CSI 5163 (95.573) ALGORITHM ANALYSIS AND DESIGN
|
|
|
- Myrtle Reynolds
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CSI 5163 (95.573) ALGORITHM ANALYSIS AND DESIGN CSI 5163 ( ) ALGORITHM ANALYSIS AND DESIGN (3 cr.) (T) Topics of curret iterest i the desig ad aalysis of computer algorithms for graphtheoretical applicatios; e.g. shortest paths, chromatic umber, etc. Lower bouds, upper bouds, ad average performace of algorithms. Complexity theory. PROFESSOR: SITE 5-031, ext.:6782 zaguia@site.uottawa.ca Office Hours: Friday11:30-13:00 LECTURES: Thursday, 18:00-21:00, LMX 339 REFERENCES Textbook: Kleiberg ad Tardos, Algorithm Desig, Addiso Wesley, 7th editio. Itroductio to algorithms, T.H. Corme, C.E. Leiserso ad R. L. Rivest, McGraw-Hill Book Compay, The desig ad aalysis of computer algorithms, A.V.Aha, M.R.Garey ad J.D.Ullma, Addiso-Wesley Combiatorial Optimizatio: algorithms ad complexity, C.H. Papadimitriou ad K. Steiglitz, Pretice Hall CSI 5163 (95.573) ALGORITHM ANALYSIS AND DESIGN COURSE OBJECTIVES This is a course o the desig ad aalysis of algorithms. Core results ad techiques are itroduced, which are useful to those plaig to specialize i other areas i computer sciece. Moreover, some fairly advaced topics will be covered. This will provide a idea of the curret research for the beefit of those who might wish to specialize i this area. I the last few lectures we will study a umber of specific applicatios. COURSE OUTLINE Itroductio: Itroductio of the course, asymptotic otatios, basic data structure Basic Graph algorithms ad Basic algorithms desig (greedy, divide ad coquer, dyamic programmig, ) More Graph algorithms: Chromatic umber, Network flow,.. 2 CSI 5163 (95.573) ALGORITHM ANALYSIS AND DESIGN Markig scheme: Report o the topic ad Research paper : 30% Oral presetatio o the Research paper : 15% Participatio durig presetatios 5% 2 Midterm Exams i Class (February 13, march 13) 50% Geeral Iformatio A readig project is required to fulfill the class requiremets. A list of papers ad topics o algorithms will be posted by Jauary 20th. You must write a report of about 15 pages about your topic ad also explaiig the results of the research paper ad their proofs. You must read you paper i depth. Your report should ot just be a codesed versio of the origial paper, but should explai why the paper is iterestig ad preset the mai ideas i the way you uderstad it best, perhaps usig examples or special cases, or perhaps reworkig a proof. Or you might fill i missig details of the origial paper. You must give a talk of about miutes explaiig the most importat ad major poits i the research paper. 3 1
2 CSI 5163 (95.573) ALGORITHM ANALYSIS AND DESIGN Evaluatio of reports. Evaluatio will be based o the followig criterio: (for the purpose of markig these criterio will be cosidered approximately equally, except where oted.) Writig quality Relevace ad icorporatio of the ideas preseted durig the lectures of this course Depth of the aalysis ad uderstadig of the paper Evaluatio of presetatios. Presetatios will be evaluated based o the format ad quality of the presetatio (orgaizatio, quality of overheads, colors, graphics, speakig clearly, maagig the allotted time of the presetatio, ) It should ot be a repetitio of materials from the paper, lecture otes or textbooks. Importat: All writig reports should be retured o March 20th before the begiig of the lecture. A copy of your presetatios (hardcopy) should be retured at the begiig of your talk. Please sed me a soft copy of the reports ad the presetatios by . 4 Asymptotic Performace Asymptotic performace How does the algorithm behave as the problem size gets very large? Ruig time Memory/storage requiremets Badwidth/power requiremets/logic gates/etc. 5 Aalysis of Algorithms Computatioal model The assumptio: geeric uiprocessor radom-access machie (RAM) All memory equally expesive to access No cocurret operatios All reasoable istructios take uit time Except, of course, fuctio calls Costat word size Uless we are explicitly maipulatig bits 6 2
3 Iput Size Time ad space complexity This is geerally a fuctio of the iput size e.g., sortig, multiplicatio How we characterize iput size depeds: Sortig: umber of iput items Multiplicatio: total umber of bits Graph algorithms: umber of odes & edges etc Number of primitive steps that are executed Except for time of executig a fuctio call, most statemets roughly require the same amout of time 7 Aalysis Worst case Provides a upper boud o ruig time A absolute guaratee Average case Provides the expected ruig time Very useful, but treat with care: what is average? Radom (equally likely) iputs Real-life iputs 8 A Example: Isertio Sort IsertioSort(A, { for i = 2 to { key = A[i] j = i - 1; while (j > 0) ad (A[j] > key) { A[j+1] = A[j] j = j - 1 } A[j+1] = key } } 9 3
4 Isertio Sort IsertioSort(A, { for i = 2 to { -1 key = A[i] 1 j = i - 1; 1 while (j > 0) ad (A[j] > key) { i-1 A[j+1] = A[j] 1 j = j } 0 A[j+1] = key 1 } 0 Average case??? } Best case: while loop body ever executed is a liear fuctio = -1 Worst case: while loop body executed for all previous elemets = 2 i (2*(i-1)+1+1+1)= 2 i (2i+1)= 2( 2 i i) + (-1) = [(+1)/2] 1 + (-1) = [ ]/2 is a quadratic fuctio 10 Simplificatios Aalysis Igore actual ad abstract statemet costs Order of growth is the iterestig measure: Highest-order term is what couts Remember, we are doig asymptotic aalysis As the iput size grows larger it is the high order term that domiates A fuctio f( is O(g() if there exist positive costats c ad 0 such that f( c g( for all 0 11 Big O Fact We say Isertio Sort s ru time is O( 2 ) A polyomial of degree k is O( k ) Suppose f( = b k k + b k-1 k b 1 + b 0 Let a i = b i f( a k k + a k-1 k a 1 + a 0 k i ai k k a i c k 12 4
5 Lower Boud Notatio A fuctio f( is (g() if there exists c 0 ad 0 such that 0 cg( f( 0 A fuctio f( is (g() if there exists c 1 0, c 2 0, ad 0 0 such that c 1 g( f( c 2 g( 0 f( is (g() iff f( is both O(g() ad (g() 13 Practical Complexity 14 Practical Complexity 500 f( = f( = log( f( = log( f( = ^2 f( = ^3 f( = 2^
6 Practical Complexity 1000 f( = f( = log( f( = log( f( = ^2 f( = ^3 f( = 2^ Practical Complexity f( = f( = log( f( = log( f( = ^2 f( = ^3 f( = 2^ Practical Complexity Order of complexity miutes 5.2 miutes 13.0 miutes secod 17.9 miutes 12.7 days 35.7 years 366 ceturies miutes 6.5 years 3855 ceturies 2x10 8 ceturies 1.3x10 13 ceturies 18 6
7 Other Asymptotic Notatios A fuctio f( is o(g() if there exists positive costats c ad 0 such that f( < c g( 0 A fuctio f( is (g() if there exists positive costats c ad 0 such that c g( < f( 0 Ituitively, o() is like < O() is like () is like > () is like () is like = 19 Aalysis of Merge Sort Solvig recurreces MergeSort(A, left, right) { if (left < right) { mid = floor((left + right) / 2); MergeSort(A, left, mid); MergeSort(A, mid+1, right); Merge(A, left, mid, right); } } (1) (1) /2) /2) ( So = (1) whe = 1, ad 2/2) + ( whe > 1 20 Review: Solvig Recurreces The expressio: c T ( 2T c is a recurrece. There are basic techiques to solve recurrece relatios. Substitutio method Iteratio method Master method 21 7
