Overview of Fourier Series (Sect. 6.2). Origins of the Fourier Series.
|
|
|
- Alicia Lucas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Overview of Fourier Series (Sect Origins of the Fourier Series. Periodic functions. Orthogonality of Sines and Cosines. Main result on Fourier Series. Origins of the Fourier Series. Summary: Daniel Bernoulli ( 1750 found solutions to the equation that describes waves propagating on a vibrating string. y 0 x u(t,x x The function u, measuring the vertical displacement of the string, is the solution to the wave equation, 2 t u(t, x = v 2 2 x u(t, x, v R, x [0,, t [0,, with initial conditions, and boundary conditions, u(0, x = f (x, t u(0, x = 0, u(t, 0 = 0, u(t, = 0.
2 Origins of the Fourier Series. Summary: Bernoulli found particular solutions to the wave equation. If the initial condition is f n (x = sin, ( vnπt then the solution is u n (t, x = sin. Bernoulli also realized that N ( vnπt U N (t, x = a n sin, a n R is also solution of the wave equation with initial condition N F N (x = a n sin. Remark: The wave equation and its solutions provide a mathematical description of music. Origins of the Fourier Series. Remarks: Bernoulli claimed he had obtained all solutions to the problem above for the wave equation. However, he did not prove that claim. A proof is: Given a function F with F (0 = F ( = 0, but otherwise arbitrary, find N and the coefficients a n such that F is approximated by an expansion F N given in the previous slide. Joseph Fourier ( 1800 provided such formula for the coefficients a n, while studying a different problem: The heat transport in a solid material. Find the temperature function u solution of the heat equation t u(t, x = k 2 x u(t, x, k > 0, x [0,, t [0,, I.C. u(0, x = f (x, B.C. u(t, 0 = 0, u(t, = 0.
3 Origins of the Fourier Series. Remarks: Fourier found particular solutions to the heat equation. If the initial condition is f n (x = sin, then the solution is u n (t, x = sin e k( nπ 2t. Fourier also realized that N U N (t, x = a n sin e k( nπ 2t, a n R is also solution of the heat equation with initial condition N F N (x = a n sin. Remark: The heat equation and its solutions provide a mathematical description of heat transport in a solid material. Origins of the Fourier Series. Remarks: However, Fourier went farther than Bernoulli. Fourier found a formula for the coefficients a n in terms of the function F. Given an initial data function F, satisfying F (0 = F ( = 0, but otherwise arbitrary, Fourier proved that one can construct an expansion F N as follows, N F N (x = a n sin, for N any positive integer, where the a n are given by a n = 2 F (x sin dx. 0 To find all solutions to the heat equation problem above one must prove one more thing: That F N approximates F for large enough N. That is, lim N F N = F. Fourier didn t show this.
4 Origins of the Fourier Series. Remarks: Based on Bernoulli and Fourier works, people have been able to prove that. Every continuous, -periodic function can be expressed as an infinite linear combination of sine and ine functions. More precisely: Every continuous, -periodic function F, there exist constants a 0, a n, b n, for n = 1, 2, such that F N (x = a N [ ( 0 2nπx 2 + a n + b n sin, satisfies lim F N(x = F (x for every x R. N Notation: F (x = a [ a n + b n sin. Origins of the Fourier Series. The main problem in our class: Given a continuous, -periodic function f, find the formulas for a n and b n such that f (x = a [ a n Remarks: We need to review two main concepts: The notion of periodic functions. + b n sin. The notion of orthogonal functions, in particular the orthogonality of Sines and Cosines.
5 Fourier Series (Sect Origins of the Fourier Series. Periodic functions. Orthogonality of Sines and Cosines. Main result on Fourier Series. Periodic functions. Definition A function f : R R is called periodic iff there exists > 0 such that for all x R holds f (x + = f (x. Remark: f is invariant under translations by. Definition A period T of a periodic function f is the smallest value of such that f (x + = f (x holds. Notation: A periodic function with period T is also called T -periodic.
6 Periodic functions. Example The following functions are periodic, with period T, f (x = sin(x, T = 2π. f (x = (x, T = 2π. f (x = tan(x, T = π. f (x = sin(ax, T = 2π a. The proof of the latter statement is the following: f ( x + 2π a ( = sin ax + a 2π a = sin(ax + 2π = sin(ax = f (x. Periodic functions. Example Show that the function below is periodic, and find its period, f (x = e x, x [0, 2, f (x 2 = f (x. Solution: We just graph the function, y y = f(x 0 1 x So the function is periodic with period T = 2.
7 Periodic functions. Theorem A linear combination of T -periodic functions is also T -periodic. Proof: If f (x + T = f (x and g(x + T = g(x, then af (x + T + bg(x + T = af (x + bg(x, so (af + bg is also T -periodic. Example f (x = 2 sin(3x + 7 (3x is periodic with period T = 2π/3. Remark: The functions below are periodic with period T = n, ( 2πnx ( 2πnx f (x =, g(x = sin, Since f and g are invariant under translations by /n, they are also invariant under translations by. Periodic functions. Corollary Any function f given by f (x = a [ a n is periodic with period. + b n sin Remark: We will show that the converse statement is true. Theorem A function f is -periodic iff holds f (x = a [ a n + b n sin.
8 Fourier Series (Sect Origins of the Fourier Series. Periodic functions. Orthogonality of Sines and Cosines. Main result on Fourier Series. Orthogonality of Sines and Cosines. Remark: From now on we work on the following domain: [,. y ( pi x / x sin ( pi x / T = 2
9 Orthogonality of Sines and Cosines. Theorem (Orthogonality The following relations hold for all n, m N, ( mπx 0 n m, dx = n = m 0, 2 n = m = 0, { ( mπx 0 n m, sin sin dx = n = m, Remark: The operation f g = ( mπx sin dx = 0. f (x g(x dx is an inner product in the vector space of functions. ike the dot product is in R 2. Two functions f, g, are orthogonal iff f g = 0. Orthogonality of Sines and Cosines. Recall: (θ (φ = 1 2 sin(θ sin(φ = 1 2 [ (θ + φ + (θ φ ; [ (θ φ (θ + φ ; sin(θ (φ = 1 2 [ sin(θ + φ + sin(θ φ. Proof: First formula: If n = m = 0, it is simple to see that ( mπx dx = dx = 2. In the case where one of n or m is non-zero, use the relation ( mπx dx = 1 [ (n + mπx dx [ (n mπx dx. 2
10 Orthogonality of Sines and Cosines. Proof: Since one of n or m is non-zero, holds 1 [ (n + mπx [ (n + mπx dx = 2 2(n + mπ sin = 0. We obtain that ( mπx dx = 1 [ (n mπx dx. 2 If we further restrict n m, then 1 [ (n mπx [ (n mπx dx = 2 2(n mπ sin = 0. If n = m 0, we have that 1 [ (n mπx dx = 1 dx =. 2 2 This establishes the first equation in the Theorem. The remaining equations are proven in a similar way. Overview of Fourier Series (Sect Origins of the Fourier Series. Periodic functions. Orthogonality of Sines and Cosines. Main result on Fourier Series.
