LECTURE # 19 Dennis Papadopoulos End of Classical Physics Quantization Bohr Atom Chapters 38 39
|
|
|
- Dwain Chandler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PHYS 270-SPRING 2011 LECTURE # 19 Dennis Papadopoulos End of Classical Physics Quantization Bohr Atom Chapters April 14,
2 HOW TO MEASURE SPECTRA
3 Spectroscopy: Unlocking the Structure of Atoms There are two types of spectra, continuous spectra and discrete spectra: Hot, self-luminous objects, such as the sun or an incandescent light bulb, emit a continuous spectrum in which a rainbow is formed by light being emitted at every possible wavelength. In contrast, the light emitted by a gas discharge tube (such as those used to make neon signs) contains only certain discrete, individual wavelengths. Such a spectrum is called a discrete spectrum.
4
5 Absorption and Emission Lines Close examination of the spectra from the Sun and other stars reveals that the rainbow of colors has many dark lines in it, called absorption lines. They are produced by the cooler thin gas in the upper layers of the stars absorbing certain colors of light produced by the hotter dense lower layers. You can also see them in the reflected light spectrum from planets. Some of the colors in the sunlight reflecting off the planets are absorbed by the molecules on the planet's surface or in its atmosphere. The spectra of hot, thin (low density) gas clouds are a series of bright lines called emission lines. In both of these types of spectra you see spectral features at certain, discrete wavelengths (or colors) and no where else.
6 See also
7 ATOMIC HYDROGEN SPECTRUM
8 Balmer Numerology λ µm Hydrogen Spectrum Balmer math schoolteacher liked to amuse himself by taking four numbers and then finding an equation that described their relationship. While playing with the four numbers he found something very interesting about the number a=3.645 µm They followed the progression 9a/5, 16a/12, 25a/21, 36a/32
9 hf = hc /λ = (hc /a) n 2 4 n 2 E 1 = (hc /a)(5 /9) 9a/5, 16a/12, 25a/21, 36a/32
10
11 Matter is composed of atoms that are a combination of positive and negative ions Current through the water decomposes it to Hydrogen and Oxygen Bubbles of them come out near electrodes Faraday: Electrolysis can be understood on the basis of atomic theory of matter Charge associated with each atom or molecule in the solution. Positive and negative ions. Cl > Cl+e
12 Battery vs. Fuel Cell
13 Gaseous Discharges 1. Current flows driving discharge 2. Discharge color depends on gas (N 2, Neon) 3. Cathode glow Independent of gas Connection between color of light and type of atoms in the discharge Unification of matter electricity light Reduce gas pressure (good pumps) 1. Bright colored glow reduces and becomes extinct 2. Cathode glow fills tube 3. Put a metal object creates shadow SPECTROSCOPY NEON EXAMPLE
14 Cathode Rays IMPROVED PUMPS >LOW PRESSURE > CATODE GLOW DOMINATES+GLASS EMITS GREENISH GLOW (FLUORESCENCE) SOMETHING BLOCKING FLOW Crooke s Tubes led to 1. Electric current associated with cathode rays 2. The rays are deflected by a magnetic field like a negative charge 3. Cathodes of any metal produce cathode rays. Ray properties independent of metal type. 4. Rays can exert forces on objects. Thin foil gets hot and glows red.
15 Are Cathode Rays Charged Particles? Enter J.J.Thomson OK for NaCl but what about He (monatomic gas) Roentgen X rays Atoms should be composed of positive and negative parts Deflection depends on q/m and v dv dt = q m ( v B ) r = mv /qb Confirmed that cathode rays were negatively charged particles but could not measure the q/m
16 Cross Field Experiment dv dt = q m ( E + v B ) dv dt = 0 v x = E /B r = mv /qb = (m /q)(e /B 2 ) Thomson found q/m=10 11 Cb/kg For Hydrogen q/m=10 8 Cb/kg Cathode ray particle has either much larger charge or much smaller mass.
17 FOUND THAT NEGATIVE PARTICLES EMITTED FROM METALS HAVE THE SAME q/m. > ELECTRONS ARE CONSTITUENT OF ALL MATTER
18 Enter Rutheford Using Thomson s technique measured radioactive rays emitted from U samples as beta rays (q/m =-e/m e similar to cathode rays electrons) penetrate.1 inch of metal as alpha rays with q/m = e/2m H. Alpha ray value indicates either singly charged H 2 (q=e m=2m H ) or doubly ionized He atom (q=2e, m=4m H Ra A few days later created a discharge and looked at the spectrum. He found He but not H Alpha particles nuclei of He
19 Rutherford and the Discovery of the Nucleus In 1896 Rutherford s experiment was set up to see if any alpha particles were deflected from gold foil at large angles. Not only were alpha particles deflected at large angles, but a very few were reflected almost straight backward toward the source!
20 Fig. 4-10, p. 120
21 The discovery of the atomic nucleus: Rutherford Back Scattering what Rutherford expected from the plum pudding model the clever experiment the (surprise!) result It was almost as incredible as if you had fired a 15-inch shell at a piece of tissue paper and it came back and hit you."
22
23 Atomic number Z number of electrons and number of positive charges nucleus Puzzle atom mass more than Zm p -> neutron
24 Into the Nucleus The atomic number Z of an element describes the number of protons in the nucleus. Elements are listed in the periodic table by their atomic number. There are a range of neutron numbers N that happily form a nucleus with Z protons, creating a series of nuclei having the same Z-value but different masses. Such a series of nuclei are called isotopes. An atom s mass number A is defined to be A = Z + N. It is the total number of protons and neutrons in a nucleus. The notation used to label isotopes is A Z, where the mass number A is given as a leading superscript. The proton number Z is not specified by an actual number but, equivalently, by the chemical symbol for that element.
25 Chemical properties controlled by Z. Isotopes 4 2 He
26 The Emission of Light Hot, self-luminous objects, such as the sun or an incandescent lightbulb, form a rainbow-like continuous spectrum in which light is emitted at every possible wavelength. The figure shows a continuous spectrum.
27 The Emission of Light The light emitted by one of Faraday s gas discharge tubes contains only certain discrete, individual wavelengths. Such a spectrum is called a discrete spectrum. Each wavelength in a discrete spectrum is called a spectral line because of its appearance in photographs such as the one shown.
28 IF MATTER COMPOSED OF ATOMS WHAT ATOMS ARE COMPOSED OF? FARADAY ELECTROLYSIS THOMSON ELECTRONS q/m MILLIKAN ELECTRONIC q RUTHERFORD NUCLEAR MODEL
29 positive charge is concentrated at the center of the atom in an area ~1/1000 th the size of the atom the mass of the electron is very small compared to the mass of the atom (one thousand times less than the hydrogen atom
30 The attractive Coulomb force between the positive nucleus and the orbiting electron could provide the attractive force which keeps the electron in it s orbit, much as the planets orbit the sun with gravity providing the centripetal force. What s wrong with this picture? Accelerating charges radiate. Could this electromagnetic radiation be the source of the spectral lines? No. This radiation must come at the expense of the kinetic energy of the orbiting electron! It will eventually spiral into the nucleus. The atom would be unstable!
