Beyond the spherical dust collapse model
|
|
|
- Noah Beverly Griffin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Beyond the spherical dust collapse model 1.5M 1.0M M= M 0.65M 0.4M 0.25M Evolution of radii of different mass shells in a simulated halo Yasushi Suto Department of Physics and RESCEU (Research Center for the early Universe) The University of Tokyo Kyoto workshop Vlasov-Poisson: towards numerical methods without particles June 2, 2015@Yukawa Institute, Kyoto University
2 Collaborators n This talk is based on my collaboration with n Daichi Suto (Univ. of Tokyo) n Ken Osato (Univ. of Tokyo), n Tetsu Kitayama (Toho Univ.) n Shin Sasaki (Tokyo Metropolitan Univ.) n Still one-going and preliminary work!
3 Spherical dust collapse (SDC) model n The most basic model of structure formation n Everybody knows that it is just a simple approximation, but still widely used even in precision cosmology: n e.g., Dark matter halo abundance vs. cluster mass and temperature functions to determine cosmological parameters n Attempts for improvement n Non-sphericity (e.g., Jing & Suto 2002) n inhomogeneities (e.g., Kawahara et al. 2007) n shell-crossing and velocity dispersions (this talk)
4 Comparison of the SDC model predictions against N-body results n Dark matter only simulations with GADGET-2 n ΛCDM with WMAP9 cosmological parameters n N= in L=360 Mpc h -1 n m= M n FOF halos identified at z=0 n compute the spherical mass M and radius R of spherical overdensity of Δ=ρ/ρ m =355.4 n Identifies the center-of-mass of the z=0 FOF halo particles at z, and compute the radius R(z) enclosing the mass M at 0<z<z initial = 99
5 The most massive halo with M= M Red: FOF particles at z=0 Black: non-fof particles Red curve: SDC prediction with δ(z=99) R / R(z=inital) of the simulation Y [comoving Mpc/h] R(z) for the (constant) mass M R(z)/R(z=99) simulation X [comoving Mpc/h] Sampled particles in a halo log (1+z)
6 Generic trends from 100 simulated halos n Very good quantitative agreement until the turn-around epoch n may be reasonable but not trivial at all, given the small-scale clumping, subhalo mergers inside, and/or the filamentary structure across the entire region n Systematic difference relative to SDC predictions after the turn-around epoch n Delay of the turn-around epoch n Larger turn-around radius n Larger virialized radius
7 Evolution of a halo(m= M ) in phase space (comoving coordinate)
8 Effect of velocity dispersions n Jeans equation for spherical collisionless system n radial velocity dispersion σ 2 r n tangential velocity dispersion σ 2 t Dv r Dt = 1 (ρσ 2 r ) ρ r + σ 2 t 2σ 2 r 2 GM r 2 n SDC assumes an initially top-hat (homogeneous) sphere n neglects small-scale inhomogeneities, shell-crossing before turn-around, and thus no σ r 2 or σ t 2 n Larger t turn-around and R virial than predicted by SDC
9 Improvement with velocity dispersions n Evaluate the velocity dispersions from simulation data and solve the Jean equation n Greatly improved! 1 (ρσ 2 r ) + σ 2 2 t 2σ r ρ r 2 [(km/s) 2 /(Mpc/h)] at R(z) that encloses the total halo mass R(z)/R(z=99) improved SC model based on Jeans equation (with velocity dispersions) 点 : シミュレーション simulation M= M log(1+z) SDC (w/o velocity dispersions) log(1+z)
10 Phase-space distribution in redshift space: line-of-sight velocity vs. projected radius M= M z=0.6 Σ(R) exp( R / R Σ ) σ 2 (R) exp( R / R σ 2 ) Σ(R)σ 2 (R) exp( R / R Σσ 2 ) Surface density Σ(R) σ los2 (R) Σ(R)σ los2 (R)
11 Phase-space distribution in redshift space: line-of-sight velocity vs. projected radius M= M z=0.2 Σ(R) exp( R / R Σ ) σ 2 (R) exp( R / R σ 2 ) Σ(R)σ 2 (R) exp( R / R Σσ 2 ) Surface density Σ(R) σ los2 (R) Σ(R)σ los2 (R)
12 Phase-space distribution in redshift space: line-of-sight velocity vs. projected radius M= M z=0.1 Σ(R) exp( R / R Σ ) σ 2 (R) exp( R / R σ 2 ) Σ(R)σ 2 (R) exp( R / R Σσ 2 ) Surface density Σ(R) σ los2 (R) Σ(R)σ los2 (R)
13 Phase-space distribution in redshift space: line-of-sight velocity vs. projected radius M= M z=0 Σ(R) exp( R / R Σ ) σ 2 (R) exp( R / R σ 2 ) Σ(R)σ 2 (R) exp( R / R Σσ 2 ) Surface density Σ(R) σ los2 (R) Σ(R)σ los2 (R)
14 Comparison among characteristic scales M= M σm (r nl z)=1 r ta (z) r Δ (z) r 200 (z) projected e-folding radius 2R Σσ2 (z) n Projected e-folding scales 2R Σσ2 (z) R Σ (z) R σ2 (z) are close to conventional virial radii (r 200 or r Δ ) n r 2nd apocenter 0.367r ta and r 3rd apocenter 0.236r ta in Bertschinger s solution (1985, ApJS, 58, 39)
15 Splashback in accreting dark halos S. Adhikari, N. Dalal & R. T. Chamberlain, arxiv: All particles Particles with v r <0.4v circ n Physical definition of halo size = splashback radius? n first apoapse after collapse n Ensemble of halos from cosmological simulation n Clear signature in density profile of ensemble of halos n Not easy to determine the splashback radius from a single halo (at least observationally)
16 The splashback radius as a physical halo boundary and the growth of halo mass S. More, B. Diemer & A. V. Kravtsov, arxiv:
17 Signature of the splashback radius? n Line-of-sight velocity of galaxies in X-ray selected clusters n Rines et al. (2013)
18 Relation to Splashback radius? M= M R Σ (z=0.2) R Σ (z=0) n n Qualitative agreement between our projected e-folding radius R and the splashback radius Our definition (e-folding scale in redshift space) is more relevant from an observational viewpoint S. Adhikari, N. Dalal & R. T. Chamberlain, arxiv:
19 Bertschinger s self-similar solution turn-around (1 st apocenter) λ r r ta (t) " ξ ln$ # 2 nd apocenter 3 rd apocenter t t ta % ' & n Self-similar shell crossing of collisionless spherical secondary infall Bertschinger 1985, ApJS, 58, 39
20 Scaled evolution of constant mass shells: r M (z) with M(<r M )=const. in the halo M= M n usual assumption (r vir =r ta /2) is not accurate n Mixing of different mass shells is not complete
21 Motion of constant mass shells for 4 different halos M= M M= M M= M M= M
22 Virialized mass shells change: not constant but oscillating 1.5M 1.0M 0.65M 0.4M 0.25M M= M M= M n Each mass shell continues to oscillate within the halo; halos are not static but dynamical
23 Virialized mass shells change: not constant but oscillating M= M M= M n Each mass shell continues to oscillate within the halo; halos are not static but dynamical
24 virialized densities within different mass shells M= M n Not constant n Large coherent modulation
25 Summary n Spherical dust collapse model for dark matter halos is oversimplified n Better model is required for cluster cosmology, and indeed already overdue n We focus on the effect of velocity dispersions n Delays the turn-around epoch, increases the virial radius n Confirmed by solving the Jeans equation n Interesting scaling behavior of halo collapse n Virialized halos are not static but dynamical, and indeed oscillating!
