The fluctuation-dissipation theorem: from statistical physics to climate dynamics?
|
|
|
- June Parker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The fluctuation-dissipation theorem: from statistical physics to climate dynamics? Peter Haynes University of Cambridge Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics (DAMTP) Cambridge Centre for Climate Science (CCfCS) Université Fédérale Toulouse Midi-Pyrénées (collaborations with Fenwick Cooper and Peter Hitchcock)
2 The climate response problem Lu et al 2008: simulations with GFDL CM2.1 model, compared with in A2 scenario. Longitudinal/time average change depends on physical processes which fluctuate in longitude and time.
3 Changes in the SH troposphere as a dynamical response to stratospheric ozone depletion Ozone perturbation applied to AGCM (Thompson and Solomon 2002, Gillett and Thompson, 2003)
4 Simple model of solar cycle effects Haigh et al (2005): response of simple troposphere to imposed changes, e.g. uniform increase in radiative equilibrium temperature in stratosphere TOP 10km U1 U5 SURFACE
5
6 Changes in eddy fluxes are a vital part of the tropospheric dynamical response (possibility of amplification ) Simpson et al (2009)
7 Can we make predictions about the response of the tropospheric circulation? Diagram from Simpson et al (2009) Can this tropospheric box really be decomposed? Analogous tropospheric response problems: ozone hole (Gillett and Thompson 2003), stratospheric perturbation (Polvani and Kushner 2002, Song and Robinson 2004), surface friction (Chen et al 2007), tropospheric heating (Butler et al 2010)
8 Reduction in surface friction in simple circulation model Chen et al (2007): two-stage adjustment (short-time in jet strength followed by longer term change in jet position)
9 Chen et al (2007) 1) As the surface drag is reduced, the zonal wind acceleration is barotropic and proportional to the surface wind in the extratropics. Meanwhile, the baroclinic eddies are weakened by the increased Surface barotropic meridional shear, Mean but zonal neither the weakening eddies nor the Friction increased meridional shears are directly implicated in the wind poleward shift. 2) The increase in the strength of the westerlies in the extratropics leads to faster eddy phase speeds, while the subtropical zonal winds barely change. Hence, the critical latitude for these eddies is displaced poleward. Structure of eddies 3) The dynamics of the wave breaking in the upper troposphere, in the presence of this poleward shift in critical latitude, shifts the eddy momentum fluxes poleward, driving a poleward shift in the surface zonal winds and the eddy-driven jet. This is particularly supported by the shallow water model results. Eddy momentum flux 4) Eddy heat fluxes, and the associated upward Eliassen Palm (EP) fluxes tend to follow this upper-level eddy activity. This shift in the baroclinic eddy production provides some positive feedback on the upper-level shift.
10 Questions What is relation between spatial pattern of forcing and the amplitude and spatial pattern of response? ( preferred response, most effective forcing ) Will different models overpredict or underpredict response (and correct pattern of response) relative to real atmosphere? Seek a unified approach to quantitative prediction of tropospheric response, rather than post-hoc explanation of each special case
11 Brownian motion Einstein (1905,1906) Smoluchowksi (1906) Observable Diffusivity of Particle: D x = hv 2 x i corr Equipartition of kinetic energy: Stokes law for viscous drag force: 1 2 mhv 2 x i = 1 2 RT N A F S = k S V = 6 µav
12 m dv x = k S V x + f R (t) dt hf R (t 1 )f R (t 2 )i = C (t 1 t 2 ) hv x (t 1 )V x (t 2 )i = hv 2 x i exp( k S t 1 t 2 /m) corr = m/k S D = RT 6N A µa EINSTEIN RELATION Time scale of fluctuations corr = m/k S Velocity response to applied force Applied force FLUCTUATION -- DISSIPATION
13 Dynamical systems approach Calculation of change in statistical measure of chaotic/random system due to applied perturbation ρ(x) X(t) UNDISTURBED SYSTEM DISTURBED SYSTEM
14 Evolution equation U(X,t) dx dt = U(X,t) is usually nonlinear and could contain explicit randomness Equilibrium statistical properties described by probability density function (x) Perturb evolution equation What is new (x)? dx dt = U(X,t)+ F(X,t) [Perturbations to individual trajectories are large perturbations to overall statistics are small.]
15 Consider small applied forcing F = f(x) (t) At t=0: (x)! + (x) ' (x) r x.(f(x) (x)) Z Z (X( )) f = dx dy (y)p(x( ) =y X(0) = x) + (x) Z Compare identity (X( )) (X(0)) Z = dx dy (y)p(x( ) = y X(0) = x) (x) (x) Hence (X( )) f (X( )) +(x) (x) x=x(0) (X( )) = (X( )) x.(f(x ) (x)) (x) and x=x(0)
16 Fluctuation-Dissipation Theorem For steady x-independent F X = Z 1 0 d X( ) x. (x) (x) x=x(0). F = L F A: General If X is Gaussian then hxi = Z 1 0 d C( )C(0) 1. F = L F B: Gaussian where C( ) =hx( )X(0)i Linear operator L given in terms of properties of undisturbed system Crude approximation hxi correlation F
17 Gritsun and Branstator (2007) Application of Gaussian FDT to predict response to localised tropical heating in GCM Individual AGCM integrations days FDT estimate constructed from 4M day integration
18 Gritsun and Branstator (2007) Success of FDT measured by pattern correlation and amplitude ratio
19 Ring and Plumb (2008): Gaussian FDT makes incorrect prediction for response to zonally symmetric thermal (!) and mechanical (") forcings
20 Practical issues in applying the FDT L = Z 1 0 d C( ) C(0) 1 EOFs (which diagonalise C(0)) are a natural choice of variable (but not the only possible choice) < C( τ ) C(0) -1 > must be estimated from available data. C(0) -1 potentially ill-conditioned number of useful EOFs may be restricted by length of data series integration from τ = 0 to τ = must be approximated by finite sum
21 Statistical requirements on application of Gaussian FDT Cooper and H D linear model FDT prediction of response
22 Study based on simple T21L20 general circulation model (Cooper and H 2012) day simulations, mean and variance Forced response +/- 1 m/s/day Forced response +/- 0.1 m/s/day
23 Application of the FDT to predict the response to forcing of a simple T21L20 general circulation model Response (m/s) Upper limit of integral (days) Response (m/s) Run length (days) x 10 4 (10 x 10 5 day integrations) (300 day upper limit to integral)
24 What is the optimal number of EOFs to include in the calculation? (T31L20 model) Response (ms 1 ) Response (m/s) Upper limit of integral (days) Number of EOFs
25 Specification of forcing L Gaussian = Z 1 0 d C( )C(0) 1 Where did the equations go? Implications of truncation e.g. Ring and Plumb (2007) u t + = F T t + =0 u t + = L(u, F)
26 Effect of using climatological u versus u=0 in L(u, F) Response (ms 1 ) Number of EOFs
27 0.015 Usefulness of Gaussian FDT may be limited by non-gaussianity?!(x) x pdfs of EOF1 in zonal wind for T21L20 and T31L20 simulations
28 The non-gaussian case a non-parametric FDT Cooper and H 2011 X = Z 1 0 d X( ) x (x) x=x(0). F (x) ˆ(x; h, N) = 1 Nh d r x ˆ(x; h, N) =... Estimate using kernel density estimator method of non-parametric statistics NX i=1 K( x X i h Bias and Uncertainty depend on h and N. ) Simplest choice for K(.) is isotropic Gaussian
29 strongly non-gaussian test case dx dt = b 1X b 2 X 3 + Perturbed and unperturbed pdfs
30
31 Application to stochastic Lorenz 1963 model Compare with Thuburn (2005) approach of solving Fokker-Planck equation
32 Response in x direction to forcing applied in different directions
33 0.015 What is a useful measure of non-gaussianity?!(x) x L L Gaussian = Z 1 0 hhx( ) X(0)i{ (x) 1 r x (x) x=x(0) X(0).C(0) 1 }i Depends on structure of time correlations as well as form of pdf
34 Summary FDT potentially provides a quantitative description of tropospheric response to forcing (e.g. ozone hole, solar cycle, greenhouse gas increase) given information on statistics of unforced circulation If model low-frequency variability (timescales and patterns) is wrong then response to forcing will be wrong Typical response to forcing will be leading singular vector of response operator (providing forcing has significant projection onto leading singular vector), not necessarily the leading EOF. In practice can FDT do better than simple estimation of timescale of leading EOF? Applications? Model assessment/intercomparison?
35 FDT confusion? FDT implies that response to forcing will have the same form as leading EOF? Not necessarily! dx = BX dt + d hd d i = Q dt BC(0) + C(0)B T + Q =0 C(0) depends on Q Analogy to system of springs with weakest spring responding preferentially? Better to consider mixing in dynamical system the longest-lived structure is the one that mixes least rapidly.
36 Deser et al (2004) heuristic approach to response problem INDIRECT DIRECT
37 Future lines of work? (Is the FDT a practical quantitative tool?) Statistical nature of FDT requires explicit information on/ estimates for bias and uncertainty Non-gaussian extension of FDT potentially extends validity (but there are challenges in implementation can we escape the curse of dimensionality or avoid it by working in a truncated system? ) FDT for truncated system is non-trivial need to consider proper effective forcing on truncated system. Clearer practical guide to implementation of FDT (How long a data record is needed for required precision? How many degrees of freedom to include?)
38 Usefulness of linear theory? depends on problem being considered but recall Haigh et al (2005) TOP 10km U1 U5 SURFACE
39 Kidston et al (2015): tropospheric response to stratosphere on different timescales
40 FDT cultural differences 20 th century physics: large systems, small fluctuations, FDT has been discussed/applied/interpreted in terms of macroscopic variables. 21 st century physics: extension to non-equilibrium small systems with large fluctuations? Dynamical systems: Formal derivation/justification of fluctuation-response operators, conditions for applicability, can problems of non-smoothness/non-differentiability be overcome? Climate/circulation: Evaluation of fluctuation-response operator from model simulation (or from data?) is a problem in statistics of large-degree-of-freedom systems. How much data is needed for required accuracy? How can effective dimensionality be most effectively reduced?
41 THE END
42 Reference list for PHH Les Houches seminar The following are papers referenced in the slides. I ve added papers by Fuchs et al (2015) and Hassanzadeh and Kuang (2016a,b) since they add significantly to some of the things that I talked about. Butler, A.H., Thompson, D. W. J., Heikes, R., 2010: The Steady-State Atmospheric Circulation Response to Climate Changelike Thermal Forcings in a Simple General Circulation Model. J. Climate, 23, , doi: /2010JCLI Chen, G., Held, I.M., Robinson, W. A., 2007: Sensitivity of the Latitude of the Surface Westerlies to Surface Friction. J. Atmos. Sci., 64, , doi: /JAS Cooper, F. C., Haynes, P. H., 2011: Climate sensitivity via a non-parametric fluctuation-dissipation theorem. J. Atmos. Sci. 68, Cooper, F. C., Haynes, P. H., 2012: Assessment of the fluctuation-dissipation theorem as an estimator of the response of the tropospheric response to forcing. (preprint). [This paper was never published. I d be pleased to a copy to anyone interested. Some of it has been significantly superseded by the papers by Fuchs et al (2015) and Hassanzadeh and Kuang (2016a,b).] Deser, C., G. Magnusdottir, R. Saravanan, and A. Phillips, 2004: The e ects of North Atlantic SST and sea ice anomalies on the winter circulation in CCM3. Part II: direct and indirect components of the response, J. Climate, 17, 877?889, doi: / (2004) :TEONAS 2.0.CO;2. Fuchs, D., S. Sherwood, and D. Hernandez, 2015: An exploration of multivariate fluctuation dissipation operators and their response to sea surface temperature perturbations. J. Atmos. Sci., 72, , doi: /jas-d Gritsun, A., Branstator, G., 2007: Climate response using a three-dimensional operator based on the fluctuation-dissipation theorem. J. Atmos. Sci., 64, Haigh, J. D., Blackburn, M., and Day, R. 2005: The response of tropospheric circulation to perturbations in lower-stratospheric temperature. J. Climate, 18, , doi: / JCLI Hassanzadeh P. and Kuang Z., 2016: The linear response function of an idealized atmosphere. Part I: Construction using Green s functions and applications, Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 79, Hassanzadeh P., Kuang Z., 2016: The linear response function of an idealized atmosphere: Part II: Implications for the practical use of the Fluctuation-Dissipation Theorem and the role of operator s nonnormality. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 79, Kidston, J., Scaife, A. A., Hardiman, S. C., Mitchell, D. M., Butchart, N., Baldwin, M. P., Gray, L. G., 2015: Stratospheric influence on tropospheric jet streams, storm tracks and surface weather. Nature Geoscience, 8, Kushner, P. J., and Polvani, L. M., 2004: Stratospheretroposphere coupling in a relatively simple AGCM: The role of eddies. J. Climate, 17, , doi: / (2004)017,0629: SCIARS.2.0.CO;2. Lu, J., Chen, G., Frierson, D.M.W, 2008: Response of the Zonal Mean Atmospheric Circulation to El Niño versus Global Warming. J. Climate, 21, , doi: /2008JCLI
43 Polvani, L. M., and P. J. Kushner, 2002: Tropospheric response to stratospheric perturbations in a relatively simple general circulation model. Geophys. Res. Lett., 29, 1114, doi: / 2001GL Ring, M. J., and Plumb, R. A. 2008: The response of a simplified GCM to axisymmetric forcings: Applicability of the fluctuation dissipation theorem. J. Atmos. Sci., 65, Simpson, I. R., Blackburn, M., and Haigh, J.D., 2009: The role of eddies in driving the tropospheric response to stratospheric heating perturbations. J. Atmos. Sci., 66, , doi: /2008jas Song, Y., Robinson, W. A., 2004: Dynamical mechanisms for stratospheric influences on the troposphere. J. Atmos. Sci., 61, Thompson, D. W. J., Solomon, S., 2002: Interpretation of Recent Southern Hemisphere Climate Change, Science, 296, Thuburn, J., 2005: Climate sensitivities via a Fokker-Plank adjoint approach. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 131,
Stratospheric Influence on Polar Climate. Paul Kushner, Dept. of Physics, University of Toronto
 Stratospheric Influence on Polar Climate Paul Kushner, Dept. of Physics, University of Toronto Aims for Today 1. Discuss different types of stratospheric influence. 2. Describe some dynamical aspects.
Stratospheric Influence on Polar Climate Paul Kushner, Dept. of Physics, University of Toronto Aims for Today 1. Discuss different types of stratospheric influence. 2. Describe some dynamical aspects.
Climate Change and Variability in the Southern Hemisphere: An Atmospheric Dynamics Perspective
 Climate Change and Variability in the Southern Hemisphere: An Atmospheric Dynamics Perspective Edwin P. Gerber Center for Atmosphere Ocean Science Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences New York University
Climate Change and Variability in the Southern Hemisphere: An Atmospheric Dynamics Perspective Edwin P. Gerber Center for Atmosphere Ocean Science Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences New York University
Math, Models, and Climate Change How shaving cream moved a jet stream, and how mathematics can help us better understand why
 Math, Models, and Climate Change How shaving cream moved a jet stream, and how mathematics can help us better understand why Edwin P. Gerber Center for Atmosphere and Ocean Science Courant Institute of
Math, Models, and Climate Change How shaving cream moved a jet stream, and how mathematics can help us better understand why Edwin P. Gerber Center for Atmosphere and Ocean Science Courant Institute of
The Steady-State Atmospheric Circulation Response to Climate Change like Thermal Forcings in a Simple General Circulation Model
 3474 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 23 The Steady-State Atmospheric Circulation Response to Climate Change like Thermal Forcings in a Simple General Circulation Model AMY H. BUTLER, DAVID W. J.
3474 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 23 The Steady-State Atmospheric Circulation Response to Climate Change like Thermal Forcings in a Simple General Circulation Model AMY H. BUTLER, DAVID W. J.
3. Midlatitude Storm Tracks and the North Atlantic Oscillation
 3. Midlatitude Storm Tracks and the North Atlantic Oscillation Copyright 2006 Emily Shuckburgh, University of Cambridge. Not to be quoted or reproduced without permission. EFS 3/1 Review of key results
3. Midlatitude Storm Tracks and the North Atlantic Oscillation Copyright 2006 Emily Shuckburgh, University of Cambridge. Not to be quoted or reproduced without permission. EFS 3/1 Review of key results
The Impact of the State of the Troposphere on the Response to Stratospheric Heating in a Simplified GCM
 6166 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 23 The Impact of the State of the Troposphere on the Response to Stratospheric Heating in a Simplified GCM ISLA R. SIMPSON Department of Physics, Imperial College
6166 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 23 The Impact of the State of the Troposphere on the Response to Stratospheric Heating in a Simplified GCM ISLA R. SIMPSON Department of Physics, Imperial College
How does the stratosphere influence the troposphere in mechanistic GCMs?
 How does the stratosphere influence the troposphere in mechanistic GCMs? Walt Robinson Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Acknowledgments: Dr. Yucheng Song, Climate
How does the stratosphere influence the troposphere in mechanistic GCMs? Walt Robinson Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Acknowledgments: Dr. Yucheng Song, Climate
Traveling planetary-scale Rossby waves in the winter stratosphere: The role of tropospheric baroclinic instability
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053684, 2012 Traveling planetary-scale Rossby waves in the winter stratosphere: The role of tropospheric baroclinic instability Daniela I. V. Domeisen
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053684, 2012 Traveling planetary-scale Rossby waves in the winter stratosphere: The role of tropospheric baroclinic instability Daniela I. V. Domeisen
Forced Annular Mode Patterns in a Simple Atmospheric General Circulation Model
 OCTOBER 2007 R I N G A N D P L U M B 3611 Forced Annular Mode Patterns in a Simple Atmospheric General Circulation Model MICHAEL J. RING AND R. ALAN PLUMB Program in Atmospheres, Oceans, and Climate, Massachusetts
OCTOBER 2007 R I N G A N D P L U M B 3611 Forced Annular Mode Patterns in a Simple Atmospheric General Circulation Model MICHAEL J. RING AND R. ALAN PLUMB Program in Atmospheres, Oceans, and Climate, Massachusetts
Traveling planetary-scale Rossby waves in the winter stratosphere: The role of tropospheric baroclinic instability
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.29/, 1 2 Traveling planetary-scale Rossby waves in the winter stratosphere: The role of tropospheric baroclinic instability Daniela I.V. Domeisen, 1 R.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.29/, 1 2 Traveling planetary-scale Rossby waves in the winter stratosphere: The role of tropospheric baroclinic instability Daniela I.V. Domeisen, 1 R.
Modeling the Downward Influence of Stratospheric Final Warming events
 Modeling the Downward Influence of Stratospheric Final Warming events Lantao Sun Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Walter A. Robinson Division of Atmospheric
Modeling the Downward Influence of Stratospheric Final Warming events Lantao Sun Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Walter A. Robinson Division of Atmospheric
DynVar Diagnostic MIP Dynamics and Variability of the Stratosphere Troposphere System
 DynVar Diagnostic MIP Dynamics and Variability of the Stratosphere Troposphere System Co-Chairs: Edwin Gerber (gerber@cims.nyu.edu) Elisa Manzini (elisa.manzini@mpimet.mpg.de) Members of the Scientific
DynVar Diagnostic MIP Dynamics and Variability of the Stratosphere Troposphere System Co-Chairs: Edwin Gerber (gerber@cims.nyu.edu) Elisa Manzini (elisa.manzini@mpimet.mpg.de) Members of the Scientific
The stratospheric response to extratropical torques and its relationship with the annular mode
 The stratospheric response to extratropical torques and its relationship with the annular mode Peter Watson 1, Lesley Gray 1,2 1. Atmospheric, Oceanic and Planetary Physics, Oxford University 2. National
The stratospheric response to extratropical torques and its relationship with the annular mode Peter Watson 1, Lesley Gray 1,2 1. Atmospheric, Oceanic and Planetary Physics, Oxford University 2. National
Schematic from Vallis: Rossby waves and the jet
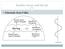 Schematic from Vallis: Rossby waves and the jet Schematic from Vallis: Rossby waves and the jet A Barotropic Model Stochastic stirring + linear damping Force barotropic vort. eqn. with white noise in storm
Schematic from Vallis: Rossby waves and the jet Schematic from Vallis: Rossby waves and the jet A Barotropic Model Stochastic stirring + linear damping Force barotropic vort. eqn. with white noise in storm
A mechanistic model study of quasi-stationary wave reflection. D.A. Ortland T.J. Dunkerton NorthWest Research Associates Bellevue WA
 A mechanistic model study of quasi-stationary wave reflection D.A. Ortland T.J. Dunkerton ortland@nwra.com NorthWest Research Associates Bellevue WA Quasi-stationary flow Describe in terms of zonal mean
A mechanistic model study of quasi-stationary wave reflection D.A. Ortland T.J. Dunkerton ortland@nwra.com NorthWest Research Associates Bellevue WA Quasi-stationary flow Describe in terms of zonal mean
Imperial College London
 Solar Influence on Stratosphere-Troposphere Dynamical Coupling Isla Simpson, Joanna D. Haigh, Space and Atmospheric Physics, Imperial College London Mike Blackburn, Department of Meteorology, University
Solar Influence on Stratosphere-Troposphere Dynamical Coupling Isla Simpson, Joanna D. Haigh, Space and Atmospheric Physics, Imperial College London Mike Blackburn, Department of Meteorology, University
On the Linkages between the Tropospheric Isentropic Slope and Eddy Fluxes of Heat during Northern Hemisphere Winter
 JUNE 2012 T H O M P S O N A N D B I R N E R 1811 On the Linkages between the Tropospheric Isentropic Slope and Eddy Fluxes of Heat during Northern Hemisphere Winter DAVID W. J. THOMPSON AND THOMAS BIRNER
JUNE 2012 T H O M P S O N A N D B I R N E R 1811 On the Linkages between the Tropospheric Isentropic Slope and Eddy Fluxes of Heat during Northern Hemisphere Winter DAVID W. J. THOMPSON AND THOMAS BIRNER
no eddies eddies Figure 3. Simulated surface winds. Surface winds no eddies u, v m/s φ0 =12 φ0 =0
 References Held, Isaac M., and Hou, A. Y., 1980: Nonlinear axially symmetric circulations in a nearly inviscid atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 37, 515-533. Held, Isaac M., and Suarez, M. J., 1994: A proposal
References Held, Isaac M., and Hou, A. Y., 1980: Nonlinear axially symmetric circulations in a nearly inviscid atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 37, 515-533. Held, Isaac M., and Suarez, M. J., 1994: A proposal
The Tropospheric Jet Response to Prescribed Zonal Forcing in an Idealized Atmospheric Model
 2254 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 65 The Tropospheric Jet Response to Prescribed Zonal Forcing in an Idealized Atmospheric Model GANG CHEN Program in Atmospheres,
2254 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 65 The Tropospheric Jet Response to Prescribed Zonal Forcing in an Idealized Atmospheric Model GANG CHEN Program in Atmospheres,
A Mechanism for the Effect of Tropospheric Jet Structure on the Annular Mode Like Response to Stratospheric Forcing
 2152 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 69 A Mechanism for the Effect of Tropospheric Jet Structure on the Annular Mode Like Response to Stratospheric Forcing ISLA R.
2152 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 69 A Mechanism for the Effect of Tropospheric Jet Structure on the Annular Mode Like Response to Stratospheric Forcing ISLA R.
Stratosphere Troposphere Coupling in a Relatively Simple AGCM: Impact of the Seasonal Cycle
 1 NOVEMBER 2006 N O T E S A N D C O R R E S P O N D E N C E 5721 Stratosphere Troposphere Coupling in a Relatively Simple AGCM: Impact of the Seasonal Cycle PAUL J. KUSHNER Department of Physics, University
1 NOVEMBER 2006 N O T E S A N D C O R R E S P O N D E N C E 5721 Stratosphere Troposphere Coupling in a Relatively Simple AGCM: Impact of the Seasonal Cycle PAUL J. KUSHNER Department of Physics, University
SPARC Dynamics and Variability Project and its Connection to C20C. Paul J. Kushner (Project Coordinator) University of Toronto
 SPARC Dynamics and Variability Project and its Connection to C20C Paul J. Kushner (Project Coordinator) University of Toronto Mark Baldwin, Neil Butchart, Norm McFarlane, Alan O Neill, Judith Perlwitz,
SPARC Dynamics and Variability Project and its Connection to C20C Paul J. Kushner (Project Coordinator) University of Toronto Mark Baldwin, Neil Butchart, Norm McFarlane, Alan O Neill, Judith Perlwitz,
Four ways of inferring the MMC. 1. direct measurement of [v] 2. vorticity balance. 3. total energy balance
![Four ways of inferring the MMC. 1. direct measurement of [v] 2. vorticity balance. 3. total energy balance Four ways of inferring the MMC. 1. direct measurement of [v] 2. vorticity balance. 3. total energy balance](/thumbs/88/114934484.jpg) Four ways of inferring the MMC 1. direct measurement of [v] 2. vorticity balance 3. total energy balance 4. eliminating time derivatives in governing equations Four ways of inferring the MMC 1. direct
Four ways of inferring the MMC 1. direct measurement of [v] 2. vorticity balance 3. total energy balance 4. eliminating time derivatives in governing equations Four ways of inferring the MMC 1. direct
Isentropic slopes, down-gradient eddy fluxes, and the extratropical atmospheric. circulation response to tropical tropospheric heating
 Isentropic slopes, down-gradient eddy fluxes, and the extratropical atmospheric circulation response to tropical tropospheric heating Amy H. Butler 1, David W.J. Thompson 2, Thomas Birner 2 1 NOAA/NWS/NCEP/Climate
Isentropic slopes, down-gradient eddy fluxes, and the extratropical atmospheric circulation response to tropical tropospheric heating Amy H. Butler 1, David W.J. Thompson 2, Thomas Birner 2 1 NOAA/NWS/NCEP/Climate
The role of stratospheric processes in large-scale teleconnections
 The role of stratospheric processes in large-scale teleconnections Judith Perlwitz NOAA/Earth System Research Laboratory and CIRES/University of Colorado Outline Introduction Comparison of features of
The role of stratospheric processes in large-scale teleconnections Judith Perlwitz NOAA/Earth System Research Laboratory and CIRES/University of Colorado Outline Introduction Comparison of features of
The influence of Southern Hemisphere sea ice extent on the latitude of the mid latitude jet stream
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl048056, 2011 The influence of Southern Hemisphere sea ice extent on the latitude of the mid latitude jet stream J. Kidston, 1 A. S. Taschetto,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl048056, 2011 The influence of Southern Hemisphere sea ice extent on the latitude of the mid latitude jet stream J. Kidston, 1 A. S. Taschetto,
High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
7 The General Circulation
 7 The General Circulation 7.1 The axisymmetric state At the beginning of the class, we discussed the nonlinear, inviscid, axisymmetric theory of the meridional structure of the atmosphere. The important
7 The General Circulation 7.1 The axisymmetric state At the beginning of the class, we discussed the nonlinear, inviscid, axisymmetric theory of the meridional structure of the atmosphere. The important
Sensitivity of zonal-mean circulation to air-sea roughness in climate models
 Sensitivity of zonal-mean circulation to air-sea roughness in climate models Inna Polichtchouk & Ted Shepherd Royal Meteorological Society National Meeting 16.11.2016 MOTIVATION Question: How sensitive
Sensitivity of zonal-mean circulation to air-sea roughness in climate models Inna Polichtchouk & Ted Shepherd Royal Meteorological Society National Meeting 16.11.2016 MOTIVATION Question: How sensitive
The role of synoptic eddies in the tropospheric response to stratospheric variability
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 4, 4933 4937, doi:1.12/grl.943, 213 The role of synoptic eddies in the tropospheric response to stratospheric variability Daniela I. V. Domeisen, 1 Lantao Sun, 2 and
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 4, 4933 4937, doi:1.12/grl.943, 213 The role of synoptic eddies in the tropospheric response to stratospheric variability Daniela I. V. Domeisen, 1 Lantao Sun, 2 and
Mechanisms for influence of the stratosphere on the troposphere
 Mechanisms for influence of the stratosphere on the troposphere Radiative Mass transfer/chemical Dynamical Alan Plumb M. I. T. Apr 2003 What dynamical effect does the stratosphere have on the troposphere?
Mechanisms for influence of the stratosphere on the troposphere Radiative Mass transfer/chemical Dynamical Alan Plumb M. I. T. Apr 2003 What dynamical effect does the stratosphere have on the troposphere?
How do we deal with uncertainty connected with atmospheric circulation?
 How do we deal with uncertainty connected with atmospheric circulation? Ted Shepherd Grantham Professor of Climate Science Department of Meteorology University of Reading Some addi-onal background Circula-on
How do we deal with uncertainty connected with atmospheric circulation? Ted Shepherd Grantham Professor of Climate Science Department of Meteorology University of Reading Some addi-onal background Circula-on
AMERICAN METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY
 AMERICAN METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences EARLY ONLINE RELEASE This is a preliminary PDF of the author-produced manuscript that has been peer-reviewed and accepted for publication.
AMERICAN METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences EARLY ONLINE RELEASE This is a preliminary PDF of the author-produced manuscript that has been peer-reviewed and accepted for publication.
Change in Occurrence Frequency of Stratospheric Sudden Warmings. with ENSO-like SST Forcing as Simulated WACCM
 Change in Occurrence Frequency of Stratospheric Sudden Warmings with ENSO-like SST Forcing as Simulated WACCM Masakazu Taguchi* and Dennis L. Hartmann Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of
Change in Occurrence Frequency of Stratospheric Sudden Warmings with ENSO-like SST Forcing as Simulated WACCM Masakazu Taguchi* and Dennis L. Hartmann Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of
The effects of North Atlantic SST and sea-ice anomalies. on the winter circulation in CCM3. Part II: Direct and indirect components of the response
 The effects of North Atlantic SST and sea-ice anomalies on the winter circulation in CCM3. Part II: Direct and indirect components of the response Clara Deser 1, Gudrun Magnusdottir 2, R. Saravanan 1 and
The effects of North Atlantic SST and sea-ice anomalies on the winter circulation in CCM3. Part II: Direct and indirect components of the response Clara Deser 1, Gudrun Magnusdottir 2, R. Saravanan 1 and
Quantifying the Eddy Feedback and the Persistence of the Zonal Index in an Idealized Atmospheric Model
 DECEMBER 2009 C H E N A N D P L U M B 3707 Quantifying the Eddy Feedback and the Persistence of the Zonal Index in an Idealized Atmospheric Model GANG CHEN AND R. ALAN PLUMB Program in Atmospheres, Oceans
DECEMBER 2009 C H E N A N D P L U M B 3707 Quantifying the Eddy Feedback and the Persistence of the Zonal Index in an Idealized Atmospheric Model GANG CHEN AND R. ALAN PLUMB Program in Atmospheres, Oceans
Thermodynamic Control on the Poleward shift of the Extratropical Jet in. Climate Change Simulations
 1 Thermodynamic Control on the Poleward shift of the Extratropical Jet in 2 Climate Change Simulations 3 Ying Li and David W. J. Thompson 4 Department of Atmospheric Science, Colorado State University,
1 Thermodynamic Control on the Poleward shift of the Extratropical Jet in 2 Climate Change Simulations 3 Ying Li and David W. J. Thompson 4 Department of Atmospheric Science, Colorado State University,
Dynamics of the Extratropical Response to Tropical Heating
 Regional and Local Climate Modeling and Analysis Research Group R e L o C l i m Dynamics of the Extratropical Response to Tropical Heating (1) Wegener Center for Climate and Global Change (WegCenter) and
Regional and Local Climate Modeling and Analysis Research Group R e L o C l i m Dynamics of the Extratropical Response to Tropical Heating (1) Wegener Center for Climate and Global Change (WegCenter) and
7 The Quasi-Biennial Oscillation (QBO)
 7 The Quasi-Biennial Oscillation (QBO) (Reviewed by Baldwin et al., Rev. Geophys., 001) Previously we noted the remarkable quasi-periodic reversal of zonal winds in the tropical stratosphere, the quasi-biennial
7 The Quasi-Biennial Oscillation (QBO) (Reviewed by Baldwin et al., Rev. Geophys., 001) Previously we noted the remarkable quasi-periodic reversal of zonal winds in the tropical stratosphere, the quasi-biennial
Lecture #2 Planetary Wave Models. Charles McLandress (Banff Summer School 7-13 May 2005)
 Lecture #2 Planetary Wave Models Charles McLandress (Banff Summer School 7-13 May 2005) 1 Outline of Lecture 1. Observational motivation 2. Forced planetary waves in the stratosphere 3. Traveling planetary
Lecture #2 Planetary Wave Models Charles McLandress (Banff Summer School 7-13 May 2005) 1 Outline of Lecture 1. Observational motivation 2. Forced planetary waves in the stratosphere 3. Traveling planetary
On the Tropospheric Response to Anomalous Stratospheric Wave Drag and Radiative Heating
 2616 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 63 On the Tropospheric Response to Anomalous Stratospheric Wave Drag and Radiative Heating DAVID W. J. THOMPSON AND JASON C. FURTADO
2616 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 63 On the Tropospheric Response to Anomalous Stratospheric Wave Drag and Radiative Heating DAVID W. J. THOMPSON AND JASON C. FURTADO
The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007
 The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007 Hiroshi Hasegawa 1, Yayoi Harada 1, Hiroshi Nakamigawa 1, Atsushi Goto 1 1 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological
The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007 Hiroshi Hasegawa 1, Yayoi Harada 1, Hiroshi Nakamigawa 1, Atsushi Goto 1 1 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological
Thermodynamic Control on the Poleward shift of the Extratropical Jet in. Climate Change Simulations - Role of systematic lifting of high clouds and
 1 Thermodynamic Control on the Poleward shift of the Extratropical Jet in 2 Climate Change Simulations - Role of systematic lifting of high clouds and 3 their radiative effects 4 Ying Li and David W. J.
1 Thermodynamic Control on the Poleward shift of the Extratropical Jet in 2 Climate Change Simulations - Role of systematic lifting of high clouds and 3 their radiative effects 4 Ying Li and David W. J.
Extremely cold and persistent stratospheric Arctic vortex in the winter of
 Article Atmospheric Science September 2013 Vol.58 No.25: 3155 3160 doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5945-5 Extremely cold and persistent stratospheric Arctic vortex in the winter of 2010 2011 HU YongYun 1* & XIA
Article Atmospheric Science September 2013 Vol.58 No.25: 3155 3160 doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5945-5 Extremely cold and persistent stratospheric Arctic vortex in the winter of 2010 2011 HU YongYun 1* & XIA
Baroclinic anomalies associated with the Southern Hemisphere Annular Mode: Roles of synoptic and low-frequency eddies
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 4, 361 366, doi:1.1/grl.5396, 13 Baroclinic anomalies associated with the Southern Hemisphere Annular Mode: Roles of synoptic and low-frequency eddies Yu Nie, 1 Yang
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 4, 361 366, doi:1.1/grl.5396, 13 Baroclinic anomalies associated with the Southern Hemisphere Annular Mode: Roles of synoptic and low-frequency eddies Yu Nie, 1 Yang
The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate
 The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate Mark P. Baldwin Northwest Research Associates, USA SORCE, 27 October 2004 Overview Climatology of the
The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate Mark P. Baldwin Northwest Research Associates, USA SORCE, 27 October 2004 Overview Climatology of the
2. Meridional atmospheric structure; heat and water transport. Recall that the most primitive equilibrium climate model can be written
 2. Meridional atmospheric structure; heat and water transport The equator-to-pole temperature difference DT was stronger during the last glacial maximum, with polar temperatures down by at least twice
2. Meridional atmospheric structure; heat and water transport The equator-to-pole temperature difference DT was stronger during the last glacial maximum, with polar temperatures down by at least twice
Influence of eddy driven jet latitude on North Atlantic jet persistence and blocking frequency in CMIP3 integrations
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl045700, 2010 Influence of eddy driven jet latitude on North Atlantic jet persistence and blocking frequency in CMIP3 integrations Elizabeth A.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl045700, 2010 Influence of eddy driven jet latitude on North Atlantic jet persistence and blocking frequency in CMIP3 integrations Elizabeth A.
What kind of stratospheric sudden warming propagates to the troposphere?
 What kind of stratospheric sudden warming propagates to the troposphere? Ken I. Nakagawa 1, and Koji Yamazaki 2 1 Sapporo District Meteorological Observatory, Japan Meteorological Agency Kita-2, Nishi-18,
What kind of stratospheric sudden warming propagates to the troposphere? Ken I. Nakagawa 1, and Koji Yamazaki 2 1 Sapporo District Meteorological Observatory, Japan Meteorological Agency Kita-2, Nishi-18,
Effect of zonal asymmetries in stratospheric ozone on simulated Southern Hemisphere climate trends
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L18701, doi:10.1029/2009gl040419, 2009 Effect of zonal asymmetries in stratospheric ozone on simulated Southern Hemisphere climate trends
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L18701, doi:10.1029/2009gl040419, 2009 Effect of zonal asymmetries in stratospheric ozone on simulated Southern Hemisphere climate trends
Influence of Doubled CO 2 on Ozone via Changes in the Brewer Dobson Circulation
 JULY 2007 N O T E S A N D C O R R E S P O N D E N C E 2751 Influence of Doubled CO 2 on Ozone via Changes in the Brewer Dobson Circulation XUN JIANG Division of Geological and Planetary Sciences, and Department
JULY 2007 N O T E S A N D C O R R E S P O N D E N C E 2751 Influence of Doubled CO 2 on Ozone via Changes in the Brewer Dobson Circulation XUN JIANG Division of Geological and Planetary Sciences, and Department
A Simulation of the Separate Climate Effects of Middle-Atmospheric and Tropospheric CO 2 Doubling
 2352 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE VOLUME 17 A Simulation of the Separate Climate Effects of Middle-Atmospheric and Tropospheric CO 2 Doubling M. SIGMOND Department of Applied Physics, Eindhoven University of Technology
2352 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE VOLUME 17 A Simulation of the Separate Climate Effects of Middle-Atmospheric and Tropospheric CO 2 Doubling M. SIGMOND Department of Applied Physics, Eindhoven University of Technology
Annular mode time scales in the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fourth Assessment Report models
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L22707, doi:10.1029/2008gl035712, 2008 Annular mode time scales in the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fourth Assessment Report
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L22707, doi:10.1029/2008gl035712, 2008 Annular mode time scales in the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fourth Assessment Report
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1. Summary of the climatic responses to the Gulf Stream. On the offshore flank of the SST front (black dashed curve) of the Gulf Stream (green long arrow), surface wind convergence associated with
Figure S1. Summary of the climatic responses to the Gulf Stream. On the offshore flank of the SST front (black dashed curve) of the Gulf Stream (green long arrow), surface wind convergence associated with
Annular Mode Like Variation in a Multilayer Quasigeostrophic Model
 2940 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 69 Annular Mode Like Variation in a Multilayer Quasigeostrophic Model YANG ZHANG, XIU-QUN YANG, AND YU NIE School of Atmospheric
2940 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 69 Annular Mode Like Variation in a Multilayer Quasigeostrophic Model YANG ZHANG, XIU-QUN YANG, AND YU NIE School of Atmospheric
A Truncated Model for Finite Amplitude Baroclinic Waves in a Channel
 A Truncated Model for Finite Amplitude Baroclinic Waves in a Channel Zhiming Kuang 1 Introduction To date, studies of finite amplitude baroclinic waves have been mostly numerical. The numerical models,
A Truncated Model for Finite Amplitude Baroclinic Waves in a Channel Zhiming Kuang 1 Introduction To date, studies of finite amplitude baroclinic waves have been mostly numerical. The numerical models,
Abrupt Circulation Responses to Tropical Upper-Tropospheric Warming in a Relatively Simple Stratosphere-Resolving AGCM
 15 JUNE 2012 W A N G E T A L. 4097 Abrupt Circulation Responses to Tropical Upper-Tropospheric Warming in a Relatively Simple Stratosphere-Resolving AGCM SHUGUANG WANG Department of Applied Physics and
15 JUNE 2012 W A N G E T A L. 4097 Abrupt Circulation Responses to Tropical Upper-Tropospheric Warming in a Relatively Simple Stratosphere-Resolving AGCM SHUGUANG WANG Department of Applied Physics and
Seasonality of the Jet Response to Arctic Warming
 Seasonality of the Jet Response to Arctic Warming Bryn Ronalds Adv: Elizabeth Barnes CVCWG Meeting: March 2, 27 The story: Midlatitude jets are fundamental to weather and climate It is generally agreed
Seasonality of the Jet Response to Arctic Warming Bryn Ronalds Adv: Elizabeth Barnes CVCWG Meeting: March 2, 27 The story: Midlatitude jets are fundamental to weather and climate It is generally agreed
Annular variability and eddy-zonal flow interactions in a simplified atmospheric GCM. Part 1: Characterization of high and low frequency behaviour
 Annular variability and eddy-zonal flow interactions in a simplified atmospheric GCM. Part 1: Characterization of high and low frequency behaviour A BC DEF B E E E A E E DE C E E E E E A E DE DD E E BE
Annular variability and eddy-zonal flow interactions in a simplified atmospheric GCM. Part 1: Characterization of high and low frequency behaviour A BC DEF B E E E A E E DE C E E E E E A E DE DD E E BE
Eddy Zonal Flow Interactions and the Persistence of the Zonal Index
 3296 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 64 Eddy Zonal Flow Interactions and the Persistence of the Zonal Index EDWIN P. GERBER Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics,
3296 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 64 Eddy Zonal Flow Interactions and the Persistence of the Zonal Index EDWIN P. GERBER Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics,
The Role of Eddies in Driving the Tropospheric Response to Stratospheric Heating Perturbations
 MAY 2009 S I M P S O N E T A L. 1347 The Role of Eddies in Driving the Tropospheric Response to Stratospheric Heating Perturbations ISLA R. SIMPSON Department of Physics, Imperial College London, London,
MAY 2009 S I M P S O N E T A L. 1347 The Role of Eddies in Driving the Tropospheric Response to Stratospheric Heating Perturbations ISLA R. SIMPSON Department of Physics, Imperial College London, London,
CHAPTER 4. THE HADLEY CIRCULATION 59 smaller than that in midlatitudes. This is illustrated in Fig. 4.2 which shows the departures from zonal symmetry
 Chapter 4 THE HADLEY CIRCULATION The early work on the mean meridional circulation of the tropics was motivated by observations of the trade winds. Halley (1686) and Hadley (1735) concluded that the trade
Chapter 4 THE HADLEY CIRCULATION The early work on the mean meridional circulation of the tropics was motivated by observations of the trade winds. Halley (1686) and Hadley (1735) concluded that the trade
A stratospheric influence on the winter NAO and North Atlantic surface climate
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L18715, doi:10.1029/2005gl023226, 2005 A stratospheric influence on the winter NAO and North Atlantic surface climate Adam A. Scaife, 1 Jeff R. Knight, 1 Geoff K.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L18715, doi:10.1029/2005gl023226, 2005 A stratospheric influence on the winter NAO and North Atlantic surface climate Adam A. Scaife, 1 Jeff R. Knight, 1 Geoff K.
Zonal Jet Structure and the Leading Mode of Variability
 15 OCTOBER 2007 E I CHELBERGER AND HARTMANN 5149 Zonal Jet Structure and the Leading Mode of Variability SCOTT J. EICHELBERGER AND DENNIS L. HARTMANN Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington,
15 OCTOBER 2007 E I CHELBERGER AND HARTMANN 5149 Zonal Jet Structure and the Leading Mode of Variability SCOTT J. EICHELBERGER AND DENNIS L. HARTMANN Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington,
The Impact of Polar Stratospheric Ozone Loss on Southern Hemisphere Stratospheric Circulation and Surface Climate
 The Impact of Polar Stratospheric Ozone Loss on Southern Hemisphere Stratospheric Circulation and Surface Climate James Keeble, Peter Braesicke, Howard Roscoe and John Pyle James.keeble@atm.ch.cam.ac.uk
The Impact of Polar Stratospheric Ozone Loss on Southern Hemisphere Stratospheric Circulation and Surface Climate James Keeble, Peter Braesicke, Howard Roscoe and John Pyle James.keeble@atm.ch.cam.ac.uk
Stratospheric control of the extratropical circulation response to surface forcing
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L21802, doi:10.1029/2007gl031626, 2007 Stratospheric control of the extratropical circulation response to surface forcing Christopher
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L21802, doi:10.1029/2007gl031626, 2007 Stratospheric control of the extratropical circulation response to surface forcing Christopher
The Interannual Relationship between the Latitude of the Eddy-Driven Jet and the Edge of the Hadley Cell
 15 JANUARY 2011 K A N G A N D P O L V A N I 563 The Interannual Relationship between the Latitude of the Eddy-Driven Jet and the Edge of the Hadley Cell SARAH M. KANG Department of Applied Physics and
15 JANUARY 2011 K A N G A N D P O L V A N I 563 The Interannual Relationship between the Latitude of the Eddy-Driven Jet and the Edge of the Hadley Cell SARAH M. KANG Department of Applied Physics and
The impacts of stochastic noise on climate models
 The impacts of stochastic noise on climate models Paul Williams Department of Meteorology, University of Reading, UK The impacts of στοχαστικός noise on climate models Paul Williams Department of Meteorology,
The impacts of stochastic noise on climate models Paul Williams Department of Meteorology, University of Reading, UK The impacts of στοχαστικός noise on climate models Paul Williams Department of Meteorology,
Response of Baroclinic Life Cycles to Barotropic Shear
 VOL. 55, NO. 3 JOURNAL OF THE ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES 1FEBRUARY 1998 Response of Baroclinic Life Cycles to Barotropic Shear DENNIS L. HARTMANN AND PETER ZUERCHER Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University
VOL. 55, NO. 3 JOURNAL OF THE ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES 1FEBRUARY 1998 Response of Baroclinic Life Cycles to Barotropic Shear DENNIS L. HARTMANN AND PETER ZUERCHER Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University
The Key Role of Lower-Level Meridional Shear in Baroclinic Wave Life Cycles
 389 The Key Role of Lower-Level Meridional Shear in Baroclinic Wave Life Cycles DENNIS L. HARTMANN Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington (Manuscript received
389 The Key Role of Lower-Level Meridional Shear in Baroclinic Wave Life Cycles DENNIS L. HARTMANN Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington (Manuscript received
The Role of Subtropical Irreversible PV Mixing in the Zonal Mean Circulation Response to Global Warming Like Thermal Forcing
 15 MARCH 2014 L U E T A L. 2297 The Role of Subtropical Irreversible PV Mixing in the Zonal Mean Circulation Response to Global Warming Like Thermal Forcing JIAN LU Pacific Northwest National Laboratory,
15 MARCH 2014 L U E T A L. 2297 The Role of Subtropical Irreversible PV Mixing in the Zonal Mean Circulation Response to Global Warming Like Thermal Forcing JIAN LU Pacific Northwest National Laboratory,
Downward propagation from the stratosphere to the troposphere: A comparison of the two hemispheres
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. D24, 4780, doi:10.1029/2003jd004077, 2003 Downward propagation from the stratosphere to the troposphere: A comparison of the two hemispheres Rune G. Graversen
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. D24, 4780, doi:10.1029/2003jd004077, 2003 Downward propagation from the stratosphere to the troposphere: A comparison of the two hemispheres Rune G. Graversen
The ozone hole indirect effect: Cloud-radiative anomalies accompanying the poleward shift of the eddy-driven jet in the Southern Hemisphere
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 4, 388 392, doi:1.12/grl.575, 213 The ozone hole indirect effect: Cloud-radiative anomalies accompanying the poleward shift of the eddy-driven jet in the Southern Hemisphere
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 4, 388 392, doi:1.12/grl.575, 213 The ozone hole indirect effect: Cloud-radiative anomalies accompanying the poleward shift of the eddy-driven jet in the Southern Hemisphere
Quantifying the annular mode dynamics in an idealized atmosphere
 Generated using the official AMS LATEX template two-column layout. FOR AUTHOR USE ONLY, NOT FOR SUBMISSION! J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S Quantifying the annular mode dynamics
Generated using the official AMS LATEX template two-column layout. FOR AUTHOR USE ONLY, NOT FOR SUBMISSION! J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S Quantifying the annular mode dynamics
The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact
 1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
General Circulation of the Atmosphere. René Garreaud
 General Circulation of the Atmosphere René Garreaud www.dgf.uchile.cl/rene General circulation of the Atmosphere Low latitude areas receive more solar energy than high latitudes (because of earth sphericity).
General Circulation of the Atmosphere René Garreaud www.dgf.uchile.cl/rene General circulation of the Atmosphere Low latitude areas receive more solar energy than high latitudes (because of earth sphericity).
Some remarks on climate modeling
 Some remarks on climate modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Selected overheads by Doug Nychka Outline Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
Some remarks on climate modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Selected overheads by Doug Nychka Outline Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
Historical trends in the jet streams
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L08803, doi:10.1029/2008gl033614, 2008 Historical trends in the jet streams Cristina L. Archer 1 and Ken Caldeira 1 Received 12 February 2008; revised 10 March 2008;
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L08803, doi:10.1029/2008gl033614, 2008 Historical trends in the jet streams Cristina L. Archer 1 and Ken Caldeira 1 Received 12 February 2008; revised 10 March 2008;
METEOROLOGY ATMOSPHERIC TELECONNECTIONS: FROM CAUSAL ATTRIBUTION TO STORYLINES OF CIRCULATION CHANGE
 METEOROLOGY ATMOSPHERIC TELECONNECTIONS: FROM CAUSAL ATTRIBUTION TO STORYLINES OF CIRCULATION CHANGE Ted Shepherd Grantham Chair of Climate Science Stratosphere-troposphere coupling: stratospheric polar
METEOROLOGY ATMOSPHERIC TELECONNECTIONS: FROM CAUSAL ATTRIBUTION TO STORYLINES OF CIRCULATION CHANGE Ted Shepherd Grantham Chair of Climate Science Stratosphere-troposphere coupling: stratospheric polar
Lecture 10a: The Hadley Cell
 Lecture 10a: The Hadley Cell Geoff Vallis; notes by Jim Thomas and Geoff J. Stanley June 27 In this short lecture we take a look at the general circulation of the atmosphere, and in particular the Hadley
Lecture 10a: The Hadley Cell Geoff Vallis; notes by Jim Thomas and Geoff J. Stanley June 27 In this short lecture we take a look at the general circulation of the atmosphere, and in particular the Hadley
Width of the Hadley cell in simple and comprehensive general circulation models
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L18804, doi:10.1029/2007gl031115, 2007 Width of the Hadley cell in simple and comprehensive general circulation models Dargan M. W. Frierson,
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L18804, doi:10.1029/2007gl031115, 2007 Width of the Hadley cell in simple and comprehensive general circulation models Dargan M. W. Frierson,
Southern Annular Mode Dynamics in Observations and Models. Part 1: the Influence of Climatological Zonal Wind Biases in a. Comprehensive GCM.
 Generated using version 3.1.2 of the official AMS L A TEX template 1 Southern Annular Mode Dynamics in Observations and Models. 2 Part 1: the Influence of Climatological Zonal Wind Biases in a 3 Comprehensive
Generated using version 3.1.2 of the official AMS L A TEX template 1 Southern Annular Mode Dynamics in Observations and Models. 2 Part 1: the Influence of Climatological Zonal Wind Biases in a 3 Comprehensive
Zonal jet structure and the. leading mode of variability
 Zonal jet structure and the leading mode of variability Scott J. Eichelberger & Dennis L. Hartmann Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington Seattle, WA January 31, 2007 corresponding
Zonal jet structure and the leading mode of variability Scott J. Eichelberger & Dennis L. Hartmann Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington Seattle, WA January 31, 2007 corresponding
Observational Zonal Mean Flow Anomalies: Vacillation or Poleward
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2013, VOL. 6, NO. 1, 1 7 Observational Zonal Mean Flow Anomalies: Vacillation or Poleward Propagation? SONG Jie The State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling for
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2013, VOL. 6, NO. 1, 1 7 Observational Zonal Mean Flow Anomalies: Vacillation or Poleward Propagation? SONG Jie The State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling for
Quantifying the eddy-jet feedback strength of the annular mode in an. idealized GCM and reanalysis data
 1 Quantifying the eddy-jet feedback strength of the annular mode in an 2 idealized GCM and reanalysis data 3 Ding Ma 4 Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts
1 Quantifying the eddy-jet feedback strength of the annular mode in an 2 idealized GCM and reanalysis data 3 Ding Ma 4 Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts
Eliassen-Palm Theory
 Eliassen-Palm Theory David Painemal MPO611 April 2007 I. Introduction The separation of the flow into its zonal average and the deviations therefrom has been a dominant paradigm for analyses of the general
Eliassen-Palm Theory David Painemal MPO611 April 2007 I. Introduction The separation of the flow into its zonal average and the deviations therefrom has been a dominant paradigm for analyses of the general
Introduction to Isentropic Coordinates:! a new view of mean meridional & eddy circulations" Cristiana Stan
 Introduction to Isentropic Coordinates:! a new view of mean meridional & eddy circulations" Cristiana Stan School and Conference on the General Circulation of the Atmosphere and Oceans: a Modern Perspective!
Introduction to Isentropic Coordinates:! a new view of mean meridional & eddy circulations" Cristiana Stan School and Conference on the General Circulation of the Atmosphere and Oceans: a Modern Perspective!
Downward migration of extratropical zonal wind anomalies
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. D7, 4223, doi:10.1029/2002jd002773, 2003 Downward migration of extratropical zonal wind anomalies R. Alan Plumb and Kirill Semeniuk 1 Department of Earth,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. D7, 4223, doi:10.1029/2002jd002773, 2003 Downward migration of extratropical zonal wind anomalies R. Alan Plumb and Kirill Semeniuk 1 Department of Earth,
Deconstructing the climate change response of the Northern
 Climate Dynamics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Deconstructing the climate change response of the Northern Hemisphere wintertime storm tracks B. J. Harvey L. C. Shaffrey T. J. Woollings
Climate Dynamics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Deconstructing the climate change response of the Northern Hemisphere wintertime storm tracks B. J. Harvey L. C. Shaffrey T. J. Woollings
(Palaeo-)climate sensitivity: ideas and definitions from the NPG literature
 (Palaeo-)climate sensitivity: ideas and definitions from the NPG literature Michel Crucifix Université catholique de Louvain & Belgian National Fund of Scientific Research Ringberg Grand Challenge Workshop:
(Palaeo-)climate sensitivity: ideas and definitions from the NPG literature Michel Crucifix Université catholique de Louvain & Belgian National Fund of Scientific Research Ringberg Grand Challenge Workshop:
Atmospheric Circulation Response to An. Instantaneous Doubling of Carbon Dioxide. Part II Atmospheric Transient Adjustment.
 Generated using version 3.1.1 of the official AMS L A TEX template 1 2 3 4 Atmospheric Circulation Response to An Instantaneous Doubling of Carbon Dioxide Part II Atmospheric Transient Adjustment and its
Generated using version 3.1.1 of the official AMS L A TEX template 1 2 3 4 Atmospheric Circulation Response to An Instantaneous Doubling of Carbon Dioxide Part II Atmospheric Transient Adjustment and its
Stratosphere Troposphere Coupling in a Relatively Simple AGCM: The Importance of Stratospheric Variability
 1920 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 22 Stratosphere Troposphere Coupling in a Relatively Simple AGCM: The Importance of Stratospheric Variability EDWIN P. GERBER Department of Applied Physics and
1920 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 22 Stratosphere Troposphere Coupling in a Relatively Simple AGCM: The Importance of Stratospheric Variability EDWIN P. GERBER Department of Applied Physics and
warmest (coldest) temperatures at summer heat dispersed upward by vertical motion Prof. Jin-Yi Yu ESS200A heated by solar radiation at the base
 Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
Responses of mesosphere and lower thermosphere temperatures to gravity wave forcing during stratospheric sudden warming
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl042351, 2010 Responses of mesosphere and lower thermosphere temperatures to gravity wave forcing during stratospheric
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl042351, 2010 Responses of mesosphere and lower thermosphere temperatures to gravity wave forcing during stratospheric
Sudden Stratospheric Warmings and Anomalous Upward Wave Activity Flux
 8 SOLA, 2017, Vol. 13A, 8 12, doi:10.2151/sola.13a-002 Sudden Stratospheric Warmings and Anomalous Upward Wave Activity Flux Thomas Birner 1 and John R. Albers 2, 3 1 Department of Atmospheric Science,
8 SOLA, 2017, Vol. 13A, 8 12, doi:10.2151/sola.13a-002 Sudden Stratospheric Warmings and Anomalous Upward Wave Activity Flux Thomas Birner 1 and John R. Albers 2, 3 1 Department of Atmospheric Science,
of Stratospheric Sudden Warming
 13 Hindcast AGCM Experiments on the Predictability of Stratospheric Sudden Warming Hitoshi Mukougawa 1, Toshihiko Hirooka 2, Tomoko Ichimaru 3 and Yuhji Kuroda 4 1 Kyoto University, Disaster Prevention
13 Hindcast AGCM Experiments on the Predictability of Stratospheric Sudden Warming Hitoshi Mukougawa 1, Toshihiko Hirooka 2, Tomoko Ichimaru 3 and Yuhji Kuroda 4 1 Kyoto University, Disaster Prevention
Changes in Southern Hemisphere rainfall, circulation and weather systems
 19th International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Perth, Australia, 12 16 December 2011 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim2011 Changes in Southern Hemisphere rainfall, circulation and weather systems Frederiksen,
19th International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Perth, Australia, 12 16 December 2011 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim2011 Changes in Southern Hemisphere rainfall, circulation and weather systems Frederiksen,
Midlatitude Storm Track Response to Increased Greenhouse Warming
 Midlatitude Storm Track Response to Increased Greenhouse Warming Yutian Wu Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Graduate School of Arts and
Midlatitude Storm Track Response to Increased Greenhouse Warming Yutian Wu Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Graduate School of Arts and
Stratospheric polar vortex influence on Northern Hemisphere winter climate variability
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L18703, doi:10.1029/2009gl039334, 2009 Stratospheric polar vortex influence on Northern Hemisphere winter climate variability H. Douville
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L18703, doi:10.1029/2009gl039334, 2009 Stratospheric polar vortex influence on Northern Hemisphere winter climate variability H. Douville
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Hydrologic Cycle and Global Warming
 Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Hydrologic Cycle and Global Warming D A R G A N M. W. F R I E R S O N U N I V E R S I T Y O F W A S H I N G T O N, D E P A R T M E N T O F A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Hydrologic Cycle and Global Warming D A R G A N M. W. F R I E R S O N U N I V E R S I T Y O F W A S H I N G T O N, D E P A R T M E N T O F A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C
