By: B. Fahimi. Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Missouri-Rolla Tel: (573) Fax: (573) EML:
|
|
|
- Roxanne Bruce
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 By: B. Fahimi Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Missouri-Rolla Tel: (573) Fax: (573) EML:
2 Basic Magnetic Configuration of SRM Drives
3 T = 1 2 i 2 dl? dθ Magnetic Behavior of SRM
4 Local and Bul Saturation in SRM Drives
5 = = = = i e i di i const i W T di i W 0 0 ), (. ), ( θ λ θ θ θ λ CLOSED LOOP DIGITAL CONTROL OF TORQUE, SPEED AND POSITION
6 Basic Principles of Operation W 1 2 dl Te =! i θ 2 dθ 2 W L E =! iω θ I θ
7 Low speed High speed
8 4-Q Operation of SRM Torque Reverse Motoring A-D-C-B Forward Motoring A-B-C-D Speed Reverse Generating A-D-C-B Forward Generating A-B-BC-D
9 Classic Power Inverter for SRM Drive
10 REGION EQUATION 1 Region I Region II Region III Region IV Region V dl di V = Ri+ ( L * + i ) di dt dl di V = Ri+( L( θ) + i ) di dt dl dl di V = ( R+ ω ) i+ ( L( θ) + i ) dθ di dt dl di V = ( R+ω ) i+ L( θ) dθ dt dl di dij V = ω i+ L(θ ) + M j dθ dt dt * Variations of the phase voltage equation in various operational region
11 Torque r dl r +ω d θ dl( θ ) L( θ ) + i di dl r +ω d θ dl r +ω d θ L(θ ) + di - M j j dt dl( θ ) L( θ ) + i di L(θ ) r Speed L * + dl i di * Dynamics of SRM drive over the entire Speed Range
12 Torque Speed
13 Advantages: Rugged construction allows high speed operation possible Control principle is simple With appropriate excitation, the drive is as efficient as other drives Disadvantages: Sensors Low power factor Torque ripple, acoustic noise New Technology safe and reliable operation Low cost manufacturing Extended constant power region
14 IM BLDC SRM SM IPM Robustness + + Motor Cost + + Efficiency + + Open-loop Control + + Closed-loop Simplicity + + Torque Ripple Wide Speed Range + ++ No Position Sensor Acoustic Noise - Comparison of SRM with Other Adjustable Speed Candidates
15 Structural Robustness Automotive Industry Fault Tolerance Aerospace Industry High Speed Capability Mining Industry Safety Low Cost Manufacturing Office Products Application Areas Sensorless Control Home Appliances
16 θ estimated / sensed General Bloc Diagram of the SRM drive
17 Correspondence between mode of control & quadrants of operation
18 Computation of commutation instants/sequence of excitation Commutation instants are to be selected such that maximum torque/ampere is achieved. That is to position the current pulse in the area with positive (motoring) or negative (generating) slope of inductance. In the single pulse mode of operation (high speeds), proper phase advancing is necessary to build up maximum current in the phase when the positive slope starts. The sequence of excitation is ey in determining the direction of rotation. SRM rotates Opposite to the direction of phase excitation on the stator.
19 TMS320F240 Processor A (15-0) D (15-0) Program ROM/ Flash Data RAM 544w x 16 16Kw x 16 C25LP CORE 16-bit T-register 16-bit Barrel 16 x 16 Multiply Shifter (L) 32-bit P-register ShiftL (0,1,4,-6) 32-bit ALU 32-bit Accumulator ShiftL (0-7) 8 Auxiliary Regs 8 Level H/W Stac 2 Status Registers Repeat Count PA (64K-0) (A 15-0, D 15-0) Three 8-bit I/O Ports 3 Timers & 1 Watchdog 9 PWM outputs 4 Input Capt/ 12 Compare outputs Quadrature Pulse control SCI& SPI 2 10-bit ADCs 16 input ch.
20 Basic Drive Electronics for a three phase drive
21 Optimization of commutation angle by online search Phase current and gating pulse without optimization: Motor terminal voltage = 50 V; Load = 120 W, Reference current = 5.5 A; Speed = 1200 RPM; Conduction angle = 30 Phase current and gating pulse with optimization: Motor terminal voltage = 50 V; Load = 120W; Reference current = 4.7 A; Speed 1200 RPM; Conduction angle = 27.25
22 Dynamics of SRM at High Speed: di dl V = ri + L( θ ) +ω i dt dθ Torque Inductance Current The main objective in control is to tune t0 and t3 such that maximum current and maximum torque match while Avoiding excessive negative torque. θ = θ d = L π N u r I V max bus ω θ (min( α d s, α r ) + α s 2 α r ) t0 t1 t2 t3 t4
23 Current pulse during generation = + = = + θ θ ω θ θ τ θ π θ ω θ θ ω π θ τ θ τ d dl L e d N dl V t i e d dl V t i N r t r Bus g t Bus m ) ( ) ( ) ( 1 ) ( ) ( ) )(1 ) ( ( ) ( ) ( ) (
24 General structure of the Torque Estimator in SRM
25 5 Torque[N-m] T ave 12 π i m 0 ( L ( i) L ) comm min idi time[sec] M 2 L comm [ mh] = 2 i i i i i 45 M Torque[N-m] time[sec] Estimated and Measured Torque Signals
26 Torque Control during motoring and generating
27 f ω[. rpm..] N = r 60 Estimation of Speed in SRM drive
28 time[sec] Speed regulation in SRM Drive
29 Start Send voltage pulse with a fixed and short enough duration to all phases Compare the magnitude of resulting currents to the region in which rotor position is located Also select the equation which should be solved. Select the phase which should be used for first excitation. Also compute the initial position of the rotor. Excite the proper phase and switch over to sensorless technique at near zero speeds. SENSORLESS AT STANDSTILL
30 Ia T B D F Ib T A C E T 0 0 { L, L } { L(7.5 ), L(15 )} I B A ( L B Ic I II III IV V VI = SENSORLESS AT STANDSTILL π LA) θ = VBUS T 24 B
31 L Sensorless Start-up routine Select the Phase/s in ON state Estimation of Position Chec for the region 2 Chec on State of Switches and Calculate Switching Function S Sensorless Routine at High Speeds Compute the following Quantities V eq, R eq, = S V = R Coil Bus + (1 S ) V + (1 + S ) R D Mosfet Perform the Digital Filtering on the Current Data ~ I ~ = αi + βi 1 Chec for the region 1 Y H Perform the following scaling: ˆ A ( ), ˆ f V = Veq, L = L( R R eq, s eq, ) Perform the search for commutation/hystersis current control and update the phase status(on/off) ~ ~ ~ Vˆ I = Lˆ ( I I ) 1 SENSORLESS AT LOW SPEEDS
32 H Estimation of Position Select the Phase/s in ON state Chec for the region 1 Chec on State of Switches and Calculate Switching Function S Sensorless Routine at Low Speeds Compute the following Quantities V eq, R eq, = S V = R Coil Bus + (1 S ) V + (1 + S ) R D Mosfet Perform the following scaling: ˆ A ˆ 2 f V = Veq, ( ), L = L( R R eq, s eq, ) Chec for the region 2 Y L Perform the search for commutation/hystersis current control and update the phase status(on/off) V ˆ I ) + ( Vˆ I ) = Lˆ ( I ) ( j j j 1 j 1 SENSORLESS AT HIGH SPEEDS
33 i R Î Estimation of Position V I d L v T 1 T 2 E Equivalent circuit of an idle phase T T 1 2 LIˆ V E LIˆ V + E T T 1 2 = V V + E E
