm 0π 0 P ( 00m) P ( 0) + 0log 34,5 Bm 0B 54,5Bm λ 4π
15 Refeence istance + fequency 41%1 $ P (, 51 + PG G λ PG G ( c/ f ) f ) (4π ) P ( t 0 t, f 0 ) L (4π ) 0 [ ] ( ) ( ) Bm t t 0log 0 L f / f 0 f00 f 0log / 0 33, * <, *, < * < + >? < *
16 Moe ealistic popagation moels 05$$ <, * *,. 9η P ( ) η -, - *, η7 If tough envionment (e.g., lots of foliage), < * / -, 9 η fo small istances (0 B/ecae) η3 to η4 (40 B/ecae) fo mobile telephone istances η *, - ), Aη, - ) - ) -, η
17 Extene fomulae P ( )( Bm) log P ( o ) + η log _ef 1 Km P_ef -51,566 Bm (PtxW; 900 MHz; 00m) o istance px (eta)px (eta3,5) px (eta4) 1-51,566-51, ,566 1, -53,1-54, ,6939 1,4-54,449-56, ,3717 1,6-55,609-58, ,6914 1,8-56,631-60, , ,547-6, ,5678, -58, , ,35,4-59, , ,7351,6-59,861-66, ,156,8-60, , , ,069-68, ,6115 3, -61,696-69, ,736 3,4-6,156-70, ,7858 3,6-6,657-70, ,7787 3,8-63,13-71, , ,5678-7, ,609 4, -63, , ,4566 4,4-64, , ,647 4,6-64, , ,0369 4,8-65, , , ,506-75, ,4854 eceive powe (Bm) η η3,5 η istance (Km)
18 Realistic scenaios $" 3 * 633* 6, *, < 3- * ) < / ) - * *, *, 6 /, < 6 / 3 * * - *, 3 * /, A * - *, ), ), < $". /, / * / 3 33 *, 33 <,.## ##,, * *, - * / <, -,,, - * / <, -,,, /,,
19 Example scenaios: LOS path non necessaily existing (an unique) : B 9* < ) -, A # 0 5# : C " 5; > 8 A D 33* A 3 * 33* 3 *
20 Example scenaios 0 5# : C " 5; > 8 % D 33* 6 3 * 6, * 0 "
21 Two-Ray Goun Popagation Moel -"η6 8 <,, -, * 0 " 3 * * * /, 3* :, <, / h t 0 3" < 3 * < h 8, * /, 33
22 Two-ay moel geomety >> h t, h θ θ iect + ( h h ) t ht h 1 + 1/ ht h eflect + ( h + h ) t ht h 1/ ht + h
23 Two ay moel path analysis ht + h 1 + eflect iect 1 ht h ht h 3$ " , E iect ay Acos πf t - * eflect ay B cosπf t - 3 * 3 * 6 iect c eflect c
24 Two ay moel fiel stength " π ϕ πf c λ.#" 0 : * ) 3, / ) < * < 8 ρ* E E E [ ] j ϕ + ρ E E iect 1 e iect E iect E 4πh h t λ [ ] j ϕ 1 e E [ 1 cos sin ] iect ϕ + j ϕ [ 1 cos cos sin ] 1/ + ϕ ϕ + ϕ iect 1 cos ϕ E iect ϕ sin
25 Two ay moel powe computation.$ F: F P 4 E iect sin ( ϕ / ) P ( ) PG t tg L λ πht h 4sin 4π λ
26 Two ay moel - conclusion -1& G 3, 3 G * - 3, λ G 3, 3* G -, sin h h h h small h h t t t λ π λ π λ π ) ( h h L PG G h h L PG G P t t t t t t λ π π λ 4 ) ( P
27 Design notes -1 1 η - 3,, *, Fee space moel η4-3, *, LOS + eflecte ay moel H,, /, * I I % (e.g., > (h t + h ))
28 Empiical moels! J ) -, * < 6- +, ) < * ), 4 < < *, 0 " 6 3 * 633* 6, *, - 3 *, -, C 7 - * < A, A, * 33* - -, 64, 6,, 6, 6 *! " # $ % & ' (
29 Okumua-Hata moel 789+&1 : " 0 *, A" - *, A. -, 0 9I 4 & f caie fequency (MHz) istance BS MS (Km) h bs (effective) heigh of base station antenna (m) h ms height of mobile antenna (m) : 33 * / "
30 Okumua-Hata: uban aea L path ( B) ( log h ) 13.8 log log h bs a bs ( h ) ms log f + + lage " # *) 34"#" cities : a small - me ( ) [ ( )] hms 3. log 11.75hms 4.97 f 400MHz : a( h ) [ 1.1log f 0.7] h [ 1.56 log f 0.8] cities ms ms
31 Okumua-Hata: sububan & ual aeas 4" sububan : ual : L L path path ( B) ( B) L L p p log 4.78 f [ ] log f log f
32 Okumua-Hata: examples path loss (B) istance (km) C K + >? 6 ), L 6, lage cities small cities sububs ual aea
33 Okumua-Hata an η!#1" +η -""#""4%"$"η η base station height (m)
34 Othe empiical moels ; J, K + > M C, *, I 4,, -, 4 *, * - + * B 4- - > "*0# C * < L + >? N 3 * * -, *, 1 4 ) < : - H 3 3" * 3* 8 * * H " 8, *, 3 * 3 ;, <,, 0# 5 * - - 3*, - ) - * * ) 3, 63, 6 3 *,, 6 *,?,? 6? 6,? 6 *?
35 Execises < $,+ ##%" ##"+#1 #1 ;++ #$"""#"#" +++"$#" -"# "$ ""$ -"$(" 6<7 %#+ "" $"5$"#"" #*1A" "#" 1$%" $*(+ " ""#A>*?+%*6+%
36 Execises 7##99+37# &,B (C( 9(#" D66 8*?,,#" # 7$""#$"" "#"(+++ #$,,A>9 8##@
37 ( #
38 Statistical natue of eceive powe 4##" Long tem faing Shot tem faing Mean value peicte by attenuation moel (constant at given ) Time (o movement)
39 Multipath: shot tem faing 4"*#, 9-3, 9,, * 3, 93 <1 # ## 1".#& e ( t) N a k k cos 1 0 ) ) ) φ ( π f t + φ ) k 3"#5 " /, 3B B 3Oλ change intefeence patten astic fluctuations in signal stength ue to constuctive/estuctive intefeence 15-0 cm fo 900 MHz "
40 Multipath analysis e ( t) ( f t + φ ) N a k k cos π 1 0 k X N ( πf 0t) a ( f t ) k k cosφk sin π 1 0 ( πf t) Y sin( πf t) cos cos k ecall cos that :cos( πf 0t + φk ) ( πf t) cos( φ ) sin( πf t) sin ( φ ) 0 N k a k sin φ k 0 k 5,, -, 9 # <, φ 4-3 <, ) - 6π 4 * ) /, - *, 0 " $ 6P -,, 6 * <, ) - / ), " / 9 X + Y. <, ) -
41 pobability istibution E 0,7 0,6 0,5 0,4 0,3 0, 0,1 0 Rayleigh istibution amplitue sigma1 sigma sigma4 σ [ ] x a x e x σ 1. 53σ Va 0 x σ π f a (x) [ ] x σ a x e σ σ 0.49σ 0 x σ π π P x σ σ / * 3$ P ; -,, / ( x a < x + x) e x x σ
42 Signal powe amplitue : a X + Y : ayleigh istibuti on powe : p a X + Y : exponential istibuti on #$& σ / / 0$. / ) 6 9 pobability ensity function: Pobability istibution function: f p F p ( x) ( x) 1 x σ e σ x σ 1 e
43 Outage pobability 1"$$ "#"" *, * ) * * < * / #$ + σ 3$""γ outage pobability : : B 9 / µ A, µ A - ) ) < B 6K Q P( p γ ) P0 ( γ ) 1 F p e : B 9 / A, A - ) ) < B 6K L Q γ
44 Long-tem faing 4#1E #" " ##""# $".&#*# 3,
45 Long-tem faing statistics lognomal istibution P ( )( Bm) log P ( o ) + η log o + F+# $"σ 11& Y f Y ' 1 ( ) σ B ( ) p Bm π σ B e p Bm P av
46 Long-tem faing an attenuation plot attenuation: η4 afte 0m; η befoe 0m -30 eceive powe (Bm) istance (m) no shaowing sigma3 B sigma8 B
47 nomal istibution 0.4 σ σ σ3 " 9 µ0; σ f X µ 1 ( x µ ) ( x) e σ π σ
48 Cumulative nomal istibution µ0; σ1 (stana) x t 1 Q e ( x) FX ( x) π t
49 ef - efc x ef ( x) e π efc( x) 1 0 t t ef ( x) Popeties: ef ( x) ef ( x) efc( x) efc( x)
