Design of digital differentiators and integrators of order 1 2
|
|
|
- Silas Hensley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ISSN , England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 4 (2008) No. 3, pp Design of digital differentiators and integrators of order 1 2 B. T. Krishna, K. V. V. S. Reddy Department of ECE, GITAM University, Visakhapatnam, India (Received March , Accepted May ) Abstract. In this paper,design of digital differentiators and integrators of order 1 2 is presented.first,the rational approximation for the fractional operator s ± 1 2 is calculated. Next, using s to z transforms it is digitized. The results obtained were closer to ideal characteristics. Keywords: continued fraction expansion, Al-Alaoui transform, fractional order, convergence, discretization 1 Introduction Fractional order integrators and differentiators are used to calculate the fractional order integral and derivative of an input signal [8, 9]. These devices find applications in instrumentation,control systems,radar, digital Image processing, bio-medical engineering and other allied fields [3]. An ideal fractional order digital differentiator is defined by the following transfer function [4], H d (jω) = (jω) α (1) where α is fractional order and j = 1. Similarly an ideal fractional order integrator is defined as, H I (jω) = 1 (jω) α (2) The key step in the digital implementation of the fractional order differentiator/integrator is its discretization [4, 5, 11]. Direct and indirect discretization are the commonly used methods for discretization. Direct discretization method involves the application of the direct power series or continued fraction expansion of s to z transform. In [4, 11], the different methods of direct discretization of the fractional order controller are discussed. In [5], Dorcak et al. have compared all these direct discretization methods. In indirect discretization method,two steps are required, i.e., fitting the transfer function first and then discretizing the fit s-domain transfer function. In this paper, first, rational approximations for s and 1 s are obtained using continued fraction expansion. Then, using s to z transformations it is discretized. The paper is organised as follows. First order s to z transforms are discussed in Section 2. Design method is presented in section 3. Section 4 deals with Simulation Results and conclusions. 2 First order s to z transforms: S to z transforms play major role in the discretization [6, 10]. The s to z transform should be such that, The imaginary axis in the s-plane be mapped onto the unit circle in z plane. Corresponding author. address: tkbattula@gmail.com. Published by World Academic Press, World Academic Union
2 World Journal of Modelling and Simulation, Vol. 4 (2008) No. 3, pp A stable analog transfer function be transformed into a stable digital transfer function. Property 1 preserves the frequency selective properties of the continuous system, whereas property 2 ensures that stable continuous systems are mapped into stable discrete systems [6, 10]. Bilinear transform and backward difference transform were the most widely used s to z transforms. In case of backward difference transform, the imaginary axis of the s-plane maps as a circle of radius 1 / 2 centered at z = 1 / 2. Bilinear transform satisfies the above two conditions but it produces warping effect.the following is the expression for bilinear transform, 2(z 1) T (z + 1) (3) A new type of s to z transform called as Al-Alaoui transform is obtained from the interpolation of backward and bilinear transforms with a tuning factor, a of value varying from 0 to 1 [2]. H N (z) = The resulting s to z transform is, at z (z + 1) + (1 a)t (z 1) 2(z 1), 0 a 1 (4) 2(z 1) T [(1 a) + (1 + a)z] (5) Substituting a = 3 4, in Eq. (5) it simplifies to, 8(z 1) 7T (z ) (6) The above transform has been proved to be less warped than bilinear transformation and less linear than backward difference transform. The Al-Alaoui Transform has shown superior performance in digital filter design compared to previously existing s to z transforms [1, 2]. 3 Design method Continued fraction expansion is used to obtain the rational approximations of the irrational functions [7]. It helps in terminating an infinite order transfer function to finite order. Since the fractional order systems were characterized by infinite memory [3], they will have an infinite order rational approximation. So, in order to have practical realization of the system it s transfer function has to be terminated to a finite order. We have the continued fraction expansion for s as [7] Consequently, a + ( s a ) = a + s + a = a + 2a + s a2 2a+ s a2 2a+ (7) a + 2a + One can re-write the continued fraction as, 2a +... [Rogers][4] (8) a + s a 2 2a 1+ s a 2 4a 2 1+ s a 2 4a The above continued fraction expansion converges in the finite complex s-plane along the negative real axis satisfying the inequality < s 0. Considering number of terms of Eq. (7), the rational approximations obtained for 1 s were summarised in Tab. 1. In order to get the rational approximation of s the (9) WJMS for subscription: info@wjms.org.uk
3 184 B. Krishna & K. Reddy: Design of digital differentiators Table 1. Rational approximations for s S. NO No. of Terms Rational Approximation 3s s s 2 +10s+1 s 2 +10s s 3 +35s 2 +21s+1 s 3 +21s 2 +35s s 4 +84s s 2 +36s+1 s 4 +36s s 2 +84s s s s s 2 +55s+1 s 5 +55s s s s+11 Fig. 1. Comparison of Magnitude and Phase Responses of Rational approximation functions with ideal s expressions has to be simply reversed. Fig. 1 compares the magnitude and phase responses of rational approximations with the ideal one. From the magnitude and phase response Plots it is evident that fifth order rational approximation is best fit in s-domain. Higher order rational approximations can be obtained by increasing the number of terms in Eq. (7). So, 11s s s s s + 1 s s s s s = s5 + 55s s s s + 11 s 11s s s s s + 1 (10) (11) In order to check for the stability of the rational approximations as defined in Eq. (8) and (9), pole-zero plot are drawn and are shown in Fig. 2 and Fig. 3. From pole-zero plots,it is evident that pole and zeros interlace on negative real axis making the system as stable. By digitizing the Eq. (8) and (9) using transforms as defined in Eq. (3) and (6), the following transfer functions were obtained. WJMS for contribution: submit@wjms.org.uk
4 World Journal of Modelling and Simulation, Vol. 4 (2008) No. 3, pp Fig. 2. Pole-Zero Plot of s Fig. 3. Pole-Zero Plot of 1 s Fig. 4. Magnitude Response, Phase Response and error plots of digital differentiators H dt (z) = z z z z z z z z z z H da (z) = z z z z z z z z z z H IT (z) = z z z z z z z z z z H IA (z) = z z z z z z z z z z (12) (13) (14) (15) WJMS for subscription: info@wjms.org.uk
5 186 B. Krishna & K. Reddy: Design of digital differentiators Fig. 5. Magnitude Response, Phase Response and error plots of digital integrators where H dt (z), H IT (z) are the transfer functions of digital differentiator and integrator obtained using bilinear transform, and H da (z), H IA (z) are the transfer functions of digital differentiator and integrator when Al- Alaoui transform is used. It is to be noted that sampling time, T = 1 sec is used in all calculations. Fig. 6. Pole-zero diagrams WJMS for contribution: submit@wjms.org.uk
