f (D) = 1 chdh h=o DESIGN OF MULTILEVEL PSEUDORANDOM SIGNALS
|
|
|
- Sheila Fleming
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
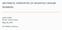
1 DESIGN OF MULTILEVEL PSEUDORANDOM SIGNALS FOR SPECIFIED HARMONIC CONTENT H. A. Barker Pseudorandom signals have been used in system identification for many years, usually in their binary form, usually for the identification of linear systems and usually because of their correlation propemes.' Pseudorandom binary signals are unsuitable for the identification of nonlinear systems but pseudorandom ternary signals have been used for the purpose, exploiting their higher-order correlation properties.2 In contrast, system identification exploiting the harmonic properties of pseudorandom signals has received considerably less attention, although the author has described how these properties can be used in the identification of both linear and nonlinear 4,5 systems. The principal factor which militates against exploiting the harmonic propemes of multilevel pseudorandom signals for system identification is the sheer complexity of the underlying theory and its dependence on the algebra of finite fields.6 The seminal paper on the generation and correlation propemes of these signals by Zierler ' is difficult enough, and there is no equivalent on harmonic properties. To some extent, these difficulties can be circumvented by constructing sum and product tables to define the algebraic operations involved.8 These tables can be constructed for any Galois field GF( q) with q field elements, where q is a power of a prime p, given by k q=p In these tables, the field elements are taken as the integers modulo-q, and for a prime field, when k = 1, the addition and multiplication operations are simply modulo-q arithmetic, as seen in Tables la and lb for the case q = 7. For an extension field, when k > 1, the field operators cannot be defined in this simple way, and it is necessary to invoke a special procedure for the construction of the tables. Once consnucted, however, the tables for an extension field may be used in the same way as those for a prime field, and an example for the case q = 9 is given in Tables 2a and 2b. In what follows, the primitive elements of a field play an important part. These elements are easily identified from the product tables as those for which the powers generate. all the nonzero elements of the field. For example, from Tables Ib and 2b the primitive elements of GF(7) are 3 and 5 and those of GF(9) are 3, 4, 6, and 8. The tables can also be used to generate a sequence { s,} by means of a recurrence relationship n h=o as shown in Figure 1. If the characteristic polynomial f(d) given by n f (D) = 1 chdh h=o (3) Professor H. A. Barker is with the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University College of Swansea, Swansea, Wales, United Kingdom 2/1
2 is primitive, then the sequence {s,} is a maximum-length m-sequence, with period P given by P=q"-l (4) Comprehensive tables of primitive polynomials are available for this purp~se.'~ lo An important characteristic of an m-sequence, which influences the harmonic content of pseudorandom signals derived from it, is that a period of P = qn - 1 members may be divided into q - 1 subperiods of (q" - 1) / (q - 1) members, and any subperiod may be formed by multiplying the members of the previous subperiod by a primitive element g. That is as shown in Figure 2. Tables 3a and 3b show 3 subperiods of m-sequences in GF(7) and GF(9) for which the primitive element multiplier is 3. If every element e of the Galois field GF(q) is now mapped into a real number x(e), then the m-sequence {si} is mapped into a pseudorandom sequence {xi}, for which {G> = (5 (5%)) ( 6) as shown in Figure 2. A period of the pseudorandom sequence {x,} will also have q - 1 subperiods, but the relationships between them will depend not only on equation 5 but also on the mapping, SO this too influences the harmonic content of the pseudorandom signal 3: (t) derived from it. The pseudorandom signals considered here are those derived from the pseudorandom sequence { z,} by using a zero-order-hold to create a stepwise-continuous signal z (t). The harmonic content of the pseudorandom signal z (t) is completely characterized by the frequency response of the zero-orderhold and the discrete Fourier transform {xk} of the pseudorandom sequence {si}, given by. P-1 1 P :=o.xk = - 1 xiexp(-2~jik/p) and it is through the magnitude 1 xk I of the transform sequence member xk that the presence or absence of the k-th harmonic of the pseudorandom signal x(t) is determined. As the period P is not normally a power of 2, the radix-2 fast Fourier transform cannot normally be used for this transformation, but efficient algorithms are nevertheless available for computing {xk} from {xi},ll, The transform sequence {X,} also has period P = qn - 1, and a consequence of the subperiodicity of the m-sequence (5,) from which it is derived is that this period may also be divided into subperiods. In the case of the transform sequence, however, a period of P = q" - 1 members divides into (qn- 1) / ( q - 1) subperiods of q - 1 members, as shown in Figure 2. With the exception of X,P, which reflects the mean value of the pseudorandom sequence {xi}, the magnitudes of corresponding members in the subperiods are equal, that is k#rp and only the phases are different. This means that there are at most q - 1 independent harmonics available for allocation in a design, and this is quite restrictive when q is small. Tables 4a and 4b show 2 subperiods of the transform sequence magnitudes of a 7-level and a 9-level pseudorandom sequence. (7) 2/2
3 To proceed further, it is necessary to use a formula derived by the author for the magnitude 1 -yk I of the k-th harmonic. This uses the discrete Fourier transform of a sequence with q - 1 members which are the levels of the pseudorandom sequence {z,} mapped from the nonzero elements of GF(q) generated as the powers of a primitive element g. that is from the sequence z (1) z(g) z (g2)... z (91)... 5 (99-2) for which the discrete Fourier transform {Mk} is given by (9) The magnitude of the k-harmonic 1 1 is then obtained as q-1 P q - l u - -1qn-1.k40 + (q"-l - 1) / (q- 1). (0) 1 q-1 n-l -- - p 4 I.& k=rp I Xk I = p q W O - (011 k = s (q - 1) # rp (10) k # s (q - 1) uskg this result, a mapping may be chosen which eliminates all harmonics that are multiples of a prime number v, that is for which If v # q - 1, this implies that M,, = 0 all r > 0 (12) This equation can always be satisfied if v is a factor of q - 1, because equation 9 can then be re-arranged as (q - 1) /U groups of v terms, so that equation 12 becomes which is satisfied when U-1 This condition does not involve z(o), but it involves all the other levels of the pseudorandom sequence {xi}, and consequently in equation 9 M O = 0 (15) Now because q - 1 and its multiples are themselves multiples of U, it is also necessary to remove the corresponding harmonics, and from equation 10 and 15 this requires that and consequently XO is also zero, thus accounting for all harmonics. 3 (0) = 0 (16) 2/3
4 Using these results it is easy to design a pseudorandom signal so that the k-th harmonic is absent, when k is a multiple of any one of a number of primes v1,v2,....vh. The number of levels, q, of the pseudorandom signal must be chosen so that q - 1 is a multiple of each of the primes, the level mapped from the zero element of the Galois field GF(q) must be zero and the levels mapped from the nonzero elements of the field must satisfy equation 14 for each of the primes 2'1, U?,..., Vh. For example, suppose that a pseudorandom signal is to be designed in which harmonics which are multiples of 2 and 3 are absent. This requires that the number of levels is at least 2 x = 7, SO the pseudorandom signal may be based on an m-sequence in GF(7), for which the sum and product tables are Tables la and lb and one of the primitive elements is 3. Equations 14 and 16 give the conditions x(0) = 0 ~(3') ~ ( 3 =z(l)+x(6)=0 ~ ) I ( (34) = 2 (3) + I(4) = 0 2 (32) + z (35) = z(2) + 5 (5) = 0 z(30) +x(32) +z(34) =z(l)+z(2)+z(4)=0 2 (3l) + I (33) + I (35) = z (3) + 5 (6) + I (5) = 0 (17) with typical solution Two subperiods of the transform sequence magnitudes of a 7-level Pseudorandom sequence with this mapping are shown in Table 5. References 1. BRIGGS, P.A.N., HAMMOND, P.H., HUGHES, M.T.G., and PLUMB, G.O. : " Correlation analysis of process dynamics using pseudo-random binary test perturbations ". Proc. Inst Mech. Engrs., Vol 179, pp 37-51, BARKER. H.A., and DAVY, R.W. : " Measurement of second-order Volterra kernels uskg pseudorandom signals ", Int. J. Control, Vol 27, pp , BARKER, H.A., and DAVY, R.W. : " System identification using pseudorandom signals and the discrete Fourier transform ", Proc. IEE, Vol 122, pp , BARKER, H.A., and DAVY, R.W. : " 2nd-order Volterra kernel measurement using pseudorandom ternary signals and their discrete Fourier transforms ", Proc. IEE, Vol 126, pp , BARKER, H.A., and AL-HILAL, M.H. : " Nonlinear system identification using pseudorandom signals with partially orthogonal transforms ". Roc. FAC Symposium on Identification and System Parameter Estimation, York, 1985, pp ALBERT, A.A. : " Fundamental concepts of higher algebra ", University of Chicago Press, Chicago, ZIEFLER, N. : " Linear recurring sequences ", J. Soc. Ind. Math., Vol 7, pp 31-48, BARKER, H.A. : " Sum and product tables for Galois fields ", Int. J. Math. Educ. Sci. Technol., Vol 17, pp , CHURCH, R. : " Tables of irreducible polynomials fnz the first four prime moduli '0 Ann. Math., Vol 36, pp , /4
5 1% ALA", J.D., and KNUTH, D.E. :" Tables of finite fields ", Sankhya, Vol 26, pp , SINGLETON, R.C. :" An algorithm for computing the mixed radix fast Fourier transform ", IEEE TEU~S., Vol AU-17, pp , WINOGRAD, S. : " On computing the discrete Fourier nansform '0 Roc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (U.S.), Vol 73, pp , SILVERMAN, H.F. : " An introduction to programming the Winograd fast Fourier transform algorithm (WFTA) ", IEEE Trans., Vol. ASSP-25, pp , I I-rt SUBPERIOD tnd SUBPERIOD Srd SUBPERIOD 4 IY 1% ( I - 1 )-th SUBPERIOD p s. ' Q 1 c I-sf SUBPERIOD 2nd SUBPERIOD 3th SUBPERIOD 6th SUBPERIOD 5-th SUBPERIOD In-' th SUBPERIOD 'k '&++l xk+.xq-l) Jt+WI-l) 'k4q-l) c- q -I Figure 2 m-sequence, pseudorandom sequence and transform sequence 2/5
6 x101112/3/415(6 olololololololo Table la Sum Table for GF(7) Table lb Product Table for GF(7) Table 2a Sum Table for GF(9) Table 3a Three subperiods of an m-sequence in GF(7) Table 3b Three subperiods of an m-sequence in GF(9) [ Table 4a Two subperiods of transform magnitudes of a 7-level pseudorandom sequence I OS I.lo OS I Table 4b Two subperiods of transform magnitudes of a 9-level pseudorandom sequence HARMONIC MAGNITUDE Table 5 Two subperiods of transform magnitudes of a 7-level pseudorandom sequence with harmonic multiples of 2 and 3 suppressed
Construction of Galois Fields of Characteristic
 Construction of Galois Fields of Characteristic Two and Irreducible Polynomials By J. D. Swift 1. Introduction. The primary purpose of this paper is to provide a practical method of constructing Galois
Construction of Galois Fields of Characteristic Two and Irreducible Polynomials By J. D. Swift 1. Introduction. The primary purpose of this paper is to provide a practical method of constructing Galois
New algebraic decoding method for the (41, 21,9) quadratic residue code
 New algebraic decoding method for the (41, 21,9) quadratic residue code Mohammed M. Al-Ashker a, Ramez Al.Shorbassi b a Department of Mathematics Islamic University of Gaza, Palestine b Ministry of education,
New algebraic decoding method for the (41, 21,9) quadratic residue code Mohammed M. Al-Ashker a, Ramez Al.Shorbassi b a Department of Mathematics Islamic University of Gaza, Palestine b Ministry of education,
CSCE 564, Fall 2001 Notes 6 Page 1 13 Random Numbers The great metaphysical truth in the generation of random numbers is this: If you want a function
 CSCE 564, Fall 2001 Notes 6 Page 1 13 Random Numbers The great metaphysical truth in the generation of random numbers is this: If you want a function that is reasonably random in behavior, then take any
CSCE 564, Fall 2001 Notes 6 Page 1 13 Random Numbers The great metaphysical truth in the generation of random numbers is this: If you want a function that is reasonably random in behavior, then take any
Galois fields/1. (M3) There is an element 1 (not equal to 0) such that a 1 = a for all a.
 Galois fields 1 Fields A field is an algebraic structure in which the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division (except by zero) can be performed, and satisfy the usual rules. More
Galois fields 1 Fields A field is an algebraic structure in which the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division (except by zero) can be performed, and satisfy the usual rules. More
M 2 + s 2. Note that the required matrix A when M 2 + s 2 was also obtained earlier by Gordon [2]. (2.2) x -alxn-l-aex n-2 an
![M 2 + s 2. Note that the required matrix A when M 2 + s 2 was also obtained earlier by Gordon [2]. (2.2) x -alxn-l-aex n-2 an M 2 + s 2. Note that the required matrix A when M 2 + s 2 was also obtained earlier by Gordon [2]. (2.2) x -alxn-l-aex n-2 an](/thumbs/94/119028444.jpg) SIAM J. ALG. DISC. METH. Vol. 1, No. 1, March 1980 1980 Society for. Industrial and Applied Mathematics 0196-52/80/0101-0014 $01.00/0 ON CONSTRUCTION OF MATRICES WITH DISTINCT SUBMATRICES* SHARAD V. KANETKAR"
SIAM J. ALG. DISC. METH. Vol. 1, No. 1, March 1980 1980 Society for. Industrial and Applied Mathematics 0196-52/80/0101-0014 $01.00/0 ON CONSTRUCTION OF MATRICES WITH DISTINCT SUBMATRICES* SHARAD V. KANETKAR"
Functions on Finite Fields, Boolean Functions, and S-Boxes
 Functions on Finite Fields, Boolean Functions, and S-Boxes Claude Shannon Institute www.shannoninstitute.ie and School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Ireland 1 July, 2013 Boolean Function
Functions on Finite Fields, Boolean Functions, and S-Boxes Claude Shannon Institute www.shannoninstitute.ie and School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Ireland 1 July, 2013 Boolean Function
17 Galois Fields Introduction Primitive Elements Roots of Polynomials... 8
 Contents 17 Galois Fields 2 17.1 Introduction............................... 2 17.2 Irreducible Polynomials, Construction of GF(q m )... 3 17.3 Primitive Elements... 6 17.4 Roots of Polynomials..........................
Contents 17 Galois Fields 2 17.1 Introduction............................... 2 17.2 Irreducible Polynomials, Construction of GF(q m )... 3 17.3 Primitive Elements... 6 17.4 Roots of Polynomials..........................
New Negative Latin Square Type Partial Difference Sets in Nonelementary Abelian 2-groups and 3-groups
 New Negative Latin Square Type Partial Difference Sets in Nonelementary Abelian 2-groups and 3-groups John Polhill Department of Mathematics, Computer Science, and Statistics Bloomsburg University Bloomsburg,
New Negative Latin Square Type Partial Difference Sets in Nonelementary Abelian 2-groups and 3-groups John Polhill Department of Mathematics, Computer Science, and Statistics Bloomsburg University Bloomsburg,
Constructions of Nonbinary Quasi-Cyclic LDPC Codes: A Finite Field Approach
 Constructions of Nonbinary Quasi-Cyclic LDPC Codes: A Finite Field Approach Shu Lin, Shumei Song, Lan Lan, Lingqi Zeng and Ying Y Tai Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of California,
Constructions of Nonbinary Quasi-Cyclic LDPC Codes: A Finite Field Approach Shu Lin, Shumei Song, Lan Lan, Lingqi Zeng and Ying Y Tai Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of California,
Some Results on the Arithmetic Correlation of Sequences
 Some Results on the Arithmetic Correlation of Sequences Mark Goresky Andrew Klapper Abstract In this paper we study various properties of arithmetic correlations of sequences. Arithmetic correlations are
Some Results on the Arithmetic Correlation of Sequences Mark Goresky Andrew Klapper Abstract In this paper we study various properties of arithmetic correlations of sequences. Arithmetic correlations are
Infinite Sequences, Series Convergence and the Discrete Time Fourier Transform over Finite Fields
 Infinite Sequences, Series Convergence and the Discrete Time Fourier Transform over Finite Fields R M Campello de Souza M M Campello de Souza H M de Oliveira M M Vasconcelos Depto de Eletrônica e Sistemas,
Infinite Sequences, Series Convergence and the Discrete Time Fourier Transform over Finite Fields R M Campello de Souza M M Campello de Souza H M de Oliveira M M Vasconcelos Depto de Eletrônica e Sistemas,
Graduate Preliminary Examination
 Graduate Preliminary Examination Algebra II 18.2.2005: 3 hours Problem 1. Prove or give a counter-example to the following statement: If M/L and L/K are algebraic extensions of fields, then M/K is algebraic.
Graduate Preliminary Examination Algebra II 18.2.2005: 3 hours Problem 1. Prove or give a counter-example to the following statement: If M/L and L/K are algebraic extensions of fields, then M/K is algebraic.
A field F is a set of numbers that includes the two numbers 0 and 1 and satisfies the properties:
 Byte multiplication 1 Field arithmetic A field F is a set of numbers that includes the two numbers 0 and 1 and satisfies the properties: F is an abelian group under addition, meaning - F is closed under
Byte multiplication 1 Field arithmetic A field F is a set of numbers that includes the two numbers 0 and 1 and satisfies the properties: F is an abelian group under addition, meaning - F is closed under
A NEW GENERAL SERIES OF BALANCED INCOMPLETE BLOCK DESIGNS
 A NEW GENERAL SERIES OF BALANCED INCOMPLETE BLOCK DESIGNS C. RAMANUJACHARYULU 0. Summary. Let v be any integer with si the least prime power factor, the other prime power factors being s2,, sm. Assume
A NEW GENERAL SERIES OF BALANCED INCOMPLETE BLOCK DESIGNS C. RAMANUJACHARYULU 0. Summary. Let v be any integer with si the least prime power factor, the other prime power factors being s2,, sm. Assume
Construction of latin squares of prime order
 Construction of latin squares of prime order Theorem. If p is prime, then there exist p 1 MOLS of order p. Construction: The elements in the latin square will be the elements of Z p, the integers modulo
Construction of latin squares of prime order Theorem. If p is prime, then there exist p 1 MOLS of order p. Construction: The elements in the latin square will be the elements of Z p, the integers modulo
Construction of PBIBD (2) Designs Using MOLS
 Intern. J. Fuzzy Mathematical Archive Vol. 3, 013, 4-49 ISSN: 30 34 (P), 30 350 (online) Published on 4 December 013 www.researchmathsci.org International Journal of R.Jaisankar 1 and M.Pachamuthu 1 Department
Intern. J. Fuzzy Mathematical Archive Vol. 3, 013, 4-49 ISSN: 30 34 (P), 30 350 (online) Published on 4 December 013 www.researchmathsci.org International Journal of R.Jaisankar 1 and M.Pachamuthu 1 Department
PETERSON'S TABLE OF IRREDUCIBLE POLYNOMIALS OVER GF(2)
 PETERSON'S TABLE OF IRREDUCIBLE POLYNOMIALS OVER GF(2) This table was taken from Error-Correcting Codes by W. Wesley Peterson, MIT Press (1970), pages 251-155. This table is to be used only by students
PETERSON'S TABLE OF IRREDUCIBLE POLYNOMIALS OVER GF(2) This table was taken from Error-Correcting Codes by W. Wesley Peterson, MIT Press (1970), pages 251-155. This table is to be used only by students
Chapter 4 Mathematics of Cryptography
 Chapter 4 Mathematics of Cryptography Part II: Algebraic Structures Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 4.1 Chapter 4 Objectives To review the concept
Chapter 4 Mathematics of Cryptography Part II: Algebraic Structures Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 4.1 Chapter 4 Objectives To review the concept
Field Theory Problems
 Field Theory Problems I. Degrees, etc. 1. Answer the following: (a Find u R such that Q(u = Q( 2, 3 5. (b Describe how you would find all w Q( 2, 3 5 such that Q(w = Q( 2, 3 5. 2. If a, b K are algebraic
Field Theory Problems I. Degrees, etc. 1. Answer the following: (a Find u R such that Q(u = Q( 2, 3 5. (b Describe how you would find all w Q( 2, 3 5 such that Q(w = Q( 2, 3 5. 2. If a, b K are algebraic
Chapter 6 Reed-Solomon Codes. 6.1 Finite Field Algebra 6.2 Reed-Solomon Codes 6.3 Syndrome Based Decoding 6.4 Curve-Fitting Based Decoding
 Chapter 6 Reed-Solomon Codes 6. Finite Field Algebra 6. Reed-Solomon Codes 6.3 Syndrome Based Decoding 6.4 Curve-Fitting Based Decoding 6. Finite Field Algebra Nonbinary codes: message and codeword symbols
Chapter 6 Reed-Solomon Codes 6. Finite Field Algebra 6. Reed-Solomon Codes 6.3 Syndrome Based Decoding 6.4 Curve-Fitting Based Decoding 6. Finite Field Algebra Nonbinary codes: message and codeword symbols
Binary Sequences with Optimal Autocorrelation
 Cunsheng DING, HKUST, Kowloon, HONG KONG, CHINA September 2008 Outline of this talk Difference sets and almost difference sets Cyclotomic classes Introduction of binary sequences with optimal autocorrelation
Cunsheng DING, HKUST, Kowloon, HONG KONG, CHINA September 2008 Outline of this talk Difference sets and almost difference sets Cyclotomic classes Introduction of binary sequences with optimal autocorrelation
Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) 4-bit LFSR
 Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) These are n-bit counters exhibiting pseudo-random behavior. Built from simple shift-registers with a small number of xor gates. Used for: random number generation
Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) These are n-bit counters exhibiting pseudo-random behavior. Built from simple shift-registers with a small number of xor gates. Used for: random number generation
Divisibility of Trinomials by Irreducible Polynomials over F 2
 Divisibility of Trinomials by Irreducible Polynomials over F 2 Ryul Kim Faculty of Mathematics and Mechanics Kim Il Sung University, Pyongyang, D.P.R.Korea Wolfram Koepf Department of Mathematics University
Divisibility of Trinomials by Irreducible Polynomials over F 2 Ryul Kim Faculty of Mathematics and Mechanics Kim Il Sung University, Pyongyang, D.P.R.Korea Wolfram Koepf Department of Mathematics University
xp = 9- ZP, yp + z y (mod p), (2) SUMMARY OF RESULTS AND PROOFS CONCERNING FERMA T'S DZPARTMZNT OF PURi MATHZMATICS, UNIVZRSITY of TExAs
 VOL. 12, 1926 MA THEMA TICS: H. S. VANDI VER 767 gether in a subcontinuum of M. A point set M is strongly connected im kleinen if for every point P of M and for every positive number e there exists a positive
VOL. 12, 1926 MA THEMA TICS: H. S. VANDI VER 767 gether in a subcontinuum of M. A point set M is strongly connected im kleinen if for every point P of M and for every positive number e there exists a positive
Arithmetic Funtions Over Rings with Zero Divisors
 BULLETIN of the Bull Malaysian Math Sc Soc (Second Series) 24 (200 81-91 MALAYSIAN MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES SOCIETY Arithmetic Funtions Over Rings with Zero Divisors 1 PATTIRA RUANGSINSAP, 1 VICHIAN LAOHAKOSOL
BULLETIN of the Bull Malaysian Math Sc Soc (Second Series) 24 (200 81-91 MALAYSIAN MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES SOCIETY Arithmetic Funtions Over Rings with Zero Divisors 1 PATTIRA RUANGSINSAP, 1 VICHIAN LAOHAKOSOL
GENERATION OF PRIMITIVE BINARY POLYNOMIALS
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON ALGEBRA, LOGIC AND DISCRETE MATHEMATICS April 14-16, 1995 Niš GENERATION OF PRIMITIVE BINARY POLYNOMIALS Miodrag Živković Let F q denote the finite field of order q = p n, where
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON ALGEBRA, LOGIC AND DISCRETE MATHEMATICS April 14-16, 1995 Niš GENERATION OF PRIMITIVE BINARY POLYNOMIALS Miodrag Živković Let F q denote the finite field of order q = p n, where
Division of Trinomials by Pentanomials and Orthogonal Arrays
 Division of Trinomials by Pentanomials and Orthogonal Arrays School of Mathematics and Statistics Carleton University daniel@math.carleton.ca Joint work with M. Dewar, L. Moura, B. Stevens and Q. Wang
Division of Trinomials by Pentanomials and Orthogonal Arrays School of Mathematics and Statistics Carleton University daniel@math.carleton.ca Joint work with M. Dewar, L. Moura, B. Stevens and Q. Wang
COMMUTATIVE SEMIFIELDS OF ORDER 243 AND 3125
 COMMUTATIVE SEMIFIELDS OF ORDER 243 AND 3125 ROBERT S. COULTER AND PAMELA KOSICK Abstract. This note summarises a recent search for commutative semifields of order 243 and 3125. For each of these two orders,
COMMUTATIVE SEMIFIELDS OF ORDER 243 AND 3125 ROBERT S. COULTER AND PAMELA KOSICK Abstract. This note summarises a recent search for commutative semifields of order 243 and 3125. For each of these two orders,
its weaknesses. The ASG consists of three subgenerators K,fl,
 ALTERNATING STEP GENERATORS CONTROLLED BY DE BRUIJN SEQUENCES C.G. Giinther Brown Boveri Research Center 5405 Baden, Switzerland ABSTRACT The alternating step generator (ASG) is a new generator of pseudo-
ALTERNATING STEP GENERATORS CONTROLLED BY DE BRUIJN SEQUENCES C.G. Giinther Brown Boveri Research Center 5405 Baden, Switzerland ABSTRACT The alternating step generator (ASG) is a new generator of pseudo-
1. Vélu s formulae GENERALIZATION OF VÉLU S FORMULAE FOR ISOGENIES BETWEEN ELLIPTIC CURVES. Josep M. Miret, Ramiro Moreno and Anna Rio
 Publ. Mat. 2007, 147 163 Proceedings of the Primeras Jornadas de Teoría de Números. GENERALIZATION OF VÉLU S FORMULAE FOR ISOGENIES BETWEEN ELLIPTIC CURVES Josep M. Miret, Ramiro Moreno and Anna Rio Abstract
Publ. Mat. 2007, 147 163 Proceedings of the Primeras Jornadas de Teoría de Números. GENERALIZATION OF VÉLU S FORMULAE FOR ISOGENIES BETWEEN ELLIPTIC CURVES Josep M. Miret, Ramiro Moreno and Anna Rio Abstract
Fields in Cryptography. Çetin Kaya Koç Winter / 30
 Fields in Cryptography http://koclab.org Çetin Kaya Koç Winter 2017 1 / 30 Field Axioms Fields in Cryptography A field F consists of a set S and two operations which we will call addition and multiplication,
Fields in Cryptography http://koclab.org Çetin Kaya Koç Winter 2017 1 / 30 Field Axioms Fields in Cryptography A field F consists of a set S and two operations which we will call addition and multiplication,
An Explicit Similarity Transform between Cellular Automata and LFSR Matrices*
 FINITE FIELDS AND THEIR APPLICATIONS 4, 239 251 (1998) ARTICLE NO FF980212 An Explicit Similarity Transform between Cellular Automata and LFSR Matrices* Kevin Cattell and Jon C Muzio Department of Computer
FINITE FIELDS AND THEIR APPLICATIONS 4, 239 251 (1998) ARTICLE NO FF980212 An Explicit Similarity Transform between Cellular Automata and LFSR Matrices* Kevin Cattell and Jon C Muzio Department of Computer
On the Cross-Correlation of a p-ary m-sequence of Period p 2m 1 and Its Decimated
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL 58, NO 3, MARCH 01 1873 On the Cross-Correlation of a p-ary m-sequence of Period p m 1 Its Decimated Sequences by (p m +1) =(p +1) Sung-Tai Choi, Taehyung Lim,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL 58, NO 3, MARCH 01 1873 On the Cross-Correlation of a p-ary m-sequence of Period p m 1 Its Decimated Sequences by (p m +1) =(p +1) Sung-Tai Choi, Taehyung Lim,
A New Algebraic Method to Search Irreducible Polynomials Using Decimal Equivalents of Polynomials over Galois Field GF(p q )
 A New Algebraic Method to Search Irreducible Polynomials Using Decimal Equivalents of Polynomials over Galois Field GF(p q ) Sankhanil Dey and Ranjan Ghosh 2 Institute of Radio Physics and Electronics
A New Algebraic Method to Search Irreducible Polynomials Using Decimal Equivalents of Polynomials over Galois Field GF(p q ) Sankhanil Dey and Ranjan Ghosh 2 Institute of Radio Physics and Electronics
IEEE P1363 / D13 (Draft Version 13). Standard Specifications for Public Key Cryptography
 IEEE P1363 / D13 (Draft Version 13). Standard Specifications for Public Key Cryptography Annex A (Informative). Number-Theoretic Background. Copyright 1999 by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics
IEEE P1363 / D13 (Draft Version 13). Standard Specifications for Public Key Cryptography Annex A (Informative). Number-Theoretic Background. Copyright 1999 by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics
ELG 5372 Error Control Coding. Lecture 5: Algebra 3: Irreducible, Primitive and Minimal Polynomials
 ELG 5372 Error Control Coding Lecture 5: Algebra 3: Irreducible, Primitive and Minimal Polynomials Irreducible Polynomials When f() is divided by g() and r() = 0, then g() is a factor of f() and we say
ELG 5372 Error Control Coding Lecture 5: Algebra 3: Irreducible, Primitive and Minimal Polynomials Irreducible Polynomials When f() is divided by g() and r() = 0, then g() is a factor of f() and we say
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 21 - Design Blocks
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 21 - Design Blocks April 3, 2012 John Wawrzynek Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec21-db3 Page 1 Fixed Shifters / Rotators fixed shifters hardwire the shift amount into the circuit.
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 21 - Design Blocks April 3, 2012 John Wawrzynek Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec21-db3 Page 1 Fixed Shifters / Rotators fixed shifters hardwire the shift amount into the circuit.
MODEL ANSWERS TO HWK #10
 MODEL ANSWERS TO HWK #10 1. (i) As x + 4 has degree one, either it divides x 3 6x + 7 or these two polynomials are coprime. But if x + 4 divides x 3 6x + 7 then x = 4 is a root of x 3 6x + 7, which it
MODEL ANSWERS TO HWK #10 1. (i) As x + 4 has degree one, either it divides x 3 6x + 7 or these two polynomials are coprime. But if x + 4 divides x 3 6x + 7 then x = 4 is a root of x 3 6x + 7, which it
New Algebraic Decoding of (17,9,5) Quadratic Residue Code by using Inverse Free Berlekamp-Massey Algorithm (IFBM)
 International Journal of Computational Intelligence Research (IJCIR). ISSN: 097-87 Volume, Number 8 (207), pp. 205 2027 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijcir.htm New Algebraic
International Journal of Computational Intelligence Research (IJCIR). ISSN: 097-87 Volume, Number 8 (207), pp. 205 2027 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijcir.htm New Algebraic
Singer and GMW constructions (or generalized GMW constructions), little else is known about p-ary two-level autocorrelation sequences. Recently, a few
 New Families of Ideal -level Autocorrelation Ternary Sequences From Second Order DHT Michael Ludkovski 1 and Guang Gong Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Waterloo Waterloo,
New Families of Ideal -level Autocorrelation Ternary Sequences From Second Order DHT Michael Ludkovski 1 and Guang Gong Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Waterloo Waterloo,
IEEE P1363 / D9 (Draft Version 9). Standard Specifications for Public Key Cryptography
 IEEE P1363 / D9 (Draft Version 9) Standard Specifications for Public Key Cryptography Annex A (informative) Number-Theoretic Background Copyright 1997,1998,1999 by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics
IEEE P1363 / D9 (Draft Version 9) Standard Specifications for Public Key Cryptography Annex A (informative) Number-Theoretic Background Copyright 1997,1998,1999 by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics
Binary Sequences with Optimal Autocorrelation
 Cunsheng DING, HKUST, Kowloon, HONG KONG, CHINA July 2004 The Autocorrelation Function The autocorrelation of a binary sequence {s(t)} of period N at shift w is C s (w) = ( 1) s(t+w) s(t). N 1 t=0 The
Cunsheng DING, HKUST, Kowloon, HONG KONG, CHINA July 2004 The Autocorrelation Function The autocorrelation of a binary sequence {s(t)} of period N at shift w is C s (w) = ( 1) s(t+w) s(t). N 1 t=0 The
Chapter 4 Finite Fields
 Chapter 4 Finite Fields Introduction will now introduce finite fields of increasing importance in cryptography AES, Elliptic Curve, IDEA, Public Key concern operations on numbers what constitutes a number
Chapter 4 Finite Fields Introduction will now introduce finite fields of increasing importance in cryptography AES, Elliptic Curve, IDEA, Public Key concern operations on numbers what constitutes a number
strengthened. In 1971, M. M. Dodson [5] showed that fl(k; p) <c 1 if p>k 2 (here and below c 1 ;c 2 ;::: are some positive constants). Various improve
![strengthened. In 1971, M. M. Dodson [5] showed that fl(k; p) <c 1 if p>k 2 (here and below c 1 ;c 2 ;::: are some positive constants). Various improve strengthened. In 1971, M. M. Dodson [5] showed that fl(k; p) <c 1 if p>k 2 (here and below c 1 ;c 2 ;::: are some positive constants). Various improve](/thumbs/83/87461611.jpg) Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, Vilnius, IMI, 1999, No 4, pp. 23-30 ON WARING'S PROBLEM FOR A PRIME MODULUS A. Dubickas Department of Mathematics and Informatics, Vilnius University, Naugarduko
Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, Vilnius, IMI, 1999, No 4, pp. 23-30 ON WARING'S PROBLEM FOR A PRIME MODULUS A. Dubickas Department of Mathematics and Informatics, Vilnius University, Naugarduko
FACTORIZATION OF POLYNOMIALS OVER FINITE FIELDS
 FACTORIZATION OF POLYNOMIALS OVER FINITE FIELDS RICHARD G. SWAN Dickson [1, Ch. V, Th. 38] has given an interesting necessary condition for a polynomial over a finite field of odd characteristic to be
FACTORIZATION OF POLYNOMIALS OVER FINITE FIELDS RICHARD G. SWAN Dickson [1, Ch. V, Th. 38] has given an interesting necessary condition for a polynomial over a finite field of odd characteristic to be
Design of Pseudo-Random Spreading Sequences for CDMA Systems
 Design of Pseudo-Random Spreading Sequences for CDMA Systems Jian Ren and Tongtong Li Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Michigan State University, 2120 Engineering Building East Lansing,
Design of Pseudo-Random Spreading Sequences for CDMA Systems Jian Ren and Tongtong Li Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Michigan State University, 2120 Engineering Building East Lansing,
Sample algebra qualifying exam
 Sample algebra qualifying exam University of Hawai i at Mānoa Spring 2016 2 Part I 1. Group theory In this section, D n and C n denote, respectively, the symmetry group of the regular n-gon (of order 2n)
Sample algebra qualifying exam University of Hawai i at Mānoa Spring 2016 2 Part I 1. Group theory In this section, D n and C n denote, respectively, the symmetry group of the regular n-gon (of order 2n)
Polynomials as Generators of Minimal Clones
 Polynomials as Generators of Minimal Clones Hajime Machida Michael Pinser Abstract A minimal clone is an atom of the lattice of clones. A minimal function is a function which generates a minimal clone.
Polynomials as Generators of Minimal Clones Hajime Machida Michael Pinser Abstract A minimal clone is an atom of the lattice of clones. A minimal function is a function which generates a minimal clone.
Number-Theoretic Transforms of Prescribed Length
 MATHEMATICS OF COMPUTATION VOLUME 47, NUMBER 176 OCTOBER 1986. PAGES 693-701 Number-Theoretic Transforms of Prescribed Length By R. Creutzburg and M. Tasche Abstract. A new constructive method for finding
MATHEMATICS OF COMPUTATION VOLUME 47, NUMBER 176 OCTOBER 1986. PAGES 693-701 Number-Theoretic Transforms of Prescribed Length By R. Creutzburg and M. Tasche Abstract. A new constructive method for finding
MATH 690 NOTES. 1. Associated graded rings
 MATH 690 NOTES 1. Associated graded rings Question 1.1. Let G = k[g 1 ] = n 0 G n be a one-dimensional standard graded ring over the field k = G 0. What are necessary and sufficient conditions in order
MATH 690 NOTES 1. Associated graded rings Question 1.1. Let G = k[g 1 ] = n 0 G n be a one-dimensional standard graded ring over the field k = G 0. What are necessary and sufficient conditions in order
Abstract Algebra, Second Edition, by John A. Beachy and William D. Blair. Corrections and clarifications
 1 Abstract Algebra, Second Edition, by John A. Beachy and William D. Blair Corrections and clarifications Note: Some corrections were made after the first printing of the text. page 9, line 8 For of the
1 Abstract Algebra, Second Edition, by John A. Beachy and William D. Blair Corrections and clarifications Note: Some corrections were made after the first printing of the text. page 9, line 8 For of the
Coding Theory: Linear-Error Correcting Codes Anna Dovzhik Math 420: Advanced Linear Algebra Spring 2014
 Anna Dovzhik 1 Coding Theory: Linear-Error Correcting Codes Anna Dovzhik Math 420: Advanced Linear Algebra Spring 2014 Sharing data across channels, such as satellite, television, or compact disc, often
Anna Dovzhik 1 Coding Theory: Linear-Error Correcting Codes Anna Dovzhik Math 420: Advanced Linear Algebra Spring 2014 Sharing data across channels, such as satellite, television, or compact disc, often
RADIX-2 FAST HARTLEY TRANSFORM REVISITED. de Oliveira, H.M.; Viviane L. Sousa, Silva, Helfarne A.N. and Campello de Souza, R.M.
 RADIX- FAST HARTLY TRASFRM RVISITD de liveira, H.M.; Viviane L. Sousa, Silva, Helfarne A.. and Campello de Souza, R.M. Federal University of Pernambuco Departamento de letrônica e Sistemas - Recife - P,
RADIX- FAST HARTLY TRASFRM RVISITD de liveira, H.M.; Viviane L. Sousa, Silva, Helfarne A.. and Campello de Souza, R.M. Federal University of Pernambuco Departamento de letrônica e Sistemas - Recife - P,
ECEN 5022 Cryptography
 Elementary Algebra and Number Theory University of Colorado Spring 2008 Divisibility, Primes Definition. N denotes the set {1, 2, 3,...} of natural numbers and Z denotes the set of integers {..., 2, 1,
Elementary Algebra and Number Theory University of Colorado Spring 2008 Divisibility, Primes Definition. N denotes the set {1, 2, 3,...} of natural numbers and Z denotes the set of integers {..., 2, 1,
ECEN 5682 Theory and Practice of Error Control Codes
 ECEN 5682 Theory and Practice of Error Control Codes Introduction to Algebra University of Colorado Spring 2007 Motivation and For convolutional codes it was convenient to express the datawords and the
ECEN 5682 Theory and Practice of Error Control Codes Introduction to Algebra University of Colorado Spring 2007 Motivation and For convolutional codes it was convenient to express the datawords and the
Irreducible Polynomials. Finite Fields of Order p m (1) Primitive Polynomials. Finite Fields of Order p m (2)
 S-72.3410 Finite Fields (2) 1 S-72.3410 Finite Fields (2) 3 Irreducible Polynomials Finite Fields of Order p m (1) The following results were discussed in the previous lecture: The order of a finite field
S-72.3410 Finite Fields (2) 1 S-72.3410 Finite Fields (2) 3 Irreducible Polynomials Finite Fields of Order p m (1) The following results were discussed in the previous lecture: The order of a finite field
Some approaches to construct MDS matrices over a finite field
 2017 6 Å 31 Å 2 ¹ June 2017 Communication on Applied Mathematics and Computation Vol.31 No.2 DOI 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6330.2017.02.001 Some approaches to construct MDS matrices over a finite field BELOV
2017 6 Å 31 Å 2 ¹ June 2017 Communication on Applied Mathematics and Computation Vol.31 No.2 DOI 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6330.2017.02.001 Some approaches to construct MDS matrices over a finite field BELOV
Finite fields: some applications Michel Waldschmidt 1
 Ho Chi Minh University of Science HCMUS Update: 16/09/2013 Finite fields: some applications Michel Waldschmidt 1 Exercises We fix an algebraic closure F p of the prime field F p of characteristic p. When
Ho Chi Minh University of Science HCMUS Update: 16/09/2013 Finite fields: some applications Michel Waldschmidt 1 Exercises We fix an algebraic closure F p of the prime field F p of characteristic p. When
B. Encryption using quasigroup
 Sequence Randomization Using Quasigroups and Number Theoretic s Vaignana Spoorthy Ella Department of Computer Science Oklahoma State University Stillwater, Oklahoma, USA spoorthyella@okstateedu Abstract
Sequence Randomization Using Quasigroups and Number Theoretic s Vaignana Spoorthy Ella Department of Computer Science Oklahoma State University Stillwater, Oklahoma, USA spoorthyella@okstateedu Abstract
Error Detection & Correction
 Error Detection & Correction Error detection & correction noisy channels techniques in networking error detection error detection capability retransmition error correction reconstruction checksums redundancy
Error Detection & Correction Error detection & correction noisy channels techniques in networking error detection error detection capability retransmition error correction reconstruction checksums redundancy
= (w 0 + w x t Up^t 9 ' 1 )-. A. "0
 5hk MINIMUM PERIODS MODULO n FOR BERNOULLI NUMBERS [Dec. for some nonzero integer U. Finally, u 0 = u p, and u n \u 0 for n = 0, 1,.... VK.00^'. By Lemma 7 and the fact that {u n } is a kth order recurrent
5hk MINIMUM PERIODS MODULO n FOR BERNOULLI NUMBERS [Dec. for some nonzero integer U. Finally, u 0 = u p, and u n \u 0 for n = 0, 1,.... VK.00^'. By Lemma 7 and the fact that {u n } is a kth order recurrent
Chapter 6. BCH Codes
 Chapter 6 BCH Codes Description of the Codes Decoding of the BCH Codes Outline Implementation of Galois Field Arithmetic Implementation of Error Correction Nonbinary BCH Codes and Reed-Solomon Codes Weight
Chapter 6 BCH Codes Description of the Codes Decoding of the BCH Codes Outline Implementation of Galois Field Arithmetic Implementation of Error Correction Nonbinary BCH Codes and Reed-Solomon Codes Weight
arxiv: v1 [cs.it] 12 Jun 2016
![arxiv: v1 [cs.it] 12 Jun 2016 arxiv: v1 [cs.it] 12 Jun 2016](/thumbs/92/109362781.jpg) New Permutation Trinomials From Niho Exponents over Finite Fields with Even Characteristic arxiv:606.03768v [cs.it] 2 Jun 206 Nian Li and Tor Helleseth Abstract In this paper, a class of permutation trinomials
New Permutation Trinomials From Niho Exponents over Finite Fields with Even Characteristic arxiv:606.03768v [cs.it] 2 Jun 206 Nian Li and Tor Helleseth Abstract In this paper, a class of permutation trinomials
Construction of some new families of nested orthogonal arrays
 isid/ms/2017/01 April 7, 2017 http://www.isid.ac.in/ statmath/index.php?module=preprint Construction of some new families of nested orthogonal arrays Tian-fang Zhang, Guobin Wu and Aloke Dey Indian Statistical
isid/ms/2017/01 April 7, 2017 http://www.isid.ac.in/ statmath/index.php?module=preprint Construction of some new families of nested orthogonal arrays Tian-fang Zhang, Guobin Wu and Aloke Dey Indian Statistical
Construction of lattice designs using MOLS
 Malaya Journal of Matematik S(1)(2013) 11 16 Construction of lattice designs using MOLS Dr.R. Jaisankar a, and M. Pachamuthu b, a Department of Statistics, Bharathiar University, Coimbatore-641046, India.
Malaya Journal of Matematik S(1)(2013) 11 16 Construction of lattice designs using MOLS Dr.R. Jaisankar a, and M. Pachamuthu b, a Department of Statistics, Bharathiar University, Coimbatore-641046, India.
Introduction to Information Security
 Introduction to Information Security Lecture 5: Number Theory 007. 6. Prof. Byoungcheon Lee sultan (at) joongbu. ac. kr Information and Communications University Contents 1. Number Theory Divisibility
Introduction to Information Security Lecture 5: Number Theory 007. 6. Prof. Byoungcheon Lee sultan (at) joongbu. ac. kr Information and Communications University Contents 1. Number Theory Divisibility
Trace Representation of Legendre Sequences
 C Designs, Codes and Cryptography, 24, 343 348, 2001 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Trace Representation of Legendre Sequences JEONG-HEON KIM School of Electrical and
C Designs, Codes and Cryptography, 24, 343 348, 2001 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Trace Representation of Legendre Sequences JEONG-HEON KIM School of Electrical and
Repeated-Root Self-Dual Negacyclic Codes over Finite Fields
 Journal of Mathematical Research with Applications May, 2016, Vol. 36, No. 3, pp. 275 284 DOI:10.3770/j.issn:2095-2651.2016.03.004 Http://jmre.dlut.edu.cn Repeated-Root Self-Dual Negacyclic Codes over
Journal of Mathematical Research with Applications May, 2016, Vol. 36, No. 3, pp. 275 284 DOI:10.3770/j.issn:2095-2651.2016.03.004 Http://jmre.dlut.edu.cn Repeated-Root Self-Dual Negacyclic Codes over
Homework 4 Solutions
 Homework 4 Solutions November 11, 2016 You were asked to do problems 3,4,7,9,10 in Chapter 7 of Lang. Problem 3. Let A be an integral domain, integrally closed in its field of fractions K. Let L be a finite
Homework 4 Solutions November 11, 2016 You were asked to do problems 3,4,7,9,10 in Chapter 7 of Lang. Problem 3. Let A be an integral domain, integrally closed in its field of fractions K. Let L be a finite
CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security
 CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 8 February 1, 2012 CPSC 467b, Lecture 8 1/42 Number Theory Needed for RSA Z n : The integers mod n Modular arithmetic GCD Relatively
CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 8 February 1, 2012 CPSC 467b, Lecture 8 1/42 Number Theory Needed for RSA Z n : The integers mod n Modular arithmetic GCD Relatively
Commutative Rings and Fields
 Commutative Rings and Fields 1-22-2017 Different algebraic systems are used in linear algebra. The most important are commutative rings with identity and fields. Definition. A ring is a set R with two
Commutative Rings and Fields 1-22-2017 Different algebraic systems are used in linear algebra. The most important are commutative rings with identity and fields. Definition. A ring is a set R with two
Section VI.33. Finite Fields
 VI.33 Finite Fields 1 Section VI.33. Finite Fields Note. In this section, finite fields are completely classified. For every prime p and n N, there is exactly one (up to isomorphism) field of order p n,
VI.33 Finite Fields 1 Section VI.33. Finite Fields Note. In this section, finite fields are completely classified. For every prime p and n N, there is exactly one (up to isomorphism) field of order p n,
ITALIAN JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS N ( ) 451
 ITALIAN JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS N. 39 2018 451 464 451 ON THE k-normal ELEMENTS AND POLYNOMIALS OVER FINITE FIELDS Mahmood Alizadeh Department of Mathematics Ahvaz Branch Islamic Azad University
ITALIAN JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS N. 39 2018 451 464 451 ON THE k-normal ELEMENTS AND POLYNOMIALS OVER FINITE FIELDS Mahmood Alizadeh Department of Mathematics Ahvaz Branch Islamic Azad University
ANTIPODAL FIXED POINT THEORY FOR VOLTERRA MAPS
 Dynamic Systems and Applications 17 (2008) 325-330 ANTIPODAL FIXED POINT THEORY FOR VOLTERRA MAPS YEOL JE CHO, DONAL O REGAN, AND SVATOSLAV STANEK Department of Mathematics Education and the RINS, College
Dynamic Systems and Applications 17 (2008) 325-330 ANTIPODAL FIXED POINT THEORY FOR VOLTERRA MAPS YEOL JE CHO, DONAL O REGAN, AND SVATOSLAV STANEK Department of Mathematics Education and the RINS, College
Analogues for Bessel Functions of the Christoffel-Darboux Identity
 Analogues for Bessel Functions of the Christoffel-Darboux Identity Mark Tygert Research Report YALEU/DCS/RR-1351 March 30, 2006 Abstract We derive analogues for Bessel functions of what is known as the
Analogues for Bessel Functions of the Christoffel-Darboux Identity Mark Tygert Research Report YALEU/DCS/RR-1351 March 30, 2006 Abstract We derive analogues for Bessel functions of what is known as the
ON THE THEORY OF ASSOCIATIVE DIVISION ALGEBRAS*
 ON THE THEORY OF ASSOCIATIVE DIVISION ALGEBRAS* BY OLIVE C. HAZLETT 1. Relation to the literature. There is a famous theorem to the effect that the only linear associative algebras over the field of all
ON THE THEORY OF ASSOCIATIVE DIVISION ALGEBRAS* BY OLIVE C. HAZLETT 1. Relation to the literature. There is a famous theorem to the effect that the only linear associative algebras over the field of all
FOURIER COEFFICIENTS OF VECTOR-VALUED MODULAR FORMS OF DIMENSION 2
 FOURIER COEFFICIENTS OF VECTOR-VALUED MODULAR FORMS OF DIMENSION 2 CAMERON FRANC AND GEOFFREY MASON Abstract. We prove the following Theorem. Suppose that F = (f 1, f 2 ) is a 2-dimensional vector-valued
FOURIER COEFFICIENTS OF VECTOR-VALUED MODULAR FORMS OF DIMENSION 2 CAMERON FRANC AND GEOFFREY MASON Abstract. We prove the following Theorem. Suppose that F = (f 1, f 2 ) is a 2-dimensional vector-valued
Almost fifth powers in arithmetic progression
 Almost fifth powers in arithmetic progression L. Hajdu and T. Kovács University of Debrecen, Institute of Mathematics and the Number Theory Research Group of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences Debrecen,
Almost fifth powers in arithmetic progression L. Hajdu and T. Kovács University of Debrecen, Institute of Mathematics and the Number Theory Research Group of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences Debrecen,
Pseudo-Random Numbers Generators. Anne GILLE-GENEST. March 1, Premia Introduction Definitions Good generators...
 14 pages 1 Pseudo-Random Numbers Generators Anne GILLE-GENEST March 1, 2012 Contents Premia 14 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Definitions............................. 2 1.2 Good generators..........................
14 pages 1 Pseudo-Random Numbers Generators Anne GILLE-GENEST March 1, 2012 Contents Premia 14 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Definitions............................. 2 1.2 Good generators..........................
MATH 3030, Abstract Algebra Winter 2012 Toby Kenney Sample Midterm Examination Model Solutions
 MATH 3030, Abstract Algebra Winter 2012 Toby Kenney Sample Midterm Examination Model Solutions Basic Questions 1. Give an example of a prime ideal which is not maximal. In the ring Z Z, the ideal {(0,
MATH 3030, Abstract Algebra Winter 2012 Toby Kenney Sample Midterm Examination Model Solutions Basic Questions 1. Give an example of a prime ideal which is not maximal. In the ring Z Z, the ideal {(0,
S. Lie has thrown much new light on this operation. The assumption
 600 MATHEMATICS: A. E. ROSS PRoc. N. A. S. The operation of finding the limit of an infinite series has been one of the most fruitful operations of all mathematics. While this is not a group operation
600 MATHEMATICS: A. E. ROSS PRoc. N. A. S. The operation of finding the limit of an infinite series has been one of the most fruitful operations of all mathematics. While this is not a group operation
State Analysis and Optimal Control of Linear. Time-Invariant Scaled Systems Using. the Chebyshev Wavelets
 Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 5, 2012, no. 2, 91-105 State Analysis and Optimal Control of Linear Time-Invariant Scaled Systems Using the Chebyshev Wavelets M. R. Fatehi a, M. Samavat b *, M.
Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 5, 2012, no. 2, 91-105 State Analysis and Optimal Control of Linear Time-Invariant Scaled Systems Using the Chebyshev Wavelets M. R. Fatehi a, M. Samavat b *, M.
EXAMPLES OF PROOFS BY INDUCTION
 EXAMPLES OF PROOFS BY INDUCTION KEITH CONRAD 1. Introduction In this handout we illustrate proofs by induction from several areas of mathematics: linear algebra, polynomial algebra, and calculus. Becoming
EXAMPLES OF PROOFS BY INDUCTION KEITH CONRAD 1. Introduction In this handout we illustrate proofs by induction from several areas of mathematics: linear algebra, polynomial algebra, and calculus. Becoming
Discrete Math. Instructor: Mike Picollelli. Day 10
 Day 10 Fibonacci Redux. Last time, we saw that F n = 1 5 (( 1 + ) n ( 5 2 1 ) n ) 5. 2 What Makes The Fibonacci Numbers So Special? The Fibonacci numbers are a particular type of recurrence relation, a
Day 10 Fibonacci Redux. Last time, we saw that F n = 1 5 (( 1 + ) n ( 5 2 1 ) n ) 5. 2 What Makes The Fibonacci Numbers So Special? The Fibonacci numbers are a particular type of recurrence relation, a
INTEGER VALUED POLYNOMIALS AND LUBIN-TATE FORMAL GROUPS
 INTEGER VALUED POLYNOMIALS AND LUBIN-TATE FORMAL GROUPS EHUD DE SHALIT AND ERAN ICELAND Abstract. If R is an integral domain and K is its field of fractions, we let Int(R) stand for the subring of K[x]
INTEGER VALUED POLYNOMIALS AND LUBIN-TATE FORMAL GROUPS EHUD DE SHALIT AND ERAN ICELAND Abstract. If R is an integral domain and K is its field of fractions, we let Int(R) stand for the subring of K[x]
THE RALEIGH GAME. Received: 1/6/06, Accepted: 6/25/06. Abstract
 INTEGERS: ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF COMBINATORIAL NUMBER THEORY 7(2) (2007), #A13 THE RALEIGH GAME Aviezri S. Fraenkel 1 Department of Computer Science and Applied Mathematics, Weizmann Institute of Science,
INTEGERS: ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF COMBINATORIAL NUMBER THEORY 7(2) (2007), #A13 THE RALEIGH GAME Aviezri S. Fraenkel 1 Department of Computer Science and Applied Mathematics, Weizmann Institute of Science,
'i I 'i ; ~ A method for the easy storage of discriminant polynomials. by RANAN B. BANERJI FIELDS
 A method for the easy storage of discriminant polynomials by RANAN B. BANERJI Case Western Reserve University Cleveland, Ohio I~TRODUCTIO~ One olthepurposes of. feature extraction is to save_ on the memory
A method for the easy storage of discriminant polynomials by RANAN B. BANERJI Case Western Reserve University Cleveland, Ohio I~TRODUCTIO~ One olthepurposes of. feature extraction is to save_ on the memory
On the computation of discrete Fourier transform using Fermat number transform
 On the computation of discrete Fourier transform using Fermat number transform Wan-Chi Siu, AP(HK), M.Phil., C.Eng., M.I.E.R.E., Mem.I.E.E.E., A.G. Constantinides, B.Sc.(Eng.), Ph.D., C.Eng., M.I.E.E.,
On the computation of discrete Fourier transform using Fermat number transform Wan-Chi Siu, AP(HK), M.Phil., C.Eng., M.I.E.R.E., Mem.I.E.E.E., A.G. Constantinides, B.Sc.(Eng.), Ph.D., C.Eng., M.I.E.E.,
Other Public-Key Cryptosystems
 Other Public-Key Cryptosystems Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse571-11/
Other Public-Key Cryptosystems Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse571-11/
arithmetic properties of weighted catalan numbers
 arithmetic properties of weighted catalan numbers Jason Chen Mentor: Dmitry Kubrak May 20, 2017 MIT PRIMES Conference background: catalan numbers Definition The Catalan numbers are the sequence of integers
arithmetic properties of weighted catalan numbers Jason Chen Mentor: Dmitry Kubrak May 20, 2017 MIT PRIMES Conference background: catalan numbers Definition The Catalan numbers are the sequence of integers
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 26 Error Correction Codes, Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs)
 EECS150 - igital esign Lecture 26 Error Correction Codes, Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) Nov 21, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS150 Lec26-ECC Page 1 Outline Error detection using parity Hamming
EECS150 - igital esign Lecture 26 Error Correction Codes, Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) Nov 21, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS150 Lec26-ECC Page 1 Outline Error detection using parity Hamming
Algebra. Modular arithmetic can be handled mathematically by introducing a congruence relation on the integers described in the above example.
 Coding Theory Massoud Malek Algebra Congruence Relation The definition of a congruence depends on the type of algebraic structure under consideration Particular definitions of congruence can be made for
Coding Theory Massoud Malek Algebra Congruence Relation The definition of a congruence depends on the type of algebraic structure under consideration Particular definitions of congruence can be made for
Algebraic function fields
 Algebraic function fields 1 Places Definition An algebraic function field F/K of one variable over K is an extension field F K such that F is a finite algebraic extension of K(x) for some element x F which
Algebraic function fields 1 Places Definition An algebraic function field F/K of one variable over K is an extension field F K such that F is a finite algebraic extension of K(x) for some element x F which
COUNTING SEPARABLE POLYNOMIALS IN Z/n[x]
![COUNTING SEPARABLE POLYNOMIALS IN Z/n[x] COUNTING SEPARABLE POLYNOMIALS IN Z/n[x]](/thumbs/92/109397678.jpg) COUNTING SEPARABLE POLYNOMIALS IN Z/n[x] JASON K.C. POLAK Abstract. For a commutative ring R, a polynomial f R[x] is called separable if R[x]/f is a separable R-algebra. We derive formulae for the number
COUNTING SEPARABLE POLYNOMIALS IN Z/n[x] JASON K.C. POLAK Abstract. For a commutative ring R, a polynomial f R[x] is called separable if R[x]/f is a separable R-algebra. We derive formulae for the number
Other Public-Key Cryptosystems
 Other Public-Key Cryptosystems Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: 10-1 Overview 1. How to exchange
Other Public-Key Cryptosystems Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: 10-1 Overview 1. How to exchange
SOLUTION TO RUBEL S QUESTION ABOUT DIFFERENTIALLY ALGEBRAIC DEPENDENCE ON INITIAL VALUES GUY KATRIEL PREPRINT NO /4
 SOLUTION TO RUBEL S QUESTION ABOUT DIFFERENTIALLY ALGEBRAIC DEPENDENCE ON INITIAL VALUES GUY KATRIEL PREPRINT NO. 2 2003/4 1 SOLUTION TO RUBEL S QUESTION ABOUT DIFFERENTIALLY ALGEBRAIC DEPENDENCE ON INITIAL
SOLUTION TO RUBEL S QUESTION ABOUT DIFFERENTIALLY ALGEBRAIC DEPENDENCE ON INITIAL VALUES GUY KATRIEL PREPRINT NO. 2 2003/4 1 SOLUTION TO RUBEL S QUESTION ABOUT DIFFERENTIALLY ALGEBRAIC DEPENDENCE ON INITIAL
#A11 INTEGERS 12 (2012) FIBONACCI VARIATIONS OF A CONJECTURE OF POLIGNAC
 #A11 INTEGERS 12 (2012) FIBONACCI VARIATIONS OF A CONJECTURE OF POLIGNAC Lenny Jones Department of Mathematics, Shippensburg University, Shippensburg, Pennsylvania lkjone@ship.edu Received: 9/17/10, Revised:
#A11 INTEGERS 12 (2012) FIBONACCI VARIATIONS OF A CONJECTURE OF POLIGNAC Lenny Jones Department of Mathematics, Shippensburg University, Shippensburg, Pennsylvania lkjone@ship.edu Received: 9/17/10, Revised:
Chapter 6 Lagrange Codes
 Chapter 6 Lagrange Codes 6. Introduction Joseph Louis Lagrange was a famous eighteenth century Italian mathematician [] credited with minimum degree polynomial interpolation amongst his many other achievements.
Chapter 6 Lagrange Codes 6. Introduction Joseph Louis Lagrange was a famous eighteenth century Italian mathematician [] credited with minimum degree polynomial interpolation amongst his many other achievements.
1 Fields and vector spaces
 1 Fields and vector spaces In this section we revise some algebraic preliminaries and establish notation. 1.1 Division rings and fields A division ring, or skew field, is a structure F with two binary
1 Fields and vector spaces In this section we revise some algebraic preliminaries and establish notation. 1.1 Division rings and fields A division ring, or skew field, is a structure F with two binary
Math 121 Homework 2 Solutions
 Math 121 Homework 2 Solutions Problem 13.2 #16. Let K/F be an algebraic extension and let R be a ring contained in K that contains F. Prove that R is a subfield of K containing F. We will give two proofs.
Math 121 Homework 2 Solutions Problem 13.2 #16. Let K/F be an algebraic extension and let R be a ring contained in K that contains F. Prove that R is a subfield of K containing F. We will give two proofs.
