Inductive and statistical learning of formal grammars
|
|
|
- Hope Gaines
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Inductive nd sttisticl lerning of forml grmmrs Pierre Dupont Grmmr Induction Mchine Lerning Gol: to give the lerning ility to mchine Design progrms the performnce of which improves over time Inductive lerning is prticulr instnce of mchine lerning Gol: to find generl lw from exmples Suprolem of theoreticl computer science, rtificil intelligence or pttern recognition Typeset y FoilTEX Pierre Dupont Grmmr Induction Outline Grmmr Induction Grmmr Induction or Grmmticl Inference Grmmr induction definition Lerning prdigms DFA lerning from positive nd negtive exmples RPNI lgorithm Proilistic DFA lerning Appliction to nturl lnguge tsk Links with Mrkov models Relted prolems nd future work Grmmr induction is prticulr cse of inductive lerning The generl lw is represented y forml grmmr or n equivlent mchine The set of exmples, known s positive smple, is usully mde of strings or sequences over specific lphet A negtive smple, i.e. set of strings not elonging to the trget lnguge, cn sometimes help the induction process Dt Induction Grmmr S >S S > λ Pierre Dupont Pierre Dupont 3
2 Grmmr Induction Exmples Grmmr Induction Chromosome clssifiction Nturl lnguge sentence Speech Centromere Chronologicl series Successive ctions of WEB user Successive moves during chess gme A musicl piece A progrm A form chrcterized y chin code grey density grey dens. derivtive Chromosome position long medin xis A iologicl sequence (DNA, proteins,...) Pierre Dupont "=====CDFDCBBBBBBBA==cdc==DGFB=cc==... ==cffc=ccc==cd==bcb==dfdc=====" String of Primitives Pierre Dupont Grmmr Induction Pttern Recognition Grmmr Induction A modeling hypothesis 5 3.cont 3.cont G Genertion Dt Induction Grmmr G 3 dc Find G s close s possile to G The induction process does not prove the existence of G It is modeling hypothesis dc: Pierre Dupont 5 Pierre Dupont
3 Grmmr Induction Grmmr Induction Identifiction in the limit Grmmr induction definition Lerning prdigms DFA lerning from positive nd negtive exmples RPNI lgorithm Proilistic DFA lerning Appliction to nturl lnguge tsk Links with Mrkov models Relted prolems nd future work G Dt Genertion Induction d d d n convergence in finite time to G G is representtion of L(G ) (exct lerning) Grmmr G G G* Pierre Dupont Pierre Dupont Grmmr Induction Lerning prdigms Grmmr Induction PAC Lerning How to chrcterize lerning? G Genertion Dt Induction Grmmr which concept clsses cn or cnnot e lerned? d d G G wht is good exmple? is it possile to lern in polynomil time? convergence to G d n G* G is close enough to G with high proility Proly Approximtely Correct lerning polynomil time complexity Pierre Dupont 9 Pierre Dupont
4 Grmmr Induction Grmmr Induction Other lernility results Define proility distriution D on set of strings Σ n L(G ) L(G* ) P [P D (L(G ) L(G )) < ɛ] > δ The sme unknown distriution D is used to generte the smple nd to mesure the error Σ Identifiction in the limit in polynomil time DFAs cnnot e efficiently identified in the limit unless we cn sk equivlence nd memership queries to n orcle PAC lerning DFAs re not PAC lernle (under some cryptogrphic limittion ssumption) unless we cn sk memership queries to n orcle The result must hold for ny distriution D (distriution free requirement) The lgorithm must return n hypothesis in polynomil time with respect to ɛ, δ, n, R(L) Pierre Dupont Pierre Dupont Grmmr Induction Identifiction in the limit: good nd d news Grmmr Induction The d one... Theorem. No superfinite clss of lnguges is identifile in the limit from positive dt only The good one... Theorem. Any dmissile clss of lnguges is identifile in the limit from positive nd negtive dt PAC lerning with simple exmples, i.e. exmples drwn ccording to the conditionl Solomonoff-Levin distriution P c (x) = λ c K(x c) K(x c) denotes the Kolmogorov complexity of x given representtion c of the concept to e lerned regulr lnguges re PACS lernle with positive exmples only ut Kolmogorov complexity is not computle! Pierre Dupont 3 Pierre Dupont 5
5 Grmmr Induction Cognitive relevnce of lerning prdigms Grmmr Induction A lrgely unsolved question Lerning prdigms seem irrelevnt to model humn lerning: Gold s identifiction in the limit frmework hs een criticized s children seem to lern nturl lnguge without negtive exmples All lerning models ssume known representtion clss Some lernility results re sed on enumertion Grmmr induction definition Lerning prdigms DFA lerning from positive nd negtive exmples RPNI lgorithm Proilistic DFA lerning Appliction to nturl lnguge tsk Links with Mrkov models Relted prolems nd future work Pierre Dupont Pierre Dupont Grmmr Induction Grmmr Induction Regulr Inference from Positive nd Negtive Dt However lerning models show tht: n orcle cn help some exmples re useless, others re good: chrcteristic smples typicl exmples lerning well is lerning efficiently Additionl hypothesis: the underlying theory is regulr grmmr or, equivlently, finite stte utomton Property. Any regulr lnguge hs cnonicl utomton A(L) which is deterministic nd miniml (miniml DFA) Exmple : L = ( ) exmple frequency mtters good exmples re simple exmples cognitive economy Pierre Dupont Pierre Dupont 9
6 Grmmr Induction A few definitions Grmmr Induction A theorem Definition. A positive smple S + is structurlly complete with respect to n utomton A if, when generting S + from A: every trnsition of A is used t lest one every finl stte is used s ccepting stte of t lest one string The positive dt cn e represented y prefix tree cceptor (PTA) Exmple : {,, } 3 5 Exmple : {,,, λ} Theorem 3. If the positive smple is structurlly complete with respect to cnonicl utomton A(L ) then there exists prtition π of the stte set of P T A such tht P T A/π = A(L ) Pierre Dupont Pierre Dupont Grmmr Induction Merging is fun Grmmr Induction A 3 5 A,,, Merging definition of prtition π on the set of sttes Exmple : {{,}, {}} If A = A /π then L(A ) L(A ) : merging sttes generlize lnguge,, How re we going to find the right prtition? Use negtive dt! Pierre Dupont Pierre Dupont 3
7 Grmmr Induction Summry Grmmr Induction A(L ) Dt Genertion Induction Grmmr PTA π PTA π? We oserve some positive nd negtive dt The positive smple S + comes from regulr lnguge L The positive smple is ssumed to e structurlly complete with respect to the cnonicl utomton A(L ) of the trget lnguge L (Not n dditionl hypothesis ut wy to restrict the serch to resonle generliztions!) We uild the Prefix Tree Acceptor of S +. By construction L(P T A) = S + Merging sttes generlize S + Grmmr induction definition Lerning prdigms DFA lerning from positive nd negtive exmples RPNI lgorithm Proilistic DFA lerning Appliction to nturl lnguge tsk Links with Mrkov models Relted prolems nd future work The negtive smple S helps to control over-generliztion Note: finding the miniml DFA consistent with S +, S is NP-complete! Pierre Dupont Pierre Dupont Grmmr Induction An utomton induction lgorithm Grmmr Induction RPNI lgorithm RPNI is prticulr instnce of the generliztion s serch prdigm Algorithm Automton Induction input S + S A P T A(S + ) // positive smple // negtive smple // PTA RPNI follows the prefix order in PTA 3 5 while (i, j) choose sttes () do if comptile (i, j, S ) then A A/π ij end if end while return A // Choose stte pir // Check for comptiility of merging i nd j Pierre Dupont 5 Polynomil time complexity with respect to smple size (S +, S ) RPNI identifies in the limit the clss of regulr lnguges A chrcteristic smple, i.e. smple such tht RPNI is gurnteed to produce the correct solution, hs qudrtic size with respect to A(L ) Additionl heuristics exist to improve performnce when such smple is not provided Pierre Dupont