8 Review: Solvig Recurreces The substitutio method : Guess the form of the aswer, the use iductio to fid the costats ad show that guessed solutio works Example: merge sort = 2/2) + c We guess that the aswer is O( lg Prove it by iductio Ca similarly show = Ω( lg, thus Θ( lg 22 Solvig Recurreces The Iteratio method 1. Expad the recurrece 2. Work some algebra to express as a summatio 3. Evaluate the summatio 23 Review: Solvig Recurreces s( = c + s(-1) = c + c + s(-2) = 2c + s(-2) = 2c + c + s(-3) = 3c + s(-3) = c + s(0) = c s( = c 0 s( c s( 1)
9 Review: Solvig Recurreces s( 0 0 s( = + s(-1) s( 1) 0 = s(-2) = (k-1) + s(-k) = s(0) 1 = i s(0) s( i Review: Solvig Recurreces = 2/2) + c c 2T c = 2(2/2/2) + c) + c = 2 2 /2 2 ) + 2c + c = 2 2 (2/2 2 /2) + c) + 3c = 2 3 /2 3 ) + 4c + 3c = 2 k /2 k ) + (2 k - 1)c = 2 lg /2 lg ) + (2 lg - 1)c = / + ( - 1)c = 1) + (-1)c = c + (-1)c = (2-1)c 26 Review: Solvig Recurreces What about this relatio: c at c b
10 Review: Solvig Recurreces = c 1 a/b) + c at c 1 a(a/b/b) + c/b) + c b a 2 /b 2 ) + c(a/b + 1) a 2 (a/b 2 /b) + c/b 2 ) + c(a/b + 1) a 3 /b 3 ) + c(a 2 /b 2 + a/b + 1) a k /b k ) + c(a k-1 /b k-1 + a k-2 /b k a 2 /b 2 +a/b +1) For k = log b, that is = b k = a k 1) + c(a k-1 /b k a 2 /b 2 + a/b + 1) = ca k /b k + c(a k-1 /b k a 2 /b 2 + a/b + 1) = c(a k /b k a 2 /b 2 + a/b + 1) 28 = c(a k /b k a 2 /b 2 + a/b + 1, (k=log b, =b k ) Recall that (x k + x k x + 1) = (x k+1-1)/(x-1) ad a log = log a k a b a b k a b 1 a b k k1 a a a k k1 b b b 1 If a = b the = c(k + 1) =c(log b + 1)=( log If a b the Review: Solvig Recurreces k1 a b a b k1 1 1 a b 1 1 If a b the a b1 1 a b = ( log a ) =c (a k / b k ) =c (a log / b log ) = c (a log / = c ( log a / = (c log a / = ( log a ) k a b 1 = c (1) = ( 1 29 Review: Solvig Recurreces So c at c b 1 1 log b log b a a b a b a b 30 10
11 The Master Theorem The Master Theorem is a very useful geeralizatio of the previous theorem: Cosider ay divide ad coquer algorithm Suppose the algorithm divides the problem of size ito a subproblems, each of size /b f( is the cost of subdividig the problem ito the subroblems plus the cost of combiig the solutios of subproblems = a/b) + f( 31 The Master Theorem if = a/b) + f( the logb a logb a log f ( f ( O f ( f ( logb a logb a af ( / b) cf ( for large 32 logb a AND 0 c 1 Usig The Master Method = 9/3) + a=9, b=3, f( = log b a = log 3 9 = ( 2 ) Need to compare f(= with log b a = ( 2 ), Sice f(= O( 2- ), where =1, case 1 applies: logb a logb a whe f ( O Thus the solutio is = ( 2 ) 33 11
12 Usig The Master Method = 3/4) + 1 ad 1)= (1) a=1, b=4/3, f( = 1 log b a = log 4/3 1 = ( 0 ) =1 Need to compare f(=1 with log b a =1, Sice f(= O( log b a ), case 2 applies: Thus the solutio is = (log 34 Usig The Master Method = 3/3) + log ad 1)= (1) a=3, b=3, f( = log log b a = log 3 3 = ( Need to compare f(= log with log b a = (, Sice log = (, case 3 is the best possibility. However there is o such that log = ( 1+ ). Thus the Master theorem caot be applied to this recurrece
Design and Analysis of ALGORITHM (Topic 2)
 DR. Gatot F. Hertoo, MSc. Desig ad Aalysis of ALGORITHM (Topic 2) Algorithms + Data Structures = Programs Lessos Leared 1 Our Machie Model: Assumptios Geeric Radom Access Machie (RAM) Executes operatios
DR. Gatot F. Hertoo, MSc. Desig ad Aalysis of ALGORITHM (Topic 2) Algorithms + Data Structures = Programs Lessos Leared 1 Our Machie Model: Assumptios Geeric Radom Access Machie (RAM) Executes operatios
Model of Computation and Runtime Analysis
 Model of Computatio ad Rutime Aalysis Model of Computatio Model of Computatio Specifies Set of operatios Cost of operatios (ot ecessarily time) Examples Turig Machie Radom Access Machie (RAM) PRAM Map
Model of Computatio ad Rutime Aalysis Model of Computatio Model of Computatio Specifies Set of operatios Cost of operatios (ot ecessarily time) Examples Turig Machie Radom Access Machie (RAM) PRAM Map
Model of Computation and Runtime Analysis
 Model of Computatio ad Rutime Aalysis Model of Computatio Model of Computatio Specifies Set of operatios Cost of operatios (ot ecessarily time) Examples Turig Machie Radom Access Machie (RAM) PRAM Map
Model of Computatio ad Rutime Aalysis Model of Computatio Model of Computatio Specifies Set of operatios Cost of operatios (ot ecessarily time) Examples Turig Machie Radom Access Machie (RAM) PRAM Map
COMP26120: Introducing Complexity Analysis (2018/19) Lucas Cordeiro
 COMP60: Itroduig Complexity Aalysis (08/9) Luas Cordeiro luas.ordeiro@mahester.a.uk Itroduig Complexity Aalysis Textbook: Algorithm Desig ad Appliatios, Goodrih, Mihael T. ad Roberto Tamassia (hapter )
COMP60: Itroduig Complexity Aalysis (08/9) Luas Cordeiro luas.ordeiro@mahester.a.uk Itroduig Complexity Aalysis Textbook: Algorithm Desig ad Appliatios, Goodrih, Mihael T. ad Roberto Tamassia (hapter )
Data Structures and Algorithm. Xiaoqing Zheng
 Data Structures ad Algorithm Xiaoqig Zheg zhegxq@fudaeduc What are algorithms? A sequece of computatioal steps that trasform the iput ito the output Sortig problem: Iput: A sequece of umbers
Data Structures ad Algorithm Xiaoqig Zheg zhegxq@fudaeduc What are algorithms? A sequece of computatioal steps that trasform the iput ito the output Sortig problem: Iput: A sequece of umbers
CS583 Lecture 02. Jana Kosecka. some materials here are based on E. Demaine, D. Luebke slides
 CS583 Lecture 02 Jaa Kosecka some materials here are based o E. Demaie, D. Luebke slides Previously Sample algorithms Exact ruig time, pseudo-code Approximate ruig time Worst case aalysis Best case aalysis
CS583 Lecture 02 Jaa Kosecka some materials here are based o E. Demaie, D. Luebke slides Previously Sample algorithms Exact ruig time, pseudo-code Approximate ruig time Worst case aalysis Best case aalysis
CS 270 Algorithms. Oliver Kullmann. Growth of Functions. Divide-and- Conquer Min-Max- Problem. Tutorial. Reading from CLRS for week 2
 Geeral remarks Week 2 1 Divide ad First we cosider a importat tool for the aalysis of algorithms: Big-Oh. The we itroduce a importat algorithmic paradigm:. We coclude by presetig ad aalysig two examples.
Geeral remarks Week 2 1 Divide ad First we cosider a importat tool for the aalysis of algorithms: Big-Oh. The we itroduce a importat algorithmic paradigm:. We coclude by presetig ad aalysig two examples.
This Lecture. Divide and Conquer. Merge Sort: Algorithm. Merge Sort Algorithm. MergeSort (Example) - 1. MergeSort (Example) - 2
 This Lecture Divide-ad-coquer techique for algorithm desig. Example the merge sort. Writig ad solvig recurreces Divide ad Coquer Divide-ad-coquer method for algorithm desig: Divide: If the iput size is
This Lecture Divide-ad-coquer techique for algorithm desig. Example the merge sort. Writig ad solvig recurreces Divide ad Coquer Divide-ad-coquer method for algorithm desig: Divide: If the iput size is
COMP26120: More on the Complexity of Recursive Programs (2018/19) Lucas Cordeiro
 COMP26120: More o the Complexity of Recursive Programs (2018/19) Lucas Cordeiro lucas.cordeiro@machester.ac.uk Divide-ad-Coquer (Recurrece) Textbook: Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, Goodrich, Michael T.