34 Apply a voltage pulse with a fixed duration of T1 Estimation of Position Measure the time it taes for current to be completely removed after the switches are turned off. T 2 Y System Is Operating in High Speed Region? N T1 T 2 N T1 T2 T + T 1 2 α HM N L T1 T 2 Y T1 T2 T + T 1 2 α LM Y L Y Y N N T2 T1 T + T 1 2 α HM N L H T2 T1 T + T 1 2 α LM Y L H Y H Detection Methodology for operational region N H
35 Current at Phase_A Current at Phase_B Current[A] Time[msec] Current[A] Time[msec] Diagnostic pulses for detection of position at stand still PHASE AT ALIGNED ACTUAL POSITION IN DETECTED POSITION IN ERROR(%) POSITION NUMBER OF PULSES NUMBER OF PULSES Phase_A 900[ ] 882[ ] 2% Phase_B 1500[ ] 1465[ ] 2.3% Phase_C 300[7.5 0 ] 288[7.2 0 ] 4% 0 Sample results for sensorless at standstill ( Overall E 1 Mech )
36 Actual Position 60 Position[mech. degree] EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS Time[msec] Estimated position Operation in High Speed Regime (n=1500 r.p.m.) 60 Position[Mech. Degree] time[msec]
37 Sensorless Startup Position[Mech. Degree] Time[msec] EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS Two example operation under sensorless Control 0 Overall E 1.5 Position[Mech. Degree] Sensorless Operation from standstill Time[msec]
38 Experimental testbed for position control
39 Web-enabled SRM Control system
40 Accomplishments:! Closed loop control of SRM drives is essential in successful application of this emerging Technology. E ( Mech)! Optimal torque control of SRM in the presence of parameter variation and system disturbances have been solved and is presented as a technology ready for applications.! Estimation of ey quantities such as torque, speed, and position will reduce the cost, dimension and unreliability of closed loop control systems.! Cost effective processors and motor controllers are ey elements in development of high grade and robust SRM drives.! Wor is underway to complete the position control of SRM drives in a closed loop format.!similar wor is being pursued for power control of SR Generators.
the machine makes analytic calculation of rotor position impossible for a given flux linkage and current value.
 COMPARISON OF FLUX LINKAGE ESTIMATORS IN POSITION SENSORLESS SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MOTOR DRIVES Erkan Mese Kocaeli University / Technical Education Faculty zmit/kocaeli-turkey email: emese@kou.edu.tr ABSTRACT
COMPARISON OF FLUX LINKAGE ESTIMATORS IN POSITION SENSORLESS SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MOTOR DRIVES Erkan Mese Kocaeli University / Technical Education Faculty zmit/kocaeli-turkey email: emese@kou.edu.tr ABSTRACT
Control of Wind Turbine Generators. James Cale Guest Lecturer EE 566, Fall Semester 2014 Colorado State University
 Control of Wind Turbine Generators James Cale Guest Lecturer EE 566, Fall Semester 2014 Colorado State University Review from Day 1 Review Last time, we started with basic concepts from physics such as
Control of Wind Turbine Generators James Cale Guest Lecturer EE 566, Fall Semester 2014 Colorado State University Review from Day 1 Review Last time, we started with basic concepts from physics such as
A High Performance DTC Strategy for Torque Ripple Minimization Using duty ratio control for SRM Drive
 A High Performance DTC Strategy for Torque Ripple Minimization Using duty ratio control for SRM Drive Veena P & Jeyabharath R 1, Rajaram M 2, S.N.Sivanandam 3 K.S.Rangasamy College of Technology, Tiruchengode-637
A High Performance DTC Strategy for Torque Ripple Minimization Using duty ratio control for SRM Drive Veena P & Jeyabharath R 1, Rajaram M 2, S.N.Sivanandam 3 K.S.Rangasamy College of Technology, Tiruchengode-637
Sunita.Ch 1, M.V.Srikanth 2 1, 2 Department of Electrical and Electronics, Shri Vishnu engineering college for women, India
 MODELING AND ANALYSIS OF 6/4 SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MOTOR WITH TORQUE RIPPLE REDUCTION Sunita.Ch 1, M.V.Srikanth 2 1, 2 Department of Electrical and Electronics, Shri Vishnu engineering college for women,
MODELING AND ANALYSIS OF 6/4 SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MOTOR WITH TORQUE RIPPLE REDUCTION Sunita.Ch 1, M.V.Srikanth 2 1, 2 Department of Electrical and Electronics, Shri Vishnu engineering college for women,
PRINCIPLE OF DESIGN OF FOUR PHASE LOW POWER SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MACHINE AIMED TO THE MAXIMUM TORQUE PRODUCTION
 Journal of ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 55, NO. 5-6, 24, 138 143 PRINCIPLE OF DESIGN OF FOUR PHASE LOW POWER SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MACHINE AIMED TO THE MAXIMUM TORQUE PRODUCTION Martin Lipták This paper
Journal of ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 55, NO. 5-6, 24, 138 143 PRINCIPLE OF DESIGN OF FOUR PHASE LOW POWER SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MACHINE AIMED TO THE MAXIMUM TORQUE PRODUCTION Martin Lipták This paper
Improved efficiency of a fan drive system without using an encoder or current sensors
 Improved efficiency of a fan drive system without using an encoder or current sensors Tian-Hua Liu, Jyun-Jie Huang Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University of Science Technology,
Improved efficiency of a fan drive system without using an encoder or current sensors Tian-Hua Liu, Jyun-Jie Huang Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University of Science Technology,
Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 3 (2009) 331 338 Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors M. Mikhov a, a Faculty of Automatics,
Applied and Computational Mechanics 3 (2009) 331 338 Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors M. Mikhov a, a Faculty of Automatics,
Sensorless Control for High-Speed BLDC Motors With Low Inductance and Nonideal Back EMF
 Sensorless Control for High-Speed BLDC Motors With Low Inductance and Nonideal Back EMF P.Suganya Assistant Professor, Department of EEE, Bharathiyar Institute of Engineering for Women Salem (DT). Abstract
Sensorless Control for High-Speed BLDC Motors With Low Inductance and Nonideal Back EMF P.Suganya Assistant Professor, Department of EEE, Bharathiyar Institute of Engineering for Women Salem (DT). Abstract
Sensorless DTC-SVM of Induction Motor by Applying Two Neural Controllers
 Sensorless DTC-SVM of Induction Motor by Applying Two Neural Controllers Abdallah Farahat Mahmoud Dept. of Electrical Engineering, Al-Azhar University, Qena, Egypt engabdallah2012@azhar.edu.eg Adel S.
Sensorless DTC-SVM of Induction Motor by Applying Two Neural Controllers Abdallah Farahat Mahmoud Dept. of Electrical Engineering, Al-Azhar University, Qena, Egypt engabdallah2012@azhar.edu.eg Adel S.
