Weighted DFT Codebook for Multiuser MIMO in Spatially Correlated Channels
|
|
|
- Helen Hancock
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Weighted DFT Codebook for Multiuser MIMO in Spatially Correlated Channels Fang Yuan, Shengqian Han, Chenyang Yang Beihang University, Beijing, China Yu Zhang, Gang Wang, Ming Lei NEC Laboratories, China {zhang yu, wang gang, lei Abstract This paper proposes a novel codebook for multiuser multiple-input multiple-output systems under spatially correlated channels. Existing codebooks designed for correlated channels either require accurate channel statistics which is not favorable for practical systems, or only perform well in highly correlated channels. In this paper, we first analyze the per-user rate loss led by using DFT codebook, then propose a two-level codebook, named weighted DFT codebook. It consists of a DFT-based codebook and a Grassmannian linear packing codebook. The proposed scheme does not need accurate channel statistics and can adapt to both correlated and uncorrelated scenarios. Simulation results show significant performance gain of the proposed codebook over the existing codebooks in various correlated channels. Index Terms Limited feedback, MU-MIMO, WDFT, Codebook I. INTRODUCTION Limited feedback techniques in multiuser (MU) multipleinput multiple-output (MIMO) systems have received much attention in the last decade [1 4], where the design of codebook plays a key role. When perfect channel state information (CSI) is known at the transmitter, MU-MIMO systems will have sum rate loss in spatially correlated channels [5]. Nonetheless, it is recognized recently that MU-MIMO systems with limited feedback perform even better in correlated channels than in uncorrelated channels [6]. This is because the spatial signature of the co-scheduled users is more separable in correlated channels hence the inter-user interference is able to be reduced. For spatially correlated channels, it has been shown that Grassmannian linear packing (GLP) codebooks are not appropriate for MIMO systems any more [6]. Optimal codebook can be designed by using vector quantization techniques [7], but it requires high complexity. A systematic codebook was designed in [8], which achieves near perfect CSI performance even with few feedback bits when transmit correlation matrix is ill-conditioned and receive correlation matrix is wellconditioned. To reduce the complexity, a suboptimal codebook referred to as the transformed codebook is proposed, which can reuse the codebook designed for uncorrelated channels []. To achieve good performance, these limited feedback This work was supported in part by NEC Laboratories, China, and by the International S&T Cooperation Program of China (ISCP) (No. 008DFA1100). schemes require accurate channel statistics information. DFT codebook does not need the feedback of channel statistics. It is shown that DFT codebook can achieve a near optimal sum rate in highly correlated channels [9,10]. However, DFT based codebooks do not perform well in less correlated channels. In practice, it is desirable to design codebooks that apply for various correlated channels without the feedback of spatial correlation matrices. In this paper, we first analyze the per-user rate loss led by DFT codebook. The results indicate that DFT codebook is only efficient for quantizing channels with small angle spread (AS). For the channels with large angle spread, increasing the size of DFT codebook does not reduce the rate loss. This is owing to the fact that a single DFT codeword is not sufficient to represent a channel with large AS. Based on this observation, we propose a novel codebook for MU- MIMO systems, named weighted DFT (WDFT) codebook. It is composed of two level codebooks, among which a DFTbased codebook is used to convey the statistical channel direction information (CDI), and a GLP codebook is applied to reflect the instantaneous fluctuation of fading channels. The proposed scheme can adapt to both correlated and uncorrelated scenarios. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed codebook outperforms DFT codebook, GLP codebook, and a popular DFT-based two-level codebook for various correlated channels. II. SYSTEM MODEL A. MU-MIMO System with Limited Feedback We consider a downlink MU-MIMO system where a BS with M antennas serves K single-antenna users. The received signal at the kth user can be expressed as y k = h H k x + n k, k =1,...,K, (1) where h k C M 1 is the channel vector of the kth user, x is the transmit signal vector of the BS to K users, and n k is the additive white Gaussian noise with zero mean and unit variance. Through capacity-limited uplink channel, each user feeds back quantized CDI and channel quality information (CQI) respectively for multiuser precoding and scheduling at the BS. We propose to use a two-level codebook consisting of C 1 and C for quantizing the statistical and instantaneous CDI, /11/$ IEEE
2 respectively. The codebook design and codeword selection issues will be discuss later. B. Correlated Channel Model We consider the widely applied virtual channel model [11] for spatially correlated channel. The channel vector of the kth user is a superposition of N uncorrelated subpaths, i.e., N h k = a k,n u(β k,n ), () n=1 where a k,n is the associated subpaths gain and u(β k,n ) = [1,e jπβ k,n,...,e jπ(m 1)β k,n ] T is the steering vector by assuming uniform linear array with omnidirectional antennas. Here, β k,n = mod (d/λ sin θ k,n, 1) [0, 1] is related to the physical angle of incidence θ k,n with respect to the BS broadside, d is the antenna spacing distance, λ is the wavelength, and mod is a mod operation. According to [11], the subpath gain a k,n is independent to the angle β k,n. The channel model can be rewritten more compactly as h k = U k a k, () where the direction matrix U k =[u(β k,1 ),...,u(β k,n )],the gain vector a k =[a k,1,...,a k,n ] T and channel average energy is normalized as E{ h k } = E{M N n=1 a k,n } =1 ( and are respectively a norm and absolute operation). III. PER-USER RATE LOSS OF DFT CODEBOOK In this section, we analyze the performance of DFT codebook by deriving its per-user rate loss. The results will quantitatively show when DFT codebook is efficient for quantizing channels for MU-MIMO systems, i.e., when the performance of MU-MIMO systems can be improved by increasing codebook size. This fact has been ignored by most existing works. We consider a DFT codebook uniformly sampling the angle domain as in [10]. The ith codeword of such a B-bit DFT codebook F has the following structure f(φ i )= 1 [1,e jπφi,...,e jπ(m 1)φi ] T, (4) M where φ i = i (i =1,..., B ) and πφ B i is the ith sample in the angle domain [0, π]. Noting that DFT codebook is a single-level codebook, we can select a codeword from C. Among all the multiuser beamforming schemes, zeroforcing beamforming (ZFBF) is considered here. Though suboptimal when user number is limited, it is of low complexity and is widely applied [4, 6]. Based on the well-established upper bound of per-user rate loss for the case K = M [4], the gap between the rate with perfect CSI and the rate with limited feedback when using ZFBF is { ( P M ΔR up (P ) E log 1+ h H i v k )} M k=1,k i ( log 1+ P M E{ h k h H k v k }) = log ( 1+ P (M 1) M D(h k, C ) ), (5) where P is the transmit power at the BS, h H i v k is the interference term caused by the nonorthogonality of beamforming vector v k to h i, and D(h k, C ) is the average distortion led by codebook C []. When DFT codebook is applied, i.e., C = F, the average distortion can be further upper bounded by (see appendix) D(h k, F) ME { c 1 min φ i N a k,n (β k,n φ i ) } + c 0, (6) n where φ i is the angle sample of codeword in F. Inbrief, we denote the angle sample of the selected DFT codeword as N β k = arg min φi n a k,n (β k,n φ i ). Two observations can be obtained from (5) and (6). On one hand, for the channels with small AS and the resolution of DFT codebook B exceeds the AS, we find that β k satisfies β k β k,n < B. Then we have ( P (M 1) ΔR up (P ) log 1+ M (c 1 B + c 0 ) ), (7) where E{M n a k,n } =1is used. In these scenarios, the rate loss is mainly constrained by the spatial resolution of DFT codebook, i.e. B. Therefore increasing the codebook size B is an effective way to improve the performance of MU-MIMO systems. On the other hand, for the channels with large AS or the cases when the size of DFT codebook is large enough such that min m,n,m n β k,n β k,m B holds for all the subpaths, we will show that the sum rate of MU-MIMO systems can not be improved with the increase of the size of DFT codebook. To see this, we consider the case when B approaches to infinity, then the angle samples φ i of DFT codebook approach continuous values. In this case, we can obtain that β n k = a k,n β k,n. By defining σ k = n a k,n n a k,n (β k,n β k ) n a k,n, (8) the rate loss in (5) is more tightly upper bounded by ( P (M 1) ΔR up (P ) log 1+ M (c 1E{σk} + c 0 ) ). (9) Note that the term E{σk } in (9) is the expectation of AS in virtual channel, thus the rate loss of DFT codebook increases with AS. This indicates that DFT codebook leads to nonnegligible quantization error in less correlated channels, which cannot be compensated by increasing the codebook size. IV. WDFT CODEBOOK DESIGN A. Principles As shown in the previous analysis, the drawbacks of DFT codebook lie in that a single DFT codeword is not sufficient to represent the channels with large AS. In this section we propose a so-called WDFT codebook to resolve this problem. Inspired by the structure of virtual channel model shown in (), where the channel is expressed as a combination of the direction matrix U k and the gain vector a k, we propose to
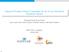
