3x + 2y 2z w = 3 x + y + z + 2w = 5 3y 3z 3w = 0. 2x + y z = 0 x + 2y + 4z = 3 2y + 6z = 4. 5x + 6y + 2z = 28 4x + 4y + z = 20 2x + 3y + z = 13
|
|
|
- Clemence Henry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Answers in blue. If you have questions or spot an error, let me know.. Use Gauss-Jordan elimination to find all solutions of the system: (a) (b) (c) (d) x t/ y z = 2 t/ 2 4t/ w t x 2t y = 2 t z t x 2 y = z x x 2 x = x 4 2s + t s t t x + 2y 2z w = x + y + z + 2w = 5 y z w = 0. 2x + y z = 0 x + 2y + 4z = 2y + 6z = 4. 5x + 6y + 2z = 28 4x + 4y + z = 20 2x + y + z = x + 6x 2 + x 2x 4 = 9 2x + 4x 2 + x x 4 = 6 2. Determine the values of k for which each system has: i) no solution, ii) a unique solution, iii) infinitely many solutions: (a) x y + 5z = 2 2x + 4y + 6z = 8 5x + y z = k + 6 There is a unique solution for all values of k.
2 (b) x + 2y = 2 2x + (k 2 5)y = k + There are infinitely many solutions for k =, no solution for k =, and a unique solution for k ±.. Let A = , B = 2 6, C = 6, D = (a) Find rref(a). 0 rref(a) = 0 2, rref(b) = I, rref(c) = , rref(d) = (b) Find rank(a). Counting leading ones, rank(a) = 2, rank(b) =, rank(c) =, and rank(d) = 2. (c) Is A invertible? If so, find A. If not, explain how you know that it isn t. A and C aren t invertible since they don t have rank. D isn t invertible since it isn t square. 8/5 /5 B = /2 8/5 /5. 0 /0 /0 (d) Compute A(2 e + e ). A(2 e + e ) = 2 4, B(2 e + e ) = , C(2 e + e ) = 4, D(2 e + e ) = 2 4. In each case below, express the vector w as a linear combination of v,..., v m or explain why you can t. [ 2 (a) w =, v ] = e, v 2 = e 2 w = 2 v + v 2 (b) w = [ ], v = [ ] [ ] 2, v 2 2 = w = v 7 v 2 2
3 7 2 0 (c) w = 2 6 = 2 2 = 0 = 4 w = v + v v 0 (d) w =, v =, v 2 = w is not a linear combination of v and v 2. If we 2 0 write w = a v + b v 2, the corresponding system of equations in the variables a and b is inconsistent. 5. For scalars a and b with a 2 + b 2 =, consider the matrix [ ] a b A =. b a (a) What is the geometrical effect of multiplying x by A? A is a reflection matrix. (b) Compute A when it exists. For what values of a and b does A not exist? Using the formula for # in Section 2. (which is good to know!), A = A (because a 2 + b 2 = ). The inverse wouldn t exist if and only if a = b = 0, but since we have the restriction a 2 + b 2 =, it always works for the values of a and b that we re considering. (c) Use geometry to explain your result in part (b). The way to undo the reflection of a vector across a line is to reflect it back across the same line, which is why A is its own inverse. [ 6. Let T be a linear transformation from R 2 to R with T ( ) = 2] [ [ 2 Compute T ( 4 ). 2] ] T ( [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] ) = T ( ) 4T ( 2 2 ) = = [ 2 2 and T ( ) = ] 7. A linear system of the form A x = 0 is called homogeneous. Justify the following facts: (a) If v and v 2 are solutions of A x = 0, then ( v + v 2 ) is a solution as well. A( v + v 2 ) = A v + A v 2 = = 0. (b) If v is a solution of A x = 0 and k is a scalar, then k v is a solution as well. A(k v) = ka v = k 0 = Classify each of the following matrices as either a scaling, an orthogonal projection, a shear, a reflection, or a rotation. (Use each option once.) [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] 0 0 A =, B =, C =, D =, E = [ ] A is a rotation, B is an orthogonal projection, C is a scaling, D is a shear, and E is a reflection.
4 9. Calculate the matrix for a rotation of θ in the counterclockwise direction around the y-axis in R. (You may assume that this transformation is linear.) Note: This problem doesn t actually have a unique solution as stated, since which direction is counterclockwise depends on whether we re looking from the positive y-axis or from the negative y-axis. I meant to say the counterclockwise direction as viewed from the positive y-axis. Oops. Sorry about that; let s pretend that that s what I said. We [ don t have a formula for this, so let s think it out. The matrix of a linear transformation is T ( e )... T ( e m ) ], so we just need to figure out what such a rotation will do to the standard cos θ cos(θ π 2 ) sin θ vectors. We have T ( e ) = 0, T ( e 2 ) = e 2, and T ( e ) = 0 = 0, so sin θ sin(θ π 2 ) cos θ cos θ 0 sin θ the matrix is 0 0. sin θ 0 cos θ (Note that this is for a right-handed coordinate system. If you prefer working in a left-handed cos θ 0 sin θ coordinate system, the answer is 0 0. As the use of right-handed coordinate sin θ 0 cos θ systems is conventional in math, you should explicitly specify if you aren t doing this.) v 0. Let v = v 2. Define the transformation T ( x) = v x (the dot product) from R to R. v (a) Show that T is a linear transformation by finding its matrix. The matrix is [ v v 2 v ]. (b) Using part (a), show that v ( u + w) = v u + v w and that v (k w) = k( v w) for all vectors u, v, and w in R and for all scalars k. Since we know that T is linear, v ( u + w) = T ( u + w) = T ( u) + T ( w) = v u + v w and v (k w) = T (k w) = kt ( w) = k( v w).. True or false: (a) If a system of equations has fewer equations than unknowns, then it has infinitely many solutions. False; it could have no solution. (b) If A in an n m matrix, then rank(a) n. True. See Example in Section.. (c) If A in [ an ] n [ n] matrix [ ] and A x = 0, then x = 0. False; this is only true if rank(a) = n. 0 e.g., = 0 (d) If a square matrix has two equal columns, then it is not invertible. True. Its rref will not be I n. (e) If a square matrix has two equal rows, then it is not invertible. True. Its rref will not be I n. 4
5 (f) There exists a 2 2 matrix A such that rank(a) = 0. True. The zero matrix. (g) There exists a 2 2 matrix A such that rank(a) = 4. False. rank(a) 2. [ ] a b (h) A matrix of the form with a b a 2 + b 2 = must be invertible. True. cf. Section 2., #. Or, note that it s a rotation, so clearly invertible by geometry (as you can invert it by rotating in the opposite direction). (i) If A is a 4 matrix, then A x = 0 has infinitely many solutions. True. It has more variables than equations, so it can t have a unique solution, and it s homogeneous, so it can t be inconsistent (as x = 0 is one solution.) [ ] (j) The solutions to x = e form a line in R 2. False. This system is inconsistent. (k) If v and w are two solutions to A x = b, then ( v + w) is a solution too. False. A( v + w) = A v + A w = b + b = 2 b. As 2 b b except when b = 0, this is not generally true. (l) If A is an upper-triangular matrix, then A is invertible. False. For example, the zero matrix is upper-triangular, but it isn t invertible. 2. Let A be an n m matrix and v and w vectors in R m. Prove that A( v + w) = A v + A w. See Theorem..0 in your book for a proof.. Let T be a linear transformation from R m to R n. Prove that the matrix of T is A = [ T ( e )... T ( e m ) ]. See Theorem 2..2 in your book. The book doesn t provide a full proof, but I gave one in class. In case you missed it: Let A = [ ] v... v m be the matrix of T (that is, v,..., v m are the columns of A.) Then T ( e i ) = A e i = v i, so that A = [ T ( e )... T ( e m ) ]. 4. Let S( x) and T ( x) be a linear transformation from R m to R n. Define R( x) = S( x) + T ( x). Prove that R( x) is a linear transformation. We need to show two things: R( v + w) = R( v) + R( w) and R(k v) = kr( v). Let v, w in R m and k be a scalar. Then: R( v+ w) = S( v+ w)+t ( v+ w) = S( v)+s( w)+t ( v)+t ( w) = S( v)+t ( v)+s( w)+t ( w) = R( v)+r( w). R(k v) = S(k v) + T (k v) = ks( v) + kt ( v) = k(s( v) + T ( v)) = kr( v). 5. Let T ( x) be a linear transformation from R m to R n and k be a scalar. Define R( x) = kt ( x). Prove that R( x) is a linear transformation. We need to show two things: R( v + w) = R( v) + R( w) and R(k v) = kr( v). Let v, w in R m and c be a scalar (c as k is already in use). Then: R( v + w) = kt ( v + w) = k(t ( v) + T ( w)) = kt ( v) + kt ( w) = R( v) + R( w). R(c v) = kt (c v) = kct ( v) = ckt ( v) = cr( v). 5
