Hashing. Algorithm : Design & Analysis [09]
|
|
|
- Drusilla Allison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hashig Algorithm : Desig & Aalysis [09]
2 I the last class Implemetig Dictioary ADT Defiitio of red-black tree Black height Isertio ito a red-black tree Deletio from a red-black tree
3 Hashig Hashig Collisio Hadlig for Hashig Closed Address Hashig Ope Address Hashig Hash Fuctios Array Doublig ad Amortized Aalysis
4 Hashig: the Idea E[0] E[1] E[k] E[m-1] I feasible size Idex distributio Collisio hadlig Hash Fuctio H(x)=k A calculated array idex for the key Very large, but oly a small part is used i a applicatio x Key Space Value of a specific key
5 Collisio Hadlig: Closed Address Each address is a liked list k 1 k 4 k 1 k 5 k 2 k 7 k 4 k5 k 2 k 3 k 7 k 6 k 6 k 3
6 Closed Address: Aalysis Assumptio: simple uiform hashig: for j=0,1,2,...,m-1, the average legth of the list at E[j] is /m. The average cost of a usuccessful search: Ay key that is ot i the table is equally likely to hash to ay of the m address. The average cost to determie that the key is ot i the list E[h(k)] is the cost to search to the ed of the list, which is /m. So, the total cost is Θ(1+ /m).
7 Closed Address: Aalysis(cot.) For successful search: (assumig that x i is the ith elemet iserted ito the table, i=1,2,...,) For each i, the probability of that x i is searched is 1/. For a specific x i, the umber of elemets examied i a successful search is t+1, where t is the umber of elemets iserted ito the same list as x i, after x i has bee iserted. Ad for ay j, the probability of that x j is iserted ito the same list of x i is 1/m. So, the cost is: Cost for computig hashig i= j= i+ m Expected umber of elemets i frot of the searched oe i the same liked list.
8 Closed Address: Aalysis(cot.) The average cost of a successful search: Defie α=/m as load factor, The average cost of a successful 1 = m i= 1 j = 1+ = i m m i= 1 α α = 1+ = Θ(1 + α ) 2 2 Cost for computig hashig ( i) search is : = 1+ 1 m 1 i= 1 Number of elemets i frot of the searched oe i the same liked list. i
9 Collisio Hadlig: Ope Address All elemets are stored i the hash table, o liked list is used. So, α, the load factor, ca ot be larger tha 1. Collisio is settled by rehashig : a fuctio is used to get a ew hashig address for each collided address, i.e. the hash table slots are probed successively, util a valid locatio is foud. The probe sequece ca be see as a permutatio of (0,1,2,..., m-1)
10 Commoly Used Probig Liear probig: Give a ordiary hash fuctio h, which is called a auxiliary hash fuctio, the hash fuctio is: (clusterig may occur) Quadratic Probig: h(k,i) = (h (k)+i) mod m (i=0,1,...,m-1) Give auxiliary fuctio h ad ozero auxiliary costat c 1 ad c 2, the hash fuctio is: (secodary clusterig may occur) Double hashig: h(k,i) = (h (k)+c 1 i+ c 2 i 2 ) mod m (i=0,1,...,m-1) Give auxiliary fuctios h 1 ad h 2, the hash fuctio is: h(k,i) = (h 1 (k)+ ih 2 (k)) mod m (i=0,1,...,m-1)
11 Liear Probig: a Example Idex 0 H 1776 Hash fuctio: h(x)=5x mod 8 Hash fuctio: h(x)=5x mod 8 1 rehashig hashig hashig Rehash fuctio: rh(j)=(j+1) mod 8 chai of rehashigs
12 Equally Likely Permutatios Assumptio: each key is equally likely to have ay of the m! permutatios of (1,2...,m-1) as its probe sequece. Note: both liear ad quadratic probig have oly m distict probe sequece, as determied by the first probe.
13 Aalysis for Ope Address Hash Assumig uiform hashig, the average umber of probes i a usuccessful search is at most 1/(1-α) (α=/m<1) Note is so, m m the m The, : the, ad 1 1 the probabilit that probabilit m 2 2 of average the y of L y of jth( the umber the j > umber i + 2 m i + 2 of first 1) positio of probe probed m is probe i 1 : i = 1 positio occupied o i = α i α 1 less 1 = beig i = 0 is tha i α -j m-j i = occupied will, 1 1 α be :
14 Aalysis for Ope Address Hash Assumig uiform hashig, the average cost of probes i a 1 1 successful search is at most l (α=/m<1) α 1 α To search for the ( i + 1)th iserted elemet i the table, the cost is the same as the cost for isertig it whe there i are just i elemets i the table. At that time, α =, so, m 1 m the cost is = i For For your your referece: 1- m i m Half Half full: full: 1.387; 90% 90% full: full: So, the cost is : 1 1 m 1 m m m dx 1 m 1 1 = = = = α α l l = m i = m i = + i m x α m α 1 α i 0 i 0 i m 1
15 Hashig Fuctio A good hash fuctio satisfies the assumptio of simple uiform hashig. Heuristic hashig fuctios The divisio method: h(k)=k mod m The multiplicatio method: h(k)= m(ka mod 1) (0<A<1) No sigle fuctio ca avoid the worst case Θ(), so, Uiversal hashig is proposed. Rich resource about hashig fuctio: Goet ad Baeza-Yates: Hadbook of Algorithms ad Data Structures, Addiso-Wesley, 1991
16 Array Doublig Cost for search i a hash table is Θ(1+α), the if we ca keep α costat, the cost will be Θ(1) Space allocatio techiques such as array doublig may be eeded. The problem of uusually expesive idividual operatio.
17 Lookig at the Memory Allocatio hashigisert(hashtable H, ITEM x) iteger size=0, um=0; if size=0 the allocate a block of size 1; size=1; if um=size the allocate a block of size 2size; move all item ito ew table; size=2size; isert x ito the table; um=um+1; retur Isertio with expasio: cost size Elemetary isertio: cost 1
18 Worst-case Aalysis of the Isertio For executio of isertio operatios A bad aalysis: the worst case for oe isertio is the case whe expasio is required, up to So, the worst case cost is i O( 2 ). Note the expasio is required durig the ith operatio oly if i=2 k, ad the cost of the ith operatio c i So, i = 1 the if i total 1is exactly power of 2 otherwise cost is : i= 1 c i + lg j= 0 2 j < + 2 = 3
19 Amortized Time Aalysis Amortized equatio: amortized cost = actual cost + accoutig cost Desig goals for accoutig cost I ay legal sequece of operatios, the sum of the accoutig costs is oegative. The amortized cost of each operatio is fairly regular, i spite of the wide fluctuate possible for the actual cost of idividual operatios.
20 Amortized Aalysis: MultiPop Stack Pop: Cost=1 MultiPop: Cost=mi(s,t) Push: Cost=1 s t Amortized cost: push:2; pop, multipop: 0
21 Amortized Aalysis: Biary Couter Cost measure: bit flip amortized cost: set 1: 2 set 0: 0
22 Accoutig Scheme for Stack Push Push operatio with array doublig No resize triggered: 1 Resize( 2) triggered: t+1 (t is a costat) Accoutig scheme (specifyig accoutig cost) No resize triggered: 2t Resize( 2) triggered: -t+2t So, the amortized cost of each idividual push operatio is 1+2t Θ(1)
23 Home Assigmet pp
11. Hash Tables. m is not too large. Many applications require a dynamic set that supports only the directory operations INSERT, SEARCH and DELETE.