8 Grmmr Induction RPNI lgorithm: pseudo-code Grmmr Induction Serch spce chrcteriztion input S +, S output A DFA consistent with S +, S egin A P T A(S + ) // N denotes the numer of sttes of P T A(S + ) π {{}, {},..., {N }} // One stte for ech prefix ccording to stndrd order < for i = to π // Loop over prtition susets π for j = to i // Loop over susets of lower rnk π π\{b j, B i }U{B i UB j } // Merging B i nd B j A/π derive (A, π ) π determ merging (A/π ) if comptile (A/π,S ) then // Deterministic prsing of S π π rek // Brek j loop end if end for // End j loop end for // End i loop return A/π Conditions on the lerning smple to gurntee the existence of solution DFA nd NFA in the lttice Chrcteriztion of the set of mximl generliztions similr to the G set from Version Spce Efficient Incrementl lttice construction is possile RPNI lgorithm Possile serch y genetic optimiztion Pierre Dupont Pierre Dupont 3 Grmmr Induction An execution step of RPNI Grmmr Induction Merge 5 nd Merge nd Merge nd Merge 9 nd Merge nd Grmmr induction definition Lerning prdigms DFA lerning from positive nd negtive exmples RPNI lgorithm Proilistic DFA lerning Appliction to nturl lnguge tsk Links with Mrkov models Relted prolems nd future work Pierre Dupont 9 Pierre Dupont 3
9 Grmmr Induction Proilistic DFA Grmmr Induction A proilistic utomton induction lgorithm. P () =...3 A structurl nd proilistic model n explicit nd noise tolernt theory A comined inductive lerning nd sttisticl estimtion prolem Lerning from positive exmples only nd frequency informtion Outside of the scope of the previous lerning prdigms..3. Algorithm Proilistic Automton Induction input S + α A P P T A(S + ) while (i, j) choose sttes () do if comptile (i, j, α) then A A/π ij end if end while return A // positive smple // precision prmeter // Proilistic PTA // Choose pir of sttes // Check for comptiility of merging i nd j Pierre Dupont 3 Pierre Dupont 3 Grmmr Induction Proilistic prefix tree cceptor (PPTA) Grmmr Induction Comptiility criterion 3 / /3 / /3 5 /3 /3 /3,3 /3 /3 5 Pierre Dupont 33 ALERGIA, RLIPS Two sttes re comptile (cn e merged) if their suffix distriutions re close enough MDI Two sttes re comptile if prior proility gin of the merged model compenstes for the likelihood loss of the dt: Byesin lerning (not strictly in this cse) sed on Kullck-Leiler divergence Pierre Dupont 35
10 Grmmr Induction ALERGIA RPNI stte merging order Grmmr Induction Kullck-Leiler divergence Comptiility mesure : q q D(P A P A ) nottion = D(A A ) = x Σ P A (x) log P A (x) P A (x) = x Σ P A (x) log P A (x) H(A ) Likelihood of x given model A : C(q,) C(q ) C(q,) C(q ) < ln ( α + A C(q ) C(q ) δ(q, ) nd δ(q, ) re α A comptile, Σ Remrks: It is recursive mesure of suffix proximity ), Σ {#} This mesure does not depend on the prefixes of q nd q locl criterion Pierre Dupont 3 Cross entropy etween A nd A : P A (x) = P (x A ) P A (x) log P A (x) When A is mximum likelihood estimte, e.g. the PPTA, cross entropy mesure the likelihood loss while going from A to A Pierre Dupont 3 Grmmr Induction Byesin lerning Grmmr Induction MDI lgorithm Find model ˆM which mximizes the likelihood of the dt P (X M) nd the prior proility of the model P (M) : ˆM = rgmx M PPTA mximizes the dt likelihood P (X M).P (M) A smller model (numer of sttes) is priori ssumed more likely RPNI stte merging order Comptiility mesure: smll divergence increse (= smll likelihood loss) with respect to size reduction (= prior proility increse) glol criterion (A, A ) A A < α M Efficient computtion of divergence increse D(A A ) = D(A A ) + (A, A ) (A, A ) = c i γ (q i, ) log γ (q i,) γ (q i,) q i Q Σ {#} Q = {q i Q B π (q i ) B π (q i )} denotes the set of sttes of A which hve een merged to get A from A Pierre Dupont 3 Pierre Dupont 39
11 Grmmr Induction Grmmr Induction Comprtive results Grmmr induction definition Lerning prdigms DFA lerning from positive nd negtive exmples RPNI lgorithm Proilistic DFA lerning Appliction to nturl lnguge tsk Links with Mrkov models Relted prolems nd future work Perplexity Trining smple size ALERGIA MDI Perplexity mesure the prediction power of the model: the smller, the etter Pierre Dupont Pierre Dupont Grmmr Induction Nturl lnguge ppliction: the ATIS tsk Grmmr Induction Perplexity Air trvel informtion system, spontneous Americn English Uh, I d like to go from, uh, Pittsurgh to Boston next Tuesdy, no wit, Wednesdy. Lexicon (lphet): 9 words Lerning smple: 3 sentences, 33 words Vlidtion set: 9 sentences, 3 words Test set: sentences, 3 words P (x j i qi ) : proility of generting x j i, the i-th symol of the j-th string from stte q i LL = S P P = perfectly predictive model S x log P (x j i qi ) j= i= P P = LL P P = Σ uniform rndom guessing over Σ Pierre Dupont Pierre Dupont 3
12 Grmmr Induction Grmmr Induction Equivlence etween PNFA nd HMM Grmmr induction definition Lerning prdigms DFA lerning from positive nd negtive exmples RPNI lgorithm Proilistic DFA lerning Appliction to nturl lnguge tsk Links with Mrkov models Relted prolems nd future work Proilistic non-deterministic utomt (PNFA), with no end-of-string proilities, re equivlent to Hidden Mrkov Models (HMMs) PNFA.. [.3]. [.].9..3 [.] [.]. [.] [.] [.9] [.] HMM with emission on trnsitions Pierre Dupont Pierre Dupont Grmmr Induction Links with Mrkov chins A suclss of regulr lnguges: the k-testle lnguges in the strict sense A k-tss lnguge is generted y n utomton such tht ll susequences shring the sme lst k symols led to the sme stte λ ˆp( ) = C() C() A proilistic k-tss lnguge is equivlent to k order Mrkov chin There exists proilistic regulr lnguges not reducile to Mrkov chins of ny finite order Grmmr Induction.. [.3]. [.].9..3 [.] [.]. [.] [.] [.9] [.] HMM with emission on trnsitions..3.9 [.] [.] [.3] [.] [.] [.9] [.] [.]...3 HMM with emission on sttes PNFA Pierre Dupont 5 Pierre Dupont
13 Grmmr Induction Grmmr Induction Grmmr induction definition Lerning prdigms DFA lerning from positive nd negtive exmples RPNI lgorithm Proilistic DFA lerning Appliction to nturl lnguge tsk Links with Mrkov models Relted prolems nd future work Grmmr induction definition Lerning prdigms DFA lerning from positive nd negtive exmples RPNI lgorithm Proilistic DFA lerning Appliction to nturl lnguge tsk Links with Mrkov models Relted prolems nd future work Pierre Dupont Pierre Dupont 5 Grmmr Induction The smoothing prolem Grmmr Induction Relted prolems nd pproches A proilistic DFA defines proility distriution over set of strings Some strings re not oserved on the trining smple ut they could e oserved their proility should e strictly positive The smoothing prolem: how to ssign resonle proility to (yet) unseen rndom events? Highly optimized smoothing techniques exist for Mrkov chins How to dpt these techniques to more generl proilistic utomt? I did not tlk out other induction prolems (NFA, CFG, tree grmmrs,...) heuristic pproches s neurl nets or genetic lgorithms how to use prior knowledge smoothing techniques how to prse nturl lnguge without grmmrs (decision trees) how to lern trnsducers enchmrks, pplictions Pierre Dupont 9 Pierre Dupont 5
14 Grmmr Induction Ongoing nd future work Definition of theoreticl frmework for inductive nd sttisticl lerning Links with HMMs: prmeter estimtion, structurl induction Smoothing techniques improvement key issue for prcticl pplictions Applictions to proilistic modeling of proteins Automtic trnsltion Applictions to Text ctegoriztion or Text mining Pierre Dupont 5
Learning Moore Machines from Input-Output Traces
 Lerning Moore Mchines from Input-Output Trces Georgios Gintmidis 1 nd Stvros Tripkis 1,2 1 Alto University, Finlnd 2 UC Berkeley, USA Motivtion: lerning models from blck boxes Inputs? Lerner Forml Model
Lerning Moore Mchines from Input-Output Trces Georgios Gintmidis 1 nd Stvros Tripkis 1,2 1 Alto University, Finlnd 2 UC Berkeley, USA Motivtion: lerning models from blck boxes Inputs? Lerner Forml Model
CS415 Compilers. Lexical Analysis and. These slides are based on slides copyrighted by Keith Cooper, Ken Kennedy & Linda Torczon at Rice University
 CS415 Compilers Lexicl Anlysis nd These slides re sed on slides copyrighted y Keith Cooper, Ken Kennedy & Lind Torczon t Rice University First Progrmming Project Instruction Scheduling Project hs een posted
CS415 Compilers Lexicl Anlysis nd These slides re sed on slides copyrighted y Keith Cooper, Ken Kennedy & Lind Torczon t Rice University First Progrmming Project Instruction Scheduling Project hs een posted