31 Bohr Atom r=n 2 a B, a B = (h/2π) 2 /(ke 2 m)=.0529 nm E n = E 1 /n 2 E 1 =13.6 ev
32 The Spectrum of Hydrogen Hydrogen is the simplest atom, with one electron orbiting a proton, and it also has the simplest atomic spectrum. The emission lines have wavelengths which correspond to two integers, m and n. Every line in the hydrogen spectrum has a wavelength given by
33 Bohr s Model of Atomic Quantization 1. An atom consists of negative electrons orbiting a very small positive nucleus. 2. Atoms can exist only in certain stationary states. Each stationary state corresponds to a particular set of electron orbits around the nucleus. These states can be numbered 2, 3, 4,..., where n is the quantum number. 3. Each stationary state has an energy E n. The stationary states of an atom are numbered in order of increasing energy: E 1 < E 2 < E 3 < 4. The lowest energy state of the atom E 1 is stable and can persist indefinitely. It is called the ground state of the atom. Other stationary states with energies E 2, E 3, E 4,... are called excited states of the atom.
34 Bohr s Model of Atomic Quantization 5. An atom can jump from one stationary state to another by emitting or absorbing a photon of frequency where h is Planck s constant and and ΔE atom = E f E i. E f and E i are the energies of the initial and final states. Such a jump is called a transition or, sometimes, a quantum jump.
35 Bohr s Model of Atomic Quantization 6. An atom can move from a lower energy state to a higher energy state by absorbing energy ΔE atom = E f E i in an inelastic collision with an electron or another atom. This process, called collisional excitation, is shown.
36 Emission Absorption
37 Emission
38 Line Spectra To explain discrete spectra, Bohr found that atoms obey three basic rules: 1. Electrons have only certain energies corresponding to particular distances from nucleus. As long as the electron is in one of those energy orbits, it will not lose or absorb any energy. The energy orbits are analogous to rungs on a ladder: electrons can be only on rungs of the ladder and not in between rungs. 2. The orbits closer to the nucleus have lower energy. 3. Atoms want to be in the lowest possible energy state called the ground state (all electrons as close to the nucleus as possible).
39
40 ABSORPTION AND EMISSION SPECTRA Notice that there are fewer absorption than emission lines
41 Matter Waves and Energy Quantization In 1924 de Broglie postulated that if a material particle of momentum p = mv has a wave like nature, then its wavelength must be given by Photons E = hf = pc λ = c / f = h / p where h is Planck s constant (h = J s). This is called the de Broglie wavelength.
42 DB considered a matter wave to be a travelling one. Suppose however that the particle is confined in a small region and cannot escape. How do the wave properties show up? λ n = 2L /n,n =1,2,3,4... λ = h /mv v n = n(h /2Lm),n =1,2,3 E n = n 2 (h 2 /8mL 2 ) n 2 E 1 Probability
43 Standing waves (harmonics) Ends (or edges) must stay fixed. That s what we call a boundary condition. This is an example of a Bessel function.
44 Quantization of Energy Consider a particle of mass m moving in one dimension as it bounces back and forth with speed v between the ends of a box of length L. We ll call this a one dimensional box; its width isn t relevant. A wave, if it reflects back and forth between two fixed points, sets up a standing wave. A standing wave of length L must have a wavelength given by
45 Quantization of Energy Using the de Broglie relationship λ = h/mv, a standing wave with wavelength λ n forms when the particle has a speed Thus the particle s energy, which is purely kinetic energy, is E n = E 1 n 2 De Broglie s hypothesis about the wave like properties of matter leads us to the remarkable conclusion that the energy of a confined particle is quantized.
46 Phase cancellation L = m e vr = n n =1,2,3... = h /2π an integer number of wavelengths fits into the circular orbit Photons p=hf/c= h/λ where λ is the de Broglie wavelength In order to understand quantum mechanics, you must understand waves!
47
48 Black Body Radiation
49 Blackbody Radiation The heat energy Q radiated in a time interval Δt by an object with surface area A and absolute temperature T is given by where σ = W/m 2 K 4 is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant. The parameter e is the emissivity of the surface, a measure of how effectively it radiates. The value of e ranges from 0 to 1. A perfectly absorbing and thus perfectly emitting object with e = 1 is called a blackbody, and the thermal radiation emitted by a blackbody is called blackbody radiation.
50 Wien law λ 1/Τ or f m ~T
51 Fig. 3-11, p. 78
52 Red oscillators Blue oscillators Green oscillators
53 B
54 Lava glows when hot
55 Blackbody Radiation The wavelength of the peak in the intensity graph is given by Wien s law (T must be in kelvin): Wien s Displacement Law
56
LECTURE # 17 Modern Optics Matter Waves
 PHYS 270-SPRING 2011 LECTURE # 17 Modern Optics Matter Waves April 5, 2011 1 Spectroscopy: Unlocking the Structure of Atoms There are two types of spectra, continuous spectra and discrete spectra: Hot,
PHYS 270-SPRING 2011 LECTURE # 17 Modern Optics Matter Waves April 5, 2011 1 Spectroscopy: Unlocking the Structure of Atoms There are two types of spectra, continuous spectra and discrete spectra: Hot,
Chapter 38. The End of Classical Physics
 Chapter 38. The End of Classical Physics Studies of the light emitted by gas discharge tubes helped bring classical physics to an end. Chapter Goal: To understand how scientists discovered the properties
Chapter 38. The End of Classical Physics Studies of the light emitted by gas discharge tubes helped bring classical physics to an end. Chapter Goal: To understand how scientists discovered the properties
Chapter 38 and Chapter 39
 Chapter 38 and Chapter 39 State of 19th and very early 20th century physics: Light: 1. E&M Maxwell s equations > waves; J. J. Thompson s double slit experiment with light 2. Does light need a medium? >
Chapter 38 and Chapter 39 State of 19th and very early 20th century physics: Light: 1. E&M Maxwell s equations > waves; J. J. Thompson s double slit experiment with light 2. Does light need a medium? >
3. Particle nature of matter
 3. Particle nature of matter 3.1 atomic nature of matter Democrit(us) 470-380 B.C.: there is only atoms and empty space, everything else is mere opinion (atoms are indivisible) Dalton (chemist) 180: chemical
3. Particle nature of matter 3.1 atomic nature of matter Democrit(us) 470-380 B.C.: there is only atoms and empty space, everything else is mere opinion (atoms are indivisible) Dalton (chemist) 180: chemical
Chapter 27 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Discovery and Properties of the electron
 Chapter 27 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom 27-1 Discovery and Properties of the electron Measure charge to mass ratio e/m (J. J. Thomson, 1897) When apply magnetic field only, the rays are
Chapter 27 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom 27-1 Discovery and Properties of the electron Measure charge to mass ratio e/m (J. J. Thomson, 1897) When apply magnetic field only, the rays are
Physics 1C Lecture 29A. Finish off Ch. 28 Start Ch. 29
 Physics 1C Lecture 29A Finish off Ch. 28 Start Ch. 29 Particle in a Box Let s consider a particle confined to a one-dimensional region in space. Following the quantum mechanics approach, we need to find