11 Main result on Fourier Series. Theorem (Fourier Series If the function f : [, R R is continuous, then f can be expressed as an infinite series f (x = a [ a n with the constants a n and b n given by a n = 1 b n = 1 f (x f (x sin + b n sin dx, n 0, dx, n 1. Furthermore, the Fourier series in Eq. (?? provides a 2-periodic extension of f from the domain [, R to R. (1
10.2-3: Fourier Series.
 10.2-3: Fourier Series. 10.2-3: Fourier Series. O. Costin: Fourier Series, 10.2-3 1 Fourier series are very useful in representing periodic functions. Examples of periodic functions. A function is periodic
10.2-3: Fourier Series. 10.2-3: Fourier Series. O. Costin: Fourier Series, 10.2-3 1 Fourier series are very useful in representing periodic functions. Examples of periodic functions. A function is periodic
Solving the Heat Equation (Sect. 10.5).
 Solving the Heat Equation Sect. 1.5. Review: The Stationary Heat Equation. The Heat Equation. The Initial-Boundary Value Problem. The separation of variables method. An example of separation of variables.
Solving the Heat Equation Sect. 1.5. Review: The Stationary Heat Equation. The Heat Equation. The Initial-Boundary Value Problem. The separation of variables method. An example of separation of variables.
Examples of the Fourier Theorem (Sect. 10.3). The Fourier Theorem: Continuous case.
 s of the Fourier Theorem (Sect. 1.3. The Fourier Theorem: Continuous case. : Using the Fourier Theorem. The Fourier Theorem: Piecewise continuous case. : Using the Fourier Theorem. The Fourier Theorem:
s of the Fourier Theorem (Sect. 1.3. The Fourier Theorem: Continuous case. : Using the Fourier Theorem. The Fourier Theorem: Piecewise continuous case. : Using the Fourier Theorem. The Fourier Theorem:
22. Periodic Functions and Fourier Series
 November 29, 2010 22-1 22. Periodic Functions and Fourier Series 1 Periodic Functions A real-valued function f(x) of a real variable is called periodic of period T > 0 if f(x + T ) = f(x) for all x R.
November 29, 2010 22-1 22. Periodic Functions and Fourier Series 1 Periodic Functions A real-valued function f(x) of a real variable is called periodic of period T > 0 if f(x + T ) = f(x) for all x R.
Physics 250 Green s functions for ordinary differential equations
 Physics 25 Green s functions for ordinary differential equations Peter Young November 25, 27 Homogeneous Equations We have already discussed second order linear homogeneous differential equations, which
Physics 25 Green s functions for ordinary differential equations Peter Young November 25, 27 Homogeneous Equations We have already discussed second order linear homogeneous differential equations, which
Mathematical Methods: Fourier Series. Fourier Series: The Basics
 1 Mathematical Methods: Fourier Series Fourier Series: The Basics Fourier series are a method of representing periodic functions. It is a very useful and powerful tool in many situations. It is sufficiently
1 Mathematical Methods: Fourier Series Fourier Series: The Basics Fourier series are a method of representing periodic functions. It is a very useful and powerful tool in many situations. It is sufficiently
Analysis II: Fourier Series
 .... Analysis II: Fourier Series Kenichi Maruno Department of Mathematics, The University of Texas - Pan American May 3, 011 K.Maruno (UT-Pan American) Analysis II May 3, 011 1 / 16 Fourier series were
.... Analysis II: Fourier Series Kenichi Maruno Department of Mathematics, The University of Texas - Pan American May 3, 011 K.Maruno (UT-Pan American) Analysis II May 3, 011 1 / 16 Fourier series were
More on Fourier Series
 More on Fourier Series R. C. Trinity University Partial Differential Equations Lecture 6.1 New Fourier series from old Recall: Given a function f (x, we can dilate/translate its graph via multiplication/addition,
More on Fourier Series R. C. Trinity University Partial Differential Equations Lecture 6.1 New Fourier series from old Recall: Given a function f (x, we can dilate/translate its graph via multiplication/addition,
Time-Frequency Analysis
 Time-Frequency Analysis Basics of Fourier Series Philippe B. aval KSU Fall 015 Philippe B. aval (KSU) Fourier Series Fall 015 1 / 0 Introduction We first review how to derive the Fourier series of a function.
Time-Frequency Analysis Basics of Fourier Series Philippe B. aval KSU Fall 015 Philippe B. aval (KSU) Fourier Series Fall 015 1 / 0 Introduction We first review how to derive the Fourier series of a function.
Fourier and Partial Differential Equations
 Chapter 5 Fourier and Partial Differential Equations 5.1 Fourier MATH 294 SPRING 1982 FINAL # 5 5.1.1 Consider the function 2x, 0 x 1. a) Sketch the odd extension of this function on 1 x 1. b) Expand the
Chapter 5 Fourier and Partial Differential Equations 5.1 Fourier MATH 294 SPRING 1982 FINAL # 5 5.1.1 Consider the function 2x, 0 x 1. a) Sketch the odd extension of this function on 1 x 1. b) Expand the
Fourier Series and the Discrete Fourier Expansion
 2 2.5.5 Fourier Series and the Discrete Fourier Expansion Matthew Lincoln Adrienne Carter sillyajc@yahoo.com December 5, 2 Abstract This article is intended to introduce the Fourier series and the Discrete
2 2.5.5 Fourier Series and the Discrete Fourier Expansion Matthew Lincoln Adrienne Carter sillyajc@yahoo.com December 5, 2 Abstract This article is intended to introduce the Fourier series and the Discrete
Bernoulli Numbers and their Applications
 Bernoulli Numbers and their Applications James B Silva Abstract The Bernoulli numbers are a set of numbers that were discovered by Jacob Bernoulli (654-75). This set of numbers holds a deep relationship
Bernoulli Numbers and their Applications James B Silva Abstract The Bernoulli numbers are a set of numbers that were discovered by Jacob Bernoulli (654-75). This set of numbers holds a deep relationship
MA 201: Differentiation and Integration of Fourier Series Applications of Fourier Series Lecture - 10
 MA 201: Differentiation and Integration of Fourier Series Applications of Fourier Series ecture - 10 Fourier Series: Orthogonal Sets We begin our treatment with some observations: For m,n = 1,2,3,... cos
MA 201: Differentiation and Integration of Fourier Series Applications of Fourier Series ecture - 10 Fourier Series: Orthogonal Sets We begin our treatment with some observations: For m,n = 1,2,3,... cos
3 rd class Mech. Eng. Dept. hamdiahmed.weebly.com Fourier Series
 Definition 1 Fourier Series A function f is said to be piecewise continuous on [a, b] if there exists finitely many points a = x 1 < x 2
Definition 1 Fourier Series A function f is said to be piecewise continuous on [a, b] if there exists finitely many points a = x 1 < x 2
Notes on Fourier Series and Integrals Fourier Series
 Notes on Fourier Series and Integrals Fourier Series et f(x) be a piecewise linear function on [, ] (This means that f(x) may possess a finite number of finite discontinuities on the interval). Then f(x)
Notes on Fourier Series and Integrals Fourier Series et f(x) be a piecewise linear function on [, ] (This means that f(x) may possess a finite number of finite discontinuities on the interval). Then f(x)
The wave equation in one dimension
 The wave equation in one dimension Prof. Joyner 1 The theory of the vibrating string touches on musical theory and the theory of oscillating waves, so has likely been a concern of scholars since ancient
The wave equation in one dimension Prof. Joyner 1 The theory of the vibrating string touches on musical theory and the theory of oscillating waves, so has likely been a concern of scholars since ancient
A Guided Tour of the Wave Equation
 A Guided Tour of the Wave Equation Background: In order to solve this problem we need to review some facts about ordinary differential equations: Some Common ODEs and their solutions: f (x) = 0 f(x) =
A Guided Tour of the Wave Equation Background: In order to solve this problem we need to review some facts about ordinary differential equations: Some Common ODEs and their solutions: f (x) = 0 f(x) =
Method of Separation of Variables
 MODUE 5: HEAT EQUATION 11 ecture 3 Method of Separation of Variables Separation of variables is one of the oldest technique for solving initial-boundary value problems (IBVP) and applies to problems, where
MODUE 5: HEAT EQUATION 11 ecture 3 Method of Separation of Variables Separation of variables is one of the oldest technique for solving initial-boundary value problems (IBVP) and applies to problems, where