6 World Journal of Modelling and Simulation, Vol. 4 (2008) No. 3, pp Results and conclusions This section presents pole-zero diagrams, magnitude and phase responses of the designed digital differentiators and integrators evaluated at, sampling time, T = 1 sec. From the magnitude plots it is to be noted that Al-Alaoui transform has shown superior performance compared to bilinear transform. The phase response is more nearer to ideal using bilinear transform. The percent relative error is very less. Poles and zeros were lying inside of the unit circle and alternate on negative real axis. So, the indirect discretization produced stable,minimum phase differentiators and integrators. References [1] M. Al-Alaoui. Novel digital integrator and differentiator. Electronics Letters, 1993, 29(4): [2] M. Al-Alaoui. Filling the gap between the bilinear and the backward difference transforms: An interactive design approach. Int. J. of Electrical Engineering Education, 1997, 34(4): [3] J. Bruce, B. Mauro, G. Paolo. Physics of Fractal operators. Springer Verilog, [4] Y. Chen, B. Vinagre. A new IIR-type digital fractional order differentiator. Signal Processing, 2003, 83: [5] L. Dorcak, I. Petras, M. Zborovjan. Comparison of the methods for discrete approximation of the fractional-order operator. Acta Montanistica Slovaca, 2003, [6] E. Ifeachor, B. Jervis. Digital signal processing-a practical approach, pearson education [7] A. Khovanskii. The application of continued fractions and their generalizations to problems in approximation theory [8] K. Miller, B. Ross. An introduction to the fractional calculus and fractional differential equations. John Wiley sons, [9] K. Oldham, J. Spanier. The Fractional Calculus. Academic Press, [10] J. Proakis, D. Manolakis. Digital signal processing, principles, algorithms, and applications. PHI Publications, [11] B. Vinagre, Y. Chen, I. Petras. Two direct tustin discretization methods for fractional-order differentiator and integrator. J. franklininst, 2003, 340(5): WJMS for subscription: info@wjms.org.uk
An Improved Design for the IIR Digital Fractional order Differential Filter using Indirect Discretization Approach
 Volume 1 Issue4 pp 05-030 July 01 www. ijsret.org ISSN 78-088 An Improved Design for the IIR Digital Fractional order Differential Filter using Indirect Discretization Approach Jay kumar Pandey 1, Mausmi
Volume 1 Issue4 pp 05-030 July 01 www. ijsret.org ISSN 78-088 An Improved Design for the IIR Digital Fractional order Differential Filter using Indirect Discretization Approach Jay kumar Pandey 1, Mausmi
Discretization of Fractional-Order Differentiators and Integrators
 Preprints of the 19th World Congress The International Federation of Automatic Control Cape Town, South Africa. August 24-29, 14 Discretization of Fractional-Order Differentiators and Integrators Reyad
Preprints of the 19th World Congress The International Federation of Automatic Control Cape Town, South Africa. August 24-29, 14 Discretization of Fractional-Order Differentiators and Integrators Reyad
2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. I Reading:
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. I Reading:
Approximating fractional derivatives through the generalized mean
 Approximating fractional derivatives through the generalized mean J.A. Tenreiro Machado, Alexandra M. Galhano, Anabela M. Oliveira, József K. Tar a b s t r a c t This paper addresses the calculation of
Approximating fractional derivatives through the generalized mean J.A. Tenreiro Machado, Alexandra M. Galhano, Anabela M. Oliveira, József K. Tar a b s t r a c t This paper addresses the calculation of
The Time-Scaled Trapezoidal Integration Rule for Discrete Fractional Order Controllers
 The Time-Scaled Trapezoidal Integration Rule for Discrete Fractional Order Controllers Chengbin Ma and Yoichi Hori Electrical Control System Engineering, Information & System Division, Institute of Industrial
The Time-Scaled Trapezoidal Integration Rule for Discrete Fractional Order Controllers Chengbin Ma and Yoichi Hori Electrical Control System Engineering, Information & System Division, Institute of Industrial
Lecture 8 - IIR Filters (II)
 Lecture 8 - IIR Filters (II) James Barnes (James.Barnes@colostate.edu) Spring 2009 Colorado State University Dept of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE423 1 / 27 Lecture 8 Outline Introduction Digital
Lecture 8 - IIR Filters (II) James Barnes (James.Barnes@colostate.edu) Spring 2009 Colorado State University Dept of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE423 1 / 27 Lecture 8 Outline Introduction Digital
The Time-Scaled Trapezoidal Integration Rule for Discrete Fractional Order Controllers
 Nonlinear Dynamics 38: 171 18, 24. C 24 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. The Time-Scaled Trapezoidal Integration Rule for Discrete Fractional Order Controllers CHENGBIN MA and YOICHI
Nonlinear Dynamics 38: 171 18, 24. C 24 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. The Time-Scaled Trapezoidal Integration Rule for Discrete Fractional Order Controllers CHENGBIN MA and YOICHI
Using Continued Fraction Expansion to Discretize Fractional Order Derivatives
 Using Continued Fraction Expansion to Discretize Fractional Order Derivatives YangQuan Chen (yqchen@ieee.org) CSOIS, Utah State University, USA Blas M. Vinagre (bvinagre@unex.es) University of Extremadura,
Using Continued Fraction Expansion to Discretize Fractional Order Derivatives YangQuan Chen (yqchen@ieee.org) CSOIS, Utah State University, USA Blas M. Vinagre (bvinagre@unex.es) University of Extremadura,
ISSN (Print) Research Article. *Corresponding author Nitin Rawal
 Scholars Journal of Engineering and Technology (SJET) Sch. J. Eng. Tech., 016; 4(1):89-94 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources) www.saspublisher.com
Scholars Journal of Engineering and Technology (SJET) Sch. J. Eng. Tech., 016; 4(1):89-94 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources) www.saspublisher.com
Time-Domain Evaluation of Fractional Order Controllers Direct Discretization Methods
 Paper Time-Domain Evaluation of Fractional Order Controllers Direct Discretization Methods Chengbin Ma Yoichi Hori Student Member Member Fractional Order Control (FOC), in which the controlled systems
Paper Time-Domain Evaluation of Fractional Order Controllers Direct Discretization Methods Chengbin Ma Yoichi Hori Student Member Member Fractional Order Control (FOC), in which the controlled systems
On the Designing of Fractional Order FIR Differentiator Using Radial Basis Function and Window
 On the Designing of Fractional Order FIR Differentiator Using Radial Basis Function and Window Manjeet Kumar Digital Signal Processing Laboratory, Room No. 135, ECE Division, Netaji Subhas Institute of
On the Designing of Fractional Order FIR Differentiator Using Radial Basis Function and Window Manjeet Kumar Digital Signal Processing Laboratory, Room No. 135, ECE Division, Netaji Subhas Institute of
