Ceramic Processing Research
|
|
|
- Pamela Bradford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
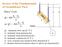
1 Journal of Ceramic Processing Research. Vol. 10, No. 2, pp. 195~201 (2009) J O U R N A L O F Ceramic Processing Research Computer simulation of a ceramics powder compaction process and optimization of process parameters Y. T. Keum a, *, J. L. Kim b and J. K. Shim b a School of Mechanical ngineering, Hanang Universit, 17 Haengdang-dong, Seongdong-ku, Seoul 1-791, South Korea b Graduate School of Mechanical ngineering, Hanang Universit, 17 Haengdang-dong, Seongdong-ku, Seoul 1-791, South Korea In order to optimize the process parameters of ceramic powder compaction, a process simulation was first performed using a finite element method. In the finite element analsis, a quasi-random multi-particle arra was introduced for modeling the non-periodic and randoml scattered powder particles with initiall-low relative densities. Homogenization theor was emploed to find the equivalent material properties associated with various porosities. The size of Al 2 O particles, amplitude of the cclic compaction pressure, and friction coefficient among powder particles were chosen as process parameters. Finite element analsis results show that relative densit becomes bigger as the process variables become smaller. Net, a regression model was found b using the response surface method, based on the results of the finite element analsis. Then, the optimal conditions of the process parameters providing the highest relative densit were pursued b emploing a grid search method. Ke word: Ceramic powder compaction, Homogenization method, Process parameter optimization, Relative densit, Response surface method, Grid search method, Finite element analsis. Introduction The characteristics of mechanical strength, phsical, and chemical properties of pol crstalline ceramic materials are affected b the arrangement of crstal directions because the are caused b the anisotrop of single crstals associated with crstal directions. Therefore, in order to make an analtical model and to perform a computer simulation for a ceramic powder compaction process, it is important to analze the deformation behavior of material microstructures. perimental research on the ceramic powder compaction process has been made in was to allow the stud of the man qualitative characteristics of a pol crstalline ceramic material during the powder compaction process. ven the quantitative analses of some ideal models are in progress using numerical methods. However, the ideal model of compact forming is different from the real model because the real powders are not regularl arraed, and the powder densit distribution and replenishment state is not uniform. Therefore, to improve the various properties of ceramic components and the efficienc of powder compaction forming processes, the modeling of compaction forming processes, which can quantitativel analze the real compaction forming process, is recommended. Furthermore, to reduce the time and numerical cost of simulation, the relationship among the relative densit and the process *Corresponding author: Tel : Fa: mail: tkeum@hanang.ac.kr parameters influenced greatl b the relative densit during the ceramic powder compaction forming has to be considered. In addition, optimal process parameter values for maimizing the relative densit should be adopted. Looking at the research trends of ceramic powder compaction forming, an ideal model in the static and repetitive compactions for compound materials was epedd. rimentall and numericall studied b Wu et al. [1] and Jiang et al. [2]. Xin et al. [] introduced a computer simulation method using eplicit FM for analzing the powder compaction phenomena of single and compound materials. Zahlan et al. [4] presented a modeling method for real products made b powder compaction forming under repetitive loads. Zipse [5] also performed research on the FM simulation of compaction forming and sintering processes of real ceramic products. Deis and Lannutti [6] and Lu and Lannutti[7-9] measured the densit slope and pore distribution during powder compact forming using an X-ra CT and mercur pore analzer and eperimentall investigated the how initial densit slope affected powder compaction forming b emploing the X-ra CT. Hassani and Hinton [10] formulated an analtical solution of homogenization theor for various material models to be used in the finite element analsis. Also Takano et al. [11-12] presented a calculation of the elastic coefficient as a function of porosit and pore shape for compound materials and porous ceramic materials using homogenization theor. In addition, as the relative densit is one of the important factors in evaluating ceramic products, much effort to get high densit products from the beginning of compact forming 195
2 196 Y. T. Keum, J. L. Kim and J. K. Shim is in progress. Recentl, researches on the optimum process parameters enabling high relative densities have been made. Roughl summarizing the researches on the parameter stud of relative densit, Jiang et al. [1-14] carried out eperiments looking at the effect of the lubricant of a metal composite, the aspect ratio of the test material and the size of particles. Rendanz and Fleck [15] used a computer simulation technique to stud the compaction of randoml distributed powders. Inter-particle friction and affined motion has been studied both for the compaction response and for the resulting ield surface. Procopio and Zavaliangos [16] simulated the multi-aial compaction for a granular media to stud relative densities related to the particle shape and size as well as material properties. Consuelo and Lannutti [17] also eamined the effect of particle size during the packing. Hassanqaur and Ghadiri [18] emploed the distinct element method to simulate the bulk deformation, based on single particle properties. Briscoe and Rough [19] carried out an eperiment to see the effect of friction between powder particles and the die. Kim et al. [20] looked into the effects of repetitive pressure, repetitive velocit, and biased pressure on powder densification under repetitive compaction in room temperature. Also Shin et al. [21] presented the forming conditions to be able to improve the reproducibilit b studing the changes in the forming densit and sintering densit in normal pressure sintering. In this stud, the arbitraril-intensified powder compact is first modeled and the equivalent material propert is introduced in the finite element analsis to simulate ceramic powder compaction. In addition, the optimal values of process parameters providing the maimum relative densit are pursued on the basis of the response surface model obtained from the analsis of the eperimental region of interest chosen b the full factorial design. Forming Process Analsis Modeling Fig. 1 is a 2-dimensional view of the powder compaction device and ceramic powders before compaction. The ceramic powders are located inside the die and base punch stationar and are compacted to the desired shapes b the upper punch operating up and down. While the base punch and dies are stationar, the upper punch is movable so that repetitive loads can be applied to the powders. Generall, homogeneous or non-homogeneous powders are modeled in the finite element analsis of a ceramic powder compaction process with the assumption that unit cells are periodicall arraed in heahedron or cubic shapes. Although the powders are not periodicall arraed in a real compaction, the powders are modeled using a quasi-random multi-particle arra, which can represent the non-periodicit and arbitrariness of the powder distribution b packing the particles one b one considering the powder arra and the Fig dimensional view of powder compaction device and ceramic powders. size distribution, position, and rearrangement of powder particles. After packing the particles to give contact between particle and particle or between tool and particles, the size and arra of the particles are adjusted to make the desired relative densit. In order to analze green compacts whose initial relative densities are 0.554, and 0.615, respectivel, the size of an Al particle is fied to 15 µm. Then Al 2 O particles whose sizes are 7.5 µm, 15 µm and 22.5 µm, respectivel, are modeled. The models whose sizes of Al 2 O are 7.5 µm, 15 µm and 22.5 µm are called Model 1, Model 2 and Model, respectivel. In ceramic powder compaction forming, an important factor to control the relative densit is the friction coefficient. Generall, the friction coefficient between the dr Al 2 O powders unlubricated is and lubricated with zinc stearate is [22]. To investigate the effect of various friction coefficients on the relative densit of powder compaction, different friction coefficients between the powders are used in the analsis of the powder compaction forming process. Formulation The finite element formulation of stress fields, which is used to analze the powder compaction forming process, is written as follows [2]: ([ K] { u} { F} ) e = 0 e= 1 (1) where [K] is the stiffness matri obtained from the homogenized theor and [F] is the force vector. Homogenization theor is introduced to find the equivalent material propert from the microscopic scale model for analzing accuratel macroscopic scale porous materials such as powder ceramics. For eample, the homogenized elastic tensor, H ijkl, is written as:
3 Computer simulation of a ceramics powder compaction process and optimization of process parameters 1 H ijkl = ---- Y Y kl χ m jikl n dy (2) where ijkl is the elastic tensor and mkl is the characteristic displacement. In the governing equation of a linear elastic problem, which is derived from the homogenization theor equations, the 2-dimensional powder compact Ω is assumed to be the assembl of micro-unit cells [2]. Forming Analsis Analsis model and homogenized material propert In this stud, the compound compact consisting of three aluminum and three alumina powder particles are modeled with 2-dimensional rods b using the quasi-random multi- 197 particle arra. A rod arra model is often emploed in numerical simulations because not onl is there no big difference in the densit, although it is less dense than a real powder compact, but also it clearl shows material behaviors and contact states [1]. For the elasto-plastic finite element analsis, powder particles are modeled with 4 node elements in a plane strain state, as seem in Fig. 2. Model 1 emplos 526 nodes and 444 finite elements. Model 2 uses 695 nodes and 598 finite elements. Model has 821 nodes and 714 finite elements. The upper punch, base punch, and die are modeled with mass elements. The densit, elastic modulus, Poisson s ratio and ield strength are the material properties used in the forming analsis. The homogenized elastic modulus is also emploed. Table 1 shows the material properties of Al and Al2O used in the analsis. Fig. 2 presents the boundar conditions used in the finite element analsis. While the dies and base punch are assumed to be rigid, namel not deformable, the upper punch presses ceramic powders, taking 0 seconds up to the peak pressure P = 200 MPa. For calculating the homogenized elastic modulus associated with porosities, the unit cell structure with a cross shaped porosit, which is similar to the porosit shape a of powder compact, is modeled with 2-dimensional finite elements (see Fig. ). Then, the relative elastic modulus r is obtained using the homogenization method from the unit cell structures Material properties of Al and Al2O Material propert Al Mass densit (ρ) 2.12(10) kg/m Yield stress (YS) 28 MPa Poisson s ratio (ν) 0.45 lastic modulus () 62 GPa Homogenized elastic modulus ( ) e GPa Table 1. Finite element modeling of ceramic powders and boundar conditions for simulating the powder compaction process. Fig. 2. Fig.. h Cross pore-solid models for calculating homogenized elastic modulus associated with porosities(f). r -4.87f Al O.89(10) kg/m 00 MPa GPa e GPa 2 r -4.87f
4 Y. T. Keum, J. L. Kim and J. K. Shim 198 Fig. 4. Formed shapes and principal stresses of 6 particles during the powder compaction. associated porosities f, and the homogenized elastic modulus h is calculated b interpolating r as follows: () h = r e 4.87f. Numerical analsis The powder compact forming process model is analzed b emploing the finite element method using both a micromechanics approach and a continuum-mechanics approach. In the micro-mechanics approach, the phsical quantities such as stress and velocit can be different from those averaged in the macroscopic approach. In this method, the powder compact is regarded as an assembl of particles. Particles and gaps occup the space inside the powder compact. Particles are defined as 1 and gap 0 in the densit function. The simulation is performed using the elastic modulus for 0 seconds taking up to the peak pressure P = 200 MPa. Fig. 4 shows the formed shapes of the 6 particles during the compaction. A micro-mechanics approach shows that the relative densit graduall increases to 0.699, 0.70, 0.769, and during the compaction. In the continuum mechanics approach, the atomic structures of materials are neglected. All phsical quantities are assumed to be represented with continuous mathematical functions. Therefore, stress and strain are defined at all points in the continuum. Using the homogenized elastic modulus associated with porosities h, as done in the micro-mechanics approach, the simulation is performed for 0 seconds. Relative densities are increased to 0.748, 0.778, 0.792, and finall to Fig. 5 shows a comparison of the relative densit between FM and the eperiment done b Jiang. [2] The relative densities obtained b the continuum approach which introduces the homogenized elastic modulus associated with porosities in the analsis are closer to the eperimental ones than those of the micro-mechanics approach. The reason for the sudden rise of relative densit when the homogenized elastic modulus h is used in the continuum approach is wh the h is small, which is calculated in the initiall low relative densit of the powder compact, namel the high porosit state, but h suddenl increases as the relative densit increases. Net, the analsis is performed under the condition Comparison of relative densities obtained from FM analses and eperiment during the powder compaction. Fig. 5. et al Comparison of relative densit among friction coefficients 0.4, 0.6, and 0.8. Fig. 6. where the friction coefficient between the powders is changed to 0.4, 0.6, and 0.8 while the friction coefficient between the powders and die is fied. Fig. 6 shows the changes in relative densities with time as the friction coefficient changes. After 0 seconds reached to the peak pressure, the relative densities are 0.816, 0.827, and 0.81 when friction coefficients are 0.4, 0.6, and 0.8, respectivel.
5 Computer simulation of a ceramics powder compaction process and optimization of process parameters Process Parameters Optimization perimental region of interest The optimization flow of process parameters of powder compaction followed in this stud is seen in Fig. 7. After the eperimental region of interest is set up b the full factorial design, the finite element analses are performed for all cases in the region. The response surface called the regression model, which is represented b the second 199 order polnomial function of process parameters, is then found from the responses obtained from the analsis results. Finall, the optimal values of process parameters providing the maimum relative densit are determined b the grid search method. The Al2O particle size, amplitude of cclic compaction, and friction coefficient are chosen as design variables and the eperimental region of interest is set up b the full factorial design, as shown in Table 2. Net, the finite element analses are performed a total of 27 times determined b the three variables and three levels. In ever finite element analsis, the relative densit and principal stress for 0, 1, 10, 100, and 1000 ccles of compaction pressure are calculated, as seen in Fig. 8, and the difference in relative densit between 1 ccle and 1000 ccles is defined as the response. Regression model The response surface method, which was introduced b Bo and Wilson [24], is to optimize approimatel the variables after representing an analsis model with eplicit functions. In this stud, the response surface method is used for optimizing the powder compact process parameters defined in the previous section. Approimatel epressing the response surface obtained from the simulations done at the eperimental points selected b the eperimental design with an objective N Process parameters and levels for optimization Levels Process parameters Al O particle size [μm] Amplitude of cclic compaction pressure[mpa] Coefficient of friction Table 2. 2 Schematic flow for optimizing process parameters of powder compaction. Fig. 7. Fig Formed shapes and principal stresses associated with pressure ccles in the case of 1 = 2 = = 0.
6 Y. T. Keum, J. L. Kim and J. K. Shim 200 function as follows: = Xβ + ε (4) Using the least square estimate about the response obtained from 27 simulations, the estimated regression model can be epressed as follows: = (5) where 1, 2, and are the process parameters defined in Table 2. The recurrence of the estimated regression model, which is evaluated through the F-test performed b variance analsis [25], is listed in Table. The regression model of q. (5) has a recurrence because of the rejection F(0.05;9,17) = 2.98 when the level of significance is 5% and F0 = (10)4. Response surface model for Al2O particle size ( 1) and coefficient of friction ( ) in the case of cclic compaction pressure amplitude 2 = 0. Fig. 10. Optimal conditions q. (5), which is derived as a result of the response surface method to optimize process parameters, can be graphicall shown in Fig. 9, Fig. 10, and Fig. 11 when the remaining third process variable has a middle level. Fig. 9 shows that the variation of relative densit increases with the Al2O particle size ( 1 direction of 1) and the amplitude of Variance analsis of regression model Degree of freedom of regression Regression sum of squares Regression mean squares Degree of freedom of error rror sum of squares Mean square error Total degree of freedom Total sum of squares Fo = Regression mean squares / Mean square error Table (10) (10) (10)4 Response surface model for amplitude of cclic compaction pressure ( 2) and coefficient of friction ( ) in the case of particle size 1 = 0. Fig. 11. cclic compaction pressure (1 direction of 2) decreases. Fig. 10 shows that the variation of relative densit when the friction coefficient becomes smaller ( 1 direction of ) is not as big as much as that when the Al2O particle size is smaller ( 1 direction of 1). Fig. 11 implies that the increase in the variation of relative densit when the amplitude of cclic compaction pressure decreases (1 direction of 2) is bigger than that when the coefficient of friction decreases ( 1 direction of ). Therefore, the response surface model eplains that the effects of the Al2O particle size and the amplitude of cclic compaction pressure on the relative densit is bigger than that of the friction coefficient in ceramic powder compaction forming. In order to find the values of design parameters associated with the maimum relative densit, the grid search method is used [26]. The optimal condition, in which the maimum relative densit is 0.990, is found when the Al2O particle size, the amplitude of cclic compaction pressure and the friction coefficient are 22.5 μm, 75 MPa and 0.110, respectivel. Response surface model for Al2O particle size ( 1) and amplitude of cclic compaction pressure ( 2) in the case of friction coefficient = 0. Fig. 9.
7 Computer simulation of a ceramics powder compaction process and optimization of process parameters 201 Conclusions Multi-scale modeling and finite element analsis were performed to predict the relative densit of ceramic powder compaction forming and the optimization of process parameters was carried out to maimize the relative densit. Through the forming analsis and optimization, the following conclusions are made: (1) The modeling of non-periodicit and arbitraries of ceramic powder particles can be successfull achieved b introducing a quasi-random multi-particle arra. (2) The ceramic powder compaction forming process can be accuratel simulated b a multi-scale model and equivalent material properties obtained b emploing the homogenization method. () The relative densit becomes bigger with the size of the Al 2 O particles, the amplitude of the cclic compaction pressure, and coefficient of friction are smaller. (4) The regression model enables to predict the relative densit associated with compaction conditions and to provide the optimal conditions of process parameters related to the highest densit of the green ceramic compact. Acknowledgements This work was supported b the research fund of Hanang Universit (HY-2006-I). The authors appreciate Prof. R.H.Wagoner for discussions leading to these results. References 1. W. Wu, G. Jiang, R.H. Wagoner and G.S. Daehn, Acta mater. 48 (2000) G. Jiang, W. Wu, G.S. Daehn and R.H. Wagoner, Acta mater. 48 (2000) X.J. Xin, P. Jaaraman, G. Jiang, R.H. Wagoner and G.S. Daehn, Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, A (2002) N. Zahlan, D.T. Knight, A. Backhouse and G.A. Leiper, Powder Technolog 114 (2001) H. Zipse, Journal of uropean Ceramic Societ 17 (1997) T.A. Deis and J.J. Lannutti, Journal of the American Ceramic Societ 81[5] (1998) P.K. Lu and J.J. Lannutti, Journal of the American Ceramic Societ 8[] (2000) P.K. Lu and J.J. Lannutti, Journal of the American Ceramic Societ 8[10] (2000) P.K. Lu and J.J. Lannutti, Journal of the American Ceramic Societ 8[6] (2000) B. Hassani and. Hinton, Comput. Str. 69 (1998) N. Takano, Y. Uetsuji, Y. Kashiwagi and M. Zako, Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. ng. 7 (1999) N. Takano, M. Zako and M. Ishizono, J. Comput.-Aided Mater. Design. 7 (2000) G. Jiang, G.S. Daehn, J.J. Lannutti, Y. Fu and R.H. Wagoner, Acta mater, 49 (2001) G. Jiang, G.S. Daehn and R.H. Wagoner, Scripta mater, 44 (2001) P. Rendanz, N.A. Fleck, Acta Materialia, 49 (2001) A.T. Procopio and A. Zavaliangos, Mechanics and Phsics of Solids, 5 (2005) M.K. Consuelo and J.J. Lannutti, Journal of the American Ceramic Societ, 8[9] (2000) A. Hassanpour and M. Ghadiri, Powder Technolog, 141 (2004) B.J. Briscoe and S.L Rough, Powder Technolog, 99 (1998) K.T. Kim, G.S. Son and J. Suh, Journal of Korean Ceramic Societ, 29[2] (1992) D.W. Shin, G.D. Kim, S.S. Park, C.S. Lim and S.W. Lee, Journal of Korean Association of Crstal Growth, 8[2] (1998) S. Turenne and P.. Mongeon, Advances in Powder Metallurg & Particulate Materials-1995 (1995) Y.T. Keum and J.W. Oh, Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and ngineering, Institute of Phsics Publishing, 1 (2005) G..P. Bo and K.B. Wilson, Journal of the Roal Statistical Societ, Series B., 1 (1951) p R.. Wapole, R.H. Mers, S.L. Mers and k. Ye, in Probabilit & Statistics for ngineers & Scientists 8th ed (Pearson education, 2006). 26. Chen, D. Liu, X. Zhou, Y. Yang, X. Lu, L. Wang and X.J. Xin, Journal of Applied Polmer Science, 76[4] (2000)
Citation Key Engineering Materials, ,
 NASITE: Nagasaki Universit's Ac Title Author(s) Interference Analsis between Crack Plate b Bod Force Method Ino, Takuichiro; Ueno, Shohei; Saim Citation Ke Engineering Materials, 577-578, Issue Date 2014
NASITE: Nagasaki Universit's Ac Title Author(s) Interference Analsis between Crack Plate b Bod Force Method Ino, Takuichiro; Ueno, Shohei; Saim Citation Ke Engineering Materials, 577-578, Issue Date 2014
Vibrational Power Flow Considerations Arising From Multi-Dimensional Isolators. Abstract
 Vibrational Power Flow Considerations Arising From Multi-Dimensional Isolators Rajendra Singh and Seungbo Kim The Ohio State Universit Columbus, OH 4321-117, USA Abstract Much of the vibration isolation
Vibrational Power Flow Considerations Arising From Multi-Dimensional Isolators Rajendra Singh and Seungbo Kim The Ohio State Universit Columbus, OH 4321-117, USA Abstract Much of the vibration isolation
MMJ1153 COMPUTATIONAL METHOD IN SOLID MECHANICS PRELIMINARIES TO FEM
 B Course Content: A INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW Numerical method and Computer-Aided Engineering; Phsical problems; Mathematical models; Finite element method;. B Elements and nodes, natural coordinates,
B Course Content: A INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW Numerical method and Computer-Aided Engineering; Phsical problems; Mathematical models; Finite element method;. B Elements and nodes, natural coordinates,
Research Article Equivalent Elastic Modulus of Asymmetrical Honeycomb
 International Scholarl Research Network ISRN Mechanical Engineering Volume, Article ID 57, pages doi:.5//57 Research Article Equivalent Elastic Modulus of Asmmetrical Honecomb Dai-Heng Chen and Kenichi
International Scholarl Research Network ISRN Mechanical Engineering Volume, Article ID 57, pages doi:.5//57 Research Article Equivalent Elastic Modulus of Asmmetrical Honecomb Dai-Heng Chen and Kenichi
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 20, 2011 Professor A. Dolovich
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 20, 2011 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS LAST NAME (printed): FIRST NAME (printed): STUDENT
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 20, 2011 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS LAST NAME (printed): FIRST NAME (printed): STUDENT
ME 323 Examination #2 April 11, 2018
 ME 2 Eamination #2 April, 2 PROBLEM NO. 25 points ma. A thin-walled pressure vessel is fabricated b welding together two, open-ended stainless-steel vessels along a 6 weld line. The welded vessel has an
ME 2 Eamination #2 April, 2 PROBLEM NO. 25 points ma. A thin-walled pressure vessel is fabricated b welding together two, open-ended stainless-steel vessels along a 6 weld line. The welded vessel has an
ANALYSIS OF BI-STABILITY AND RESIDUAL STRESS RELAXATION IN HYBRID UNSYMMETRIC LAMINATES
 ANALYSIS OF BI-STABILITY AND RESIDUAL STRESS RELAXATION IN HYBRID UNSYMMETRIC LAMINATES Fuhong Dai*, Hao Li, Shani Du Center for Composite Material and Structure, Harbin Institute of Technolog, China,5
ANALYSIS OF BI-STABILITY AND RESIDUAL STRESS RELAXATION IN HYBRID UNSYMMETRIC LAMINATES Fuhong Dai*, Hao Li, Shani Du Center for Composite Material and Structure, Harbin Institute of Technolog, China,5
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 103 (2015 ) 52 59
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 103 (2015 ) 52 59 The 13 th Hpervelocit Impact Smposium Guided Impact Mitigation in 2D and 3D Granular Crstals Haden A. Burgone
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 103 (2015 ) 52 59 The 13 th Hpervelocit Impact Smposium Guided Impact Mitigation in 2D and 3D Granular Crstals Haden A. Burgone
CONTINUOUS SPATIAL DATA ANALYSIS
 CONTINUOUS SPATIAL DATA ANALSIS 1. Overview of Spatial Stochastic Processes The ke difference between continuous spatial data and point patterns is that there is now assumed to be a meaningful value, s
CONTINUOUS SPATIAL DATA ANALSIS 1. Overview of Spatial Stochastic Processes The ke difference between continuous spatial data and point patterns is that there is now assumed to be a meaningful value, s
KINEMATIC RELATIONS IN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS
 Chapter 8 KINEMATIC RELATIONS IN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS Figure 8.1: 195 196 CHAPTER 8. KINEMATIC RELATIONS IN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS 8.1 Motivation In Chapter 3, the conservation of linear momentum for a
Chapter 8 KINEMATIC RELATIONS IN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS Figure 8.1: 195 196 CHAPTER 8. KINEMATIC RELATIONS IN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS 8.1 Motivation In Chapter 3, the conservation of linear momentum for a
Stability Analysis of a Geometrically Imperfect Structure using a Random Field Model
 Stabilit Analsis of a Geometricall Imperfect Structure using a Random Field Model JAN VALEŠ, ZDENĚK KALA Department of Structural Mechanics Brno Universit of Technolog, Facult of Civil Engineering Veveří
Stabilit Analsis of a Geometricall Imperfect Structure using a Random Field Model JAN VALEŠ, ZDENĚK KALA Department of Structural Mechanics Brno Universit of Technolog, Facult of Civil Engineering Veveří
Vibration Analysis of Isotropic and Orthotropic Plates with Mixed Boundary Conditions
 Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 7-6 (003) 7 Vibration Analsis of Isotropic and Orthotropic Plates with Mied Boundar Conditions Ming-Hung Hsu epartment of Electronic Engineering
Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 7-6 (003) 7 Vibration Analsis of Isotropic and Orthotropic Plates with Mied Boundar Conditions Ming-Hung Hsu epartment of Electronic Engineering
Data Repository Hampel et al., page 1/5
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2138 Data Repositor Hampel et al., page 1/5 SETUP OF THE FINITE-ELEMENT MODEL The finite-element models were created with the software ABAQUS and consist of a 1-km-thick lithosphere,
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2138 Data Repositor Hampel et al., page 1/5 SETUP OF THE FINITE-ELEMENT MODEL The finite-element models were created with the software ABAQUS and consist of a 1-km-thick lithosphere,
Numerical simulations for isostatic and die compaction of powder by the discrete element method
 Numerical simulations for isostatic and die compaction of powder by the discrete element method J.-F. Jerier 1, B. Harthong 1, V. Richefeu 1, D. Imbault 1, F.-V. Donzé 1,1, P. Dorémus 1 a University of
Numerical simulations for isostatic and die compaction of powder by the discrete element method J.-F. Jerier 1, B. Harthong 1, V. Richefeu 1, D. Imbault 1, F.-V. Donzé 1,1, P. Dorémus 1 a University of
Fringe Analysis for Photoelasticity Using Image Processing Techniques
 International Journal of Software Engineering and Its pplications, pp.91-102 http://d.doi.org/10.14257/ijseia.2014.8.4.11 Fringe nalsis for Photoelasticit Using Image Processing Techniques Tae Hun Baek
International Journal of Software Engineering and Its pplications, pp.91-102 http://d.doi.org/10.14257/ijseia.2014.8.4.11 Fringe nalsis for Photoelasticit Using Image Processing Techniques Tae Hun Baek
ANSYS-Based Birefringence Property Analysis of Side-Hole Fiber Induced by Pressure and Temperature
 PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 8, No. 1, 2018: 13 21 ANSYS-Based Birefringence Propert Analsis of Side-Hole Fiber Induced b Pressure and Temperature Xinbang ZHOU 1 and Zhenfeng GONG 2* 1 School of Ocean Science
PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 8, No. 1, 2018: 13 21 ANSYS-Based Birefringence Propert Analsis of Side-Hole Fiber Induced b Pressure and Temperature Xinbang ZHOU 1 and Zhenfeng GONG 2* 1 School of Ocean Science
The Numerical Analysis and Experiment of Shock Processing for Bouef
 Int. Jnl. of Multiphsics Volume 4 Number 4 2010 329 The Numerical Analsis and Eperiment of Shock Processing for Bouef Yusuke YAMASHITA*, Asuka ODA*, Takeshi HUJII*, Hironori MAEHARA*, M Moatamedi**, Shigeru
Int. Jnl. of Multiphsics Volume 4 Number 4 2010 329 The Numerical Analsis and Eperiment of Shock Processing for Bouef Yusuke YAMASHITA*, Asuka ODA*, Takeshi HUJII*, Hironori MAEHARA*, M Moatamedi**, Shigeru
Survey of Wave Types and Characteristics
 Seminar: Vibrations and Structure-Borne Sound in Civil Engineering Theor and Applications Surve of Wave Tpes and Characteristics Xiuu Gao April 1 st, 2006 Abstract Mechanical waves are waves which propagate
Seminar: Vibrations and Structure-Borne Sound in Civil Engineering Theor and Applications Surve of Wave Tpes and Characteristics Xiuu Gao April 1 st, 2006 Abstract Mechanical waves are waves which propagate
Engineering Solid Mechanics
 Engineering Solid Mechanics 7 (019) 71-8 Contents lists available at GrowingScience Engineering Solid Mechanics homepage: www.growingscience.com/esm A method for determination of uivalent limit load surface
Engineering Solid Mechanics 7 (019) 71-8 Contents lists available at GrowingScience Engineering Solid Mechanics homepage: www.growingscience.com/esm A method for determination of uivalent limit load surface
Proceedings of the ASME th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2016 June 19-24, 2016, Busan, South Korea
 Proceedings of the ASME 26 35th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE26 June 9-24, 26, Busan, South Korea OMAE26-54554 LOCAL STRAIN AND STRESS CALCULATION METHODS OF IRREGULAR
Proceedings of the ASME 26 35th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE26 June 9-24, 26, Busan, South Korea OMAE26-54554 LOCAL STRAIN AND STRESS CALCULATION METHODS OF IRREGULAR
Title. Author(s)Tamura, Shin-ichiro; Tanaka, Yukihiro; Maris, Humphr. CitationPHYSICAL REVIEW B, 60(4): Issue Date
 Title Phonon group velocit and thermal conduction in supe Author(s)Tamura, Shin-ichiro; Tanaka, Yukihiro; Maris, Humphr CitationPHYSICAL REVIEW B, 60(4): 2627-2630 Issue Date 1999-07-15 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/5917
Title Phonon group velocit and thermal conduction in supe Author(s)Tamura, Shin-ichiro; Tanaka, Yukihiro; Maris, Humphr CitationPHYSICAL REVIEW B, 60(4): 2627-2630 Issue Date 1999-07-15 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/5917
Constants of Metal Rubber Material
 Constants of Metal Rubber Material Modern Applied Science; Vol. 8, No. 5; 014 ISSN 1913-1844 E-ISSN 1913-185 Published b Canadian Center of Science and Education Aleander Mikhailovich Ulanov 1 1 Samara
Constants of Metal Rubber Material Modern Applied Science; Vol. 8, No. 5; 014 ISSN 1913-1844 E-ISSN 1913-185 Published b Canadian Center of Science and Education Aleander Mikhailovich Ulanov 1 1 Samara
A PROTOCOL FOR DETERMINATION OF THE ADHESIVE FRACTURE TOUGHNESS OF FLEXIBLE LAMINATES BY PEEL TESTING: FIXED ARM AND T-PEEL METHODS
 1 A PROTOCOL FOR DETERMINATION OF THE ADHESIVE FRACTURE TOUGHNESS OF FLEXIBLE LAMINATES BY PEEL TESTING: FIXED ARM AND T-PEEL METHODS An ESIS Protocol Revised June 2007, Nov 2010 D R Moore, J G Williams
1 A PROTOCOL FOR DETERMINATION OF THE ADHESIVE FRACTURE TOUGHNESS OF FLEXIBLE LAMINATES BY PEEL TESTING: FIXED ARM AND T-PEEL METHODS An ESIS Protocol Revised June 2007, Nov 2010 D R Moore, J G Williams
THE GENERAL ELASTICITY PROBLEM IN SOLIDS
 Chapter 10 TH GNRAL LASTICITY PROBLM IN SOLIDS In Chapters 3-5 and 8-9, we have developed equilibrium, kinematic and constitutive equations for a general three-dimensional elastic deformable solid bod.
Chapter 10 TH GNRAL LASTICITY PROBLM IN SOLIDS In Chapters 3-5 and 8-9, we have developed equilibrium, kinematic and constitutive equations for a general three-dimensional elastic deformable solid bod.
3.032 Problem Set 2 Solutions Fall 2007 Due: Start of Lecture,
 3.032 Problem Set 2 Solutions Fall 2007 Due: Start of Lecture, 09.21.07 1. In the beam considered in PS1, steel beams carried the distributed weight of the rooms above. To reduce stress on the beam, it
3.032 Problem Set 2 Solutions Fall 2007 Due: Start of Lecture, 09.21.07 1. In the beam considered in PS1, steel beams carried the distributed weight of the rooms above. To reduce stress on the beam, it
A NUMERICAL STUDY OF PILED RAFT FOUNDATIONS
 Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, Vol. 9, No. 6, pp. 191-197 (6) 191 Short Paper A NUMERICAL STUDY OF PILED RAFT FOUNDATIONS Der-Gue Lin and Zheng-Yi Feng* ABSTRACT This paper presents raft-pile-soil
Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, Vol. 9, No. 6, pp. 191-197 (6) 191 Short Paper A NUMERICAL STUDY OF PILED RAFT FOUNDATIONS Der-Gue Lin and Zheng-Yi Feng* ABSTRACT This paper presents raft-pile-soil
ME 7502 Lecture 2 Effective Properties of Particulate and Unidirectional Composites
 ME 75 Lecture Effective Properties of Particulate and Unidirectional Composites Concepts from Elasticit Theor Statistical Homogeneit, Representative Volume Element, Composite Material Effective Stress-
ME 75 Lecture Effective Properties of Particulate and Unidirectional Composites Concepts from Elasticit Theor Statistical Homogeneit, Representative Volume Element, Composite Material Effective Stress-
RESEARCH ON PIEZOELECTRIC QUARTZ UNDER MULTIDIMENSIONAL FORCES
 aterials Phsics and echanics (015) 94-100 eceived: October 31, 014 ESEACH ON PIEZOELECTIC QUATZ UNDE ULTIDIENSIONAL OCES ei Wang *, uji Wang, Zongjin en, Zhenuan Jia, Liqi Zhao, Dong Li Ke Laborator for
aterials Phsics and echanics (015) 94-100 eceived: October 31, 014 ESEACH ON PIEZOELECTIC QUATZ UNDE ULTIDIENSIONAL OCES ei Wang *, uji Wang, Zongjin en, Zhenuan Jia, Liqi Zhao, Dong Li Ke Laborator for
Friction Properties of Surface with Circular Micro-patterns
 Friction Properties of Surface with Circular Micro-patterns Hideo Koguchi Mechanical Engineering, 603- Kamitomioka, Nagaoka Univ. of Tech., Nagaoka, Niigata, Japan Email: koguchi@mech.nagaokaut.ac.jp Takayoshi
Friction Properties of Surface with Circular Micro-patterns Hideo Koguchi Mechanical Engineering, 603- Kamitomioka, Nagaoka Univ. of Tech., Nagaoka, Niigata, Japan Email: koguchi@mech.nagaokaut.ac.jp Takayoshi
Prediction of Elastic Constants on 3D Four-directional Braided
 Prediction of Elastic Constants on 3D Four-directional Braided Composites Prediction of Elastic Constants on 3D Four-directional Braided Composites Liang Dao Zhou 1,2,* and Zhuo Zhuang 1 1 School of Aerospace,
Prediction of Elastic Constants on 3D Four-directional Braided Composites Prediction of Elastic Constants on 3D Four-directional Braided Composites Liang Dao Zhou 1,2,* and Zhuo Zhuang 1 1 School of Aerospace,
ELECTROMECHANICAL RESPONSE OF PIEZOELECTRIC FOAMS
 18 TH INTRNATIONAL CONFRNC ON COMPOSIT MATRIALS LCTROMCHANICAL RSPONS OF PIZOLCTRIC FOAMS K.S. Challagulla 1 *, T.A. Venkatesh 1 School of ngineering, Laurentian University, Sudbury, Canada, Department
18 TH INTRNATIONAL CONFRNC ON COMPOSIT MATRIALS LCTROMCHANICAL RSPONS OF PIZOLCTRIC FOAMS K.S. Challagulla 1 *, T.A. Venkatesh 1 School of ngineering, Laurentian University, Sudbury, Canada, Department
Topology Optimization of Compliant Mechanism with Geometrical Advantage
 610 Topology Optimization of Compliant Mechanism with Geometrical Advantage Seungjae MIN and Younggi KIM A compliant mechanism is a mechanism that produces its motion by the flexibility of some or all
610 Topology Optimization of Compliant Mechanism with Geometrical Advantage Seungjae MIN and Younggi KIM A compliant mechanism is a mechanism that produces its motion by the flexibility of some or all
Estimation Of Linearised Fluid Film Coefficients In A Rotor Bearing System Subjected To Random Excitation
 Estimation Of Linearised Fluid Film Coefficients In A Rotor Bearing Sstem Subjected To Random Ecitation Arshad. Khan and Ahmad A. Khan Department of Mechanical Engineering Z.. College of Engineering &
Estimation Of Linearised Fluid Film Coefficients In A Rotor Bearing Sstem Subjected To Random Ecitation Arshad. Khan and Ahmad A. Khan Department of Mechanical Engineering Z.. College of Engineering &
4 Strain true strain engineering strain plane strain strain transformation formulae
 4 Strain The concept of strain is introduced in this Chapter. The approimation to the true strain of the engineering strain is discussed. The practical case of two dimensional plane strain is discussed,
4 Strain The concept of strain is introduced in this Chapter. The approimation to the true strain of the engineering strain is discussed. The practical case of two dimensional plane strain is discussed,
Vibration of Plate on Foundation with Four Edges Free by Finite Cosine Integral Transform Method
 854 Vibration of Plate on Foundation with Four Edges Free b Finite Cosine Integral Transform Method Abstract The analtical solutions for the natural frequencies and mode shapes of the rectangular plate
854 Vibration of Plate on Foundation with Four Edges Free b Finite Cosine Integral Transform Method Abstract The analtical solutions for the natural frequencies and mode shapes of the rectangular plate
Effect of Magnetic Field and a Mode-I Crack 3D-Problem in Micropolar Thermoelastic Cubic Medium Possessing Under Three Theories
 Journal of Solid Mechanics Vol. 5, No. () pp. 5-69 Effect of Magnetic Field and a Mode-I Crack D-Problem in Micropolar Thermoelastic Cubic Medium Possessing Under Three Theories Kh. Lotf,,, N. Yahia Department
Journal of Solid Mechanics Vol. 5, No. () pp. 5-69 Effect of Magnetic Field and a Mode-I Crack D-Problem in Micropolar Thermoelastic Cubic Medium Possessing Under Three Theories Kh. Lotf,,, N. Yahia Department
2.2 Relation Between Mathematical & Engineering Constants Isotropic Materials Orthotropic Materials
 Chapter : lastic Constitutive quations of a Laminate.0 Introduction quations of Motion Symmetric of Stresses Tensorial and ngineering Strains Symmetry of Constitutive quations. Three-Dimensional Constitutive
Chapter : lastic Constitutive quations of a Laminate.0 Introduction quations of Motion Symmetric of Stresses Tensorial and ngineering Strains Symmetry of Constitutive quations. Three-Dimensional Constitutive
Bending of Shear Deformable Plates Resting on Winkler Foundations According to Trigonometric Plate Theory
 J. Appl. Comput. ech., 4(3) (018) 187-01 DOI: 10.055/JAC.017.3057.1148 ISSN: 383-4536 jacm.scu.ac.ir Bending of Shear Deformable Plates Resting on Winkler Foundations According to Trigonometric Plate Theor
J. Appl. Comput. ech., 4(3) (018) 187-01 DOI: 10.055/JAC.017.3057.1148 ISSN: 383-4536 jacm.scu.ac.ir Bending of Shear Deformable Plates Resting on Winkler Foundations According to Trigonometric Plate Theor
EVALUATION OF FAILURE CRITERIA IN WOOD MEMBERS
 EVALUATION OF FAILURE CRITERIA IN WOOD MEMBERS José M. Cabrero 1, Kifle G. Gebremedhin ABSTRACT: Multi-aial stress conditions eist in almost all engineering applications, but design procedures, in most
EVALUATION OF FAILURE CRITERIA IN WOOD MEMBERS José M. Cabrero 1, Kifle G. Gebremedhin ABSTRACT: Multi-aial stress conditions eist in almost all engineering applications, but design procedures, in most
Research Design - - Topic 15a Introduction to Multivariate Analyses 2009 R.C. Gardner, Ph.D.
 Research Design - - Topic 15a Introduction to Multivariate Analses 009 R.C. Gardner, Ph.D. Major Characteristics of Multivariate Procedures Overview of Multivariate Techniques Bivariate Regression and
Research Design - - Topic 15a Introduction to Multivariate Analses 009 R.C. Gardner, Ph.D. Major Characteristics of Multivariate Procedures Overview of Multivariate Techniques Bivariate Regression and
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF DISLOCATION DYNAMICS BY MEANS OF PARAMETRIC APPROACH
 Proceedings of Czech Japanese Seminar in Applied Mathematics August -7,, Czech Technical Universit in Prague http://geraldine.fjfi.cvut.cz pp. 1 13 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF DISLOCATION DYNAMICS BY MEANS
Proceedings of Czech Japanese Seminar in Applied Mathematics August -7,, Czech Technical Universit in Prague http://geraldine.fjfi.cvut.cz pp. 1 13 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF DISLOCATION DYNAMICS BY MEANS
The Plane Stress Problem
 . 4 The Plane Stress Problem 4 Chapter 4: THE PLANE STRESS PROBLEM 4 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 4.. INTRODUCTION 4 3 4... Plate in Plane Stress............... 4 3 4... Mathematical Model.............. 4 4
. 4 The Plane Stress Problem 4 Chapter 4: THE PLANE STRESS PROBLEM 4 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 4.. INTRODUCTION 4 3 4... Plate in Plane Stress............... 4 3 4... Mathematical Model.............. 4 4
Design and characterization of broadband acoustic composite metamaterials
 Design and characterization of broadband acoustic composite metamaterials Bogdan-Ioan Popa* and Steven A. Cummer Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Duke Universit, Durham, North Carolina
Design and characterization of broadband acoustic composite metamaterials Bogdan-Ioan Popa* and Steven A. Cummer Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Duke Universit, Durham, North Carolina
x y plane is the plane in which the stresses act, yy xy xy Figure 3.5.1: non-zero stress components acting in the x y plane
 3.5 Plane Stress This section is concerned with a special two-dimensional state of stress called plane stress. It is important for two reasons: () it arises in real components (particularl in thin components
3.5 Plane Stress This section is concerned with a special two-dimensional state of stress called plane stress. It is important for two reasons: () it arises in real components (particularl in thin components
3-D Finite Element Analysis of Instrumented Indentation of Transversely Isotropic Materials
 3-D Finite Element Analysis of Instrumented Indentation of Transversely Isotropic Materials Abstract: Talapady S. Bhat and T. A. Venkatesh Department of Material Science and Engineering Stony Brook University,
3-D Finite Element Analysis of Instrumented Indentation of Transversely Isotropic Materials Abstract: Talapady S. Bhat and T. A. Venkatesh Department of Material Science and Engineering Stony Brook University,
Fig. 1. Circular fiber and interphase between the fiber and the matrix.
 Finite element unit cell model based on ABAQUS for fiber reinforced composites Tian Tang Composites Manufacturing & Simulation Center, Purdue University West Lafayette, IN 47906 1. Problem Statement In
Finite element unit cell model based on ABAQUS for fiber reinforced composites Tian Tang Composites Manufacturing & Simulation Center, Purdue University West Lafayette, IN 47906 1. Problem Statement In
Consider a slender rod, fixed at one end and stretched, as illustrated in Fig ; the original position of the rod is shown dotted.
 4.1 Strain If an object is placed on a table and then the table is moved, each material particle moves in space. The particles undergo a displacement. The particles have moved in space as a rigid bod.
4.1 Strain If an object is placed on a table and then the table is moved, each material particle moves in space. The particles undergo a displacement. The particles have moved in space as a rigid bod.
Stress and Strain ( , 3.14) MAE 316 Strength of Mechanical Components NC State University Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
 (3.8-3.1, 3.14) MAE 316 Strength of Mechanical Components NC State Universit Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering 1 Introduction MAE 316 is a continuation of MAE 314 (solid mechanics) Review
(3.8-3.1, 3.14) MAE 316 Strength of Mechanical Components NC State Universit Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering 1 Introduction MAE 316 is a continuation of MAE 314 (solid mechanics) Review
Review of the Fundamentals of Groundwater Flow
 Review of te Fundamentals of Groundwater Flow Darc s Law 1 A 1 L A or L 1 datum L : volumetric flow rate [L 3 T -1 ] 1 : draulic ead upstream [L] A : draulic ead downstream [L] : draulic conductivit [L
Review of te Fundamentals of Groundwater Flow Darc s Law 1 A 1 L A or L 1 datum L : volumetric flow rate [L 3 T -1 ] 1 : draulic ead upstream [L] A : draulic ead downstream [L] : draulic conductivit [L
Chapter 2 Overview of the Simulation Methodology
 Chapter Overview of the Simulation Methodolog. Introduction This chapter presents an overview of the simulation methodolog that comprises both the art and science involved in simulating phsical phenomena.
Chapter Overview of the Simulation Methodolog. Introduction This chapter presents an overview of the simulation methodolog that comprises both the art and science involved in simulating phsical phenomena.
Three-Dimensional Explicit Parallel Finite Element Analysis of Functionally Graded Solids under Impact Loading. Ganesh Anandakumar and Jeong-Ho Kim
 Three-Dimensional Eplicit Parallel Finite Element Analsis of Functionall Graded Solids under Impact Loading Ganesh Anandaumar and Jeong-Ho Kim Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Universit
Three-Dimensional Eplicit Parallel Finite Element Analsis of Functionall Graded Solids under Impact Loading Ganesh Anandaumar and Jeong-Ho Kim Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Universit
Analytical study of sandwich structures using Euler Bernoulli beam equation
 Analtical stud of sandwich structures using Euler Bernoulli beam equation Hui Xue and H. Khawaja Citation: AIP Conference Proceedings 1798, 020076 (2017); doi: 10.1063/1.4972668 View online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4972668
Analtical stud of sandwich structures using Euler Bernoulli beam equation Hui Xue and H. Khawaja Citation: AIP Conference Proceedings 1798, 020076 (2017); doi: 10.1063/1.4972668 View online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4972668
LATERAL BUCKLING ANALYSIS OF ANGLED FRAMES WITH THIN-WALLED I-BEAMS
 Journal of arine Science and J.-D. Technolog, Yau: ateral Vol. Buckling 17, No. Analsis 1, pp. 9-33 of Angled (009) Frames with Thin-Walled I-Beams 9 ATERA BUCKING ANAYSIS OF ANGED FRAES WITH THIN-WAED
Journal of arine Science and J.-D. Technolog, Yau: ateral Vol. Buckling 17, No. Analsis 1, pp. 9-33 of Angled (009) Frames with Thin-Walled I-Beams 9 ATERA BUCKING ANAYSIS OF ANGED FRAES WITH THIN-WAED
Archetype-Blending Multiscale Continuum Method
 Archetype-Blending Multiscale Continuum Method John A. Moore Professor Wing Kam Liu Northwestern University Mechanical Engineering 3/27/2014 1 1 Outline Background and Motivation Archetype-Blending Continuum
Archetype-Blending Multiscale Continuum Method John A. Moore Professor Wing Kam Liu Northwestern University Mechanical Engineering 3/27/2014 1 1 Outline Background and Motivation Archetype-Blending Continuum
Post Graduate Diploma in Mechanical Engineering Computational mechanics using finite element method
 9210-220 Post Graduate Diploma in Mechanical Engineering Computational mechanics using finite element method You should have the following for this examination one answer book scientific calculator No
9210-220 Post Graduate Diploma in Mechanical Engineering Computational mechanics using finite element method You should have the following for this examination one answer book scientific calculator No
Flow and Transport. c(s, t)s ds,
 Flow and Transport 1. The Transport Equation We shall describe the transport of a dissolved chemical by water that is traveling with uniform velocity ν through a long thin tube G with uniform cross section
Flow and Transport 1. The Transport Equation We shall describe the transport of a dissolved chemical by water that is traveling with uniform velocity ν through a long thin tube G with uniform cross section
EVALUATION OF STRESS IN BMI-CARBON FIBER LAMINATE TO DETERMINE THE ONSET OF MICROCRACKING
 EVALUATION OF STRESS IN BMI-CARBON FIBER LAMINATE TO DETERMINE THE ONSET OF MICROCRACKING A Thesis b BRENT DURRELL PICKLE Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Teas A&M Universit in partial fulfillment
EVALUATION OF STRESS IN BMI-CARBON FIBER LAMINATE TO DETERMINE THE ONSET OF MICROCRACKING A Thesis b BRENT DURRELL PICKLE Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Teas A&M Universit in partial fulfillment
Study on Nonlinear Vibration and Crack Fault of Rotor-bearing-seal Coupling System
 Sensors & Transducers 04 b IFSA Publishing S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Stud on Nonlinear Vibration and Crack Fault of Rotor-bearing-seal Coupling Sstem Yuegang LUO Songhe ZHANG Bin WU Wanlei WANG
Sensors & Transducers 04 b IFSA Publishing S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Stud on Nonlinear Vibration and Crack Fault of Rotor-bearing-seal Coupling Sstem Yuegang LUO Songhe ZHANG Bin WU Wanlei WANG
Exercise solutions: concepts from chapter 5
 1) Stud the oöids depicted in Figure 1a and 1b. a) Assume that the thin sections of Figure 1 lie in a principal plane of the deformation. Measure and record the lengths and orientations of the principal
1) Stud the oöids depicted in Figure 1a and 1b. a) Assume that the thin sections of Figure 1 lie in a principal plane of the deformation. Measure and record the lengths and orientations of the principal
Mechanical Spring Reliability Assessments Based on FEA Generated Fatigue Stresses and Monte Carlo Simulated Stress/Strength Distributions
 Purdue Universit Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 4 Mechanical Spring Reliabilit Assessments Based on FEA Generated Fatigue Stresses and Monte
Purdue Universit Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 4 Mechanical Spring Reliabilit Assessments Based on FEA Generated Fatigue Stresses and Monte
Shock wave speed and stress-strain relation of aluminium honeycombs under dynamic compression
 EPJ Web of Conferences 83, 7 (8) DYMAT 8 https://doi.org/.5/epjconf/8837 Shock wave speed and stress-strain relation of aluminium honeycombs under dynamic compression Peng Wang,*, Jun Zhang, Haiying Huang,
EPJ Web of Conferences 83, 7 (8) DYMAT 8 https://doi.org/.5/epjconf/8837 Shock wave speed and stress-strain relation of aluminium honeycombs under dynamic compression Peng Wang,*, Jun Zhang, Haiying Huang,
With appropriate conditions from constitutive relations, the stress distribution can be found by fitting the boundary
 Lecture Note 3 Stress Functions First Semester, Academic Year Department of Mechanical ngineering Chulalongkorn Universit Objectives # Describe the equation of equilibrium using D/3D stress elements Set
Lecture Note 3 Stress Functions First Semester, Academic Year Department of Mechanical ngineering Chulalongkorn Universit Objectives # Describe the equation of equilibrium using D/3D stress elements Set
The Diagnosis and Optimization of Scroll Compressor Noise Based on the Theory of Near- Field Acoustical Holography
 Purdue Universit Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference chool of Mechanical Engineering 2010 The Diagnosis and Optimiation of croll Compressor oise Based on the Theor of ear- Field
Purdue Universit Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference chool of Mechanical Engineering 2010 The Diagnosis and Optimiation of croll Compressor oise Based on the Theor of ear- Field
Modeling of the Bending Stiffness of a Bimaterial Beam by the Approximation of One-Dimensional of Laminated Theory
 . Flores-Domínguez Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Applications RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS odeling of the Bending Stiffness of a Bimaterial Beam by the Approimation of One-Dimensional of Laminated
. Flores-Domínguez Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Applications RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS odeling of the Bending Stiffness of a Bimaterial Beam by the Approimation of One-Dimensional of Laminated
MAE4700/5700 Finite Element Analysis for Mechanical and Aerospace Design
 MAE4700/5700 Finite Element Analsis for Mechanical and Aerospace Design Cornell Universit, Fall 2009 Nicholas Zabaras Materials Process Design and Control Laborator Sible School of Mechanical and Aerospace