COMP26120: More o the Complexity of Recursive Programs (2018/19) Lucas Cordeiro lucas.cordeiro@machester.ac.uk Divide-ad-Coquer (Recurrece) Textbook: Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, Goodrich, Michael T.
Algorithms and Data Structures Lecture IV
 Algorithms ad Data Structures Lecture IV Simoas Šalteis Aalborg Uiversity simas@cs.auc.dk September 5, 00 1 This Lecture Aalyzig the ruig time of recursive algorithms (such as divide-ad-coquer) Writig
Algorithms ad Data Structures Lecture IV Simoas Šalteis Aalborg Uiversity simas@cs.auc.dk September 5, 00 1 This Lecture Aalyzig the ruig time of recursive algorithms (such as divide-ad-coquer) Writig
Ch3. Asymptotic Notation
 Ch. Asymptotic Notatio copyright 006 Preview of Chapters Chapter How to aalyze the space ad time complexities of program Chapter Review asymptotic otatios such as O, Ω, Θ, o for simplifyig the aalysis
Ch. Asymptotic Notatio copyright 006 Preview of Chapters Chapter How to aalyze the space ad time complexities of program Chapter Review asymptotic otatios such as O, Ω, Θ, o for simplifyig the aalysis
Analysis of Algorithms. Introduction. Contents
 Itroductio The focus of this module is mathematical aspects of algorithms. Our mai focus is aalysis of algorithms, which meas evaluatig efficiecy of algorithms by aalytical ad mathematical methods. We
Itroductio The focus of this module is mathematical aspects of algorithms. Our mai focus is aalysis of algorithms, which meas evaluatig efficiecy of algorithms by aalytical ad mathematical methods. We
Examples: data compression, path-finding, game-playing, scheduling, bin packing
 Algorithms - Basic Cocepts Algorithms so what is a algorithm, ayway? The dictioary defiitio: A algorithm is a well-defied computatioal procedure that takes iput ad produces output. This class will deal
Algorithms - Basic Cocepts Algorithms so what is a algorithm, ayway? The dictioary defiitio: A algorithm is a well-defied computatioal procedure that takes iput ad produces output. This class will deal
CS161 Design and Analysis of Algorithms. Administrative
 CS161 Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms Da Boeh 1 Admiistrative Lecture 1, April 3, 1 Web page http://theory.staford.edu/~dabo/cs161» Hadouts» Aoucemets» Late breakig ews Gradig ad course requiremets» Midterm/fial/hw»
CS161 Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms Da Boeh 1 Admiistrative Lecture 1, April 3, 1 Web page http://theory.staford.edu/~dabo/cs161» Hadouts» Aoucemets» Late breakig ews Gradig ad course requiremets» Midterm/fial/hw»
Algorithm Analysis. Chapter 3
 Data Structures Dr Ahmed Rafat Abas Computer Sciece Dept, Faculty of Computer ad Iformatio, Zagazig Uiversity arabas@zu.edu.eg http://www.arsaliem.faculty.zu.edu.eg/ Algorithm Aalysis Chapter 3 3. Itroductio
Data Structures Dr Ahmed Rafat Abas Computer Sciece Dept, Faculty of Computer ad Iformatio, Zagazig Uiversity arabas@zu.edu.eg http://www.arsaliem.faculty.zu.edu.eg/ Algorithm Aalysis Chapter 3 3. Itroductio
Classification of problem & problem solving strategies. classification of time complexities (linear, logarithmic etc)
 Classificatio of problem & problem solvig strategies classificatio of time complexities (liear, arithmic etc) Problem subdivisio Divide ad Coquer strategy. Asymptotic otatios, lower boud ad upper boud:
Classificatio of problem & problem solvig strategies classificatio of time complexities (liear, arithmic etc) Problem subdivisio Divide ad Coquer strategy. Asymptotic otatios, lower boud ad upper boud:
CS 332: Algorithms. Linear-Time Sorting. Order statistics. Slide credit: David Luebke (Virginia)
 1 CS 332: Algorithms Liear-Time Sortig. Order statistics. Slide credit: David Luebke (Virgiia) Quicksort: Partitio I Words Partitio(A, p, r): Select a elemet to act as the pivot (which?) Grow two regios,
1 CS 332: Algorithms Liear-Time Sortig. Order statistics. Slide credit: David Luebke (Virgiia) Quicksort: Partitio I Words Partitio(A, p, r): Select a elemet to act as the pivot (which?) Grow two regios,
Chapter 22 Developing Efficient Algorithms
 Chapter Developig Efficiet Algorithms 1 Executig Time Suppose two algorithms perform the same task such as search (liear search vs. biary search). Which oe is better? Oe possible approach to aswer this
Chapter Developig Efficiet Algorithms 1 Executig Time Suppose two algorithms perform the same task such as search (liear search vs. biary search). Which oe is better? Oe possible approach to aswer this
Test One (Answer Key)
 CS395/Ma395 (Sprig 2005) Test Oe Name: Page 1 Test Oe (Aswer Key) CS395/Ma395: Aalysis of Algorithms This is a closed book, closed otes, 70 miute examiatio. It is worth 100 poits. There are twelve (12)
CS395/Ma395 (Sprig 2005) Test Oe Name: Page 1 Test Oe (Aswer Key) CS395/Ma395: Aalysis of Algorithms This is a closed book, closed otes, 70 miute examiatio. It is worth 100 poits. There are twelve (12)
Advanced Course of Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Differet complexity measures Advaced Course of Algorithm Desig ad Aalysis Asymptotic complexity Big-Oh otatio Properties of O otatio Aalysis of simple algorithms A algorithm may may have differet executio
Differet complexity measures Advaced Course of Algorithm Desig ad Aalysis Asymptotic complexity Big-Oh otatio Properties of O otatio Aalysis of simple algorithms A algorithm may may have differet executio
Sorting Algorithms. Algorithms Kyuseok Shim SoEECS, SNU.
 Sortig Algorithms Algorithms Kyuseo Shim SoEECS, SNU. Desigig Algorithms Icremetal approaches Divide-ad-Coquer approaches Dyamic programmig approaches Greedy approaches Radomized approaches You are ot
Sortig Algorithms Algorithms Kyuseo Shim SoEECS, SNU. Desigig Algorithms Icremetal approaches Divide-ad-Coquer approaches Dyamic programmig approaches Greedy approaches Radomized approaches You are ot
Recursive Algorithms. Recurrences. Recursive Algorithms Analysis
 Recursive Algorithms Recurreces Computer Sciece & Egieerig 35: Discrete Mathematics Christopher M Bourke cbourke@cseuledu A recursive algorithm is oe i which objects are defied i terms of other objects
Recursive Algorithms Recurreces Computer Sciece & Egieerig 35: Discrete Mathematics Christopher M Bourke cbourke@cseuledu A recursive algorithm is oe i which objects are defied i terms of other objects
Fundamental Algorithms
 Fudametal Algorithms Chapter 2b: Recurreces Michael Bader Witer 2014/15 Chapter 2b: Recurreces, Witer 2014/15 1 Recurreces Defiitio A recurrece is a (i-equality that defies (or characterizes a fuctio i
Fudametal Algorithms Chapter 2b: Recurreces Michael Bader Witer 2014/15 Chapter 2b: Recurreces, Witer 2014/15 1 Recurreces Defiitio A recurrece is a (i-equality that defies (or characterizes a fuctio i
Hand Out: Analysis of Algorithms. September 8, Bud Mishra. In general, there can be several algorithms to solve a problem; and one is faced
 Had Out Aalysis of Algorithms September 8, 998 Bud Mishra c Mishra, February 9, 986 Itroductio I geeral, there ca be several algorithms to solve a problem; ad oe is faced with the problem of choosig a
Had Out Aalysis of Algorithms September 8, 998 Bud Mishra c Mishra, February 9, 986 Itroductio I geeral, there ca be several algorithms to solve a problem; ad oe is faced with the problem of choosig a
CIS 121 Data Structures and Algorithms with Java Spring Code Snippets and Recurrences Monday, February 4/Tuesday, February 5
 CIS 11 Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 019 Code Sippets ad Recurreces Moday, February 4/Tuesday, February 5 Learig Goals Practice provig asymptotic bouds with code sippets Practice solvig
CIS 11 Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 019 Code Sippets ad Recurreces Moday, February 4/Tuesday, February 5 Learig Goals Practice provig asymptotic bouds with code sippets Practice solvig
CSE 4095/5095 Topics in Big Data Analytics Spring 2017; Homework 1 Solutions
 CSE 09/09 Topics i ig Data Aalytics Sprig 2017; Homework 1 Solutios Note: Solutios to problems,, ad 6 are due to Marius Nicolae. 1. Cosider the followig algorithm: for i := 1 to α log e do Pick a radom
CSE 09/09 Topics i ig Data Aalytics Sprig 2017; Homework 1 Solutios Note: Solutios to problems,, ad 6 are due to Marius Nicolae. 1. Cosider the followig algorithm: for i := 1 to α log e do Pick a radom
Data Structures Lecture 9
 Fall 2017 Fag Yu Software Security Lab. Dept. Maagemet Iformatio Systems, Natioal Chegchi Uiversity Data Structures Lecture 9 Midterm o Dec. 7 (9:10-12:00am, 106) Lec 1-9, TextBook Ch1-8, 11,12 How to
Fall 2017 Fag Yu Software Security Lab. Dept. Maagemet Iformatio Systems, Natioal Chegchi Uiversity Data Structures Lecture 9 Midterm o Dec. 7 (9:10-12:00am, 106) Lec 1-9, TextBook Ch1-8, 11,12 How to
4.3 Growth Rates of Solutions to Recurrences
 4.3. GROWTH RATES OF SOLUTIONS TO RECURRENCES 81 4.3 Growth Rates of Solutios to Recurreces 4.3.1 Divide ad Coquer Algorithms Oe of the most basic ad powerful algorithmic techiques is divide ad coquer.