3 Fig. 1. Illustration of WDFT codebook design: using two DFT codewords to quantize a two-subpath channel. use two-level codebook, C 1 and C, to respectively quantize the direction matrix U k and the gain vector a k. Since a steering vector of uniform linear array has the same structure as a DFT codeword, we use multiple DFT codewords to construct the first level codebook C 1, which targets to quantize multiple resolvable directions of the channel. According to the law of central limit, the gain of each resolvable direction approaches to a complex Gaussian vector when many subpaths are covered by each resolvable direction. Thus GLP codebook or Random vector quantization (RVQ) codebook can be used as the second level codebook C. The principle of WDFT codebook is illustrated in Fig. 1, where the array response of a channel consisting of two subpaths is plotted, and two DFT codewords are used for quantizing the resolvable directions of two subpaths. More specifically, the first level B 1 -bit codebook C 1 can be reconstructed by an original B 1 -bit DFT codebook F with angle sample set A = {φ i φ i = i,i = }. B 1 1,...,B1 Codeword w 1 C 1 constructed by R DFT codewords f F can be written in a matrix form as w 1 (i, ΔΦ,R)=[f(φ i +Δφ 1 ),...,f(φ i +Δφ R )], (10) where Δφ r (1 r R) are the relative deviations from the central direction φ i of the codeword. Both the values of φ i and Δφ r are restricted within the discrete angle sample set A, which is known by both the BS and users. Define the deviation vector ΔΦ = [Δφ 1,...,Δφ R ], then the first level codebook depends on two parameters: ΔΦ and R. The joint chosen of R and ΔΦ will be discussed in subsection IV-B. Correspondingly, the B -bit second level codebook could be a GLP as in [1] or RVQ codebook as in [4] with proper dimension. The overall codeword in the proposed WDFT codebook can be generated by w 1 C 1 and C as G(w 1, )= w 1 }{{} }{{} size M R size R 1 / w 1. (11) In practical scenarios, the resolvable directions vary slowly, while the gain coefficients on these directions change fast. To match the channel characteristic, in the WDFT scheme the first level codebook C 1 can be used as a statistic CDI feedback while the second level codebook C can be used as an instantaneous feedback to reflect fast fading. Through this decomposition, the total feedback overhead is significantly reduced. Since we employ GLP or RVQ as the second level codebook, we only need to design the first level codebook C 1, which will be discussed in next subsection. Given the codeword for statistical CDI w opt 1 C 1, the instantaneous codeword C can be selected at the user side as w opt = arg max C h H k G(w opt 1, ). (1) Denoting the channel vector space that is closest to the overall codeword G(w 1, ) as S w 1 ={h k h H k G(w 1, ) h H k G(w 1, w ), (1) w 1 w 1, w }, then the codeword for quantizing statistical CDI information can be selected as w opt 1 = arg max h H w 1 C 1 w h C k S w k G(w 1, ) p(h k )dh k, 1 (14) where p(h k ) is the probability density function (PDF) of channel vector. B. Optimal Design According to (10) and (11), constructing a WDFT codebook at the BS requires each user to feedback the parameters ΔΦ and R. When the optimal values of ΔΦ and R are given, the optimal codebook C 1 is then determined. To reflect the dependence of the codebook on these two parameters, we denote the overall codebook built by the first level codebook C 1 and the second level codebook C as G(ΔΦ,R) in the following. According to (5), the optimal codebook design problem minimizing the per-user rate loss upper bound can be formulated as min ΔΦ,R D( h k, G(ΔΦ,R) ) () s.t. R {1,,..., B1 }, ΔΦ = [Δφ 1,...,Δφ R ], with Δφ r A,r =1,,R. The design in (), though optimal, is with a large search space which leads to a very high computation load as well as heavy feedback overhead. To address this issue, we consider a suboptimal candidate with equally spaced resolvable directions, i.e., Δφ r+1 Δφ r =Δφ. Then the optimization problem in () reduces to min Δφ,R D( h k, G(Δφ, R) ) (16a) s.t. R {1,,..., B1 }, (16b) Δφ { B1, B1+1,...,1/}. (16c) Compared with (), (16) has much lower complexity since multiple parameters ΔΦ in () becomes a single parameter
4 Δφ in (16). This also leads to lower feedback overhead of channel statistics. By contrast to the well-known Lloyd methods [7], the solution of the problem in (16) does not require explicit channel statistics at the BS. Only the feedback of R and Δφ is enough for the construction of the overall WDFT codebook scheme. C. A Heuristic Method Unfortunately, although we can expect to deign codebooks with good performance by choosing R and Δφ from the optimal problem in (16), it is feasible only when the PDF of channel vector is available at the user. Moreover, since C 1 and C is coupled as in (1) and (14), it is hard to have a closed-form solution to the problem (16). From practical application, a simpler scheme where C 1 is directly designed according to the spatial correlation matrix R h = E{hh H } is highly preferred. Here, we propose a heuristic method for designing the first level codebook with only the information of spatial correlation matrix. To this end, we view the problem shown in (16) as a statistical spatial fitting problem. Conceptually, the average CDI is less dependent on the gain vector. Therefore, we first separately find a CDI candidates set from the basic DFT codebook based on the spatial correlation matrix. Then, we strive for finding the optimal R and Δφ based on the candidate set and given the constraint that the second level codebook is GLP or RVQ codebook. In summary, the WDFT codebook feedback scheme can be implemented in the following two steps. The first step is to find the first level codebook and codeword for each user given the second codebook: 1) Each user selects a DFT codeword as its average CDI from a B 1 -bit DFT codebook F through i = arg max f(φ j ) H R h f(φ j ). j=1,..., B 1 ) Then each user finds R and Δφ as follows { {Δφ opt, R opt } = arg max max Δφ,R w ηwh C (R) } w H 1 (i, Δφ, R)R h w 1 (i, Δφ, R), 1 where η = w 1(i,Δφ,R) is a normalization factor, and the parameter R and Δφ are constrained by (16b) and (16c). The second step is feedback: 1) Each user feeds back the first level codeword w 1 (i, Δφ, R) in a long period, i.e., to feedback the index i and the two scalar parameters Δφ and R 1. ) Each user feeds back the second level codeword to the BS in a short period, which is selected according to (11) and (1). 1 In practice, the average CDI may change faster than the channel AS. In this scenario each user does not need to feedback i, Δφ and R in the same period. By contrast, the user can feed back the later two parameters in a longer period, with which the BS obtains the first level codebook. When the BS receives the two codewords, it can obtain the overall codeword by using (11). Note that such a solution does not require channel correlation matrix at the BS. Only the feedback of R and Δφ is enough to construct the first level codebook. V. SIMULATION RESULTS In the simulations, we evaluate the performance of the proposed WDFT codebook with Spatial Channel Model (SCM) [1]. The BS is equipped with a 4-antenna uniform linear array with a half wavelength antenna separation, which serves in total 10 single-antenna users by ZFBF based on limited feedback and greedy user scheduling [1]. The CQI is fed back as suggested in [14] and user speed is km/h, which is commonly used for performance evaluation in MU-MIMO systems. Two typical scenarios are studied here: one is highly correlated scenario, which has an AS of 8 degrees as defined in [1], and the other is less correlated scenario with an AS of 5 degrees. In simulations, the first level codeword is fed back every 100 ms while the second level codeword is fed back every 5 ms. In addition, a feedback delay of 1 ms is considered. The first simulation is to compare the performance of the proposed codebook with existing codebooks under different feedback overhead. Besides the proposed WDFT codebook with optimal design in (16) and the heuristic solution, two schemes are also provided here for comparison: DFT codebook in [9], and a two-level DFT-based codebook proposed by SamSung in []. The basic idea of SamSung s codebook is using the first level statistic codebook to find a rough CDI range and using the second level instantaneous codebook to quantize the CDI within the range. Therefore, it is equivalent to a DFT codebook with more feedback bits. For two-level codebooks including WDFT and SamSung s, the first level codebook has a size of B 1 =8bits. The size of the instantaneous codebook B is the same for all codebooks, which is shown in the x-axis. The average signal to noise ratio (SNR) is set to be 5 db. As shown in Fig., for the channels with both 8- and 5-degree AS, the proposed WDFT codebook with both optimal design and heuristic solution outperforms the DFT codebook as well as the codebook proposed by SamSung. Moreover, with the increase of the second level feedback bits, a performance bottleneck for DFT and SamSung s codebook is observed in both scenarios, as indicated by our analysis in Section III. The second simulation evaluates the performance of the proposed codebook and existing codebooks under different SNR for two different correlated channels. The codebooks in the simulation include the optimal WDFT codebook, the heuristic WDFT codebook, the SamSung s codebook and the GLP codebook proposed in [1]. DFT codebook is not shown here since it is inferior to the SamSung s scheme. The size of instantaneous codebook is set to be 6 bits. As shown in Fig., for the channels with both 8- and 5-degree angle spread, the proposed WDFT codebooks with both optimal design and heuristic solution outperform GLP and SamSung s codebooks.
