Will it float? The New Keynesian Phillips curve tested on OECD panel data
|
|
|
- Wilfrid Walsh
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Phillips curve Roger Bjørnstad Research Department Statistics Norway 2 Department of Economics University of Oslo 31 October 2006
2 Outline
3 Outline
4 Outline
5 Outline
6 Outline
7 The debatable The hybrid Phillips Curve, hereafter, is an integral part (in fact the supply side ) of the standard model of monetary policy. Impact due to: p t = a f 0 pe t+1 + ab 0 p t 1 + b 0 ws t, Micro foundations with rational expectations a "structural" macro equation. Empirical success: on euro area and US data, as stated by Gali, and Gertler López-Salido (2001) and (2005), GGL hereafter.
8 The debatable, cont d Nevertheless a debate. A categorization of arguments can be made with reference to statistical and scientific inference (Koopmans and Reiersøl (1950)): Statistical inference: from sample to population eg. the question of the right estimation method. Scientific inference: interpretation of the population in terms of theory and existing knowledge a concern for all the properties and implications of a chosen or maintained interpretation of the correlations (not just chosen favourable traits), and also a mindfulness of alternatives. GGL engage in the debate about statistical inference, and claim that nothing can overturn their. But of scientific inference may be just at important: alternative models exist already, and encompassing tests should therefore accompany statistical inference.
9 The debatable, cont d For example: Bårdsen, Jansen and Nymoen (2004) test the encompassing capabilities of the on both GGL s original euro area data and on Norwegian and UK time series data. The show that the has little encompassing power: it does not explain existing findings. Others have done even more careful s, for example Boug, Cappelen and Swensen (2006). Here, we assess the hybrid on a set from OECD countries.
10 The theoretical The hybrid is given as p t = a f 0 pe t+1 + ab 0 p t 1 + b 0 ws t, (1) where pt+1 e is expected inflation one period ahead, in our application the period is annual, conditional on the information available in period t 1. 1 ws is the log of the wage-share, as an operational definition of marginal costs. 1 p e t = E( p t+1 I t j ) the mathematical expectation given information available in time period t j. It has become custom to assume that j = 0.
11 The typical empirical The typical estimated by GGL gives the following : 1. The two null hypotheses a f = 0 and a b = 0 are firmly rejected both individually and jointly. 2. The hypothesis a f + a b = 1 is typically not rejected at conventional levels of significance, although the estimated sum is usually a little less than one. 3. The estimated value of a f is larger than a b, hence forward-looking behavior is dominant. a b is usually estimated in the range of 0.2 to When real marginal costs are proxied by the wage-share, as already assumed, the coefficient b is positive and significantly different from zero at conventional levels of significance. In the paper we show that all features depend crucially on not taking into consideration alternative and existing explanations and models.
12 OECD panel and the open economy We make use of data from 20 OECD countries. Because each country is an open economy, the closed economy equation (1) framework is a limitation. However: p t = a f 0 pe t+1 + ab 0 p t 1 + b 0 ws t + c x t, (2) where x t contains the open-economy variables, and c denotes the corresponding coefficient vector. The change in the real import price, (pi t p t ) is the single most important open economy augmentation of the. The empirical of the open economy variant align perfectly with the typical properties above.
13 Testable hypotheses Start from: ws t = ulc t pd t, (3) where ulc denotes unit labour costs (in logs) and pd is the log of the price level on domestic goods and services. Let (1 γ) denote a constant import share, then the aggregate price level is defined as p t = γ pd t + (1 γ) pi t (4) Using (3) and (4) we can re-write the as:
14 or p t = a f ( ) p 1 + b t+1 e + γ a b ( 1 + b γ ) p t 1 b (γ + b) [p t 1 γ ulc t 1 (1 γ) pi t 1 ] + γ b (γ + b) ulc t + b (1 γ) (γ + b) pi t + γ c (γ + b) x t, p t = α f p e t+1 + αb p t 1 (5) +β(ulc t 1 p t 1 ) β (1 γ) (ulc t 1 pi t 1 ) +β γ ulc t + β (1 γ) pi t + ψx t, where we have defined α f, α b, β and ψ as new coefficients for simplification.
15 This equation shows out that the has an interpretation as an equilibrium correction model (ECM), of the price level, but with two important remarks: 1. The usual ECM for inflation is extended by the inclusion of the forward-looking term p e t The -ECM contains more parameter restriction than ususal since the coefficients of ulc t, pi t and the ECM terms, (ulc t 1 p t 1 ) and (ulc t 1 pi t 1 ), are restricted to be functions of b and γ.
16 encompassing hypotheses An alternative model for price and wage formation is the imperfect competition model, ICM. The specification and evaluation of the ICM was developed in the last 2 decades before the coming of the. In simplified form the ICM implies a price equation: p t = α f pt+1 e + αb p t 1 +β 1 (ulc t 1 p t 1 ) + β 2 (ulc t 1 pi t 1 ) (6) +β 3 ulc t + β 4 pi t + ψx t. The implies restrictions on the coefficients: H a 0 : β 3 = β 1 + β 2 and H b 0 : β 4 = β 2. The ICM requires only that β 1 > 0 and β 1 > β 2. The rejection of H0 a and/or Hb 0 would therefore appear to be telling evidence against the.
17 Additional hypotheses In addition to H0 a and Hb 0 we can test: H0 c: αf = 0 and H d 0 : αb = 0. This is essentially the usual assessment of the on country (or area) data. Notice that the ICM does not imply H c : α f = 0 though. Hence a ICM with elements of forward-looking behavior is a possible alternative to both the and the ICM with (only) backward-looking expectations.
18 The OECD data set We use a data set for annual wages and prices for 20 OECD countries, for the time period For some of the countries the time period is shorter, so the panel is unbalanced. Because of one lead and one lag we loose the observations from 1960 and We use the OECD unit labour cost index that covers the whole economy. The import price index is constructed by taking the ratio of the value and the volume of imported goods and services. We use the consumer price index as a measure for p t
19 The benchmark model, M1 As a benchmark model we first estimate the model (2) with the following variables in the x vector: the rate of change in the oil price ( po t ), the change in the indirect tax rate ( VAT t ), and the change in the real import price (pi t p t ). The resulting equation is denoted M1 in the section.
20 The more general inflation equation, M2 The open economy inflation equation (6), which we repeat here as p i,t = θ i + α f p e i,t+1 + αb p i,t 1 + β 1 (ulc i,t 1 p i,t 1 ) +β 2 (ulc i,t 1 pi i,t 1 ) + β 3 ulc i,t + β 4 pi i,t +ψ 1 po i,t + ψ 2 VAT i,t + ε i,t. We have added an extra subscript i for each country, country-specific fixed effects, θ i, and a stochastic error term ε i,t. This model is denoted M2 in the next section.
21 Some Induced MA disturbances GMM estimation Identification instruments lagged two periods Common shocks we include explicit common explanatory variables (oil price), and also use SURE estimation to check our main, as an alternative to time dummies Homogenous slope coefficients Time series properties, cointegration
22 Estimation method The models are estimated using GMM, where p i,t+1, ulc i,t and (pi i,t p i,t ) are treated as endogenous explanatory variables. Instruments in all models: p i,t 2, pi i,t 1, po i,t 1, ulc i,t 1 and ws i,t 1, the gross replacement rate (BRR) and its lags, and an index of employment protection (EP) and its lags. (ulc i,t 1 pi i,t 1 ) and (ulc i,t 1 p i,t 1 ) are additional instruments in M1 and M1. Ordinary GMM estimation, and, for robustness, GMM with Cross-Section SUR (PCSE) corrections of standard errors and covariances.