4.3. GROWTH RATES OF SOLUTIONS TO RECURRENCES 81 4.3 Growth Rates of Solutios to Recurreces 4.3.1 Divide ad Coquer Algorithms Oe of the most basic ad powerful algorithmic techiques is divide ad coquer.
Lecture 3: Asymptotic Analysis + Recurrences
 Lecture 3: Asymptotic Aalysis + Recurreces Data Structures ad Algorithms CSE 373 SU 18 BEN JONES 1 Warmup Write a model ad fid Big-O for (it i = 0; i < ; i++) { for (it j = 0; j < i; j++) { System.out.pritl(
Lecture 3: Asymptotic Aalysis + Recurreces Data Structures ad Algorithms CSE 373 SU 18 BEN JONES 1 Warmup Write a model ad fid Big-O for (it i = 0; i < ; i++) { for (it j = 0; j < i; j++) { System.out.pritl(
ITEC 360 Data Structures and Analysis of Algorithms Spring for n 1
 ITEC 360 Data Structures ad Aalysis of Algorithms Sprig 006 1. Prove that f () = 60 + 5 + 1 is Θ ( ). 60 + 5 + 1 60 + 5 + = 66 for 1 Take C 1 = 66 f () = 60 + 5 + 1 is O( ) Sice 60 + 5 + 1 60 for 1 If
ITEC 360 Data Structures ad Aalysis of Algorithms Sprig 006 1. Prove that f () = 60 + 5 + 1 is Θ ( ). 60 + 5 + 1 60 + 5 + = 66 for 1 Take C 1 = 66 f () = 60 + 5 + 1 is O( ) Sice 60 + 5 + 1 60 for 1 If
Recurrence Relations
 Recurrece Relatios Aalysis of recursive algorithms, such as: it factorial (it ) { if (==0) retur ; else retur ( * factorial(-)); } Let t be the umber of multiplicatios eeded to calculate factorial(). The
Recurrece Relatios Aalysis of recursive algorithms, such as: it factorial (it ) { if (==0) retur ; else retur ( * factorial(-)); } Let t be the umber of multiplicatios eeded to calculate factorial(). The
Algorithms 演算法. Multi-threaded Algorithms
 演算法 Multi-threaded Professor Chie-Mo James Li 李建模 Graduate Istitute of Electroics Egieerig Natioal aiwa Uiversity Outlie Multithreaded, CH7 7. Basics 7. Matrix Multiplicatio 7.3 Merge sort Leoardo Fiboacci
演算法 Multi-threaded Professor Chie-Mo James Li 李建模 Graduate Istitute of Electroics Egieerig Natioal aiwa Uiversity Outlie Multithreaded, CH7 7. Basics 7. Matrix Multiplicatio 7.3 Merge sort Leoardo Fiboacci
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms CSE 53 Lecture 9 Media ad Order Statistics Juzhou Huag, Ph.D. Departmet of Computer Sciece ad Egieerig Dept. CSE, UT Arligto CSE53 Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms Medias ad
Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms CSE 53 Lecture 9 Media ad Order Statistics Juzhou Huag, Ph.D. Departmet of Computer Sciece ad Egieerig Dept. CSE, UT Arligto CSE53 Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms Medias ad
COMP285 Midterm Exam Department of Mathematics
 COMP85 Midterm Exam Departmet of Mathematics Fall 010/011 - November 8, 010 Name: Studet Number: Please fiish withi 90 miutes. All poits above 100 are cosidered as bous poit. You ca reach maximal 1 poits.
COMP85 Midterm Exam Departmet of Mathematics Fall 010/011 - November 8, 010 Name: Studet Number: Please fiish withi 90 miutes. All poits above 100 are cosidered as bous poit. You ca reach maximal 1 poits.
Matriculation number: You have 90 minutes to complete the exam of InformatikIIb. The following rules apply:
 Departmet of Iformatics Prof. Dr. Michael Böhle Bizmühlestrasse 14 8050 Zurich Phoe: +41 44 635 4333 Email: boehle@ifi.uzh.ch AlgoDat Midterm1 Sprig 016 08.04.016 Name: Matriculatio umber: Advice You have
Departmet of Iformatics Prof. Dr. Michael Böhle Bizmühlestrasse 14 8050 Zurich Phoe: +41 44 635 4333 Email: boehle@ifi.uzh.ch AlgoDat Midterm1 Sprig 016 08.04.016 Name: Matriculatio umber: Advice You have
Mathematical Foundation. CSE 6331 Algorithms Steve Lai
 Mathematical Foudatio CSE 6331 Algorithms Steve Lai Complexity of Algorithms Aalysis of algorithm: to predict the ruig time required by a algorithm. Elemetary operatios: arithmetic & boolea operatios:
Mathematical Foudatio CSE 6331 Algorithms Steve Lai Complexity of Algorithms Aalysis of algorithm: to predict the ruig time required by a algorithm. Elemetary operatios: arithmetic & boolea operatios:
Analysis of Algorithms -Quicksort-
 Aalysis of Algorithms -- Adreas Ermedahl MRTC (Mälardales Real-Time Research Ceter) adreas.ermedahl@mdh.se Autum 2004 Proposed by C.A.R. Hoare i 962 Worst- case ruig time: Θ( 2 ) Expected ruig time: Θ(
Aalysis of Algorithms -- Adreas Ermedahl MRTC (Mälardales Real-Time Research Ceter) adreas.ermedahl@mdh.se Autum 2004 Proposed by C.A.R. Hoare i 962 Worst- case ruig time: Θ( 2 ) Expected ruig time: Θ(
CS161: Algorithm Design and Analysis Handout #10 Stanford University Wednesday, 10 February 2016
 CS161: Algorithm Desig ad Aalysis Hadout #10 Staford Uiversity Wedesday, 10 February 2016 Lecture #11: Wedesday, 10 February 2016 Topics: Example midterm problems ad solutios from a log time ago Sprig
CS161: Algorithm Desig ad Aalysis Hadout #10 Staford Uiversity Wedesday, 10 February 2016 Lecture #11: Wedesday, 10 February 2016 Topics: Example midterm problems ad solutios from a log time ago Sprig
A recurrence equation is just a recursive function definition. It defines a function at one input in terms of its value on smaller inputs.
