Compact star crust: relativistic versus Skyrme nuclear models
|
|
|
- Laurence Richards
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Problem How do relativistic models, used to build EoS of compact stars, behave at subsaturation densities? EoS at subsaturation densities/crust of compact stars: how do relativistic and Skyrme nuclear models compare? Can we constrain the temperature and isospin dependence of the nuclear EoS studying the subsaturation density behaviour of the EoS of ANM?
2 Compact star crust: relativistic versus Skyrme nuclear models Camille Ducoin, Philippe Chomaz, Alexandre Santos, Constança Providência, Universidade de Coimbra, Portugal The Complex Physics of Compact Stars Ladek Zdroj, February 28
3 Outline Energy functionals Skyrme interactions Relativistic Mean-Field Nuclear Models Equilibrium properties Thermodynamical instabilities Dynamical instabilities Formalism Instability Region Stellar Matter Summary Conclusions
4 Skyrme Functional The Skyrme energy-density functional homogeneous, spin-saturated matter, no Coulomb interaction H = K + H + H 3 + H eff K = 2 2m τ H = C ρ 2 + D ρ 2 3 H 3 = C 3 ρ σ+2 + D 3 ρ σ ρ 2 3 H eff = C eff ρτ + D eff ρ 3 τ 3
5 Skyrme Functional: parametrizations chosen SIII - fitted to double magic nuclei(beiner et al A238 76(1974)) SGII - with spin and pairing effects and constraints on K (Van Giai et al NPA371(1982)) Sly23a - improves the isospin description (Chabanat et al NPA627 (1997)) LNS -fitted to a Brueckner-Hartree-Fock calculation extended to spin and isospin polarized homogeneous matter (Cao et al PRC 76(26)) NRAPR- fitted to the APR EoS obtained from a variational microscopic calculation (Steiner et al PhysRep 411(25))
6 Skyrme Functional: parametrizations chosen Model B/A ρ K E sym M /M (MeV) (fm ) (MeV) (MeV) (MeV) SIII SGII SLy23a NRAPR LNS
7 RMF Lagrangian for npe matter Lagrangian density L NLWM = L i + L mesons + L γ + L e, i=p,n Nucleon contribution: Li = ψ i [γ µ D µ M ] ψ i, D µ = i µ g v V µ gρ 2 τ bµ ea µ 1+τ 3 2 M = M g s φ g δ τ δ. Meson contribution L mesons = L σ + L ω + L ρ + L δ + L non linear... Electromagnetic contribution: Lγ = 1 4 F µνf µν Electron contribution: Le = ψ e [γ µ (i µ + ea µ ) m e ]ψ e
8 Relativistic Nuclear Models Parametrizations tested: NL3: includes non-linear σ terms (Lalazissis et al PRC55(1997)) Density Dependent Hadron Models: TW, DDME2 (Typel & Wolter, NPA656, Niksic PRC66 (22)) The coupling meson-nucleon parameters are density dependent Thermodynamical consistency: requires the inclusion of a rearrangement contribution Σ R in the self-energies NLδ, DDHδ: include the δ meson (Greco et al PRC67 (23), Gaitanos et al NPA732 (24)) Isovector channel has a saturation mechanism similar to isoscalar channel The symmetry energy at larger densities increases faster
9 Relativistic Nuclear Models Model B/A ρ K E sym M /M (MeV) (fm ) (MeV) (MeV) (MeV) NL NLδ TW DD-ME DDHδ
10 Isoscalar channel Binding energy: E/A Pressure: P = ρ 2 (E/A)/ ρ Incompressibility: K = 9 P/ ρ
11 Isoscalar channel E/A (MeV) ) P (MeV fm SIII SGII Sly23a NRAPR LNS ρ (fm ) P (MeV fm ) E/A (MeV) NL3 TW DDME NL δ TW δ ρ (fm ) ρ (fm ) ρ (fm ) K (MeV) 2 1 K (MeV) ρ (fm ) ρ (fm )
12 Density of upper spinodal border ρ s ρ (fm ) (fm ) Sly23a SGII SIII RATP NR-APR NLS NL NLδ TW DDHδ ME
13 Isovector channel Symmetry energy: a s = F y 2, Slope of symmetry energy: L = 3ρ a s Symmetry incompressibility: K sym = 9ρ 2 a s, y = ρ 3 /ρ
14 Symmetry energy 5 SIII SGII Sly23a NRAPR 4 LNS (MeV) a s ρ (fm )
15 Symmetry energy (MeV) a s 5 SIII SGII Sly23a NRAPR 4 LNS NL3 ME2 3 TW 2 1 NL δ TWδ ρ (fm )
16 Slope of the symmetry energy L = 3ρ a s L (MeV) SIII SGII Sly23a NRAPR LNS NL3 ME2 TW TWδ NL δ ρ (fm )
17 Symmetry incompressibility K sym = 9ρ 2 a s, (MeV) SIII SGII Sly23a NRAPR LNS K sym 2 25 NL3 ME2 TW TW δ NL δ
18 Isovector chemical potential µ 3 = µ n µ p = 2 F/ ρ 3 parabolic approximation: µ par 3 = 4 a s ρ 3 /rho para 3 /µ 3 µ SIII SGII Sly23a LNS NRAPR NL3 TW DDME2 ρ =.5 fm para 3 /µ 3 µ ρ =.3 fm ρ /ρ ρ /ρ 3
19 Thermodynamical Stability Conditions Stability condition: the free energy curvature matrix C is positive. ( 2 ) F C ij = F ij = ρ i ρ j The free energy curvature matrix: C = ( µn ρ n µ p ρ n µ n ρ p µ p ρ p Stability conditions for asymmetric nuclear matter (ANM) : T ) Tr(C) >, Det(C) >.,
20 Thermodynamical instability: RMF ρ (fm ) ρ (fm ) ρ (fm ) NL3 TM1 TW NL δ DDHρδ δ T= MeV T=1 MeV T=14 MeV Largest differences: at finite T and large δ Avancini et al PRC7 (24)
21 Thermodynamical Spinodal (ρ p, ρ n ) Curvature at ρ s : 2 det C(ρ s,) ρ 2 3 = 4 ρ 4 [ a s (ρ 2 a s + 2ρa s) 2(ρa s) 2 ] SIII SGII Sly23a NRAPR LNS T=.6 ρ p ρ (fm ) n
22 Thermodynamical Spinodal (ρ p, ρ n ) SIII SGII Sly23a NRAPR LNS NL3 TW DD ME2 T= p ρ ρ n (fm )
23 Thermodynamical Spinodal (ρ p, ρ n ): meson δ.12 ) (fm p ρ NL3 TW DD ME2 NL TW δ δ ρ (fm ) n
24 Thermodynamical instability direction the crossing of the spinodal with the axis of symmetric matter: ρ s corresponds to the zero of the incompressibility function K(ρ) Skyrme interaction predict larger instability regions. At low densities all spinodals reach high asymmetry and cannot be distinguished.