Applicatin of the α-approximation for Discretization of Analogue Systems
 FACTA UNIVERSITATIS (NIŠ) SER.: ELEC. ENERG. vol. 8, no. 3, December 5, 57-586 Applicatin of the α-approximation for Discretization of Analogue Systems Tomislav B. Šekara and Milić R. Stojić Abstract:
FACTA UNIVERSITATIS (NIŠ) SER.: ELEC. ENERG. vol. 8, no. 3, December 5, 57-586 Applicatin of the α-approximation for Discretization of Analogue Systems Tomislav B. Šekara and Milić R. Stojić Abstract:
Design of Higher Order LP and HP Digital IIR Filter Using the Concept of Teaching-Learning Based Optimization
 Design of Higher Order LP and HP Digital IIR Filter Using the Concept of Teaching-Learning Based Optimization DAMANPREET SINGH, J.S. DHILLON Department of Computer Science & Engineering Department of Electrical
Design of Higher Order LP and HP Digital IIR Filter Using the Concept of Teaching-Learning Based Optimization DAMANPREET SINGH, J.S. DHILLON Department of Computer Science & Engineering Department of Electrical
EE482: Digital Signal Processing Applications
 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu EE482: Digital Signal Processing Applications Spring 2014 TTh 14:30-15:45 CBC C222 Lecture 05 IIR Design 14/03/04 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ee482/
Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu EE482: Digital Signal Processing Applications Spring 2014 TTh 14:30-15:45 CBC C222 Lecture 05 IIR Design 14/03/04 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ee482/
Lecture 9 Infinite Impulse Response Filters
 Lecture 9 Infinite Impulse Response Filters Outline 9 Infinite Impulse Response Filters 9 First-Order Low-Pass Filter 93 IIR Filter Design 5 93 CT Butterworth filter design 5 93 Bilinear transform 7 9
Lecture 9 Infinite Impulse Response Filters Outline 9 Infinite Impulse Response Filters 9 First-Order Low-Pass Filter 93 IIR Filter Design 5 93 CT Butterworth filter design 5 93 Bilinear transform 7 9
Fibonacci tan-sec method for construction solitary wave solution to differential-difference equations
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 7 (2011) No. 1, pp. 52-57 Fibonacci tan-sec method for construction solitary wave solution to differential-difference equations
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 7 (2011) No. 1, pp. 52-57 Fibonacci tan-sec method for construction solitary wave solution to differential-difference equations
Lecture 8 - IIR Filters (II)
 Lecture 8 - IIR Filters (II) James Barnes (James.Barnes@colostate.edu) Spring 24 Colorado State University Dept of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE423 1 / 29 Lecture 8 Outline Introduction Digital
Lecture 8 - IIR Filters (II) James Barnes (James.Barnes@colostate.edu) Spring 24 Colorado State University Dept of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE423 1 / 29 Lecture 8 Outline Introduction Digital
EE 521: Instrumentation and Measurements
 Aly El-Osery Electrical Engineering Department, New Mexico Tech Socorro, New Mexico, USA November 1, 2009 1 / 27 1 The z-transform 2 Linear Time-Invariant System 3 Filter Design IIR Filters FIR Filters
Aly El-Osery Electrical Engineering Department, New Mexico Tech Socorro, New Mexico, USA November 1, 2009 1 / 27 1 The z-transform 2 Linear Time-Invariant System 3 Filter Design IIR Filters FIR Filters
Chapter 13 Z Transform
 Chapter 13 Z Transform 1. -transform 2. Inverse -transform 3. Properties of -transform 4. Solution to Difference Equation 5. Calculating output using -transform 6. DTFT and -transform 7. Stability Analysis
Chapter 13 Z Transform 1. -transform 2. Inverse -transform 3. Properties of -transform 4. Solution to Difference Equation 5. Calculating output using -transform 6. DTFT and -transform 7. Stability Analysis
Approximate solution of linear integro-differential equations by using modified Taylor expansion method
 ISSN 1 746-7233, Engl, UK World Journal of Modelling Simulation Vol 9 (213) No 4, pp 289-31 Approximate solution of linear integro-differential equations by using modified Taylor expansion method Jalil
ISSN 1 746-7233, Engl, UK World Journal of Modelling Simulation Vol 9 (213) No 4, pp 289-31 Approximate solution of linear integro-differential equations by using modified Taylor expansion method Jalil
Influence and analysis of escape posture for different launch tube spiral angles
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 3 (2007) No. 3, pp. 230-234 Influence and analysis of escape posture for different launch tube spiral angles Young Fung 1, Zhigang
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 3 (2007) No. 3, pp. 230-234 Influence and analysis of escape posture for different launch tube spiral angles Young Fung 1, Zhigang
Acceleration of Levenberg-Marquardt method training of chaotic systems fuzzy modeling
 ISSN 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 3 (2007) No. 4, pp. 289-298 Acceleration of Levenberg-Marquardt method training of chaotic systems fuzzy modeling Yuhui Wang, Qingxian
ISSN 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 3 (2007) No. 4, pp. 289-298 Acceleration of Levenberg-Marquardt method training of chaotic systems fuzzy modeling Yuhui Wang, Qingxian
Trade-off Adjustment of Fractional Order Low-pass Filter for Vibration Suppression Control of Torsional System
 Trade-off Adjustment of Fractional Order Low-pass Filter for Vibration Suppression Control of Torsional System Chengbin Ma, Yoichi Hori 2 Department of Electrical Engineering, the University of Tokyo,
Trade-off Adjustment of Fractional Order Low-pass Filter for Vibration Suppression Control of Torsional System Chengbin Ma, Yoichi Hori 2 Department of Electrical Engineering, the University of Tokyo,
Digital Signal Processing IIR Filter Design via Bilinear Transform
 Digital Signal Processing IIR Filter Design via Bilinear Transform D. Richard Brown III D. Richard Brown III 1 / 12 Basic Procedure We assume here that we ve already decided to use an IIR filter. The basic
Digital Signal Processing IIR Filter Design via Bilinear Transform D. Richard Brown III D. Richard Brown III 1 / 12 Basic Procedure We assume here that we ve already decided to use an IIR filter. The basic
A new condition based maintenance model with random improvements on the system after maintenance actions: Optimizing by monte carlo simulation
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 4 (2008) No. 3, pp. 230-236 A new condition based maintenance model with random improvements on the system after maintenance
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 4 (2008) No. 3, pp. 230-236 A new condition based maintenance model with random improvements on the system after maintenance
Lecture 7 Discrete Systems
 Lecture 7 Discrete Systems EE 52: Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture Notes Update on November, 29 Aly El-Osery, Electrical Engineering Dept., New Mexico Tech 7. Contents The z-transform 2 Linear
Lecture 7 Discrete Systems EE 52: Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture Notes Update on November, 29 Aly El-Osery, Electrical Engineering Dept., New Mexico Tech 7. Contents The z-transform 2 Linear
A simple model based control of self excited induction generators over a wide speed range