14 Fourier analysis. Read: Boas Ch. 7.
 14 Fourier analysis Read: Boas Ch. 7. 14.1 Function spaces A function can be thought of as an element of a kind of vector space. After all, a function f(x) is merely a set of numbers, one for each point
14 Fourier analysis Read: Boas Ch. 7. 14.1 Function spaces A function can be thought of as an element of a kind of vector space. After all, a function f(x) is merely a set of numbers, one for each point
Math Assignment 14
 Math 2280 - Assignment 14 Dylan Zwick Spring 2014 Section 9.5-1, 3, 5, 7, 9 Section 9.6-1, 3, 5, 7, 14 Section 9.7-1, 2, 3, 4 1 Section 9.5 - Heat Conduction and Separation of Variables 9.5.1 - Solve the
Math 2280 - Assignment 14 Dylan Zwick Spring 2014 Section 9.5-1, 3, 5, 7, 9 Section 9.6-1, 3, 5, 7, 14 Section 9.7-1, 2, 3, 4 1 Section 9.5 - Heat Conduction and Separation of Variables 9.5.1 - Solve the
u tt = a 2 u xx u tt = a 2 (u xx + u yy )
 10.7 The wave equation 10.7 The wave equation O. Costin: 10.7 1 This equation describes the propagation of waves through a medium: in one dimension, such as a vibrating string u tt = a 2 u xx 1 This equation
10.7 The wave equation 10.7 The wave equation O. Costin: 10.7 1 This equation describes the propagation of waves through a medium: in one dimension, such as a vibrating string u tt = a 2 u xx 1 This equation
Definition 1. A set V is a vector space over the scalar field F {R, C} iff. there are two operations defined on V, called vector addition
 6 Vector Spaces with Inned Product Basis and Dimension Section Objective(s): Vector Spaces and Subspaces Linear (In)dependence Basis and Dimension Inner Product 6 Vector Spaces and Subspaces Definition
6 Vector Spaces with Inned Product Basis and Dimension Section Objective(s): Vector Spaces and Subspaces Linear (In)dependence Basis and Dimension Inner Product 6 Vector Spaces and Subspaces Definition
Fourier Series. Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta
 1 Lecture Notes on Partial Differential Equations Chapter IV Fourier Series Ilyasse Aksikas Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta aksikas@ualberta.ca DEFINITIONS 2 Before
1 Lecture Notes on Partial Differential Equations Chapter IV Fourier Series Ilyasse Aksikas Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta aksikas@ualberta.ca DEFINITIONS 2 Before
Periodic functions: simple harmonic oscillator
 Periodic functions: simple harmonic oscillator Recall the simple harmonic oscillator (e.g. mass-spring system) d 2 y dt 2 + ω2 0y = 0 Solution can be written in various ways: y(t) = Ae iω 0t y(t) = A cos
Periodic functions: simple harmonic oscillator Recall the simple harmonic oscillator (e.g. mass-spring system) d 2 y dt 2 + ω2 0y = 0 Solution can be written in various ways: y(t) = Ae iω 0t y(t) = A cos
2.2 The derivative as a Function
 2.2 The derivative as a Function Recall: The derivative of a function f at a fixed number a: f a f a+h f(a) = lim h 0 h Definition (Derivative of f) For any number x, the derivative of f is f x f x+h f(x)
2.2 The derivative as a Function Recall: The derivative of a function f at a fixed number a: f a f a+h f(a) = lim h 0 h Definition (Derivative of f) For any number x, the derivative of f is f x f x+h f(x)
Vibrating-string problem
 EE-2020, Spring 2009 p. 1/30 Vibrating-string problem Newton s equation of motion, m u tt = applied forces to the segment (x, x, + x), Net force due to the tension of the string, T Sinθ 2 T Sinθ 1 T[u
EE-2020, Spring 2009 p. 1/30 Vibrating-string problem Newton s equation of motion, m u tt = applied forces to the segment (x, x, + x), Net force due to the tension of the string, T Sinθ 2 T Sinθ 1 T[u
Chapter 10: Partial Differential Equations
 1.1: Introduction Chapter 1: Partial Differential Equations Definition: A differential equations whose dependent variable varies with respect to more than one independent variable is called a partial differential
1.1: Introduction Chapter 1: Partial Differential Equations Definition: A differential equations whose dependent variable varies with respect to more than one independent variable is called a partial differential
# Points Score Total 100
 Name: PennID: Math 241 Make-Up Final Exam January 19, 2016 Instructions: Turn off and put away your cell phone. Please write your Name and PennID on the top of this page. Please sign and date the pledge
Name: PennID: Math 241 Make-Up Final Exam January 19, 2016 Instructions: Turn off and put away your cell phone. Please write your Name and PennID on the top of this page. Please sign and date the pledge
Math 489AB A Very Brief Intro to Fourier Series Fall 2008
 Math 489AB A Very Brief Intro to Fourier Series Fall 8 Contents Fourier Series. The coefficients........................................ Convergence......................................... 4.3 Convergence
Math 489AB A Very Brief Intro to Fourier Series Fall 8 Contents Fourier Series. The coefficients........................................ Convergence......................................... 4.3 Convergence
PHYS 502 Lecture 3: Fourier Series
 PHYS 52 Lecture 3: Fourier Series Fourier Series Introduction In mathematics, a Fourier series decomposes periodic functions or periodic signals into the sum of a (possibly infinite) set of simple oscillating
PHYS 52 Lecture 3: Fourier Series Fourier Series Introduction In mathematics, a Fourier series decomposes periodic functions or periodic signals into the sum of a (possibly infinite) set of simple oscillating
6.1 The Inverse Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Functions Objectives
 Objectives 1. Find the Exact Value of an Inverse Sine, Cosine, or Tangent Function. 2. Find an Approximate Value of an Inverse Sine Function. 3. Use Properties of Inverse Functions to Find Exact Values
Objectives 1. Find the Exact Value of an Inverse Sine, Cosine, or Tangent Function. 2. Find an Approximate Value of an Inverse Sine Function. 3. Use Properties of Inverse Functions to Find Exact Values
Chapter 2: Differentiation
 Chapter 2: Differentiation Winter 2016 Department of Mathematics Hong Kong Baptist University 1 / 75 2.1 Tangent Lines and Their Slopes This section deals with the problem of finding a straight line L
Chapter 2: Differentiation Winter 2016 Department of Mathematics Hong Kong Baptist University 1 / 75 2.1 Tangent Lines and Their Slopes This section deals with the problem of finding a straight line L
7.2 Trigonometric Integrals