Lecture 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices
 Lecture 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Math 19620 Outline of Course Linear Equations and Matrices Linear Transformations, Inverses Bases, Linear Independence, Subspaces Abstract Vector Spaces
Lecture 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Math 19620 Outline of Course Linear Equations and Matrices Linear Transformations, Inverses Bases, Linear Independence, Subspaces Abstract Vector Spaces
Lecture 2 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices, Continued
 Lecture 2 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices, Continued Math 19620 Outline of Lecture Algorithm for putting a matrix in row reduced echelon form - i.e. Gauss-Jordan Elimination Number of Solutions
Lecture 2 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices, Continued Math 19620 Outline of Lecture Algorithm for putting a matrix in row reduced echelon form - i.e. Gauss-Jordan Elimination Number of Solutions
is Use at most six elementary row operations. (Partial
 MATH 235 SPRING 2 EXAM SOLUTIONS () (6 points) a) Show that the reduced row echelon form of the augmented matrix of the system x + + 2x 4 + x 5 = 3 x x 3 + x 4 + x 5 = 2 2x + 2x 3 2x 4 x 5 = 3 is. Use
MATH 235 SPRING 2 EXAM SOLUTIONS () (6 points) a) Show that the reduced row echelon form of the augmented matrix of the system x + + 2x 4 + x 5 = 3 x x 3 + x 4 + x 5 = 2 2x + 2x 3 2x 4 x 5 = 3 is. Use
Final Review Sheet. B = (1, 1 + 3x, 1 + x 2 ) then 2 + 3x + 6x 2
 Final Review Sheet The final will cover Sections Chapters 1,2,3 and 4, as well as sections 5.1-5.4, 6.1-6.2 and 7.1-7.3 from chapters 5,6 and 7. This is essentially all material covered this term. Watch
Final Review Sheet The final will cover Sections Chapters 1,2,3 and 4, as well as sections 5.1-5.4, 6.1-6.2 and 7.1-7.3 from chapters 5,6 and 7. This is essentially all material covered this term. Watch
MATH 15a: Linear Algebra Exam 1, Solutions
 MATH 5a: Linear Algebra Exam, Solutions. Let T : R 3 R 4 be the linear transformation with T( e ) = 2 e + e 2 + 3 e 3 4 e 4, T( e 2 ) = e e 2 +2 e 3 +6 e 4, and T( e 3 ) = 4 e e 2 +7 e 3 +8 e 4. (a) (6
MATH 5a: Linear Algebra Exam, Solutions. Let T : R 3 R 4 be the linear transformation with T( e ) = 2 e + e 2 + 3 e 3 4 e 4, T( e 2 ) = e e 2 +2 e 3 +6 e 4, and T( e 3 ) = 4 e e 2 +7 e 3 +8 e 4. (a) (6
3.4 Elementary Matrices and Matrix Inverse
 Math 220: Summer 2015 3.4 Elementary Matrices and Matrix Inverse A n n elementary matrix is a matrix which is obtained from the n n identity matrix I n n by a single elementary row operation. Elementary
Math 220: Summer 2015 3.4 Elementary Matrices and Matrix Inverse A n n elementary matrix is a matrix which is obtained from the n n identity matrix I n n by a single elementary row operation. Elementary
Answers in blue. If you have questions or spot an error, let me know. 1. Find all matrices that commute with A =. 4 3
 Answers in blue. If you have questions or spot an error, let me know. 3 4. Find all matrices that commute with A =. 4 3 a b If we set B = and set AB = BA, we see that 3a + 4b = 3a 4c, 4a + 3b = 3b 4d,
Answers in blue. If you have questions or spot an error, let me know. 3 4. Find all matrices that commute with A =. 4 3 a b If we set B = and set AB = BA, we see that 3a + 4b = 3a 4c, 4a + 3b = 3b 4d,
February 20 Math 3260 sec. 56 Spring 2018
 February 20 Math 3260 sec. 56 Spring 2018 Section 2.2: Inverse of a Matrix Consider the scalar equation ax = b. Provided a 0, we can solve this explicity x = a 1 b where a 1 is the unique number such that
February 20 Math 3260 sec. 56 Spring 2018 Section 2.2: Inverse of a Matrix Consider the scalar equation ax = b. Provided a 0, we can solve this explicity x = a 1 b where a 1 is the unique number such that
MTH 102A - Linear Algebra II Semester
 MTH 0A - Linear Algebra - 05-6-II Semester Arbind Kumar Lal P Field A field F is a set from which we choose our coefficients and scalars Expected properties are ) a+b and a b should be defined in it )
MTH 0A - Linear Algebra - 05-6-II Semester Arbind Kumar Lal P Field A field F is a set from which we choose our coefficients and scalars Expected properties are ) a+b and a b should be defined in it )
MATH 15a: Applied Linear Algebra Practice Exam 1
 MATH 5a: Applied Linear Algebra Practice Exam Note: this practice test is NOT a guarantee of what the actual midterm will look like!. Say whether the following functions are linear. If so, write down the
MATH 5a: Applied Linear Algebra Practice Exam Note: this practice test is NOT a guarantee of what the actual midterm will look like!. Say whether the following functions are linear. If so, write down the
SUMMARY OF MATH 1600
 SUMMARY OF MATH 1600 Note: The following list is intended as a study guide for the final exam. It is a continuation of the study guide for the midterm. It does not claim to be a comprehensive list. You
SUMMARY OF MATH 1600 Note: The following list is intended as a study guide for the final exam. It is a continuation of the study guide for the midterm. It does not claim to be a comprehensive list. You
Math 416, Spring 2010 Matrix multiplication; subspaces February 2, 2010 MATRIX MULTIPLICATION; SUBSPACES. 1. Announcements
 Math 416, Spring 010 Matrix multiplication; subspaces February, 010 MATRIX MULTIPLICATION; SUBSPACES 1 Announcements Office hours on Wednesday are cancelled because Andy will be out of town If you email
Math 416, Spring 010 Matrix multiplication; subspaces February, 010 MATRIX MULTIPLICATION; SUBSPACES 1 Announcements Office hours on Wednesday are cancelled because Andy will be out of town If you email
Math 4A Notes. Written by Victoria Kala Last updated June 11, 2017
 Math 4A Notes Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu Last updated June 11, 2017 Systems of Linear Equations A linear equation is an equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 +...