Assignment 1 Automata, Languages, and Computability. 1 Finite State Automata and Regular Languages
 Deprtment of Computer Science, Austrlin Ntionl University COMP2600 Forml Methods for Softwre Engineering Semester 2, 206 Assignment Automt, Lnguges, nd Computility Smple Solutions Finite Stte Automt nd
Deprtment of Computer Science, Austrlin Ntionl University COMP2600 Forml Methods for Softwre Engineering Semester 2, 206 Assignment Automt, Lnguges, nd Computility Smple Solutions Finite Stte Automt nd
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018
 Finite Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 10 An Bove April 23rd 2018 Recp: Regulr Lnguges We cn convert between FA nd RE; Hence both FA nd RE ccept/generte regulr lnguges; More
Finite Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 10 An Bove April 23rd 2018 Recp: Regulr Lnguges We cn convert between FA nd RE; Hence both FA nd RE ccept/generte regulr lnguges; More
Chapter Five: Nondeterministic Finite Automata. Formal Language, chapter 5, slide 1
 Chpter Five: Nondeterministic Finite Automt Forml Lnguge, chpter 5, slide 1 1 A DFA hs exctly one trnsition from every stte on every symol in the lphet. By relxing this requirement we get relted ut more
Chpter Five: Nondeterministic Finite Automt Forml Lnguge, chpter 5, slide 1 1 A DFA hs exctly one trnsition from every stte on every symol in the lphet. By relxing this requirement we get relted ut more
Nondeterminism and Nodeterministic Automata
 Nondeterminism nd Nodeterministic Automt 61 Nondeterminism nd Nondeterministic Automt The computtionl mchine models tht we lerned in the clss re deterministic in the sense tht the next move is uniquely
Nondeterminism nd Nodeterministic Automt 61 Nondeterminism nd Nondeterministic Automt The computtionl mchine models tht we lerned in the clss re deterministic in the sense tht the next move is uniquely
Minimal DFA. minimal DFA for L starting from any other
 Miniml DFA Among the mny DFAs ccepting the sme regulr lnguge L, there is exctly one (up to renming of sttes) which hs the smllest possile numer of sttes. Moreover, it is possile to otin tht miniml DFA
Miniml DFA Among the mny DFAs ccepting the sme regulr lnguge L, there is exctly one (up to renming of sttes) which hs the smllest possile numer of sttes. Moreover, it is possile to otin tht miniml DFA
The University of Nottingham SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE A LEVEL 2 MODULE, SPRING SEMESTER LANGUAGES AND COMPUTATION ANSWERS
 The University of Nottinghm SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE LEVEL 2 MODULE, SPRING SEMESTER 2016 2017 LNGUGES ND COMPUTTION NSWERS Time llowed TWO hours Cndidtes my complete the front cover of their nswer ook
The University of Nottinghm SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE LEVEL 2 MODULE, SPRING SEMESTER 2016 2017 LNGUGES ND COMPUTTION NSWERS Time llowed TWO hours Cndidtes my complete the front cover of their nswer ook
Foundations of XML Types: Tree Automata
 1 / 43 Foundtions of XML Types: Tree Automt Pierre Genevès CNRS (slides mostly sed on slides y W. Mrtens nd T. Schwentick) University of Grenole Alpes, 2017 2018 2 / 43 Why Tree Automt? Foundtions of XML
1 / 43 Foundtions of XML Types: Tree Automt Pierre Genevès CNRS (slides mostly sed on slides y W. Mrtens nd T. Schwentick) University of Grenole Alpes, 2017 2018 2 / 43 Why Tree Automt? Foundtions of XML
Chapter 2 Finite Automata
 Chpter 2 Finite Automt 28 2.1 Introduction Finite utomt: first model of the notion of effective procedure. (They lso hve mny other pplictions). The concept of finite utomton cn e derived y exmining wht
Chpter 2 Finite Automt 28 2.1 Introduction Finite utomt: first model of the notion of effective procedure. (They lso hve mny other pplictions). The concept of finite utomton cn e derived y exmining wht
Designing finite automata II
 Designing finite utomt II Prolem: Design DFA A such tht L(A) consists of ll strings of nd which re of length 3n, for n = 0, 1, 2, (1) Determine wht to rememer out the input string Assign stte to ech of
Designing finite utomt II Prolem: Design DFA A such tht L(A) consists of ll strings of nd which re of length 3n, for n = 0, 1, 2, (1) Determine wht to rememer out the input string Assign stte to ech of
Gold s algorithm. Acknowledgements. Why would this be true? Gold's Algorithm. 1 Key ideas. Strings as states
 Acknowledgements Gold s lgorithm Lurent Miclet, Jose Oncin nd Tim Otes for previous versions of these slides. Rfel Crrsco, Pco Cscuert, Rémi Eyrud, Philippe Ezequel, Henning Fernu, Thierry Murgue, Frnck
Acknowledgements Gold s lgorithm Lurent Miclet, Jose Oncin nd Tim Otes for previous versions of these slides. Rfel Crrsco, Pco Cscuert, Rémi Eyrud, Philippe Ezequel, Henning Fernu, Thierry Murgue, Frnck
CS103B Handout 18 Winter 2007 February 28, 2007 Finite Automata
 CS103B ndout 18 Winter 2007 Ferury 28, 2007 Finite Automt Initil text y Mggie Johnson. Introduction Severl childrens gmes fit the following description: Pieces re set up on plying ord; dice re thrown or
CS103B ndout 18 Winter 2007 Ferury 28, 2007 Finite Automt Initil text y Mggie Johnson. Introduction Severl childrens gmes fit the following description: Pieces re set up on plying ord; dice re thrown or
Formal languages, automata, and theory of computation
 Mälrdlen University TEN1 DVA337 2015 School of Innovtion, Design nd Engineering Forml lnguges, utomt, nd theory of computtion Thursdy, Novemer 5, 14:10-18:30 Techer: Dniel Hedin, phone 021-107052 The exm
Mälrdlen University TEN1 DVA337 2015 School of Innovtion, Design nd Engineering Forml lnguges, utomt, nd theory of computtion Thursdy, Novemer 5, 14:10-18:30 Techer: Dniel Hedin, phone 021-107052 The exm
Theory of Computation Regular Languages. (NTU EE) Regular Languages Fall / 38
 Theory of Computtion Regulr Lnguges (NTU EE) Regulr Lnguges Fll 2017 1 / 38 Schemtic of Finite Automt control 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 Figure: Schemtic of Finite Automt A finite utomton hs finite set of control
Theory of Computtion Regulr Lnguges (NTU EE) Regulr Lnguges Fll 2017 1 / 38 Schemtic of Finite Automt control 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 Figure: Schemtic of Finite Automt A finite utomton hs finite set of control
FABER Formal Languages, Automata and Models of Computation
 DVA337 FABER Forml Lnguges, Automt nd Models of Computtion Lecture 5 chool of Innovtion, Design nd Engineering Mälrdlen University 2015 1 Recp of lecture 4 y definition suset construction DFA NFA stte
DVA337 FABER Forml Lnguges, Automt nd Models of Computtion Lecture 5 chool of Innovtion, Design nd Engineering Mälrdlen University 2015 1 Recp of lecture 4 y definition suset construction DFA NFA stte
Theory of Computation Regular Languages
 Theory of Computtion Regulr Lnguges Bow-Yw Wng Acdemi Sinic Spring 2012 Bow-Yw Wng (Acdemi Sinic) Regulr Lnguges Spring 2012 1 / 38 Schemtic of Finite Automt control 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 Figure: Schemtic of
Theory of Computtion Regulr Lnguges Bow-Yw Wng Acdemi Sinic Spring 2012 Bow-Yw Wng (Acdemi Sinic) Regulr Lnguges Spring 2012 1 / 38 Schemtic of Finite Automt control 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 Figure: Schemtic of
A likelihood-ratio test for identifying probabilistic deterministic real-time automata from positive data
 A likelihood-rtio test for identifying proilistic deterministic rel-time utomt from positive dt Sicco Verwer 1, Mthijs de Weerdt 2, nd Cees Witteveen 2 1 Eindhoven University of Technology 2 Delft University
A likelihood-rtio test for identifying proilistic deterministic rel-time utomt from positive dt Sicco Verwer 1, Mthijs de Weerdt 2, nd Cees Witteveen 2 1 Eindhoven University of Technology 2 Delft University
CS 330 Formal Methods and Models
 CS 330 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, George Mson University, Spring 2017 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Ferury 2 1. Prove ((( p q) q) p) is tutology () (3pts) y truth tle. p q p q