25 Thermodynamical Spinodal (µ 3, ρ) (MeV) 1 5 SIII SGII Sly23a NRAPR LNS (MeV) µ NL3 TW DD ME2 TWδ NLδ µ ρ (fm ) ρ (fm ) (ρ,µ 3 ) spinodal: all models are distinct at all densities,
26 Spinodal Surface The eigenvalues of the stability matrix are given by λ ± = 1 ( ) Tr(F) ± Tr(F) 2 2 4Det(F), with eigenvectors δρ ± δρ ± i δρ ± j = λ ± F jj F ji, i, j = p, n The largest eigenvalue λ + is always positive The smallest λ becomes negative at subsaturation densities
27 Distillation Effect T = MeV, y p =.2, ρ p /ρ n = δρ p /δρ n.7 NL3 TM1.6 NL δ TW DDH δ ρ (fm ) Avancini et al PRC74 (26)
28 Distillation Effect T = MeV, y p =.2, δρ p /δρ n.8.7 NL3 TW Λ=.25 no rearr Avancini et al PRC74 (26) ρ (fm )
29 Thermodynamical instability direction /δρ 3 δρ Distillation effect if δρ 3 /δρ <.4 for Z/A= Z/A=.3, T= SIII SGII Sly23a LNS NRAPR ρ (fm ) NL δ TW δ DDME2 NL3 TW Avancini et al PRC74 (26)
30 Thermodynamical instability direction Common trend: reduction of the distillation effect with density. DD-ME2 follows quite closely the Skyrme parametrization Sly23a with the smallest distillation effect TW follows the general trend of all the other models. NL3 and NLδ: distillation effect with density increases with density Multifragmentation heavy-ion collisions: isospin content of large fragments sensitive to δρ 3 /δρ
31 Dynamical instabilities The Relativistic Vlasov Equation The time evolution of f i is described by the Vlasov equation df i dt =, i = p, n, e f i t + {f i, h i } =, i = p, n, e
32 Small perturbation of the system Equilibrium state characterized by: P Fn, P Fp, P Fe Charge neutrality: P Fe = P Fp Perturbed fields: F i = F i + δf i, Perturbed distribution function: f = f + δf, δf i = {S i, f i } Generating function: S(r, p, t) = diag(s p, S n, S e ),
33 Linearized Equations of Motion The linearized relativistic Vlasov equation ds i dt + {S i, h i } = δh i Longitudinal fluctuations: ( Si δf j δρ i δh i ) = ( Sω,i (x) δf ω,j δρ ω,i δh ω,i ) e i(q r ωt) x = cos(p q), i = e, p, n, j = σ,ω,ρ,γ
34 Linearized Equations of Motion One-body hamiltonian variation Electrons [ δh e = e δa p δa ], ǫ e nucleons: relativistic models δh i = g s δφ M ǫ + δv i p δv i ǫ, i = p, n nucleons: Skyrme interactions δh i = [ ] U (1) ij + xu (2) ij δρ j j
35 Finite size instabilities: npe matter The instability growth ratio and direction of the unstable mode 1 1/τ ((fm/c) SIII SGII Sly23a LNS NRAPR NL3 TW ME2 ρ=.5 fm, Z/A=.3, T= Vlasov /δρ 3 δρ NL3 TW DD ME q (MeV/c) q (MeV/c)
36 Instability growth rates/ Direction of instability Sly23a: the smallest growth rates of the Skyrme interactions Relativistic models: smaller growth rates, and q ranges Low q: all models similar behavior defined by electromagnetic interaction anti-distillation is model dependent ( δρ3 /δρ>.4) no anti-distillation: NL3 and DDME2 Large q behavior: defined by the finite range of the nuclear force Distillation behavior: NL3 shows the strongest distillation TW and DDME2 behave like Skyrme interactions
37 Stellar Matter β-equilibrium matter: neutrino free DU SIII SGII Sly23a NRAPR LNS Y i (p, µ ) NL3 TW DDME2 DU DU p p, µ= Y i p µ p, µ= ρ (fm ) ρ (fm )
38 β-equilibrium matter: neutrino trapped Y i Y l =.4 SIII SGII Sly23a LNS NRAPR ρ (fm ) Y i (ν e e p) p ν NL ρ (fm ) TW, DDME2
39 Barionic density at µ onset model ρ (fm ) SIII.19 SGII.137 Sly23a.112 LNS.118 NRAPR.111 NL3.112 TW.115 DDME2.114 For SIII the muons disappear at ρ > fm
40 β-equilibrium npeν e matter/ Instability region β-equilibrium EoS with/without neutrinos and the dynamical spinodal surface por npe matter T=1 MeV (MeV) e +µ p µ t SIII SGII Sly23a LNS NRAPR NL µ t (MeV) n β-equilibrium EoS without neutrinos: no crossing.
41 Edge of outer/inner crust Crossing of the β-equilibrium EoS with/without neutrinos with the dynamical spinodal surface por npe matter = ν ρ Y l =.4 SIII SGII Sly223a LNS NRAPR NL3 cros b ρ T (MeV)
42 Eos/dynamical spinodal crossing The behavior of different models follows the trend of the thermodynamical spinodals: at the larger densities and very asymmetric matter the Sl23a spinodal extends to larger asymmetries and the NL3 to smaller ones. 1 5 (MeV) 3 µ ρ (fm )
43 Edge of inner crust: T = MeV Densities at the inner edge of the crust (fm ) from spinodal of pne matter for k = 8 MeV/c Y ν = Y L =.4 model ρ cross,sup ρ cross,sup SIII SGII SLy23a LNS NRAPR NL TW DD-ME
44 Size of clusters Half-wave-length of the most unstable mode inside the instability region, along a path of β-equilibrium ) λ /2 (fm ρ =, T= ν NL3 TW ME2 SIII SGII Sly23a LNS NRAPR ) λ /2 (fm Y l =.4, T=1 MeV NL3 SIII SGII Sly23a LNS NRAPR 4 2 Vlasov 4 2 Vlasov ρ (fm b ) ρ (fm b )
45 Most Unstable Modes Neutrino free: relativistic models predict larger clusters > 6 fm, Skyrme forces clusters with 4 fm may appear high density border: all models predict similar sizes. Neutrino trapped matter at T=1 MeV: The size of the clusters does not change much with density Mean value depends on the model, ranging from 5 fm for SIII to 8 fm for NL3 and SLy23a
46 Conclusions RMF/DDH versus Skyrme Equilibrium properties: larger differences in the isovector channel RMF/DDH: smaller thermodynamical spinodal regions RMF: distillation effect increases with density Skyrme/DDH: distillation effect decreases with density ρ >.1fm RMF/DDH: larger cluster in the crust Dynamic properties differ: RMF/DDH larger clusters, smaller growth rates, instabilities extend to smaller q. What do other approachs starting from NN interaction, including correlations, etc.. predict for the quantities discussed? Could transport calculations for isospin diffusion currents, isospin content of fragments, etc.. distinguish models?
Symmetry Energy within the Brueckner-Hartree-Fock approximation
 Symmetry Energy within the Brueckner-Hartree-Fock approximation Isaac Vidaña CFC, University of Coimbra International Symposium on Nuclear Symmetry Energy Smith College, Northampton ( Massachusetts) June
Symmetry Energy within the Brueckner-Hartree-Fock approximation Isaac Vidaña CFC, University of Coimbra International Symposium on Nuclear Symmetry Energy Smith College, Northampton ( Massachusetts) June
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 17 Dec 2008
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 17 Dec 2008 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 17 Dec 2008](/thumbs/93/113195425.jpg) The pasta phase within density dependent hadronic models S. S. Avancini, 1 L. Brito, 2 J.R.Marinelli, 1 D.P.Menezes, 1 M.M.W. de Moraes, 1 C. Providência, 2 and A.M.Santos 2 1 Depto de Física - CFM - Universidade
The pasta phase within density dependent hadronic models S. S. Avancini, 1 L. Brito, 2 J.R.Marinelli, 1 D.P.Menezes, 1 M.M.W. de Moraes, 1 C. Providência, 2 and A.M.Santos 2 1 Depto de Física - CFM - Universidade
The crust-core transition and the stellar matter equation of state
 The crust-core transition and the stellar matter equation of state Helena Pais CFisUC, University of Coimbra, Portugal Nuclear Physics, Compact Stars, and Compact Star Mergers YITP, Kyoto, Japan, October
The crust-core transition and the stellar matter equation of state Helena Pais CFisUC, University of Coimbra, Portugal Nuclear Physics, Compact Stars, and Compact Star Mergers YITP, Kyoto, Japan, October
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 30 Mar 2015
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 30 Mar 2015 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 30 Mar 2015](/thumbs/83/88958643.jpg) Compact Stars in the QCD Phase Diagram IV (CSQCD IV) September 26-30, 2014, Prerow, Germany http://www.ift.uni.wroc.pl/~csqcdiv Core-collapse supernova matter: light clusters, pasta phase and phase transitions
