Collective modes and transport In Weyl semimetals. Dima Pesin, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, USA
|
|
|
- Sherman Hart
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Collective modes and transport In Weyl semimetals Dima Pesin, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, USA TAMU, College Station, TX 11/06/2014
2 Life in the time of Topologitis QHE Strong TI Bulk Insulators QSHE (taken from A. Schnyder et al. in Proceedings of the L.D.Landau Memorial Conference "Advances in Theoretical Physics", June 22-26, 2008, Chernogolovka, Moscow region, Russia) Newer* stuff: gapless topological phases *) circ s
3 No epidemic plateau seen yet APS MM abstracts (BiTe) (Majorana?)
4 Weyl semimetals are off to a good start (Cd 3 As 2 )
5 Weyl Semimetal (WS) is a collection of nondegenerate band touchings in 3D k-space 3D Graphene Conduction band Weyl points Valence band (Herring 37, Abrikosov&Beneslavsky 71, Wan et al 11, Burkov&Balents 11) Two bands => the spin degeneracy is lifted, either by T or I breaking
6 Where does one get a WS? (in a lattice system) Ir-based pyrochlores: (Wan, Turner, Vishwanath&Savrasov 11) Ln 2 Ir 2 O 7 : LDA+U TI-based heterostructures: (Burkov&Balents 11)
7 Where does one get a WS? (continued) Recently: Cd 3 As 2 is a Dirac semimetal? 1) Wang et al., (first principles calc) 2) Borisenko et al., (Cava s group) 3) Neupane et al., (Hasan s group)
8 Weyl semimetals (WS) are gapless phases with nontrivial topology (review: Turner&Vishwanath, cond-mat: ) Conduction band Valence band 1. Nodes are stable due to topology, not symmetry (as, say, in graphene) 2. There are protected surface states( arcs ), which cannot be realized in a 2DEG. 3. Hall response is determined by the distance between nodes, and nothing else. 4. The chiral anomaly is also a topo. response
9 The chiral anomaly is the nonconservation of valley charges in the presence of EM fields 1D Example: Apply yet (!)
10 In the 3D case, the B-field reduces the problem to a collection of 1D ones graphene gap 3D chiral anomaly
11 Practical problem: symmetry-wise, WS are no different from more conventional phases, thus exhibit the same responses, in principle.
12 Practical problem: symmetry-wise, WS are no different from more conventional phases, thus exhibit the same responses, in principle. How does one detect them then? There are a few ways out of this complication: 1) Look for unusual magnitude of effect 2) Unusual sign (Son, Spivak, 2012 negative classical magnetoresistance) 3) Unusual parameter dependence. (Parameswaran et al. 2011, quantum-critical conductivity,
13 Q: How to distinguish a WS from a small-gap semiconductor? Both in principle, and in practice. A: The chiral anomaly [1] is a good candidate. It provides a nonlocal transport signature. The latter is absent in the usual small gap semiconductors. [1] S. L. Adler, Phys. Rev. 177, 2426 (1969 ); J. S. Bell and R. Jackiw, Il Nuovo Cimento A 60, 47 (1969).
14 How to see the chiral anomaly: The only known existing condensed matter measurement is for 3 He-A. (T.D.C. Proposals Bevan, for A.J. crystalline Manninen, J.B. systems: Cook, J.R. Hook, H.E. Hall, T. Vachaspati, G.E. Volovik, 1997) - via anisotropies in the conductivity (Nielsen&Ninomiya, 1983; Aji, 2012) - via large classical magnetoresistance (Son&Spivak, 2012) - via magnon-plasmon coupling (Liu,Ye&Qi, 2012)
15 We would like to have an easily observable effect that does not exist without the chiral anomaly. PRX 4, (2014) Sid Parameswaran Tarun Grover Dmitry Abanin Ashvin Vishwanath Berkeley/UC Irvine KITP, UCSB Perimeter Institute UC Berkeley
16 We will use the chiral anomaly to generate and detect nonlocal voltages, sensitive to magnetic field magnitude and direction.
17 In the presence of a magnetic field, transport current generates valley imbalance SOURCE DRAIN
18 Inverse effect: In the presence of a magnetic field AND valley imbalance, there is a topbottom voltage SOURCE DRAIN
19 Summary so far: 1. Four-terminal nonlocal geometry can help detect electric signals due to the presence of the chiral anomaly: 2. Should employ either tunneling leads, or this: 3. Locally applied B-fields are preferred 4. Detectors can be made non-invasive, if they are not too long
20 Transport theory = bulk transport equations + boundary conditions The currents include the chiral modes contributions: (Vilenkin, 1980) The continuity equations include the anomalous divergences: The final stationary transport equations contain only
21 Boundary conditions: The simplest set of physically sound ones would suffice here Top surface: Assumption: no intervalley scattering under a lead. Bottom surface:
22 The nonlocal voltages reach afar, and depend on the orientation of the B-fields SOURCE DRAIN
23 Tunneling contacts are beneficial, since leads act as shorts between valleys LEAD Good contact; bad for imbalance generation. Effective relaxation time can be as short as the diffusion time through the bulk. Poor contact; good for imbalance generation. Intervalley scattering relaxes imbalances. Means almost no voltage drop across the bulk.
24 Local B-fields (i) reduce intervalley scattering, (ii) provide additional sensitivity to the C.A. SOURCE VACUUM DRAIN SOURCE VS Up-moving chiral mode cannot back - scatter into the same valley. DRAIN In B-field, open surfaces must induce intervalley scattering
25 Local B-fields (i) reduce intervalley scattering, (ii) provide additional sensitivity to the C.A. SOURCE DRAIN SOURCE VS DRAIN
26 When is the detector non-invasive? LEAD, This condition is not very restrictive, since well within the applicability range of the theory. is
27 Does chiral anomaly manifest itself in the spectrum of collective modes? I. Panfilov, A. Burkov, DP Phys. Rev. B 89, (2014) (see also Son&Spivak 12) Are there any new modes? Hydrodynamics plasmons? ( yes - Son&Spivak 12)
28 Hydrodynamic plasmons? No Equations of motion with a self-consistent electric field:
29 Hydrodynamic plasmons? Only for large B. Dispersion relation: Solutions with a real part exist if It is unlikely to satisfy this condition for
30 Undoped case: WS becomes compessible at any finite B-field Unitary limit, Screening by non-zero Landau levels Does not depend on e This translates into a non-analytic in B correction at finite doping:
31 Conclusions 1. Weyl semimetals are gapless topological phases 2. The Adler-Bell-Jackiw (chiral) anomaly provides a topological response. 3. In clean samples this response is measurable via a simple nonlocal electric measurement. 4. The chiral anomaly leads to new collective modes. The plasmon analog of the first sound does not exist at small magnetic fields though.
3D Weyl metallic states realized in the Bi 1-x Sb x alloy and BiTeI. Heon-Jung Kim Department of Physics, Daegu University, Korea
 3D Weyl metallic states realized in the Bi 1-x Sb x alloy and BiTeI Heon-Jung Kim Department of Physics, Daegu University, Korea Content 3D Dirac metals Search for 3D generalization of graphene Bi 1-x
3D Weyl metallic states realized in the Bi 1-x Sb x alloy and BiTeI Heon-Jung Kim Department of Physics, Daegu University, Korea Content 3D Dirac metals Search for 3D generalization of graphene Bi 1-x
Weyl semimetals from chiral anomaly to fractional chiral metal
 Weyl semimetals from chiral anomaly to fractional chiral metal Jens Hjörleifur Bárðarson Max Planck Institute for the Physics of Complex Systems, Dresden KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm J.