CS 330 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, George Mson University, Spring 2017 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Ferury 2 1. Prove ((( p q) q) p) is tutology () (3pts) y truth tle. p q p q
Bayesian Networks: Approximate Inference
 pproches to inference yesin Networks: pproximte Inference xct inference Vrillimintion Join tree lgorithm pproximte inference Simplify the structure of the network to mkxct inferencfficient (vritionl methods,
pproches to inference yesin Networks: pproximte Inference xct inference Vrillimintion Join tree lgorithm pproximte inference Simplify the structure of the network to mkxct inferencfficient (vritionl methods,
Non-Deterministic Finite Automata. Fall 2018 Costas Busch - RPI 1
 Non-Deterministic Finite Automt Fll 2018 Costs Busch - RPI 1 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet ={} q q2 1 q 0 q 3 Fll 2018 Costs Busch - RPI 2 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet
Non-Deterministic Finite Automt Fll 2018 Costs Busch - RPI 1 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet ={} q q2 1 q 0 q 3 Fll 2018 Costs Busch - RPI 2 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet
12.1 Nondeterminism Nondeterministic Finite Automata. a a b ε. CS125 Lecture 12 Fall 2014
 CS125 Lecture 12 Fll 2014 12.1 Nondeterminism The ide of nondeterministic computtions is to llow our lgorithms to mke guesses, nd only require tht they ccept when the guesses re correct. For exmple, simple
CS125 Lecture 12 Fll 2014 12.1 Nondeterminism The ide of nondeterministic computtions is to llow our lgorithms to mke guesses, nd only require tht they ccept when the guesses re correct. For exmple, simple
CS 330 Formal Methods and Models Dana Richards, George Mason University, Spring 2016 Quiz Solutions
 CS 330 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, George Mson University, Spring 2016 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Ferury 9 1. (4pts) ((p q) (q r)) (p r), prove tutology using truth tles. p
CS 330 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, George Mson University, Spring 2016 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Ferury 9 1. (4pts) ((p q) (q r)) (p r), prove tutology using truth tles. p
Harvard University Computer Science 121 Midterm October 23, 2012
 Hrvrd University Computer Science 121 Midterm Octoer 23, 2012 This is closed-ook exmintion. You my use ny result from lecture, Sipser, prolem sets, or section, s long s you quote it clerly. The lphet is
Hrvrd University Computer Science 121 Midterm Octoer 23, 2012 This is closed-ook exmintion. You my use ny result from lecture, Sipser, prolem sets, or section, s long s you quote it clerly. The lphet is
Model Reduction of Finite State Machines by Contraction
 Model Reduction of Finite Stte Mchines y Contrction Alessndro Giu Dip. di Ingegneri Elettric ed Elettronic, Università di Cgliri, Pizz d Armi, 09123 Cgliri, Itly Phone: +39-070-675-5892 Fx: +39-070-675-5900
Model Reduction of Finite Stte Mchines y Contrction Alessndro Giu Dip. di Ingegneri Elettric ed Elettronic, Università di Cgliri, Pizz d Armi, 09123 Cgliri, Itly Phone: +39-070-675-5892 Fx: +39-070-675-5900
Non-deterministic Finite Automata
 Non-deterministic Finite Automt Eliminting non-determinism Rdoud University Nijmegen Non-deterministic Finite Automt H. Geuvers nd T. vn Lrhoven Institute for Computing nd Informtion Sciences Intelligent
Non-deterministic Finite Automt Eliminting non-determinism Rdoud University Nijmegen Non-deterministic Finite Automt H. Geuvers nd T. vn Lrhoven Institute for Computing nd Informtion Sciences Intelligent
NFAs continued, Closure Properties of Regular Languages
 Algorithms & Models of Computtion CS/ECE 374, Fll 2017 NFAs continued, Closure Properties of Regulr Lnguges Lecture 5 Tuesdy, Septemer 12, 2017 Sriel Hr-Peled (UIUC) CS374 1 Fll 2017 1 / 31 Regulr Lnguges,
Algorithms & Models of Computtion CS/ECE 374, Fll 2017 NFAs continued, Closure Properties of Regulr Lnguges Lecture 5 Tuesdy, Septemer 12, 2017 Sriel Hr-Peled (UIUC) CS374 1 Fll 2017 1 / 31 Regulr Lnguges,
Regular Languages and Applications
 Regulr Lnguges nd Applictions Yo-Su Hn Deprtment of Computer Science Yonsei University 1-1 SNU 4/14 Regulr Lnguges An old nd well-known topic in CS Kleene Theorem in 1959 FA (finite-stte utomton) constructions:
Regulr Lnguges nd Applictions Yo-Su Hn Deprtment of Computer Science Yonsei University 1-1 SNU 4/14 Regulr Lnguges An old nd well-known topic in CS Kleene Theorem in 1959 FA (finite-stte utomton) constructions:
Convert the NFA into DFA
 Convert the NF into F For ech NF we cn find F ccepting the sme lnguge. The numer of sttes of the F could e exponentil in the numer of sttes of the NF, ut in prctice this worst cse occurs rrely. lgorithm:
Convert the NF into F For ech NF we cn find F ccepting the sme lnguge. The numer of sttes of the F could e exponentil in the numer of sttes of the NF, ut in prctice this worst cse occurs rrely. lgorithm:
Myhill-Nerode Theorem
 Overview Myhill-Nerode Theorem Correspondence etween DA s nd MN reltions Cnonicl DA for L Computing cnonicl DFA Myhill-Nerode Theorem Deepk D Souz Deprtment of Computer Science nd Automtion Indin Institute
Overview Myhill-Nerode Theorem Correspondence etween DA s nd MN reltions Cnonicl DA for L Computing cnonicl DFA Myhill-Nerode Theorem Deepk D Souz Deprtment of Computer Science nd Automtion Indin Institute
CS 301. Lecture 04 Regular Expressions. Stephen Checkoway. January 29, 2018
 CS 301 Lecture 04 Regulr Expressions Stephen Checkowy Jnury 29, 2018 1 / 35 Review from lst time NFA N = (Q, Σ, δ, q 0, F ) where δ Q Σ P (Q) mps stte nd n lphet symol (or ) to set of sttes We run n NFA
CS 301 Lecture 04 Regulr Expressions Stephen Checkowy Jnury 29, 2018 1 / 35 Review from lst time NFA N = (Q, Σ, δ, q 0, F ) where δ Q Σ P (Q) mps stte nd n lphet symol (or ) to set of sttes We run n NFA
First Midterm Examination
 24-25 Fll Semester First Midterm Exmintion ) Give the stte digrm of DFA tht recognizes the lnguge A over lphet Σ = {, } where A = {w w contins or } 2) The following DFA recognizes the lnguge B over lphet
24-25 Fll Semester First Midterm Exmintion ) Give the stte digrm of DFA tht recognizes the lnguge A over lphet Σ = {, } where A = {w w contins or } 2) The following DFA recognizes the lnguge B over lphet
Regular expressions, Finite Automata, transition graphs are all the same!!
 CSI 3104 /Winter 2011: Introduction to Forml Lnguges Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Regulr expressions, Finite Automt, trnsition grphs re ll the sme!! Dr. Neji Zgui CSI3104-W11 1
CSI 3104 /Winter 2011: Introduction to Forml Lnguges Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Regulr expressions, Finite Automt, trnsition grphs re ll the sme!! Dr. Neji Zgui CSI3104-W11 1
Formal Language and Automata Theory (CS21004)
 Forml Lnguge nd Automt Forml Lnguge nd Automt Theory (CS21004) Khrgpur Khrgpur Khrgpur Forml Lnguge nd Automt Tle of Contents Forml Lnguge nd Automt Khrgpur 1 2 3 Khrgpur Forml Lnguge nd Automt Forml Lnguge
Forml Lnguge nd Automt Forml Lnguge nd Automt Theory (CS21004) Khrgpur Khrgpur Khrgpur Forml Lnguge nd Automt Tle of Contents Forml Lnguge nd Automt Khrgpur 1 2 3 Khrgpur Forml Lnguge nd Automt Forml Lnguge
CS 330 Formal Methods and Models
 CS 330 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, section 003, George Mson University, Fll 2017 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Septemer 7 1. Prove (p q) (p q), () (5pts) using truth tles. p q
CS 330 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, section 003, George Mson University, Fll 2017 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Septemer 7 1. Prove (p q) (p q), () (5pts) using truth tles. p q
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation
 9/6/28 Stereotypicl computer CISC 49 Theory of Computtion Finite stte mchines & Regulr lnguges Professor Dniel Leeds dleeds@fordhm.edu JMH 332 Centrl processing unit (CPU) performs ll the instructions
9/6/28 Stereotypicl computer CISC 49 Theory of Computtion Finite stte mchines & Regulr lnguges Professor Dniel Leeds dleeds@fordhm.edu JMH 332 Centrl processing unit (CPU) performs ll the instructions