Physics 1C Lecture 29A Finish off Ch. 28 Start Ch. 29 Particle in a Box Let s consider a particle confined to a one-dimensional region in space. Following the quantum mechanics approach, we need to find
Lecture 32 April
 Lecture 32 April 08. 2016. Hydrogen Discharge Tube and Emission of Discrete Wavelengths Description of the discrete Hydrogen Emission Spectrum by the Balmer (1884) Rydberg Ritz formula (1908) Cathode Ray
Lecture 32 April 08. 2016. Hydrogen Discharge Tube and Emission of Discrete Wavelengths Description of the discrete Hydrogen Emission Spectrum by the Balmer (1884) Rydberg Ritz formula (1908) Cathode Ray
Final Exam: Thursday 05/02 7:00 9:00 pm in STEW 183
 Final Exam: Thursday 05/02 7:00 9:00 pm in STEW 183 Covers all readings, lectures, homework from Chapters 17 through 30 Be sure to bring your student ID card, calculator, pencil, and up to three onepage
Final Exam: Thursday 05/02 7:00 9:00 pm in STEW 183 Covers all readings, lectures, homework from Chapters 17 through 30 Be sure to bring your student ID card, calculator, pencil, and up to three onepage
LECTURE 23 SPECTROSCOPY AND ATOMIC MODELS. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 23 SPECTROSCOPY AND ATOMIC MODELS Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 23 2 29.1 Spectroscopy 29.2 Atoms The first nuclear physics experiment Using the nuclear model 29.3 Bohr s model of atomic quantization
LECTURE 23 SPECTROSCOPY AND ATOMIC MODELS Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 23 2 29.1 Spectroscopy 29.2 Atoms The first nuclear physics experiment Using the nuclear model 29.3 Bohr s model of atomic quantization
Chapter 28. Atomic Physics
 Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Sir Joseph John Thomson J. J. Thomson 1856-1940 Discovered the electron Did extensive work with cathode ray deflections 1906 Nobel Prize for discovery of electron Early Models
Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Sir Joseph John Thomson J. J. Thomson 1856-1940 Discovered the electron Did extensive work with cathode ray deflections 1906 Nobel Prize for discovery of electron Early Models
The Atom. Result for Hydrogen. For example: the emission spectrum of Hydrogen: Screen. light. Hydrogen gas. Diffraction grating (or prism)
 The Atom What was know about the atom in 1900? First, the existence of atoms was not universally accepted at this time, but for those who did think atoms existed, they knew: 1. Atoms are small, but they
The Atom What was know about the atom in 1900? First, the existence of atoms was not universally accepted at this time, but for those who did think atoms existed, they knew: 1. Atoms are small, but they
1 The Cathode Rays experiment is associated. with: Millikan A B. Thomson. Townsend. Plank Compton
 1 The Cathode Rays experiment is associated with: A B C D E Millikan Thomson Townsend Plank Compton 1 2 The electron charge was measured the first time in: A B C D E Cathode ray experiment Photoelectric
1 The Cathode Rays experiment is associated with: A B C D E Millikan Thomson Townsend Plank Compton 1 2 The electron charge was measured the first time in: A B C D E Cathode ray experiment Photoelectric
From Last Time Pearson Education, Inc.
 From Last Time Light: Absorption, Emission, Transmission, Reflection, and Scattering c=λ x f E=h x f Light (electromagnetic radiation) extends from gamma rays (high E, high f, small λ) to radio waves (small
From Last Time Light: Absorption, Emission, Transmission, Reflection, and Scattering c=λ x f E=h x f Light (electromagnetic radiation) extends from gamma rays (high E, high f, small λ) to radio waves (small
Quantum and Atomic Physics - Multiple Choice
 PSI AP Physics 2 Name 1. The Cathode Ray Tube experiment is associated with: (A) J. J. Thomson (B) J. S. Townsend (C) M. Plank (D) A. H. Compton 2. The electron charge was measured the first time in: (A)
PSI AP Physics 2 Name 1. The Cathode Ray Tube experiment is associated with: (A) J. J. Thomson (B) J. S. Townsend (C) M. Plank (D) A. H. Compton 2. The electron charge was measured the first time in: (A)
General Physics (PHY 2140)
 General Physics (PHY 140) Lecture 33 Modern Physics Atomic Physics Atomic spectra Bohr s theory of hydrogen http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy140/ Chapter 8 1 Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Atomic
General Physics (PHY 140) Lecture 33 Modern Physics Atomic Physics Atomic spectra Bohr s theory of hydrogen http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy140/ Chapter 8 1 Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Atomic
1. Historical perspective
 Atomic and Molecular Physics/Lecture notes presented by Dr. Fouad Attia Majeed/Third year students/college of Education (Ibn Hayyan)/Department of Physics/University of Babylon. 1. Historical perspective
Atomic and Molecular Physics/Lecture notes presented by Dr. Fouad Attia Majeed/Third year students/college of Education (Ibn Hayyan)/Department of Physics/University of Babylon. 1. Historical perspective
Particle Nature of Matter. Chapter 4
 Particle Nature of Matter Chapter 4 Modern physics When my grandfather was born, atoms were just an idea. That year, 1897, was marked by the discovery of the electron by J.J. Thomson. The nuclear model
Particle Nature of Matter Chapter 4 Modern physics When my grandfather was born, atoms were just an idea. That year, 1897, was marked by the discovery of the electron by J.J. Thomson. The nuclear model
like firing a 16 shell at a piece of tissue paper and seeing it bounce back. - E Rutherford
 Black body radiation [const.] λ max = T E radiated surf. area Planck E f hf = T E W KE 4 ROY G BIV Einstein Photo-electric effect- Photons Thompson electron identification B + F v R +q 2 mv F= =qvb=f R
Black body radiation [const.] λ max = T E radiated surf. area Planck E f hf = T E W KE 4 ROY G BIV Einstein Photo-electric effect- Photons Thompson electron identification B + F v R +q 2 mv F= =qvb=f R
Models of the Atom. Spencer Clelland & Katelyn Mason
 Models of the Atom Spencer Clelland & Katelyn Mason First Things First Electrons were accepted to be part of the atom structure by scientists in the1900 s. The first model of the atom was visualized as
Models of the Atom Spencer Clelland & Katelyn Mason First Things First Electrons were accepted to be part of the atom structure by scientists in the1900 s. The first model of the atom was visualized as
Chapter 28. Atomic Physics
 Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Quantum Numbers and Atomic Structure The characteristic wavelengths emitted by a hot gas can be understood using quantum numbers. No two electrons can have the same set of quantum
Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Quantum Numbers and Atomic Structure The characteristic wavelengths emitted by a hot gas can be understood using quantum numbers. No two electrons can have the same set of quantum
Physics 30 Modern Physics Unit: Atomic Basics
 Physics 30 Modern Physics Unit: Atomic Basics Models of the Atom The Greeks believed that if you kept dividing matter into smaller and smaller pieces, you would eventually come to a bit of matter that
Physics 30 Modern Physics Unit: Atomic Basics Models of the Atom The Greeks believed that if you kept dividing matter into smaller and smaller pieces, you would eventually come to a bit of matter that
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Planck s Quantum Hypothesis; Blackbody Radiation Photon Theory of Light and the Photoelectric Effect Energy, Mass, and Momentum of a Photon Compton
