arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 30 Jul 2013
|
|
|
- Britney Perry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BOUNDAY CONCENTATION OF A GAUGED NONLINEA SCHÖDINGE EQUATION ON LAGE BALLS ALESSIO POMPONIO 1 AND DAVID UIZ axiv:137815v1 [mathap] 3 Jul 13 ABSTACT Thi pape i motivated by a gauged Schödinge equation in dimenion including the o-called Chen-Simon tem The adially ymmetic cae lead to an elliptic poblem with a nonlocal defocuing tem, in competition with a local focuing nonlineaity In thi wok we poe the equation in a ball unde homogeneou Diichlet bounday condition By uing ingula petubation agument we pove exitence of olution fo lage value of the adiu Thoe olution ae located cloe to the bounday and the limit pofile i given 1 INTODUCTION Let u conide a gauged Nonlinea Schödinge Equation in the plane: 1 id φ + D 1 D 1 + D D φ + φ p 1 φ = Hee t, x = x 1, x, φ : C i the cala field, A µ : ae the component of the gauge potential and D µ = µ + ia µ i the covaiant deivative µ =, 1, The natual equation fo the gauge potential A µ ae the Maxwell equation Howeve, the modified gauge field equation popoe to include alo the o-called Chen-Simon tem, that i, µ F µν + 1 κɛναβ F αβ = j ν, with F µν = µ A ν ν A µ In the above equation, κ i a paamete that meaue the tength of the Chen- Simon tem A uual, ɛ ναβ i the Levi-Civita teno, and upe-indice ae elated to the Minkowki metic with ignatue 1, 1, 1 Finally, j µ i the coneved matte cuent, j = φ, j i = Im φdi φ At low enegie, the Maxwell tem become negligible and can be dopped, giving ie to: 1 κɛναβ F αβ = j ν See [6, 7, 11, 1, 13] and [15, Chapte 1] fo the dicuion above 1 Mathematic Subject Claification 35J, 35Q55 Key wod and phae Gauged Schödinge Equation, Lyapunov-Schmidt eduction AP i uppoted by MIU - PIN Metodi vaiazionali e topologici nello tudio di fenomeni non lineai, by GNAMPA Poject Metodi Vaiazionali e Poblemi Ellittici Non Lineai and by FA11 Equazioni ellittiche di tipo Bon-Infeld D i uppoted by the Spanih Minity of Science and Innovation unde Gant MTM and by J Andalucia FQM 116 1
2 POMPONIO AND UIZ Fo the ake of implicity, let u nomalize o that κ = Equation 1 and lead u to the poblem: 3 id φ + D 1 D 1 + D D φ + φ p 1 φ =, A 1 1 A = Im φd φ, A A = Im φd 1 φ, 1 A A 1 = 1 φ A uual in Chen-Simon theoy, poblem 3 i invaiant unde gauge tanfomation, φ φe iχ, A µ A µ µ χ fo any abitay C function χ Thi model wa fit popoed and tudied in [11, 1, 13], and ometime ha eceived the name of Chen-Simon-Schödinge equation The initial value poblem, a well a global exitence and blow-up, ha been addeed in [, 8, 1] fo the cae p = 3 The exitence of tationay tate fo 3 and geneal p > 1 ha been tudied ecently in [5, 9, 1] By uing the anatz: φt, x = u x e iωt, A x = A x, A 1 t, x = x x h x, A t, x = x 1 x h x, and afte ome manipulation, in [5] it i found that: ux+ ω + h x + h x + u d ux = ux p 1 ux, in, whee Hee A take the fom: x h = 1 u d h A = u d Obeve that i a nonlocal equation Moeove, in [5] it i hown that i indeed the Eule-Lagange equation of the enegy functional: I : H 1, defined a Iu = 1 ux + ωu x dx + 1 u x 8 x u d dx 1 ux p+1 dx p + 1 Hee H 1 i the Sobolev pace of adially ymmetic function In [5, 9, 1] citical point of I ae found by uing vaiational method It i hown that the value p = 3 i citical fo thi poblem Indeed, fo p > 3 the enegy functional i unbounded fom below and atifie a mountain-pa geomety Even if the PS popety i not known to be atified, poitive olution ae found in [5] Intead, fo p 1, 3 the global behavio of I i diffeent and depend on the paamete ω In [1] we how that I i bounded fom below if and only if ω ω, whee the thehold value ω i explicit, namely: ω = 3 p 3 + p 3 p 1 3 p 3 p m 3 + p p 1 p 1 3 p
3 BOUNDAY CONCENTATION OF A GAUGED NONLINEA SCHÖDINGE EQUATION 3 Hee m = w 1 d, and w 1 i the unique poitive even olution of the poblem w + w = w p in, ie, 1 p 1 5 w 1 = p + 1 coh 1 p In thi pape we tudy poitive olution fo the Diichlet poblem poed on a ball B,, that i: 6 ux + ux =, whee, a above, ω + h x x + x h u d ux = u p x, x B,, x B,, h = 1 u d Let u denote by H = H,B, 1 the Sobolev Space of adially ymmetic function Again, 6 i the Eule-Lagange equation of the functional I : H, I = I H A fit motivation fo thi tudy come fom the poof of [1] It i not difficult to how that I i coecive fo any fixed So, thee exit a minimize u of I In ode to pove boundedne of u when +, the poblem i the poible lo of ma at infinity In [1] we pove that, if unbounded, the equence u actually behave a a oliton, when u i intepeted a a function of a ingle eal vaiable Then, the enegy functional I admit a natual appoximation though a convenient limit functional J, ee Section fo detail Moeove, the olution of that limit functional, and thei enegy, can be found explicitly, and thi lead u to a contadiction if ω ω In thi pape we how that thi kind of olution actually exit fo ω < ω Moeove, thei enegy tend to a +, and they eem to be local minima of I Theefoe, they could coepond to global minima of I, which i an inteeting phenomenon: the minima of the enegy tend to aggegate nea the bounday of the domain A econd motivation come fom efeence [3] Obeve that fo any u, the function: h x x + x h u d, i deceaing in x Theefoe, a olution like in [3] could exit Howeve hee the poblem i completely diffeent, ince h itelf depend on u in a nonlocal fahion Indeed, natual etiction on ω and p appea, a commented above The main eult of thi pape i the following: Theoem 11 Aume p 1, 3, ω, ω Then, fo lage enough, poblem 6 admit a poitive olution ũ U, with U = k 1 p 1 w 1 k Hee w 1 i given by 5 and k i the laget poitive oot of the equation: k = ω + 1 m k 5 p p 1, k > Finally, 1 k log
4 POMPONIO AND UIZ A commented above, the aumption ω, ω i natual fo thi eult Moeove, obeve that ω i well defined only fo p 1, 3, and it tend to a p tend to 3 The poof ue a ingula petubation method baed on a Lyapunov-Schmidt eduction, which ha become a well-known technique in thi kind of poblem Howeve, thee ae ome new apect on the poblem unde conideation Fit, ou poblem involve a nonlocal tem which make the agument of the poof moe complicated We point out that it i not jut a technical difficulty, ince the exitence eult depend heavily on the nonlocal tem Indeed, thoe olution do not exit fo the autonomou Nonlinea Schödinge Equation, and ae a pecial featue of the model tudied in thi pape Moeove, the limit functional i diffeent fom the uual one in Nonlinea Schödinge Equation and contain alo a nonlocal tem A a conequence, we alo need to pove the non-degeneacy of the limit olution, which in thi cae coepond to a global minimum of the limit functional The et of the pape i oganized a follow Section i devoted to ome peliminay eult The limit functional and it popetie ae expoed hee Moeove, we pove that the limit olution i non-degeneate The lat two ection ae devoted to the poof of Theoem 11 Section 3 i devoted to olve the auxiliay equation in the Lyapunov-Schmidt eduction, wheea in Section we pove the exitence of a minimum fo the educed functional Acknowledgement Thi wok ha been patially caied out duing a tay of AP in Ganada He would like to expe hi deep gatitude to the Depatamento de Análii Matemático fo the uppot and wam hopitality PELIMINAIES Let u fit fix ome notation We denote by H = H 1,B, the Sobolev pace of adially ymmetic function We ue, to denote it uual cala poduct and nom, wheea othe nom, like Lebegue nom in B,, will be indicated with a ubcipt Moeove, H 1 a,b, H 1 a,b ae ued to indicate the cala poduct and nom of the Sobolev pace of dimenion 1 If nothing i pecified, tong and weak convegence of equence of function ae aumed in the pace H In ou etimate, we will fequently denote by C >, c > fixed contant, that may change fom line to line, but ae alway independent of the vaiable unde conideation We alo ue the notation O1, o1, Oε, oε to decibe the aymptotic behavio of quantitie in a tandad way Finally the lette x indicate a two-dimenional vaiable, and,, t denote one-dimenional vaiable Let u tat with the following popoition: Popoition 1 I i a C 1 functional, and it citical point coepond to claical olution of 6
5 BOUNDAY CONCENTATION OF A GAUGED NONLINEA SCHÖDINGE EQUATION 5 Thi wa poved in [5] fo the poblem et in ; the ame agument apply to ou cae Moeove, the deivative of I i: 7 I z[u] π = z u + ωzu z p zu d zu z d d z z tt dt zu d d If in the lat tem we ue Fubini Theoem in the vaiable,, and afte that we intechange the name of the vaiable, we obtain: 8 I z[u] π = z u + ωzu z p zu d zu z d d z zu z tt dt d In thi pape we will make ue of both expeion fo I, depending on the cae Ou poof of Theoem 11 ue a Lyapunov-Schmidt eduction to pove exitence of a citical point fo I In ode to do that, ome knowledge of the limit functional i needed Fit of all, let u give a heuitic deivation of thi enegy functional Conide u a fixed function, and define u = u Let u now etimate Iu a + ; afte the change of vaiable +, we obtain: Iu π = u + ωu + d u + u d d 1 + p + 1 d u p+1 + d We etimate the above expeion by imply eplacing the expeion +, + with the contant : π 1 Iu [ 1 = [ 1 u + ωu d u + ωu d + 1 u u d d 1 ] + u p+1 d p u d 1 ] + u p+1 d p + 1 Theefoe, it i natual to conide the limit functional J : H 1, 9 Ju = 1 u + ωu d u d 1 u p+1 d p + 1 Clealy, the Eule-Lagange equation of 9 i the following limit poblem: 1 u + ωu + 1 u d u = u p 1 u, in Befoe going on with the tudy of 1, we need ome well-known fact concening the poblem 11 w + kw = w p in, k >
6 6 POMPONIO AND UIZ We denote by w k H 1 k > the unique poitive even olution of 11 Obeve that equation 11 i integable and the Hamiltonian of w k i equal to, that i, 1 1 w k + k w k 1 p + 1 wp+1 k =, fo all It i alo known that any poitive olution of 11 i of the fom u = w k ξ, fo ome ξ Moeove, 13 w k = k 1 p 1 w1 1 p 1 k, and w 1 = p + 1 coh 1 p Notice that w k and w k decay exponentially to zeo at infinity In what follow we define 1 m = 15 w 1 d The following elation ae alo well known, and can be deduced fom 1: w 1 d = p 1 p + 3 m, w p+1 p d = p + 3 m Let u now come back to equation 1 Conide u a poitive olution of 1, and define k = ω d u Then, u i a olution of u + ku = u p, o u = w k ξ fo ome ξ By uing 13, we obtain: k = ω + 1 w k d = ω + 1 k p 1 w1 k d A change of vaiable lead u to the identity: 16 k = ω + 1 m k 5 p p 1, k > Theefoe, the exitence of olution fo 1 educe to the exitence of olution of the algebaic equation 16 Moeove, we ae alo inteeted in the enegy of thoe olution, a we hall ee in Section Thoe quetion have been teated in [1, Section 3], whee the following eult wee obtained: Popoition Aume p 1, 3 and take m a in 1 Define: ω = 3 p 3 + p 3 p 1 3 p 3 p m p 1 3 p 3 + p, p 1 5 pm p 1 3 p m 5 p 5 pm 3 p ω 1 = p 1 p 1 The following hold: 1 < ω < ω 1 ; if ω > ω 1, equation 16 ha no olution and thee i no nontivial olution of 1; 3 if ω = ω 1, equation 16 ha only one olution k and w k i the only poitive olution of 1 apat fom tanlation; if ω, ω 1, equation 16 ha two olution k 1 ω < k ω and w k1, w k ae the only two poitive olution of 1 apat fom tanlation; 5 fo any ω, ω 1, Jw k1 >
7 BOUNDAY CONCENTATION OF A GAUGED NONLINEA SCHÖDINGE EQUATION 7 6 Jw k < if and only if ω, ω In uch cae, w k i a global minimize fo J emak 3 In geneal, we cannot obtain a moe explicit expeion of m depending on p, but it can be eaily appoximated by uing ome oftwae In Figue 1 the map ω p and ω 1 p have been plotted FIGUE 1 The value ω p < ω 1 p, fo p 1, 3 Fo ome pecific value of p, m can be explicitly computed, and hence ω and ω 1 Fo intance, if p =, m = 6, ω 1 = 9 and ω 3 = 5 15 A commented in the intoduction, in Section 3 we will ue the above olution a a limit pofile of olution of 6 via a Lyapunov-Schmidt eduction On that pupoe, the non-degeneacy of the limit olution i equied We ay that a olution u of 1 i degeneate if the poblem: 17 φ + ωφ u d φ ha a olution φ H 1 diffeent fom c u, c Next popoition i devoted to thi quetion u d uφ d u pu p 1 φ = Popoition Let ω 1, k, k 1, k a in Popoition Then: 1 If ω = ω 1, w k i a degeneate olution of 1 If ω, ω 1, both w k1 and w k ae non-degeneate olution of 1 Poof Take w k a olution of 1, and φ a olution of 17 Define α = wk d w k φ d Then, φ i a olution of the poblem: φ + ωφ + 1 w k d φ pw p 1 k φ = αw k
8 8 POMPONIO AND UIZ Wite φ = ψw k : then, ψ = ψ w k w k + αw k w k Thi i a linea equation of fit ode in ψ, which can be olved by vaiation of contant: ψ C = w k + α wk w k, C Obeve that if C, then φ = ψw k tend to + at infinity, which i not poible if φ H 1 So, C mut be equal to, and we ae led to: ψ = α w k w k By uing 1, the above equation can be explicitly integated: ψ = α w k k p 1 w k + + β, with β Theefoe, φ = α k p 1 w k + w k + βw k Clealy, w k i degeneate if and only if α can take value diffeent fom zeo Take β =, and ecall now the definition of α: α = α w k k d p 1 w k + w kw k d By integation by pat, w kw k d = 1 Then, eithe α = o 1 = m k 6 p 5 p p 1 p 1 Thi, togethe with 16, implie that ω = ω 1 and k = k w k d = 1 k 5 p p 1 m Obeve that, due to the nonlocal chaacte of ou poblem, the lineaized poblem 17 doe not have the fom of a Schödinge opeato Then, ome moe wok i needed in ode to accomplih a Lyapunov-Schmidt eduction Let u define the following opeato: [ T [φ] = φ + ω + 1 ] u d pu p 1 φ, K[φ] = u d uφ d u, L[φ] = T [φ] + K[φ] Obeve that L, T, K : H 1 {u } H 1 {u } Of coue, hee othogonality i undetood fo the cala poduct H 1 Coollay 5 Aume ω, ω 1 Then the opeato L defined above i a bijection fo u = w k1 o u = w k Moeove, if ω < ω and u = w k, thee exit c > o that: 18 L[φ], φ H 1 c φ H 1 fo any φ H1 {u }
9 BOUNDAY CONCENTATION OF A GAUGED NONLINEA SCHÖDINGE EQUATION 9 Poof It i well-known that T i a bijection Since the image of K i of dimenion 1, K i obviouly a compact opeato Moeove, by Popoition, L i injective By Fedholm altenative, L i a bijection Moeove, by Popoition, we know that w k i a minimize of J with nondegeneate econd deivative Fom thi, 18 follow 3 THE AUXILIAY EQUATION In thi ection we begin the poof of Theoem 11, which ue a ingula petubation agument baed on a Lyapunov-Schmidt eduction So, let u aume p 1, 3 and ω, ω thoughout the et of the pape The contuction of ou appoximating olution i lagely inpied by [3] We et U = w k, whee k i the econd oot of equation 16 ee Popoition We will denote U = U, and V = U e k Fo late ue, obeve that U olve the equation 19 U + ωu + 1 wheea V atifie V + ωv + 1 U d U = U p, in, U d V =, in We define ou appoximating olution a z = φ U V H, whee φ : [, + [, 1] i a mooth function uch that { if, /, φ =, φ 1 if /,, C Let u define the inteval [ I = β log, α ] k log, k whee α, β ae fixed contant atifying: { 1 1 max, 1 } < α < 1, 1 < β < min{, p}α p We ae inteeted in finding citical point fo I nea the manifold of appoximating olution: Z = {z, I } Fo any z Z, conide T z Z the tangent pace, panned by the function: ż := z = φ U + U e k Take alo W = W z = T z Z, and let P, Q denote the othogonal pojection onto the pace W and T z Z, epectively We then decompoe the equation: { I z P I + w = z + w = auxiliay equation, QI z + w = bifucation equation In thi ection we ue the Banach contaction pinciple to find a olution w of the auxiliay equation fo any I In ode to do that, ome etimate ae in ode Ou fit eult i an etimate on I z, which meaue in which ene z i an appoximating olution
10 1 POMPONIO AND UIZ Lemma 31 Fo any I, we have that O e k I z = O e p k Poof Let u ecall that, by 8, I z [u] π = + z u + ωz u d + z u Let u evaluate all thee integal in [, /] We have z u d C 1 e k d, if p,, if p < z u z d d z t z t dt d d zu p d 1 u C 1 e k u Analogouly, ωz u d C 1 e k u Moeove z u z d d C e k d C e k C 1 e k 3 u z d 3 1 We can alo etimate z t z u z t dt d d C zd Ce k u z u u d z u d Finally zu p d C p p+1 e p k u Theefoe I z [u] π = + z u + ωz u d + z z u + oe k 5 u z u z d d t z t dt d d zu p d
11 BOUNDAY CONCENTATION OF A GAUGED NONLINEA SCHÖDINGE EQUATION 11 Let u pove that [ I z [u] = z π u + ωz u d + 1 z u z d d + 1 z u z zt dt d d zu p ] d 3 Indeed we have z u d Theefoe + O 1/ u Analogouly, we get 5 6 z u d z d z u d = z u d = z p u d = = 1 u 1 z d u + z u d + O 1/ u z u d + O 1/ u, z p u d + O 1/ u Let u tudy the nonlocal tem; z u z d d 1 = z u 1 z d d We have I z u + 1 [ ] z u z d z d d II + z u 1 z d d I C III z u C z z u d 1 d u z d d C u C u 1 z d d
12 1 POMPONIO AND UIZ Moeove and II 1 C III z u C z d z u d C u, z u z u d + + z d d 1 z d d C u Theefoe, taking alo in account the exponential decay of z, 7 z u Analogouly z d d = z z u z u = z z u z u = O 1/ u z u z z u + O 1/ u t z t dt d d z 1 t z t dt z 1 t t z u z and o, again by the exponential decay of z, 8 z z u = z u z + O 1/ u z t dt d d d d t z t dt d d z t dt d d zt dt d d 1 z d d 1 z t dt d d 1 z t dt d d
13 BOUNDAY CONCENTATION OF A GAUGED NONLINEA SCHÖDINGE EQUATION 13 Then, by, 5, 6, 7 and 8, we get 3 Let u obeve that z u d = z u d = Theefoe, by 19 and, we have I z [u] = z + ωz + z π + O 1/ u [ = z + ωz + z z u d + O 1/ u z u d + o 1/ u [ ] z d + z zt dt d z p u d ] z d z p u d + O 1/ u [ ] = U d U d U u d A [ ] U d U d V u d U d U V d U u d B C + U d V d U u d D [ U V p U p ] u d } {{ } E + o e k u Let u evaluate evey tem in the peviou fomula Since we infe that U d U d = O e k, A = O e k u, B = o e k u
14 1 POMPONIO AND UIZ Moeove, by [1, Lemma 37], The etimate of D i diect: C = O e k u D = O e k u Finally, by the Mean Value Theoem we can etimate: Again by [1, Lemma 37], we have E U V p U p CU p 1 V 1 [ U V p U p ] d u O e k u, if p >, 1 = O e k u, if p =, O e p k u, if p < Hence we get the concluion U p 1 V d Ou next eult concen the non-degeneacy of I z, and make ue of Coollay 5 in an eential way Lemma 3 Thee exit C > c > uch that fo lage and fo any I, c u I z [u, u] C u, fo all u T z Z Poof Let u H uch that u T z Z Take a [, ] uch that a+1 a u + ωu d u Take ψ a cut-off function uch that if a, ψ = a if a a + 1, 1 if a + 1 Since u = ψu + 1 ψu, we have Moeove u = ψu + 1 ψu + ψu, 1 ψu I z [u, u] = I z [ψu, ψu] + I z [1 ψu, 1 ψu] + I z [ψu, 1 ψu] Fo that ake of bevity, we et v = ψu and w = 1 ψu By 35, we infe that 9 3 I z [v, w] = v, w + o1 u = o1 u, I z [w, w] = w + o1 u Befoe evaluating I z [v, v], let u obeve that ince u T z Z, then 31 v, ż = w, ż = o e 1/3 u We now extend v to in all, and etimate v, U H 1 On that pupoe, it i eay to ee that: 3 v, U H1 v, U = O 1/ v 1 u
15 BOUNDAY CONCENTATION OF A GAUGED NONLINEA SCHÖDINGE EQUATION 15 Moeove, by uing, 33 v, ż + U = U v, e k = U O v Putting togethe 31, 3 and 33, we conclude that 3 v, U H1 = o 1/ v, We now tudy I z [v, v]; hee we will deive I fom expeion 8, obtaining the expeion: 35 I z [u, v] = π u v uv + ωuv d + z d d z u z d z v d d z t uv z t dt d d z v z u tz t dt d d z z u tz tvt dt d d p z p 1 uv d Aguing a in the poof of Lemma 31, we can ubtitute,, t with committing negligible eo: moe peciely, we have I z [v, v] = π Let u obeve that, p v v + ωv d + z d d z v z d z v d d v z zt dt d d v + ωv d p = z v z v zt dt d d z v z z tvt dt d d z p 1 v d + o1 u z p 1 v d v + ωv d p U p 1 v d + o1 u
16 16 POMPONIO AND UIZ Setting F = z d, ince F = z, we get v z d d + v z zt dt d d = z d v d = U d v d + o1 u Setting, moeove, G = z v d, ince G = z v, we have z v z d z v d d + z v z v zt dt d d Theefoe, by 3: + z v z z tvt dt d d = z d z v d = U d U v d + o1 u I z [v, v] = L[v, v] + o1 u By Coollay 5 we have that c v H 1 L[v, v] C v H 1 Obeve moeove that v H 1 = v + o1 v Thee etimate, togethe with 9 and 3, yield the concluion Ou next etimate implie that the peviou non-degeneacy eult applie alo fo I z + w if w i ufficiently mall Lemma 33 Thee exit C > uch that I z [u, u] I z + w[u, u] C w + w p 1 u, fo all u, w H, ufficiently lage and I Poof Fo thi etimate, we ue the fom of I z deived fom 7, that i: I z [u, u] = π u + ωu d p z p 1 u d z z d u d d z u z u d z d d u z z d d + z u d d
17 BOUNDAY CONCENTATION OF A GAUGED NONLINEA SCHÖDINGE EQUATION 17 Fo the etimate of the local tem, we ue the inequalitie: C a q 1 + b q 1 b if q > 1, a + b q a q b q if q, 1] Then, if p >, we ue the L bound of z to get:, a, b If p 1, ], z + w p 1 z p 1 u d C z + w p 1 z p 1 u d w + w p 1 u d 1/ 1/ C w + w p 1 d u d w d w p 1 u d p 1 3 p u 3 p d Let u now conide the nonlocal tem Obeve that each of thoe tem i of ode in z The etimate of each tem i elatively eay, but the whole computation i lengthy Let u explain in detail ome of them Fo intance, let u define: Qz 1, z, z 3, z = z 1 z z 3 z d u d d Clealy Q i linea in each vaiable Theefoe, we need to etimate: Qz 1, z, z 3, z whee z i = w i A, z i = z i / A, fo any non-empty A {1,, 3, } Fo intance, we etimate: z Qz, z, z, w = z w d u d d z d z d z w d z d 1 u d w L u C w L u L The cae whee w appea moe than once ae eaie Slightly moe difficult i the etimate of Kz, z, z, w, with z 1 u Kz 1, z, z 3, z = z u d z 3 z d d Indeed, in thi cae z appea in the thee integal Then, we need to hae the vaiable, a follow: z u Kz, z, z, w = z u d z w d d z u d C u L w L z u d z w d d
18 18 POMPONIO AND UIZ The othe tem can be etimated in an analogou way We ae now in condition of tating the main eult of thi ection Popoition 3 Fo ufficiently lage and any I, thee exit a unique w H uch that: 1 z + w olve the auxiliay equation P I z + w = The map w i C 1 3 w = O O log, if p,, if p < 1 α 1 pα Poof The poof i quite tandad in Lyapunov-Schmidt eduction By Lemma 31, and taking into account 1, we obtain that I z = o1 Thi, togethe with the etimate of Lemma 3, 33, make it poible to cay out the contaction agument Moeove, the C 1 egulaity of the map w can be deduced fom the Implicit Function Theoem See [], Section 3,, fo detail Moeove, by taking into account that I, we conclude that: O I z = O log, if p,, if p < 1 α 1 pα Theefoe, the ame etimate fo w hold emak 35 It i impotant to obeve that mot of the eult of thi ection hold with the ame poof if we conide ω, ω 1, and alo if we take U = w k1 intead of w k Lemma 3 hould be etated fo U = w k1, ince thi i not a minimize fo J In next ection, though, we will obtain a olution of the bifucation equation only if JU < Thi i the eaon why we need ω, ω, U = w k, accoding to Popoition But thoe etiction ae natual, a commented in the Intoduction Let u define: THE EDUCED FUNCTIONAL Z = {z + w : I, w a in Popoition 3} It i well-known ee [] that Z i a natual containt fo I o, in othe wod, that citical point of I Z coepond to olution of the bifucation equation, and hence they ae tue citical point of I Thi ection i devoted to pove the exitence of a minimum fo I Z, which eceive the name of educed functional Lemma 1 Fo any I, we have Poof We have I z = πju + π k e k + o I z π = 1 1 p + 1 z + ωz 1 d + 8 z p+1 d e k z z d d
19 BOUNDAY CONCENTATION OF A GAUGED NONLINEA SCHÖDINGE EQUATION 19 Let u evaluate all thee integal in [, /] We have z d Ce k Ce k Analogouly, Theefoe I z π = 1 Let u check that 36 I z = 1 π Indeed and hence 37 Analogouly ωz d Ce k, z z d d Ce 3 k 1 p + 1 z + ωz 1 d + 8, z p+1 d Ce p+1 k z p+1 d + oe k 5 z + ωz 1 d + z d z d z d = z d = z p+1 d = z z d d 3 z d 1 p + 1 z p+1 z d C, z d + O1 z d + O1, z p+1 d + O1 d +O1 Moeove z z d d z z d d 1 = z 1 z d d I + 1 [ ] z z d z d d II
20 POMPONIO AND UIZ Since I C II C z z d d C z z d + z d d C, we have z z d d = z z d d + O1 3 = z 3 d + O1 Hence 36 follow by 37, 38, 39 and By 36, we infe that I z π [ 1 3 = U + ωu 1 d + U d 1 U p+1 d p + 1 A U V + ωu V d 1 U d U V d + U p V d B + 1 V + ωv 1 d + U d V d 8 C 1 ] U V p+1 U p+1 + p + 1U p V d p + 1 D + O e k We have to evaluate each tem of the peviou fomula Fitly, let u obeve that U d = k U d e + oe k k
21 BOUNDAY CONCENTATION OF A GAUGED NONLINEA SCHÖDINGE EQUATION 1 Since U i a olution of 19, we have A = 1 3 U + ωu U d + 1 U d 1 U p+1 d p U U + o e k = 1 3 U d U d U d U p+1 d p k e k + o e k = U d U p+1 d 1 k e k p o e k = JU 1 k e k + o e k Again, being U a olution of 19, B = U + ωu V d 1 e k U d U V d + V U + o = 1 U d U V d 1 U d U V d + k e k + o e k = k e k + o e k Moeove, ince V i a olution of, C = 1 V + ωv V d + 1 U d 8 + o e k = 1 U d V d + 1 U d k e k + o e k = 1 k e k + o e k U p V d V d + 1 V V V d Finally, ince U V p+1 U p+1 + p + 1U p V we have Then the concluion follow D = o e k pp + 1 U p 1 V, The poof of Theoem 11 i completed with the following popoition
22 POMPONIO AND UIZ Popoition Let u define Φ : I a Φ = I z + w Then, Φ = πju + π k e k + o e k Moeove, Φ attain a global minimum in the inteio of I fo ufficiently lage Poof Fit, we ue Taylo expanion to get, fo ome ξ, 1, I z + w = I z + I z [w ] + 1 I z + ξ w [w, w ] = I z + I z [w ] + 1 I z [w, w ] + 1 I z + ξ w I z [w, w ] By uing Lemma 31, 3, 33, we obtain that: I z + w = I z + O w Popoition 3 and 1 imply that the eo w i negligible, o that Φ = πju + π k e k + o e k Fo the ake of bevity, we et α = α k log, 1 = 1 k log, β = β k log We will pove that Φ ha a minimum in the inteio of I, howing that Φ β Φ 1 + and Φ α Φ 1 +, a + Indeed Φ β Φ 1 = π1 βju k log + O1, Φ α Φ 1 = π k 1 α + o 1 α emak 3 The olution that we have found coepond to a minimum of the educed functional, and ecall that w k i alo a minimize fo the limit functional J Theefoe, it i eaonable to think that ou olution coepond to a local minimum of I Moeove, it enegy divege negatively a +, o it could be the global minimize fo I Indeed, by the agument in [1], the global minimize of I mut contain a tem like U, fo ome Howeve, it i not clea if the global minimize could alo have a localized pat EFEENCES [1] A Amboetti, E Coloado and D uiz, Multi-bump oliton to linealy coupled ytem of nonlinea Schödinge equation, Calc Va Patial Diffeential Equation 3 7, [] A Amboetti and A Malchiodi, Petubation method and emilinea elliptic poblem on N, Poge in Mathematic, Bikhäue Velag, Bael, 6 [3] A Amboetti, A Malchiodi and W-M Ni, Singulaly petubed elliptic equation with ymmety: exitence of olution concentating on phee II, Indiana Univ Math J 53, [] L Begé, A de Bouad and J C Saut, Blowing up time-dependent olution of the plana Chen- Simon gauged nonlinea Schödinge equation, Nonlineaity , [5] J Byeon, H Huh, and J Seok, Standing wave of nonlinea Schödinge equation with the gauge field, J Funct Anal 63 1, no 6, [6] C Hagen, A new gauge theoy without an elementay photon, Ann of Phy , [7] C Hagen, otational anomalie without anyon, Phy eview D , [8] H Huh, Blow-up olution of the Chen-Simon-Schödinge equation, Nonlineaity
23 BOUNDAY CONCENTATION OF A GAUGED NONLINEA SCHÖDINGE EQUATION 3 [9] H Huh, Standing wave of the Schödinge equation coupled with the Chen-Simon gauge field J Math Phy 53 1, no 6, 637, 8 pp [1] H Huh, Enegy Solution to the Chen-Simon-Schödinge Equation, Abtact and Applied Analyi Volume 13, Aticle ID 59653, 7 page [11] Jackiw and S-Y Pi, Soliton olution to the gauged nonlinea Schödinge Equation, Phy eview Lette 6 199, [1] Jackiw and S-Y Pi, Claical and quantal nonelativitic Chen-Simon theoy, Phy ev D [13] Jackiw and S-Y Pi, Self-dual Chen-Simon oliton, Pog Theoet Phy Suppl [1] A Pomponio and D uiz, A Vaiational Analyi of a Gauged Nonlinea Schödinge Equation, pepint axiv:13651 [15] G Taantello, Self-Dual Gauge Field Votice: An Analytical Appoach, PNLDE 7, Bikhäue Boton, Inc, Boton, MA, 7 1 DIPATIMENTO DI MECCANICA, MATEMATICA E MANAGEMENT, POLITECNICO DI BAI, VIA E OABONA, 715 BAI, ITALY DPTO ANÁLISIS MATEMÁTICO, GANADA, 1871 SPAIN adde: apomponio@polibait, dauiz@uge
arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 9 Jun 2013
![arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 9 Jun 2013 arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 9 Jun 2013](/thumbs/86/93353853.jpg) A VARIATIONAL ANALYSIS OF A GAUGED NONLINEAR SCHRÖDINGER EQUATION ALESSIO POMPONIO 1 AND DAVID RUIZ axiv:136.51v1 [math.ap] 9 Jun 13 ABSTRACT. This pape is motivated by a gauged Schödinge equation in dimension