1. For each of the following theorems, give a two or three sentence sketch of how the proof goes or why it is not true.
 York University CSE 2 Unit 3. DFA Clsses Converting etween DFA, NFA, Regulr Expressions, nd Extended Regulr Expressions Instructor: Jeff Edmonds Don t chet y looking t these nswers premturely.. For ech
York University CSE 2 Unit 3. DFA Clsses Converting etween DFA, NFA, Regulr Expressions, nd Extended Regulr Expressions Instructor: Jeff Edmonds Don t chet y looking t these nswers premturely.. For ech
CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computation. Lecture #31: What DFA s Can and Can t Do David Mix Barrington 9 April 2014
 CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computtion Lecture #31: Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Dvid Mix Brrington 9 April 2014 Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Deterministic Finite Automt Forml Definition of DFA s Exmples of DFA
CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computtion Lecture #31: Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Dvid Mix Brrington 9 April 2014 Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Deterministic Finite Automt Forml Definition of DFA s Exmples of DFA
Deterministic Finite Automata
 Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt H. Geuvers nd J. Rot Institute for Computing nd Informtion Sciences Version: fll 2016 J. Rot Version: fll 2016 Tlen en Automten 1 / 21 Outline Finite Automt Finite
Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt H. Geuvers nd J. Rot Institute for Computing nd Informtion Sciences Version: fll 2016 J. Rot Version: fll 2016 Tlen en Automten 1 / 21 Outline Finite Automt Finite
Worked out examples Finite Automata
 Worked out exmples Finite Automt Exmple Design Finite Stte Automton which reds inry string nd ccepts only those tht end with. Since we re in the topic of Non Deterministic Finite Automt (NFA), we will
Worked out exmples Finite Automt Exmple Design Finite Stte Automton which reds inry string nd ccepts only those tht end with. Since we re in the topic of Non Deterministic Finite Automt (NFA), we will
Lecture 09: Myhill-Nerode Theorem
 CS 373: Theory of Computtion Mdhusudn Prthsrthy Lecture 09: Myhill-Nerode Theorem 16 Ferury 2010 In this lecture, we will see tht every lnguge hs unique miniml DFA We will see this fct from two perspectives
CS 373: Theory of Computtion Mdhusudn Prthsrthy Lecture 09: Myhill-Nerode Theorem 16 Ferury 2010 In this lecture, we will see tht every lnguge hs unique miniml DFA We will see this fct from two perspectives
AUTOMATA AND LANGUAGES. Definition 1.5: Finite Automaton
 25. Finite Automt AUTOMATA AND LANGUAGES A system of computtion tht only hs finite numer of possile sttes cn e modeled using finite utomton A finite utomton is often illustrted s stte digrm d d d. d q
25. Finite Automt AUTOMATA AND LANGUAGES A system of computtion tht only hs finite numer of possile sttes cn e modeled using finite utomton A finite utomton is often illustrted s stte digrm d d d. d q
DFA minimisation using the Myhill-Nerode theorem
 DFA minimistion using the Myhill-Nerode theorem Johnn Högerg Lrs Lrsson Astrct The Myhill-Nerode theorem is n importnt chrcteristion of regulr lnguges, nd it lso hs mny prcticl implictions. In this chpter,
DFA minimistion using the Myhill-Nerode theorem Johnn Högerg Lrs Lrsson Astrct The Myhill-Nerode theorem is n importnt chrcteristion of regulr lnguges, nd it lso hs mny prcticl implictions. In this chpter,
Revision Sheet. (a) Give a regular expression for each of the following languages:
 Theoreticl Computer Science (Bridging Course) Dr. G. D. Tipldi F. Bonirdi Winter Semester 2014/2015 Revision Sheet University of Freiurg Deprtment of Computer Science Question 1 (Finite Automt, 8 + 6 points)
Theoreticl Computer Science (Bridging Course) Dr. G. D. Tipldi F. Bonirdi Winter Semester 2014/2015 Revision Sheet University of Freiurg Deprtment of Computer Science Question 1 (Finite Automt, 8 + 6 points)
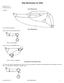
Let's start with an example:
 Finite Automt Let's strt with n exmple: Here you see leled circles tht re sttes, nd leled rrows tht re trnsitions. One of the sttes is mrked "strt". One of the sttes hs doule circle; this is terminl stte
Finite Automt Let's strt with n exmple: Here you see leled circles tht re sttes, nd leled rrows tht re trnsitions. One of the sttes is mrked "strt". One of the sttes hs doule circle; this is terminl stte
Hybrid Control and Switched Systems. Lecture #2 How to describe a hybrid system? Formal models for hybrid system
 Hyrid Control nd Switched Systems Lecture #2 How to descrie hyrid system? Forml models for hyrid system João P. Hespnh University of Cliforni t Snt Brr Summry. Forml models for hyrid systems: Finite utomt
Hyrid Control nd Switched Systems Lecture #2 How to descrie hyrid system? Forml models for hyrid system João P. Hespnh University of Cliforni t Snt Brr Summry. Forml models for hyrid systems: Finite utomt
Compiler Design. Fall Lexical Analysis. Sample Exercises and Solutions. Prof. Pedro C. Diniz
 University of Southern Cliforni Computer Science Deprtment Compiler Design Fll Lexicl Anlysis Smple Exercises nd Solutions Prof. Pedro C. Diniz USC / Informtion Sciences Institute 4676 Admirlty Wy, Suite
University of Southern Cliforni Computer Science Deprtment Compiler Design Fll Lexicl Anlysis Smple Exercises nd Solutions Prof. Pedro C. Diniz USC / Informtion Sciences Institute 4676 Admirlty Wy, Suite
80 CHAPTER 2. DFA S, NFA S, REGULAR LANGUAGES. 2.6 Finite State Automata With Output: Transducers
 80 CHAPTER 2. DFA S, NFA S, REGULAR LANGUAGES 2.6 Finite Stte Automt With Output: Trnsducers So fr, we hve only considered utomt tht recognize lnguges, i.e., utomt tht do not produce ny output on ny input
80 CHAPTER 2. DFA S, NFA S, REGULAR LANGUAGES 2.6 Finite Stte Automt With Output: Trnsducers So fr, we hve only considered utomt tht recognize lnguges, i.e., utomt tht do not produce ny output on ny input
NFA DFA Example 3 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Equivalence of DFAs and NFAs. Equivalence of DFAs and NFAs (cont.