Compact Stars in the QCD Phase Diagram IV (CSQCD IV) September 26-30, 2014, Prerow, Germany http://www.ift.uni.wroc.pl/~csqcdiv Core-collapse supernova matter: light clusters, pasta phase and phase transitions
arxiv:nucl-th/ v2 12 Jan 2005
 Neutron stars with isovector scalar correlations B. Liu 1,2, H. Guo 1,3, M. Di Toro 4, V. Greco 4,5 1 Center of Theoretical Nuclear Physics, National Laboratory of Heavy Ion Accelerator, Lanzhou 73, China
Neutron stars with isovector scalar correlations B. Liu 1,2, H. Guo 1,3, M. Di Toro 4, V. Greco 4,5 1 Center of Theoretical Nuclear Physics, National Laboratory of Heavy Ion Accelerator, Lanzhou 73, China
Nuclear symmetry energy and Neutron star cooling
 Nuclear symmetry energy and Neutron star cooling Yeunhwan Lim 1 1 Daegu University. July 26, 2013 In Collaboration with J.M. Lattimer (SBU), C.H. Hyun (Daegu), C-H Lee (PNU), and T-S Park (SKKU) NuSYM13
Nuclear symmetry energy and Neutron star cooling Yeunhwan Lim 1 1 Daegu University. July 26, 2013 In Collaboration with J.M. Lattimer (SBU), C.H. Hyun (Daegu), C-H Lee (PNU), and T-S Park (SKKU) NuSYM13
Nuclear symmetry energy deduced from dipole excitations: comparison with other constraints
 Nuclear symmetry energy deduced from dipole excitations: a comparison with other constraints G. Colò June 15th, 2010 This work is part of a longer-term research plan. The goal is: understanding which are
Nuclear symmetry energy deduced from dipole excitations: a comparison with other constraints G. Colò June 15th, 2010 This work is part of a longer-term research plan. The goal is: understanding which are
Clusters in Dense Matter and the Equation of State
 Clusters in Dense Matter and the Equation of State Excellence Cluster Universe, Technische Universität München GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung, Darmstadt in collaboration with Gerd Röpke
Clusters in Dense Matter and the Equation of State Excellence Cluster Universe, Technische Universität München GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung, Darmstadt in collaboration with Gerd Röpke
Toward a unified description of equilibrium and dynamics of neutron star matter
 Toward a unified description of equilibrium and dynamics of neutron star matter Omar Benhar INFN and Department of Physics Sapienza Università di Roma I-00185 Roma, Italy Based on work done in collaboration
Toward a unified description of equilibrium and dynamics of neutron star matter Omar Benhar INFN and Department of Physics Sapienza Università di Roma I-00185 Roma, Italy Based on work done in collaboration
The Vlasov formalism for extended relativistic mean field models: the crust-core transition and the stellar matter equation of state
 The Vlasov formalism for extended relativistic mean field models: the crust-core transition and the stellar matter equation of state Helena Pais and Constança Providência CFisUC, Department of Physics,
The Vlasov formalism for extended relativistic mean field models: the crust-core transition and the stellar matter equation of state Helena Pais and Constança Providência CFisUC, Department of Physics,
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 15 Dec 2004
 Reaction Dynamics with Exotic Nuclei V. Baran a,1, M.Colonna a, V.Greco b, M.Di Toro a,, arxiv:nucl-th/0412060v1 15 Dec 2004 a Laboratori Nazionali del Sud INFN, Via S. Sofia 62, I-95123 Catania, Italy
Reaction Dynamics with Exotic Nuclei V. Baran a,1, M.Colonna a, V.Greco b, M.Di Toro a,, arxiv:nucl-th/0412060v1 15 Dec 2004 a Laboratori Nazionali del Sud INFN, Via S. Sofia 62, I-95123 Catania, Italy
The role of stangeness in hadronic matter (in)stability: from hypernuclei to compact stars
 The role of stangeness in hadronic matter (in)stability: from hypernuclei to compact stars James R. Torres (former Ph.D. student), Francesca Gulminelli and DPM Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina (Brazil)
The role of stangeness in hadronic matter (in)stability: from hypernuclei to compact stars James R. Torres (former Ph.D. student), Francesca Gulminelli and DPM Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina (Brazil)
Nuclear Matter Incompressibility and Giant Monopole Resonances
 Nuclear Matter Incompressibility and Giant Monopole Resonances C.A. Bertulani Department of Physics and Astronomy Texas A&M University-Commerce Collaborator: Paolo Avogadro 27th Texas Symposium on Relativistic
Nuclear Matter Incompressibility and Giant Monopole Resonances C.A. Bertulani Department of Physics and Astronomy Texas A&M University-Commerce Collaborator: Paolo Avogadro 27th Texas Symposium on Relativistic
Isospin-dependent clusterization of Neutron-Star Matter
 Isospin-dependent clusterization of Neutron-Star Matter C. Ducoin, P. Chomaz, F. Gulminelli To cite this version: C. Ducoin, P. Chomaz, F. Gulminelli. Isospin-dependent clusterization of Neutron-Star Matter.
Isospin-dependent clusterization of Neutron-Star Matter C. Ducoin, P. Chomaz, F. Gulminelli To cite this version: C. Ducoin, P. Chomaz, F. Gulminelli. Isospin-dependent clusterization of Neutron-Star Matter.
Symmetry energy within the BHF approach
 Symmetry energy within the BHF approach Isaac Vidaña 1, Constança Providência 1, A. Polls 3 and Arnau Rios 3 1 Centro de Física Computacional. Deparment of Physics, University of Coimbra, PT-34-516 Coimbra
Symmetry energy within the BHF approach Isaac Vidaña 1, Constança Providência 1, A. Polls 3 and Arnau Rios 3 1 Centro de Física Computacional. Deparment of Physics, University of Coimbra, PT-34-516 Coimbra
Parity-Violating Asymmetry for 208 Pb
 Parity-Violating Asymmetry for 208 Pb Matteo Vorabbi Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia INFN - Sezione di Pavia Rome - 2015 January 15 Matteo Vorabbi (Università di Pavia) Parity-Violating Asymmetry
Parity-Violating Asymmetry for 208 Pb Matteo Vorabbi Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia INFN - Sezione di Pavia Rome - 2015 January 15 Matteo Vorabbi (Università di Pavia) Parity-Violating Asymmetry
Density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy estimated from neutron skin thickness in finite nuclei
 Density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy estimated from neutron skin thickness in finite nuclei X. Viñas a M. Centelles a M. Warda a,b X. Roca-Maza a,c a Departament d Estructura i Constituents
Density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy estimated from neutron skin thickness in finite nuclei X. Viñas a M. Centelles a M. Warda a,b X. Roca-Maza a,c a Departament d Estructura i Constituents
AMD. Skyrme ( ) 2009/03/ / 22
 2009 3 25 26 AMD Skyrme ( ) 2009/03/25 26 1 / 22 (?) ( ) 2009/03/25 26 2 / 22 Nuclear Matter in Nuclear Collisions and Neutron Stars 0 60 E sym [MeV] 40 20 0 0 NL3 ChPT DBHF DD ρδ DD TW var AV18+ δ V+3
2009 3 25 26 AMD Skyrme ( ) 2009/03/25 26 1 / 22 (?) ( ) 2009/03/25 26 2 / 22 Nuclear Matter in Nuclear Collisions and Neutron Stars 0 60 E sym [MeV] 40 20 0 0 NL3 ChPT DBHF DD ρδ DD TW var AV18+ δ V+3
Stochastic Mean Field (SMF) description TRANSPORT Maria Colonna INFN - Laboratori Nazionali del Sud (Catania)
 Stochastic Mean Field (SMF) description TRANSPORT 2017 March 27-30, 2017 FRIB-MSU, East Lansing, Michigan, USA Maria Colonna INFN - Laboratori Nazionali del Sud (Catania) Dynamics of many-body system I
Stochastic Mean Field (SMF) description TRANSPORT 2017 March 27-30, 2017 FRIB-MSU, East Lansing, Michigan, USA Maria Colonna INFN - Laboratori Nazionali del Sud (Catania) Dynamics of many-body system I
Clusters in Nuclear Matter
 Clusters in Nuclear Matter Excellence Cluster Universe, Technische Universität München GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung, Darmstadt in collaboration with Gerd Röpke (Universität Rostock) Thomas
Clusters in Nuclear Matter Excellence Cluster Universe, Technische Universität München GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung, Darmstadt in collaboration with Gerd Röpke (Universität Rostock) Thomas
Density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy estimated from neutron skin thickness in finite nuclei
 Density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy estimated from neutron skin thickness in finite nuclei X. Roca-Maza a,c X. Viñas a M. Centelles a M. Warda a,b a Departament d Estructura i Constituents
Density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy estimated from neutron skin thickness in finite nuclei X. Roca-Maza a,c X. Viñas a M. Centelles a M. Warda a,b a Departament d Estructura i Constituents
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 24 Apr 2001
 Neutron Star Structure and the Neutron Radius of 208 Pb C. J. Horowitz Nuclear Theory Center and Dept. of Physics, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN 47405 J. Piekarewicz Department of Physics Florida
Neutron Star Structure and the Neutron Radius of 208 Pb C. J. Horowitz Nuclear Theory Center and Dept. of Physics, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN 47405 J. Piekarewicz Department of Physics Florida
Phase transitions in dilute stellar matter. Francesca Gulminelli & Adriana Raduta
 Phase transitions in dilute stellar matter Francesca Gulminelli & Adriana Raduta LPC Caen, France IFIN Bucharest Supernova remnant and neutron star in Puppis A (ROSAT x-ray) χ 1/2 Τ 10 12 Κ Motivation:
Phase transitions in dilute stellar matter Francesca Gulminelli & Adriana Raduta LPC Caen, France IFIN Bucharest Supernova remnant and neutron star in Puppis A (ROSAT x-ray) χ 1/2 Τ 10 12 Κ Motivation:
Neutron Rich Nuclei in Heaven and Earth
 First Prev Next Last Go Back Neutron Rich Nuclei in Heaven and Earth Jorge Piekarewicz with Bonnie Todd-Rutel Tallahassee, Florida, USA Page 1 of 15 Cassiopeia A: Chandra 08/23/04 Workshop on Nuclear Incompressibility
First Prev Next Last Go Back Neutron Rich Nuclei in Heaven and Earth Jorge Piekarewicz with Bonnie Todd-Rutel Tallahassee, Florida, USA Page 1 of 15 Cassiopeia A: Chandra 08/23/04 Workshop on Nuclear Incompressibility
Symmetry energy and the neutron star core-crust transition with Gogny forces
 Symmetry energy and the neutron star core-crust transition with Gogny forces Claudia Gonzalez-Boquera, 1 M. Centelles, 1 X. Viñas 1 and A. Rios 2 1 Departament de Física Quàntica i Astrofísica and Institut
Symmetry energy and the neutron star core-crust transition with Gogny forces Claudia Gonzalez-Boquera, 1 M. Centelles, 1 X. Viñas 1 and A. Rios 2 1 Departament de Física Quàntica i Astrofísica and Institut
Nucelon self-energy in nuclear matter and how to probe ot with RIBs
 Nucelon self-energy in nuclear matter and how to probe ot with RIBs Christian Fuchs University of Tübingen Germany Christian Fuchs - Uni Tübingen p.1/?? Outline relativistic dynamics E/A [MeV] 6 5 4 3
Nucelon self-energy in nuclear matter and how to probe ot with RIBs Christian Fuchs University of Tübingen Germany Christian Fuchs - Uni Tübingen p.1/?? Outline relativistic dynamics E/A [MeV] 6 5 4 3
Isospin asymmetry in stable and exotic nuclei
 Isospin asymmetry in stable and exotic nuclei Xavier Roca Maza 6 May 2010 Advisors: Xavier Viñas i Gausí and Mario Centelles i Aixalà Motivation: Nuclear Chart Relative Neutron excess I (N Z )/(N + Z )
Isospin asymmetry in stable and exotic nuclei Xavier Roca Maza 6 May 2010 Advisors: Xavier Viñas i Gausí and Mario Centelles i Aixalà Motivation: Nuclear Chart Relative Neutron excess I (N Z )/(N + Z )
Liquid-Gas Phase Transition of Supernova Matter and Its Relation to Nucleosynthesis
 Liquid-Gas Phase Transition of Supernova Matter and Its Relation to Nucleosynthesis C. Ishizuka a, A. Ohnishi a and K. Sumiyoshi b a Division of Physics, Graduate School of Science, Hokkaido University,
Liquid-Gas Phase Transition of Supernova Matter and Its Relation to Nucleosynthesis C. Ishizuka a, A. Ohnishi a and K. Sumiyoshi b a Division of Physics, Graduate School of Science, Hokkaido University,
in covariant density functional theory.
 Nuclear Particle ISTANBUL-06 Density vibrational Functional coupling Theory for Excited States. in covariant density functional theory. Beijing, Sept. 8, 2011 Beijing, May 9, 2011 Peter Peter Ring Ring
Nuclear Particle ISTANBUL-06 Density vibrational Functional coupling Theory for Excited States. in covariant density functional theory. Beijing, Sept. 8, 2011 Beijing, May 9, 2011 Peter Peter Ring Ring
Equations of State of Relativistic Mean-Field Models with Different Parametrisations of Density Dependent Couplings
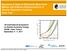 Equations of State of Relativistic Mean-Field Models with Different Parametrisations of Density Dependent Couplings Stefan Typel 100 7th International Symposium on Nuclear Symmetry Energy GANIL, Caen,
Equations of State of Relativistic Mean-Field Models with Different Parametrisations of Density Dependent Couplings Stefan Typel 100 7th International Symposium on Nuclear Symmetry Energy GANIL, Caen,
Nuclear & Particle Physics of Compact Stars
 Nuclear & Particle Physics of Compact Stars Madappa Prakash Ohio University, Athens, OH National Nuclear Physics Summer School July 24-28, 2006, Bloomington, Indiana 1/30 How Neutron Stars are Formed Lattimer
Nuclear & Particle Physics of Compact Stars Madappa Prakash Ohio University, Athens, OH National Nuclear Physics Summer School July 24-28, 2006, Bloomington, Indiana 1/30 How Neutron Stars are Formed Lattimer
Relativistic point-coupling models for finite nuclei
 Relativistic point-coupling models for finite nuclei T. J. Buervenich 1, D. G. Madland 1, J. A. Maruhn 2, and P.-G. Reinhard 3 1 Los Alamos National Laboratory 2 University of Frankfurt 3 University of
Relativistic point-coupling models for finite nuclei T. J. Buervenich 1, D. G. Madland 1, J. A. Maruhn 2, and P.-G. Reinhard 3 1 Los Alamos National Laboratory 2 University of Frankfurt 3 University of
Equation of state for supernovae and neutron stars
 Equation of state for supernovae and neutron stars H. Shen Nankai University, Tianjin, China 申虹南開大学天津中国 In collaboration with H. Toki RCNP, Osaka University, Japan K. Sumiyoshi Numazu College of Technology,
Equation of state for supernovae and neutron stars H. Shen Nankai University, Tianjin, China 申虹南開大学天津中国 In collaboration with H. Toki RCNP, Osaka University, Japan K. Sumiyoshi Numazu College of Technology,
Some new developments in relativistic point-coupling models
 Some new developments in relativistic point-coupling models T. J. Buervenich 1, D. G. Madland 1, J. A. Maruhn 2, and P.-G. Reinhard 3 1 Los Alamos National Laboratory 2 University of Frankfurt 3 University
Some new developments in relativistic point-coupling models T. J. Buervenich 1, D. G. Madland 1, J. A. Maruhn 2, and P.-G. Reinhard 3 1 Los Alamos National Laboratory 2 University of Frankfurt 3 University
Nuclear equation of state with realistic nuclear forces
 Nuclear equation of state with realistic nuclear forces Hajime Togashi (RIKEN) Collaborators: M. Takano, K. Nakazato, Y. Takehara, S. Yamamuro, K. Sumiyoshi, H. Suzuki, E. Hiyama 1:Introduction Outline