23 Main, GMM, OECD p i,t (0.03) p i,t (0.03) M1 M1 M (0.03) 0.46 (0.02) 0.01 (0.12) 0.38 (0.03) ws i,t (0.01) (ulc i,t p i,t ) (0.008) (ulc i,t 1 p i,t 1 ) (0.014) (ulc i,t 1 pi i,t 1 ) (0.006) ulc i,t 0.32 (0.06) pi i,t 0.11 (0.014) (pi i,t p i,t ) 0.05 (0.01) 0.05 (0.01) po i,t (0.002) (0.002) (0.002) VAT i,t
24 Main, cont d M1 M1 M2 # observ ˆσ χ 2 ival 41.49[0.000] 41.96[0.000] 10.96[0.204] N AR [0.002] 3.02[0.002] 0.26[0.81] N AR [0.019] 2.35[0.019] 0.30[0.76]
25 Encompassing tests 1. Significance of the forward-term in M1 should carry over to M2 if the is the right theoretical framework. We observe the opposite: the hypothesis H c 0 : αf = 0 is not rejected in M2. 2. The dominance of the forward term in M1 is thus due to p i,t+1 being correlated with (ulc i,t 1 p i,t 1 ) and (ulc i,t 1 pi i,t 1 ); there is no genuine correlation between the predictable part of p i,t+1 and p i,t. 3. The t-statistics are 46.8 and 8.4 for H a 0 and Hb 0, respectively. 4. The diagnostics test of M1 also rejects their respective nulls: χ 2 ival is significant, and there is indication of significant residual autocorrelation (also of 2nd order). No such problems for M2
26 GGL claim that the represents a significant advance in inflation modelling which finally substantiates the dominance of forward-looking behavior in price adjustment. We take the testing of the model from the calm waters of US and euro area data to the vast data ocean represented by a set from 20 OECD countries We replicate all typical features of estimated model the appears to float. However, this result is to be expected also when the is encompassed by the imperfect competition model (ICM). Specifically, when the main explanatory variables of the ICM is introduced: the dominance of the forward term disappears completely the sinks
The New Keynesian Phillips Curve: The joint evidence can imply refutation
 The New Keynesian Phillips Curve: The joint evidence can imply refutation Ragnar Nymoen University of Oslo Anders Rygh Swensen University of Oslo February 2008. Eivind Tveter Statistics Norway Abstract
The New Keynesian Phillips Curve: The joint evidence can imply refutation Ragnar Nymoen University of Oslo Anders Rygh Swensen University of Oslo February 2008. Eivind Tveter Statistics Norway Abstract
Wage and price setting. Slides for 26. August 2003 lecture
 1 B&W s derivation of the Phillips curve Wage and price setting. Slides for 26. August 2003 lecture Ragnar Nymoen University of Oslo, Department of Economics Ch 12.3: The Battle of the mark-ups as a framework
1 B&W s derivation of the Phillips curve Wage and price setting. Slides for 26. August 2003 lecture Ragnar Nymoen University of Oslo, Department of Economics Ch 12.3: The Battle of the mark-ups as a framework
Testing the New Keynesian Phillips curve
 Testing the New Keynesian Phillips curve Gunnar Bårdsen Norwegian University of Science and Technology and Norges Bank EilevS.Jansen Norges Bank, University of Oslo, and Norwegian University of Science
Testing the New Keynesian Phillips curve Gunnar Bårdsen Norwegian University of Science and Technology and Norges Bank EilevS.Jansen Norges Bank, University of Oslo, and Norwegian University of Science
Slides to Lecture 3 of Introductory Dynamic Macroeconomics. Linear Dynamic Models (Ch 2 of IDM)
 Partial recap of lecture 2 1. We used the ADL model to make precise the concept of dynamic multiplier. Slides to Lecture 3 of Introductory Dynamic Macroeconomics. Linear Dynamic Models (Ch 2 of IDM) Ragnar
Partial recap of lecture 2 1. We used the ADL model to make precise the concept of dynamic multiplier. Slides to Lecture 3 of Introductory Dynamic Macroeconomics. Linear Dynamic Models (Ch 2 of IDM) Ragnar
UNIVERSITY OF OSLO DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS
 UNIVERSITY OF OSLO DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS Exam: ECON3150/ECON4150 Introductory Econometrics Date of exam: Wednesday, May 15, 013 Grades are given: June 6, 013 Time for exam: :30 p.m. 5:30 p.m. The problem
UNIVERSITY OF OSLO DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS Exam: ECON3150/ECON4150 Introductory Econometrics Date of exam: Wednesday, May 15, 013 Grades are given: June 6, 013 Time for exam: :30 p.m. 5:30 p.m. The problem
GCOE Discussion Paper Series
 GCOE Discussion Paper Series Global COE Program Human Behavior and Socioeconomic Dynamics Discussion Paper No.34 Inflation Inertia and Optimal Delegation of Monetary Policy Keiichi Morimoto February 2009
GCOE Discussion Paper Series Global COE Program Human Behavior and Socioeconomic Dynamics Discussion Paper No.34 Inflation Inertia and Optimal Delegation of Monetary Policy Keiichi Morimoto February 2009
Oil price and macroeconomy in Russia. Abstract
 Oil price and macroeconomy in Russia Katsuya Ito Fukuoka University Abstract In this note, using the VEC model we attempt to empirically investigate the effects of oil price and monetary shocks on the
Oil price and macroeconomy in Russia Katsuya Ito Fukuoka University Abstract In this note, using the VEC model we attempt to empirically investigate the effects of oil price and monetary shocks on the
The empirical relevance of the New Keynesian Phillips curve
 The empirical relevance of the New Keynesian Phillips curve Gunnar Bårdsen Norwegian University of Science and Technology and Norges Bank Eilev S. Jansen Norges Bank, University of Oslo, and Norwegian
The empirical relevance of the New Keynesian Phillips curve Gunnar Bårdsen Norwegian University of Science and Technology and Norges Bank Eilev S. Jansen Norges Bank, University of Oslo, and Norwegian
Modelling Czech and Slovak labour markets: A DSGE model with labour frictions
 Modelling Czech and Slovak labour markets: A DSGE model with labour frictions Daniel Němec Faculty of Economics and Administrations Masaryk University Brno, Czech Republic nemecd@econ.muni.cz ESF MU (Brno)
Modelling Czech and Slovak labour markets: A DSGE model with labour frictions Daniel Němec Faculty of Economics and Administrations Masaryk University Brno, Czech Republic nemecd@econ.muni.cz ESF MU (Brno)
Econometrics of Panel Data
 Econometrics of Panel Data Jakub Mućk Meeting # 6 Jakub Mućk Econometrics of Panel Data Meeting # 6 1 / 36 Outline 1 The First-Difference (FD) estimator 2 Dynamic panel data models 3 The Anderson and Hsiao
Econometrics of Panel Data Jakub Mućk Meeting # 6 Jakub Mućk Econometrics of Panel Data Meeting # 6 1 / 36 Outline 1 The First-Difference (FD) estimator 2 Dynamic panel data models 3 The Anderson and Hsiao
Answer all questions from part I. Answer two question from part II.a, and one question from part II.b.