Three phase induction motor using direct torque control by Matlab Simulink
 Three phase induction motor using direct torque control by Matlab Simulink Arun Kumar Yadav 1, Dr. Vinod Kumar Singh 2 1 Reaserch Scholor SVU Gajraula Amroha, U.P. 2 Assistant professor ABSTRACT Induction
Three phase induction motor using direct torque control by Matlab Simulink Arun Kumar Yadav 1, Dr. Vinod Kumar Singh 2 1 Reaserch Scholor SVU Gajraula Amroha, U.P. 2 Assistant professor ABSTRACT Induction
Sensorless Control of Two-phase Switched Reluctance Drive in the Whole Speed Range
 Sensorless Control of Two-phase Switched Reluctance Drive in the Whole Speed Range Dmitry Aliamkin, Alecksey Anuchin, Maxim Lashkevich Electric Drives Department of Moscow Power Engineering Institute,
Sensorless Control of Two-phase Switched Reluctance Drive in the Whole Speed Range Dmitry Aliamkin, Alecksey Anuchin, Maxim Lashkevich Electric Drives Department of Moscow Power Engineering Institute,
Doubly salient reluctance machine or, as it is also called, switched reluctance machine. [Pyrhönen et al 2008]
![Doubly salient reluctance machine or, as it is also called, switched reluctance machine. [Pyrhönen et al 2008] Doubly salient reluctance machine or, as it is also called, switched reluctance machine. [Pyrhönen et al 2008]](/thumbs/86/93665357.jpg) Doubly salient reluctance machine or, as it is also called, switched reluctance machine [Pyrhönen et al 2008] Pros and contras of a switched reluctance machine Advantages Simple robust rotor with a small
Doubly salient reluctance machine or, as it is also called, switched reluctance machine [Pyrhönen et al 2008] Pros and contras of a switched reluctance machine Advantages Simple robust rotor with a small
Simulation of Direct Torque Control of Induction motor using Space Vector Modulation Methodology
 International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Simulation of Direct Torque Control of Induction motor using Space Vector Modulation Methodology Arpit S. Bhugul 1, Dr. Archana
International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Simulation of Direct Torque Control of Induction motor using Space Vector Modulation Methodology Arpit S. Bhugul 1, Dr. Archana
3 d Calculate the product of the motor constant and the pole flux KΦ in this operating point. 2 e Calculate the torque.
 Exam Electrical Machines and Drives (ET4117) 11 November 011 from 14.00 to 17.00. This exam consists of 5 problems on 4 pages. Page 5 can be used to answer problem 4 question b. The number before a question
Exam Electrical Machines and Drives (ET4117) 11 November 011 from 14.00 to 17.00. This exam consists of 5 problems on 4 pages. Page 5 can be used to answer problem 4 question b. The number before a question
AC Induction Motor Stator Resistance Estimation Algorithm
 7th WSEAS International Conference on Electric Power Systems, High Voltages, Electric Machines, Venice, Italy, November 21-23, 27 86 AC Induction Motor Stator Resistance Estimation Algorithm PETR BLAHA
7th WSEAS International Conference on Electric Power Systems, High Voltages, Electric Machines, Venice, Italy, November 21-23, 27 86 AC Induction Motor Stator Resistance Estimation Algorithm PETR BLAHA
Speed Sensorless Control of a Long-Stator Linear Synchronous-Motor arranged by Multiple Sections
 Speed Sensorless Control of a Long-Stator Linear Synchronous-Motor arranged by Multiple Sections Roberto Leidhold Peter Mutschler Department of Power Electronics and Control of Drives Darmsta University
Speed Sensorless Control of a Long-Stator Linear Synchronous-Motor arranged by Multiple Sections Roberto Leidhold Peter Mutschler Department of Power Electronics and Control of Drives Darmsta University
APPLICATION OF A SLIDING MODE OBSERVER FOR SENSORLESS OPERATION OF SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MOTORS. Stefan Brock
 APPLICATION OF A SLIDING MODE OBSERVER FOR SENSORLESS OPERATION OF SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MOTORS Stefan Brock Poznań University of Technology, Institute of Control and Information Engineering Piotrowo 3a,
APPLICATION OF A SLIDING MODE OBSERVER FOR SENSORLESS OPERATION OF SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MOTORS Stefan Brock Poznań University of Technology, Institute of Control and Information Engineering Piotrowo 3a,
Lecture 8: Sensorless Synchronous Motor Drives
 1 / 22 Lecture 8: Sensorless Synchronous Motor Drives ELEC-E8402 Control of Electric Drives and Power Converters (5 ECTS) Marko Hinkkanen Spring 2017 2 / 22 Learning Outcomes After this lecture and exercises
1 / 22 Lecture 8: Sensorless Synchronous Motor Drives ELEC-E8402 Control of Electric Drives and Power Converters (5 ECTS) Marko Hinkkanen Spring 2017 2 / 22 Learning Outcomes After this lecture and exercises
A Direct Torque Controlled Induction Motor with Variable Hysteresis Band
 UKSim 2009: th International Conference on Computer Modelling and Simulation A Direct Torque Controlled Induction Motor with Variable Hysteresis Band Kanungo Barada Mohanty Electrical Engineering Department,
UKSim 2009: th International Conference on Computer Modelling and Simulation A Direct Torque Controlled Induction Motor with Variable Hysteresis Band Kanungo Barada Mohanty Electrical Engineering Department,
MODELLING ANALYSIS & DESIGN OF DSP BASED NOVEL SPEED SENSORLESS VECTOR CONTROLLER FOR INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE
 International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET) Volume 6, Issue 3, March, 2015, pp. 70-81, Article ID: IJARET_06_03_008 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijaret/issues.asp?jtypeijaret&vtype=6&itype=3
International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET) Volume 6, Issue 3, March, 2015, pp. 70-81, Article ID: IJARET_06_03_008 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijaret/issues.asp?jtypeijaret&vtype=6&itype=3
Novel DTC-SVM for an Adjustable Speed Sensorless Induction Motor Drive
 Novel DTC-SVM for an Adjustable Speed Sensorless Induction Motor Drive Nazeer Ahammad S1, Sadik Ahamad Khan2, Ravi Kumar Reddy P3, Prasanthi M4 1*Pursuing M.Tech in the field of Power Electronics 2*Working
Novel DTC-SVM for an Adjustable Speed Sensorless Induction Motor Drive Nazeer Ahammad S1, Sadik Ahamad Khan2, Ravi Kumar Reddy P3, Prasanthi M4 1*Pursuing M.Tech in the field of Power Electronics 2*Working
Motors Automation Energy Transmission & Distribution Coatings. Servo Drive SCA06 V1.5X. Addendum to the Programming Manual SCA06 V1.