50 ef ( x-) efc e ef π x 0 t t #, ) - µ 6σ, 7 ef ( x) π 1 x x t t e t e t 0 π x π 1 ( 1/ ) x x e t ( 1/ ) t 1 ef ( x) 1 efc( x) x
51 ef - efc F X ( m, σ ) ( x) 1 m x efc PX0, σ 1 > m x σ ef efc an nomal stana istibution: F X (0,1) 1 1 ( x) efc 1 efc x nomal stana istibution to efc: 1 x efc 1 FX (0,1) ( x) x
52 Cumulative nomal (st) istibution an efc 1 x efc efc x x
53 Outage pobability examples aveage eceive powe (Bm) -80 lognomal stana eviation (B) 6 outage theshol outage pob ,87% -88 9,1% -90 4,78% -9,8% -94 0,98% -96 0,38% -98 0,13% -0 0,04% : B * * - 9 DISTRIB.NORM( th, me,stev, VERO) ; *, * - 9 H /,!, γ g th P γ σ B av < 0 > 0 : / - ) 6 R : 3 : 3γ - : 3 : 3* : 3 : 3
54 Nomal istibution (stana) -4 0,003% -3,9 0,005% -3,8 0,007% -3,7 0,011% -3,6 0,016% -3,5 0,03% -3,4 0,034% -3,3 0,048% -3, 0,069% -3,1 0,097% -3 0,135% -,9 0,187% -,8 0,56% -,7 0,347% -,6 0,466% -,5 0,61% -,4 0,80% -,3 1,07% -, 1,390% -,1 1,786% -,75% -1,9,87% -1,8 3,593% -1,7 4,457% -1,6 5,480% -1,5 6,681% -1,4 8,076% -1,3 9,680% -1, 11,507% -1,1 13,567% -1 15,866% outage pob 0,000%,000% 1,000% 0,0% 0,0% 0,001% n x sigma
55 Esecizi & σ! "!#"$!#"% &'#()* &! " # ##$ #!% &'(σ)*&)+ (& ' σ),##$ # - % " ##$ #./ # 01
TELE4652 Mobile and Satellite Communications
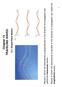
 Mobile and Satellite Communications Lectue 3 Radio Channel Modelling Channel Models If one was to walk away fom a base station, and measue the powe level eceived, a plot would like this: Channel Models
Mobile and Satellite Communications Lectue 3 Radio Channel Modelling Channel Models If one was to walk away fom a base station, and measue the powe level eceived, a plot would like this: Channel Models
Chapter 3 Problem Solutions
 Chate Poblem Solutions Poblem A Equation (5) gives P P G G log h log h L 4 log d t t t sys Substituting gives P log 6 log log 4 log 875 m B The wavelength is given by 8 The fee-sace ath loss is then 9
Chate Poblem Solutions Poblem A Equation (5) gives P P G G log h log h L 4 log d t t t sys Substituting gives P log 6 log log 4 log 875 m B The wavelength is given by 8 The fee-sace ath loss is then 9
Introduction to Arrays
 Intoduction to Aays Page 1 Intoduction to Aays The antennas we have studied so fa have vey low diectivity / gain. While this is good fo boadcast applications (whee we want unifom coveage), thee ae cases
Intoduction to Aays Page 1 Intoduction to Aays The antennas we have studied so fa have vey low diectivity / gain. While this is good fo boadcast applications (whee we want unifom coveage), thee ae cases
Supplementary Information for On characterizing protein spatial clusters with correlation approaches
 Supplementay Infomation fo On chaacteizing potein spatial clustes with coelation appoaches A. Shivananan, J. Unnikishnan, A. Raenovic Supplementay Notes Contents Deivation of expessions fo p = a t................................
Supplementay Infomation fo On chaacteizing potein spatial clustes with coelation appoaches A. Shivananan, J. Unnikishnan, A. Raenovic Supplementay Notes Contents Deivation of expessions fo p = a t................................
Applications of radars: Sensing of clouds and precipitation.
 Lectue 1 Applications of adas: Sensing of clouds and pecipitation. Ojectives: 1. aticle ackscatteing and ada equation.. Sensing of pecipitation and clouds with adas (weathe adas, space adas: TMM and CloudSat).
Lectue 1 Applications of adas: Sensing of clouds and pecipitation. Ojectives: 1. aticle ackscatteing and ada equation.. Sensing of pecipitation and clouds with adas (weathe adas, space adas: TMM and CloudSat).
Mobile Radio Communications
 Course 3: Radio wave propagation Session 3, page 1 Propagation mechanisms free space propagation reflection diffraction scattering LARGE SCALE: average attenuation SMALL SCALE: short-term variations in
Course 3: Radio wave propagation Session 3, page 1 Propagation mechanisms free space propagation reflection diffraction scattering LARGE SCALE: average attenuation SMALL SCALE: short-term variations in
( )( )( ) ( ) + ( ) ( ) ( )
 3.7. Moel: The magnetic fiel is that of a moving chage paticle. Please efe to Figue Ex3.7. Solve: Using the iot-savat law, 7 19 7 ( ) + ( ) qvsinθ 1 T m/a 1.6 1 C. 1 m/s sin135 1. 1 m 1. 1 m 15 = = = 1.13
3.7. Moel: The magnetic fiel is that of a moving chage paticle. Please efe to Figue Ex3.7. Solve: Using the iot-savat law, 7 19 7 ( ) + ( ) qvsinθ 1 T m/a 1.6 1 C. 1 m/s sin135 1. 1 m 1. 1 m 15 = = = 1.13
PHYSICS PAPER 2. Name: Class: ( ) Question-Answer Book 2014-HFC PHY PAPER 2. Time allowed: ¾ hour This paper must be answered in English INSTRUCTIONS
 014-HF PHY PAPER Name: lass: ( ) HO FUNG OLLEGE (SPONSORE Y SIK SIK YUEN) FINAL EXAMINATION 014 PHYSIS PAPER Question-Answe ook Time allowe: ¾ hou This pape must be answee in English INSTRUTIONS (1) Afte
014-HF PHY PAPER Name: lass: ( ) HO FUNG OLLEGE (SPONSORE Y SIK SIK YUEN) FINAL EXAMINATION 014 PHYSIS PAPER Question-Answe ook Time allowe: ¾ hou This pape must be answee in English INSTRUTIONS (1) Afte
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University. ECE 303: Electromagnetic Fields and Waves. Fall 2007
 School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 303: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 007 Homewok 8 Due on Oct. 19, 007 by 5:00 PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes.
School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 303: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 007 Homewok 8 Due on Oct. 19, 007 by 5:00 PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes.