26 Future outlook n Observational signature of the oscillating feature? n affects the gas dynamics as well? n Hydro-dynamical simulations to check? n X-ray vs. weak lensing? n Toy model to describe the oscillation? n Empirical scaling model? n Modeling velocity dispersions?
cluster scaling relations and mass definitions
 cluster scaling relations and mass definitions Andrey Kravtsov Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics The University of Chicago Abell 85 SDSS Abell 85 SDSS/ Abell
cluster scaling relations and mass definitions Andrey Kravtsov Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics The University of Chicago Abell 85 SDSS Abell 85 SDSS/ Abell
Splashback radius as a physical boundary of clusters
 Splashback radius as a physical boundary of clusters Andrey Kravtsov Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics The University of Chicago Abell 85 SDSS/ Chandra galaxy
Splashback radius as a physical boundary of clusters Andrey Kravtsov Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics The University of Chicago Abell 85 SDSS/ Chandra galaxy
The edge of darkness, and other halo surprises
 The edge of darkness, and other halo surprises Benedikt Diemer ITC Fellow, Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (in collaboration with Andrey Kravtsov and Surhud More) APEC Seminar IPMU 4/7/26 Strength
The edge of darkness, and other halo surprises Benedikt Diemer ITC Fellow, Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (in collaboration with Andrey Kravtsov and Surhud More) APEC Seminar IPMU 4/7/26 Strength
The Los Cabos Lectures
 January 2009 The Los Cabos Lectures Dark Matter Halos: 2 Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics EPS statistics for the standard ΛCDM cosmology Millennium Simulation cosmology: Ωm = 0.25, ΩΛ
January 2009 The Los Cabos Lectures Dark Matter Halos: 2 Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics EPS statistics for the standard ΛCDM cosmology Millennium Simulation cosmology: Ωm = 0.25, ΩΛ
pseudo- evolution of halo mass and observable-mass relations Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago
 pseudo- evolution of halo mass and observable-mass relations Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Baseline model for cluster scaling relations Kaiser 1986, 1991 If mass is defined within a spherical
pseudo- evolution of halo mass and observable-mass relations Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Baseline model for cluster scaling relations Kaiser 1986, 1991 If mass is defined within a spherical
Origin of Structure Formation of Structure. Projected slice of 200,000 galaxies, with thickness of a few degrees.
 Origin of Structure Formation of Structure Projected slice of 200,000 galaxies, with thickness of a few degrees. Redshift Surveys Modern survey: Sloan Digital Sky Survey, probes out to nearly 1000 Mpc.
Origin of Structure Formation of Structure Projected slice of 200,000 galaxies, with thickness of a few degrees. Redshift Surveys Modern survey: Sloan Digital Sky Survey, probes out to nearly 1000 Mpc.
The Milky Way in the cosmological context. Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago
 The Milky Way in the cosmological context Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Milky Way and Its Stars, KITP, 2 February 2015 Cosmological context: hierarchical structure formation from a Gaussian
The Milky Way in the cosmological context Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Milky Way and Its Stars, KITP, 2 February 2015 Cosmological context: hierarchical structure formation from a Gaussian
Simulating non-linear structure formation in dark energy cosmologies
 Simulating non-linear structure formation in dark energy cosmologies Volker Springel Distribution of WIMPS in the Galaxy Early Dark Energy Models (Margherita Grossi) Coupled Dark Energy (Marco Baldi) Fifth
Simulating non-linear structure formation in dark energy cosmologies Volker Springel Distribution of WIMPS in the Galaxy Early Dark Energy Models (Margherita Grossi) Coupled Dark Energy (Marco Baldi) Fifth
THE EDGES OF DARK MATTER HALOS: THEORY AND OBSERVATIONS
 THE EDGES OF DARK MATTER HALOS: THEORY AND OBSERVATIONS SURHUD MORE (KAVLI IPMU) Collaborators : Benedikt Diemer, Andrey Kravtsov, Philip Mansfield, Masahiro Takada, Hironao Miyatake, Neal Dalal, Rachel
THE EDGES OF DARK MATTER HALOS: THEORY AND OBSERVATIONS SURHUD MORE (KAVLI IPMU) Collaborators : Benedikt Diemer, Andrey Kravtsov, Philip Mansfield, Masahiro Takada, Hironao Miyatake, Neal Dalal, Rachel
Signatures of MG on. linear scales. non- Fabian Schmidt MPA Garching. Lorentz Center Workshop, 7/15/14
 Signatures of MG on non- linear scales Fabian Schmidt MPA Garching Lorentz Center Workshop, 7/15/14 Tests of gravity Smooth Dark Energy (DE): unique prediction for growth factor given w(a) Use evolution
Signatures of MG on non- linear scales Fabian Schmidt MPA Garching Lorentz Center Workshop, 7/15/14 Tests of gravity Smooth Dark Energy (DE): unique prediction for growth factor given w(a) Use evolution
The Caustic Technique An overview
 The An overview Ana Laura Serra Torino, July 30, 2010 Why the mass of? Small scales assumption of dynamical equilibrium Mass distribution on intermediate scales (1 10 Mpc/h) Large scales small over densities
The An overview Ana Laura Serra Torino, July 30, 2010 Why the mass of? Small scales assumption of dynamical equilibrium Mass distribution on intermediate scales (1 10 Mpc/h) Large scales small over densities
Princeton December 2009 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos
 Princeton December 2009 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The dark matter structure of CDM halos A rich galaxy cluster halo Springel et al
Princeton December 2009 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The dark matter structure of CDM halos A rich galaxy cluster halo Springel et al
The Current Status of Too Big To Fail problem! based on Warm Dark Matter cosmology
 The Current Status of Too Big To Fail problem! based on Warm Dark Matter cosmology 172th Astronomical Seminar Dec.3 2013 Chiba Lab.M2 Yusuke Komuro Key Word s Too Big To Fail TBTF Cold Dark Matter CDM
The Current Status of Too Big To Fail problem! based on Warm Dark Matter cosmology 172th Astronomical Seminar Dec.3 2013 Chiba Lab.M2 Yusuke Komuro Key Word s Too Big To Fail TBTF Cold Dark Matter CDM
DETECTION OF HALO ASSEMBLY BIAS AND THE SPLASHBACK RADIUS
 DETECTION OF HALO ASSEMBLY BIAS AND THE SPLASHBACK RADIUS Surhud More (Kavli-IPMU) Collaborators: Hironao Miyatake (JPL), Masahiro Takada (Kavli IPMU), David Spergel (Princeton), Rachel Mandelbaum (CMU),
DETECTION OF HALO ASSEMBLY BIAS AND THE SPLASHBACK RADIUS Surhud More (Kavli-IPMU) Collaborators: Hironao Miyatake (JPL), Masahiro Takada (Kavli IPMU), David Spergel (Princeton), Rachel Mandelbaum (CMU),
QUENCHING AND MORPHOLOGICAL TRANSFORMATIONS. Physics of Groups IAP Mike Hudson, U. Waterloo
 QUENCHING AND MORPHOLOGICAL TRANSFORMATIONS Physics of Groups Conference @ IAP Mike Hudson, U. Waterloo 1 EFFECT OF THE ENVIRONMENT Star-formation quenching via:! Ram-pressure stripping cold gas hot gas
QUENCHING AND MORPHOLOGICAL TRANSFORMATIONS Physics of Groups Conference @ IAP Mike Hudson, U. Waterloo 1 EFFECT OF THE ENVIRONMENT Star-formation quenching via:! Ram-pressure stripping cold gas hot gas
Probing Dark Matter Halos with Satellite Kinematics & Weak Lensing
 Probing Dark Matter Halos with & Weak Lensing Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Surhud More, Marcello Cacciato UMass, August 2008 Probing Dark Matter Halos - p. 1/35 Galaxy Formation in a Nutshell
Probing Dark Matter Halos with & Weak Lensing Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Surhud More, Marcello Cacciato UMass, August 2008 Probing Dark Matter Halos - p. 1/35 Galaxy Formation in a Nutshell
You may not start to read the questions printed on the subsequent pages until instructed to do so by the Invigilator.