Math 4A Notes Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu Last updated June 11, 2017 Systems of Linear Equations A linear equation is an equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 +...
MATH 221: SOLUTIONS TO SELECTED HOMEWORK PROBLEMS
 MATH 221: SOLUTIONS TO SELECTED HOMEWORK PROBLEMS 1. HW 1: Due September 4 1.1.21. Suppose v, w R n and c is a scalar. Prove that Span(v + cw, w) = Span(v, w). We must prove two things: that every element
MATH 221: SOLUTIONS TO SELECTED HOMEWORK PROBLEMS 1. HW 1: Due September 4 1.1.21. Suppose v, w R n and c is a scalar. Prove that Span(v + cw, w) = Span(v, w). We must prove two things: that every element
Math 265 Midterm 2 Review
 Math 65 Midterm Review March 6, 06 Things you should be able to do This list is not meant to be ehaustive, but to remind you of things I may ask you to do on the eam. These are roughly in the order they
Math 65 Midterm Review March 6, 06 Things you should be able to do This list is not meant to be ehaustive, but to remind you of things I may ask you to do on the eam. These are roughly in the order they
Number of solutions of a system
 Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 3: Linear systems and matrices Section 7 Number of solutions of a system What you need to know already: How to solve a linear system by using Gauss- Jordan elimination.
Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 3: Linear systems and matrices Section 7 Number of solutions of a system What you need to know already: How to solve a linear system by using Gauss- Jordan elimination.
Math 314H EXAM I. 1. (28 points) The row reduced echelon form of the augmented matrix for the system. is the matrix
 Math 34H EXAM I Do all of the problems below. Point values for each of the problems are adjacent to the problem number. Calculators may be used to check your answer but not to arrive at your answer. That
Math 34H EXAM I Do all of the problems below. Point values for each of the problems are adjacent to the problem number. Calculators may be used to check your answer but not to arrive at your answer. That
Examples True or false: 3. Let A be a 3 3 matrix. Then there is a pattern in A with precisely 4 inversions.
 The exam will cover Sections 6.-6.2 and 7.-7.4: True/False 30% Definitions 0% Computational 60% Skip Minors and Laplace Expansion in Section 6.2 and p. 304 (trajectories and phase portraits) in Section
The exam will cover Sections 6.-6.2 and 7.-7.4: True/False 30% Definitions 0% Computational 60% Skip Minors and Laplace Expansion in Section 6.2 and p. 304 (trajectories and phase portraits) in Section
Spring 2014 Midterm 1 02/26/14 Lecturer: Jesus Martinez Garcia
 Math 0 Spring 04 Midterm 0/6/4 Lecturer: Jesus Martinez Garcia Time Limit: 50 minutes Name (Print: Teaching Assistant This exam contains 9 pages (including this cover page and 4 problems Check to see if
Math 0 Spring 04 Midterm 0/6/4 Lecturer: Jesus Martinez Garcia Time Limit: 50 minutes Name (Print: Teaching Assistant This exam contains 9 pages (including this cover page and 4 problems Check to see if
Chapter 2: Matrices and Linear Systems
 Chapter 2: Matrices and Linear Systems Paul Pearson Outline Matrices Linear systems Row operations Inverses Determinants Matrices Definition An m n matrix A = (a ij ) is a rectangular array of real numbers
Chapter 2: Matrices and Linear Systems Paul Pearson Outline Matrices Linear systems Row operations Inverses Determinants Matrices Definition An m n matrix A = (a ij ) is a rectangular array of real numbers
Spring 2015 Midterm 1 03/04/15 Lecturer: Jesse Gell-Redman
 Math 0 Spring 05 Midterm 03/04/5 Lecturer: Jesse Gell-Redman Time Limit: 50 minutes Name (Print): Teaching Assistant This exam contains pages (including this cover page) and 5 problems. Check to see if
Math 0 Spring 05 Midterm 03/04/5 Lecturer: Jesse Gell-Redman Time Limit: 50 minutes Name (Print): Teaching Assistant This exam contains pages (including this cover page) and 5 problems. Check to see if
Solutions of Linear system, vector and matrix equation
 Goals: Solutions of Linear system, vector and matrix equation Solutions of linear system. Vectors, vector equation. Matrix equation. Math 112, Week 2 Suggested Textbook Readings: Sections 1.3, 1.4, 1.5
Goals: Solutions of Linear system, vector and matrix equation Solutions of linear system. Vectors, vector equation. Matrix equation. Math 112, Week 2 Suggested Textbook Readings: Sections 1.3, 1.4, 1.5
Lecture 4: Gaussian Elimination and Homogeneous Equations
 Lecture 4: Gaussian Elimination and Homogeneous Equations Reduced Row Echelon Form An augmented matrix associated to a system of linear equations is said to be in Reduced Row Echelon Form (RREF) if the
Lecture 4: Gaussian Elimination and Homogeneous Equations Reduced Row Echelon Form An augmented matrix associated to a system of linear equations is said to be in Reduced Row Echelon Form (RREF) if the
18.06 Problem Set 3 - Solutions Due Wednesday, 26 September 2007 at 4 pm in
 8.6 Problem Set 3 - s Due Wednesday, 26 September 27 at 4 pm in 2-6. Problem : (=2+2+2+2+2) A vector space is by definition a nonempty set V (whose elements are called vectors) together with rules of addition
8.6 Problem Set 3 - s Due Wednesday, 26 September 27 at 4 pm in 2-6. Problem : (=2+2+2+2+2) A vector space is by definition a nonempty set V (whose elements are called vectors) together with rules of addition
1 Last time: multiplying vectors matrices
 MATH Linear algebra (Fall 7) Lecture Last time: multiplying vectors matrices Given a matrix A = a a a n a a a n and a vector v = a m a m a mn Av = v a a + v a a v v + + Rn we define a n a n a m a m a mn
MATH Linear algebra (Fall 7) Lecture Last time: multiplying vectors matrices Given a matrix A = a a a n a a a n and a vector v = a m a m a mn Av = v a a + v a a v v + + Rn we define a n a n a m a m a mn
Inverting Matrices. 1 Properties of Transpose. 2 Matrix Algebra. P. Danziger 3.2, 3.3
 3., 3.3 Inverting Matrices P. Danziger 1 Properties of Transpose Transpose has higher precedence than multiplication and addition, so AB T A ( B T and A + B T A + ( B T As opposed to the bracketed expressions
3., 3.3 Inverting Matrices P. Danziger 1 Properties of Transpose Transpose has higher precedence than multiplication and addition, so AB T A ( B T and A + B T A + ( B T As opposed to the bracketed expressions
ANSWERS (5 points) Let A be a 2 2 matrix such that A =. Compute A. 2
 MATH 7- Final Exam Sample Problems Spring 7 ANSWERS ) ) ). 5 points) Let A be a matrix such that A =. Compute A. ) A = A ) = ) = ). 5 points) State ) the definition of norm, ) the Cauchy-Schwartz inequality
MATH 7- Final Exam Sample Problems Spring 7 ANSWERS ) ) ). 5 points) Let A be a matrix such that A =. Compute A. ) A = A ) = ) = ). 5 points) State ) the definition of norm, ) the Cauchy-Schwartz inequality
Solutions to Math 51 First Exam April 21, 2011
 Solutions to Math 5 First Exam April,. ( points) (a) Give the precise definition of a (linear) subspace V of R n. (4 points) A linear subspace V of R n is a subset V R n which satisfies V. If x, y V then
Solutions to Math 5 First Exam April,. ( points) (a) Give the precise definition of a (linear) subspace V of R n. (4 points) A linear subspace V of R n is a subset V R n which satisfies V. If x, y V then
Topic 2 Quiz 2. choice C implies B and B implies C. correct-choice C implies B, but B does not imply C
 Topic 1 Quiz 1 text A reduced row-echelon form of a 3 by 4 matrix can have how many leading one s? choice must have 3 choice may have 1, 2, or 3 correct-choice may have 0, 1, 2, or 3 choice may have 0,
Topic 1 Quiz 1 text A reduced row-echelon form of a 3 by 4 matrix can have how many leading one s? choice must have 3 choice may have 1, 2, or 3 correct-choice may have 0, 1, 2, or 3 choice may have 0,
Math 416, Spring 2010 Coordinate systems and Change of Basis February 16, 2010 COORDINATE SYSTEMS AND CHANGE OF BASIS. 1.