Nuclear equation of state with realistic nuclear forces Hajime Togashi (RIKEN) Collaborators: M. Takano, K. Nakazato, Y. Takehara, S. Yamamuro, K. Sumiyoshi, H. Suzuki, E. Hiyama 1:Introduction Outline
Dipole Polarizability and the neutron skin thickness
 Dipole Polarizability and the neutron skin thickness Xavier Roca-Maza Università degli Studi di Milano and INFN MITP Scientific Program Neutron Skins of Nuclei May 17th-27th 2016. 1 Table of contents:
Dipole Polarizability and the neutron skin thickness Xavier Roca-Maza Università degli Studi di Milano and INFN MITP Scientific Program Neutron Skins of Nuclei May 17th-27th 2016. 1 Table of contents:
Localized form of Fock terms in nuclear covariant density functional theory
 Computational Advances in Nuclear and Hadron Physics September 21 October 3, 215, YITP, Kyoto, Japan Localized form of Fock terms in nuclear covariant density functional theory Haozhao Liang ùíî RIKEN
Computational Advances in Nuclear and Hadron Physics September 21 October 3, 215, YITP, Kyoto, Japan Localized form of Fock terms in nuclear covariant density functional theory Haozhao Liang ùíî RIKEN
Gianluca Colò. Density Functional Theory for isovector observables: from nuclear excitations to neutron stars. Università degli Studi and INFN, MIlano
 Density Functional Theory for isovector observables: from nuclear excitations to neutron stars Gianluca Colò NSMAT2016, Tohoku University, Sendai 1 Outline Energy density functionals (EDFs): a short introduction
Density Functional Theory for isovector observables: from nuclear excitations to neutron stars Gianluca Colò NSMAT2016, Tohoku University, Sendai 1 Outline Energy density functionals (EDFs): a short introduction
Self-consistent study of spin-isospin resonances and its application in astrophysics
 Tensor Interaction in Nuclear and Hadron Physics November 1 3, Beihang University, Beijing, China Self-consistent study of spin-isospin resonances and its application in astrophysics Haozhao Liang School
Tensor Interaction in Nuclear and Hadron Physics November 1 3, Beihang University, Beijing, China Self-consistent study of spin-isospin resonances and its application in astrophysics Haozhao Liang School
Heavy-ion reactions and the Nuclear Equation of State
 Heavy-ion reactions and the Nuclear Equation of State S. J. Yennello Texas A&M University D. Shetty, G. Souliotis, S. Soisson, Chen, M. Veselsky, A. Keksis, E. Bell, M. Jandel Studying Nuclear Equation
Heavy-ion reactions and the Nuclear Equation of State S. J. Yennello Texas A&M University D. Shetty, G. Souliotis, S. Soisson, Chen, M. Veselsky, A. Keksis, E. Bell, M. Jandel Studying Nuclear Equation
Fine structure of nuclear spin-dipole excitations in covariant density functional theory
 1 o3iø(œ April 12 16, 2012, Huzhou, China Fine structure of nuclear spin-dipole excitations in covariant density functional theory ùíî (Haozhao Liang) ŒÆÔnÆ 2012 c 4 13 F ÜŠöµ Š # Ç!Nguyen Van Giai Ç!ë+
1 o3iø(œ April 12 16, 2012, Huzhou, China Fine structure of nuclear spin-dipole excitations in covariant density functional theory ùíî (Haozhao Liang) ŒÆÔnÆ 2012 c 4 13 F ÜŠöµ Š # Ç!Nguyen Van Giai Ç!ë+
Modeling the EOS. Christian Fuchs 1 & Hermann Wolter 2. 1 University of Tübingen/Germany. 2 University of München/Germany
 Modeling the EOS Christian Fuchs 1 & Hermann Wolter 2 1 University of Tübingen/Germany 2 University of München/Germany Christian Fuchs - Uni Tübingen p.1/20 Outline Christian Fuchs - Uni Tübingen p.2/20
Modeling the EOS Christian Fuchs 1 & Hermann Wolter 2 1 University of Tübingen/Germany 2 University of München/Germany Christian Fuchs - Uni Tübingen p.1/20 Outline Christian Fuchs - Uni Tübingen p.2/20
Microscopic calculation of the neutrino mean free path inside hot neutron matter Isaac Vidaña CFisUC, University of Coimbra
 Microscopic calculation of the neutrino mean free path inside hot neutron matter Isaac Vidaña CFisUC, University of Coimbra Landau Fermi liquid theory in nuclear & many-body theory May 22 nd 26 th 2017,
Microscopic calculation of the neutrino mean free path inside hot neutron matter Isaac Vidaña CFisUC, University of Coimbra Landau Fermi liquid theory in nuclear & many-body theory May 22 nd 26 th 2017,
Peter Ring. ISTANBUL-06 New developments in covariant density functional theory. Saariselkä April 20, 2009
 ISTANBUL-06 New developments in covariant density functional theory Saariselkä April 20, 2009 Peter Ring Technical University Munich Universidad Autónoma de Madrid 1 Content Covariant density functionals
ISTANBUL-06 New developments in covariant density functional theory Saariselkä April 20, 2009 Peter Ring Technical University Munich Universidad Autónoma de Madrid 1 Content Covariant density functionals
Nuclear equation of state for supernovae and neutron stars
 Nuclear equation of state for supernovae and neutron stars H. Shen 申虹 In collaboration with Nankai University, Tianjin, China 南開大学 天津 中国 H. Toki RCNP, Osaka University, Japan K. Sumiyoshi Numazu College
Nuclear equation of state for supernovae and neutron stars H. Shen 申虹 In collaboration with Nankai University, Tianjin, China 南開大学 天津 中国 H. Toki RCNP, Osaka University, Japan K. Sumiyoshi Numazu College
Effects of U boson on the inner edge of neutron star crusts
 Effects of U boson on the inner edge of neutron star crusts Reporter : Hao Zheng ( 郑皓 ) ( INPAC & Department of Physics, Shanghai Jiao Tong University) Supervisor : Lie-Wen Chen Outline Neutron Star introduction
Effects of U boson on the inner edge of neutron star crusts Reporter : Hao Zheng ( 郑皓 ) ( INPAC & Department of Physics, Shanghai Jiao Tong University) Supervisor : Lie-Wen Chen Outline Neutron Star introduction
Nuclear structure Anatoli Afanasjev Mississippi State University
 Nuclear structure Anatoli Afanasjev Mississippi State University 1. Nuclear theory selection of starting point 2. What can be done exactly (ab-initio calculations) and why we cannot do that systematically?
Nuclear structure Anatoli Afanasjev Mississippi State University 1. Nuclear theory selection of starting point 2. What can be done exactly (ab-initio calculations) and why we cannot do that systematically?
An empirical Equation of State for nuclear physics and astrophysics
 An empirical Equation of State for nuclear physics and astrophysics Collaborators: Debarati Chatterjee LPC/ENSICAEN, caen, france Francesca Gulminelli Jerome Margueron Adriana Raduta Sofija Antic Debora
An empirical Equation of State for nuclear physics and astrophysics Collaborators: Debarati Chatterjee LPC/ENSICAEN, caen, france Francesca Gulminelli Jerome Margueron Adriana Raduta Sofija Antic Debora
Nuclear Structure for the Crust of Neutron Stars
 Nuclear Structure for the Crust of Neutron Stars Peter Gögelein with Prof. H. Müther Institut for Theoretical Physics University of Tübingen, Germany September 11th, 2007 Outline Neutron Stars Pasta in
Nuclear Structure for the Crust of Neutron Stars Peter Gögelein with Prof. H. Müther Institut for Theoretical Physics University of Tübingen, Germany September 11th, 2007 Outline Neutron Stars Pasta in
Equation-of-State of Nuclear Matter with Light Clusters
 Equation-of-State of Nuclear Matter with Light Clusters rmann Wolter Faculty of Physics, University of Munich, D-878 Garching, Germany E-mail: hermann.wolter@lmu.de The nuclear equation-of-state (EoS)
Equation-of-State of Nuclear Matter with Light Clusters rmann Wolter Faculty of Physics, University of Munich, D-878 Garching, Germany E-mail: hermann.wolter@lmu.de The nuclear equation-of-state (EoS)
Collective excitations in nuclei away from the valley of stability
 Collective excitations in nuclei away from the valley of stability A. Horvat 1, N. Paar 16.7.14, CSSP 14, Sinaia, Romania 1 Institut für Kernphysik, TU Darmstadt, Germany (for the R3B-LAND collaboration)
Collective excitations in nuclei away from the valley of stability A. Horvat 1, N. Paar 16.7.14, CSSP 14, Sinaia, Romania 1 Institut für Kernphysik, TU Darmstadt, Germany (for the R3B-LAND collaboration)
The Nuclear Equation of State
 The Nuclear Equation of State Theoretical models for nuclear structure studies Xavier Roca-Maza Università degli Studi di Milano e INFN, sezione di Milano Terzo Incontro Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare LNF,
The Nuclear Equation of State Theoretical models for nuclear structure studies Xavier Roca-Maza Università degli Studi di Milano e INFN, sezione di Milano Terzo Incontro Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare LNF,
Symmetry energy, masses and T=0 np-pairing
 Symmetry energy, masses and T=0 np-pairing Can we measure the T=0 pair gap? Do the moments of inertia depend on T=0 pairing? Do masses evolve like T(T+1) or T^2 (N-Z)^2? Origin of the linear term in mean
Symmetry energy, masses and T=0 np-pairing Can we measure the T=0 pair gap? Do the moments of inertia depend on T=0 pairing? Do masses evolve like T(T+1) or T^2 (N-Z)^2? Origin of the linear term in mean
Nuclear phase transition and thermodynamic instabilities in dense nuclear matter
 Nuclear phase transition and thermodynamic instabilities in dense nuclear matter A. Lavagno a 1 Department of Applied Science and Technology, Politecnico di Torino, I-10129 Torino, Italy 2 Istituto Nazionale
Nuclear phase transition and thermodynamic instabilities in dense nuclear matter A. Lavagno a 1 Department of Applied Science and Technology, Politecnico di Torino, I-10129 Torino, Italy 2 Istituto Nazionale
Pygmy dipole resonances in stable and unstable nuclei
 Pygmy dipole resonances in stable and unstable nuclei Xavier Roca-Maza INFN, Sezione di Milano, Via Celoria 16, I-2133, Milano (Italy) Collaborators: Giacomo Pozzi, Marco Brenna, Kazhuito Mizuyama and
Pygmy dipole resonances in stable and unstable nuclei Xavier Roca-Maza INFN, Sezione di Milano, Via Celoria 16, I-2133, Milano (Italy) Collaborators: Giacomo Pozzi, Marco Brenna, Kazhuito Mizuyama and
Density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy estimated from neutron skin thickness in finite nuclei
 Density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy estimated from neutron skin thickness in finite nuclei X. Roca-Maza a,b X. Viñas b M. Centelles b M. Warda b,c a INFN sezione di Milano. Via Celoria 16,
Density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy estimated from neutron skin thickness in finite nuclei X. Roca-Maza a,b X. Viñas b M. Centelles b M. Warda b,c a INFN sezione di Milano. Via Celoria 16,
Pure Neutron Matter Constraints and Nuclear Symmetry Energy
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Pure Neutron Matter Constraints and Nuclear Symmetry Energy To cite this article: F J Fattoyev et al 2013 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 420 012108 View the article online for
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Pure Neutron Matter Constraints and Nuclear Symmetry Energy To cite this article: F J Fattoyev et al 2013 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 420 012108 View the article online for
T. GAITANOS, H.H. WOLTER Sektion Physik der Universität München Am Coulombwall 1, D Garching, Germany
 NON-EQUILIBRIUM AND COLLECTIVE FLOW EFFECTS IN RELATIVISTIC HEAVY ION COLLISIONS T. GAITANOS, H.H. WOLTER Sektion Physik der Universität München Am Coulombwall 1, D-85748 Garching, Germany AND C. FUCHS
NON-EQUILIBRIUM AND COLLECTIVE FLOW EFFECTS IN RELATIVISTIC HEAVY ION COLLISIONS T. GAITANOS, H.H. WOLTER Sektion Physik der Universität München Am Coulombwall 1, D-85748 Garching, Germany AND C. FUCHS
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 10 Apr 2015
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 10 Apr 2015 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 10 Apr 2015](/thumbs/79/79354788.jpg) Compact Stars in the QCD Phase Diagram IV (CSQCD IV) September 6-30, 014, Prerow, Germany http://www.ift.uni.wroc.pl/~csqcdiv Many-body forces, isospin asymmetry and dense hyperonic matter R.O. Gomes 1,
Compact Stars in the QCD Phase Diagram IV (CSQCD IV) September 6-30, 014, Prerow, Germany http://www.ift.uni.wroc.pl/~csqcdiv Many-body forces, isospin asymmetry and dense hyperonic matter R.O. Gomes 1,
The Nuclear Many-Body Problem
 The Nuclear Many-Body Problem relativistic heavy ions vacuum electron scattering quarks gluons radioactive beams heavy few nuclei body quark-gluon soup QCD nucleon QCD few body systems many body systems
The Nuclear Many-Body Problem relativistic heavy ions vacuum electron scattering quarks gluons radioactive beams heavy few nuclei body quark-gluon soup QCD nucleon QCD few body systems many body systems
Shape of Lambda Hypernuclei within the Relativistic Mean-Field Approach
 Universities Research Journal 2011, Vol. 4, No. 4 Shape of Lambda Hypernuclei within the Relativistic Mean-Field Approach Myaing Thi Win 1 and Kouichi Hagino 2 Abstract Self-consistent mean-field theory
Universities Research Journal 2011, Vol. 4, No. 4 Shape of Lambda Hypernuclei within the Relativistic Mean-Field Approach Myaing Thi Win 1 and Kouichi Hagino 2 Abstract Self-consistent mean-field theory
PAIRING PROPERTIES OF SYMMETRIC NUCLEAR MATTER IN RELATIVISTIC MEAN FIELD THEORY
 International Journal of Modern Physics E Vol. 17, No. 8 (2008) 1441 1452 c World Scientific Publishing Company PAIRING PROPERTIES OF SYMMETRIC NUCLEAR MATTER IN RELATIVISTIC MEAN FIELD THEORY J. LI, B.
International Journal of Modern Physics E Vol. 17, No. 8 (2008) 1441 1452 c World Scientific Publishing Company PAIRING PROPERTIES OF SYMMETRIC NUCLEAR MATTER IN RELATIVISTIC MEAN FIELD THEORY J. LI, B.
Transport in the Outer Core of Neutron Stars
 Stephan Stetina Institute for Theoretical Physics Vienna UT Transport in the Outer Core of Neutron Stars SEWM 018, Barcelona Ermal Rrapaj (University of Guelph), Sanjay Reddy (INT Seattle) [S. Stetina,
Stephan Stetina Institute for Theoretical Physics Vienna UT Transport in the Outer Core of Neutron Stars SEWM 018, Barcelona Ermal Rrapaj (University of Guelph), Sanjay Reddy (INT Seattle) [S. Stetina,
Investigations on Nuclei near Z = 82 in Relativistic Mean Field Theory with FSUGold
 Plasma Science and Technology, Vol.14, No.6, Jun. 2012 Investigations on Nuclei near Z = 82 in Relativistic Mean Field Theory with FSUGold SHENG Zongqiang ( ) 1,2, REN Zhongzhou ( ) 1,2,3 1 Department
Plasma Science and Technology, Vol.14, No.6, Jun. 2012 Investigations on Nuclei near Z = 82 in Relativistic Mean Field Theory with FSUGold SHENG Zongqiang ( ) 1,2, REN Zhongzhou ( ) 1,2,3 1 Department
QRPA Calculations of Charge Exchange Reactions and Weak Interaction Rates. N. Paar
 Strong, Weak and Electromagnetic Interactions to probe Spin-Isospin Excitations ECT*, Trento, 28 September - 2 October 2009 QRPA Calculations of Charge Exchange Reactions and Weak Interaction Rates N.
Strong, Weak and Electromagnetic Interactions to probe Spin-Isospin Excitations ECT*, Trento, 28 September - 2 October 2009 QRPA Calculations of Charge Exchange Reactions and Weak Interaction Rates N.
