MPM1D0 UNIT 4 - LINEAR RELATIONS
|
|
|
- August Gordon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MPM1D0 UNIT 4 - LINEAR RELATIONS MPM1D0 UNIT 4 - LINEAR RELATIONS... 1 INTRODUCTION WHAT YOU SHOULD ALREADY KNOW... 3 SLOPES, INTERCEPTS AND THEIR MEANINGS... 3 APPLICATIONS OF SLOPES AND INTERCEPTS... 3 EQUATIONS OF LINES DISCOVERY ACTIVITY... 5 WRITING EQUATIONS OF LINES IN STANDARD FORM AND SLOPE-INTERCEPT FORM... 9 DEFINITIONS... 9 EXAMPLES... 9 HOMEWORK USING INTERCEPTS TO SKETCH THE GRAPHS OF LINEAR RELATIONS EXAMPLE Solution EXAMPLE Solution SUMMARY EQUATIONS OF LINEAR RELATIONS... 1 HOMEWORK... 1 MID-UNIT SUMMARY... 1 PRACTICE: CONSOLODATING YOUR SKILLS WHY DID ZORNA POUR KETCHUP ON HER BROTHER S HAND? WHAT DID THE APE THINK OF THE GRAPE S HOUSE? WHOM SHOULD YOU SEE AT THE BANK IF YOU NEED TO BORROW MONEY? DID YOU HEAR ABOUT REVIEW OF ANALYTIC GEOMETRY AND RELATIONS SLOPES OF PARALLEL AND PERPENDICULAR LINES HOW THE SLOPES OF PERPENDICULAR LINES ARE RELATED HOW THE SLOPES OF PARALLEL LINES ARE RELATED... 0 EXAMPLE EXAMPLE... 0 Solution... 0 HOMEWORK... 0 FINDING EQUATIONS OF LINES GIVEN A SLOPE AND A POINT OR GIVEN TWO POINTS... 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 EXAMPLES... 1 HOMEWORK... 3 IMPORTANT PROBLEM SET... 4 LINEAR SYSTEMS (SOLVING SYSTEMS OF TWO LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO UNKNOWNS)... 7 DEFINITION... 7 EXAMPLE EXAMPLE... 8 SOLVING SYSTEMS OF TWO LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO UNKNOWNS APPLICATIONS... 9 Problem Problem Problem HOMEWORK EQAO PRACTICE TASKS... 3 TASK 1: BOWLING... 3 TASK : BABYSITTERS CLUB TASK 3: BERRIES FOR PICKING Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-1
2 VERY IMPORTANT REVIEW OF LINEAR RELATIONS PRACTICE TEST PRACTICE TEST Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-
3 INTRODUCTION WHAT YOU SHOULD ALREADY KNOW Slopes, Intercepts and their MEANINGS 1. The slope of a line is a measure of the line s. Slope also measures the of the variable with respect to the variable. For example, in the graph ( x, y ) 1 1 ( 0,1) y y y shown at the right, slope = m = = = =. This x x x means that for every increase in the independent variable ( x value ) by units, the dependent variable ( y value ) y x ( 3, 4) ( x, y ) by units.. The y-intercept or vertical intercept is the y-co-ordinate of the point at which the graph the y-axis. The meaning of the y-intercept is. In the graph shown above, the line intersects the y-axis at the point with co-ordinates, which means that the y-intercept must be. The x-co-ordinate of the point at which the graph intersects the y-axis must be zero because. Applications of Slopes and Intercepts 1. Fisherman in the Finger Lakes Region have been recording the dead fish they encounter while fishing in the region. The Department of Environmental Conservation monitors the pollution index for the Finger Lakes Region. The mathematical model for the number of fish deaths D for a given pollution index I is D= 9.607I (a) Use the equation to identify the slope and the y-intercept of the given linear relation. slope = m = y-intercept = b = (b) Mark the y-intercept on the graph. In addition, draw a right triangle that shows rise and run of the given line. (c) What is the meaning of the y-intercept? D D= 9.607I I (d) What is the meaning of the slope? (Hint: slope = rate of change) Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-3
4 . The WeTalkALot long distance company charges $5.00 each month for its special $0.05 per minute rate on long distance. (a) Let C represent the total monthly long distance cost and let t represent the total number of minutes used for long distance calls. Write an equation that expresses C in terms of t. (b) State the slope, y-intercept and their meanings. slope = m = Meaning: y-intercept = b = Meaning: (c) Use the provided grid to sketch a graph of C versus t. Use a scale of 0 to 00 minutes for the horizontal axis and scale of 0 to 0 dollars for the vertical axis. Don t forget to label the axes! (d) The WeTalkEvenMore long distance company charges $7.00 per month for its special $0.03 per minute rate on long distance. Using the same grid given above, sketch a graph of C versus t for WeTalkEvenMore. (e) If you have sketched both graphs correctly, you should find that they intersect (cross) at approximately the point with co-ordinates ( 100,10 ). Explain the meaning of this point of intersection. (f) Under what circumstances is the WeTalkALot long distance plan a better deal? Under what circumstances is the WeTalkEvenMore plan a better deal? (g) The BlahBlahBlah long distance company offers a unique plan. Each month, the first 0 minutes are free but thereafter, the calls cost $0.10 per minute. Using the same grid given above, sketch a graph of C versus t for BlahBlahBlah. (h) If you have sketched the graph for BlahBlahBlah correctly, you will see that it has an x-intercept of 0. What is the meaning of the x-intercept? (i) Under what circumstances is the BlahBlahBlah plan a better deal than either of the others? Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-4
5 EQUATIONS OF LINES DISCOVERY ACTIVITY A F B y C 1. Which of the lines shown at the left (a) have positive slope? (b) have negative slope? D (c) have zero slope? x (d) have undefined slope?. Which line is steeper, (a) A or B? (b) E or C? E (c) D or F? (d) A or C? (e) B or E? 3. For each of the lines shown above, carefully select two points that lie on the line. Then use those two points to calculate the slope of the line. Important Note: Make sure that the points that you choose lie where two grid lines intersect. y y y1 y y A. slope = m = = = = y1 D. slope = m = = = = x x x x x x 1 1 y y y1 B. slope = m = = = = x x x 1 y y y1 C. slope = m = = = = x x x 1 4. For each of the lines shown above, identify the y-intercept. A. y-intercept = b = B. y-intercept = b = C. y-intercept = b = y y y1 E. slope = m = = = = x x x 1 y y y1 F. slope = m = = = = x x x 1 D. y-intercept = b = E. y-intercept = b = F. y-intercept = b = 5. For each of the lines shown above, write an equation in the form y = mx + b (i.e. slope-y-intercept form). A. B. C. D. E. F. 6. For each of the lines shown above, sketch a diagram showing both the rise and the run. In each case, indicate the signs of x and y (i.e. whether the rise and run are positive or negative). Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-5
6 y 7. Use the provided grid to sketch lines passing through the point 3, 4 and having ( ) (a) a slope of. Label this line A. 5 (b) a slope of 5. Label this line B. x (c) a slope of 3. Label this line C. 7 (d) a slope of 7. Label this line D Using your sketches, estimate the y-intercepts of each of the lines that you sketched in question 7. A. b B. b C. b D. b 9. Using the example given below for line A as a model, calculate the y-intercepts of each of the lines in question 7. Then write an equation of each line in the form y = mx + b. (This is called the slope-y-intercept equation of a line.) A. Since the slope of this line is known to be, 5 the equation of the line must be of the form y = x+ b. It s also given that the point 5 3, 4 lies on the line. Therefore, the ( ) co-ordinates of this point must satisfy the equation. This means that when the values of x and y are substituted into the equation, the lefthand side must agree with the right-hand side. 3 4 = + b = + b = + b = b = b 5 B. C. D. The slope-y-intercept equation of line A must be 14 y = x Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-6
7 10. Carefully check your answers to questions 8 and 9. Summarize your results in the following table. If your answers to question 8 do not agree with your answers to question 9, then find out what went wrong and correct your mistakes! 8A. b 8B. b 8C. b 8D. b 9A. b = 9B. b = 9C. b = 9D. b = Answers Agree? (Yes / No) Answers Agree? (Yes / No) Answers Agree? (Yes / No) Answers Agree? (Yes / No) 11. Consider the linear relation with slope-y-intercept equation (a) Describe the relation in words. Specifically, what does the equation tell you about the relationship between the x-co-ordinate and the y-co-ordinate of any point that lies on the line? 3 7 (c) Sketch the graph of y = x using only the slope and y-intercept. y 3 7 y = x. (b) Complete the following table of values: 3 7 x y = x (d) Sketch the graph of y = x using only the table of values from (b). y x x (e) Check carefully to ensure that the graphs in (c) and (d) are identical. If they are, then check with some classmates to see if your graphs agree. (f) Summarize what you have learned from exercises 7 to 11. If all the graphs agree, then they are probably correct. If any do not agree, then check your work and correct any mistakes. Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-7
8 1. In this question you will explore various forms of equations for linear relations. The forms that you need to know are summarized in the table given below. Slope-y-intercept Form Standard Form Modified Standard Form y = mx + b m and b are constants representing the slope and y-intercept respectively e.g. y = 3x 5 slope = m = 3, y-intercept = b= 5 Advantage Very easy to sketch the graph. Disadvantage Cannot be used with lines that have an undefined slope. Ax + By + C = 0 (A > 0, no fractions) A, B and C are constants that do not by themselves represent geometric features of the graph e.g. x 5y 3= 0 A =, B = 5, C = 3 Advantage Can be used even if slope is undefined. Disadvantage More difficult to sketch the graph. Ax + By = C (A > 0, no fractions) A, B and C are constants that do not by themselves represent geometric features of the graph e.g. x 5y = 3 A =, B = 5, C = 3 Advantage Can be used even if slope is undefined. Disadvantage More difficult to sketch the graph. (a) Use your knowledge of rearranging equations to write 3 7 y = x in standard form. (Hint: Eliminate the fractions first!) (c) By now you should have the correct answer to (b). Rewrite the equation in the form Ax + By = C. Then use the equation to complete the following table. Show all your work! x y (b) Check your answer to (a) by completing the following table of values. x y (Calculated using 3 7 y = x ) 5/ 1/ 7/ 13/ 19/ y (Calculated using the equation in standard form obtained in (a)) (d) Use the table in (c) to sketch the graph. Your graph must be identical to the graphs in 11(c) and 11(d). y 0 x 0 (e) Use the first two columns of the table in (b) to explain why the relation must be linear. Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-8