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 10 (2014) No. 3, pp. 206-213 A simple model based control of self excited induction generators over a wide speed range Krishna
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 10 (2014) No. 3, pp. 206-213 A simple model based control of self excited induction generators over a wide speed range Krishna
Butterworth Filter Properties
 OpenStax-CNX module: m693 Butterworth Filter Properties C. Sidney Burrus This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3. This section develops the properties
OpenStax-CNX module: m693 Butterworth Filter Properties C. Sidney Burrus This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3. This section develops the properties
Application of homotopy perturbation method to non-homogeneous parabolic partial and non linear differential equations
 ISSN 1 746-733, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 5 (009) No. 3, pp. 5-31 Application of homotopy perturbation method to non-homogeneous parabolic partial and non linear differential
ISSN 1 746-733, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 5 (009) No. 3, pp. 5-31 Application of homotopy perturbation method to non-homogeneous parabolic partial and non linear differential
Design and Realization of Quantum based Digital Integrator
 International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174, Volume 7, Number 5 (2014), pp. 449-454 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Design and Realization
International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174, Volume 7, Number 5 (2014), pp. 449-454 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Design and Realization
LCPI method to find optimal solutions of nonlinear programming problems
 ISSN 1 746-7233, Engl, UK World Journal of Modelling Simulation Vol. 14 2018) No. 1, pp. 50-57 LCPI method to find optimal solutions of nonlinear programming problems M.H. Noori Skari, M. Ghaznavi * Faculty
ISSN 1 746-7233, Engl, UK World Journal of Modelling Simulation Vol. 14 2018) No. 1, pp. 50-57 LCPI method to find optimal solutions of nonlinear programming problems M.H. Noori Skari, M. Ghaznavi * Faculty
New Iterative Method for Time-Fractional Schrödinger Equations
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 9 2013) No. 2, pp. 89-95 New Iterative Method for Time-Fractional Schrödinger Equations Ambreen Bibi 1, Abid Kamran 2, Umer Hayat
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 9 2013) No. 2, pp. 89-95 New Iterative Method for Time-Fractional Schrödinger Equations Ambreen Bibi 1, Abid Kamran 2, Umer Hayat
Direct torque control of induction motor fed by two level inverter using space vector pulse width modulation
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 9 (2013) No. 1, pp. 59-67 Direct torque control of induction motor fed by two level inverter using space vector pulse width modulation
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 9 (2013) No. 1, pp. 59-67 Direct torque control of induction motor fed by two level inverter using space vector pulse width modulation
Reliability evaluation of a repairable system under fuzziness
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 12 (2016) No. 1, pp. 48-58 Reliability evaluation of a repairable system under fuzziness Kalika Patrai 1, Indu Uprety 2 1 Department
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 12 (2016) No. 1, pp. 48-58 Reliability evaluation of a repairable system under fuzziness Kalika Patrai 1, Indu Uprety 2 1 Department
ELEG 305: Digital Signal Processing
 ELEG 305: Digital Signal Processing Lecture : Design of Digital IIR Filters (Part I) Kenneth E. Barner Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Delaware Fall 008 K. E. Barner (Univ.
ELEG 305: Digital Signal Processing Lecture : Design of Digital IIR Filters (Part I) Kenneth E. Barner Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Delaware Fall 008 K. E. Barner (Univ.
Digital Signal Processing Module 6 Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)
 Objective: Digital Signal Processing Module 6 Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) 1. To analyze finite duration sequences using Discrete Fourier Transform. 2. To understand the characteristics and importance
Objective: Digital Signal Processing Module 6 Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) 1. To analyze finite duration sequences using Discrete Fourier Transform. 2. To understand the characteristics and importance
2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Massachusetts
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Massachusetts
Today. ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing. IIR Filter Design. Impulse Invariance. Impulse Invariance. Impulse Invariance. ω < π.
 Today ESE 53: Digital Signal Processing! IIR Filter Design " Lec 8: March 30, 207 IIR Filters and Adaptive Filters " Bilinear Transformation! Transformation of DT Filters! Adaptive Filters! LMS Algorithm
Today ESE 53: Digital Signal Processing! IIR Filter Design " Lec 8: March 30, 207 IIR Filters and Adaptive Filters " Bilinear Transformation! Transformation of DT Filters! Adaptive Filters! LMS Algorithm
Controlling a Novel Chaotic Attractor using Linear Feedback
 ISSN 746-7659, England, UK Journal of Information and Computing Science Vol 5, No,, pp 7-4 Controlling a Novel Chaotic Attractor using Linear Feedback Lin Pan,, Daoyun Xu 3, and Wuneng Zhou College of
ISSN 746-7659, England, UK Journal of Information and Computing Science Vol 5, No,, pp 7-4 Controlling a Novel Chaotic Attractor using Linear Feedback Lin Pan,, Daoyun Xu 3, and Wuneng Zhou College of
Exercise 5.1: Introduction To Euclid s Geometry
 Exercise 5.1: Introduction To Euclid s Geometry Email: info@mywayteaching.com Q1. Which of the following statements are true and which are false? Give reasons for your answers. (i)only one line can pass
Exercise 5.1: Introduction To Euclid s Geometry Email: info@mywayteaching.com Q1. Which of the following statements are true and which are false? Give reasons for your answers. (i)only one line can pass
Simulations and calculations of stochastic differential equations and backward stochastic differential equations
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 3 (2007) No. 1, pp. 3-9 Simulations and calculations of stochastic differential equations and backward stochastic differential
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 3 (2007) No. 1, pp. 3-9 Simulations and calculations of stochastic differential equations and backward stochastic differential
Pseudo-fractional ARMA modelling using a double Levinson recursion
 Pseudo-fractional ARA modelling using a double Levinson recursion.d. Ortigueira and A.J. Serralheiro Abstract: The modelling of fractional linear systems through ARA models is addressed. To perform this
Pseudo-fractional ARA modelling using a double Levinson recursion.d. Ortigueira and A.J. Serralheiro Abstract: The modelling of fractional linear systems through ARA models is addressed. To perform this
UNIT - III PART A. 2. Mention any two techniques for digitizing the transfer function of an analog filter?
 UNIT - III PART A. Mention the important features of the IIR filters? i) The physically realizable IIR filters does not have linear phase. ii) The IIR filter specification includes the desired characteristics
UNIT - III PART A. Mention the important features of the IIR filters? i) The physically realizable IIR filters does not have linear phase. ii) The IIR filter specification includes the desired characteristics
New independence definition of fuzzy random variable and random fuzzy variable
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 2 (2006) No. 5, pp. 338-342 New independence definition of fuzzy random variable and random fuzzy variable Xiang Li, Baoding
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 2 (2006) No. 5, pp. 338-342 New independence definition of fuzzy random variable and random fuzzy variable Xiang Li, Baoding
EXACT TRAVELING WAVE SOLUTIONS FOR NONLINEAR FRACTIONAL PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS USING THE IMPROVED (G /G) EXPANSION METHOD
 Jan 4. Vol. 4 No. 7-4 EAAS & ARF. All rights reserved ISSN5-869 EXACT TRAVELIN WAVE SOLUTIONS FOR NONLINEAR FRACTIONAL PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS USIN THE IMPROVED ( /) EXPANSION METHOD Elsayed M.
Jan 4. Vol. 4 No. 7-4 EAAS & ARF. All rights reserved ISSN5-869 EXACT TRAVELIN WAVE SOLUTIONS FOR NONLINEAR FRACTIONAL PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS USIN THE IMPROVED ( /) EXPANSION METHOD Elsayed M.
Robust sliding mode speed controller for hybrid SVPWM based direct torque control of induction motor
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 3 (2007) No. 3, pp. 180-188 Robust sliding mode speed controller for hybrid SVPWM based direct torque control of induction motor
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 3 (2007) No. 3, pp. 180-188 Robust sliding mode speed controller for hybrid SVPWM based direct torque control of induction motor
Control System Design
 ELEC ENG 4CL4: Control System Design Notes for Lecture #27 Wednesday, March 17, 2004 Dr. Ian C. Bruce Room: CRL-229 Phone ext.: 26984 Email: ibruce@mail.ece.mcmaster.ca Discrete Delta Domain Models The
ELEC ENG 4CL4: Control System Design Notes for Lecture #27 Wednesday, March 17, 2004 Dr. Ian C. Bruce Room: CRL-229 Phone ext.: 26984 Email: ibruce@mail.ece.mcmaster.ca Discrete Delta Domain Models The
Digital Signal Processing Lecture 8 - Filter Design - IIR
 Digital Signal Processing - Filter Design - IIR Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville October 20, 2015 Overview 1 2 3 4 5 6 Roadmap Discrete-time signals and systems
Digital Signal Processing - Filter Design - IIR Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville October 20, 2015 Overview 1 2 3 4 5 6 Roadmap Discrete-time signals and systems
ECE 410 DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING D. Munson University of Illinois Chapter 12
 . ECE 40 DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING D. Munson University of Illinois Chapter IIR Filter Design ) Based on Analog Prototype a) Impulse invariant design b) Bilinear transformation ( ) ~ widely used ) Computer-Aided
. ECE 40 DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING D. Munson University of Illinois Chapter IIR Filter Design ) Based on Analog Prototype a) Impulse invariant design b) Bilinear transformation ( ) ~ widely used ) Computer-Aided
Design of IIR filters
 Design of IIR filters Standard methods of design of digital infinite impulse response (IIR) filters usually consist of three steps, namely: 1 design of a continuous-time (CT) prototype low-pass filter;
Design of IIR filters Standard methods of design of digital infinite impulse response (IIR) filters usually consist of three steps, namely: 1 design of a continuous-time (CT) prototype low-pass filter;
The Müntz-Legendre Tau method for Weakly singular Volterra integral equations
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 14 (218) No. 3, pp. 199-28 The Müntz-Legendre Tau method for Weakly singular Volterra integral equations Ali Tahmasbi 1 *, Behruz
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 14 (218) No. 3, pp. 199-28 The Müntz-Legendre Tau method for Weakly singular Volterra integral equations Ali Tahmasbi 1 *, Behruz
DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING. Chapter 6 IIR Filter Design
 DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Chapter 6 IIR Filter Design OER Digital Signal Processing by Dr. Norizam Sulaiman work is under licensed Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International
DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Chapter 6 IIR Filter Design OER Digital Signal Processing by Dr. Norizam Sulaiman work is under licensed Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International
LECTURE NOTES DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING III B.TECH II SEMESTER (JNTUK R 13)
 LECTURE NOTES ON DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING III B.TECH II SEMESTER (JNTUK R 13) FACULTY : B.V.S.RENUKA DEVI (Asst.Prof) / Dr. K. SRINIVASA RAO (Assoc. Prof) DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS
LECTURE NOTES ON DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING III B.TECH II SEMESTER (JNTUK R 13) FACULTY : B.V.S.RENUKA DEVI (Asst.Prof) / Dr. K. SRINIVASA RAO (Assoc. Prof) DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS
Design of Stable IIR filters with prescribed flatness and approximately linear phase
 Design of Stable IIR filters with prescribed flatness and approximately linear phase YASUNORI SUGITA Nagaoka University of Technology Dept. of Electrical Engineering Nagaoka city, Niigata-pref., JAPAN
Design of Stable IIR filters with prescribed flatness and approximately linear phase YASUNORI SUGITA Nagaoka University of Technology Dept. of Electrical Engineering Nagaoka city, Niigata-pref., JAPAN
PS403 - Digital Signal processing
 PS403 - Digital Signal processing 6. DSP - Recursive (IIR) Digital Filters Key Text: Digital Signal Processing with Computer Applications (2 nd Ed.) Paul A Lynn and Wolfgang Fuerst, (Publisher: John Wiley
PS403 - Digital Signal processing 6. DSP - Recursive (IIR) Digital Filters Key Text: Digital Signal Processing with Computer Applications (2 nd Ed.) Paul A Lynn and Wolfgang Fuerst, (Publisher: John Wiley
A computerized analytical model for evaluating hydrocarbon fluids as natural alternative refrigerants
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 5 (2009) No. 3, pp. 232-240 A computerized analytical model for evaluating hydrocarbon fluids as natural alternative refrigerants
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 5 (2009) No. 3, pp. 232-240 A computerized analytical model for evaluating hydrocarbon fluids as natural alternative refrigerants
Bubble radius function-non isothermal film blowing
 ISSN 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 3 (2007) No. 2, pp. 2-29 Bubble radius function-non isothermal film blowing I. M. R. Pinheiro PO BOX 2396, ABeckett st., Melbourne,
ISSN 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 3 (2007) No. 2, pp. 2-29 Bubble radius function-non isothermal film blowing I. M. R. Pinheiro PO BOX 2396, ABeckett st., Melbourne,
A new FOC technique based on predictive current control for PMSM drive
 ISSN 1 746-7, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 5 (009) No. 4, pp. 87-94 A new FOC technique based on predictive current control for PMSM drive F. Heydari, A. Sheikholeslami, K.