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Friday 8 June 2001 1.30 to 4.30 PAPER 41 PHYSICAL COSMOLOGY Answer any THREE questions. The questions carry equal weight. You may not start to read the questions printed on
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Friday 8 June 2001 1.30 to 4.30 PAPER 41 PHYSICAL COSMOLOGY Answer any THREE questions. The questions carry equal weight. You may not start to read the questions printed on
2. What are the largest objects that could have formed so far? 3. How do the cosmological parameters influence structure formation?
 Einführung in die beobachtungsorientierte Kosmologie I / Introduction to observational Cosmology I LMU WS 2009/10 Rene Fassbender, MPE Tel: 30000-3319, rfassben@mpe.mpg.de 1. Cosmological Principles, Newtonian
Einführung in die beobachtungsorientierte Kosmologie I / Introduction to observational Cosmology I LMU WS 2009/10 Rene Fassbender, MPE Tel: 30000-3319, rfassben@mpe.mpg.de 1. Cosmological Principles, Newtonian
The mass of a halo. M. White
 A&A 367, 27 32 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20000357 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics The mass of a halo M. White Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Cambridge, MA 02138, USA e-mail: mwhite@cfa.harvard.edu
A&A 367, 27 32 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20000357 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics The mass of a halo M. White Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Cambridge, MA 02138, USA e-mail: mwhite@cfa.harvard.edu
The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters
 IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
4. Structure of Dark Matter halos. Hence the halo mass, virial radius, and virial velocity are related by
 13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-1 13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-1 13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 18 Nov 2009
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 18 Nov 2009 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 18 Nov 2009](/thumbs/72/67298474.jpg) Draft version November 22, 2013 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 11/26/04 ASSEMBLY BIAS AND THE DYNAMICAL STRUCTURE OF DARK MATTER HALOS Andreas Faltenbacher 1,2,3 and Simon D. M. White
Draft version November 22, 2013 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 11/26/04 ASSEMBLY BIAS AND THE DYNAMICAL STRUCTURE OF DARK MATTER HALOS Andreas Faltenbacher 1,2,3 and Simon D. M. White
A tool to test galaxy formation theories. Joe Wolf (UC Irvine)
 A tool to test galaxy formation theories Joe Wolf (UC Irvine) SF09 Cosmology Summer Workshop July 7 2009 Team Irvine: Greg Martinez James Bullock Manoj Kaplinghat Frank Avedo KIPAC: Louie Strigari Haverford:
A tool to test galaxy formation theories Joe Wolf (UC Irvine) SF09 Cosmology Summer Workshop July 7 2009 Team Irvine: Greg Martinez James Bullock Manoj Kaplinghat Frank Avedo KIPAC: Louie Strigari Haverford:
N-body Simulations. Initial conditions: What kind of Dark Matter? How much Dark Matter? Initial density fluctuations P(k) GRAVITY
 N-body Simulations N-body Simulations N-body Simulations Initial conditions: What kind of Dark Matter? How much Dark Matter? Initial density fluctuations P(k) GRAVITY Final distribution of dark matter.
N-body Simulations N-body Simulations N-body Simulations Initial conditions: What kind of Dark Matter? How much Dark Matter? Initial density fluctuations P(k) GRAVITY Final distribution of dark matter.
The Los Cabos Lectures
 January 2009 The Los Cabos Lectures Dark Matter Halos: 3 Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Shapes of halo equidensity surfaces Group Jing & Suto 2002 Galaxy δ 100 2500 6250 Shapes of halo
January 2009 The Los Cabos Lectures Dark Matter Halos: 3 Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Shapes of halo equidensity surfaces Group Jing & Suto 2002 Galaxy δ 100 2500 6250 Shapes of halo
4. Structure of Dark Matter halos. Hence the halo mass, virial radius, and virial velocity are related by
 6-4-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c04-1 6-4-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
6-4-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c04-1 6-4-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
DA(z) from Strong Lenses. Eiichiro Komatsu, Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik Inaugural MIAPP Workshop on Extragalactic Distance Scale May 26, 2014
 DA(z) from Strong Lenses Eiichiro Komatsu, Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik Inaugural MIAPP Workshop on Extragalactic Distance Scale May 26, 2014 This presentation is based on: Measuring angular diameter
DA(z) from Strong Lenses Eiichiro Komatsu, Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik Inaugural MIAPP Workshop on Extragalactic Distance Scale May 26, 2014 This presentation is based on: Measuring angular diameter
Future evolution of bound supercluster in an accelerating Universe
 Future evolution of bound supercluster in an accelerating Universe P.A. Araya-Melo, A. Reisenegger, A. Meza, R. van de Weygaert, R. Dünner and H. Quintana August 27, 2010 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 399,97-120
Future evolution of bound supercluster in an accelerating Universe P.A. Araya-Melo, A. Reisenegger, A. Meza, R. van de Weygaert, R. Dünner and H. Quintana August 27, 2010 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 399,97-120
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 27 Nov 2000
 A&A manuscript no. (will be inserted by hand later) Your thesaurus codes are: 02 (3.13.18) - methods: N-body simulations ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS The mass of a halo Martin White arxiv:astro-ph/0011495v1
A&A manuscript no. (will be inserted by hand later) Your thesaurus codes are: 02 (3.13.18) - methods: N-body simulations ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS The mass of a halo Martin White arxiv:astro-ph/0011495v1
The inside-out Growth of the Stellar Mass Distribution in Galaxy Clusters since z 1
 The inside-out Growth of the Stellar Mass Distribution in Galaxy Clusters since z 1 Remco van der Burg CEA Saclay, France A&A in press (ArXiv:1412.2137) Henk Hoekstra, Adam Muzzin, Cristóbal Sifón, Michael
The inside-out Growth of the Stellar Mass Distribution in Galaxy Clusters since z 1 Remco van der Burg CEA Saclay, France A&A in press (ArXiv:1412.2137) Henk Hoekstra, Adam Muzzin, Cristóbal Sifón, Michael
arxiv:astro-ph/ v3 13 May 2008
 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 0/09/06 FORMATION AND EOLUTION OF GALAXY DARK MATTER HALOS AND THEIR SUBSTRUCTURE Jürg Diemand,, Michael Kuhlen, & Piero Madau, arxiv:astro-ph/0707v May
Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 0/09/06 FORMATION AND EOLUTION OF GALAXY DARK MATTER HALOS AND THEIR SUBSTRUCTURE Jürg Diemand,, Michael Kuhlen, & Piero Madau, arxiv:astro-ph/0707v May
The Distribution of Stellar Mass in Galaxy Clusters since z=1
 The Distribution of Stellar Mass in Galaxy Clusters since z=1 Remco van der Burg CEA Saclay, France Adam Muzzin, Henk Hoekstra, Monique Arnaud, Hervé Aussel, Gabriel Pratt, JeanBaptiste Melin, Sean McGee,
The Distribution of Stellar Mass in Galaxy Clusters since z=1 Remco van der Burg CEA Saclay, France Adam Muzzin, Henk Hoekstra, Monique Arnaud, Hervé Aussel, Gabriel Pratt, JeanBaptiste Melin, Sean McGee,
Summary So Far! M87van der Maerl! NGC4342! van den Bosch! rotation velocity!