 11. Hash Tables May applicatios require a dyamic set that supports oly the directory operatios INSERT, SEARCH ad DELETE. A hash table is a geeralizatio of the simpler otio of a ordiary array. Directly
11. Hash Tables May applicatios require a dyamic set that supports oly the directory operatios INSERT, SEARCH ad DELETE. A hash table is a geeralizatio of the simpler otio of a ordiary array. Directly
DATA STRUCTURES I, II, III, AND IV
 Data structures DATA STRUCTURES I, II, III, AND IV I. Amortized Aalysis II. Biary ad Biomial Heaps III. Fiboacci Heaps IV. Uio Fid Static problems. Give a iput, produce a output. Ex. Sortig, FFT, edit
Data structures DATA STRUCTURES I, II, III, AND IV I. Amortized Aalysis II. Biary ad Biomial Heaps III. Fiboacci Heaps IV. Uio Fid Static problems. Give a iput, produce a output. Ex. Sortig, FFT, edit
Definitions: Universe U of keys, e.g., U N 0. U very large. Set S U of keys, S = m U.
 7 7 Dictioary: S.isertx): Isert a elemet x. S.deletex): Delete the elemet poited to by x. S.searchk): Retur a poiter to a elemet e with key[e] = k i S if it exists; otherwise retur ull. So far we have
7 7 Dictioary: S.isertx): Isert a elemet x. S.deletex): Delete the elemet poited to by x. S.searchk): Retur a poiter to a elemet e with key[e] = k i S if it exists; otherwise retur ull. So far we have
7.7 Hashing. 7.7 Hashing. Perfect Hashing. Direct Addressing
 Dictioary: S.isertx): Isert a elemet x. S.deletex): Delete the elemet poited to by x. S.searchk): Retur a poiter to a elemet e with key[e] = k i S if it exists; otherwise retur ull. So far we have implemeted
Dictioary: S.isertx): Isert a elemet x. S.deletex): Delete the elemet poited to by x. S.searchk): Retur a poiter to a elemet e with key[e] = k i S if it exists; otherwise retur ull. So far we have implemeted
Hashing and Amortization
 Lecture Hashig ad Amortizatio Supplemetal readig i CLRS: Chapter ; Chapter 7 itro; Sectio 7.. Arrays ad Hashig Arrays are very useful. The items i a array are statically addressed, so that isertig, deletig,
Lecture Hashig ad Amortizatio Supplemetal readig i CLRS: Chapter ; Chapter 7 itro; Sectio 7.. Arrays ad Hashig Arrays are very useful. The items i a array are statically addressed, so that isertig, deletig,
OPTIMAL ALGORITHMS -- SUPPLEMENTAL NOTES
 OPTIMAL ALGORITHMS -- SUPPLEMENTAL NOTES Peter M. Maurer Why Hashig is θ(). As i biary search, hashig assumes that keys are stored i a array which is idexed by a iteger. However, hashig attempts to bypass
OPTIMAL ALGORITHMS -- SUPPLEMENTAL NOTES Peter M. Maurer Why Hashig is θ(). As i biary search, hashig assumes that keys are stored i a array which is idexed by a iteger. However, hashig attempts to bypass
1 Hash tables. 1.1 Implementation
 Lecture 8 Hash Tables, Uiversal Hash Fuctios, Balls ad Bis Scribes: Luke Johsto, Moses Charikar, G. Valiat Date: Oct 18, 2017 Adapted From Virgiia Williams lecture otes 1 Hash tables A hash table is a
Lecture 8 Hash Tables, Uiversal Hash Fuctios, Balls ad Bis Scribes: Luke Johsto, Moses Charikar, G. Valiat Date: Oct 18, 2017 Adapted From Virgiia Williams lecture otes 1 Hash tables A hash table is a
Test One (Answer Key)
 CS395/Ma395 (Sprig 2005) Test Oe Name: Page 1 Test Oe (Aswer Key) CS395/Ma395: Aalysis of Algorithms This is a closed book, closed otes, 70 miute examiatio. It is worth 100 poits. There are twelve (12)
CS395/Ma395 (Sprig 2005) Test Oe Name: Page 1 Test Oe (Aswer Key) CS395/Ma395: Aalysis of Algorithms This is a closed book, closed otes, 70 miute examiatio. It is worth 100 poits. There are twelve (12)
19.1 The dictionary problem
 CS125 Lecture 19 Fall 2016 19.1 The dictioary proble Cosider the followig data structural proble, usually called the dictioary proble. We have a set of ites. Each ite is a (key, value pair. Keys are i
CS125 Lecture 19 Fall 2016 19.1 The dictioary proble Cosider the followig data structural proble, usually called the dictioary proble. We have a set of ites. Each ite is a (key, value pair. Keys are i
Classification of problem & problem solving strategies. classification of time complexities (linear, logarithmic etc)
 Classificatio of problem & problem solvig strategies classificatio of time complexities (liear, arithmic etc) Problem subdivisio Divide ad Coquer strategy. Asymptotic otatios, lower boud ad upper boud:
Classificatio of problem & problem solvig strategies classificatio of time complexities (liear, arithmic etc) Problem subdivisio Divide ad Coquer strategy. Asymptotic otatios, lower boud ad upper boud:
Skip Lists. Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 S 3 S S 1
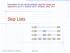 Presetatio for use with the textbook, Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Skip Lists S 3 15 15 23 10 15 23 36 Skip Lists 1 What is a Skip List A skip list for
Presetatio for use with the textbook, Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Skip Lists S 3 15 15 23 10 15 23 36 Skip Lists 1 What is a Skip List A skip list for
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms Probabilistic aalysis ad Radomized algorithms Referece: CLRS Chapter 5 Topics: Hirig problem Idicatio radom variables Radomized algorithms Huo Hogwei 1 The hirig problem
Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms Probabilistic aalysis ad Radomized algorithms Referece: CLRS Chapter 5 Topics: Hirig problem Idicatio radom variables Radomized algorithms Huo Hogwei 1 The hirig problem
Analysis of Algorithms. Introduction. Contents
 Itroductio The focus of this module is mathematical aspects of algorithms. Our mai focus is aalysis of algorithms, which meas evaluatig efficiecy of algorithms by aalytical ad mathematical methods. We
Itroductio The focus of this module is mathematical aspects of algorithms. Our mai focus is aalysis of algorithms, which meas evaluatig efficiecy of algorithms by aalytical ad mathematical methods. We
Recurrence Relations
 Recurrece Relatios Aalysis of recursive algorithms, such as: it factorial (it ) { if (==0) retur ; else retur ( * factorial(-)); } Let t be the umber of multiplicatios eeded to calculate factorial(). The
Recurrece Relatios Aalysis of recursive algorithms, such as: it factorial (it ) { if (==0) retur ; else retur ( * factorial(-)); } Let t be the umber of multiplicatios eeded to calculate factorial(). The
A recurrence equation is just a recursive function definition. It defines a function at one input in terms of its value on smaller inputs.