 Motors Automation Energy Transmission & Distribution Coatings Servo Drive SCA06 V1.5X SCA06 V1.4X Series: SCA06 Language: English Document Number: 10003604017 / 01 Software Version: V1.5X Publication Date:
Motors Automation Energy Transmission & Distribution Coatings Servo Drive SCA06 V1.5X SCA06 V1.4X Series: SCA06 Language: English Document Number: 10003604017 / 01 Software Version: V1.5X Publication Date:
Lezione 9 30 March. Scribes: Arianna Marangon, Matteo Vitturi, Riccardo Prota
 Control Laboratory: a.a. 2015/2016 Lezione 9 30 March Instructor: Luca Schenato Scribes: Arianna Marangon, Matteo Vitturi, Riccardo Prota What is left to do is how to design the low pass pole τ L for the
Control Laboratory: a.a. 2015/2016 Lezione 9 30 March Instructor: Luca Schenato Scribes: Arianna Marangon, Matteo Vitturi, Riccardo Prota What is left to do is how to design the low pass pole τ L for the
COMPARISION BETWEEN TWO LEVEL AND THREE LEVEL INVERTER FOR DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE
 COMPARISION BETWEEN TWO LEVEL AND THREE LEVEL INVERTER FOR DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE Shailesh B. Kadu 1, Prof. J.G. Choudhari 2 Research Scholar (Department of Electrical Engineering,
COMPARISION BETWEEN TWO LEVEL AND THREE LEVEL INVERTER FOR DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE Shailesh B. Kadu 1, Prof. J.G. Choudhari 2 Research Scholar (Department of Electrical Engineering,
A Novel Adaptive Estimation of Stator and Rotor Resistance for Induction Motor Drives
 A Novel Adaptive Estimation of Stator and Rotor Resistance for Induction Motor Drives Nagaraja Yadav Ponagani Asst.Professsor, Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Dhurva Institute of Engineering
A Novel Adaptive Estimation of Stator and Rotor Resistance for Induction Motor Drives Nagaraja Yadav Ponagani Asst.Professsor, Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Dhurva Institute of Engineering
A Novel Three-phase Matrix Converter Based Induction Motor Drive Using Power Factor Control
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 8(4) Special 214, Pages: 49-417 AENSI Journals Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences ISSN:1991-8178 Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com A Novel
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 8(4) Special 214, Pages: 49-417 AENSI Journals Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences ISSN:1991-8178 Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com A Novel
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development SIMULATION OF FIELD ORIENTED CONTROL OF PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor(SJIF): 3.134 e-issn(o): 2348-4470 p-issn(p): 2348-6406 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 2,Issue 4, April -2015 SIMULATION
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor(SJIF): 3.134 e-issn(o): 2348-4470 p-issn(p): 2348-6406 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 2,Issue 4, April -2015 SIMULATION
Measurement of Flux Linkage and Inductance Profile of SRM
 Measurement of Flux Linkage and Inductance Profile of SRM Rakesh Saxena, Bhim Singh and Yogesh Pahariya Abstract The main goal in modeling of SRM is to provide a good accuracy over the entire speed and
Measurement of Flux Linkage and Inductance Profile of SRM Rakesh Saxena, Bhim Singh and Yogesh Pahariya Abstract The main goal in modeling of SRM is to provide a good accuracy over the entire speed and
MODELLING ANALYSIS & DESIGN OF DSP BASED NOVEL SPEED SENSORLESS VECTOR CONTROLLER FOR INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 6480(Print), ISSN 0976 6499(Online), AND TECHNOLOGY
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 6480(Print), ISSN 0976 6499(Online), AND TECHNOLOGY
DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF SENSORLESS SPEED CONTROL FOR INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE USING AN OPTIMIZED EXTENDED KALMAN FILTER
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJECET) International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology (IJECET), ISSN 0976 ISSN 0976 6464(Print)
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJECET) International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology (IJECET), ISSN 0976 ISSN 0976 6464(Print)
Simplified EKF Based Sensorless Direct Torque Control of Permanent Magnet Brushless AC Drives
 International Journal of Automation and Computing (24) 35-4 Simplified EKF Based Sensorless Direct Torque Control of Permanent Magnet Brushless AC Drives Yong Liu, Ziqiang Zhu, David Howe Department of
International Journal of Automation and Computing (24) 35-4 Simplified EKF Based Sensorless Direct Torque Control of Permanent Magnet Brushless AC Drives Yong Liu, Ziqiang Zhu, David Howe Department of
Comparison Between Direct and Indirect Field Oriented Control of Induction Motor
 Comparison Between Direct and Indirect Field Oriented Control of Induction Motor Venu Gopal B T Research Scholar, Department of Electrical Engineering UVCE, Bangalore University, Bengaluru ABSTRACT - Vector
Comparison Between Direct and Indirect Field Oriented Control of Induction Motor Venu Gopal B T Research Scholar, Department of Electrical Engineering UVCE, Bangalore University, Bengaluru ABSTRACT - Vector
ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012
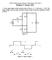 ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012 1. In the single-phase rectifier shown below in Fig 1a., s = 1mH and I d = 10A. The input voltage v s has the pulse waveform shown
ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012 1. In the single-phase rectifier shown below in Fig 1a., s = 1mH and I d = 10A. The input voltage v s has the pulse waveform shown
EE Branch GATE Paper 2010
 Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where, is equal to 0 1 e 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector field is 3 1/r 3. The period of the signal x(t) = 8 is 0.4
Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where, is equal to 0 1 e 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector field is 3 1/r 3. The period of the signal x(t) = 8 is 0.4
Sensorless Speed Control for PMSM Based On the DTC Method with Adaptive System R. Balachandar 1, S. Vinoth kumar 2, C. Vignesh 3
 Sensorless Speed Control for PMSM Based On the DTC Method with Adaptive System R. Balachandar 1, S. Vinoth kumar 2, C. Vignesh 3 P.G Scholar, Sri Subramanya College of Engg & Tech, Palani, Tamilnadu, India
Sensorless Speed Control for PMSM Based On the DTC Method with Adaptive System R. Balachandar 1, S. Vinoth kumar 2, C. Vignesh 3 P.G Scholar, Sri Subramanya College of Engg & Tech, Palani, Tamilnadu, India
Control of an Induction Motor Drive
 Control of an Induction Motor Drive 1 Introduction This assignment deals with control of an induction motor drive. First, scalar control (or Volts-per-Hertz control) is studied in Section 2, where also
Control of an Induction Motor Drive 1 Introduction This assignment deals with control of an induction motor drive. First, scalar control (or Volts-per-Hertz control) is studied in Section 2, where also
Digital Control of Electric Drives. Induction Motor Vector Control. Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering
 Digital Control of Electric Drives Induction Motor Vector Control Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering BE1M14DEP O. Zoubek, J. Zdenek 1 Induction Motor Control Methods
Digital Control of Electric Drives Induction Motor Vector Control Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering BE1M14DEP O. Zoubek, J. Zdenek 1 Induction Motor Control Methods
Torque Ripple Reduction Method with Minimized Current RMS Value for SRM Based on Mathematical Model of Magnetization Characteristic