 Math 46 Spring Coordinate systems and Change of asis February 6 COORDINAE SYSEMS AND CHANGE OF ASIS Announcements Don t forget that we have a quiz on hursday and test coming up the following hursday Finishing
Math 46 Spring Coordinate systems and Change of asis February 6 COORDINAE SYSEMS AND CHANGE OF ASIS Announcements Don t forget that we have a quiz on hursday and test coming up the following hursday Finishing
MATH 15a: Linear Algebra Practice Exam 2
 MATH 5a: Linear Algebra Practice Exam 2 Write all answers in your exam booklet. Remember that you must show all work and justify your answers for credit. No calculators are allowed. Good luck!. Compute
MATH 5a: Linear Algebra Practice Exam 2 Write all answers in your exam booklet. Remember that you must show all work and justify your answers for credit. No calculators are allowed. Good luck!. Compute
Chapter 4 & 5: Vector Spaces & Linear Transformations
 Chapter 4 & 5: Vector Spaces & Linear Transformations Philip Gressman University of Pennsylvania Philip Gressman Math 240 002 2014C: Chapters 4 & 5 1 / 40 Objective The purpose of Chapter 4 is to think
Chapter 4 & 5: Vector Spaces & Linear Transformations Philip Gressman University of Pennsylvania Philip Gressman Math 240 002 2014C: Chapters 4 & 5 1 / 40 Objective The purpose of Chapter 4 is to think
Lecture Notes in Mathematics. Arkansas Tech University Department of Mathematics. The Basics of Linear Algebra
 Lecture Notes in Mathematics Arkansas Tech University Department of Mathematics The Basics of Linear Algebra Marcel B. Finan c All Rights Reserved Last Updated November 30, 2015 2 Preface Linear algebra
Lecture Notes in Mathematics Arkansas Tech University Department of Mathematics The Basics of Linear Algebra Marcel B. Finan c All Rights Reserved Last Updated November 30, 2015 2 Preface Linear algebra
YORK UNIVERSITY. Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH M Test #1. July 11, 2013 Solutions
 YORK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH 222 3. M Test # July, 23 Solutions. For each statement indicate whether it is always TRUE or sometimes FALSE. Note: For
YORK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH 222 3. M Test # July, 23 Solutions. For each statement indicate whether it is always TRUE or sometimes FALSE. Note: For
LECTURES 4/5: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS
 LECTURES 4/5: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS MA1111: LINEAR ALGEBRA I, MICHAELMAS 2016 1 Linear equations We now switch gears to discuss the topic of solving linear equations, and more interestingly, systems
LECTURES 4/5: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS MA1111: LINEAR ALGEBRA I, MICHAELMAS 2016 1 Linear equations We now switch gears to discuss the topic of solving linear equations, and more interestingly, systems
Math x + 3y 5z = 14 3x 2y + 3z = 17 4x + 3y 2z = 1
 Math 210 1. Solve the system: x + y + z = 1 2x + 3y + 4z = 5 (a z = 2, y = 1 and x = 0 (b z =any value, y = 3 2z and x = z 2 (c z =any value, y = 3 2z and x = z + 2 (d z =any value, y = 3 + 2z and x =
Math 210 1. Solve the system: x + y + z = 1 2x + 3y + 4z = 5 (a z = 2, y = 1 and x = 0 (b z =any value, y = 3 2z and x = z 2 (c z =any value, y = 3 2z and x = z + 2 (d z =any value, y = 3 + 2z and x =
Matrices and systems of linear equations
 Matrices and systems of linear equations Samy Tindel Purdue University Differential equations and linear algebra - MA 262 Taken from Differential equations and linear algebra by Goode and Annin Samy T.
Matrices and systems of linear equations Samy Tindel Purdue University Differential equations and linear algebra - MA 262 Taken from Differential equations and linear algebra by Goode and Annin Samy T.
4 Elementary matrices, continued
 4 Elementary matrices, continued We have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. If you check the previous examples, you ll find that these matrices are constructed
4 Elementary matrices, continued We have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. If you check the previous examples, you ll find that these matrices are constructed
Section Gaussian Elimination
 Section. - Gaussian Elimination A matrix is said to be in row echelon form (REF) if it has the following properties:. The first nonzero entry in any row is a. We call this a leading one or pivot one..
Section. - Gaussian Elimination A matrix is said to be in row echelon form (REF) if it has the following properties:. The first nonzero entry in any row is a. We call this a leading one or pivot one..
