One Dimensional Motion (Motion in a Straight Line)
|
|
|
- Annabella Little
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 One Dimensional Motion (Motion in a Straight Line) Chapter MOTION QUANTITIES 1
2 Kinematics - Intro Mechanics generally consists of two parts: Kinematics and Dynamics. Mechanics Kinematics Description of Motion Dynamics Cause of Motion Vectors and Scalars Some quantities that we measure have only a magnitude (or size). We call these quantities scalars. Some quantities that we measure have both magnitude and direction. We call these quantities vectors.
3 Vectors and Scalars We designate that a quantity is a vector by drawing an arrow hat over the variable that represents that quantity. Below are some examples: Velocity = v Acceleration = a Force = F Note: Because it is often difficult to place arrows over text, I will often use a BOLDED variable to signify a vector Position and Displacement Position is defined as the location of an object relative to some assigned origin or point of reference. Variable: x or y Units: m (meters) 3
4 Position and Displacement An easy way to represent position in one dimension is to use a number line, as shown below. The origin or point of reference is designated by the X (meters) Sample 1 Below you see two objects A and B. a) What are their positions, relative to the origin? b) Does it make sense to say that B is at a greater position than A? Explain. A - + B X (meters) 4
5 Position and Displacement Displacement is defined as the change in position. Variable: Dx Equation: Dx = x f x Distance is the scalar counterpart to displacement. It tells use how far an object has moved. Sample a) If an object moves from point A to point B, what is its displacement? b) If an object moves from point B to point A, what is its displacement? A B X (meters)
6 Sample 3 An object moves from point B to point A and then to point C. a) What is the total distance that it traveled? b) What is the total displacement of the object? A C X (meters) B Checkpoint 1 Here are three pairs of initial and final positions, respectively, along an x axis. Which pairs give a negative displacement? a) -3 m, + m b) -3 m, -7 m c) 7 m, -3 m 6
7 v Velocity ( ) is defined as the rate of change of position. A rate is how fast something changes over time. In the case of velocity, it is the position that changes. Mathematically, we can write this as: Dx x f x x f x v Dt t t t This equation states that the velocity is defined as the change in position divided by the time interval or change in time. Units: m/s Velocity and Speed f Velocity and Speed Speed (v or s) is the scalar counterpart to velocity Speed is defined mathematically as: v d t x t Speed is a scalar and, like distance, has no direction and cannot be negative. 7
8 Average, Instantaneous and Uniform We can characterize velocity in different ways, depending on how it is measured. Average velocity (which you are most familiar with) is defined as the change in position over the change in time over a long time. v avg = Dx Dt where Dt is a long time. Average, Instantaneous and Uniform In contrast, we can define an instantaneous velocity as a velocity at an instant. Mathematically, we would write this as: Dx dx vinst lim Dt Dt dt This means that the instantaneous velocity is just the average velocity as the time interval (Dt) approaches zero, i.e. at an instant. Instantaneous velocity is the derivative of position. Note: when we just say velocity we typically mean instantaneous velocity. 8
9 Sample 4 The position of a particle moving an an x axis is given by x = t -.1t 3, with x in meters and t in seconds. a) What is its velocity at t = 3. s? b) Is the velocity constant, or is it continuously changing? Sample You leave your house and drive a beat-up pickup truck along a straight road for 8.4 km at 7 km/h, at which point the truck runs out of gasoline and stops. Over the next 3 minutes, you walk another. km farther along the road to a gas station. a) What is your overall displacement from the beginning of your drive to your arrival at the station? b) What is the time interval Δt from the beginning of your drive to your arrival at the station? c) What is your average velocity from the beginning of your drive to your arrival at the station? Find it both numerically and graphically. d) Suppose that to pump the gasoline, pay for it, and walk back to the truck takes you another 4 minutes. What is your average speed from the beginning of your drive to your return to the truck with the gasoline? 9
10 Checkpoint In Sample, suppose that right after refueling the truck, exasperated, you drive back to your house. What is your velocity for your entire trip? Checkpoint 3 The following equations give the position x(t) of a particle in four situations (in each equation, x is in meters, t is in seconds, and t > ): 1) x = 3t - ) x = -4t 3) x = /t 4) x = - a) In which situation is the velocity v of the particle constant? b) In which is v in the negative x direction? 1
11 Acceleration Acceleration ( a ) is defined as the rate of change of velocity. In other words, acceleration is how fast the velocity changes. Mathematically, the definition of acceleration is Dv Dt a avg = = v f t f - - v i = t i v f - t v i Units: m/s Acceleration Instantaneous acceleration is defined as the derivative of velocity or the second derivative of position. a lim Dt Dv Dt dv dt d dt dx dt d x dt 11
12 An Acceleration s Sign In common language, the sign of an acceleration has a non-scientific meaning: positive acceleration means that the speed of an object is increasing, and negative acceleration means that the speed is decreasing (the object is decelerating ). However in physics, the sign of the acceleration indicates a direction, not whether an object s speed is increasing or decreasing. The proper way to interpret the signs: If the signs of the velocity and acceleration or a particle are the same, the speed of the particle increases. If the signs are opposite, the speed decreases. Checkpoint 4 A wombat moves along an x axis. What is the sign of its acceleration if it is moving a) in the positive direction with increasing speed b) in the positive direction with decreasing speed c) in the negative direction with increasing speed d) in the negative direction with decreasing speed 1
13 Sample 6 A particle s position on the x axis is given by x = 4 7t + t 3, with x in meters and t in seconds. a) Find the particles velocity function v(t) and acceleration function a(t). b) Is there ever a time when v =? c) Describe the particle s motion for t. GRAPHING MOTION QUANTITIES 13