 CS23 Algorithms Hadout #6 Prof Ly Turbak September 8, 200 Wellesley College RECURRENCES This hadout summarizes highlights of CLRS Chapter 4 ad Appedix A (CLR Chapters 3 & 4) Two-Step Strategy for Aalyzig
CS23 Algorithms Hadout #6 Prof Ly Turbak September 8, 200 Wellesley College RECURRENCES This hadout summarizes highlights of CLRS Chapter 4 ad Appedix A (CLR Chapters 3 & 4) Two-Step Strategy for Aalyzig
CSI 2101 Discrete Structures Winter Homework Assignment #4 (100 points, weight 5%) Due: Thursday, April 5, at 1:00pm (in lecture)
 CSI 101 Discrete Structures Witer 01 Prof. Lucia Moura Uiversity of Ottawa Homework Assigmet #4 (100 poits, weight %) Due: Thursday, April, at 1:00pm (i lecture) Program verificatio, Recurrece Relatios
CSI 101 Discrete Structures Witer 01 Prof. Lucia Moura Uiversity of Ottawa Homework Assigmet #4 (100 poits, weight %) Due: Thursday, April, at 1:00pm (i lecture) Program verificatio, Recurrece Relatios
Algorithm Analysis. Algorithms that are equally correct can vary in their utilization of computational resources
 Algorithm Aalysis Algorithms that are equally correct ca vary i their utilizatio of computatioal resources time ad memory a slow program it is likely ot to be used a program that demads too much memory
Algorithm Aalysis Algorithms that are equally correct ca vary i their utilizatio of computatioal resources time ad memory a slow program it is likely ot to be used a program that demads too much memory
Chapter 6. Advanced Counting Techniques
 Chapter 6 Advaced Coutig Techiques 6.: Recurrece Relatios Defiitio: A recurrece relatio for the sequece {a } is a equatio expressig a i terms of oe or more of the previous terms of the sequece: a,a2,a3,,a
Chapter 6 Advaced Coutig Techiques 6.: Recurrece Relatios Defiitio: A recurrece relatio for the sequece {a } is a equatio expressig a i terms of oe or more of the previous terms of the sequece: a,a2,a3,,a
CS:3330 (Prof. Pemmaraju ): Assignment #1 Solutions. (b) For n = 3, we will have 3 men and 3 women with preferences as follows: m 1 : w 3 > w 1 > w 2
 Shiyao Wag CS:3330 (Prof. Pemmaraju ): Assigmet #1 Solutios Problem 1 (a) Cosider iput with me m 1, m,..., m ad wome w 1, w,..., w with the followig prefereces: All me have the same prefereces for wome:
Shiyao Wag CS:3330 (Prof. Pemmaraju ): Assigmet #1 Solutios Problem 1 (a) Cosider iput with me m 1, m,..., m ad wome w 1, w,..., w with the followig prefereces: All me have the same prefereces for wome:
Algorithms Design & Analysis. Divide & Conquer
 Algorithms Desig & Aalysis Divide & Coquer Recap Direct-accessible table Hash tables Hash fuctios Uiversal hashig Perfect Hashig Ope addressig 2 Today s topics The divide-ad-coquer desig paradigm Revised
Algorithms Desig & Aalysis Divide & Coquer Recap Direct-accessible table Hash tables Hash fuctios Uiversal hashig Perfect Hashig Ope addressig 2 Today s topics The divide-ad-coquer desig paradigm Revised
Divide & Conquer. Divide-and-conquer algorithms. Conventional product of polynomials. Conventional product of polynomials.
 Divide-ad-coquer algorithms Divide & Coquer Strategy: Divide the problem ito smaller subproblems of the same type of problem Solve the subproblems recursively Combie the aswers to solve the origial problem
Divide-ad-coquer algorithms Divide & Coquer Strategy: Divide the problem ito smaller subproblems of the same type of problem Solve the subproblems recursively Combie the aswers to solve the origial problem
OPTIMAL ALGORITHMS -- SUPPLEMENTAL NOTES
 OPTIMAL ALGORITHMS -- SUPPLEMENTAL NOTES Peter M. Maurer Why Hashig is θ(). As i biary search, hashig assumes that keys are stored i a array which is idexed by a iteger. However, hashig attempts to bypass
OPTIMAL ALGORITHMS -- SUPPLEMENTAL NOTES Peter M. Maurer Why Hashig is θ(). As i biary search, hashig assumes that keys are stored i a array which is idexed by a iteger. However, hashig attempts to bypass
Introduction to Algorithms 6.046J/18.401J LECTURE 3 Divide and conquer Binary search Powering a number Fibonacci numbers Matrix multiplication
 Itroductio to Algorithms 6.046J/8.40J LECTURE 3 Divide ad coquer Biary search Powerig a umber Fiboacci umbers Matrix multiplicatio Strasse s algorithm VLSI tree layout Prof. Charles E. Leiserso The divide-ad-coquer
Itroductio to Algorithms 6.046J/8.40J LECTURE 3 Divide ad coquer Biary search Powerig a umber Fiboacci umbers Matrix multiplicatio Strasse s algorithm VLSI tree layout Prof. Charles E. Leiserso The divide-ad-coquer
CSE Introduction to Parallel Processing. Chapter 3. Parallel Algorithm Complexity
 Dr. Izadi CSE-40533 Itroductio to Parallel Processig Chapter 3 Parallel Algorithm Complexity Review algorithm complexity ad various complexity classes Itroduce the otios of time ad time-cost optimality
Dr. Izadi CSE-40533 Itroductio to Parallel Processig Chapter 3 Parallel Algorithm Complexity Review algorithm complexity ad various complexity classes Itroduce the otios of time ad time-cost optimality
CS 332: Algorithms. Quicksort
 CS 33: Aorithms Quicsort David Luebe //03 Homewor Assiged today, due ext Wedesday Will be o web page shortly after class Go over ow David Luebe //03 Review: Quicsort Sorts i place Sorts O( ) i the average
CS 33: Aorithms Quicsort David Luebe //03 Homewor Assiged today, due ext Wedesday Will be o web page shortly after class Go over ow David Luebe //03 Review: Quicsort Sorts i place Sorts O( ) i the average
CSE 5311 Notes 1: Mathematical Preliminaries
 Chapter 1 - Algorithms Computig CSE 5311 Notes 1: Mathematical Prelimiaries Last updated 1/20/18 12:56 PM) Relatioship betwee complexity classes, eg log,, log, 2, 2, etc Chapter 2 - Gettig Started Loop
Chapter 1 - Algorithms Computig CSE 5311 Notes 1: Mathematical Prelimiaries Last updated 1/20/18 12:56 PM) Relatioship betwee complexity classes, eg log,, log, 2, 2, etc Chapter 2 - Gettig Started Loop
2. ALGORITHM ANALYSIS
 2. ALGORITHM ANALYSIS computatioal tractability survey of commo ruig times 2. ALGORITHM ANALYSIS computatioal tractability survey of commo ruig times Lecture slides by Kevi Waye Copyright 2005 Pearso-Addiso
2. ALGORITHM ANALYSIS computatioal tractability survey of commo ruig times 2. ALGORITHM ANALYSIS computatioal tractability survey of commo ruig times Lecture slides by Kevi Waye Copyright 2005 Pearso-Addiso
A New Solution Method for the Finite-Horizon Discrete-Time EOQ Problem
 This is the Pre-Published Versio. A New Solutio Method for the Fiite-Horizo Discrete-Time EOQ Problem Chug-Lu Li Departmet of Logistics The Hog Kog Polytechic Uiversity Hug Hom, Kowloo, Hog Kog Phoe: +852-2766-7410
This is the Pre-Published Versio. A New Solutio Method for the Fiite-Horizo Discrete-Time EOQ Problem Chug-Lu Li Departmet of Logistics The Hog Kog Polytechic Uiversity Hug Hom, Kowloo, Hog Kog Phoe: +852-2766-7410
Sequences, Mathematical Induction, and Recursion. CSE 2353 Discrete Computational Structures Spring 2018
 CSE 353 Discrete Computatioal Structures Sprig 08 Sequeces, Mathematical Iductio, ad Recursio (Chapter 5, Epp) Note: some course slides adopted from publisher-provided material Overview May mathematical
CSE 353 Discrete Computatioal Structures Sprig 08 Sequeces, Mathematical Iductio, ad Recursio (Chapter 5, Epp) Note: some course slides adopted from publisher-provided material Overview May mathematical
Mathematics review for CSCI 303 Spring Department of Computer Science College of William & Mary Robert Michael Lewis
 Mathematics review for CSCI 303 Sprig 019 Departmet of Computer Sciece College of William & Mary Robert Michael Lewis Copyright 018 019 Robert Michael Lewis Versio geerated: 13 : 00 Jauary 17, 019 Cotets
Mathematics review for CSCI 303 Sprig 019 Departmet of Computer Sciece College of William & Mary Robert Michael Lewis Copyright 018 019 Robert Michael Lewis Versio geerated: 13 : 00 Jauary 17, 019 Cotets
Lecture 9: Hierarchy Theorems
 IAS/PCMI Summer Sessio 2000 Clay Mathematics Udergraduate Program Basic Course o Computatioal Complexity Lecture 9: Hierarchy Theorems David Mix Barrigto ad Alexis Maciel July 27, 2000 Most of this lecture
IAS/PCMI Summer Sessio 2000 Clay Mathematics Udergraduate Program Basic Course o Computatioal Complexity Lecture 9: Hierarchy Theorems David Mix Barrigto ad Alexis Maciel July 27, 2000 Most of this lecture
CS / MCS 401 Homework 3 grader solutions
 CS / MCS 401 Homework 3 grader solutios assigmet due July 6, 016 writte by Jāis Lazovskis maximum poits: 33 Some questios from CLRS. Questios marked with a asterisk were ot graded. 1 Use the defiitio of
CS / MCS 401 Homework 3 grader solutios assigmet due July 6, 016 writte by Jāis Lazovskis maximum poits: 33 Some questios from CLRS. Questios marked with a asterisk were ot graded. 1 Use the defiitio of
The Growth of Functions. Theoretical Supplement
 The Growth of Fuctios Theoretical Supplemet The Triagle Iequality The triagle iequality is a algebraic tool that is ofte useful i maipulatig absolute values of fuctios. The triagle iequality says that
The Growth of Fuctios Theoretical Supplemet The Triagle Iequality The triagle iequality is a algebraic tool that is ofte useful i maipulatig absolute values of fuctios. The triagle iequality says that
Skip Lists. Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 S 3 S S 1
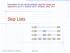 Presetatio for use with the textbook, Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Skip Lists S 3 15 15 23 10 15 23 36 Skip Lists 1 What is a Skip List A skip list for
Presetatio for use with the textbook, Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Skip Lists S 3 15 15 23 10 15 23 36 Skip Lists 1 What is a Skip List A skip list for
Intensive Algorithms Lecture 11. DFT and DP. Lecturer: Daniel A. Spielman February 20, f(n) O(g(n) log c g(n)).