 B203: Quantitative Methods Answer all questions from part I. Answer two question from part II.a, and one question from part II.b. Part I: Compulsory Questions. Answer all questions. Each question carries
B203: Quantitative Methods Answer all questions from part I. Answer two question from part II.a, and one question from part II.b. Part I: Compulsory Questions. Answer all questions. Each question carries
Perceived productivity and the natural rate of interest
 Perceived productivity and the natural rate of interest Gianni Amisano and Oreste Tristani European Central Bank IRF 28 Frankfurt, 26 June Amisano-Tristani (European Central Bank) Productivity and the
Perceived productivity and the natural rate of interest Gianni Amisano and Oreste Tristani European Central Bank IRF 28 Frankfurt, 26 June Amisano-Tristani (European Central Bank) Productivity and the
Lecture 8: Aggregate demand and supply dynamics, closed economy case.
 Lecture 8: Aggregate demand and supply dynamics, closed economy case. Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics, University of Oslo October 20, 2008 1 Ch 17, 19 and 20 in IAM Since our primary concern is to
Lecture 8: Aggregate demand and supply dynamics, closed economy case. Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics, University of Oslo October 20, 2008 1 Ch 17, 19 and 20 in IAM Since our primary concern is to
Department of Economics, UCSB UC Santa Barbara
 Department of Economics, UCSB UC Santa Barbara Title: Past trend versus future expectation: test of exchange rate volatility Author: Sengupta, Jati K., University of California, Santa Barbara Sfeir, Raymond,
Department of Economics, UCSB UC Santa Barbara Title: Past trend versus future expectation: test of exchange rate volatility Author: Sengupta, Jati K., University of California, Santa Barbara Sfeir, Raymond,
Global Value Chain Participation and Current Account Imbalances
 Global Value Chain Participation and Current Account Imbalances Johannes Brumm University of Zurich Georgios Georgiadis European Central Bank Johannes Gräb European Central Bank Fabian Trottner Princeton
Global Value Chain Participation and Current Account Imbalances Johannes Brumm University of Zurich Georgios Georgiadis European Central Bank Johannes Gräb European Central Bank Fabian Trottner Princeton
On inflation expectations in the NKPC model
 Empir Econ https://doi.org/10.1007/s00181-018-1417-8 On inflation expectations in the NKPC model Philip Hans Franses 1 Received: 24 November 2017 / Accepted: 9 May 2018 The Author(s) 2018 Abstract To create
Empir Econ https://doi.org/10.1007/s00181-018-1417-8 On inflation expectations in the NKPC model Philip Hans Franses 1 Received: 24 November 2017 / Accepted: 9 May 2018 The Author(s) 2018 Abstract To create
The regression model with one stochastic regressor (part II)
 The regression model with one stochastic regressor (part II) 3150/4150 Lecture 7 Ragnar Nymoen 6 Feb 2012 We will finish Lecture topic 4: The regression model with stochastic regressor We will first look
The regression model with one stochastic regressor (part II) 3150/4150 Lecture 7 Ragnar Nymoen 6 Feb 2012 We will finish Lecture topic 4: The regression model with stochastic regressor We will first look
ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I
 Name: Students ID: ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I I. Short Questions (21/2 points each) Mark the following statements as True (T) or False (F) and give a brief explanation of your answer in each case. 1. 2.
Name: Students ID: ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I I. Short Questions (21/2 points each) Mark the following statements as True (T) or False (F) and give a brief explanation of your answer in each case. 1. 2.
Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle
 Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle David de la Croix 1,3 Gregory de Walque 2 Rafael Wouters 2,1 1 dept. of economics, Univ. cath. Louvain 2 National Bank of Belgium
Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle David de la Croix 1,3 Gregory de Walque 2 Rafael Wouters 2,1 1 dept. of economics, Univ. cath. Louvain 2 National Bank of Belgium
ECON 4160: Econometrics-Modelling and Systems Estimation Lecture 9: Multiple equation models II
 ECON 4160: Econometrics-Modelling and Systems Estimation Lecture 9: Multiple equation models II Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics University of Oslo 9 October 2018 The reference to this lecture is:
ECON 4160: Econometrics-Modelling and Systems Estimation Lecture 9: Multiple equation models II Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics University of Oslo 9 October 2018 The reference to this lecture is:
Identification of the New Keynesian Phillips Curve: Problems and Consequences
 MACROECONOMIC POLICY WORKSHOP: CENTRAL BANK OF CHILE The Relevance of the New Keynesian Phillips Curve Identification of the New Keynesian Phillips Curve: Problems and Consequences James. H. Stock Harvard
MACROECONOMIC POLICY WORKSHOP: CENTRAL BANK OF CHILE The Relevance of the New Keynesian Phillips Curve Identification of the New Keynesian Phillips Curve: Problems and Consequences James. H. Stock Harvard
Inflation Dynamics in the Euro Area Jensen, Henrik
 university of copenhagen Inflation Dynamics in the Euro Area Jensen, Henrik Publication date: 2010 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Citation for published version (APA):
university of copenhagen Inflation Dynamics in the Euro Area Jensen, Henrik Publication date: 2010 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Citation for published version (APA):
Shortfalls of Panel Unit Root Testing. Jack Strauss Saint Louis University. And. Taner Yigit Bilkent University. Abstract
 Shortfalls of Panel Unit Root Testing Jack Strauss Saint Louis University And Taner Yigit Bilkent University Abstract This paper shows that (i) magnitude and variation of contemporaneous correlation are
Shortfalls of Panel Unit Root Testing Jack Strauss Saint Louis University And Taner Yigit Bilkent University Abstract This paper shows that (i) magnitude and variation of contemporaneous correlation are
MEMORANDUM. Department of Economics University of Oslo. Testing the Invariance of Expectations Models of Inflation
 MEMORANDUM No 21/2010 Testing the Invariance of Expectations Models of Inflation Jennifer L. Castle Jurgen A. Doornik David F. Hendry Ragnar Nymoen ISSN: 0809-8786 Department of Economics University of
MEMORANDUM No 21/2010 Testing the Invariance of Expectations Models of Inflation Jennifer L. Castle Jurgen A. Doornik David F. Hendry Ragnar Nymoen ISSN: 0809-8786 Department of Economics University of
Purchasing power parity over two centuries: strengthening the case for real exchange rate stability A reply to Cuddington and Liang
 Journal of International Money and Finance 19 (2000) 759 764 www.elsevier.nl/locate/econbase Purchasing power parity over two centuries: strengthening the case for real exchange rate stability A reply
Journal of International Money and Finance 19 (2000) 759 764 www.elsevier.nl/locate/econbase Purchasing power parity over two centuries: strengthening the case for real exchange rate stability A reply
The New Keynesian Phillips Curve When Inflation Is Non-Stationary: The Case for Canada
 The New Keynesian Phillips Curve When Inflation Is Non-Stationary: The Case for Canada Bergljot BjØrnson Barkbu and Nicoletta Batini* Introduction The assumption that inflation is stationary, however,
The New Keynesian Phillips Curve When Inflation Is Non-Stationary: The Case for Canada Bergljot BjØrnson Barkbu and Nicoletta Batini* Introduction The assumption that inflation is stationary, however,
ARDL Cointegration Tests for Beginner