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Planck s Quantum Hypothesis; Blackbody Radiation Photon Theory of Light and the Photoelectric Effect Energy, Mass, and Momentum of a Photon Compton
Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom
 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Electron Discharge tube (circa 1900 s) There is something ( cathode rays ) which is emitted by the cathode and causes glowing Unlike light, these rays are deflected
Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Electron Discharge tube (circa 1900 s) There is something ( cathode rays ) which is emitted by the cathode and causes glowing Unlike light, these rays are deflected
Atomic Structure Discovered. Dalton s Atomic Theory. Discovery of the Electron 10/30/2012
 Atomic Structure Discovered Ancient Greeks Democritus (460-362 BC) - indivisible particles called atoms Prevailing argument (Plato and Aristotle) - matter is continuously and infinitely divisible John
Atomic Structure Discovered Ancient Greeks Democritus (460-362 BC) - indivisible particles called atoms Prevailing argument (Plato and Aristotle) - matter is continuously and infinitely divisible John
Chapter 27 Lecture Notes
 Chapter 27 Lecture Notes Physics 2424 - Strauss Formulas: λ P T = 2.80 10-3 m K E = nhf = nhc/λ fλ = c hf = K max + W 0 λ = h/p λ - λ = (h/mc)(1 - cosθ) 1/λ = R(1/n 2 f - 1/n 2 i ) Lyman Series n f = 1,
Chapter 27 Lecture Notes Physics 2424 - Strauss Formulas: λ P T = 2.80 10-3 m K E = nhf = nhc/λ fλ = c hf = K max + W 0 λ = h/p λ - λ = (h/mc)(1 - cosθ) 1/λ = R(1/n 2 f - 1/n 2 i ) Lyman Series n f = 1,
Atom Physics. Chapter 30. DR JJ UiTM-Cutnell & Johnson 7th ed. 1. Model of an atom-the recent model. Nuclear radius r m
 Chapter 30 Atom Physics DR JJ UiTM-Cutnell & Johnson 7th ed. 1 30.1 Rutherford Scattering and the Nuclear Atom Model of an atom-the recent model Nuclear radius r 10-15 m Electron s position radius r 10-10
Chapter 30 Atom Physics DR JJ UiTM-Cutnell & Johnson 7th ed. 1 30.1 Rutherford Scattering and the Nuclear Atom Model of an atom-the recent model Nuclear radius r 10-15 m Electron s position radius r 10-10
Historical Background of Quantum Mechanics
 Historical Background of Quantum Mechanics The Nature of Light The Structure of Matter Dr. Sabry El-Taher 1 The Nature of Light Dr. Sabry El-Taher 2 In 1801 Thomas Young: gave experimental evidence for
Historical Background of Quantum Mechanics The Nature of Light The Structure of Matter Dr. Sabry El-Taher 1 The Nature of Light Dr. Sabry El-Taher 2 In 1801 Thomas Young: gave experimental evidence for
Spectroscopy. Hot self-luminous objects light the Sun or a light bulb emit a continuous spectrum of wavelengths.
 Hot self-luminous objects light the Sun or a light bulb emit a continuous spectrum of wavelengths. In contract, light emitted in low=pressure gas discharge contains only discrete individual wavelengths,
Hot self-luminous objects light the Sun or a light bulb emit a continuous spectrum of wavelengths. In contract, light emitted in low=pressure gas discharge contains only discrete individual wavelengths,
PHY293 Lecture #15. November 27, Quantum Mechanics and the Atom
 PHY293 Lecture #15 November 27, 2017 1. Quantum Mechanics and the Atom The Thompson/Plum Pudding Model Thompson discovered the electron in 1894 (Nobel Prize in 1906) Heating materials (metals) causes corpuscles
PHY293 Lecture #15 November 27, 2017 1. Quantum Mechanics and the Atom The Thompson/Plum Pudding Model Thompson discovered the electron in 1894 (Nobel Prize in 1906) Heating materials (metals) causes corpuscles
Chapter 39. Particles Behaving as Waves
 Chapter 39 Particles Behaving as Waves 39.1 Electron Waves Light has a dual nature. Light exhibits both wave and particle characteristics. Louis de Broglie postulated in 1924 that if nature is symmetric,
Chapter 39 Particles Behaving as Waves 39.1 Electron Waves Light has a dual nature. Light exhibits both wave and particle characteristics. Louis de Broglie postulated in 1924 that if nature is symmetric,
Nicholas J. Giordano. Chapter 29. Atomic Theory. Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 29 Atomic Theory Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Atomic Theory Matter is composed of atoms Atoms are assembled from electrons,
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 29 Atomic Theory Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Atomic Theory Matter is composed of atoms Atoms are assembled from electrons,
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom
 Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Units of Chapter 37 37-7 Wave Nature of Matter 37-8 Electron Microscopes 37-9 Early Models of the Atom 37-10 Atomic Spectra: Key to the Structure
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Units of Chapter 37 37-7 Wave Nature of Matter 37-8 Electron Microscopes 37-9 Early Models of the Atom 37-10 Atomic Spectra: Key to the Structure
Earlier we learned that hot, opaque objects produce continuous spectra of radiation of different wavelengths.
 Section7: The Bohr Atom Earlier we learned that hot, opaque objects produce continuous spectra of radiation of different wavelengths. Continuous Spectrum Everyone has seen the spectrum produced when white
Section7: The Bohr Atom Earlier we learned that hot, opaque objects produce continuous spectra of radiation of different wavelengths. Continuous Spectrum Everyone has seen the spectrum produced when white
Planck s Quantum Hypothesis Blackbody Radiation
 Planck s Quantum Hypothesis Blackbody Radiation The spectrum of blackbody radiation has been measured(next slide); it is found that the frequency of peak intensity increases linearly with temperature.
Planck s Quantum Hypothesis Blackbody Radiation The spectrum of blackbody radiation has been measured(next slide); it is found that the frequency of peak intensity increases linearly with temperature.
Chapter 7: The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom
 C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 7 P a g e 1 Chapter 7: The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom Homework: Read Chapter 7. Work out sample/practice exercises Check for the MasteringChemistry.com assignment
C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 7 P a g e 1 Chapter 7: The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom Homework: Read Chapter 7. Work out sample/practice exercises Check for the MasteringChemistry.com assignment
Radiation can be defined as the propagation of energy through matter or space. It can be in the form of electromagnetic waves or energetic particles.
 Lecture 1: Overview; History of Radiation Radiation can be defined as the propagation of energy through matter or space. It can be in the form of electromagnetic waves or energetic particles. Source: Lawrence
Lecture 1: Overview; History of Radiation Radiation can be defined as the propagation of energy through matter or space. It can be in the form of electromagnetic waves or energetic particles. Source: Lawrence
Physics 1C. Lecture 28D
 Physics 1C Lecture 28D "I ask you to look both ways. For the road to a knowledge of the stars leads through the atom; and important knowledge of the atom has been reached through the stars." --Sir Arthur
Physics 1C Lecture 28D "I ask you to look both ways. For the road to a knowledge of the stars leads through the atom; and important knowledge of the atom has been reached through the stars." --Sir Arthur
PSI AP Physics How was it determined that cathode rays possessed a negative charge?
 PSI AP Physics 2 Name Chapter Questions 1. How was it determined that cathode rays possessed a negative charge? 2. J. J. Thomson found that cathode rays were really particles, which were subsequently named
PSI AP Physics 2 Name Chapter Questions 1. How was it determined that cathode rays possessed a negative charge? 2. J. J. Thomson found that cathode rays were really particles, which were subsequently named
CHAPTER 27 Quantum Physics
 CHAPTER 27 Quantum Physics Units Discovery and Properties of the Electron Planck s Quantum Hypothesis; Blackbody Radiation Photon Theory of Light and the Photoelectric Effect Energy, Mass, and Momentum
CHAPTER 27 Quantum Physics Units Discovery and Properties of the Electron Planck s Quantum Hypothesis; Blackbody Radiation Photon Theory of Light and the Photoelectric Effect Energy, Mass, and Momentum
Blackbody radiation The photoelectric effect Compton effect Line spectra Nuclear physics/bohr model Lasers Quantum mechanics
 Blackbody radiation The photoelectric effect Compton effect Line spectra Nuclear physics/bohr model Lasers Quantum mechanics Phys 2435: Chap. 38, Pg 1 Blackbody radiation New Topic Phys 2435: Chap. 38,
Blackbody radiation The photoelectric effect Compton effect Line spectra Nuclear physics/bohr model Lasers Quantum mechanics Phys 2435: Chap. 38, Pg 1 Blackbody radiation New Topic Phys 2435: Chap. 38,
Atomic Models. 1) Students will be able to describe the evolution of atomic models.
 Atomic Models 1) Students will be able to describe the evolution of atomic models. 2) Students will be able to describe the role of experimental evidence in changing models of the atom. 3) Students will
Atomic Models 1) Students will be able to describe the evolution of atomic models. 2) Students will be able to describe the role of experimental evidence in changing models of the atom. 3) Students will
Physics 116. Nov 22, Session 32 Models of atoms. R. J. Wilkes
 Physics 116 Session 32 Models of atoms Nov 22, 2011 Thomson Rutherford R. J. Wilkes Email: ph116@u.washington.edu Announcements Exam 3 next week (Tuesday, 11/29) Usual format and procedures I ll post example
Physics 116 Session 32 Models of atoms Nov 22, 2011 Thomson Rutherford R. J. Wilkes Email: ph116@u.washington.edu Announcements Exam 3 next week (Tuesday, 11/29) Usual format and procedures I ll post example
Physics: Quanta to Quarks Option (99.95 ATAR)
 HSC Physics Year 2016 Mark 95.00 Pages 22 Published Jan 15, 2017 Physics: Quanta to Quarks Option (99.95 ATAR) By Edward (99.95 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Edward. Edward
HSC Physics Year 2016 Mark 95.00 Pages 22 Published Jan 15, 2017 Physics: Quanta to Quarks Option (99.95 ATAR) By Edward (99.95 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Edward. Edward
Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 5 June 1, 2018
 www.astro.yale.edu/astro120 Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 5 June 1, 2018 to understand how we know stuff about the universe we need to understand: 1. the spectral analysis of light 2. how light interacts with
www.astro.yale.edu/astro120 Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 5 June 1, 2018 to understand how we know stuff about the universe we need to understand: 1. the spectral analysis of light 2. how light interacts with
THE NATURE OF THE ATOM. alpha particle source
 chapter THE NATURE OF THE ATOM www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) Section 30.1 Rutherford Scattering and the Nuclear Atom 1. Which model of atomic structure
chapter THE NATURE OF THE ATOM www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) Section 30.1 Rutherford Scattering and the Nuclear Atom 1. Which model of atomic structure
UNIT VIII ATOMS AND NUCLEI
 UNIT VIII ATOMS AND NUCLEI Weightage Marks : 06 Alpha-particles scattering experiment, Rutherford s model of atom, Bohr Model, energy levels, Hydrogen spectrum. Composition and size of Nucleus, atomic
UNIT VIII ATOMS AND NUCLEI Weightage Marks : 06 Alpha-particles scattering experiment, Rutherford s model of atom, Bohr Model, energy levels, Hydrogen spectrum. Composition and size of Nucleus, atomic
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 27 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 27 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 27 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
The Atom. Describe a model of the atom that features a small nucleus surrounded by electrons.
 The Atom Describe a model of the atom that features a small nucleus surrounded by electrons. A guy by the name of Bohr created a model for the atom that consisted of an small nucleus surrounded by orbiting
The Atom Describe a model of the atom that features a small nucleus surrounded by electrons. A guy by the name of Bohr created a model for the atom that consisted of an small nucleus surrounded by orbiting
Rhonda Alexander IC Science Robert E. Lee
 Rhonda Alexander IC Science Robert E. Lee Atom The smallest particle of an element that retains all of the chemical properties of the element. The Theory & Evidence for John Dalton s Atomic Theory: Around
Rhonda Alexander IC Science Robert E. Lee Atom The smallest particle of an element that retains all of the chemical properties of the element. The Theory & Evidence for John Dalton s Atomic Theory: Around
ATOM. Rich -Paradis. Early Thoughts Aristotle-- Continuous theory. Matter can be divided indefinitely. Greeks
 ATOM Early Thoughts Aristotle-- Continuous theory Greeks Matter can be divided indefinitely matter is made up of particles--4 elements 4 elements --air--fire--water- -- earth Democritus --Discontinuous
ATOM Early Thoughts Aristotle-- Continuous theory Greeks Matter can be divided indefinitely matter is made up of particles--4 elements 4 elements --air--fire--water- -- earth Democritus --Discontinuous
Chapter 27 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom
 Chapter 27 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Modern Physics 19th century physics had so many great successes, that most people felt nature was almost fully understood. Just a few small clouds
Chapter 27 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Modern Physics 19th century physics had so many great successes, that most people felt nature was almost fully understood. Just a few small clouds
General Physics (PHY 2140)
 General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 32 Modern Physics Atomic Physics Early models of the atom Atomic spectra http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2140/ Chapter 28 1 If you want to know your progress
General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 32 Modern Physics Atomic Physics Early models of the atom Atomic spectra http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2140/ Chapter 28 1 If you want to know your progress
SECTION A Quantum Physics and Atom Models
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Modern Physics SECTION A Quantum Physics and Atom Models 1. Light of a single frequency falls on a photoelectric material but no electrons are emitted. Electrons may
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Modern Physics SECTION A Quantum Physics and Atom Models 1. Light of a single frequency falls on a photoelectric material but no electrons are emitted. Electrons may
Exam 2 Development of Quantum Mechanics
 PHYS40 (Spring 00) Riq Parra Exam # (Friday, April 1 th, 00) Exam Development of Quantum Mechanics Do NOT write your name on this exam. Write your class ID number on the top right hand corner of each problem
PHYS40 (Spring 00) Riq Parra Exam # (Friday, April 1 th, 00) Exam Development of Quantum Mechanics Do NOT write your name on this exam. Write your class ID number on the top right hand corner of each problem
Quantum Physics and Atomic Models Chapter Questions. 1. How was it determined that cathode rays possessed a negative charge?