Weyl semimetals from chiral anomaly to fractional chiral metal Jens Hjörleifur Bárðarson Max Planck Institute for the Physics of Complex Systems, Dresden KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm J.
Weyl semi-metal: a New Topological State in Condensed Matter
 Weyl semi-metal: a New Topological State in Condensed Matter Sergey Savrasov Department of Physics, University of California, Davis Xiangang Wan Nanjing University Ari Turner and Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley
Weyl semi-metal: a New Topological State in Condensed Matter Sergey Savrasov Department of Physics, University of California, Davis Xiangang Wan Nanjing University Ari Turner and Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley
Supplementary Figure 1. Magneto-transport characteristics of topological semimetal Cd 3 As 2 microribbon. (a) Measured resistance (R) as a function
 Supplementary Figure 1. Magneto-transport characteristics of topological semimetal Cd 3 As 2 microribbon. (a) Measured resistance (R) as a function of temperature (T) at zero magnetic field. (b) Magnetoresistance
Supplementary Figure 1. Magneto-transport characteristics of topological semimetal Cd 3 As 2 microribbon. (a) Measured resistance (R) as a function of temperature (T) at zero magnetic field. (b) Magnetoresistance
Dirac and Weyl fermions in condensed matter systems: an introduction
 Dirac and Weyl fermions in condensed matter systems: an introduction Fa Wang ( 王垡 ) ICQM, Peking University 第二届理论物理研讨会 Preamble: Dirac/Weyl fermions Dirac equation: reconciliation of special relativity
Dirac and Weyl fermions in condensed matter systems: an introduction Fa Wang ( 王垡 ) ICQM, Peking University 第二届理论物理研讨会 Preamble: Dirac/Weyl fermions Dirac equation: reconciliation of special relativity
Emergent topological phenomena in antiferromagnets with noncoplanar spins
 Emergent topological phenomena in antiferromagnets with noncoplanar spins - Surface quantum Hall effect - Dimensional crossover Bohm-Jung Yang (RIKEN, Center for Emergent Matter Science (CEMS), Japan)
Emergent topological phenomena in antiferromagnets with noncoplanar spins - Surface quantum Hall effect - Dimensional crossover Bohm-Jung Yang (RIKEN, Center for Emergent Matter Science (CEMS), Japan)
can be moved in energy/momentum but not individually destroyed; in general: topological Fermi surfaces
 nodes protected against gapping can be moved in energy/momentum but not individually destroyed; in general: topological Fermi surfaces physical realization: stacked 2d topological insulators C=1 3d top
nodes protected against gapping can be moved in energy/momentum but not individually destroyed; in general: topological Fermi surfaces physical realization: stacked 2d topological insulators C=1 3d top
Weyl fermions and the Anomalous Hall Effect
 Weyl fermions and the Anomalous Hall Effect Anton Burkov CAP congress, Montreal, May 29, 2013 Outline Introduction: Weyl fermions in condensed matter, Weyl semimetals. Anomalous Hall Effect in ferromagnets
Weyl fermions and the Anomalous Hall Effect Anton Burkov CAP congress, Montreal, May 29, 2013 Outline Introduction: Weyl fermions in condensed matter, Weyl semimetals. Anomalous Hall Effect in ferromagnets
1. Chiral anomaly in Na 3 Bi and the half-heusler GdPtBi 2. Thermopower of Weyl fermions 3. Prelim results on nonsymmorphic semimetal KHgSb
 Workshop Topological Quantum Matter, KITP-UCSB Oct. 2016 The chiral anomaly in Dirac and Weyl Semimetals Jun Xiong Kushwaha Tian Liang Jason Krizan Hirschberger Zhijun Wang Quinn Gibson Cano Bradlyn S.H.
Workshop Topological Quantum Matter, KITP-UCSB Oct. 2016 The chiral anomaly in Dirac and Weyl Semimetals Jun Xiong Kushwaha Tian Liang Jason Krizan Hirschberger Zhijun Wang Quinn Gibson Cano Bradlyn S.H.
TOPOLOGY IN CONDENSED MATTER SYSTEMS: MAJORANA MODES AND WEYL SEMIMETALS. Jan 23, 2012, University of Illinois, Urbana-Chamapaign
 TOPOLOGY IN CONDENSED MATTER SYSTEMS: MAJORANA MODES AND WEYL SEMIMETALS Pavan Hosur UC Berkeley Jan 23, 2012, University of Illinois, Urbana-Chamapaign Acknowledgements Advisor: Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley
TOPOLOGY IN CONDENSED MATTER SYSTEMS: MAJORANA MODES AND WEYL SEMIMETALS Pavan Hosur UC Berkeley Jan 23, 2012, University of Illinois, Urbana-Chamapaign Acknowledgements Advisor: Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley
Symmetry Protected Topological Insulators and Semimetals
 Symmetry Protected Topological Insulators and Semimetals I. Introduction : Many examples of topological band phenomena II. Recent developments : - Line node semimetal Kim, Wieder, Kane, Rappe, PRL 115,
Symmetry Protected Topological Insulators and Semimetals I. Introduction : Many examples of topological band phenomena II. Recent developments : - Line node semimetal Kim, Wieder, Kane, Rappe, PRL 115,
Topological Insulators and Ferromagnets: appearance of flat surface bands
 Topological Insulators and Ferromagnets: appearance of flat surface bands Thomas Dahm University of Bielefeld T. Paananen and T. Dahm, PRB 87, 195447 (2013) T. Paananen et al, New J. Phys. 16, 033019 (2014)
Topological Insulators and Ferromagnets: appearance of flat surface bands Thomas Dahm University of Bielefeld T. Paananen and T. Dahm, PRB 87, 195447 (2013) T. Paananen et al, New J. Phys. 16, 033019 (2014)
Quantum Hall effect. Quantization of Hall resistance is incredibly precise: good to 1 part in I believe. WHY?? G xy = N e2 h.
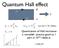 Quantum Hall effect V1 V2 R L I I x = N e2 h V y V x =0 G xy = N e2 h n.b. h/e 2 = 25 kohms Quantization of Hall resistance is incredibly precise: good to 1 part in 10 10 I believe. WHY?? Robustness Why
Quantum Hall effect V1 V2 R L I I x = N e2 h V y V x =0 G xy = N e2 h n.b. h/e 2 = 25 kohms Quantization of Hall resistance is incredibly precise: good to 1 part in 10 10 I believe. WHY?? Robustness Why
Dirac semimetal in three dimensions
 Dirac semimetal in three dimensions Steve M. Young, Saad Zaheer, Jeffrey C. Y. Teo, Charles L. Kane, Eugene J. Mele, and Andrew M. Rappe University of Pennsylvania 6/7/12 1 Dirac points in Graphene Without
Dirac semimetal in three dimensions Steve M. Young, Saad Zaheer, Jeffrey C. Y. Teo, Charles L. Kane, Eugene J. Mele, and Andrew M. Rappe University of Pennsylvania 6/7/12 1 Dirac points in Graphene Without
Topological Defects in the Topological Insulator
 Topological Defects in the Topological Insulator Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley arxiv:0810.5121 YING RAN Frank YI ZHANG Quantum Hall States Exotic Band Topology Topological band Insulators (quantum spin
Topological Defects in the Topological Insulator Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley arxiv:0810.5121 YING RAN Frank YI ZHANG Quantum Hall States Exotic Band Topology Topological band Insulators (quantum spin
Topological Defects inside a Topological Band Insulator
 Topological Defects inside a Topological Band Insulator Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley Refs: Ran, Zhang A.V., Nature Physics 5, 289 (2009). Hosur, Ryu, AV arxiv: 0908.2691 Part 1: Outline A toy model of
Topological Defects inside a Topological Band Insulator Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley Refs: Ran, Zhang A.V., Nature Physics 5, 289 (2009). Hosur, Ryu, AV arxiv: 0908.2691 Part 1: Outline A toy model of
Part 1. March 5, 2014 Quantum Hadron Physics Laboratory, RIKEN, Wako, Japan 2
 MAR 5, 2014 Part 1 March 5, 2014 Quantum Hadron Physics Laboratory, RIKEN, Wako, Japan 2 ! Examples of relativistic matter Electrons, protons, quarks inside compact stars (white dwarfs, neutron, hybrid
MAR 5, 2014 Part 1 March 5, 2014 Quantum Hadron Physics Laboratory, RIKEN, Wako, Japan 2 ! Examples of relativistic matter Electrons, protons, quarks inside compact stars (white dwarfs, neutron, hybrid
Heusler compounds: Tunable materials with non trivial topologies. Claudia Felser
 Heusler compounds: Tunable materials with non trivial topologies Claudia Felser Tunability of Heusler compounds Tuning the band gap Tuning spin orbit coupling Trivial and topological Heusler Adding spins
Heusler compounds: Tunable materials with non trivial topologies Claudia Felser Tunability of Heusler compounds Tuning the band gap Tuning spin orbit coupling Trivial and topological Heusler Adding spins
Weyl Semimetals, Fermi Arcs and Chiral Anomalies (A Short Review)
 Weyl Semimetals, Fermi Arcs and Chiral Anomalies (A Short Review) Shuang Jia, 1,2 Su-Yang Xu, 3 and M. Zahid Hasan 3,4 arxiv:1612.00416v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 7 Dec 2016 1 International Center for Quantum
Weyl Semimetals, Fermi Arcs and Chiral Anomalies (A Short Review) Shuang Jia, 1,2 Su-Yang Xu, 3 and M. Zahid Hasan 3,4 arxiv:1612.00416v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 7 Dec 2016 1 International Center for Quantum
Dirac fermions in condensed matters
 Dirac fermions in condensed matters Bohm Jung Yang Department of Physics and Astronomy, Seoul National University Outline 1. Dirac fermions in relativistic wave equations 2. How do Dirac fermions appear
Dirac fermions in condensed matters Bohm Jung Yang Department of Physics and Astronomy, Seoul National University Outline 1. Dirac fermions in relativistic wave equations 2. How do Dirac fermions appear
Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter. Andrea Cappelli INFN, Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti)
 Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter Andrea Cappelli INFN, Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Topological States of Matter System with bulk gap but non-trivial at energies below
Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter Andrea Cappelli INFN, Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Topological States of Matter System with bulk gap but non-trivial at energies below
Structure and Topology of Band Structures in the 1651 Magnetic Space Groups
 Structure and Topology of Band Structures in the 1651 Magnetic Space Groups Haruki Watanabe University of Tokyo [Noninteracting] Sci Adv (2016) PRL (2016) Nat Commun (2017) (New) arxiv:1707.01903 [Interacting]
Structure and Topology of Band Structures in the 1651 Magnetic Space Groups Haruki Watanabe University of Tokyo [Noninteracting] Sci Adv (2016) PRL (2016) Nat Commun (2017) (New) arxiv:1707.01903 [Interacting]
Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter
 Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter Andrea Cappelli, INFN Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Outline Topological states of matter Quantum Hall effect: bulk and edge Effective field
Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter Andrea Cappelli, INFN Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Outline Topological states of matter Quantum Hall effect: bulk and edge Effective field
5 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry
 Phys62.nb 63 5 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry It is impossible to have quantum Hall effect without breaking the time-reversal symmetry. xy xy. If we want xy to be invariant under, xy
Phys62.nb 63 5 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry It is impossible to have quantum Hall effect without breaking the time-reversal symmetry. xy xy. If we want xy to be invariant under, xy
Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry
 Phys620.nb 101 7 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry Q: Can we get a topological insulator that preserves the time-reversal symmetry? A: Yes, with the help of the spin degree of freedom.
Phys620.nb 101 7 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry Q: Can we get a topological insulator that preserves the time-reversal symmetry? A: Yes, with the help of the spin degree of freedom.
Stability of semi-metals : (partial) classification of semi-metals
 : (partial) classification of semi-metals Eun-Gook Moon Department of Physics, UCSB EQPCM 2013 at ISSP, Jun 20, 2013 Collaborators Cenke Xu, UCSB Yong Baek, Kim Univ. of Toronto Leon Balents, KITP B.J.
: (partial) classification of semi-metals Eun-Gook Moon Department of Physics, UCSB EQPCM 2013 at ISSP, Jun 20, 2013 Collaborators Cenke Xu, UCSB Yong Baek, Kim Univ. of Toronto Leon Balents, KITP B.J.
Fully symmetric and non-fractionalized Mott insulators at fractional site-filling
 Fully symmetric and non-fractionalized Mott insulators at fractional site-filling Itamar Kimchi University of California, Berkeley EQPCM @ ISSP June 19, 2013 PRL 2013 (kagome), 1207.0498...[PNAS] (honeycomb)
Fully symmetric and non-fractionalized Mott insulators at fractional site-filling Itamar Kimchi University of California, Berkeley EQPCM @ ISSP June 19, 2013 PRL 2013 (kagome), 1207.0498...[PNAS] (honeycomb)
Notes on Topological Insulators and Quantum Spin Hall Effect. Jouko Nieminen Tampere University of Technology.
 Notes on Topological Insulators and Quantum Spin Hall Effect Jouko Nieminen Tampere University of Technology. Not so much discussed concept in this session: topology. In math, topology discards small details
Notes on Topological Insulators and Quantum Spin Hall Effect Jouko Nieminen Tampere University of Technology. Not so much discussed concept in this session: topology. In math, topology discards small details
Introductory lecture on topological insulators. Reza Asgari
 Introductory lecture on topological insulators Reza Asgari Workshop on graphene and topological insulators, IPM. 19-20 Oct. 2011 Outlines -Introduction New phases of materials, Insulators -Theory quantum
Introductory lecture on topological insulators Reza Asgari Workshop on graphene and topological insulators, IPM. 19-20 Oct. 2011 Outlines -Introduction New phases of materials, Insulators -Theory quantum
Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field
 Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field by B. I. Halperin Nano-QT 2016 Kyiv October 11, 2016 Based on work with So Takei (CUNY), Yaroslav Tserkovnyak (UCLA), and Amir Yacoby (Harvard)
Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field by B. I. Halperin Nano-QT 2016 Kyiv October 11, 2016 Based on work with So Takei (CUNY), Yaroslav Tserkovnyak (UCLA), and Amir Yacoby (Harvard)
Nanostructured Carbon Allotropes as Weyl-Like Semimetals
 Nanostructured Carbon Allotropes as Weyl-Like Semimetals Shengbai Zhang Department of Physics, Applied Physics & Astronomy Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute symmetry In quantum mechanics, symmetry can be
Nanostructured Carbon Allotropes as Weyl-Like Semimetals Shengbai Zhang Department of Physics, Applied Physics & Astronomy Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute symmetry In quantum mechanics, symmetry can be
From graphene to Z2 topological insulator
 From graphene to Z2 topological insulator single Dirac topological AL mass U U valley WL ordinary mass or ripples WL U WL AL AL U AL WL Rashba Ken-Ichiro Imura Condensed-Matter Theory / Tohoku Univ. Dirac
From graphene to Z2 topological insulator single Dirac topological AL mass U U valley WL ordinary mass or ripples WL U WL AL AL U AL WL Rashba Ken-Ichiro Imura Condensed-Matter Theory / Tohoku Univ. Dirac
Topological Physics in Band Insulators II
 Topological Physics in Band Insulators II Gene Mele University of Pennsylvania Topological Insulators in Two and Three Dimensions The canonical list of electric forms of matter is actually incomplete Conductor
Topological Physics in Band Insulators II Gene Mele University of Pennsylvania Topological Insulators in Two and Three Dimensions The canonical list of electric forms of matter is actually incomplete Conductor
Dirac matter: Magneto-optical studies
 Dirac matter: Magneto-optical studies Marek Potemski Laboratoire National des Champs Magnétiques Intenses Grenoble High Magnetic Field Laboratory CNRS/UGA/UPS/INSA/EMFL MOMB nd International Conference
Dirac matter: Magneto-optical studies Marek Potemski Laboratoire National des Champs Magnétiques Intenses Grenoble High Magnetic Field Laboratory CNRS/UGA/UPS/INSA/EMFL MOMB nd International Conference
arxiv: v3 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 18 Feb 2015
![arxiv: v3 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 18 Feb 2015 arxiv: v3 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 18 Feb 2015](/thumbs/77/76275752.jpg) Observation of Fermi Arc Surface States in a Topological Metal: A New Type of 2D Electron Gas Su-Yang Xu, 1 Chang Liu, 1 Satya K. Kushwaha, 2 Raman Sankar, 3 Jason W. Krizan, 2 arxiv:1501.01249v3 [cond-mat.mes-hall]
Observation of Fermi Arc Surface States in a Topological Metal: A New Type of 2D Electron Gas Su-Yang Xu, 1 Chang Liu, 1 Satya K. Kushwaha, 2 Raman Sankar, 3 Jason W. Krizan, 2 arxiv:1501.01249v3 [cond-mat.mes-hall]
IRG-1 CEM CENTER FOR EMERGENT MATERIALS SPIN-ORBIT COUPLING IN CORRELATED MATERIALS: SEARCH FOR NOVEL PHASES AND PHENOMENA
 IRG-1 SPIN-ORBIT COUPLING IN CORRELATED MATERIALS: SEARCH FOR NOVEL PHASES AND PHENOMENA Co-leads: N. Trivedi & P. M. Woodward 3 June 2014 Center for Emergent Materials an NSF MRSEC IRG-1 1 Spin orbit
IRG-1 SPIN-ORBIT COUPLING IN CORRELATED MATERIALS: SEARCH FOR NOVEL PHASES AND PHENOMENA Co-leads: N. Trivedi & P. M. Woodward 3 June 2014 Center for Emergent Materials an NSF MRSEC IRG-1 1 Spin orbit
Effective Field Theories of Topological Insulators
 Effective Field Theories of Topological Insulators Eduardo Fradkin University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Workshop on Field Theoretic Computer Simulations for Particle Physics and Condensed Matter
Effective Field Theories of Topological Insulators Eduardo Fradkin University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Workshop on Field Theoretic Computer Simulations for Particle Physics and Condensed Matter
Visualizing "Fermi arcs" in the Weyl semimetal TaAs
 Visualizing "Fermi arcs" in the Weyl semimetal TaAs Rajib Batabyal 1, Noam Morali 1, Nurit Avraham 1, Yan Sun 2, Marcus Schmidt 2, Claudia Felser 2, Ady Stern 1, Binghai Yan 2, Haim Beidenkopf 1 1 Department
Visualizing "Fermi arcs" in the Weyl semimetal TaAs Rajib Batabyal 1, Noam Morali 1, Nurit Avraham 1, Yan Sun 2, Marcus Schmidt 2, Claudia Felser 2, Ady Stern 1, Binghai Yan 2, Haim Beidenkopf 1 1 Department
ARPES experiments on 3D topological insulators. Inna Vishik Physics 250 (Special topics: spectroscopies of quantum materials) UC Davis, Fall 2016
 ARPES experiments on 3D topological insulators Inna Vishik Physics 250 (Special topics: spectroscopies of quantum materials) UC Davis, Fall 2016 Outline Using ARPES to demonstrate that certain materials
ARPES experiments on 3D topological insulators Inna Vishik Physics 250 (Special topics: spectroscopies of quantum materials) UC Davis, Fall 2016 Outline Using ARPES to demonstrate that certain materials
Topological response in Weyl metals. Anton Burkov
 Topological response in Weyl metals Anton Burkov NanoPiter, Saint-Petersburg, Russia, June 26, 2014 Outline Introduction: Weyl semimetal as a 3D generalization of IQHE. Anomalous Hall Effect in metallic
Topological response in Weyl metals Anton Burkov NanoPiter, Saint-Petersburg, Russia, June 26, 2014 Outline Introduction: Weyl semimetal as a 3D generalization of IQHE. Anomalous Hall Effect in metallic
Konstantin Y. Bliokh, Daria Smirnova, Franco Nori. Center for Emergent Matter Science, RIKEN, Japan. Science 348, 1448 (2015)
 Konstantin Y. Bliokh, Daria Smirnova, Franco Nori Center for Emergent Matter Science, RIKEN, Japan Science 348, 1448 (2015) QSHE and topological insulators The quantum spin Hall effect means the presence
Konstantin Y. Bliokh, Daria Smirnova, Franco Nori Center for Emergent Matter Science, RIKEN, Japan Science 348, 1448 (2015) QSHE and topological insulators The quantum spin Hall effect means the presence
Topological insulator (TI)
 Topological insulator (TI) Haldane model: QHE without Landau level Quantized spin Hall effect: 2D topological insulators: Kane-Mele model for graphene HgTe quantum well InAs/GaSb quantum well 3D topological
Topological insulator (TI) Haldane model: QHE without Landau level Quantized spin Hall effect: 2D topological insulators: Kane-Mele model for graphene HgTe quantum well InAs/GaSb quantum well 3D topological
Superconductivities of doped Weyl semimetals
 UIUC, Feb 5 th (2013) Superconductivities of doped Weyl semimetals Phys. Rev. B. 86, 214514 (2012) - Editors suggestion Gil Young Cho UC Berkeley Jens H Bardarson Yuan-Ming Lu Joel E Moore Plan. Part 1
UIUC, Feb 5 th (2013) Superconductivities of doped Weyl semimetals Phys. Rev. B. 86, 214514 (2012) - Editors suggestion Gil Young Cho UC Berkeley Jens H Bardarson Yuan-Ming Lu Joel E Moore Plan. Part 1
Cenke Xu. Quantum Phase Transitions between Bosonic Symmetry Protected Topological States without sign problem 许岑珂
 Quantum Phase Transitions between Bosonic Symmetry Protected Topological States without sign problem Cenke Xu 许岑珂 University of California, Santa Barbara Quantum Phase Transitions between bosonic Symmetry
Quantum Phase Transitions between Bosonic Symmetry Protected Topological States without sign problem Cenke Xu 许岑珂 University of California, Santa Barbara Quantum Phase Transitions between bosonic Symmetry
Symmetric Surfaces of Topological Superconductor
 Symmetric Surfaces of Topological Superconductor Sharmistha Sahoo Zhao Zhang Jeffrey Teo Outline Introduction Brief description of time reversal symmetric topological superconductor. Coupled wire model
Symmetric Surfaces of Topological Superconductor Sharmistha Sahoo Zhao Zhang Jeffrey Teo Outline Introduction Brief description of time reversal symmetric topological superconductor. Coupled wire model
Helicity/Chirality. Helicities of (ultra-relativistic) massless particles are (approximately) conserved Right-handed
 Helicity/Chirality Helicities of (ultra-relativistic) massless particles are (approximately) conserved Right-handed Left-handed Conservation of chiral charge is a property of massless Dirac theory (classically)
Helicity/Chirality Helicities of (ultra-relativistic) massless particles are (approximately) conserved Right-handed Left-handed Conservation of chiral charge is a property of massless Dirac theory (classically)
ASHVIN VISHWANATH HARVARD UNIVERSITY, USA.
 BOULDER SUMMER SCHOOL LECTURE NOTES TOPOLOGICAL SEMIMETALS AND SYMMETRY PROTECTED TOPOLOGICAL PHASES ASHVIN VISHWANATH HARVARD UNIVERSITY, USA. In the previous lectures you have heard about topological
BOULDER SUMMER SCHOOL LECTURE NOTES TOPOLOGICAL SEMIMETALS AND SYMMETRY PROTECTED TOPOLOGICAL PHASES ASHVIN VISHWANATH HARVARD UNIVERSITY, USA. In the previous lectures you have heard about topological
3.14. The model of Haldane on a honeycomb lattice
 4 Phys60.n..7. Marginal case: 4 t Dirac points at k=(,). Not an insulator. No topological index...8. case IV: 4 t All the four special points has z 0. We just use u I for the whole BZ. No singularity.
4 Phys60.n..7. Marginal case: 4 t Dirac points at k=(,). Not an insulator. No topological index...8. case IV: 4 t All the four special points has z 0. We just use u I for the whole BZ. No singularity.
Topological Insulators
 Topological Insulators A new state of matter with three dimensional topological electronic order L. Andrew Wray Lawrence Berkeley National Lab Princeton University Surface States (Topological Order in
Topological Insulators A new state of matter with three dimensional topological electronic order L. Andrew Wray Lawrence Berkeley National Lab Princeton University Surface States (Topological Order in
Photoinduced Anomalous Hall Effect in Weyl Semimetal
 Photoinduced Anomalous Hall Effect in Weyl Semimetal Jung Hoon Han (Sungkyunkwan U) * Intense circularly polarized light will modify the band structure of WSM, its Berry curvature distribution, and leads
Photoinduced Anomalous Hall Effect in Weyl Semimetal Jung Hoon Han (Sungkyunkwan U) * Intense circularly polarized light will modify the band structure of WSM, its Berry curvature distribution, and leads
Composite Dirac liquids
 Composite Dirac liquids Composite Fermi liquid non-interacting 3D TI surface Interactions Composite Dirac liquid ~ Jason Alicea, Caltech David Mross, Andrew Essin, & JA, Physical Review X 5, 011011 (2015)
Composite Dirac liquids Composite Fermi liquid non-interacting 3D TI surface Interactions Composite Dirac liquid ~ Jason Alicea, Caltech David Mross, Andrew Essin, & JA, Physical Review X 5, 011011 (2015)
Luttinger Liquid at the Edge of a Graphene Vacuum
 Luttinger Liquid at the Edge of a Graphene Vacuum H.A. Fertig, Indiana University Luis Brey, CSIC, Madrid I. Introduction: Graphene Edge States (Non-Interacting) II. III. Quantum Hall Ferromagnetism and
Luttinger Liquid at the Edge of a Graphene Vacuum H.A. Fertig, Indiana University Luis Brey, CSIC, Madrid I. Introduction: Graphene Edge States (Non-Interacting) II. III. Quantum Hall Ferromagnetism and
PhD Thesis. Theory of quantum transport in three-dimensional Weyl electron systems. Yuya Ominato
 PhD Thesis Theory of quantum transport in three-dimensional Weyl electron systems Yuya Ominato Department of Physics, Graduate School of Science Tohoku University 2015 Contents 1 Introduction 9 1.1 3D
PhD Thesis Theory of quantum transport in three-dimensional Weyl electron systems Yuya Ominato Department of Physics, Graduate School of Science Tohoku University 2015 Contents 1 Introduction 9 1.1 3D
Weyl semimetals and topological phase transitions
 Weyl semimetals and topological phase transitions Shuichi Murakami 1 Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology 2 TIES, Tokyo Institute of Technology 3 CREST, JST Collaborators: R. Okugawa (Tokyo
Weyl semimetals and topological phase transitions Shuichi Murakami 1 Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology 2 TIES, Tokyo Institute of Technology 3 CREST, JST Collaborators: R. Okugawa (Tokyo
Topological Insulators and Superconductors. Tokyo 2010 Shoucheng Zhang, Stanford University
 Topological Insulators and Superconductors Tokyo 2010 Shoucheng Zhang, Stanford University Colloborators Stanford group: Xiaoliang Qi, Andrei Bernevig, Congjun Wu, Chaoxing Liu, Taylor Hughes, Sri Raghu,
Topological Insulators and Superconductors Tokyo 2010 Shoucheng Zhang, Stanford University Colloborators Stanford group: Xiaoliang Qi, Andrei Bernevig, Congjun Wu, Chaoxing Liu, Taylor Hughes, Sri Raghu,
Minimal Update of Solid State Physics
 Minimal Update of Solid State Physics It is expected that participants are acquainted with basics of solid state physics. Therefore here we will refresh only those aspects, which are absolutely necessary
Minimal Update of Solid State Physics It is expected that participants are acquainted with basics of solid state physics. Therefore here we will refresh only those aspects, which are absolutely necessary
Topological Electromagnetic and Thermal Responses of Time-Reversal Invariant Superconductors and Chiral-Symmetric band insulators
 Topological Electromagnetic and Thermal Responses of Time-Reversal Invariant Superconductors and Chiral-Symmetric band insulators Satoshi Fujimoto Dept. Phys., Kyoto University Collaborator: Ken Shiozaki
Topological Electromagnetic and Thermal Responses of Time-Reversal Invariant Superconductors and Chiral-Symmetric band insulators Satoshi Fujimoto Dept. Phys., Kyoto University Collaborator: Ken Shiozaki
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 17 Sep 2013
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 17 Sep 2013 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 17 Sep 2013](/thumbs/93/114319874.jpg) Recent developments in transport phenomena in Weyl semimetals Pavan Hosur Department of Physics, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA arxiv:1309.4464v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 17 Sep 2013 Abstract Xiaoliang
Recent developments in transport phenomena in Weyl semimetals Pavan Hosur Department of Physics, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA arxiv:1309.4464v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 17 Sep 2013 Abstract Xiaoliang
Nonlinear electrodynamics in Weyl semimetals: Floquet bands and photocurrent generation
 Oct 26, 2017 Nonlinear electrodynamics in Weyl semimetals: Floquet bands and photocurrent generation Theory Patrick Lee (MIT) Experiment Ching-Kit Chan University of California Los Angeles Su-Yang Xu,
Oct 26, 2017 Nonlinear electrodynamics in Weyl semimetals: Floquet bands and photocurrent generation Theory Patrick Lee (MIT) Experiment Ching-Kit Chan University of California Los Angeles Su-Yang Xu,
Topological Insulators in 3D and Bosonization
 Topological Insulators in 3D and Bosonization Andrea Cappelli, INFN Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Outline Topological states of matter: bulk and edge Fermions and bosons on the (1+1)-dimensional
Topological Insulators in 3D and Bosonization Andrea Cappelli, INFN Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Outline Topological states of matter: bulk and edge Fermions and bosons on the (1+1)-dimensional
Topological Photonics with Heavy-Photon Bands
 Topological Photonics with Heavy-Photon Bands Vassilios Yannopapas Dept. of Physics, National Technical University of Athens (NTUA) Quantum simulations and many-body physics with light, 4-11/6/2016, Hania,
Topological Photonics with Heavy-Photon Bands Vassilios Yannopapas Dept. of Physics, National Technical University of Athens (NTUA) Quantum simulations and many-body physics with light, 4-11/6/2016, Hania,
Topological Heterostructures by Molecular Beam Epitaxy
 Topological Heterostructures by Molecular Beam Epitaxy Susanne Stemmer Materials Department, University of California, Santa Barbara Fine Lecture, Northwestern University February 20, 2018 Stemmer Group
Topological Heterostructures by Molecular Beam Epitaxy Susanne Stemmer Materials Department, University of California, Santa Barbara Fine Lecture, Northwestern University February 20, 2018 Stemmer Group
Emergent technology based on Fermi-arcs?
 Emergent technology based on Fermi-arcs? Transport evidence for Fermi-arc-mediated chirality transfer in the Dirac semimetal Cd 3 As 2 P. J. W. Moll, N. L. Nair, T. Helm, A. C. Potter, I. Kimchi, A. Vishwanath,
Emergent technology based on Fermi-arcs? Transport evidence for Fermi-arc-mediated chirality transfer in the Dirac semimetal Cd 3 As 2 P. J. W. Moll, N. L. Nair, T. Helm, A. C. Potter, I. Kimchi, A. Vishwanath,
Emergent Frontiers in Quantum Materials:
 Emergent Frontiers in Quantum Materials: High Temperature superconductivity and Topological Phases Jiun-Haw Chu University of Washington The nature of the problem in Condensed Matter Physics Consider a
Emergent Frontiers in Quantum Materials: High Temperature superconductivity and Topological Phases Jiun-Haw Chu University of Washington The nature of the problem in Condensed Matter Physics Consider a
Graphite, graphene and relativistic electrons
 Graphite, graphene and relativistic electrons Introduction Physics of E. graphene Y. Andrei Experiments Rutgers University Transport electric field effect Quantum Hall Effect chiral fermions STM Dirac
Graphite, graphene and relativistic electrons Introduction Physics of E. graphene Y. Andrei Experiments Rutgers University Transport electric field effect Quantum Hall Effect chiral fermions STM Dirac
Helicity/Chirality. Helicities of (ultra-relativistic) massless particles are (approximately) conserved Right-handed
 Helicity/Chirality Helicities of (ultra-relativistic) massless particles are (approximately) conserved Right-handed Left-handed Conservation of chiral charge is a property of massless Dirac theory (classically)
Helicity/Chirality Helicities of (ultra-relativistic) massless particles are (approximately) conserved Right-handed Left-handed Conservation of chiral charge is a property of massless Dirac theory (classically)
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 27 Feb 2014
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 27 Feb 2014 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 27 Feb 2014](/thumbs/74/70548915.jpg) Dirac and Weyl Superconductors in Three Dimensions Shengyuan A. Yang, 1 Hui Pan, 2 3, 4, and Fan Zhang 1 ngineering Product Development, Singapore University of Technology and Design, Singapore 138682,
Dirac and Weyl Superconductors in Three Dimensions Shengyuan A. Yang, 1 Hui Pan, 2 3, 4, and Fan Zhang 1 ngineering Product Development, Singapore University of Technology and Design, Singapore 138682,
Topological Obstructions to Band Insulator Behavior in Non-symmorphic Crystals
 Topological Obstructions to Band Insulator Behavior in Non-symmorphic Crystals D. P. Arovas, UCSD Siddharth Parameswaran UC Berkeley UC Irvine Ari Turner Univ. Amsterdam JHU Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley
Topological Obstructions to Band Insulator Behavior in Non-symmorphic Crystals D. P. Arovas, UCSD Siddharth Parameswaran UC Berkeley UC Irvine Ari Turner Univ. Amsterdam JHU Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley
Universe Heavy-ion collisions Compact stars Dirac semimetals, graphene, etc.
 NOV 23, 2015 MAGNETIC FIELDS EVERYWHERE [Miransky & Shovkovy, Physics Reports 576 (2015) pp. 1-209] Universe Heavy-ion collisions Compact stars Dirac semimetals, graphene, etc. November 23, 2015 Magnetic
NOV 23, 2015 MAGNETIC FIELDS EVERYWHERE [Miransky & Shovkovy, Physics Reports 576 (2015) pp. 1-209] Universe Heavy-ion collisions Compact stars Dirac semimetals, graphene, etc. November 23, 2015 Magnetic
The uses of Instantons for classifying Topological Phases
 The uses of Instantons for classifying Topological Phases - anomaly-free and chiral fermions Juven Wang, Xiao-Gang Wen (arxiv:1307.7480, arxiv:140?.????) MIT/Perimeter Inst. 2014 @ APS March A Lattice
The uses of Instantons for classifying Topological Phases - anomaly-free and chiral fermions Juven Wang, Xiao-Gang Wen (arxiv:1307.7480, arxiv:140?.????) MIT/Perimeter Inst. 2014 @ APS March A Lattice
Two Dimensional Chern Insulators, the Qi-Wu-Zhang and Haldane Models
 Two Dimensional Chern Insulators, the Qi-Wu-Zhang and Haldane Models Matthew Brooks, Introduction to Topological Insulators Seminar, Universität Konstanz Contents QWZ Model of Chern Insulators Haldane
Two Dimensional Chern Insulators, the Qi-Wu-Zhang and Haldane Models Matthew Brooks, Introduction to Topological Insulators Seminar, Universität Konstanz Contents QWZ Model of Chern Insulators Haldane
Studying Topological Insulators. Roni Ilan UC Berkeley
 Studying Topological Insulators via time reversal symmetry breaking and proximity effect Roni Ilan UC Berkeley Joel Moore, Jens Bardarson, Jerome Cayssol, Heung-Sun Sim Topological phases Insulating phases
Studying Topological Insulators via time reversal symmetry breaking and proximity effect Roni Ilan UC Berkeley Joel Moore, Jens Bardarson, Jerome Cayssol, Heung-Sun Sim Topological phases Insulating phases
Physics in two dimensions in the lab
 Physics in two dimensions in the lab Nanodevice Physics Lab David Cobden PAB 308 Collaborators at UW Oscar Vilches (Low Temperature Lab) Xiaodong Xu (Nanoscale Optoelectronics Lab) Jiun Haw Chu (Quantum
Physics in two dimensions in the lab Nanodevice Physics Lab David Cobden PAB 308 Collaborators at UW Oscar Vilches (Low Temperature Lab) Xiaodong Xu (Nanoscale Optoelectronics Lab) Jiun Haw Chu (Quantum
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 29 Jul 2010
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 29 Jul 2010 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 29 Jul 2010](/thumbs/94/121300146.jpg) Discovery of several large families of Topological Insulator classes with backscattering-suppressed spin-polarized single-dirac-cone on the surface arxiv:1007.5111v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 29 Jul 2010 Su-Yang
Discovery of several large families of Topological Insulator classes with backscattering-suppressed spin-polarized single-dirac-cone on the surface arxiv:1007.5111v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 29 Jul 2010 Su-Yang
arxiv: v2 [hep-ph] 21 Oct 2016
![arxiv: v2 [hep-ph] 21 Oct 2016 arxiv: v2 [hep-ph] 21 Oct 2016](/thumbs/72/67189080.jpg) Quantized chiral magnetic current from reconnections of magnetic flux Yuji Hirono, 1 Dmitri E. Kharzeev, 1, 2, 3 and Yi Yin 1 1 Department of Physics, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, New York 11973-5000
Quantized chiral magnetic current from reconnections of magnetic flux Yuji Hirono, 1 Dmitri E. Kharzeev, 1, 2, 3 and Yi Yin 1 1 Department of Physics, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, New York 11973-5000
Spin Hall and quantum spin Hall effects. Shuichi Murakami Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology PRESTO, JST
 YKIS2007 (Kyoto) Nov.16, 2007 Spin Hall and quantum spin Hall effects Shuichi Murakami Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology PRESTO, JST Introduction Spin Hall effect spin Hall effect in
YKIS2007 (Kyoto) Nov.16, 2007 Spin Hall and quantum spin Hall effects Shuichi Murakami Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology PRESTO, JST Introduction Spin Hall effect spin Hall effect in
Topological states of matter in correlated electron systems
 Seminar @ Tsinghua, Dec.5/2012 Topological states of matter in correlated electron systems Qiang-Hua Wang National Lab of Solid State Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China Collaborators:Dunghai
Seminar @ Tsinghua, Dec.5/2012 Topological states of matter in correlated electron systems Qiang-Hua Wang National Lab of Solid State Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China Collaborators:Dunghai
Surface Majorana Fermions in Topological Superconductors. ISSP, Univ. of Tokyo. Nagoya University Masatoshi Sato
 Surface Majorana Fermions in Topological Superconductors ISSP, Univ. of Tokyo Nagoya University Masatoshi Sato Kyoto Tokyo Nagoya In collaboration with Satoshi Fujimoto (Kyoto University) Yoshiro Takahashi
Surface Majorana Fermions in Topological Superconductors ISSP, Univ. of Tokyo Nagoya University Masatoshi Sato Kyoto Tokyo Nagoya In collaboration with Satoshi Fujimoto (Kyoto University) Yoshiro Takahashi
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 11 Oct 2016
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 11 Oct 2016 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 11 Oct 2016](/thumbs/77/74977843.jpg) Nonsymmorphic symmetry-required band crossings in topological semimetals arxiv:1606.03698v [cond-mat.mes-hall] 11 Oct 016 Y. X. Zhao 1, and Andreas P. Schnyder 1, 1 Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State
Nonsymmorphic symmetry-required band crossings in topological semimetals arxiv:1606.03698v [cond-mat.mes-hall] 11 Oct 016 Y. X. Zhao 1, and Andreas P. Schnyder 1, 1 Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State
Exotic Phenomena in Topological Insulators and Superconductors
 SPICE Workshop on Spin Dynamics in the Dirac System Schloss Waldthausen, Mainz, 6 June 2017 Exotic Phenomena in Topological Insulators and Superconductors Yoichi Ando Physics Institute II, University of
SPICE Workshop on Spin Dynamics in the Dirac System Schloss Waldthausen, Mainz, 6 June 2017 Exotic Phenomena in Topological Insulators and Superconductors Yoichi Ando Physics Institute II, University of
SPT: a window into highly entangled phases
 SPT: a window into highly entangled phases T. Senthil (MIT) Collaborators: Chong Wang, A. Potter Why study SPT? 1. Because it may be there... Focus on electronic systems with realistic symmetries in d
SPT: a window into highly entangled phases T. Senthil (MIT) Collaborators: Chong Wang, A. Potter Why study SPT? 1. Because it may be there... Focus on electronic systems with realistic symmetries in d
Topological insulators
 http://www.physik.uni-regensburg.de/forschung/fabian Topological insulators Jaroslav Fabian Institute for Theoretical Physics University of Regensburg Stara Lesna, 21.8.212 DFG SFB 689 what are topological
http://www.physik.uni-regensburg.de/forschung/fabian Topological insulators Jaroslav Fabian Institute for Theoretical Physics University of Regensburg Stara Lesna, 21.8.212 DFG SFB 689 what are topological
Floquet Topological Insulators and Majorana Modes
 Floquet Topological Insulators and Majorana Modes Manisha Thakurathi Journal Club Centre for High Energy Physics IISc Bangalore January 17, 2013 References Floquet Topological Insulators by J. Cayssol
Floquet Topological Insulators and Majorana Modes Manisha Thakurathi Journal Club Centre for High Energy Physics IISc Bangalore January 17, 2013 References Floquet Topological Insulators by J. Cayssol
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 5 Jan 2015
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 5 Jan 2015 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 5 Jan 2015](/thumbs/88/117638152.jpg) Weyl semimetal phase in non-centrosymmetric transition metal monophosphides Hongming Weng, 1, 2, Chen Fang, 3 Zhong Fang, 1, 2 Andrei Bernevig, 4 and Xi Dai 1, 2 1 Beijing National Laboratory for Condensed
Weyl semimetal phase in non-centrosymmetric transition metal monophosphides Hongming Weng, 1, 2, Chen Fang, 3 Zhong Fang, 1, 2 Andrei Bernevig, 4 and Xi Dai 1, 2 1 Beijing National Laboratory for Condensed
Classification theory of topological insulators with Clifford algebras and its application to interacting fermions. Takahiro Morimoto.