 CS23 Algorithms Hadout #6 Prof Ly Turbak September 8, 200 Wellesley College RECURRENCES This hadout summarizes highlights of CLRS Chapter 4 ad Appedix A (CLR Chapters 3 & 4) Two-Step Strategy for Aalyzig
CS23 Algorithms Hadout #6 Prof Ly Turbak September 8, 200 Wellesley College RECURRENCES This hadout summarizes highlights of CLRS Chapter 4 ad Appedix A (CLR Chapters 3 & 4) Two-Step Strategy for Aalyzig
CS / MCS 401 Homework 3 grader solutions
 CS / MCS 401 Homework 3 grader solutios assigmet due July 6, 016 writte by Jāis Lazovskis maximum poits: 33 Some questios from CLRS. Questios marked with a asterisk were ot graded. 1 Use the defiitio of
CS / MCS 401 Homework 3 grader solutios assigmet due July 6, 016 writte by Jāis Lazovskis maximum poits: 33 Some questios from CLRS. Questios marked with a asterisk were ot graded. 1 Use the defiitio of
Design and Analysis of ALGORITHM (Topic 2)
 DR. Gatot F. Hertoo, MSc. Desig ad Aalysis of ALGORITHM (Topic 2) Algorithms + Data Structures = Programs Lessos Leared 1 Our Machie Model: Assumptios Geeric Radom Access Machie (RAM) Executes operatios
DR. Gatot F. Hertoo, MSc. Desig ad Aalysis of ALGORITHM (Topic 2) Algorithms + Data Structures = Programs Lessos Leared 1 Our Machie Model: Assumptios Geeric Radom Access Machie (RAM) Executes operatios
CS 332: Algorithms. Linear-Time Sorting. Order statistics. Slide credit: David Luebke (Virginia)
 1 CS 332: Algorithms Liear-Time Sortig. Order statistics. Slide credit: David Luebke (Virgiia) Quicksort: Partitio I Words Partitio(A, p, r): Select a elemet to act as the pivot (which?) Grow two regios,
1 CS 332: Algorithms Liear-Time Sortig. Order statistics. Slide credit: David Luebke (Virgiia) Quicksort: Partitio I Words Partitio(A, p, r): Select a elemet to act as the pivot (which?) Grow two regios,
Lecture 3: Asymptotic Analysis + Recurrences
 Lecture 3: Asymptotic Aalysis + Recurreces Data Structures ad Algorithms CSE 373 SU 18 BEN JONES 1 Warmup Write a model ad fid Big-O for (it i = 0; i < ; i++) { for (it j = 0; j < i; j++) { System.out.pritl(
Lecture 3: Asymptotic Aalysis + Recurreces Data Structures ad Algorithms CSE 373 SU 18 BEN JONES 1 Warmup Write a model ad fid Big-O for (it i = 0; i < ; i++) { for (it j = 0; j < i; j++) { System.out.pritl(
Recursive Algorithms. Recurrences. Recursive Algorithms Analysis
 Recursive Algorithms Recurreces Computer Sciece & Egieerig 35: Discrete Mathematics Christopher M Bourke cbourke@cseuledu A recursive algorithm is oe i which objects are defied i terms of other objects
Recursive Algorithms Recurreces Computer Sciece & Egieerig 35: Discrete Mathematics Christopher M Bourke cbourke@cseuledu A recursive algorithm is oe i which objects are defied i terms of other objects
CS161: Algorithm Design and Analysis Handout #10 Stanford University Wednesday, 10 February 2016
 CS161: Algorithm Desig ad Aalysis Hadout #10 Staford Uiversity Wedesday, 10 February 2016 Lecture #11: Wedesday, 10 February 2016 Topics: Example midterm problems ad solutios from a log time ago Sprig
CS161: Algorithm Desig ad Aalysis Hadout #10 Staford Uiversity Wedesday, 10 February 2016 Lecture #11: Wedesday, 10 February 2016 Topics: Example midterm problems ad solutios from a log time ago Sprig
Data Structures and Algorithm. Xiaoqing Zheng
 Data Structures ad Algorithm Xiaoqig Zheg zhegxq@fudaeduc What are algorithms? A sequece of computatioal steps that trasform the iput ito the output Sortig problem: Iput: A sequece of umbers
Data Structures ad Algorithm Xiaoqig Zheg zhegxq@fudaeduc What are algorithms? A sequece of computatioal steps that trasform the iput ito the output Sortig problem: Iput: A sequece of umbers
CS583 Lecture 02. Jana Kosecka. some materials here are based on E. Demaine, D. Luebke slides
 CS583 Lecture 02 Jaa Kosecka some materials here are based o E. Demaie, D. Luebke slides Previously Sample algorithms Exact ruig time, pseudo-code Approximate ruig time Worst case aalysis Best case aalysis
CS583 Lecture 02 Jaa Kosecka some materials here are based o E. Demaie, D. Luebke slides Previously Sample algorithms Exact ruig time, pseudo-code Approximate ruig time Worst case aalysis Best case aalysis
Mathematical Foundation. CSE 6331 Algorithms Steve Lai
 Mathematical Foudatio CSE 6331 Algorithms Steve Lai Complexity of Algorithms Aalysis of algorithm: to predict the ruig time required by a algorithm. Elemetary operatios: arithmetic & boolea operatios:
Mathematical Foudatio CSE 6331 Algorithms Steve Lai Complexity of Algorithms Aalysis of algorithm: to predict the ruig time required by a algorithm. Elemetary operatios: arithmetic & boolea operatios:
ADVANCED SOFTWARE ENGINEERING
 ADVANCED SOFTWARE ENGINEERING COMP 3705 Exercise Usage-based Testig ad Reliability Versio 1.0-040406 Departmet of Computer Ssciece Sada Narayaappa, Aeliese Adrews Versio 1.1-050405 Departmet of Commuicatio
ADVANCED SOFTWARE ENGINEERING COMP 3705 Exercise Usage-based Testig ad Reliability Versio 1.0-040406 Departmet of Computer Ssciece Sada Narayaappa, Aeliese Adrews Versio 1.1-050405 Departmet of Commuicatio
Examples: data compression, path-finding, game-playing, scheduling, bin packing
 Algorithms - Basic Cocepts Algorithms so what is a algorithm, ayway? The dictioary defiitio: A algorithm is a well-defied computatioal procedure that takes iput ad produces output. This class will deal
Algorithms - Basic Cocepts Algorithms so what is a algorithm, ayway? The dictioary defiitio: A algorithm is a well-defied computatioal procedure that takes iput ad produces output. This class will deal
Advanced Course of Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Differet complexity measures Advaced Course of Algorithm Desig ad Aalysis Asymptotic complexity Big-Oh otatio Properties of O otatio Aalysis of simple algorithms A algorithm may may have differet executio
Differet complexity measures Advaced Course of Algorithm Desig ad Aalysis Asymptotic complexity Big-Oh otatio Properties of O otatio Aalysis of simple algorithms A algorithm may may have differet executio
Amortized Analysis - Part 2 - Dynamic Tables. Objective: In this lecture, we shall explore Dynamic tables and its amortized analysis in detail.