 Summary So Far Fundamental plane connects luminosity, scale length, surface brightness, stellar dynamics. age and chemical composition Elliptical galaxies are not randomly distributed within the 3D space
Summary So Far Fundamental plane connects luminosity, scale length, surface brightness, stellar dynamics. age and chemical composition Elliptical galaxies are not randomly distributed within the 3D space
halo merger histories
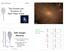 Physics 463, Spring 07 Lecture 5 The Growth and Structure of Dark Mater Halos z=7! z=3! z=1! expansion scalefactor z=0! ~milky way M>3e12M! /h c vir ~13 ~virgo cluster M>3e14M! /h, c vir ~6 halo merger
Physics 463, Spring 07 Lecture 5 The Growth and Structure of Dark Mater Halos z=7! z=3! z=1! expansion scalefactor z=0! ~milky way M>3e12M! /h c vir ~13 ~virgo cluster M>3e14M! /h, c vir ~6 halo merger
THE BOLSHOI COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS
 GALAXY FORMATION - Durham -18 July 2011 THE BOLSHOI COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS JOEL PRIMACK, UCSC ΛCDM Cosmological Parameters for Bolshoi and BigBolshoi Halo Mass Function is 10x
GALAXY FORMATION - Durham -18 July 2011 THE BOLSHOI COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS JOEL PRIMACK, UCSC ΛCDM Cosmological Parameters for Bolshoi and BigBolshoi Halo Mass Function is 10x
Elad Zinger Hebrew University Jerusalem Spineto, 12 June Collaborators: Avishai Dekel, Yuval Birnboim, Daisuke Nagai & Andrey Kravtsov
 Elad Zinger Hebrew University Jerusalem IGM@50, Spineto, 12 June 2015 Collaborators: Avishai Dekel, Yuval Birnboim, Daisuke Nagai & Andrey Kravtsov They re still there! Account for most of the accretion.
Elad Zinger Hebrew University Jerusalem IGM@50, Spineto, 12 June 2015 Collaborators: Avishai Dekel, Yuval Birnboim, Daisuke Nagai & Andrey Kravtsov They re still there! Account for most of the accretion.
(Toward) A Solution to the Hydrostatic Mass Bias Problem in Galaxy Clusters. Eiichiro Komatsu (MPA) UTAP Seminar, December 22, 2014
 (Toward) A Solution to the Hydrostatic Mass Bias Problem in Galaxy Clusters Eiichiro Komatsu (MPA) UTAP Seminar, December 22, 2014 References Shi & EK, MNRAS, 442, 512 (2014) Shi, EK, Nelson & Nagai, arxiv:1408.3832
(Toward) A Solution to the Hydrostatic Mass Bias Problem in Galaxy Clusters Eiichiro Komatsu (MPA) UTAP Seminar, December 22, 2014 References Shi & EK, MNRAS, 442, 512 (2014) Shi, EK, Nelson & Nagai, arxiv:1408.3832
arxiv:astro-ph/ v3 10 Oct 2000
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 1 February 2008 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) Profiles of dark haloes: evolution, scatter, and environment arxiv:astro-ph/9908159v3 10 Oct 2000 J. S.
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 1 February 2008 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) Profiles of dark haloes: evolution, scatter, and environment arxiv:astro-ph/9908159v3 10 Oct 2000 J. S.
Lecture 6: Dark Matter Halos
 Lecture 6: Dark Matter Halos Houjun Mo February 23, 2004 Hierarchical clustering, the matter in the universe condenses to form quasiequilibrium objects (dark halos) of increasing masses in the passage
Lecture 6: Dark Matter Halos Houjun Mo February 23, 2004 Hierarchical clustering, the matter in the universe condenses to form quasiequilibrium objects (dark halos) of increasing masses in the passage
Baryon Census in Hydrodynamical Simulations of Galaxy Clusters
 Baryon Census in Hydrodynamical Simulations of Galaxy Clusters Susana Planelles (Univ.Trieste-INAF) Collaborators: S.Borgani (Univ. Trieste-INAF), G.Murante (INAF Torino), L.Tornatore (Univ. Trieste),
Baryon Census in Hydrodynamical Simulations of Galaxy Clusters Susana Planelles (Univ.Trieste-INAF) Collaborators: S.Borgani (Univ. Trieste-INAF), G.Murante (INAF Torino), L.Tornatore (Univ. Trieste),
Galaxy Cluster Mergers
 Galaxy Cluster Mergers Alexia Schulz Institute for Advanced Study Andrew Wetzel Daniel Holz Mike Warren Talk Overview! Introduction " Why are cluster mergers of interest? " Where will mergers complicate
Galaxy Cluster Mergers Alexia Schulz Institute for Advanced Study Andrew Wetzel Daniel Holz Mike Warren Talk Overview! Introduction " Why are cluster mergers of interest? " Where will mergers complicate
8.1 Structure Formation: Introduction and the Growth of Density Perturbations
 8.1 Structure Formation: Introduction and the Growth of Density Perturbations 1 Structure Formation and Evolution From this (Δρ/ρ ~ 10-6 ) to this (Δρ/ρ ~ 10 +2 ) to this (Δρ/ρ ~ 10 +6 ) 2 Origin of Structure
8.1 Structure Formation: Introduction and the Growth of Density Perturbations 1 Structure Formation and Evolution From this (Δρ/ρ ~ 10-6 ) to this (Δρ/ρ ~ 10 +2 ) to this (Δρ/ρ ~ 10 +6 ) 2 Origin of Structure
Non-linear structure in the Universe Cosmology on the Beach
 Non-linear structure in the Universe Cosmology on the Beach Puerto Vallarta January, 2011 Martin White UC Berkeley/LBNL (http://mwhite.berkeley.edu/talks) Strong non-linearity Martin White UCB/LBNL Limited
Non-linear structure in the Universe Cosmology on the Beach Puerto Vallarta January, 2011 Martin White UC Berkeley/LBNL (http://mwhite.berkeley.edu/talks) Strong non-linearity Martin White UCB/LBNL Limited
AY202a Galaxies & Dynamics Lecture 7: Jeans Law, Virial Theorem Structure of E Galaxies
 AY202a Galaxies & Dynamics Lecture 7: Jeans Law, Virial Theorem Structure of E Galaxies Jean s Law Star/Galaxy Formation is most simply defined as the process of going from hydrostatic equilibrium to gravitational
AY202a Galaxies & Dynamics Lecture 7: Jeans Law, Virial Theorem Structure of E Galaxies Jean s Law Star/Galaxy Formation is most simply defined as the process of going from hydrostatic equilibrium to gravitational
Why is the Universe Expanding?