A survey of the relativistic mean field approach
 A survey of the relativistic mean field approach B. D. Serot and J. D. Walecka, The relativistic nuclear many body problem. Adv. Nuc. Phys., 16:1, 1986. Non relativistic mean field Small potentials (a
A survey of the relativistic mean field approach B. D. Serot and J. D. Walecka, The relativistic nuclear many body problem. Adv. Nuc. Phys., 16:1, 1986. Non relativistic mean field Small potentials (a
4 November Master 2 APIM. Le problème à N corps nucléaire: structure nucléaire
 4 November 2010. Master 2 APIM Le problème à N corps nucléaire: structure nucléaire The atomic nucleus is a self-bound quantum many-body (manynucleon) system Rich phenomenology for nuclei Mean field Which
4 November 2010. Master 2 APIM Le problème à N corps nucléaire: structure nucléaire The atomic nucleus is a self-bound quantum many-body (manynucleon) system Rich phenomenology for nuclei Mean field Which
Neutrino Mean Free Path in Neutron Stars
 1 Neutrino Mean Free Path in Neutron Stars U. Lombardo a, Caiwan Shen a,n.vangiai b,w.zuo c a INFN-LNS,via S.Sofia 44 95129 Catania, Italy b Institut de Physique Nucléaire,F-91406, Orsay France c Institute
1 Neutrino Mean Free Path in Neutron Stars U. Lombardo a, Caiwan Shen a,n.vangiai b,w.zuo c a INFN-LNS,via S.Sofia 44 95129 Catania, Italy b Institut de Physique Nucléaire,F-91406, Orsay France c Institute
Nuclear Symmetry Energy Constrained by Cluster Radioactivity. Chang Xu ( 许昌 ) Department of Physics, Nanjing University
 Nuclear Symmetry Energy Constrained by Cluster Radioactivity Chang Xu ( 许昌 ) Department of Physics, Nanjing University 2016.6.13-18@NuSym2016 Outline 1. Cluster radioactivity: brief review and our recent
Nuclear Symmetry Energy Constrained by Cluster Radioactivity Chang Xu ( 许昌 ) Department of Physics, Nanjing University 2016.6.13-18@NuSym2016 Outline 1. Cluster radioactivity: brief review and our recent
Dynamics of Phase Transitions in Asymmetric Nuclear Matter
 1 Dynamics of Phase Transitions in Asymmetric Nuclear Matter M.Di Toro a,v.baran a, M.Colonna a, A.Drago b,t.gaitanos a V.Greco c,and A.Lavagno d a Laboratori Nazionali del Sud INFN, Via S. Sofia 44, I-95123
1 Dynamics of Phase Transitions in Asymmetric Nuclear Matter M.Di Toro a,v.baran a, M.Colonna a, A.Drago b,t.gaitanos a V.Greco c,and A.Lavagno d a Laboratori Nazionali del Sud INFN, Via S. Sofia 44, I-95123
Skyrme Hartree-Fock Methods and the Saclay-Lyon Forces
 Skyrme Hartree-Fock Methods and the Saclay-Lyon Forces K. Bennaceur, IPNL UCB Lyon-1 / CEA ESNT The SLy force, quick overview Beyond the standard parameterization: new terms... Extended density dependence
Skyrme Hartree-Fock Methods and the Saclay-Lyon Forces K. Bennaceur, IPNL UCB Lyon-1 / CEA ESNT The SLy force, quick overview Beyond the standard parameterization: new terms... Extended density dependence
Neutron Skins with α-clusters
 Neutron Skins with α-clusters GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung, Darmstadt Nuclear Astrophysics Virtual Institute Hirschegg 2015 Nuclear Structure and Reactions: Weak, Strange and Exotic International
Neutron Skins with α-clusters GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung, Darmstadt Nuclear Astrophysics Virtual Institute Hirschegg 2015 Nuclear Structure and Reactions: Weak, Strange and Exotic International
Influence of phase-transition scenarios on the abrupt changes in the characteristics of compact stars
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Influence of phase-transition scenarios on the abrupt changes in the characteristics of compact stars To cite this article: G B Alaverdyan 2014 J. Phys.:
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Influence of phase-transition scenarios on the abrupt changes in the characteristics of compact stars To cite this article: G B Alaverdyan 2014 J. Phys.:
Probing the Nuclear Symmetry Energy and Neutron Skin from Collective Excitations. N. Paar
 Calcium Radius Experiment (CREX) Workshop at Jefferson Lab, March 17-19, 2013 Probing the Nuclear Symmetry Energy and Neutron Skin from Collective Excitations N. Paar Physics Department Faculty of Science
Calcium Radius Experiment (CREX) Workshop at Jefferson Lab, March 17-19, 2013 Probing the Nuclear Symmetry Energy and Neutron Skin from Collective Excitations N. Paar Physics Department Faculty of Science
Nuclear Equation of State for High Density Matter. Matthias Hempel, Basel University NuPECC meeting Basel,
 Nuclear Equation of State for High Density Matter, Basel University NuPECC meeting Basel, 12.06.2015 Equation of State for Compact Stars neutron stars core-collapse supernova explosions MH Liebendörfer
Nuclear Equation of State for High Density Matter, Basel University NuPECC meeting Basel, 12.06.2015 Equation of State for Compact Stars neutron stars core-collapse supernova explosions MH Liebendörfer
The pygmy dipole strength, the neutron skin thickness and the symmetry energy
 The pygmy dipole strength, the neutron skin thickness and the symmetry energy Xavier Roca-Maza INFN, Sezione di Milano, Via Celoria 16, I-2133, Milano (Italy) Giacomo Pozzi Marco Brenna Kazhuito Mizuyama
The pygmy dipole strength, the neutron skin thickness and the symmetry energy Xavier Roca-Maza INFN, Sezione di Milano, Via Celoria 16, I-2133, Milano (Italy) Giacomo Pozzi Marco Brenna Kazhuito Mizuyama
Constraining the symmetry energy and effective mass splitting from HICs
 INT Program INT-16-2b, The Phases of Dense Matter July 11 - August 12, 2016 Constraining the symmetry energy and effective mass splitting from HICs Yingxun Zhang ( 张英逊 ) China Institute of Atomic Energy
INT Program INT-16-2b, The Phases of Dense Matter July 11 - August 12, 2016 Constraining the symmetry energy and effective mass splitting from HICs Yingxun Zhang ( 张英逊 ) China Institute of Atomic Energy
Probing the EoS of Asymmetric Matter
 Probing the EoS of Asymmetric Matter William Lynch, NSCL MSU Motivations Sources of constraints on the EOS and symmetry energy. Astrophysics Nuclear experiments Laboratory constraints from nuclear collisions
Probing the EoS of Asymmetric Matter William Lynch, NSCL MSU Motivations Sources of constraints on the EOS and symmetry energy. Astrophysics Nuclear experiments Laboratory constraints from nuclear collisions
Correlations between Saturation Properties of Isospin Symmetric and Asymmetric Nuclear Matter in a Nonlinear σ-ω-ρ Mean-field Approximation
 Adv. Studies Theor. Phys., Vol. 2, 2008, no. 11, 519-548 Correlations between Saturation Properties of Isospin Symmetric and Asymmetric Nuclear Matter in a Nonlinear σ-ω-ρ Mean-field Approximation Hiroshi
Adv. Studies Theor. Phys., Vol. 2, 2008, no. 11, 519-548 Correlations between Saturation Properties of Isospin Symmetric and Asymmetric Nuclear Matter in a Nonlinear σ-ω-ρ Mean-field Approximation Hiroshi
The isospin dependence of the nuclear force and its impact on the many-body system
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS The isospin dependence of the nuclear force and its impact on the many-body system To cite this article: F Sammarruca et al 2015 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 580
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS The isospin dependence of the nuclear force and its impact on the many-body system To cite this article: F Sammarruca et al 2015 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 580
Interaction of antiprotons with nuclei
 Interaction of antiprotons with nuclei Jaroslava Hrtánková Nuclear Physics Institute, eº, Czech Republic (Nucl. Phys. A 945 (2016) 197) LEAP conference, Kanazawa, March 6-11, 2016 Introduction 2 Introduction
Interaction of antiprotons with nuclei Jaroslava Hrtánková Nuclear Physics Institute, eº, Czech Republic (Nucl. Phys. A 945 (2016) 197) LEAP conference, Kanazawa, March 6-11, 2016 Introduction 2 Introduction
The Nuclear Equation of State: a Tool to Constrain In-Medium Hadronic Interactions
 The Nuclear Equation of State: a Tool to Constrain In-Medium Hadronic Interactions F. Sammarruca 1 and P. G. Krastev 2 1 Physics Department, University of Idaho, Moscow, ID 83844-0903, U.S.A. 2 Physics
The Nuclear Equation of State: a Tool to Constrain In-Medium Hadronic Interactions F. Sammarruca 1 and P. G. Krastev 2 1 Physics Department, University of Idaho, Moscow, ID 83844-0903, U.S.A. 2 Physics
NN-Correlations in the spin symmetry energy of neutron matter
 NN-Correlations in the spin symmetry energy of neutron matter Symmetry energy of nuclear matter Spin symmetry energy of neutron matter. Kinetic and potential energy contributions. A. Rios, I. Vidaña, A.
NN-Correlations in the spin symmetry energy of neutron matter Symmetry energy of nuclear matter Spin symmetry energy of neutron matter. Kinetic and potential energy contributions. A. Rios, I. Vidaña, A.