A VARIATIONAL ANALYSIS OF A GAUGED NONLINEAR SCHRÖDINGER EQUATION ALESSIO POMPONIO 1 AND DAVID RUIZ axiv:136.51v1 [math.ap] 9 Jun 13 ABSTRACT. This pape is motivated by a gauged Schödinge equation in dimension
Gravity. David Barwacz 7778 Thornapple Bayou SE, Grand Rapids, MI David Barwacz 12/03/2003
 avity David Bawacz 7778 Thonapple Bayou, and Rapid, MI 495 David Bawacz /3/3 http://membe.titon.net/daveb Uing the concept dicued in the peceding pape ( http://membe.titon.net/daveb ), I will now deive
avity David Bawacz 7778 Thonapple Bayou, and Rapid, MI 495 David Bawacz /3/3 http://membe.titon.net/daveb Uing the concept dicued in the peceding pape ( http://membe.titon.net/daveb ), I will now deive
Fall 2004/05 Solutions to Assignment 5: The Stationary Phase Method Provided by Mustafa Sabri Kilic. I(x) = e ixt e it5 /5 dt (1) Z J(λ) =
 8.35 Fall 24/5 Solution to Aignment 5: The Stationay Phae Method Povided by Mutafa Sabi Kilic. Find the leading tem fo each of the integal below fo λ >>. (a) R eiλt3 dt (b) R e iλt2 dt (c) R eiλ co t dt
8.35 Fall 24/5 Solution to Aignment 5: The Stationay Phae Method Povided by Mutafa Sabi Kilic. Find the leading tem fo each of the integal below fo λ >>. (a) R eiλt3 dt (b) R e iλt2 dt (c) R eiλ co t dt
ON A SINGULAR PERTURBED PROBLEM IN AN ANNULUS
 ON A SINGULAR PERTURBE PROBLEM IN AN ANNULUS SANJIBAN SANTRA AN JUNCHENG WEI Abtact. In thi pape, we extend the eult obtained by Ruf Sikanth 8. We pove the exitence of poitive olution unde iichlet and
ON A SINGULAR PERTURBE PROBLEM IN AN ANNULUS SANJIBAN SANTRA AN JUNCHENG WEI Abtact. In thi pape, we extend the eult obtained by Ruf Sikanth 8. We pove the exitence of poitive olution unde iichlet and
Inference for A One Way Factorial Experiment. By Ed Stanek and Elaine Puleo
 Infeence fo A One Way Factoial Expeiment By Ed Stanek and Elaine Puleo. Intoduction We develop etimating equation fo Facto Level mean in a completely andomized one way factoial expeiment. Thi development
Infeence fo A One Way Factoial Expeiment By Ed Stanek and Elaine Puleo. Intoduction We develop etimating equation fo Facto Level mean in a completely andomized one way factoial expeiment. Thi development
Estimation and Confidence Intervals: Additional Topics
 Chapte 8 Etimation and Confidence Inteval: Additional Topic Thi chapte imply follow the method in Chapte 7 fo foming confidence inteval The text i a bit dioganized hee o hopefully we can implify Etimation:
Chapte 8 Etimation and Confidence Inteval: Additional Topic Thi chapte imply follow the method in Chapte 7 fo foming confidence inteval The text i a bit dioganized hee o hopefully we can implify Etimation:
arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 7 Nov 2018
![arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 7 Nov 2018 arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 7 Nov 2018](/thumbs/90/101586781.jpg) INTERMEDIATE HANKEL OPERATORS ON THE FOCK SPACE OLIVIA CONSTANTIN axiv:181103137v1 [mathcv] 7 Nov 2018 Abtact We contuct a natual equence of middle Hankel opeato on the Fock pace, ie opeato which ae intemediate
INTERMEDIATE HANKEL OPERATORS ON THE FOCK SPACE OLIVIA CONSTANTIN axiv:181103137v1 [mathcv] 7 Nov 2018 Abtact We contuct a natual equence of middle Hankel opeato on the Fock pace, ie opeato which ae intemediate
On the quadratic support of strongly convex functions
 Int. J. Nonlinea Anal. Appl. 7 2016 No. 1, 15-20 ISSN: 2008-6822 electonic http://dx.doi.og/10.22075/ijnaa.2015.273 On the quadatic uppot of tongly convex function S. Abbazadeh a,b,, M. Ehaghi Godji a
Int. J. Nonlinea Anal. Appl. 7 2016 No. 1, 15-20 ISSN: 2008-6822 electonic http://dx.doi.og/10.22075/ijnaa.2015.273 On the quadatic uppot of tongly convex function S. Abbazadeh a,b,, M. Ehaghi Godji a
Chapter 19 Webassign Help Problems
 Chapte 9 Webaign Help Poblem 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Poblem 4: The pictue fo thi poblem i a bit mileading. They eally jut give you the pictue fo Pat b. So let fix that. Hee i the pictue fo Pat (a): Pat (a) imply
Chapte 9 Webaign Help Poblem 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Poblem 4: The pictue fo thi poblem i a bit mileading. They eally jut give you the pictue fo Pat b. So let fix that. Hee i the pictue fo Pat (a): Pat (a) imply
ASTR 3740 Relativity & Cosmology Spring Answers to Problem Set 4.
 ASTR 3740 Relativity & Comology Sping 019. Anwe to Poblem Set 4. 1. Tajectoie of paticle in the Schwazchild geomety The equation of motion fo a maive paticle feely falling in the Schwazchild geomety ae
ASTR 3740 Relativity & Comology Sping 019. Anwe to Poblem Set 4. 1. Tajectoie of paticle in the Schwazchild geomety The equation of motion fo a maive paticle feely falling in the Schwazchild geomety ae
Dynamic Systems and Applications 26 (2017) xx-xx. GRADIENT NONLINEAR ELLIPTIC SYSTEMS DRIVEN BY A (p, q)-laplacian OPERATOR
 Dynamic Sytem and Application 26 207 xx-xx GRADIENT NONLINEAR ELLIPTIC SYSTEMS DRIVEN BY A p, -LAPLACIAN OPERATOR DIEGO AVERNA a, GABRIELE BONANNO b, AND ELISABETTA TORNATORE c a Dipatimento di Matematica
Dynamic Sytem and Application 26 207 xx-xx GRADIENT NONLINEAR ELLIPTIC SYSTEMS DRIVEN BY A p, -LAPLACIAN OPERATOR DIEGO AVERNA a, GABRIELE BONANNO b, AND ELISABETTA TORNATORE c a Dipatimento di Matematica
Math 124B February 02, 2012
 Math 24B Febuay 02, 202 Vikto Gigoyan 8 Laplace s equation: popeties We have aleady encounteed Laplace s equation in the context of stationay heat conduction and wave phenomena. Recall that in two spatial
Math 24B Febuay 02, 202 Vikto Gigoyan 8 Laplace s equation: popeties We have aleady encounteed Laplace s equation in the context of stationay heat conduction and wave phenomena. Recall that in two spatial
Several new identities involving Euler and Bernoulli polynomials
 Bull. Math. Soc. Sci. Math. Roumanie Tome 9107 No. 1, 016, 101 108 Seveal new identitie involving Eule and Benoulli polynomial by Wang Xiaoying and Zhang Wenpeng Abtact The main pupoe of thi pape i uing
Bull. Math. Soc. Sci. Math. Roumanie Tome 9107 No. 1, 016, 101 108 Seveal new identitie involving Eule and Benoulli polynomial by Wang Xiaoying and Zhang Wenpeng Abtact The main pupoe of thi pape i uing
Theorem 2: Proof: Note 1: Proof: Note 2:
 A New 3-Dimenional Polynomial Intepolation Method: An Algoithmic Appoach Amitava Chattejee* and Rupak Bhattachayya** A new 3-dimenional intepolation method i intoduced in thi pape. Coeponding to the method
A New 3-Dimenional Polynomial Intepolation Method: An Algoithmic Appoach Amitava Chattejee* and Rupak Bhattachayya** A new 3-dimenional intepolation method i intoduced in thi pape. Coeponding to the method
Then the number of elements of S of weight n is exactly the number of compositions of n into k parts.
 Geneating Function In a geneal combinatoial poblem, we have a univee S of object, and we want to count the numbe of object with a cetain popety. Fo example, if S i the et of all gaph, we might want to
Geneating Function In a geneal combinatoial poblem, we have a univee S of object, and we want to count the numbe of object with a cetain popety. Fo example, if S i the et of all gaph, we might want to
A THREE CRITICAL POINTS THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS TO THE ORDINARY DIRICHLET PROBLEM
 A THREE CRITICAL POINTS THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS TO THE ORDINARY DIRICHLET PROBLEM DIEGO AVERNA AND GABRIELE BONANNO Abstact. The aim of this pape is twofold. On one hand we establish a thee citical
A THREE CRITICAL POINTS THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS TO THE ORDINARY DIRICHLET PROBLEM DIEGO AVERNA AND GABRIELE BONANNO Abstact. The aim of this pape is twofold. On one hand we establish a thee citical
RADIAL POSITIVE SOLUTIONS FOR A NONPOSITONE PROBLEM IN AN ANNULUS
 Electonic Jounal of Diffeential Equations, Vol. 04 (04), o. 9, pp. 0. ISS: 07-669. UL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu o http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu ADIAL POSITIVE SOLUTIOS FO A OPOSITOE
Electonic Jounal of Diffeential Equations, Vol. 04 (04), o. 9, pp. 0. ISS: 07-669. UL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu o http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu ADIAL POSITIVE SOLUTIOS FO A OPOSITOE
SOME SOLVABILITY THEOREMS FOR NONLINEAR EQUATIONS
 Fixed Point Theoy, Volume 5, No. 1, 2004, 71-80 http://www.math.ubbcluj.o/ nodeacj/sfptcj.htm SOME SOLVABILITY THEOREMS FOR NONLINEAR EQUATIONS G. ISAC 1 AND C. AVRAMESCU 2 1 Depatment of Mathematics Royal
Fixed Point Theoy, Volume 5, No. 1, 2004, 71-80 http://www.math.ubbcluj.o/ nodeacj/sfptcj.htm SOME SOLVABILITY THEOREMS FOR NONLINEAR EQUATIONS G. ISAC 1 AND C. AVRAMESCU 2 1 Depatment of Mathematics Royal
Precision Spectrophotometry
 Peciion Spectophotomety Pupoe The pinciple of peciion pectophotomety ae illutated in thi expeiment by the detemination of chomium (III). ppaatu Spectophotomete (B&L Spec 20 D) Cuvette (minimum 2) Pipet:
Peciion Spectophotomety Pupoe The pinciple of peciion pectophotomety ae illutated in thi expeiment by the detemination of chomium (III). ppaatu Spectophotomete (B&L Spec 20 D) Cuvette (minimum 2) Pipet:
A Variational Analysis of a Gauged Nonlinear Schrödinger Equation
 A Variational Analysis of a Gauged Nonlinear Schrödinger Equation Alessio Pomponio, joint work with David Ruiz Dipartimento di Meccanica, Matematica e Management, Politecnico di Bari Variational and Topological
A Variational Analysis of a Gauged Nonlinear Schrödinger Equation Alessio Pomponio, joint work with David Ruiz Dipartimento di Meccanica, Matematica e Management, Politecnico di Bari Variational and Topological
22.615, MHD Theory of Fusion Systems Prof. Freidberg Lecture 18
 .65, MHD Theoy of Fuion Sytem Pof. Feidbeg Lectue 8. Deive δw fo geneal cew pinch. Deive Suydam citeion Scew Pinch Equilibia μ p + + ( ) = μ J = μ J= Stability ( ) m k ξ=ξ e ι +ι ξ=ξ e +ξ e +ξ e =ξ +ξ
.65, MHD Theoy of Fuion Sytem Pof. Feidbeg Lectue 8. Deive δw fo geneal cew pinch. Deive Suydam citeion Scew Pinch Equilibia μ p + + ( ) = μ J = μ J= Stability ( ) m k ξ=ξ e ι +ι ξ=ξ e +ξ e +ξ e =ξ +ξ
Determining the Best Linear Unbiased Predictor of PSU Means with the Data. included with the Random Variables. Ed Stanek
 Detemining te Bet Linea Unbiaed Pedicto of PSU ean wit te Data included wit te andom Vaiable Ed Stanek Intoduction We develop te equation fo te bet linea unbiaed pedicto of PSU mean in a two tage andom
Detemining te Bet Linea Unbiaed Pedicto of PSU ean wit te Data included wit te andom Vaiable Ed Stanek Intoduction We develop te equation fo te bet linea unbiaed pedicto of PSU mean in a two tage andom
Approximately intertwining mappings
 J. Math. Anal. Appl. 332 (2007) 171 178 www.elevie.com/locate/jmaa Appoximately intetwining mapping Mohammad Sal Molehian a,b,1 a Depatment of Mathematic, Fedowi Univeity, PO Box 1159, Mahhad 91775, Ian
J. Math. Anal. Appl. 332 (2007) 171 178 www.elevie.com/locate/jmaa Appoximately intetwining mapping Mohammad Sal Molehian a,b,1 a Depatment of Mathematic, Fedowi Univeity, PO Box 1159, Mahhad 91775, Ian
arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 28 May 2013
![arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 28 May 2013 arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 28 May 2013](/thumbs/86/94949337.jpg) Rotationally ymmetic p-hamonic flow fom D 2 to S 2 : local well-poedne and finite time blow-up axiv:35.6552v [math.ap] 28 May 23 Razvan Gabiel Iaga, Salvado Moll, Abtact We tudy the p-hamonic flow fom
Rotationally ymmetic p-hamonic flow fom D 2 to S 2 : local well-poedne and finite time blow-up axiv:35.6552v [math.ap] 28 May 23 Razvan Gabiel Iaga, Salvado Moll, Abtact We tudy the p-hamonic flow fom
FI 2201 Electromagnetism
 FI Electomagnetim Aleande A. Ikanda, Ph.D. Phyic of Magnetim and Photonic Reeach Goup ecto Analyi CURILINEAR COORDINAES, DIRAC DELA FUNCION AND HEORY OF ECOR FIELDS Cuvilinea Coodinate Sytem Cateian coodinate:
FI Electomagnetim Aleande A. Ikanda, Ph.D. Phyic of Magnetim and Photonic Reeach Goup ecto Analyi CURILINEAR COORDINAES, DIRAC DELA FUNCION AND HEORY OF ECOR FIELDS Cuvilinea Coodinate Sytem Cateian coodinate:
ON INDEPENDENT SETS IN PURELY ATOMIC PROBABILITY SPACES WITH GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION. 1. Introduction. 1 r r. r k for every set E A, E \ {0},
 ON INDEPENDENT SETS IN PURELY ATOMIC PROBABILITY SPACES WITH GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION E. J. IONASCU and A. A. STANCU Abstact. We ae inteested in constucting concete independent events in puely atomic pobability
ON INDEPENDENT SETS IN PURELY ATOMIC PROBABILITY SPACES WITH GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION E. J. IONASCU and A. A. STANCU Abstact. We ae inteested in constucting concete independent events in puely atomic pobability
New problems in universal algebraic geometry illustrated by boolean equations
 New poblems in univesal algebaic geomety illustated by boolean equations axiv:1611.00152v2 [math.ra] 25 Nov 2016 Atem N. Shevlyakov Novembe 28, 2016 Abstact We discuss new poblems in univesal algebaic
New poblems in univesal algebaic geomety illustated by boolean equations axiv:1611.00152v2 [math.ra] 25 Nov 2016 Atem N. Shevlyakov Novembe 28, 2016 Abstact We discuss new poblems in univesal algebaic
 This aticle was oiginally published in a jounal published by Elsevie, the attached copy is povided by Elsevie fo the autho s benefit fo the benefit of the autho s institution, fo non-commecial eseach educational
This aticle was oiginally published in a jounal published by Elsevie, the attached copy is povided by Elsevie fo the autho s benefit fo the benefit of the autho s institution, fo non-commecial eseach educational
Noether Theorem, Noether Charge and All That
 Noethe Theoem, Noethe Chage and All That Ceated fo PF by Samalkhaiat 10 Tanfomation Let G be a Lie goup whoe action on Minkowki pace-time fomally ealized by coodinate tanfomation ( ) ( 1,3,η) M i Infiniteimally,
Noethe Theoem, Noethe Chage and All That Ceated fo PF by Samalkhaiat 10 Tanfomation Let G be a Lie goup whoe action on Minkowki pace-time fomally ealized by coodinate tanfomation ( ) ( 1,3,η) M i Infiniteimally,
SIMPLE LOW-ORDER AND INTEGRAL-ACTION CONTROLLER SYNTHESIS FOR MIMO SYSTEMS WITH TIME DELAYS
 Appl. Comput. Math., V.10, N.2, 2011, pp.242-249 SIMPLE LOW-ORDER AND INTEGRAL-ACTION CONTROLLER SYNTHESIS FOR MIMO SYSTEMS WITH TIME DELAYS A.N. GÜNDEŞ1, A.N. METE 2 Abtact. A imple finite-dimenional
Appl. Comput. Math., V.10, N.2, 2011, pp.242-249 SIMPLE LOW-ORDER AND INTEGRAL-ACTION CONTROLLER SYNTHESIS FOR MIMO SYSTEMS WITH TIME DELAYS A.N. GÜNDEŞ1, A.N. METE 2 Abtact. A imple finite-dimenional
Rotational Kinetic Energy
 Add Impotant Rotational Kinetic Enegy Page: 353 NGSS Standad: N/A Rotational Kinetic Enegy MA Cuiculum Famewok (006):.1,.,.3 AP Phyic 1 Leaning Objective: N/A, but olling poblem have appeaed on peviou
Add Impotant Rotational Kinetic Enegy Page: 353 NGSS Standad: N/A Rotational Kinetic Enegy MA Cuiculum Famewok (006):.1,.,.3 AP Phyic 1 Leaning Objective: N/A, but olling poblem have appeaed on peviou
GROWTH ESTIMATES THROUGH SCALING FOR QUASILINEAR PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 Annales Academiæ Scientiaum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 32, 2007, 595 599 GROWTH ESTIMATES THROUGH SCALING FOR QUASILINEAR PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Teo Kilpeläinen, Henik Shahgholian and Xiao Zhong
Annales Academiæ Scientiaum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 32, 2007, 595 599 GROWTH ESTIMATES THROUGH SCALING FOR QUASILINEAR PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Teo Kilpeläinen, Henik Shahgholian and Xiao Zhong
On the undulatory theory of positive and negative electrons
 Su la théoie ondulatoie de électon poitif and negatif J. Phy. et le Rad. 7 (1936) 347-353. On the undulatoy theoy of poitive and negative electon By AL. PROCA Intitut Heni Poincaé Pai Tanlated by D. H.
Su la théoie ondulatoie de électon poitif and negatif J. Phy. et le Rad. 7 (1936) 347-353. On the undulatoy theoy of poitive and negative electon By AL. PROCA Intitut Heni Poincaé Pai Tanlated by D. H.
On Locally Convex Topological Vector Space Valued Null Function Space c 0 (S,T, Φ, ξ, u) Defined by Semi Norm and Orlicz Function
 Jounal of Intitute of Science and Technology, 204, 9(): 62-68, Intitute of Science and Technology, T.U. On Locally Convex Topological Vecto Space Valued Null Function Space c 0 (S,T, Φ, ξ, u) Defined by
Jounal of Intitute of Science and Technology, 204, 9(): 62-68, Intitute of Science and Technology, T.U. On Locally Convex Topological Vecto Space Valued Null Function Space c 0 (S,T, Φ, ξ, u) Defined by
Solutions Practice Test PHYS 211 Exam 2
 Solution Pactice Tet PHYS 11 Exam 1A We can plit thi poblem up into two pat, each one dealing with a epaate axi. Fo both the x- and y- axe, we have two foce (one given, one unknown) and we get the following
Solution Pactice Tet PHYS 11 Exam 1A We can plit thi poblem up into two pat, each one dealing with a epaate axi. Fo both the x- and y- axe, we have two foce (one given, one unknown) and we get the following
arxiv: v1 [math.na] 8 Feb 2013
![arxiv: v1 [math.na] 8 Feb 2013 arxiv: v1 [math.na] 8 Feb 2013](/thumbs/96/127989960.jpg) A mixed method fo Diichlet poblems with adial basis functions axiv:1302.2079v1 [math.na] 8 Feb 2013 Nobet Heue Thanh Tan Abstact We pesent a simple discetization by adial basis functions fo the Poisson
A mixed method fo Diichlet poblems with adial basis functions axiv:1302.2079v1 [math.na] 8 Feb 2013 Nobet Heue Thanh Tan Abstact We pesent a simple discetization by adial basis functions fo the Poisson
Second Order Fuzzy S-Hausdorff Spaces
 Inten J Fuzzy Mathematical Achive Vol 1, 013, 41-48 ISSN: 30-34 (P), 30-350 (online) Publihed on 9 Febuay 013 wwweeachmathciog Intenational Jounal o Second Ode Fuzzy S-Haudo Space AKalaichelvi Depatment
Inten J Fuzzy Mathematical Achive Vol 1, 013, 41-48 ISSN: 30-34 (P), 30-350 (online) Publihed on 9 Febuay 013 wwweeachmathciog Intenational Jounal o Second Ode Fuzzy S-Haudo Space AKalaichelvi Depatment
PROBLEM SET #1 SOLUTIONS by Robert A. DiStasio Jr.