14 Graphing Motion Quantities You should be able to sketch graphs of any of the three motion quantities given a plot of any of the other quantities. Derivatives [i.e. x(t) v(t)] Use slope Integrals [i.e. v(t) x(t)] Use area Graphing Velocity Graphically, the velocity at any point is the slope of the curve of x(t) at that point. X (m) 4 3 v (m/s) m = 1 m/s 1 v = 1 m/s t (s) t (s) 14
15 Sample 7 The graph below shows an x(t) plot for an elevator cab that is initially stationary, then moves upward (which we take to be the positive direction of x), and then stops. Plot v(t). Graphing Acceleration Graphically, the acceleration at any point is the slope of the curve of v(t) at that point. X (m) V (m/s) v = 1 m/s a (m/s ) t (s) t (s)
16 Sample 8 For the scenario described in Sample 7, plot a(t). Sample 9 Given the position function below, sketch a graph of the velocity function. X (m) v (m/s) t (s) t (s) 16
17 Sample 1 Given the velocity function below, sketch a graph of the position function. x (m) v (m/s) t (s) t (s) Sample 11 In one test to study neck injury in rear-end collisions, a volunteer was strapped to a seat that was then moved abruptly to simulate a collision by a rear car moving at 1. km/h. The figure on the next slide gives the accelerations of the volunteer s torso and head during the collision, which began at time t =. The torso acceleration was delayed by 4 ms because during that time interval the seat back had to compress against the volunteer. The head acceleration was delayed by an additional 7 ms. What was the torso speed when the head began to accelerate? 17
18 Graphing Uniform Acceleration What do you think a graph of uniform acceleration would look like on an acceleration vs. time graph? Assume the acceleration is a constant m/s. Then complete the velocity and position graphs. X (m) V (m/s) a (m/s ) t (s) t (s) t (s) 18
19 A Special Case CONSTANT ACCELERATION Derivations of Equations for Constant Accelerated Motion 19
20 Equations for Motion with Constant Acceleration Equation Missing Quantity v = v + at x x x x = v t + ½at v v = v + a(x - x ) x x = ½(v v)t t a x x v *Note: You may only use these equations when ACCELERATION IS CONSTANT Checkpoint The following equations give the position x(t) of a particle in four situations: 1) x = 3t -4 ) x = -t 3 + 4t + 6 3) x = /t 4) x = t 3 To which of these situations do the constant accelerated motion equations apply?
21 Sample 1 Spotting a police car, you brake a Porsche from a speed of 1 km/h to a speed of 8. km/h during a displacement of 88. m, at a constant acceleration. a) What is that acceleration? b) How much time is required for the given decrease in speed? FREE-FALL 1
22 Free-Fall Acceleration If the effects of air are eliminated, all objects accelerate downwards at a certain constant rate known and the free-fall acceleration. The magnitude of free-fall acceleration is represented by g and has a value of 9.8 m/s. The constant accelerated motion equations apply to objects in free-fall. Sample 13 On September 6, 1993, Dave Munday went over the Canadian edge of Niagara Falls in a steel ball equipped with an air hole and then fell 48 m to the water (and rocks). Assume his initial velocity was zero, and neglect the effect of the air on the ball during the fall. a) How long did Munday fall to reach the water surface? b) Munday could count off the three seconds of free fall but could not see how far he had fallen with each count. Determine his position at each full second. c) What was Munday s velocity as he reached the water surface? d) What was Munday s velocity at each count of one full second?
23 Sample 14 In the provided figure, a pitcher tosses a baseball up along a y axis, with an initial speed of 1 m/s. a) How long does the ball take to reach its maximum height? b) What is the ball s maximum height above its release point? c) How long does the ball take to reach a point. m above its release point? Checkpoint 6 In sample 13: a) What is the sign of the ball s displacement for the ascent, from the release point to the highest point? b) What is it for the descent, from the highest point back to the release point? c) What is the ball s acceleration at its highest point? 3
Chapter 2. Motion along a Straight Line
 Chapter 2 Motion along a Straight Line 1 2.1 Motion Everything in the universe, from atoms to galaxies, is in motion. A first step to study motion is to consider simplified cases. In this chapter we study
Chapter 2 Motion along a Straight Line 1 2.1 Motion Everything in the universe, from atoms to galaxies, is in motion. A first step to study motion is to consider simplified cases. In this chapter we study
Motion Along a Straight Line
 C H A P T E R 2 Motion Along a Straight Line 2- POSITION, DISPLACEMENT, AND AVERAGE VELOCITY Learning Objectives After reading this module, you should be able to 2. Identify that if all parts of an object
C H A P T E R 2 Motion Along a Straight Line 2- POSITION, DISPLACEMENT, AND AVERAGE VELOCITY Learning Objectives After reading this module, you should be able to 2. Identify that if all parts of an object
Chapter 2: Motion a Straight Line
 Formula Memorization: Displacement What is a vector? Average Velocity Average Speed Instanteous Velocity Average Acceleration Instantaneous Acceleration Constant Acceleration Equation (List all five of
Formula Memorization: Displacement What is a vector? Average Velocity Average Speed Instanteous Velocity Average Acceleration Instantaneous Acceleration Constant Acceleration Equation (List all five of
BELL RINGER: Define Displacement. Define Velocity. Define Speed. Define Acceleration. Give an example of constant acceleration.
 BELL RINGER: Define Displacement. Define Velocity. Define Speed. Define Acceleration. Give an example of constant acceleration. What does the below equation tell us? v = d t NOTES 2.1: ONE-DIMENSIONAL
BELL RINGER: Define Displacement. Define Velocity. Define Speed. Define Acceleration. Give an example of constant acceleration. What does the below equation tell us? v = d t NOTES 2.1: ONE-DIMENSIONAL
Chapter 2: Motion along a straight line
 Chapter 2: Motion along a straight line This chapter uses the definitions of length and time to study the motions of particles in space. This task is at the core of physics and applies to all objects irregardless
Chapter 2: Motion along a straight line This chapter uses the definitions of length and time to study the motions of particles in space. This task is at the core of physics and applies to all objects irregardless
DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION. AP Physics Section 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement
 DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION AP Physics Section 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement Model the velocity of the ball from the time it leaves my hand till the time it hits the ground?
DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION AP Physics Section 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement Model the velocity of the ball from the time it leaves my hand till the time it hits the ground?
DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION. AP Physics Section 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement
 DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION AP Physics Section 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement Model the velocity of the ball from the time it leaves my hand till the time it hits the ground?
DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION AP Physics Section 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement Model the velocity of the ball from the time it leaves my hand till the time it hits the ground?
Chapter 2. Motion along a straight line
 Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line Introduction: Study of the motion of objects Physics studies: Properties of matter and energy: solid state physics, thermal physics/ thermodynamics, atomic physics,
Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line Introduction: Study of the motion of objects Physics studies: Properties of matter and energy: solid state physics, thermal physics/ thermodynamics, atomic physics,
Motion Along a Straight Line
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER Motion Along a Straight Line Position & displacement Average & instantaneous velocity Average & instantaneous acceleration Constant acceleration Free fall Graphical
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER Motion Along a Straight Line Position & displacement Average & instantaneous velocity Average & instantaneous acceleration Constant acceleration Free fall Graphical
acceleration versus time. LO Determine a particle s change in position by graphical integration on a graph of velocity versus time.
 Chapter: Chapter 2 Learning Objectives LO 2.1.0 Solve problems related to position, displacement, and average velocity to solve problems. LO 2.1.1 Identify that if all parts of an object move in the same
Chapter: Chapter 2 Learning Objectives LO 2.1.0 Solve problems related to position, displacement, and average velocity to solve problems. LO 2.1.1 Identify that if all parts of an object move in the same
HRW 7e Chapter 2 Page 1 of 13
 HRW 7e Chapter Page of 3 Halliday/Resnick/Walker 7e Chapter. Huber s speed is v 0 =(00 m)/(6.509 s)=30.7 m/s = 0.6 km/h, where we have used the conversion factor m/s = 3.6 km/h. Since Whittingham beat
HRW 7e Chapter Page of 3 Halliday/Resnick/Walker 7e Chapter. Huber s speed is v 0 =(00 m)/(6.509 s)=30.7 m/s = 0.6 km/h, where we have used the conversion factor m/s = 3.6 km/h. Since Whittingham beat
Motion along a straight line. Physics 11a. 4 Basic Quantities in Kinematics. Motion
 Physics 11a Motion along a straight line Motion Position and Average velocity and average speed Instantaneous velocity and speed Acceleration Constant acceleration: A special case Free fall acceleration
Physics 11a Motion along a straight line Motion Position and Average velocity and average speed Instantaneous velocity and speed Acceleration Constant acceleration: A special case Free fall acceleration
Forces and Motion in One Dimension. Chapter 3
 Forces and Motion in One Dimension Chapter 3 Constant velocity on an x-versus-t graph Velocity and Position In general, the average velocity is the slope of the line segment that connects the positions
Forces and Motion in One Dimension Chapter 3 Constant velocity on an x-versus-t graph Velocity and Position In general, the average velocity is the slope of the line segment that connects the positions
What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction
 What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction We frequently use vectors when solving problems in Physics Example: Change in position (displacement) Velocity
What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction We frequently use vectors when solving problems in Physics Example: Change in position (displacement) Velocity
Motion Along a Straight Line (Motion in One-Dimension)
 Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line (Motion in One-Dimension) Learn the concepts of displacement, velocity, and acceleration in one-dimension. Describe motions at constant acceleration. Be able to graph
Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line (Motion in One-Dimension) Learn the concepts of displacement, velocity, and acceleration in one-dimension. Describe motions at constant acceleration. Be able to graph
1.1 Graphing Motion. IB Physics 11 Kinematics
 IB Physics 11 Kinematics 1.1 Graphing Motion Kinematics is the study of motion without reference to forces and masses. We will need to learn some definitions: A Scalar quantity is a measurement that has
IB Physics 11 Kinematics 1.1 Graphing Motion Kinematics is the study of motion without reference to forces and masses. We will need to learn some definitions: A Scalar quantity is a measurement that has
Chapter 2: 1D Kinematics
 Chapter 2: 1D Kinematics Description of motion involves the relationship between position, displacement, velocity, and acceleration. A fundamental goal of 1D kinematics is to determine x(t) if given initial
Chapter 2: 1D Kinematics Description of motion involves the relationship between position, displacement, velocity, and acceleration. A fundamental goal of 1D kinematics is to determine x(t) if given initial
Physics 101 Lecture 3 Motion in 1D Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN
 Physics 101 Lecture 3 Motion in 1D Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department Motion along a straight line q Motion q Position and displacement q Average velocity and average speed q Instantaneous velocity and
Physics 101 Lecture 3 Motion in 1D Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department Motion along a straight line q Motion q Position and displacement q Average velocity and average speed q Instantaneous velocity and
12/06/2010. Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension. 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement. 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement
 Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement Any measurement of position, distance, or speed must be made with respect to a reference frame. For example,
Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement Any measurement of position, distance, or speed must be made with respect to a reference frame. For example,
2/18/2019. Position-versus-Time Graphs. Below is a motion diagram, made at 1 frame per minute, of a student walking to school.