Wireless Communications
 Wireless Communications Cannel Moeling Large Scale Hami Barami Electrical & Computer Engineering EM Spectrum Raio Wave l Raio wave: a form of electromagnetic raiation, create wenever a carge object accelerates
Wireless Communications Cannel Moeling Large Scale Hami Barami Electrical & Computer Engineering EM Spectrum Raio Wave l Raio wave: a form of electromagnetic raiation, create wenever a carge object accelerates
CHAPTER 2 DERIVATION OF STATE EQUATIONS AND PARAMETER DETERMINATION OF AN IPM MACHINE. 2.1 Derivation of Machine Equations
 1 CHAPTER DERIVATION OF STATE EQUATIONS AND PARAMETER DETERMINATION OF AN IPM MACHINE 1 Deivation of Machine Equations A moel of a phase PM machine is shown in Figue 1 Both the abc an the q axes ae shown
1 CHAPTER DERIVATION OF STATE EQUATIONS AND PARAMETER DETERMINATION OF AN IPM MACHINE 1 Deivation of Machine Equations A moel of a phase PM machine is shown in Figue 1 Both the abc an the q axes ae shown
ANTENNAS. Vector and Scalar Potentials. Maxwell's Equations. D = εe. For a linear, homogeneous, isotropic medium µ and ε are contant.
 ANTNNAS Vecto and Scala Potentials Maxwell's quations jωb J + jωd D ρ B (M) (M) (M3) (M4) D ε B Fo a linea, homogeneous, isotopic medium and ε ae contant. Since B, thee exists a vecto A such that B A and
ANTNNAS Vecto and Scala Potentials Maxwell's quations jωb J + jωd D ρ B (M) (M) (M3) (M4) D ε B Fo a linea, homogeneous, isotopic medium and ε ae contant. Since B, thee exists a vecto A such that B A and
Momentum is conserved if no external force
 Goals: Lectue 13 Chapte 9 v Employ consevation of momentum in 1 D & 2D v Examine foces ove time (aka Impulse) Chapte 10 v Undestand the elationship between motion and enegy Assignments: l HW5, due tomoow
Goals: Lectue 13 Chapte 9 v Employ consevation of momentum in 1 D & 2D v Examine foces ove time (aka Impulse) Chapte 10 v Undestand the elationship between motion and enegy Assignments: l HW5, due tomoow
TRAVELING WAVES. Chapter Simple Wave Motion. Waves in which the disturbance is parallel to the direction of propagation are called the
 Chapte 15 RAVELING WAVES 15.1 Simple Wave Motion Wave in which the ditubance i pependicula to the diection of popagation ae called the tanvee wave. Wave in which the ditubance i paallel to the diection
Chapte 15 RAVELING WAVES 15.1 Simple Wave Motion Wave in which the ditubance i pependicula to the diection of popagation ae called the tanvee wave. Wave in which the ditubance i paallel to the diection
556: MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS I
 556: MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS I CHAPTER 5: STOCHASTIC CONVERGENCE The following efinitions ae state in tems of scala anom vaiables, but exten natually to vecto anom vaiables efine on the same obability
556: MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS I CHAPTER 5: STOCHASTIC CONVERGENCE The following efinitions ae state in tems of scala anom vaiables, but exten natually to vecto anom vaiables efine on the same obability
A Lattice Energy Calculation for LiH
 A Lattice Enegy Calculation fo LiH Fank Riou Lithium hyie is a white cystalline soli with the face-centee cubic cystal stuctue (see lattice shown below). The moel fo LiH(s) popose in this stuy constists
A Lattice Enegy Calculation fo LiH Fank Riou Lithium hyie is a white cystalline soli with the face-centee cubic cystal stuctue (see lattice shown below). The moel fo LiH(s) popose in this stuy constists
Waves and Polarization in General
 Waves and Polaization in Geneal Wave means a distubance in a medium that tavels. Fo light, the medium is the electomagnetic field, which can exist in vacuum. The tavel pat defines a diection. The distubance
Waves and Polaization in Geneal Wave means a distubance in a medium that tavels. Fo light, the medium is the electomagnetic field, which can exist in vacuum. The tavel pat defines a diection. The distubance
Analytical calculation of the power dissipated in the LHC liner. Stefano De Santis - LBNL and Andrea Mostacci - CERN
 Analytical calculation of the powe dissipated in the LHC line Stefano De Santis - LBNL and Andea Mostacci - CERN Contents What is the Modified Bethe s Diffaction Theoy? Some inteesting consequences of
Analytical calculation of the powe dissipated in the LHC line Stefano De Santis - LBNL and Andea Mostacci - CERN Contents What is the Modified Bethe s Diffaction Theoy? Some inteesting consequences of
EKT 345 MICROWAVE ENGINEERING CHAPTER 2: PLANAR TRANSMISSION LINES
 EKT 345 MICROWAVE ENGINEERING CHAPTER : PLANAR TRANSMISSION LINES 1 Tansmission Lines A device used to tansfe enegy fom one point to anothe point efficiently Efficiently minimum loss, eflection and close
EKT 345 MICROWAVE ENGINEERING CHAPTER : PLANAR TRANSMISSION LINES 1 Tansmission Lines A device used to tansfe enegy fom one point to anothe point efficiently Efficiently minimum loss, eflection and close
Retrieval of three-dimensional distribution of rainfall parameters for rain attenuation correction using multi-parameter radar
 Retieval of thee-dimensional distibution of ainfall paametes fo ain attenuation coection using multi-paamete ada Dong-Soon Kim 1, Dong-In Lee 1, Masayuki Maki 2 and Ji-Young Gu 1 1 Depatment of Envionmental
Retieval of thee-dimensional distibution of ainfall paametes fo ain attenuation coection using multi-paamete ada Dong-Soon Kim 1, Dong-In Lee 1, Masayuki Maki 2 and Ji-Young Gu 1 1 Depatment of Envionmental
EKT 356 MICROWAVE COMMUNICATIONS CHAPTER 2: PLANAR TRANSMISSION LINES
 EKT 356 MICROWAVE COMMUNICATIONS CHAPTER : PLANAR TRANSMISSION LINES 1 Tansmission Lines A device used to tansfe enegy fom one point to anothe point efficiently Efficiently minimum loss, eflection and
EKT 356 MICROWAVE COMMUNICATIONS CHAPTER : PLANAR TRANSMISSION LINES 1 Tansmission Lines A device used to tansfe enegy fom one point to anothe point efficiently Efficiently minimum loss, eflection and
Question 1. Typical Cellular System. Some geometry TELE4353. About cellular system. About cellular system (2)
 TELE4353 Moble a atellte Commucato ystems Tutoal 1 (week 3-4 4 Questo 1 ove that fo a hexagoal geomety, the co-chael euse ato s gve by: Q (3 N Whee N + j + j 1/ 1 Typcal Cellula ystem j cells up cells
TELE4353 Moble a atellte Commucato ystems Tutoal 1 (week 3-4 4 Questo 1 ove that fo a hexagoal geomety, the co-chael euse ato s gve by: Q (3 N Whee N + j + j 1/ 1 Typcal Cellula ystem j cells up cells
Lecture 04: HFK Propagation Physical Optics II (Optical Sciences 330) (Updated: Friday, April 29, 2005, 8:05 PM) W.J. Dallas
 C:\Dallas\0_Couses\0_OpSci_330\0 Lectue Notes\04 HfkPopagation.doc: Page of 9 Lectue 04: HFK Popagation Physical Optics II (Optical Sciences 330) (Updated: Fiday, Apil 9, 005, 8:05 PM) W.J. Dallas The
C:\Dallas\0_Couses\0_OpSci_330\0 Lectue Notes\04 HfkPopagation.doc: Page of 9 Lectue 04: HFK Popagation Physical Optics II (Optical Sciences 330) (Updated: Fiday, Apil 9, 005, 8:05 PM) W.J. Dallas The
Chapter 5. Applying Newton s Laws. Newton s Laws. r r. 1 st Law: An object at rest or traveling in uniform. 2 nd Law:
 Chapte 5 Applying Newton s Laws Newton s Laws st Law: An object at est o taveling in unifom motion will emain at est o taveling in unifom motion unless and until an extenal foce is applied net ma nd Law:
Chapte 5 Applying Newton s Laws Newton s Laws st Law: An object at est o taveling in unifom motion will emain at est o taveling in unifom motion unless and until an extenal foce is applied net ma nd Law:
Lecture 2 Date:
 Lectue 2 Date: 5.1.217 Definition of Some TL Paametes Examples of Tansmission Lines Tansmission Lines (contd.) Fo a lossless tansmission line the second ode diffeential equation fo phasos ae: LC 2 d I
Lectue 2 Date: 5.1.217 Definition of Some TL Paametes Examples of Tansmission Lines Tansmission Lines (contd.) Fo a lossless tansmission line the second ode diffeential equation fo phasos ae: LC 2 d I