Neutrino Interactions in Neutron Star Matter
 Neutrino Interactions in Neutron Star Matter Omar Benhar INFN and Department of Physics Sapienza Università di Roma I-00185 Roma, Italy Based on work done in collaboration with Andrea Cipollone, Alessandro
Neutrino Interactions in Neutron Star Matter Omar Benhar INFN and Department of Physics Sapienza Università di Roma I-00185 Roma, Italy Based on work done in collaboration with Andrea Cipollone, Alessandro
Potential Model Approaches to the Equation of State
 Potential Model Approaches to the Equation of State C. Constantinou IKP, FZ Jülich Wednesday, December 3, 214 PALS: M. Prakash, B. Muccioli & J.M. Lattimer Workshop on NEOS for Compact Stars and Supernovae
Potential Model Approaches to the Equation of State C. Constantinou IKP, FZ Jülich Wednesday, December 3, 214 PALS: M. Prakash, B. Muccioli & J.M. Lattimer Workshop on NEOS for Compact Stars and Supernovae
Discerning the symmetry energy and neutron star properties from nuclear collective excitations
 International Workshop XLV on Gross Properties of Nuclei and Nuclear Excitations Hirschegg, Kleinwalsertal, Austria, January 15-21, 2017 Discerning the symmetry energy and neutron star properties from
International Workshop XLV on Gross Properties of Nuclei and Nuclear Excitations Hirschegg, Kleinwalsertal, Austria, January 15-21, 2017 Discerning the symmetry energy and neutron star properties from
The Nuclear Equation of State and the neutron skin thickness in nuclei
 The Nuclear Equation of State and the neutron skin thickness in nuclei Xavier Roca-Maza Università degli Studi di Milano e INFN, sezione di Milano Physics beyond the standard model and precision nucleon
The Nuclear Equation of State and the neutron skin thickness in nuclei Xavier Roca-Maza Università degli Studi di Milano e INFN, sezione di Milano Physics beyond the standard model and precision nucleon
b - stable matter of protoneutron star
 Mean-field study of the hot b - stable matter of protoneutron star Dao Tien Khoa INST Hanoi, VINATOM EOS of hot nuclear matter with a high neutron-proton asymmetry. EOS of hot b - stable baryon-lepton
Mean-field study of the hot b - stable matter of protoneutron star Dao Tien Khoa INST Hanoi, VINATOM EOS of hot nuclear matter with a high neutron-proton asymmetry. EOS of hot b - stable baryon-lepton
Extracting symmetry energy information with transport models
 Extracting symmetry energy information with transport models Yingxun Zhang China Institute of Atomic Energy Collaborator: Zhuxia Li (CIAE) M.B.Tsang, P. Danielewicz, W.G. Lynch (MSU/NSCL) Fei Lu (PKU)
Extracting symmetry energy information with transport models Yingxun Zhang China Institute of Atomic Energy Collaborator: Zhuxia Li (CIAE) M.B.Tsang, P. Danielewicz, W.G. Lynch (MSU/NSCL) Fei Lu (PKU)
Dipole Polarizability and the neutron skin thickness
 Dipole Polarizability and the neutron skin thickness Xavier Roca-Maza Università degli Studi di Milano and INFN Joint LIA COLL-AGAIN, COPIGAL, and POLITA Workshop, April 26th-29th 2016. 1 Table of contents:
Dipole Polarizability and the neutron skin thickness Xavier Roca-Maza Università degli Studi di Milano and INFN Joint LIA COLL-AGAIN, COPIGAL, and POLITA Workshop, April 26th-29th 2016. 1 Table of contents:
Compact stars and the symmetry energy
 Compact stars and the symmetry energy Constana Providência, Rafael Cavagnoli, Debora P. Menezes, Prafulla K. Panda,3, Aziz Rabhi,4 Centro de Física Computacional, Department of Physics, University of Coimbra,
Compact stars and the symmetry energy Constana Providência, Rafael Cavagnoli, Debora P. Menezes, Prafulla K. Panda,3, Aziz Rabhi,4 Centro de Física Computacional, Department of Physics, University of Coimbra,
Nuclear Symmetry Energy and its Density Dependence. Chang Xu Department of Physics, Nanjing University. Wako, Japan
 Nuclear Symmetry Energy and its Density Dependence Chang Xu Department of Physics, Nanjing University 2016.8.17-21@RIKEN, Wako, Japan Outline 1. Brief Review: Nuclear symmetry energy 2. What determines
Nuclear Symmetry Energy and its Density Dependence Chang Xu Department of Physics, Nanjing University 2016.8.17-21@RIKEN, Wako, Japan Outline 1. Brief Review: Nuclear symmetry energy 2. What determines
Study of the spin orbit force using a bubble nucleus O. Sorlin (GANIL)
 Study of the spin orbit force using a bubble nucleus O. Sorlin (GANIL) I. General introduction to the atomic nucleus Charge density, nuclear orbits Shell gaps-> magic nuclei II. The spin orbit force History
Study of the spin orbit force using a bubble nucleus O. Sorlin (GANIL) I. General introduction to the atomic nucleus Charge density, nuclear orbits Shell gaps-> magic nuclei II. The spin orbit force History
Neutron star structure explored with a family of unified equations of state of neutron star matter
 Neutron star structure explored with a family of unified equations of state of neutron star matter Department of Human Informatics, ichi Shukutoku University, 2-9 Katahira, Nagakute, 48-1197, Japan E-mail:
Neutron star structure explored with a family of unified equations of state of neutron star matter Department of Human Informatics, ichi Shukutoku University, 2-9 Katahira, Nagakute, 48-1197, Japan E-mail:
Transport studies of heavy ion collisions and antiproton-induced reactions on nuclei at FAIR energies
 Transport studies of heavy ion collisions and antiproton-induced reactions on nuclei at FAIR energies A.B. Larionov Outline: 1) Motivation. 2) The GiBUU model: kinetic equations with relativistic mean
Transport studies of heavy ion collisions and antiproton-induced reactions on nuclei at FAIR energies A.B. Larionov Outline: 1) Motivation. 2) The GiBUU model: kinetic equations with relativistic mean
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 6 Dec 2003
 Observable effects of symmetry energy in heavy-ion collisions at RIA energies Bao-An Li arxiv:nucl-th/322v 6 Dec 23 Department of Chemistry and Physics P.O. Box 49, Arkansas State University State University,
Observable effects of symmetry energy in heavy-ion collisions at RIA energies Bao-An Li arxiv:nucl-th/322v 6 Dec 23 Department of Chemistry and Physics P.O. Box 49, Arkansas State University State University,
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 17 Sep 2003
 Asymmetric nuclear matter in the relativistic mean field approach with vector cross-interaction Juraj Kotulič Bunta and Štefan Gmuca Institute of Physics, Slovak Academy of Sciences, Dubravska cesta 9,
Asymmetric nuclear matter in the relativistic mean field approach with vector cross-interaction Juraj Kotulič Bunta and Štefan Gmuca Institute of Physics, Slovak Academy of Sciences, Dubravska cesta 9,
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 7 Apr 2009
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 7 Apr 2009 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 7 Apr 2009](/thumbs/90/103476070.jpg) Thermodynamic properties of nuclear matter with three-body forces V. Somà, and P. Bożek,, Institute of Nuclear Physics PAN, PL-- Kraków, Poland Institute of Physics, Rzeszów University, PL--99 Rzeszów,
Thermodynamic properties of nuclear matter with three-body forces V. Somà, and P. Bożek,, Institute of Nuclear Physics PAN, PL-- Kraków, Poland Institute of Physics, Rzeszów University, PL--99 Rzeszów,
Nature of low-energy dipole states in exotic nuclei
 Nature of low-energy dipole states in exotic nuclei Xavier Roca-Maza Università degli Studi di Milano, Via Celoria 16, I-133, Milano SPES One-day Workshop on "Collective Excitations of Exotic Nuclei" December
Nature of low-energy dipole states in exotic nuclei Xavier Roca-Maza Università degli Studi di Milano, Via Celoria 16, I-133, Milano SPES One-day Workshop on "Collective Excitations of Exotic Nuclei" December
Effects of n-p Mass Splitting on Symmetry Energy
 Effects of n-p Mass Splitting on Symmetry Energy Li Ou1,2 Zhuxia Li3 Bao-An Li1 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy Texas A&M University-Commerce, USA 2 College of Physics and Technology Guangxi Normal
Effects of n-p Mass Splitting on Symmetry Energy Li Ou1,2 Zhuxia Li3 Bao-An Li1 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy Texas A&M University-Commerce, USA 2 College of Physics and Technology Guangxi Normal