 Torque Ripple Reduction Method with Minimized Current RMS Value for SRM Based on Mathematical Model of Magnetization Characteristic Takahiro Kumagai, Keisuke Kusaka, Jun-ichi Itoh Nagaoka University of
Torque Ripple Reduction Method with Minimized Current RMS Value for SRM Based on Mathematical Model of Magnetization Characteristic Takahiro Kumagai, Keisuke Kusaka, Jun-ichi Itoh Nagaoka University of
Generators for wind power conversion
 Generators for wind power conversion B. G. Fernandes Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Email : bgf@ee.iitb.ac.in Outline of The Talk Introduction Constant speed
Generators for wind power conversion B. G. Fernandes Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Email : bgf@ee.iitb.ac.in Outline of The Talk Introduction Constant speed
CHAPTER 2 MODELLING OF INTERIOR PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR
 21 CHAPTER 2 MODELLING OF INTERIOR PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR 2.1 INTRODUCTION The need for adjustable speed drives in industrial applications has been increasing progressively. The variable speed
21 CHAPTER 2 MODELLING OF INTERIOR PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR 2.1 INTRODUCTION The need for adjustable speed drives in industrial applications has been increasing progressively. The variable speed
Sensorless Torque and Speed Control of Traction Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for Railway Applications based on Model Reference Adaptive System
 5 th SASTech 211, Khavaran Higher-education Institute, Mashhad, Iran. May 12-14. 1 Sensorless Torue and Speed Control of Traction Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for Railway Applications based on Model
5 th SASTech 211, Khavaran Higher-education Institute, Mashhad, Iran. May 12-14. 1 Sensorless Torue and Speed Control of Traction Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for Railway Applications based on Model
Research on Control Method of Brushless DC Motor Based on Continuous Three-Phase Current
 6th International onference on Measurement, Instrumentation and Automation (IMIA 017 Research on ontrol Method of Brushless D Motor Based on ontinuous hree-phase urrent Li Ding 1,Mingliang Hu, Jun Zhao
6th International onference on Measurement, Instrumentation and Automation (IMIA 017 Research on ontrol Method of Brushless D Motor Based on ontinuous hree-phase urrent Li Ding 1,Mingliang Hu, Jun Zhao
Modelling of Closed Loop Speed Control for Pmsm Drive
 Modelling of Closed Loop Speed Control for Pmsm Drive Vikram S. Sathe, Shankar S. Vanamane M. Tech Student, Department of Electrical Engg, Walchand College of Engineering, Sangli. Associate Prof, Department
Modelling of Closed Loop Speed Control for Pmsm Drive Vikram S. Sathe, Shankar S. Vanamane M. Tech Student, Department of Electrical Engg, Walchand College of Engineering, Sangli. Associate Prof, Department
Prediction of Electromagnetic Forces and Vibrations in SRMs Operating at Steady State and Transient Speeds
 Prediction of Electromagnetic Forces and Vibrations in SRMs Operating at Steady State and Transient Speeds Zhangjun Tang Stryker Instruments Kalamazoo, MI 491 Phone: 269-323-77 Ext.363 Fax: 269-323-394
Prediction of Electromagnetic Forces and Vibrations in SRMs Operating at Steady State and Transient Speeds Zhangjun Tang Stryker Instruments Kalamazoo, MI 491 Phone: 269-323-77 Ext.363 Fax: 269-323-394
Switched Reluctance Machine Modeling Applied on a MRAC Scheme
 Switched Reluctance Machine Modeling Applied on a MRAC Scheme Arnaldo Matute a, Julio Viola b,c, José Restrepo a,b,c, José Manuel Aller a,b,c, Flavio Quizhpi c a Universidad Simón Bolívar. Caracas, Venezuela
Switched Reluctance Machine Modeling Applied on a MRAC Scheme Arnaldo Matute a, Julio Viola b,c, José Restrepo a,b,c, José Manuel Aller a,b,c, Flavio Quizhpi c a Universidad Simón Bolívar. Caracas, Venezuela
Modeling and Analysis of Dynamic Systems
 Modeling and Analysis of Dynamic Systems by Dr. Guillaume Ducard Fall 2016 Institute for Dynamic Systems and Control ETH Zurich, Switzerland 1/22 Outline 1 Lecture 5: Hydraulic Systems Pelton Turbine:
Modeling and Analysis of Dynamic Systems by Dr. Guillaume Ducard Fall 2016 Institute for Dynamic Systems and Control ETH Zurich, Switzerland 1/22 Outline 1 Lecture 5: Hydraulic Systems Pelton Turbine:
Synchronous Machines
 Synchronous Machines Synchronous Machines n 1 Φ f n 1 Φ f I f I f I f damper (run-up) winding Stator: similar to induction (asynchronous) machine ( 3 phase windings that forms a rotational circular magnetic
Synchronous Machines Synchronous Machines n 1 Φ f n 1 Φ f I f I f I f damper (run-up) winding Stator: similar to induction (asynchronous) machine ( 3 phase windings that forms a rotational circular magnetic
A New Predictive Control Strategy Dedicated to Salient Pole Synchronous Machines
 A New Predictive Control Strategy Dedicated to Salient Pole Synchronous Machines Nicolas Patin Member IEEE University of Technology of Compiègne Laboratoire d Electromécanique de Compiègne Rue Personne
A New Predictive Control Strategy Dedicated to Salient Pole Synchronous Machines Nicolas Patin Member IEEE University of Technology of Compiègne Laboratoire d Electromécanique de Compiègne Rue Personne
Inductance profile estimation of high-speed Switched Reluctance Machine with rotor eccentricity
 Inductance profile estimation of high-speed Switched Reluctance Machine with rotor eccentricity Rajdeep Banerjee, Parthasarathi Sensarma Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Kanpur, India Email: brajdeep@iitk.ac.in,
Inductance profile estimation of high-speed Switched Reluctance Machine with rotor eccentricity Rajdeep Banerjee, Parthasarathi Sensarma Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Kanpur, India Email: brajdeep@iitk.ac.in,
Variable Sampling Effect for BLDC Motors using Fuzzy PI Controller
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(35), DOI:10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i35/68960, December 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Variable Sampling Effect BLDC Motors using Fuzzy
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(35), DOI:10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i35/68960, December 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Variable Sampling Effect BLDC Motors using Fuzzy
ECE 585 Power System Stability
 Homework 1, Due on January 29 ECE 585 Power System Stability Consider the power system below. The network frequency is 60 Hz. At the pre-fault steady state (a) the power generated by the machine is 400
Homework 1, Due on January 29 ECE 585 Power System Stability Consider the power system below. The network frequency is 60 Hz. At the pre-fault steady state (a) the power generated by the machine is 400
DEVELOPMENT OF DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL MODELWITH USING SVI FOR THREE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR
 DEVELOPMENT OF DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL MODELWITH USING SVI FOR THREE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR MUKESH KUMAR ARYA * Electrical Engg. Department, Madhav Institute of Technology & Science, Gwalior, Gwalior, 474005,
DEVELOPMENT OF DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL MODELWITH USING SVI FOR THREE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR MUKESH KUMAR ARYA * Electrical Engg. Department, Madhav Institute of Technology & Science, Gwalior, Gwalior, 474005,
A new FOC technique based on predictive current control for PMSM drive
 ISSN 1 746-7, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 5 (009) No. 4, pp. 87-94 A new FOC technique based on predictive current control for PMSM drive F. Heydari, A. Sheikholeslami, K.
ISSN 1 746-7, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 5 (009) No. 4, pp. 87-94 A new FOC technique based on predictive current control for PMSM drive F. Heydari, A. Sheikholeslami, K.