 ARDL Cointegration Tests for Beginner Tuck Cheong TANG Department of Economics, Faculty of Economics & Administration University of Malaya Email: tangtuckcheong@um.edu.my DURATION: 3 HOURS On completing
ARDL Cointegration Tests for Beginner Tuck Cheong TANG Department of Economics, Faculty of Economics & Administration University of Malaya Email: tangtuckcheong@um.edu.my DURATION: 3 HOURS On completing
Investigating weak identification in estimates of the Taylor rule for the Norwegian economy
 Investigating weak identification in estimates of the Taylor rule for the Norwegian economy Anders Merckoll Helseth Master s Thesis, Department of Economics University of Oslo May 2015 Anders Merckoll
Investigating weak identification in estimates of the Taylor rule for the Norwegian economy Anders Merckoll Helseth Master s Thesis, Department of Economics University of Oslo May 2015 Anders Merckoll
Adverse Effects of Monetary Policy Signalling
 Adverse Effects of Monetary Policy Signalling Jan FILÁČEK and Jakub MATĚJŮ Monetary Department Czech National Bank CNB Research Open Day, 18 th May 21 Outline What do we mean by adverse effects of monetary
Adverse Effects of Monetary Policy Signalling Jan FILÁČEK and Jakub MATĚJŮ Monetary Department Czech National Bank CNB Research Open Day, 18 th May 21 Outline What do we mean by adverse effects of monetary
Econometrics - ECON4160 Exercises (GiveWin & PcGive) 1. Exercises to PcGive lectures 15. January 2009
 Econometrics - ECON4160 Exercises (GiveWin & PcGive) 1 Exercises to PcGive lectures 15. January 2009 We outline 10 exercises for this course in econometrics. The exercises have been designed such that
Econometrics - ECON4160 Exercises (GiveWin & PcGive) 1 Exercises to PcGive lectures 15. January 2009 We outline 10 exercises for this course in econometrics. The exercises have been designed such that
FORECAST ERRORS IN PRICES AND WAGES: THE EXPERIENCE WITH THREE PROGRAMME COUNTRIES
 Escola de Economia e Gestão Universidade do Minho e NIPE fjveiga@eeg.uminho.pt FORECAST ERRORS IN PRICES AND WAGES: THE EXPERIENCE WITH THREE PROGRAMME COUNTRIES ABSTRACT This paper evaluates the accuracy
Escola de Economia e Gestão Universidade do Minho e NIPE fjveiga@eeg.uminho.pt FORECAST ERRORS IN PRICES AND WAGES: THE EXPERIENCE WITH THREE PROGRAMME COUNTRIES ABSTRACT This paper evaluates the accuracy
Resolving the Missing Deflation Puzzle. June 7, 2018
 Resolving the Missing Deflation Puzzle Jesper Lindé Sveriges Riksbank Mathias Trabandt Freie Universität Berlin June 7, 218 Motivation Key observations during the Great Recession: Extraordinary contraction
Resolving the Missing Deflation Puzzle Jesper Lindé Sveriges Riksbank Mathias Trabandt Freie Universität Berlin June 7, 218 Motivation Key observations during the Great Recession: Extraordinary contraction
Financial Econometrics
 Financial Econometrics Long-run Relationships in Finance Gerald P. Dwyer Trinity College, Dublin January 2016 Outline 1 Long-Run Relationships Review of Nonstationarity in Mean Cointegration Vector Error
Financial Econometrics Long-run Relationships in Finance Gerald P. Dwyer Trinity College, Dublin January 2016 Outline 1 Long-Run Relationships Review of Nonstationarity in Mean Cointegration Vector Error
Autoregressive distributed lag models
 Introduction In economics, most cases we want to model relationships between variables, and often simultaneously. That means we need to move from univariate time series to multivariate. We do it in two
Introduction In economics, most cases we want to model relationships between variables, and often simultaneously. That means we need to move from univariate time series to multivariate. We do it in two
1 Estimation of Persistent Dynamic Panel Data. Motivation
 1 Estimation of Persistent Dynamic Panel Data. Motivation Consider the following Dynamic Panel Data (DPD) model y it = y it 1 ρ + x it β + µ i + v it (1.1) with i = {1, 2,..., N} denoting the individual
1 Estimation of Persistent Dynamic Panel Data. Motivation Consider the following Dynamic Panel Data (DPD) model y it = y it 1 ρ + x it β + µ i + v it (1.1) with i = {1, 2,..., N} denoting the individual
Økonomisk Kandidateksamen 2004 (II) Econometrics 2 June 14, 2004
 Økonomisk Kandidateksamen 2004 (II) Econometrics 2 June 14, 2004 This is a four hours closed-book exam (uden hjælpemidler). Answer all questions! The questions 1 to 4 have equal weight. Within each question,
Økonomisk Kandidateksamen 2004 (II) Econometrics 2 June 14, 2004 This is a four hours closed-book exam (uden hjælpemidler). Answer all questions! The questions 1 to 4 have equal weight. Within each question,
The Predictability of Aggregate Consumption Growth in OECD Countries: A Panel Data Analysis
 The Predictability of Aggregate Consumption Growth in OECD Countries: A Panel Data Analysis Gerdie Everaert a1 and Lorenzo Pozzi b2 1 SHERPPA, Ghent University 2 Department of Economics, Erasmus University
The Predictability of Aggregate Consumption Growth in OECD Countries: A Panel Data Analysis Gerdie Everaert a1 and Lorenzo Pozzi b2 1 SHERPPA, Ghent University 2 Department of Economics, Erasmus University
Macroeconomics II. Dynamic AD-AS model
 Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Dynamic AD-AS model vs. AD-AS model Notes. Dynamic AD-AS model in a few words Notes. Notation to incorporate time-dimension Notes
 Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Another Look at the Boom and Bust of Financial Bubbles
 ANNALS OF ECONOMICS AND FINANCE 16-2, 417 423 (2015) Another Look at the Boom and Bust of Financial Bubbles Andrea Beccarini University of Münster, Department of Economics, Am Stadtgraben 9, 48143, Münster,
ANNALS OF ECONOMICS AND FINANCE 16-2, 417 423 (2015) Another Look at the Boom and Bust of Financial Bubbles Andrea Beccarini University of Münster, Department of Economics, Am Stadtgraben 9, 48143, Münster,
Econometrics - ECON4160 Exercises (GiveWin & PcGive) 1. Exercises to PcGive lectures 5th February 2004
 Econometrics - ECON4160 Exercises (GiveWin & PcGive) 1 Exercises to PcGive lectures 5th February 2004 We outline 10 exercises for this course in econometrics. The exercises have been designed such that
Econometrics - ECON4160 Exercises (GiveWin & PcGive) 1 Exercises to PcGive lectures 5th February 2004 We outline 10 exercises for this course in econometrics. The exercises have been designed such that
The regression model with one fixed regressor cont d
 The regression model with one fixed regressor cont d 3150/4150 Lecture 4 Ragnar Nymoen 27 January 2012 The model with transformed variables Regression with transformed variables I References HGL Ch 2.8
The regression model with one fixed regressor cont d 3150/4150 Lecture 4 Ragnar Nymoen 27 January 2012 The model with transformed variables Regression with transformed variables I References HGL Ch 2.8
University of Groningen. A regional analysis of inflation dynamics in Turkey Yesilyurt, Filiz; Elhorst, Paul. Published in: Annals of Regional Science
 University of Groningen A regional analysis of inflation dynamics in Turkey Yesilyurt, Filiz; Elhorst, Paul Published in: Annals of Regional Science DOI: 10.1007/s00168-013-0570-4 IMPORTANT NOTE: You are
University of Groningen A regional analysis of inflation dynamics in Turkey Yesilyurt, Filiz; Elhorst, Paul Published in: Annals of Regional Science DOI: 10.1007/s00168-013-0570-4 IMPORTANT NOTE: You are
Fiscal Multipliers in a Nonlinear World
 Fiscal Multipliers in a Nonlinear World Jesper Lindé Sveriges Riksbank Mathias Trabandt Freie Universität Berlin November 28, 2016 Lindé and Trabandt Multipliers () in Nonlinear Models November 28, 2016
Fiscal Multipliers in a Nonlinear World Jesper Lindé Sveriges Riksbank Mathias Trabandt Freie Universität Berlin November 28, 2016 Lindé and Trabandt Multipliers () in Nonlinear Models November 28, 2016
The Price Puzzle: Mixing the Temporary and Permanent Monetary Policy Shocks.