9 WRITING EQUATIONS OF LINES IN STANDARD FORM AND SLOPE-INTERCEPT FORM Definitions Slope-y-intercept Form y = mx + b m and b represent the slope and y-intercept respectively. e.g. y = 3x 5 slope = m = 3 = 3, 1 y-intercept = b= 5 Meaning of the Slope: The y-co-ordinate (dependent variable) decreases by 3 units for every increase of 1 unit in the x-co-ordinate (independent variable). Meaning of the y-intercept: The y-co-ordinate is 5 when the x-co-ordinate is zero. A > 0 Standard Form Ax + By + C = If possible, A, B and C should be integers (i.e. no fractions) A, B and C are constants that do not by themselves represent geometric features of the graph. However, A, B and C are related to m and b. e.g. x 5y 3= 0 A =, B = 5, C = 3 0 Note: Slope-y -Intercept Form is also called Slope-Intercept Form Examples 1. Write the equation of each line in both slope-y-intercept form and standard form. (a) (b) Solution Since ( 0, 5) lies on the line, b = 5 Since ( 6, 1) also lies on the line, y m = x y y1 = x x1 1 5 = = 6 = 3 ( ) Therefore, the slope-y-intercept form of the equation is y = x 5. 3 Solution Since both m and b are undefined, it is not possible to write the equation of a vertical line in slope-y-intercept form. However, it is possible to write the equation of this line in standard form. Observe that any point on the line has x-co-ordinate but there is no restriction at all on the y-co-ordinate. Therefore, the equation turns out to be extremely simple: x = This equation simply means that the x-co-ordinate must be. Since y does not appear in the equation, it is understood that y can have any value. To make this equation conform to the format of the standard form in can be written as follows: 1x+ 0y = 0 Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-9
10 Continuation of Example 1(a) To write y = x 5 in standard form, use the same techniques that you used to rearrange (manipulate) formulas: 3 y = x y = x 3( 5) (Multiply both sides by 3.) 1 3 3y = x 15 3y x+ 15 = x 15 x+ 15 x+ 3y+ 15 = 0 ( x) ( 1)( 3y) ( 1)( 15) ( 0) = 1 x 3y 15 = 0 This is almost in standard form. The only problem is that the coefficient of x is negative. To write the equation with a positive coefficient of x, simply multiply both sides by 1. The standard form of the equation is x 3y 15 = 0.. Write the equation 5x 7y+ 3= 0 in slope-y-intercept form. Solution The goal is to isolate y. Once again, use the techniques that you learned to rearrange equations. 5x 7y+ 3= 0 5x 7y+ 3 5x 3 = 0 5x 3 7y = 5x 3 7y 5x 3 = y = x+ 7 7 Homework pp # 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 11 (Divide both sides by 7.) Artwork by Daniel Dhillon PRACTICE is the key to success in mathematics and just about anything else that is meaningful and worthwhile. So do your homework every day, ask questions about anything that you do not understand and do your best to understand the meaning of all the concepts that you learn. If you choose to do otherwise, the consequences are too frightening to contemplate! MUHAHAHAHAHAHAHAHAHAHAHA! Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-10
11 USING INTERCEPTS TO SKETCH THE GRAPHS OF LINEAR RELATIONS Example 1 Determine the intercepts of the linear relation with equation y = x 3. Solution Because the equation is given in the form y = mx + b, we can immediately conclude the following: slope = m = y-intercept = b = 3 However, the y = mx + b form of the equation does not directly tell us what the x-intercept is. From the graph, it appears that the x-intercept is 1.5 but this is only an estimate. The equation can be used to calculate the exact value of the x-intercept but first, it is necessary to understand the following important principle: Any point lying on the x-axis must have a y-co-ordinate of zero! ( 0, 3) The x-intercept is 1.5. y = x 3 ( 1.5,0) The y-intercept is 3. (In addition, any point lying on the y-axis must have an x-co-ordinate of zero. We don t need this at the moment to calculate the x-intercept but we will need it later to calculate the y-intercept when the equation is given in a form other than the slope-y-intercept form.) Therefore, to find the x-intercept, we simply set y = 0 and solve for x: If y = 0 then 0= x 3 3= x 3 x = 3 x = Therefore, the x-intercept is 3 = 1.5 (agrees with estimate) and the y-intercept is 3. (Of course, this means that the line intersects the 3 x-axis at the point with co-ordinates,0 and the y-axis at the point with co-ordinates ( 0, 3).) Example Use the intercepts of the linear relation 5x+ y = 10 to sketch its graph. Solution The graph of 5x+ y = 10 could be sketched by first rewriting the equation in slope-y-intercept form. However, there is a much faster approach! 5x+ y = 10 Any point on the y-axis must have x-co-ordinate zero because there is no horizontal movement. Any point on the x-axis must have y-co-ordinate zero because there is no vertical movement. x-intercept y = 0 y-intercept x = 0 5x+ y = 10 5x+ y = 10 5x + ( 0) = 10 5( 0) + y = 10 5x = 10 y = 10 x = y = 5 (,0) lies on the graph ( 0,5) lies on the graph Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-11
12 Summary Equations of Linear Relations As shown below, equations of lines can be written in various forms. Regardless of the form, however, the equation must be satisfied by the co-ordinates of any point that lies on the line. That is, if ( xy, ) lies on the line, when the values of the x and y co-ordinates are substituted into the equation, the left and right sides of the equation must agree! (a) Slope-y-intercept Form: y = mx + b } m = slope = rate of change of y with respect to x = steepness b = y-intercept = vertical intercept = initial value = value of y when x = 0 (b) Standard Form: Ax + By + C = 0 (c) Modified Standard Form: Ax + By = C } A, B and C do not directly represent any geometric features of the graph. However, m and b are related to A, B and C. Homework pp # C1, C, C3, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 13, 15 MID-UNIT SUMMARY Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-1
13 Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-13
14 PRACTICE: CONSOLODATING YOUR SKILLS Why did Zorna Pour Ketchup on her Brother s Hand? Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-14
15 What Did the Ape think of the Grape s House? Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-15
16 Whom Should you See at the Bank if you Need to Borrow Money? Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-16
17 Did you Hear About Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-17
18 REVIEW OF ANALYTIC GEOMETRY AND RELATIONS 1. For a taxi ride, a Toronto taxi company charges $5.00 plus $1.50 per kilometre travelled. (a) Complete the following table of values: d = distance (km), C = cost ($) d C C (1 st differences) (b) Is this relation an example of direct variation or partial variation? Explain. (c) Explain why the relation between C and d must be linear. In addition, state the slope and the y-intercept. (d) Which variable is the dependent variable? Explain. (e) Graph the relation. (f) Write an equation, in the form y = mx + b, that relates C to d. (g) Interpret the slope as a rate of change. (i) Describe the relation between C and d in words. (k) Convert the equation that you obtained in (f) to standard form. (h) Interpret the y-intercept as an initial value. (j) How much would it cost to take a 100 km taxi ride? (l) Is there an easy way to determine the slope and y-intercept from the standard form of a linear relation?. Write an equation for each of the following. Positive Slope Positive Rate of Change As x increases, y increases. Negative Slope Negative Rate of Change As x increases, y decreases. Zero Slope Zero Rate of Change As x increases, y is constant. Undefined Slope Undefined Rate of Change x is constant, y varies freely. Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-18
19 SLOPES OF PARALLEL AND PERPENDICULAR LINES How the Slopes of Perpendicular Lines are Related Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-19
20 How the Slopes of Parallel Lines are Related Example 1 Example Find an equation of the line passing through the point 4,5 and perpendicular to the line with equation ( ) y = x Solution Required Line: m =?, b =?, passes through ( 4,5) From the result of the previous example, we can conclude that 3 m =. Thus, the equation of the line must be of the form 3 y = x+ b. Since ( 4,5) lies on the required line, the co-ordinates of this point must satisfy the equation. Therefore, = + b 1 5= 6+ b = 6 + b = b The slope-y-intercept equation of the line must be 3 y = x+ 11. Homework pp # 1,, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 1, 14 Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-0
21 FINDING EQUATIONS OF LINES GIVEN A SLOPE AND A POINT OR GIVEN TWO POINTS Introduction Examples Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-1
22 Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-
23 Homework pp # C1, C, 1,, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 11 pp # 1cd,, 3, 5, 6, 7, 9 Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-3
24 1. Line A passes through the point ( ) y IMPORTANT PROBLEM SET 9,9 and is perpendicular to the line with equation 9x+ 11y 99 = 0. (a) Using the provided set of axes, sketch the graph of 9x+ 11y 99 = 0. The fastest approach is to use the intercepts method. (b) On the same set of axes, carefully sketch the graph of 9,9 and line A. Make sure that line A passes through ( ) that it is perpendicular to 9x+ 11y 99 = 0. (c) Use your sketch of line A to estimate its slope and y-intercept. m b x (d) Determine the exact slope of the line 9x+ 11y 99 = 0. Show your work and state a conclusion. Therefore, the slope of 9x+ 11y 99 = 0 is. (e) Use your answer from (d) to determine the slope of line A. For line A, m = because. (f) Use your answer from (e) and the fact that line A passes through the point ( 9,9 ) to determine the equation of line A. (g) Now check your answer to (f) by using the equation that you obtained in (f) to sketch the graph of line A. Does it agree with the graph that you obtained in y x (h) Now summarize your results. Estimates from (c) Actual Values from (f) Conclusion(s): Is your equation for line A correct? m m = b b = Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-4
25 . Line A passes through the point ( 9,9 ) and is parallel to the line with equation 9x+ 11y 99 = 0. Determine an equation of line A. 3. The equation n E+ 15 = 0 describes the amount earned per hour in a certain factory. In this equation, E represents the amount earned per hour in dollars and n represents the number of years of experience. Calculate the hourly earnings of a beginning factory worker as well as one with five years of experience. 4. The equation 9C 5F = 0 describes the relationship between temperature, C, in degrees Celsius and temperature, F, in degrees Fahrenheit. (a) Express the equation in the form C = mf + b. 5. Plot the points A ( 1,1), B(, 5) and ( 3, ) C to form ABC. Is ABC a right triangle? Justify your answer using mathematical reasoning. (b) Explain the meaning of the slope and the vertical intercept. 6. Given that A and k are one-digit numbers, determine the numbers of pairs of values for which the lines Ax 3y + 15 = 0 and y = kx + 7 are (a) parallel (b) perpendicular (c) coincident (the same line) Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-5
26 7. Anil is driving to his home in Toronto at a constant speed. At 4:30 P.M., he spots a sign indicating that Toronto is 40 km away. At 7:00 P.M., he notices another sign indicating that Toronto is 40 km away. (a) Plot a graph showing Anil s distance from Toronto versus time elapsed since 4:30 P.M. d (b) Do you expect the relation between distance from Toronto and time to be linear? Explain. (c) Let t represent time in hours and d represent distance from Toronto in km. Write an equation relating d to t. Show all work! t (d) How fast is Anil travelling? Explain. (e) Explain the meaning of the y-intercept of the graph in (a). (f) Explain the meaning of the x-intercept of the graph in (a). (g) At 5:45 P.M., how far from Toronto was Anil? Determine this by using both the graph and the equation. Make sure that your answers agree! Estimate from Graph: Exact Distance using Equation (Show all Work) (h) At what time did Anil arrive in Toronto? Determine this by using both the graph and the equation. Make sure that your answers agree! Estimate from Graph: Exact Time using Equation (Show all Work) (i) Anil was rushing home to Toronto because he did not want to miss watching the Maple Leafs lose yet another game. If the opening faceoff was to take place at 7:45 P.M., did Anil make it home in time? Explain. Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-6
27 LINEAR SYSTEMS (SOLVING SYSTEMS OF TWO LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO UNKNOWNS) Definition Example 1 Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-7
28 Example Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-8
29 Solving Systems of Two Linear Equations in Two Unknowns Applications Problem 1 d) State the point of intersection of the two lines. e) What does the point of intersection mean in this situation? f) By looking at the graph, determine if All Natural will make money or lose money if 100 L of gas are sold. What is the profit/loss? Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-9
30 Problem Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-30
31 Problem 3 Homework pp # C, 1,, 3, 7, 9, 10, 11, 14, 15 Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-31
32 Task 1: Bowling EQAO PRACTICE TASKS Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-3
33 Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-33
34 Task : Babysitters Club Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-34
35 Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-35
36 Task 3: Berries for Picking Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-36
37 Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-37
38 VERY IMPORTANT REVIEW OF LINEAR RELATIONS 1. Find an equation of the line with slope 6 and having x-intercept 8. (a) Make a sketch and use it to estimate the equation of the required line. (b) Use an algebraic method to find the exact equation of the required line. Estimate of Equation:. Find an equation of the line that passes through ( 5, 0) and (5, 6). (a) Make a sketch and use it to estimate the equation of the required line. (b) Use an algebraic method to find the exact equation of the required line. Estimate of Equation: Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-38
39 3. A line is parallel to 5x + y 8 = 0 and has the same y-intercept as x + 4y 1 = 0. Find an equation of the line. (a) Make a sketch and use it to estimate the equation of the required line. (b) Use an algebraic method to find the exact equation of the required line. Estimate of Equation: 4. A line is perpendicular to x + 3y 4 = 0 and has the same y-intercept as x + 5y 0 = 0. Find an equation of the line. (a) Make a sketch and use it to estimate the equation of the required line. (b) Use an algebraic method to find the exact equation of the required line. Estimate of Equation: Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-39
40 Multiple Choice PRACTICE TEST 1 For each question, select the best answer. 1. Which are the slope and y-intercept of the line y = 5x + 3? A m = 3, b = 5 B m = 3, b = 5 C m = 5, b = 3 D m = 5, b = 3 7. Erynn used a motion sensor to create this distancetime graph.. What are the x- and y-intercepts of the line 5x 4y = 0? A x-intercept = 4, y-intercept = 5 B x-intercept = 4, y-intercept = 5 C x-intercept = 4, y-intercept = 5 D x-intercept = 4, y-intercept = 5 3. What is the slope of a line parallel to x + y = 4? A B C 1 D 1 4. What is the slope of a line perpendicular to x + y = 4? A B C 1 D 1 5. Which is the solution to the linear system y = 6 x and y = x 4? A (1, 5) B (5, 1) C ( 1, 5) D ( 5, 1) Short Response 6. Write x y + 4 = 0 in the form y = mx + b. a) Find the slope and d-intercept. What information does each of these give us about Erynn s motion? b) Write an equation that describes this distance-time relationship. 8. Find an equation for a line a) with slope 1 passing through (, ) b) that passes through (10, 3) and (5, 6) Extend Show all your work. 9. A line is perpendicular to x + 3y 4 = 0 and has the same y-intercept as x + 5y 0 = 0. Find an equation for the line. 10. A fitness club offers two membership plans. Plan A: $30 per month Plan B: $18 per month plus $ for each visit a) Graph the linear system. When would the cost of the two membership plans be the same? b) Describe a situation under which you would choose each plan. Answers 1. D. A 3. D 4. A 5. B 6. y = 1 x + 7. a) slope: 1.; d-intercept: 1 b) d = 1.t a) y = x + 4 b) y = 3 x y =3x a) When you make 6 visits per month, the cost for both plans is $30. b) I would choose Plan A if I go to the gym more than 6 times each month. If I thought I would go fewer than 6 times per month, I would choose Plan B (or not get a membership). Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-40
41 Multiple Choice For each question, select the best answer. 1. Which are the slope and y-intercept of the line y = x 4? A m = 0, b = 4 B m = 0, b = 4 C m = 1, b = 4 D m = 1, b = 4. What are the x- and y-intercepts of the line 3x + y = 1? A x-intercept = 4, y-intercept = 6 B x-intercept = 4, y-intercept = 6 C x-intercept = 4, y-intercept = 6 D x-intercept = 4, y-intercept = 6 3. What is the slope of a line parallel to 4x + y = 7? A B C 1 D 1 4. What is the slope of a line perpendicular to x y = 3? A B 1 1 C D 5. Which is the solution to the linear system y = x and y = x + 4? A (4, 1) B (4, ) C (4, 8) D (4, 4) Short Response 6. Write 8x + y + 11 = 0 in the form y = mx + b. Answers 1. D. D 3. B 4. D 5. C 6. y = 4x a) 3 m b) Away; approximately.1 m/s c) d =.1t a) y = 6x + 10 b) y = 3 x y = 5 x + 3 PRACTICE TEST 7. Frank recorded his motion with a motion sensor and produced this graph. a) How far was Frank from the motion sensor when he started moving? b) Was Frank moving toward the motion sensor or away from it? How fast was he moving? c) Write an equation that describes this distance-time relationship. 8. Find an equation for a line a) with slope 6 passing through ( 1, 4) b) that passes through ( 5, 0) and (5, 6) Extend Show all your work. 9. A line is parallel to 5x + y 8 = 0 and has the same y-intercept as x + 4y 1 = 0. Find an equation of the line. 10. A retail store offers two different hourly pay plans: Plan A: $9.00 per hour Plan B: $7.50 per hour plus a $4.50 shift bonus. 10. a) The earnings per shift under both plans are $7 when you work 3 h. b) I would choose Plan A if I usually work more than 3 h each shift. If I work fewer than 3 h per shift, I would choose Plan B. a) Graph the linear system. When would the earnings from the two plans be the same? b) Describe a situation under which you would choose each plan. Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D0 Unit 4 Linear Relations LR-41
Algebra 1 Spencer Unit 4 Notes: Inequalities and Graphing Linear Equations. Unit Calendar
 Algebra 1 Spencer Unit 4 Notes: Inequalities and Graphing Linear Equations Unit Calendar Date Topic Homework Nov 5 (A ) 6.1 Solving Linear Inequalities +/- 6.2 Solving Linear Inequalities x/ 6.3 Solving
Algebra 1 Spencer Unit 4 Notes: Inequalities and Graphing Linear Equations Unit Calendar Date Topic Homework Nov 5 (A ) 6.1 Solving Linear Inequalities +/- 6.2 Solving Linear Inequalities x/ 6.3 Solving
Unit 3 Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey
 HW#1 Name Algebra II Unit Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey 1) In each of the following, the variable pair given are proportional to one another. Find the missing value. (a) b = 8 when a = 16 b =? when a = 18
HW#1 Name Algebra II Unit Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey 1) In each of the following, the variable pair given are proportional to one another. Find the missing value. (a) b = 8 when a = 16 b =? when a = 18
G.3 Forms of Linear Equations in Two Variables
 section G 2 G. Forms of Linear Equations in Two Variables Forms of Linear Equations Linear equations in two variables can take different forms. Some forms are easier to use for graphing, while others are
section G 2 G. Forms of Linear Equations in Two Variables Forms of Linear Equations Linear equations in two variables can take different forms. Some forms are easier to use for graphing, while others are
COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
 COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 1 8 4 Lesson 1: Writing Equations Using Symbols Write each of the following statements using symbolic language. 1. When you square five times a number you get
COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 1 8 4 Lesson 1: Writing Equations Using Symbols Write each of the following statements using symbolic language. 1. When you square five times a number you get
Complete Week 18 Package
 Complete Week 18 Package Jeanette Stein Table of Contents Unit 4 Pacing Chart -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 Day 86 Bellringer --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Complete Week 18 Package Jeanette Stein Table of Contents Unit 4 Pacing Chart -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 Day 86 Bellringer --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chapter 3: Linear Functions & Their Algebra
 Chapter 3: Linear Functions & Their Algebra Lesson 1: Direct Variation Lesson 2: Average Rate of Change Lesson 3: Forms of a Line Lesson 4: Linear Modeling Lesson 5: Inverse of Linear Functions Lesson
Chapter 3: Linear Functions & Their Algebra Lesson 1: Direct Variation Lesson 2: Average Rate of Change Lesson 3: Forms of a Line Lesson 4: Linear Modeling Lesson 5: Inverse of Linear Functions Lesson
Graphing and Writing Linear Equations Review 3.1, 3.3, & 4.4. Name: Date: Period:
 Graphing and Writing Linear Equations Review.1,., 4.1-4. & 4.4 Algebra I Name: Date: Period: Quest Topics Section.1 linear versus nonlinear rewrite linear equations in standard form: Ax By C find and use
Graphing and Writing Linear Equations Review.1,., 4.1-4. & 4.4 Algebra I Name: Date: Period: Quest Topics Section.1 linear versus nonlinear rewrite linear equations in standard form: Ax By C find and use
SOLVING EQUATIONS CONTAINING FRACTIONS GENERAL PROCEDURE FOR SOLVING LINEAR EQUATIONS EXAMPLES Try This One!...
 UNIT EQUATIONS: POWERFUL PROBLEM SOLVING TOOLS UNIT EQUATIONS: POWERFUL PROBLEM SOLVING TOOLS... 1 INTRODUCTION TO EQUATIONS... WHAT IS AN EXPRESSION... WHAT IS AN EQUATION?... WHAT DOES AN EQUATION LOOK
UNIT EQUATIONS: POWERFUL PROBLEM SOLVING TOOLS UNIT EQUATIONS: POWERFUL PROBLEM SOLVING TOOLS... 1 INTRODUCTION TO EQUATIONS... WHAT IS AN EXPRESSION... WHAT IS AN EQUATION?... WHAT DOES AN EQUATION LOOK
Unit #6 Part II: Slope, Intercepts & Linear Relations
 Name: Block: Teacher: Miss Zukowski Date Submitted: / / 2018 Unit #6 Part II: Slope, Intercepts & Linear Relations Submission Checklist: (make sure you have included all components for full marks) Cover
Name: Block: Teacher: Miss Zukowski Date Submitted: / / 2018 Unit #6 Part II: Slope, Intercepts & Linear Relations Submission Checklist: (make sure you have included all components for full marks) Cover
SOLVING LINEAR INEQUALITIES
 Topic 15: Solving linear inequalities 65 SOLVING LINEAR INEQUALITIES Lesson 15.1 Inequalities on the number line 15.1 OPENER Consider the inequality x > 7. 1. List five numbers that make the inequality
Topic 15: Solving linear inequalities 65 SOLVING LINEAR INEQUALITIES Lesson 15.1 Inequalities on the number line 15.1 OPENER Consider the inequality x > 7. 1. List five numbers that make the inequality
Chapter 1 Skills Points and Linear Equations
 Example 1. Solve We have Chapter 1 Skills Points and Linear Equations t = 3 t t = 3 t for t. = ( t)( t) = ( t) = 3( t) = 4 4t = 6 3t = = t t = 3 ( t)( t) t Example. Solve We have = A + Bt A Bt for t. =
Example 1. Solve We have Chapter 1 Skills Points and Linear Equations t = 3 t t = 3 t for t. = ( t)( t) = ( t) = 3( t) = 4 4t = 6 3t = = t t = 3 ( t)( t) t Example. Solve We have = A + Bt A Bt for t. =
Algebra. Topic: Manipulate simple algebraic expressions.
 30-4-10 Algebra Days: 1 and 2 Topic: Manipulate simple algebraic expressions. You need to be able to: Use index notation and simple instances of index laws. Collect like terms Multiply a single term over
30-4-10 Algebra Days: 1 and 2 Topic: Manipulate simple algebraic expressions. You need to be able to: Use index notation and simple instances of index laws. Collect like terms Multiply a single term over
MATH 60 Course Notebook Chapter #1
 MATH 60 Course Notebook Chapter #1 Integers and Real Numbers Before we start the journey into Algebra, we need to understand more about the numbers and number concepts, which form the foundation of Algebra.
MATH 60 Course Notebook Chapter #1 Integers and Real Numbers Before we start the journey into Algebra, we need to understand more about the numbers and number concepts, which form the foundation of Algebra.
Copyright, Nick E. Nolfi MPM1D9 Unit 6 Statistics (Data Analysis) STA-1
 UNIT 6 STATISTICS (DATA ANALYSIS) UNIT 6 STATISTICS (DATA ANALYSIS)... 1 INTRODUCTION TO STATISTICS... 2 UNDERSTANDING STATISTICS REQUIRES A CHANGE IN MINDSET... 2 UNDERSTANDING SCATTER PLOTS #1... 3 UNDERSTANDING
UNIT 6 STATISTICS (DATA ANALYSIS) UNIT 6 STATISTICS (DATA ANALYSIS)... 1 INTRODUCTION TO STATISTICS... 2 UNDERSTANDING STATISTICS REQUIRES A CHANGE IN MINDSET... 2 UNDERSTANDING SCATTER PLOTS #1... 3 UNDERSTANDING
Unit 5. Linear equations and inequalities OUTLINE. Topic 13: Solving linear equations. Topic 14: Problem solving with slope triangles
 Unit 5 Linear equations and inequalities In this unit, you will build your understanding of the connection between linear functions and linear equations and inequalities that can be used to represent and
Unit 5 Linear equations and inequalities In this unit, you will build your understanding of the connection between linear functions and linear equations and inequalities that can be used to represent and
Polynomials. Lesson 6
 Polynomials Lesson 6 MPMD Principles of Mathematics Unit Lesson 6 Lesson Six Concepts Introduction to polynomials Like terms Addition and subtraction of polynomials Distributive law Multiplication and
Polynomials Lesson 6 MPMD Principles of Mathematics Unit Lesson 6 Lesson Six Concepts Introduction to polynomials Like terms Addition and subtraction of polynomials Distributive law Multiplication and
Unit 5. Linear equations and inequalities OUTLINE. Topic 13: Solving linear equations. Topic 14: Problem solving with slope triangles
 Unit 5 Linear equations and inequalities In this unit, you will build your understanding of the connection between linear functions and linear equations and inequalities that can be used to represent and
Unit 5 Linear equations and inequalities In this unit, you will build your understanding of the connection between linear functions and linear equations and inequalities that can be used to represent and
STEP 1: Ask Do I know the SLOPE of the line? (Notice how it s needed for both!) YES! NO! But, I have two NO! But, my line is
 EQUATIONS OF LINES 1. Writing Equations of Lines There are many ways to define a line, but for today, let s think of a LINE as a collection of points such that the slope between any two of those points
EQUATIONS OF LINES 1. Writing Equations of Lines There are many ways to define a line, but for today, let s think of a LINE as a collection of points such that the slope between any two of those points
 Twitter: @Owen134866 www.mathsfreeresourcelibrary.com Prior Knowledge Check 1) Find the point of intersection for each pair of lines: a) y = 4x + 7 and 5y = 2x 1 b) y = 5x 1 and 3x + 7y = 11 c) 2x 5y =
Twitter: @Owen134866 www.mathsfreeresourcelibrary.com Prior Knowledge Check 1) Find the point of intersection for each pair of lines: a) y = 4x + 7 and 5y = 2x 1 b) y = 5x 1 and 3x + 7y = 11 c) 2x 5y =
Algebra 1 ECA Remediation Diagnostic Homework Review #2
 Lesson 1 1. Simplify the expression. (r 6) +10r A1.1.3.1 Algebra 1 ECA Remediation Diagnostic Homework Review # Lesson. Solve the equation. 5x + 4x = 10 +6x + x A1..1 Lesson 3. Solve the equation. 1 +
Lesson 1 1. Simplify the expression. (r 6) +10r A1.1.3.1 Algebra 1 ECA Remediation Diagnostic Homework Review # Lesson. Solve the equation. 5x + 4x = 10 +6x + x A1..1 Lesson 3. Solve the equation. 1 +
Sample: Do Not Reproduce LF6 STUDENT PAGES LINEAR FUNCTIONS STUDENT PACKET 6: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS. Name Period Date
 Name Period Date LINEAR FUNCTIONS STUDENT PACKET 6: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS LF6.1 LF6.2 LF6.3 Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations Understand the definition of a system of linear equations Understand
Name Period Date LINEAR FUNCTIONS STUDENT PACKET 6: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS LF6.1 LF6.2 LF6.3 Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations Understand the definition of a system of linear equations Understand
Chapter 9: Roots and Irrational Numbers
 Chapter 9: Roots and Irrational Numbers Index: A: Square Roots B: Irrational Numbers C: Square Root Functions & Shifting D: Finding Zeros by Completing the Square E: The Quadratic Formula F: Quadratic
Chapter 9: Roots and Irrational Numbers Index: A: Square Roots B: Irrational Numbers C: Square Root Functions & Shifting D: Finding Zeros by Completing the Square E: The Quadratic Formula F: Quadratic
Eureka Math. Grade 8, Module 4. Student File_B. Contains Exit Ticket, and Assessment Materials
 A Story of Ratios Eureka Math Grade 8, Module 4 Student File_B Contains, and Assessment Materials Published by the non-profit Great Minds. Copyright 2015 Great Minds. No part of this work may be reproduced,
A Story of Ratios Eureka Math Grade 8, Module 4 Student File_B Contains, and Assessment Materials Published by the non-profit Great Minds. Copyright 2015 Great Minds. No part of this work may be reproduced,
Algebra. CLCnet. Page Topic Title. Revision Websites. GCSE Revision 2006/7 - Mathematics. Add your favourite websites and school software here.
 Section 2 Page Topic Title 54-57 12. Basic algebra 58-61 13. Solving equations 62-64 14. Forming and solving equations from written information 65-67 15. Trial and improvement 68-72 16. Formulae 73-76
Section 2 Page Topic Title 54-57 12. Basic algebra 58-61 13. Solving equations 62-64 14. Forming and solving equations from written information 65-67 15. Trial and improvement 68-72 16. Formulae 73-76
Algebra 1 Enriched- Midterm Review
 Algebra 1 Enriched- Midterm Review Know all vocabulary, pay attention to the highlighted words in the text, and understand the various types of directions in each of the sections of the textbook. Practice
Algebra 1 Enriched- Midterm Review Know all vocabulary, pay attention to the highlighted words in the text, and understand the various types of directions in each of the sections of the textbook. Practice
Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Paper Reference(s) 666/0 Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C Gold Level G Time: hour 0 minutes Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included with question papers Nil Candidates
Paper Reference(s) 666/0 Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C Gold Level G Time: hour 0 minutes Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included with question papers Nil Candidates
Name: Teacher: School: Contents:
 Name: Teacher: School: Contents: Key Words... 1 Tools and Strategies... 2 Open Response Rubric... 3 EQAO Formula Sheet... 5 Sample Questions from the 2014 Assessment... 7 Sample Questions from the 2013
Name: Teacher: School: Contents: Key Words... 1 Tools and Strategies... 2 Open Response Rubric... 3 EQAO Formula Sheet... 5 Sample Questions from the 2014 Assessment... 7 Sample Questions from the 2013
Section 3.4 Writing the Equation of a Line
 Chapter Linear Equations and Functions Section.4 Writing the Equation of a Line Writing Equations of Lines Critical to a thorough understanding of linear equations and functions is the ability to write
Chapter Linear Equations and Functions Section.4 Writing the Equation of a Line Writing Equations of Lines Critical to a thorough understanding of linear equations and functions is the ability to write
Name: Date: Period: Activity 4.5.1: Direct Variation
 Name: Date: Period: Activity 4.5.1: Direct Variation 1.) When building a roof, carpenters place posts every 2 feet along the horizontal support beam starting at the eave. The diagram below illustrates
Name: Date: Period: Activity 4.5.1: Direct Variation 1.) When building a roof, carpenters place posts every 2 feet along the horizontal support beam starting at the eave. The diagram below illustrates
Math 112 Group Activity: The Vertical Speed of a Shell
 Name: Section: Math 112 Group Activity: The Vertical Speed of a Shell A shell is fired straight up by a mortar. The graph below shows its altitude as a function of time. 400 300 altitude (in feet) 200
Name: Section: Math 112 Group Activity: The Vertical Speed of a Shell A shell is fired straight up by a mortar. The graph below shows its altitude as a function of time. 400 300 altitude (in feet) 200
Math 8 Unit 4: A Study of Linear Equations
 Math 8 Unit 4: A Study of Linear Equations By the end of this unit, students should be able to: 1) Show that the slope of a line can be calculated as rise/run. Explain why the slope is the same between
Math 8 Unit 4: A Study of Linear Equations By the end of this unit, students should be able to: 1) Show that the slope of a line can be calculated as rise/run. Explain why the slope is the same between
Section 8 Topic 1 Comparing Linear, Quadratic, and Exponential Functions Part 1
 Section 8: Summary of Functions Section 8 Topic 1 Comparing Linear, Quadratic, and Exponential Functions Part 1 Complete the table below to describe the characteristics of linear functions. Linear Functions
Section 8: Summary of Functions Section 8 Topic 1 Comparing Linear, Quadratic, and Exponential Functions Part 1 Complete the table below to describe the characteristics of linear functions. Linear Functions
Using Linear Equations to Solve Problems
 Chapter 5: Writing Linear Equations Sections 1-4 Name Algebra Notes Using Linear Equations to Solve Problems Slope-Intercept Point Slope Standard Form y = mx + b y- y 1 = m ( x = x 1 ) Ax + By = C So,
Chapter 5: Writing Linear Equations Sections 1-4 Name Algebra Notes Using Linear Equations to Solve Problems Slope-Intercept Point Slope Standard Form y = mx + b y- y 1 = m ( x = x 1 ) Ax + By = C So,
4. The table shows the number of toll booths driven through compared to the cost of using a Toll Tag.
 ALGEBRA 1 Fall 2016 Semester Exam Review Name 1. According to the data shown below, which would be the best prediction of the average cost of a -bedroom house in Georgetown in the year 2018? Year Average
ALGEBRA 1 Fall 2016 Semester Exam Review Name 1. According to the data shown below, which would be the best prediction of the average cost of a -bedroom house in Georgetown in the year 2018? Year Average
LINEAR EQUATIONS Modeling Linear Equations Common Core Standards
 E Linear Equations, Lesson 1, Modeling Linear Functions (r. 2018) LINEAR EQUATIONS Modeling Linear Equations Common Core Standards F-BF.A.1 Write a function that describes a relationship between two quantities.
E Linear Equations, Lesson 1, Modeling Linear Functions (r. 2018) LINEAR EQUATIONS Modeling Linear Equations Common Core Standards F-BF.A.1 Write a function that describes a relationship between two quantities.
Lesson 26: Characterization of Parallel Lines
 Student Outcomes Students know that when a system of linear equations has no solution, i.e., no point of intersection of the lines, then the lines are parallel. Lesson Notes The discussion that begins
Student Outcomes Students know that when a system of linear equations has no solution, i.e., no point of intersection of the lines, then the lines are parallel. Lesson Notes The discussion that begins
First Differences WS 5.1. Rate of Change WS 5.2. Slope/Rate of Change WS 5.3. Partial Variation WS 5.5. Mid Chapter Review & EQAO Practice
 UNIT 5 - LINEAR RELATIONS Date Lesson Topic HW Nov. 22 5.1 First Differences WS 5.1 Nov. 22 5.2 Rate of Change WS 5.2 Nov. 27 5.3 Slope/Rate of Change WS 5.3 Nov. 28 5.4 Direct Variation QUIZ (5.1-5.2)
UNIT 5 - LINEAR RELATIONS Date Lesson Topic HW Nov. 22 5.1 First Differences WS 5.1 Nov. 22 5.2 Rate of Change WS 5.2 Nov. 27 5.3 Slope/Rate of Change WS 5.3 Nov. 28 5.4 Direct Variation QUIZ (5.1-5.2)
ALGEBRA I SEMESTER EXAMS PRACTICE MATERIALS SEMESTER Use the diagram below. 9.3 cm. A = (9.3 cm) (6.2 cm) = cm 2. 6.
 1. Use the diagram below. 9.3 cm A = (9.3 cm) (6.2 cm) = 57.66 cm 2 6.2 cm A rectangle s sides are measured to be 6.2 cm and 9.3 cm. What is the rectangle s area rounded to the correct number of significant
1. Use the diagram below. 9.3 cm A = (9.3 cm) (6.2 cm) = 57.66 cm 2 6.2 cm A rectangle s sides are measured to be 6.2 cm and 9.3 cm. What is the rectangle s area rounded to the correct number of significant
Polynomials. Lesson 6
 Polynomials Lesson 6 MFMP Foundations of Mathematics Unit Lesson 6 Lesson Six Concepts Overall Expectations Simplify numerical and polynomial expressions in one variable, and solve simple first-degree
Polynomials Lesson 6 MFMP Foundations of Mathematics Unit Lesson 6 Lesson Six Concepts Overall Expectations Simplify numerical and polynomial expressions in one variable, and solve simple first-degree
TEST 150 points
 Math 130 Spring 008 Name: TEST #1 @ 150 points Write neatly. Show all work. Write all responses on separate paper. Clearly label the exercises. 1. A piecewise-defined function is given. 1- x if x< f (
Math 130 Spring 008 Name: TEST #1 @ 150 points Write neatly. Show all work. Write all responses on separate paper. Clearly label the exercises. 1. A piecewise-defined function is given. 1- x if x< f (
Sect 2.4 Linear Functions
 36 Sect 2.4 Linear Functions Objective 1: Graphing Linear Functions Definition A linear function is a function in the form y = f(x) = mx + b where m and b are real numbers. If m 0, then the domain and
36 Sect 2.4 Linear Functions Objective 1: Graphing Linear Functions Definition A linear function is a function in the form y = f(x) = mx + b where m and b are real numbers. If m 0, then the domain and
Linear vs. Exponential Word Problems
 Linear vs. Eponential Word Problems At separate times in the course, you ve learned about linear functions and eponential functions, and done word problems involving each type of function. Today s assignment
Linear vs. Eponential Word Problems At separate times in the course, you ve learned about linear functions and eponential functions, and done word problems involving each type of function. Today s assignment
Lesson: Slope. Warm Up. Unit #2: Linear Equations. 2) If f(x) = 7x 5, find the value of the following: f( 2) f(3) f(0)
 Warm Up 1) 2) If f(x) = 7x 5, find the value of the following: f( 2) f(3) f(0) Oct 15 10:21 AM Unit #2: Linear Equations Lesson: Slope Oct 15 10:05 AM 1 Students will be able to find the slope Oct 16 12:19
Warm Up 1) 2) If f(x) = 7x 5, find the value of the following: f( 2) f(3) f(0) Oct 15 10:21 AM Unit #2: Linear Equations Lesson: Slope Oct 15 10:05 AM 1 Students will be able to find the slope Oct 16 12:19
Keystone Exam Practice Test # 3
 Name: Date: Part 1 Multiple Choice Keystone Exam Practice Test # 1) Evan always drives between 45 and 60 miles per hour on his commute. The distance he travels can be represented in the system of inequalities
Name: Date: Part 1 Multiple Choice Keystone Exam Practice Test # 1) Evan always drives between 45 and 60 miles per hour on his commute. The distance he travels can be represented in the system of inequalities
Sect The Slope-Intercept Form
 0 Concepts # and # Sect. - The Slope-Intercept Form Slope-Intercept Form of a line Recall the following definition from the beginning of the chapter: Let a, b, and c be real numbers where a and b are not
0 Concepts # and # Sect. - The Slope-Intercept Form Slope-Intercept Form of a line Recall the following definition from the beginning of the chapter: Let a, b, and c be real numbers where a and b are not
Topic 1. Solving Equations and Inequalities 1. Solve the following equation
 Topic 1. Solving Equations and Inequalities 1. Solve the following equation Algebraically 2( x 3) = 12 Graphically 2( x 3) = 12 2. Solve the following equations algebraically a. 5w 15 2w = 2(w 5) b. 1
Topic 1. Solving Equations and Inequalities 1. Solve the following equation Algebraically 2( x 3) = 12 Graphically 2( x 3) = 12 2. Solve the following equations algebraically a. 5w 15 2w = 2(w 5) b. 1
Elementary Algebra Sample Final Exam Spring 2017
 Elementary Algebra NAME: Sample Final Exam Spring 2017 You will have 2 hours to complete this exam. You may use a calculator but must show all algebraic work in the space provided to receive full credit.
Elementary Algebra NAME: Sample Final Exam Spring 2017 You will have 2 hours to complete this exam. You may use a calculator but must show all algebraic work in the space provided to receive full credit.
Chapter 2: Linear Functions
 Chapter 2: Linear Functions Chapter one was a window that gave us a peek into the entire course. Our goal was to understand the basic structure of functions and function notation, the toolkit functions,
Chapter 2: Linear Functions Chapter one was a window that gave us a peek into the entire course. Our goal was to understand the basic structure of functions and function notation, the toolkit functions,
Name: Period: Date: Algebra 1 1st Semester Review Which best describes the solution(s) for this equation? 3 ( 8x 12) = 33 2x
 Name: Period: ate: lgebra 1 1st Semester Review 2011 1 Which algebraic expression could NOT match the pictorial representation below? 5 Which best describes the solution(s) for this equation? 3 ( 8x 12)
Name: Period: ate: lgebra 1 1st Semester Review 2011 1 Which algebraic expression could NOT match the pictorial representation below? 5 Which best describes the solution(s) for this equation? 3 ( 8x 12)
The Celsius temperature scale is based on the freezing point and the boiling point of water. 12 degrees Celsius below zero would be written as
 Prealgebra, Chapter 2 - Integers, Introductory Algebra 2.1 Integers In the real world, numbers are used to represent real things, such as the height of a building, the cost of a car, the temperature of
Prealgebra, Chapter 2 - Integers, Introductory Algebra 2.1 Integers In the real world, numbers are used to represent real things, such as the height of a building, the cost of a car, the temperature of
MFM2P Foundations of Mathematics Unit 3 Lesson 11
 The Line Lesson MFMP Foundations of Mathematics Unit Lesson Lesson Eleven Concepts Introduction to the line Using standard form of an equation Using y-intercept form of an equation x and y intercept Recognizing
The Line Lesson MFMP Foundations of Mathematics Unit Lesson Lesson Eleven Concepts Introduction to the line Using standard form of an equation Using y-intercept form of an equation x and y intercept Recognizing
LESSON #11 - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
Chapter 0.B.3. [More than Just] Lines.
![Chapter 0.B.3. [More than Just] Lines. Chapter 0.B.3. [More than Just] Lines.](/thumbs/84/90640295.jpg) Chapter 0.B.3. [More than Just] Lines. Of course you've studied lines before, so why repeat it one more time? Haven't you seen this stuff about lines enough to skip this section? NO! But why? It is true
Chapter 0.B.3. [More than Just] Lines. Of course you've studied lines before, so why repeat it one more time? Haven't you seen this stuff about lines enough to skip this section? NO! But why? It is true
Item Specification Sheet Algebra I Semester Exam
 Item Specification Sheet Algebra I Semester Exam Free Response: 1. Illustrating Mathematical Properties 2. Equations with Infinitely Many Solutions or No Solution 3. Relations and Functions 4. Application
Item Specification Sheet Algebra I Semester Exam Free Response: 1. Illustrating Mathematical Properties 2. Equations with Infinitely Many Solutions or No Solution 3. Relations and Functions 4. Application
ALGEBRA 2 Summer Review Assignments Graphing
 ALGEBRA 2 Summer Review Assignments Graphing To be prepared for algebra two, and all subsequent math courses, you need to be able to accurately and efficiently find the slope of any line, be able to write
ALGEBRA 2 Summer Review Assignments Graphing To be prepared for algebra two, and all subsequent math courses, you need to be able to accurately and efficiently find the slope of any line, be able to write
Name: Date: Page 1 of 7. Direct Variation. Post Horizontal distance from post Height of Post Ratio y x
 Name: Date: Page 1 of 7 Direct Variation 1. When building a roof, carpenters place posts every 2 feet along the horizontal support beam starting at the eave. The diagram below illustrates this. Eave 4.5
Name: Date: Page 1 of 7 Direct Variation 1. When building a roof, carpenters place posts every 2 feet along the horizontal support beam starting at the eave. The diagram below illustrates this. Eave 4.5
Mathematics GRADE 8 Teacher Packet
 COMMON CORE Standards Plus Mathematics GRADE 8 Teacher Packet Copyright 01 Learning Plus Associates All Rights Reserved; International Copyright Secured. Permission is hereby granted to teachers to reprint
COMMON CORE Standards Plus Mathematics GRADE 8 Teacher Packet Copyright 01 Learning Plus Associates All Rights Reserved; International Copyright Secured. Permission is hereby granted to teachers to reprint
TEST BANK. How TO USE THIS TEST BANK
 TEST BANK How TO USE THIS TEST BANK In this section you will find one chap-ter test for each of the 14 chapters in Algebra: Themes, Tools, Concepts. For Chapters 3, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, and 13, you will also
TEST BANK How TO USE THIS TEST BANK In this section you will find one chap-ter test for each of the 14 chapters in Algebra: Themes, Tools, Concepts. For Chapters 3, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, and 13, you will also
LHS Algebra Pre-Test
 Your Name Teacher Block Grade (please circle): 9 10 11 12 Course level (please circle): Honors Level 1 Instructions LHS Algebra Pre-Test The purpose of this test is to see whether you know Algebra 1 well
Your Name Teacher Block Grade (please circle): 9 10 11 12 Course level (please circle): Honors Level 1 Instructions LHS Algebra Pre-Test The purpose of this test is to see whether you know Algebra 1 well
Graphing Equations Chapter Test
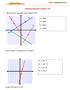 1. Which line on the graph has a slope of 2/3? Graphing Equations Chapter Test A. Line A B. Line B C. Line C D. Line D 2. Which equation is represented on the graph? A. y = 4x 6 B. y = -4x 6 C. y = 4x
1. Which line on the graph has a slope of 2/3? Graphing Equations Chapter Test A. Line A B. Line B C. Line C D. Line D 2. Which equation is represented on the graph? A. y = 4x 6 B. y = -4x 6 C. y = 4x
Grade 8 + DIGITAL. EL Strategies. DOK 1-4 RTI Tiers 1-3. Flexible Supplemental K-8 ELA & Math Online & Print
 Standards PLUS Flexible Supplemental K-8 ELA & Math Online & Print Grade 8 SAMPLER Mathematics EL Strategies DOK 1-4 RTI Tiers 1-3 15-20 Minute Lessons Assessments Consistent with CA Testing Technology
Standards PLUS Flexible Supplemental K-8 ELA & Math Online & Print Grade 8 SAMPLER Mathematics EL Strategies DOK 1-4 RTI Tiers 1-3 15-20 Minute Lessons Assessments Consistent with CA Testing Technology
Midterm Review Packet
 Algebra 1 CHAPTER 1 Midterm Review Packet Name Date Match the following with the appropriate property. 1. x y y x A. Distributive Property. 6 u v 6u 1v B. Commutative Property of Multiplication. m n 5
Algebra 1 CHAPTER 1 Midterm Review Packet Name Date Match the following with the appropriate property. 1. x y y x A. Distributive Property. 6 u v 6u 1v B. Commutative Property of Multiplication. m n 5
CHAPTER 5-1. Regents Exam Questions - PH Algebra Chapter 5 Page a, P.I. 8.G.13 What is the slope of line shown in the
 Regents Exam Questions - PH Algebra Chapter Page 1 CHAPTER -1 SLOPE AND DIRECT VARIATION 4. 069918a, P.I. 8.G.1 What is the slope of line shown in the accompanying diagram? 1. 080417a, P.I. A.A. If the
Regents Exam Questions - PH Algebra Chapter Page 1 CHAPTER -1 SLOPE AND DIRECT VARIATION 4. 069918a, P.I. 8.G.1 What is the slope of line shown in the accompanying diagram? 1. 080417a, P.I. A.A. If the
Math 8 Honors Coordinate Geometry part 1 Unit Updated July 29, 2016
 Reviewing the basics The number line A number line is a visual representation of all real numbers. Each of the images below are examples of number lines. The top left one includes only positive whole numbers,
Reviewing the basics The number line A number line is a visual representation of all real numbers. Each of the images below are examples of number lines. The top left one includes only positive whole numbers,
Mathematics 10C. UNIT FIVE Linear Functions. Unit. Student Workbook. y 2. - y 1 x 2. rise. m = - x 1 run. y = mx + b. m = m original. 1 moriginal.
 Mathematics 10C Student Workbook Unit m = y 2 - y 1 x 2 - x 1 run rise Lesson 1: Slope of a Line Approximate Completion Time: 2 Days y = mx + b Lesson 2: Slope-Intercept Form Approximate Completion Time:
Mathematics 10C Student Workbook Unit m = y 2 - y 1 x 2 - x 1 run rise Lesson 1: Slope of a Line Approximate Completion Time: 2 Days y = mx + b Lesson 2: Slope-Intercept Form Approximate Completion Time:
FOR STUDENTS WHO HAVE COMPLETED ALGEBRA 1 (Students entering Geometry)
 FOR STUDENTS WHO HAVE COMPLETED ALGEBRA (Students entering Geometry) Dear Parent/Guardian and Student, Name: Date: Period: Attached you will find a review packet of skills which each student is expected
FOR STUDENTS WHO HAVE COMPLETED ALGEBRA (Students entering Geometry) Dear Parent/Guardian and Student, Name: Date: Period: Attached you will find a review packet of skills which each student is expected
Algebra 1 ECA Remediation Diagnostic Homework Review #1
 Algebra 1 ECA Remediation Diagnostic Homework Review #1 Lesson 1 1. Simplify the expression. 8 5(7 r) A1.1.3.1 Lesson. Solve the equation. 4x 1 = 9 x A1..1 Lesson 3. Solve the equation. 1.6n 5.95 = 11.7
Algebra 1 ECA Remediation Diagnostic Homework Review #1 Lesson 1 1. Simplify the expression. 8 5(7 r) A1.1.3.1 Lesson. Solve the equation. 4x 1 = 9 x A1..1 Lesson 3. Solve the equation. 1.6n 5.95 = 11.7
The steps in Raya s solution to 2.5 (6.25x + 0.5) = 11 are shown. Select the correct reason for line 4 of Raya s solution.
 A.CED.1 Create equations and inequalities in one variable and use them to solve problems. Include equations arising from linear functions. Unit 2: Reasoning with Linear Equations and Inequalities The perimeter
A.CED.1 Create equations and inequalities in one variable and use them to solve problems. Include equations arising from linear functions. Unit 2: Reasoning with Linear Equations and Inequalities The perimeter
Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by David Rennie. Adapted from the Georgia Department of Education Frameworks
 Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by David Rennie Adapted from the Georgia Department of Education Frameworks Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by
Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by David Rennie Adapted from the Georgia Department of Education Frameworks Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by
Mathematics Level D: Lesson 2 Representations of a Line
 Mathematics Level D: Lesson 2 Representations of a Line Targeted Student Outcomes Students graph a line specified by a linear function. Students graph a line specified by an initial value and rate of change
Mathematics Level D: Lesson 2 Representations of a Line Targeted Student Outcomes Students graph a line specified by a linear function. Students graph a line specified by an initial value and rate of change
MAT 135. In Class Assignments
 MAT 15 In Class Assignments 1 Chapter 1 1. Simplify each expression: a) 5 b) (5 ) c) 4 d )0 6 4. a)factor 4,56 into the product of prime factors b) Reduce 4,56 5,148 to lowest terms.. Translate each statement
MAT 15 In Class Assignments 1 Chapter 1 1. Simplify each expression: a) 5 b) (5 ) c) 4 d )0 6 4. a)factor 4,56 into the product of prime factors b) Reduce 4,56 5,148 to lowest terms.. Translate each statement
CORE. Chapter 3: Interacting Linear Functions, Linear Systems. Algebra Assessments
 CORE Algebra Assessments Chapter 3: Interacting Linear Functions, Linear Systems 97 98 Bears Band Booster Club The Bears Band Booster Club has decided to sell calendars to the band members and their parents.
CORE Algebra Assessments Chapter 3: Interacting Linear Functions, Linear Systems 97 98 Bears Band Booster Club The Bears Band Booster Club has decided to sell calendars to the band members and their parents.
Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Paper Reference(s) 666/0 Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C Gold Level G Time: hour 0 minutes Materials required for examination papers Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included with question Nil Candidates
Paper Reference(s) 666/0 Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C Gold Level G Time: hour 0 minutes Materials required for examination papers Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included with question Nil Candidates
Chapter 3 Representations of a Linear Relation
 Chapter 3 Representations of a Linear Relation The purpose of this chapter is to develop fluency in the ways of representing a linear relation, and in extracting information from these representations.
Chapter 3 Representations of a Linear Relation The purpose of this chapter is to develop fluency in the ways of representing a linear relation, and in extracting information from these representations.
LESSON #12 - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
4. Based on the table below, what is the joint relative frequency of the people surveyed who do not have a job and have a savings account?
 Name: Period: Date: Algebra 1 Common Semester 1 Final Review 1. How many surveyed do not like PS4 and do not like X-Box? 2. What percent of people surveyed like the X-Box, but not the PS4? 3. What is the
Name: Period: Date: Algebra 1 Common Semester 1 Final Review 1. How many surveyed do not like PS4 and do not like X-Box? 2. What percent of people surveyed like the X-Box, but not the PS4? 3. What is the
Mathematics Success Grade 8
 T538 Mathematics Success Grade 8 [OBJECTIVE] The student will compare functions represented algebraically, graphically, with verbal descriptions or in tables and identify functions as linear or non-linear.
T538 Mathematics Success Grade 8 [OBJECTIVE] The student will compare functions represented algebraically, graphically, with verbal descriptions or in tables and identify functions as linear or non-linear.
Chapter 1: January 26 January 30
 Chapter : January 26 January 30 Section.7: Inequalities As a diagnostic quiz, I want you to go through the first ten problems of the Chapter Test on page 32. These will test your knowledge of Sections.
Chapter : January 26 January 30 Section.7: Inequalities As a diagnostic quiz, I want you to go through the first ten problems of the Chapter Test on page 32. These will test your knowledge of Sections.
East Greenwich Mathematics Summer Review Material for Students Entering Algebra I, Part II Directions:
 East Greenwich Mathematics Summer Review Material for Students Entering Algebra I, Part II 2016-2017 Directions: In order to earn full credit, show all work in the spaces provided. Do all work without
East Greenwich Mathematics Summer Review Material for Students Entering Algebra I, Part II 2016-2017 Directions: In order to earn full credit, show all work in the spaces provided. Do all work without
Outline. Lesson 3: Linear Functions. Objectives:
 Lesson 3: Linear Functions Objectives: Outline I can determine the dependent and independent variables in a linear function. I can read and interpret characteristics of linear functions including x- and
Lesson 3: Linear Functions Objectives: Outline I can determine the dependent and independent variables in a linear function. I can read and interpret characteristics of linear functions including x- and
Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Academic Standards Mathematics
 ALGEBRA 1 Standard 1 Operations with Real Numbers Students simplify and compare expressions. They use rational exponents, and simplify square roots. A1.1.1 A1.1.2 A1.1.3 A1.1.4 A1.1.5 Compare real number
ALGEBRA 1 Standard 1 Operations with Real Numbers Students simplify and compare expressions. They use rational exponents, and simplify square roots. A1.1.1 A1.1.2 A1.1.3 A1.1.4 A1.1.5 Compare real number
4. Solve for x: 5. Use the FOIL pattern to multiply (4x 2)(x + 3). 6. Simplify using exponent rules: (6x 3 )(2x) 3
 SUMMER REVIEW FOR STUDENTS COMPLETING ALGEBRA I WEEK 1 1. Write the slope-intercept form of an equation of a. Write a definition of slope. 7 line with a slope of, and a y-intercept of 3. 11 3. You want
SUMMER REVIEW FOR STUDENTS COMPLETING ALGEBRA I WEEK 1 1. Write the slope-intercept form of an equation of a. Write a definition of slope. 7 line with a slope of, and a y-intercept of 3. 11 3. You want
Pre-AP Algebra II Summer Packet
 Summer Packet Pre-AP Algebra II Name Period Pre-AP Algebra II 2018-2019 Summer Packet The purpose of this packet is to make sure that you have the mathematical skills you will need to succeed in Pre-AP
Summer Packet Pre-AP Algebra II Name Period Pre-AP Algebra II 2018-2019 Summer Packet The purpose of this packet is to make sure that you have the mathematical skills you will need to succeed in Pre-AP
Math 8 Unit 5. Writing Equations. Tuesday, November 27; 7:30am Tuesday, December 4; 7:30am. Date Lesson Topic Homework
 Math 8 Unit 5 Writing Equations Extra Help: Tuesday, November 20; 2:40pm Tuesday, November 27; 7:30am Tuesday, December 4; 7:30am Date Lesson Topic Homework M 11/19 1 Types of Slope Lesson 1 -Page 6 T
Math 8 Unit 5 Writing Equations Extra Help: Tuesday, November 20; 2:40pm Tuesday, November 27; 7:30am Tuesday, December 4; 7:30am Date Lesson Topic Homework M 11/19 1 Types of Slope Lesson 1 -Page 6 T
Lesson 7: Slopes and Functions: Speed and Velocity
 Lesson 7: Slopes and Functions: Speed and Velocity 7.1 Observe and Represent Another way of comparing trend lines is by calculating the slope of each line and comparing the numerical values of the slopes.
Lesson 7: Slopes and Functions: Speed and Velocity 7.1 Observe and Represent Another way of comparing trend lines is by calculating the slope of each line and comparing the numerical values of the slopes.
Eureka Math. Grade, Module 4. Student File_B Contains Sprint and Fluency, Exit Ticket, and Assessment Materials
 A Story of Eureka Math Grade, Module 4 Student File_B Contains Sprint and Fluency,, and Assessment Materials Published by the non-profit Great Minds. Copyright 2015 Great Minds. No part of this work may
A Story of Eureka Math Grade, Module 4 Student File_B Contains Sprint and Fluency,, and Assessment Materials Published by the non-profit Great Minds. Copyright 2015 Great Minds. No part of this work may
Chapter 2 Linear Relationships. Vocabulary
 Chapter 2 Linear Relationships Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Sept. 2 Lesson: 2.1.1/2.1.2 Sept. 3 Lesson: 2.1.3/2.1.4 Sept. 4 Lesson: 2.2.2 HW: Day 1 2-6 2-10 2-19 2-24 HW: Day 2 2-31 2-35 2-41
Chapter 2 Linear Relationships Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Sept. 2 Lesson: 2.1.1/2.1.2 Sept. 3 Lesson: 2.1.3/2.1.4 Sept. 4 Lesson: 2.2.2 HW: Day 1 2-6 2-10 2-19 2-24 HW: Day 2 2-31 2-35 2-41
Sample Assessment Materials
 Edexcel Awards Mathematics Sample Assessment Materials Edexcel Level Award in Algebra (AAL0) Edexcel Level 3 Award in Algebra (AAL30) For first teaching from October 01 Pearson Education Limited is a registered
Edexcel Awards Mathematics Sample Assessment Materials Edexcel Level Award in Algebra (AAL0) Edexcel Level 3 Award in Algebra (AAL30) For first teaching from October 01 Pearson Education Limited is a registered
MAT 135 In-Class Assignments Answer Key
 MAT 135 In-Class Assignments Answer Key Answers are listed under the heading of each section. Where a section was continued on multiple pages, the answers are all listed under the section heading. If there
MAT 135 In-Class Assignments Answer Key Answers are listed under the heading of each section. Where a section was continued on multiple pages, the answers are all listed under the section heading. If there
3.1 Exercises. Amount saved A (dollars) Section 3.1 Linear Models 233
 Section 3.1 Linear Models 233 3.1 Exercises 1. Jodiah is saving his money to buy a Playstation 3 gaming system. He estimates that he will need $950 to buy the unit itself, accessories, and a few games.
Section 3.1 Linear Models 233 3.1 Exercises 1. Jodiah is saving his money to buy a Playstation 3 gaming system. He estimates that he will need $950 to buy the unit itself, accessories, and a few games.
BETHLEHEM CATHOLIC HIGH SCHOOL
 BETHLEHEM CATHOLIC HIGH SCHOOL ALGEBRA SUMMER ASSIGNMENT NAME: - Variables and Expressions For Exercises, choose the correct letter.. The word minus corresponds to which symbol? A. B. C. D.. The phrase
BETHLEHEM CATHOLIC HIGH SCHOOL ALGEBRA SUMMER ASSIGNMENT NAME: - Variables and Expressions For Exercises, choose the correct letter.. The word minus corresponds to which symbol? A. B. C. D.. The phrase
Solving Systems of Linear Equations
 Section 2.3 Solving Systems of Linear Equations TERMINOLOGY 2.3 Previously Used: Equivalent Equations Literal Equation Properties of Equations Substitution Principle Prerequisite Terms: Coordinate Axes
Section 2.3 Solving Systems of Linear Equations TERMINOLOGY 2.3 Previously Used: Equivalent Equations Literal Equation Properties of Equations Substitution Principle Prerequisite Terms: Coordinate Axes
Overview Ratios, Rates, Proportions, and Percents Polynomials Equations Overview Statistics...
 Overview... 5 1. Integers and Real Numbers... 6 2. Ratios, Rates, Proportions, and Percents... 10 3. Laws of Exponents... 14 4. Algebraic Expressions... 18 5. Polynomials... 22 6. Equations... 26 7. Graphs
Overview... 5 1. Integers and Real Numbers... 6 2. Ratios, Rates, Proportions, and Percents... 10 3. Laws of Exponents... 14 4. Algebraic Expressions... 18 5. Polynomials... 22 6. Equations... 26 7. Graphs
Lesson 3: Working With Linear Relations Day 3 Unit 1 Linear Relations
 (A) Lesson Context BIG PICTURE of this UNIT: CONTEXT of this LESSON: mastery with algebraic manipulations/calculations involving linear relations proficiency in working with graphic and numeric representations
(A) Lesson Context BIG PICTURE of this UNIT: CONTEXT of this LESSON: mastery with algebraic manipulations/calculations involving linear relations proficiency in working with graphic and numeric representations
Please allow yourself one to two hours to complete the following sections of the packet. College Integrated Geometry Honors Integrated Geometry
 Incoming Integrated Geometry Summer Work Dear Incoming Integrated Geometry Students, To better prepare for your high school mathematics entry process, summer work is assigned to ensure an easier transition
Incoming Integrated Geometry Summer Work Dear Incoming Integrated Geometry Students, To better prepare for your high school mathematics entry process, summer work is assigned to ensure an easier transition
Review for MIDTERM. Ensure your Survival Guides are complete and corrected. These you may use on PART #1 (but not on PART #2)
 1 M i d t e r m 10P Date: Name: Review for MIDTERM MIDTERM TASK #1 date MIDTERM TASK # date Success Criteria Students on IEP if ou will need more time to finish, arrange a ride afterschool on these das
1 M i d t e r m 10P Date: Name: Review for MIDTERM MIDTERM TASK #1 date MIDTERM TASK # date Success Criteria Students on IEP if ou will need more time to finish, arrange a ride afterschool on these das
This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 4 from the book Beginning Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0).
 This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 4 from the book Beginning Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 4 from the book Beginning Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
Number System Chapter Questions
 Number System Chapter Questions. What is an integer?. Explain what absolute value represents.. Create an owing money example for comparing two negative numbers.. What is the Cartesian (Coordinate) plane?
Number System Chapter Questions. What is an integer?. Explain what absolute value represents.. Create an owing money example for comparing two negative numbers.. What is the Cartesian (Coordinate) plane?
Chapter 5: Writing Linear Equations Study Guide (REG)
 Chapter 5: Writing Linear Equations Study Guide (REG) 5.1: Write equations of lines given slope and y intercept or two points Write the equation of the line with the given information: Ex: Slope: 0, y
Chapter 5: Writing Linear Equations Study Guide (REG) 5.1: Write equations of lines given slope and y intercept or two points Write the equation of the line with the given information: Ex: Slope: 0, y
Edexcel New GCE A Level Maths workbook
 Edexcel New GCE A Level Maths workbook Straight line graphs Parallel and Perpendicular lines. Edited by: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebly.com Straight line graphs A LEVEL LINKS Scheme of work: a. Straight-line
Edexcel New GCE A Level Maths workbook Straight line graphs Parallel and Perpendicular lines. Edited by: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebly.com Straight line graphs A LEVEL LINKS Scheme of work: a. Straight-line