6 PROBABILITY GENERATING FUNCTIONS
 6 PROBABILITY GENERATING FUNCTIONS Cetain deivations pesented in this couse have been somewhat heavy on algeba. Fo example, detemining the expectation of the Binomial distibution (page 5.1 tuned out to
6 PROBABILITY GENERATING FUNCTIONS Cetain deivations pesented in this couse have been somewhat heavy on algeba. Fo example, detemining the expectation of the Binomial distibution (page 5.1 tuned out to
A path-integral approach to CMB
 A path-integal appoach to CMB Based on PHR and L. R. Abamo, CMB and Random Flights: tempeatue and polaization in position space, JCAP6(3)43 Paulo Henique Reimbeg IF-USP II JBPCosmo, 4/3, Peda Azul, ES
A path-integal appoach to CMB Based on PHR and L. R. Abamo, CMB and Random Flights: tempeatue and polaization in position space, JCAP6(3)43 Paulo Henique Reimbeg IF-USP II JBPCosmo, 4/3, Peda Azul, ES
Qualifying Examination Electricity and Magnetism Solutions January 12, 2006
 1 Qualifying Examination Electicity and Magnetism Solutions Januay 12, 2006 PROBLEM EA. a. Fist, we conside a unit length of cylinde to find the elationship between the total chage pe unit length λ and
1 Qualifying Examination Electicity and Magnetism Solutions Januay 12, 2006 PROBLEM EA. a. Fist, we conside a unit length of cylinde to find the elationship between the total chage pe unit length λ and
F-IF Logistic Growth Model, Abstract Version
 F-IF Logistic Gowth Model, Abstact Vesion Alignments to Content Standads: F-IFB4 Task An impotant example of a model often used in biology o ecology to model population gowth is called the logistic gowth
F-IF Logistic Gowth Model, Abstact Vesion Alignments to Content Standads: F-IFB4 Task An impotant example of a model often used in biology o ecology to model population gowth is called the logistic gowth
III. Spherical Waves and Radiation
 III. Spherical Waves and Radiation Antennas radiate spherical waves into free space Receiving antennas, reciprocity, path gain and path loss Noise as a limit to reception Ray model for antennas above a
III. Spherical Waves and Radiation Antennas radiate spherical waves into free space Receiving antennas, reciprocity, path gain and path loss Noise as a limit to reception Ray model for antennas above a
PH126 Exam I Solutions
 PH6 Exam I Solutions q Q Q q. Fou positively chage boies, two with chage Q an two with chage q, ae connecte by fou unstetchable stings of equal length. In the absence of extenal foces they assume the equilibium
PH6 Exam I Solutions q Q Q q. Fou positively chage boies, two with chage Q an two with chage q, ae connecte by fou unstetchable stings of equal length. In the absence of extenal foces they assume the equilibium
Random Variables and Probability Distribution Random Variable
 Random Vaiables and Pobability Distibution Random Vaiable Random vaiable: If S is the sample space P(S) is the powe set of the sample space, P is the pobability of the function then (S, P(S), P) is called
Random Vaiables and Pobability Distibution Random Vaiable Random vaiable: If S is the sample space P(S) is the powe set of the sample space, P is the pobability of the function then (S, P(S), P) is called
Physics 121 Hour Exam #5 Solution
 Physics 2 Hou xam # Solution This exam consists of a five poblems on five pages. Point values ae given with each poblem. They add up to 99 points; you will get fee point to make a total of. In any given
Physics 2 Hou xam # Solution This exam consists of a five poblems on five pages. Point values ae given with each poblem. They add up to 99 points; you will get fee point to make a total of. In any given
ECE 6340 Intermediate EM Waves. Fall Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE. Notes 4
 ECE 6340 Intemediate EM Waves Fall 016 Pof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE Notes 4 1 Debye Model This model explains molecula effects. y We conside an electic field applied in the x diection. Molecule:
ECE 6340 Intemediate EM Waves Fall 016 Pof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE Notes 4 1 Debye Model This model explains molecula effects. y We conside an electic field applied in the x diection. Molecule:
Equilibria of a cylindrical plasma
 // Miscellaneous Execises Cylinical equilibia Equilibia of a cylinical plasma Consie a infinitely long cyline of plasma with a stong axial magnetic fiel (a geat fusion evice) Plasma pessue will cause the
// Miscellaneous Execises Cylinical equilibia Equilibia of a cylinical plasma Consie a infinitely long cyline of plasma with a stong axial magnetic fiel (a geat fusion evice) Plasma pessue will cause the
1. Review of Probability.
 1. Review of Pobability. What is pobability? Pefom an expeiment. The esult is not pedictable. One of finitely many possibilities R 1, R 2,, R k can occu. Some ae pehaps moe likely than othes. We assign
1. Review of Pobability. What is pobability? Pefom an expeiment. The esult is not pedictable. One of finitely many possibilities R 1, R 2,, R k can occu. Some ae pehaps moe likely than othes. We assign
Lecture 28: Convergence of Random Variables and Related Theorems
 EE50: Pobability Foundations fo Electical Enginees July-Novembe 205 Lectue 28: Convegence of Random Vaiables and Related Theoems Lectue:. Kishna Jagannathan Scibe: Gopal, Sudhasan, Ajay, Swamy, Kolla An
EE50: Pobability Foundations fo Electical Enginees July-Novembe 205 Lectue 28: Convegence of Random Vaiables and Related Theoems Lectue:. Kishna Jagannathan Scibe: Gopal, Sudhasan, Ajay, Swamy, Kolla An
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation
 1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physical insight in the sound geneation mechanism can be gained by consideing simple analytical solutions to the wave equation. One example is to conside acoustic
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physical insight in the sound geneation mechanism can be gained by consideing simple analytical solutions to the wave equation. One example is to conside acoustic
Solution to HW 3, Ma 1a Fall 2016
 Solution to HW 3, Ma a Fall 206 Section 2. Execise 2: Let C be a subset of the eal numbes consisting of those eal numbes x having the popety that evey digit in the decimal expansion of x is, 3, 5, o 7.
Solution to HW 3, Ma a Fall 206 Section 2. Execise 2: Let C be a subset of the eal numbes consisting of those eal numbes x having the popety that evey digit in the decimal expansion of x is, 3, 5, o 7.
Math 1105: Calculus I (Math/Sci majors) MWF 11am / 12pm, Campion 235 Written homework 3
 Math : alculus I Math/Sci majos MWF am / pm, ampion Witten homewok Review: p 94, p 977,8,9,6, 6: p 46, 6: p 4964b,c,69, 6: p 47,6 p 94, Evaluate the following it by identifying the integal that it epesents:
Math : alculus I Math/Sci majos MWF am / pm, ampion Witten homewok Review: p 94, p 977,8,9,6, 6: p 46, 6: p 4964b,c,69, 6: p 47,6 p 94, Evaluate the following it by identifying the integal that it epesents:
4. Compare the electric force holding the electron in orbit ( r = 0.53
 Electostatics WS Electic Foce an Fiel. Calculate the magnitue of the foce between two 3.60-µ C point chages 9.3 cm apat.. How many electons make up a chage of 30.0 µ C? 3. Two chage ust paticles exet a
Electostatics WS Electic Foce an Fiel. Calculate the magnitue of the foce between two 3.60-µ C point chages 9.3 cm apat.. How many electons make up a chage of 30.0 µ C? 3. Two chage ust paticles exet a
Problem 1. Part b. Part a. Wayne Witzke ProblemSet #1 PHY 361. Calculate x, the expected value of x, defined by
 Poblem Pat a The nomal distibution Gaussian distibution o bell cuve has the fom f Ce µ Calculate the nomalization facto C by equiing the distibution to be nomalized f Substituting in f, defined above,
Poblem Pat a The nomal distibution Gaussian distibution o bell cuve has the fom f Ce µ Calculate the nomalization facto C by equiing the distibution to be nomalized f Substituting in f, defined above,
10/04/18. P [P(x)] 1 negl(n).