 QMath13, 10 th October 2016 Classification theory of topological insulators with Clifford algebras and its application to interacting fermions Takahiro Morimoto UC Berkeley Collaborators Akira Furusaki
QMath13, 10 th October 2016 Classification theory of topological insulators with Clifford algebras and its application to interacting fermions Takahiro Morimoto UC Berkeley Collaborators Akira Furusaki
Spins and spin-orbit coupling in semiconductors, metals, and nanostructures
 B. Halperin Spin lecture 1 Spins and spin-orbit coupling in semiconductors, metals, and nanostructures Behavior of non-equilibrium spin populations. Spin relaxation and spin transport. How does one produce
B. Halperin Spin lecture 1 Spins and spin-orbit coupling in semiconductors, metals, and nanostructures Behavior of non-equilibrium spin populations. Spin relaxation and spin transport. How does one produce
Proximity-induced magnetization dynamics, interaction effects, and phase transitions on a topological surface
 Proximity-induced magnetization dynamics, interaction effects, and phase transitions on a topological surface Ilya Eremin Theoretische Physik III, Ruhr-Uni Bochum Work done in collaboration with: F. Nogueira
Proximity-induced magnetization dynamics, interaction effects, and phase transitions on a topological surface Ilya Eremin Theoretische Physik III, Ruhr-Uni Bochum Work done in collaboration with: F. Nogueira
Influence of tetragonal distortion on the topological electronic structure. of the half-heusler compound LaPtBi from first principles
 Influence of tetragonal distortion on the topological electronic structure of the half-heusler compound LaPtBi from first principles X. M. Zhang, 1,3 W. H. Wang, 1, a) E. K. Liu, 1 G. D. Liu, 3 Z. Y. Liu,
Influence of tetragonal distortion on the topological electronic structure of the half-heusler compound LaPtBi from first principles X. M. Zhang, 1,3 W. H. Wang, 1, a) E. K. Liu, 1 G. D. Liu, 3 Z. Y. Liu,
Quantitative Mappings from Symmetry to Topology
 Z. Song, Z. Fang and CF, PRL 119, 246402 (2017) CF and L. Fu, arxiv:1709.01929 Z. Song, T. Zhang, Z. Fang and CF arxiv:1711.11049 Z. Song, T. Zhang and CF arxiv:1711.11050 Quantitative Mappings from Symmetry
Z. Song, Z. Fang and CF, PRL 119, 246402 (2017) CF and L. Fu, arxiv:1709.01929 Z. Song, T. Zhang, Z. Fang and CF arxiv:1711.11049 Z. Song, T. Zhang and CF arxiv:1711.11050 Quantitative Mappings from Symmetry
Weyl Semimetal Phase in Noncentrosymmetric Transition-Metal Monophosphides
 PHYSICAL REVIEW X 5, 1129 (215) Weyl Semimetal Phase in Noncentrosymmetric Transition-Metal Monophosphides Hongming Weng, 1,2,* Chen Fang, 3 hong Fang, 1,2 B. Andrei Bernevig, 4 and Xi Dai 1,2 1 Beijing
PHYSICAL REVIEW X 5, 1129 (215) Weyl Semimetal Phase in Noncentrosymmetric Transition-Metal Monophosphides Hongming Weng, 1,2,* Chen Fang, 3 hong Fang, 1,2 B. Andrei Bernevig, 4 and Xi Dai 1,2 1 Beijing
Time Reversal Invariant Ζ 2 Topological Insulator
 Time Reversal Invariant Ζ Topological Insulator D Bloch Hamiltonians subject to the T constraint 1 ( ) ΘH Θ = H( ) with Θ = 1 are classified by a Ζ topological invariant (ν =,1) Understand via Bul-Boundary
Time Reversal Invariant Ζ Topological Insulator D Bloch Hamiltonians subject to the T constraint 1 ( ) ΘH Θ = H( ) with Θ = 1 are classified by a Ζ topological invariant (ν =,1) Understand via Bul-Boundary
Quantum Hall Effect in Graphene p-n Junctions
 Quantum Hall Effect in Graphene p-n Junctions Dima Abanin (MIT) Collaboration: Leonid Levitov, Patrick Lee, Harvard and Columbia groups UIUC January 14, 2008 Electron transport in graphene monolayer New
Quantum Hall Effect in Graphene p-n Junctions Dima Abanin (MIT) Collaboration: Leonid Levitov, Patrick Lee, Harvard and Columbia groups UIUC January 14, 2008 Electron transport in graphene monolayer New
2015 Summer School on Emergent Phenomena in Quantum Materials. Program Overview
 Emergent Phenomena in Quantum Materials Program Overview Each talk to be 45min with 15min Q&A. Monday 8/3 8:00AM Registration & Breakfast 9:00-9:10 Welcoming Remarks 9:10-10:10 Eugene Demler Harvard University
Emergent Phenomena in Quantum Materials Program Overview Each talk to be 45min with 15min Q&A. Monday 8/3 8:00AM Registration & Breakfast 9:00-9:10 Welcoming Remarks 9:10-10:10 Eugene Demler Harvard University
Dirac-Fermion-Induced Parity Mixing in Superconducting Topological Insulators. Nagoya University Masatoshi Sato
 Dirac-Fermion-Induced Parity Mixing in Superconducting Topological Insulators Nagoya University Masatoshi Sato In collaboration with Yukio Tanaka (Nagoya University) Keiji Yada (Nagoya University) Ai Yamakage
Dirac-Fermion-Induced Parity Mixing in Superconducting Topological Insulators Nagoya University Masatoshi Sato In collaboration with Yukio Tanaka (Nagoya University) Keiji Yada (Nagoya University) Ai Yamakage
Electronic transport in topological insulators
 Electronic transport in topological insulators Reinhold Egger Institut für Theoretische Physik, Düsseldorf Alex Zazunov, Alfredo Levy Yeyati Trieste, November 011 To the memory of my dear friend Please
Electronic transport in topological insulators Reinhold Egger Institut für Theoretische Physik, Düsseldorf Alex Zazunov, Alfredo Levy Yeyati Trieste, November 011 To the memory of my dear friend Please
Massive Dirac Fermion on the Surface of a magnetically doped Topological Insulator
 SLAC-PUB-14357 Massive Dirac Fermion on the Surface of a magnetically doped Topological Insulator Y. L. Chen 1,2,3, J.-H. Chu 1,2, J. G. Analytis 1,2, Z. K. Liu 1,2, K. Igarashi 4, H.-H. Kuo 1,2, X. L.
SLAC-PUB-14357 Massive Dirac Fermion on the Surface of a magnetically doped Topological Insulator Y. L. Chen 1,2,3, J.-H. Chu 1,2, J. G. Analytis 1,2, Z. K. Liu 1,2, K. Igarashi 4, H.-H. Kuo 1,2, X. L.
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 22 Oct 2018
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 22 Oct 2018 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 22 Oct 2018](/thumbs/88/114697358.jpg) Pseudo topological insulators C. Yuce Department of Physics, Anadolu University, Turkey Department of Physics, Eskisehir Technical University, Turkey (Dated: October 23, 2018) arxiv:1808.07862v2 [cond-mat.str-el]
Pseudo topological insulators C. Yuce Department of Physics, Anadolu University, Turkey Department of Physics, Eskisehir Technical University, Turkey (Dated: October 23, 2018) arxiv:1808.07862v2 [cond-mat.str-el]
Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley
 TOPOLOGY + LOCALIZATION: QUANTUM COHERENCE IN HOT MATTER Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley arxiv:1307.4092 (to appear in Nature Comm.) Thanks to David Huse for inspiring discussions Yasaman Bahri (Berkeley)
TOPOLOGY + LOCALIZATION: QUANTUM COHERENCE IN HOT MATTER Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley arxiv:1307.4092 (to appear in Nature Comm.) Thanks to David Huse for inspiring discussions Yasaman Bahri (Berkeley)
2D Materials with Strong Spin-orbit Coupling: Topological and Electronic Transport Properties
 2D Materials with Strong Spin-orbit Coupling: Topological and Electronic Transport Properties Artem Pulkin California Institute of Technology (Caltech), Pasadena, CA 91125, US Institute of Physics, Ecole
2D Materials with Strong Spin-orbit Coupling: Topological and Electronic Transport Properties Artem Pulkin California Institute of Technology (Caltech), Pasadena, CA 91125, US Institute of Physics, Ecole