 POBLM S # SOLUIONS by obet A. DiStasio J. Q. he Bon-Oppenheime appoximation is the standad way of appoximating the gound state of a molecula system. Wite down the conditions that detemine the tonic and
POBLM S # SOLUIONS by obet A. DiStasio J. Q. he Bon-Oppenheime appoximation is the standad way of appoximating the gound state of a molecula system. Wite down the conditions that detemine the tonic and
< 1. max x B(0,1) f. ν ds(y) Use Poisson s formula for the ball to prove. (r x ) x y n ds(y) (x B0 (0, r)). 1 nα(n)r n 1
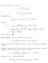 7 On the othe hand, u x solves { u n in U u on U, so which implies that x G(x, y) x n ng(x, y) < n (x B(, )). Theefoe u(x) fo all x B(, ). G ν ds(y) + max g G x ν ds(y) + C( max g + max f ) f(y)g(x, y)
7 On the othe hand, u x solves { u n in U u on U, so which implies that x G(x, y) x n ng(x, y) < n (x B(, )). Theefoe u(x) fo all x B(, ). G ν ds(y) + max g G x ν ds(y) + C( max g + max f ) f(y)g(x, y)
15 Solving the Laplace equation by Fourier method
 5 Solving the Laplace equation by Fouie method I aleady intoduced two o thee dimensional heat equation, when I deived it, ecall that it taes the fom u t = α 2 u + F, (5.) whee u: [0, ) D R, D R is the
5 Solving the Laplace equation by Fouie method I aleady intoduced two o thee dimensional heat equation, when I deived it, ecall that it taes the fom u t = α 2 u + F, (5.) whee u: [0, ) D R, D R is the
Estimates on Invariant Tori near an Elliptic Equilibrium Point of a Hamiltonian System
 jounal of diffeential equation 131, 277303 (1996) aticle no. 0165 Etimate on Invaiant Toi nea an Elliptic Equilibium Point of a Hamiltonian Sytem Amadeu Delham* Depatament de Matema tica Aplicada I, Univeitat
jounal of diffeential equation 131, 277303 (1996) aticle no. 0165 Etimate on Invaiant Toi nea an Elliptic Equilibium Point of a Hamiltonian Sytem Amadeu Delham* Depatament de Matema tica Aplicada I, Univeitat
Section 25 Describing Rotational Motion
 Section 25 Decibing Rotational Motion What do object do and wh do the do it? We have a ve thoough eplanation in tem of kinematic, foce, eneg and momentum. Thi include Newton thee law of motion and two
Section 25 Decibing Rotational Motion What do object do and wh do the do it? We have a ve thoough eplanation in tem of kinematic, foce, eneg and momentum. Thi include Newton thee law of motion and two
Syntactical content of nite approximations of partial algebras 1 Wiktor Bartol Inst. Matematyki, Uniw. Warszawski, Warszawa (Poland)
 Syntactical content of nite appoximations of patial algebas 1 Wikto Batol Inst. Matematyki, Uniw. Waszawski, 02-097 Waszawa (Poland) batol@mimuw.edu.pl Xavie Caicedo Dep. Matematicas, Univ. de los Andes,
Syntactical content of nite appoximations of patial algebas 1 Wikto Batol Inst. Matematyki, Uniw. Waszawski, 02-097 Waszawa (Poland) batol@mimuw.edu.pl Xavie Caicedo Dep. Matematicas, Univ. de los Andes,
Brief summary of functional analysis APPM 5440 Fall 2014 Applied Analysis
 Bief summay of functional analysis APPM 5440 Fall 014 Applied Analysis Stephen Becke, stephen.becke@coloado.edu Standad theoems. When necessay, I used Royden s and Keyzsig s books as a efeence. Vesion
Bief summay of functional analysis APPM 5440 Fall 014 Applied Analysis Stephen Becke, stephen.becke@coloado.edu Standad theoems. When necessay, I used Royden s and Keyzsig s books as a efeence. Vesion
Numerical approximation to ζ(2n+1)
 Illinois Wesleyan Univesity Fom the SelectedWoks of Tian-Xiao He 6 Numeical appoximation to ζ(n+1) Tian-Xiao He, Illinois Wesleyan Univesity Michael J. Dancs Available at: https://woks.bepess.com/tian_xiao_he/6/
Illinois Wesleyan Univesity Fom the SelectedWoks of Tian-Xiao He 6 Numeical appoximation to ζ(n+1) Tian-Xiao He, Illinois Wesleyan Univesity Michael J. Dancs Available at: https://woks.bepess.com/tian_xiao_he/6/
Two-Body Problem with Varying Mass in Case. of Isotropic Mass Loss
 Adv Theo Appl Mech Vol no 69-8 Two-Body Poblem with Vaying Ma in Cae of Iotopic Ma o W A Rahoma M K Ahmed and I A El-Tohamy Caio Univeity Faculty of Science Dept of Atonomy Caio 6 Egypt FA Abd El-Salam
Adv Theo Appl Mech Vol no 69-8 Two-Body Poblem with Vaying Ma in Cae of Iotopic Ma o W A Rahoma M K Ahmed and I A El-Tohamy Caio Univeity Faculty of Science Dept of Atonomy Caio 6 Egypt FA Abd El-Salam
Simulation of Spatially Correlated Large-Scale Parameters and Obtaining Model Parameters from Measurements
 Simulation of Spatially Coelated Lage-Scale Paamete and Obtaining Model Paamete fom PER ZETTERBERG Stockholm Septembe 8 TRITA EE 8:49 Simulation of Spatially Coelated Lage-Scale Paamete and Obtaining Model
Simulation of Spatially Coelated Lage-Scale Paamete and Obtaining Model Paamete fom PER ZETTERBERG Stockholm Septembe 8 TRITA EE 8:49 Simulation of Spatially Coelated Lage-Scale Paamete and Obtaining Model
Exceptional regular singular points of second-order ODEs. 1. Solving second-order ODEs
 (May 14, 2011 Exceptional egula singula points of second-ode ODEs Paul Gaett gaett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ gaett/ 1. Solving second-ode ODEs 2. Examples 3. Convegence Fobenius method fo solving
(May 14, 2011 Exceptional egula singula points of second-ode ODEs Paul Gaett gaett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ gaett/ 1. Solving second-ode ODEs 2. Examples 3. Convegence Fobenius method fo solving
3. Perturbation of Kerr BH
 3. Petubation of Ke BH hoizon at Δ = 0 ( = ± ) Unfotunately, it i technically fomidable to deal with the metic petubation of Ke BH becaue of coupling between and θ Nevethele, thee exit a fomalim (Newman-Penoe
3. Petubation of Ke BH hoizon at Δ = 0 ( = ± ) Unfotunately, it i technically fomidable to deal with the metic petubation of Ke BH becaue of coupling between and θ Nevethele, thee exit a fomalim (Newman-Penoe
Solution to HW 3, Ma 1a Fall 2016
 Solution to HW 3, Ma a Fall 206 Section 2. Execise 2: Let C be a subset of the eal numbes consisting of those eal numbes x having the popety that evey digit in the decimal expansion of x is, 3, 5, o 7.
Solution to HW 3, Ma a Fall 206 Section 2. Execise 2: Let C be a subset of the eal numbes consisting of those eal numbes x having the popety that evey digit in the decimal expansion of x is, 3, 5, o 7.
3.1 Random variables
 3 Chapte III Random Vaiables 3 Random vaiables A sample space S may be difficult to descibe if the elements of S ae not numbes discuss how we can use a ule by which an element s of S may be associated
3 Chapte III Random Vaiables 3 Random vaiables A sample space S may be difficult to descibe if the elements of S ae not numbes discuss how we can use a ule by which an element s of S may be associated
ψ - exponential type orbitals, Frictional
 ew develoment in theoy of Laguee olynomial I. I. Gueinov Deatment of Phyic, Faculty of At and Science, Onekiz Mat Univeity, Çanakkale, Tukey Abtact The new comlete othonomal et of L -Laguee tye olynomial
ew develoment in theoy of Laguee olynomial I. I. Gueinov Deatment of Phyic, Faculty of At and Science, Onekiz Mat Univeity, Çanakkale, Tukey Abtact The new comlete othonomal et of L -Laguee tye olynomial
Lecture 28: Convergence of Random Variables and Related Theorems
 EE50: Pobability Foundations fo Electical Enginees July-Novembe 205 Lectue 28: Convegence of Random Vaiables and Related Theoems Lectue:. Kishna Jagannathan Scibe: Gopal, Sudhasan, Ajay, Swamy, Kolla An
EE50: Pobability Foundations fo Electical Enginees July-Novembe 205 Lectue 28: Convegence of Random Vaiables and Related Theoems Lectue:. Kishna Jagannathan Scibe: Gopal, Sudhasan, Ajay, Swamy, Kolla An
Measure Estimates of Nodal Sets of Polyharmonic Functions
 Chin. Ann. Math. Se. B 39(5), 08, 97 93 DOI: 0.007/s40-08-004-6 Chinese Annals of Mathematics, Seies B c The Editoial Office of CAM and Spinge-Velag Belin Heidelbeg 08 Measue Estimates of Nodal Sets of
Chin. Ann. Math. Se. B 39(5), 08, 97 93 DOI: 0.007/s40-08-004-6 Chinese Annals of Mathematics, Seies B c The Editoial Office of CAM and Spinge-Velag Belin Heidelbeg 08 Measue Estimates of Nodal Sets of
Quantum Mechanics II
 Quantum Mechanics II Pof. Bois Altshule Apil 25, 2 Lectue 25 We have been dicussing the analytic popeties of the S-matix element. Remembe the adial wave function was u kl () = R kl () e ik iπl/2 S l (k)e
Quantum Mechanics II Pof. Bois Altshule Apil 25, 2 Lectue 25 We have been dicussing the analytic popeties of the S-matix element. Remembe the adial wave function was u kl () = R kl () e ik iπl/2 S l (k)e
On the integration of the equations of hydrodynamics
 Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
Symmetry of Lagrangians of holonomic systems in terms of quasi-coordinates
 Vol 18 No 8, Augut 009 c 009 Chin. Phy. Soc. 1674-1056/009/1808/3145-05 Chinee Phyic B an IOP Publihing Lt Symmety of Lagangian of holonomic ytem in tem of quai-cooinate Wu Hui-Bin an Mei Feng-Xiang School
Vol 18 No 8, Augut 009 c 009 Chin. Phy. Soc. 1674-1056/009/1808/3145-05 Chinee Phyic B an IOP Publihing Lt Symmety of Lagangian of holonomic ytem in tem of quai-cooinate Wu Hui-Bin an Mei Feng-Xiang School
AE 423 Space Technology I Chapter 2 Satellite Dynamics
 AE 43 Space Technology I Chapte Satellite Dynamic.1 Intoduction In thi chapte we eview ome dynamic elevant to atellite dynamic and we etablih ome of the baic popetie of atellite dynamic.. Dynamic of a
AE 43 Space Technology I Chapte Satellite Dynamic.1 Intoduction In thi chapte we eview ome dynamic elevant to atellite dynamic and we etablih ome of the baic popetie of atellite dynamic.. Dynamic of a
On Chern-Simons-Schrödinger equations including a vortex point
 On Chern-Simons-Schrödinger equations including a vortex point Alessio Pomponio Dipartimento di Meccanica, Matematica e Management, Politecnico di Bari Workshop in Nonlinear PDEs Brussels, September 7
On Chern-Simons-Schrödinger equations including a vortex point Alessio Pomponio Dipartimento di Meccanica, Matematica e Management, Politecnico di Bari Workshop in Nonlinear PDEs Brussels, September 7
(U) vanishes. A special case of system (1.1), (1.2) is given by the equations for compressible flow in a variable area duct, a ρv2,
 MEHODS AND APPLICAIONS OF ANALYSIS. c 2003 Intenational Pe Vol. 10, No. 2, pp. 279 294, June 2003 007 HE GENERIC SOLUION OF HE RIEMANN PROBLEM IN A NEIGHBORHOOD OF A POIN OF RESONANCE FOR SYSEMS OF NONLINEAR
MEHODS AND APPLICAIONS OF ANALYSIS. c 2003 Intenational Pe Vol. 10, No. 2, pp. 279 294, June 2003 007 HE GENERIC SOLUION OF HE RIEMANN PROBLEM IN A NEIGHBORHOOD OF A POIN OF RESONANCE FOR SYSEMS OF NONLINEAR
A note on rescalings of the skew-normal distribution
 Poyeccione Jounal of Mathematic Vol. 31, N o 3, pp. 197-07, Septembe 01. Univeidad Católica del Note Antofagata - Chile A note on ecaling of the kew-nomal ditibution OSVALDO VENEGAS Univeidad Católica
Poyeccione Jounal of Mathematic Vol. 31, N o 3, pp. 197-07, Septembe 01. Univeidad Católica del Note Antofagata - Chile A note on ecaling of the kew-nomal ditibution OSVALDO VENEGAS Univeidad Católica
Regularity for Fully Nonlinear Elliptic Equations with Neumann Boundary Data
 Communications in Patial Diffeential Equations, 31: 1227 1252, 2006 Copyight Taylo & Fancis Goup, LLC ISSN 0360-5302 pint/1532-4133 online DOI: 10.1080/03605300600634999 Regulaity fo Fully Nonlinea Elliptic
Communications in Patial Diffeential Equations, 31: 1227 1252, 2006 Copyight Taylo & Fancis Goup, LLC ISSN 0360-5302 pint/1532-4133 online DOI: 10.1080/03605300600634999 Regulaity fo Fully Nonlinea Elliptic
QUADRATIC DEPENDENCE MEASURE FOR NONLINEAR BLIND SOURCES SEPARATION
 QUADRATI DPNDN MASUR FR NNLINAR BLIND SURS SPARATIN Sophie Achad Dinh Tuan Pham Univ. of Genoble Laboatoy of Modeling and omputation IMAG.N.R.S. B.P. 5X 84 Genoble edex Fance Sophie.Achad@imag.f Dinh-Tuan.Pham@imag.f
QUADRATI DPNDN MASUR FR NNLINAR BLIND SURS SPARATIN Sophie Achad Dinh Tuan Pham Univ. of Genoble Laboatoy of Modeling and omputation IMAG.N.R.S. B.P. 5X 84 Genoble edex Fance Sophie.Achad@imag.f Dinh-Tuan.Pham@imag.f
d 2 x 0a d d =0. Relative to an arbitrary (accelerating frame) specified by x a = x a (x 0b ), the latter becomes: d 2 x a d 2 + a dx b dx c
 Chapte 6 Geneal Relativity 6.1 Towads the Einstein equations Thee ae seveal ways of motivating the Einstein equations. The most natual is pehaps though consideations involving the Equivalence Pinciple.