 Why is the Universe Expanding? In general relativity, mass warps space. Warped space makes matter move, which changes the structure of space. Thus the universe should be dynamic! Gravity tries to collapse
Why is the Universe Expanding? In general relativity, mass warps space. Warped space makes matter move, which changes the structure of space. Thus the universe should be dynamic! Gravity tries to collapse
Halo Model. Vinicius Miranda. Cosmology Course - Astro 321, Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics University of Chicago
 Introduction program Thanks Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics University of Chicago Cosmology Course - Astro 321, 2011 Introduction program Thanks Outline 1 Introduction 2 Linear Theory Press -
Introduction program Thanks Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics University of Chicago Cosmology Course - Astro 321, 2011 Introduction program Thanks Outline 1 Introduction 2 Linear Theory Press -
The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos
 COSMO11, Porto, August 2011 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos Simon White Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics COSMO11, Porto, August 2011 Mark Vogelsberger The fine-scale structure of dark
COSMO11, Porto, August 2011 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos Simon White Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics COSMO11, Porto, August 2011 Mark Vogelsberger The fine-scale structure of dark
The Iguaçu Lectures. Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures
 April 2006 The Iguaçu Lectures Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics z = 0 Dark Matter ROT EVOL Cluster structure
April 2006 The Iguaçu Lectures Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics z = 0 Dark Matter ROT EVOL Cluster structure
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 7 Jul 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 7 Jul 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 7 Jul 2018](/thumbs/81/84518293.jpg) Splashback radius of non-spherical dark matter halos from cosmic density and velocity fields arxiv:1807.02669v1 [astro-ph.co] 7 Jul 2018 Teppei Okumura, 1, 2, Takahiro Nishimichi, 2, 3 Keiichi Umetsu,
Splashback radius of non-spherical dark matter halos from cosmic density and velocity fields arxiv:1807.02669v1 [astro-ph.co] 7 Jul 2018 Teppei Okumura, 1, 2, Takahiro Nishimichi, 2, 3 Keiichi Umetsu,
The Clustering of Dark Matter in ΛCDM on Scales Both Large and Small
 The Clustering of Dark Matter in ΛCDM on Scales Both Large and Small Large Scales by Chris Orban May 19, 2008 Galaxy-redshift Survey Small Scales 0. Dark Matter Exists! 1. Large-Scale Structure What is
The Clustering of Dark Matter in ΛCDM on Scales Both Large and Small Large Scales by Chris Orban May 19, 2008 Galaxy-redshift Survey Small Scales 0. Dark Matter Exists! 1. Large-Scale Structure What is
Cosmology and Astrophysics with Galaxy Clusters Recent Advances and Future Challenges
 Cosmology and Astrophysics with Galaxy Clusters Recent Advances and Future Challenges Daisuke Nagai Yale University IPMU, July 15 th, 2010 Large-scale structure in the Universe SDSS (optical) Today δρ/ρ>>1
Cosmology and Astrophysics with Galaxy Clusters Recent Advances and Future Challenges Daisuke Nagai Yale University IPMU, July 15 th, 2010 Large-scale structure in the Universe SDSS (optical) Today δρ/ρ>>1
dark matter haloes and galaxy formation
 dark matter haloes and galaxy formation cosmology lecture (chapter 12) Haus der Astronomie and Centre for Astronomy Fakultät für Physik und Astronomie, Universität Heidelberg August 1, 2013 outline 1 repetition
dark matter haloes and galaxy formation cosmology lecture (chapter 12) Haus der Astronomie and Centre for Astronomy Fakultät für Physik und Astronomie, Universität Heidelberg August 1, 2013 outline 1 repetition
The impact of primordial supersonic flows on early structure formation, reionization and the lowest-mass dwarf galaxies
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 412, L40 L44 (2011) doi:10.1111/j.1745-3933.2010.01001.x The impact of primordial supersonic flows on early structure formation, reionization and the lowest-mass dwarf galaxies
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 412, L40 L44 (2011) doi:10.1111/j.1745-3933.2010.01001.x The impact of primordial supersonic flows on early structure formation, reionization and the lowest-mass dwarf galaxies
Theory of galaxy formation
 Theory of galaxy formation Bibliography: Galaxy Formation and Evolution (Mo, van den Bosch, White 2011) Lectures given by Frank van den Bosch in Yale http://www.astro.yale.edu/vdbosch/teaching.html Theory
Theory of galaxy formation Bibliography: Galaxy Formation and Evolution (Mo, van den Bosch, White 2011) Lectures given by Frank van den Bosch in Yale http://www.astro.yale.edu/vdbosch/teaching.html Theory
The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection
 The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection constraining cosmology & galaxy formation Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang (SHAO) Marcello Cacciato, Surhud More (MPIA) Kunming,
The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection constraining cosmology & galaxy formation Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang (SHAO) Marcello Cacciato, Surhud More (MPIA) Kunming,
Galaxies 626. Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star
 Galaxies 626 Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star Galaxies 626 Firstly, some very brief cosmology for background and notation: Summary: Foundations of Cosmology 1. Universe is homogenous and isotropic