 The Price Puzzle: Mixing the Temporary and Permanent Monetary Policy Shocks. Ida Wolden Bache Norges Bank Kai Leitemo Norwegian School of Management BI September 2, 2008 Abstract We argue that the correct
The Price Puzzle: Mixing the Temporary and Permanent Monetary Policy Shocks. Ida Wolden Bache Norges Bank Kai Leitemo Norwegian School of Management BI September 2, 2008 Abstract We argue that the correct
Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded areas indicate US recessions research.stlouisfed.org
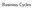 Business Cycles 0 Real Gross Domestic Product 18,000 16,000 (Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars) 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 1940 1960 1980 2000 Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded
Business Cycles 0 Real Gross Domestic Product 18,000 16,000 (Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars) 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 1940 1960 1980 2000 Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded
General Examination in Macroeconomic Theory SPRING 2013
 HARVARD UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS General Examination in Macroeconomic Theory SPRING 203 You have FOUR hours. Answer all questions Part A (Prof. Laibson): 48 minutes Part B (Prof. Aghion): 48
HARVARD UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS General Examination in Macroeconomic Theory SPRING 203 You have FOUR hours. Answer all questions Part A (Prof. Laibson): 48 minutes Part B (Prof. Aghion): 48
Graduate Macro Theory II: Notes on Quantitative Analysis in DSGE Models
 Graduate Macro Theory II: Notes on Quantitative Analysis in DSGE Models Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Spring 2011 This note describes very briefly how to conduct quantitative analysis on a linearized
Graduate Macro Theory II: Notes on Quantitative Analysis in DSGE Models Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Spring 2011 This note describes very briefly how to conduct quantitative analysis on a linearized
ECO 310: Empirical Industrial Organization Lecture 2 - Estimation of Demand and Supply
 ECO 310: Empirical Industrial Organization Lecture 2 - Estimation of Demand and Supply Dimitri Dimitropoulos Fall 2014 UToronto 1 / 55 References RW Section 3. Wooldridge, J. (2008). Introductory Econometrics:
ECO 310: Empirical Industrial Organization Lecture 2 - Estimation of Demand and Supply Dimitri Dimitropoulos Fall 2014 UToronto 1 / 55 References RW Section 3. Wooldridge, J. (2008). Introductory Econometrics:
Volume 31, Issue 1. Mean-reverting behavior of consumption-income ratio in OECD countries: evidence from SURADF panel unit root tests
 Volume 3, Issue Mean-reverting behavior of consumption-income ratio in OECD countries: evidence from SURADF panel unit root tests Shu-Yi Liao Department of Applied Economics, National Chung sing University,
Volume 3, Issue Mean-reverting behavior of consumption-income ratio in OECD countries: evidence from SURADF panel unit root tests Shu-Yi Liao Department of Applied Economics, National Chung sing University,
Identifying the Monetary Policy Shock Christiano et al. (1999)
 Identifying the Monetary Policy Shock Christiano et al. (1999) The question we are asking is: What are the consequences of a monetary policy shock a shock which is purely related to monetary conditions
Identifying the Monetary Policy Shock Christiano et al. (1999) The question we are asking is: What are the consequences of a monetary policy shock a shock which is purely related to monetary conditions
The multiple regression model; Indicator variables as regressors
 The multiple regression model; Indicator variables as regressors Ragnar Nymoen University of Oslo 28 February 2013 1 / 21 This lecture (#12): Based on the econometric model specification from Lecture 9
The multiple regression model; Indicator variables as regressors Ragnar Nymoen University of Oslo 28 February 2013 1 / 21 This lecture (#12): Based on the econometric model specification from Lecture 9
Stagnation Traps. Gianluca Benigno and Luca Fornaro
 Stagnation Traps Gianluca Benigno and Luca Fornaro May 2015 Research question and motivation Can insu cient aggregate demand lead to economic stagnation? This question goes back, at least, to the Great
Stagnation Traps Gianluca Benigno and Luca Fornaro May 2015 Research question and motivation Can insu cient aggregate demand lead to economic stagnation? This question goes back, at least, to the Great
ENERGY CONSUMPTION AND ECONOMIC GROWTH IN SWEDEN: A LEVERAGED BOOTSTRAP APPROACH, ( ) HATEMI-J, Abdulnasser * IRANDOUST, Manuchehr
 ENERGY CONSUMPTION AND ECONOMIC GROWTH IN SWEDEN: A LEVERAGED BOOTSTRAP APPROACH, (1965-2000) HATEMI-J, Abdulnasser * IRANDOUST, Manuchehr Abstract The causal interaction between energy consumption, real
ENERGY CONSUMPTION AND ECONOMIC GROWTH IN SWEDEN: A LEVERAGED BOOTSTRAP APPROACH, (1965-2000) HATEMI-J, Abdulnasser * IRANDOUST, Manuchehr Abstract The causal interaction between energy consumption, real
Warwick Business School Forecasting System. Summary. Ana Galvao, Anthony Garratt and James Mitchell November, 2014
 Warwick Business School Forecasting System Summary Ana Galvao, Anthony Garratt and James Mitchell November, 21 The main objective of the Warwick Business School Forecasting System is to provide competitive
Warwick Business School Forecasting System Summary Ana Galvao, Anthony Garratt and James Mitchell November, 21 The main objective of the Warwick Business School Forecasting System is to provide competitive
ECON 4160: Econometrics-Modelling and Systems Estimation Lecture 7: Single equation models
 ECON 4160: Econometrics-Modelling and Systems Estimation Lecture 7: Single equation models Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics University of Oslo 25 September 2018 The reference to this lecture is: Chapter
ECON 4160: Econometrics-Modelling and Systems Estimation Lecture 7: Single equation models Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics University of Oslo 25 September 2018 The reference to this lecture is: Chapter
4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models. Basic Economic Models
 4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models Basic Economic Models In Economics, we use theoretical models to explain the economic processes in the real world. These models de ne a relation
4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models Basic Economic Models In Economics, we use theoretical models to explain the economic processes in the real world. These models de ne a relation
Modeling Nonlinearities in Interest Rate Setting
 The United Kingdom 1970:2006 riedel@wiwi.hu-berlin.de Institut für Statistik and Ökonometrie, C2 Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin June 27, 2007 Aim Estimation of an augmented Taylor Rule for interest rates
The United Kingdom 1970:2006 riedel@wiwi.hu-berlin.de Institut für Statistik and Ökonometrie, C2 Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin June 27, 2007 Aim Estimation of an augmented Taylor Rule for interest rates
G. S. Maddala Kajal Lahiri. WILEY A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd., Publication
 G. S. Maddala Kajal Lahiri WILEY A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd., Publication TEMT Foreword Preface to the Fourth Edition xvii xix Part I Introduction and the Linear Regression Model 1 CHAPTER 1 What is Econometrics?