![10/04/18. P [P(x)] 1 negl(n). 10/04/18. P [P(x)] 1 negl(n).](/thumbs/92/110495316.jpg) Mastemath, Sping 208 Into to Lattice lgs & Cypto Lectue 0 0/04/8 Lectues: D. Dadush, L. Ducas Scibe: K. de Boe Intoduction In this lectue, we will teat two main pats. Duing the fist pat we continue the
Mastemath, Sping 208 Into to Lattice lgs & Cypto Lectue 0 0/04/8 Lectues: D. Dadush, L. Ducas Scibe: K. de Boe Intoduction In this lectue, we will teat two main pats. Duing the fist pat we continue the
DIMENSIONALITY LOSS IN MIMO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 DIMENSIONALITY LOSS IN MIMO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Segey Loya, Amma Koui School of Infomation Technology and Engineeing (SITE) Univesity of Ottawa, 6 Louis Pasteu, Ottawa, Ontaio, Canada, KN 6N5 Email:
DIMENSIONALITY LOSS IN MIMO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Segey Loya, Amma Koui School of Infomation Technology and Engineeing (SITE) Univesity of Ottawa, 6 Louis Pasteu, Ottawa, Ontaio, Canada, KN 6N5 Email:
A Deep Convolutional Neural Network Based on Nested Residue Number System
 A Deep Convolutional Neual Netwok Based on Nested Residue Numbe System Hioki Nakahaa Ehime Univesity, Japan Tsutomu Sasao Meiji Univesity, Japan Abstact A pe-tained deep convolutional neual netwok (DCNN)
A Deep Convolutional Neual Netwok Based on Nested Residue Numbe System Hioki Nakahaa Ehime Univesity, Japan Tsutomu Sasao Meiji Univesity, Japan Abstact A pe-tained deep convolutional neual netwok (DCNN)
2. Radiation Field Basics I. Specific Intensity
 . Raiation Fiel Basics Rutten:. Basic efinitions of intensity, flux Enegy ensity, aiation pessue E Specific ntensity t Pencil beam of aiation at position, iection n, caying enegy E, pasg though aea, between
. Raiation Fiel Basics Rutten:. Basic efinitions of intensity, flux Enegy ensity, aiation pessue E Specific ntensity t Pencil beam of aiation at position, iection n, caying enegy E, pasg though aea, between
3. Electromagnetic Waves II
 Lectue 3 - Electomagnetic Waves II 9 3. Electomagnetic Waves II Last time, we discussed the following. 1. The popagation of an EM wave though a macoscopic media: We discussed how the wave inteacts with
Lectue 3 - Electomagnetic Waves II 9 3. Electomagnetic Waves II Last time, we discussed the following. 1. The popagation of an EM wave though a macoscopic media: We discussed how the wave inteacts with
Circular-Rotational Motion Mock Exam. Instructions: (92 points) Answer the following questions. SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK.
 AP Physics C Sping, 2017 Cicula-Rotational Motion Mock Exam Name: Answe Key M. Leonad Instuctions: (92 points) Answe the following questions. SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK. ( ) 1. A stuntman dives a motocycle
AP Physics C Sping, 2017 Cicula-Rotational Motion Mock Exam Name: Answe Key M. Leonad Instuctions: (92 points) Answe the following questions. SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK. ( ) 1. A stuntman dives a motocycle
Nuclear Medicine Physics 02 Oct. 2007
 Nuclea Medicine Physics Oct. 7 Counting Statistics and Eo Popagation Nuclea Medicine Physics Lectues Imaging Reseach Laboatoy, Radiology Dept. Lay MacDonald 1//7 Statistics (Summaized in One Slide) Type
Nuclea Medicine Physics Oct. 7 Counting Statistics and Eo Popagation Nuclea Medicine Physics Lectues Imaging Reseach Laboatoy, Radiology Dept. Lay MacDonald 1//7 Statistics (Summaized in One Slide) Type
Acoustic Impedances of Audiometric Earphones Coupled to Different Loads
 Acoustic Impeances of Auiometic Eaphones Couple to Diffeent Loas Dejan Ćiić, Dote Hammeshøi Depatment of Acoustics, Aalbog Univesity, DK-9 Aalbog, Feeik Bajes Vej 7B 5, Denmak, {c, h}@acoustics.aau.k The
Acoustic Impeances of Auiometic Eaphones Couple to Diffeent Loas Dejan Ćiić, Dote Hammeshøi Depatment of Acoustics, Aalbog Univesity, DK-9 Aalbog, Feeik Bajes Vej 7B 5, Denmak, {c, h}@acoustics.aau.k The
Mutual impedance between linear elements: The induced EMF method. Persa Kyritsi September 29th, 2005 FRB7, A1-104
 Mutual impedance between linea elements: The induced EMF method Septembe 9th, 5 FRB7, A-4 Outline Septembe 9, 5 Reminde: self impedance nduced EMF method Nea-field of a dipole Self impedance vs. Mutual
Mutual impedance between linea elements: The induced EMF method Septembe 9th, 5 FRB7, A-4 Outline Septembe 9, 5 Reminde: self impedance nduced EMF method Nea-field of a dipole Self impedance vs. Mutual
ELECTRON ENERGY DISTRIBUTIONS AND NON-COLLISIONAL HEATING IN MAGNETICALLY ENHANCED INDUCTIVELY COUPLED PLASMAS*
 ELECTRON ENERGY DISTRIUTIONS AND NON-COLLISIONAL HEATING IN MAGNETICALLY ENHANCED INDUCTIVELY COUPLED PLASMAS* Ronald L. Kinde and Mak J. Kushne Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing Ubana, IL
ELECTRON ENERGY DISTRIUTIONS AND NON-COLLISIONAL HEATING IN MAGNETICALLY ENHANCED INDUCTIVELY COUPLED PLASMAS* Ronald L. Kinde and Mak J. Kushne Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing Ubana, IL
DOING PHYSICS WITH MATLAB COMPUTATIONAL OPTICS
 DOING PHYIC WITH MTLB COMPUTTIONL OPTIC FOUNDTION OF CLR DIFFRCTION THEORY Ian Coope chool of Physics, Univesity of ydney ian.coope@sydney.edu.au DOWNLOD DIRECTORY FOR MTLB CRIPT View document: Numeical
DOING PHYIC WITH MTLB COMPUTTIONL OPTIC FOUNDTION OF CLR DIFFRCTION THEORY Ian Coope chool of Physics, Univesity of ydney ian.coope@sydney.edu.au DOWNLOD DIRECTORY FOR MTLB CRIPT View document: Numeical
15. SIMPLE MHD EQUILIBRIA
 15. SIMPLE MHD EQUILIBRIA In this Section we will examine some simple examples of MHD equilibium configuations. These will all be in cylinical geomety. They fom the basis fo moe the complicate equilibium
15. SIMPLE MHD EQUILIBRIA In this Section we will examine some simple examples of MHD equilibium configuations. These will all be in cylinical geomety. They fom the basis fo moe the complicate equilibium
Empirical Prediction of Fitting Densities in Industrial Workrooms for Ray Tracing. 1 Introduction. 2 Ray Tracing using DRAYCUB
 Empiical Pediction of Fitting Densities in Industial Wokooms fo Ray Tacing Katina Scheebnyj, Muay Hodgson Univesity of Bitish Columbia, SOEH-MECH, Acoustics and Noise Reseach Goup, 226 East Mall, Vancouve,
Empiical Pediction of Fitting Densities in Industial Wokooms fo Ray Tacing Katina Scheebnyj, Muay Hodgson Univesity of Bitish Columbia, SOEH-MECH, Acoustics and Noise Reseach Goup, 226 East Mall, Vancouve,
Tidal forces. m r. m 1 m 2. x r 2. r 1
 Tidal foces Befoe we look at fee waves on the eath, let s fist exaine one class of otion that is diectly foced: astonoic tides. Hee we will biefly conside soe of the tidal geneating foces fo -body systes.