Definitions. Main Results
 Definitions Pivot of A Basis of V Main Results A column in rref(a) which contains a leading one has a corresponding column in A, called a pivot column of A. It is an independent set v 1,..., v k from data
Definitions Pivot of A Basis of V Main Results A column in rref(a) which contains a leading one has a corresponding column in A, called a pivot column of A. It is an independent set v 1,..., v k from data
4 Elementary matrices, continued
 4 Elementary matrices, continued We have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. To repeat the recipe: These matrices are constructed by performing the given row
4 Elementary matrices, continued We have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. To repeat the recipe: These matrices are constructed by performing the given row
Solutions to Exam I MATH 304, section 6
 Solutions to Exam I MATH 304, section 6 YOU MUST SHOW ALL WORK TO GET CREDIT. Problem 1. Let A = 1 2 5 6 1 2 5 6 3 2 0 0 1 3 1 1 2 0 1 3, B =, C =, I = I 0 0 0 1 1 3 4 = 4 4 identity matrix. 3 1 2 6 0
Solutions to Exam I MATH 304, section 6 YOU MUST SHOW ALL WORK TO GET CREDIT. Problem 1. Let A = 1 2 5 6 1 2 5 6 3 2 0 0 1 3 1 1 2 0 1 3, B =, C =, I = I 0 0 0 1 1 3 4 = 4 4 identity matrix. 3 1 2 6 0
1 9/5 Matrices, vectors, and their applications
 1 9/5 Matrices, vectors, and their applications Algebra: study of objects and operations on them. Linear algebra: object: matrices and vectors. operations: addition, multiplication etc. Algorithms/Geometric
1 9/5 Matrices, vectors, and their applications Algebra: study of objects and operations on them. Linear algebra: object: matrices and vectors. operations: addition, multiplication etc. Algorithms/Geometric
If A is a 4 6 matrix and B is a 6 3 matrix then the dimension of AB is A. 4 6 B. 6 6 C. 4 3 D. 3 4 E. Undefined
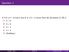 Question 1 If A is a 4 6 matrix and B is a 6 3 matrix then the dimension of AB is A. 4 6 B. 6 6 C. 4 3 D. 3 4 E. Undefined Quang T. Bach Math 18 October 18, 2017 1 / 17 Question 2 1 2 Let A = 3 4 1 2 3
Question 1 If A is a 4 6 matrix and B is a 6 3 matrix then the dimension of AB is A. 4 6 B. 6 6 C. 4 3 D. 3 4 E. Undefined Quang T. Bach Math 18 October 18, 2017 1 / 17 Question 2 1 2 Let A = 3 4 1 2 3
9.1 - Systems of Linear Equations: Two Variables
 9.1 - Systems of Linear Equations: Two Variables Recall that a system of equations consists of two or more equations each with two or more variables. A solution to a system in two variables is an ordered
9.1 - Systems of Linear Equations: Two Variables Recall that a system of equations consists of two or more equations each with two or more variables. A solution to a system in two variables is an ordered
Extra Problems: Chapter 1
 MA131 (Section 750002): Prepared by Asst.Prof.Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 1 Extra Problems: Chapter 1 1. In each of the following answer true if the statement is always true and false otherwise in the space
MA131 (Section 750002): Prepared by Asst.Prof.Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 1 Extra Problems: Chapter 1 1. In each of the following answer true if the statement is always true and false otherwise in the space
Practice Exam. 2x 1 + 4x 2 + 2x 3 = 4 x 1 + 2x 2 + 3x 3 = 1 2x 1 + 3x 2 + 4x 3 = 5
 Practice Exam. Solve the linear system using an augmented matrix. State whether the solution is unique, there are no solutions or whether there are infinitely many solutions. If the solution is unique,
Practice Exam. Solve the linear system using an augmented matrix. State whether the solution is unique, there are no solutions or whether there are infinitely many solutions. If the solution is unique,
Basis, Dimension, Kernel, Image
 Basis, Dimension, Kernel, Image Definitions: Pivot, Basis, Rank and Nullity Main Results: Dimension, Pivot Theorem Main Results: Rank-Nullity, Row Rank, Pivot Method Definitions: Kernel, Image, rowspace,
Basis, Dimension, Kernel, Image Definitions: Pivot, Basis, Rank and Nullity Main Results: Dimension, Pivot Theorem Main Results: Rank-Nullity, Row Rank, Pivot Method Definitions: Kernel, Image, rowspace,
Math 22AL Lab #4. 1 Objectives. 2 Header. 0.1 Notes
 Math 22AL Lab #4 0.1 Notes Green typewriter text represents comments you must type. Each comment is worth one point. Blue typewriter text represents commands you must type. Each command is worth one point.
Math 22AL Lab #4 0.1 Notes Green typewriter text represents comments you must type. Each comment is worth one point. Blue typewriter text represents commands you must type. Each command is worth one point.
Math Computation Test 1 September 26 th, 2016 Debate: Computation vs. Theory Whatever wins, it ll be Huuuge!
 Math 5- Computation Test September 6 th, 6 Debate: Computation vs. Theory Whatever wins, it ll be Huuuge! Name: Answer Key: Making Math Great Again Be sure to show your work!. (8 points) Consider the following
Math 5- Computation Test September 6 th, 6 Debate: Computation vs. Theory Whatever wins, it ll be Huuuge! Name: Answer Key: Making Math Great Again Be sure to show your work!. (8 points) Consider the following
Notes on Row Reduction
 Notes on Row Reduction Francis J. Narcowich Department of Mathematics Texas A&M University September The Row-Reduction Algorithm The row-reduced form of a matrix contains a great deal of information, both
Notes on Row Reduction Francis J. Narcowich Department of Mathematics Texas A&M University September The Row-Reduction Algorithm The row-reduced form of a matrix contains a great deal of information, both
CSL361 Problem set 4: Basic linear algebra
 CSL361 Problem set 4: Basic linear algebra February 21, 2017 [Note:] If the numerical matrix computations turn out to be tedious, you may use the function rref in Matlab. 1 Row-reduced echelon matrices
CSL361 Problem set 4: Basic linear algebra February 21, 2017 [Note:] If the numerical matrix computations turn out to be tedious, you may use the function rref in Matlab. 1 Row-reduced echelon matrices
Midterm 1 Review. Written by Victoria Kala SH 6432u Office Hours: R 12:30 1:30 pm Last updated 10/10/2015
 Midterm 1 Review Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu SH 6432u Office Hours: R 12:30 1:30 pm Last updated 10/10/2015 Summary This Midterm Review contains notes on sections 1.1 1.5 and 1.7 in your
Midterm 1 Review Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu SH 6432u Office Hours: R 12:30 1:30 pm Last updated 10/10/2015 Summary This Midterm Review contains notes on sections 1.1 1.5 and 1.7 in your
Basis, Dimension, Kernel, Image
 Basis, Dimension, Kernel, Image Definitions: Pivot, Basis, Rank and Nullity Main Results: Dimension, Pivot Theorem Main Results: Rank-Nullity, Row Rank, Pivot Method Definitions: Kernel, Image, rowspace,
Basis, Dimension, Kernel, Image Definitions: Pivot, Basis, Rank and Nullity Main Results: Dimension, Pivot Theorem Main Results: Rank-Nullity, Row Rank, Pivot Method Definitions: Kernel, Image, rowspace,
MATH 260 LINEAR ALGEBRA EXAM III Fall 2014
 MAH 60 LINEAR ALGEBRA EXAM III Fall 0 Instructions: the use of built-in functions of your calculator such as det( ) or RREF is permitted ) Consider the table and the vectors and matrices given below Fill
MAH 60 LINEAR ALGEBRA EXAM III Fall 0 Instructions: the use of built-in functions of your calculator such as det( ) or RREF is permitted ) Consider the table and the vectors and matrices given below Fill
b for the linear system x 1 + x 2 + a 2 x 3 = a x 1 + x 3 = 3 x 1 + x 2 + 9x 3 = 3 ] 1 1 a 2 a
![b for the linear system x 1 + x 2 + a 2 x 3 = a x 1 + x 3 = 3 x 1 + x 2 + 9x 3 = 3 ] 1 1 a 2 a b for the linear system x 1 + x 2 + a 2 x 3 = a x 1 + x 3 = 3 x 1 + x 2 + 9x 3 = 3 ] 1 1 a 2 a](/thumbs/71/65559666.jpg) Practice Exercises for Exam Exam will be on Monday, September 8, 7. The syllabus for Exam consists of Sections One.I, One.III, Two.I, and Two.II. You should know the main definitions, results and computational
Practice Exercises for Exam Exam will be on Monday, September 8, 7. The syllabus for Exam consists of Sections One.I, One.III, Two.I, and Two.II. You should know the main definitions, results and computational
Multiple Choice Questions
 Multiple Choice Questions There is no penalty for guessing. Three points per question, so a total of 48 points for this section.. What is the complete relationship between homogeneous linear systems of
Multiple Choice Questions There is no penalty for guessing. Three points per question, so a total of 48 points for this section.. What is the complete relationship between homogeneous linear systems of
Math 51, Homework-2 Solutions
 SSEA Summer 27 Math 5, Homework-2 Solutions Write the parametric equation of the plane that contains the following point and line: 3 2, 4 2 + t 3 t R 5 4 By substituting t = and t =, we get two points
SSEA Summer 27 Math 5, Homework-2 Solutions Write the parametric equation of the plane that contains the following point and line: 3 2, 4 2 + t 3 t R 5 4 By substituting t = and t =, we get two points
S09 MTH 371 Linear Algebra NEW PRACTICE QUIZ 4, SOLUTIONS Prof. G.Todorov February 15, 2009 Please, justify your answers.