G. S. Maddala Kajal Lahiri WILEY A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd., Publication TEMT Foreword Preface to the Fourth Edition xvii xix Part I Introduction and the Linear Regression Model 1 CHAPTER 1 What is Econometrics?
Monetary Policy Regimes and Economic Performance: The Historical Record,
 Monetary Policy Regimes and Economic Performance: The Historical Record, 1979-2008 Luca Benati Charles Goodhart European Central Bank London School of Economics Conference on: Key developments in monetary
Monetary Policy Regimes and Economic Performance: The Historical Record, 1979-2008 Luca Benati Charles Goodhart European Central Bank London School of Economics Conference on: Key developments in monetary
Interest Rate Determination & the Taylor Rule JARED BERRY & JAIME MARQUEZ JOHNS HOPKINS SCHOOL OF ADVANCED INTERNATIONAL STUDIES JANURY 2017
 Interest Rate Determination & the Taylor Rule JARED BERRY & JAIME MARQUEZ JOHNS HOPKINS SCHOOL OF ADVANCED INTERNATIONAL STUDIES JANURY 2017 Monetary Policy Rules Policy rules form part of the modern approach
Interest Rate Determination & the Taylor Rule JARED BERRY & JAIME MARQUEZ JOHNS HOPKINS SCHOOL OF ADVANCED INTERNATIONAL STUDIES JANURY 2017 Monetary Policy Rules Policy rules form part of the modern approach
Macroeconometric Modelling
 Macroeconometric Modelling 4 General modelling and some examples Gunnar Bårdsen CREATES 16-17 November 2009 From system... I Standard procedure see (?), Hendry (1995), Johansen (1995), Johansen (2006),
Macroeconometric Modelling 4 General modelling and some examples Gunnar Bårdsen CREATES 16-17 November 2009 From system... I Standard procedure see (?), Hendry (1995), Johansen (1995), Johansen (2006),
The US Phillips Curve and inflation expectations: A State. Space Markov-Switching explanatory model.
 The US Phillips Curve and inflation expectations: A State Space Markov-Switching explanatory model. Guillaume Guerrero Nicolas Million February 2004 We are grateful to P.Y Hénin, for helpful ideas and
The US Phillips Curve and inflation expectations: A State Space Markov-Switching explanatory model. Guillaume Guerrero Nicolas Million February 2004 We are grateful to P.Y Hénin, for helpful ideas and
Econometrics Summary Algebraic and Statistical Preliminaries
 Econometrics Summary Algebraic and Statistical Preliminaries Elasticity: The point elasticity of Y with respect to L is given by α = ( Y/ L)/(Y/L). The arc elasticity is given by ( Y/ L)/(Y/L), when L
Econometrics Summary Algebraic and Statistical Preliminaries Elasticity: The point elasticity of Y with respect to L is given by α = ( Y/ L)/(Y/L). The arc elasticity is given by ( Y/ L)/(Y/L), when L
Christopher Dougherty London School of Economics and Political Science
 Introduction to Econometrics FIFTH EDITION Christopher Dougherty London School of Economics and Political Science OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents INTRODU CTION 1 Why study econometrics? 1 Aim of this
Introduction to Econometrics FIFTH EDITION Christopher Dougherty London School of Economics and Political Science OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents INTRODU CTION 1 Why study econometrics? 1 Aim of this
What Happened to the Phillips Curve in the 1990s in Canada?
 What Happened to the Phillips Curve in the 1990s in Canada? Paul Beaudry and Matthew Doyle* Introduction There are at least two broad categories of interpretation to consider when examining observations
What Happened to the Phillips Curve in the 1990s in Canada? Paul Beaudry and Matthew Doyle* Introduction There are at least two broad categories of interpretation to consider when examining observations
Econometrics in a nutshell: Variation and Identification Linear Regression Model in STATA. Research Methods. Carlos Noton.
 1/17 Research Methods Carlos Noton Term 2-2012 Outline 2/17 1 Econometrics in a nutshell: Variation and Identification 2 Main Assumptions 3/17 Dependent variable or outcome Y is the result of two forces:
1/17 Research Methods Carlos Noton Term 2-2012 Outline 2/17 1 Econometrics in a nutshell: Variation and Identification 2 Main Assumptions 3/17 Dependent variable or outcome Y is the result of two forces:
Co-integration rank determination in partial systems using information criteria
 Co-integration rank determination in partial systems using information criteria Giuseppe Cavaliere Luca Fanelli Luca De Angelis Department of Statistical Sciences, University of Bologna February 15, 2016
Co-integration rank determination in partial systems using information criteria Giuseppe Cavaliere Luca Fanelli Luca De Angelis Department of Statistical Sciences, University of Bologna February 15, 2016
Are Policy Counterfactuals Based on Structural VARs Reliable?