 7.2 1 7.2 Trigonometric Integrals Products of Powers of Sines and Cosines We wish to evaluate integrals of the form: sin m x cos n xdx where m and n are nonnegative integers. Recall the double angle formulas
7.2 1 7.2 Trigonometric Integrals Products of Powers of Sines and Cosines We wish to evaluate integrals of the form: sin m x cos n xdx where m and n are nonnegative integers. Recall the double angle formulas
Lecture Notes for MAE 3100: Introduction to Applied Mathematics
 ecture Notes for MAE 31: Introduction to Applied Mathematics Richard H. Rand Cornell University Ithaca NY 14853 rhr2@cornell.edu http://audiophile.tam.cornell.edu/randdocs/ version 17 Copyright 215 by
ecture Notes for MAE 31: Introduction to Applied Mathematics Richard H. Rand Cornell University Ithaca NY 14853 rhr2@cornell.edu http://audiophile.tam.cornell.edu/randdocs/ version 17 Copyright 215 by
Lecture Notes for Math 251: ODE and PDE. Lecture 32: 10.2 Fourier Series
 Lecture Notes for Math 251: ODE and PDE. Lecture 32: 1.2 Fourier Series Shawn D. Ryan Spring 212 Last Time: We studied the heat equation and the method of Separation of Variabes. We then used Separation
Lecture Notes for Math 251: ODE and PDE. Lecture 32: 1.2 Fourier Series Shawn D. Ryan Spring 212 Last Time: We studied the heat equation and the method of Separation of Variabes. We then used Separation
MATH 220: INNER PRODUCT SPACES, SYMMETRIC OPERATORS, ORTHOGONALITY
 MATH 22: INNER PRODUCT SPACES, SYMMETRIC OPERATORS, ORTHOGONALITY When discussing separation of variables, we noted that at the last step we need to express the inhomogeneous initial or boundary data as
MATH 22: INNER PRODUCT SPACES, SYMMETRIC OPERATORS, ORTHOGONALITY When discussing separation of variables, we noted that at the last step we need to express the inhomogeneous initial or boundary data as
Continuum Limit and Fourier Series
 Chapter 6 Continuum Limit and Fourier Series Continuous is in the eye of the beholder Most systems that we think of as continuous are actually made up of discrete pieces In this chapter, we show that a
Chapter 6 Continuum Limit and Fourier Series Continuous is in the eye of the beholder Most systems that we think of as continuous are actually made up of discrete pieces In this chapter, we show that a
FOURIER TRANSFORMS. At, is sometimes taken as 0.5 or it may not have any specific value. Shifting at
 Chapter 2 FOURIER TRANSFORMS 2.1 Introduction The Fourier series expresses any periodic function into a sum of sinusoids. The Fourier transform is the extension of this idea to non-periodic functions by
Chapter 2 FOURIER TRANSFORMS 2.1 Introduction The Fourier series expresses any periodic function into a sum of sinusoids. The Fourier transform is the extension of this idea to non-periodic functions by
Ma 221 Eigenvalues and Fourier Series
 Ma Eigenvalues and Fourier Series Eigenvalue and Eigenfunction Examples Example Find the eigenvalues and eigenfunctions for y y 47 y y y5 Solution: The characteristic equation is r r 47 so r 44 447 6 Thus
Ma Eigenvalues and Fourier Series Eigenvalue and Eigenfunction Examples Example Find the eigenvalues and eigenfunctions for y y 47 y y y5 Solution: The characteristic equation is r r 47 so r 44 447 6 Thus
Fourier Series and Integrals
 Fourier Series and Integrals Fourier Series et f(x) beapiece-wiselinearfunctionon[, ] (Thismeansthatf(x) maypossessa finite number of finite discontinuities on the interval). Then f(x) canbeexpandedina
Fourier Series and Integrals Fourier Series et f(x) beapiece-wiselinearfunctionon[, ] (Thismeansthatf(x) maypossessa finite number of finite discontinuities on the interval). Then f(x) canbeexpandedina
Chapter 2: Differentiation
 Chapter 2: Differentiation Spring 2018 Department of Mathematics Hong Kong Baptist University 1 / 82 2.1 Tangent Lines and Their Slopes This section deals with the problem of finding a straight line L
Chapter 2: Differentiation Spring 2018 Department of Mathematics Hong Kong Baptist University 1 / 82 2.1 Tangent Lines and Their Slopes This section deals with the problem of finding a straight line L
Vectors in Function Spaces
 Jim Lambers MAT 66 Spring Semester 15-16 Lecture 18 Notes These notes correspond to Section 6.3 in the text. Vectors in Function Spaces We begin with some necessary terminology. A vector space V, also
Jim Lambers MAT 66 Spring Semester 15-16 Lecture 18 Notes These notes correspond to Section 6.3 in the text. Vectors in Function Spaces We begin with some necessary terminology. A vector space V, also
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3 Remark is a new function derived from called derivative. 2.2 The derivative as a Function
 Slide 1 2.2 The derivative as a Function Slide 2 Recall: The derivative of a function number : at a fixed Definition (Derivative of ) For any number, the derivative of is Slide 3 Remark is a new function
Slide 1 2.2 The derivative as a Function Slide 2 Recall: The derivative of a function number : at a fixed Definition (Derivative of ) For any number, the derivative of is Slide 3 Remark is a new function
1. Partial differential equations. Chapter 12: Partial Differential Equations. Examples. 2. The one-dimensional wave equation
 1. Partial differential equations Definitions Examples A partial differential equation PDE is an equation giving a relation between a function of two or more variables u and its partial derivatives. The
1. Partial differential equations Definitions Examples A partial differential equation PDE is an equation giving a relation between a function of two or more variables u and its partial derivatives. The
Analysis II: Basic knowledge of real analysis: Part V, Power Series, Differentiation, and Taylor Series
 .... Analysis II: Basic knowledge of real analysis: Part V, Power Series, Differentiation, and Taylor Series Kenichi Maruno Department of Mathematics, The University of Texas - Pan American March 4, 20
.... Analysis II: Basic knowledge of real analysis: Part V, Power Series, Differentiation, and Taylor Series Kenichi Maruno Department of Mathematics, The University of Texas - Pan American March 4, 20
Consequences of Orthogonality
 Consequences of Orthogonality Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Consequences of Orthogonality Today 1 / 23 Introduction The three kind of examples we did above involved Dirichlet, Neumann
Consequences of Orthogonality Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Consequences of Orthogonality Today 1 / 23 Introduction The three kind of examples we did above involved Dirichlet, Neumann
CHAPTER 10 NOTES DAVID SEAL