 S09 MTH 37 Linear Algebra NEW PRACTICE QUIZ 4, SOLUTIONS Prof. G.Todorov February, 009 Please, justify your answers. 3 0. Let A = 0 3. 7 Determine whether the column vectors of A are dependent or independent.
S09 MTH 37 Linear Algebra NEW PRACTICE QUIZ 4, SOLUTIONS Prof. G.Todorov February, 009 Please, justify your answers. 3 0. Let A = 0 3. 7 Determine whether the column vectors of A are dependent or independent.
Math 220: Summer Midterm 1 Questions
 Math 220: Summer 2015 Midterm 1 Questions MOST questions will either look a lot like a Homework questions This lists draws your attention to some important types of HW questions. SOME questions will have
Math 220: Summer 2015 Midterm 1 Questions MOST questions will either look a lot like a Homework questions This lists draws your attention to some important types of HW questions. SOME questions will have
This MUST hold matrix multiplication satisfies the distributive property.
 The columns of AB are combinations of the columns of A. The reason is that each column of AB equals A times the corresponding column of B. But that is a linear combination of the columns of A with coefficients
The columns of AB are combinations of the columns of A. The reason is that each column of AB equals A times the corresponding column of B. But that is a linear combination of the columns of A with coefficients
Linear Algebra Homework and Study Guide
 Linear Algebra Homework and Study Guide Phil R. Smith, Ph.D. February 28, 20 Homework Problem Sets Organized by Learning Outcomes Test I: Systems of Linear Equations; Matrices Lesson. Give examples of
Linear Algebra Homework and Study Guide Phil R. Smith, Ph.D. February 28, 20 Homework Problem Sets Organized by Learning Outcomes Test I: Systems of Linear Equations; Matrices Lesson. Give examples of
Linear Algebra Highlights
 Linear Algebra Highlights Chapter 1 A linear equation in n variables is of the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n. We can have m equations in n variables, a system of linear equations, which we want to
Linear Algebra Highlights Chapter 1 A linear equation in n variables is of the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n. We can have m equations in n variables, a system of linear equations, which we want to
Vectors Summary. can slide along the line of action. not restricted, defined by magnitude & direction but can be anywhere.
 Vectors Summary A vector includes magnitude (size) and direction. Academic Skills Advice Types of vectors: Line vector: Free vector: Position vector: Unit vector (n ): can slide along the line of action.
Vectors Summary A vector includes magnitude (size) and direction. Academic Skills Advice Types of vectors: Line vector: Free vector: Position vector: Unit vector (n ): can slide along the line of action.
Chapter SSM: Linear Algebra. 5. Find all x such that A x = , so that x 1 = x 2 = 0.
 Chapter Find all x such that A x : Chapter, so that x x ker(a) { } Find all x such that A x ; note that all x in R satisfy the equation, so that ker(a) R span( e, e ) 5 Find all x such that A x 5 ; x x
Chapter Find all x such that A x : Chapter, so that x x ker(a) { } Find all x such that A x ; note that all x in R satisfy the equation, so that ker(a) R span( e, e ) 5 Find all x such that A x 5 ; x x
Math 1314 Week #14 Notes
 Math 3 Week # Notes Section 5.: A system of equations consists of two or more equations. A solution to a system of equations is a point that satisfies all the equations in the system. In this chapter,
Math 3 Week # Notes Section 5.: A system of equations consists of two or more equations. A solution to a system of equations is a point that satisfies all the equations in the system. In this chapter,
MTH Linear Algebra. Study Guide. Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education
 MTH 3 Linear Algebra Study Guide Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education June 3, ii Contents Table of Contents iii Matrix Algebra. Real Life
MTH 3 Linear Algebra Study Guide Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education June 3, ii Contents Table of Contents iii Matrix Algebra. Real Life
Math 416, Spring 2010 More on Algebraic and Geometric Properties January 21, 2010 MORE ON ALGEBRAIC AND GEOMETRIC PROPERTIES
 Math 46, Spring 2 More on Algebraic and Geometric Properties January 2, 2 MORE ON ALGEBRAIC AND GEOMETRIC PROPERTIES Algebraic properties Algebraic properties of matrix/vector multiplication Last time
Math 46, Spring 2 More on Algebraic and Geometric Properties January 2, 2 MORE ON ALGEBRAIC AND GEOMETRIC PROPERTIES Algebraic properties Algebraic properties of matrix/vector multiplication Last time
Math 217 Midterm 1. Winter Solutions. Question Points Score Total: 100
 Math 7 Midterm Winter 4 Solutions Name: Section: Question Points Score 8 5 3 4 5 5 6 8 7 6 8 8 Total: Math 7 Solutions Midterm, Page of 7. Write complete, precise definitions for each of the following
Math 7 Midterm Winter 4 Solutions Name: Section: Question Points Score 8 5 3 4 5 5 6 8 7 6 8 8 Total: Math 7 Solutions Midterm, Page of 7. Write complete, precise definitions for each of the following
Elementary matrices, continued. To summarize, we have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding
 Elementary matrices, continued To summarize, we have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. If you check the previous examples, you ll find that these matrices
Elementary matrices, continued To summarize, we have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. If you check the previous examples, you ll find that these matrices
BASIC NOTIONS. x + y = 1 3, 3x 5y + z = A + 3B,C + 2D, DC are not defined. A + C =
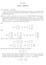 CHAPTER I BASIC NOTIONS (a) 8666 and 8833 (b) a =6,a =4 will work in the first case, but there are no possible such weightings to produce the second case, since Student and Student 3 have to end up with
CHAPTER I BASIC NOTIONS (a) 8666 and 8833 (b) a =6,a =4 will work in the first case, but there are no possible such weightings to produce the second case, since Student and Student 3 have to end up with
After we have found an eigenvalue λ of an n n matrix A, we have to find the vectors v in R n such that
 7.3 FINDING THE EIGENVECTORS OF A MATRIX After we have found an eigenvalue λ of an n n matrix A, we have to find the vectors v in R n such that A v = λ v or (λi n A) v = 0 In other words, we have to find