ISSN 1 746-7, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 5 (009) No. 4, pp. 87-94 A new FOC technique based on predictive current control for PMSM drive F. Heydari, A. Sheikholeslami, K.
Bifurcation and Stability Analysis of a Prey-predator System with a Reserved Area
 ISSN 746-733, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 8 ( No. 4, pp. 85-9 Bifurcation and Stability Analysis of a Prey-predator System with a Reserved Area Debasis Mukherjee Department
ISSN 746-733, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 8 ( No. 4, pp. 85-9 Bifurcation and Stability Analysis of a Prey-predator System with a Reserved Area Debasis Mukherjee Department
INFINITE-IMPULSE RESPONSE DIGITAL FILTERS Classical analog filters and their conversion to digital filters 4. THE BUTTERWORTH ANALOG FILTER
 INFINITE-IMPULSE RESPONSE DIGITAL FILTERS Classical analog filters and their conversion to digital filters. INTRODUCTION 2. IIR FILTER DESIGN 3. ANALOG FILTERS 4. THE BUTTERWORTH ANALOG FILTER 5. THE CHEBYSHEV-I
INFINITE-IMPULSE RESPONSE DIGITAL FILTERS Classical analog filters and their conversion to digital filters. INTRODUCTION 2. IIR FILTER DESIGN 3. ANALOG FILTERS 4. THE BUTTERWORTH ANALOG FILTER 5. THE CHEBYSHEV-I
Inverse optimal control of hyperchaotic finance system
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 10 (2014) No. 2, pp. 83-91 Inverse optimal control of hyperchaotic finance system Changzhong Chen 1,3, Tao Fan 1,3, Bangrong
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 10 (2014) No. 2, pp. 83-91 Inverse optimal control of hyperchaotic finance system Changzhong Chen 1,3, Tao Fan 1,3, Bangrong
Design IIR Butterworth Filters Using 12 Lines of Code
 db Design IIR Butterworth Filters Using 12 Lines of Code While there are plenty of canned functions to design Butterworth IIR filters [1], it s instructive and not that complicated to design them from
db Design IIR Butterworth Filters Using 12 Lines of Code While there are plenty of canned functions to design Butterworth IIR filters [1], it s instructive and not that complicated to design them from
Lecture 3 - Design of Digital Filters
 Lecture 3 - Design of Digital Filters 3.1 Simple filters In the previous lecture we considered the polynomial fit as a case example of designing a smoothing filter. The approximation to an ideal LPF can
Lecture 3 - Design of Digital Filters 3.1 Simple filters In the previous lecture we considered the polynomial fit as a case example of designing a smoothing filter. The approximation to an ideal LPF can
Recursive, Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) Digital Filters:
 Recursive, Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) Digital Filters: Filters defined by Laplace Domain transfer functions (analog devices) can be easily converted to Z domain transfer functions (digital, sampled
Recursive, Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) Digital Filters: Filters defined by Laplace Domain transfer functions (analog devices) can be easily converted to Z domain transfer functions (digital, sampled
Question 1: Is zero a rational number? Can you write it in the form p, where p and q are integers and q 0?
 Class IX - NCERT Maths Exercise (.) Question : Is zero a rational number? Can you write it in the form p, where p and q are integers and q 0? q Solution : Consider the definition of a rational number.
Class IX - NCERT Maths Exercise (.) Question : Is zero a rational number? Can you write it in the form p, where p and q are integers and q 0? q Solution : Consider the definition of a rational number.
Math 110 (S & E) Textbook: Calculus Early Transcendentals by James Stewart, 7 th Edition
 Math 110 (S & E) Textbook: Calculus Early Transcendentals by James Stewart, 7 th Edition 1 Appendix A : Numbers, Inequalities, and Absolute Values Sets A set is a collection of objects with an important
Math 110 (S & E) Textbook: Calculus Early Transcendentals by James Stewart, 7 th Edition 1 Appendix A : Numbers, Inequalities, and Absolute Values Sets A set is a collection of objects with an important
Advanced Digital Signal Processing -Introduction
 Advanced Digital Signal Processing -Introduction LECTURE-2 1 AP9211- ADVANCED DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING UNIT I DISCRETE RANDOM SIGNAL PROCESSING Discrete Random Processes- Ensemble Averages, Stationary
Advanced Digital Signal Processing -Introduction LECTURE-2 1 AP9211- ADVANCED DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING UNIT I DISCRETE RANDOM SIGNAL PROCESSING Discrete Random Processes- Ensemble Averages, Stationary
2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 2008
 MI OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu.6 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 008 For information about citing these materials or our erms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Massachusetts
MI OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu.6 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete Fall 008 For information about citing these materials or our erms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Massachusetts
DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING UNIT III INFINITE IMPULSE RESPONSE DIGITAL FILTERS. 3.6 Design of Digital Filter using Digital to Digital
 DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING UNIT III INFINITE IMPULSE RESPONSE DIGITAL FILTERS Contents: 3.1 Introduction IIR Filters 3.2 Transformation Function Derivation 3.3 Review of Analog IIR Filters 3.3.1 Butterworth
DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING UNIT III INFINITE IMPULSE RESPONSE DIGITAL FILTERS Contents: 3.1 Introduction IIR Filters 3.2 Transformation Function Derivation 3.3 Review of Analog IIR Filters 3.3.1 Butterworth
Soliton solution of the Kadomtse-Petviashvili equation by homotopy perturbation method
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 5 (2009) No. 1, pp. 38-44 Soliton solution of the Kadomtse-Petviashvili equation by homotopy perturbation method H. Mirgolbabaei
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 5 (2009) No. 1, pp. 38-44 Soliton solution of the Kadomtse-Petviashvili equation by homotopy perturbation method H. Mirgolbabaei
DESIGN OF QUANTIZED FIR FILTER USING COMPENSATING ZEROS
 DESIGN OF QUANTIZED FIR FILTER USING COMPENSATING ZEROS Nivedita Yadav, O.P. Singh, Ashish Dixit Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Amity University, Lucknow Campus, Lucknow, (India)
DESIGN OF QUANTIZED FIR FILTER USING COMPENSATING ZEROS Nivedita Yadav, O.P. Singh, Ashish Dixit Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Amity University, Lucknow Campus, Lucknow, (India)
Digital Signal Processing
 COMP ENG 4TL4: Digital Signal Processing Notes for Lecture #21 Friday, October 24, 2003 Types of causal FIR (generalized) linear-phase filters: Type I: Symmetric impulse response: with order M an even
COMP ENG 4TL4: Digital Signal Processing Notes for Lecture #21 Friday, October 24, 2003 Types of causal FIR (generalized) linear-phase filters: Type I: Symmetric impulse response: with order M an even
Backlash Vibration Suppression Control of Torsional System by Novel Fractional Order PID k Controller
 Paper Backlash Vibration Suppression Control of Torsional System by Novel Fractional Order PID k Controller Chengbin Ma Yoichi Hori Student Member Member This paper proposes a novel fractional order PID
Paper Backlash Vibration Suppression Control of Torsional System by Novel Fractional Order PID k Controller Chengbin Ma Yoichi Hori Student Member Member This paper proposes a novel fractional order PID
Circles & Interval & Set Notation.notebook. November 16, 2009 CIRCLES. OBJECTIVE Graph a Circle given the equation in standard form.
 OBJECTIVE Graph a Circle given the equation in standard form. Write the equation of a circle in standard form given a graph or two points (one being the center). Students will be able to write the domain
OBJECTIVE Graph a Circle given the equation in standard form. Write the equation of a circle in standard form given a graph or two points (one being the center). Students will be able to write the domain
Discrete-Time David Johns and Ken Martin University of Toronto
 Discrete-Time David Johns and Ken Martin University of Toronto (johns@eecg.toronto.edu) (martin@eecg.toronto.edu) University of Toronto 1 of 40 Overview of Some Signal Spectra x c () t st () x s () t xn
Discrete-Time David Johns and Ken Martin University of Toronto (johns@eecg.toronto.edu) (martin@eecg.toronto.edu) University of Toronto 1 of 40 Overview of Some Signal Spectra x c () t st () x s () t xn
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION CORE COURSE. B.Sc. MATHEMATICS V SEMESTER. (2011 Admission onwards) BASIC MATHEMATICAL ANALYSIS
 UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION CORE COURSE B.Sc. MATHEMATICS V SEMESTER (2011 Admission onwards) BASIC MATHEMATICAL ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK 1. Find the number of elements in the power
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION CORE COURSE B.Sc. MATHEMATICS V SEMESTER (2011 Admission onwards) BASIC MATHEMATICAL ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK 1. Find the number of elements in the power
A New Least-Squares Approach to Differintegration. Modeling
 A New Least-Squares Approach to Differintegration Modeling Manuel D Ortigueira 1,2 António J Serralheiro 2, 3 mdo@deefctunlpt antonioserralheiro@inesc-idpt Abstract In this paper a new least-squares (LS)
A New Least-Squares Approach to Differintegration Modeling Manuel D Ortigueira 1,2 António J Serralheiro 2, 3 mdo@deefctunlpt antonioserralheiro@inesc-idpt Abstract In this paper a new least-squares (LS)
Digital Signal Processing
 COMP ENG 4TL4: Digital Signal Processing Notes for Lecture #24 Tuesday, November 4, 2003 6.8 IIR Filter Design Properties of IIR Filters: IIR filters may be unstable Causal IIR filters with rational system
COMP ENG 4TL4: Digital Signal Processing Notes for Lecture #24 Tuesday, November 4, 2003 6.8 IIR Filter Design Properties of IIR Filters: IIR filters may be unstable Causal IIR filters with rational system
Digital Signal Processing Module 1 Analysis of Discrete time Linear Time - Invariant Systems
 Digital Signal Processing Module 1 Analysis of Discrete time Linear Time - Invariant Systems Objective: 1. To understand the representation of Discrete time signals 2. To analyze the causality and stability
Digital Signal Processing Module 1 Analysis of Discrete time Linear Time - Invariant Systems Objective: 1. To understand the representation of Discrete time signals 2. To analyze the causality and stability
Responses of Digital Filters Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes:
 Responses of Digital Filters Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Understanding the relationships between impulse response, frequency response, difference equation and transfer function in characterizing
Responses of Digital Filters Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Understanding the relationships between impulse response, frequency response, difference equation and transfer function in characterizing
Rational Implementation of Distributed Delay Using Extended Bilinear Transformations
 Rational Implementation of Distributed Delay Using Extended Bilinear Transformations Qing-Chang Zhong zhongqc@ieee.org, http://come.to/zhongqc School of Electronics University of Glamorgan United Kingdom
Rational Implementation of Distributed Delay Using Extended Bilinear Transformations Qing-Chang Zhong zhongqc@ieee.org, http://come.to/zhongqc School of Electronics University of Glamorgan United Kingdom
Modelling and Estimation of Climatic Variable using Time Series Trigonometric Analysis
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 14 (2018) No. 3, pp. 192-198 Modelling and Estimation of Climatic Variable using Time Series Trigonometric Analysis T.O. Olatayo,A.
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 14 (2018) No. 3, pp. 192-198 Modelling and Estimation of Climatic Variable using Time Series Trigonometric Analysis T.O. Olatayo,A.
A LITTLE REAL ANALYSIS AND TOPOLOGY
 A LITTLE REAL ANALYSIS AND TOPOLOGY 1. NOTATION Before we begin some notational definitions are useful. (1) Z = {, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, }is the set of integers. (2) Q = { a b : aεz, bεz {0}} is the set
A LITTLE REAL ANALYSIS AND TOPOLOGY 1. NOTATION Before we begin some notational definitions are useful. (1) Z = {, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, }is the set of integers. (2) Q = { a b : aεz, bεz {0}} is the set
April 28, 2017 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length
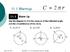 11.1 Warmup April 28, 2017 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length 1 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length mbhaub@mpsaz.org 11.1 Essential Question How can you find the length of a circular arc?
11.1 Warmup April 28, 2017 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length 1 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length mbhaub@mpsaz.org 11.1 Essential Question How can you find the length of a circular arc?
Number Systems. Exercise 1.1. Question 1. Is zero a rational number? Can you write it in the form p q,
 s Exercise. Question. Is zero a rational number? Can you write it in the form p q, where p and q are integers and q 0? Solution Yes, write 0 (where 0 and are integers and q which is not equal to zero).
s Exercise. Question. Is zero a rational number? Can you write it in the form p q, where p and q are integers and q 0? Solution Yes, write 0 (where 0 and are integers and q which is not equal to zero).
Basic properties of real numbers. Solving equations and inequalities. Homework. Solve and write linear equations.