 CHAPTER 1 NOTES DAVID SEA 1. Two Point Boundary Value Problems All of the problems listed in 14 2 ask you to find eigenfunctions for the problem (1 y + λy = with some prescribed data on the boundary. To
CHAPTER 1 NOTES DAVID SEA 1. Two Point Boundary Value Problems All of the problems listed in 14 2 ask you to find eigenfunctions for the problem (1 y + λy = with some prescribed data on the boundary. To
Course 2BA1, Section 11: Periodic Functions and Fourier Series
 Course BA, 8 9 Section : Periodic Functions and Fourier Series David R. Wikins Copyright c David R. Wikins 9 Contents Periodic Functions and Fourier Series 74. Fourier Series of Even and Odd Functions...........
Course BA, 8 9 Section : Periodic Functions and Fourier Series David R. Wikins Copyright c David R. Wikins 9 Contents Periodic Functions and Fourier Series 74. Fourier Series of Even and Odd Functions...........
Review Problems for Test 2
 Review Problems for Test Math 0 009 These problems are meant to help you study. The presence of a problem on this sheet does not imply that there will be a similar problem on the test. And the absence
Review Problems for Test Math 0 009 These problems are meant to help you study. The presence of a problem on this sheet does not imply that there will be a similar problem on the test. And the absence
1 + lim. n n+1. f(x) = x + 1, x 1. and we check that f is increasing, instead. Using the quotient rule, we easily find that. 1 (x + 1) 1 x (x + 1) 2 =
 Chapter 5 Sequences and series 5. Sequences Definition 5. (Sequence). A sequence is a function which is defined on the set N of natural numbers. Since such a function is uniquely determined by its values
Chapter 5 Sequences and series 5. Sequences Definition 5. (Sequence). A sequence is a function which is defined on the set N of natural numbers. Since such a function is uniquely determined by its values
Lecture 1: Interpolation and approximation
 ecture notes on Variational and Approximate Methods in Applied Mathematics - A Peirce UBC ecture : Interpolation and approximation (Compiled 6 August 207 In this lecture we introduce the concept of approximation
ecture notes on Variational and Approximate Methods in Applied Mathematics - A Peirce UBC ecture : Interpolation and approximation (Compiled 6 August 207 In this lecture we introduce the concept of approximation
State Precalculus/Trigonometry Contest 2008
 State Precalculus/Trigonometry Contest 008 Select the best answer for each of the following questions and mark it on the answer sheet provided. Be sure to read all the answer choices before making your
State Precalculus/Trigonometry Contest 008 Select the best answer for each of the following questions and mark it on the answer sheet provided. Be sure to read all the answer choices before making your
Boundary value problems for partial differential equations
 Boundary value problems for partial differential equations Henrik Schlichtkrull March 11, 213 1 Boundary value problem 2 1 Introduction This note contains a brief introduction to linear partial differential
Boundary value problems for partial differential equations Henrik Schlichtkrull March 11, 213 1 Boundary value problem 2 1 Introduction This note contains a brief introduction to linear partial differential
THE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO. Applied Mathematics 375a Instructor: Matt Davison. Final Examination December 14, :00 12:00 a.m.
 THE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO London Ontario Applied Mathematics 375a Instructor: Matt Davison Final Examination December 4, 22 9: 2: a.m. 3 HOURS Name: Stu. #: Notes: ) There are 8 question worth
THE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO London Ontario Applied Mathematics 375a Instructor: Matt Davison Final Examination December 4, 22 9: 2: a.m. 3 HOURS Name: Stu. #: Notes: ) There are 8 question worth
X b n sin nπx L. n=1 Fourier Sine Series Expansion. a n cos nπx L 2 + X. n=1 Fourier Cosine Series Expansion ³ L. n=1 Fourier Series Expansion
 3 Fourier Series 3.1 Introduction Although it was not apparent in the early historical development of the method of separation of variables what we are about to do is the analog for function spaces of
3 Fourier Series 3.1 Introduction Although it was not apparent in the early historical development of the method of separation of variables what we are about to do is the analog for function spaces of
Instructor s Solutions Manual PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS. with FOURIER SERIES and BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS. NAKHLÉ H. ASMAR University of Missouri
 Instructor s Solutions Manual PARTIA DIFFERENTIA EQUATIONS with FOURIER SERIES and BOUNDARY VAUE PROBEMS Second Edition NAKHÉ H. ASMAR University of Missouri Contents Preface Errata v vi A Preview of Applications
Instructor s Solutions Manual PARTIA DIFFERENTIA EQUATIONS with FOURIER SERIES and BOUNDARY VAUE PROBEMS Second Edition NAKHÉ H. ASMAR University of Missouri Contents Preface Errata v vi A Preview of Applications
Differential Equations
 Differential Equations Problem Sheet 1 3 rd November 2011 First-Order Ordinary Differential Equations 1. Find the general solutions of the following separable differential equations. Which equations are
Differential Equations Problem Sheet 1 3 rd November 2011 First-Order Ordinary Differential Equations 1. Find the general solutions of the following separable differential equations. Which equations are
AP Calculus (BC) Chapter 9 Test No Calculator Section Name: Date: Period:
 WORKSHEET: Series, Taylor Series AP Calculus (BC) Chapter 9 Test No Calculator Section Name: Date: Period: 1 Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions (5 points each; please circle the correct answer.) 1. The
WORKSHEET: Series, Taylor Series AP Calculus (BC) Chapter 9 Test No Calculator Section Name: Date: Period: 1 Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions (5 points each; please circle the correct answer.) 1. The
Math 201 Assignment #11
 Math 21 Assignment #11 Problem 1 (1.5 2) Find a formal solution to the given initial-boundary value problem. = 2 u x, < x < π, t > 2 u(, t) = u(π, t) =, t > u(x, ) = x 2, < x < π Problem 2 (1.5 5) Find
Math 21 Assignment #11 Problem 1 (1.5 2) Find a formal solution to the given initial-boundary value problem. = 2 u x, < x < π, t > 2 u(, t) = u(π, t) =, t > u(x, ) = x 2, < x < π Problem 2 (1.5 5) Find
Math 2Z03 - Tutorial # 6. Oct. 26th, 27th, 28th, 2015