 NFA DFA Exmple 3 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges NFA {B,D,E {A,E {C,D {E Finite Automt, con't. R = { {A,E, {B,D,E, {C,D, {E 2 Equivlence of DFAs nd NFAs Any string from {A to either {D or {CD
NFA DFA Exmple 3 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges NFA {B,D,E {A,E {C,D {E Finite Automt, con't. R = { {A,E, {B,D,E, {C,D, {E 2 Equivlence of DFAs nd NFAs Any string from {A to either {D or {CD
12.1 Nondeterminism Nondeterministic Finite Automata. a a b ε. CS125 Lecture 12 Fall 2016
 CS125 Lecture 12 Fll 2016 12.1 Nondeterminism The ide of nondeterministic computtions is to llow our lgorithms to mke guesses, nd only require tht they ccept when the guesses re correct. For exmple, simple
CS125 Lecture 12 Fll 2016 12.1 Nondeterminism The ide of nondeterministic computtions is to llow our lgorithms to mke guesses, nd only require tht they ccept when the guesses re correct. For exmple, simple
Grammar. Languages. Content 5/10/16. Automata and Languages. Regular Languages. Regular Languages
 5//6 Grmmr Automt nd Lnguges Regulr Grmmr Context-free Grmmr Context-sensitive Grmmr Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering L. The University of Aizu Jpn Regulr Lnguges Context Free Lnguges Context Sensitive
5//6 Grmmr Automt nd Lnguges Regulr Grmmr Context-free Grmmr Context-sensitive Grmmr Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering L. The University of Aizu Jpn Regulr Lnguges Context Free Lnguges Context Sensitive
1.3 Regular Expressions
 56 1.3 Regulr xpressions These hve n importnt role in describing ptterns in serching for strings in mny pplictions (e.g. wk, grep, Perl,...) All regulr expressions of lphbet re 1.Ønd re regulr expressions,
56 1.3 Regulr xpressions These hve n importnt role in describing ptterns in serching for strings in mny pplictions (e.g. wk, grep, Perl,...) All regulr expressions of lphbet re 1.Ønd re regulr expressions,
Speech Recognition Lecture 2: Finite Automata and Finite-State Transducers. Mehryar Mohri Courant Institute and Google Research
 Speech Recognition Lecture 2: Finite Automt nd Finite-Stte Trnsducers Mehryr Mohri Cournt Institute nd Google Reserch mohri@cims.nyu.com Preliminries Finite lphet Σ, empty string. Set of ll strings over
Speech Recognition Lecture 2: Finite Automt nd Finite-Stte Trnsducers Mehryr Mohri Cournt Institute nd Google Reserch mohri@cims.nyu.com Preliminries Finite lphet Σ, empty string. Set of ll strings over
1.4 Nonregular Languages
 74 1.4 Nonregulr Lnguges The number of forml lnguges over ny lphbet (= decision/recognition problems) is uncountble On the other hnd, the number of regulr expressions (= strings) is countble Hence, ll
74 1.4 Nonregulr Lnguges The number of forml lnguges over ny lphbet (= decision/recognition problems) is uncountble On the other hnd, the number of regulr expressions (= strings) is countble Hence, ll
Speech Recognition Lecture 2: Finite Automata and Finite-State Transducers
 Speech Recognition Lecture 2: Finite Automt nd Finite-Stte Trnsducers Eugene Weinstein Google, NYU Cournt Institute eugenew@cs.nyu.edu Slide Credit: Mehryr Mohri Preliminries Finite lphet, empty string.
Speech Recognition Lecture 2: Finite Automt nd Finite-Stte Trnsducers Eugene Weinstein Google, NYU Cournt Institute eugenew@cs.nyu.edu Slide Credit: Mehryr Mohri Preliminries Finite lphet, empty string.
Homework 3 Solutions
 CS 341: Foundtions of Computer Science II Prof. Mrvin Nkym Homework 3 Solutions 1. Give NFAs with the specified numer of sttes recognizing ech of the following lnguges. In ll cses, the lphet is Σ = {,1}.
CS 341: Foundtions of Computer Science II Prof. Mrvin Nkym Homework 3 Solutions 1. Give NFAs with the specified numer of sttes recognizing ech of the following lnguges. In ll cses, the lphet is Σ = {,1}.
Normal Forms for Context-free Grammars
 Norml Forms for Context-free Grmmrs 1 Linz 6th, Section 6.2 wo Importnt Norml Forms, pges 171--178 2 Chomsky Norml Form All productions hve form: A BC nd A vrile vrile terminl 3 Exmples: S AS S AS S S
Norml Forms for Context-free Grmmrs 1 Linz 6th, Section 6.2 wo Importnt Norml Forms, pges 171--178 2 Chomsky Norml Form All productions hve form: A BC nd A vrile vrile terminl 3 Exmples: S AS S AS S S
Lecture 08: Feb. 08, 2019
 4CS4-6:Theory of Computtion(Closure on Reg. Lngs., regex to NDFA, DFA to regex) Prof. K.R. Chowdhry Lecture 08: Fe. 08, 2019 : Professor of CS Disclimer: These notes hve not een sujected to the usul scrutiny
4CS4-6:Theory of Computtion(Closure on Reg. Lngs., regex to NDFA, DFA to regex) Prof. K.R. Chowdhry Lecture 08: Fe. 08, 2019 : Professor of CS Disclimer: These notes hve not een sujected to the usul scrutiny
NFAs continued, Closure Properties of Regular Languages
 lgorithms & Models of omputtion S/EE 374, Spring 209 NFs continued, losure Properties of Regulr Lnguges Lecture 5 Tuesdy, Jnury 29, 209 Regulr Lnguges, DFs, NFs Lnguges ccepted y DFs, NFs, nd regulr expressions
lgorithms & Models of omputtion S/EE 374, Spring 209 NFs continued, losure Properties of Regulr Lnguges Lecture 5 Tuesdy, Jnury 29, 209 Regulr Lnguges, DFs, NFs Lnguges ccepted y DFs, NFs, nd regulr expressions
Non Deterministic Automata. Linz: Nondeterministic Finite Accepters, page 51
 Non Deterministic Automt Linz: Nondeterministic Finite Accepters, pge 51 1 Nondeterministic Finite Accepter (NFA) Alphbet ={} q 1 q2 q 0 q 3 2 Nondeterministic Finite Accepter (NFA) Alphbet ={} Two choices
Non Deterministic Automt Linz: Nondeterministic Finite Accepters, pge 51 1 Nondeterministic Finite Accepter (NFA) Alphbet ={} q 1 q2 q 0 q 3 2 Nondeterministic Finite Accepter (NFA) Alphbet ={} Two choices
CS 275 Automata and Formal Language Theory
 CS 275 utomt nd Forml Lnguge Theory Course Notes Prt II: The Recognition Prolem (II) Chpter II.5.: Properties of Context Free Grmmrs (14) nton Setzer (Bsed on ook drft y J. V. Tucker nd K. Stephenson)
CS 275 utomt nd Forml Lnguge Theory Course Notes Prt II: The Recognition Prolem (II) Chpter II.5.: Properties of Context Free Grmmrs (14) nton Setzer (Bsed on ook drft y J. V. Tucker nd K. Stephenson)
First Midterm Examination
 Çnky University Deprtment of Computer Engineering 203-204 Fll Semester First Midterm Exmintion ) Design DFA for ll strings over the lphet Σ = {,, c} in which there is no, no nd no cc. 2) Wht lnguge does
Çnky University Deprtment of Computer Engineering 203-204 Fll Semester First Midterm Exmintion ) Design DFA for ll strings over the lphet Σ = {,, c} in which there is no, no nd no cc. 2) Wht lnguge does
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages
 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 CMSC 330 1 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic
CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 CMSC 330 1 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic
Finite-State Automata: Recap
 Finite-Stte Automt: Recp Deepk D Souz Deprtment of Computer Science nd Automtion Indin Institute of Science, Bnglore. 09 August 2016 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Forml Definitions nd Nottion 3 Closure under
Finite-Stte Automt: Recp Deepk D Souz Deprtment of Computer Science nd Automtion Indin Institute of Science, Bnglore. 09 August 2016 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Forml Definitions nd Nottion 3 Closure under
The size of subsequence automaton
 Theoreticl Computer Science 4 (005) 79 84 www.elsevier.com/locte/tcs Note The size of susequence utomton Zdeněk Troníček,, Ayumi Shinohr,c Deprtment of Computer Science nd Engineering, FEE CTU in Prgue,
Theoreticl Computer Science 4 (005) 79 84 www.elsevier.com/locte/tcs Note The size of susequence utomton Zdeněk Troníček,, Ayumi Shinohr,c Deprtment of Computer Science nd Engineering, FEE CTU in Prgue,
Today. Recap: Reasoning Over Time. Demo Bonanza! CS 188: Artificial Intelligence. Advanced HMMs. Speech recognition. HMMs. Start machine learning
 CS 188: Artificil Intelligence Advnced HMMs Dn Klein, Pieter Aeel University of Cliforni, Berkeley Demo Bonnz! Tody HMMs Demo onnz! Most likely explntion queries Speech recognition A mssive HMM! Detils
CS 188: Artificil Intelligence Advnced HMMs Dn Klein, Pieter Aeel University of Cliforni, Berkeley Demo Bonnz! Tody HMMs Demo onnz! Most likely explntion queries Speech recognition A mssive HMM! Detils
Some Theory of Computation Exercises Week 1
 Some Theory of Computtion Exercises Week 1 Section 1 Deterministic Finite Automt Question 1.3 d d d d u q 1 q 2 q 3 q 4 q 5 d u u u u Question 1.4 Prt c - {w w hs even s nd one or two s} First we sk whether
Some Theory of Computtion Exercises Week 1 Section 1 Deterministic Finite Automt Question 1.3 d d d d u q 1 q 2 q 3 q 4 q 5 d u u u u Question 1.4 Prt c - {w w hs even s nd one or two s} First we sk whether
Finite Automata-cont d
 Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges Professor Leslie Lnder Lecture # 6 Finite Automt-cont d The Pumping Lemm WEB SITE: http://ingwe.inghmton.edu/ ~lnder/cs573.html Septemer 18, 2000 Exmple 1 Consider L = {ww
Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges Professor Leslie Lnder Lecture # 6 Finite Automt-cont d The Pumping Lemm WEB SITE: http://ingwe.inghmton.edu/ ~lnder/cs573.html Septemer 18, 2000 Exmple 1 Consider L = {ww
ɛ-closure, Kleene s Theorem,
 DEGefW5wiGH2XgYMEzUKjEmtCDUsRQ4d 1 A nice pper relevnt to this course is titled The Glory of the Pst 2 NICTA Resercher, Adjunct t the Austrlin Ntionl University nd Griffith University ɛ-closure, Kleene
DEGefW5wiGH2XgYMEzUKjEmtCDUsRQ4d 1 A nice pper relevnt to this course is titled The Glory of the Pst 2 NICTA Resercher, Adjunct t the Austrlin Ntionl University nd Griffith University ɛ-closure, Kleene
Overview HC9. Parsing: Top-Down & LL(1) Context-Free Grammars (1) Introduction. CFGs (3) Context-Free Grammars (2) Vertalerbouw HC 9: Ch.