Chapte 6 Geneal Relativity 6.1 Towads the Einstein equations Thee ae seveal ways of motivating the Einstein equations. The most natual is pehaps though consideations involving the Equivalence Pinciple.
Boise State University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE470 Electric Machines
 Boie State Univeity Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing ECE470 Electic Machine Deivation of the Pe-Phae Steady-State Equivalent Cicuit of a hee-phae Induction Machine Nomenclatue θ: oto haft
Boie State Univeity Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing ECE470 Electic Machine Deivation of the Pe-Phae Steady-State Equivalent Cicuit of a hee-phae Induction Machine Nomenclatue θ: oto haft
arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 2013
![arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 2013 arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 2013](/thumbs/89/100795062.jpg) A note on the electostatic enegy of two point chages axiv:1306.0401v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 013 A C Tot Instituto de Física Univesidade Fedeal do io de Janeio Caixa Postal 68.58; CEP 1941-97 io de Janeio,
A note on the electostatic enegy of two point chages axiv:1306.0401v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 013 A C Tot Instituto de Física Univesidade Fedeal do io de Janeio Caixa Postal 68.58; CEP 1941-97 io de Janeio,
A Bijective Approach to the Permutational Power of a Priority Queue
 A Bijective Appoach to the Pemutational Powe of a Pioity Queue Ia M. Gessel Kuang-Yeh Wang Depatment of Mathematics Bandeis Univesity Waltham, MA 02254-9110 Abstact A pioity queue tansfoms an input pemutation
A Bijective Appoach to the Pemutational Powe of a Pioity Queue Ia M. Gessel Kuang-Yeh Wang Depatment of Mathematics Bandeis Univesity Waltham, MA 02254-9110 Abstact A pioity queue tansfoms an input pemutation
Classical Mechanics Homework set 7, due Nov 8th: Solutions
 Classical Mechanics Homewok set 7, due Nov 8th: Solutions 1. Do deivation 8.. It has been asked what effect does a total deivative as a function of q i, t have on the Hamiltonian. Thus, lets us begin with
Classical Mechanics Homewok set 7, due Nov 8th: Solutions 1. Do deivation 8.. It has been asked what effect does a total deivative as a function of q i, t have on the Hamiltonian. Thus, lets us begin with
KOEBE DOMAINS FOR THE CLASSES OF FUNCTIONS WITH RANGES INCLUDED IN GIVEN SETS
 Jounal of Applied Analysis Vol. 14, No. 1 2008), pp. 43 52 KOEBE DOMAINS FOR THE CLASSES OF FUNCTIONS WITH RANGES INCLUDED IN GIVEN SETS L. KOCZAN and P. ZAPRAWA Received Mach 12, 2007 and, in evised fom,
Jounal of Applied Analysis Vol. 14, No. 1 2008), pp. 43 52 KOEBE DOMAINS FOR THE CLASSES OF FUNCTIONS WITH RANGES INCLUDED IN GIVEN SETS L. KOCZAN and P. ZAPRAWA Received Mach 12, 2007 and, in evised fom,
arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 29 Sep 2017
![arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 29 Sep 2017 arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 29 Sep 2017](/thumbs/77/76346489.jpg) A duality pinciple fo the multi-block entanglement entopy of fee femion ytem J.A. Caaco 1,+, F. Finkel 1,+, A. González-López 1,+,*, and P. Tempeta 1,,+ 1 Depatamento de Fíica Teóica II, Univeidad Complutene
A duality pinciple fo the multi-block entanglement entopy of fee femion ytem J.A. Caaco 1,+, F. Finkel 1,+, A. González-López 1,+,*, and P. Tempeta 1,,+ 1 Depatamento de Fíica Teóica II, Univeidad Complutene
arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 20 Feb 2015
![arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 20 Feb 2015 arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 20 Feb 2015](/thumbs/93/113092535.jpg) STANDING WAVES FOR A GAUGED NONLINEAR SCHRÖDINGER EQUATION WITH A VORTEX POINT YONGSHENG JIANG 1, ALESSIO POMPONIO, AND DAVID RUIZ 3 axiv:15.5867v1 [math.ap] Feb 15 ABSTRACT. This pape is motivated by
STANDING WAVES FOR A GAUGED NONLINEAR SCHRÖDINGER EQUATION WITH A VORTEX POINT YONGSHENG JIANG 1, ALESSIO POMPONIO, AND DAVID RUIZ 3 axiv:15.5867v1 [math.ap] Feb 15 ABSTRACT. This pape is motivated by
MATH 220: SECOND ORDER CONSTANT COEFFICIENT PDE. We consider second order constant coefficient scalar linear PDEs on R n. These have the form
 MATH 220: SECOND ORDER CONSTANT COEFFICIENT PDE ANDRAS VASY We conside second ode constant coefficient scala linea PDEs on R n. These have the fom Lu = f L = a ij xi xj + b i xi + c i whee a ij b i and
MATH 220: SECOND ORDER CONSTANT COEFFICIENT PDE ANDRAS VASY We conside second ode constant coefficient scala linea PDEs on R n. These have the fom Lu = f L = a ij xi xj + b i xi + c i whee a ij b i and
EM Boundary Value Problems
 EM Bounday Value Poblems 10/ 9 11/ By Ilekta chistidi & Lee, Seung-Hyun A. Geneal Desciption : Maxwell Equations & Loentz Foce We want to find the equations of motion of chaged paticles. The way to do
EM Bounday Value Poblems 10/ 9 11/ By Ilekta chistidi & Lee, Seung-Hyun A. Geneal Desciption : Maxwell Equations & Loentz Foce We want to find the equations of motion of chaged paticles. The way to do
Problems with Mannheim s conformal gravity program
 Poblems with Mannheim s confomal gavity pogam June 4, 18 Youngsub Yoon axiv:135.163v6 [g-qc] 7 Jul 13 Depatment of Physics and Astonomy Seoul National Univesity, Seoul 151-747, Koea Abstact We show that
Poblems with Mannheim s confomal gavity pogam June 4, 18 Youngsub Yoon axiv:135.163v6 [g-qc] 7 Jul 13 Depatment of Physics and Astonomy Seoul National Univesity, Seoul 151-747, Koea Abstact We show that
Compactly Supported Radial Basis Functions
 Chapte 4 Compactly Suppoted Radial Basis Functions As we saw ealie, compactly suppoted functions Φ that ae tuly stictly conditionally positive definite of ode m > do not exist The compact suppot automatically
Chapte 4 Compactly Suppoted Radial Basis Functions As we saw ealie, compactly suppoted functions Φ that ae tuly stictly conditionally positive definite of ode m > do not exist The compact suppot automatically
On absence of solutions of a semi-linear elliptic equation with biharmonic operator in the exterior of a ball
 Tansactions of NAS of Azebaijan, Issue Mathematics, 36, 63-69 016. Seies of Physical-Technical and Mathematical Sciences. On absence of solutions of a semi-linea elliptic euation with bihamonic opeato
Tansactions of NAS of Azebaijan, Issue Mathematics, 36, 63-69 016. Seies of Physical-Technical and Mathematical Sciences. On absence of solutions of a semi-linea elliptic euation with bihamonic opeato
Mean Curvature and Shape Operator of Slant Immersions in a Sasakian Space Form
 Mean Cuvatue and Shape Opeato of Slant Immesions in a Sasakian Space Fom Muck Main Tipathi, Jean-Sic Kim and Son-Be Kim Abstact Fo submanifolds, in a Sasakian space fom, which ae tangential to the stuctue
Mean Cuvatue and Shape Opeato of Slant Immesions in a Sasakian Space Fom Muck Main Tipathi, Jean-Sic Kim and Son-Be Kim Abstact Fo submanifolds, in a Sasakian space fom, which ae tangential to the stuctue
Bogoliubov Transformation in Classical Mechanics
 Bogoliubov Tranformation in Claical Mechanic Canonical Tranformation Suppoe we have a et of complex canonical variable, {a j }, and would like to conider another et of variable, {b }, b b ({a j }). How
Bogoliubov Tranformation in Claical Mechanic Canonical Tranformation Suppoe we have a et of complex canonical variable, {a j }, and would like to conider another et of variable, {b }, b b ({a j }). How
Basic propositional and. The fundamentals of deduction
 Baic ooitional and edicate logic The fundamental of deduction 1 Logic and it alication Logic i the tudy of the atten of deduction Logic lay two main ole in comutation: Modeling : logical entence ae the
Baic ooitional and edicate logic The fundamental of deduction 1 Logic and it alication Logic i the tudy of the atten of deduction Logic lay two main ole in comutation: Modeling : logical entence ae the
THE CONE THEOREM JOEL A. TROPP. Abstract. We prove a fixed point theorem for functions which are positive with respect to a cone in a Banach space.