5 Rate (bps/hz) Rate (bps/hz) WDFT (optimal) WDFT (heuristic) B (AS = 8 degree) SamSung 0 DFT B (AS = 5 degree) Fig.. Sum rate of different codebooks as a function of B for two different correlated channels. Rate (bps/hz) WDFT (optimal) AS = 8 WDFT (heuristic) AS = 8 SamSung AS = 8 GLP AS = 8 WDFT (optimal) AS = 5 WDFT (heuristic) AS = 5 Samsung AS = 5 GLP AS = SNR (in db) Fig.. Sum rate of different codebooks as a function of SNR for two different correlated channels (B =6). At the SNR of 5 db, a performance gain of 5 bps/hz and 4 bps/hz respectively achieved by optimal and heuristic WDFT can be observed over SamSung s codebook in both channels. VI. CONCLUSION In this paper we have studied the codebook design method for correlated MU-MIMO channels. We propose a novel weighted DFT (WDFT) codebook, which can adapt to different correlated channel scenarios by judiciously designing feedback information for channel statistics. The overall WDFT codebook is simple and can be easily implemented for the prevalent MU-MIMO systems. Simulation results have shown that our method is effective in different channels without requiring too much feedback overhead. APPENDIX In the following, the average distortion led by codebook F is analyzed (the subscript k is ignored for simplification). D(h, F) = E { h } E { h H f opt } =1 1 M E{ max φ i n ah n u H (β n )f(φ i ) } (17a) 1 1 M E{ max φ i n ah n u H (β n )f(φ i ) } +E { n m>n ah n a m } (17b) =1 1 M E{ max a n sin (Mπ(β n φ i ))} φ i n sin +c0 (π(β n φ i )) =1 c 1 ME { max a n (β n φ i ) } + c 0, (17c) φ i n where channel energy E{ h } is normalized to one in (17a) and c 0 =E{ n m>n ah n a m }. In the above derivations, (17b) is followed by the facts that n x n n x n n m>n x nx m and u H (β n )f(φ i ) M. In (17c), the inequality sin (Mπx) M (1 c sin (πx) 1 x ) is applied (c 1 x < 1), where c 1 = d sin (Mπx) dx M sin (πx) x=0 = (M 1) π, which is not hard to be derived. REFERENCES [1] D. J. Love, J. Heath, R. W., and T. Strohmer, Grassmannian beamforming for multiple-input multiple-output wireless systems, in Proc. IEEE Int. Communi. Conf. (IEEE ICC), vol. 4, 00. [] D. Gesbert, M. Kountouris, R. W. Heath, C.-B. Chae, and T. Salzer, From single user to multiuser: Shifting the MIMO paradigm, IEEE Signal Processing Mag., vol. 4, no. 5, pp. 6 46, 007. [] D. J. Love and R. W. Heath, Limited feedback diversity techniques for correlated channels, IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol., vol. 55, no., pp , 006. [4] N. Jindal, MIMO broadcast channels with finite-rate feedback, IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, vol. 5, no. 11, pp , 006. [5] T. Y. Al-Naffouri, M. Sharif, and B. Hassibi, How much does transmit correlation affect the sum-rate of MIMO downlink channels? in Proc. IEEE Int Information Theory Symp (IEEE ISIT), 006. [6] B. Clerckx, G. Kim, and S. Kim, Correlated fading in broadcast MIMO channels: Curse or blessing? in Proc. IEEE Global Telecommun. Conf. (IEEE GLOBECOM), 008. [7] A. Gersho and R. M. Gray, Vector Quantization and Signal Compression. Kluwer, 199. [8] R. W. Heath, T. Wu, and A. C. K. Soong, Progressive refinement for high resolution limited feedback multiuser MIMO beamforming, in Proc. 4nd Asilomar Conf. Signals, Systems and Computers, 008. [9] N. Ravindran, N. Jindal, and H. C. Huang, Beamforming with finite rate feedback for los MIMO downlink channels, in Proc. IEEE Global Telecommun. Conf. (IEEE GLOBECOM), 007. [10] D. Yang, L.-L. Yang, and L. Hanzo, DFT-based beamforming weightvector codebook design for spatially correlated channels in the unitary precoding aided multiuser downlink, in Proc. IEEE Int. Communi. Conf. (IEEE ICC), 010. [11] A. M. Sayeed, Deconstructing multi-antenna fading channels, IEEE Trans. Signal Processing, vol. 50, no. 10, pp , 00. [1] Spatial channel model for MIMO simulations, GPP TR V6.1.0, 00. [1] G. Dimic and N. D. Sidiropoulos, On downlink beamforming with greedy user selection: performance analysis and a simple new algorithm, IEEE Trans. Signal Processing, vol. 5, no. 10, pp , 005. [14] T. Yoo, N. Jindal, and A. Goldsmith, Multi-antenna downlink channels with limited feedback and user selection, IEEE J. Select. Areas Commun., vol. 5, no. 7, pp , 007. [] Views on the feedback framework for Rel. 10, SamSung, GPP TSG RAN 1, meeting #61, R1-1077, 010.
On the Design of Scalar Feedback Techniques for MIMO Broadcast Scheduling
 On the Design of Scalar Feedback Techniques for MIMO Broadcast Scheduling Ruben de Francisco and Dirk T.M. Slock Eurecom Institute Sophia-Antipolis, France Email: {defranci, slock}@eurecom.fr Abstract
On the Design of Scalar Feedback Techniques for MIMO Broadcast Scheduling Ruben de Francisco and Dirk T.M. Slock Eurecom Institute Sophia-Antipolis, France Email: {defranci, slock}@eurecom.fr Abstract
I. Introduction. Index Terms Multiuser MIMO, feedback, precoding, beamforming, codebook, quantization, OFDM, OFDMA.
 Zero-Forcing Beamforming Codebook Design for MU- MIMO OFDM Systems Erdem Bala, Member, IEEE, yle Jung-Lin Pan, Member, IEEE, Robert Olesen, Member, IEEE, Donald Grieco, Senior Member, IEEE InterDigital
Zero-Forcing Beamforming Codebook Design for MU- MIMO OFDM Systems Erdem Bala, Member, IEEE, yle Jung-Lin Pan, Member, IEEE, Robert Olesen, Member, IEEE, Donald Grieco, Senior Member, IEEE InterDigital
Limited Feedback-based Unitary Precoder Design in Rician MIMO Channel via Trellis Exploration Algorithm
 Limited Feedback-based Unitary Precoder Design in Rician MIMO Channel via Trellis Exploration Algorithm Dalin Zhu Department of Wireless Communications NEC Laboratories China NLC) 11F Bld.A Innovation
Limited Feedback-based Unitary Precoder Design in Rician MIMO Channel via Trellis Exploration Algorithm Dalin Zhu Department of Wireless Communications NEC Laboratories China NLC) 11F Bld.A Innovation
Two-Stage Channel Feedback for Beamforming and Scheduling in Network MIMO Systems
 Two-Stage Channel Feedback for Beamforming and Scheduling in Network MIMO Systems Behrouz Khoshnevis and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario,
Two-Stage Channel Feedback for Beamforming and Scheduling in Network MIMO Systems Behrouz Khoshnevis and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario,
Mode Selection for Multi-Antenna Broadcast Channels
 Mode Selection for Multi-Antenna Broadcast Channels Gill November 22, 2011 Gill (University of Delaware) November 22, 2011 1 / 25 Part I Mode Selection for MISO BC with Perfect/Imperfect CSI [1]-[3] Gill
Mode Selection for Multi-Antenna Broadcast Channels Gill November 22, 2011 Gill (University of Delaware) November 22, 2011 1 / 25 Part I Mode Selection for MISO BC with Perfect/Imperfect CSI [1]-[3] Gill
Multi-User Diversity vs. Accurate Channel State Information in MIMO Downlink Channels
 1 Multi-User Diversity vs. Accurate Channel State Information in MIMO Downlink Channels Niranjay Ravindran and Nihar Jindal University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455 Email: {ravi0022, nihar}@umn.edu
1 Multi-User Diversity vs. Accurate Channel State Information in MIMO Downlink Channels Niranjay Ravindran and Nihar Jindal University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455 Email: {ravi0022, nihar}@umn.edu
The Optimality of Beamforming: A Unified View
 The Optimality of Beamforming: A Unified View Sudhir Srinivasa and Syed Ali Jafar Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of California Irvine, Irvine, CA 92697-2625 Email: sudhirs@uciedu,
The Optimality of Beamforming: A Unified View Sudhir Srinivasa and Syed Ali Jafar Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of California Irvine, Irvine, CA 92697-2625 Email: sudhirs@uciedu,
Nash Bargaining in Beamforming Games with Quantized CSI in Two-user Interference Channels
 Nash Bargaining in Beamforming Games with Quantized CSI in Two-user Interference Channels Jung Hoon Lee and Huaiyu Dai Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, North Carolina State University,
Nash Bargaining in Beamforming Games with Quantized CSI in Two-user Interference Channels Jung Hoon Lee and Huaiyu Dai Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, North Carolina State University,
CHANNEL FEEDBACK QUANTIZATION METHODS FOR MISO AND MIMO SYSTEMS
 CHANNEL FEEDBACK QUANTIZATION METHODS FOR MISO AND MIMO SYSTEMS June Chul Roh and Bhaskar D Rao Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 9293 47,
CHANNEL FEEDBACK QUANTIZATION METHODS FOR MISO AND MIMO SYSTEMS June Chul Roh and Bhaskar D Rao Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 9293 47,
Explicit vs. Implicit Feedback for SU and MU-MIMO
 This full text paper was peer reviewed at the direction of IEEE Communications Society subject matter experts for publication in the IEEE Globecom 010 proceedings. Explicit vs. Implicit Feedback for SU
This full text paper was peer reviewed at the direction of IEEE Communications Society subject matter experts for publication in the IEEE Globecom 010 proceedings. Explicit vs. Implicit Feedback for SU
USING multiple antennas has been shown to increase the
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 55, NO. 1, JANUARY 2007 11 A Comparison of Time-Sharing, DPC, and Beamforming for MIMO Broadcast Channels With Many Users Masoud Sharif, Member, IEEE, and Babak
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 55, NO. 1, JANUARY 2007 11 A Comparison of Time-Sharing, DPC, and Beamforming for MIMO Broadcast Channels With Many Users Masoud Sharif, Member, IEEE, and Babak
THE CAPACITY region for the multiple-input multipleoutput
 IEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 26, NO. 8, OCTOBER 2008 1505 Coordinated Beamforming with Limited Feedback in the MIMO Broadcast Channel Chan-Byoung Chae, Student Member, IEEE, David
IEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 26, NO. 8, OCTOBER 2008 1505 Coordinated Beamforming with Limited Feedback in the MIMO Broadcast Channel Chan-Byoung Chae, Student Member, IEEE, David
Secure Multiuser MISO Communication Systems with Quantized Feedback
 Secure Multiuser MISO Communication Systems with Quantized Feedback Berna Özbek*, Özgecan Özdoğan*, Güneş Karabulut Kurt** *Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Izmir Institute of Technology,Turkey
Secure Multiuser MISO Communication Systems with Quantized Feedback Berna Özbek*, Özgecan Özdoğan*, Güneş Karabulut Kurt** *Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Izmir Institute of Technology,Turkey
Vector Channel Capacity with Quantized Feedback
 Vector Channel Capacity with Quantized Feedback Sudhir Srinivasa and Syed Ali Jafar Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of California Irvine, Irvine, CA 9697-65 Email: syed@ece.uci.edu,
Vector Channel Capacity with Quantized Feedback Sudhir Srinivasa and Syed Ali Jafar Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of California Irvine, Irvine, CA 9697-65 Email: syed@ece.uci.edu,
Codebook Design for Channel Feedback in Lens-Based Millimeter-Wave Massive MIMO Systems
 1 Codebook Design for Channel Feedback in Lens-Based Millimeter-Wave Massive MIMO Systems Wenqian Shen, Student Member, IEEE, Linglong Dai, Senior Member, IEEE, Yang Yang, Member, IEEE, Yue Li, Member,
1 Codebook Design for Channel Feedback in Lens-Based Millimeter-Wave Massive MIMO Systems Wenqian Shen, Student Member, IEEE, Linglong Dai, Senior Member, IEEE, Yang Yang, Member, IEEE, Yue Li, Member,
Dirty Paper Coding vs. TDMA for MIMO Broadcast Channels
 TO APPEAR IEEE INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COUNICATIONS, JUNE 004 1 Dirty Paper Coding vs. TDA for IO Broadcast Channels Nihar Jindal & Andrea Goldsmith Dept. of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University
TO APPEAR IEEE INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COUNICATIONS, JUNE 004 1 Dirty Paper Coding vs. TDA for IO Broadcast Channels Nihar Jindal & Andrea Goldsmith Dept. of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University
Title. Author(s)Tsai, Shang-Ho. Issue Date Doc URL. Type. Note. File Information. Equal Gain Beamforming in Rayleigh Fading Channels
 Title Equal Gain Beamforming in Rayleigh Fading Channels Author(s)Tsai, Shang-Ho Proceedings : APSIPA ASC 29 : Asia-Pacific Signal Citationand Conference: 688-691 Issue Date 29-1-4 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/39789
Title Equal Gain Beamforming in Rayleigh Fading Channels Author(s)Tsai, Shang-Ho Proceedings : APSIPA ASC 29 : Asia-Pacific Signal Citationand Conference: 688-691 Issue Date 29-1-4 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/39789
Limited Feedback in Wireless Communication Systems
 Limited Feedback in Wireless Communication Systems - Summary of An Overview of Limited Feedback in Wireless Communication Systems Gwanmo Ku May 14, 17, and 21, 2013 Outline Transmitter Ant. 1 Channel N
Limited Feedback in Wireless Communication Systems - Summary of An Overview of Limited Feedback in Wireless Communication Systems Gwanmo Ku May 14, 17, and 21, 2013 Outline Transmitter Ant. 1 Channel N
Low-High SNR Transition in Multiuser MIMO
 Low-High SNR Transition in Multiuser MIMO Malcolm Egan 1 1 Agent Technology Center, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic. 1 Abstract arxiv:1409.4393v1
Low-High SNR Transition in Multiuser MIMO Malcolm Egan 1 1 Agent Technology Center, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic. 1 Abstract arxiv:1409.4393v1
On the Required Accuracy of Transmitter Channel State Information in Multiple Antenna Broadcast Channels
 On the Required Accuracy of Transmitter Channel State Information in Multiple Antenna Broadcast Channels Giuseppe Caire University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA, USA Email: caire@usc.edu Nihar
On the Required Accuracy of Transmitter Channel State Information in Multiple Antenna Broadcast Channels Giuseppe Caire University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA, USA Email: caire@usc.edu Nihar
NOMA: Principles and Recent Results
 NOMA: Principles and Recent Results Jinho Choi School of EECS GIST September 2017 (VTC-Fall 2017) 1 / 46 Abstract: Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) becomes a key technology in 5G as it can improve
NOMA: Principles and Recent Results Jinho Choi School of EECS GIST September 2017 (VTC-Fall 2017) 1 / 46 Abstract: Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) becomes a key technology in 5G as it can improve
VECTOR QUANTIZATION TECHNIQUES FOR MULTIPLE-ANTENNA CHANNEL INFORMATION FEEDBACK
 VECTOR QUANTIZATION TECHNIQUES FOR MULTIPLE-ANTENNA CHANNEL INFORMATION FEEDBACK June Chul Roh and Bhaskar D. Rao Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, San Diego La
VECTOR QUANTIZATION TECHNIQUES FOR MULTIPLE-ANTENNA CHANNEL INFORMATION FEEDBACK June Chul Roh and Bhaskar D. Rao Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, San Diego La
Hybrid Pilot/Quantization based Feedback in Multi-Antenna TDD Systems
 Hybrid Pilot/Quantization based Feedback in Multi-Antenna TDD Systems Umer Salim, David Gesbert, Dirk Slock, Zafer Beyaztas Mobile Communications Department Eurecom, France Abstract The communication between
Hybrid Pilot/Quantization based Feedback in Multi-Antenna TDD Systems Umer Salim, David Gesbert, Dirk Slock, Zafer Beyaztas Mobile Communications Department Eurecom, France Abstract The communication between
How Much Training and Feedback are Needed in MIMO Broadcast Channels?
 How uch raining and Feedback are Needed in IO Broadcast Channels? ari Kobayashi, SUPELEC Gif-sur-Yvette, France Giuseppe Caire, University of Southern California Los Angeles CA, 989 USA Nihar Jindal University
How uch raining and Feedback are Needed in IO Broadcast Channels? ari Kobayashi, SUPELEC Gif-sur-Yvette, France Giuseppe Caire, University of Southern California Los Angeles CA, 989 USA Nihar Jindal University
On the Throughput of Proportional Fair Scheduling with Opportunistic Beamforming for Continuous Fading States
 On the hroughput of Proportional Fair Scheduling with Opportunistic Beamforming for Continuous Fading States Andreas Senst, Peter Schulz-Rittich, Gerd Ascheid, and Heinrich Meyr Institute for Integrated
On the hroughput of Proportional Fair Scheduling with Opportunistic Beamforming for Continuous Fading States Andreas Senst, Peter Schulz-Rittich, Gerd Ascheid, and Heinrich Meyr Institute for Integrated
MASSIVE multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) can
 IEEE ICC 017 Signal Processing for Communications Symposium AoD-Adaptive Subspace Codebook for Channel Feedback in FDD assive IO Systems Wenqian Shen, Linglong Dai, Guan Gui, Zhaocheng Wang, Robert W.
IEEE ICC 017 Signal Processing for Communications Symposium AoD-Adaptive Subspace Codebook for Channel Feedback in FDD assive IO Systems Wenqian Shen, Linglong Dai, Guan Gui, Zhaocheng Wang, Robert W.
Sum-Rate Analysis of MIMO Broadcast Channel with Random Unitary Beamforming
 This full text paper was peer reviewed at the direction of IEEE Communications Society subject matter experts for publication in the WCNC 8 proceedings. Sum-Rate Analysis of IO Broadcast Channel with Random
This full text paper was peer reviewed at the direction of IEEE Communications Society subject matter experts for publication in the WCNC 8 proceedings. Sum-Rate Analysis of IO Broadcast Channel with Random
(Article begins on next page)
 Chalmers Publication Library Copyright Notice 2010 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for
Chalmers Publication Library Copyright Notice 2010 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for
Degrees-of-Freedom Robust Transmission for the K-user Distributed Broadcast Channel
 /33 Degrees-of-Freedom Robust Transmission for the K-user Distributed Broadcast Channel Presented by Paul de Kerret Joint work with Antonio Bazco, Nicolas Gresset, and David Gesbert ESIT 2017 in Madrid,
/33 Degrees-of-Freedom Robust Transmission for the K-user Distributed Broadcast Channel Presented by Paul de Kerret Joint work with Antonio Bazco, Nicolas Gresset, and David Gesbert ESIT 2017 in Madrid,
User Scheduling for Millimeter Wave MIMO Communications with Low-Resolution ADCs
 User Scheduling for Millimeter Wave MIMO Communications with Low-Resolution ADCs Jinseok Choi and Brian L. Evans Wireless Networking and Communication Group, The University of Texas at Austin E-mail: jinseokchoi89@utexas.edu,
User Scheduling for Millimeter Wave MIMO Communications with Low-Resolution ADCs Jinseok Choi and Brian L. Evans Wireless Networking and Communication Group, The University of Texas at Austin E-mail: jinseokchoi89@utexas.edu,
Transmitter-Receiver Cooperative Sensing in MIMO Cognitive Network with Limited Feedback
 IEEE INFOCOM Workshop On Cognitive & Cooperative Networks Transmitter-Receiver Cooperative Sensing in MIMO Cognitive Network with Limited Feedback Chao Wang, Zhaoyang Zhang, Xiaoming Chen, Yuen Chau. Dept.of
IEEE INFOCOM Workshop On Cognitive & Cooperative Networks Transmitter-Receiver Cooperative Sensing in MIMO Cognitive Network with Limited Feedback Chao Wang, Zhaoyang Zhang, Xiaoming Chen, Yuen Chau. Dept.of
PERFORMANCE COMPARISON OF DATA-SHARING AND COMPRESSION STRATEGIES FOR CLOUD RADIO ACCESS NETWORKS. Pratik Patil, Binbin Dai, and Wei Yu
 PERFORMANCE COMPARISON OF DATA-SHARING AND COMPRESSION STRATEGIES FOR CLOUD RADIO ACCESS NETWORKS Pratik Patil, Binbin Dai, and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto,
PERFORMANCE COMPARISON OF DATA-SHARING AND COMPRESSION STRATEGIES FOR CLOUD RADIO ACCESS NETWORKS Pratik Patil, Binbin Dai, and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto,
Linear precoding design for massive MIMO based on the minimum mean square error algorithm
 Ge and Haiyan EURASIP Journal on Embedded Systems (2017) 2017:20 DOI 10.1186/s13639-016-0064-4 EURASIP Journal on Embedded Systems REVIEW Linear precoding design for massive MIMO based on the minimum mean
Ge and Haiyan EURASIP Journal on Embedded Systems (2017) 2017:20 DOI 10.1186/s13639-016-0064-4 EURASIP Journal on Embedded Systems REVIEW Linear precoding design for massive MIMO based on the minimum mean
Improved MU-MIMO Performance for Future Systems Using Differential Feedback
 Improved MU-MIMO Performance for Future 80. Systems Using Differential Feedback Ron Porat, Eric Ojard, Nihar Jindal, Matthew Fischer, Vinko Erceg Broadcom Corp. {rporat, eo, njindal, mfischer, verceg}@broadcom.com
Improved MU-MIMO Performance for Future 80. Systems Using Differential Feedback Ron Porat, Eric Ojard, Nihar Jindal, Matthew Fischer, Vinko Erceg Broadcom Corp. {rporat, eo, njindal, mfischer, verceg}@broadcom.com
Multiple Antenna Broadcast Channels with Shape Feedback and Limited Feedback
 Multiple Antenna Broadcast Channels with Shape Feedback and Limited Feedback Peilu Ding, David J. Love, and Michael D. Zoltowski School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University West Lafayette,
Multiple Antenna Broadcast Channels with Shape Feedback and Limited Feedback Peilu Ding, David J. Love, and Michael D. Zoltowski School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University West Lafayette,
Comparison of Linear Precoding Schemes for Downlink Massive MIMO
 Comparison of Linear Precoding Schemes for Downlink Massive MIMO Jakob Hoydis, Stephan ten Brink, and Mérouane Debbah Department of Telecommunications and Alcatel-Lucent Chair on Flexible Radio, Supélec,
Comparison of Linear Precoding Schemes for Downlink Massive MIMO Jakob Hoydis, Stephan ten Brink, and Mérouane Debbah Department of Telecommunications and Alcatel-Lucent Chair on Flexible Radio, Supélec,
Hybrid Pilot/Quantization based Feedback in Multi-Antenna TDD Systems
 Hybrid Pilot/Quantization based Feedback in Multi-Antenna TDD Systems Umer Salim, David Gesbert, Dirk Slock and Zafer Beyaztas Mobile Communications Department Eurecom, France Email: {salim, gesbert, slock}@eurecom.fr
Hybrid Pilot/Quantization based Feedback in Multi-Antenna TDD Systems Umer Salim, David Gesbert, Dirk Slock and Zafer Beyaztas Mobile Communications Department Eurecom, France Email: {salim, gesbert, slock}@eurecom.fr
On the Impact of Quantized Channel Feedback in Guaranteeing Secrecy with Artificial Noise
 On the Impact of Quantized Channel Feedback in Guaranteeing Secrecy with Artificial Noise Ya-Lan Liang, Yung-Shun Wang, Tsung-Hui Chang, Y.-W. Peter Hong, and Chong-Yung Chi Institute of Communications
On the Impact of Quantized Channel Feedback in Guaranteeing Secrecy with Artificial Noise Ya-Lan Liang, Yung-Shun Wang, Tsung-Hui Chang, Y.-W. Peter Hong, and Chong-Yung Chi Institute of Communications
Incremental Grassmannian Feedback Schemes for Multi-User MIMO Systems
 1130 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 63, NO. 5, MARCH 1, 2015 Incremental Grassmannian Feedback Schemes for Multi-User MIMO Systems Ahmed Medra and Timothy N. Davidson Abstract The communication
1130 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 63, NO. 5, MARCH 1, 2015 Incremental Grassmannian Feedback Schemes for Multi-User MIMO Systems Ahmed Medra and Timothy N. Davidson Abstract The communication
Quantifying the Performance Gain of Direction Feedback in a MISO System
 Quantifying the Performance Gain of Direction Feedback in a ISO System Shengli Zhou, Jinhong Wu, Zhengdao Wang 3, and ilos Doroslovacki Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Connecticut
Quantifying the Performance Gain of Direction Feedback in a ISO System Shengli Zhou, Jinhong Wu, Zhengdao Wang 3, and ilos Doroslovacki Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Connecticut
On the Capacity of MIMO Rician Broadcast Channels
 On the Capacity of IO Rician Broadcast Channels Alireza Bayesteh Email: alireza@shannon2.uwaterloo.ca Kamyar oshksar Email: kmoshksa@shannon2.uwaterloo.ca Amir K. Khani Email: khani@shannon2.uwaterloo.ca
On the Capacity of IO Rician Broadcast Channels Alireza Bayesteh Email: alireza@shannon2.uwaterloo.ca Kamyar oshksar Email: kmoshksa@shannon2.uwaterloo.ca Amir K. Khani Email: khani@shannon2.uwaterloo.ca
Upper Bounds on MIMO Channel Capacity with Channel Frobenius Norm Constraints
 Upper Bounds on IO Channel Capacity with Channel Frobenius Norm Constraints Zukang Shen, Jeffrey G. Andrews, Brian L. Evans Wireless Networking Communications Group Department of Electrical Computer Engineering
Upper Bounds on IO Channel Capacity with Channel Frobenius Norm Constraints Zukang Shen, Jeffrey G. Andrews, Brian L. Evans Wireless Networking Communications Group Department of Electrical Computer Engineering
Performance Analysis of Multiple Antenna Systems with VQ-Based Feedback
 Performance Analysis of Multiple Antenna Systems with VQ-Based Feedback June Chul Roh and Bhaskar D. Rao Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla,
Performance Analysis of Multiple Antenna Systems with VQ-Based Feedback June Chul Roh and Bhaskar D. Rao Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla,
On the Performance of Random Vector Quantization Limited Feedback Beamforming in a MISO System
 1 On the Performance of Random Vector Quantization Limited Feedback Beamforming in a MISO System Chun Kin Au-Yeung, Student Member, IEEE, and David J. Love, Member, IEEE Abstract In multiple antenna wireless
1 On the Performance of Random Vector Quantization Limited Feedback Beamforming in a MISO System Chun Kin Au-Yeung, Student Member, IEEE, and David J. Love, Member, IEEE Abstract In multiple antenna wireless
A New SLNR-based Linear Precoding for. Downlink Multi-User Multi-Stream MIMO Systems
 A New SLNR-based Linear Precoding for 1 Downlin Multi-User Multi-Stream MIMO Systems arxiv:1008.0730v1 [cs.it] 4 Aug 2010 Peng Cheng, Meixia Tao and Wenjun Zhang Abstract Signal-to-leaage-and-noise ratio
A New SLNR-based Linear Precoding for 1 Downlin Multi-User Multi-Stream MIMO Systems arxiv:1008.0730v1 [cs.it] 4 Aug 2010 Peng Cheng, Meixia Tao and Wenjun Zhang Abstract Signal-to-leaage-and-noise ratio
Coordinated Regularized Zero-Forcing Precoding for Multicell MISO Systems with Limited Feedback
 DRAFT 1 Coordinated Regularized Zero-Forcing Precoding for Multicell MISO Systems with Limited Feedbac Jawad Mirza, Student Member, IEEE, Peter J. Smith, Fellow, IEEE, Pawel A. Dmochowsi, Senior Member,
DRAFT 1 Coordinated Regularized Zero-Forcing Precoding for Multicell MISO Systems with Limited Feedbac Jawad Mirza, Student Member, IEEE, Peter J. Smith, Fellow, IEEE, Pawel A. Dmochowsi, Senior Member,
Research Article A Design Framework for Scalar Feedback in MIMO Broadcast Channels
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing Volume 8, Article ID 5778, pages doi:.55/8/5778 Research Article A Design Framework for Scalar Feedback in MIMO Broadcast
Hindawi Publishing Corporation EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing Volume 8, Article ID 5778, pages doi:.55/8/5778 Research Article A Design Framework for Scalar Feedback in MIMO Broadcast
Morning Session Capacity-based Power Control. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland
 Morning Session Capacity-based Power Control Şennur Ulukuş Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland So Far, We Learned... Power control with SIR-based QoS guarantees Suitable
Morning Session Capacity-based Power Control Şennur Ulukuş Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland So Far, We Learned... Power control with SIR-based QoS guarantees Suitable
Achievable Outage Rate Regions for the MISO Interference Channel
 Achievable Outage Rate Regions for the MISO Interference Channel Johannes Lindblom, Eleftherios Karipidis and Erik G. Larsson Linköping University Post Print N.B.: When citing this work, cite the original
Achievable Outage Rate Regions for the MISO Interference Channel Johannes Lindblom, Eleftherios Karipidis and Erik G. Larsson Linköping University Post Print N.B.: When citing this work, cite the original
OVER the past ten years, research (see the references in
 766 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 54, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2006 Duplex Distortion Models for Limited Feedback MIMO Communication David J. Love, Member, IEEE Abstract The use of limited feedback
766 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 54, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2006 Duplex Distortion Models for Limited Feedback MIMO Communication David J. Love, Member, IEEE Abstract The use of limited feedback
Achievable rates of MIMO downlink beamforming with non-perfect CSI: a comparison between quantized and analog feedback
 Achievable rates of MIMO downlink beamforming with non-perfect CSI: a comparison between quantized and ana feedback Giuseppe Caire University of Sourthern California Los Angeles CA, 989 USA Nihar Jindal
Achievable rates of MIMO downlink beamforming with non-perfect CSI: a comparison between quantized and ana feedback Giuseppe Caire University of Sourthern California Los Angeles CA, 989 USA Nihar Jindal
Joint Power Control and Beamforming Codebook Design for MISO Channels with Limited Feedback
 Joint Power Control and Beamforming Codebook Design for MISO Channels with Limited Feedback Behrouz Khoshnevis and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto, Toronto,
Joint Power Control and Beamforming Codebook Design for MISO Channels with Limited Feedback Behrouz Khoshnevis and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto, Toronto,
Tranceiver Design using Linear Precoding in a Multiuser MIMO System with Limited Feedback
 IET Communications Tranceiver Design using Linear Precoding in a Multiuser MIMO System with Limited Feedback Journal: IET Communications Manuscript ID: Draft Manuscript Type: Research Paper Date Submitted
IET Communications Tranceiver Design using Linear Precoding in a Multiuser MIMO System with Limited Feedback Journal: IET Communications Manuscript ID: Draft Manuscript Type: Research Paper Date Submitted
Optimum Power Allocation in Fading MIMO Multiple Access Channels with Partial CSI at the Transmitters
 Optimum Power Allocation in Fading MIMO Multiple Access Channels with Partial CSI at the Transmitters Alkan Soysal Sennur Ulukus Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland,
Optimum Power Allocation in Fading MIMO Multiple Access Channels with Partial CSI at the Transmitters Alkan Soysal Sennur Ulukus Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland,
Duality, Achievable Rates, and Sum-Rate Capacity of Gaussian MIMO Broadcast Channels
 2658 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL 49, NO 10, OCTOBER 2003 Duality, Achievable Rates, and Sum-Rate Capacity of Gaussian MIMO Broadcast Channels Sriram Vishwanath, Student Member, IEEE, Nihar
2658 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL 49, NO 10, OCTOBER 2003 Duality, Achievable Rates, and Sum-Rate Capacity of Gaussian MIMO Broadcast Channels Sriram Vishwanath, Student Member, IEEE, Nihar
On the Optimization of Two-way AF MIMO Relay Channel with Beamforming
 On the Optimization of Two-way AF MIMO Relay Channel with Beamforming Namjeong Lee, Chan-Byoung Chae, Osvaldo Simeone, Joonhyuk Kang Information and Communications Engineering ICE, KAIST, Korea Email:
On the Optimization of Two-way AF MIMO Relay Channel with Beamforming Namjeong Lee, Chan-Byoung Chae, Osvaldo Simeone, Joonhyuk Kang Information and Communications Engineering ICE, KAIST, Korea Email:
Limited Feedback Hybrid Precoding for. Multi-User Millimeter Wave Systems
 Limited Feedback Hybrid Precoding for 1 Multi-ser Millimeter Wave Systems Ahmed Alkhateeb, Geert Leus, and Robert W. Heath Jr. arxiv:1409.5162v2 [cs.it] 5 Mar 2015 Abstract Antenna arrays will be an important
Limited Feedback Hybrid Precoding for 1 Multi-ser Millimeter Wave Systems Ahmed Alkhateeb, Geert Leus, and Robert W. Heath Jr. arxiv:1409.5162v2 [cs.it] 5 Mar 2015 Abstract Antenna arrays will be an important
Joint FEC Encoder and Linear Precoder Design for MIMO Systems with Antenna Correlation
 Joint FEC Encoder and Linear Precoder Design for MIMO Systems with Antenna Correlation Chongbin Xu, Peng Wang, Zhonghao Zhang, and Li Ping City University of Hong Kong 1 Outline Background Mutual Information
Joint FEC Encoder and Linear Precoder Design for MIMO Systems with Antenna Correlation Chongbin Xu, Peng Wang, Zhonghao Zhang, and Li Ping City University of Hong Kong 1 Outline Background Mutual Information
ON BEAMFORMING WITH FINITE RATE FEEDBACK IN MULTIPLE ANTENNA SYSTEMS
 ON BEAMFORMING WITH FINITE RATE FEEDBACK IN MULTIPLE ANTENNA SYSTEMS KRISHNA KIRAN MUKKAVILLI ASHUTOSH SABHARWAL ELZA ERKIP BEHNAAM AAZHANG Abstract In this paper, we study a multiple antenna system where
ON BEAMFORMING WITH FINITE RATE FEEDBACK IN MULTIPLE ANTENNA SYSTEMS KRISHNA KIRAN MUKKAVILLI ASHUTOSH SABHARWAL ELZA ERKIP BEHNAAM AAZHANG Abstract In this paper, we study a multiple antenna system where
DFT-Based Hybrid Beamforming Multiuser Systems: Rate Analysis and Beam Selection
 1 DFT-Based Hybrid Beamforming Multiuser Systems: Rate Analysis and Beam Selection Yu Han, Shi Jin, Jun Zhang, Jiayi Zhang, and Kai-Kit Wong National Mobile Communications Research Laboratory, Southeast
1 DFT-Based Hybrid Beamforming Multiuser Systems: Rate Analysis and Beam Selection Yu Han, Shi Jin, Jun Zhang, Jiayi Zhang, and Kai-Kit Wong National Mobile Communications Research Laboratory, Southeast
NOMA: An Information Theoretic Perspective
 NOMA: An Information Theoretic Perspective Peng Xu, Zhiguo Ding, Member, IEEE, Xuchu Dai and H. Vincent Poor, Fellow, IEEE arxiv:54.775v2 cs.it] 2 May 25 Abstract In this letter, the performance of non-orthogonal
NOMA: An Information Theoretic Perspective Peng Xu, Zhiguo Ding, Member, IEEE, Xuchu Dai and H. Vincent Poor, Fellow, IEEE arxiv:54.775v2 cs.it] 2 May 25 Abstract In this letter, the performance of non-orthogonal
MIMO Broadcast Channels with Spatial Heterogeneity
 I TRANSACTIONS ON WIRLSS COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 9, NO. 8, AUGUST 449 MIMO Broadcast Channels with Spatial Heterogeneity Illsoo Sohn, Member, I, Jeffrey G. Andrews, Senior Member, I, and wang Bok Lee, Senior
I TRANSACTIONS ON WIRLSS COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 9, NO. 8, AUGUST 449 MIMO Broadcast Channels with Spatial Heterogeneity Illsoo Sohn, Member, I, Jeffrey G. Andrews, Senior Member, I, and wang Bok Lee, Senior
Interference Alignment under Training and Feedback Constraints
 Interference Alignment under Training and Feedbac Constraints Baile Xie, Student Member, IEEE, Yang Li, Student Member, IEEE, Hlaing Minn, Senior Member, IEEE, and Aria Nosratinia, Fellow, IEEE The University
Interference Alignment under Training and Feedbac Constraints Baile Xie, Student Member, IEEE, Yang Li, Student Member, IEEE, Hlaing Minn, Senior Member, IEEE, and Aria Nosratinia, Fellow, IEEE The University
IEEE C802.16e-05/142 Project. IEEE Broadband Wireless Access Working Group <
 Project IEEE 80.6 Broadband Wireless Access Working Group Title Date Submitted Per Stream Power Control in CQICH Enhanced Allocation IE 005-03-09 Source(s) Re: Xiangyang (Jeff) Zhuang
Project IEEE 80.6 Broadband Wireless Access Working Group Title Date Submitted Per Stream Power Control in CQICH Enhanced Allocation IE 005-03-09 Source(s) Re: Xiangyang (Jeff) Zhuang
IN this paper, we show that the scalar Gaussian multiple-access
 768 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 50, NO. 5, MAY 2004 On the Duality of Gaussian Multiple-Access and Broadcast Channels Nihar Jindal, Student Member, IEEE, Sriram Vishwanath, and Andrea
768 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 50, NO. 5, MAY 2004 On the Duality of Gaussian Multiple-Access and Broadcast Channels Nihar Jindal, Student Member, IEEE, Sriram Vishwanath, and Andrea
Generalized MMSE Beamforming for Downlink MIMO Systems
 Generalized MMSE Beamforming for Downlin MIMO Systems youngjoo Lee, Illsoo Sohn, Donghyun Kim, and Kwang Bo Lee School of Electrical Engineering and INMC, Seoul National University (SNU, Seoul, Korea.
Generalized MMSE Beamforming for Downlin MIMO Systems youngjoo Lee, Illsoo Sohn, Donghyun Kim, and Kwang Bo Lee School of Electrical Engineering and INMC, Seoul National University (SNU, Seoul, Korea.
Massive MU-MIMO Downlink TDD Systems with Linear Precoding and Downlink Pilots
 Massive MU-MIMO Downlink TDD Systems with Linear Precoding and Downlink Pilots Hien Quoc Ngo, Erik G. Larsson, and Thomas L. Marzetta Department of Electrical Engineering (ISY) Linköping University, 58
Massive MU-MIMO Downlink TDD Systems with Linear Precoding and Downlink Pilots Hien Quoc Ngo, Erik G. Larsson, and Thomas L. Marzetta Department of Electrical Engineering (ISY) Linköping University, 58
Lattice Reduction Aided Precoding for Multiuser MIMO using Seysen s Algorithm
 Lattice Reduction Aided Precoding for Multiuser MIMO using Seysen s Algorithm HongSun An Student Member IEEE he Graduate School of I & Incheon Korea ahs3179@gmail.com Manar Mohaisen Student Member IEEE
Lattice Reduction Aided Precoding for Multiuser MIMO using Seysen s Algorithm HongSun An Student Member IEEE he Graduate School of I & Incheon Korea ahs3179@gmail.com Manar Mohaisen Student Member IEEE
Capacity of Memoryless Channels and Block-Fading Channels With Designable Cardinality-Constrained Channel State Feedback
 2038 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 50, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2004 Capacity of Memoryless Channels and Block-Fading Channels With Designable Cardinality-Constrained Channel State Feedback Vincent
2038 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 50, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2004 Capacity of Memoryless Channels and Block-Fading Channels With Designable Cardinality-Constrained Channel State Feedback Vincent
Optimal Power Allocation for Parallel Gaussian Broadcast Channels with Independent and Common Information
 SUBMIED O IEEE INERNAIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON INFORMAION HEORY, DE. 23 1 Optimal Power Allocation for Parallel Gaussian Broadcast hannels with Independent and ommon Information Nihar Jindal and Andrea Goldsmith
SUBMIED O IEEE INERNAIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON INFORMAION HEORY, DE. 23 1 Optimal Power Allocation for Parallel Gaussian Broadcast hannels with Independent and ommon Information Nihar Jindal and Andrea Goldsmith
Approximate capacity region of the two-pair bidirectional Gaussian relay network
 Approximate capacity region of the two-pair bidirectional Gaussian relay network Aydin Sezgin UC Irvine CA USA asezgin@uci.edu M. Amin Khajehnejad Caltech Pasadena CA USA amin@caltech.edu A. Salman Avestimehr
Approximate capacity region of the two-pair bidirectional Gaussian relay network Aydin Sezgin UC Irvine CA USA asezgin@uci.edu M. Amin Khajehnejad Caltech Pasadena CA USA amin@caltech.edu A. Salman Avestimehr
On the Duality of Gaussian Multiple-Access and Broadcast Channels
 On the Duality of Gaussian ultiple-access and Broadcast Channels Xiaowei Jin I. INTODUCTION Although T. Cover has been pointed out in [] that one would have expected a duality between the broadcast channel(bc)
On the Duality of Gaussian ultiple-access and Broadcast Channels Xiaowei Jin I. INTODUCTION Although T. Cover has been pointed out in [] that one would have expected a duality between the broadcast channel(bc)
DEVICE-TO-DEVICE COMMUNICATIONS: THE PHYSICAL LAYER SECURITY ADVANTAGE
 DEVICE-TO-DEVICE COMMUNICATIONS: THE PHYSICAL LAYER SECURITY ADVANTAGE Daohua Zhu, A. Lee Swindlehurst, S. Ali A. Fakoorian, Wei Xu, Chunming Zhao National Mobile Communications Research Lab, Southeast
DEVICE-TO-DEVICE COMMUNICATIONS: THE PHYSICAL LAYER SECURITY ADVANTAGE Daohua Zhu, A. Lee Swindlehurst, S. Ali A. Fakoorian, Wei Xu, Chunming Zhao National Mobile Communications Research Lab, Southeast
Multi-User Gain Maximum Eigenmode Beamforming, and IDMA. Peng Wang and Li Ping City University of Hong Kong
 Multi-User Gain Maximum Eigenmode Beamforming, and IDMA Peng Wang and Li Ping City University of Hong Kong 1 Contents Introduction Multi-user gain (MUG) Maximum eigenmode beamforming (MEB) MEB performance
Multi-User Gain Maximum Eigenmode Beamforming, and IDMA Peng Wang and Li Ping City University of Hong Kong 1 Contents Introduction Multi-user gain (MUG) Maximum eigenmode beamforming (MEB) MEB performance
Capacity Region of the Two-Way Multi-Antenna Relay Channel with Analog Tx-Rx Beamforming
 Capacity Region of the Two-Way Multi-Antenna Relay Channel with Analog Tx-Rx Beamforming Authors: Christian Lameiro, Alfredo Nazábal, Fouad Gholam, Javier Vía and Ignacio Santamaría University of Cantabria,
Capacity Region of the Two-Way Multi-Antenna Relay Channel with Analog Tx-Rx Beamforming Authors: Christian Lameiro, Alfredo Nazábal, Fouad Gholam, Javier Vía and Ignacio Santamaría University of Cantabria,
Random Beamforming in Spatially Correlated Multiuser MISO Channels
 andom Beamforming in Spatially Correlated Multiuser MISO Channels Jae-Yun Ko and Yong-Hwan ee School of lectrical ngineering and INMC Seoul National University Kwana P. O. Box 34 Seoul 5-600 Korea Abstract
andom Beamforming in Spatially Correlated Multiuser MISO Channels Jae-Yun Ko and Yong-Hwan ee School of lectrical ngineering and INMC Seoul National University Kwana P. O. Box 34 Seoul 5-600 Korea Abstract
Comparisons of Performance of Various Transmission Schemes of MIMO System Operating under Rician Channel Conditions
 Comparisons of Performance of Various ransmission Schemes of MIMO System Operating under ician Channel Conditions Peerapong Uthansakul and Marek E. Bialkowski School of Information echnology and Electrical
Comparisons of Performance of Various ransmission Schemes of MIMO System Operating under ician Channel Conditions Peerapong Uthansakul and Marek E. Bialkowski School of Information echnology and Electrical
Cooperative Transmission for Wireless Relay Networks Using Limited Feedback
 1 Cooperative Transmission for Wireless Relay Networks Using Limited Feedback Javier M. Paredes, Babak H. Khalaj, and Alex B. Gershman arxiv:0904.1369v2 [cs.it] 29 Jul 2009 Abstract To achieve the available
1 Cooperative Transmission for Wireless Relay Networks Using Limited Feedback Javier M. Paredes, Babak H. Khalaj, and Alex B. Gershman arxiv:0904.1369v2 [cs.it] 29 Jul 2009 Abstract To achieve the available
Transmission Schemes for Lifetime Maximization in Wireless Sensor Networks: Uncorrelated Source Observations
 Transmission Schemes for Lifetime Maximization in Wireless Sensor Networks: Uncorrelated Source Observations Xiaolu Zhang, Meixia Tao and Chun Sum Ng Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering National
Transmission Schemes for Lifetime Maximization in Wireless Sensor Networks: Uncorrelated Source Observations Xiaolu Zhang, Meixia Tao and Chun Sum Ng Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering National
Lecture 6: Modeling of MIMO Channels Theoretical Foundations of Wireless Communications 1
 Fading : Theoretical Foundations of Wireless Communications 1 Thursday, May 3, 2018 9:30-12:00, Conference Room SIP 1 Textbook: D. Tse and P. Viswanath, Fundamentals of Wireless Communication 1 / 23 Overview
Fading : Theoretical Foundations of Wireless Communications 1 Thursday, May 3, 2018 9:30-12:00, Conference Room SIP 1 Textbook: D. Tse and P. Viswanath, Fundamentals of Wireless Communication 1 / 23 Overview
Under sum power constraint, the capacity of MIMO channels
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL 6, NO 9, SEPTEMBER 22 242 Iterative Mode-Dropping for the Sum Capacity of MIMO-MAC with Per-Antenna Power Constraint Yang Zhu and Mai Vu Abstract We propose an
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL 6, NO 9, SEPTEMBER 22 242 Iterative Mode-Dropping for the Sum Capacity of MIMO-MAC with Per-Antenna Power Constraint Yang Zhu and Mai Vu Abstract We propose an
Low Resolution Adaptive Compressed Sensing for mmwave MIMO receivers
 Low Resolution Adaptive Compressed Sensing for mmwave MIMO receivers Cristian Rusu, Nuria González-Prelcic and Robert W. Heath Motivation 2 Power consumption at mmwave in a MIMO receiver Power at 60 GHz
Low Resolution Adaptive Compressed Sensing for mmwave MIMO receivers Cristian Rusu, Nuria González-Prelcic and Robert W. Heath Motivation 2 Power consumption at mmwave in a MIMO receiver Power at 60 GHz
Short-Packet Communications in Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access Systems
 Short-Packet Communications in Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access Systems Xiaofang Sun, Shihao Yan, Nan Yang, Zhiguo Ding, Chao Shen, and Zhangdui Zhong State Key Lab of Rail Traffic Control and Safety, Beijing
Short-Packet Communications in Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access Systems Xiaofang Sun, Shihao Yan, Nan Yang, Zhiguo Ding, Chao Shen, and Zhangdui Zhong State Key Lab of Rail Traffic Control and Safety, Beijing
Lecture 6: Modeling of MIMO Channels Theoretical Foundations of Wireless Communications 1. Overview. CommTh/EES/KTH
 : Theoretical Foundations of Wireless Communications 1 Wednesday, May 11, 2016 9:00-12:00, Conference Room SIP 1 Textbook: D. Tse and P. Viswanath, Fundamentals of Wireless Communication 1 / 1 Overview
: Theoretical Foundations of Wireless Communications 1 Wednesday, May 11, 2016 9:00-12:00, Conference Room SIP 1 Textbook: D. Tse and P. Viswanath, Fundamentals of Wireless Communication 1 / 1 Overview
Research Article Scheduling for Multiuser MIMO Downlink Channels with Ranking-Based Feedback
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing Volume 28, Article ID 85412, 14 pages doi:1.1155/28/85412 Research Article Scheduling for Multiuser MIMO Downlink Channels
Hindawi Publishing Corporation EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing Volume 28, Article ID 85412, 14 pages doi:1.1155/28/85412 Research Article Scheduling for Multiuser MIMO Downlink Channels
Robust Learning-Based ML Detection for Massive MIMO Systems with One-Bit Quantized Signals
 Robust Learning-Based ML Detection for Massive MIMO Systems with One-Bit Quantized Signals Jinseok Choi, Yunseong Cho, Brian L. Evans, and Alan Gatherer Wireless Networking and Communications Group, The
Robust Learning-Based ML Detection for Massive MIMO Systems with One-Bit Quantized Signals Jinseok Choi, Yunseong Cho, Brian L. Evans, and Alan Gatherer Wireless Networking and Communications Group, The
Performance Analysis for Transmit-Beamforming with Finite-Rate Feedback
 24 Conference on Information Sciences and Systems, Princeton University, arch 7-9, 24 Performance Analysis for Transmit-Beamforming with Finite-Rate Feedback Shengli Zhou, Zhengdao Wang 2, and Georgios
24 Conference on Information Sciences and Systems, Princeton University, arch 7-9, 24 Performance Analysis for Transmit-Beamforming with Finite-Rate Feedback Shengli Zhou, Zhengdao Wang 2, and Georgios
MIMO Spatial Multiplexing Systems with Limited Feedback
 MIMO Spatial Multiplexing Systems with Limited eedback June Chul Roh and Bhaskar D. Rao Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 92093 0407, USA
MIMO Spatial Multiplexing Systems with Limited eedback June Chul Roh and Bhaskar D. Rao Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 92093 0407, USA
Schur-convexity of the Symbol Error Rate in Correlated MIMO Systems with Precoding and Space-time Coding
 Schur-convexity of the Symbol Error Rate in Correlated MIMO Systems with Precoding and Space-time Coding RadioVetenskap och Kommunikation (RVK 08) Proceedings of the twentieth Nordic Conference on Radio
Schur-convexity of the Symbol Error Rate in Correlated MIMO Systems with Precoding and Space-time Coding RadioVetenskap och Kommunikation (RVK 08) Proceedings of the twentieth Nordic Conference on Radio
Approximately achieving the feedback interference channel capacity with point-to-point codes
 Approximately achieving the feedback interference channel capacity with point-to-point codes Joyson Sebastian*, Can Karakus*, Suhas Diggavi* Abstract Superposition codes with rate-splitting have been used
Approximately achieving the feedback interference channel capacity with point-to-point codes Joyson Sebastian*, Can Karakus*, Suhas Diggavi* Abstract Superposition codes with rate-splitting have been used
Exploiting Quantized Channel Norm Feedback Through Conditional Statistics in Arbitrarily Correlated MIMO Systems
 Exploiting Quantized Channel Norm Feedback Through Conditional Statistics in Arbitrarily Correlated MIMO Systems IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING Volume 57, Issue 10, Pages 4027-4041, October 2009.
Exploiting Quantized Channel Norm Feedback Through Conditional Statistics in Arbitrarily Correlated MIMO Systems IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING Volume 57, Issue 10, Pages 4027-4041, October 2009.
Optimal Power Allocation for Cognitive Radio under Primary User s Outage Loss Constraint
 This full text paper was peer reviewed at the direction of IEEE Communications Society subject matter experts for publication in the IEEE ICC 29 proceedings Optimal Power Allocation for Cognitive Radio
This full text paper was peer reviewed at the direction of IEEE Communications Society subject matter experts for publication in the IEEE ICC 29 proceedings Optimal Power Allocation for Cognitive Radio
Grassmannian Beamforming for Multiple-Input Multiple-Output Wireless Systems
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 49, NO. 0, OCTOBER 003 735 Grassmannian Beamforming for Multiple-Input Multiple-Output Wireless Systems David J. Love, Student Member, IEEE, Robert W. Heath,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 49, NO. 0, OCTOBER 003 735 Grassmannian Beamforming for Multiple-Input Multiple-Output Wireless Systems David J. Love, Student Member, IEEE, Robert W. Heath,
Outage-Efficient Downlink Transmission Without Transmit Channel State Information
 1 Outage-Efficient Downlink Transmission Without Transmit Channel State Information Wenyi Zhang, Member, IEEE, Shivaprasad Kotagiri, Student Member, IEEE, and J. Nicholas Laneman, Senior Member, IEEE arxiv:0711.1573v1
1 Outage-Efficient Downlink Transmission Without Transmit Channel State Information Wenyi Zhang, Member, IEEE, Shivaprasad Kotagiri, Student Member, IEEE, and J. Nicholas Laneman, Senior Member, IEEE arxiv:0711.1573v1
On the Optimality of Multiuser Zero-Forcing Precoding in MIMO Broadcast Channels
 On the Optimality of Multiuser Zero-Forcing Precoding in MIMO Broadcast Channels Saeed Kaviani and Witold A. Krzymień University of Alberta / TRLabs, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada T6G 2V4 E-mail: {saeed,wa}@ece.ualberta.ca
On the Optimality of Multiuser Zero-Forcing Precoding in MIMO Broadcast Channels Saeed Kaviani and Witold A. Krzymień University of Alberta / TRLabs, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada T6G 2V4 E-mail: {saeed,wa}@ece.ualberta.ca
2318 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 54, NO. 6, JUNE Mai Vu, Student Member, IEEE, and Arogyaswami Paulraj, Fellow, IEEE
 2318 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 54, NO. 6, JUNE 2006 Optimal Linear Precoders for MIMO Wireless Correlated Channels With Nonzero Mean in Space Time Coded Systems Mai Vu, Student Member,
2318 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 54, NO. 6, JUNE 2006 Optimal Linear Precoders for MIMO Wireless Correlated Channels With Nonzero Mean in Space Time Coded Systems Mai Vu, Student Member,
Pilot Optimization and Channel Estimation for Multiuser Massive MIMO Systems
 1 Pilot Optimization and Channel Estimation for Multiuser Massive MIMO Systems Tadilo Endeshaw Bogale and Long Bao Le Institute National de la Recherche Scientifique (INRS) Université de Québec, Montréal,
1 Pilot Optimization and Channel Estimation for Multiuser Massive MIMO Systems Tadilo Endeshaw Bogale and Long Bao Le Institute National de la Recherche Scientifique (INRS) Université de Québec, Montréal,
IEEE Broadband Wireless Access Working Group <
 Project Title IEEE 802.6 Broadband Wireless Access Working Group Codebook based pre-coding MIMO Date Submitted Source(s) 2008-05-05 Jaewan Kim, Wookbong Lee, Bin-chul Ihm Voice:
Project Title IEEE 802.6 Broadband Wireless Access Working Group Codebook based pre-coding MIMO Date Submitted Source(s) 2008-05-05 Jaewan Kim, Wookbong Lee, Bin-chul Ihm Voice:
Correspondence. MIMO Broadcast Channels With Finite-Rate Feedback
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORATION THEORY, VO. 5, NO., NOVEBER 6 545 Correspondence IO Broadcast Channels With Finite-Rate Feedbac Nihar Jindal, ember, IEEE Abstract ultiple transmit antennas in a downlin
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORATION THEORY, VO. 5, NO., NOVEBER 6 545 Correspondence IO Broadcast Channels With Finite-Rate Feedbac Nihar Jindal, ember, IEEE Abstract ultiple transmit antennas in a downlin
Reflected Simplex Codebooks for Limited Feedback MIMO Beamforming
 Reflected Simplex Codebooks for Limited Feedback MIMO Beamforming Daniel J. Ryan 1, Iain B. Collings 2 and Jean-Marc Valin 3 1 Dept. of Electronics & Telecommunications., Norwegian University of Science
Reflected Simplex Codebooks for Limited Feedback MIMO Beamforming Daniel J. Ryan 1, Iain B. Collings 2 and Jean-Marc Valin 3 1 Dept. of Electronics & Telecommunications., Norwegian University of Science