 Itesive Algorithms Lecture 11 DFT ad DP Lecturer: Daiel A. Spielma February 20, 2018 11.1 Itroductio The purpose of this lecture is to lear how use the Discrete Fourier Trasform to save space i Dyamic
Itesive Algorithms Lecture 11 DFT ad DP Lecturer: Daiel A. Spielma February 20, 2018 11.1 Itroductio The purpose of this lecture is to lear how use the Discrete Fourier Trasform to save space i Dyamic
Some special clique problems
 Some special clique problems Reate Witer Istitut für Iformatik Marti-Luther-Uiversität Halle-Witteberg Vo-Seckedorff-Platz, D 0620 Halle Saale Germay Abstract: We cosider graphs with cliques of size k
Some special clique problems Reate Witer Istitut für Iformatik Marti-Luther-Uiversität Halle-Witteberg Vo-Seckedorff-Platz, D 0620 Halle Saale Germay Abstract: We cosider graphs with cliques of size k
Department of Informatics Prof. Dr. Michael Böhlen Binzmühlestrasse Zurich Phone:
 Departmet of Iformatics Prof. Dr. Michael Böhle Bizmühlestrasse 14 8050 Zurich Phoe: +41 44 635 4333 Email: boehle@ifi.uzh.ch Iformatik II Midterm1 Sprig 018 3.03.018 Advice You have 90 miutes to complete
Departmet of Iformatics Prof. Dr. Michael Böhle Bizmühlestrasse 14 8050 Zurich Phoe: +41 44 635 4333 Email: boehle@ifi.uzh.ch Iformatik II Midterm1 Sprig 018 3.03.018 Advice You have 90 miutes to complete
A New Method to Order Functions by Asymptotic Growth Rates Charlie Obimbo Dept. of Computing and Information Science University of Guelph
 A New Method to Order Fuctios by Asymptotic Growth Rates Charlie Obimbo Dept. of Computig ad Iformatio Sciece Uiversity of Guelph ABSTRACT A ew method is described to determie the complexity classes of
A New Method to Order Fuctios by Asymptotic Growth Rates Charlie Obimbo Dept. of Computig ad Iformatio Sciece Uiversity of Guelph ABSTRACT A ew method is described to determie the complexity classes of
CSE 202 Homework 1 Matthias Springer, A Yes, there does always exist a perfect matching without a strong instability.
 CSE 0 Homework 1 Matthias Spriger, A9950078 1 Problem 1 Notatio a b meas that a is matched to b. a < b c meas that b likes c more tha a. Equality idicates a tie. Strog istability Yes, there does always
CSE 0 Homework 1 Matthias Spriger, A9950078 1 Problem 1 Notatio a b meas that a is matched to b. a < b c meas that b likes c more tha a. Equality idicates a tie. Strog istability Yes, there does always
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures ad Algorithms Autum 2017-2018 Outlie 1 Sortig Algorithms (cotd) Outlie Sortig Algorithms (cotd) 1 Sortig Algorithms (cotd) Heapsort Sortig Algorithms (cotd) Have see that we ca build a
Data Structures ad Algorithms Autum 2017-2018 Outlie 1 Sortig Algorithms (cotd) Outlie Sortig Algorithms (cotd) 1 Sortig Algorithms (cotd) Heapsort Sortig Algorithms (cotd) Have see that we ca build a
CS 253: Algorithms. Syllabus. Chapter 1. Appendix A
 CS 5: Algorithms Syllabus Chapter Appedi A Syllabus Istructor : Firet Ercal - Office: CS 4 Phoe: 4-4857 E-mail & URL : ercal@mst.edu http://web.mst.edu/~ercal/ide.html Meetig Times : :50 pm. M W F Office
CS 5: Algorithms Syllabus Chapter Appedi A Syllabus Istructor : Firet Ercal - Office: CS 4 Phoe: 4-4857 E-mail & URL : ercal@mst.edu http://web.mst.edu/~ercal/ide.html Meetig Times : :50 pm. M W F Office
Amortized Analysis - Part 2 - Dynamic Tables. Objective: In this lecture, we shall explore Dynamic tables and its amortized analysis in detail.