7.3 FINDING THE EIGENVECTORS OF A MATRIX After we have found an eigenvalue λ of an n n matrix A, we have to find the vectors v in R n such that A v = λ v or (λi n A) v = 0 In other words, we have to find
Question Total Score
 Math - Winter - Midterm Exam I Name: Student ID: Circle your section: Nick Haber James Zhao Henry Adams : AM : AM : AM : PM : PM : PM Ralph Furmaniak Jeremy Miller Ha Pham : AM : AM : AM : PM : PM : PM
Math - Winter - Midterm Exam I Name: Student ID: Circle your section: Nick Haber James Zhao Henry Adams : AM : AM : AM : PM : PM : PM Ralph Furmaniak Jeremy Miller Ha Pham : AM : AM : AM : PM : PM : PM
Example: 2x y + 3z = 1 5y 6z = 0 x + 4z = 7. Definition: Elementary Row Operations. Example: Type I swap rows 1 and 3
 Math 0 Row Reduced Echelon Form Techniques for solving systems of linear equations lie at the heart of linear algebra. In high school we learn to solve systems with or variables using elimination and substitution
Math 0 Row Reduced Echelon Form Techniques for solving systems of linear equations lie at the heart of linear algebra. In high school we learn to solve systems with or variables using elimination and substitution
Math 315: Linear Algebra Solutions to Assignment 7
 Math 5: Linear Algebra s to Assignment 7 # Find the eigenvalues of the following matrices. (a.) 4 0 0 0 (b.) 0 0 9 5 4. (a.) The characteristic polynomial det(λi A) = (λ )(λ )(λ ), so the eigenvalues are
Math 5: Linear Algebra s to Assignment 7 # Find the eigenvalues of the following matrices. (a.) 4 0 0 0 (b.) 0 0 9 5 4. (a.) The characteristic polynomial det(λi A) = (λ )(λ )(λ ), so the eigenvalues are
Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 4: Matrix Algebra Section 7. Inverse matrices
 Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 4: Matrix Algebra Section 7 Inverse matrices What you need to know already: How to add and multiply matrices. What elementary matrices are. What you can learn
Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 4: Matrix Algebra Section 7 Inverse matrices What you need to know already: How to add and multiply matrices. What elementary matrices are. What you can learn
We could express the left side as a sum of vectors and obtain the Vector Form of a Linear System: a 12 a x n. a m2
 Week 22 Equations, Matrices and Transformations Coefficient Matrix and Vector Forms of a Linear System Suppose we have a system of m linear equations in n unknowns a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + + a 1n x n b 1
Week 22 Equations, Matrices and Transformations Coefficient Matrix and Vector Forms of a Linear System Suppose we have a system of m linear equations in n unknowns a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + + a 1n x n b 1
Chapter 6 Page 1 of 10. Lecture Guide. Math College Algebra Chapter 6. to accompany. College Algebra by Julie Miller
 Chapter 6 Page 1 of 10 Lecture Guide Math 105 - College Algebra Chapter 6 to accompany College Algebra by Julie Miller Corresponding Lecture Videos can be found at Prepared by Stephen Toner & Nichole DuBal
Chapter 6 Page 1 of 10 Lecture Guide Math 105 - College Algebra Chapter 6 to accompany College Algebra by Julie Miller Corresponding Lecture Videos can be found at Prepared by Stephen Toner & Nichole DuBal
Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations
 What is a linear equation? Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations We are now going to discuss solving systems of two or more linear equations with two variables. Recall that solving an equation
What is a linear equation? Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations We are now going to discuss solving systems of two or more linear equations with two variables. Recall that solving an equation
Recall, we solved the system below in a previous section. Here, we learn another method. x + 4y = 14 5x + 3y = 2
 We will learn how to use a matrix to solve a system of equations. College algebra Class notes Matrices and Systems of Equations (section 6.) Recall, we solved the system below in a previous section. Here,
We will learn how to use a matrix to solve a system of equations. College algebra Class notes Matrices and Systems of Equations (section 6.) Recall, we solved the system below in a previous section. Here,
CS123 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER GRAPHICS. Linear Algebra 1/33
 Linear Algebra 1/33 Vectors A vector is a magnitude and a direction Magnitude = v Direction Also known as norm, length Represented by unit vectors (vectors with a length of 1 that point along distinct
Linear Algebra 1/33 Vectors A vector is a magnitude and a direction Magnitude = v Direction Also known as norm, length Represented by unit vectors (vectors with a length of 1 that point along distinct
Math 54 HW 4 solutions
 Math 54 HW 4 solutions 2.2. Section 2.2 (a) False: Recall that performing a series of elementary row operations A is equivalent to multiplying A by a series of elementary matrices. Suppose that E,...,
Math 54 HW 4 solutions 2.2. Section 2.2 (a) False: Recall that performing a series of elementary row operations A is equivalent to multiplying A by a series of elementary matrices. Suppose that E,...,
Example: 2x y + 3z = 1 5y 6z = 0 x + 4z = 7. Definition: Elementary Row Operations. Example: Type I swap rows 1 and 3
 Linear Algebra Row Reduced Echelon Form Techniques for solving systems of linear equations lie at the heart of linear algebra. In high school we learn to solve systems with or variables using elimination
Linear Algebra Row Reduced Echelon Form Techniques for solving systems of linear equations lie at the heart of linear algebra. In high school we learn to solve systems with or variables using elimination
2 Systems of Linear Equations
 2 Systems of Linear Equations A system of equations of the form or is called a system of linear equations. x + 2y = 7 2x y = 4 5p 6q + r = 4 2p + 3q 5r = 7 6p q + 4r = 2 Definition. An equation involving
2 Systems of Linear Equations A system of equations of the form or is called a system of linear equations. x + 2y = 7 2x y = 4 5p 6q + r = 4 2p + 3q 5r = 7 6p q + 4r = 2 Definition. An equation involving
LINEAR ALGEBRA KNOWLEDGE SURVEY
 LINEAR ALGEBRA KNOWLEDGE SURVEY Instructions: This is a Knowledge Survey. For this assignment, I am only interested in your level of confidence about your ability to do the tasks on the following pages.
LINEAR ALGEBRA KNOWLEDGE SURVEY Instructions: This is a Knowledge Survey. For this assignment, I am only interested in your level of confidence about your ability to do the tasks on the following pages.