 Position-versus-Time Graphs Below is a motion diagram, made at 1 frame per minute, of a student walking to school. A motion diagram is one way to represent the student s motion. Another way is to make
Position-versus-Time Graphs Below is a motion diagram, made at 1 frame per minute, of a student walking to school. A motion diagram is one way to represent the student s motion. Another way is to make
Chapter 2: 1-D Kinematics. Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University
 Chapter 2: 1-D Kinematics Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Displacement Levels of Formalism The Cartesian axis One dimension: the number line Mathematical definition of displacement: Δx = x f
Chapter 2: 1-D Kinematics Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Displacement Levels of Formalism The Cartesian axis One dimension: the number line Mathematical definition of displacement: Δx = x f
Chapter 2: 1-D Kinematics
 Chapter : 1-D Kinematics Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Displacement Levels of Formalism The Cartesian axis One dimension: the number line Mathematical definition of displacement: Δx = x f x
Chapter : 1-D Kinematics Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Displacement Levels of Formalism The Cartesian axis One dimension: the number line Mathematical definition of displacement: Δx = x f x
2.2 Average vs. Instantaneous Description
 2 KINEMATICS 2.2 Average vs. Instantaneous Description Name: 2.2 Average vs. Instantaneous Description 2.2.1 Average vs. Instantaneous Velocity In the previous activity, you figured out that you can calculate
2 KINEMATICS 2.2 Average vs. Instantaneous Description Name: 2.2 Average vs. Instantaneous Description 2.2.1 Average vs. Instantaneous Velocity In the previous activity, you figured out that you can calculate
Chapter 2. Motion in One Dimension. Professor Wa el Salah
 Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Kinematics Describes motion while ignoring the external agents that might have caused or modified the motion For now, will consider motion in one dimension Along a straight
Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Kinematics Describes motion while ignoring the external agents that might have caused or modified the motion For now, will consider motion in one dimension Along a straight
Calculating Acceleration
 Calculating Acceleration Textbook pages 392 405 Before You Read Section 9. 2 Summary How do you think a velocity-time graph might differ from the position-time graph you learned about in the previous chapter?
Calculating Acceleration Textbook pages 392 405 Before You Read Section 9. 2 Summary How do you think a velocity-time graph might differ from the position-time graph you learned about in the previous chapter?
Position-versus-Time Graphs
 Position-versus-Time Graphs Below is a motion diagram, made at 1 frame per minute, of a student walking to school. A motion diagram is one way to represent the student s motion. Another way is to make
Position-versus-Time Graphs Below is a motion diagram, made at 1 frame per minute, of a student walking to school. A motion diagram is one way to represent the student s motion. Another way is to make
Chapter 2. Motion along a straight line
 Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line 2.2 Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Examples: The Earth orbits around the Sun A roadway moves with Earth s
Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line 2.2 Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Examples: The Earth orbits around the Sun A roadway moves with Earth s
Chapter 3. Motion in One Dimension
 Chapter 3 Motion in One Dimension Outline 3.1 Position, Velocity and Speed 3.2 Instantaneous Velocity and Speed 3.3 Acceleration 3.4 Motion Diagrams 3.5 One-Dimensional Motion with Constant Acceleration
Chapter 3 Motion in One Dimension Outline 3.1 Position, Velocity and Speed 3.2 Instantaneous Velocity and Speed 3.3 Acceleration 3.4 Motion Diagrams 3.5 One-Dimensional Motion with Constant Acceleration
Kinematics and One Dimensional Motion
 Kinematics and One Dimensional Motion Kinematics Vocabulary Kinema means movement Mathematical description of motion Position Time Interval Displacement Velocity; absolute value: speed Acceleration Averages
Kinematics and One Dimensional Motion Kinematics Vocabulary Kinema means movement Mathematical description of motion Position Time Interval Displacement Velocity; absolute value: speed Acceleration Averages
Lecture 2. 1D motion with Constant Acceleration. Vertical Motion.
 Lecture 2 1D motion with Constant Acceleration. Vertical Motion. Types of motion Trajectory is the line drawn to track the position of an abject in coordinates space (no time axis). y 1D motion: Trajectory
Lecture 2 1D motion with Constant Acceleration. Vertical Motion. Types of motion Trajectory is the line drawn to track the position of an abject in coordinates space (no time axis). y 1D motion: Trajectory
Lecture 2. 1D motion with Constant Acceleration. Vertical Motion.
 Lecture 2 1D motion with Constant Acceleration. Vertical Motion. Types of motion Trajectory is the line drawn to track the position of an abject in coordinates space (no time axis). y 1D motion: Trajectory
Lecture 2 1D motion with Constant Acceleration. Vertical Motion. Types of motion Trajectory is the line drawn to track the position of an abject in coordinates space (no time axis). y 1D motion: Trajectory
State the condition under which the distance covered and displacement of moving object will have the same magnitude.
 Exercise CBSE-Class IX Science Motion General Instructions: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Question no. 1-15 are very short answer questions. These are required to be answered in one sentence each. Questions no.
Exercise CBSE-Class IX Science Motion General Instructions: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Question no. 1-15 are very short answer questions. These are required to be answered in one sentence each. Questions no.
CHAPTER 2 LINEAR MOTION
 0 CHAPTER LINEAR MOTION HAPTER LINEAR MOTION 1 Motion o an object is the continuous change in the position o that object. In this chapter we shall consider the motion o a particle in a straight line, which
0 CHAPTER LINEAR MOTION HAPTER LINEAR MOTION 1 Motion o an object is the continuous change in the position o that object. In this chapter we shall consider the motion o a particle in a straight line, which
Chapter 8 : Motion. KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ]
![Chapter 8 : Motion. KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ] Chapter 8 : Motion. KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ]](/thumbs/77/76428187.jpg) Chapter 8 : Motion KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ] 1 Motion **** 2 Graphical Representation of Motion *** & Graphs 3 Equation of motion **** 4 Uniform Circular Motion ** 1 Motion
Chapter 8 : Motion KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ] 1 Motion **** 2 Graphical Representation of Motion *** & Graphs 3 Equation of motion **** 4 Uniform Circular Motion ** 1 Motion
QuickCheck. A cart slows down while moving away from the origin. What do the position and velocity graphs look like? Slide 2-65
 QuickCheck A cart slows down while moving away from the origin. What do the position and velocity graphs look like? Slide 2-65 QuickCheck A cart speeds up toward the origin. What do the position and velocity
QuickCheck A cart slows down while moving away from the origin. What do the position and velocity graphs look like? Slide 2-65 QuickCheck A cart speeds up toward the origin. What do the position and velocity
Chapter 2. Motion in One Dimension
 Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Types of Motion Translational An example is a car traveling on a highway. Rotational An example is the Earth s spin on its axis. Vibrational An example is the back-and-forth
Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Types of Motion Translational An example is a car traveling on a highway. Rotational An example is the Earth s spin on its axis. Vibrational An example is the back-and-forth
Physics I Exam 1 Spring 2015 (version A)
 95.141 Physics I Exam 1 Spring 015 (version A) Section Number Section instructor Last/First Name (PRINT) / Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Answer all questions, beginning each new question in the space
95.141 Physics I Exam 1 Spring 015 (version A) Section Number Section instructor Last/First Name (PRINT) / Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Answer all questions, beginning each new question in the space
Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics Units of Chapter 2 Position, Distance, and Displacement Average Speed and Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Applications
Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics Units of Chapter 2 Position, Distance, and Displacement Average Speed and Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Applications
Introduction to Kinematics. Motion, Forces and Energy
 Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False Answer: B Var: 1
 University Physics, 13e (Young/Freedman) Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line 2.1 Conceptual Questions 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
University Physics, 13e (Young/Freedman) Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line 2.1 Conceptual Questions 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
1. The speed (assumed constant) is (90 km/h)(1000 m/km) (3600 s/h) = 25 m/s. Thus, during 0.50 s, the car travels (0.50)(25) 13 m.
 . The speed (assumed constant) is (90 km/h)(000 m/km) (3600 s/h) = 5 m/s. Thus, during 0.50 s, the car travels (0.50)(5) 3 m. . Huber s speed is v 0 =(00 m)/(6.509 s)=30.7 m/s = 0.6 km/h, where we have
. The speed (assumed constant) is (90 km/h)(000 m/km) (3600 s/h) = 5 m/s. Thus, during 0.50 s, the car travels (0.50)(5) 3 m. . Huber s speed is v 0 =(00 m)/(6.509 s)=30.7 m/s = 0.6 km/h, where we have
Motion Unit Review 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a
 Motion Unit Review 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a A motion sensor.b low- g accelerometer. C potential difference
Motion Unit Review 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a A motion sensor.b low- g accelerometer. C potential difference
1.1 Motion and Motion Graphs
 Figure 1 A highway is a good example of the physics of motion in action. kinematics the study of motion without considering the forces that produce the motion dynamics the study of the causes of motion
Figure 1 A highway is a good example of the physics of motion in action. kinematics the study of motion without considering the forces that produce the motion dynamics the study of the causes of motion
Kinematics II Mathematical Analysis of Motion
 AP Physics Kinematics II Mathematical Analysis of Motion Introduction: Everything in the universe is in a state of motion. It might seem impossible to find a simple way to describe and understand the motion
AP Physics Kinematics II Mathematical Analysis of Motion Introduction: Everything in the universe is in a state of motion. It might seem impossible to find a simple way to describe and understand the motion
Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension:
 Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension: Vector / Scaler Quantities Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration Graphing Motion Distance vs Time Graphs Velocity vs Time Graphs Solving Problems Free Falling Objects
Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension: Vector / Scaler Quantities Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration Graphing Motion Distance vs Time Graphs Velocity vs Time Graphs Solving Problems Free Falling Objects
2 Representing Motion 4 How Fast? MAINIDEA Write the Main Idea for this section.
 2 Representing Motion 4 How Fast? MAINIDEA Write the Main Idea for this section. REVIEW VOCABULARY absolute value Recall and write the definition of the Review Vocabulary term. absolute value NEW VOCABULARY
2 Representing Motion 4 How Fast? MAINIDEA Write the Main Idea for this section. REVIEW VOCABULARY absolute value Recall and write the definition of the Review Vocabulary term. absolute value NEW VOCABULARY
Jan 31 8:19 PM. Chapter 9: Uniform Rectilinear Motion
 Unit 3: Kinematics Uniform Rectilinear Motion (velocity is constant) Uniform Accelerated Rectilinear Motion The Motion of Projectiles Jan 31 8:19 PM Chapter 9: Uniform Rectilinear Motion Position: point
Unit 3: Kinematics Uniform Rectilinear Motion (velocity is constant) Uniform Accelerated Rectilinear Motion The Motion of Projectiles Jan 31 8:19 PM Chapter 9: Uniform Rectilinear Motion Position: point
PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension
 PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension August 13, 2012 www.njctl.org 1 Motion in One Dimension Return to Table of Contents 2 Distance We all know what the distance between two objects is... So what is it?
PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension August 13, 2012 www.njctl.org 1 Motion in One Dimension Return to Table of Contents 2 Distance We all know what the distance between two objects is... So what is it?
Chapter 2. Motion along a straight line
 Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line 2.2 Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Examples: The Earth orbits around the Sun A roadway moves with Earth s
Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line 2.2 Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Examples: The Earth orbits around the Sun A roadway moves with Earth s
PH Exam 1. Name
 PH105-007 Exam 1 Name 1) The figure shows the graph of the position x as a function of time for an object moving in the straight line (the x-axis). Which of the following graphs best describes the velocity
PH105-007 Exam 1 Name 1) The figure shows the graph of the position x as a function of time for an object moving in the straight line (the x-axis). Which of the following graphs best describes the velocity
Unit 1 Test Review Physics Basics, Movement, and Vectors Chapters 2-3
 A.P. Physics B Unit 1 Test Review Physics Basics, Movement, and Vectors Chapters - 3 * In studying for your test, make sure to study this review sheet along with your quizzes and homework assignments.
A.P. Physics B Unit 1 Test Review Physics Basics, Movement, and Vectors Chapters - 3 * In studying for your test, make sure to study this review sheet along with your quizzes and homework assignments.