 Quantum Physics and Atomic Models Chapter Questions 1. How was it determined that cathode rays possessed a negative charge? 2. J. J. Thomson found that cathode rays were really particles, which were subsequently
Quantum Physics and Atomic Models Chapter Questions 1. How was it determined that cathode rays possessed a negative charge? 2. J. J. Thomson found that cathode rays were really particles, which were subsequently
LIGHT. Question. Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light.
 LIGHT Question Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light. What kind of information can we get from light? 1 Light
LIGHT Question Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light. What kind of information can we get from light? 1 Light
Physics 102: Lecture 24. Bohr vs. Correct Model of Atom. Physics 102: Lecture 24, Slide 1
 Physics 102: Lecture 24 Bohr vs. Correct Model of Atom Physics 102: Lecture 24, Slide 1 Plum Pudding Early Model for Atom positive and negative charges uniformly distributed throughout the atom like plums
Physics 102: Lecture 24 Bohr vs. Correct Model of Atom Physics 102: Lecture 24, Slide 1 Plum Pudding Early Model for Atom positive and negative charges uniformly distributed throughout the atom like plums
Physics 1C. Modern Physics Lecture
 Physics 1C Modern Physics Lecture "I ask you to look both ways. For the road to a knowledge of the stars leads through the atom; and important knowledge of the atom has been reached through the stars."
Physics 1C Modern Physics Lecture "I ask you to look both ways. For the road to a knowledge of the stars leads through the atom; and important knowledge of the atom has been reached through the stars."
Particle nature of light & Quantization
 Particle nature of light & Quantization A quantity is quantized if its possible values are limited to a discrete set. An example from classical physics is the allowed frequencies of standing waves on a
Particle nature of light & Quantization A quantity is quantized if its possible values are limited to a discrete set. An example from classical physics is the allowed frequencies of standing waves on a
Particle Detectors and Quantum Physics (2) Stefan Westerhoff Columbia University NYSPT Summer Institute 2002
 Particle Detectors and Quantum Physics (2) Stefan Westerhoff Columbia University NYSPT Summer Institute 2002 More Quantum Physics We know now how to detect light (or photons) One possibility to detect
Particle Detectors and Quantum Physics (2) Stefan Westerhoff Columbia University NYSPT Summer Institute 2002 More Quantum Physics We know now how to detect light (or photons) One possibility to detect
Nuclear Chemistry. Atomic Structure Notes Start on Slide 20 from the second class lecture
 Nuclear Chemistry Atomic Structure Notes Start on Slide 20 from the second class lecture The Birth of an Idea Democritus, 400 B.C. coined the term atom If you divide matter into smaller and smaller pieces,
Nuclear Chemistry Atomic Structure Notes Start on Slide 20 from the second class lecture The Birth of an Idea Democritus, 400 B.C. coined the term atom If you divide matter into smaller and smaller pieces,
College Physics B - PHY2054C
 of College - PHY2054C The of 11/17/2014 My Office Hours: Tuesday 10:00 AM - Noon 206 Keen Building Outline of 1 2 of 3 4 of Puzzling The blackbody intensity falls to zero at both long and short wavelengths,
of College - PHY2054C The of 11/17/2014 My Office Hours: Tuesday 10:00 AM - Noon 206 Keen Building Outline of 1 2 of 3 4 of Puzzling The blackbody intensity falls to zero at both long and short wavelengths,
Particle and Nuclear Physics. Outline. Structure of the Atom. History of Atomic Structure. 1 Structure of the Atom
 Outline of 1 of Atomic Spectra of Helium Classical Atom of Existence of spectral lines required new model of atom, so that only certain amounts of energy could be emitted or absorbed. By about 1890, most
Outline of 1 of Atomic Spectra of Helium Classical Atom of Existence of spectral lines required new model of atom, so that only certain amounts of energy could be emitted or absorbed. By about 1890, most
 CHAPTER 5 ATOMIC STRUCTURE SHORT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Q.1 Why it is necessary to decrease the pressure in the discharge tube to get the cathode rays? The current does not flow through the gas at ordinary
CHAPTER 5 ATOMIC STRUCTURE SHORT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Q.1 Why it is necessary to decrease the pressure in the discharge tube to get the cathode rays? The current does not flow through the gas at ordinary
The atom cont. +Investigating EM radiation
 The atom cont. +Investigating EM radiation Announcements: First midterm is 7:30pm on Sept 26, 2013 Will post a past midterm exam from 2011 today. We are covering Chapter 3 today. (Started on Wednesday)
The atom cont. +Investigating EM radiation Announcements: First midterm is 7:30pm on Sept 26, 2013 Will post a past midterm exam from 2011 today. We are covering Chapter 3 today. (Started on Wednesday)
What is a theory? An organized system of accepted knowledge that applies in a variety of circumstances to explain a specific set of phenomena
 Atomic Structure What is a theory? An organized system of accepted knowledge that applies in a variety of circumstances to explain a specific set of phenomena Early Theories Democritus: 4 B.C.: atom He
Atomic Structure What is a theory? An organized system of accepted knowledge that applies in a variety of circumstances to explain a specific set of phenomena Early Theories Democritus: 4 B.C.: atom He
Professor K. Atomic structure
 Professor K Atomic structure Review Reaction- the formation and breaking of chemical bonds Bond- a transfer or sharing of electrons Electrons Abbreviated e - What are they? How were they discovered? Early
Professor K Atomic structure Review Reaction- the formation and breaking of chemical bonds Bond- a transfer or sharing of electrons Electrons Abbreviated e - What are they? How were they discovered? Early
Discovery of the Atomic Nucleus. Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition. Discovery of the Electron. Discovery of the Atomic Nucleus
 Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Chapter 32: THE ATOM AND THE QUANTUM Discovery of the Atomic Nucleus These alpha particles must have hit something relatively massive but what? Rutherford reasoned that
Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Chapter 32: THE ATOM AND THE QUANTUM Discovery of the Atomic Nucleus These alpha particles must have hit something relatively massive but what? Rutherford reasoned that
Astronomy 1 Winter 2011
 Astronomy 1 Winter 2011 Lecture 8; January 24 2011 Previously on Astro 1 Light as a wave The Kelvin Temperature scale What is a blackbody? Wien s law: λ max (in meters) = (0.0029 K m)/t. The Stefan-Boltzmann
Astronomy 1 Winter 2011 Lecture 8; January 24 2011 Previously on Astro 1 Light as a wave The Kelvin Temperature scale What is a blackbody? Wien s law: λ max (in meters) = (0.0029 K m)/t. The Stefan-Boltzmann
ASTRONOMY. Chapter 5 RADIATION AND SPECTRA PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 ASTRONOMY Chapter 5 RADIATION AND SPECTRA PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 5.1 Our Sun in Ultraviolet Light. This photograph of the Sun was taken at several different wavelengths of ultraviolet, which
ASTRONOMY Chapter 5 RADIATION AND SPECTRA PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 5.1 Our Sun in Ultraviolet Light. This photograph of the Sun was taken at several different wavelengths of ultraviolet, which
Chapter 29 Atomic Physics. Looking Ahead. Slide 29-1
 Chapter 29 Atomic Physics Looking Ahead Slide 29-1 Atomic Spectra and the Bohr Model In the mid 1800s it became apparent that the spectra of atomic gases is comprised of individual emission lines. Slide
Chapter 29 Atomic Physics Looking Ahead Slide 29-1 Atomic Spectra and the Bohr Model In the mid 1800s it became apparent that the spectra of atomic gases is comprised of individual emission lines. Slide
Today. Kirchoff s Laws. Emission and Absorption. Stellar Spectra & Composition. Doppler Effect & Motion. Extrasolar Planets
 Today Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Stellar Spectra & Composition Doppler Effect & Motion Extrasolar Planets Three basic types of spectra Continuous Spectrum Intensity Emission Line Spectrum
Today Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Stellar Spectra & Composition Doppler Effect & Motion Extrasolar Planets Three basic types of spectra Continuous Spectrum Intensity Emission Line Spectrum
Democritus & Leucippus (~400 BC) Greek philosophers: first to propose that matter is made up of particles called atomos, the Greek word for atoms
 Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block The Evolution of the Atomic Model Since atoms are too small to see even with a very powerful microscope, scientists rely upon indirect evidence and models to help them
Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block The Evolution of the Atomic Model Since atoms are too small to see even with a very powerful microscope, scientists rely upon indirect evidence and models to help them
From Last Time. Electron diffraction. Making a particle out of waves. Planetary model of atom. Using quantum mechanics ev 1/ 2 nm E kinetic
 From Last Time All objects show both wave-like properties and particle-like properties. Electromagnetic radiation (e.g. light) shows interference effects (wave-like properties), but also comes in discrete
From Last Time All objects show both wave-like properties and particle-like properties. Electromagnetic radiation (e.g. light) shows interference effects (wave-like properties), but also comes in discrete
Chapter 5 Light and Matter
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter Stars and galaxies are too far for us to send a spacecraft or to visit (in our lifetimes). All we can receive from them is light But there is much we can learn (composition,
Chapter 5 Light and Matter Stars and galaxies are too far for us to send a spacecraft or to visit (in our lifetimes). All we can receive from them is light But there is much we can learn (composition,
Quantum Mechanics and Stellar Spectroscopy.
 Quantum Mechanics and Stellar Spectroscopy http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ Recall the electric force. Like gravity it is a 1/r 2 force/ That is: F elec = Z 1 Z 2 e2 r 2 where Z 1 and Z 2 are the (integer) numbers
Quantum Mechanics and Stellar Spectroscopy http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ Recall the electric force. Like gravity it is a 1/r 2 force/ That is: F elec = Z 1 Z 2 e2 r 2 where Z 1 and Z 2 are the (integer) numbers
Today. Spectra. Thermal Radiation. Wien s Law. Stefan-Boltzmann Law. Kirchoff s Laws. Emission and Absorption. Spectra & Composition
 Today Spectra Thermal Radiation Wien s Law Stefan-Boltzmann Law Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Spectra & Composition Spectrum Originally, the range of colors obtained by passing sunlight through
Today Spectra Thermal Radiation Wien s Law Stefan-Boltzmann Law Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Spectra & Composition Spectrum Originally, the range of colors obtained by passing sunlight through
Experimental Basis for QM Ch3
 Experimental Basis for QM Ch3 This chapter describes the early evidence for quantization including Blackbody radiation Photoelectric effect Compton scattering X-rays and their spectra We ll see how early
Experimental Basis for QM Ch3 This chapter describes the early evidence for quantization including Blackbody radiation Photoelectric effect Compton scattering X-rays and their spectra We ll see how early
Atoms and Spectroscopy
 Atoms and Spectroscopy Lecture 3 1 ONE SMALL STEP FOR MAN ONE GIANT LEAP FOR MANKIND 2 FROM ATOMS TO STARS AND GALAXIES HOW DO WE KNOW? Observations The Scientific Method Hypothesis Verifications LAW 3
Atoms and Spectroscopy Lecture 3 1 ONE SMALL STEP FOR MAN ONE GIANT LEAP FOR MANKIND 2 FROM ATOMS TO STARS AND GALAXIES HOW DO WE KNOW? Observations The Scientific Method Hypothesis Verifications LAW 3
Physics 1C Lecture 29B
 Physics 1C Lecture 29B Emission Spectra! The easiest gas to analyze is hydrogen gas.! Four prominent visible lines were observed, as well as several ultraviolet lines.! In 1885, Johann Balmer, found a
Physics 1C Lecture 29B Emission Spectra! The easiest gas to analyze is hydrogen gas.! Four prominent visible lines were observed, as well as several ultraviolet lines.! In 1885, Johann Balmer, found a
Chapter 7 QUANTUM THEORY & ATOMIC STRUCTURE Brooks/Cole - Thomson
 Chapter 7 QUANTUM THEORY & ATOMIC STRUCTURE 1 7.1 The Nature of Light 2 Most subatomic particles behave as PARTICLES and obey the physics of waves. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation Light consists
Chapter 7 QUANTUM THEORY & ATOMIC STRUCTURE 1 7.1 The Nature of Light 2 Most subatomic particles behave as PARTICLES and obey the physics of waves. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation Light consists
Physics 2D Lecture Slides Feb. 2, Sunil Sinha UCSD Physics
 Physics D Lecture Slides Feb., 010 Sunil Sinha UCSD Physics Thomson s Determination of e/m of the Electron In E Field alone, electron lands at D In B field alone, electron lands at E When E and B field
Physics D Lecture Slides Feb., 010 Sunil Sinha UCSD Physics Thomson s Determination of e/m of the Electron In E Field alone, electron lands at D In B field alone, electron lands at E When E and B field
Chapter 31 Atomic Physics
 100 92 86 100 92 84 100 92 84 98 92 83 97 92 82 96 91 80 96 91 76 95 91 74 95 90 68 95 89 67 95 89 66 94 87 93 86 No. of Students in Range Exam 3 Score Distribution 25 22 20 15 10 10 5 3 2 0 0 0 0 0 0
100 92 86 100 92 84 100 92 84 98 92 83 97 92 82 96 91 80 96 91 76 95 91 74 95 90 68 95 89 67 95 89 66 94 87 93 86 No. of Students in Range Exam 3 Score Distribution 25 22 20 15 10 10 5 3 2 0 0 0 0 0 0
CONCEPT MAP ATOMS. Atoms. 1.Thomson model 2.Rutherford model 3.Bohr model. 6. Hydrogen spectrum
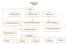 CONCEPT MAP ATOMS Atoms 1.Thomson model 2.Rutherford model 3.Bohr model 4.Emission line spectra 2a. Alpha scattering experiment 3a. Bohr s postulates 6. Hydrogen spectrum 8. De Broglie s explanation 5.Absorption
CONCEPT MAP ATOMS Atoms 1.Thomson model 2.Rutherford model 3.Bohr model 4.Emission line spectra 2a. Alpha scattering experiment 3a. Bohr s postulates 6. Hydrogen spectrum 8. De Broglie s explanation 5.Absorption
Early Atomic Theories and the Origins of Quantum Theory. Chapter 3.1
 Early Atomic Theories and the Origins of Quantum Theory Chapter 3.1 What is Matter Made of? People have wondered about the answer to this question for thousands of years Philosophers Matter is composed