 Are Policy Counterfactuals Based on Structural VARs Reliable? Luca Benati European Central Bank 2nd International Conference in Memory of Carlo Giannini 20 January 2010 The views expressed herein are personal,
Are Policy Counterfactuals Based on Structural VARs Reliable? Luca Benati European Central Bank 2nd International Conference in Memory of Carlo Giannini 20 January 2010 The views expressed herein are personal,
The Econometrics of Macroeconomic Modelling GUNNAR BÅRDSEN ØYVIND EITRHEIM EILEV S. JANSEN AND RAGNAR NYMOEN
 The Econometrics of Macroeconomic Modelling GUNNAR BÅRDSEN ØYVIND EITRHEIM EILEV S. JANSEN AND RAGNAR NYMOEN 1 Contents List of Figures List of Tables List of Abbreviations xv xix xxi 1 Introduction 1
The Econometrics of Macroeconomic Modelling GUNNAR BÅRDSEN ØYVIND EITRHEIM EILEV S. JANSEN AND RAGNAR NYMOEN 1 Contents List of Figures List of Tables List of Abbreviations xv xix xxi 1 Introduction 1
DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS AND FINANCE COLLEGE OF BUSINESS AND ECONOMICS UNIVERSITY OF CANTERBURY CHRISTCHURCH, NEW ZEALAND
 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS AND FINANCE COLLEGE OF BUSINESS AND ECONOMICS UNIVERSITY OF CANTERBURY CHRISTCHURCH, NEW ZEALAND Testing For Unit Roots With Cointegrated Data NOTE: This paper is a revision of
DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS AND FINANCE COLLEGE OF BUSINESS AND ECONOMICS UNIVERSITY OF CANTERBURY CHRISTCHURCH, NEW ZEALAND Testing For Unit Roots With Cointegrated Data NOTE: This paper is a revision of
LECTURE 9: GENTLE INTRODUCTION TO
 LECTURE 9: GENTLE INTRODUCTION TO REGRESSION WITH TIME SERIES From random variables to random processes (cont d) 2 in cross-sectional regression, we were making inferences about the whole population based
LECTURE 9: GENTLE INTRODUCTION TO REGRESSION WITH TIME SERIES From random variables to random processes (cont d) 2 in cross-sectional regression, we were making inferences about the whole population based
Dynamic Factor Models Cointegration and Error Correction Mechanisms
 Dynamic Factor Models Cointegration and Error Correction Mechanisms Matteo Barigozzi Marco Lippi Matteo Luciani LSE EIEF ECARES Conference in memory of Carlo Giannini Pavia 25 Marzo 2014 This talk Statement
Dynamic Factor Models Cointegration and Error Correction Mechanisms Matteo Barigozzi Marco Lippi Matteo Luciani LSE EIEF ECARES Conference in memory of Carlo Giannini Pavia 25 Marzo 2014 This talk Statement
Cointegration and Tests of Purchasing Parity Anthony Mac Guinness- Senior Sophister
 Cointegration and Tests of Purchasing Parity Anthony Mac Guinness- Senior Sophister Most of us know Purchasing Power Parity as a sensible way of expressing per capita GNP; that is taking local price levels
Cointegration and Tests of Purchasing Parity Anthony Mac Guinness- Senior Sophister Most of us know Purchasing Power Parity as a sensible way of expressing per capita GNP; that is taking local price levels
Aggregate Supply. A Nonvertical AS Curve. implications for unemployment, rms pricing behavior, the real wage and the markup
 A Nonvertical AS Curve nominal wage rigidity nominal price rigidity labor and goods markets implications for unemployment, rms pricing behavior, the real wage and the markup Case 1: Sticky W, Flexible
A Nonvertical AS Curve nominal wage rigidity nominal price rigidity labor and goods markets implications for unemployment, rms pricing behavior, the real wage and the markup Case 1: Sticky W, Flexible
TERMS OF TRADE: THE AGRICULTURE-INDUSTRY INTERACTION IN THE CARIBBEAN
 (Draft- February 2004) TERMS OF TRADE: THE AGRICULTURE-INDUSTRY INTERACTION IN THE CARIBBEAN Chandra Sitahal-Aleong Delaware State University, Dover, Delaware, USA John Aleong, University of Vermont, Burlington,
(Draft- February 2004) TERMS OF TRADE: THE AGRICULTURE-INDUSTRY INTERACTION IN THE CARIBBEAN Chandra Sitahal-Aleong Delaware State University, Dover, Delaware, USA John Aleong, University of Vermont, Burlington,
1. Constant-elasticity-of-substitution (CES) or Dixit-Stiglitz aggregators. Consider the following function J: J(x) = a(j)x(j) ρ dj
 Macro II (UC3M, MA/PhD Econ) Professor: Matthias Kredler Problem Set 1 Due: 29 April 216 You are encouraged to work in groups; however, every student has to hand in his/her own version of the solution.
Macro II (UC3M, MA/PhD Econ) Professor: Matthias Kredler Problem Set 1 Due: 29 April 216 You are encouraged to work in groups; however, every student has to hand in his/her own version of the solution.
Econometrics of Panel Data
 Econometrics of Panel Data Jakub Mućk Meeting # 9 Jakub Mućk Econometrics of Panel Data Meeting # 9 1 / 22 Outline 1 Time series analysis Stationarity Unit Root Tests for Nonstationarity 2 Panel Unit Root
Econometrics of Panel Data Jakub Mućk Meeting # 9 Jakub Mućk Econometrics of Panel Data Meeting # 9 1 / 22 Outline 1 Time series analysis Stationarity Unit Root Tests for Nonstationarity 2 Panel Unit Root
1.2. Structural VARs
 1. Shocks Nr. 1 1.2. Structural VARs How to identify A 0? A review: Choleski (Cholesky?) decompositions. Short-run restrictions. Inequality restrictions. Long-run restrictions. Then, examples, applications,
1. Shocks Nr. 1 1.2. Structural VARs How to identify A 0? A review: Choleski (Cholesky?) decompositions. Short-run restrictions. Inequality restrictions. Long-run restrictions. Then, examples, applications,
Testing for Unit Roots with Cointegrated Data
 Discussion Paper No. 2015-57 August 19, 2015 http://www.economics-ejournal.org/economics/discussionpapers/2015-57 Testing for Unit Roots with Cointegrated Data W. Robert Reed Abstract This paper demonstrates
Discussion Paper No. 2015-57 August 19, 2015 http://www.economics-ejournal.org/economics/discussionpapers/2015-57 Testing for Unit Roots with Cointegrated Data W. Robert Reed Abstract This paper demonstrates
Introduction to Econometrics
 Introduction to Econometrics T H I R D E D I T I O N Global Edition James H. Stock Harvard University Mark W. Watson Princeton University Boston Columbus Indianapolis New York San Francisco Upper Saddle
Introduction to Econometrics T H I R D E D I T I O N Global Edition James H. Stock Harvard University Mark W. Watson Princeton University Boston Columbus Indianapolis New York San Francisco Upper Saddle
Toulouse School of Economics, Macroeconomics II Franck Portier. Homework 1. Problem I An AD-AS Model
 Toulouse School of Economics, 2009-2010 Macroeconomics II Franck Portier Homework 1 Problem I An AD-AS Model Let us consider an economy with three agents (a firm, a household and a government) and four
Toulouse School of Economics, 2009-2010 Macroeconomics II Franck Portier Homework 1 Problem I An AD-AS Model Let us consider an economy with three agents (a firm, a household and a government) and four
Macroeconomics Field Exam. August 2007
 Macroeconomics Field Exam August 2007 Answer all questions in the exam. Suggested times correspond to the questions weights in the exam grade. Make your answers as precise as possible, using graphs, equations,
Macroeconomics Field Exam August 2007 Answer all questions in the exam. Suggested times correspond to the questions weights in the exam grade. Make your answers as precise as possible, using graphs, equations,
Strict and Flexible Inflation Forecast Targets: An Empirical Investigation
 Strict and Flexible Inflation Forecast Targets: An Empirical Investigation Graham Voss University of Victoria, Canada Glenn Otto University of New South Wales, Australia Inflation Targets Bank of Canada
Strict and Flexible Inflation Forecast Targets: An Empirical Investigation Graham Voss University of Victoria, Canada Glenn Otto University of New South Wales, Australia Inflation Targets Bank of Canada