Chapter 2. Motion along a straight line
 Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line 2.2 Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Specifically, the description of motion. Examples: The Earth orbits around
Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line 2.2 Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Specifically, the description of motion. Examples: The Earth orbits around
Physics 30S Unit 2 Motion Graphs. Mrs. Kornelsen Teulon Collegiate Institute
 Physics 30S Unit 2 Motion Graphs Mrs. Kornelsen Teulon Collegiate Institute 1 Grade 11 Physics Graphing Properties Property d-t Graph v-t Graph a-t Graph Not Moving Does Not Apply Constant Velocity Change
Physics 30S Unit 2 Motion Graphs Mrs. Kornelsen Teulon Collegiate Institute 1 Grade 11 Physics Graphing Properties Property d-t Graph v-t Graph a-t Graph Not Moving Does Not Apply Constant Velocity Change
Chapter 2 Solutions. = 16.1 m/s. = 11.5 m/s m. 180 km = ( ) h. = 2.5 m/s. = 3.3 m/s
 Chapter Solutions *.1 (a) v.30 m/s v x 57.5 m 9.0 m 3.00 s 16.1 m/s (c) v x 57.5 m 0 m 5.00 s 11.5 m/s. (a) Displacement (8.50 10 4 m/h) 35.0 60.0 h + 130 103 m x (49.6 + 130) 10 3 m 180 km Average velocity
Chapter Solutions *.1 (a) v.30 m/s v x 57.5 m 9.0 m 3.00 s 16.1 m/s (c) v x 57.5 m 0 m 5.00 s 11.5 m/s. (a) Displacement (8.50 10 4 m/h) 35.0 60.0 h + 130 103 m x (49.6 + 130) 10 3 m 180 km Average velocity
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 2 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th Edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 2 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th Edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 2 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th Edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
What does the lab partner observe during the instant the student pushes off?
 Motion Unit Review State Test Questions 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a A motion sensor.b low- g accelerometer.
Motion Unit Review State Test Questions 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a A motion sensor.b low- g accelerometer.
General Physics. Linear Motion. Life is in infinite motion; at the same time it is motionless. Debasish Mridha
 General Physics Linear Motion Life is in infinite motion; at the same time it is motionless. Debasish Mridha High Throw How high can a human throw something? Mechanics The study of motion Kinematics Description
General Physics Linear Motion Life is in infinite motion; at the same time it is motionless. Debasish Mridha High Throw How high can a human throw something? Mechanics The study of motion Kinematics Description
Chapter 2. Motion In One Dimension
 I. Displacement, Position, and Distance Chapter 2. Motion In One Dimension 1. John (Mike, Fred, Joe, Tom, Derek, Dan, James) walks (jogs, runs, drives) 10 m north. After that he turns around and walks
I. Displacement, Position, and Distance Chapter 2. Motion In One Dimension 1. John (Mike, Fred, Joe, Tom, Derek, Dan, James) walks (jogs, runs, drives) 10 m north. After that he turns around and walks
Kinematics in One Dimension
 Honors Physics Kinematics in One Dimension Life is in infinite motion; at the same time it is motionless. Debasish Mridha Mechanics The study of motion Kinematics Description of how things move Dynamics
Honors Physics Kinematics in One Dimension Life is in infinite motion; at the same time it is motionless. Debasish Mridha Mechanics The study of motion Kinematics Description of how things move Dynamics
Motion in One Dimension
 Motion in One Dimension Much of the physics we ll learn this semester will deal with the motion of objects We start with the simple case of one-dimensional motion Or, motion in x: As always, we begin by
Motion in One Dimension Much of the physics we ll learn this semester will deal with the motion of objects We start with the simple case of one-dimensional motion Or, motion in x: As always, we begin by
Chapter 3 Acceleration
 Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration AP style
 Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration AP style Linear Motion Position- the location of an object relative to a reference point. IF the position is one-dimension only, we often use the letter x to represent
Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration AP style Linear Motion Position- the location of an object relative to a reference point. IF the position is one-dimension only, we often use the letter x to represent
2. (a) Using the fact that time = distance/velocity while the velocity is constant, we find m 73.2 m 1.74 m/s m 73.2 m v m. 1.
 Chapter. The speed (assumed constant) is v = (9 km/h)( m/km) (36 s/h) = 5 m/s. Thus, in.5 s, the car travels a distance d = vt = (5 m/s)(.5 s) 3 m.. (a) Using the fact that time = distance/velocity while
Chapter. The speed (assumed constant) is v = (9 km/h)( m/km) (36 s/h) = 5 m/s. Thus, in.5 s, the car travels a distance d = vt = (5 m/s)(.5 s) 3 m.. (a) Using the fact that time = distance/velocity while
Chapter 3 Acceleration
 Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
ONE-DIMENSIONAL KINEMATICS
 ONE-DIMENSIONAL KINEMATICS Chapter 2 Units of Chapter 2 Position, Distance, and Displacement Average Speed and Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Applications
ONE-DIMENSIONAL KINEMATICS Chapter 2 Units of Chapter 2 Position, Distance, and Displacement Average Speed and Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Applications
Physics 1120: 1D Kinematics Solutions
 Questions: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Physics 1120: 1D Kinematics Solutions 1. Initially, a ball has a speed of 5.0 m/s as it rolls up an incline. Some time later, at a distance of 5.5 m up the incline, the ball has
Questions: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Physics 1120: 1D Kinematics Solutions 1. Initially, a ball has a speed of 5.0 m/s as it rolls up an incline. Some time later, at a distance of 5.5 m up the incline, the ball has
PUM Physics II - Kinematics Lesson 12 Solutions Page 1 of 16
 PUM Physics II - Kinematics Lesson 12 Solutions Page 1 of 16 12.1 Hypothesize (Derive a Mathematical Model) Graphically we know that the area beneath a velocity vs. time graph line represents the displacement
PUM Physics II - Kinematics Lesson 12 Solutions Page 1 of 16 12.1 Hypothesize (Derive a Mathematical Model) Graphically we know that the area beneath a velocity vs. time graph line represents the displacement
Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter One-Dimensional Kinematics Units of Chapter Position, Distance, and Displacement Average Speed and Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Applications of
Chapter One-Dimensional Kinematics Units of Chapter Position, Distance, and Displacement Average Speed and Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Applications of
Lecture 2- Linear Motion Chapter 10
 1 / 37 Lecture 2- Linear Motion Chapter 10 Instructor: Prof. Noronha-Hostler Course Administrator: Prof. Roy Montalvo PHY-123 ANALYTICAL PHYSICS IA Phys- 123 Sep. 12 th, 2018 Contact Already read the syllabus
1 / 37 Lecture 2- Linear Motion Chapter 10 Instructor: Prof. Noronha-Hostler Course Administrator: Prof. Roy Montalvo PHY-123 ANALYTICAL PHYSICS IA Phys- 123 Sep. 12 th, 2018 Contact Already read the syllabus
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION
 CHAPTER 2 DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: state from memory the meaning of the key terms and phrases
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: state from memory the meaning of the key terms and phrases
Motion along a straight line
 1 Motion along a straight line Relativeness of motion Activity: Observations from inside and outside of a moving bus. When you look outside a moving bus, do the trees and houses appear to move backwards?