22A-2 SUMMER 2014 LECTURE 5
 A- SUMMER 0 LECTURE 5 NATHANIEL GALLUP Agenda Elimination to the identity matrix Inverse matrices LU factorization Elimination to the identity matrix Previously, we have used elimination to get a system
A- SUMMER 0 LECTURE 5 NATHANIEL GALLUP Agenda Elimination to the identity matrix Inverse matrices LU factorization Elimination to the identity matrix Previously, we have used elimination to get a system
MATH240: Linear Algebra Review for exam #1 6/10/2015 Page 1
 MATH24: Linear Algebra Review for exam # 6//25 Page No review sheet can cover everything that is potentially fair game for an exam, but I tried to hit on all of the topics with these questions, as well
MATH24: Linear Algebra Review for exam # 6//25 Page No review sheet can cover everything that is potentially fair game for an exam, but I tried to hit on all of the topics with these questions, as well
Section 6.2 Larger Systems of Linear Equations
 Section 6.2 Larger Systems of Linear Equations Gaussian Elimination In general, to solve a system of linear equations using its augmented matrix, we use elementary row operations to arrive at a matrix
Section 6.2 Larger Systems of Linear Equations Gaussian Elimination In general, to solve a system of linear equations using its augmented matrix, we use elementary row operations to arrive at a matrix
Gauss-Jordan Row Reduction and Reduced Row Echelon Form
 Gauss-Jordan Row Reduction and Reduced Row Echelon Form If we put the augmented matrix of a linear system in reduced row-echelon form, then we don t need to back-substitute to solve the system. To put
Gauss-Jordan Row Reduction and Reduced Row Echelon Form If we put the augmented matrix of a linear system in reduced row-echelon form, then we don t need to back-substitute to solve the system. To put
2/27/2018 FIRST HOURLY PRACTICE 9 Math 21b, Spring Name:
 2/27/208 FIRST HOURLY PRACTICE 9 Math 2b, Spring 208 Name: MWF 9 Oliver Knill MWF 0 Jeremy Hahn MWF 0 Hunter Spink MWF Matt Demers MWF Yu-Wen Hsu MWF Ben Knudsen MWF Sander Kupers MWF 2 Hakim Walker TTH
2/27/208 FIRST HOURLY PRACTICE 9 Math 2b, Spring 208 Name: MWF 9 Oliver Knill MWF 0 Jeremy Hahn MWF 0 Hunter Spink MWF Matt Demers MWF Yu-Wen Hsu MWF Ben Knudsen MWF Sander Kupers MWF 2 Hakim Walker TTH
Handout 1 EXAMPLES OF SOLVING SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS
 22M:33 J. Simon page 1 of 7 22M:33 Summer 06 J. Simon Example 1. Handout 1 EXAMPLES OF SOLVING SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS 2x 1 + 3x 2 5x 3 = 10 3x 1 + 5x 2 + 6x 3 = 16 x 1 + 5x 2 x 3 = 10 Step 1. Write
22M:33 J. Simon page 1 of 7 22M:33 Summer 06 J. Simon Example 1. Handout 1 EXAMPLES OF SOLVING SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS 2x 1 + 3x 2 5x 3 = 10 3x 1 + 5x 2 + 6x 3 = 16 x 1 + 5x 2 x 3 = 10 Step 1. Write
Math 54 Homework 3 Solutions 9/
 Math 54 Homework 3 Solutions 9/4.8.8.2 0 0 3 3 0 0 3 6 2 9 3 0 0 3 0 0 3 a a/3 0 0 3 b b/3. c c/3 0 0 3.8.8 The number of rows of a matrix is the size (dimension) of the space it maps to; the number of
Math 54 Homework 3 Solutions 9/4.8.8.2 0 0 3 3 0 0 3 6 2 9 3 0 0 3 0 0 3 a a/3 0 0 3 b b/3. c c/3 0 0 3.8.8 The number of rows of a matrix is the size (dimension) of the space it maps to; the number of
Reduction to the associated homogeneous system via a particular solution
 June PURDUE UNIVERSITY Study Guide for the Credit Exam in (MA 5) Linear Algebra This study guide describes briefly the course materials to be covered in MA 5. In order to be qualified for the credit, one
June PURDUE UNIVERSITY Study Guide for the Credit Exam in (MA 5) Linear Algebra This study guide describes briefly the course materials to be covered in MA 5. In order to be qualified for the credit, one
a s 1.3 Matrix Multiplication. Know how to multiply two matrices and be able to write down the formula
 Syllabus for Math 308, Paul Smith Book: Kolman-Hill Chapter 1. Linear Equations and Matrices 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations Definition of a linear equation and a solution to a linear equations. Meaning
Syllabus for Math 308, Paul Smith Book: Kolman-Hill Chapter 1. Linear Equations and Matrices 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations Definition of a linear equation and a solution to a linear equations. Meaning
1. What is the determinant of the following matrix? a 1 a 2 4a 3 2a 2 b 1 b 2 4b 3 2b c 1. = 4, then det
 What is the determinant of the following matrix? 3 4 3 4 3 4 4 3 A 0 B 8 C 55 D 0 E 60 If det a a a 3 b b b 3 c c c 3 = 4, then det a a 4a 3 a b b 4b 3 b c c c 3 c = A 8 B 6 C 4 D E 3 Let A be an n n matrix
What is the determinant of the following matrix? 3 4 3 4 3 4 4 3 A 0 B 8 C 55 D 0 E 60 If det a a a 3 b b b 3 c c c 3 = 4, then det a a 4a 3 a b b 4b 3 b c c c 3 c = A 8 B 6 C 4 D E 3 Let A be an n n matrix
Math 415 Exam I. Name: Student ID: Calculators, books and notes are not allowed!
 Math 415 Exam I Calculators, books and notes are not allowed! Name: Student ID: Score: Math 415 Exam I (20pts) 1. Let A be a square matrix satisfying A 2 = 2A. Find the determinant of A. Sol. From A 2
Math 415 Exam I Calculators, books and notes are not allowed! Name: Student ID: Score: Math 415 Exam I (20pts) 1. Let A be a square matrix satisfying A 2 = 2A. Find the determinant of A. Sol. From A 2
Chapter 1: Linear Equations
 Chapter : Linear Equations (Last Updated: September, 6) The material for these notes is derived primarily from Linear Algebra and its applications by David Lay (4ed).. Systems of Linear Equations Before
Chapter : Linear Equations (Last Updated: September, 6) The material for these notes is derived primarily from Linear Algebra and its applications by David Lay (4ed).. Systems of Linear Equations Before
TBP MATH33A Review Sheet. November 24, 2018
 TBP MATH33A Review Sheet November 24, 2018 General Transformation Matrices: Function Scaling by k Orthogonal projection onto line L Implementation If we want to scale I 2 by k, we use the following: [
TBP MATH33A Review Sheet November 24, 2018 General Transformation Matrices: Function Scaling by k Orthogonal projection onto line L Implementation If we want to scale I 2 by k, we use the following: [
In this LAB you will explore the following topics using MATLAB. Investigate properties of the column space of a matrix.
 MATH 22AL Lab # 6 Objectives In this LAB you will explore the following topics using MATLAB. Investigate properties of the null space of a matrix. Learn how to find a basis for null-space of a matrix.
MATH 22AL Lab # 6 Objectives In this LAB you will explore the following topics using MATLAB. Investigate properties of the null space of a matrix. Learn how to find a basis for null-space of a matrix.
Elementary operation matrices: row addition
 Elementary operation matrices: row addition For t a, let A (n,t,a) be the n n matrix such that { A (n,t,a) 1 if r = c, or if r = t and c = a r,c = 0 otherwise A (n,t,a) = I + e t e T a Example: A (5,2,4)
Elementary operation matrices: row addition For t a, let A (n,t,a) be the n n matrix such that { A (n,t,a) 1 if r = c, or if r = t and c = a r,c = 0 otherwise A (n,t,a) = I + e t e T a Example: A (5,2,4)