Tidal foces Befoe we look at fee waves on the eath, let s fist exaine one class of otion that is diectly foced: astonoic tides. Hee we will biefly conside soe of the tidal geneating foces fo -body systes.
Energy Savings Achievable in Connection Preserving Energy Saving Algorithms
 Enegy Savings Achievable in Connection Peseving Enegy Saving Algoithms Seh Chun Ng School of Electical and Infomation Engineeing Univesity of Sydney National ICT Austalia Limited Sydney, Austalia Email:
Enegy Savings Achievable in Connection Peseving Enegy Saving Algoithms Seh Chun Ng School of Electical and Infomation Engineeing Univesity of Sydney National ICT Austalia Limited Sydney, Austalia Email:
Rate Splitting is Approximately Optimal for Fading Gaussian Interference Channels
 Rate Splitting is Appoximately Optimal fo Fading Gaussian Intefeence Channels Joyson Sebastian, Can Kaakus, Suhas Diggavi, I-Hsiang Wang Abstact In this pape, we study the -use Gaussian intefeence-channel
Rate Splitting is Appoximately Optimal fo Fading Gaussian Intefeence Channels Joyson Sebastian, Can Kaakus, Suhas Diggavi, I-Hsiang Wang Abstact In this pape, we study the -use Gaussian intefeence-channel
σ = neμ = v D = E H, the Hall Field B Z E Y = ee y Determining n and μ: The Hall Effect V x, E x I, J x E y B z F = qe + qv B F y
 Detemining n and μ: The Hall Effect V x, E x + + + + + + + + + + + --------- E y I, J x F = qe + qv B F y = ev D B z F y = ee y B z In steady state, E Y = v D B Z = E H, the Hall Field Since v D =-J x
Detemining n and μ: The Hall Effect V x, E x + + + + + + + + + + + --------- E y I, J x F = qe + qv B F y = ev D B z F y = ee y B z In steady state, E Y = v D B Z = E H, the Hall Field Since v D =-J x
Uniform Circular Motion
 Unifom Cicula Motion constant speed Pick a point in the objects motion... What diection is the velocity? HINT Think about what diection the object would tavel if the sting wee cut Unifom Cicula Motion
Unifom Cicula Motion constant speed Pick a point in the objects motion... What diection is the velocity? HINT Think about what diection the object would tavel if the sting wee cut Unifom Cicula Motion
Electric Potential and Gauss s Law, Configuration Energy Challenge Problem Solutions
 Poblem 1: Electic Potential an Gauss s Law, Configuation Enegy Challenge Poblem Solutions Consie a vey long o, aius an chage to a unifom linea chage ensity λ a) Calculate the electic fiel eveywhee outsie
Poblem 1: Electic Potential an Gauss s Law, Configuation Enegy Challenge Poblem Solutions Consie a vey long o, aius an chage to a unifom linea chage ensity λ a) Calculate the electic fiel eveywhee outsie
angular momentum Angular Momentum in Halos & Galaxies how do galaxies get their spin? the spin parameter
 Physics 46, Sping 7 Lectue 11 angula momentum Angula Momentum in Halos & Galaxies Tial toque theoy Halo spin The angula momentum istibution in halos Gas conensation & Disk fomation The AM poblems gas AM
Physics 46, Sping 7 Lectue 11 angula momentum Angula Momentum in Halos & Galaxies Tial toque theoy Halo spin The angula momentum istibution in halos Gas conensation & Disk fomation The AM poblems gas AM
The Substring Search Problem
 The Substing Seach Poblem One algoithm which is used in a vaiety of applications is the family of substing seach algoithms. These algoithms allow a use to detemine if, given two chaacte stings, one is
The Substing Seach Poblem One algoithm which is used in a vaiety of applications is the family of substing seach algoithms. These algoithms allow a use to detemine if, given two chaacte stings, one is
Electrodynamics Subject Exam Prep Quiz, Tuesday, May 2, 2017
 Electodynamics ubject Exam Pep Quiz, Tuesday, May, 017 a ( b c ) b( a c ) c ( a b), a ( b c ) b ( c a ) c ( a b), ( a b) ( c d) ( a c )( b d) ( a d)( b c ), ( ψ) 0, ( a ) 0, ( a ) ( a ) a, (ψ a) a ψ +
Electodynamics ubject Exam Pep Quiz, Tuesday, May, 017 a ( b c ) b( a c ) c ( a b), a ( b c ) b ( c a ) c ( a b), ( a b) ( c d) ( a c )( b d) ( a d)( b c ), ( ψ) 0, ( a ) 0, ( a ) ( a ) a, (ψ a) a ψ +
Gravitational Radiation from Oscillating Gravitational Dipole
 Gavitational Radiation fom Oscillating Gavitational Dipole Fan De Aquino Maanhao State Univesity, Physics Depatment, S.Luis/MA, Bazil. deaquino@uema.b Abstact. The concept of Gavitational Dipole is intoduced
Gavitational Radiation fom Oscillating Gavitational Dipole Fan De Aquino Maanhao State Univesity, Physics Depatment, S.Luis/MA, Bazil. deaquino@uema.b Abstact. The concept of Gavitational Dipole is intoduced
1.2 Differential cross section
 .2. DIFFERENTIAL CROSS SECTION Febuay 9, 205 Lectue VIII.2 Diffeential coss section We found that the solution to the Schodinge equation has the fom e ik x ψ 2π 3/2 fk, k + e ik x and that fk, k = 2 m
.2. DIFFERENTIAL CROSS SECTION Febuay 9, 205 Lectue VIII.2 Diffeential coss section We found that the solution to the Schodinge equation has the fom e ik x ψ 2π 3/2 fk, k + e ik x and that fk, k = 2 m
Double-angle & power-reduction identities. Elementary Functions. Double-angle & power-reduction identities. Double-angle & power-reduction identities
 Double-angle & powe-eduction identities Pat 5, Tigonomety Lectue 5a, Double Angle and Powe Reduction Fomulas In the pevious pesentation we developed fomulas fo cos( β) and sin( β) These fomulas lead natually
Double-angle & powe-eduction identities Pat 5, Tigonomety Lectue 5a, Double Angle and Powe Reduction Fomulas In the pevious pesentation we developed fomulas fo cos( β) and sin( β) These fomulas lead natually
Chapter 2 Classical propagation
 Chapte Classical popagation Model: Light: electomagnetic wave Atom and molecule: classical dipole oscillato n. / / t c nz i z t z k i e e c i n k e t z Two popagation paametes: n. Popagation of light in
Chapte Classical popagation Model: Light: electomagnetic wave Atom and molecule: classical dipole oscillato n. / / t c nz i z t z k i e e c i n k e t z Two popagation paametes: n. Popagation of light in
4/18/2005. Statistical Learning Theory
 Statistical Leaning Theoy Statistical Leaning Theoy A model of supevised leaning consists of: a Envionment - Supplying a vecto x with a fixed but unknown pdf F x (x b Teache. It povides a desied esponse
Statistical Leaning Theoy Statistical Leaning Theoy A model of supevised leaning consists of: a Envionment - Supplying a vecto x with a fixed but unknown pdf F x (x b Teache. It povides a desied esponse
Electromagnetic scattering. Graduate Course Electrical Engineering (Communications) 1 st Semester, Sharif University of Technology
 Electomagnetic scatteing Gaduate Couse Electical Engineeing (Communications) 1 st Semeste, 1390-1391 Shaif Univesity of Technology Geneal infomation Infomation about the instucto: Instucto: Behzad Rejaei
Electomagnetic scatteing Gaduate Couse Electical Engineeing (Communications) 1 st Semeste, 1390-1391 Shaif Univesity of Technology Geneal infomation Infomation about the instucto: Instucto: Behzad Rejaei
Quantum tunneling: α-decay
 Announcements: Quantum tunneling: α-decay Exam 2 solutions ae posted on CULean Homewok solutions will be posted by 7pm tonight Next weeks homewok will be available by noon tomoow Homewok aveage fo set
Announcements: Quantum tunneling: α-decay Exam 2 solutions ae posted on CULean Homewok solutions will be posted by 7pm tonight Next weeks homewok will be available by noon tomoow Homewok aveage fo set
11) A thin, uniform rod of mass M is supported by two vertical strings, as shown below.