 Idia Istitute of Iformatio Techology Desig ad Maufacturig, Kacheepuram Cheai 600 17, Idia A Autoomous Istitute uder MHRD, Govt of Idia http://www.iiitdm.ac.i COM 501 Advaced Data Structures ad Algorithms
Idia Istitute of Iformatio Techology Desig ad Maufacturig, Kacheepuram Cheai 600 17, Idia A Autoomous Istitute uder MHRD, Govt of Idia http://www.iiitdm.ac.i COM 501 Advaced Data Structures ad Algorithms
Divide and Conquer. 1 Overview. 2 Multiplying Bit Strings. COMPSCI 330: Design and Analysis of Algorithms 1/19/2016 and 1/21/2016
 COMPSCI 330: Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms 1/19/2016 ad 1/21/2016 Lecturer: Debmalya Paigrahi Divide ad Coquer Scribe: Tiaqi Sog 1 Overview I this lecture, a importat algorithm desig techique called divide-ad-coquer
COMPSCI 330: Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms 1/19/2016 ad 1/21/2016 Lecturer: Debmalya Paigrahi Divide ad Coquer Scribe: Tiaqi Sog 1 Overview I this lecture, a importat algorithm desig techique called divide-ad-coquer
Polynomial Multiplication and Fast Fourier Transform
 Polyomial Multiplicatio ad Fast Fourier Trasform Com S 477/577 Notes Ya-Bi Jia Sep 19, 2017 I this lecture we will describe the famous algorithm of fast Fourier trasform FFT, which has revolutioized digital
Polyomial Multiplicatio ad Fast Fourier Trasform Com S 477/577 Notes Ya-Bi Jia Sep 19, 2017 I this lecture we will describe the famous algorithm of fast Fourier trasform FFT, which has revolutioized digital
TEACHER CERTIFICATION STUDY GUIDE
 COMPETENCY 1. ALGEBRA SKILL 1.1 1.1a. ALGEBRAIC STRUCTURES Kow why the real ad complex umbers are each a field, ad that particular rigs are ot fields (e.g., itegers, polyomial rigs, matrix rigs) Algebra
COMPETENCY 1. ALGEBRA SKILL 1.1 1.1a. ALGEBRAIC STRUCTURES Kow why the real ad complex umbers are each a field, ad that particular rigs are ot fields (e.g., itegers, polyomial rigs, matrix rigs) Algebra
Chapter 2. Asymptotic Notation
 Asyptotic Notatio 3 Chapter Asyptotic Notatio Goal : To siplify the aalysis of ruig tie by gettig rid of details which ay be affected by specific ipleetatio ad hardware. [1] The Big Oh (O-Notatio) : It
Asyptotic Notatio 3 Chapter Asyptotic Notatio Goal : To siplify the aalysis of ruig tie by gettig rid of details which ay be affected by specific ipleetatio ad hardware. [1] The Big Oh (O-Notatio) : It
Ma 530 Introduction to Power Series
 Ma 530 Itroductio to Power Series Please ote that there is material o power series at Visual Calculus. Some of this material was used as part of the presetatio of the topics that follow. What is a Power
Ma 530 Itroductio to Power Series Please ote that there is material o power series at Visual Calculus. Some of this material was used as part of the presetatio of the topics that follow. What is a Power
The picture in figure 1.1 helps us to see that the area represents the distance traveled. Figure 1: Area represents distance travelled
 1 Lecture : Area Area ad distace traveled Approximatig area by rectagles Summatio The area uder a parabola 1.1 Area ad distace Suppose we have the followig iformatio about the velocity of a particle, how
1 Lecture : Area Area ad distace traveled Approximatig area by rectagles Summatio The area uder a parabola 1.1 Area ad distace Suppose we have the followig iformatio about the velocity of a particle, how
Time-Domain Representations of LTI Systems
 2.1 Itroductio Objectives: 1. Impulse resposes of LTI systems 2. Liear costat-coefficiets differetial or differece equatios of LTI systems 3. Bloc diagram represetatios of LTI systems 4. State-variable
2.1 Itroductio Objectives: 1. Impulse resposes of LTI systems 2. Liear costat-coefficiets differetial or differece equatios of LTI systems 3. Bloc diagram represetatios of LTI systems 4. State-variable
Spectral Partitioning in the Planted Partition Model
 Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 21 Spectral Partitioig i the Plated Partitio Model Daiel A. Spielma November 11, 2009 21.1 Itroductio I this lecture, we will perform a crude aalysis of the performace of
Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 21 Spectral Partitioig i the Plated Partitio Model Daiel A. Spielma November 11, 2009 21.1 Itroductio I this lecture, we will perform a crude aalysis of the performace of
Lecture 4 Recursive Algorithm Analysis. Merge Sort Solving Recurrences The Master Theorem
 Lecture 4 Recursive Algorithm Alysis Merge Sort Solvig Recurreces The Mster Theorem Merge Sort MergeSortA, left, right) { if left < right) { mid floorleft right) / 2); MergeSortA, left, mid); MergeSortA,
Lecture 4 Recursive Algorithm Alysis Merge Sort Solvig Recurreces The Mster Theorem Merge Sort MergeSortA, left, right) { if left < right) { mid floorleft right) / 2); MergeSortA, left, mid); MergeSortA,
Recursive Algorithm for Generating Partitions of an Integer. 1 Preliminary
 Recursive Algorithm for Geeratig Partitios of a Iteger Sug-Hyuk Cha Computer Sciece Departmet, Pace Uiversity 1 Pace Plaza, New York, NY 10038 USA scha@pace.edu Abstract. This article first reviews the
Recursive Algorithm for Geeratig Partitios of a Iteger Sug-Hyuk Cha Computer Sciece Departmet, Pace Uiversity 1 Pace Plaza, New York, NY 10038 USA scha@pace.edu Abstract. This article first reviews the
ECE-S352 Introduction to Digital Signal Processing Lecture 3A Direct Solution of Difference Equations
 ECE-S352 Itroductio to Digital Sigal Processig Lecture 3A Direct Solutio of Differece Equatios Discrete Time Systems Described by Differece Equatios Uit impulse (sample) respose h() of a DT system allows
ECE-S352 Itroductio to Digital Sigal Processig Lecture 3A Direct Solutio of Differece Equatios Discrete Time Systems Described by Differece Equatios Uit impulse (sample) respose h() of a DT system allows
Linear Programming and the Simplex Method
 Liear Programmig ad the Simplex ethod Abstract This article is a itroductio to Liear Programmig ad usig Simplex method for solvig LP problems i primal form. What is Liear Programmig? Liear Programmig is
Liear Programmig ad the Simplex ethod Abstract This article is a itroductio to Liear Programmig ad usig Simplex method for solvig LP problems i primal form. What is Liear Programmig? Liear Programmig is
Algorithms. Elementary Sorting. Dong Kyue Kim Hanyang University
 Algorithms Elemetary Sortig Dog Kyue Kim Hayag Uiversity dqkim@hayag.a.kr Cotets Sortig problem Elemetary sortig algorithms Isertio sort Merge sort Seletio sort Bubble sort Sortig problem Iput A sequee
Algorithms Elemetary Sortig Dog Kyue Kim Hayag Uiversity dqkim@hayag.a.kr Cotets Sortig problem Elemetary sortig algorithms Isertio sort Merge sort Seletio sort Bubble sort Sortig problem Iput A sequee
Infinite Sequences and Series
 Chapter 6 Ifiite Sequeces ad Series 6.1 Ifiite Sequeces 6.1.1 Elemetary Cocepts Simply speakig, a sequece is a ordered list of umbers writte: {a 1, a 2, a 3,...a, a +1,...} where the elemets a i represet
Chapter 6 Ifiite Sequeces ad Series 6.1 Ifiite Sequeces 6.1.1 Elemetary Cocepts Simply speakig, a sequece is a ordered list of umbers writte: {a 1, a 2, a 3,...a, a +1,...} where the elemets a i represet
COMPUTING SUMS AND THE AVERAGE VALUE OF THE DIVISOR FUNCTION (x 1) + x = n = n.