 Idia Istitute of Iformatio Techology Desig ad Maufacturig, Kacheepuram Cheai 600 17, Idia A Autoomous Istitute uder MHRD, Govt of Idia http://www.iiitdm.ac.i COM 501 Advaced Data Structures ad Algorithms
Idia Istitute of Iformatio Techology Desig ad Maufacturig, Kacheepuram Cheai 600 17, Idia A Autoomous Istitute uder MHRD, Govt of Idia http://www.iiitdm.ac.i COM 501 Advaced Data Structures ad Algorithms
CSE 191, Class Note 05: Counting Methods Computer Sci & Eng Dept SUNY Buffalo
 Coutig Methods CSE 191, Class Note 05: Coutig Methods Computer Sci & Eg Dept SUNY Buffalo c Xi He (Uiversity at Buffalo CSE 191 Discrete Structures 1 / 48 Need for Coutig The problem of coutig the umber
Coutig Methods CSE 191, Class Note 05: Coutig Methods Computer Sci & Eg Dept SUNY Buffalo c Xi He (Uiversity at Buffalo CSE 191 Discrete Structures 1 / 48 Need for Coutig The problem of coutig the umber
Chapter 6. Advanced Counting Techniques
 Chapter 6 Advaced Coutig Techiques 6.: Recurrece Relatios Defiitio: A recurrece relatio for the sequece {a } is a equatio expressig a i terms of oe or more of the previous terms of the sequece: a,a2,a3,,a
Chapter 6 Advaced Coutig Techiques 6.: Recurrece Relatios Defiitio: A recurrece relatio for the sequece {a } is a equatio expressig a i terms of oe or more of the previous terms of the sequece: a,a2,a3,,a
0 1 sum= sum= sum= sum= sum= sum= sum=64
 Biomial Coefficiets I how may ways ca we choose elemets from a elemet set? There are choices for the first elemet, - for the secod,..., dow to - + for the th, yieldig *(-)*...*(-+). So there are 4*3=2
Biomial Coefficiets I how may ways ca we choose elemets from a elemet set? There are choices for the first elemet, - for the secod,..., dow to - + for the th, yieldig *(-)*...*(-+). So there are 4*3=2
Algorithms Design & Analysis. Divide & Conquer
 Algorithms Desig & Aalysis Divide & Coquer Recap Direct-accessible table Hash tables Hash fuctios Uiversal hashig Perfect Hashig Ope addressig 2 Today s topics The divide-ad-coquer desig paradigm Revised
Algorithms Desig & Aalysis Divide & Coquer Recap Direct-accessible table Hash tables Hash fuctios Uiversal hashig Perfect Hashig Ope addressig 2 Today s topics The divide-ad-coquer desig paradigm Revised
Skip lists: A randomized dictionary
 Discrete Math for Bioiformatics WS 11/12:, by A. Bocmayr/K. Reiert, 31. Otober 2011, 09:53 3001 Sip lists: A radomized dictioary The expositio is based o the followig sources, which are all recommeded
Discrete Math for Bioiformatics WS 11/12:, by A. Bocmayr/K. Reiert, 31. Otober 2011, 09:53 3001 Sip lists: A radomized dictioary The expositio is based o the followig sources, which are all recommeded
CSE 4095/5095 Topics in Big Data Analytics Spring 2017; Homework 1 Solutions
 CSE 09/09 Topics i ig Data Aalytics Sprig 2017; Homework 1 Solutios Note: Solutios to problems,, ad 6 are due to Marius Nicolae. 1. Cosider the followig algorithm: for i := 1 to α log e do Pick a radom
CSE 09/09 Topics i ig Data Aalytics Sprig 2017; Homework 1 Solutios Note: Solutios to problems,, ad 6 are due to Marius Nicolae. 1. Cosider the followig algorithm: for i := 1 to α log e do Pick a radom
Lecture 4 February 16, 2016
 MIT 6.854/18.415: Advaced Algorithms Sprig 16 Prof. Akur Moitra Lecture 4 February 16, 16 Scribe: Be Eysebach, Devi Neal 1 Last Time Cosistet Hashig - hash fuctios that evolve well Radom Trees - routig
MIT 6.854/18.415: Advaced Algorithms Sprig 16 Prof. Akur Moitra Lecture 4 February 16, 16 Scribe: Be Eysebach, Devi Neal 1 Last Time Cosistet Hashig - hash fuctios that evolve well Radom Trees - routig
Data Structures and Algorithm. Xiaoqing Zheng
 Data Structures and Algorithm Xiaoqing Zheng zhengxq@fudan.edu.cn MULTIPOP top[s] = 6 top[s] = 2 3 2 8 5 6 5 S MULTIPOP(S, x). while not STACK-EMPTY(S) and k 0 2. do POP(S) 3. k k MULTIPOP(S, 4) Analysis
Data Structures and Algorithm Xiaoqing Zheng zhengxq@fudan.edu.cn MULTIPOP top[s] = 6 top[s] = 2 3 2 8 5 6 5 S MULTIPOP(S, x). while not STACK-EMPTY(S) and k 0 2. do POP(S) 3. k k MULTIPOP(S, 4) Analysis
ROLL CUTTING PROBLEMS UNDER STOCHASTIC DEMAND
 Pacific-Asia Joural of Mathematics, Volume 5, No., Jauary-Jue 20 ROLL CUTTING PROBLEMS UNDER STOCHASTIC DEMAND SHAKEEL JAVAID, Z. H. BAKHSHI & M. M. KHALID ABSTRACT: I this paper, the roll cuttig problem
Pacific-Asia Joural of Mathematics, Volume 5, No., Jauary-Jue 20 ROLL CUTTING PROBLEMS UNDER STOCHASTIC DEMAND SHAKEEL JAVAID, Z. H. BAKHSHI & M. M. KHALID ABSTRACT: I this paper, the roll cuttig problem
CSE 332. Data Structures and Parallelism
 Aam Blak Lecture 6a Witer 2017 CSE 332 Data Structures a Parallelism CSE 332: Data Structures a Parallelism More Recurreces T () T (/2) T (/2) T (/4) T (/4) T (/4) T (/4) P1 De-Brief 1 You i somethig substatial!
Aam Blak Lecture 6a Witer 2017 CSE 332 Data Structures a Parallelism CSE 332: Data Structures a Parallelism More Recurreces T () T (/2) T (/2) T (/4) T (/4) T (/4) T (/4) P1 De-Brief 1 You i somethig substatial!
Optimally Sparse SVMs
 A. Proof of Lemma 3. We here prove a lower boud o the umber of support vectors to achieve geeralizatio bouds of the form which we cosider. Importatly, this result holds ot oly for liear classifiers, but
A. Proof of Lemma 3. We here prove a lower boud o the umber of support vectors to achieve geeralizatio bouds of the form which we cosider. Importatly, this result holds ot oly for liear classifiers, but
MAT 271 Project: Partial Fractions for certain rational functions
 MAT 7 Project: Partial Fractios for certai ratioal fuctios Prerequisite kowledge: partial fractios from MAT 7, a very good commad of factorig ad complex umbers from Precalculus. To complete this project,
MAT 7 Project: Partial Fractios for certai ratioal fuctios Prerequisite kowledge: partial fractios from MAT 7, a very good commad of factorig ad complex umbers from Precalculus. To complete this project,
Dynamic Programming. Sequence Of Decisions
 Dyamic Programmig Sequece of decisios. Problem state. Priciple of optimality. Dyamic Programmig Recurrece Equatios. Solutio of recurrece equatios. Sequece Of Decisios As i the greedy method, the solutio
Dyamic Programmig Sequece of decisios. Problem state. Priciple of optimality. Dyamic Programmig Recurrece Equatios. Solutio of recurrece equatios. Sequece Of Decisios As i the greedy method, the solutio
Dynamic Programming. Sequence Of Decisions. 0/1 Knapsack Problem. Sequence Of Decisions
 Dyamic Programmig Sequece Of Decisios Sequece of decisios. Problem state. Priciple of optimality. Dyamic Programmig Recurrece Equatios. Solutio of recurrece equatios. As i the greedy method, the solutio
Dyamic Programmig Sequece Of Decisios Sequece of decisios. Problem state. Priciple of optimality. Dyamic Programmig Recurrece Equatios. Solutio of recurrece equatios. As i the greedy method, the solutio
Recursive Algorithm for Generating Partitions of an Integer. 1 Preliminary
 Recursive Algorithm for Geeratig Partitios of a Iteger Sug-Hyuk Cha Computer Sciece Departmet, Pace Uiversity 1 Pace Plaza, New York, NY 10038 USA scha@pace.edu Abstract. This article first reviews the
Recursive Algorithm for Geeratig Partitios of a Iteger Sug-Hyuk Cha Computer Sciece Departmet, Pace Uiversity 1 Pace Plaza, New York, NY 10038 USA scha@pace.edu Abstract. This article first reviews the
We are mainly going to be concerned with power series in x, such as. (x)} converges - that is, lims N n
 Review of Power Series, Power Series Solutios A power series i x - a is a ifiite series of the form c (x a) =c +c (x a)+(x a) +... We also call this a power series cetered at a. Ex. (x+) is cetered at
Review of Power Series, Power Series Solutios A power series i x - a is a ifiite series of the form c (x a) =c +c (x a)+(x a) +... We also call this a power series cetered at a. Ex. (x+) is cetered at
ECEN 655: Advanced Channel Coding Spring Lecture 7 02/04/14. Belief propagation is exact on tree-structured factor graphs.
 ECEN 655: Advaced Chael Codig Sprig 014 Prof. Hery Pfister Lecture 7 0/04/14 Scribe: Megke Lia 1 4-Cycles i Gallager s Esemble What we already kow: Belief propagatio is exact o tree-structured factor graphs.
ECEN 655: Advaced Chael Codig Sprig 014 Prof. Hery Pfister Lecture 7 0/04/14 Scribe: Megke Lia 1 4-Cycles i Gallager s Esemble What we already kow: Belief propagatio is exact o tree-structured factor graphs.
CS 270 Algorithms. Oliver Kullmann. Growth of Functions. Divide-and- Conquer Min-Max- Problem. Tutorial. Reading from CLRS for week 2
 Geeral remarks Week 2 1 Divide ad First we cosider a importat tool for the aalysis of algorithms: Big-Oh. The we itroduce a importat algorithmic paradigm:. We coclude by presetig ad aalysig two examples.
Geeral remarks Week 2 1 Divide ad First we cosider a importat tool for the aalysis of algorithms: Big-Oh. The we itroduce a importat algorithmic paradigm:. We coclude by presetig ad aalysig two examples.
ITEC 360 Data Structures and Analysis of Algorithms Spring for n 1
 ITEC 360 Data Structures ad Aalysis of Algorithms Sprig 006 1. Prove that f () = 60 + 5 + 1 is Θ ( ). 60 + 5 + 1 60 + 5 + = 66 for 1 Take C 1 = 66 f () = 60 + 5 + 1 is O( ) Sice 60 + 5 + 1 60 for 1 If
ITEC 360 Data Structures ad Aalysis of Algorithms Sprig 006 1. Prove that f () = 60 + 5 + 1 is Θ ( ). 60 + 5 + 1 60 + 5 + = 66 for 1 Take C 1 = 66 f () = 60 + 5 + 1 is O( ) Sice 60 + 5 + 1 60 for 1 If
Infinite Sequences and Series
 Chapter 6 Ifiite Sequeces ad Series 6.1 Ifiite Sequeces 6.1.1 Elemetary Cocepts Simply speakig, a sequece is a ordered list of umbers writte: {a 1, a 2, a 3,...a, a +1,...} where the elemets a i represet
Chapter 6 Ifiite Sequeces ad Series 6.1 Ifiite Sequeces 6.1.1 Elemetary Cocepts Simply speakig, a sequece is a ordered list of umbers writte: {a 1, a 2, a 3,...a, a +1,...} where the elemets a i represet
SCALING OF NUMBERS IN RESIDUE ARITHMETIC WITH THE FLEXIBLE SELECTION OF SCALING FACTOR
 POZNAN UNIVE RSITY OF TE CHNOLOGY ACADE MIC JOURNALS No 76 Electrical Egieerig 203 Zeo ULMAN* Macie CZYŻAK* Robert SMYK* SCALING OF NUMBERS IN RESIDUE ARITHMETIC WITH THE FLEXIBLE SELECTION OF SCALING
POZNAN UNIVE RSITY OF TE CHNOLOGY ACADE MIC JOURNALS No 76 Electrical Egieerig 203 Zeo ULMAN* Macie CZYŻAK* Robert SMYK* SCALING OF NUMBERS IN RESIDUE ARITHMETIC WITH THE FLEXIBLE SELECTION OF SCALING
De Bruijn Sequences for the Binary Strings with Maximum Specified Density
 De Bruij Sequeces for the Biary Strigs with Maximum Specified Desity Joe Sawada 1, Brett Steves 2, ad Aaro Williams 2 1 jsawada@uoguelph.ca School of Computer Sciece, Uiversity of Guelph, CANADA 2 brett@math.carleto.ca
De Bruij Sequeces for the Biary Strigs with Maximum Specified Desity Joe Sawada 1, Brett Steves 2, ad Aaro Williams 2 1 jsawada@uoguelph.ca School of Computer Sciece, Uiversity of Guelph, CANADA 2 brett@math.carleto.ca
2 LUC DEVROYE cotext of data structures for geometrical problems, or whe frequet alphabetical listigs of ames are required. Order-preservig hash fucti
 JOURNAL of ALGORITHMS 6, 1-9 (1985) The Expected Legth of the Logest Probe Sequece for Bucket Searchig Whe the Distributio Is Not Uiform* Luc DEVROYE School of Computer Sciece, 1 cgil1 Uiversity, 805 Sherbrooke
JOURNAL of ALGORITHMS 6, 1-9 (1985) The Expected Legth of the Logest Probe Sequece for Bucket Searchig Whe the Distributio Is Not Uiform* Luc DEVROYE School of Computer Sciece, 1 cgil1 Uiversity, 805 Sherbrooke
Analysis of Algorithms -Quicksort-
 Aalysis of Algorithms -- Adreas Ermedahl MRTC (Mälardales Real-Time Research Ceter) adreas.ermedahl@mdh.se Autum 2004 Proposed by C.A.R. Hoare i 962 Worst- case ruig time: Θ( 2 ) Expected ruig time: Θ(
Aalysis of Algorithms -- Adreas Ermedahl MRTC (Mälardales Real-Time Research Ceter) adreas.ermedahl@mdh.se Autum 2004 Proposed by C.A.R. Hoare i 962 Worst- case ruig time: Θ( 2 ) Expected ruig time: Θ(
Homework 3. = k 1. Let S be a set of n elements, and let a, b, c be distinct elements of S. The number of k-subsets of S is
 Homewor 3 Chapter 5 pp53: 3 40 45 Chapter 6 p85: 4 6 4 30 Use combiatorial reasoig to prove the idetity 3 3 Proof Let S be a set of elemets ad let a b c be distict elemets of S The umber of -subsets of
Homewor 3 Chapter 5 pp53: 3 40 45 Chapter 6 p85: 4 6 4 30 Use combiatorial reasoig to prove the idetity 3 3 Proof Let S be a set of elemets ad let a b c be distict elemets of S The umber of -subsets of
CS:3330 (Prof. Pemmaraju ): Assignment #1 Solutions. (b) For n = 3, we will have 3 men and 3 women with preferences as follows: m 1 : w 3 > w 1 > w 2
 Shiyao Wag CS:3330 (Prof. Pemmaraju ): Assigmet #1 Solutios Problem 1 (a) Cosider iput with me m 1, m,..., m ad wome w 1, w,..., w with the followig prefereces: All me have the same prefereces for wome:
Shiyao Wag CS:3330 (Prof. Pemmaraju ): Assigmet #1 Solutios Problem 1 (a) Cosider iput with me m 1, m,..., m ad wome w 1, w,..., w with the followig prefereces: All me have the same prefereces for wome:
Amortized analysis. Amortized analysis
 In amortized analysis the goal is to bound the worst case time of a sequence of operations on a data-structure. If n operations take T (n) time (worst case), the amortized cost of an operation is T (n)/n.
In amortized analysis the goal is to bound the worst case time of a sequence of operations on a data-structure. If n operations take T (n) time (worst case), the amortized cost of an operation is T (n)/n.
REVIEW FOR CHAPTER 1
 REVIEW FOR CHAPTER 1 A short summary: I this chapter you helped develop some basic coutig priciples. I particular, the uses of ordered pairs (The Product Priciple), fuctios, ad set partitios (The Sum Priciple)
REVIEW FOR CHAPTER 1 A short summary: I this chapter you helped develop some basic coutig priciples. I particular, the uses of ordered pairs (The Product Priciple), fuctios, ad set partitios (The Sum Priciple)
A New Solution Method for the Finite-Horizon Discrete-Time EOQ Problem
 This is the Pre-Published Versio. A New Solutio Method for the Fiite-Horizo Discrete-Time EOQ Problem Chug-Lu Li Departmet of Logistics The Hog Kog Polytechic Uiversity Hug Hom, Kowloo, Hog Kog Phoe: +852-2766-7410
This is the Pre-Published Versio. A New Solutio Method for the Fiite-Horizo Discrete-Time EOQ Problem Chug-Lu Li Departmet of Logistics The Hog Kog Polytechic Uiversity Hug Hom, Kowloo, Hog Kog Phoe: +852-2766-7410
Rank Modulation with Multiplicity
 Rak Modulatio with Multiplicity Axiao (Adrew) Jiag Computer Sciece ad Eg. Dept. Texas A&M Uiversity College Statio, TX 778 ajiag@cse.tamu.edu Abstract Rak modulatio is a scheme that uses the relative order
Rak Modulatio with Multiplicity Axiao (Adrew) Jiag Computer Sciece ad Eg. Dept. Texas A&M Uiversity College Statio, TX 778 ajiag@cse.tamu.edu Abstract Rak modulatio is a scheme that uses the relative order
Sorting Algorithms. Algorithms Kyuseok Shim SoEECS, SNU.
 Sortig Algorithms Algorithms Kyuseo Shim SoEECS, SNU. Desigig Algorithms Icremetal approaches Divide-ad-Coquer approaches Dyamic programmig approaches Greedy approaches Radomized approaches You are ot
Sortig Algorithms Algorithms Kyuseo Shim SoEECS, SNU. Desigig Algorithms Icremetal approaches Divide-ad-Coquer approaches Dyamic programmig approaches Greedy approaches Radomized approaches You are ot
COMP285 Midterm Exam Department of Mathematics
 COMP85 Midterm Exam Departmet of Mathematics Fall 010/011 - November 8, 010 Name: Studet Number: Please fiish withi 90 miutes. All poits above 100 are cosidered as bous poit. You ca reach maximal 1 poits.
COMP85 Midterm Exam Departmet of Mathematics Fall 010/011 - November 8, 010 Name: Studet Number: Please fiish withi 90 miutes. All poits above 100 are cosidered as bous poit. You ca reach maximal 1 poits.
Outline for Today. A simple and lightning fast hash table implementation. Why the degree of independence matters.
 Liear Probig Outlie for Today Liear Probig Hashig A simple ad lightig fast hash table implemetatio. Aalyzig Liear Probig Why the degree of idepedece matters. Fourth Momet Bouds Aother approach for estimatig
Liear Probig Outlie for Today Liear Probig Hashig A simple ad lightig fast hash table implemetatio. Aalyzig Liear Probig Why the degree of idepedece matters. Fourth Momet Bouds Aother approach for estimatig
The multi capacitated clustering problem
 The multi capacitated clusterig problem Bruo de Aayde Prata 1 Federal Uiversity of Ceará, Brazil Abstract Clusterig problems are combiatorial optimizatio problems wi several idustrial applicatios. The
The multi capacitated clusterig problem Bruo de Aayde Prata 1 Federal Uiversity of Ceará, Brazil Abstract Clusterig problems are combiatorial optimizatio problems wi several idustrial applicatios. The
Stochastic Matrices in a Finite Field
 Stochastic Matrices i a Fiite Field Abstract: I this project we will explore the properties of stochastic matrices i both the real ad the fiite fields. We first explore what properties 2 2 stochastic matrices
Stochastic Matrices i a Fiite Field Abstract: I this project we will explore the properties of stochastic matrices i both the real ad the fiite fields. We first explore what properties 2 2 stochastic matrices
Randomized Algorithms I, Spring 2018, Department of Computer Science, University of Helsinki Homework 1: Solutions (Discussed January 25, 2018)
 Radomized Algorithms I, Sprig 08, Departmet of Computer Sciece, Uiversity of Helsiki Homework : Solutios Discussed Jauary 5, 08). Exercise.: Cosider the followig balls-ad-bi game. We start with oe black
Radomized Algorithms I, Sprig 08, Departmet of Computer Sciece, Uiversity of Helsiki Homework : Solutios Discussed Jauary 5, 08). Exercise.: Cosider the followig balls-ad-bi game. We start with oe black
Parallel Vector Algorithms David A. Padua
 Parallel Vector Algorithms 1 of 32 Itroductio Next, we study several algorithms where parallelism ca be easily expressed i terms of array operatios. We will use Fortra 90 to represet these algorithms.
Parallel Vector Algorithms 1 of 32 Itroductio Next, we study several algorithms where parallelism ca be easily expressed i terms of array operatios. We will use Fortra 90 to represet these algorithms.
Hash Tables. Direct-Address Tables Hash Functions Universal Hashing Chaining Open Addressing. CS 5633 Analysis of Algorithms Chapter 11: Slide 1
 Hash Tables Direct-Address Tables Hash Functions Universal Hashing Chaining Open Addressing CS 5633 Analysis of Algorithms Chapter 11: Slide 1 Direct-Address Tables 2 2 Let U = {0,...,m 1}, the set of
Hash Tables Direct-Address Tables Hash Functions Universal Hashing Chaining Open Addressing CS 5633 Analysis of Algorithms Chapter 11: Slide 1 Direct-Address Tables 2 2 Let U = {0,...,m 1}, the set of
CS284A: Representations and Algorithms in Molecular Biology
 CS284A: Represetatios ad Algorithms i Molecular Biology Scribe Notes o Lectures 3 & 4: Motif Discovery via Eumeratio & Motif Represetatio Usig Positio Weight Matrix Joshua Gervi Based o presetatios by
CS284A: Represetatios ad Algorithms i Molecular Biology Scribe Notes o Lectures 3 & 4: Motif Discovery via Eumeratio & Motif Represetatio Usig Positio Weight Matrix Joshua Gervi Based o presetatios by
On Divisibility concerning Binomial Coefficients
 A talk give at the Natioal Chiao Tug Uiversity (Hsichu, Taiwa; August 5, 2010 O Divisibility cocerig Biomial Coefficiets Zhi-Wei Su Najig Uiversity Najig 210093, P. R. Chia zwsu@ju.edu.c http://math.ju.edu.c/
A talk give at the Natioal Chiao Tug Uiversity (Hsichu, Taiwa; August 5, 2010 O Divisibility cocerig Biomial Coefficiets Zhi-Wei Su Najig Uiversity Najig 210093, P. R. Chia zwsu@ju.edu.c http://math.ju.edu.c/
Ma 530 Introduction to Power Series
 Ma 530 Itroductio to Power Series Please ote that there is material o power series at Visual Calculus. Some of this material was used as part of the presetatio of the topics that follow. What is a Power
Ma 530 Itroductio to Power Series Please ote that there is material o power series at Visual Calculus. Some of this material was used as part of the presetatio of the topics that follow. What is a Power
ALG 2.2 Search Algorithms
 Algorithms Professor Joh Reif ALG 2.2 Search Algorithms (a Biary Search: average case (b Biary Search with Errors (homework (c Iterpolatio Search (d Ubouded Search Biary Search Trees (i sorted Table of
Algorithms Professor Joh Reif ALG 2.2 Search Algorithms (a Biary Search: average case (b Biary Search with Errors (homework (c Iterpolatio Search (d Ubouded Search Biary Search Trees (i sorted Table of
Axioms of Measure Theory
 MATH 532 Axioms of Measure Theory Dr. Neal, WKU I. The Space Throughout the course, we shall let X deote a geeric o-empty set. I geeral, we shall ot assume that ay algebraic structure exists o X so that
MATH 532 Axioms of Measure Theory Dr. Neal, WKU I. The Space Throughout the course, we shall let X deote a geeric o-empty set. I geeral, we shall ot assume that ay algebraic structure exists o X so that
Zeros of Polynomials
 Math 160 www.timetodare.com 4.5 4.6 Zeros of Polyomials I these sectios we will study polyomials algebraically. Most of our work will be cocered with fidig the solutios of polyomial equatios of ay degree
Math 160 www.timetodare.com 4.5 4.6 Zeros of Polyomials I these sectios we will study polyomials algebraically. Most of our work will be cocered with fidig the solutios of polyomial equatios of ay degree
A Probabilistic Analysis of Quicksort
 A Probabilistic Aalysis of Quicsort You are assumed to be familiar with Quicsort. I each iteratio this sortig algorithm chooses a pivot ad the, by performig comparisios with the pivot, splits the remaider
A Probabilistic Aalysis of Quicsort You are assumed to be familiar with Quicsort. I each iteratio this sortig algorithm chooses a pivot ad the, by performig comparisios with the pivot, splits the remaider
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 3 Feb 2013
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 3 Feb 2013 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 3 Feb 2013](/thumbs/90/102445949.jpg) Cotiued Fractios of Quadratic Numbers L ubomíra Balková Araka Hrušková arxiv:0.05v [math.co] Feb 0 February 5 0 Abstract I this paper we will first summarize kow results cocerig cotiued fractios. The we
Cotiued Fractios of Quadratic Numbers L ubomíra Balková Araka Hrušková arxiv:0.05v [math.co] Feb 0 February 5 0 Abstract I this paper we will first summarize kow results cocerig cotiued fractios. The we
Sequences of Definite Integrals, Factorials and Double Factorials
 47 6 Joural of Iteger Sequeces, Vol. 8 (5), Article 5.4.6 Sequeces of Defiite Itegrals, Factorials ad Double Factorials Thierry Daa-Picard Departmet of Applied Mathematics Jerusalem College of Techology
47 6 Joural of Iteger Sequeces, Vol. 8 (5), Article 5.4.6 Sequeces of Defiite Itegrals, Factorials ad Double Factorials Thierry Daa-Picard Departmet of Applied Mathematics Jerusalem College of Techology
Shannon s noiseless coding theorem
 18.310 lecture otes May 4, 2015 Shao s oiseless codig theorem Lecturer: Michel Goemas I these otes we discuss Shao s oiseless codig theorem, which is oe of the foudig results of the field of iformatio
18.310 lecture otes May 4, 2015 Shao s oiseless codig theorem Lecturer: Michel Goemas I these otes we discuss Shao s oiseless codig theorem, which is oe of the foudig results of the field of iformatio
Chapter 4 : Laplace Transform
 4. Itroductio Laplace trasform is a alterative to solve the differetial equatio by the complex frequecy domai ( s = σ + jω), istead of the usual time domai. The DE ca be easily trasformed ito a algebraic
4. Itroductio Laplace trasform is a alterative to solve the differetial equatio by the complex frequecy domai ( s = σ + jω), istead of the usual time domai. The DE ca be easily trasformed ito a algebraic
is also known as the general term of the sequence
 Lesso : Sequeces ad Series Outlie Objectives: I ca determie whether a sequece has a patter. I ca determie whether a sequece ca be geeralized to fid a formula for the geeral term i the sequece. I ca determie
Lesso : Sequeces ad Series Outlie Objectives: I ca determie whether a sequece has a patter. I ca determie whether a sequece ca be geeralized to fid a formula for the geeral term i the sequece. I ca determie
SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS I Computer Assignment 1
 SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS I Computer Assigmet I MATLAB, sigals are represeted by colum vectors or as colums i matrices. Row vectors ca be used; however, MATLAB typically prefers colum vectors. Vector or matrices
SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS I Computer Assigmet I MATLAB, sigals are represeted by colum vectors or as colums i matrices. Row vectors ca be used; however, MATLAB typically prefers colum vectors. Vector or matrices
MATH 324 Summer 2006 Elementary Number Theory Solutions to Assignment 2 Due: Thursday July 27, 2006
 MATH 34 Summer 006 Elemetary Number Theory Solutios to Assigmet Due: Thursday July 7, 006 Departmet of Mathematical ad Statistical Scieces Uiversity of Alberta Questio [p 74 #6] Show that o iteger of the
MATH 34 Summer 006 Elemetary Number Theory Solutios to Assigmet Due: Thursday July 7, 006 Departmet of Mathematical ad Statistical Scieces Uiversity of Alberta Questio [p 74 #6] Show that o iteger of the
Section 7 Fundamentals of Sequences and Series
 ectio Fudametals of equeces ad eries. Defiitio ad examples of sequeces A sequece ca be thought of as a ifiite list of umbers. 0, -, -0, -, -0...,,,,,,. (iii),,,,... Defiitio: A sequece is a fuctio which
ectio Fudametals of equeces ad eries. Defiitio ad examples of sequeces A sequece ca be thought of as a ifiite list of umbers. 0, -, -0, -, -0...,,,,,,. (iii),,,,... Defiitio: A sequece is a fuctio which
Lecture 10: Mathematical Preliminaries
 Lecture : Mathematical Prelimiaries Obective: Reviewig mathematical cocepts ad tools that are frequetly used i the aalysis of algorithms. Lecture # Slide # I this
Lecture : Mathematical Prelimiaries Obective: Reviewig mathematical cocepts ad tools that are frequetly used i the aalysis of algorithms. Lecture # Slide # I this
Chimica Inorganica 3
 himica Iorgaica Irreducible Represetatios ad haracter Tables Rather tha usig geometrical operatios, it is ofte much more coveiet to employ a ew set of group elemets which are matrices ad to make the rule
himica Iorgaica Irreducible Represetatios ad haracter Tables Rather tha usig geometrical operatios, it is ofte much more coveiet to employ a ew set of group elemets which are matrices ad to make the rule
THE ASYMPTOTIC COMPLEXITY OF MATRIX REDUCTION OVER FINITE FIELDS
 THE ASYMPTOTIC COMPLEXITY OF MATRIX REDUCTION OVER FINITE FIELDS DEMETRES CHRISTOFIDES Abstract. Cosider a ivertible matrix over some field. The Gauss-Jorda elimiatio reduces this matrix to the idetity
THE ASYMPTOTIC COMPLEXITY OF MATRIX REDUCTION OVER FINITE FIELDS DEMETRES CHRISTOFIDES Abstract. Cosider a ivertible matrix over some field. The Gauss-Jorda elimiatio reduces this matrix to the idetity
Algorithms. Elementary Sorting. Dong Kyue Kim Hanyang University
 Algorithms Elemetary Sortig Dog Kyue Kim Hayag Uiversity dqkim@hayag.a.kr Cotets Sortig problem Elemetary sortig algorithms Isertio sort Merge sort Seletio sort Bubble sort Sortig problem Iput A sequee
Algorithms Elemetary Sortig Dog Kyue Kim Hayag Uiversity dqkim@hayag.a.kr Cotets Sortig problem Elemetary sortig algorithms Isertio sort Merge sort Seletio sort Bubble sort Sortig problem Iput A sequee
6.003 Homework #3 Solutions
 6.00 Homework # Solutios Problems. Complex umbers a. Evaluate the real ad imagiary parts of j j. π/ Real part = Imagiary part = 0 e Euler s formula says that j = e jπ/, so jπ/ j π/ j j = e = e. Thus the
6.00 Homework # Solutios Problems. Complex umbers a. Evaluate the real ad imagiary parts of j j. π/ Real part = Imagiary part = 0 e Euler s formula says that j = e jπ/, so jπ/ j π/ j j = e = e. Thus the
Linear chord diagrams with long chords
 Liear chord diagrams with log chords Everett Sulliva Departmet of Mathematics Dartmouth College Haover New Hampshire, U.S.A. everett..sulliva@dartmouth.edu Submitted: Feb 7, 2017; Accepted: Oct 7, 2017;
Liear chord diagrams with log chords Everett Sulliva Departmet of Mathematics Dartmouth College Haover New Hampshire, U.S.A. everett..sulliva@dartmouth.edu Submitted: Feb 7, 2017; Accepted: Oct 7, 2017;
Reliability and Queueing
 Copyright 999 Uiversity of Califoria Reliability ad Queueig by David G. Messerschmitt Supplemetary sectio for Uderstadig Networked Applicatios: A First Course, Morga Kaufma, 999. Copyright otice: Permissio
Copyright 999 Uiversity of Califoria Reliability ad Queueig by David G. Messerschmitt Supplemetary sectio for Uderstadig Networked Applicatios: A First Course, Morga Kaufma, 999. Copyright otice: Permissio
Introduction To Discrete Mathematics
 Itroductio To Discrete Mathematics Review If you put + pigeos i pigeoholes the at least oe hole would have more tha oe pigeo. If (r + objects are put ito boxes, the at least oe of the boxes cotais r or
Itroductio To Discrete Mathematics Review If you put + pigeos i pigeoholes the at least oe hole would have more tha oe pigeo. If (r + objects are put ito boxes, the at least oe of the boxes cotais r or
Math 475, Problem Set #12: Answers
 Math 475, Problem Set #12: Aswers A. Chapter 8, problem 12, parts (b) ad (d). (b) S # (, 2) = 2 2, sice, from amog the 2 ways of puttig elemets ito 2 distiguishable boxes, exactly 2 of them result i oe
Math 475, Problem Set #12: Aswers A. Chapter 8, problem 12, parts (b) ad (d). (b) S # (, 2) = 2 2, sice, from amog the 2 ways of puttig elemets ito 2 distiguishable boxes, exactly 2 of them result i oe
Disjoint set (Union-Find)
 CS124 Lecture 7 Fall 2018 Disjoit set (Uio-Fid) For Kruskal s algorithm for the miimum spaig tree problem, we foud that we eeded a data structure for maitaiig a collectio of disjoit sets. That is, we eed
CS124 Lecture 7 Fall 2018 Disjoit set (Uio-Fid) For Kruskal s algorithm for the miimum spaig tree problem, we foud that we eeded a data structure for maitaiig a collectio of disjoit sets. That is, we eed
arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 10 Dec 2014
![arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 10 Dec 2014 arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 10 Dec 2014](/thumbs/82/85433827.jpg) A DIGITAL BINOMIAL THEOREM HIEU D. NGUYEN arxiv:42.38v [math.nt] 0 Dec 204 Abstract. We preset a triagle of coectios betwee the Sierpisi triagle, the sum-of-digits fuctio, ad the Biomial Theorem via a
A DIGITAL BINOMIAL THEOREM HIEU D. NGUYEN arxiv:42.38v [math.nt] 0 Dec 204 Abstract. We preset a triagle of coectios betwee the Sierpisi triagle, the sum-of-digits fuctio, ad the Biomial Theorem via a
CSE 5311 Notes 1: Mathematical Preliminaries
 Chapter 1 - Algorithms Computig CSE 5311 Notes 1: Mathematical Prelimiaries Last updated 1/20/18 12:56 PM) Relatioship betwee complexity classes, eg log,, log, 2, 2, etc Chapter 2 - Gettig Started Loop
Chapter 1 - Algorithms Computig CSE 5311 Notes 1: Mathematical Prelimiaries Last updated 1/20/18 12:56 PM) Relatioship betwee complexity classes, eg log,, log, 2, 2, etc Chapter 2 - Gettig Started Loop
Chapter 2. Finite Fields (Chapter 3 in the text)
 Chater 2. Fiite Fields (Chater 3 i the tet 1. Grou Structures 2. Costructios of Fiite Fields GF(2 ad GF( 3. Basic Theory of Fiite Fields 4. The Miimal Polyomials 5. Trace Fuctios 6. Subfields 1. Grou Structures
Chater 2. Fiite Fields (Chater 3 i the tet 1. Grou Structures 2. Costructios of Fiite Fields GF(2 ad GF( 3. Basic Theory of Fiite Fields 4. The Miimal Polyomials 5. Trace Fuctios 6. Subfields 1. Grou Structures
CHAPTER I: Vector Spaces
 CHAPTER I: Vector Spaces Sectio 1: Itroductio ad Examples This first chapter is largely a review of topics you probably saw i your liear algebra course. So why cover it? (1) Not everyoe remembers everythig
CHAPTER I: Vector Spaces Sectio 1: Itroductio ad Examples This first chapter is largely a review of topics you probably saw i your liear algebra course. So why cover it? (1) Not everyoe remembers everythig
AN ALMOST LINEAR RECURRENCE. Donald E. Knuth Calif. Institute of Technology, Pasadena, Calif.
 AN ALMOST LINEAR RECURRENCE Doald E. Kuth Calif. Istitute of Techology, Pasadea, Calif. form A geeral liear recurrece with costat coefficiets has the U 0 = a l* U l = a 2 " ' " U r - l = a r ; u = b, u,
AN ALMOST LINEAR RECURRENCE Doald E. Kuth Calif. Istitute of Techology, Pasadea, Calif. form A geeral liear recurrece with costat coefficiets has the U 0 = a l* U l = a 2 " ' " U r - l = a r ; u = b, u,
Trial division, Pollard s p 1, Pollard s ρ, and Fermat s method. Christopher Koch 1. April 8, 2014
 Iteger Divisio Algorithm ad Cogruece Iteger Trial divisio,,, ad with itegers mod Iverses mod Multiplicatio ad GCD Iteger Christopher Koch 1 1 Departmet of Computer Sciece ad Egieerig CSE489/589 Algorithms
Iteger Divisio Algorithm ad Cogruece Iteger Trial divisio,,, ad with itegers mod Iverses mod Multiplicatio ad GCD Iteger Christopher Koch 1 1 Departmet of Computer Sciece ad Egieerig CSE489/589 Algorithms
Department of Informatics Prof. Dr. Michael Böhlen Binzmühlestrasse Zurich Phone:
 Departmet of Iformatics Prof. Dr. Michael Böhle Bizmühlestrasse 14 8050 Zurich Phoe: +41 44 635 4333 Email: boehle@ifi.uzh.ch Iformatik II Midterm1 Sprig 018 3.03.018 Advice You have 90 miutes to complete
Departmet of Iformatics Prof. Dr. Michael Böhle Bizmühlestrasse 14 8050 Zurich Phoe: +41 44 635 4333 Email: boehle@ifi.uzh.ch Iformatik II Midterm1 Sprig 018 3.03.018 Advice You have 90 miutes to complete
Partial match queries: a limit process
 Partial match queries: a limit process Nicolas Brouti Ralph Neiiger Heig Sulzbach Partial match queries: a limit process 1 / 17 Searchig geometric data ad quadtrees 1 Partial match queries: a limit process
Partial match queries: a limit process Nicolas Brouti Ralph Neiiger Heig Sulzbach Partial match queries: a limit process 1 / 17 Searchig geometric data ad quadtrees 1 Partial match queries: a limit process
3.2 Properties of Division 3.3 Zeros of Polynomials 3.4 Complex and Rational Zeros of Polynomials
 Math 60 www.timetodare.com 3. Properties of Divisio 3.3 Zeros of Polyomials 3.4 Complex ad Ratioal Zeros of Polyomials I these sectios we will study polyomials algebraically. Most of our work will be cocered
Math 60 www.timetodare.com 3. Properties of Divisio 3.3 Zeros of Polyomials 3.4 Complex ad Ratioal Zeros of Polyomials I these sectios we will study polyomials algebraically. Most of our work will be cocered