 Fall 2007 Qualifie Pat II 12 minute questions 11) A thin, unifom od of mass M is suppoted by two vetical stings, as shown below. Find the tension in the emaining sting immediately afte one of the stings
Fall 2007 Qualifie Pat II 12 minute questions 11) A thin, unifom od of mass M is suppoted by two vetical stings, as shown below. Find the tension in the emaining sting immediately afte one of the stings
Revision of Lecture Eight
 Revision of Lectue Eight Baseband equivalent system and equiements of optimal tansmit and eceive filteing: (1) achieve zeo ISI, and () maximise the eceive SNR Thee detection schemes: Theshold detection
Revision of Lectue Eight Baseband equivalent system and equiements of optimal tansmit and eceive filteing: (1) achieve zeo ISI, and () maximise the eceive SNR Thee detection schemes: Theshold detection
FREE SPACE OPTICS - MEASUREMENT OF TRANSMISSION QUALITY LINK PARAMETERS
 FREE SPACE OPTICS - MEASUREMENT OF TRANSMISSION QUALITY LINK PARAMETERS Pavel Hovořák, Otaka Wilfet Depatment of Radioelectonics, Bno Univesity of Technology, Faculty of Electical Engineeing and Communication,
FREE SPACE OPTICS - MEASUREMENT OF TRANSMISSION QUALITY LINK PARAMETERS Pavel Hovořák, Otaka Wilfet Depatment of Radioelectonics, Bno Univesity of Technology, Faculty of Electical Engineeing and Communication,
Newton s Laws, Kepler s Laws, and Planetary Orbits
 Newton s Laws, Keple s Laws, and Planetay Obits PROBLEM SET 4 DUE TUESDAY AT START OF LECTURE 28 Septembe 2017 ASTRONOMY 111 FALL 2017 1 Newton s & Keple s laws and planetay obits Unifom cicula motion
Newton s Laws, Keple s Laws, and Planetay Obits PROBLEM SET 4 DUE TUESDAY AT START OF LECTURE 28 Septembe 2017 ASTRONOMY 111 FALL 2017 1 Newton s & Keple s laws and planetay obits Unifom cicula motion
I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION
 I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION The Helmohltz equation in 4 dimensions is 4 + k G 4 x, x = δ 4 x x. In this equation, G is the Geen s function and 4 efes to the dimensionality. In the vey end,
I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION The Helmohltz equation in 4 dimensions is 4 + k G 4 x, x = δ 4 x x. In this equation, G is the Geen s function and 4 efes to the dimensionality. In the vey end,
CHAPTER IV RADIATION BY SIMPLE ACOUSTIC SOURCE. or by vibratory forces acting directly on the fluid, or by the violent motion of the fluid itself.
 CHAPTER IV RADIATION BY SIMPLE ACOUSTIC SOURCE 4.1 POINT SOURCE Sound waves ae geneated by the vibation of any solid body in contact with the fluid medium o by vibatoy foces acting diectly on the fluid,
CHAPTER IV RADIATION BY SIMPLE ACOUSTIC SOURCE 4.1 POINT SOURCE Sound waves ae geneated by the vibation of any solid body in contact with the fluid medium o by vibatoy foces acting diectly on the fluid,
Inverse Square Law and Polarization
 Invese Squae Law and Polaization Objectives: To show that light intensity is invesely popotional to the squae of the distance fom a point light souce and to show that the intensity of the light tansmitted
Invese Squae Law and Polaization Objectives: To show that light intensity is invesely popotional to the squae of the distance fom a point light souce and to show that the intensity of the light tansmitted
Homework Set 3 Physics 319 Classical Mechanics
 Homewok Set 3 Phsics 319 lassical Mechanics Poblem 5.13 a) To fin the equilibium position (whee thee is no foce) set the eivative of the potential to zeo U 1 R U0 R U 0 at R R b) If R is much smalle than
Homewok Set 3 Phsics 319 lassical Mechanics Poblem 5.13 a) To fin the equilibium position (whee thee is no foce) set the eivative of the potential to zeo U 1 R U0 R U 0 at R R b) If R is much smalle than
Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism
 Physics C: Electicity an Magnetism TABLE OF INFORMATION FOR CONSTANTS AND CONVERSION FACTORS - unifie atomic mass unit, u =. 66 7 kg = 93 MeV/ c Poton mass, m p = 67. 7 kg Neuton mass, m n = 67. 7 kg Electon
Physics C: Electicity an Magnetism TABLE OF INFORMATION FOR CONSTANTS AND CONVERSION FACTORS - unifie atomic mass unit, u =. 66 7 kg = 93 MeV/ c Poton mass, m p = 67. 7 kg Neuton mass, m n = 67. 7 kg Electon
Much that has already been said about changes of variable relates to transformations between different coordinate systems.
 MULTIPLE INTEGRLS I P Calculus Cooinate Sstems Much that has alea been sai about changes of vaiable elates to tansfomations between iffeent cooinate sstems. The main cooinate sstems use in the solution
MULTIPLE INTEGRLS I P Calculus Cooinate Sstems Much that has alea been sai about changes of vaiable elates to tansfomations between iffeent cooinate sstems. The main cooinate sstems use in the solution
The Great Wave Hokusai. LO: Recognize physical principles associated with terms in sonar equation.
 Sona Equation: The Wave Equation The Geat Wave Hokusai LO: Recognize hysical inciles associated with tems in sona equation. the Punchline If density too high to esolve individual oganisms, then: E[enegy
Sona Equation: The Wave Equation The Geat Wave Hokusai LO: Recognize hysical inciles associated with tems in sona equation. the Punchline If density too high to esolve individual oganisms, then: E[enegy
Flow of Energy and Momentum inthenearzoneofahertziandipole
 1 Poblem Flow of Enegy and Momentum intheneazoneofahetziandipole Kik T. McDonald Joseph Heny Laboatoies, Pinceton Univesity, Pinceton, NJ 08544 Apil 11, 2007; updated May 13, 2014) Discuss the density
1 Poblem Flow of Enegy and Momentum intheneazoneofahetziandipole Kik T. McDonald Joseph Heny Laboatoies, Pinceton Univesity, Pinceton, NJ 08544 Apil 11, 2007; updated May 13, 2014) Discuss the density
MONTE CARLO SIMULATION OF FLUID FLOW
 MONTE CARLO SIMULATION OF FLUID FLOW M. Ragheb 3/7/3 INTRODUCTION We conside the situation of Fee Molecula Collisionless and Reflective Flow. Collisionless flows occu in the field of aefied gas dynamics.
MONTE CARLO SIMULATION OF FLUID FLOW M. Ragheb 3/7/3 INTRODUCTION We conside the situation of Fee Molecula Collisionless and Reflective Flow. Collisionless flows occu in the field of aefied gas dynamics.
EXAM NMR (8N090) November , am
 EXA NR (8N9) Novembe 5 9, 9. 1. am Remaks: 1. The exam consists of 8 questions, each with 3 pats.. Each question yields the same amount of points. 3. You ae allowed to use the fomula sheet which has been
EXA NR (8N9) Novembe 5 9, 9. 1. am Remaks: 1. The exam consists of 8 questions, each with 3 pats.. Each question yields the same amount of points. 3. You ae allowed to use the fomula sheet which has been
That is, the acceleration of the electron is larger than the acceleration of the proton by the same factor the electron is lighter than the proton.