Galaxies 626 Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star Galaxies 626 Firstly, some very brief cosmology for background and notation: Summary: Foundations of Cosmology 1. Universe is homogenous and isotropic
The motion of emptiness
 The motion of emptiness Dynamics and evolution of cosmic voids Laura Ceccarelli IATE, Observatorio Astronómico de Córdoba Large scale structure and galaxy flows Quy Nhon, July 2016 Motivations Universe
The motion of emptiness Dynamics and evolution of cosmic voids Laura Ceccarelli IATE, Observatorio Astronómico de Córdoba Large scale structure and galaxy flows Quy Nhon, July 2016 Motivations Universe
EFFECT OF MERGERS ON THE SIZE EVOLUTION OF EARLY-TYPE GALAXIES
 EFFECT OF MERGERS ON THE SIZE EVOLUTION OF EARLY-TYPE GALAXIES CARLO NIPOTI BOLOGNA UNIVERSITY Getting a Grip on Galaxy Girths, Tokyo, February 2015 NGC 474(Credit: Duc Atlas3D) Dry and wet galaxy mergers
EFFECT OF MERGERS ON THE SIZE EVOLUTION OF EARLY-TYPE GALAXIES CARLO NIPOTI BOLOGNA UNIVERSITY Getting a Grip on Galaxy Girths, Tokyo, February 2015 NGC 474(Credit: Duc Atlas3D) Dry and wet galaxy mergers
Milky Way s Mass and Stellar Halo Velocity Dispersion Profiles
 Milky Way s Mass and Stellar Halo Velocity Dispersion Profiles Shanghai Astronomical Observatory In collaboration with Juntai Shen, Xiang Xiang Xue, Chao Liu, Chris Flynn, Ling Zhu, Jie Wang Contents 1
Milky Way s Mass and Stellar Halo Velocity Dispersion Profiles Shanghai Astronomical Observatory In collaboration with Juntai Shen, Xiang Xiang Xue, Chao Liu, Chris Flynn, Ling Zhu, Jie Wang Contents 1
Exponential Profile Formation in Simple Models of Scattering Processes
 Exponential Profile Formation in Simple Models of Scattering Processes Curtis Struck Iowa State Univ. Work in collab. with B. G. Elmegreen, D. Hunter, H. Salo Lowell Workshop, Oct. 2014 Exponential profiles
Exponential Profile Formation in Simple Models of Scattering Processes Curtis Struck Iowa State Univ. Work in collab. with B. G. Elmegreen, D. Hunter, H. Salo Lowell Workshop, Oct. 2014 Exponential profiles
Testing the cold dark matter model with gravitational lensing
 Testing the cold dark matter model with gravitational lensing Priyamvada Natarajan Departments of Astronomy & Physics Yale University In Memoriam: Vera Rubin New Directions in Theoretical Physics, January
Testing the cold dark matter model with gravitational lensing Priyamvada Natarajan Departments of Astronomy & Physics Yale University In Memoriam: Vera Rubin New Directions in Theoretical Physics, January
The cosmological principle is not in the sky
 The 7th KIAS Workshop on Cosmology and Structure Formation Oct. 30 Nov. 4 2016 The cosmological principle is not in the sky Chan-Gyung Park (Division of Science Education, Chonbuk National University)
The 7th KIAS Workshop on Cosmology and Structure Formation Oct. 30 Nov. 4 2016 The cosmological principle is not in the sky Chan-Gyung Park (Division of Science Education, Chonbuk National University)
Phase Space Structure of Dark Matter Halos
 Phase Space Structure of Dark Matter Halos Monica Valluri University of Michigan Collaborators Ileana Vass (U. Florida, Gainesville) Andrey Kravtsov (KICP, U. Chicago) Stelios Kazantzidis (CCAPP, Ohio
Phase Space Structure of Dark Matter Halos Monica Valluri University of Michigan Collaborators Ileana Vass (U. Florida, Gainesville) Andrey Kravtsov (KICP, U. Chicago) Stelios Kazantzidis (CCAPP, Ohio
Preliminaries. Growth of Structure. Today s measured power spectrum, P(k) Simple 1-D example of today s P(k) Growth in roughness: δρ/ρ. !(r) =!!
 Growth of Structure Notes based on Teaching Company lectures, and associated undergraduate text with some additional material added. For a more detailed discussion, see the article by Peacock taken from
Growth of Structure Notes based on Teaching Company lectures, and associated undergraduate text with some additional material added. For a more detailed discussion, see the article by Peacock taken from
Satellite Galaxy Evolution in Groups & Clusters
 Satellite Galaxy Evolution in Groups & Clusters Andrew Wetzel Yale University Jeremy Tinker (NYU) & Charlie Conroy (Harvard/CfA) Tinker, Wetzel & Conroy 2011, ArXiv 1107.5046 Wetzel, Tinker & Conroy 2011,
Satellite Galaxy Evolution in Groups & Clusters Andrew Wetzel Yale University Jeremy Tinker (NYU) & Charlie Conroy (Harvard/CfA) Tinker, Wetzel & Conroy 2011, ArXiv 1107.5046 Wetzel, Tinker & Conroy 2011,
Massimo Meneghetti 1, Elena Torri 1, Matthias Bartelmann 2, Lauro Moscardini 3, Elena Rasia 1 and Giuseppe Tormen 1,
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 73, 23 c SAIt 2002 Memorie della! "$# %&'()*+,(+ -. Massimo Meneghetti 1, Elena Torri 1, Matthias Bartelmann 2, Lauro Moscardini 3, Elena Rasia 1 and Giuseppe Tormen 1, 1 Dipartimento
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 73, 23 c SAIt 2002 Memorie della! "$# %&'()*+,(+ -. Massimo Meneghetti 1, Elena Torri 1, Matthias Bartelmann 2, Lauro Moscardini 3, Elena Rasia 1 and Giuseppe Tormen 1, 1 Dipartimento
A look into the Dark Universe
 Zentrum für Astronomie, Institut für Theoretische Astrophysik Universität Heidelberg Dark Energy dark energy: assumed to drive accelerated cosmic expansion scalar field having negative pressure? early
Zentrum für Astronomie, Institut für Theoretische Astrophysik Universität Heidelberg Dark Energy dark energy: assumed to drive accelerated cosmic expansion scalar field having negative pressure? early
How many arcmin-separation lenses are expected in the 2dF QSO survey?