 THE ONE THEOEM JOEL A. TOPP Abstact. We pove a fixed point theoem fo functions which ae positive with espect to a cone in a Banach space. 1. Definitions Definition 1. Let X be a eal Banach space. A subset
THE ONE THEOEM JOEL A. TOPP Abstact. We pove a fixed point theoem fo functions which ae positive with espect to a cone in a Banach space. 1. Definitions Definition 1. Let X be a eal Banach space. A subset
A STABILITY RESULT FOR p-harmonic SYSTEMS WITH DISCONTINUOUS COEFFICIENTS. Bianca Stroffolini. 0. Introduction
 Electonic Jounal of Diffeential Equations, Vol. 2001(2001), No. 02, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu o http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) A STABILITY RESULT
Electonic Jounal of Diffeential Equations, Vol. 2001(2001), No. 02, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu o http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) A STABILITY RESULT
Energy Levels Of Hydrogen Atom Using Ladder Operators. Ava Khamseh Supervisor: Dr. Brian Pendleton The University of Edinburgh August 2011
 Enegy Levels Of Hydogen Atom Using Ladde Opeatos Ava Khamseh Supeviso: D. Bian Pendleton The Univesity of Edinbugh August 11 1 Abstact The aim of this pape is to fist use the Schödinge wavefunction methods
Enegy Levels Of Hydogen Atom Using Ladde Opeatos Ava Khamseh Supeviso: D. Bian Pendleton The Univesity of Edinbugh August 11 1 Abstact The aim of this pape is to fist use the Schödinge wavefunction methods
ONE-POINT CODES USING PLACES OF HIGHER DEGREE
 ONE-POINT CODES USING PLACES OF HIGHER DEGREE GRETCHEN L. MATTHEWS AND TODD W. MICHEL DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES CLEMSON UNIVERSITY CLEMSON, SC 29634-0975 U.S.A. E-MAIL: GMATTHE@CLEMSON.EDU, TMICHEL@CLEMSON.EDU
ONE-POINT CODES USING PLACES OF HIGHER DEGREE GRETCHEN L. MATTHEWS AND TODD W. MICHEL DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES CLEMSON UNIVERSITY CLEMSON, SC 29634-0975 U.S.A. E-MAIL: GMATTHE@CLEMSON.EDU, TMICHEL@CLEMSON.EDU
Geometry of the homogeneous and isotropic spaces
 Geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces H. Sonoda Septembe 2000; last evised Octobe 2009 Abstact We summaize the aspects of the geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces which ae most elevant
Geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces H. Sonoda Septembe 2000; last evised Octobe 2009 Abstact We summaize the aspects of the geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces which ae most elevant
ESSENTIAL NORM OF AN INTEGRAL-TYPE OPERATOR ON THE UNIT BALL. Juntao Du and Xiangling Zhu
 Opuscula Math. 38, no. 6 (8), 89 839 https://doi.og/.7494/opmath.8.38.6.89 Opuscula Mathematica ESSENTIAL NORM OF AN INTEGRAL-TYPE OPERATOR FROM ω-bloch SPACES TO µ-zygmund SPACES ON THE UNIT BALL Juntao
Opuscula Math. 38, no. 6 (8), 89 839 https://doi.og/.7494/opmath.8.38.6.89 Opuscula Mathematica ESSENTIAL NORM OF AN INTEGRAL-TYPE OPERATOR FROM ω-bloch SPACES TO µ-zygmund SPACES ON THE UNIT BALL Juntao
A Relativistic Electron in a Coulomb Potential
 A Relativistic Electon in a Coulomb Potential Alfed Whitehead Physics 518, Fall 009 The Poblem Solve the Diac Equation fo an electon in a Coulomb potential. Identify the conseved quantum numbes. Specify
A Relativistic Electon in a Coulomb Potential Alfed Whitehead Physics 518, Fall 009 The Poblem Solve the Diac Equation fo an electon in a Coulomb potential. Identify the conseved quantum numbes. Specify
Last time: S n xt y where T tpijq 1 i j nu.
 Lat time: Let G ü A. ( ) The obit of an element a P A i O a tg a g P Gu. ( ) The tabilize of an element a P A i G a tg P G g a au, and i a ubgoup of G. ( ) The kenel of the action i ke tg P G g a a fo
Lat time: Let G ü A. ( ) The obit of an element a P A i O a tg a g P Gu. ( ) The tabilize of an element a P A i G a tg P G g a au, and i a ubgoup of G. ( ) The kenel of the action i ke tg P G g a a fo
Shrinkage Estimation of Reliability Function for Some Lifetime Distributions
 Ameican Jounal of Computational and Applied Mathematic 4, 4(3): 9-96 DOI:.593/j.ajcam.443.4 Shinkage Etimation of eliability Function fo Some Lifetime Ditibution anjita Pandey Depatment of Statitic, niveity
Ameican Jounal of Computational and Applied Mathematic 4, 4(3): 9-96 DOI:.593/j.ajcam.443.4 Shinkage Etimation of eliability Function fo Some Lifetime Ditibution anjita Pandey Depatment of Statitic, niveity
Bifurcation Analysis for the Delay Logistic Equation with Two Delays
 IOSR Jounal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578, p-issn: 39-765X. Volume, Issue 5 Ve. IV (Sep. - Oct. 05), PP 53-58 www.iosjounals.og Bifucation Analysis fo the Delay Logistic Equation with Two Delays
IOSR Jounal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578, p-issn: 39-765X. Volume, Issue 5 Ve. IV (Sep. - Oct. 05), PP 53-58 www.iosjounals.og Bifucation Analysis fo the Delay Logistic Equation with Two Delays
Is there a magnification paradox in gravitational lensing?
 Is thee a magnification paadox in gavitational ing? Olaf Wucknitz wucknitz@asto.uni-bonn.de Astophysics semina/colloquium, Potsdam, 6 Novembe 7 Is thee a magnification paadox in gavitational ing? gavitational
Is thee a magnification paadox in gavitational ing? Olaf Wucknitz wucknitz@asto.uni-bonn.de Astophysics semina/colloquium, Potsdam, 6 Novembe 7 Is thee a magnification paadox in gavitational ing? gavitational
An analytical proof of Hardy-like inequalities related to the Dirac operator
 An analytical poof of Hady-like inequalities elated to the Diac opeato Jean Dolbeault a,1 Maia J. Esteban a,1 Michael Loss b,2 Luis Vega c,1 a CEREMADE, Univesité Pais-Dauphine, 75775 Pais Cedex 16, Fance
An analytical poof of Hady-like inequalities elated to the Diac opeato Jean Dolbeault a,1 Maia J. Esteban a,1 Michael Loss b,2 Luis Vega c,1 a CEREMADE, Univesité Pais-Dauphine, 75775 Pais Cedex 16, Fance
EKR Sets for Large n and r
 EKR Set fo Lage n and The MIT Faculty ha made thi aticle openly available. Pleae hae how thi acce benefit you. You toy matte. Citation A Publihed Publihe Bond, Benjamin. "EKR Set fo Lage n and." Gaph and
EKR Set fo Lage n and The MIT Faculty ha made thi aticle openly available. Pleae hae how thi acce benefit you. You toy matte. Citation A Publihed Publihe Bond, Benjamin. "EKR Set fo Lage n and." Gaph and
Derivations in Classical Electrodynamics
 Deivation in Claical Electodynamic Andew Foete Januay 8, 009 Content Explanation Idea 3 Integation 3. A Special Integation by Pat.................................. 3 3. Anothe Special Integation by Pat...............................
Deivation in Claical Electodynamic Andew Foete Januay 8, 009 Content Explanation Idea 3 Integation 3. A Special Integation by Pat.................................. 3 3. Anothe Special Integation by Pat...............................
Hölder Continuity for Local Minimizers of a Nonconvex Variational Problem
 Jounal of Convex Analysis Volume 10 003), No., 389 408 Hölde Continuity fo Local Minimizes of a Nonconvex Vaiational Poblem Giovanni Cupini Dipatimento di Matematica U. Dini, Univesità di Fienze, Viale
Jounal of Convex Analysis Volume 10 003), No., 389 408 Hölde Continuity fo Local Minimizes of a Nonconvex Vaiational Poblem Giovanni Cupini Dipatimento di Matematica U. Dini, Univesità di Fienze, Viale
Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics
 Jounal of Inequalities in Pue and Applied Mathematics COEFFICIENT INEQUALITY FOR A FUNCTION WHOSE DERIVATIVE HAS A POSITIVE REAL PART S. ABRAMOVICH, M. KLARIČIĆ BAKULA AND S. BANIĆ Depatment of Mathematics
Jounal of Inequalities in Pue and Applied Mathematics COEFFICIENT INEQUALITY FOR A FUNCTION WHOSE DERIVATIVE HAS A POSITIVE REAL PART S. ABRAMOVICH, M. KLARIČIĆ BAKULA AND S. BANIĆ Depatment of Mathematics
γ from B D(Kπ)K and B D(KX)K, X=3π or ππ 0
 fom and X, X= o 0 Jim Libby, Andew Powell and Guy Wilkinon Univeity of Oxfod 8th Januay 007 Gamma meeting 1 Outline The AS technique to meaue Uing o 0 : intoducing the coheence facto Meauing the coheence
fom and X, X= o 0 Jim Libby, Andew Powell and Guy Wilkinon Univeity of Oxfod 8th Januay 007 Gamma meeting 1 Outline The AS technique to meaue Uing o 0 : intoducing the coheence facto Meauing the coheence
A New Approach to General Relativity
 Apeion, Vol. 14, No. 3, July 7 7 A New Appoach to Geneal Relativity Ali Rıza Şahin Gaziosmanpaşa, Istanbul Tukey E-mail: aizasahin@gmail.com Hee we pesent a new point of view fo geneal elativity and/o
Apeion, Vol. 14, No. 3, July 7 7 A New Appoach to Geneal Relativity Ali Rıza Şahin Gaziosmanpaşa, Istanbul Tukey E-mail: aizasahin@gmail.com Hee we pesent a new point of view fo geneal elativity and/o
( ) [ ] [ ] [ ] δf φ = F φ+δφ F. xdx.
![( ) [ ] [ ] [ ] δf φ = F φ+δφ F. xdx. ( ) [ ] [ ] [ ] δf φ = F φ+δφ F. xdx.](/thumbs/90/103689049.jpg) 9. LAGRANGIAN OF THE ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD In the pevious section the Lagangian and Hamiltonian of an ensemble of point paticles was developed. This appoach is based on a qt. This discete fomulation can
9. LAGRANGIAN OF THE ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD In the pevious section the Lagangian and Hamiltonian of an ensemble of point paticles was developed. This appoach is based on a qt. This discete fomulation can
Surveillance Points in High Dimensional Spaces
 Société de Calcul Mathématique SA Tools fo decision help since 995 Suveillance Points in High Dimensional Spaces by Benad Beauzamy Januay 06 Abstact Let us conside any compute softwae, elying upon a lage
Société de Calcul Mathématique SA Tools fo decision help since 995 Suveillance Points in High Dimensional Spaces by Benad Beauzamy Januay 06 Abstact Let us conside any compute softwae, elying upon a lage
New Analysis for The FGM Thick Cylinders Under Combined Pressure and Temperature Loading
 Ameican Jounal of Applied Science 5 (7): 85-859, 008 ISSN 546-939 008 Science Publication New Analyi fo The FGM Thick Cylinde Unde Combined Peue and Tempeatue Loading K. Abinia, H. Naee, F. Sadeghi and
Ameican Jounal of Applied Science 5 (7): 85-859, 008 ISSN 546-939 008 Science Publication New Analyi fo The FGM Thick Cylinde Unde Combined Peue and Tempeatue Loading K. Abinia, H. Naee, F. Sadeghi and