 PHY 8 Test Pactice Solutions Sping Q: [] A poton an an electon attact each othe electically so, when elease fom est, they will acceleate towa each othe. Which paticle will have a lage acceleation? (Neglect
PHY 8 Test Pactice Solutions Sping Q: [] A poton an an electon attact each othe electically so, when elease fom est, they will acceleate towa each othe. Which paticle will have a lage acceleation? (Neglect
Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors
 Sensos an ctuatos Intouction to sensos Sane Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Depatment of Electical Engineeing Electonic Systems PITIE SENSORS (hapte 3., 7., 9.,.6, 3., 3.) 3 Senso classification type / quantity
Sensos an ctuatos Intouction to sensos Sane Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Depatment of Electical Engineeing Electonic Systems PITIE SENSORS (hapte 3., 7., 9.,.6, 3., 3.) 3 Senso classification type / quantity
Wireless Communications
 NETW701 Wireless Communications Dr. Wassim Alexan Winter 2018 Lecture 2 NETW705 Mobile Communication Networks Dr. Wassim Alexan Winter 2018 Lecture 2 Wassim Alexan 2 Reflection When a radio wave propagating
NETW701 Wireless Communications Dr. Wassim Alexan Winter 2018 Lecture 2 NETW705 Mobile Communication Networks Dr. Wassim Alexan Winter 2018 Lecture 2 Wassim Alexan 2 Reflection When a radio wave propagating
Movie Review Part One due Tuesday (in class) please print
 Movie Review Pat One due Tuesday (in class) please pint Test in class on Fiday. You may stat at 8:30 if you want. (The topic of powe is not on test.) Chaptes 4-6 Main Ideas in Class Today Afte class, you
Movie Review Pat One due Tuesday (in class) please pint Test in class on Fiday. You may stat at 8:30 if you want. (The topic of powe is not on test.) Chaptes 4-6 Main Ideas in Class Today Afte class, you
Improvement in Accuracy for Design of Multidielectric Layers Microstrip Patch Antenna
 498 Impovement in Accuacy fo Design of Multidielectic Layes Micostip Patch Antenna Sami Dev Gupta*, Anvesh Gag and Anuag P. Saan Jaypee Institute of Infomation Technology Univesity Noida, Utta Padesh,
498 Impovement in Accuacy fo Design of Multidielectic Layes Micostip Patch Antenna Sami Dev Gupta*, Anvesh Gag and Anuag P. Saan Jaypee Institute of Infomation Technology Univesity Noida, Utta Padesh,
Answers to Coursebook questions Chapter 2.11
 Answes to Couseook questions Chapte 11 1 he net foe on the satellite is F = G Mm and this plays the ole of the entipetal foe on the satellite, ie mv mv Equating the two gives π Fo iula motion we have that
Answes to Couseook questions Chapte 11 1 he net foe on the satellite is F = G Mm and this plays the ole of the entipetal foe on the satellite, ie mv mv Equating the two gives π Fo iula motion we have that
= 4 3 π( m) 3 (5480 kg m 3 ) = kg.
 CHAPTER 11 THE GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Newton s Law of Gavitation m 1 m A foce of attaction occus between two masses given by Newton s Law of Gavitation Inetial mass and gavitational mass Gavitational potential
CHAPTER 11 THE GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Newton s Law of Gavitation m 1 m A foce of attaction occus between two masses given by Newton s Law of Gavitation Inetial mass and gavitational mass Gavitational potential
COMPUTATIONS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS RADIATED FROM COMPLEX LIGHTNING CHANNELS
 Pogess In Electomagnetics Reseach, PIER 73, 93 105, 2007 COMPUTATIONS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS RADIATED FROM COMPLEX LIGHTNING CHANNELS T.-X. Song, Y.-H. Liu, and J.-M. Xiong School of Mechanical Engineeing
Pogess In Electomagnetics Reseach, PIER 73, 93 105, 2007 COMPUTATIONS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS RADIATED FROM COMPLEX LIGHTNING CHANNELS T.-X. Song, Y.-H. Liu, and J.-M. Xiong School of Mechanical Engineeing
Sensor and Simulation Notes. Note 525. Oct Lens Design for a Prolate-Spheroidal Impulse radiating Antenna (IRA)
 Senso and Simulation Notes Note 55 Oct 7 Lens Design fo a Polate-Spheoidal Impulse adiating Antenna (IRA) Sehat Altunc, Cal E. Baum, Chistos G. Chistodoulou and Edl Schamiloglu Univesity of New Mexico
Senso and Simulation Notes Note 55 Oct 7 Lens Design fo a Polate-Spheoidal Impulse adiating Antenna (IRA) Sehat Altunc, Cal E. Baum, Chistos G. Chistodoulou and Edl Schamiloglu Univesity of New Mexico
Computer Propagation Analysis Tools
 Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools. Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools Inoducion By now you ae pobably geing he idea ha pedicing eceived signal sengh is a eally impoan as in he design of a wieless communicaion
Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools. Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools Inoducion By now you ae pobably geing he idea ha pedicing eceived signal sengh is a eally impoan as in he design of a wieless communicaion
4.3 Area of a Sector. Area of a Sector Section
 ea of a Secto Section 4. 9 4. ea of a Secto In geomety you leaned that the aea of a cicle of adius is π 2. We will now lean how to find the aea of a secto of a cicle. secto is the egion bounded by a cental
ea of a Secto Section 4. 9 4. ea of a Secto In geomety you leaned that the aea of a cicle of adius is π 2. We will now lean how to find the aea of a secto of a cicle. secto is the egion bounded by a cental
ECE Spring Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 1
 ECE 6345 ping 5 Po. David. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes Oveview In this set o notes we discuss the CAD model o the micostip antenna. Discuss complex esonance equency Deive omula o Q Deive omula o input impedance
ECE 6345 ping 5 Po. David. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes Oveview In this set o notes we discuss the CAD model o the micostip antenna. Discuss complex esonance equency Deive omula o Q Deive omula o input impedance
Wave Incidence. Dr. Cruz-Pol. Normal Incidence. Ex.1. Light traveling in air encounters the water; another medium.
 D. Cu-Pol Ex.1. Light taveling in ai encountes the wate; anothe medium. Wave Incidence [Chapte 10 cont, Sadiku] D. Sanda Cu-Pol Electical and Compute Engineeing Dept. UPR-Maagüe Ex.1. Light encountes atmosphee,
D. Cu-Pol Ex.1. Light taveling in ai encountes the wate; anothe medium. Wave Incidence [Chapte 10 cont, Sadiku] D. Sanda Cu-Pol Electical and Compute Engineeing Dept. UPR-Maagüe Ex.1. Light encountes atmosphee,
SPH4UI 28/02/2011. Total energy = K + U is constant! Electric Potential Mr. Burns. GMm
 8//11 Electicity has Enegy SPH4I Electic Potential M. Buns To sepaate negative an positive chages fom each othe, wok must be one against the foce of attaction. Theefoe sepeate chages ae in a higheenegy
8//11 Electicity has Enegy SPH4I Electic Potential M. Buns To sepaate negative an positive chages fom each othe, wok must be one against the foce of attaction. Theefoe sepeate chages ae in a higheenegy
Advanced Subsidiary GCE (H157) Advanced GCE (H557) Physics B (Advancing Physics) Data, Formulae and Relationships Booklet
 Advanced Subsidiay GCE (H57) Advanced GCE (H557) Physics B (Advancing Physics) Data, Fomulae and Relationships Booklet The infomation in this booklet is fo the use of candidates following the Advanced
Advanced Subsidiay GCE (H57) Advanced GCE (H557) Physics B (Advancing Physics) Data, Fomulae and Relationships Booklet The infomation in this booklet is fo the use of candidates following the Advanced