 Overview H9 Vertlerouw H 9: Prsing: op-down & LL(1) do 3 mei 2001 56 heo Ruys h. 8 - Prsing 8.1 ontext-free Grmmrs 8.2 op-down Prsing 8.3 LL(1) Grmmrs See lso [ho, Sethi & Ullmn 1986] for more thorough
Overview H9 Vertlerouw H 9: Prsing: op-down & LL(1) do 3 mei 2001 56 heo Ruys h. 8 - Prsing 8.1 ontext-free Grmmrs 8.2 op-down Prsing 8.3 LL(1) Grmmrs See lso [ho, Sethi & Ullmn 1986] for more thorough
Non-deterministic Finite Automata
 Non-deterministic Finite Automt From Regulr Expressions to NFA- Eliminting non-determinism Rdoud University Nijmegen Non-deterministic Finite Automt H. Geuvers nd J. Rot Institute for Computing nd Informtion
Non-deterministic Finite Automt From Regulr Expressions to NFA- Eliminting non-determinism Rdoud University Nijmegen Non-deterministic Finite Automt H. Geuvers nd J. Rot Institute for Computing nd Informtion
Formal Languages and Automata
 Moile Computing nd Softwre Engineering p. 1/5 Forml Lnguges nd Automt Chpter 2 Finite Automt Chun-Ming Liu cmliu@csie.ntut.edu.tw Deprtment of Computer Science nd Informtion Engineering Ntionl Tipei University
Moile Computing nd Softwre Engineering p. 1/5 Forml Lnguges nd Automt Chpter 2 Finite Automt Chun-Ming Liu cmliu@csie.ntut.edu.tw Deprtment of Computer Science nd Informtion Engineering Ntionl Tipei University
Finite Automata. Informatics 2A: Lecture 3. John Longley. 22 September School of Informatics University of Edinburgh
 Lnguges nd Automt Finite Automt Informtics 2A: Lecture 3 John Longley School of Informtics University of Edinburgh jrl@inf.ed.c.uk 22 September 2017 1 / 30 Lnguges nd Automt 1 Lnguges nd Automt Wht is
Lnguges nd Automt Finite Automt Informtics 2A: Lecture 3 John Longley School of Informtics University of Edinburgh jrl@inf.ed.c.uk 22 September 2017 1 / 30 Lnguges nd Automt 1 Lnguges nd Automt Wht is
13 Learning with Queries
 13 Lerning with Queries Among the more interesting remining theoreticl questions re: inference in the presence of noise, generl strtegies for interctive presenttion nd the inference of systems with semntics.
13 Lerning with Queries Among the more interesting remining theoreticl questions re: inference in the presence of noise, generl strtegies for interctive presenttion nd the inference of systems with semntics.
State Minimization for DFAs
 Stte Minimiztion for DFAs Red K & S 2.7 Do Homework 10. Consider: Stte Minimiztion 4 5 Is this miniml mchine? Step (1): Get rid of unrechle sttes. Stte Minimiztion 6, Stte is unrechle. Step (2): Get rid
Stte Minimiztion for DFAs Red K & S 2.7 Do Homework 10. Consider: Stte Minimiztion 4 5 Is this miniml mchine? Step (1): Get rid of unrechle sttes. Stte Minimiztion 6, Stte is unrechle. Step (2): Get rid
CS 310 (sec 20) - Winter Final Exam (solutions) SOLUTIONS
 CS 310 (sec 20) - Winter 2003 - Finl Exm (solutions) SOLUTIONS 1. (Logic) Use truth tles to prove the following logicl equivlences: () p q (p p) (q q) () p q (p q) (p q) () p q p q p p q q (q q) (p p)
CS 310 (sec 20) - Winter 2003 - Finl Exm (solutions) SOLUTIONS 1. (Logic) Use truth tles to prove the following logicl equivlences: () p q (p p) (q q) () p q (p q) (p q) () p q p q p p q q (q q) (p p)
On Determinisation of History-Deterministic Automata.
 On Deterministion of History-Deterministic Automt. Denis Kupererg Mich l Skrzypczk University of Wrsw YR-ICALP 2014 Copenhgen Introduction Deterministic utomt re centrl tool in utomt theory: Polynomil
On Deterministion of History-Deterministic Automt. Denis Kupererg Mich l Skrzypczk University of Wrsw YR-ICALP 2014 Copenhgen Introduction Deterministic utomt re centrl tool in utomt theory: Polynomil
Learning Regular Languages over Large Alphabets
 Irini-Eleftheri Mens VERIMAG, University of Grenoble-Alpes Lerning Regulr Lnguges over Lrge Alphbets 10 October 2017 Jury Members Oded Mler Directeur de thèse Lurent Fribourg Exminteur Dn Angluin Rpporteur
Irini-Eleftheri Mens VERIMAG, University of Grenoble-Alpes Lerning Regulr Lnguges over Lrge Alphbets 10 October 2017 Jury Members Oded Mler Directeur de thèse Lurent Fribourg Exminteur Dn Angluin Rpporteur
NFAs and Regular Expressions. NFA-ε, continued. Recall. Last class: Today: Fun:
 CMPU 240 Lnguge Theory nd Computtion Spring 2019 NFAs nd Regulr Expressions Lst clss: Introduced nondeterministic finite utomt with -trnsitions Tody: Prove n NFA- is no more powerful thn n NFA Introduce
CMPU 240 Lnguge Theory nd Computtion Spring 2019 NFAs nd Regulr Expressions Lst clss: Introduced nondeterministic finite utomt with -trnsitions Tody: Prove n NFA- is no more powerful thn n NFA Introduce
Finite Automata. Informatics 2A: Lecture 3. Mary Cryan. 21 September School of Informatics University of Edinburgh
 Finite Automt Informtics 2A: Lecture 3 Mry Cryn School of Informtics University of Edinburgh mcryn@inf.ed.c.uk 21 September 2018 1 / 30 Lnguges nd Automt Wht is lnguge? Finite utomt: recp Some forml definitions
Finite Automt Informtics 2A: Lecture 3 Mry Cryn School of Informtics University of Edinburgh mcryn@inf.ed.c.uk 21 September 2018 1 / 30 Lnguges nd Automt Wht is lnguge? Finite utomt: recp Some forml definitions
Talen en Automaten Test 1, Mon 7 th Dec, h45 17h30
 Tlen en Automten Test 1, Mon 7 th Dec, 2015 15h45 17h30 This test consists of four exercises over 5 pges. Explin your pproch, nd write your nswer to ech exercise on seprte pge. You cn score mximum of 100
Tlen en Automten Test 1, Mon 7 th Dec, 2015 15h45 17h30 This test consists of four exercises over 5 pges. Explin your pproch, nd write your nswer to ech exercise on seprte pge. You cn score mximum of 100
Nondeterministic Biautomata and Their Descriptional Complexity
 Nondeterministic Biutomt nd Their Descriptionl Complexity Mrkus Holzer nd Sestin Jkoi Institut für Informtik Justus-Lieig-Universität Arndtstr. 2, 35392 Gießen, Germny 23. Theorietg Automten und Formle
Nondeterministic Biutomt nd Their Descriptionl Complexity Mrkus Holzer nd Sestin Jkoi Institut für Informtik Justus-Lieig-Universität Arndtstr. 2, 35392 Gießen, Germny 23. Theorietg Automten und Formle
Learning probabilistic finite automata
 Lerning probbilistic finite utomt Colin de l Higuer University of Nntes Zdr, August 00 Acknowledgements Lurent Miclet, Jose Oncin, Tim Otes, Rfel Crrsco, Pco Cscubert, Rémi Eyrud, Philippe Ezequel, Henning
Lerning probbilistic finite utomt Colin de l Higuer University of Nntes Zdr, August 00 Acknowledgements Lurent Miclet, Jose Oncin, Tim Otes, Rfel Crrsco, Pco Cscubert, Rémi Eyrud, Philippe Ezequel, Henning
Genetic Programming. Outline. Evolutionary Strategies. Evolutionary strategies Genetic programming Summary
 Outline Genetic Progrmming Evolutionry strtegies Genetic progrmming Summry Bsed on the mteril provided y Professor Michel Negnevitsky Evolutionry Strtegies An pproch simulting nturl evolution ws proposed
Outline Genetic Progrmming Evolutionry strtegies Genetic progrmming Summry Bsed on the mteril provided y Professor Michel Negnevitsky Evolutionry Strtegies An pproch simulting nturl evolution ws proposed
Regular Expressions (RE) Regular Expressions (RE) Regular Expressions (RE) Regular Expressions (RE) Kleene-*
 Regulr Expressions (RE) Regulr Expressions (RE) Empty set F A RE denotes the empty set Opertion Nottion Lnguge UNIX Empty string A RE denotes the set {} Alterntion R +r L(r ) L(r ) r r Symol Alterntion
Regulr Expressions (RE) Regulr Expressions (RE) Empty set F A RE denotes the empty set Opertion Nottion Lnguge UNIX Empty string A RE denotes the set {} Alterntion R +r L(r ) L(r ) r r Symol Alterntion
Types of Finite Automata. CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Comparing DFAs and NFAs. NFA for (a b)*abb.