 COMPUTING SUMS AND THE AVERAGE VALUE OF THE DIVISOR FUNCTION Abstract. We itroduce a method for computig sums of the form f( where f( is ice. We apply this method to study the average value of d(, where
COMPUTING SUMS AND THE AVERAGE VALUE OF THE DIVISOR FUNCTION Abstract. We itroduce a method for computig sums of the form f( where f( is ice. We apply this method to study the average value of d(, where
Northwest High School s Algebra 2/Honors Algebra 2 Summer Review Packet
 Northwest High School s Algebra /Hoors Algebra Summer Review Packet This packet is optioal! It will NOT be collected for a grade et school year! This packet has bee desiged to help you review various mathematical
Northwest High School s Algebra /Hoors Algebra Summer Review Packet This packet is optioal! It will NOT be collected for a grade et school year! This packet has bee desiged to help you review various mathematical
An Introduction to Randomized Algorithms
 A Itroductio to Radomized Algorithms The focus of this lecture is to study a radomized algorithm for quick sort, aalyze it usig probabilistic recurrece relatios, ad also provide more geeral tools for aalysis
A Itroductio to Radomized Algorithms The focus of this lecture is to study a radomized algorithm for quick sort, aalyze it usig probabilistic recurrece relatios, ad also provide more geeral tools for aalysis
Math 2784 (or 2794W) University of Connecticut
 ORDERS OF GROWTH PAT SMITH Math 2784 (or 2794W) Uiversity of Coecticut Date: Mar. 2, 22. ORDERS OF GROWTH. Itroductio Gaiig a ituitive feel for the relative growth of fuctios is importat if you really
ORDERS OF GROWTH PAT SMITH Math 2784 (or 2794W) Uiversity of Coecticut Date: Mar. 2, 22. ORDERS OF GROWTH. Itroductio Gaiig a ituitive feel for the relative growth of fuctios is importat if you really
Problem Set 1 Solutions
 V R N N N R f ] R S Itroductio to Algorithms September 12, 2003 Massachusetts Istitute of echology 6046J/18410J rofessors Shafi Goldwasser ad Silvio Micali Hadout 7 roblem Set 1 Solutios roblem 1-1 Recurrece
V R N N N R f ] R S Itroductio to Algorithms September 12, 2003 Massachusetts Istitute of echology 6046J/18410J rofessors Shafi Goldwasser ad Silvio Micali Hadout 7 roblem Set 1 Solutios roblem 1-1 Recurrece
Sums, products and sequences
 Sums, products ad sequeces How to write log sums, e.g., 1+2+ (-1)+ cocisely? i=1 Sum otatio ( sum from 1 to ): i 3 = 1 + 2 + + If =3, i=1 i = 1+2+3=6. The ame ii does ot matter. Could use aother letter
Sums, products ad sequeces How to write log sums, e.g., 1+2+ (-1)+ cocisely? i=1 Sum otatio ( sum from 1 to ): i 3 = 1 + 2 + + If =3, i=1 i = 1+2+3=6. The ame ii does ot matter. Could use aother letter
CS161 Handout 05 Summer 2013 July 10, 2013 Mathematical Terms and Identities
 CS161 Hadout 05 Summer 2013 July 10, 2013 Mathematical Terms ad Idetities Thaks to Ady Nguye ad Julie Tibshirai for their advice o this hadout. This hadout covers mathematical otatio ad idetities that
CS161 Hadout 05 Summer 2013 July 10, 2013 Mathematical Terms ad Idetities Thaks to Ady Nguye ad Julie Tibshirai for their advice o this hadout. This hadout covers mathematical otatio ad idetities that
Optimization Methods MIT 2.098/6.255/ Final exam
 Optimizatio Methods MIT 2.098/6.255/15.093 Fial exam Date Give: December 19th, 2006 P1. [30 pts] Classify the followig statemets as true or false. All aswers must be well-justified, either through a short
Optimizatio Methods MIT 2.098/6.255/15.093 Fial exam Date Give: December 19th, 2006 P1. [30 pts] Classify the followig statemets as true or false. All aswers must be well-justified, either through a short
CS166 Handout 02 Spring 2018 April 3, 2018 Mathematical Terms and Identities
 CS166 Hadout 02 Sprig 2018 April 3, 2018 Mathematical Terms ad Idetities Thaks to Ady Nguye ad Julie Tibshirai for their advice o this hadout. This hadout covers mathematical otatio ad idetities that may
CS166 Hadout 02 Sprig 2018 April 3, 2018 Mathematical Terms ad Idetities Thaks to Ady Nguye ad Julie Tibshirai for their advice o this hadout. This hadout covers mathematical otatio ad idetities that may
CSE 1400 Applied Discrete Mathematics Number Theory and Proofs
 CSE 1400 Applied Discrete Mathematics Number Theory ad Proofs Departmet of Computer Scieces College of Egieerig Florida Tech Sprig 01 Problems for Number Theory Backgroud Number theory is the brach of
CSE 1400 Applied Discrete Mathematics Number Theory ad Proofs Departmet of Computer Scieces College of Egieerig Florida Tech Sprig 01 Problems for Number Theory Backgroud Number theory is the brach of
Average-Case Analysis of QuickSort
 Average-Case Aalysis of QuickSort Comp 363 Fall Semester 003 October 3, 003 The purpose of this documet is to itroduce the idea of usig recurrece relatios to do average-case aalysis. The average-case ruig
Average-Case Aalysis of QuickSort Comp 363 Fall Semester 003 October 3, 003 The purpose of this documet is to itroduce the idea of usig recurrece relatios to do average-case aalysis. The average-case ruig
Recurrences: Methods and Examples
 Reurrees: Methods ad Examples CSE 30 Algorithms ad Data Strutures Alexadra Stefa Uiversity of exas at Arligto Updated: 308 Summatios Review Review slides o Summatios Reurrees Reursive algorithms It may
Reurrees: Methods ad Examples CSE 30 Algorithms ad Data Strutures Alexadra Stefa Uiversity of exas at Arligto Updated: 308 Summatios Review Review slides o Summatios Reurrees Reursive algorithms It may
Machine Learning Theory Tübingen University, WS 2016/2017 Lecture 12
 Machie Learig Theory Tübige Uiversity, WS 06/07 Lecture Tolstikhi Ilya Abstract I this lecture we derive risk bouds for kerel methods. We will start by showig that Soft Margi kerel SVM correspods to miimizig
Machie Learig Theory Tübige Uiversity, WS 06/07 Lecture Tolstikhi Ilya Abstract I this lecture we derive risk bouds for kerel methods. We will start by showig that Soft Margi kerel SVM correspods to miimizig
Optimally Sparse SVMs
 A. Proof of Lemma 3. We here prove a lower boud o the umber of support vectors to achieve geeralizatio bouds of the form which we cosider. Importatly, this result holds ot oly for liear classifiers, but
A. Proof of Lemma 3. We here prove a lower boud o the umber of support vectors to achieve geeralizatio bouds of the form which we cosider. Importatly, this result holds ot oly for liear classifiers, but
Zhicheng Gao School of Mathematics and Statistics, Carleton University, Ottawa, Canada
 #A3 INTEGERS 4A (04) THE R TH SMALLEST PART SIZE OF A RANDOM INTEGER PARTITION Zhicheg Gao School of Mathematics ad Statistics, arleto Uiversity, Ottawa, aada zgao@math.carleto.ca orado Martiez Departamet
#A3 INTEGERS 4A (04) THE R TH SMALLEST PART SIZE OF A RANDOM INTEGER PARTITION Zhicheg Gao School of Mathematics ad Statistics, arleto Uiversity, Ottawa, aada zgao@math.carleto.ca orado Martiez Departamet
1 Hash tables. 1.1 Implementation
 Lecture 8 Hash Tables, Uiversal Hash Fuctios, Balls ad Bis Scribes: Luke Johsto, Moses Charikar, G. Valiat Date: Oct 18, 2017 Adapted From Virgiia Williams lecture otes 1 Hash tables A hash table is a
Lecture 8 Hash Tables, Uiversal Hash Fuctios, Balls ad Bis Scribes: Luke Johsto, Moses Charikar, G. Valiat Date: Oct 18, 2017 Adapted From Virgiia Williams lecture otes 1 Hash tables A hash table is a
(3) If you replace row i of A by its sum with a multiple of another row, then the determinant is unchanged! Expand across the i th row:
 Math 50-004 Tue Feb 4 Cotiue with sectio 36 Determiats The effective way to compute determiats for larger-sized matrices without lots of zeroes is to ot use the defiitio, but rather to use the followig
Math 50-004 Tue Feb 4 Cotiue with sectio 36 Determiats The effective way to compute determiats for larger-sized matrices without lots of zeroes is to ot use the defiitio, but rather to use the followig
In number theory we will generally be working with integers, though occasionally fractions and irrationals will come into play.
 Number Theory Math 5840 otes. Sectio 1: Axioms. I umber theory we will geerally be workig with itegers, though occasioally fractios ad irratioals will come ito play. Notatio: Z deotes the set of all itegers
Number Theory Math 5840 otes. Sectio 1: Axioms. I umber theory we will geerally be workig with itegers, though occasioally fractios ad irratioals will come ito play. Notatio: Z deotes the set of all itegers
Merge and Quick Sort
 Merge ad Quick Sort Merge Sort Merge Sort Tree Implemetatio Quick Sort Pivot Item Radomized Quick Sort Adapted from: Goodrich ad Tamassia, Data Structures ad Algorithms i Java, Joh Wiley & So (1998). Ruig
Merge ad Quick Sort Merge Sort Merge Sort Tree Implemetatio Quick Sort Pivot Item Radomized Quick Sort Adapted from: Goodrich ad Tamassia, Data Structures ad Algorithms i Java, Joh Wiley & So (1998). Ruig
ECE 669 Parallel Computer Architecture
 ECE 669 Parallel Computer Architecture Lecture 4 Parallel Applicatios Outlie Motivatig Problems (applicatio case studies) Classifyig problems Parallelizig applicatios Examiig tradeoffs Uderstadig commuicatio
ECE 669 Parallel Computer Architecture Lecture 4 Parallel Applicatios Outlie Motivatig Problems (applicatio case studies) Classifyig problems Parallelizig applicatios Examiig tradeoffs Uderstadig commuicatio