1 Motion along a straight line Relativeness of motion Activity: Observations from inside and outside of a moving bus. When you look outside a moving bus, do the trees and houses appear to move backwards?
Introduction to 1-D Motion Distance versus Displacement
 Introduction to 1-D Motion Distance versus Displacement Kinematics! Kinematics is the branch of mechanics that describes the motion of objects without necessarily discussing what causes the motion.! 1-Dimensional
Introduction to 1-D Motion Distance versus Displacement Kinematics! Kinematics is the branch of mechanics that describes the motion of objects without necessarily discussing what causes the motion.! 1-Dimensional
Chapter 2: Kinematics
 Section 1 Chapter 2: Kinematics To simplify the concept of motion, we will first consider motion that takes place in one direction. To measure motion, you must choose a frame of reference. Frame of reference
Section 1 Chapter 2: Kinematics To simplify the concept of motion, we will first consider motion that takes place in one direction. To measure motion, you must choose a frame of reference. Frame of reference
t 2 (60 km / h) Both displacements are in the same direction, so the total displacement is v avg (2.0 h)
 . We use Eq. - and Eq. -3. During a time t c when the velocity remains a positive constant, speed is equivalent to velocity, and distance is equivalent to displacement, with Δx = v t c. (a) During the
. We use Eq. - and Eq. -3. During a time t c when the velocity remains a positive constant, speed is equivalent to velocity, and distance is equivalent to displacement, with Δx = v t c. (a) During the
Chapter 2. Motion in One Dimension. AIT AP Physics C
 Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Kinematics Describes motion while ignoring the agents that caused the motion For now, will consider motion in one dimension Along a straight line Will use the particle
Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Kinematics Describes motion while ignoring the agents that caused the motion For now, will consider motion in one dimension Along a straight line Will use the particle
Chapter 2 1D KINEMATICS
 Chapter 2 1D KINEMATICS The motion of an American kestrel through the air can be described by the bird s displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration. When it flies in a straight line without any change
Chapter 2 1D KINEMATICS The motion of an American kestrel through the air can be described by the bird s displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration. When it flies in a straight line without any change
Chapter 2. Kinematics in One Dimension
 Register Clickers Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension Kinematics deals with the concepts that are needed to describe motion. Dynamics deals with the effect that forces have on motion. Together, kinematics
Register Clickers Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension Kinematics deals with the concepts that are needed to describe motion. Dynamics deals with the effect that forces have on motion. Together, kinematics
KINETICS: MOTION ON A STRAIGHT LINE. VELOCITY, ACCELERATION. FREELY FALLING BODIES
 014.08.06. KINETICS: MOTION ON A STRAIGHT LINE. VELOCITY, ACCELERATION. FREELY FALLING BODIES www.biofizika.aok.pte.hu Premedical course 04.08.014. Fluids Kinematics Dynamics MECHANICS Velocity and acceleration
014.08.06. KINETICS: MOTION ON A STRAIGHT LINE. VELOCITY, ACCELERATION. FREELY FALLING BODIES www.biofizika.aok.pte.hu Premedical course 04.08.014. Fluids Kinematics Dynamics MECHANICS Velocity and acceleration
Mathematical review trigonometry vectors Motion in one dimension
 Mathematical review trigonometry vectors Motion in one dimension Used to describe the position of a point in space Coordinate system (frame) consists of a fixed reference point called the origin specific
Mathematical review trigonometry vectors Motion in one dimension Used to describe the position of a point in space Coordinate system (frame) consists of a fixed reference point called the origin specific
INTRODUCTION & RECTILINEAR KINEMATICS: CONTINUOUS MOTION
 INTRODUCTION & RECTILINEAR KINEMATICS: CONTINUOUS MOTION (Sections 12.1-12.2) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to find the kinematic quantities (position, displacement, velocity, and acceleration)
INTRODUCTION & RECTILINEAR KINEMATICS: CONTINUOUS MOTION (Sections 12.1-12.2) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to find the kinematic quantities (position, displacement, velocity, and acceleration)
Lesson 12: Position of an Accelerating Object as a Function of Time
 Lesson 12: Position of an Accelerating Object as a Function of Time 12.1 Hypothesize (Derive a Mathematical Model) Recall the initial position and clock reading data from the previous lab. When considering
Lesson 12: Position of an Accelerating Object as a Function of Time 12.1 Hypothesize (Derive a Mathematical Model) Recall the initial position and clock reading data from the previous lab. When considering
1. (a) As the man continues to remain at the same place with respect to the gym, it is obvious that his net displacement is zero.
 . (a) As the man continues to remain at the same place with respect to the gym, it is obvious that his net displacement is zero. (b) In 5 min, the average velocity is v avg ( x x ) 0.0 0.0 = = = 0.0. (
. (a) As the man continues to remain at the same place with respect to the gym, it is obvious that his net displacement is zero. (b) In 5 min, the average velocity is v avg ( x x ) 0.0 0.0 = = = 0.0. (
Chapter 2. Motion along a straight line. We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics.
 Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line 2.2 Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Examples: The Earth orbits around the Sun A roadway moves with Earth s
Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line 2.2 Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Examples: The Earth orbits around the Sun A roadway moves with Earth s
A. VOCABULARY REVIEWS On the line, write the term that correctly completes each statement. Use each term once.
 PART III. KINEMATICS A. VOCABULARY REVIEWS On the line, write the term that correctly completes each statement. Use each term once. 1. rise (Δy) The vertical separation of any two points on a curve is
PART III. KINEMATICS A. VOCABULARY REVIEWS On the line, write the term that correctly completes each statement. Use each term once. 1. rise (Δy) The vertical separation of any two points on a curve is
INTRODUCTION. 1. One-Dimensional Kinematics
 INTRODUCTION Mechanics is the area of physics most apparent to us in our everyday lives Raising an arm, standing up, sitting down, throwing a ball, opening a door etc all governed by laws of mechanics
INTRODUCTION Mechanics is the area of physics most apparent to us in our everyday lives Raising an arm, standing up, sitting down, throwing a ball, opening a door etc all governed by laws of mechanics
Course Name : Physics I Course # PHY 107. Note - 3 : Motion in One Dimension
 Course Name : Physics I Course # PHY 107 Note - 3 : Motion in One Dimension Abu Mohammad Khan Department of Mathematics and Physics North South University https://abukhan.weebly.com Copyright: It is unlawful
Course Name : Physics I Course # PHY 107 Note - 3 : Motion in One Dimension Abu Mohammad Khan Department of Mathematics and Physics North South University https://abukhan.weebly.com Copyright: It is unlawful
Chapter 3 Acceleration
 Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 PackBack The first answer gives a good physical picture. The video was nice, and worth the second answer. https://www.youtube.com/w atch?v=m57cimnj7fc Slide 3-2 Slide 3-3
Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 PackBack The first answer gives a good physical picture. The video was nice, and worth the second answer. https://www.youtube.com/w atch?v=m57cimnj7fc Slide 3-2 Slide 3-3
 CHAPTER 1. We find the average speed from average speed = d/t = (30 km)/(3.5 h) = 70.8 km/h.. We find the time from average speed = d/t; 5 km/h = (15 km)/t, which gives t = 0.60 h (36 min). 3. We find
CHAPTER 1. We find the average speed from average speed = d/t = (30 km)/(3.5 h) = 70.8 km/h.. We find the time from average speed = d/t; 5 km/h = (15 km)/t, which gives t = 0.60 h (36 min). 3. We find
Motion Along a Straight Line
 Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line 2.1 Displacement, Time, and Average Velocity 1D motion. Very often it is convenient to model an object whose motion you analyze e.g. car, runner, stone, etc.) as
Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line 2.1 Displacement, Time, and Average Velocity 1D motion. Very often it is convenient to model an object whose motion you analyze e.g. car, runner, stone, etc.) as
MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without
 MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without considering the cause of the motion). Distance vs. Displacement
MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without considering the cause of the motion). Distance vs. Displacement
VELOCITY. If you have a graph of position and you take the derivative, what would the derivative represent? Position. Time
 VELOCITY If you have a graph of position and you take the derivative, what would the derivative represent? Position Time Average rate of Change What is the average rate of change of temperature over the
VELOCITY If you have a graph of position and you take the derivative, what would the derivative represent? Position Time Average rate of Change What is the average rate of change of temperature over the
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration?
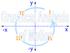 Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
Class 11 Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Motion in a Straight Line
 Class 11 Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Motion in a Straight Line Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. Among the four graphs shown in the figure, there is only one graph for which
Class 11 Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Motion in a Straight Line Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. Among the four graphs shown in the figure, there is only one graph for which
Position, Speed and Velocity Position is a variable that gives your location relative to an origin. The origin is the place where position equals 0.
 Position, Speed and Velocity Position is a variable that gives your location relative to an origin. The origin is the place where position equals 0. The position of this car at 50 cm describes where the
Position, Speed and Velocity Position is a variable that gives your location relative to an origin. The origin is the place where position equals 0. The position of this car at 50 cm describes where the
4.1 Motion Is Relative. An object is moving if its position relative to a fixed point is changing. You can describe the motion of an object by its
 4.1 Motion Is Relative You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. An object is moving if its position relative to a fixed point is changing. 4.1 Motion
4.1 Motion Is Relative You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. An object is moving if its position relative to a fixed point is changing. 4.1 Motion
Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension
 Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension Units of Chapter 2 Reference Frames and Displacement Average Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion at Constant Acceleration Solving
Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension Units of Chapter 2 Reference Frames and Displacement Average Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion at Constant Acceleration Solving
Summary of motion graphs Object is moving to the right (in positive direction) v = 0 a = 0
 Summary of motion graphs Object is moving to the right (in positive direction) Object at rest (not moving) Position is constant v (m/s) a (m/s 2 ) v = 0 a = 0 Constant velocity Position increases at constant
Summary of motion graphs Object is moving to the right (in positive direction) Object at rest (not moving) Position is constant v (m/s) a (m/s 2 ) v = 0 a = 0 Constant velocity Position increases at constant
Kinematics II Mathematical Analysis of Motion
 AP Physics-B Kinematics II Mathematical Analysis of Motion Introduction: Everything in the universe is in a state of motion. It might seem impossible to find a simple way to describe and understand the
AP Physics-B Kinematics II Mathematical Analysis of Motion Introduction: Everything in the universe is in a state of motion. It might seem impossible to find a simple way to describe and understand the
1. A sphere with a radius of 1.7 cm has a volume of: A) m 3 B) m 3 C) m 3 D) 0.11 m 3 E) 21 m 3
 1. A sphere with a radius of 1.7 cm has a volume of: A) 2.1 10 5 m 3 B) 9.1 10 4 m 3 C) 3.6 10 3 m 3 D) 0.11 m 3 E) 21 m 3 2. A 25-N crate slides down a frictionless incline that is 25 above the horizontal.
1. A sphere with a radius of 1.7 cm has a volume of: A) 2.1 10 5 m 3 B) 9.1 10 4 m 3 C) 3.6 10 3 m 3 D) 0.11 m 3 E) 21 m 3 2. A 25-N crate slides down a frictionless incline that is 25 above the horizontal.