 Math 2Z03 - Tutorial # 6 Oct. 26th, 27th, 28th, 2015 Tutorial Info: Tutorial Website: http://ms.mcmaster.ca/ dedieula/2z03.html Office Hours: Mondays 3pm - 5pm (in the Math Help Centre) Tutorial #6: 3.4
Math 2Z03 - Tutorial # 6 Oct. 26th, 27th, 28th, 2015 Tutorial Info: Tutorial Website: http://ms.mcmaster.ca/ dedieula/2z03.html Office Hours: Mondays 3pm - 5pm (in the Math Help Centre) Tutorial #6: 3.4
Boundary-value Problems in Rectangular Coordinates
 Boundary-value Problems in Rectangular Coordinates 2009 Outline Separation of Variables: Heat Equation on a Slab Separation of Variables: Vibrating String Separation of Variables: Laplace Equation Review
Boundary-value Problems in Rectangular Coordinates 2009 Outline Separation of Variables: Heat Equation on a Slab Separation of Variables: Vibrating String Separation of Variables: Laplace Equation Review
Math Computer Lab 4 : Fourier Series
 Math 227 - Computer Lab 4 : Fourier Series Dylan Zwick Fall 212 This lab should be a pretty quick lab. It s goal is to introduce you to one of the coolest ideas in mathematics, the Fourier series, and
Math 227 - Computer Lab 4 : Fourier Series Dylan Zwick Fall 212 This lab should be a pretty quick lab. It s goal is to introduce you to one of the coolest ideas in mathematics, the Fourier series, and
Midterm 2: Sample solutions Math 118A, Fall 2013
 Midterm 2: Sample solutions Math 118A, Fall 213 1. Find all separated solutions u(r,t = F(rG(t of the radially symmetric heat equation u t = k ( r u. r r r Solve for G(t explicitly. Write down an ODE for
Midterm 2: Sample solutions Math 118A, Fall 213 1. Find all separated solutions u(r,t = F(rG(t of the radially symmetric heat equation u t = k ( r u. r r r Solve for G(t explicitly. Write down an ODE for
Fourier Series. Now we need to take a theoretical excursion to build up the mathematics that makes separation of variables possible.
 Fourier Series Now we need to take a theoretical excursion to build up the mathematics that makes separation of variables possible Periodic functions Definition: A function f is periodic with period p
Fourier Series Now we need to take a theoretical excursion to build up the mathematics that makes separation of variables possible Periodic functions Definition: A function f is periodic with period p
Mathematics 324 Riemann Zeta Function August 5, 2005
 Mathematics 324 Riemann Zeta Function August 5, 25 In this note we give an introduction to the Riemann zeta function, which connects the ideas of real analysis with the arithmetic of the integers. Define
Mathematics 324 Riemann Zeta Function August 5, 25 In this note we give an introduction to the Riemann zeta function, which connects the ideas of real analysis with the arithmetic of the integers. Define
11.10a Taylor and Maclaurin Series
 11.10a 1 11.10a Taylor and Maclaurin Series Let y = f(x) be a differentiable function at x = a. In first semester calculus we saw that (1) f(x) f(a)+f (a)(x a), for all x near a The right-hand side of
11.10a 1 11.10a Taylor and Maclaurin Series Let y = f(x) be a differentiable function at x = a. In first semester calculus we saw that (1) f(x) f(a)+f (a)(x a), for all x near a The right-hand side of
Boundary Value Problems (Sect. 10.1). Two-point Boundary Value Problem.
 Boundary Value Problems (Sect. 10.1). Two-point BVP. from physics. Comparison: IVP vs BVP. Existence, uniqueness of solutions to BVP. Particular case of BVP: Eigenvalue-eigenfunction problem. Two-point
Boundary Value Problems (Sect. 10.1). Two-point BVP. from physics. Comparison: IVP vs BVP. Existence, uniqueness of solutions to BVP. Particular case of BVP: Eigenvalue-eigenfunction problem. Two-point
Inner products. Theorem (basic properties): Given vectors u, v, w in an inner product space V, and a scalar k, the following properties hold:
 Inner products Definition: An inner product on a real vector space V is an operation (function) that assigns to each pair of vectors ( u, v) in V a scalar u, v satisfying the following axioms: 1. u, v
Inner products Definition: An inner product on a real vector space V is an operation (function) that assigns to each pair of vectors ( u, v) in V a scalar u, v satisfying the following axioms: 1. u, v
6 Non-homogeneous Heat Problems
 6 Non-homogeneous Heat Problems Up to this point all the problems we have considered for the heat or wave equation we what we call homogeneous problems. This means that for an interval < x < l the problems
6 Non-homogeneous Heat Problems Up to this point all the problems we have considered for the heat or wave equation we what we call homogeneous problems. This means that for an interval < x < l the problems
FOURIER ANALYSIS. (a) Fourier Series
 (a) Fourier Series FOURIER ANAYSIS (b) Fourier Transforms Useful books: 1. Advanced Mathematics for Engineers and Scientists, Schaum s Outline Series, M. R. Spiegel - The course text. We follow their notation
(a) Fourier Series FOURIER ANAYSIS (b) Fourier Transforms Useful books: 1. Advanced Mathematics for Engineers and Scientists, Schaum s Outline Series, M. R. Spiegel - The course text. We follow their notation
Chapter 4 Sequences and Series
 Chapter 4 Sequences and Series 4.1 Sequence Review Sequence: a set of elements (numbers or letters or a combination of both). The elements of the set all follow the same rule (logical progression). The
Chapter 4 Sequences and Series 4.1 Sequence Review Sequence: a set of elements (numbers or letters or a combination of both). The elements of the set all follow the same rule (logical progression). The
5.4 Continuity: Preliminary Notions
 5.4. CONTINUITY: PRELIMINARY NOTIONS 181 5.4 Continuity: Preliminary Notions 5.4.1 Definitions The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language defines continuity as an uninterrupted succession,
5.4. CONTINUITY: PRELIMINARY NOTIONS 181 5.4 Continuity: Preliminary Notions 5.4.1 Definitions The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language defines continuity as an uninterrupted succession,
Formulas to remember
 Complex numbers Let z = x + iy be a complex number The conjugate z = x iy Formulas to remember The real part Re(z) = x = z+z The imaginary part Im(z) = y = z z i The norm z = zz = x + y The reciprocal
Complex numbers Let z = x + iy be a complex number The conjugate z = x iy Formulas to remember The real part Re(z) = x = z+z The imaginary part Im(z) = y = z z i The norm z = zz = x + y The reciprocal
Solved Examples. Given are two sets A {1, 2, -2, 3} and B = {1, 2, 3, 5}. Is the function f(x) = 2x - 1 defined from A to B?
 Solved Examples Example 1: Given are two sets A {1, 2, -2, 3} and B = {1, 2, 3, 5}. Is the function f(x) = 2x - 1 defined from A to B? Solution : Out of all the ordered pairs, the ordered pairs which are
Solved Examples Example 1: Given are two sets A {1, 2, -2, 3} and B = {1, 2, 3, 5}. Is the function f(x) = 2x - 1 defined from A to B? Solution : Out of all the ordered pairs, the ordered pairs which are
Inverse Trig Functions
 6.6i Inverse Trigonometric Functions Inverse Sine Function Does g(x) = sin(x) have an inverse? What restriction would we need to make so that at least a piece of this function has an inverse? Given f (x)
6.6i Inverse Trigonometric Functions Inverse Sine Function Does g(x) = sin(x) have an inverse? What restriction would we need to make so that at least a piece of this function has an inverse? Given f (x)
Math 121A: Homework 6 solutions
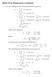 Math A: Homework 6 solutions. (a) The coefficients of the Fourier sine series are given by b n = π f (x) sin nx dx = x(π x) sin nx dx π = (π x) cos nx dx nπ nπ [x(π x) cos nx]π = n ( )(sin nx) dx + π n
Math A: Homework 6 solutions. (a) The coefficients of the Fourier sine series are given by b n = π f (x) sin nx dx = x(π x) sin nx dx π = (π x) cos nx dx nπ nπ [x(π x) cos nx]π = n ( )(sin nx) dx + π n
Practice 14. imathesis.com By Carlos Sotuyo
 Practice 4 imathesis.com By Carlos Sotuyo Suggested solutions for Miscellaneous exercises 0, problems 5-0, pages 53 to 55 from Pure Mathematics, by Hugh Neil and Douglas Quailing, Cambridge University
Practice 4 imathesis.com By Carlos Sotuyo Suggested solutions for Miscellaneous exercises 0, problems 5-0, pages 53 to 55 from Pure Mathematics, by Hugh Neil and Douglas Quailing, Cambridge University
Solutions to Exercises 8.1
 Section 8. Partial Differential Equations in Physics and Engineering 67 Solutions to Exercises 8.. u xx +u xy u is a second order, linear, and homogeneous partial differential equation. u x (,y) is linear
Section 8. Partial Differential Equations in Physics and Engineering 67 Solutions to Exercises 8.. u xx +u xy u is a second order, linear, and homogeneous partial differential equation. u x (,y) is linear
b n x n + b n 1 x n b 1 x + b 0
 Math Partial Fractions Stewart 7.4 Integrating basic rational functions. For a function f(x), we have examined several algebraic methods for finding its indefinite integral (antiderivative) F (x) = f(x)
Math Partial Fractions Stewart 7.4 Integrating basic rational functions. For a function f(x), we have examined several algebraic methods for finding its indefinite integral (antiderivative) F (x) = f(x)
SEISMIC WAVE PROPAGATION. Lecture 2: Fourier Analysis
 SEISMIC WAVE PROPAGATION Lecture 2: Fourier Analysis Fourier Series & Fourier Transforms Fourier Series Review of trigonometric identities Analysing the square wave Fourier Transform Transforms of some
SEISMIC WAVE PROPAGATION Lecture 2: Fourier Analysis Fourier Series & Fourier Transforms Fourier Series Review of trigonometric identities Analysing the square wave Fourier Transform Transforms of some
AP Calculus Testbank (Chapter 9) (Mr. Surowski)
 AP Calculus Testbank (Chapter 9) (Mr. Surowski) Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions n 1 1. The series will converge, provided that n 1+p + n + 1 (A) p > 1 (B) p > 2 (C) p >.5 (D) p 0 2. The series
AP Calculus Testbank (Chapter 9) (Mr. Surowski) Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions n 1 1. The series will converge, provided that n 1+p + n + 1 (A) p > 1 (B) p > 2 (C) p >.5 (D) p 0 2. The series
swapneel/207
 Partial differential equations Swapneel Mahajan www.math.iitb.ac.in/ swapneel/207 1 1 Power series For a real number x 0 and a sequence (a n ) of real numbers, consider the expression a n (x x 0 ) n =
Partial differential equations Swapneel Mahajan www.math.iitb.ac.in/ swapneel/207 1 1 Power series For a real number x 0 and a sequence (a n ) of real numbers, consider the expression a n (x x 0 ) n =
MATH 251 Final Examination August 14, 2015 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Final Examination August 14, 2015 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 11 questions for a total of 150 points. Show all your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
MATH 251 Final Examination August 14, 2015 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 11 questions for a total of 150 points. Show all your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
Chapter 3a Topics in differentiation. Problems in differentiation. Problems in differentiation. LC Abueg: mathematical economics
 Chapter 3a Topics in differentiation Lectures in Mathematical Economics L Cagandahan Abueg De La Salle University School of Economics Problems in differentiation Problems in differentiation Problem 1.
Chapter 3a Topics in differentiation Lectures in Mathematical Economics L Cagandahan Abueg De La Salle University School of Economics Problems in differentiation Problems in differentiation Problem 1.