A Horse-Race Contest of Selected Economic Indicators & Their Potential Prediction Abilities on GDP
 A Horse-Race Contest of Selected Economic Indicators & Their Potential Prediction Abilities on GDP Tahmoures Afshar, Woodbury University, USA ABSTRACT This paper empirically investigates, in the context
A Horse-Race Contest of Selected Economic Indicators & Their Potential Prediction Abilities on GDP Tahmoures Afshar, Woodbury University, USA ABSTRACT This paper empirically investigates, in the context
Applied Microeconometrics (L5): Panel Data-Basics
 Applied Microeconometrics (L5): Panel Data-Basics Nicholas Giannakopoulos University of Patras Department of Economics ngias@upatras.gr November 10, 2015 Nicholas Giannakopoulos (UPatras) MSc Applied Economics
Applied Microeconometrics (L5): Panel Data-Basics Nicholas Giannakopoulos University of Patras Department of Economics ngias@upatras.gr November 10, 2015 Nicholas Giannakopoulos (UPatras) MSc Applied Economics
Taylor Rules and Technology Shocks
 Taylor Rules and Technology Shocks Eric R. Sims University of Notre Dame and NBER January 17, 2012 Abstract In a standard New Keynesian model, a Taylor-type interest rate rule moves the equilibrium real
Taylor Rules and Technology Shocks Eric R. Sims University of Notre Dame and NBER January 17, 2012 Abstract In a standard New Keynesian model, a Taylor-type interest rate rule moves the equilibrium real
Inflation dynamics, marginal cost, and the output gap: Evidence from three countries
 Inflation dynamics, marginal cost, and the output gap: Evidence from three countries Katharine S. Neiss a and Edward Nelson b a Monetary Analysis, Bank of England, London EC2R 8AH, U.K. b Monetary Policy
Inflation dynamics, marginal cost, and the output gap: Evidence from three countries Katharine S. Neiss a and Edward Nelson b a Monetary Analysis, Bank of England, London EC2R 8AH, U.K. b Monetary Policy
Reliability of inference (1 of 2 lectures)
 Reliability of inference (1 of 2 lectures) Ragnar Nymoen University of Oslo 5 March 2013 1 / 19 This lecture (#13 and 14): I The optimality of the OLS estimators and tests depend on the assumptions of
Reliability of inference (1 of 2 lectures) Ragnar Nymoen University of Oslo 5 March 2013 1 / 19 This lecture (#13 and 14): I The optimality of the OLS estimators and tests depend on the assumptions of
12 TH RESEARCH MEETING OF NIPFP-DEA RESEARCH PROGRAMME
 AN UNOBSERVED COMPONENTS PHILLIPS CURVE FOR INDIA 12 TH RESEARCH MEETING OF NIPFP-DEA RESEARCH PROGRAMME Ananya Kotia University of Oxford March 2014 UC Phillips Curve for India 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 What
AN UNOBSERVED COMPONENTS PHILLIPS CURVE FOR INDIA 12 TH RESEARCH MEETING OF NIPFP-DEA RESEARCH PROGRAMME Ananya Kotia University of Oxford March 2014 UC Phillips Curve for India 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 What
Introduction to Econometrics
 Introduction to Econometrics STAT-S-301 Introduction to Time Series Regression and Forecasting (2016/2017) Lecturer: Yves Dominicy Teaching Assistant: Elise Petit 1 Introduction to Time Series Regression
Introduction to Econometrics STAT-S-301 Introduction to Time Series Regression and Forecasting (2016/2017) Lecturer: Yves Dominicy Teaching Assistant: Elise Petit 1 Introduction to Time Series Regression
The Dark Corners of the Labor Market
 The Dark Corners of the Labor Market Vincent Sterk Conference on Persistent Output Gaps: Causes and Policy Remedies EABCN / University of Cambridge / INET University College London September 2015 Sterk
The Dark Corners of the Labor Market Vincent Sterk Conference on Persistent Output Gaps: Causes and Policy Remedies EABCN / University of Cambridge / INET University College London September 2015 Sterk
This is a repository copy of Estimating Quarterly GDP for the Interwar UK Economy: An Application to the Employment Function.
 This is a repository copy of Estimating Quarterly GDP for the Interwar UK Economy: n pplication to the Employment Function. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/9884/
This is a repository copy of Estimating Quarterly GDP for the Interwar UK Economy: n pplication to the Employment Function. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/9884/
LECTURE 11. Introduction to Econometrics. Autocorrelation
 LECTURE 11 Introduction to Econometrics Autocorrelation November 29, 2016 1 / 24 ON PREVIOUS LECTURES We discussed the specification of a regression equation Specification consists of choosing: 1. correct
LECTURE 11 Introduction to Econometrics Autocorrelation November 29, 2016 1 / 24 ON PREVIOUS LECTURES We discussed the specification of a regression equation Specification consists of choosing: 1. correct
Advanced Macroeconomics II. Monetary Models with Nominal Rigidities. Jordi Galí Universitat Pompeu Fabra April 2018
 Advanced Macroeconomics II Monetary Models with Nominal Rigidities Jordi Galí Universitat Pompeu Fabra April 208 Motivation Empirical Evidence Macro evidence on the e ects of monetary policy shocks (i)
Advanced Macroeconomics II Monetary Models with Nominal Rigidities Jordi Galí Universitat Pompeu Fabra April 208 Motivation Empirical Evidence Macro evidence on the e ects of monetary policy shocks (i)
Markov-Switching Models with Endogenous Explanatory Variables. Chang-Jin Kim 1
 Markov-Switching Models with Endogenous Explanatory Variables by Chang-Jin Kim 1 Dept. of Economics, Korea University and Dept. of Economics, University of Washington First draft: August, 2002 This version:
Markov-Switching Models with Endogenous Explanatory Variables by Chang-Jin Kim 1 Dept. of Economics, Korea University and Dept. of Economics, University of Washington First draft: August, 2002 This version:
Volume 30, Issue 1. Measuring the Intertemporal Elasticity of Substitution for Consumption: Some Evidence from Japan
 Volume 30, Issue 1 Measuring the Intertemporal Elasticity of Substitution for Consumption: Some Evidence from Japan Akihiko Noda Graduate School of Business and Commerce, Keio University Shunsuke Sugiyama
Volume 30, Issue 1 Measuring the Intertemporal Elasticity of Substitution for Consumption: Some Evidence from Japan Akihiko Noda Graduate School of Business and Commerce, Keio University Shunsuke Sugiyama
Fiscal Multipliers in a Nonlinear World
 Fiscal Multipliers in a Nonlinear World Jesper Lindé and Mathias Trabandt ECB-EABCN-Atlanta Nonlinearities Conference, December 15-16, 2014 Sveriges Riksbank and Federal Reserve Board December 16, 2014
Fiscal Multipliers in a Nonlinear World Jesper Lindé and Mathias Trabandt ECB-EABCN-Atlanta Nonlinearities Conference, December 15-16, 2014 Sveriges Riksbank and Federal Reserve Board December 16, 2014
Empirical Approach to Modelling and Forecasting Inflation in Ghana
 Current Research Journal of Economic Theory 4(3): 83-87, 2012 ISSN: 2042-485X Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2012 Submitted: April 13, 2012 Accepted: May 06, 2012 Published: June 30, 2012 Empirical Approach
Current Research Journal of Economic Theory 4(3): 83-87, 2012 ISSN: 2042-485X Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2012 Submitted: April 13, 2012 Accepted: May 06, 2012 Published: June 30, 2012 Empirical Approach
ECON 4230 Intermediate Econometric Theory Exam
 ECON 4230 Intermediate Econometric Theory Exam Multiple Choice (20 pts). Circle the best answer. 1. The Classical assumption of mean zero errors is satisfied if the regression model a) is linear in the
ECON 4230 Intermediate Econometric Theory Exam Multiple Choice (20 pts). Circle the best answer. 1. The Classical assumption of mean zero errors is satisfied if the regression model a) is linear in the