Early Atomic Theories and the Origins of Quantum Theory Chapter 3.1 What is Matter Made of? People have wondered about the answer to this question for thousands of years Philosophers Matter is composed
From Last Time. Summary of Photoelectric effect. Photon properties of light
 Exam 3 is Tuesday Nov. 25 5:30-7 pm, 203 Ch (here) Students w / scheduled academic conflict please stay after class Tues. Nov. 8 (TODAY) to arrange alternate time. From Last Time Photoelectric effect and
Exam 3 is Tuesday Nov. 25 5:30-7 pm, 203 Ch (here) Students w / scheduled academic conflict please stay after class Tues. Nov. 8 (TODAY) to arrange alternate time. From Last Time Photoelectric effect and
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 7-1A DISCRETE ENERGY Essential Idea: In the microscopic world energy is discrete. Theory Of Knowledge: The role of luck/serendipity in
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 7-1A DISCRETE ENERGY Essential Idea: In the microscopic world energy is discrete. Theory Of Knowledge: The role of luck/serendipity in
Section 3.1 Substances Are Made of Atoms
 Section 3.1 Substances Are Made of Atoms Objectives: 1. State the three laws that support the existence of atoms. 2. List the five principles of John Dalton s atomic theory. Vocabulary: law of definite
Section 3.1 Substances Are Made of Atoms Objectives: 1. State the three laws that support the existence of atoms. 2. List the five principles of John Dalton s atomic theory. Vocabulary: law of definite
Topics Covered in Chapter. Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation. A Subatomic Interlude II. A Subatomic Interlude. A Subatomic Interlude III
 Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation Topics Covered in Chapter 1.Structure of Atoms 2.Origins of Electromagnetic Radiation 3.Objects with Different Temperature and their Electromagnetic Radiation
Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation Topics Covered in Chapter 1.Structure of Atoms 2.Origins of Electromagnetic Radiation 3.Objects with Different Temperature and their Electromagnetic Radiation
Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation
 Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation 1 Topics Covered in Chapter 1.Structure of Atoms 2.Origins of Electromagnetic Radiation 3.Objects with Different Temperature and their Electromagnetic Radiation
Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation 1 Topics Covered in Chapter 1.Structure of Atoms 2.Origins of Electromagnetic Radiation 3.Objects with Different Temperature and their Electromagnetic Radiation
2/28/2016 ATOMS) ATOMS. Physics 2D. PHYS 342 Modern Physics Atom I: Rutherford Model and Bohr Model
 PHYS 342 Modern Physics Atom I: Rutherford Model and Bohr Model Today Contents: a) Basic Properties of Atoms b) Rutherford Model and Scattering Experiments c) Bohr Model and Line Spectra Physics 2D Subfields
PHYS 342 Modern Physics Atom I: Rutherford Model and Bohr Model Today Contents: a) Basic Properties of Atoms b) Rutherford Model and Scattering Experiments c) Bohr Model and Line Spectra Physics 2D Subfields
Preview. Atomic Physics Section 1. Section 1 Quantization of Energy. Section 2 Models of the Atom. Section 3 Quantum Mechanics
 Atomic Physics Section 1 Preview Section 1 Quantization of Energy Section 2 Models of the Atom Section 3 Quantum Mechanics Atomic Physics Section 1 TEKS The student is expected to: 8A describe the photoelectric
Atomic Physics Section 1 Preview Section 1 Quantization of Energy Section 2 Models of the Atom Section 3 Quantum Mechanics Atomic Physics Section 1 TEKS The student is expected to: 8A describe the photoelectric
is the minimum stopping potential for which the current between the plates reduces to zero.
 Module 1 :Quantum Mechanics Chapter 2 : Introduction to Quantum ideas Introduction to Quantum ideas We will now consider some experiments and their implications, which introduce us to quantum ideas. The
Module 1 :Quantum Mechanics Chapter 2 : Introduction to Quantum ideas Introduction to Quantum ideas We will now consider some experiments and their implications, which introduce us to quantum ideas. The
298 Chapter 6 Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties of Elements
 98 Chapter 6 Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties of Elements 6. The Bohr Model By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom Use the Rydberg equation
98 Chapter 6 Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties of Elements 6. The Bohr Model By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom Use the Rydberg equation
X Rays must be viewed from space used for detecting exotic objects such as neutron stars and black holes also observing the Sun.
 6/25 How do we get information from the telescope? 1. Galileo drew pictures. 2. With the invention of photography, we began taking pictures of the view in the telescope. With telescopes that would rotate
6/25 How do we get information from the telescope? 1. Galileo drew pictures. 2. With the invention of photography, we began taking pictures of the view in the telescope. With telescopes that would rotate
HISTORY OF THE ATOM ATOMA
 S.MORRIS 2006 HISTORY OF THE ATOM 460 BC Democritus develops the idea of atoms he pounded up materials in his pestle and mortar until he had reduced them to smaller and smaller particles which he called
S.MORRIS 2006 HISTORY OF THE ATOM 460 BC Democritus develops the idea of atoms he pounded up materials in his pestle and mortar until he had reduced them to smaller and smaller particles which he called
UNIT : QUANTUM THEORY AND THE ATOM
 Name St.No. Date(YY/MM/DD) / / Section UNIT 102-10: QUANTUM THEORY AND THE ATOM OBJECTIVES Atomic Spectra for Hydrogen, Mercury and Neon. 1. To observe various atomic spectra with a diffraction grating
Name St.No. Date(YY/MM/DD) / / Section UNIT 102-10: QUANTUM THEORY AND THE ATOM OBJECTIVES Atomic Spectra for Hydrogen, Mercury and Neon. 1. To observe various atomic spectra with a diffraction grating
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos. How do we experience light? Colors of Light. How do light and matter interact?
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos How do we experience light? The warmth of sunlight tells us that light is a form of energy We can measure the amount of energy emitted by a
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos How do we experience light? The warmth of sunlight tells us that light is a form of energy We can measure the amount of energy emitted by a
AP Physics Study Guide Modern Physics I. Atomic Physics and Quantum Effects 1. Who is generally credited with the discovery of the electron?
 AP Physics Study Guide Modern Physics I. Atomic Physics and Quantum Effects 1. Who is generally credited with the discovery of the electron? 2. What was it that J. J. Thomson actually measured? 3. Regarding
AP Physics Study Guide Modern Physics I. Atomic Physics and Quantum Effects 1. Who is generally credited with the discovery of the electron? 2. What was it that J. J. Thomson actually measured? 3. Regarding
The Nature of Light. Chapter Five
 The Nature of Light Chapter Five Guiding Questions 1. How fast does light travel? How can this speed be measured? 2. Why do we think light is a wave? What kind of wave is it? 3. How is the light from an
The Nature of Light Chapter Five Guiding Questions 1. How fast does light travel? How can this speed be measured? 2. Why do we think light is a wave? What kind of wave is it? 3. How is the light from an