Direct torque control of induction motor fed by two level inverter using space vector pulse width modulation
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 9 (2013) No. 1, pp. 59-67 Direct torque control of induction motor fed by two level inverter using space vector pulse width modulation
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 9 (2013) No. 1, pp. 59-67 Direct torque control of induction motor fed by two level inverter using space vector pulse width modulation
Design and implementation of a sliding-mode observer of the rotor flux and rotor speed in induction machines
 1 Design and implementation of a sliding-mode observer of the rotor flux and rotor speed in induction machines João Ferraz, Paulo Branco Phd. Abstract A sliding-mode observer for the rotor flux and speed
1 Design and implementation of a sliding-mode observer of the rotor flux and rotor speed in induction machines João Ferraz, Paulo Branco Phd. Abstract A sliding-mode observer for the rotor flux and speed
CHAPTER 6 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF SINGLE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS
 79 CHAPTER 6 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF SINGLE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 6.. INTRODUCTION The steady-state analysis of six-phase and three-phase self-excited induction generators has been presented
79 CHAPTER 6 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF SINGLE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 6.. INTRODUCTION The steady-state analysis of six-phase and three-phase self-excited induction generators has been presented
Offline Parameter Identification of an Induction Machine Supplied by Impressed Stator Voltages
 POSTER 2016, PRAGUE MAY 24 1 Offline Parameter Identification of an Induction Machine Supplied by Impressed Stator Voltages Tomáš KOŠŤÁL Dept. of Electric Drives and Traction, Czech Technical University,
POSTER 2016, PRAGUE MAY 24 1 Offline Parameter Identification of an Induction Machine Supplied by Impressed Stator Voltages Tomáš KOŠŤÁL Dept. of Electric Drives and Traction, Czech Technical University,
Lecture 7: Synchronous Motor Drives
 1 / 46 Lecture 7: Synchronous Motor Drives ELEC-E8402 Control of Electric Drives and Power Converters (5 ECTS) Marko Hinkkanen Spring 2017 2 / 46 Learning Outcomes After this lecture and exercises you
1 / 46 Lecture 7: Synchronous Motor Drives ELEC-E8402 Control of Electric Drives and Power Converters (5 ECTS) Marko Hinkkanen Spring 2017 2 / 46 Learning Outcomes After this lecture and exercises you
Comparative Analysis of Speed Control of Induction Motor by DTC over Scalar Control Technique
 Comparative Analysis of Speed Control of Induction Motor by DTC over Scalar Control Technique S.Anuradha 1, N.Amarnadh Reddy 2 M.Tech (PE), Dept. of EEE, VNRVJIET, T.S, India 1 Assistant Professor, Dept.
Comparative Analysis of Speed Control of Induction Motor by DTC over Scalar Control Technique S.Anuradha 1, N.Amarnadh Reddy 2 M.Tech (PE), Dept. of EEE, VNRVJIET, T.S, India 1 Assistant Professor, Dept.
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Technology 25 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Technology 25 (2016 ) 801 807 Global Colloquium in Recent Advancement and Effectual Researches in Engineering, Science and Technology (RAEREST
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Technology 25 (2016 ) 801 807 Global Colloquium in Recent Advancement and Effectual Researches in Engineering, Science and Technology (RAEREST
Chapter 5 Three phase induction machine (1) Shengnan Li
 Chapter 5 Three phase induction machine (1) Shengnan Li Main content Structure of three phase induction motor Operating principle of three phase induction motor Rotating magnetic field Graphical representation
Chapter 5 Three phase induction machine (1) Shengnan Li Main content Structure of three phase induction motor Operating principle of three phase induction motor Rotating magnetic field Graphical representation
Evaluation Method to Estimate Position Control Error in Position Sensorless Control Based on Pattern Matching Method
 IEEJ Journal of Industry Applications Vol.7 No.1 pp.73 79 DOI: 10.1541/ieejjia.7.73 Paper Evaluation Method to Estimate Position Control Error in Position Sensorless Control Based on Pattern Matching Method
IEEJ Journal of Industry Applications Vol.7 No.1 pp.73 79 DOI: 10.1541/ieejjia.7.73 Paper Evaluation Method to Estimate Position Control Error in Position Sensorless Control Based on Pattern Matching Method
Speed Sensor less DTC of VSI fed Induction Motor with Simple Flux Regulation for Improving State Estimation at Low Speed
 Speed Sensor less DTC of VSI fed Induction Motor with Simple Flux Regulation for Improving State Estimation at Low Speed K. Farzand Ali 1, S.Sridhar 2 1 PG Scholar, Dept. Of Electrical & Electronics Engineering,
Speed Sensor less DTC of VSI fed Induction Motor with Simple Flux Regulation for Improving State Estimation at Low Speed K. Farzand Ali 1, S.Sridhar 2 1 PG Scholar, Dept. Of Electrical & Electronics Engineering,
The University of Southern Queensland
 New Design Methodologies for Printed Circuit Axial Field Brushless DC Motors by Daniele Marco Gambetta, MPhil, B.Sc (Hons) Dissertation Submitted in Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor
New Design Methodologies for Printed Circuit Axial Field Brushless DC Motors by Daniele Marco Gambetta, MPhil, B.Sc (Hons) Dissertation Submitted in Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor
Chapter 14. Reluctance Drives: Stepper-Motor and Switched- Reluctance Drives
 Chapter 14 Reluctance Drives: tepper-motor and witched- Reluctance Drives Reluctance Drives 14-1 tepper Motor and witched Reluctance Drives q Reluctance Drives tepper Motor drives - ccurate position control
Chapter 14 Reluctance Drives: tepper-motor and witched- Reluctance Drives Reluctance Drives 14-1 tepper Motor and witched Reluctance Drives q Reluctance Drives tepper Motor drives - ccurate position control
Speed Behaviour of PI and SMC Based DTC of BLDC Motor
 Speed Behaviour of PI and SMC Based DTC of BLDC Motor Dr.T.Vamsee Kiran 1, M.Prasanthi 2 Professor, Dept. of EEE, DVR &Dr. HS MIC College of Technology, Andhra Pradesh, India 1 PG Student [PE], Dept. of
Speed Behaviour of PI and SMC Based DTC of BLDC Motor Dr.T.Vamsee Kiran 1, M.Prasanthi 2 Professor, Dept. of EEE, DVR &Dr. HS MIC College of Technology, Andhra Pradesh, India 1 PG Student [PE], Dept. of
Deriving a Fast and Accurate PMSM Motor Model from Finite Element Analysis The MathWorks, Inc. 1
 Deriving a Fast and Accurate PMSM Motor Model from Finite Element Analysis Dakai Hu, Ph.D Haiwei Cai, Ph.D MathWorks Application Engineer ANSYS Application Engineer 2017 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Motivation
Deriving a Fast and Accurate PMSM Motor Model from Finite Element Analysis Dakai Hu, Ph.D Haiwei Cai, Ph.D MathWorks Application Engineer ANSYS Application Engineer 2017 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Motivation
Water-Cooled Direct Drive Permanent Magnet Motor Design in Consideration of its Efficiency and Structural Strength
 Journal of Magnetics 18(2), 125-129 (2013) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 http://dx.doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2013.18.2.125 Water-Cooled Direct Drive Permanent Magnet Motor Design in Consideration
Journal of Magnetics 18(2), 125-129 (2013) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 http://dx.doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2013.18.2.125 Water-Cooled Direct Drive Permanent Magnet Motor Design in Consideration
A NOVEL CONTROL APPROACH FOR SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MOTORS BASED ON FUZZY LOGIC AND PARTICLE SWARM OPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUES
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series C, Vol. 78, Iss. 3, 216 ISSN 2286-354 A NOVEL CONTROL APPROACH FOR SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MOTORS BASED ON FUZZY LOGIC AND PARTICLE SWARM OPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUES Thi Mai Phuong DAO
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series C, Vol. 78, Iss. 3, 216 ISSN 2286-354 A NOVEL CONTROL APPROACH FOR SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MOTORS BASED ON FUZZY LOGIC AND PARTICLE SWARM OPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUES Thi Mai Phuong DAO
Automatic Control Systems. -Lecture Note 15-
 -Lecture Note 15- Modeling of Physical Systems 5 1/52 AC Motors AC Motors Classification i) Induction Motor (Asynchronous Motor) ii) Synchronous Motor 2/52 Advantages of AC Motors i) Cost-effective ii)
-Lecture Note 15- Modeling of Physical Systems 5 1/52 AC Motors AC Motors Classification i) Induction Motor (Asynchronous Motor) ii) Synchronous Motor 2/52 Advantages of AC Motors i) Cost-effective ii)
Sensorless Control of Double-sided Linear Switched Reluctance Motor Based on Simplified Flux Linkage Method
 246 CES TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRICAL MACHINES AND SYSTEMS, VOL. 1, NO. 3, SEPTEMBER 2017 Sensorless Control of Double-sided Linear Switched Reluctance Motor Based on Simplified Flux Linkage Method Wenkai
246 CES TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRICAL MACHINES AND SYSTEMS, VOL. 1, NO. 3, SEPTEMBER 2017 Sensorless Control of Double-sided Linear Switched Reluctance Motor Based on Simplified Flux Linkage Method Wenkai
MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY. Modeling a Servo Motor System
 Modeling a Servo Motor System Definitions Motor: A device that receives a continuous (Analog) signal and operates continuously in time. Digital Controller: Discretizes the amplitude of the signal and also
Modeling a Servo Motor System Definitions Motor: A device that receives a continuous (Analog) signal and operates continuously in time. Digital Controller: Discretizes the amplitude of the signal and also
Speed Control of Induction Motor Drives using Nonlinear Adaptive Controller
 Speed Control of Induction Motor Drives using Nonlinear Adaptive Controller 1 Sarojini.P, 2 Mr. R Issan Raj M.E Control and Instrumentation Engineering Valliammai Engineering College Kancheepuram District
Speed Control of Induction Motor Drives using Nonlinear Adaptive Controller 1 Sarojini.P, 2 Mr. R Issan Raj M.E Control and Instrumentation Engineering Valliammai Engineering College Kancheepuram District
GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering
 GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe dx, is equal to (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) e (D) 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector
GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe dx, is equal to (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) e (D) 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector
6) Motors and Encoders
 6) Motors and Encoders Electric motors are by far the most common component to supply mechanical input to a linear motion system. Stepper motors and servo motors are the popular choices in linear motion
6) Motors and Encoders Electric motors are by far the most common component to supply mechanical input to a linear motion system. Stepper motors and servo motors are the popular choices in linear motion
THE approach of sensorless speed control of induction motors
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRY APPLICATIONS, VOL. 41, NO. 4, JULY/AUGUST 2005 1039 An Adaptive Sliding-Mode Observer for Induction Motor Sensorless Speed Control Jingchuan Li, Longya Xu, Fellow, IEEE, and
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRY APPLICATIONS, VOL. 41, NO. 4, JULY/AUGUST 2005 1039 An Adaptive Sliding-Mode Observer for Induction Motor Sensorless Speed Control Jingchuan Li, Longya Xu, Fellow, IEEE, and
Robust Controller Design for Speed Control of an Indirect Field Oriented Induction Machine Drive
 Leonardo Electronic Journal of Practices and Technologies ISSN 1583-1078 Issue 6, January-June 2005 p. 1-16 Robust Controller Design for Speed Control of an Indirect Field Oriented Induction Machine Drive
Leonardo Electronic Journal of Practices and Technologies ISSN 1583-1078 Issue 6, January-June 2005 p. 1-16 Robust Controller Design for Speed Control of an Indirect Field Oriented Induction Machine Drive
Independent Control of Speed and Torque in a Vector Controlled Induction Motor Drive using Predictive Current Controller and SVPWM
 Independent Control of Speed and Torque in a Vector Controlled Induction Motor Drive using Predictive Current Controller and SVPWM Vandana Peethambaran 1, Dr.R.Sankaran 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of
Independent Control of Speed and Torque in a Vector Controlled Induction Motor Drive using Predictive Current Controller and SVPWM Vandana Peethambaran 1, Dr.R.Sankaran 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of
user's manual nx frequency converters resolver option board opt-bc
 user's manual nx frequency converters resolver option board opt-bc INDEX Document code: ud01039d Date: 18.2.2011 1. Resolver option board OPT-BC... 3 1.1 Resolver basics... 3 1.2 Resolver board features...
user's manual nx frequency converters resolver option board opt-bc INDEX Document code: ud01039d Date: 18.2.2011 1. Resolver option board OPT-BC... 3 1.1 Resolver basics... 3 1.2 Resolver board features...
EE 410/510: Electromechanical Systems Chapter 4
 EE 410/510: Electromechanical Systems Chapter 4 Chapter 4. Direct Current Electric Machines and Motion Devices Permanent Magnet DC Electric Machines Radial Topology Simulation and Experimental Studies
EE 410/510: Electromechanical Systems Chapter 4 Chapter 4. Direct Current Electric Machines and Motion Devices Permanent Magnet DC Electric Machines Radial Topology Simulation and Experimental Studies
DESIGN AND MODELLING OF SENSORLESS VECTOR CONTROLLED INDUCTION MOTOR USING MODEL REFERENCE ADAPTIVE SYSTEMS
 DESIGN AND MODELLING OF SENSORLESS VECTOR CONTROLLED INDUCTION MOTOR USING MODEL REFERENCE ADAPTIVE SYSTEMS Janaki Pakalapati 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of EEE, Avanthi Institute of Engineering and Technology,
DESIGN AND MODELLING OF SENSORLESS VECTOR CONTROLLED INDUCTION MOTOR USING MODEL REFERENCE ADAPTIVE SYSTEMS Janaki Pakalapati 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of EEE, Avanthi Institute of Engineering and Technology,
A Microscopic Investigation of Force Generation in a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine
 A Microscopic Investigation of Force Generation in a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine S. Pekarek, Purdue University (W. Zhu UM-Rolla), (B. Fahimi University of Texas-Arlington) February 7, 25 1 Outline
A Microscopic Investigation of Force Generation in a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine S. Pekarek, Purdue University (W. Zhu UM-Rolla), (B. Fahimi University of Texas-Arlington) February 7, 25 1 Outline
An Approach for Sensorless Position Estimation for Switched Reluctance Motors Using Artifical Neural Networks
 An Approach for Sensorless Position Estimation for Switched Reluctance Motors Using Artifical Neural Networks Erkan Mese David A. Torrey Department of Electric Power Engineering Rensselaer Polytechnic
An Approach for Sensorless Position Estimation for Switched Reluctance Motors Using Artifical Neural Networks Erkan Mese David A. Torrey Department of Electric Power Engineering Rensselaer Polytechnic
An adaptive sliding mode control scheme for induction motor drives
 An adaptive sliding mode control scheme for induction motor drives Oscar Barambones, Patxi Alkorta, Aitor J. Garrido, I. Garrido and F.J. Maseda ABSTRACT An adaptive sliding-mode control system, which