 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt () Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic Finite Automt
CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt () Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic Finite Automt
Random subgroups of a free group
 Rndom sugroups of free group Frédérique Bssino LIPN - Lortoire d Informtique de Pris Nord, Université Pris 13 - CNRS Joint work with Armndo Mrtino, Cyril Nicud, Enric Ventur et Pscl Weil LIX My, 2015 Introduction
Rndom sugroups of free group Frédérique Bssino LIPN - Lortoire d Informtique de Pris Nord, Université Pris 13 - CNRS Joint work with Armndo Mrtino, Cyril Nicud, Enric Ventur et Pscl Weil LIX My, 2015 Introduction
Types of Finite Automata. CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Comparing DFAs and NFAs. Comparing DFAs and NFAs (cont.) Finite Automata 2
 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt () Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic Finite Automt
CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt () Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic Finite Automt
Automata Theory 101. Introduction. Outline. Introduction Finite Automata Regular Expressions ω-automata. Ralf Huuck.
 Outline Automt Theory 101 Rlf Huuck Introduction Finite Automt Regulr Expressions ω-automt Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 1 Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 2 Acknowledgement Some slides re sed on Wolfgng Thoms excellent
Outline Automt Theory 101 Rlf Huuck Introduction Finite Automt Regulr Expressions ω-automt Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 1 Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 2 Acknowledgement Some slides re sed on Wolfgng Thoms excellent
3 Regular expressions
 3 Regulr expressions Given n lphet Σ lnguge is set of words L Σ. So fr we were le to descrie lnguges either y using set theory (i.e. enumertion or comprehension) or y n utomton. In this section we shll
3 Regulr expressions Given n lphet Σ lnguge is set of words L Σ. So fr we were le to descrie lnguges either y using set theory (i.e. enumertion or comprehension) or y n utomton. In this section we shll
5. (±±) Λ = fw j w is string of even lengthg [ 00 = f11,00g 7. (11 [ 00)± Λ = fw j w egins with either 11 or 00g 8. (0 [ ffl)1 Λ = 01 Λ [ 1 Λ 9.
 Regulr Expressions, Pumping Lemm, Right Liner Grmmrs Ling 106 Mrch 25, 2002 1 Regulr Expressions A regulr expression descries or genertes lnguge: it is kind of shorthnd for listing the memers of lnguge.
Regulr Expressions, Pumping Lemm, Right Liner Grmmrs Ling 106 Mrch 25, 2002 1 Regulr Expressions A regulr expression descries or genertes lnguge: it is kind of shorthnd for listing the memers of lnguge.
More on automata. Michael George. March 24 April 7, 2014
 More on utomt Michel George Mrch 24 April 7, 2014 1 Automt constructions Now tht we hve forml model of mchine, it is useful to mke some generl constructions. 1.1 DFA Union / Product construction Suppose
More on utomt Michel George Mrch 24 April 7, 2014 1 Automt constructions Now tht we hve forml model of mchine, it is useful to mke some generl constructions. 1.1 DFA Union / Product construction Suppose
a,b a 1 a 2 a 3 a,b 1 a,b a,b 2 3 a,b a,b a 2 a,b CS Determinisitic Finite Automata 1
 CS4 45- Determinisitic Finite Automt -: Genertors vs. Checkers Regulr expressions re one wy to specify forml lnguge String Genertor Genertes strings in the lnguge Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) re nother
CS4 45- Determinisitic Finite Automt -: Genertors vs. Checkers Regulr expressions re one wy to specify forml lnguge String Genertor Genertes strings in the lnguge Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) re nother
2. Lexical Analysis. Oscar Nierstrasz
 2. Lexicl Anlysis Oscr Nierstrsz Thnks to Jens Plserg nd Tony Hosking for their kind permission to reuse nd dpt the CS132 nd CS502 lecture notes. http://www.cs.ucl.edu/~plserg/ http://www.cs.purdue.edu/homes/hosking/
2. Lexicl Anlysis Oscr Nierstrsz Thnks to Jens Plserg nd Tony Hosking for their kind permission to reuse nd dpt the CS132 nd CS502 lecture notes. http://www.cs.ucl.edu/~plserg/ http://www.cs.purdue.edu/homes/hosking/
Synchronizing Automata with Random Inputs
 Synchronizing Automt with Rndom Inputs Vldimir Gusev Url Federl University, Ekterinurg, Russi 9 August, 14 Vldimir Gusev (UrFU) Synchronizing Automt with Rndom Input 9 August, 14 1 / 13 Introduction Synchronizing
Synchronizing Automt with Rndom Inputs Vldimir Gusev Url Federl University, Ekterinurg, Russi 9 August, 14 Vldimir Gusev (UrFU) Synchronizing Automt with Rndom Input 9 August, 14 1 / 13 Introduction Synchronizing
1 Nondeterministic Finite Automata
 1 Nondeterministic Finite Automt Suppose in life, whenever you hd choice, you could try oth possiilities nd live your life. At the end, you would go ck nd choose the one tht worked out the est. Then you
1 Nondeterministic Finite Automt Suppose in life, whenever you hd choice, you could try oth possiilities nd live your life. At the end, you would go ck nd choose the one tht worked out the est. Then you
GNFA GNFA GNFA GNFA GNFA
 DFA RE NFA DFA -NFA REX GNFA Definition GNFA A generlize noneterministic finite utomton (GNFA) is grph whose eges re lele y regulr expressions, with unique strt stte with in-egree, n unique finl stte with
DFA RE NFA DFA -NFA REX GNFA Definition GNFA A generlize noneterministic finite utomton (GNFA) is grph whose eges re lele y regulr expressions, with unique strt stte with in-egree, n unique finl stte with
Faster Regular Expression Matching. Philip Bille Mikkel Thorup
 Fster Regulr Expression Mtching Philip Bille Mikkel Thorup Outline Definition Applictions History tour of regulr expression mtching Thompson s lgorithm Myers lgorithm New lgorithm Results nd extensions
Fster Regulr Expression Mtching Philip Bille Mikkel Thorup Outline Definition Applictions History tour of regulr expression mtching Thompson s lgorithm Myers lgorithm New lgorithm Results nd extensions
Scanner. Specifying patterns. Specifying patterns. Operations on languages. A scanner must recognize the units of syntax Some parts are easy:
 Scnner Specifying ptterns source code tokens scnner prser IR A scnner must recognize the units of syntx Some prts re esy: errors mps chrcters into tokens the sic unit of syntx x = x + y; ecomes
Scnner Specifying ptterns source code tokens scnner prser IR A scnner must recognize the units of syntx Some prts re esy: errors mps chrcters into tokens the sic unit of syntx x = x + y; ecomes
In-depth introduction to main models, concepts of theory of computation:
 CMPSCI601: Introduction Lecture 1 In-depth introduction to min models, concepts of theory of computtion: Computility: wht cn e computed in principle Logic: how cn we express our requirements Complexity:
CMPSCI601: Introduction Lecture 1 In-depth introduction to min models, concepts of theory of computtion: Computility: wht cn e computed in principle Logic: how cn we express our requirements Complexity:
