y = sin x Chapter 9 Overview: Types and Traits of Parent Trigonometric Functions
|
|
|
- Francis Bates
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 9 Overview: Types and Traits of Parent Trigonometric Functions In many Precalculus courses (and in Physics), a great deal of time is spent looking at the trigonometric graphs as transformations of a parent function. The six trigonometric parent functions look like this: y = sin x y = cosx y = csc x y = sec x 510
2 y = tan x y = cot x The transformations are shifts (translations) or stretching/shrinking (dilations) which are caused by introducing numbers into the parent function by multiplication or addition, either inside or outside the functions. These translation and dilation numbers are: Amplitude Period Vertical Shift Horizontal Shift (Note: Since this book consistently uses the word traits for the collective characteristics which overarch the families of functions, the same word will not be used to refer to these translations and dilations. They will just be referred to as characteristics.) The sine and cosine waves, in particular, can be used to model many real world problems, especially those that are periodic in nature (i.e., those where the y-values repeat with constancy). The analysis of trigonometric functions in order to use them to predict behavior will be explored. 511
3 9-1: Graphing Trigonometric Functions by Calculator Now that geometric trigonometry has been fully reviewed and used to build a base of analytic trigonometry, it is time to leave triangles behind and explore the nature of the six trigonometric functions as functions (like polynomials, etc.) rather than as operations. A common vocabulary must be established. Much of it comes directly from Algebra 1 and 2. Vocabulary: 1. Domain Defn: the set of values of the independent variable Means: the set of x-values that can be substituted into the equation to get a real y value (i.e., no zero denominator, no negative under an even radical, and no non-positive number in a logarithm) 2. Range Defn: the set of values of the dependent variable Means: the set of y-values that can come from the equation 3. Relation Defn: a set of ordered pairs Means: the equation that creates/defines the pairs 4. Function Defn: a relation for which there is exactly one value of the dependent variable for each value of the independent variable Means: an equation where every x gets only one y 5. Critical Value the x-coordinate of the maximum or minimum points 6. Extreme Value the y-coordinate of the maximum or minimum points One of the main differences between trigonometric functions and the algebraic functions (polynomials, rationals, etc.) is that trigonometric functions are periodic. This means the curve repeats itself just as trigonometric values repeat for coterminal angles. Vocabulary: 7. Parent Function a non-transformed version indicative of a family of functions; the most basic version 8. Trigonometric Function a relation in degrees between x and y based on six trigonometric operations 9. Sinusoidal Function functions involving sine or cosine 10. Cycle one section of curve without repeating values 11. Primary Cycle the cycle beginning with the horizontal (a.k.a. phase) shift 512
4 12. Period the width of one cycle 13. Sinusoidal Axis imaginary horizontal centerline of the curve 14. Axis Points the points where the curve crosses the sinusoidal axis The graphs of y = cosx and y = sin x look like this, respectively: LEARNING OUTCOMES Explore the relationship between the equation and the graph of a sinusoidal. Use a graphing calculator to find the graph of a trigonometric equation. In-class Assignment: Graph each equation on your calculator and sketch it, indicating the window used. Be sure the mode is RADIANS. 1. y = cosx 2. y = 3cosx 3. y = 2+ cosx 4. y = 2! cosx 5. y = cos( 2x)! 6. y = cos 1 2 x " % & 513
5 7. y = cos( x! 2) 8. y = cos( x + 2) 9. y =1+ 4cos! 3 x " 2 & % ' ( 10. y = sin x 11. y = 3sin x 12. y = 2+ sin x 13. y = 2! sin x 14. y = sin( 2x)! 15. y = sin 1 2 x " % & 16. y = sin( x! 2) 17. y = sin( x + 2) 18. y = 3+ 2sin! 2 x " 2 & % ' ( 19. If the general equation of a sinusoidal is y = k + Ai f " B x! h, how does % each of the constants A, B, h, and k affect the graph? Analysis of these graphs reveals certain conclusions about the introduction of constants in the places of A, B, h, and k in the general equation. A = stretches or shrinks the curve vertically B = stretches or shrinks the curve horizontally k = shifts the curve vertically h = shifts the curve horizontally 514
6 General Equation: y = k + Ai f " B x! h % where and A = amplitude vertical distance from extreme value to the sinusoidal axis B = angular velocity* 2! B = period** 1 period = frequency k = vertical shift h = horizontal shift (a.k.a. phase shift) f = the sinusoidal function *Note that B itself is not used overtly in graphing the equation, but it is the number of cycles between 0 and 2π. **Tangent and cotangent functions have a different period. Note that negative values of h will shift the curve left and negative values of k will shift the curve down. Negative values of A will mirror the curve vertically (and negative values of B will mirror the curve horizontally, with the exception of cosine and secant, although we will not consider this case). LEARNING OUTCOMES Find the graph from the equation of a sinusoidal without a graphing calculator. Given a sinusoidal graph or its traits, find its equation. 515
7 EX 1 Sketch the graph of the sinusoidal with maximum value of 12 at x = 3 and x = 7, and minimum value of 4 at x = 5. The easiest way to look at this is problem is to note that three ordered pairs are given: ( 3, 12), ( 5, 4), and ( 7, 12) Plot the three points and connect them sinusoidally. 516
8 EX 2 Sketch the primary cycle of y = 3+ 2cos! 4 x "1 & % (. Amplitude = 2 Period = 2!! 4 = 8 Vertical Shift = 3 Horizontal shift = 1 517
9 " EX 3 Sketch the primary cycle of y = 2 + 3sin! 6 x + 3 %. & Amplitude = 3 Period = 2!! 6 =12 Vertical Shift = 2 Phase shift = "3 518
10 EX 4 Sketch the primary cycle of y =!4cos 1 6 x +" & % (. Amplitude =!4 Period = 2" 1 6 =12" Vertical Shift = 0 Phase shift =!" Note that a negative A value means the graph will be mirrored vertically. 519
11 EX 5 Find one sine and one cosine equation for this graph. Amplitude = 4 Period = 2! 3, so b = 3 Vertical Shift = 0 Cosine crosses the y-axis at its maximum, so there is no phase shift for the cosine equation. The cosine equation for this graph is y = 4cos3x. Sine has a phase shift 1 4 of the period to the left of cosine. Since the period is 2! 3, the shift is!. The sine equation for this graph is 6 " y = 4sin3 x +! % 6 & '. 520
12 9-1 Multiple Choice Homework 1. In the figure r sin! equals (a) a (b) b (c) a (d) b (e) a + b 2. The vertical distance between the minimum and maximum values of the function y =! 2 sin 3x is (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) sin!1 ( cos100 ) (a) 1.0 (b) 1.4 (c) 0.2 (d) 1.4 (e) The graph of the curve represented by " % x = 3sin! & ' y = 3sin! ( is (a) a line (b) a horizontal line segment (c) a circle (d) a line segment 3 units long (e) a line segment with slope 1 521
13 5. What is the amplitude of the graph of y = acos x + bsin x? a + b (a) 2 (b) a + b (c) ab (d) a 2 + b 2 (e) ( a + b) Free Response Homework 1. The temperature at a location on a distant planet is given by T =! sin " ( 7 x!5 & % )( where T is temperature in Fahrenheit and x is time of day in hours. Determine whether each statement is true or false and EXPLAIN your choice. Reference the equation in your explanation. a) The location is ALWAYS freezing (below 32ºF). b) A day on this planet is 24 hours long. c) At midnight x = 0, the location is at its coldest point. d) The temperature will equal 10ºF twice every day. Identify the period, amplitude, vertical shift and horizontal (phase) shift, and sketch the primary cycle of each of these equations. 2. y = 4+ sin! 8 x " 3 & " % ( 3. y = 2 + 3cos! 4 x % & 4. y =1+5sin 1 2 x!" & % ( 5. y =1! 3sin " x % & 6. y =!3cos " 6 x + 2 & % ( 7. y = 2+ cos! 2 x " 2 & % ( 522
14 8. y =!2! 4sin " ( 5 x! 2 & % ) ( 9. y = 2! 2cos ) 1 2 x + " &, + % 2 ' (. * + -. Find one sine and one cosine equation for each of these graphs
15
16
17 9-2: Solving Sinusoidal Equations LEARNING OUTCOME Given a sinusoidal equation, find values of y from x and vice versa. The algebraic process of solving a trig equation is not too difficult; it is just a matter of isolating the variable. EX 1 If f x = 2 + 3cos! ( 4 x "1 ) % & ' (, find f ( 2.3). Since f ( x) is already isolated, this can be done on the calculator. = 2+ 3cos! ( 4 2.3"1 ) f 2.3 % f ( 2.3) = & ' ( Remember that these functions are periodic and that isolating for x will yield multiple answers. REMEMBER: cos!1 x r = % calculator ± 2" n '% ( &%!calculator ± 2" n)% sin!1 y r = % calculator ± 2" n '% ( &% "! calculator ± 2" n)% " 1± 6n & So if, for example, x = ', this means there is an infinite number of %!3± 6n( answers, namely "...!11,!5, 1, 7, 13,... & x = ' %...!15,! 9,! 3, 3, 9,...( It is likely specific solutions will be solicited. 526
18 EX 2 If f x f ( x) = 4. = 2 + 3cos! ( 4 x "1 ) % & ' (, find the first three positive values where 4 = 2+ 3cos! 4 x "1 & % ' ( 2 = 3cos! 4 x "1 & % ' ( 2 3 = cos! ( 4 x "1 & ) % ' ( cos "1 2& % 3' ( =! 4 x "1 The first three positive x-values are ) ± 2! n-+ *.,+ "0.841± 2! n =! /+ 4 x "1 ) ± 8n-+ *.,+ "1.071± 8n = x "1 /+ ) ± 8n-+ *.,+ "0.071± 8n = x /+ x = { 2.071, 7.929, } Notice that if the function in EX 1 and 2 are sketched, the points involved are: The x-values of the points of intersection with the line y = 4 appear to be at the approximate location of the solutions to EX
19 EX 3 For f ( x) =1! 4sin " ( 2 x +1 &! 2 % )(, find a) f " 3% &, and b) the first three negative values of x, closest to zero, where f x! 2 a) f " 3% & =1' 4sin ) (! , + " % &. * + -. = 2. b) 2 =1! 4sin " 2 x +1 & % (! 1 4 = sin " ( 2 x +1 & % )( sin!1 )! 1, * = " ( 2 x +1 ) / 1!0.253± 2" n ± 2" n = " 51 2 x +1 / 1!0.161± 4n ± 4n = x / 1!1.161± 4n ± 4n = x 51! 2 f " 3% & = '1 The first three negative x-values, closest to zero, are x = {!1.161,! 2.839,!5.161} 528
20 9-2 Multiple Choice Homework " 1. What is the smallest positive x-intercept of the graph of y = 3sin 2 x + 2! 3 (a) 0 (b) 2.09 (c) 1.05 (d) 0.52 (e) The smallest positive value of x satisfying the equation tan 5x =!2 is closest to (a) 13 (b) 31 (c) 23 (d) 49 (e) 63 % & '? 3. As x increases from! " 4 to 3! 4, the value of cos x (a) always increases (b) always decreases (c) increases then decreases (d) decreases then increases (e) does none of the above 4. The graph of the curve represented by (a) a line (b) a hyperbola (c) an ellipse (d) a line segment (e) a portion of a hyperbola " % x = sec! & ' y = cos! ( is 529
21 5. The figure below shows the graph of y = sin 3x. What is the value of x at point P?! (a) 3 2! (b) 3 (c) 2! (d) 3! (e) 6! 9-2 Free Response Homework For each of the following, find a) y if x =!2.7, and b) the smallest three positive values of x where y = 0. " 1. y = 2+ 3cos! 4 x % 2. y = 4! cos " & 4 x!12 & % ( 3. y =1+5sin 1 ( 2 x!" & % ) ( 4. y = 3+ 7cos ) 1 3 x! " &, + % 2 ' (. * + -. For each of the following, find a) y if x = 4.8, and b) the first four negative values of x, closest to zero, where y = y =!3cos " 6 x + 21 & % ( 6. y = 2+ cos! 2 x "5 & % ( 7. y = sin! 8 x " 3 & % ( 8. y =1! 3sin " x % & 530
22 9-3: Mathematical Modeling with Sinusoidals Vocabulary: (variation word problem phrases) 1. Dependent Variable the unknown that varies 2. Independent Variable the unknown that the dependent varies with 3. y varies directly as x y = kx 4. y varies inversely as x y = k x 5. f varies jointly with x and y f = kxy ( ) or 6. y varies sinusoidally with t y = k + Acos B t! h y = k + Asin B t! h LEARNING OUTCOME Model and solve sinusoidal situations. EX 1 In a Chemistry experiment, researchers find that the temperature of a compound varies sinusoidally with time. 17 minutes after they start timing, the temperature is its highest, which is 56 Celsius. 12 minutes after it has reached its maximum, the temperature hits its minimum, which is 40 Celsius. a) Sketch a graph of the temperature as a function of time and write a sinusoidal equation that describes the temperature y in terms of time t. b) What was the temperature at the start of the experiment? c) What are the first three times that the temperature is 51? a) In this situation, the high and low values are at 56 and 40 respectively. So the sinusoidal axis is at 48 and A = 8. The high point occurs at 17 minutes therefore h = 17. It takes 12 minutes to get from high to low point, so period = 24 minutes and B =!
23 The sketch is:! and the equation is y = 48+8cos ( 12 t "17 & % )(.! b) y = 48+8cos ( 12 0"17 & % )(! c) 51= 48+8cos ( 12 t "17 & % )(! 3= 8cos ( 12 t "17 & % )( 3 8 = cos! ( 12 t "17 & % )( ) ± 2! n -+ *.,+ "1.186 ± 2! n =! /+ 12 t "17 ) ± 24n -+ *.,+ " ± 24n = t "17 /+ ) ± 24n-+ *., ± 24n = t /+ y( 0) = The first three times are t = { , , } minutes. 532
24 EX 2 A tropical flower closes and opens at different times of the day. The diameter of the petals varies sinusoidally with time. At midnight, the petals of the flower completely open to an 8 inch diameter. At 6am, they completely close to a diameter of 2 inches. a) Sketch two cycles. b) Find the equation of the sinusoidal. c) What is the diameter at 10:45am? d) What are the times of the day when the petals are 3 inches open? a) " b) y = 5+ 3cos! 6 t % & c) " y = 5+ 3cos! ( % )' & =
25 " d) 3= 5+ 3cos! 6 t % & " 3 = 5+ 3cos! 6 t % & ( 2 3 = cos "! 6 t % & ) ± 2!n -+ *.,+ ( 2.301± 2!n =! /+ 6 t ) ±12n-+ *.,+ ( ±12n = t /+ t = 4.394, 7.606, , The times of day are 4:24am, 7:36am, 4:24pm, and 7:36pm. 534
26 9-3 Multiple Choice Homework 1. When the graph of y = sin 2x is drawn for all values of x between 10 and 350, it crosses the x-axis (a) zero times (b) one time (c) two times (d) three times (e) six times 2. As x increases from! " 4 to 3! 4, the value of sin x (a) always increases (b) always decreases (c) increases then decreases (d) decreases then increases (e) does none of the above 3. Which of the following equations has the graph shown in the figure below? (a) y = sin x (b) y = sin 2x (c) y = 2sin x 2 (d) y = 2sin x (e) y = 2sin 2x 4. The primary period of the function f ( x) = 2 cos 2 3x is (a) 2π (b)! 3 (c) π (d)! 2 (e) 3π 535
27 5. x > sin x for (a) all x > 0 (b) all x < 0 (c) all x for which x! 0 (d) all x (e) all for which! " 2 < x < Free Response Homework 1. A particular weight attached to a spring bounces up and down such that the height of the weight from the table varies sinusoidally with time. The furthest the weight gets from the table is 10 inches and the closest is 2 inches. The weight is at its highest point at 0.2 seconds and goes from highest to lowest point and back to the highest point in 0.5 seconds. a) Sketch a graph of the movement. b) Find a sinusoidal function to represent the graph. c) How high is the weight at 0 seconds, 1.2 seconds, and 3.7 seconds? d) When are the first three times that the weight is at 8 inches? 2. The height of a seat on a Ferris wheel from the ground varies sinusoidally with time. The wheel goes around once every 60 seconds and the seat is 45 feet off the ground when you start timing the motion. At its lowest, the seat is 2 feet above the ground. The diameter of the wheel is 50 feet. a) Sketch a graph of the movement. b) Find a sinusoidal function to represent the graph. c) How high is the seat at 35 seconds, 85 seconds, and 2 minutes? d) When is the fifth time the seat is at its lowest? 536
28 3. Todd is meditating; he is concentrating on his breathing. His breathing varies sinusoidally with time. His lung capacity is 68 cubic centimeters at minimum capacity (exhale). When he inhales completely, his lung capacity is 128 cubic centimeters. At 2 seconds, his lung capacity is at its lowest, and he is back to his lowest 8 seconds later. a) Sketch a graph of the situation and find a sinusoidal function to represent the situation. b) Find his lung capacity at 0 seconds, 3 seconds, and 10 seconds. c) Use your graph to predict the first three times that his lung capacity is at its highest. 4. The new roller coaster, the Raging Behemoth, contains many loops and swoops. Its height on one of the loops varies sinusoidally with time. At its highest, the coaster is 85 feet off the ground 15 seconds after the start of the ride. After five seconds, it reaches its lowest point, 5 feet off the ground. Sketch a graph of this section of the coaster, find an equation for that graph and determine when the coaster is 78' up. 5. One Saturday you and a friend are watching some dolphins jump around in the water. You immediately recognize that their height above and below the water varies sinusoidally with time. After four seconds of watching a particular dolphin, you observe that it is five feet below the surface of the water and that this is the lowest point seconds later, it is at its highest point, five feet above the water. Sketch the graph of the situation; write an equation in terms of sine for the graph, then write a second equation in terms of cosine. Find the height of the dolphin at time 0 seconds, 2.56 seconds, and 3.68 seconds, and verify that the heights are the same for both equations. 537
29 6. On a Saturday afternoon, Billy decides to go on a swing to kill some time. He notices that his deflection from the center of the swing varies sinusoidally with time. He also notices that his height varies sinusoidally with time as well. In other words, there are two variations occurring simultaneously. He is at the lowest point 2 feet off the ground at 1.5 seconds, and the next time he hits the highest point of 8 feet high is 0.74 seconds later. He is at his furthest deflection from the center at 2.24 seconds and 6 feet from the center, and he is back at the same spot in 2.96 seconds. a) Sketch two cycles of each curve. b) Find an equation to represent Billy s height and another to represent Billy s deflection from center situation. c) Find the first three times Billy is at a height of 4 feet. d) Find his deflections at times of 1, 2, and 3 seconds. 7. A particular teacher s ability to reach her students varies sinusoidally with time. One month after the start of school, in September, she is teaching her best reaching all 100 of her students. Three months later she reaches her lowest, only 50 of her students. a) Sketch a graph of the number of students reached as a function of months after school starts. b) Write a sinusoidal equation that describes the number of students reached in terms of months after school starts. c) How many students were reached at the start of school (in months)? d) When are the first two times in terms of months she will reach 85 students? 8. A person jumping on a trampoline will bounce sinusoidally with time. The surface of the trampoline is 45 cm above the ground. At 0.20 seconds, she reaches her highest point of 110 cm above the surface of the trampoline seconds later she is at the lowest point, 20 cm below the surface of the trampoline. Sketch the graph of 4 cycles of this function. Find an equation that fits this model. Find the first four times she is at a height of 1 meter above the ground. 538
30 9. A patient in a hospital is experiencing fluctuations in his blood pressure. His pressure seems to be varying sinusoidally with time. Over 24 hours, it varies from 90 to 150 and back twice. At 9 am, the pressure is 120 and is on the rise. a) Sketch a graph of the pressure P t b) Write a sinusoidal equation that describes the P t as a function of time. in terms of time t. c) What would you expect the pressure at 1:15 pm? d) What are the first three times of day when P t =130? 10. Tsunamis are tidal waves in the Pacific Ocean caused by earthquakes in various places around the Pacific Rim. In 1946, 159 people were killed by a tsunami caused by an earthquake in the Aleutian Islands, Alaska. The sea level first dropped 55 feet, exposing the seabed which is normally 25 feet below sea level and then the water rose an equal distance above sea level. Many school children were drowned when the walked out into the exposed area, not knowing the sea when would be rushing back in. The cycles took roughly 12 minutes. Assuming the waves conform to a sine graph (i.e., the height of the wave y varies sinusoidally with time), determine an equation to describe this phenomenon and predict how long the seabed would be exposed. 539
31 9-4: Reciprocal and Quotient Curves As with the sinusoidals, the other four trig functions have graphs that are periodic. The Quotient Curves: y = tan x y = cot x Notice the tan x and cot x curves repeat more often than the sinusoidals. If the period is considered to be the width of one section of curve without repeated! 2! y-values, the period on these curves is, instead of, as it is for the B B other four trig functions. Note that the curves drawn above show more than one cycle. The primary cycle is still considered to be the one starting with h and ending at h + the period, just as with the sinusoidals. Some authors (and teachers) prefer a more aesthetic graph and will start at an asymptote, regardless of h. This might be helpful when considering inverse functions later, but, for now, consistency with the sinusoidals will be maintained. However, if your teacher prefers the aesthetic approach, do as he or she requires. 540
32 The Reciprocal Curves: y = sec x 4 6 y = csc x All the facts learned in a previous section about A, B, h and k will remain the same with the new graphs, except that the period for y = tan x and y = cot x is. LEARNING OUTCOME Find the graph from the equation of tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant functions. EX 1 Identify the period, amplitude, vertical shift and phase shift and sketch the "! % 1 primary cycle of y = 2 + tan x '. 2 6 & Vertical shift = 2 Amplitude = Phase shift = Period = 541! =6! 6
33 EX 2 Identify the period, amplitude, vertical shift and phase shift and sketch the primary cycle of y = 3+ 2csc! ( 6 x "1 & % )(. Vertical shift = 3 Horizontal shift = 1 Amplitude = 2 Period = 2!! 6 =12 542
34 9-4 Multiple Choice Homework 1. If tan x = 3, the numerical value of csc x is (a) 0.97 (b) 1.03 (c) 1.78 (d) 3.16 (e) The period of the function f x (a) 2 1 (b) 2 (c) 1 1 (d) 4 (e) 4 = k cos kx is! 543. The amplitude of f is 2 3. What is the period of the graph of the function y = sin x 1 + cos x? (a) 2! (b)!! (c) 2! (d) 4 (e) 4! 4. Compared to the graph of y = f ( x), the graph of y = f ( x + 2)! 3 is (a) shifted 2 units right and 3 units down (b) shifted 2 units left and 3 units down (c) shifted 2 units rights and 3 units up (d) shifted 2 units right and 3 units down (e) none of the above
35 5. What is the smallest positive angle that will make 5! sin x + " & % 6 ' ( a maximum? (a) 1.05 (b) 2.09 (c) 1.57 (d) 4.19 (e) Free Response Homework Identify the period, amplitude, vertical shift and phase shift and sketch (without using a calculator) the primary cycle each of these equations. 1. y = 2 + 3sec! 6 x "1 & % ( 2. y = 2+ 3csc! 6 x "1 & % ( 3. y = 2+ 3tan! 4 x " 2 & % ( 4. y = 2+ 3cot! 4 x " 2 & % ( 5. y =!3sec 1 4 x +" & % ( 6. y =1! csc " 2 x +1 & % ( 7. y =1! tan " ( 8 x + 2 & " 1 % )( 8. y = 2 + cot ( 4 x +! % )' & 9. y = 4! 2sec " 8 x +1 & % ( 10. y = 3+ csc 1 3 x!" & % ( 11. y = 4! 1 2 tan x 12. y = cot "! 6 x + 2 % & 544
36 Parent Trigonometric Functions Practice Test CALCULATOR REQUIRED Round to 3 decimal places. Show all work. Multiple Choice (3 pts. each) 1. Which equation can be used to model the graph of the function shown? (a) y = sin2x + 3 (b) y = 2sin x + 3 (c) y = sin2x! 3 (d) y = 2sin x! 3 (e) y = 2sin2x + 3 " 2. The y-intercept of y = 2csc3 x +! % 5 & ' is (a) 0.22 (b) 1.49 (c) 4.58 (d) 0.67 (e) The interval(s) of decreasing for the sine function in the interval from 0 to 2! is (are) (a) x! ", 2" (b) x! 0, " (c) x! " 2, 3" & % 2 ' ( (d) x! 0, " & % 2 ' 3" 2, 2" & % ' ( (e) x!( 0, " )(", 2" ) 545
37 4. During one cycle, a sinusoid has a minimum at 18, 44 ( 30, 68). What is the amplitude of this sinusoid? (a) 6 (b) 12 (c) 22 (d) 48 (e) 56 and a maximum at 5. In the following diagram, an old car tire is swinging back and forth on a rope. The following graph compares its distance from the vertical wall and the time. Using the diagram answer the following question: How long does it take for the tire to swing from its closest distance to the wall to its farthest distance from the wall? (a) 1.2 seconds (b) 1.4 seconds (c) 2.4 seconds (d) 2.8 seconds (e) 3.2 seconds Free Response (10 pts. each) Identify k, A, period, and h. Label the 5 coordinates. 1. Sketch the primary cycle of y =!2+ 3sin " ( 7 x!1 & % )(. 546
38 2. Sketch the primary cycle of y = 2! 3sec 1 7 x +" & % (. 3. Sketch the primary cycle of y =!2! 3cot " 7 x!1 & % (. 547
39 4. In front of the Antique Sewing Machine Museum in Arlington, Texas, is the largest sewing machine in the world. The flywheel, which turns as the machine sews, is 5 feet in diameter. Write a model for the height h (in feet) of the handle on the flywheel as a function of the time t (in seconds), assuming that the wheel makes a complete revolution every 2 seconds and that the handle starts at its minimum height of 4 feet above the ground. a) Sketch a model for the height h (in feet) of the handle on the flywheel as a function of time t (in seconds). b) Find an equation for the graph you sketched in part a). c) What is the height of the handle of the flywheel at 7 seconds? d) What are the first four times the height of the handle of the flywheel is 6 ft? 548
40 Parent Trigonometric Functions Homework Answer Key 9-1 Multiple Choice Homework 1. B 2. A 3. E 4. E 5. D 9-1 Free Response Homework 1a. True b. False c. False d. True 2. A = 1 period = 16 k = 4 h = 3 4. A = 5 period = 4π k = 1 h =! 5. A = 3 period = 2 k = 1 h = 0 3. A = 3 period = 8 k = 2 h = 0 6. A = 3 period = 12 k = 0 h =!2 549
41 7. A = 1 period = 4 k = 2 h = y = 2 + cos! ( 5 x " 3.5 ) y = 2 + sin! ( 5 x "1 ) 12. y = 4cos! ( 2 x " 3 ) y = 4sin! ( 2 x " 2 ) 8. A = 4 period = 10 k =!2 h = y =!2+ 4cos 2 ( 3 x! 2" ) y =!2+ 4sin 2 3 x! 5" & % 4 ' ( 14. y =!2+ 2cos2" x! 1 & % 2' ( y =!2 + 2sin2" x! 1 & % 4' ( 9. A =!2 period = 4π k = 2 h =! " y =!2 + cos " ( 7 x! 6 ) y =!2+ sin " 7 x! 5 & % 2' ( 10. y = 2 + 3cos! ( 4 x " 4 ) y = 2+ 3sin! ( 4 x " 2 ) 9-2 Multiple Choice Homework 1. C 2. C 3. C 4. E 5. B 9-2 Free Response Homework 1a b , 5.071,
42 2a b. No solutions 3a b , 9.827, a b , , a b. 6, 12, 18, 24 6a b. No solutions 7a b , , a b , 1.892, 3.108, Multiple Choice Homework 1. D 2. C 3. E 4. B 5. A 9-3 Free Response Homework 1a. ( ) = inches, h( 1.2) =10 inches, h( 3.7) =10 inches b. h = 6+ 4cos 4! t " 0.2 c. h 0 d , 0.283, seconds 2a. b. h = cos! 30 t " & % ' ( = 4.455feet, h( 85) = feet, h( 120) = feet c. h 35 d seconds 3a. y = cos! 4 t " 6 & % ' ( Saint Ignatius 4/9/14 2:11 PM Deleted: 033 Saint Ignatius 4/9/14 2:11 PM Deleted: 367 Saint Ignatius 4/9/14 2:11 PM Deleted:
43 b. t = 0 seconds y = 98 cm 3 t = 3 seconds y = cm 3 t = 10 seconds y = 98 cm 3 c. highest at t = 6, 14, 22 seconds 6a. 4. y = 40cos! 5 t "15 & % ' ( + 45, t!" 15, 20 % 5. y =!5cos 50" ( 143 t! 4 & ) % ' (, y = 5sin 50! ( 143 t "5.43 & ) % ' ( t = 0 seconds y = feet t = 2.56 seconds y = feet t = 3.68 seconds t =!4.694 feet b. h = 5+ 3cos 50! ( 37 t " 2.24 & ) % ' ( d = 6cos 25! ( 9 t " 2.96 & ) % ' ( c. h = 4 feet at t = 0.310, 1.210, seconds d. t =1! d = "1.042 feet t = 2! d = "3 feet t = 3! d = feet 552
44 7a. 9a. b. y = cos! 3 t "1) & % ( c students d. t = 2.107!and! b. P( t) = sin! 6 t " 9) & % ( c mmhg d. 2:21 am, 9:39 am, 2:21 pm 10. = cos 25! h t 3 t " 0.2 & ' ( % h =100 cm! t = 0.019, 0.222, 0.259, seconds y =!55sin " 6 t & % ( 4 minutes 11.9 seconds 553
45 9-4 Multiple Choice Homework 1. B 2. E 3. A 4. B 5. D 3. A = 3 period = 4 k = 2 h = Free Response Homework 1. A = 3 period = 12 k = 2 h = 1 4. A = 3 period = 4 k = 2 h = 2 2. A = 3 period = 12 k = 2 h = 1 5. A = 3 period = 8π k = 0 h =!" 554
46 6. A = 1 period = 4 k = 1 h =!1 9. A =!2 period = 16 k = 4 h =!1 7. A = 1 period = 8 k = 1 h =!2 10. A = 1 period = 6π k = 3 h =! 8. A = 1 period = 4π k = 2 h =!" 555
47 11. A =! 1 2 period = π k = 4 h = A = 1 period = 6 k = 0 h =!2 Multiple Choice 1. A 2. B 3. C 4. B 5. A Trigonometric Functions Practice Test Answer Key 556
48 Free Response 1. k =!2, A = 3, period = 14, h = 1 2. k = 2, A = 3, period = 14!, h = "! 557
49 3. k =!2, A = 3, period = 7, h = 1 4a. b. h = 6.5! 2.5cos " t! 0 % & c. 9 feet d. t = 0.436, 1.537, 2.463, sec 558
50 559
Honors Algebra 2 Chapter 14 Page 1
 Section. (Introduction) Graphs of Trig Functions Objectives:. To graph basic trig functions using t-bar method. A. Sine and Cosecant. y = sinθ y y y y 0 --- --- 80 --- --- 30 0 0 300 5 35 5 35 60 50 0
Section. (Introduction) Graphs of Trig Functions Objectives:. To graph basic trig functions using t-bar method. A. Sine and Cosecant. y = sinθ y y y y 0 --- --- 80 --- --- 30 0 0 300 5 35 5 35 60 50 0
Honors Precalculus Semester 1 Review
 Honors Precalculus Semester 1 Review Name: UNIT 1 1. For each sequence, find the explicit and recursive formulas. Show your work. a) 45, 39, 33, 27 b) 8 3, 16 9 32 27, 64 81 Explicit formula: Explicit
Honors Precalculus Semester 1 Review Name: UNIT 1 1. For each sequence, find the explicit and recursive formulas. Show your work. a) 45, 39, 33, 27 b) 8 3, 16 9 32 27, 64 81 Explicit formula: Explicit
Unit 3 Trigonometry. 3.4 Graph and analyze the trigonometric functions sine, cosine, and tangent to solve problems.
 1 General Outcome: Develop trigonometric reasoning. Specific Outcomes: Unit 3 Trigonometry 3.1 Demonstrate an understanding of angles in standard position, expressed in degrees and radians. 3.2 Develop
1 General Outcome: Develop trigonometric reasoning. Specific Outcomes: Unit 3 Trigonometry 3.1 Demonstrate an understanding of angles in standard position, expressed in degrees and radians. 3.2 Develop
Functions and their Graphs
 Chapter One Due Monday, December 12 Functions and their Graphs Functions Domain and Range Composition and Inverses Calculator Input and Output Transformations Quadratics Functions A function yields a specific
Chapter One Due Monday, December 12 Functions and their Graphs Functions Domain and Range Composition and Inverses Calculator Input and Output Transformations Quadratics Functions A function yields a specific
Section 6.1 Sinusoidal Graphs
 Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a right triangle, and related to points on a circle We noticed how the x and y values
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a right triangle, and related to points on a circle We noticed how the x and y values
Section 6.1 Angles and Radian Measure Review If you measured the distance around a circle in terms of its radius, what is the unit of measure?
 Section 6.1 Angles and Radian Measure Review If you measured the distance around a circle in terms of its radius, what is the unit of measure? In relationship to a circle, if I go half way around the edge
Section 6.1 Angles and Radian Measure Review If you measured the distance around a circle in terms of its radius, what is the unit of measure? In relationship to a circle, if I go half way around the edge
Chapter 11B: Trig Graphing Review Sheet Test Wednesday 05/17/2017
 Chapter 11B: Trig Graphing Review Sheet Test Wednesday 05/17/2017 1. The terminal ray of an angle drawn in standard position on the unit circle that measures 30 has 3 1 coordinates of,. Based on this information,
Chapter 11B: Trig Graphing Review Sheet Test Wednesday 05/17/2017 1. The terminal ray of an angle drawn in standard position on the unit circle that measures 30 has 3 1 coordinates of,. Based on this information,
Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions
 Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions Overview: 4.1 Radian and Degree Measure 4.2 Trigonometric Functions: The Unit Circle 4.3 Right Triangle Trigonometry 4.4 Trigonometric Functions of Any Angle 4.5 Graphs
Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions Overview: 4.1 Radian and Degree Measure 4.2 Trigonometric Functions: The Unit Circle 4.3 Right Triangle Trigonometry 4.4 Trigonometric Functions of Any Angle 4.5 Graphs
Dover-Sherborn High School Mathematics Curriculum Pre-Calculus Level 1/CP
 Mathematics Curriculum A. DESCRIPTION This course is an extension of Algebra II with the emphasis in Trigonometry and introductory calculus topics. All major areas covered in Algebra II are reinforced
Mathematics Curriculum A. DESCRIPTION This course is an extension of Algebra II with the emphasis in Trigonometry and introductory calculus topics. All major areas covered in Algebra II are reinforced
Summer Work Packet for MPH Math Classes
 Summer Work Packet for MPH Math Classes Students going into AP Calculus AB Sept. 018 Name: This packet is designed to help students stay current with their math skills. Each math class expects a certain
Summer Work Packet for MPH Math Classes Students going into AP Calculus AB Sept. 018 Name: This packet is designed to help students stay current with their math skills. Each math class expects a certain
MAC 1114: Trigonometry Notes
 MAC 1114: Trigonometry Notes Instructor: Brooke Quinlan Hillsborough Community College Section 7.1 Angles and Their Measure Greek Letters Commonly Used in Trigonometry Quadrant II Quadrant III Quadrant
MAC 1114: Trigonometry Notes Instructor: Brooke Quinlan Hillsborough Community College Section 7.1 Angles and Their Measure Greek Letters Commonly Used in Trigonometry Quadrant II Quadrant III Quadrant
Chapter 4/5 Part 1- Trigonometry in Radians
 Chapter 4/5 Part 1- Trigonometry in Radians WORKBOOK MHF4U W1 4.1 Radian Measure MHF4U Jensen 1) Determine mentally the exact radian measure for each angle, given that 30 is exactly π 6 radians. a) 60
Chapter 4/5 Part 1- Trigonometry in Radians WORKBOOK MHF4U W1 4.1 Radian Measure MHF4U Jensen 1) Determine mentally the exact radian measure for each angle, given that 30 is exactly π 6 radians. a) 60
Algebra 2 Khan Academy Video Correlations By SpringBoard Activity
 SB Activity Activity 1 Creating Equations 1-1 Learning Targets: Create an equation in one variable from a real-world context. Solve an equation in one variable. 1-2 Learning Targets: Create equations in
SB Activity Activity 1 Creating Equations 1-1 Learning Targets: Create an equation in one variable from a real-world context. Solve an equation in one variable. 1-2 Learning Targets: Create equations in
Algebra 2 Khan Academy Video Correlations By SpringBoard Activity
 SB Activity Activity 1 Creating Equations 1-1 Learning Targets: Create an equation in one variable from a real-world context. Solve an equation in one variable. 1-2 Learning Targets: Create equations in
SB Activity Activity 1 Creating Equations 1-1 Learning Targets: Create an equation in one variable from a real-world context. Solve an equation in one variable. 1-2 Learning Targets: Create equations in
Precalculus Honors Problem Set: Elementary Trigonometry
 Precalculus Honors Problem Set: Elementary Trigonometry Mr. Warkentin 03 Sprague Hall 017-018 Academic Year Directions: These questions are not presented in order of difficulty. Some of these questions
Precalculus Honors Problem Set: Elementary Trigonometry Mr. Warkentin 03 Sprague Hall 017-018 Academic Year Directions: These questions are not presented in order of difficulty. Some of these questions
Halldorson Honors Pre Calculus Name 4.1: Angles and Their Measures
 Halldorson Honors Pre Calculus Name 4.1: Angles and Their Measures 1. Approximate each angle in terms of decimal degrees to the nearest ten thousandth. a. θ = 56 34'53" b. θ = 35 48'. Approximate each
Halldorson Honors Pre Calculus Name 4.1: Angles and Their Measures 1. Approximate each angle in terms of decimal degrees to the nearest ten thousandth. a. θ = 56 34'53" b. θ = 35 48'. Approximate each
Honors Precalculus A. Semester Exam Review
 Semester Eam Review Honors Precalculus A Semester Eam Review 015-016 MCPS 015 016 1 Semester Eam Review The semester A eamination for Honors Precalculus consists of two parts. Part 1 is selected response
Semester Eam Review Honors Precalculus A Semester Eam Review 015-016 MCPS 015 016 1 Semester Eam Review The semester A eamination for Honors Precalculus consists of two parts. Part 1 is selected response
I. Degrees and Radians minutes equal 1 degree seconds equal 1 minute. 3. Also, 3600 seconds equal 1 degree. 3.
 0//0 I. Degrees and Radians A. A degree is a unit of angular measure equal to /80 th of a straight angle. B. A degree is broken up into minutes and seconds (in the DMS degree minute second sstem) as follows:.
0//0 I. Degrees and Radians A. A degree is a unit of angular measure equal to /80 th of a straight angle. B. A degree is broken up into minutes and seconds (in the DMS degree minute second sstem) as follows:.
Unit 3 Trigonometry Note Package. Name:
 MAT40S Unit 3 Trigonometry Mr. Morris Lesson Unit 3 Trigonometry Note Package Homework 1: Converting and Arc Extra Practice Sheet 1 Length 2: Unit Circle and Angles Extra Practice Sheet 2 3: Determining
MAT40S Unit 3 Trigonometry Mr. Morris Lesson Unit 3 Trigonometry Note Package Homework 1: Converting and Arc Extra Practice Sheet 1 Length 2: Unit Circle and Angles Extra Practice Sheet 2 3: Determining
Halldorson Honors Pre Calculus Name 4.1: Angles and Their Measures
 .: Angles and Their Measures. Approximate each angle in terms of decimal degrees to the nearest ten thousandth. a. θ = 5 '5" b. θ = 5 8'. Approximate each angle in terms of degrees, minutes, and seconds
.: Angles and Their Measures. Approximate each angle in terms of decimal degrees to the nearest ten thousandth. a. θ = 5 '5" b. θ = 5 8'. Approximate each angle in terms of degrees, minutes, and seconds
Polynomials and Rational Functions. Quadratic Equations and Inequalities. Remainder and Factor Theorems. Rational Root Theorem
 Pre-Calculus Pre-AP Scope and Sequence - Year at a Glance Pre-Calculus Pre-AP - First Semester Pre-calculus with Limits; Larson/Hostetler Three Weeks 1 st 3 weeks 2 nd 3 weeks 3 rd 3 weeks 4 th 3 weeks
Pre-Calculus Pre-AP Scope and Sequence - Year at a Glance Pre-Calculus Pre-AP - First Semester Pre-calculus with Limits; Larson/Hostetler Three Weeks 1 st 3 weeks 2 nd 3 weeks 3 rd 3 weeks 4 th 3 weeks
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions
 Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y values
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y values
Precalculus Review. Functions to KNOW! 1. Polynomial Functions. Types: General form Generic Graph and unique properties. Constants. Linear.
 Precalculus Review Functions to KNOW! 1. Polynomial Functions Types: General form Generic Graph and unique properties Constants Linear Quadratic Cubic Generalizations for Polynomial Functions - The domain
Precalculus Review Functions to KNOW! 1. Polynomial Functions Types: General form Generic Graph and unique properties Constants Linear Quadratic Cubic Generalizations for Polynomial Functions - The domain
The function is a periodic function. That means that the functions repeats its values in regular intervals, which we call the period.
 Section 5.4 - Inverse Trigonometric Functions The Inverse Sine Function Consider the graph of the sine function f ( x) sin( x). The function is a periodic function. That means that the functions repeats
Section 5.4 - Inverse Trigonometric Functions The Inverse Sine Function Consider the graph of the sine function f ( x) sin( x). The function is a periodic function. That means that the functions repeats
Math Section 4.3 Unit Circle Trigonometry
 Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
6.1 Solutions to Exercises
 Last edited 3/1/13 6.1 Solutions to Exercises 1. There is a vertical stretch with a factor of 3, and a horizontal reflection. 3. There is a vertical stretch with a factor of. 5. Period:. Amplitude: 3.
Last edited 3/1/13 6.1 Solutions to Exercises 1. There is a vertical stretch with a factor of 3, and a horizontal reflection. 3. There is a vertical stretch with a factor of. 5. Period:. Amplitude: 3.
A2T Trig Packet Unit 1
 A2T Trig Packet Unit 1 Name: Teacher: Pd: Table of Contents Day 1: Right Triangle Trigonometry SWBAT: Solve for missing sides and angles of right triangles Pages 1-7 HW: Pages 8 and 9 in Packet Day 2:
A2T Trig Packet Unit 1 Name: Teacher: Pd: Table of Contents Day 1: Right Triangle Trigonometry SWBAT: Solve for missing sides and angles of right triangles Pages 1-7 HW: Pages 8 and 9 in Packet Day 2:
Pre-Calculus MATH 119 Fall Section 1.1. Section objectives. Section 1.3. Section objectives. Section A.10. Section objectives
 Pre-Calculus MATH 119 Fall 2013 Learning Objectives Section 1.1 1. Use the Distance Formula 2. Use the Midpoint Formula 4. Graph Equations Using a Graphing Utility 5. Use a Graphing Utility to Create Tables
Pre-Calculus MATH 119 Fall 2013 Learning Objectives Section 1.1 1. Use the Distance Formula 2. Use the Midpoint Formula 4. Graph Equations Using a Graphing Utility 5. Use a Graphing Utility to Create Tables
CHINO VALLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE TRIGONOMETRY / PRE-CALCULUS
 CHINO VALLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE TRIGONOMETRY / PRE-CALCULUS Course Number 5121 Department Mathematics Qualification Guidelines Successful completion of both semesters of Algebra
CHINO VALLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE TRIGONOMETRY / PRE-CALCULUS Course Number 5121 Department Mathematics Qualification Guidelines Successful completion of both semesters of Algebra
Precalculus Midterm Review
 Precalculus Midterm Review Date: Time: Length of exam: 2 hours Type of questions: Multiple choice (4 choices) Number of questions: 50 Format of exam: 30 questions no calculator allowed, then 20 questions
Precalculus Midterm Review Date: Time: Length of exam: 2 hours Type of questions: Multiple choice (4 choices) Number of questions: 50 Format of exam: 30 questions no calculator allowed, then 20 questions
PRE-CALCULUS FORM IV. Textbook: Precalculus with Limits, A Graphing Approach. 4 th Edition, 2005, Larson, Hostetler & Edwards, Cengage Learning.
 PRE-CALCULUS FORM IV Tetbook: Precalculus with Limits, A Graphing Approach. 4 th Edition, 2005, Larson, Hostetler & Edwards, Cengage Learning. Course Description: This course is designed to prepare students
PRE-CALCULUS FORM IV Tetbook: Precalculus with Limits, A Graphing Approach. 4 th Edition, 2005, Larson, Hostetler & Edwards, Cengage Learning. Course Description: This course is designed to prepare students
CHAPTER 6. Section Two angles are supplementary. 2. Two angles are complementary if the sum of their measures is 90 radians
 SECTION 6-5 CHAPTER 6 Section 6. Two angles are complementary if the sum of their measures is 90 radians. Two angles are supplementary if the sum of their measures is 80 ( radians).. A central angle of
SECTION 6-5 CHAPTER 6 Section 6. Two angles are complementary if the sum of their measures is 90 radians. Two angles are supplementary if the sum of their measures is 80 ( radians).. A central angle of
ALGEBRA & TRIGONOMETRY FOR CALCULUS MATH 1340
 ALGEBRA & TRIGONOMETRY FOR CALCULUS Course Description: MATH 1340 A combined algebra and trigonometry course for science and engineering students planning to enroll in Calculus I, MATH 1950. Topics include:
ALGEBRA & TRIGONOMETRY FOR CALCULUS Course Description: MATH 1340 A combined algebra and trigonometry course for science and engineering students planning to enroll in Calculus I, MATH 1950. Topics include:
Section 6.1 Exercises
 Section 6.1 Sinusoidal Graphs 97 Section 6.1 Exercises 1. Sketch a graph of f x 3sinx 2. Sketch a graph of f x 4sinx 3. Sketch a graph of f x 2cosx 4. Sketch a graph of f x 4cosx For the graphs below,
Section 6.1 Sinusoidal Graphs 97 Section 6.1 Exercises 1. Sketch a graph of f x 3sinx 2. Sketch a graph of f x 4sinx 3. Sketch a graph of f x 2cosx 4. Sketch a graph of f x 4cosx For the graphs below,
Math 1303 Part II. The opening of one of 360 equal central angles of a circle is what we chose to represent 1 degree
 Math 1303 Part II We have discussed two ways of measuring angles; degrees and radians The opening of one of 360 equal central angles of a circle is what we chose to represent 1 degree We defined a radian
Math 1303 Part II We have discussed two ways of measuring angles; degrees and radians The opening of one of 360 equal central angles of a circle is what we chose to represent 1 degree We defined a radian
Exam Review. Completion Complete each statement. 1. The maximum value of the function is. 2. The period of the function is.
 Exam Review Completion Complete each statement. 1. The maximum value of the function is. 2. The period of the function is. 3. If and, then the domain of the function is. Matching Match each equation with
Exam Review Completion Complete each statement. 1. The maximum value of the function is. 2. The period of the function is. 3. If and, then the domain of the function is. Matching Match each equation with
SESSION 6 Trig. Equations and Identities. Math 30-1 R 3. (Revisit, Review and Revive)
 SESSION 6 Trig. Equations and Identities Math 30-1 R 3 (Revisit, Review and Revive) 1 P a g e 2 P a g e Mathematics 30-1 Learning Outcomes Specific Outcome 5: Solve, algebraically and graphically, first
SESSION 6 Trig. Equations and Identities Math 30-1 R 3 (Revisit, Review and Revive) 1 P a g e 2 P a g e Mathematics 30-1 Learning Outcomes Specific Outcome 5: Solve, algebraically and graphically, first
Precalculus PreAP/D Rev A: Simple Harmonic Motion. apply the rules of trigonometry and solve using simple harmonic motion.
 4.8A: Simple Harmonic Motion I WILL apply the rules of trigonometry and solve using simple harmonic motion. Precalculus PreAP/D I. Simple Harmonic Motion A. Simple harmonic motion is a special kind of
4.8A: Simple Harmonic Motion I WILL apply the rules of trigonometry and solve using simple harmonic motion. Precalculus PreAP/D I. Simple Harmonic Motion A. Simple harmonic motion is a special kind of
Chapter 5 The Next Wave: MORE MODELING AND TRIGONOMETRY
 ANSWERS Mathematics (Mathematical Analysis) page 1 Chapter The Next Wave: MORE MODELING AND TRIGONOMETRY NW-1. TI-8, points; Casio, points a) An infinite number of them. b) 17p, - 7p c) Add p n to p, p
ANSWERS Mathematics (Mathematical Analysis) page 1 Chapter The Next Wave: MORE MODELING AND TRIGONOMETRY NW-1. TI-8, points; Casio, points a) An infinite number of them. b) 17p, - 7p c) Add p n to p, p
Next, we ll use all of the tools we ve covered in our study of trigonometry to solve some equations.
 Section 6.3 - Solving Trigonometric Equations Next, we ll use all of the tools we ve covered in our study of trigonometry to solve some equations. These are equations from algebra: Linear Equation: Solve:
Section 6.3 - Solving Trigonometric Equations Next, we ll use all of the tools we ve covered in our study of trigonometry to solve some equations. These are equations from algebra: Linear Equation: Solve:
Pre AP Algebra. Mathematics Standards of Learning Curriculum Framework 2009: Pre AP Algebra
 Pre AP Algebra Mathematics Standards of Learning Curriculum Framework 2009: Pre AP Algebra 1 The content of the mathematics standards is intended to support the following five goals for students: becoming
Pre AP Algebra Mathematics Standards of Learning Curriculum Framework 2009: Pre AP Algebra 1 The content of the mathematics standards is intended to support the following five goals for students: becoming
Summer Review Packet for Students Entering AP Calculus BC. Complex Fractions
 Summer Review Packet for Students Entering AP Calculus BC Comple Fractions When simplifying comple fractions, multiply by a fraction equal to 1 which has a numerator and denominator composed of the common
Summer Review Packet for Students Entering AP Calculus BC Comple Fractions When simplifying comple fractions, multiply by a fraction equal to 1 which has a numerator and denominator composed of the common
DuVal High School Summer Review Packet AP Calculus
 DuVal High School Summer Review Packet AP Calculus Welcome to AP Calculus AB. This packet contains background skills you need to know for your AP Calculus. My suggestion is, you read the information and
DuVal High School Summer Review Packet AP Calculus Welcome to AP Calculus AB. This packet contains background skills you need to know for your AP Calculus. My suggestion is, you read the information and
( ) b.! = 7" 3 has coordinates 1
 Chapter 4: Circular Functions Lesson 4.. 4-. a.! b.! c. i. 0!! " radians 80! = " 6 radians 4-. a. and b. ii. iii. 45!! " radians 80! = " 4 radians 60!! " radians 80! = " radians 4-. Possible patterns that
Chapter 4: Circular Functions Lesson 4.. 4-. a.! b.! c. i. 0!! " radians 80! = " 6 radians 4-. a. and b. ii. iii. 45!! " radians 80! = " 4 radians 60!! " radians 80! = " radians 4-. Possible patterns that
1. Graph each of the given equations, state the domain and range, and specify all intercepts and symmetry. a) y 3x
 MATH 94 Final Exam Review. Graph each of the given equations, state the domain and range, and specify all intercepts and symmetry. a) y x b) y x 4 c) y x 4. Determine whether or not each of the following
MATH 94 Final Exam Review. Graph each of the given equations, state the domain and range, and specify all intercepts and symmetry. a) y x b) y x 4 c) y x 4. Determine whether or not each of the following
PHASE 1 CURRICULUM MAP M. Fellmeth Course/Subject: Honors Precalculus Grade: 11 th Teacher: M. Hart
 Month: September 1. How to describe angles using different units of measure and how to find the lengths associated with those angles. 2.3.11 A Select and use appropriate units and tools to measure to the
Month: September 1. How to describe angles using different units of measure and how to find the lengths associated with those angles. 2.3.11 A Select and use appropriate units and tools to measure to the
correlated to the Indiana Academic Standards for Precalculus CC2
 correlated to the Indiana Academic Standards for Precalculus CC2 6/2003 2003 Introduction to Advanced Mathematics 2003 by Richard G. Brown Advanced Mathematics offers comprehensive coverage of precalculus
correlated to the Indiana Academic Standards for Precalculus CC2 6/2003 2003 Introduction to Advanced Mathematics 2003 by Richard G. Brown Advanced Mathematics offers comprehensive coverage of precalculus
PreCalculus. Curriculum (447 topics additional topics)
 PreCalculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
PreCalculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
Name Date Period. Calculater Permitted MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 PreAP Precalculus Spring Final Exam Review Name Date Period Calculater Permitted MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplify the expression.
PreAP Precalculus Spring Final Exam Review Name Date Period Calculater Permitted MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplify the expression.
CK- 12 Algebra II with Trigonometry Concepts 1
 14.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine 1. A.,1 B. (, 1) C. 3,0 D. 11 1, 6 E. (, 1) F. G. H. 11, 4 7, 1 11, 3. 3. 5 9,,,,,,, 4 4 4 4 3 5 3, and, 3 3 CK- 1 Algebra II with Trigonometry Concepts 1 4.ans-1401-01 5.
14.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine 1. A.,1 B. (, 1) C. 3,0 D. 11 1, 6 E. (, 1) F. G. H. 11, 4 7, 1 11, 3. 3. 5 9,,,,,,, 4 4 4 4 3 5 3, and, 3 3 CK- 1 Algebra II with Trigonometry Concepts 1 4.ans-1401-01 5.
SANDERSON HIGH SCHOOL AP CALCULUS AB/BC SUMMER REVIEW PACKET
 SANDERSON HIGH SCHOOL AP CALCULUS AB/BC SUMMER REVIEW PACKET 017-018 Name: 1. This packet is to be handed in on Monday August 8, 017.. All work must be shown on separate paper attached to the packet. 3.
SANDERSON HIGH SCHOOL AP CALCULUS AB/BC SUMMER REVIEW PACKET 017-018 Name: 1. This packet is to be handed in on Monday August 8, 017.. All work must be shown on separate paper attached to the packet. 3.
AFM Midterm Review I Fall Determine if the relation is a function. 1,6, 2. Determine the domain of the function. . x x
 AFM Midterm Review I Fall 06. Determine if the relation is a function.,6,,, 5,. Determine the domain of the function 7 h ( ). 4. Sketch the graph of f 4. Sketch the graph of f 5. Sketch the graph of f
AFM Midterm Review I Fall 06. Determine if the relation is a function.,6,,, 5,. Determine the domain of the function 7 h ( ). 4. Sketch the graph of f 4. Sketch the graph of f 5. Sketch the graph of f
Marking Period 1 Marking Period 3. Marking Period 2 Marking Period 4
 DEPARTMENT: Mathematics COURSE: Precalculus Marking Period 1 Marking Period 3 1 Functions 19 Angles & Their Measures- Unit Circle 2 Functions 20 Angles & Their Measures- Unit Circle 3 Functions 21 Angles
DEPARTMENT: Mathematics COURSE: Precalculus Marking Period 1 Marking Period 3 1 Functions 19 Angles & Their Measures- Unit Circle 2 Functions 20 Angles & Their Measures- Unit Circle 3 Functions 21 Angles
PreCalculus. Curriculum (637 topics additional topics)
 PreCalculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
PreCalculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
HHS Pre-Calculus Reference Book
 HHS Pre-Calculus Reference Book Purpose: To create a reference book to review topics for your final exam and to prepare you for Calculus. Instructions: Students are to compose a reference book containing
HHS Pre-Calculus Reference Book Purpose: To create a reference book to review topics for your final exam and to prepare you for Calculus. Instructions: Students are to compose a reference book containing
CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW
 NAME CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW Slope of a non vertical line: rise y y y m run Point Slope Equation: y y m( ) The slope is m and a point on your line is, ). ( y Slope-Intercept Equation: y m b slope=
NAME CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW Slope of a non vertical line: rise y y y m run Point Slope Equation: y y m( ) The slope is m and a point on your line is, ). ( y Slope-Intercept Equation: y m b slope=
5.1: Angles and Radian Measure Date: Pre-Calculus
 5.1: Angles and Radian Measure Date: Pre-Calculus *Use Section 5.1 (beginning on pg. 482) to complete the following Trigonometry: measurement of triangles An angle is formed by two rays that have a common
5.1: Angles and Radian Measure Date: Pre-Calculus *Use Section 5.1 (beginning on pg. 482) to complete the following Trigonometry: measurement of triangles An angle is formed by two rays that have a common
I IV II III 4.1 RADIAN AND DEGREE MEASURES (DAY ONE) COMPLEMENTARY angles add to90 SUPPLEMENTARY angles add to 180
 4.1 RADIAN AND DEGREE MEASURES (DAY ONE) TRIGONOMETRY: the study of the relationship between the angles and sides of a triangle from the Greek word for triangle ( trigonon) (trigonon ) and measure ( metria)
4.1 RADIAN AND DEGREE MEASURES (DAY ONE) TRIGONOMETRY: the study of the relationship between the angles and sides of a triangle from the Greek word for triangle ( trigonon) (trigonon ) and measure ( metria)
Class Syllabus. Accessible Topic - Topics accessible to visually impaired students using a screen reader.
 Class Syllabus Class: MATH 1112 Spring 2019 Pilot - MWF 9:05 to 9:55 am Subject : College Algebra with Trigonometry Class Code: WQJQT-3GQW4 Inst ruct or: Ritter Class Dat es: 01/04/2019-05/10/2019 Class
Class Syllabus Class: MATH 1112 Spring 2019 Pilot - MWF 9:05 to 9:55 am Subject : College Algebra with Trigonometry Class Code: WQJQT-3GQW4 Inst ruct or: Ritter Class Dat es: 01/04/2019-05/10/2019 Class
Pre-Calculus Chapter 0. Solving Equations and Inequalities 0.1 Solving Equations with Absolute Value 0.2 Solving Quadratic Equations
 Pre-Calculus Chapter 0. Solving Equations and Inequalities 0.1 Solving Equations with Absolute Value 0.1.1 Solve Simple Equations Involving Absolute Value 0.2 Solving Quadratic Equations 0.2.1 Use the
Pre-Calculus Chapter 0. Solving Equations and Inequalities 0.1 Solving Equations with Absolute Value 0.1.1 Solve Simple Equations Involving Absolute Value 0.2 Solving Quadratic Equations 0.2.1 Use the
A-Level Mathematics TRIGONOMETRY. G. David Boswell - R2S Explore 2019
 A-Level Mathematics TRIGONOMETRY G. David Boswell - R2S Explore 2019 1. Graphs the functions sin kx, cos kx, tan kx, where k R; In these forms, the value of k determines the periodicity of the trig functions.
A-Level Mathematics TRIGONOMETRY G. David Boswell - R2S Explore 2019 1. Graphs the functions sin kx, cos kx, tan kx, where k R; In these forms, the value of k determines the periodicity of the trig functions.
Math Review. Name:
 Math 30-1 Name: Review 1. Given the graph of : Sketch the graph of the given transformation on the same grid Describe how the transformed graph relates to the graph of Write the equation of the image of
Math 30-1 Name: Review 1. Given the graph of : Sketch the graph of the given transformation on the same grid Describe how the transformed graph relates to the graph of Write the equation of the image of
The six trigonometric functions
 PRE-CALCULUS: by Finney,Demana,Watts and Kennedy Chapter 4: Trigonomic Functions 4.: Trigonomic Functions of Acute Angles What you'll Learn About Right Triangle Trigonometry/ Two Famous Triangles Evaluating
PRE-CALCULUS: by Finney,Demana,Watts and Kennedy Chapter 4: Trigonomic Functions 4.: Trigonomic Functions of Acute Angles What you'll Learn About Right Triangle Trigonometry/ Two Famous Triangles Evaluating
Catholic Central High School
 Catholic Central High School Course: Basic Algebra 2 Department: Mathematics Length: One year Credit: 1 Prerequisite: Completion of Basic Algebra 1 or Algebra 1, Basic Plane Geometry or Plane Geometry,
Catholic Central High School Course: Basic Algebra 2 Department: Mathematics Length: One year Credit: 1 Prerequisite: Completion of Basic Algebra 1 or Algebra 1, Basic Plane Geometry or Plane Geometry,
2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with a graph. f(x) = 25 x 2
 29 April PreCalculus Final Review 1. Find the slope and y-intercept (if possible) of the equation of the line. Sketch the line: y = 3x + 13 2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with
29 April PreCalculus Final Review 1. Find the slope and y-intercept (if possible) of the equation of the line. Sketch the line: y = 3x + 13 2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with
Unit 10 Prerequisites for Next Year (Calculus)
 Unit 0 Prerequisites for Net Year (Calculus) The following Study Guide is the required INDEPENDENT review for you to work through for your final unit. You WILL have a test that covers this material after
Unit 0 Prerequisites for Net Year (Calculus) The following Study Guide is the required INDEPENDENT review for you to work through for your final unit. You WILL have a test that covers this material after
PreCalculus First Semester Exam Review
 PreCalculus First Semester Eam Review Name You may turn in this eam review for % bonus on your eam if all work is shown (correctly) and answers are correct. Please show work NEATLY and bo in or circle
PreCalculus First Semester Eam Review Name You may turn in this eam review for % bonus on your eam if all work is shown (correctly) and answers are correct. Please show work NEATLY and bo in or circle
1. Evaluate the function at each specified value of the independent variable and simplify. f 2a.)
 Honors Pre-Calculus Midterm Eam Review Name: January 04 Chapter : Functions and Their Graphs. Evaluate the function at each specified value of the independent variable and simplify. f ( ) f () b. f ( )
Honors Pre-Calculus Midterm Eam Review Name: January 04 Chapter : Functions and Their Graphs. Evaluate the function at each specified value of the independent variable and simplify. f ( ) f () b. f ( )
Topic Outline for Algebra 2 & and Trigonometry One Year Program
 Topic Outline for Algebra 2 & and Trigonometry One Year Program Algebra 2 & and Trigonometry - N - Semester 1 1. Rational Expressions 17 Days A. Factoring A2.A.7 B. Rationals A2.N.3 A2.A.17 A2.A.16 A2.A.23
Topic Outline for Algebra 2 & and Trigonometry One Year Program Algebra 2 & and Trigonometry - N - Semester 1 1. Rational Expressions 17 Days A. Factoring A2.A.7 B. Rationals A2.N.3 A2.A.17 A2.A.16 A2.A.23
List of PreCalculus Algebra Mathematical Concept Practice Sheets (Updated Spring 2015)
 List of PreCalculus Algebra Mathematical Concept Practice Sheets (Updated Spring 2015) MAT 155P MAT 155 1 Absolute Value Equations P 7 P 3 2 Absolute Value Inequalities P 9 P 4 3 Algebraic Expressions:
List of PreCalculus Algebra Mathematical Concept Practice Sheets (Updated Spring 2015) MAT 155P MAT 155 1 Absolute Value Equations P 7 P 3 2 Absolute Value Inequalities P 9 P 4 3 Algebraic Expressions:
Composition of and the Transformation of Functions
 1 3 Specific Outcome Demonstrate an understanding of operations on, and compositions of, functions. Demonstrate an understanding of the effects of horizontal and vertical translations on the graphs of
1 3 Specific Outcome Demonstrate an understanding of operations on, and compositions of, functions. Demonstrate an understanding of the effects of horizontal and vertical translations on the graphs of
Trigonometric Functions. Section 1.6
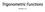 Trigonometric Functions Section 1.6 Quick Review Radian Measure The radian measure of the angle ACB at the center of the unit circle equals the length of the arc that ACB cuts from the unit circle. Radian
Trigonometric Functions Section 1.6 Quick Review Radian Measure The radian measure of the angle ACB at the center of the unit circle equals the length of the arc that ACB cuts from the unit circle. Radian
The Other Trigonometric
 The Other Trigonometric Functions By: OpenStaxCollege A wheelchair ramp that meets the standards of the Americans with Disabilities Act must make an angle with the ground whose tangent is or less, regardless
The Other Trigonometric Functions By: OpenStaxCollege A wheelchair ramp that meets the standards of the Americans with Disabilities Act must make an angle with the ground whose tangent is or less, regardless
Milford Public Schools Curriculum. Department: Mathematics Course Name: Precalculus Level 1
 Milford Public Schools Curriculum Department: Mathematics Course Name: Precalculus Level 1 UNIT 1 Unit Description: Students will construct polynomial graphs with zeros and end behavior, and apply limit
Milford Public Schools Curriculum Department: Mathematics Course Name: Precalculus Level 1 UNIT 1 Unit Description: Students will construct polynomial graphs with zeros and end behavior, and apply limit
Math Section 4.3 Unit Circle Trigonometry
 Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Dover- Sherborn High School Mathematics Curriculum Pre- Calculus CP 1
 Dover- Sherborn High School Mathematics Curriculum Pre- Calculus CP 1 A. DESCRIPTION This course is an extension of Algebra II with the emphasis in Trigonometry and introductory calculus topics. All major
Dover- Sherborn High School Mathematics Curriculum Pre- Calculus CP 1 A. DESCRIPTION This course is an extension of Algebra II with the emphasis in Trigonometry and introductory calculus topics. All major
Level 1 Advanced Mathematics Final Exam June 19, 2007
 Level Advanced Mathematics Final Exam June 9, 007 NAME: Instructions WRITE ANSWERS IN THE SPACES PROVIDED AND SHOW ALL WORK. Partial credit will not be given if work is not shown. Ask for extra paper if
Level Advanced Mathematics Final Exam June 9, 007 NAME: Instructions WRITE ANSWERS IN THE SPACES PROVIDED AND SHOW ALL WORK. Partial credit will not be given if work is not shown. Ask for extra paper if
Sophomore Year: Algebra II Textbook: Algebra II, Common Core Edition Larson, Boswell, Kanold, Stiff Holt McDougal 2012
 Sophomore Year: Algebra II Tetbook: Algebra II, Common Core Edition Larson, Boswell, Kanold, Stiff Holt McDougal 2012 Course Description: The purpose of this course is to give students a strong foundation
Sophomore Year: Algebra II Tetbook: Algebra II, Common Core Edition Larson, Boswell, Kanold, Stiff Holt McDougal 2012 Course Description: The purpose of this course is to give students a strong foundation
Monday, October 24, Trigonometry, Period 3
 Monday, Trigonometry, Period 3 Lesson Overview: Warm Up Go over homework Writing Sinusoidal Functions to Model Simple Harmonic Motion 1 Recap: The past few classes, we ve been talking about simple harmonic
Monday, Trigonometry, Period 3 Lesson Overview: Warm Up Go over homework Writing Sinusoidal Functions to Model Simple Harmonic Motion 1 Recap: The past few classes, we ve been talking about simple harmonic
n power Name: NOTES 2.5, Date: Period: Mrs. Nguyen s Initial: LESSON 2.5 MODELING VARIATION
 NOTES 2.5, 6.1 6.3 Name: Date: Period: Mrs. Nguyen s Initial: LESSON 2.5 MODELING VARIATION Direct Variation y mx b when b 0 or y mx or y kx y kx and k 0 - y varies directly as x - y is directly proportional
NOTES 2.5, 6.1 6.3 Name: Date: Period: Mrs. Nguyen s Initial: LESSON 2.5 MODELING VARIATION Direct Variation y mx b when b 0 or y mx or y kx y kx and k 0 - y varies directly as x - y is directly proportional
PRECALCULUS BISHOP KELLY HIGH SCHOOL BOISE, IDAHO. Prepared by Kristina L. Gazdik. March 2005
 PRECALCULUS BISHOP KELLY HIGH SCHOOL BOISE, IDAHO Prepared by Kristina L. Gazdik March 2005 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Course Description.3 Scope and Sequence 4 Content Outlines UNIT I: FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS
PRECALCULUS BISHOP KELLY HIGH SCHOOL BOISE, IDAHO Prepared by Kristina L. Gazdik March 2005 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Course Description.3 Scope and Sequence 4 Content Outlines UNIT I: FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS
NYS Algebra II and Trigonometry Suggested Sequence of Units (P.I's within each unit are NOT in any suggested order)
 1 of 6 UNIT P.I. 1 - INTEGERS 1 A2.A.1 Solve absolute value equations and inequalities involving linear expressions in one variable 1 A2.A.4 * Solve quadratic inequalities in one and two variables, algebraically
1 of 6 UNIT P.I. 1 - INTEGERS 1 A2.A.1 Solve absolute value equations and inequalities involving linear expressions in one variable 1 A2.A.4 * Solve quadratic inequalities in one and two variables, algebraically
1 Chapter 2 Perform arithmetic operations with polynomial expressions containing rational coefficients 2-2, 2-3, 2-4
 NYS Performance Indicators Chapter Learning Objectives Text Sections Days A.N. Perform arithmetic operations with polynomial expressions containing rational coefficients. -, -5 A.A. Solve absolute value
NYS Performance Indicators Chapter Learning Objectives Text Sections Days A.N. Perform arithmetic operations with polynomial expressions containing rational coefficients. -, -5 A.A. Solve absolute value
a) Draw the angle in standard position. b) determine an angle that is co-terminal to c) Determine the reference angle of
 1. a) Draw the angle in standard position. b) determine an angle that is co-terminal to c) Determine the reference angle of 2. Which pair of angles are co-terminal with? a., b., c., d., 3. During a routine,
1. a) Draw the angle in standard position. b) determine an angle that is co-terminal to c) Determine the reference angle of 2. Which pair of angles are co-terminal with? a., b., c., d., 3. During a routine,
Section 6.5 Modeling with Trigonometric Functions
 Section 6.5 Modeling with Trigonometric Functions 441 Section 6.5 Modeling with Trigonometric Functions Solving right triangles for angles In Section 5.5, we used trigonometry on a right triangle to solve
Section 6.5 Modeling with Trigonometric Functions 441 Section 6.5 Modeling with Trigonometric Functions Solving right triangles for angles In Section 5.5, we used trigonometry on a right triangle to solve
(c) cos Arctan ( 3) ( ) PRECALCULUS ADVANCED REVIEW FOR FINAL FIRST SEMESTER
 PRECALCULUS ADVANCED REVIEW FOR FINAL FIRST SEMESTER Work the following on notebook paper ecept for the graphs. Do not use our calculator unless the problem tells ou to use it. Give three decimal places
PRECALCULUS ADVANCED REVIEW FOR FINAL FIRST SEMESTER Work the following on notebook paper ecept for the graphs. Do not use our calculator unless the problem tells ou to use it. Give three decimal places
1.1 Angles, Degrees, and Arcs
 MA140 Trig 2015 Homework p. 1 Name: 1.1 Angles, Degrees, and Arcs Find the fraction of a counterclockwise revolution that will form an angle with the indicated number of degrees. 3(a). 45 3(b). 150 3(c).
MA140 Trig 2015 Homework p. 1 Name: 1.1 Angles, Degrees, and Arcs Find the fraction of a counterclockwise revolution that will form an angle with the indicated number of degrees. 3(a). 45 3(b). 150 3(c).
Pre-Calc Trigonometry
 Slide 1 / 207 Slide 2 / 207 Pre-Calc Trigonometry 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 207 Table of Contents Unit Circle Graphing Law of Sines Law of Cosines Pythagorean Identities Angle Sum/Difference Double
Slide 1 / 207 Slide 2 / 207 Pre-Calc Trigonometry 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 207 Table of Contents Unit Circle Graphing Law of Sines Law of Cosines Pythagorean Identities Angle Sum/Difference Double
Pre-calculus 12 Curriculum Outcomes Framework (110 hours)
 Curriculum Outcomes Framework (110 hours) Trigonometry (T) (35 40 hours) General Curriculum Outcome: Students will be expected to develop trigonometric reasoning. T01 Students will be expected to T01.01
Curriculum Outcomes Framework (110 hours) Trigonometry (T) (35 40 hours) General Curriculum Outcome: Students will be expected to develop trigonometric reasoning. T01 Students will be expected to T01.01
Pre-Calculus and Trigonometry Capacity Matrix
 Review Polynomials A1.1.4 A1.2.5 Add, subtract, multiply and simplify polynomials and rational expressions Solve polynomial equations and equations involving rational expressions Review Chapter 1 and their
Review Polynomials A1.1.4 A1.2.5 Add, subtract, multiply and simplify polynomials and rational expressions Solve polynomial equations and equations involving rational expressions Review Chapter 1 and their
Mth 133 Trigonometry Review Problems for the Final Examination
 Mth 1 Trigonometry Review Problems for the Final Examination Thomas W. Judson Stephen F. Austin State University Fall 017 Final Exam Details The final exam for MTH 1 will is comprehensive and will cover
Mth 1 Trigonometry Review Problems for the Final Examination Thomas W. Judson Stephen F. Austin State University Fall 017 Final Exam Details The final exam for MTH 1 will is comprehensive and will cover
One of the powerful themes in trigonometry is that the entire subject emanates from a very simple idea: locating a point on the unit circle.
 2.24 Tanz and the Reciprocals Derivatives of Other Trigonometric Functions One of the powerful themes in trigonometry is that the entire subject emanates from a very simple idea: locating a point on the
2.24 Tanz and the Reciprocals Derivatives of Other Trigonometric Functions One of the powerful themes in trigonometry is that the entire subject emanates from a very simple idea: locating a point on the
Algebra II Learning Targets
 Chapter 0 Preparing for Advanced Algebra LT 0.1 Representing Functions Identify the domain and range of functions LT 0.2 FOIL Use the FOIL method to multiply binomials LT 0.3 Factoring Polynomials Use
Chapter 0 Preparing for Advanced Algebra LT 0.1 Representing Functions Identify the domain and range of functions LT 0.2 FOIL Use the FOIL method to multiply binomials LT 0.3 Factoring Polynomials Use
Prentice Hall: Algebra 2 with Trigonometry 2006 Correlated to: California Mathematics Content Standards for Trigonometry (Grades 9-12)
 California Mathematics Content Standards for Trigonometry (Grades 9-12) Trigonometry uses the techniques that students have previously learned from the study of algebra and geometry. The trigonometric
California Mathematics Content Standards for Trigonometry (Grades 9-12) Trigonometry uses the techniques that students have previously learned from the study of algebra and geometry. The trigonometric
Precalculus Table of Contents Unit 1 : Algebra Review Lesson 1: (For worksheet #1) Factoring Review Factoring Using the Distributive Laws Factoring
 Unit 1 : Algebra Review Factoring Review Factoring Using the Distributive Laws Factoring Trinomials Factoring the Difference of Two Squares Factoring Perfect Square Trinomials Factoring the Sum and Difference
Unit 1 : Algebra Review Factoring Review Factoring Using the Distributive Laws Factoring Trinomials Factoring the Difference of Two Squares Factoring Perfect Square Trinomials Factoring the Sum and Difference
Sketch a possible graph of a polynomial function with the given zeros. (lesson 6-1, 6-7)
 NAME DATE PERIOD REVIEW: End of Course Final algebra 2 Find the slope and y-intercept of each function described below. (lesson 2-3, 2-4) y = 1 2 x 3 y = 4x + 1 1 2 3 x y 4 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 5 4x 2y = 10
NAME DATE PERIOD REVIEW: End of Course Final algebra 2 Find the slope and y-intercept of each function described below. (lesson 2-3, 2-4) y = 1 2 x 3 y = 4x + 1 1 2 3 x y 4 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 5 4x 2y = 10
As we know, the three basic trigonometric functions are as follows: Figure 1
 Trigonometry Basic Functions As we know, the three basic trigonometric functions are as follows: sin θ = cos θ = opposite hypotenuse adjacent hypotenuse tan θ = opposite adjacent Where θ represents an
Trigonometry Basic Functions As we know, the three basic trigonometric functions are as follows: sin θ = cos θ = opposite hypotenuse adjacent hypotenuse tan θ = opposite adjacent Where θ represents an
Indiana Academic Standards for Precalculus
 PRECALCULUS correlated to the Indiana Academic Standards for Precalculus CC2 6/2003 2004 Introduction to Precalculus 2004 by Roland E. Larson and Robert P. Hostetler Precalculus thoroughly explores topics
PRECALCULUS correlated to the Indiana Academic Standards for Precalculus CC2 6/2003 2004 Introduction to Precalculus 2004 by Roland E. Larson and Robert P. Hostetler Precalculus thoroughly explores topics
Honors Accelerated Pre-Calculus Midterm Exam Review Name: January 2010 Chapter 1: Functions and Their Graphs
 Honors Accelerated Pre-Calculus Midterm Eam Review Name: January 010 Chapter 1: Functions and Their Graphs 1. Evaluate the function at each specified value of the independent variable and simplify. 1 f
Honors Accelerated Pre-Calculus Midterm Eam Review Name: January 010 Chapter 1: Functions and Their Graphs 1. Evaluate the function at each specified value of the independent variable and simplify. 1 f
Benchmark Computation The student models, performs, and explains computation with complex numbers and polynomials in a variety of situations.
 Standard Number and Computation The student uses numerical and computational concepts and procedures in a variety of situations. Indicator/Objective Critical Vocabulary Knowledge Indicators The student
Standard Number and Computation The student uses numerical and computational concepts and procedures in a variety of situations. Indicator/Objective Critical Vocabulary Knowledge Indicators The student