MAE4700/5700 Finite Element Analsis for Mechanical and Aerospace Design Cornell Universit, Fall 2009 Nicholas Zabaras Materials Process Design and Control Laborator Sible School of Mechanical and Aerospace
Modeling of Failure along Predefined Planes in Fractured Reservoirs
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirt-Ninth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford Universit, Stanford, California, Februar 24-26, 2014 SGP-TR-202 Modeling of Failure along Predefined Planes in Fractured Reservoirs
PROCEEDINGS, Thirt-Ninth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford Universit, Stanford, California, Februar 24-26, 2014 SGP-TR-202 Modeling of Failure along Predefined Planes in Fractured Reservoirs
Modeling the Dynamic Propagation of Shear Bands in Bulk Metallic Glasses
 Modeling the Dynamic Propagation of Shear Bands in Bulk Metallic Glasses B.J. Edwards, K. Feigl, M.L. Morrison*, B. Yang*, P.K. Liaw*, and R.A. Buchanan* Dept. of Chemical Engineering, The University of
Modeling the Dynamic Propagation of Shear Bands in Bulk Metallic Glasses B.J. Edwards, K. Feigl, M.L. Morrison*, B. Yang*, P.K. Liaw*, and R.A. Buchanan* Dept. of Chemical Engineering, The University of
SHADOW AND BACKGROUND ORIENTED SCHLIEREN INVESTIGATION OF SHOCK WAVES IN GAS-DISCHARGE MEDIUM
 SHADOW AND BACKGROUND ORIENTED SCHLIEREN INVESTIGATION OF SHOCK WAVES IN GAS-DISCHARGE MEDIUM J. JIN 1, I.V. MURSENKOVA 1,c, N. N. SYSOEV 1 and I.A. ZNAMENSKAYA 1 1 Department of Phsics, Lomonosov Moscow
SHADOW AND BACKGROUND ORIENTED SCHLIEREN INVESTIGATION OF SHOCK WAVES IN GAS-DISCHARGE MEDIUM J. JIN 1, I.V. MURSENKOVA 1,c, N. N. SYSOEV 1 and I.A. ZNAMENSKAYA 1 1 Department of Phsics, Lomonosov Moscow
Velocity Limit in DPD Simulations of Wall-Bounded Flows
 Velocit Limit in DPD Simulations of Wall-Bounded Flows Dmitr A. Fedosov, Igor V. Pivkin and George Em Karniadakis Division of Applied Mathematics, Brown Universit, Providence, RI 2912 USA Abstract Dissipative
Velocit Limit in DPD Simulations of Wall-Bounded Flows Dmitr A. Fedosov, Igor V. Pivkin and George Em Karniadakis Division of Applied Mathematics, Brown Universit, Providence, RI 2912 USA Abstract Dissipative
Study on Energy Dissipation Law in the Process of Coal and Gas Outburst
 6th International Conference on lectronics, Mechanics, Culture and Medicine (MCM 05) Stud on nerg Dissipation Law in the Process of Coal and Gas Outburst Shugang Li,a, Ning Wang,b * and Tianjun Zhang,c
6th International Conference on lectronics, Mechanics, Culture and Medicine (MCM 05) Stud on nerg Dissipation Law in the Process of Coal and Gas Outburst Shugang Li,a, Ning Wang,b * and Tianjun Zhang,c
SHORT PLANE BEARINGS LUBRICATION APPLIED ON SILENT CHAIN JOINTS
 Bulletin of the Transilvania Universit of Braşov Vol. 9 (58) No. - Special Issue 016 Series I: Engineering Sciences SHORT PLANE BEARINGS LUBRICATION APPLIED ON SILENT CHAIN JOINTS L. JURJ 1 R. VELICU Abstract:
Bulletin of the Transilvania Universit of Braşov Vol. 9 (58) No. - Special Issue 016 Series I: Engineering Sciences SHORT PLANE BEARINGS LUBRICATION APPLIED ON SILENT CHAIN JOINTS L. JURJ 1 R. VELICU Abstract:
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA Department of Civil Engineering
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA Department of Civil Engineering ON THE REFLECTION OF ELASTIC WAVES IN A POROELASTIC HALF-SPACE SATURATED WITH NON-VISCOUS FLUID b Chi-Hsin Lin, Vincent W. Lee and Mihailo
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA Department of Civil Engineering ON THE REFLECTION OF ELASTIC WAVES IN A POROELASTIC HALF-SPACE SATURATED WITH NON-VISCOUS FLUID b Chi-Hsin Lin, Vincent W. Lee and Mihailo
The stiffness tailoring of megawatt wind turbine
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS The stiffness tailoring of megawatt wind turbine To cite this article: Z M Li et al 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 52 052008
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS The stiffness tailoring of megawatt wind turbine To cite this article: Z M Li et al 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 52 052008
EVALUATION OF THERMAL TRANSPORT PROPERTIES USING A MICRO-CRACKING MODEL FOR WOVEN COMPOSITE LAMINATES
 EVALUATION OF THERMAL TRANSPORT PROPERTIES USING A MICRO-CRACKING MODEL FOR WOVEN COMPOSITE LAMINATES C. Luo and P. E. DesJardin* Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Universit at Buffalo,
EVALUATION OF THERMAL TRANSPORT PROPERTIES USING A MICRO-CRACKING MODEL FOR WOVEN COMPOSITE LAMINATES C. Luo and P. E. DesJardin* Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Universit at Buffalo,
Mathematical aspects of mechanical systems eigentones
 Seminar: Vibrations and Structure-Borne Sound in Civil Engineering Theor and Applications Mathematical aspects of mechanical sstems eigentones Andre Kuzmin April st 6 Abstract Computational methods of
Seminar: Vibrations and Structure-Borne Sound in Civil Engineering Theor and Applications Mathematical aspects of mechanical sstems eigentones Andre Kuzmin April st 6 Abstract Computational methods of
Effect of Bi-axial Residual Stresses on the Micro-Indentation Behaviour of Bulk Materials
 Effect of Bi-axial Residual Stresses on the Micro-Indentation Behaviour of Bulk Materials Prakash Jadhav Department of Mechanical Engineering CMR Institute of Technolog, Bangalore, India Prakash.k@cmrit.ac.in
Effect of Bi-axial Residual Stresses on the Micro-Indentation Behaviour of Bulk Materials Prakash Jadhav Department of Mechanical Engineering CMR Institute of Technolog, Bangalore, India Prakash.k@cmrit.ac.in
MAE 323: Chapter 4. Plane Stress and Plane Strain. The Stress Equilibrium Equation
 The Stress Equilibrium Equation As we mentioned in Chapter 2, using the Galerkin formulation and a choice of shape functions, we can derive a discretized form of most differential equations. In Structural
The Stress Equilibrium Equation As we mentioned in Chapter 2, using the Galerkin formulation and a choice of shape functions, we can derive a discretized form of most differential equations. In Structural
Shear and torsion correction factors of Timoshenko beam model for generic cross sections
 Shear and torsion correction factors of Timoshenko beam model for generic cross sections Jouni Freund*, Alp Karakoç Online Publication Date: 15 Oct 2015 URL: http://www.jresm.org/archive/resm2015.19me0827.html
Shear and torsion correction factors of Timoshenko beam model for generic cross sections Jouni Freund*, Alp Karakoç Online Publication Date: 15 Oct 2015 URL: http://www.jresm.org/archive/resm2015.19me0827.html
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
 NATIONAL NIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE FINAL EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B.ENG ME 444 - DYNAMICS AND CONTROL OF ROBOTIC SYSTEMS October/November 994 - Time Allowed: 3 Hours INSTRCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:. This
NATIONAL NIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE FINAL EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B.ENG ME 444 - DYNAMICS AND CONTROL OF ROBOTIC SYSTEMS October/November 994 - Time Allowed: 3 Hours INSTRCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:. This
Department of Physics and Astronomy 2 nd Year Laboratory. L2 Light Scattering
 nd ear laborator script L Light Scattering Department o Phsics and Astronom nd Year Laborator L Light Scattering Scientiic aims and objectives To determine the densit o nano-spheres o polstrene suspended
nd ear laborator script L Light Scattering Department o Phsics and Astronom nd Year Laborator L Light Scattering Scientiic aims and objectives To determine the densit o nano-spheres o polstrene suspended
Stiffness and Strength Tailoring in Uniform Space-Filling Truss Structures
 NASA Technical Paper 3210 April 1992 Stiffness and Strength Tailoring in Uniform Space-Filling Truss Structures Mark S. Lake Summar This paper presents a deterministic procedure for tailoring the continuum
NASA Technical Paper 3210 April 1992 Stiffness and Strength Tailoring in Uniform Space-Filling Truss Structures Mark S. Lake Summar This paper presents a deterministic procedure for tailoring the continuum
Prediction of geometric dimensions for cold forgings using the finite element method
 Journal of Materials Processing Technology 189 (2007) 459 465 Prediction of geometric dimensions for cold forgings using the finite element method B.Y. Jun a, S.M. Kang b, M.C. Lee c, R.H. Park b, M.S.
Journal of Materials Processing Technology 189 (2007) 459 465 Prediction of geometric dimensions for cold forgings using the finite element method B.Y. Jun a, S.M. Kang b, M.C. Lee c, R.H. Park b, M.S.
Stability Analysis of Laminated Composite Thin-Walled Beam Structures
 Paper 224 Civil-Comp Press, 2012 Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Computational Structures echnolog, B.H.V. opping, (Editor), Civil-Comp Press, Stirlingshire, Scotland Stabilit nalsis
Paper 224 Civil-Comp Press, 2012 Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Computational Structures echnolog, B.H.V. opping, (Editor), Civil-Comp Press, Stirlingshire, Scotland Stabilit nalsis
FULL FIELD MAPPING OF FOAM DEFORMATION PATTERN AT MICROSCALES
 FULL FIELD MAPPING OF FOAM DEFORMATION PATTERN AT MICROSCALES F.P. Chiang Ston Brook Universit Department of Mechanical Engineering Ston Brook, NY 794-300 Fu-pen.chiang@stonbrook.edu SUMMARY The multi-scale
FULL FIELD MAPPING OF FOAM DEFORMATION PATTERN AT MICROSCALES F.P. Chiang Ston Brook Universit Department of Mechanical Engineering Ston Brook, NY 794-300 Fu-pen.chiang@stonbrook.edu SUMMARY The multi-scale
Mahamadou Tembely, Matthew N. O. Sadiku, Sarhan M. Musa, John O. Attia, and Pamela Obiomon
 Journal of Multidisciplinar Engineering Science and Technolog (JMEST) Electromagnetic Scattering B Random Two- Dimensional Rough Surface Using The Joint Probabilit Distribution Function And Monte Carlo
Journal of Multidisciplinar Engineering Science and Technolog (JMEST) Electromagnetic Scattering B Random Two- Dimensional Rough Surface Using The Joint Probabilit Distribution Function And Monte Carlo
The response of an idealized granular material to an incremental shear strain
 The response of an idealized granular material to an incremental shear strain Luigi La Ragione and Vanessa Magnanimo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile e Ambientale, Politecnico di Bari, Italy E-mail: l.laragione@poliba.it;
The response of an idealized granular material to an incremental shear strain Luigi La Ragione and Vanessa Magnanimo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile e Ambientale, Politecnico di Bari, Italy E-mail: l.laragione@poliba.it;
CHAPTER 7 EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE OF INELASTIC SYSTEMS. Base shear force in a linearly elastic system due to ground excitation is Vb
 CHAPTER 7 EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE OF INELASTIC SYSTEMS Base shear force in a linearl elastic sstem due to ground excitation is Vb = ( A/ g) w where A is the pseudo-acceleration corresponding to natural period
CHAPTER 7 EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE OF INELASTIC SYSTEMS Base shear force in a linearl elastic sstem due to ground excitation is Vb = ( A/ g) w where A is the pseudo-acceleration corresponding to natural period
MODELING GEOMATERIALS ACROSS SCALES JOSÉ E. ANDRADE DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING EPS SEMINAR SERIES MARCH 2008
 MODELING GEOMATERIALS ACROSS SCALES JOSÉ E. ANDRADE DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING EPS SEMINAR SERIES MARCH 2008 COLLABORATORS: DR XUXIN TU AND MR KIRK ELLISON THE ROADMAP MOTIVATION
MODELING GEOMATERIALS ACROSS SCALES JOSÉ E. ANDRADE DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING EPS SEMINAR SERIES MARCH 2008 COLLABORATORS: DR XUXIN TU AND MR KIRK ELLISON THE ROADMAP MOTIVATION
Chapter 2: Elasticity
 OHP 1 Mechanical Properties of Materials Chapter 2: lasticity Prof. Wenjea J. Tseng ( 曾文甲 ) Department of Materials ngineering National Chung Hsing University wenjea@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Reference: W.F.
OHP 1 Mechanical Properties of Materials Chapter 2: lasticity Prof. Wenjea J. Tseng ( 曾文甲 ) Department of Materials ngineering National Chung Hsing University wenjea@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Reference: W.F.
Viktor Shkolnikov, Juan G. Santiago*
 Supplementar Information: Coupling Isotachophoresis with Affinit Chromatograph for Rapid and Selective Purification with High Column Utilization. Part I: Theor Viktor Shkolnikov, Juan G. Santiago* Department
Supplementar Information: Coupling Isotachophoresis with Affinit Chromatograph for Rapid and Selective Purification with High Column Utilization. Part I: Theor Viktor Shkolnikov, Juan G. Santiago* Department
CSE 546 Midterm Exam, Fall 2014
 CSE 546 Midterm Eam, Fall 2014 1. Personal info: Name: UW NetID: Student ID: 2. There should be 14 numbered pages in this eam (including this cover sheet). 3. You can use an material ou brought: an book,
CSE 546 Midterm Eam, Fall 2014 1. Personal info: Name: UW NetID: Student ID: 2. There should be 14 numbered pages in this eam (including this cover sheet). 3. You can use an material ou brought: an book,
NUMERICAL SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS OF INTERFERENCE EFFECTS ON THE PORT CONTAINER GROUP
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS OF INTERFERENCE EFFECTS ON THE PORT CONTAINER GROUP Chun-hui Zhang, Wei Sun, Xing-qian Peng Graduate student, College of Civil Engineering, Huaqiao Universit, Quanzhou,
NUMERICAL SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS OF INTERFERENCE EFFECTS ON THE PORT CONTAINER GROUP Chun-hui Zhang, Wei Sun, Xing-qian Peng Graduate student, College of Civil Engineering, Huaqiao Universit, Quanzhou,
Effects of geometry and properties of fibre and matrix on overall. composite parameters
 Int. Journal of Applied Sciences and ngineering Research, ol. 3, Issue 4, 2014 www.ijaser.com 2014 by the authors Licensee IJASR- Under Creative Commons License 3.0 editorial@ijaser.com Research article
Int. Journal of Applied Sciences and ngineering Research, ol. 3, Issue 4, 2014 www.ijaser.com 2014 by the authors Licensee IJASR- Under Creative Commons License 3.0 editorial@ijaser.com Research article
Mechanical Engineering Letters
 13456789 Bulletin of the JSME Mechanical Engineering Letters Vol.1, 15 Stochastic homogeniation analysis of FIB-SEM image-based hierarchical model of sprayed porous ZrO uma MIAUCI*, Naoki TAKANO** and
13456789 Bulletin of the JSME Mechanical Engineering Letters Vol.1, 15 Stochastic homogeniation analysis of FIB-SEM image-based hierarchical model of sprayed porous ZrO uma MIAUCI*, Naoki TAKANO** and
FATIGUE ANALYSIS: THE SUPER-NEUBER TECHNIQUE FOR CORRECTION OF LINEAR ELASTIC FE RESULTS
 6 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES FATIGUE ANALYSIS: THE SUPER-NEUBER TECHNIQUE FOR CORRECTION OF LINEAR ELASTIC FE RESULTS L. Samuelsson * * Volvo Aero Corporation, Sweden Kewords:
6 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES FATIGUE ANALYSIS: THE SUPER-NEUBER TECHNIQUE FOR CORRECTION OF LINEAR ELASTIC FE RESULTS L. Samuelsson * * Volvo Aero Corporation, Sweden Kewords:
EFFECT OF DAMPING AND THERMAL GRADIENT ON VIBRATIONS OF ORTHOTROPIC RECTANGULAR PLATE OF VARIABLE THICKNESS
 Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 193-9466 Vol. 1, Issue 1 (June 17), pp. 1-16 Applications and Applied Mathematics: An International Journal (AAM) EFFECT OF DAMPING AND THERMAL
Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 193-9466 Vol. 1, Issue 1 (June 17), pp. 1-16 Applications and Applied Mathematics: An International Journal (AAM) EFFECT OF DAMPING AND THERMAL
Mechanics Departmental Exam Last updated November 2013
 Mechanics Departmental Eam Last updated November 213 1. Two satellites are moving about each other in circular orbits under the influence of their mutual gravitational attractions. The satellites have
Mechanics Departmental Eam Last updated November 213 1. Two satellites are moving about each other in circular orbits under the influence of their mutual gravitational attractions. The satellites have
Combined Isotropic-Kinematic Hardening Laws with Anisotropic Back-stress Evolution for Orthotropic Fiber-Reinforced Composites
 Combined Isotropic-Kinematic Hardening Laws with Antropic Back-stress Evolution for Orthotropic Fiber- Reinforced Composites Combined Isotropic-Kinematic Hardening Laws with Antropic Back-stress Evolution
Combined Isotropic-Kinematic Hardening Laws with Antropic Back-stress Evolution for Orthotropic Fiber- Reinforced Composites Combined Isotropic-Kinematic Hardening Laws with Antropic Back-stress Evolution
Chapter 5 Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Objectives
 Chapter 5 Equilibrium of a Rigid Bod Objectives Develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid bod Concept of the free-bod diagram for a rigid bod Solve rigid-bod equilibrium problems using the equations
Chapter 5 Equilibrium of a Rigid Bod Objectives Develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid bod Concept of the free-bod diagram for a rigid bod Solve rigid-bod equilibrium problems using the equations
Submarine sand ripples formation in a viscous fluid: 2D and 3D linear stability analysis
 Marine Sandwave and River Dune Dnamics 1 & April 4 - Enschede, the Netherlands Submarine sand ripples formation in a viscous fluid: D and 3D linear stabilit analsis V. Langlois (1) and A. Valance (1) Groupe
Marine Sandwave and River Dune Dnamics 1 & April 4 - Enschede, the Netherlands Submarine sand ripples formation in a viscous fluid: D and 3D linear stabilit analsis V. Langlois (1) and A. Valance (1) Groupe