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 339, L23 L27 (2003) How many arcmin-separation lenses are expected in the 2dF QSO survey? Masamune Oguri Department of Physics, School of Science, University of Tokyo, Tokyo 113-0033,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 339, L23 L27 (2003) How many arcmin-separation lenses are expected in the 2dF QSO survey? Masamune Oguri Department of Physics, School of Science, University of Tokyo, Tokyo 113-0033,
The Full Strength of Cluster Gravitational Lensing: Mass Distribution in and around Cosmic Giants from the CLASH Survey
 The Full Strength of Cluster Gravitational Lensing: Mass Distribution in and around Cosmic Giants from the CLASH Survey Cluster Lensing And Supernova survey with Hubble Keiichi Umetsu (ASIAA, Taiwan) Contents
The Full Strength of Cluster Gravitational Lensing: Mass Distribution in and around Cosmic Giants from the CLASH Survey Cluster Lensing And Supernova survey with Hubble Keiichi Umetsu (ASIAA, Taiwan) Contents
Structure and substructure in dark matter halos
 Satellites and Tidal Streams ING IAC joint Conference La Palma, May 2003 Structure and substructure in dark matter halos Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics 500 kpc A CDM Milky Way Does
Satellites and Tidal Streams ING IAC joint Conference La Palma, May 2003 Structure and substructure in dark matter halos Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics 500 kpc A CDM Milky Way Does
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 3 Oct 2001
 AiBA 2001: High-z Clusters, issing Baryons, and CB Polarization ASP Conference Series, Vol. 999, 2002 L-W Chen, C-P a, K-W Ng and U-L Pen, eds Clustering of Dark atter Halos on the Light-cone arxiv:astro-ph/0110073v1
AiBA 2001: High-z Clusters, issing Baryons, and CB Polarization ASP Conference Series, Vol. 999, 2002 L-W Chen, C-P a, K-W Ng and U-L Pen, eds Clustering of Dark atter Halos on the Light-cone arxiv:astro-ph/0110073v1
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 20 Jul 2018
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 20 Jul 2018 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 20 Jul 2018](/thumbs/88/115716006.jpg) Splashback radius of nonspherical dark matter halos from cosmic density and velocity fields arxiv:1807.02669v2 [astro-ph.co] 20 Jul 2018 Teppei Okumura, 1, 2, Takahiro Nishimichi, 2, 3 Keiichi Umetsu,
Splashback radius of nonspherical dark matter halos from cosmic density and velocity fields arxiv:1807.02669v2 [astro-ph.co] 20 Jul 2018 Teppei Okumura, 1, 2, Takahiro Nishimichi, 2, 3 Keiichi Umetsu,
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies
 Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies Gerry Gilmore H47 email: gil@ast.cam.ac.uk Lectures: Monday 12:10-13:00 Wednesday 11:15-12:05 Friday 12:10-13:00 Books: Binney & Tremaine Galactic Dynamics Princeton
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies Gerry Gilmore H47 email: gil@ast.cam.ac.uk Lectures: Monday 12:10-13:00 Wednesday 11:15-12:05 Friday 12:10-13:00 Books: Binney & Tremaine Galactic Dynamics Princeton
Dependence of the inner dark matter profile on the halo mass
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 344, 1237 1249 (2003) Dependence of the inner dark matter profile on the halo mass Massimo Ricotti Institute of Astronomy, Madingley Road, Cambridge CB3 0HA Accepted 2003 June
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 344, 1237 1249 (2003) Dependence of the inner dark matter profile on the halo mass Massimo Ricotti Institute of Astronomy, Madingley Road, Cambridge CB3 0HA Accepted 2003 June
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen The impact of primordial supersonic flows on early structure formation, reionization and the lowest-mass dwarf galaxies Maio, Umberto; Koopmans, Leon V.; Ciardi, Benedetta Published
University of Groningen The impact of primordial supersonic flows on early structure formation, reionization and the lowest-mass dwarf galaxies Maio, Umberto; Koopmans, Leon V.; Ciardi, Benedetta Published
Galaxies are not distributed randomly in space. 800 Mpc. 400 Mpc
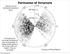 Formation Origin of of Structure Galaxies are not distributed randomly in space. 800 Mpc 400 Mpc If one galaxy has comoving coordinate, x, then the probability of finding another galaxy in the vicinity
Formation Origin of of Structure Galaxies are not distributed randomly in space. 800 Mpc 400 Mpc If one galaxy has comoving coordinate, x, then the probability of finding another galaxy in the vicinity
Clusters: Context and Background
 Clusters: Context and Background We re about to embark on a subject rather different from what we ve treated before, so it is useful to step back and think again about what we want to accomplish in this
Clusters: Context and Background We re about to embark on a subject rather different from what we ve treated before, so it is useful to step back and think again about what we want to accomplish in this
CLUMPY: A public code for γ-ray and ν signals from dark matter structures.
 CLUMPY: A public code for γ-ray and ν signals from dark matter structures. Moritz Hütten, DESY Zeuthen for the CLUMPY developers: Vincent Bonnivard, Moritz Hütten, Emmanuel Nezri, Aldée Charbonnier, Céline
CLUMPY: A public code for γ-ray and ν signals from dark matter structures. Moritz Hütten, DESY Zeuthen for the CLUMPY developers: Vincent Bonnivard, Moritz Hütten, Emmanuel Nezri, Aldée Charbonnier, Céline
Physics of the Large Scale Structure. Pengjie Zhang. Department of Astronomy Shanghai Jiao Tong University
 1 Physics of the Large Scale Structure Pengjie Zhang Department of Astronomy Shanghai Jiao Tong University The observed galaxy distribution of the nearby universe Observer 0.7 billion lys The observed
1 Physics of the Large Scale Structure Pengjie Zhang Department of Astronomy Shanghai Jiao Tong University The observed galaxy distribution of the nearby universe Observer 0.7 billion lys The observed
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 9 Feb 2005
 SDSS galaxy bias from halo mass-bias relation and its cosmological implications Uroš Seljak 1, Alexey Makarov 1, Rachel Mandelbaum 1, Christopher M. Hirata 1, Nikhil Padmanabhan 1, Patrick McDonald 1,
SDSS galaxy bias from halo mass-bias relation and its cosmological implications Uroš Seljak 1, Alexey Makarov 1, Rachel Mandelbaum 1, Christopher M. Hirata 1, Nikhil Padmanabhan 1, Patrick McDonald 1,
Structure Formation and Evolution"
 Structure Formation and Evolution" From this (Δρ/ρ ~ 10-6 )! to this! (Δρ/ρ ~ 10 +2 )! to this! (Δρ/ρ ~ 10 +6 )! How Long Does It Take?" The (dissipationless) gravitational collapse timescale is on the
Structure Formation and Evolution" From this (Δρ/ρ ~ 10-6 )! to this! (Δρ/ρ ~ 10 +2 )! to this! (Δρ/ρ ~ 10 +6 )! How Long Does It Take?" The (dissipationless) gravitational collapse timescale is on the
Cosmology with high (z>1) redshift galaxy surveys
 Cosmology with high (z>1) redshift galaxy surveys Donghui Jeong Texas Cosmology Center and Astronomy Department University of Texas at Austin Ph. D. thesis defense talk, 17 May 2010 Cosmology with HETDEX
Cosmology with high (z>1) redshift galaxy surveys Donghui Jeong Texas Cosmology Center and Astronomy Department University of Texas at Austin Ph. D. thesis defense talk, 17 May 2010 Cosmology with HETDEX
Precision Cosmology with X-ray and SZE Galaxy Cluster Surveys?