 August Equations and inequalities S. 1.1a,1.2a,1.3a, 2.1a, 2.3 a-c, 6.2a. Simplifying expressions. Algebra II Honors Textbook Glencoe McGraw Hill Algebra II and supplements McDougal Littell Houghton Miffin
August Equations and inequalities S. 1.1a,1.2a,1.3a, 2.1a, 2.3 a-c, 6.2a. Simplifying expressions. Algebra II Honors Textbook Glencoe McGraw Hill Algebra II and supplements McDougal Littell Houghton Miffin
(i) 2-5 (ii) (3 + 23) - 23 (v) 2π
 Number System - Worksheet Question 1: Express the following in the form p/q, where p and q are integers and q 0. Question 2: Express 0.99999... in the form p/q. Are you surprised by your answer? With your
Number System - Worksheet Question 1: Express the following in the form p/q, where p and q are integers and q 0. Question 2: Express 0.99999... in the form p/q. Are you surprised by your answer? With your
Applied Mathematics Letters
 Applied Mathematics Letters 24 (211) 219 223 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Applied Mathematics Letters journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/aml Laplace transform and fractional differential
Applied Mathematics Letters 24 (211) 219 223 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Applied Mathematics Letters journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/aml Laplace transform and fractional differential
A ROBUST STABILITY TEST PROCEDURE FOR A CLASS OF UNCERTAIN LTI FRACTIONAL ORDER SYSTEMS
 International Carpathian Control Conference ICCC 22 MALENOVICE, CZECH REPUBLIC May 27-, 22 A ROBUST STABILITY TEST PROCEDURE FOR A CLASS OF UNCERTAIN LTI FRACTIONAL ORDER SYSTEMS Ivo PETRÁŠ, YangQuan CHEN
International Carpathian Control Conference ICCC 22 MALENOVICE, CZECH REPUBLIC May 27-, 22 A ROBUST STABILITY TEST PROCEDURE FOR A CLASS OF UNCERTAIN LTI FRACTIONAL ORDER SYSTEMS Ivo PETRÁŠ, YangQuan CHEN
Poles and Zeros in z-plane
 M58 Mixed Signal Processors page of 6 Poles and Zeros in z-plane z-plane Response of discrete-time system (i.e. digital filter at a particular frequency ω is determined by the distance between its poles
M58 Mixed Signal Processors page of 6 Poles and Zeros in z-plane z-plane Response of discrete-time system (i.e. digital filter at a particular frequency ω is determined by the distance between its poles
Simultaneous Accumulation Points to Sets of d-tuples
 ISSN 1749-3889 print, 1749-3897 online International Journal of Nonlinear Science Vol.92010 No.2,pp.224-228 Simultaneous Accumulation Points to Sets of d-tuples Zhaoxin Yin, Meifeng Dai Nonlinear Scientific
ISSN 1749-3889 print, 1749-3897 online International Journal of Nonlinear Science Vol.92010 No.2,pp.224-228 Simultaneous Accumulation Points to Sets of d-tuples Zhaoxin Yin, Meifeng Dai Nonlinear Scientific
Parameter Derivation of Type-2 Discrete-Time Phase-Locked Loops Containing Feedback Delays
 Parameter Derivation of Type- Discrete-Time Phase-Locked Loops Containing Feedback Delays Joey Wilson, Andrew Nelson, and Behrouz Farhang-Boroujeny joey.wilson@utah.edu, nelson@math.utah.edu, farhang@ece.utah.edu
Parameter Derivation of Type- Discrete-Time Phase-Locked Loops Containing Feedback Delays Joey Wilson, Andrew Nelson, and Behrouz Farhang-Boroujeny joey.wilson@utah.edu, nelson@math.utah.edu, farhang@ece.utah.edu
Optimal Controllers with Complex Order Derivatives
 Optimal Controllers with Complex Order Derivatives J.A. Tenreiro Machado Abstract This paper studies the optimization of complex-order algorithms for the discrete-time control of linear and nonlinear systems.
Optimal Controllers with Complex Order Derivatives J.A. Tenreiro Machado Abstract This paper studies the optimization of complex-order algorithms for the discrete-time control of linear and nonlinear systems.
THERE are two major approaches to designing infinite impulse
 338 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 54, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2007 Novel Approach to Analog-to-Digital Transforms Mohamad Adnan Al-Alaoui, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract A novel
338 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 54, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2007 Novel Approach to Analog-to-Digital Transforms Mohamad Adnan Al-Alaoui, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract A novel
Signals and Systems. Lecture 11 Wednesday 22 nd November 2017 DR TANIA STATHAKI
 Signals and Systems Lecture 11 Wednesday 22 nd November 2017 DR TANIA STATHAKI READER (ASSOCIATE PROFFESOR) IN SIGNAL PROCESSING IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Effect on poles and zeros on frequency response
Signals and Systems Lecture 11 Wednesday 22 nd November 2017 DR TANIA STATHAKI READER (ASSOCIATE PROFFESOR) IN SIGNAL PROCESSING IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Effect on poles and zeros on frequency response
Department of Mathematics Faculty of Natural Science, Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi-25
 Department of Mathematics Faculty of Natural Science, Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi-25 Course Structure of U.G. under CBCS* (Only for those students who have not taken mathematics as a core or subsidiary
Department of Mathematics Faculty of Natural Science, Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi-25 Course Structure of U.G. under CBCS* (Only for those students who have not taken mathematics as a core or subsidiary
Free convection modeling over a vertical flat plate embedded in saturated porous medium with a variable heat source and radiation flux
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 9 (2013) No. 3, pp. 163-172 Free convection modeling over a vertical flat plate embedded in saturated porous medium with a variable
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 9 (2013) No. 3, pp. 163-172 Free convection modeling over a vertical flat plate embedded in saturated porous medium with a variable
Design and Realization of Fractional Low-Pass Filter of 1.5 Order Using a Single Operational Transresistance Amplifier
 Vol.9, No.9, (2016), pp.69-76 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijsip.2016.9.9.07 Design and Realization of Fractional Low-Pass Filter of 1.5 Order Using a Single Operational Transresistance Amplifier Piyush
Vol.9, No.9, (2016), pp.69-76 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijsip.2016.9.9.07 Design and Realization of Fractional Low-Pass Filter of 1.5 Order Using a Single Operational Transresistance Amplifier Piyush
SOME APPROXIMATIONS OF FRACTIONAL ORDER OPERATORS USED IN CONTROL THEORY AND APPLICATIONS. Abstract
 SOME APPROXIMATIONS OF FRACTIONAL ORDER OPERATORS USED IN CONTROL THEORY AND APPLICATIONS B. M. Vinagre, I. Podlubny, A. Hernández, V. Feliu Abstract In this paper, starting from the formulation of some
SOME APPROXIMATIONS OF FRACTIONAL ORDER OPERATORS USED IN CONTROL THEORY AND APPLICATIONS B. M. Vinagre, I. Podlubny, A. Hernández, V. Feliu Abstract In this paper, starting from the formulation of some
