Chapter 1: Linear Equations and Functions
|
|
|
- Eustace Eaton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter : Answers to Eercises Chapter : Linear Equations and Functions Eercise.. 7= = = = 8( + ). + 8= = = 0 = 0 9 = = = () = 96 = 7. ( 7) = ( + ) 9.. = + + = + = 9 = 9 7 = = 6 6 = 7 = 7 = 7 7 = + = 6 + = 6 + = = = = =.. 7. ( ) = () = = = =? Check: = () 0? = = = is the solution. = + (+ ) Multipl each term b 6( + ). = (8+ 0) 8 = 0 = or = ( )? Check: = + + ( ) ( )? = + 0 = and = 0 = is the solution. + = = 6 ( ) + = There is no solution.
2 Chapter : Answers to Eercises =.8( ) = = = = =.( ) = = = = = = + = + =. 9+ = () 8+ = = 8+ = S = P+ Prt Prt = S P S P t = Pr 9. ( ) < < < <. > 9 > 8 ( )( ) > 8( ) <. ( ) ( ) (. ( ) > + > + > + > > 6 ( )( ) > 6( ) ) < > > ( ) > 6 > 6 ( )( ) > 6( ) < ( )( ) < ( )( ) ( ) < 6 9 < 8 ( ) 9 < < + 8 < 8 < < = 68, , 000 = 68, = 68, , 000 = 6, 000 6,000 = = months 800
3 Chapter : Answers to Eercises. I = r 7.9 I = I = = I = I = $6.0. R = C for breakeven point 0 = = 790 ( ) = 0 packs or 0,000 CD's 7. 70,00 = , 00 = = $9, C 00I = 6.8 ( ) 99C 00 7 = C 7000 = C = 76.8 C = 78.68% FE + FE = 90 6 FE + 8 = 0 FE = 9 FE = 96 A 96 is the lowest grade that can be earned on the final.. = amount in safe fund,000 = amount in risk fund Yield: (,000 ) =, , =, = 600 = 90,000 = $90,000 in 9% fund, = $0,000 in % fund.. Reduced salar: (000) = $800 Increased salar: (800) = $60 60 = R% of R = = $60 is an 8% increase > > 600 > t 900.7t 0 t.6 He could bu tapes. 6. a = b t > 0 c. 008.t >.79 t >.8 6. A = h a h.h 9.8 h 0.8 b h < 0.h < 9.8 h < 0. Eercise.. a. For each value of there is onl one. b. D = { 7,,0,,.,9,,,8, } R = { 0,,,9,,,,60}. f(0) =, f() =. This is a function, since for each there is onl,,,8, 9 R =,,6 one. D = { }, { } 7. The vertical line test shows that graph (a) is a function of, and that graph (b) is not a function of.
4 Chapter : Answers to Eercises 9. If =, then is a function of.. If =, then is not a function. If, for eample, =, there are two possible values for.. R() = 8 a. R(0) = 8(0) = b. R() = 8() = 6 c. R( ) = 8( ) = d. R(.6) = 8(.6) = C a. b. c. d. ( ) = f( ) a. b. c. C (0) = (0) = C( ) = ( ) = C( ) = ( ) = C = = 6 = f = = + 8 = 8 f () = = 8 = 6 f ( ) = ( ) = 8 + = 6 f ( ) = + + a. f ( + ) = f() = + + = f() + f() = 7 + = f() + f() f( + ) b. f ( + h) = + ( + h) + ( + h) c. No. This is equivalent to a. d. f ( ) + h = h e. No. f( + h) f( ) + h 6 8 f( + h) = + ( + h) + ( + h) = + + h+ + h+ h f( ) = + + f( + h) f( ) = h+ h+ h = h(+ + h) f( + h) f( ) = + + h h. f ( ) = a. b. f( + h) = ( + h) ( + h) = + + f( + h) f( ) h h h = + + ( h) ( h) ( ) = + h h h + = h h h f( + h) f( ) h h h = h h = h. Since (9, ) and (, 6) are points on the graph: a. f (9) = b. f () = 6. a. The ordered pair (a, b) satisfies the equation. Thus b= a a. b. The coordinates of Q = (, ). Since the point is on the curve, the coordinates satisf the equation. c. The coordinates of R = (, ). The satisf the equation. d. The values are 0 and. These values are also solutions of = = + There is no division b zero or square roots. Domain is all the reals, i.e., { : Reals}. Since 0, +, the range is reals or { : }. 9. = + There is no division b zero. To get a real number, we must have + 0 or. Domain:. The square root is alwas nonnegative. Thus, the range is : reals, 0.. D: { :, }. D: { : 7 7}. f( ) =, a. b. c. g( ) { } = ( f + g)( ) = + ( f g)( ) = ( f g)( ) = = f g d. ( ) = =
5 Chapter : Answers to Eercises 7. f ( ) =, a. b. c. g( ) = ( f + g)( ) = + ( f g)( ) = ( )( ) = = f g f d. ( ) = g 9. f( ) = ( ), g( ) = a. b. c. d. ( f g)( ) = f( ) = ( ) = 8 ( g f)( ) = g(( ) ) = ( ) f( f( )) = f(( ) ) = [( ) ] 6 ( f f)( ) = ( ) ( ) = ( ). f ( ) =, a. b. ( f f )( ) f ( f( ) ) g ( ) = + ( f g)( ) f( ) = + = + = = + ( g f)( ) g( ) ( ) = + 6 c. f ( f( )) = f( ) = d. ( f f)( ) = = ( f f )( ) f ( f( ) ). a. f (0) =, 000 means it will take 0 ears to pa off a debt of $,000 (at $800 per month and 7.% compounded monthl.) b. f( + ) = f() = 69, 000 ; f() + f() = 80, 000 ; No. c. It will take ears to pa off the debt, i.e., 89,000 = f ().. a. f (90) = 6. means that in 90 there were 6. workers supporting each person receiving Social Securit benefits. b. f (990) =. c. The points based on known data must be the same and those based on projections might be the same. d. Domain: 90 t 00 Range:.9 n a. f(9) =,000,000, g(9) = 600,000 b. f (0) =, 00,000. This was the number of prisoners in 000. c. g (90) = 00, 000. This was the number of parolees in 990. d. ( f g)(0) =,00, ,000 = 00,000. There were this man more in prison than were out on parole. f g (9) = 900, ,000 = 00,000 e. ( ) ( f g) (98) =,0, ,000 = 00,000 ( f g)(98) is greater. Possible reason is increased prison capacit but parolee level is constant. 9. a. Since the wind speed cannot be negative, s 0... b. f () = () 9.6 = 9. At a temperature of F and a wind speed of mph, the temperature feels like 9. F. c. f (0) =.69, but f (0) should equal the air temperature, F. C a. ( ) = () 00() 0.() 0 C = + + = (0) + 0 = = $ b. The value C(0) is the total cost of producing 0 units. c. C (0) = 00(0) + 0.(0) p C( p) = 0 p = $, 00 a. Domain: { p: 0 p< 0} b. c. d. e. 700() 8,00 C () = = = $ (90) 67,000 C (90) = = = $6, (99) 7,700 C (99) = = = $7, (99.6) 77,080 C (99.6) = = = $,87, In each case above, to remove p% of the particulate pollution would cost C( p).
6 6 Chapter : Answers to Eercises. a. A is a function of. b. A() = (0 ) = 96 sq ft A(0) = 0(0 0) = 600 sq ft c. For the problem to have meaning we have 0 < < a. Pqt ( ( )) = P(00+ t) (00 + t) = 80(00 + t) 00 0 = 69, t t b. q() = 00 + () = 0 P(q()) = $9,7 9. R = f( C) C = g( A) a. ( )( ) ( ) f g = f C = R b. ( g f )( ) is not defined. c. A is the independent variable and R is the dependent variable. Revenue depends on mone spent for advertising. 6. length = width = L = = or = L = + = + 6. Revenue = (no. of people)(price per person) Eample: R = 0 R = 9.80 R = 9.60 Solution: R = (0 + )( 0.0) Eercise.. + = -intercept: = 0 then =. -intercept: = 0 then =.. + = 0 -intercept: = 0 then = 0 Likewise, -intercept is = 0. + = -. 8 = 60 -intercept: = 0 then -intercept: = 0 then = 60 =. = (, ) and (, 7) 7 8 m = = = 7 = 9. (, ) and (, ) 0 m = = = = 0 ( ). A horizontal line has a slope of 0.. (, ) and (, ) The rate of change is equivalent to the slope of the line. 0 m = = = = 0. a. Slope is negative. b. Slope is undefined.
7 Chapter : Answers to Eercises =, m =, b = = 6. m =, b = = = or = 0+, m = 0, b = 6 = - - = m =, b = = +. = 8 Slope is undefined. There is no -intercept. = 8 - = P(, 0), m = ( ) 0= = +. + = 6 or = +, m =, b =. 6 + = =
8 8 Chapter : Answers to Eercises,, m = = ( ( ) ) 9 = +. P( ) P(, ), m is undefined = =. P = (, ), P = (, 6) 6 m = = = ( ) = 9 = = 6 = 6 = + = Lines are perpendicular since =.. 6 = 6 = or = Lines are the same. = 6 =. If + =, then = +. So, m =. A line parallel will have the same slope. Thus, m = and P = (, 7) gives ( 7) = ( ( )) which simplifies to =.. If 6 =, then =. Slope of the perpendicular line is. Thus m = and 6 P = (, ) gives = ( ) which 6 simplifies to = P = (7, ), P = ( 6, ) m = = = 6 7 = ( 7) 7 = + = + or + =
9 Chapter : Answers to Eercises 9 7. a. 60,000 80,000 = 60, b. 0 = 60, = = 0 months 00 In 0 months, the building will be completel depreciated. c. (60, 70,000) means that after 60 months the value of the building will be $70, =.7+.6 a. m =.7, b =.6 b. In 99, when = 0,.6% of the U.S. population had Internet. c. The percentage of the U.S. population with Internet is changing at the rate of.7% per ear.. M( ) = a. m= 0.76 b= 8.8 b. In 90, 8% of the unmarried women became married. c. The annual rate of change is 0.76%. For each passing ear the percent of unmarried women who get married decreases b 0.76%.. F = 0.M a. m = 0. b. For each $ increase in male earnings, the female s earning increases onl b $0.. F 0 = c. ( ) ( ) = 8.80 thousands =$8,80. = Both units are in dollars B 7 = a. m = = 0.69 and ( 676, 7) ( W ) B = 0.690W B (80) = b. ( ) = $ a. ( 980,8. ) and ( 00,79.9 ) m = = = =. 980 ( ) = b. The consumer price inde for urban consumers increases at the rate of $. per ear. 6. (, p) is the reference. (0, 8000) is one point. 700 m = = 700 p 8,000 = 700( 0) or p = , (t, R) is the ordered pair. 7 P =,, P = (6,9) m = = = =. 7 6 R 9 =.( t 6) or R =.t or R =.t P = (00, ) P = (0, 9) 9 m = = = = 0.8( 00) or = 0.8 7
10 0 Chapter : Answers to Eercises Eercise.. = + +. = a. = = b. 000 = a. + = = = + b. Standard Window + = = 0 7. a. -intercept = 0.0 -intercept: 0.00 = 0.0 b. 0. = 0 = =
11 Chapter : Answers to Eercises 9. Complete graphs can be seen with different windows. A hint is to look at the equation and tr to determine the ma and/or min of. Also, find the - intercepts. 9. ( ) = There is no min. Ma value of =. -intercepts: 0 0.(.) = = 0. = + (.) = ± ± 8 =. ± 8 or =. or 8. ( ) = If = 0, =. A suggested window is shown below. = = 6 6 = + = + f ( ) = + ( ) ( ) = + f ( ) = + = 8 + = 8 f = + = 0.77 Use our graphing calculator, and evaluate the function at these two points. If either of our answers differ, can ou eplain the difference?. As gets large, approaches. When = 0, =, intercepts at ±.. = + 6 ( )( + ) = = ( + )( + ) What happens to as approaches??. = 8 = = = = + = + = 8. 6 = = 7 = = 6 = 0 ( )( ) + = 0 = or = + 9. Find the zeros and find the -intercepts are equivalent statements. Use a graphing calculator s TRACE or ZERO. a.-b. Graphing calculator approimation is =.98, 8.98.
12 Chapter : Answers to Eercises. a. 0 F = 0. M b. If males average $0,000, then females earn $,. F 6. =.99 thousand = $,00 c. ( ) d. p = a. E =,000p 0 p 00, a. e. The percentage decreases before 000 and increases after ,000 8, 000 C = 80 p 0 0, a. b. E 0 when 0 p 0. 0, R = 8, , 000 b. The rate is As more people become aware of the product, there are fewer to learn about it. 7. a. -min = 0, -ma = b. -min = 0, -ma = 70 c. p = a. b. Near p = 0, cost grows without bound. c. The coordinates of the point mean that the cost of obtaining stream water with % of the current pollution levels would cost $8,0. d. The p-intercept means that the cost of stream water with 0% of the current pollution levels would cost $0., = b. Increasing. The per capita federal ta burden is increasing. 0 0 Eercise.. Solution: (, ). Infinitel man solutions. : = + : + = : = : = +
13 Chapter : Answers to Eercises. Solution: (, ) 7. Solution: No solution since the graphs do not : = + : = intersect. : = : = 9.. = 6 = 8 Solve for. = = Substitute for this variable in ()=6 first equation and solve for = 6 + = the other variable. The solution of the sstem is = = 8 = and =, or,. + = 6 Solve for. = ( ) Substitute for this variable in + = 6 second equation and solve for = 6 the other variable. = 6 Solve for : = = 6 6 The solution of the sstem is = and =, or,.. + = Multipl st equation b. 9+ = = Multipl nd equation b. 8 = 8 Add the two equations. 7 = Solve for the variable. = Substitute for this variable in () + = either original equation and = 8 solve for the other variable. = The solution of the sstem is = and =, or (, ). = /. + = Multipl first equation b. + 9 = = Multipl second equation b. 8 = 6 Add the two equations. = Substitute for this variable in + () = either original equation and = 8 solve for the other variable. = The solution of the sstem is = and =.
14 Chapter : Answers to Eercises = =. =. Multipl nd equation b = 0.6 The solution of the sstem is Subtract the two equations. 0.9 =.6 Solve for the variable. Substitute, solve for. = = = and =, or, = Multipl first equation b 6. = = Multipl second equation b = 77 Add the two equations. 7 = 7 Substitute for this variable in = either original equation and 8() + = solve for the other variable. = The solution of the sstem is = and =, or (, ). =. + 6 = + 6 = + = Multipl second equation b. 6 = Add the two equations: 0 = 0 There are infinitel man solutions. The sstem is dependent. Solve for one of the variables in terms of the remaining variable: =. Then a general solution is c, c, where an value of c will give a particular solution. Use the standard window and graph each equation. Use the TRACE or INTERSECT feature to find the solution.. = 8 = = + 8. :+ = :+ 7 = = = = Solution: (, ) Solution: (, )
15 Chapter : Answers to Eercises Eq. + + z = Steps,, and of the sstematic Eq. + z = 8 procedure are completed. Eq. z = Step : z = From Eq. + () = 8 or = 7 From Eq. + (7) + = or = 7 The solution is = 7, = 7, z =. Eq. 8z = 0 Steps and of the sstematic Eq. + z = 8 procedure are completed. Eq. + z = Step : ( ) Eq added to Eq. gives z = or z =. From Eq. + ( ) = 8 or = From Eq. 8( ) = 0 or = The solution is =, =, z = or (,, ). Eq. + z = 9 Step is completed. Eq. + + z = Eq. + 8z = Step : + z = 9 Eq. Eq. + z = ( ) Eq. added to Eq. Eq. 6z = ( ) Eq. added to Eq. Step is also completed. Step : z = from Eq.. From Eq. + = or = 9 From Eq. + ( 9) = 9 or = The solution is =, = 9, z = or, 9,. f( ) = , h( ) = = = 7.9 ( ) f ( ) =. during 998 h. =. = $8.67 billion
16 6 Chapter : Answers to Eercises. a. + = 800 Total number of tickets b. 0 = revenue from $0 tickets c. 0 = revenue from $0 tickets d =, 000 Total Revenue e. Multipl equation from part (a) b = = 000 = 6000 = 600 Substitution into equation from part (a) gives = 0. Sell 0 of the $0 tickets and 600 of the $0 tickets. 7. = amount of safe investment. = amount of risk investment. + =,600 Total amount invested = 0,000 Income from investments The solution is the solution of the above sstem of equations. + =, = 00,000 () second equation 0.8 =, 00 Subtract equations = 68,000 Solve for or amount of risk investment. Substituting = 68,000 into one of the original equations we have + 68,000 =,600 or = $77,600. Solution: Put $77,600 in a safe investment and $68,000 in a risk investment. 9. = amount invested at %. = amount invested at %. + =,000 Total amount invested =,000 Investment income Solve the sstem of equation: + =, =,00 () second equation 0. = 0,000 Subtract equations = 0,000 Solve for Substituting into the first equation we have + 0,000 =,000 or =,000. Thus, $,000 is invested at % and $0,000 is invested at %.
17 Chapter : Answers to Eercises 7. A = ounces of substance A. B = ounces of substance B. A Required ratio = gives A B = 0. B Required nutrition is %A + %B = 0%. This gives A + B = 0. The % notation can be trouble. Be careful! Now we can solve the sstem. A B = 0 A+ B = 0 B = 0 Subtract first equation from second. 0 0 B = = 0 Substituting into the original equation gives A = 0 or A=. The solution is ounces of substance A and 6 ounces of substance B.. = population of species A. = population of species B. + =,600 units of first nutrient + = 9,60 units of second nutrient 8+ =,00 () first equation + = 9,60 =,70 Subtract = 0 Solve for Substituting = 0 into an original equation we have (0) + =,600. So, = 00. Solution is 0 of species A and 00 of species B.. = amount of 0% concentration. = amount of % concentration. + = amount of solution = 0.() concentration of medicine Solving this sstem of equations: + = + 0. = 7.7 () second equation 0.7 =. Subtract equations = Solve for Substituting into the first equation we have + = or = 7. The solution is cc of % concentration and 7 cc of 0% concentration. 7. = number of $0 tickets. = number of $0 tickets. + = 6,000 total number of tickets = 80,000 total revenue To solve the sstem of equations multipl Eq. b = 80, = 80,000 = 0,000 or =,000 Substituting into the first equation gives = Sell,000 tickets for $0 each and 6000 tickets for $0 each.
18 8 Chapter : Answers to Eercises 9. = amount of 0% solution to be added. 0.0 = concentration of nutrient in 0% solution. 0.0(0) = is the concentration of nutrient in % solution = 0.( + 0) 0.0+ = = 8 or = 80cc of 0% solution is needed.. = ounces of substance A, = ounces of substance B, and z = ounces of substance C. + + z = 0 Nutrition requirements = z = z Digestive restrictions Digestive restrictions Since both and are in terms of z, we can substitute in the first equation and solve for z. So, z + z + z = 0 or 0z = 0. So, z =. Now, since = z, we have =. Since = z, we have =. The solution is ounces of substance A, ounce of substance B, and ounces of substance C.. A = number of A tpe clients. B = number of B tpe clients. C = number of C tpe clients. A + B + C = 00 Total clients 00A + 00B + 00C = 0,000 Counseling costs 00A + 00B + 0C = 0,000 Food and shelter To find the solution we must solve the sstem of equations. Eq. A+ B+ C = 00 Eq. A+ B+ C = 00 Original equation divided b 0 Eq. A+ B+ C = 00 Original equation divided b 0 A+ B+ C = 00 Eq. Eq. B+ C = 00 ( ) Eq. added to Eq. Eq. B C = 00 ( ) Eq. added to Eq. A+ B+ C = 00 Eq. B+ C = 00 Eq. C = Eq. added to Eq C = = 00 Substituting C = 00 into Eq. gives B + 00 = 00 or B = 00. So, B = 0. Substituting C = 00 and B = 0 into Eq. gives A = 00. So, A = 00. Thus, the solution is 00 tpe A clients, 0 tpe B clients, and 00 tpe C clients.
19 Chapter : Answers to Eercises 9 Eercise.6. a. P ( ) = R ( ) C ( ) ( ) = = 7 00 P 00 = = $700 b. ( ) ( ). a. P ( ) = R ( ) C ( ) b. c. = 80 (+ 80) = 7 80 P (0) = 7(0) 80 = $70 The total costs are more than the revenue. P ( ) = 0 or 7 80 = 0 80 So, = = 0 units is the break-even 7 point.. C() = + 0 a. m =, C-intercept: 0 b. MC = means that each additional unit produced costs $. c. Slope = marginal cost. C-intercept =fied costs. d. $, $ ( MC = at ever point) 7. R = 7 a. m = 7 b. 7; each additional unit sold ields $7 in revenue. c. In each case, one more unit ields $7. 9. R() = 7, C() = + 0 a. P ( ) = 7 (+ 0) = 0 b. m = c. Marginal profit is. d. Each additional unit sold gives a profit of $. To maimize profit sell all that ou can produce. Note that this is not alwas true.. (, P) is the correct form. P = (00, 0) P = (0, 6000) m = = P 0 = 8( 00) or P = The marginal profit is 8.. a. TC = H b. TR = 60H c. P = R C ( H ) = 60H = H 6600 C 00 = d. ( ) ( ) = $,600 cost of 00 helmets ( 00) 60( 00) R = = $,000 revenue from 00 helmets ( 00) = ( 00) ( 00) P R C = $, 000, 600 = $600 loss from 00 helmets e. C (00) = (00) = $7,0 cost of 00 helmets R (00) = 60(00) = $8,000 revenue from 00 helmets P(00) = R(00) C(00) = 8, 000 7,0 = $900 profit from 00 helmets f. The marginal profit is $. Each additional helmet sold gives a profit of $.. a. The revenue function is the graph that passes through the origin. b. At a production of zero the fied costs are $000. c. From the graph, the break-even point is 00 units and $000 in revenue or costs d. Marginal cost = = Marginal revenue = = R() = C() = 8 = + 60 or 0 = 60 or =. Thus, necklaces must be sold to break even. 9. a. R() =, C() = b. R() = C() if = or = 600 or = 00. It takes 00 units to break even.. a. P ( ) = R ( ) C ( ) = (8+ 600) = 600 b. B setting P() = 0 we get = 00. Same as 9(b).
20 0 Chapter : Answers to Eercises. a. TC =.0 + b. TR = c. P = R C ( ) =.0 + =.0 d. Breakeven also means P = 0..0 = 0.0 =. a. R() =.90 b. P = (000, 0000) P = (800, ) 7. a. = 90 units to break even, 0, 000 7,880 m = = = , 000 =.90( 000) or =.90+ 0, 00 = C( ) c. From.90 = ,00 we have = 0 units to break even. $ BE TR P VC b. TR starts at the origin and intersects TC at the break-even (BE). FC is a horizontal line from the vertical intercept of TC. VC starts at the origin and is parallel to TC. 9. If price increases, then the demand for the product decreases.. a. If p = $0, then q = 600 (approimatel). b. If p = $0, then q = 00. c. There is a shortage since more is demanded. TC FC. Demand: p+ q = 00 (60) + q = 00 q = 80 q = 6 Suppl: p q = 60 q = q = 0 q = There will be a surplus of 9 units at a price of $ Remember that (q, p) is the correct form. P = (0, 900) P = (, 80) m = = = 0 7 Note: m < 0 for demand equations. p 900 = ( q 0) or p = q (q, p) is the correct form. P = (000,.0) P = (000,.00) m = = = Note: m > 0 for suppl equations. p = 0.000(q 000) or p = 0.000q a. The decreasing function is the demand curve. The increasing function is the suppl curve. b. Reading the graph, we have equilibrium at q = 0 and p =.. a. Reading the graph, at p = 0 we have 0 units supplied. b. Reading the graph, at p = 0 we have 0 units demanded. c. At p = 0 there is a shortage of 0 units.. B observing the graph in the figure, we see that a price below the equilibrium price results in a shortage.
21 Chapter : Answers to Eercises. q+ 8 = q+ Required condition. 7. q+ 68 = q+ 68 Multipl both sides b 6 to simplif. q = 0 q = 0 Substituting into one of the original equations gives Thus, the equilibrium point is (q, p) = (0, 8). q+ 0 = q+ 0 Required condition. 90 = 9q p = (0) + 8 = 8. q = Solve for q. Substituting q = into one of the original equations gives p = 80. Thus, the equilibrium point is (q, p) = (, 80) Demand: (80, 0) and (, 00) are two points. m = = 80 p p = m( q q) or p 00 = ( q ) or p = q Suppl: (60, 80) and (0, 70) are two points. m = = p p = m( q q) or p 80 = ( q 60) or p = q Now, set these two equations for p equal to each other and solve for q. 9 q+. = q+ 0 Required for equilibrium. 8 9q+ 700 = q+ 600 Multipl both sides b 8 to simplif. 9q = 900 q = 0 Substituting q = 0 into one of the original equations gives p =. Thus, the equilibrium point is (q, p) = (0, ).. a. Reading the graph, we have that the ta is $. b. From the graph, the original equilibrium was (0, 0). c. From the graph, the new equilibrium is (0, ). d. The supplier suffers because the increased price reduces the demand.. New suppl price: p = q = q + 68 q+ 68 = q+ 0 Required condition 9q = q = 8 Substituting q = 8 into one of the original equations gives p = 88. Thus, the new equilibrium point is (q, p) = (8, 88). q q. New suppl price: p = + + = = + 6 Required condition q q 0 0 q+ 00 = q+ 00 q = 00 q = 00 Thus, p = + = The new equilibrium point is (00, 0).
22 Chapter : Answers to Eercises q + 0 q Demand: p = Suppl: p = 60 q+ 0 q q+ 600 New suppl: p = + = + = = q+ 600 q Required condition q+ 600 = q+ 00 Multipl both sides b q = 600 q = 0 Thus, p = = The new equilibrium quantit is 0. The new equilibrium price is $.
Chapter 1: Linear Equations and Functions
 Chapter : Linear Equations and Functions Eercise.. 7 8+ 7+ 7 8 8+ + 7 8. + 8 8( + ) + 8 8+ 8 8 8 8 7 0 0. 8( ) ( ) 8 8 8 8 + 0 8 8 0 7. ( ) 8. 8. ( 7) ( + ) + + +. 7 7 7 7 7 7 ( ). 8 8 0 0 7. + + + 8 +
Chapter : Linear Equations and Functions Eercise.. 7 8+ 7+ 7 8 8+ + 7 8. + 8 8( + ) + 8 8+ 8 8 8 8 7 0 0. 8( ) ( ) 8 8 8 8 + 0 8 8 0 7. ( ) 8. 8. ( 7) ( + ) + + +. 7 7 7 7 7 7 ( ). 8 8 0 0 7. + + + 8 +
Chapter 2: Quadratic and Other Special Functions. Exercises 2.1. x 2 11x 10 0 x 2 10x x ( x 10)(x 1) 0 x 10 0 or x 1 0
 Mathematical Applications for the Management Life and Social Sciences 11th Edition Harshbarger SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/mathematical-applications-managementlife-social-sciences-11th-edition-harshbarger-solutions-manual/
Mathematical Applications for the Management Life and Social Sciences 11th Edition Harshbarger SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/mathematical-applications-managementlife-social-sciences-11th-edition-harshbarger-solutions-manual/
Systems of Linear Equations: Solving by Graphing
 8.1 Sstems of Linear Equations: Solving b Graphing 8.1 OBJECTIVE 1. Find the solution(s) for a set of linear equations b graphing NOTE There is no other ordered pair that satisfies both equations. From
8.1 Sstems of Linear Equations: Solving b Graphing 8.1 OBJECTIVE 1. Find the solution(s) for a set of linear equations b graphing NOTE There is no other ordered pair that satisfies both equations. From
8.4. If we let x denote the number of gallons pumped, then the price y in dollars can $ $1.70 $ $1.70 $ $1.70 $ $1.
 8.4 An Introduction to Functions: Linear Functions, Applications, and Models We often describe one quantit in terms of another; for eample, the growth of a plant is related to the amount of light it receives,
8.4 An Introduction to Functions: Linear Functions, Applications, and Models We often describe one quantit in terms of another; for eample, the growth of a plant is related to the amount of light it receives,
CHAPTER 1 Functions, Graphs, and Limits
 CHAPTER Functions, Graphs, and Limits Section. The Cartesian Plane and the Distance Formula... Section. Graphs of Equations...8 Section. Lines in the Plane and Slope... Mid-Chapter Quiz Solutions... Section.
CHAPTER Functions, Graphs, and Limits Section. The Cartesian Plane and the Distance Formula... Section. Graphs of Equations...8 Section. Lines in the Plane and Slope... Mid-Chapter Quiz Solutions... Section.
Chapter 5: Systems of Equations
 Chapter : Sstems of Equations Section.: Sstems in Two Variables... 0 Section. Eercises... 9 Section.: Sstems in Three Variables... Section. Eercises... Section.: Linear Inequalities... Section.: Eercises.
Chapter : Sstems of Equations Section.: Sstems in Two Variables... 0 Section. Eercises... 9 Section.: Sstems in Three Variables... Section. Eercises... Section.: Linear Inequalities... Section.: Eercises.
Can a system of linear equations have no solution? Can a system of linear equations have many solutions?
 5. Solving Special Sstems of Linear Equations Can a sstem of linear equations have no solution? Can a sstem of linear equations have man solutions? ACTIVITY: Writing a Sstem of Linear Equations Work with
5. Solving Special Sstems of Linear Equations Can a sstem of linear equations have no solution? Can a sstem of linear equations have man solutions? ACTIVITY: Writing a Sstem of Linear Equations Work with
6. 5x Division Property. CHAPTER 2 Linear Models, Equations, and Inequalities. Toolbox Exercises. 1. 3x = 6 Division Property
 CHAPTER Linear Models, Equations, and Inequalities CHAPTER Linear Models, Equations, and Inequalities Toolbox Exercises. x = 6 Division Property x 6 = x =. x 7= Addition Property x 7= x 7+ 7= + 7 x = 8.
CHAPTER Linear Models, Equations, and Inequalities CHAPTER Linear Models, Equations, and Inequalities Toolbox Exercises. x = 6 Division Property x 6 = x =. x 7= Addition Property x 7= x 7+ 7= + 7 x = 8.
Linear and Nonlinear Systems of Equations. The Method of Substitution. Equation 1 Equation 2. Check (2, 1) in Equation 1 and Equation 2: 2x y 5?
 3330_070.qd 96 /5/05 Chapter 7 7. 9:39 AM Page 96 Sstems of Equations and Inequalities Linear and Nonlinear Sstems of Equations What ou should learn Use the method of substitution to solve sstems of linear
3330_070.qd 96 /5/05 Chapter 7 7. 9:39 AM Page 96 Sstems of Equations and Inequalities Linear and Nonlinear Sstems of Equations What ou should learn Use the method of substitution to solve sstems of linear
Introduction Direct Variation Rates of Change Scatter Plots. Introduction. EXAMPLE 1 A Mathematical Model
 APPENDIX B Mathematical Modeling B1 Appendi B Mathematical Modeling B.1 Modeling Data with Linear Functions Introduction Direct Variation Rates of Change Scatter Plots Introduction The primar objective
APPENDIX B Mathematical Modeling B1 Appendi B Mathematical Modeling B.1 Modeling Data with Linear Functions Introduction Direct Variation Rates of Change Scatter Plots Introduction The primar objective
Essential Question How can you use a scatter plot and a line of fit to make conclusions about data?
 . Scatter Plots and Lines of Fit Essential Question How can ou use a scatter plot and a line of fit to make conclusions about data? A scatter plot is a graph that shows the relationship between two data
. Scatter Plots and Lines of Fit Essential Question How can ou use a scatter plot and a line of fit to make conclusions about data? A scatter plot is a graph that shows the relationship between two data
P.4 Lines in the Plane
 28 CHAPTER P Prerequisites P.4 Lines in the Plane What ou ll learn about Slope of a Line Point-Slope Form Equation of a Line Slope-Intercept Form Equation of a Line Graphing Linear Equations in Two Variables
28 CHAPTER P Prerequisites P.4 Lines in the Plane What ou ll learn about Slope of a Line Point-Slope Form Equation of a Line Slope-Intercept Form Equation of a Line Graphing Linear Equations in Two Variables
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 2-1 Solving Linear Equations and Inequalities
 A Read To Go n? Skills Intervention -1 Solving Linear Equations and Inequalities Find these vocabular words in Lesson -1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular equation solution of an equation linear
A Read To Go n? Skills Intervention -1 Solving Linear Equations and Inequalities Find these vocabular words in Lesson -1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular equation solution of an equation linear
Math098 Practice Final Test
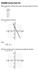 Math098 Practice Final Test Find an equation of the line that contains the points listed in the table. 1) 0-6 1-2 -4 3-3 4-2 Find an equation of the line. 2) 10-10 - 10 - -10 Solve. 3) 2 = 3 + 4 Find the
Math098 Practice Final Test Find an equation of the line that contains the points listed in the table. 1) 0-6 1-2 -4 3-3 4-2 Find an equation of the line. 2) 10-10 - 10 - -10 Solve. 3) 2 = 3 + 4 Find the
DMA 50 Worksheet #1 Introduction to Graphs: Analyzing, Interpreting, and Creating Graphs
 DMA 0 Worksheet #1 Introduction to Graphs: Analzing, Interpreting, and Creating Graphs A graph will be given followed b a set of questions to answer. Show our work. The bar graph below shows the number
DMA 0 Worksheet #1 Introduction to Graphs: Analzing, Interpreting, and Creating Graphs A graph will be given followed b a set of questions to answer. Show our work. The bar graph below shows the number
Systems of Linear Equations
 Sstems of Linear Equations Monetar Sstems Overload Lesson 3-1 Learning Targets: Use graphing, substitution, and elimination to solve sstems of linear equations in two variables. Formulate sstems of linear
Sstems of Linear Equations Monetar Sstems Overload Lesson 3-1 Learning Targets: Use graphing, substitution, and elimination to solve sstems of linear equations in two variables. Formulate sstems of linear
Intermediate Algebra. Exam 1 Review (Chapters 1, 2, and 3)
 Eam Review (Chapters,, and ) Intermediate Algebra Name. Epress the set in roster form. { N and 7}. Epress the set in set builder form. {-, 0,,,, }. Epress in set builder notation each set of numbers that
Eam Review (Chapters,, and ) Intermediate Algebra Name. Epress the set in roster form. { N and 7}. Epress the set in set builder form. {-, 0,,,, }. Epress in set builder notation each set of numbers that
M122 College Algebra Review for Final Exam
 M1 College Algebra Review for Final Eam Revised Fall 017 for College Algebra - Beecher All answers should include our work (this could be a written eplanation of the result, a graph with the relevant feature
M1 College Algebra Review for Final Eam Revised Fall 017 for College Algebra - Beecher All answers should include our work (this could be a written eplanation of the result, a graph with the relevant feature
Practice A ( 1, 3 ( 0, 1. Match the function with its graph. 3 x. Explain how the graph of g can be obtained from the graph of f. 5 x.
 8. Practice A For use with pages 65 7 Match the function with its graph.. f. f.. f 5. f 6. f f Lesson 8. A. B. C. (, 6) (0, ) (, ) (0, ) ( 0, ) (, ) D. E. F. (0, ) (, 6) ( 0, ) (, ) (, ) (0, ) Eplain how
8. Practice A For use with pages 65 7 Match the function with its graph.. f. f.. f 5. f 6. f f Lesson 8. A. B. C. (, 6) (0, ) (, ) (0, ) ( 0, ) (, ) D. E. F. (0, ) (, 6) ( 0, ) (, ) (, ) (0, ) Eplain how
Systems of Linear Equations
 Sstems of Linear Equations Monetar Sstems Overload Lesson 3-1 Learning Targets: Use graphing, substitution, and elimination to solve sstems of linear equations in two variables. Formulate sstems of linear
Sstems of Linear Equations Monetar Sstems Overload Lesson 3-1 Learning Targets: Use graphing, substitution, and elimination to solve sstems of linear equations in two variables. Formulate sstems of linear
STANDARD FORM is a QUADRATIC FUNCTION and its graph is a PARABOLA. The domain of a quadratic function is the set of all real numbers.
 EXERCISE 2-3 Things to remember: 1. QUADRATIC FUNCTION If a, b, and c are real numbers with a 0, then the function f() = a 2 + b + c STANDARD FORM is a QUADRATIC FUNCTION and its graph is a PARABOLA. The
EXERCISE 2-3 Things to remember: 1. QUADRATIC FUNCTION If a, b, and c are real numbers with a 0, then the function f() = a 2 + b + c STANDARD FORM is a QUADRATIC FUNCTION and its graph is a PARABOLA. The
Systems of Linear Equations Monetary Systems Overload
 Sstems of Linear Equations SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Shared Reading, Close Reading, Interactive Word Wall Have ou ever noticed that when an item is popular and man people want to bu it, the price
Sstems of Linear Equations SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Shared Reading, Close Reading, Interactive Word Wall Have ou ever noticed that when an item is popular and man people want to bu it, the price
CHAPTER 1 Functions and Their Graphs
 PART I CHAPTER Functions and Their Graphs Section. Lines in the Plane....................... Section. Functions........................... Section. Graphs of Functions..................... Section. Shifting,
PART I CHAPTER Functions and Their Graphs Section. Lines in the Plane....................... Section. Functions........................... Section. Graphs of Functions..................... Section. Shifting,
Graphing Linear Equations
 1-3 BJECTIVES Graph linear equations. Find the - and -intercepts of a line. Find the slope of a line through two points. Find zeros of linear functions. Graphing Linear Equations AGRICULTURE American farmers
1-3 BJECTIVES Graph linear equations. Find the - and -intercepts of a line. Find the slope of a line through two points. Find zeros of linear functions. Graphing Linear Equations AGRICULTURE American farmers
3.2 Introduction to Functions
 8 CHAPTER Graphs and Functions Write each statement as an equation in two variables. Then graph each equation. 97. The -value is more than three times the -value. 98. The -value is - decreased b twice
8 CHAPTER Graphs and Functions Write each statement as an equation in two variables. Then graph each equation. 97. The -value is more than three times the -value. 98. The -value is - decreased b twice
LESSON #28 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 1 LESSON #8 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
1 LESSON #8 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
CONSUMER CHOICES Madison is thinking about leasing a car for. Example 1 Solve the system of equations by graphing.
 2-1 BJECTIVES Solve sstems of equations graphicall. Solve sstems of equations algebraicall. Solving Sstems of Equations in Two Variables CNSUMER CHICES Madison is thinking about leasing a car for two ears.
2-1 BJECTIVES Solve sstems of equations graphicall. Solve sstems of equations algebraicall. Solving Sstems of Equations in Two Variables CNSUMER CHICES Madison is thinking about leasing a car for two ears.
MATH 021 UNIT 1 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS
 MATH 01 UNIT 1 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS General Instructions You will notice that most of the homework assignments for a section have more than one part. Usuall, the part (A) questions ask for eplanations,
MATH 01 UNIT 1 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS General Instructions You will notice that most of the homework assignments for a section have more than one part. Usuall, the part (A) questions ask for eplanations,
Reteaching (continued)
 Zero and Negative Eponents Eercises Write each epression as an integer, a simple fraction, or an epression that contains onl positive eponents. Simplif...3 0. 0-0,000 3. a -5. 3.7 0 a 5 5. 9-6. 3-3 9 p
Zero and Negative Eponents Eercises Write each epression as an integer, a simple fraction, or an epression that contains onl positive eponents. Simplif...3 0. 0-0,000 3. a -5. 3.7 0 a 5 5. 9-6. 3-3 9 p
C H A P T E R 3 Polynomial Functions
 C H A P T E R Polnomial Functions Section. Quadratic Functions and Models............. 9 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree......... Section. Polnomial and Snthetic Division............ 8 Section.
C H A P T E R Polnomial Functions Section. Quadratic Functions and Models............. 9 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree......... Section. Polnomial and Snthetic Division............ 8 Section.
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Name Date Chapter 5 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc Graph the equation. 1. + =. = 3 3. 5 + = 10. 3 = 5. 3 = 6. 3 + = 1 Solve the inequalit. Graph the solution. 7. a 3 > 8. c 9. d 5 < 3 10. 8 3r 5 r
Name Date Chapter 5 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc Graph the equation. 1. + =. = 3 3. 5 + = 10. 3 = 5. 3 = 6. 3 + = 1 Solve the inequalit. Graph the solution. 7. a 3 > 8. c 9. d 5 < 3 10. 8 3r 5 r
LESSON #24 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 1 LESSON #4 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
1 LESSON #4 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
Algebra 1B Assignments Exponential Functions (All graphs must be drawn on graph paper!)
 Name Score Algebra 1B Assignments Eponential Functions (All graphs must be drawn on graph paper!) 8-6 Pages 463-465: #1-17 odd, 35, 37-40, 43, 45-47, 50, 51, 54, 55-61 odd 8-7 Pages 470-473: #1-11 odd,
Name Score Algebra 1B Assignments Eponential Functions (All graphs must be drawn on graph paper!) 8-6 Pages 463-465: #1-17 odd, 35, 37-40, 43, 45-47, 50, 51, 54, 55-61 odd 8-7 Pages 470-473: #1-11 odd,
Graphing and Optimization
 BARNMC_33886.QXD //7 :7 Page 74 Graphing and Optimization CHAPTER - First Derivative and Graphs - Second Derivative and Graphs -3 L Hôpital s Rule -4 Curve-Sketching Techniques - Absolute Maima and Minima
BARNMC_33886.QXD //7 :7 Page 74 Graphing and Optimization CHAPTER - First Derivative and Graphs - Second Derivative and Graphs -3 L Hôpital s Rule -4 Curve-Sketching Techniques - Absolute Maima and Minima
Chapter Start Thinking! For use before Activity 6.1. For use before Activity Start Thinking! For use before Lesson
 . Enrichment and Etension. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b is an number ecept.. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. Check students work.. Puzzle PAY HIM Etension. Start Thinking! For use before
. Enrichment and Etension. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b is an number ecept.. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. Check students work.. Puzzle PAY HIM Etension. Start Thinking! For use before
Fair Game Review. Chapter = How many calculators are sold when the profit is $425? Solve the equation. Check your solution.
 Name Date Chapter 4 Fair Game Review Solve the equation. Check our solution.. 8 3 = 3 2. 4a + a = 2 3. 9 = 4( 3k 4) 7k 4. ( m) 2 5 6 2 = 8 5. 5 t + 8t = 3 6. 3 5h 2 h + 4 = 0 2 7. The profit P (in dollars)
Name Date Chapter 4 Fair Game Review Solve the equation. Check our solution.. 8 3 = 3 2. 4a + a = 2 3. 9 = 4( 3k 4) 7k 4. ( m) 2 5 6 2 = 8 5. 5 t + 8t = 3 6. 3 5h 2 h + 4 = 0 2 7. The profit P (in dollars)
Algebra 1 CP Semester Exam Review
 Name: Hr: Algebra CP Semester Eam Review GET ORGANIZED. Successful studing begins with being organized. Bring this packet with ou to class ever da. DO NOT FALL BEHIND. Do the problems that are assigned
Name: Hr: Algebra CP Semester Eam Review GET ORGANIZED. Successful studing begins with being organized. Bring this packet with ou to class ever da. DO NOT FALL BEHIND. Do the problems that are assigned
3.2 Understanding Relations and Functions-NOTES
 Name Class Date. Understanding Relations and Functions-NOTES Essential Question: How do ou represent relations and functions? Eplore A1.1.A decide whether relations represented verball, tabularl, graphicall,
Name Class Date. Understanding Relations and Functions-NOTES Essential Question: How do ou represent relations and functions? Eplore A1.1.A decide whether relations represented verball, tabularl, graphicall,
5) In a local election, 48,900 people voted. This was an increase of 6% over the last election. How many people voted in the last election?
 Final Eam Review (2018-2019) Math 11000 1) Evaluate the epression 6 - (a - b) 2, when a = 13 and b = 3 2) Simplif using the distributive law and combining like terms. -3(2t - ) - (t - ) + t 3) Solve: -9
Final Eam Review (2018-2019) Math 11000 1) Evaluate the epression 6 - (a - b) 2, when a = 13 and b = 3 2) Simplif using the distributive law and combining like terms. -3(2t - ) - (t - ) + t 3) Solve: -9
CHAPTER 2 Differentiation
 CHAPTER Differentiation Section. The Derivative and the Slope of a Graph............. 6 Section. Some Rules for Differentiation.................. 69 Section. Rates of Change: Velocit and Marginals.............
CHAPTER Differentiation Section. The Derivative and the Slope of a Graph............. 6 Section. Some Rules for Differentiation.................. 69 Section. Rates of Change: Velocit and Marginals.............
Full download all chapters instantly please go to Solutions Manual, Test Bank site: testbanklive.com
 Essentials of College Algebra 11th Edition Lial Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/essentials-of-college-algebra-11th-edition-lial-test-bank/ MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative
Essentials of College Algebra 11th Edition Lial Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/essentials-of-college-algebra-11th-edition-lial-test-bank/ MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative
CHAPTER 1 Functions Graphs, and Models; Linear Functions. Algebra Toolbox Exercises. 1. {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8} and
 CHAPTER Algebra Toolbox CHAPTER Functions Graphs, and Models; Linear Functions Algebra Toolbox Exercises. {,,,4,,6,7,8} and { xx< 9, x } Remember that x means that x is a natural number.. Yes.. Yes. Every
CHAPTER Algebra Toolbox CHAPTER Functions Graphs, and Models; Linear Functions Algebra Toolbox Exercises. {,,,4,,6,7,8} and { xx< 9, x } Remember that x means that x is a natural number.. Yes.. Yes. Every
Chapter 8 Notes SN AA U2C8
 Chapter 8 Notes SN AA U2C8 Name Period Section 8-: Eploring Eponential Models Section 8-2: Properties of Eponential Functions In Chapter 7, we used properties of eponents to determine roots and some of
Chapter 8 Notes SN AA U2C8 Name Period Section 8-: Eploring Eponential Models Section 8-2: Properties of Eponential Functions In Chapter 7, we used properties of eponents to determine roots and some of
13.1 2X2 Systems of Equations
 . X Sstems of Equations In this section we want to spend some time reviewing sstems of equations. Recall there are two basic techniques we use for solving a sstem of equations: Elimination and Substitution.
. X Sstems of Equations In this section we want to spend some time reviewing sstems of equations. Recall there are two basic techniques we use for solving a sstem of equations: Elimination and Substitution.
Lecture Guide. Math 90 - Intermediate Algebra. Stephen Toner. Intermediate Algebra, 2nd edition. Miller, O'Neill, & Hyde. Victor Valley College
 Lecture Guide Math 90 - Intermediate Algebra to accompan Intermediate Algebra, 2nd edition Miller, O'Neill, & Hde Prepared b Stephen Toner Victor Valle College Last updated: 11/24/10 0 1.1 Sets of Numbers
Lecture Guide Math 90 - Intermediate Algebra to accompan Intermediate Algebra, 2nd edition Miller, O'Neill, & Hde Prepared b Stephen Toner Victor Valle College Last updated: 11/24/10 0 1.1 Sets of Numbers
The speed the speed of light is 30,000,000,000 m/s. Write this number in scientific notation.
 Chapter 1 Section 1.1 Scientific Notation Powers of Ten 1 1 1.1.1.1.1 Standard Scientific Notation N n where 1 N and n is an integers Eamples of numbers in scientific notation. 8.17 11 Using Scientific
Chapter 1 Section 1.1 Scientific Notation Powers of Ten 1 1 1.1.1.1.1 Standard Scientific Notation N n where 1 N and n is an integers Eamples of numbers in scientific notation. 8.17 11 Using Scientific
Identify the domain and the range of the relation from the graph. 8)
 INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR TEST Use the given conditions to write an equation for the line. 1) a) Passing through (, -) and parallel to = - +. b) Passing through (, 7) and parallel to - 3 = 10 c)
INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR TEST Use the given conditions to write an equation for the line. 1) a) Passing through (, -) and parallel to = - +. b) Passing through (, 7) and parallel to - 3 = 10 c)
Math 20 Spring 2005 Final Exam Practice Problems (Set 2)
 Math 2 Spring 2 Final Eam Practice Problems (Set 2) 1. Find the etreme values of f(, ) = 2 2 + 3 2 4 on the region {(, ) 2 + 2 16}. 2. Allocation of Funds: A new editor has been allotted $6, to spend on
Math 2 Spring 2 Final Eam Practice Problems (Set 2) 1. Find the etreme values of f(, ) = 2 2 + 3 2 4 on the region {(, ) 2 + 2 16}. 2. Allocation of Funds: A new editor has been allotted $6, to spend on
Math 50 - Elementary Algebra Final Exam, Fall 2010
 Math - Elementar Algebra Final Eam, Fall Name: Date: Score: / Show the necessar work on the test cop. For an of the graphs use a straightedge to receive full credit. Place our answers in the blanks provided
Math - Elementar Algebra Final Eam, Fall Name: Date: Score: / Show the necessar work on the test cop. For an of the graphs use a straightedge to receive full credit. Place our answers in the blanks provided
Essential Question How can you use a quadratic function to model a real-life situation?
 3. TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS A..A A..E A..A A..B A..C Modeling with Quadratic Functions Essential Question How can ou use a quadratic function to model a real-life situation? Work with a partner.
3. TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS A..A A..E A..A A..B A..C Modeling with Quadratic Functions Essential Question How can ou use a quadratic function to model a real-life situation? Work with a partner.
Section 3.1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing
 Section 3.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Name: Period: Objective(s): Solve a sstem of linear equations in two variables using graphing. Essential Question: Eplain how to tell from a graph of a sstem
Section 3.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Name: Period: Objective(s): Solve a sstem of linear equations in two variables using graphing. Essential Question: Eplain how to tell from a graph of a sstem
REVIEW. log e. log. 3 k. x 4. log ( x+ 3) log x= ,if x 2 y. . h
 Math REVIEW Part I: Problems Simplif (without the use of calculators) ln log 000 e 0 k = k = k 7 log ( ) 8 lo g (log ) Solve the following equations/inequalities Check when necessar 8 =0 9 0 + = log (
Math REVIEW Part I: Problems Simplif (without the use of calculators) ln log 000 e 0 k = k = k 7 log ( ) 8 lo g (log ) Solve the following equations/inequalities Check when necessar 8 =0 9 0 + = log (
Chapter 11. Systems of Equations Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Graphing
 Chapter 11 Sstems of Equations 11.1 Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing Learning Objectives: A. Decide whether an ordered pair is a solution of a sstem of linear equations. B. Solve a sstem of
Chapter 11 Sstems of Equations 11.1 Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing Learning Objectives: A. Decide whether an ordered pair is a solution of a sstem of linear equations. B. Solve a sstem of
Essential Question How can you solve a system of linear equations? $15 per night. Cost, C (in dollars) $75 per Number of. Revenue, R (in dollars)
 5.1 Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing Essential Question How can ou solve a sstem of linear equations? Writing a Sstem of Linear Equations Work with a partner. Your famil opens a bed-and-breakfast.
5.1 Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing Essential Question How can ou solve a sstem of linear equations? Writing a Sstem of Linear Equations Work with a partner. Your famil opens a bed-and-breakfast.
Study Unit 2 : Linear functions Chapter 2 : Sections and 2.6
 1 Study Unit 2 : Linear functions Chapter 2 : Sections 2.1 2.4 and 2.6 1. Function Humans = relationships Function = mathematical form of a relationship Temperature and number of ice cream sold Independent
1 Study Unit 2 : Linear functions Chapter 2 : Sections 2.1 2.4 and 2.6 1. Function Humans = relationships Function = mathematical form of a relationship Temperature and number of ice cream sold Independent
3.2 LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS
 Section. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 7. LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS Ariel Skelle/Corbis What ou should learn Recognize and evaluate logarithmic functions with base a. Graph logarithmic
Section. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 7. LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS Ariel Skelle/Corbis What ou should learn Recognize and evaluate logarithmic functions with base a. Graph logarithmic
Math 1325 Final Exam Review. (Set it up, but do not simplify) lim
 . Given f( ), find Math 5 Final Eam Review f h f. h0 h a. If f ( ) 5 (Set it up, but do not simplify) If c. If f ( ) 5 f (Simplify) ( ) 7 f (Set it up, but do not simplify) ( ) 7 (Simplify) d. If f. Given
. Given f( ), find Math 5 Final Eam Review f h f. h0 h a. If f ( ) 5 (Set it up, but do not simplify) If c. If f ( ) 5 f (Simplify) ( ) 7 f (Set it up, but do not simplify) ( ) 7 (Simplify) d. If f. Given
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Practice Test 1-0312-Chap. 2.4,2.7, 3.1-3.6,4.1,.4,. Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Write an inequalit statement involving the
Practice Test 1-0312-Chap. 2.4,2.7, 3.1-3.6,4.1,.4,. Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Write an inequalit statement involving the
Woodland Community College: Math Practice Test
 Woodland Communit College: Math Practice Test Elementar Algebra Math Test The following problems are recommended practice problems for the elementar algebra section of the placement test. Some of the problems
Woodland Communit College: Math Practice Test Elementar Algebra Math Test The following problems are recommended practice problems for the elementar algebra section of the placement test. Some of the problems
Chapter 9 Vocabulary Check
 9 CHAPTER 9 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Find the inverse function of each one-to-one function. See Section 9.. 67. f = + 68. f = - CONCEPT EXTENSIONS The formula = 0 e kt gives the population
9 CHAPTER 9 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Find the inverse function of each one-to-one function. See Section 9.. 67. f = + 68. f = - CONCEPT EXTENSIONS The formula = 0 e kt gives the population
Chapter 4. Chapter 4 Opener. Section 4.1. Big Ideas Math Blue Worked-Out Solutions. x 2. Try It Yourself (p. 147) x 0 1. y ( ) x 2
 Chapter Chapter Opener Tr It Yourself (p. 7). As the input decreases b, the output increases b.. Input As the input increases b, the output increases b.. As the input decreases b, the output decreases
Chapter Chapter Opener Tr It Yourself (p. 7). As the input decreases b, the output increases b.. Input As the input increases b, the output increases b.. As the input decreases b, the output decreases
Intermediate Algebra Review for Exam 1 - Spring 2005
 Intermediate Algebra Review for Eam - Spring 00 Use mathematical smbols to translate the phrase. ) a) 9 more than half of some number b) 0 less than a number c) 37 percent of some number Evaluate the epression.
Intermediate Algebra Review for Eam - Spring 00 Use mathematical smbols to translate the phrase. ) a) 9 more than half of some number b) 0 less than a number c) 37 percent of some number Evaluate the epression.
Fair Game Review. Chapter 5. feet and the length is 2x feet. Find the. perimeter of the garden. 24x 5 3. Name Date. Simplify the expression. 6.
 Name Date Chapter 5 Fair Game Review Simplif the expression. 1. 2x + 5 x 2. 4 + 2d 4d 3. 7 8 + 6 3 4. 5 + 4z 3 + 3z 5. 4( s + 2) + s 1 6. ( ) 24x 5 3 7. The width of a garden is ( 4x 1) perimeter of the
Name Date Chapter 5 Fair Game Review Simplif the expression. 1. 2x + 5 x 2. 4 + 2d 4d 3. 7 8 + 6 3 4. 5 + 4z 3 + 3z 5. 4( s + 2) + s 1 6. ( ) 24x 5 3 7. The width of a garden is ( 4x 1) perimeter of the
ACTIVITY: Using a Table to Plot Points
 .5 Graphing Linear Equations in Standard Form equation a + b = c? How can ou describe the graph of the ACTIVITY: Using a Table to Plot Points Work with a partner. You sold a total of $6 worth of tickets
.5 Graphing Linear Equations in Standard Form equation a + b = c? How can ou describe the graph of the ACTIVITY: Using a Table to Plot Points Work with a partner. You sold a total of $6 worth of tickets
Chapter 1. Functions, Graphs, and Limits
 Chapter 1 Functions, Graphs, and Limits MA1103 Business Mathematics I Semester I Year 016/017 SBM International Class Lecturer: Dr. Rinovia Simanjuntak 1.1 Functions Function A function is a rule that
Chapter 1 Functions, Graphs, and Limits MA1103 Business Mathematics I Semester I Year 016/017 SBM International Class Lecturer: Dr. Rinovia Simanjuntak 1.1 Functions Function A function is a rule that
Lesson Remember. Finding Domain and Range from a Graph EXAMPLE. Key Vocabulary
 0. Lesson Ke Vocabular function domain range function form Functions A function is a relationship that pairs each input with eactl one output. The domain is the set of all possible input values. The range
0. Lesson Ke Vocabular function domain range function form Functions A function is a relationship that pairs each input with eactl one output. The domain is the set of all possible input values. The range
1. Simplify each expression and write all answers without negative exponents. for variable L.
 MATH 0: PRACTICE FINAL Spring, 007 Chapter # :. Simplif each epression and write all answers without negative eponents. ( ab ) Ans. b 9 7a 6 Ans.. Solve each equation. 5( ) = 5 5 Ans. man solutions + 7
MATH 0: PRACTICE FINAL Spring, 007 Chapter # :. Simplif each epression and write all answers without negative eponents. ( ab ) Ans. b 9 7a 6 Ans.. Solve each equation. 5( ) = 5 5 Ans. man solutions + 7
Chapter 4. Introduction to Mathematical Modeling. Types of Modeling. 1) Linear Modeling 2) Quadratic Modeling 3) Exponential Modeling
 Chapter 4 Introduction to Mathematical Modeling Tpes of Modeling 1) Linear Modeling ) Quadratic Modeling ) Eponential Modeling Each tpe of modeling in mathematics is determined b the graph of equation
Chapter 4 Introduction to Mathematical Modeling Tpes of Modeling 1) Linear Modeling ) Quadratic Modeling ) Eponential Modeling Each tpe of modeling in mathematics is determined b the graph of equation
10.4 Nonlinear Inequalities and Systems of Inequalities. OBJECTIVES 1 Graph a Nonlinear Inequality. 2 Graph a System of Nonlinear Inequalities.
 Section 0. Nonlinear Inequalities and Sstems of Inequalities 6 CONCEPT EXTENSIONS For the eercises below, see the Concept Check in this section.. Without graphing, how can ou tell that the graph of + =
Section 0. Nonlinear Inequalities and Sstems of Inequalities 6 CONCEPT EXTENSIONS For the eercises below, see the Concept Check in this section.. Without graphing, how can ou tell that the graph of + =
Math Final Review. 1. Match the following functions with the given graphs without using your calculator: f 5 (x) = 5x3 25 x.
 Mat 5 Final Review. Matc te following functions wit te given graps witout using our calculator: f () = /3 f () = /3 f 3 () = 4 5 (A) f 4 () = 54 5 + 5 (B) f 5 () = 53 5 + 5 (C) (D) f 6 () = 5 5 + 5 (E)
Mat 5 Final Review. Matc te following functions wit te given graps witout using our calculator: f () = /3 f () = /3 f 3 () = 4 5 (A) f 4 () = 54 5 + 5 (B) f 5 () = 53 5 + 5 (C) (D) f 6 () = 5 5 + 5 (E)
Functions. Introduction CHAPTER OUTLINE
 Functions,00 P,000 00 0 970 97 980 98 990 99 000 00 00 Figure Standard and Poor s Inde with dividends reinvested (credit "bull": modification of work b Praitno Hadinata; credit "graph": modification of
Functions,00 P,000 00 0 970 97 980 98 990 99 000 00 00 Figure Standard and Poor s Inde with dividends reinvested (credit "bull": modification of work b Praitno Hadinata; credit "graph": modification of
Solve each system by graphing. Check your solution. y =-3x x + y = 5 y =-7
 Practice Solving Sstems b Graphing Solve each sstem b graphing. Check our solution. 1. =- + 3 = - (1, ). = 1 - (, 1) =-3 + 5 3. = 3 + + = 1 (, 3). =-5 = - 7. = 3-5 3 - = 0 (1, 5) 5. -3 + = 5 =-7 (, 7).
Practice Solving Sstems b Graphing Solve each sstem b graphing. Check our solution. 1. =- + 3 = - (1, ). = 1 - (, 1) =-3 + 5 3. = 3 + + = 1 (, 3). =-5 = - 7. = 3-5 3 - = 0 (1, 5) 5. -3 + = 5 =-7 (, 7).
Systems of Equations and Inequalities
 Sstems of Equations and Inequalities 7 7. Linear and Nonlinear Sstems of Equations 7. Two-Variable Linear Sstems 7.3 Multivariable Linear Sstems 7. Partial Fractions 7.5 Sstems of Inequalities 7.6 Linear
Sstems of Equations and Inequalities 7 7. Linear and Nonlinear Sstems of Equations 7. Two-Variable Linear Sstems 7.3 Multivariable Linear Sstems 7. Partial Fractions 7.5 Sstems of Inequalities 7.6 Linear
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 2) A) Not defined B) - 2 5
 Stud Guide for TEST I Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the slope of the line passing through the given pair of points. )
Stud Guide for TEST I Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the slope of the line passing through the given pair of points. )
Review for Intermediate Algebra (MATD 0390) Final Exam Oct 2009
 Review for Intermediate Algebra (MATD 090) Final Eam Oct 009 Students are epected to know all relevant formulas, including: All special factoring formulas Equation of a circle All formulas for linear equations
Review for Intermediate Algebra (MATD 090) Final Eam Oct 009 Students are epected to know all relevant formulas, including: All special factoring formulas Equation of a circle All formulas for linear equations
1.1. Use a Problem Solving Plan. Read a problem and make a plan. Goal p Use a problem solving plan to solve problems. VOCABULARY. Formula.
 . Georgia Performance Standard(s) MMPd, MMPa Your Notes Use a Problem Solving Plan Goal p Use a problem solving plan to solve problems. VOCABULARY Formula A PROBLEM SOLVING PLAN Step Read the problem carefull.
. Georgia Performance Standard(s) MMPd, MMPa Your Notes Use a Problem Solving Plan Goal p Use a problem solving plan to solve problems. VOCABULARY Formula A PROBLEM SOLVING PLAN Step Read the problem carefull.
MAT 120 Test 1 May 20, 2013 (4:00 4:50 PM)
 Name: Academic Integrit Signature: I have abided b the UNCG Academic Integrit Polic. Read all of the following information before starting the eam: It is to our advantage to answer ALL of the 0 questions.
Name: Academic Integrit Signature: I have abided b the UNCG Academic Integrit Polic. Read all of the following information before starting the eam: It is to our advantage to answer ALL of the 0 questions.
Logarithms. Bacteria like Staph aureus are very common.
 UNIT 10 Eponentials and Logarithms Bacteria like Staph aureus are ver common. Copright 009, K1 Inc. All rights reserved. This material ma not be reproduced in whole or in part, including illustrations,
UNIT 10 Eponentials and Logarithms Bacteria like Staph aureus are ver common. Copright 009, K1 Inc. All rights reserved. This material ma not be reproduced in whole or in part, including illustrations,
Chapter 4 Page 1 of 16. Lecture Guide. Math College Algebra Chapter 4. to accompany. College Algebra by Julie Miller
 Chapter 4 Page 1 of 16 Lecture Guide Math 105 - College Algebra Chapter 4 to accompan College Algebra b Julie Miller Corresponding Lecture Videos can be found at Prepared b Stephen Toner & Nichole DuBal
Chapter 4 Page 1 of 16 Lecture Guide Math 105 - College Algebra Chapter 4 to accompan College Algebra b Julie Miller Corresponding Lecture Videos can be found at Prepared b Stephen Toner & Nichole DuBal
c) domain {x R, x 3}, range {y R}
 Answers Chapter 1 Functions 1.1 Functions, Domain, and Range 1. a) Yes, no vertical line will pass through more than one point. b) No, an vertical line between = 6 and = 6 will pass through two points..
Answers Chapter 1 Functions 1.1 Functions, Domain, and Range 1. a) Yes, no vertical line will pass through more than one point. b) No, an vertical line between = 6 and = 6 will pass through two points..
CHAPTER 1 Functions, Graphs, and Limits
 CHAPTER Functions, Graphs, and Limits Section. The Cartesian Plane and the Distance Formula.......... Section. Graphs of Equations........................ 8 Section. Lines in the Plane and Slope....................
CHAPTER Functions, Graphs, and Limits Section. The Cartesian Plane and the Distance Formula.......... Section. Graphs of Equations........................ 8 Section. Lines in the Plane and Slope....................
NCC Precalculus Partnership Program Final Examination, 2004
 NCC Precalculus Partnership Program Final Eamination, 2004 Part I: Answer onl 20 of the 25 questions below. Each question is worth 2 points. Place our answers on the answer sheet provided. Write the word
NCC Precalculus Partnership Program Final Eamination, 2004 Part I: Answer onl 20 of the 25 questions below. Each question is worth 2 points. Place our answers on the answer sheet provided. Write the word
MATH 1710 College Algebra Final Exam Review
 MATH 7 College Algebra Final Eam Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. ) There were 80 people at a pla. The admission price was $
MATH 7 College Algebra Final Eam Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. ) There were 80 people at a pla. The admission price was $
MATH 112 Final Exam Study Questions
 MATH Final Eam Study Questions Spring 08 Note: Certain eam questions have been more challenging for students. Questions marked (***) are similar to those challenging eam questions.. A company produces
MATH Final Eam Study Questions Spring 08 Note: Certain eam questions have been more challenging for students. Questions marked (***) are similar to those challenging eam questions.. A company produces
Fair Game Review. Chapter 2. and y = 5. Evaluate the expression when x = xy 2. 4x. Evaluate the expression when a = 9 and b = 4.
 Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Evaluate the epression when = and =.... 0 +. 8( ) Evaluate the epression when a = 9 and b =.. ab. a ( b + ) 7. b b 7 8. 7b + ( ab ) 9. You go to the movies with five
Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Evaluate the epression when = and =.... 0 +. 8( ) Evaluate the epression when a = 9 and b =.. ab. a ( b + ) 7. b b 7 8. 7b + ( ab ) 9. You go to the movies with five
Essential Question How can you determine the number of solutions of a linear system?
 .1 TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS A.3.A A.3.B Solving Linear Sstems Using Substitution Essential Question How can ou determine the number of solutions of a linear sstem? A linear sstem is consistent
.1 TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS A.3.A A.3.B Solving Linear Sstems Using Substitution Essential Question How can ou determine the number of solutions of a linear sstem? A linear sstem is consistent
x. 4. 2x 10 4x. 10 x
 CCGPS UNIT Semester 1 COORDINATE ALGEBRA Page 1 of Reasoning with Equations and Quantities Name: Date: Understand solving equations as a process of reasoning and eplain the reasoning MCC9-1.A.REI.1 Eplain
CCGPS UNIT Semester 1 COORDINATE ALGEBRA Page 1 of Reasoning with Equations and Quantities Name: Date: Understand solving equations as a process of reasoning and eplain the reasoning MCC9-1.A.REI.1 Eplain
Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions 5.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs
 Ch 5 Alg Note Sheet Ke Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions 5.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs Definition: Standard Form of a Quadratic Function The
Ch 5 Alg Note Sheet Ke Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions 5.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs Definition: Standard Form of a Quadratic Function The
Math 084 Spring 2014 Exam 3 (Final) Preperation Ch 4 et al v01 Dressler. Name
 Math 0 Spring 01 Eam 3 (Final) Preperation Ch et al v01 Dressler Name Determine whether the ordered pair is a solution of the sstem. 1) (-3, ) + = 3 - = -9 Solve the sstem b graphing. If there is no solution
Math 0 Spring 01 Eam 3 (Final) Preperation Ch et al v01 Dressler Name Determine whether the ordered pair is a solution of the sstem. 1) (-3, ) + = 3 - = -9 Solve the sstem b graphing. If there is no solution
One of your primary goals in mathematics should be to become a good problem solver. It helps to approach a problem with a plan.
 PROBLEM SOLVING One of our primar goals in mathematics should be to become a good problem solver. It helps to approach a problem with a plan. Step Step Step Step Understand the problem. Read the problem
PROBLEM SOLVING One of our primar goals in mathematics should be to become a good problem solver. It helps to approach a problem with a plan. Step Step Step Step Understand the problem. Read the problem
Review of Elementary Algebra Content
 Review of Elementar Algebra Content 0 1 Table of Contents Fractions...1 Integers...5 Order of Operations...9 Eponents...11 Polnomials...18 Factoring... Solving Linear Equations...1 Solving Linear Inequalities...
Review of Elementar Algebra Content 0 1 Table of Contents Fractions...1 Integers...5 Order of Operations...9 Eponents...11 Polnomials...18 Factoring... Solving Linear Equations...1 Solving Linear Inequalities...
Functions. Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of an exponential function? ) x e. f (x) = ( 1 3 ) x f.
 7. TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS A..A Eponential Growth and Deca Functions Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of an eponential function? You can use a graphing
7. TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS A..A Eponential Growth and Deca Functions Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of an eponential function? You can use a graphing
a. In the statement "Height is a function of weight," which is the independent variable and which is the dependent variable?
 1. The weights and heights of si mathematics students are given in the table. Answer parts a through e. Weight (lb.) Height (cm) 157 19 11 155 1 11 175 17 157 15 17 17 a. In the statement "Height is a
1. The weights and heights of si mathematics students are given in the table. Answer parts a through e. Weight (lb.) Height (cm) 157 19 11 155 1 11 175 17 157 15 17 17 a. In the statement "Height is a
9 (0, 3) and solve equations to earn full credit.
 Math 0 Intermediate Algebra II Final Eam Review Page of Instructions: (6, ) Use our own paper for the review questions. For the final eam, show all work on the eam. (-6, ) This is an algebra class do not
Math 0 Intermediate Algebra II Final Eam Review Page of Instructions: (6, ) Use our own paper for the review questions. For the final eam, show all work on the eam. (-6, ) This is an algebra class do not
Algebra Semester 1 Final Exam Review Name: Hour: Date:
 Algebra Semester Final Exam Review Name: Hour: Date: CHAPTER Learning Target: I can appl the order of operations to evaluate expressions. Simplif the following expressions (combine like terms). x + x +
Algebra Semester Final Exam Review Name: Hour: Date: CHAPTER Learning Target: I can appl the order of operations to evaluate expressions. Simplif the following expressions (combine like terms). x + x +
1.5. Analyzing Graphs of Functions. The Graph of a Function. What you should learn. Why you should learn it. 54 Chapter 1 Functions and Their Graphs
 0_005.qd /7/05 8: AM Page 5 5 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs.5 Analzing Graphs of Functions What ou should learn Use the Vertical Line Test for functions. Find the zeros of functions. Determine intervals
0_005.qd /7/05 8: AM Page 5 5 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs.5 Analzing Graphs of Functions What ou should learn Use the Vertical Line Test for functions. Find the zeros of functions. Determine intervals
4.2 Start Thinking. 4.2 Warm Up. 4.2 Cumulative Review Warm Up
 . Start Thinking How can ou find a linear equation from a graph for which ou do not know the -intercept? Describe a situation in which ou might know the slope but not the -intercept. Provide a graph of
. Start Thinking How can ou find a linear equation from a graph for which ou do not know the -intercept? Describe a situation in which ou might know the slope but not the -intercept. Provide a graph of
Skills Practice 8-9. Solving Systems of Equations. (1, 2) no solution (0, 2) (1, 3) infinitely many ( 2, 0) (4, 3) (2, 2) (12, 4) (3, 2) (13, 3)
 8-9 NME TE PERI Skills Practice Solving Sstems of Equations Solve each sstem of equations b graphing. 1. 4.. 4 8 (1, ) 4 8 (0, ) (1, ) no solution (0, ) 4. 4 5. 4 1 6. 4 1 4 4 1 (1, ) 4 4 (, 0) 4 (1, )
8-9 NME TE PERI Skills Practice Solving Sstems of Equations Solve each sstem of equations b graphing. 1. 4.. 4 8 (1, ) 4 8 (0, ) (1, ) no solution (0, ) 4. 4 5. 4 1 6. 4 1 4 4 1 (1, ) 4 4 (, 0) 4 (1, )
3-1. Solving Systems Using Tables and Graphs. Concept Summary. Graphical Solutions of Linear Systems VOCABULARY TEKS FOCUS ESSENTIAL UNDERSTANDING
 3- Solving Sstems Using Tables and Graphs TEKS FOCUS VOCABULARY Foundational to TEKS (3)(A) Formulate sstems of equations, including sstems consisting of three linear equations in three variables and sstems
3- Solving Sstems Using Tables and Graphs TEKS FOCUS VOCABULARY Foundational to TEKS (3)(A) Formulate sstems of equations, including sstems consisting of three linear equations in three variables and sstems
c. x x < 60 d. x x =9. What are the first four terms of the sequence? a. 12, 21, 30, 39 b.
 Algebra I Unit Reasoning with Linear Equations and Inequalities Post Test... A famil s cell phone plan costs $ per month for, minutes and cents per minute over the limit. This month, the famil paid $..
Algebra I Unit Reasoning with Linear Equations and Inequalities Post Test... A famil s cell phone plan costs $ per month for, minutes and cents per minute over the limit. This month, the famil paid $..