(x 3)(x + 5) = (x 3)(x 1) = x + 5. sin 2 x e ax bx 1 = 1 2. lim
 SMT Calculus Test Solutions February, x + x 5 Compute x x x + Answer: Solution: Note that x + x 5 x x + x )x + 5) = x )x ) = x + 5 x x + 5 Then x x = + 5 = Compute all real values of b such that, for fx)
SMT Calculus Test Solutions February, x + x 5 Compute x x x + Answer: Solution: Note that x + x 5 x x + x )x + 5) = x )x ) = x + 5 x x + 5 Then x x = + 5 = Compute all real values of b such that, for fx)
University of Connecticut Lecture Notes for ME5507 Fall 2014 Engineering Analysis I Part III: Fourier Analysis
 University of Connecticut Lecture Notes for ME557 Fall 24 Engineering Analysis I Part III: Fourier Analysis Xu Chen Assistant Professor United Technologies Engineering Build, Rm. 382 Department of Mechanical
University of Connecticut Lecture Notes for ME557 Fall 24 Engineering Analysis I Part III: Fourier Analysis Xu Chen Assistant Professor United Technologies Engineering Build, Rm. 382 Department of Mechanical
Power series solutions for 2nd order linear ODE s (not necessarily with constant coefficients) a n z n. n=0
 Lecture 22 Power series solutions for 2nd order linear ODE s (not necessarily with constant coefficients) Recall a few facts about power series: a n z n This series in z is centered at z 0. Here z can
Lecture 22 Power series solutions for 2nd order linear ODE s (not necessarily with constant coefficients) Recall a few facts about power series: a n z n This series in z is centered at z 0. Here z can
Wave Equation in One Dimension: Vibrating Strings and Pressure Waves
 BENG 1: Mathematical Methods in Bioengineering Lecture 19 Wave Equation in One Dimension: Vibrating Strings and Pressure Waves References Haberman APDE, Ch. 4 and Ch. 1. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/wave_equation
BENG 1: Mathematical Methods in Bioengineering Lecture 19 Wave Equation in One Dimension: Vibrating Strings and Pressure Waves References Haberman APDE, Ch. 4 and Ch. 1. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/wave_equation
Branch: Name of the Student: Unit I (Fourier Series) Fourier Series in the interval (0,2 l) Engineering Mathematics Material SUBJECT NAME
 13 SUBJECT NAME SUBJECT CODE MATERIAL NAME MATERIAL CODE UPDATED ON : Transforms and Partial Differential Equation : MA11 : University Questions :SKMA13 : May June 13 Name of the Student: Branch: Unit
13 SUBJECT NAME SUBJECT CODE MATERIAL NAME MATERIAL CODE UPDATED ON : Transforms and Partial Differential Equation : MA11 : University Questions :SKMA13 : May June 13 Name of the Student: Branch: Unit
Mathematics for Chemists 2 Lecture 14: Fourier analysis. Fourier series, Fourier transform, DFT/FFT
 Mathematics for Chemists 2 Lecture 14: Fourier analysis Fourier series, Fourier transform, DFT/FFT Johannes Kepler University Summer semester 2012 Lecturer: David Sevilla Fourier analysis 1/25 Remembering
Mathematics for Chemists 2 Lecture 14: Fourier analysis Fourier series, Fourier transform, DFT/FFT Johannes Kepler University Summer semester 2012 Lecturer: David Sevilla Fourier analysis 1/25 Remembering
MA Chapter 10 practice
 MA 33 Chapter 1 practice NAME INSTRUCTOR 1. Instructor s names: Chen. Course number: MA33. 3. TEST/QUIZ NUMBER is: 1 if this sheet is yellow if this sheet is blue 3 if this sheet is white 4. Sign the scantron
MA 33 Chapter 1 practice NAME INSTRUCTOR 1. Instructor s names: Chen. Course number: MA33. 3. TEST/QUIZ NUMBER is: 1 if this sheet is yellow if this sheet is blue 3 if this sheet is white 4. Sign the scantron
Hilbert Spaces. Contents
 Hilbert Spaces Contents 1 Introducing Hilbert Spaces 1 1.1 Basic definitions........................... 1 1.2 Results about norms and inner products.............. 3 1.3 Banach and Hilbert spaces......................
Hilbert Spaces Contents 1 Introducing Hilbert Spaces 1 1.1 Basic definitions........................... 1 1.2 Results about norms and inner products.............. 3 1.3 Banach and Hilbert spaces......................
Partial Differential Equations Summary
 Partial Differential Equations Summary 1. The heat equation Many physical processes are governed by partial differential equations. temperature of a rod. In this chapter, we will examine exactly that.
Partial Differential Equations Summary 1. The heat equation Many physical processes are governed by partial differential equations. temperature of a rod. In this chapter, we will examine exactly that.
(1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3
 Math 127 Introduction and Review (1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3 MATH 127 Introduction to Calculus III
Math 127 Introduction and Review (1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3 MATH 127 Introduction to Calculus III
Separation of Variables. A. Three Famous PDE s
 Separation of Variables c 14, Philip D. Loewen A. Three Famous PDE s 1. Wave Equation. Displacement u depends on position and time: u = u(x, t. Concavity drives acceleration: u tt = c u xx.. Heat Equation.
Separation of Variables c 14, Philip D. Loewen A. Three Famous PDE s 1. Wave Equation. Displacement u depends on position and time: u = u(x, t. Concavity drives acceleration: u tt = c u xx.. Heat Equation.
Fourier series
 11.1-11.2. Fourier series Yurii Lyubarskii, NTNU September 5, 2016 Periodic functions Function f defined on the whole real axis has period p if Properties f (t) = f (t + p) for all t R If f and g have
11.1-11.2. Fourier series Yurii Lyubarskii, NTNU September 5, 2016 Periodic functions Function f defined on the whole real axis has period p if Properties f (t) = f (t + p) for all t R If f and g have
Disturbance Decoupling Problem
 DISC Systems and Control Theory of Nonlinear Systems, 21 1 Disturbance Decoupling Problem Lecture 4 Nonlinear Dynamical Control Systems, Chapter 7 The disturbance decoupling problem is a typical example
DISC Systems and Control Theory of Nonlinear Systems, 21 1 Disturbance Decoupling Problem Lecture 4 Nonlinear Dynamical Control Systems, Chapter 7 The disturbance decoupling problem is a typical example
x 2 = 1 Clearly, this equation is not true for all real values of x. Nevertheless, we can solve it by taking careful steps:
 Sec. 01 notes Solving Trig Equations: The Easy Ones Main Idea We are now ready to discuss the solving of trigonometric equations. Recall that, generally speaking, identities are equations which hold true
Sec. 01 notes Solving Trig Equations: The Easy Ones Main Idea We are now ready to discuss the solving of trigonometric equations. Recall that, generally speaking, identities are equations which hold true
Introduction Derivation General formula List of series Convergence Applications Test SERIES 4 INU0114/514 (MATHS 1)
 MACLAURIN SERIES SERIES 4 INU0114/514 (MATHS 1) Dr Adrian Jannetta MIMA CMath FRAS Maclaurin Series 1/ 21 Adrian Jannetta Recap: Binomial Series Recall that some functions can be rewritten as a power series
MACLAURIN SERIES SERIES 4 INU0114/514 (MATHS 1) Dr Adrian Jannetta MIMA CMath FRAS Maclaurin Series 1/ 21 Adrian Jannetta Recap: Binomial Series Recall that some functions can be rewritten as a power series
Emily Jennings. Georgia Institute of Technology. Nebraska Conference for Undergraduate Women in Mathematics, 2012
 δ 2 Transform and Fourier Series of Functions with Multiple Jumps Georgia Institute of Technology Nebraska Conference for Undergraduate Women in Mathematics, 2012 Work performed at Kansas State University
δ 2 Transform and Fourier Series of Functions with Multiple Jumps Georgia Institute of Technology Nebraska Conference for Undergraduate Women in Mathematics, 2012 Work performed at Kansas State University