An adaptive sliding mode control scheme for induction motor drives Oscar Barambones, Patxi Alkorta, Aitor J. Garrido, I. Garrido and F.J. Maseda ABSTRACT An adaptive sliding-mode control system, which
Nonlinear dynamic simulation model of switched reluctance linear machine
 Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 1 (2009) 1320 1324 Procedia Earth and Planetary Science www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia The 6 th International Conference on Mining Science & Technology Nonlinear
Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 1 (2009) 1320 1324 Procedia Earth and Planetary Science www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia The 6 th International Conference on Mining Science & Technology Nonlinear
PRECISION CONTROL OF LINEAR MOTOR DRIVEN HIGH-SPEED/ACCELERATION ELECTRO-MECHANICAL SYSTEMS. Bin Yao
 PRECISION CONTROL OF LINEAR MOTOR DRIVEN HIGH-SPEED/ACCELERATION ELECTRO-MECHANICAL SYSTEMS Bin Yao Intelligent and Precision Control Laboratory School of Mechanical Engineering Purdue University West
PRECISION CONTROL OF LINEAR MOTOR DRIVEN HIGH-SPEED/ACCELERATION ELECTRO-MECHANICAL SYSTEMS Bin Yao Intelligent and Precision Control Laboratory School of Mechanical Engineering Purdue University West
LAB REPORT: THREE-PHASE INDUCTION MACHINE
 LAB REPORT: THREE-PHASE INDUCTION MACHINE ANDY BENNETT 1. Summary This report details the operation, modelling and characteristics of a three-phase induction machine. It attempts to provide a concise overview
LAB REPORT: THREE-PHASE INDUCTION MACHINE ANDY BENNETT 1. Summary This report details the operation, modelling and characteristics of a three-phase induction machine. It attempts to provide a concise overview
FEEDBACK CONTROL SYSTEMS
 FEEDBAC CONTROL SYSTEMS. Control System Design. Open and Closed-Loop Control Systems 3. Why Closed-Loop Control? 4. Case Study --- Speed Control of a DC Motor 5. Steady-State Errors in Unity Feedback Control
FEEDBAC CONTROL SYSTEMS. Control System Design. Open and Closed-Loop Control Systems 3. Why Closed-Loop Control? 4. Case Study --- Speed Control of a DC Motor 5. Steady-State Errors in Unity Feedback Control
Analysis of Sensorless Controlled One Phase Brushless DC Motor
 nalysis of Sensorless Controlled One Phase Brushless DC Motor BDEL-KRIM DUD Electrical and Computer Engineering Department Palestine Polytechnic University (PPU) P.O. Box 98 Hebron, el:+97--89, Fax:+97--78
nalysis of Sensorless Controlled One Phase Brushless DC Motor BDEL-KRIM DUD Electrical and Computer Engineering Department Palestine Polytechnic University (PPU) P.O. Box 98 Hebron, el:+97--89, Fax:+97--78
PARAMETER SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF AN INDUCTION MOTOR
 HUNGARIAN JOURNAL OF INDUSTRIAL CHEMISTRY VESZPRÉM Vol. 39(1) pp. 157-161 (2011) PARAMETER SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF AN INDUCTION MOTOR P. HATOS, A. FODOR, A. MAGYAR University of Pannonia, Department of
HUNGARIAN JOURNAL OF INDUSTRIAL CHEMISTRY VESZPRÉM Vol. 39(1) pp. 157-161 (2011) PARAMETER SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF AN INDUCTION MOTOR P. HATOS, A. FODOR, A. MAGYAR University of Pannonia, Department of
Electric Machines I Three Phase Induction Motor. Dr. Firas Obeidat
 Electric Machines I Three Phase Induction Motor Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of contents 1 General Principles 2 Construction 3 Production of Rotating Field 4 Why Does the Rotor Rotate 5 The Slip and Rotor
Electric Machines I Three Phase Induction Motor Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of contents 1 General Principles 2 Construction 3 Production of Rotating Field 4 Why Does the Rotor Rotate 5 The Slip and Rotor
DC motors. 1. Parallel (shunt) excited DC motor
 DC motors 1. Parallel (shunt) excited DC motor A shunt excited DC motor s terminal voltage is 500 V. The armature resistance is 0,5 Ω, field resistance is 250 Ω. On a certain load it takes 20 A current
DC motors 1. Parallel (shunt) excited DC motor A shunt excited DC motor s terminal voltage is 500 V. The armature resistance is 0,5 Ω, field resistance is 250 Ω. On a certain load it takes 20 A current
Anakapalli Andhra Pradesh, India I. INTRODUCTION
 Robust MRAS Based Sensorless Rotor Speed Measurement of Induction Motor against Variations in Stator Resistance Using Combination of Back Emf and Reactive Power Methods Srikanth Mandarapu Pydah College
Robust MRAS Based Sensorless Rotor Speed Measurement of Induction Motor against Variations in Stator Resistance Using Combination of Back Emf and Reactive Power Methods Srikanth Mandarapu Pydah College
CHAPTER 8 DC MACHINERY FUNDAMENTALS
 CHAPTER 8 DC MACHINERY FUNDAMENTALS Summary: 1. A Simple Rotating Loop between Curved Pole Faces - The Voltage Induced in a Rotating Loop - Getting DC voltage out of the Rotating Loop - The Induced Torque
CHAPTER 8 DC MACHINERY FUNDAMENTALS Summary: 1. A Simple Rotating Loop between Curved Pole Faces - The Voltage Induced in a Rotating Loop - Getting DC voltage out of the Rotating Loop - The Induced Torque
LECTURE 8 Fundamental Models of Pulse-Width Modulated DC-DC Converters: f(d)
 1 ECTURE 8 Fundamental Models of Pulse-Width Modulated DC-DC Converters: f(d) I. Quasi-Static Approximation A. inear Models/ Small Signals/ Quasistatic I V C dt Amp-Sec/Farad V I dt Volt-Sec/Henry 1. Switched
1 ECTURE 8 Fundamental Models of Pulse-Width Modulated DC-DC Converters: f(d) I. Quasi-Static Approximation A. inear Models/ Small Signals/ Quasistatic I V C dt Amp-Sec/Farad V I dt Volt-Sec/Henry 1. Switched
Chapter 7: Stepper Motors. (Revision 6.0, 27/10/2014)
 Chapter 7 Stepper Motors (Revision 6.0, 7/10/014) 1. Stepping Angle Analysis The following analysis derives the formula for the stepping angle of the stepper motor. It has been reproduced and edited from
Chapter 7 Stepper Motors (Revision 6.0, 7/10/014) 1. Stepping Angle Analysis The following analysis derives the formula for the stepping angle of the stepper motor. It has been reproduced and edited from
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF 3-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR
 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF 3-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR 1 A.PANDIAN, 2 Dr.R.DHANASEKARAN 1 Associate Professor., Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Angel College of
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF 3-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR 1 A.PANDIAN, 2 Dr.R.DHANASEKARAN 1 Associate Professor., Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Angel College of
SSC-JE EE POWER SYSTEMS: GENERATION, TRANSMISSION & DISTRIBUTION SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL
 1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems:
1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems:
Static Characteristics of Switched Reluctance Motor 6/4 By Finite Element Analysis
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(9): 1403-1411, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 Static Characteristics of Switched Reluctance Motor 6/4 By Finite Element Analysis 1 T. Jahan. 2 M.B.B. Sharifian
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(9): 1403-1411, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 Static Characteristics of Switched Reluctance Motor 6/4 By Finite Element Analysis 1 T. Jahan. 2 M.B.B. Sharifian
FUZZY LOGIC BASED ADAPTATION MECHANISM FOR ADAPTIVE LUENBERGER OBSERVER SENSORLESS DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF INDUCTION MOTOR
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol., No. (26) 46-59 School of Engineering, Taylor s University FUZZY LOGIC BASED ADAPTATION MECHANISM FOR ADAPTIVE LUENBERGER OBSERVER SENSORLESS DIRECT TORQUE
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol., No. (26) 46-59 School of Engineering, Taylor s University FUZZY LOGIC BASED ADAPTATION MECHANISM FOR ADAPTIVE LUENBERGER OBSERVER SENSORLESS DIRECT TORQUE