 Precision Cosmology with X-ray and SZE Galaxy Cluster Surveys? Joe Mohr University of Illinois Outline SZE and X-ray Observations of Clusters Cluster survey yields and cosmology Precision cosmology and
Precision Cosmology with X-ray and SZE Galaxy Cluster Surveys? Joe Mohr University of Illinois Outline SZE and X-ray Observations of Clusters Cluster survey yields and cosmology Precision cosmology and
RHAPSODY: II. SUBHALO PROPERTIES AND THE IMPACT OF TIDAL STRIPPING FROM A STATISTICAL SAMPLE OF CLUSTER-SIZE HALOS
 Draft version October 23, 212 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 SLAC-PUB-15314 RHAPSODY: II. SUBHALO PROPERTIES AND THE IMPACT OF TIDAL STRIPPING FROM A STATISTICAL SAMPLE OF
Draft version October 23, 212 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 SLAC-PUB-15314 RHAPSODY: II. SUBHALO PROPERTIES AND THE IMPACT OF TIDAL STRIPPING FROM A STATISTICAL SAMPLE OF
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 21 Aug 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 21 Aug 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 21 Aug 2017](/thumbs/96/128978234.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed August 22, 2017 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Haloes at the ragged edge: The importance of the splashback radius arxiv:1708.06181v1 [astro-ph.ga] 21 Aug
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed August 22, 2017 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Haloes at the ragged edge: The importance of the splashback radius arxiv:1708.06181v1 [astro-ph.ga] 21 Aug
AST4320: LECTURE 10 M. DIJKSTRA
 AST4320: LECTURE 10 M. DIJKSTRA 1. The Mass Power Spectrum P (k) 1.1. Introduction: the Power Spectrum & Transfer Function. The power spectrum P (k) emerged in several of our previous lectures: It fully
AST4320: LECTURE 10 M. DIJKSTRA 1. The Mass Power Spectrum P (k) 1.1. Introduction: the Power Spectrum & Transfer Function. The power spectrum P (k) emerged in several of our previous lectures: It fully
Galaxies in dark matter halos: luminosity-velocity relation, abundance and baryon content
 Galaxies in dark matter halos: luminosity-velocity relation, abundance and baryon content arxiv:1005.1289 arxiv:1002.3660 S. Trujillo-Gomez (NMSU) in collaboration with: A. Klypin (NMSU), J. Primack (UCSC)
Galaxies in dark matter halos: luminosity-velocity relation, abundance and baryon content arxiv:1005.1289 arxiv:1002.3660 S. Trujillo-Gomez (NMSU) in collaboration with: A. Klypin (NMSU), J. Primack (UCSC)
The distribution and kinematics of early high-σ peaks in present-day haloes: implications for rare objects and old stellar populations
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 19 (2005) Printed 20 April 2006 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The distribution and kinematics of early high-σ peaks in present-day haloes: implications for rare objects and
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 19 (2005) Printed 20 April 2006 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The distribution and kinematics of early high-σ peaks in present-day haloes: implications for rare objects and
The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection
 The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection constraining cosmology & galaxy formation Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang (SHAO) Marcello Cacciato, Surhud More, Simone Weinmann
The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection constraining cosmology & galaxy formation Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang (SHAO) Marcello Cacciato, Surhud More, Simone Weinmann
The Masses of Galaxies from the Galaxy-Halo Connection
 with Charlie Conroy (Princeton) Peter Behroozi (KIPAC/Stanford) R isa Wechsler The Masses of Galaxies from the Galaxy-Halo Connection The Basic Idea Theory: We now have a reasonable accounting for the
with Charlie Conroy (Princeton) Peter Behroozi (KIPAC/Stanford) R isa Wechsler The Masses of Galaxies from the Galaxy-Halo Connection The Basic Idea Theory: We now have a reasonable accounting for the
Cosmology from Topology of Large Scale Structure of the Universe
 RESCEU 2008 Cosmology from Topology of Large Scale Structure of the Universe RESCEU Symposium on Astroparticle Physics and Cosmology 11-14, November 2008 Changbom Park (Korea Institute for Advanced Study)
RESCEU 2008 Cosmology from Topology of Large Scale Structure of the Universe RESCEU Symposium on Astroparticle Physics and Cosmology 11-14, November 2008 Changbom Park (Korea Institute for Advanced Study)
f GR (z) dlng GR dlna
 Precision Cosmology With Large Scale Structure, Ohio State University ICTP Cosmology Summer School 2015 Lecture 2: Theoretical Approaches Dark Matter Clustering If collisionless dark matter were the only
Precision Cosmology With Large Scale Structure, Ohio State University ICTP Cosmology Summer School 2015 Lecture 2: Theoretical Approaches Dark Matter Clustering If collisionless dark matter were the only
Embedded Spiral Patterns in the massive galaxy cluster Abell 1835
 2017/06/08 X-ray Universe @ Rome Embedded Spiral Patterns in the massive galaxy cluster Abell 1835 Shutaro Ueda (ISAS/JAXA), Tetsu Kitayama (Toho University), Tadayasu Dotani (ISAS/JAXA, SOKENDAI) This
2017/06/08 X-ray Universe @ Rome Embedded Spiral Patterns in the massive galaxy cluster Abell 1835 Shutaro Ueda (ISAS/JAXA), Tetsu Kitayama (Toho University), Tadayasu Dotani (ISAS/JAXA, SOKENDAI) This
The angular homogeneity scale of the Universe
 The angular homogeneity scale of the Universe Alicia Bueno Belloso Work in collaboration with: David Alonso, Juan García-Bellido, Eusebio Sánchez and Javier Sánchez in preparation 12 th of September 2013
The angular homogeneity scale of the Universe Alicia Bueno Belloso Work in collaboration with: David Alonso, Juan García-Bellido, Eusebio Sánchez and Javier Sánchez in preparation 12 th of September 2013
Preheating in the Universe Suppressing High Energy Gamma-rays from Structure Formation
 Preheating in the Universe Suppressing High Energy Gamma-rays from Structure Formation Tomonori Totani and Susumu Inoue Division of Theoretical Astrophysics, National Astronomical Observatory, Mitaka,
Preheating in the Universe Suppressing High Energy Gamma-rays from Structure Formation Tomonori Totani and Susumu Inoue Division of Theoretical Astrophysics, National Astronomical Observatory, Mitaka,
You may not start to read the questions printed on the subsequent pages until instructed to do so by the Invigilator.
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday 3 June, 2004 9 to 12 PAPER 67 PHYSICAL COSMOLOGY Attempt THREE questions. There are four questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. You may not start to
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday 3 June, 2004 9 to 12 PAPER 67 PHYSICAL COSMOLOGY Attempt THREE questions. There are four questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. You may not start to
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 4 Sep 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 4 Sep 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 4 Sep 2009](/thumbs/78/77012841.jpg) Spherical collapse model with and without curvature Seokcheon Lee 1,2 arxiv:99.826v1 [astro-ph.co] 4 Sep 29 1 Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica, Taipei, Taiwan 11529, R.O.C. 2 Leung Center for Cosmology
Spherical collapse model with and without curvature Seokcheon Lee 1,2 arxiv:99.826v1 [astro-ph.co] 4 Sep 29 1 Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica, Taipei, Taiwan 11529, R.O.C. 2 Leung Center for Cosmology
The angular homogeneity scale of the Universe
 The angular homogeneity scale of the Universe Alicia Bueno Belloso ITP, Heidelberg Work in collaboration with: David Alonso, Juan García-Bellido, Eusebio Sánchez and Javier Sánchez in preparation 2 nd
The angular homogeneity scale of the Universe Alicia Bueno Belloso ITP, Heidelberg Work in collaboration with: David Alonso, Juan García-Bellido, Eusebio Sánchez and Javier Sánchez in preparation 2 nd
The Merging Systems Identification (MeSsI) Algorithm.
 The Merging Systems Identification (MeSsI) Algorithm. July 10, 2016 Table of contents 1 Why searching merging galaxy clusters? 2 The MeSsI Algorithm Machine learning algorithm applied for identification
The Merging Systems Identification (MeSsI) Algorithm. July 10, 2016 Table of contents 1 Why searching merging galaxy clusters? 2 The MeSsI Algorithm Machine learning algorithm applied for identification
Cosmological Constraints from a Combined Analysis of Clustering & Galaxy-Galaxy Lensing in the SDSS. Frank van den Bosch.
 Cosmological Constraints from a Combined Analysis of Clustering & Galaxy-Galaxy Lensing in the SDSS In collaboration with: Marcello Cacciato (Leiden), Surhud More (IPMU), Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang
Cosmological Constraints from a Combined Analysis of Clustering & Galaxy-Galaxy Lensing in the SDSS In collaboration with: Marcello Cacciato (Leiden), Surhud More (IPMU), Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang
