2011 Cayley Contest. The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING. Solutions. Thursday, February 24, (Grade 10)
|
|
|
- Hannah Knight
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING 0 Cayley Contest (Grade 0) Thursday, February, 0 Solutions 00 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing
2 0 Cayley Contest Solutions Page. We regroup (5 + ) + (8 + 6) + ( + 7) + (3 + ) as 5 + ( + 8) + (6 + ) + (7 + 3) +, which equals or 37. We could add the numbers directly instead.. Since ( )()(x)() =, then 8x = or x = 8 = Solution Since P RS is an exterior angle to P QR, then P QR+ QP R = P RS or x +75 = 5. Thus, x + 75 = 5 or x = 50. Solution Since QRS is a straight line, then P RQ = 80 P RS = 80 5 = 55. Since the sum of the angles in a triangle is 80, then x = 80 or x + 30 = 80 or x = 50.. Solution To get back to the original number, we undo the given operations. We add 5 to 6 to obtain and then divide by 3 to obtain 7. These are the inverse operations of decreasing by 5 and multiplying by 3. Solution Suppose that the original number is x. After tripling and decreasing by 5, the result is 3x 5. Therefore, 3x 5 = 6 or 3x = or x = 7. Answer: (C) 5. We evaluate from the inside towards the outside: = = = = 6 = Answer: (D) 6. A graph that is linear with a slope of 0 is a horizontal straight line. This is Graph Q. 7. With a fair die that has faces numbered from to 6, the probability of rolling each of to 6 is 6. We calculate the probability for each of the five choices. There are values of x that satisfy x >, so the probability is 6 = 3. There are values of x that satisfy x = or x = 5, so the probability is 6 = 3. There are 3 values of x that are even, so the probability is 3 6 =. There are values of x that satisfy x < 3, so the probability is 6 = 3. There is value of x that satisfies x = 3, so the probability is 6. Therefore, the most likely of the five choices is that x is greater than.
3 0 Cayley Contest Solutions Page 3 8. When. 0 8 is doubled, the result is. 0 8 = Answer: (C) 9. Since the face of a foonie has area 5 cm and its thickness is 0.5 cm, then the volume of one foonie is =.5 cm 3. If a stack of foonies has a volume of 50 cm 3 and each foonie has a volume of.5 cm 3, then there are 50.5 = 0 foonies in the stack. Answer: (D) 0. In order to make the playoffs, the Athenas must win at least 60% of their games. That is, they must win at least 0.6 = 6. games. Since they must win an integer number of games, then the smallest number of games that they can win to make the playoffs is the smallest integer larger than 6., or 7. Since they have won 0 games so far, then they must win 7 0 = 7 of their remaining games to make the playoffs. Answer: (E). From the definition, (3, ) (, ) = (3)() + ()() = + =. Answer: (D). Since the angle in the sector representing cookies is 90, then this sector represents of the total circle. Therefore, 5% of the students chose cookies as their favourite food. Thus, the percentage of students who chose sandwiches was 00% 30% 5% 35% = 0%. Since there are 00 students in total, then 00 0 = 0 students said that their favourite 00 food was sandwiches. 3. Solution We work from right to left as we would if doing this calculation by hand. In the units column, we have L giving. Thus, L =. (There is no borrowing required.) In the tens column, we have 3 N giving 5. Since 5 is larger than 3, we must borrow from the hundreds column. Thus, 3 N gives 5, which means N = 8. This gives K 3 5 K 3 M 8 5 In the hundreds column, we have (K ) giving, which means K = 9. This gives M 8 5 In the thousands column, we have 5 (with nothing borrowed) minus M giving. Thus, 5 M = or M =. This gives = 5, which is correct. Finally, K + L + M + N = = 0.
4 0 Cayley Contest Solutions Page Solution Since 5K3L MN = 5, then M N K 3 L We start from the units column and work towards the left. Considering the units column, the sum + has a units digit of L. Thus, L =. (There is no carry to the tens column.) Considering the tens column, the sum N + 5 has a units digit of 3. Thus, N = 8. (There is a carry of to the hundreds column.) This gives M K 3 Considering the hundreds column, the sum + plus the carry of from the tens column has a units digit of K. Therefore, K = + + = 9. There is no carry from the hundreds column to the thousands column. Considering the thousands column, the sum M + equals 5. Therefore, M =. This gives which is equivalent to = 8, which is correct. Finally, K + L + M + N = = 0.. The difference between and is = =, so LP =. 6 6 Since LP is divided into three equal parts, then this distance is divided into three equal parts, each equal to 3 = 3 = Therefore, M is located to the right of L. Thus, the value at M is + 36 = = 36 = 9. Answer: (C) 5. We plot the first three vertices on a graph. We see that one possible location for the fourth vertex, V, is in the second quadrant: y V R (, 0) S (0, ) Q (, ) x
5 0 Cayley Contest Solutions Page 5 If V SQR is a parallelogram, then SV is parallel and equal to QR. To get from Q to R, we go left units and up unit. Therefore, to get from S to V, we also go left units and up unit. Since the coordinates of S are (0, ), then the coordinates of V are (0, + ) = (, ). This is choice (A). There are two other possible locations for the fourth vertex, which we can find in a similar way. These are U(0, ) and W (, 0). Using these points, we can see that SQUR and SW QR are parallelograms. But (0, ) and (, 0) are not among the possible answers. Therefore, of the given choices, the only one that completes a parallelogram is (, ). 6. It is possible that after buying 7 gumballs, Wally has received red, blue, white, and green gumballs. This is the largest number of each colour that he could receive without having three gumballs of any one colour. If Wally buys another gumball, he will receive a blue or a green or a red gumball. In each of these cases, he will have at least 3 gumballs of one colour. In summary, if Wally buys 7 gumballs, he is not guaranteed to have 3 of any one colour; if Wally buys 8 gumballs, he is guaranteed to have 3 of at least one colour. Therefore, the least number that he must buy to guarantee receiving 3 of the same colour is 8. Answer: (E) 7. Suppose that each of the smaller rectangles has a longer side of length x cm and a shorter side of length y cm. y x y x x y x y Since the perimeter of each of the rectangles is 0 cm, then x + y = 0 or x + y = 0. But the side length of the large square is x + y cm. Therefore, the area of the large square is (x + y) = 0 = 00 cm. Answer: (C) 8. Solution When a number n is divided by x, the remainder is the difference between n and the largest multiple of x less than n. When 00 is divided by a positive integer x, the remainder is 0. This means that 00 0 = 90 is exactly divisible by x. It also means that x is larger than 0, otherwise the remainder would be smaller than 0. Since 90 is exactly divisible by x, then 90 = 990 is also exactly divisible by x. Since x > 0, then the next multiple of x is x, which is larger than 000. Thus, 990 is the largest multiple of x less than 000, and so the remainder when 000 is divided by x is = 0.
6 0 Cayley Contest Solutions Page 6 Solution When 00 is divided by a positive integer x, the remainder is 0. The remainder is the difference between 00 and the largest multiple of x less than 00. Therefore, the largest multiple of x less than 00 is 00 0 = 90. It also means that x is larger than 0, otherwise the remainder would be smaller than 0. We can choose x = 5, since 6 5 = 90 and 5 is larger than 0. What is the remainder when 000 is divided by 5? Using a calculator, = and 66 5 = 990. Thus, the difference between 000 and the largest multiple of 5 less than 000 (that is, 990) equals 0 and so the remainder is equal to Let XY W = θ. Since XY W is isosceles with W X = W Y, then Y XW = XY W = θ. Since the sum of the angles in XY W is 80, then XW Y = 80 θ. Since XW Y + ZW Y = 80, then ZW Y = 80 (80 θ) = θ. Since Y W Z is isosceles with Y W = Y Z, then Y ZW = ZW Y = θ. Since XY Z is isosceles, with XY = XZ, then XY Z = XZY = θ. Since the sum of the angles in XY Z is 80, then XY Z + XZY + Y XZ = 80 or θ + θ + θ = 80, or 5θ = 80, or θ = 36. Answer: (D) 0. For n 3 + 5n to be the square of an integer, n 3 + 5n must be an integer. We know that n 3 + 5n = n (n + 5) = n n + 5 = n n + 5. For n n + 5 to be an integer, n + 5 must be an integer. In other words, n + 5 must be a perfect square. Since n is between and 00, then n + 5 is between 6 and 05. The perfect squares in this range are 3 = 9, = 6,..., 0 = 00. Thus, there are 8 perfect squares in this range. Therefore, there are 8 values of n for which n + 5 is an integer, and thus for which n 3 + 5n is the square of an integer.. Solution If we multiply the second and third equations together, we obtain x(y + )y(y + ) = xy(x + )(x + ) = From the first equation, xy =. 9 Therefore, 35 (x + )(y + ) = 9 6 or (x + )(y + ) = 9( 35 6 ) = Solution If we expand the left side of the second equation, we obtain xy + x = 7 9. Since xy = 9 (from the first equation), then x = 7 9 xy = = 3. If we expand the left side of the third equation, we obtain xy + y = 5 Since xy = 5 (from the first equation), then y = xy = 5 = 3 = Therefore, (x + )(y + ) = ( + )( + ) = 5 7 = Answer: (E) 8. 8 or. Suppose that the crease intersects P S at X, QR at Y, and the line P R at Z. We want to determine the length of XY.
7 0 Cayley Contest Solutions Page 7 P Q Y Z X S R Since P folds on top of R, then line segment P Z folds on top of line segment RZ, since after the fold Z corresponds with itself and P corresponds with R. This means that P Z = RZ and P R must be perpendicular to XY at point Z. Since P S = RQ and SR = QP, then right-angled triangles P SR and RQP are congruent (side-angle-side). Therefore, XP Z = Y RZ. Since P Z = RZ, then right-angled triangles P ZX and RZY are congruent too (angle-sideangle). Thus, XZ = ZY and so XY = XZ. Since P SR is right-angled at S, then by the Pythagorean Theorem, since P R > 0. Since P Z = RZ, then P Z = P R = 5. P R = P S + SR = = 00 = 0 Now P ZX is similar to P SR (common angle at P and right angle), so XZ P Z = RS P S or XZ = 5 6 = 30 = Therefore, XY = XZ = 5, so the length of the fold is 5 or 7.5. Answer: (C) 3. First, we calculate the number of pairs that can be formed from the integers from to n. One way to form a pair is to choose one number to be the first item of the pair (n choices) and then a different number to be the second item of the pair (n choices). There are n(n ) ways to choose these two items in this way. But this counts each pair twice; for example, we could choose then 3 and we could also choose 3 then. So we have double-counted the pairs, meaning that there are n(n ) pairs that can be formed. Next, we examine the number of rows in the table. Since each row has three entries, then each row includes three pairs (first and second numbers, first and third numbers, second and third numbers). Suppose that the completed table has r rows. Then the total number of pairs in the table is 3r. Since each pair of the numbers from to n appears exactly once in the table and the total number of pairs from these numbers is n(n ), then 3r = n(n ), which tells us that n(n ) must be divisible by 3, since 3r is divisible by 3. We make a table listing the possible values of n and the corresponding values of n(n ): n n(n )
8 0 Cayley Contest Solutions Page 8 Since n(n ) must be divisible by 3, then the possible values of n are 3,, 6, 7, 9, 0, and. Next, consider a fixed number m from the list to n. In each row that m appears, it will belong to pairs (one with each of the other two numbers in its row). If the number m appears in s rows, then it will belong to s pairs. Therefore, each number m must belong to an even number of pairs. But each number m from the list of integers from to n must appear in n pairs (one with each other number in the list), so n must be even, and so n is odd. Therefore, the possible values of n are 3, 7, 9. Finally, we must verify that we can create a Fano table for each of these values of n. We are given the Fano table for n = 7. Since the total number of pairs when n = 3 is 3 and when n = 9 is 36, then a Fano table for n = 3 will have 3 3 = row and a Fano table for n = 9 will have 36 3 = rows. For n = 3 and n = 9, possible tables are shown below: In total, there are 3 values of n in this range for which a Fano table can be created.. First, we note that the three people are interchangeable in this problem, so it does not matter who rides and who walks at any given moment. We abbreviate the three people as D, M and P. We call their starting point A and their ending point B. Here is a strategy where all three people are moving at all times and all three arrive at B at the same time: D and M get on the motorcycle while P walks. D and M ride the motorcycle to a point Y before B. D drops off M and rides back while P and M walk toward B. D meets P at point X. D picks up P and they drive back to B meeting M at B. Point Y is chosen so that D, M and P arrive at B at the same time. Suppose that the distance from A to X is a km, from X to Y is d km, and the distance from Y to B is b km.
9 0 Cayley Contest Solutions Page 9 A X Y a d b B In the time that it takes P to walk from A to X at 6 km/h, D rides from A to Y and back to X at 90 km/h. The distance from A to X is a km. The distance from A to Y and back to X is a + d + d = a + d km. Since the time taken by P and by D is equal, then a 6 = a + d or 5a = a + d or 7a = d. 90 In the time that it takes M to walk from Y to B at 6 km/h, D rides from Y to X and back to B at 90 km/h. The distance from Y to B is b km, and the distance from Y to X and back to B is d+d+b = b+d km. Since the time taken by M and by D is equal, then b 6 = b + d or 5b = b + d or 7b = d. 90 Therefore, d = 7a = 7b, and so we can write d = 7a and b = a. Thus, the total distance from A to B is a + d + b = a + 7a + a = 9a km. However, we know that this total distance is 35 km, so 9a = 35 or a = 5. Finally, D rides from A to Y to X to B, a total distance of (a + 7a) + 7a + (7a + a) = 3a km. Since a = 5 km and D rides at 90 km/h, then the total time taken for this strategy is 3 5 = h Since we have a strategy that takes 3.83 h, then the smallest possible time is no more than 3.83 h. Can you explain why this is actually the smallest possible time? If we didn t think of this strategy, another strategy that we might try would be: D and M get on the motorcycle while P walks. D and M ride the motorcycle to B. D drops off M at B and rides back to meet P, who is still walking. D picks up P and they drive back to B. (M rests at B.) This strategy actually takes.5 h, which is longer than the strategy shown above, since M is actually sitting still for some of the time. 5. By definition, if 0 a <, then A = 0 and if a, then A =. Similarly, if 0 b <, then B = 0 and if b, then B =. We keep track of our information on a set of axes, labelled a and b. b A = 0 B = A = 0 B = 0 A = B = A = B = 0 a
10 0 Cayley Contest Solutions Page 0 The area of the region of possible pairs (a, b) is, since the region is a square with side length. Next, we determine the sets of points where C = A + B and calculate the combined area of these regions. We consider the four sub-regions case by case. In each case, we will encounter lines of the form a + b = Z for some number Z. We can rewrite these equations as b = a + Z which shows that this equation is the equation of the line with slope and b-intercept Z. Since the slope is, the a-intercept is also Z. Case : A = 0 and B = 0 For C to equal A + B, we need C = 0. Since C is obtained by rounding c, then we need 0 c <. Since c = a + b by definition, this is true when 0 a + b < or 0 a + b <. This is the set of points in this subregion above the line a + b = 0 and below the line a + b =. Case : A = 0 and B = For C to equal A + B, we need C =. Since C is obtained by rounding c, then we need 3 c < 5. Since c = a + b by definition, this is true when 3 a + b < 5 or 3 a + b < 5. This is the set of points in this subregion above the line a + b = 3 and below the line a + b = 5. Case 3: A = and B = 0 For C to equal A + B, we need C =. Since C is obtained by rounding c, then we need 3 c < 5. Since c = a + b by definition, this is true when 3 a + b < 5 or 3 a + b < 5. This is the set of points in this subregion above the line a + b = 3 and below the line a + b = 5. Case : A = and B = For C to equal A + B, we need C =. Since C is obtained by rounding c, then we need 7 c < 9. Since c = a + b by definition, this is true when 7 a + b < 9 or 7 a + b < 9. This is the set of points in this subregion above the line a + b = 7 and below the line a + b = 9. We shade the appropriate set of points in each of the subregions:
11 0 Cayley Contest Solutions Page b Case 3 Case Case Case 3 C = 0 C = C = C = 3 C = a The shaded regions are the regions of points (a, b) where A + B = C. To determine the required probability, we calculate the combined area of these regions and divide by the total area of the set of all possible points (a, b). This total area is, so the probability will actually be equal to the combined area of the shaded regions. The region from Case is a triangle with height and base, so has area = The region from Case is also a triangle with height and base. This is because the line a + b = 7 intersects the top side of the square (the line b = ) when a = 3 and the right side of the square (the line a = ) when b = 3. The regions from Case and Case 3 have identical shapes and so have the same area. We calculate the area of the region from Case by subtracting the unshaded area from the area of the entire subregion (which is ). Each unshaded portion of this subregion is a triangle with height and base. We can confirm this by calculating points of intersection as in Case. Therefore, the area of the shaded region in Case is = = Therefore, the combined area of the shaded regions is = = Thus, the required probability is 7. 6 (Note that because calculating the probability is equivalent to calculating areas in this problem, we do not have to pay special attention as to whether points on the boundaries of the various regions are included or excluded.) Answer: (D) 6. 3.
2011 Fermat Contest (Grade 11)
 Te CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING 011 Fermat Contest (Grade 11) Tursday, February 4, 011 Solutions 010 Centre for Education in Matematics and Computing 011 Fermat Contest Solutions Page
Te CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING 011 Fermat Contest (Grade 11) Tursday, February 4, 011 Solutions 010 Centre for Education in Matematics and Computing 011 Fermat Contest Solutions Page
2016 Pascal Contest (Grade 9)
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 06 Pascal Contest (Grade 9) Wednesday, February, 06 (in North America and South America) Thursday, February, 06 (outside of North
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 06 Pascal Contest (Grade 9) Wednesday, February, 06 (in North America and South America) Thursday, February, 06 (outside of North
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca Cayley Contest. (Grade 10) Thursday, February 20, 2014
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 2014 Cayley Contest (Grade 10) Thursday, February 20, 2014 (in North America and South America) Friday, February 21, 2014 (outside
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 2014 Cayley Contest (Grade 10) Thursday, February 20, 2014 (in North America and South America) Friday, February 21, 2014 (outside
2005 Pascal Contest (Grade 9)
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 005 Pascal Contest (Grade 9) Wednesday, February 3, 005
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 005 Pascal Contest (Grade 9) Wednesday, February 3, 005
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca Cayley Contest. (Grade 10) Tuesday, February 27, 2018
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 018 Cayley Contest (Grade 10) Tuesday, February 7, 018 (in North America and South America) Wednesday, February 8, 018 (outside of
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 018 Cayley Contest (Grade 10) Tuesday, February 7, 018 (in North America and South America) Wednesday, February 8, 018 (outside of
2018 Pascal Contest (Grade 9)
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 018 Pascal Contest (Grade 9) Tuesday, February 7, 018 (in North America and South America) Wednesday, February 8, 018 (outside of
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 018 Pascal Contest (Grade 9) Tuesday, February 7, 018 (in North America and South America) Wednesday, February 8, 018 (outside of
2015 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 205 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest April 205 Solutions 205 University of Waterloo 205 CTMC Solutions Page 2 Individual Problems.
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 205 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest April 205 Solutions 205 University of Waterloo 205 CTMC Solutions Page 2 Individual Problems.
2009 Cayley Contest. Solutions
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 2009 Cayley Contest (Grade 10) Wednesday, February 18, 2009
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 2009 Cayley Contest (Grade 10) Wednesday, February 18, 2009
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca Cayley Contest. (Grade 10) Tuesday, February 28, 2017
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 2017 Cayley Contest (Grade 10) Tuesday, February 28, 2017 (in North America and South America) Wednesday, March 1, 2017 (outside
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 2017 Cayley Contest (Grade 10) Tuesday, February 28, 2017 (in North America and South America) Wednesday, March 1, 2017 (outside
2012 Fermat Contest (Grade 11)
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING www.cemc.uwaterloo.ca 01 Fermat Contest (Grade 11) Thursday, February 3, 01 (in North America and South America) Friday, February 4, 01 (outside of
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING www.cemc.uwaterloo.ca 01 Fermat Contest (Grade 11) Thursday, February 3, 01 (in North America and South America) Friday, February 4, 01 (outside of
2005 Cayley Contest. Solutions
 anadian Mathematics ompetition n activity of the entre for Education in Mathematics and omputing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 005 ayley ontest (Grade 10) Wednesday, February 3, 005 Solutions
anadian Mathematics ompetition n activity of the entre for Education in Mathematics and omputing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 005 ayley ontest (Grade 10) Wednesday, February 3, 005 Solutions
2010 Fermat Contest (Grade 11)
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 010 Fermat Contest (Grade 11) Thursday, February 5, 010
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 010 Fermat Contest (Grade 11) Thursday, February 5, 010
2016 Canadian Senior Mathematics Contest
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 2016 Canadian Senior Mathematics Contest Wednesday, November 23, 2016 (in North America and South America) Thursday, November 24,
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 2016 Canadian Senior Mathematics Contest Wednesday, November 23, 2016 (in North America and South America) Thursday, November 24,
2009 Euclid Contest. Solutions
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 009 Euclid Contest Tuesday, April 7, 009 Solutions c 009
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 009 Euclid Contest Tuesday, April 7, 009 Solutions c 009
2017 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 017 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest April 017 Solutions 017 University of Waterloo 017 CTMC Solutions Page Individual Problems
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 017 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest April 017 Solutions 017 University of Waterloo 017 CTMC Solutions Page Individual Problems
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca Euclid Contest. Thursday, April 6, 2017
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 017 Euclid Contest Thursday, April 6, 017 (in North America and South America) Friday, April 7, 017 (outside of North America and
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 017 Euclid Contest Thursday, April 6, 017 (in North America and South America) Friday, April 7, 017 (outside of North America and
2007 Fermat Contest (Grade 11)
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 007 Fermat Contest (Grade 11) Tuesday, February 0, 007 Solutions
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 007 Fermat Contest (Grade 11) Tuesday, February 0, 007 Solutions
2017 Pascal Contest (Grade 9)
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 2017 Pascal Contest (Grade 9) Tuesday, February 28, 2017 (in North America and South America) Wednesday, March 1, 2017 (outside of
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 2017 Pascal Contest (Grade 9) Tuesday, February 28, 2017 (in North America and South America) Wednesday, March 1, 2017 (outside of
2005 Euclid Contest. Solutions
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 2005 Euclid Contest Tuesday, April 19, 2005 Solutions c
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 2005 Euclid Contest Tuesday, April 19, 2005 Solutions c
Grade 6 Math Circles March 22-23, 2016 Contest Prep - Geometry
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles March 22-23, 2016 Contest Prep - Geometry Today we will be focusing on how to solve
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles March 22-23, 2016 Contest Prep - Geometry Today we will be focusing on how to solve
PRE-ALGEBRA SUMMARY WHOLE NUMBERS
 PRE-ALGEBRA SUMMARY WHOLE NUMBERS Introduction to Whole Numbers and Place Value Digits Digits are the basic symbols of the system 0,,,, 4,, 6, 7, 8, and 9 are digits Place Value The value of a digit in
PRE-ALGEBRA SUMMARY WHOLE NUMBERS Introduction to Whole Numbers and Place Value Digits Digits are the basic symbols of the system 0,,,, 4,, 6, 7, 8, and 9 are digits Place Value The value of a digit in
2008 Euclid Contest. Solutions. Canadian Mathematics Competition. Tuesday, April 15, c 2008 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 008 Euclid Contest Tuesday, April 5, 008 Solutions c 008
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 008 Euclid Contest Tuesday, April 5, 008 Solutions c 008
UNC Charlotte 2005 Comprehensive March 7, 2005
 March 7, 2005 1. The numbers x and y satisfy 2 x = 15 and 15 y = 32. What is the value xy? (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 (E) none of A, B, C or D Solution: C. Note that (2 x ) y = 15 y = 32 so 2 xy = 2 5 and
March 7, 2005 1. The numbers x and y satisfy 2 x = 15 and 15 y = 32. What is the value xy? (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 (E) none of A, B, C or D Solution: C. Note that (2 x ) y = 15 y = 32 so 2 xy = 2 5 and
2008 Pascal Contest (Grade 9)
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 008 Pascal Contest (Grade 9) Tuesday, February 19, 008 Solutions
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 008 Pascal Contest (Grade 9) Tuesday, February 19, 008 Solutions
Some practice questions for CIMC.
 1. Determine the value of {2008 Cayley #2} Some practice questions for CIMC. 25 16 25 16. 25 16 25 16 = 9 5 4 = 3 1 = 3 2. In the diagram, P T and QS are straight lines intersecting at R such that QP =
1. Determine the value of {2008 Cayley #2} Some practice questions for CIMC. 25 16 25 16. 25 16 25 16 = 9 5 4 = 3 1 = 3 2. In the diagram, P T and QS are straight lines intersecting at R such that QP =
2007 Pascal Contest (Grade 9)
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 2007 Pascal Contest (Grade 9) Tuesday, February 20, 2007
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 2007 Pascal Contest (Grade 9) Tuesday, February 20, 2007
(A) 20% (B) 25% (C) 30% (D) % (E) 50%
 ACT 2017 Name Date 1. The population of Green Valley, the largest suburb of Happyville, is 50% of the rest of the population of Happyville. The population of Green Valley is what percent of the entire
ACT 2017 Name Date 1. The population of Green Valley, the largest suburb of Happyville, is 50% of the rest of the population of Happyville. The population of Green Valley is what percent of the entire
48th AHSME If a is 50% larger than c, and b is 25% larger than c, then a is what percent larger than b?
 48th HSME 1997 2 1 If a and b are digits for which then a + b = 2 a b 6 9 9 2 9 8 9 () () 4 () 7 () 9 (E) 12 2 The adjacent sides of the decagon shown meet at right angles What is its perimeter? () 22
48th HSME 1997 2 1 If a and b are digits for which then a + b = 2 a b 6 9 9 2 9 8 9 () () 4 () 7 () 9 (E) 12 2 The adjacent sides of the decagon shown meet at right angles What is its perimeter? () 22
HIGH SCHOOL - SOLUTIONS = n = 2315
 PURPLE COMET! MATH MEET April 018 HIGH SCHOOL - SOLUTIONS Copyright c Titu Andreescu and Jonathan Kane Problem 1 Find the positive integer n such that 1 3 + 5 6 7 8 + 9 10 11 1 = n 100. Answer: 315 1 3
PURPLE COMET! MATH MEET April 018 HIGH SCHOOL - SOLUTIONS Copyright c Titu Andreescu and Jonathan Kane Problem 1 Find the positive integer n such that 1 3 + 5 6 7 8 + 9 10 11 1 = n 100. Answer: 315 1 3
Arithmetic with Whole Numbers and Money Variables and Evaluation (page 6)
 LESSON Name 1 Arithmetic with Whole Numbers and Money Variables and Evaluation (page 6) Counting numbers or natural numbers are the numbers we use to count: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ) Whole numbers are the counting
LESSON Name 1 Arithmetic with Whole Numbers and Money Variables and Evaluation (page 6) Counting numbers or natural numbers are the numbers we use to count: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ) Whole numbers are the counting
Solutions Math is Cool HS Championships Mental Math
 Mental Math 9/11 Answer Solution 1 30 There are 5 such even numbers and the formula is n(n+1)=5(6)=30. 2 3 [ways] HHT, HTH, THH. 3 6 1x60, 2x30, 3x20, 4x15, 5x12, 6x10. 4 9 37 = 3x + 10, 27 = 3x, x = 9.
Mental Math 9/11 Answer Solution 1 30 There are 5 such even numbers and the formula is n(n+1)=5(6)=30. 2 3 [ways] HHT, HTH, THH. 3 6 1x60, 2x30, 3x20, 4x15, 5x12, 6x10. 4 9 37 = 3x + 10, 27 = 3x, x = 9.
Practice Test 1 BLACKLINE MASTERS
 Practice Test 1 BLACKLINE MASTERS Name Date Chapter 1: The Number System Answer the questions that follow. 1. Which of the numbers below is not irrational? A. 5 C. 2 9 B. D. 1.34344344434444 2. Which of
Practice Test 1 BLACKLINE MASTERS Name Date Chapter 1: The Number System Answer the questions that follow. 1. Which of the numbers below is not irrational? A. 5 C. 2 9 B. D. 1.34344344434444 2. Which of
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca Euclid Contest. Tuesday, April 12, 2016
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 016 Euclid Contest Tuesday, April 1, 016 (in North America and South America) Wednesday, April 13, 016 (outside of North America
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 016 Euclid Contest Tuesday, April 1, 016 (in North America and South America) Wednesday, April 13, 016 (outside of North America
**** NO CALCULATORS IN THIS ROUND ****
 A) Evaluate 8 8. CONTEST NOVEMBER 0 ROUN COMLEX NUMBERS (No Trig) ANSWERS A) B) I II III IV C) **** NO CALCULATORS IN THIS ROUN **** B) Let z = x + yi be represented by the point (x, y). In what quadrant
A) Evaluate 8 8. CONTEST NOVEMBER 0 ROUN COMLEX NUMBERS (No Trig) ANSWERS A) B) I II III IV C) **** NO CALCULATORS IN THIS ROUN **** B) Let z = x + yi be represented by the point (x, y). In what quadrant
Mad Hatter Part I.
 Question 1. Mad Hatter 11-12. Part I. When a triangle s base is increased by 10%, and the altitude to this base is decreased by 10%, the change in area is Math Field Day. California State University, Fresno.
Question 1. Mad Hatter 11-12. Part I. When a triangle s base is increased by 10%, and the altitude to this base is decreased by 10%, the change in area is Math Field Day. California State University, Fresno.
BRITISH COLUMBIA SECONDARY SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST,
 BRITISH COLUMBIA SECONDARY SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST, 014 Solutions Junior Preliminary 1. Rearrange the sum as (014 + 01 + 010 + + ) (013 + 011 + 009 + + 1) = (014 013) + (01 011) + + ( 1) = 1 + 1 + +
BRITISH COLUMBIA SECONDARY SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST, 014 Solutions Junior Preliminary 1. Rearrange the sum as (014 + 01 + 010 + + ) (013 + 011 + 009 + + 1) = (014 013) + (01 011) + + ( 1) = 1 + 1 + +
Pre Algebra. Curriculum (634 topics)
 Pre Algebra This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
Pre Algebra This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
2015 Hypatia Contest
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 015 Hypatia Contest Thursday, April 16, 015 (in North America and South America) Friday, April 17, 015 (outside of North America
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 015 Hypatia Contest Thursday, April 16, 015 (in North America and South America) Friday, April 17, 015 (outside of North America
2015 Canadian Intermediate Mathematics Contest
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 015 Canadian Intermediate Mathematics Contest Wednesday, November 5, 015 (in North America and South America) Thursday, November
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 015 Canadian Intermediate Mathematics Contest Wednesday, November 5, 015 (in North America and South America) Thursday, November
State Math Contest (Junior)
 Name: Student ID: State Math Contest (Junior) Instructions: Do not turn this page until your proctor tells you. Enter your name, grade, and school information following the instructions given by your proctor.
Name: Student ID: State Math Contest (Junior) Instructions: Do not turn this page until your proctor tells you. Enter your name, grade, and school information following the instructions given by your proctor.
ACT MATH MUST-KNOWS Pre-Algebra and Elementary Algebra: 24 questions
 Pre-Algebra and Elementary Algebra: 24 questions Basic operations using whole numbers, integers, fractions, decimals and percents Natural (Counting) Numbers: 1, 2, 3 Whole Numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3 Integers:
Pre-Algebra and Elementary Algebra: 24 questions Basic operations using whole numbers, integers, fractions, decimals and percents Natural (Counting) Numbers: 1, 2, 3 Whole Numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3 Integers:
2007 Cayley Contest. Solutions
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 007 Cayley Contest (Grade 10) Tuesday, February 0, 007 Solutions
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 007 Cayley Contest (Grade 10) Tuesday, February 0, 007 Solutions
2011 Hypatia Contest
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING 011 Hypatia Contest Wednesday, April 1, 011 Solutions 011 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing 011 Hypatia Contest Solutions Page 1. (a)
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING 011 Hypatia Contest Wednesday, April 1, 011 Solutions 011 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing 011 Hypatia Contest Solutions Page 1. (a)
Glossary. Glossary Hawkes Learning Systems. All rights reserved.
 A Glossary Absolute value The distance a number is from 0 on a number line Acute angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute triangle A triangle in which all three angles are acute Addends The
A Glossary Absolute value The distance a number is from 0 on a number line Acute angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute triangle A triangle in which all three angles are acute Addends The
Foundations 5 Curriculum Guide
 1. Review: Natural Numbers...3 2. Reading and Writing Natural Numbers...6 3. Lines, Rays, and Line Segments...8 4. Comparing Natural Numbers... 12 5. Rounding Numbers... 15 6. Adding Natural Numbers...
1. Review: Natural Numbers...3 2. Reading and Writing Natural Numbers...6 3. Lines, Rays, and Line Segments...8 4. Comparing Natural Numbers... 12 5. Rounding Numbers... 15 6. Adding Natural Numbers...
California 3 rd Grade Standards / Excel Math Correlation by Lesson Number
 California 3 rd Grade Standards / Lesson (Activity) L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 L7 L8 Excel Math Lesson Objective Learning about the tens place and the ones place; adding and subtracting two-digit numbers; learning
California 3 rd Grade Standards / Lesson (Activity) L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 L7 L8 Excel Math Lesson Objective Learning about the tens place and the ones place; adding and subtracting two-digit numbers; learning
BRITISH COLUMBIA SECONDARY SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST, 2017 Junior Preliminary Problems & Solutions
 BRITISH COLUMBIA SECONDARY SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST, 017 Junior Preliminary Problems & s 1. If x is a number larger than, which of the following expressions is the smallest? (A) /(x 1) (B) /x (C) /(x
BRITISH COLUMBIA SECONDARY SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST, 017 Junior Preliminary Problems & s 1. If x is a number larger than, which of the following expressions is the smallest? (A) /(x 1) (B) /x (C) /(x
= How many four-digit numbers between 6000 and 7000 are there for which the thousands digits equal the sum of the other three digits?
 March 5, 2007 1. Maya deposited 1000 dollars at 6% interest compounded annually. What is the number of dollars in the account after four years? (A) $1258.47 (B) $1260.18 (C) $1262.48 (D) $1263.76 (E) $1264.87
March 5, 2007 1. Maya deposited 1000 dollars at 6% interest compounded annually. What is the number of dollars in the account after four years? (A) $1258.47 (B) $1260.18 (C) $1262.48 (D) $1263.76 (E) $1264.87
Course Readiness and Skills Review Handbook (Topics 1-10, 17) (240 topics, due. on 09/11/2015) Course Readiness (55 topics)
 Course Name: Gr. 8 Fall 2015 Course Code: C6HNH-TEK9E ALEKS Course: Middle School Math Course 3 Instructor: Mr. Fernando Course Dates: Begin: 08/31/2015 End: 06/17/2016 Course Content: 642 Topics (637
Course Name: Gr. 8 Fall 2015 Course Code: C6HNH-TEK9E ALEKS Course: Middle School Math Course 3 Instructor: Mr. Fernando Course Dates: Begin: 08/31/2015 End: 06/17/2016 Course Content: 642 Topics (637
Concours Fermat 2016 (11 e année Secondaire V)
 Le CENTRE d ÉDUCATION en MATHÉMATIQUES et en INFORMATIQUE cemc.uwaterloo.ca Concours Fermat 016 (11 e année Secondaire V) le mercredi 4 février 016 (Amérique du Nord et Amérique du Sud) le jeudi 5 février
Le CENTRE d ÉDUCATION en MATHÉMATIQUES et en INFORMATIQUE cemc.uwaterloo.ca Concours Fermat 016 (11 e année Secondaire V) le mercredi 4 février 016 (Amérique du Nord et Amérique du Sud) le jeudi 5 février
State Math Contest Senior Exam SOLUTIONS
 State Math Contest Senior Exam SOLUTIONS 1. The following pictures show two views of a non standard die (however the numbers 1-6 are represented on the die). How many dots are on the bottom face of figure?
State Math Contest Senior Exam SOLUTIONS 1. The following pictures show two views of a non standard die (however the numbers 1-6 are represented on the die). How many dots are on the bottom face of figure?
Glossary. Glossary 981. Hawkes Learning Systems. All rights reserved.
 A Glossary Absolute value The distance a number is from 0 on a number line Acute angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Addends The numbers being added in an addition problem Addition principle
A Glossary Absolute value The distance a number is from 0 on a number line Acute angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Addends The numbers being added in an addition problem Addition principle
To Find the Product of Monomials. ax m bx n abx m n. Let s look at an example in which we multiply two monomials. (3x 2 y)(2x 3 y 5 )
 5.4 E x a m p l e 1 362SECTION 5.4 OBJECTIVES 1. Find the product of a monomial and a polynomial 2. Find the product of two polynomials 3. Square a polynomial 4. Find the product of two binomials that
5.4 E x a m p l e 1 362SECTION 5.4 OBJECTIVES 1. Find the product of a monomial and a polynomial 2. Find the product of two polynomials 3. Square a polynomial 4. Find the product of two binomials that
Math Contest, Fall 2017 BC EXAM , z =
 Math Contest, Fall 017 BC EXAM 1. List x, y, z in order from smallest to largest fraction: x = 111110 111111, y = 1 3, z = 333331 333334 Consider 1 x = 1 111111, 1 y = thus 1 x > 1 z > 1 y, and so x
Math Contest, Fall 017 BC EXAM 1. List x, y, z in order from smallest to largest fraction: x = 111110 111111, y = 1 3, z = 333331 333334 Consider 1 x = 1 111111, 1 y = thus 1 x > 1 z > 1 y, and so x
California 5 th Grade Standards / Excel Math Correlation by Lesson Number
 (Activity) L1 L2 L3 Excel Math Objective Recognizing numbers less than a million given in words or place value; recognizing addition and subtraction fact families; subtracting 2 threedigit numbers with
(Activity) L1 L2 L3 Excel Math Objective Recognizing numbers less than a million given in words or place value; recognizing addition and subtraction fact families; subtracting 2 threedigit numbers with
Math is Cool Masters
 Sponsored by: GENIE Industries 7 th Grade November 19, 2005 Individual Contest Express all answers as reduced fractions unless stated otherwise. Leave answers in terms of π where applicable. Do not round
Sponsored by: GENIE Industries 7 th Grade November 19, 2005 Individual Contest Express all answers as reduced fractions unless stated otherwise. Leave answers in terms of π where applicable. Do not round
DO NOT ROUND YOUR ANSWERS
 Directions: Write your answers on the answer sheet. DO NOT detach the answer sheet from your exam. Answers can be given as integers, fractions or in decimal form. The answers which are given in decimal
Directions: Write your answers on the answer sheet. DO NOT detach the answer sheet from your exam. Answers can be given as integers, fractions or in decimal form. The answers which are given in decimal
2016 Canadian Intermediate Mathematics Contest
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 2016 Canadian Intermediate Mathematics Contest Wednesday, November 23, 2016 (in North America and South America) Thursday, November
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 2016 Canadian Intermediate Mathematics Contest Wednesday, November 23, 2016 (in North America and South America) Thursday, November
Intermediate Math Circles February 14, 2018 Contest Prep: Number Theory
 Intermediate Math Circles February 14, 2018 Contest Prep: Number Theory Part 1: Prime Factorization A prime number is an integer greater than 1 whose only positive divisors are 1 and itself. An integer
Intermediate Math Circles February 14, 2018 Contest Prep: Number Theory Part 1: Prime Factorization A prime number is an integer greater than 1 whose only positive divisors are 1 and itself. An integer
2 BAMO 2015 Problems and Solutions February 26, 2015
 17TH AY AREA MATHEMATIAL OLYMPIAD PROLEMS AND SOLUTIONS A: There are 7 boxes arranged in a row and numbered 1 through 7. You have a stack of 2015 cards, which you place one by one in the boxes. The first
17TH AY AREA MATHEMATIAL OLYMPIAD PROLEMS AND SOLUTIONS A: There are 7 boxes arranged in a row and numbered 1 through 7. You have a stack of 2015 cards, which you place one by one in the boxes. The first
Grade 8 Mathematics MCA Item Sampler Teacher Guide
 Grade 8 Mathematics MCA Item Sampler Teacher Guide Overview of Item Samplers Item samplers are one type of student resource provided to help students and educators prepare for test administration. While
Grade 8 Mathematics MCA Item Sampler Teacher Guide Overview of Item Samplers Item samplers are one type of student resource provided to help students and educators prepare for test administration. While
Preliminary chapter: Review of previous coursework. Objectives
 Preliminary chapter: Review of previous coursework Objectives By the end of this chapter the student should be able to recall, from Books 1 and 2 of New General Mathematics, the facts and methods that
Preliminary chapter: Review of previous coursework Objectives By the end of this chapter the student should be able to recall, from Books 1 and 2 of New General Mathematics, the facts and methods that
The problems in this booklet are organized into strands. A problem often appears in multiple strands. The problems are suitable for most students in
 The problems in this booklet are organized into strands. A problem often appears in multiple strands. The problems are suitable for most students in Grade 11 or higher. Problem E What s Your Angle? A
The problems in this booklet are organized into strands. A problem often appears in multiple strands. The problems are suitable for most students in Grade 11 or higher. Problem E What s Your Angle? A
2008 Cayley Contest. Solutions
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 008 Cayley Contest (Grade 10) Tuesday, February 19, 008
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 008 Cayley Contest (Grade 10) Tuesday, February 19, 008
State Math Contest (Senior)
 Name: Student I: State Math ontest (Senior) Instructions: o not turn this page until your proctor tells you. nter your name, grade, and school information following the instructions given by your proctor.
Name: Student I: State Math ontest (Senior) Instructions: o not turn this page until your proctor tells you. nter your name, grade, and school information following the instructions given by your proctor.
OBJECTIVES UNIT 1. Lesson 1.0
 OBJECTIVES UNIT 1 Lesson 1.0 1. Define "set," "element," "finite set," and "infinite set," "empty set," and "null set" and give two examples of each term. 2. Define "subset," "universal set," and "disjoint
OBJECTIVES UNIT 1 Lesson 1.0 1. Define "set," "element," "finite set," and "infinite set," "empty set," and "null set" and give two examples of each term. 2. Define "subset," "universal set," and "disjoint
Math is Cool Championships
 Individual Contest Express all answers as reduced fractions unless stated otherwise. Leave answers in terms of π where applicable. Do not round any answers unless stated otherwise. Record all answers on
Individual Contest Express all answers as reduced fractions unless stated otherwise. Leave answers in terms of π where applicable. Do not round any answers unless stated otherwise. Record all answers on
2015 Fall Startup Event Solutions
 1. Evaluate: 829 7 The standard division algorithm gives 1000 + 100 + 70 + 7 = 1177. 2. What is the remainder when 86 is divided by 9? Again, the standard algorithm gives 20 + 1 = 21 with a remainder of
1. Evaluate: 829 7 The standard division algorithm gives 1000 + 100 + 70 + 7 = 1177. 2. What is the remainder when 86 is divided by 9? Again, the standard algorithm gives 20 + 1 = 21 with a remainder of
Solve for the variable by transforming equations:
 Cantwell Sacred Heart of Mary High School Math Department Study Guide for the Algebra 1 (or higher) Placement Test Name: Date: School: Solve for the variable by transforming equations: 1. y + 3 = 9. 1
Cantwell Sacred Heart of Mary High School Math Department Study Guide for the Algebra 1 (or higher) Placement Test Name: Date: School: Solve for the variable by transforming equations: 1. y + 3 = 9. 1
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca Euclid Contest. Wednesday, April 15, 2015
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 015 Euclid Contest Wednesday, April 15, 015 (in North America and South America) Thursday, April 16, 015 (outside of North America
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 015 Euclid Contest Wednesday, April 15, 015 (in North America and South America) Thursday, April 16, 015 (outside of North America
Algebra II Polynomials: Operations and Functions
 Slide 1 / 276 Slide 2 / 276 Algebra II Polynomials: Operations and Functions 2014-10-22 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 276 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Properties of Exponents Review
Slide 1 / 276 Slide 2 / 276 Algebra II Polynomials: Operations and Functions 2014-10-22 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 276 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Properties of Exponents Review
UNC Charlotte 2004 Algebra with solutions
 with solutions March 8, 2004 1. Let z denote the real number solution to of the digits of z? (A) 13 (B) 14 (C) 15 (D) 16 (E) 17 3 + x 1 = 5. What is the sum Solution: E. Square both sides twice to get
with solutions March 8, 2004 1. Let z denote the real number solution to of the digits of z? (A) 13 (B) 14 (C) 15 (D) 16 (E) 17 3 + x 1 = 5. What is the sum Solution: E. Square both sides twice to get
3. A square has 4 sides, so S = 4. A pentagon has 5 vertices, so P = 5. Hence, S + P = 9. = = 5 3.
 JHMMC 01 Grade Solutions October 1, 01 1. By counting, there are 7 words in this question.. (, 1, ) = 1 + 1 + = 9 + 1 + =.. A square has sides, so S =. A pentagon has vertices, so P =. Hence, S + P = 9..
JHMMC 01 Grade Solutions October 1, 01 1. By counting, there are 7 words in this question.. (, 1, ) = 1 + 1 + = 9 + 1 + =.. A square has sides, so S =. A pentagon has vertices, so P =. Hence, S + P = 9..
Destination Math California Intervention
 Destination Math California Intervention correlated to the California Intervention 4 7 s McDougal Littell Riverdeep STANDARDS MAPS for a Mathematics Intervention Program (Grades 4-7) The standards maps
Destination Math California Intervention correlated to the California Intervention 4 7 s McDougal Littell Riverdeep STANDARDS MAPS for a Mathematics Intervention Program (Grades 4-7) The standards maps
Grade 6 Math Circles. Gauss Contest Preparation - Solutions
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles March 25/26, 2014 Gauss Contest Preparation - Solutions General Information The Gauss
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles March 25/26, 2014 Gauss Contest Preparation - Solutions General Information The Gauss
Math Challengers Provincial 2016 Blitz and Bull s-eye rounds.
 Math hallengers Provincial 016 litz and ull s-eye rounds. Solutions proposed by Sean Wang from Point Grey litz 1. What is the sum of all single digit primes? Solution: Recall that a prime number only has
Math hallengers Provincial 016 litz and ull s-eye rounds. Solutions proposed by Sean Wang from Point Grey litz 1. What is the sum of all single digit primes? Solution: Recall that a prime number only has
Math 46 Final Exam Review Packet
 Math 46 Final Exam Review Packet Question 1. Perform the indicated operation. Simplify if possible. 7 x x 2 2x + 3 2 x Question 2. The sum of a number and its square is 72. Find the number. Question 3.
Math 46 Final Exam Review Packet Question 1. Perform the indicated operation. Simplify if possible. 7 x x 2 2x + 3 2 x Question 2. The sum of a number and its square is 72. Find the number. Question 3.
2018 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 08 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest April 08 Solutions 08 University of Waterloo 08 CTMC Solutions Page Individual Problems. Since
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 08 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest April 08 Solutions 08 University of Waterloo 08 CTMC Solutions Page Individual Problems. Since
2001 Solutions Pascal Contest (Grade 9)
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of The Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 00 s Pascal Contest (Grade 9) for The CENTRE for EDUCATION
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of The Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 00 s Pascal Contest (Grade 9) for The CENTRE for EDUCATION
Intermediate Math Circles February 22, 2012 Contest Preparation II
 Intermediate Math Circles February, 0 Contest Preparation II Answers: Problem Set 6:. C. A 3. B 4. [-6,6] 5. T 3, U and T 8, U 6 6. 69375 7. C 8. A 9. C 0. E Australian Mathematics Competition - Intermediate
Intermediate Math Circles February, 0 Contest Preparation II Answers: Problem Set 6:. C. A 3. B 4. [-6,6] 5. T 3, U and T 8, U 6 6. 69375 7. C 8. A 9. C 0. E Australian Mathematics Competition - Intermediate
ABE Math Review Package
 P a g e ABE Math Review Package This material is intended as a review of skills you once learned and wish to review before your assessment. Before studying Algebra, you should be familiar with all of the
P a g e ABE Math Review Package This material is intended as a review of skills you once learned and wish to review before your assessment. Before studying Algebra, you should be familiar with all of the
South Carolina Alternate Assessments Performance Level Descriptors. Mathematics. Revised: June 29, 2018
 South Carolina Alternate Assessments Performance Level Descriptors Mathematics Revised: June 29, 2018 Contents Standards Reference Number Abbreviations... 1 Grade 3... 2 Grade 4... 6 Grade 5... 9 Grade
South Carolina Alternate Assessments Performance Level Descriptors Mathematics Revised: June 29, 2018 Contents Standards Reference Number Abbreviations... 1 Grade 3... 2 Grade 4... 6 Grade 5... 9 Grade
Due to the detail of some problems, print the contests using a normal or high quality setting.
 General Contest Guidelines: Keep the contests secure. Discussion about contest questions is not permitted prior to giving the contest. Due to the detail of some problems, print the contests using a normal
General Contest Guidelines: Keep the contests secure. Discussion about contest questions is not permitted prior to giving the contest. Due to the detail of some problems, print the contests using a normal
SOLUTIONS OF 2012 MATH OLYMPICS LEVEL II T 3 T 3 1 T 4 T 4 1
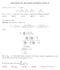 SOLUTIONS OF 0 MATH OLYMPICS LEVEL II. If T n = + + 3 +... + n and P n = T T T 3 T 3 T 4 T 4 T n T n for n =, 3, 4,..., then P 0 is the closest to which of the following numbers? (a).9 (b).3 (c) 3. (d).6
SOLUTIONS OF 0 MATH OLYMPICS LEVEL II. If T n = + + 3 +... + n and P n = T T T 3 T 3 T 4 T 4 T n T n for n =, 3, 4,..., then P 0 is the closest to which of the following numbers? (a).9 (b).3 (c) 3. (d).6
Senior Math Circles November 19, 2008 Probability II
 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Senior Math Circles November 9, 2008 Probability II Probability Counting There are many situations where
University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Senior Math Circles November 9, 2008 Probability II Probability Counting There are many situations where
2013 Canadian Senior Mathematics Contest
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 2013 Canadian Senior Mathematics Contest Thursday, November 21, 2013 (in North America and South America) Friday, November 22, 2013
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 2013 Canadian Senior Mathematics Contest Thursday, November 21, 2013 (in North America and South America) Friday, November 22, 2013
1. What is the difference between the sum of the first 2003 even counting numbers and the sum of the first 2003 odd counting numbers?
 4 th AMC 0 A 200 2. What is the difference between the sum of the first 200 even counting numbers and the sum of the first 200 odd counting numbers? (A) 0 (B) (C) 2 (D) 200 (E) 4006 2. Members of the Rockham
4 th AMC 0 A 200 2. What is the difference between the sum of the first 200 even counting numbers and the sum of the first 200 odd counting numbers? (A) 0 (B) (C) 2 (D) 200 (E) 4006 2. Members of the Rockham
Pre Algebra and Introductory Algebra
 Pre Algebra and Introductory Algebra This course covers the topics outlined below and is available for use with integrated, interactive ebooks. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to
Pre Algebra and Introductory Algebra This course covers the topics outlined below and is available for use with integrated, interactive ebooks. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to
Florida Math 0022 Correlation of the ALEKS course Florida Math 0022 to the Florida Mathematics Competencies - Lower and Upper
 Florida Math 0022 Correlation of the ALEKS course Florida Math 0022 to the Florida Mathematics Competencies - Lower and Upper Whole Numbers MDECL1: Perform operations on whole numbers (with applications,
Florida Math 0022 Correlation of the ALEKS course Florida Math 0022 to the Florida Mathematics Competencies - Lower and Upper Whole Numbers MDECL1: Perform operations on whole numbers (with applications,
2013 Junior High Mathematics Contest. Solutions: 7 th Grade Individual Contest:
 Solutions: 7 th Grade Individual Contest: 1) Solve for x. The roots are -1/3 and 5/2. (-1/3)*(5/2) = -5/6 2) The difference between each even and odd term is 1. Since there are 1000 of them, our answer
Solutions: 7 th Grade Individual Contest: 1) Solve for x. The roots are -1/3 and 5/2. (-1/3)*(5/2) = -5/6 2) The difference between each even and odd term is 1. Since there are 1000 of them, our answer
 Q 1 Find the square root of 729. 6. Squares and Square Roots Q 2 Fill in the blank using the given pattern. 7 2 = 49 67 2 = 4489 667 2 = 444889 6667 2 = Q 3 Without adding find the sum of 1 + 3 + 5 + 7
Q 1 Find the square root of 729. 6. Squares and Square Roots Q 2 Fill in the blank using the given pattern. 7 2 = 49 67 2 = 4489 667 2 = 444889 6667 2 = Q 3 Without adding find the sum of 1 + 3 + 5 + 7
High School Math Contest
 High School Math Contest University of South Carolina February th, 017 Problem 1. If (x y) = 11 and (x + y) = 169, what is xy? (a) 11 (b) 1 (c) 1 (d) (e) 8 Solution: Note that xy = (x + y) (x y) = 169
High School Math Contest University of South Carolina February th, 017 Problem 1. If (x y) = 11 and (x + y) = 169, what is xy? (a) 11 (b) 1 (c) 1 (d) (e) 8 Solution: Note that xy = (x + y) (x y) = 169
2018 LEHIGH UNIVERSITY HIGH SCHOOL MATH CONTEST
 08 LEHIGH UNIVERSITY HIGH SCHOOL MATH CONTEST. A right triangle has hypotenuse 9 and one leg. What is the length of the other leg?. Don is /3 of the way through his run. After running another / mile, he
08 LEHIGH UNIVERSITY HIGH SCHOOL MATH CONTEST. A right triangle has hypotenuse 9 and one leg. What is the length of the other leg?. Don is /3 of the way through his run. After running another / mile, he
2017 SUMMER REVIEW FOR STUDENTS ENTERING GEOMETRY
 2017 SUMMER REVIEW FOR STUDENTS ENTERING GEOMETRY The following are topics that you will use in Geometry and should be retained throughout the summer. Please use this practice to review the topics you
2017 SUMMER REVIEW FOR STUDENTS ENTERING GEOMETRY The following are topics that you will use in Geometry and should be retained throughout the summer. Please use this practice to review the topics you
Olympiad M aclaurin Paper
 4 Olympiad M aclaurin Paper A l candidates must be in SchoolYear (England and W ales), S4(Scotland), or SchoolYear (Northern Ireland).. How many different ways are there to express 5 in the form a + b,
4 Olympiad M aclaurin Paper A l candidates must be in SchoolYear (England and W ales), S4(Scotland), or SchoolYear (Northern Ireland).. How many different ways are there to express 5 in the form a + b,
GRE Quantitative Reasoning Practice Questions
 GRE Quantitative Reasoning Practice Questions y O x 7. The figure above shows the graph of the function f in the xy-plane. What is the value of f (f( ))? A B C 0 D E Explanation Note that to find f (f(
GRE Quantitative Reasoning Practice Questions y O x 7. The figure above shows the graph of the function f in the xy-plane. What is the value of f (f( ))? A B C 0 D E Explanation Note that to find f (f(
BRITISH COLUMBIA COLLEGES High School Mathematics Contest 2003 Solutions
 BRITISH COLUMBIA COLLEGES High School Mathematics Contest 3 Solutions Junior Preliminary. Solve the equation x = Simplify the complex fraction by multiplying numerator and denominator by x. x = = x = (x
BRITISH COLUMBIA COLLEGES High School Mathematics Contest 3 Solutions Junior Preliminary. Solve the equation x = Simplify the complex fraction by multiplying numerator and denominator by x. x = = x = (x
Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Academic Standards Mathematics
 8 th GRADE Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Standard 1 - Number Sense Students know the properties of rational* and irrational* numbers expressed in a variety of forms. They understand and use
8 th GRADE Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Standard 1 - Number Sense Students know the properties of rational* and irrational* numbers expressed in a variety of forms. They understand and use
Name: Geometry & Intermediate Algebra Summer Assignment
 Name: Geometry & Intermediate Algebra Summer Assignment Instructions: This packet contains material that you have seen in your previous math courses (Pre- Algebra and/or Algebra 1). We understand that
Name: Geometry & Intermediate Algebra Summer Assignment Instructions: This packet contains material that you have seen in your previous math courses (Pre- Algebra and/or Algebra 1). We understand that
MMC Sectoral Level, Category B. March 24, 2017
 MMC 017 Sectoral Level, Category B March 4, 017 Disclaimer: inexact wording. I was not able to attend the actual round, so I must rely on transcriptions, which may affect the accuracy. I can vouch for
MMC 017 Sectoral Level, Category B March 4, 017 Disclaimer: inexact wording. I was not able to attend the actual round, so I must rely on transcriptions, which may affect the accuracy. I can vouch for
