Name: Mrs. Krasniak 2014/15 Regents Chemistry
|
|
|
- Arnold McCoy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Mrs. Krasniak 2014/15 Regents Chemistry Unit 0 Math, Measurement and Lab Safety Unit 0? Yes! Before we can begin our discussion of Chemistry, we must brush up on some basic math skills that you will be using throughout the course. We also need to make sure that you can work safely and competently in the lab. Read through the objectives to see what is expected of you. Objectives: At the completion of the unit, you - will know and observe lab safety rules. will be able to make measurements of mass, length and volume to the appropriate precision based on the measurement tool. will be able to make calculations with measurements and record answers to the appropriate precision. will be able to work with very large and very small numbers utilizing scientific notation. will be able to convert a measurement in one measurement system to an equivalent measurement in a different measurement system or with different units. Chemistry Reference Tables: C, D and T Period Date Description 1 9/3/14 W Course Description and Policies Introduction to Chemistry Math Homework: Obtain course materials by Monday 9/8. Get Course Information Sheet and Safety Contract signed by Monday 9/8. Algebra Review Problems, page 16 2 Lab Laboratory Safety and Equipment Lab 3 9/4/14 Th 4 9/5/14 F Measurements in Chemistry Rules for Significant Figures Homework: Significant Figures Worksheet, pages 17 and 18 Scientific Notation and Using Scientific Notation with significant Figures. Homework: Scientific Notation Worksheet, pages 19 and 20 5 Lab Exploring the Metric System Activity 6 9/8/14 M Dimensional Analysis to convert measurements Work Due Today Laboratory Safety and Equipment Lab Homework: Dimensional Analysis Worksheet, pages 21 and /9/14 T More Dimensional Analysis Practice Got Calcium? Homework: Study for Safety, Measurement and Math Quiz 8 Lab Measurement and Unit Conversions Lab 9 9/10/14 Unit 1 The Structure of the Atom W 10 9/11/14 Th Quiz on Safety, Measurement and Chemistry Math (20 minutes) Work Due Today Measurement and Unit Conversions Lab 1 P a g e
2 2 P a g e
3 A Review of Algebra Skills Being comfortable with algebra is a requirement for success in regents chemistry. To make sure everyone is up to speed, let s review some of the important aspects: Steps to solving a word problem: 1. Read the problem. Then read it again, before writing anything down. 2. Write down all known information with units. Write down what needs to be found. 3. Write down the appropriate equation. 4. Rearrange the equation algebraically so that the variable being solved for is one side and all given information is on the other. 5. Substitute the known information into the equation with units. 6. Solve the equation. Record your answer with units and the appropriate number of significant figures. 7. CHECK your answer! The main idea of algebra is to find a number that satisfies an equation. Let's look at examples from chemistry. 1. A student measures the temperature of 20.0 ml of acetic acid and finds that it is 36.2 C. What is the temperature in Kelvin? 2. A sample of aluminum has a mass of 27.0 g. Aluminum has a density of 2.7 g/ml. What is the volume of this sample of aluminum? 3. How many moles of solute are needed to make 2.0 Liters of a 3.0 M solution? 3 P a g e
4 Direct and Inverse Relationships between Variables In nature, a change in one quantity usually leads to a change in another quantity. If second quantity undergoes the same change, this is a direct relationship. If the second quantity undergoes the opposite change, this is an inverse relationship. Example 1: Concentration of lemonade = powder water What happens to the concentration of lemonade if you add more powder, while keeping the same amount of water? What happens to the concentration if you add more water, while keeping the same amount of powder? Example 2: D = m V What happens to the value of D as m increases and V is constant? What happens to D when m decreases? What happens to the value of D as V increases and m is constant? When V decreases? Practice: spectators were at a B-Mets game. How many players were there? S = 10P 2. How many moles of solute are needed to make 5.0 Liters of a 3.0 M solution? 3. A balloon of Helium initially has a volume of 1.50 Liters at atmospheric pressure. The balloon is then placed in a hyperbaric chamber that is increased to twice atmospheric pressure. What is the new volume? P1 V1 = P2 V2 4 P a g e
5 Measurement Activity: Measurement is - Group Group Group Accuracy Precision Which set of data was most precise and why? Using the accepted values given, which set of data was the most accurate? 5 P a g e
6 How to make a Scientific Measurement 1. There is in EVERY scientific measurement. 2. The certainty of the measurement depends on the being used. 3. Every scientific measurement needs: and 4. The significant figures of a measurement include all of the known digits, plus an estimate for the last digit. 5. The accuracy of a measurement can be expressed in terms of. 6. The formula is: 6 P a g e
7 Significant Figures Rules for Significant Figures Example: 3. Example: 4. Example: Example: Exceptions: Practice: How many significant figures do each of the following measurements have? g 2.50 ml 105,210 um 15 people g 7 P a g e
8 Adding and Subtracting with Significant Figures Rule: Example: Practice: g g g g g g g g Multiplying and Dividing with Significant Figures Rule: Example: Practice: 6.25 cm x 15 cm = 7320 g 2440 ml = m x 10 m = cm cm = m x 5321 m = m m = 8 P a g e
9 Review of Scientific Notation You have already seen and possibly used scientific notation in past math and science courses. This will be a review of the very LARGE and small numbers you will encounter throughout this course. Definition: Rules for Scientific Notation: 1. A number is expressed as the product of a coefficient and 10 raised to a certain power. Example: 6.02 x 10 23, 6.02 is the coefficient. 2. The coefficient must always be greater than or equal to 1, and less than 10. The decimal point is always located between the first and second digits. The first digit should never be 0! 3. The coefficient shows all of the significant figures in a measurement. Example: 300. = 3.00x = 3x10 2 Powers of Ten: 10 x Meaning x greater than 0 Represents number greater than 1 (10, 100, 1000, etc) x less than 0 Represents a fraction (.1,.01,.001) x= 0 By definition 10 0 = 1 Practice Problems: 1. Place the following numbers into scientific notation: a b c d P a g e
10 2. Convert the following numbers from scientific notation to standard notation: a. 1.2 x b x 10-4 c x 10-3 Mathematical Operations with Scientific Notation Multiplication: Add the exponents and multiply the coefficients. Then put the answer into proper form. Example: (6.0 x 10 5 )(5.0 x ) (6.0 x 5.0)( ) 30. x x Division: Subtract the exponents and divide the coefficients. Then put the answer into proper form. Example: (2.0 x 10 5 ) (4.0 x ) ( )( ) 0.5 x x 10-6 Addition and Subtraction: Convert the numbers to the same power of ten and then add or subtract the coeffieicnts. Then put the answer into proper form. Example: (6.0 x 10 5 )+(5.0 x 10 6 ) (6.0 x 10 5 )+(50. x 10 5 ) 56 x 10 5 Practice Problems: Solve the following problems. Make sure that your answer has the proper number of significant figures and is in proper scientific notation form. a. (6.03 x 10 5 )(3.2 x 10 1 )= b. (6.03 x 10 5 )(3.2 x )= d x 10 5 e x x x 10 4 c. (6.03 x 10 5 ) (3.2 x 10 6 )= 10 P a g e
11 Name: Date: Period: Fill in the blanks lines and boxes: What s in an Identity? 1 meter stick glue sticks blocks paper clip widths _1 meter (m)_ 1 meterstick 1 ( )_ 1 glue stick 1 ( ) 1 block 1 ( )_ 1 paper clip width 1 meter (m) 1 m _ 1 dm_ dm m 1 m _ 1 cm_ cm m 1 m _ 1 mm_ mm m We can use these relationships to convert from one unit to another unit. 1) How many centimeters are in 11.7 meters? 2) How many millimeters are in 3.2 meters? 11 P a g e
12 Making Cents of it All: Dimensional Analysis aka Factor Label Method In science (and in life) it is frequently necessary to convert between units of measurement. A good example is converting between dollars and quarters, dimes, or nickels: $1.00 = 1 dollar bill = 4 quarters = 10 dimes = 20 nickels Each expression above shows the same monetary value, simply in different units. Notice that as the units get smaller and smaller, the number needed to equal a dollar becomes larger and larger. A nickel is 1/20 the size of a dollar, therefore you need 20 times as many nickel to have the same total amount of money. This comparison of the units nickel and dollar is helpful in creating a conversion factor. Conversion Factor: We know that 20 nickels are needed for every dollar. Therefore our ratio is: 20 nickels or 1 dollar 1 dollar 20 nickels Both ratios are correct, and both ratios equal one. So when do we use each? Know where you re starting and where you are headed! In order to know which ratio to use you have to know which units you re starting with, and which you re ending with. For example, if I want to make 3 dollars into nickels, I d use the following equation: 3 dollars x 20 nickels = 60 nickels 1 dollar Let's try this one: ** Note - The unit I want to end up with is in the numerator and the unit I began with is in the denominator. When setting up a conversion factor you should always have the unit you want to get rid of in the place where it will cancel out. How many quarters are in $6.25? 12 P a g e
13 Dimensional Analysis Practice: 1. Convert $229 dollars into British Pounds. $1 =.57 Pounds (as of 9/9/2008) 2. Convert 15 inches into centimeters. 1 inch = 2.54 cm 3. Using problem 3, convert 15 inches into millimeters. 4. Convert 5 pounds into kilograms Kg = 1 lb. 5. Convert 50 oz into kilograms. 1 lb = 16 oz. 6. Convert 28 days into seconds. 7. Convert 1.5 x 10 9 years into seconds. Be sure to give your answer in scientific notation. 13 P a g e
14 Got Calcium? (adapted from NASA's Imagine the Universe) Except on Earth, the Milky Way galaxy doesn't contain any milk. But it sure does have a lot of calcium. There's enough calcium floating between the stars to fortify trillions upon trillions of gallons of milk. Calcium comes from stars. In fact, all of the elements that make up your body and the planet Earth itself, other than hydrogen and helium, were made in stars or during explosions of massive stars. Stars are like mighty chemical factories. They burn hydrogen and helium through a process of nuclear fusion, which produces a tremendous amount of heat energy. In addition to energy, the fusion process in massive stars (stars having more than 8 times the mass of our sun) results in carbon, nitrogen, iron and other atoms. As iron accumulates in the stellar core, the fusion process no longer produces heat energy. At this point in the life of a massive star, the core collapses and the star explodes, sending all those atoms racing into space. Some atoms bump into each other in the fury, fusing to create even heavier atoms such as gold, silver and uranium. These atoms spread across the galaxy over the course of billions of years. Cassiopeia A is a star that exploded about 320 years ago. No astronomer recorded the explosion at the time, but we can still see the remains of the explosion today in the form of a colorful supernova remnant. By measuring the motion of the gas in the remnant, astronomers deduce its age. Optical: Visible light image of Cassiopeia A (from a telescope on Earth) X-ray image of Cassiopeia A (from Chandra X-ray Observatory X-ray image showing only the calcium present in Cassiopeia A The Michigan-Dartmouth-Massachusetts Institute of Technology Observatory on Kitt Peak, Arizona, captured a beautiful image of Cassiopeia A in visible light (above, left). In an image accumulated over a million seconds, The Chandra X-ray Observatory, an earth-orbiting satellite, saw the hot X-ray-emitting gas from the explosion (above, middle). This gas is hotter than the surface of the sun. Chandra was also able to see the individual elements within the explosion. For example, researchers at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center created an image showing only the element calcium (above, right). 14 P a g e
15 How much calcium is in Cassiopeia A? Use the following information to find out: The star that produced the supernova remnant Cassiopeia A was about 20 times more massive than the Sun. It was largely made up of hydrogen but also contained some calcium and other elements. When the star exploded, the hydrogen, calcium, and other elements produced by fusion during the life of the star fly off into space. The explosion creates more of these and other elements. The total amount of calcium is equal to about 0.05% of the mass of the original star. One glass of milk (8 fluid oz. or 237 ml) contains approximately 300 mg of calcium. There are 8.44 x 10 6 milk cows in the United States. On average, each cow produces 26.3 kg of milk/ day. Using this information, answer the following questions. Use dimensional analysis and show all your work. 1. The mass of the sun is 2.0 x kg. What is the mass of Cassiopeia A? 2. How many kilograms of calcium are in the supernova remnant Cassiopeia A? 3. How many 8-ounce glasses of milk would this equal? 4. How long must the cows in the United States be milked to produce this number of glasses of milk? 15 P a g e
16 Alegbra Review Worksheet Name: Date: Period: Solve for the unknown quantity in each of the following questions. Make sure to follow the 7 steps for solving problems and make sure to use the appropriate units. 1. A sample of a substance is found that has a mass of 21.0 g and a volume of 7.01 ml. What is the density of the substance? 2. A different sample of the same substance has a density of 3.0 g/ml and a mass of 93.0 g. What is the volume of this sample? Joules (J) of heat is added to a 200 gram (g) sample of water. The heat capacity of pure water is 4.18 J/g K. How much did the temperature of the water change when 125 J of heat was added? 4. How much did the temperature change in question 3 in degrees Celsius? 16 P a g e
17 Significant Figures Worksheet Name: Date: Period: Determine the number of significant figures in each of the following numbers g g cm lb g g cm ml g lb cm cm x x oz g mg x x x 10 3 Add the following measurements and record the answer with the appropriate number of significant figures cm cm cm = cm cm = g g g g = g g g g = cm cm cm cm = 17 P a g e
18 Subtract the following measurements and record the answer with the appropriate number of significant figures cm cm = g 43.7 g = ml = 28.9 ml = g 39.9 g = ml ml = Multiply the following measurements and record the answer with the appropriate number of significant figures cm x 4.01 cm = cm x 6.2 cm = m x 1.2 m = mm x mm = dm x dm = Divide the following measurements and record the answer with the appropriate number of significant figures cm cm = m m = ,789.4 km km = mm mm = cm cm = 18 P a g e
19 Scientific Notation Worksheet Name: Date: Period: Express each of the following numbers in scientific notation with the appropriate number of significant figures = = 2. 50,000. = ,000,000 = = = ,000 = = Express each of the following as common numbers x 10 5 = x 10-4 = x 10 5 = x 10-3 = x = x = 19 P a g e
20 Perform each of the following operations using scientific notation. Your answers should have the appropriate number of significant figures. 15. (2.3 x 10 3 )(4 x 10 5 ) = 16. (9.6 x 10-1 )(5.21 x 10 2 ) = 17. (4.56 x 10-6 )(3.1 x 10-3 ) = 18. (5.7 x 10 8 )(2.3 x 10-4 ) = x 10 2 = 1.3 x x 10 4 = 9.0 x (1.3 x 10 5 )(8.2 x 10-2 ) = 7.4 x x x x x x x x x P a g e
21 Dimensional Analysis Worksheet Name: Date: Period: Directions: Answer the following questions using dimensional analysis. Be sure to report your answer with the appropriate number of significant figures. You must show your work!! 1. A bottle of water holds 0.5 liters. How many cl of water is this? 2. The world record for the long jump is 8.95 meters. How many decimeters is that? 3. A standard tennis ball has a mass of 57.0 grams. How many micrograms is that? 4. The heaviest weight ever lifted by a human is 51.7 kg. How many grams is that? 5. According to the Village of Endicott s annual water report, one of the wells that supplies water to residents contains 89.6 mg/l of sodium. How many g/l of sodium does the water contain? 6. The Pacific Giant Kelp is the longest growing kelp at 600 cm long. How many inches long is it? ( 1 inch =2.54 cm) 7. The biggest piece of fudge ever created weighted 1367 kg. How many pounds was it? (1 lb =.454 kg) 21 P a g e
22 8. Carbonated beverage bottlers usually put 355 ml of soda in a can. How many cups is that? (1 oz = ml and 8 oz = cup) 9. How many seconds old are you? (round your age to the nearest.1 year) 10. Each liter of air has a mass of 1.80 grams. How many liters of air are contained in 2500 kg of air? grams of Doritos contains 5.0 calories. Each bag of Doritos contains 28.0 grams. How many bags would you need to eat in order to consume 2150 Calories? 12. The moon is 384,403 km from the earth. Estimate how many quarters laid end to end it would take to reach the moon if a quarter has a diameter of 2.3 cm. 22 P a g e
Name Date Class MEASUREMENTS AND THEIR UNCERTAINTY
 3.1 MEASUREMENTS AND THEIR UNCERTAINTY Section Review Objectives Convert measurements to scientific notation Distinguish among the accuracy, precision, and error of a measurement Identify the number of
3.1 MEASUREMENTS AND THEIR UNCERTAINTY Section Review Objectives Convert measurements to scientific notation Distinguish among the accuracy, precision, and error of a measurement Identify the number of
Co Curricular Data Analysis Review
 Chapter Vocabulary Co Curricular Data Analysis Review Base Unit Second (s) Meter (m) Kilogram (kg) Kelvin (K) Derived unit Liter Density Scientific notation Dimensional analysis (Equality) not in book
Chapter Vocabulary Co Curricular Data Analysis Review Base Unit Second (s) Meter (m) Kilogram (kg) Kelvin (K) Derived unit Liter Density Scientific notation Dimensional analysis (Equality) not in book
Chapter 3 Metric Units and Conversions
 Chapter 3 Metric Units and Conversions 3.1 The Metric System and Prefixes Metric system: a simple decimal system of measurement that uses the following basic units: Quantity Basic Unit Symbol length meter
Chapter 3 Metric Units and Conversions 3.1 The Metric System and Prefixes Metric system: a simple decimal system of measurement that uses the following basic units: Quantity Basic Unit Symbol length meter
Name Period Date. Measurements. Fill-in the blanks during the PowerPoint presentation in class.
 Name Period Date Measurements Fill-in the blanks during the PowerPoint presentation in class. What is Scientific Notation? Scientific notation is a way of expressing big numbers and small numbers. It is
Name Period Date Measurements Fill-in the blanks during the PowerPoint presentation in class. What is Scientific Notation? Scientific notation is a way of expressing big numbers and small numbers. It is
Scientific Measurement
 Scientific Measurement Quantifying Matter For students using the Foundation edition, assign problems 2 4, 7, 8, 10 16, 18 24. 3.1 Using and Expressing Measurements Essential Understanding In science, measurements
Scientific Measurement Quantifying Matter For students using the Foundation edition, assign problems 2 4, 7, 8, 10 16, 18 24. 3.1 Using and Expressing Measurements Essential Understanding In science, measurements
Section 1 Scientific Method. Describe the purpose of the scientific method. Distinguish between qualitative and quantitative observations.
 Section 1 Scientific Method Objectives Describe the purpose of the scientific method. Distinguish between qualitative and quantitative observations. Describe the differences between hypotheses, theories,
Section 1 Scientific Method Objectives Describe the purpose of the scientific method. Distinguish between qualitative and quantitative observations. Describe the differences between hypotheses, theories,
Chemistry 104 Chapter Two PowerPoint Notes
 Measurements in Chemistry Chapter 2 Physical Quantities Measurable physical properties such as height, volume, and temperature are called Physical quantity. A number and a unit of defined size is required
Measurements in Chemistry Chapter 2 Physical Quantities Measurable physical properties such as height, volume, and temperature are called Physical quantity. A number and a unit of defined size is required
CHAPTER TWO: MEASUREMENTS AND PROBLEM SOLVING
 CHAPTER TWO: MEASUREMENTS AND PROBLEM SOLVING Measurements: Our Starting Point! Why should we begin our study of chemistry with the topic of measurement?! Much of the laboratory work in this course is
CHAPTER TWO: MEASUREMENTS AND PROBLEM SOLVING Measurements: Our Starting Point! Why should we begin our study of chemistry with the topic of measurement?! Much of the laboratory work in this course is
Unit 1 Part 1: Significant Figures and Scientific Notation. Objective understand significant figures and their rules. Be able to use scientific
 Unit 1 Part 1: Significant Figures and Scientific Notation. Objective understand significant figures and their rules. Be able to use scientific notation in calculations. Significant figures - consist of
Unit 1 Part 1: Significant Figures and Scientific Notation. Objective understand significant figures and their rules. Be able to use scientific notation in calculations. Significant figures - consist of
Chapter 5 Assessment. 164 Chapter 5 Measurements and Calculations. 8. Write each of the following numbers in standard scientific notation. a.
 Chapter 5 Assessment All exercises with blue numbers have answers in the back of this book. 5.1 Scientific Notation and Units A. Scientific Notation 1. When the number 98,145 is written in standard scientific
Chapter 5 Assessment All exercises with blue numbers have answers in the back of this book. 5.1 Scientific Notation and Units A. Scientific Notation 1. When the number 98,145 is written in standard scientific
Unit I: Measurements A. Significant figures B. Rounding numbers C. Scientific notation D. Using electronic calculators E.
 Unit I: Measurements A. Significant figures B. Rounding numbers C. Scientific notation D. Using electronic calculators E. Using sig figs in arithmetic operations F. The metric system G. Problem solving
Unit I: Measurements A. Significant figures B. Rounding numbers C. Scientific notation D. Using electronic calculators E. Using sig figs in arithmetic operations F. The metric system G. Problem solving
Ch. 3 Notes---Scientific Measurement
 Ch. 3 Notes---Scientific Measurement Qualitative vs. Quantitative Qualitative measurements give results in a descriptive nonnumeric form. (The result of a measurement is an describing the object.) *Examples:,,
Ch. 3 Notes---Scientific Measurement Qualitative vs. Quantitative Qualitative measurements give results in a descriptive nonnumeric form. (The result of a measurement is an describing the object.) *Examples:,,
Chapter 2 Measurements and Solving Problems
 History of Measurement Chapter 2 Measurements and Solving Problems Humans once used handy items as standards or reference tools for measurement. Ex: foot, cubit, hand, yard. English System the one we use.
History of Measurement Chapter 2 Measurements and Solving Problems Humans once used handy items as standards or reference tools for measurement. Ex: foot, cubit, hand, yard. English System the one we use.
General Chemistry Unit 8 Measurement ( )
 General Chemistry Unit 8 Measurement (2017-2018) Significant Figures Scientific Notation Unit Analysis Unit of Measure Accuracy and Precision Density Percent Error 1 Adding Numbers: Add numbers as you
General Chemistry Unit 8 Measurement (2017-2018) Significant Figures Scientific Notation Unit Analysis Unit of Measure Accuracy and Precision Density Percent Error 1 Adding Numbers: Add numbers as you
Chemistry Day 39. Friday, December 14 th Monday, December 17 th, 2018
 Chemistry Day 39 Friday, December 14 th Monday, December 17 th, 2018 Do-Now: Reactions Quiz Do-Now 1. Write down today s FLT 2. Copy: KCl + H 2 O à? 3. Identify the type of reaction in #2. 4. Predict the
Chemistry Day 39 Friday, December 14 th Monday, December 17 th, 2018 Do-Now: Reactions Quiz Do-Now 1. Write down today s FLT 2. Copy: KCl + H 2 O à? 3. Identify the type of reaction in #2. 4. Predict the
Scientific Method. Why Study Chemistry? Why Study Chemistry? Chemistry has many applications to our everyday world. 1. Materials. Areas of Chemistry
 August 12, 2012 Introduction to Chemistry and Scientific Measurement What is Chemistry? Chemistry: is the study of the composition of matter and the changes that matter undergoes. Chapters 1 and 3 Why
August 12, 2012 Introduction to Chemistry and Scientific Measurement What is Chemistry? Chemistry: is the study of the composition of matter and the changes that matter undergoes. Chapters 1 and 3 Why
3.2 Units of Measurement > Chapter 3 Scientific Measurement. 3.2 Units of Measurement. 3.1 Using and Expressing Measurements
 Chapter 3 Scientific Measurement 3.1 Using and Expressing Measurements 3.2 Units of Measurement 3.3 Solving Conversion Problems 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
Chapter 3 Scientific Measurement 3.1 Using and Expressing Measurements 3.2 Units of Measurement 3.3 Solving Conversion Problems 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
MEASUREMENTS. Significant Figures
 SIGNIFICANT FIGURES MEASUREMENTS Significant Figures Every measured value, that you record on paper, reflects the precision of the measuring device used to obtain that value. Every calculated value that
SIGNIFICANT FIGURES MEASUREMENTS Significant Figures Every measured value, that you record on paper, reflects the precision of the measuring device used to obtain that value. Every calculated value that
The number of stars in a galaxy is an example of an estimate that should be expressed in scientific notation.
 3.1 Using and Expressing Measurements A measurement is a quantity that has both a number and a unit. Using and Expressing Measurements In scientific notation, a given number is written as the product of
3.1 Using and Expressing Measurements A measurement is a quantity that has both a number and a unit. Using and Expressing Measurements In scientific notation, a given number is written as the product of
2 Standards of Measurement
 What You ll Learn the SI units and symbols for length, volume, mass, density, time, and temperature how to convert related SI units 2 Standards of Measurement (A), 2(D), 2(C), 2(E) Before You Read If someone
What You ll Learn the SI units and symbols for length, volume, mass, density, time, and temperature how to convert related SI units 2 Standards of Measurement (A), 2(D), 2(C), 2(E) Before You Read If someone
2 Standards for Measurement. Careful and accurate measurements of ingredients are important both when cooking and in the chemistry laboratory!
 2 Standards for Measurement Careful and accurate measurements of ingredients are important both when cooking and in the chemistry laboratory! Chapter Outline 2.1 Scientific Notation 2.2 Measurement and
2 Standards for Measurement Careful and accurate measurements of ingredients are important both when cooking and in the chemistry laboratory! Chapter Outline 2.1 Scientific Notation 2.2 Measurement and
International System of Units 3.2. Slide 1of 33
 International System 3.2 1of 33 3.2 The International System In the signs shown here, the distances are listed as numbers with no units attached. Without the units, it is impossible to communicate the
International System 3.2 1of 33 3.2 The International System In the signs shown here, the distances are listed as numbers with no units attached. Without the units, it is impossible to communicate the
Measurement and Calculations
 Measurement and Calculations Quantitative Observation How much? Need Measurement Measurement is the comparison of a physical quantity to be measured with a unit of measurement-that is a fixed standard
Measurement and Calculations Quantitative Observation How much? Need Measurement Measurement is the comparison of a physical quantity to be measured with a unit of measurement-that is a fixed standard
A supernova is the explosion of a star. It is the largest explosion that takes place in space.
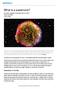 What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
Module 4 Conversion Factors
 Module 4 Conversion Factors Prerequisites: Module 4 requires knowledge of exponential math and metric fundamentals in Lessons 1A, 1B, 2A, and 2B. The other lessons in Modules 1-3 will be helpful, but not
Module 4 Conversion Factors Prerequisites: Module 4 requires knowledge of exponential math and metric fundamentals in Lessons 1A, 1B, 2A, and 2B. The other lessons in Modules 1-3 will be helpful, but not
Every physical or chemical change in matter involves a change in energy.
 Sec. 2.1 Energy Objectives: 1. Explain that physical and chemical changes in matter involve transfers of energy 2. Apply the law of conservation of energy to analyze changes in matter 3. Distinguish between
Sec. 2.1 Energy Objectives: 1. Explain that physical and chemical changes in matter involve transfers of energy 2. Apply the law of conservation of energy to analyze changes in matter 3. Distinguish between
3.2 The International System of Units HR/Name. temperature: Celsius scale: Kelvin scale: Vocabulary. absolute zero:
 temperature: Celsius scale: Kelvin scale: Reading Assignment: pages 73-79 Vocabulary International System of s (SI): absolute zero: meter (m): energy: liter (L): joule (J): kilogram: gram (g): calorie
temperature: Celsius scale: Kelvin scale: Reading Assignment: pages 73-79 Vocabulary International System of s (SI): absolute zero: meter (m): energy: liter (L): joule (J): kilogram: gram (g): calorie
Pre-Lab 0.2 Reading: Measurement
 Name Block Pre-Lab 0.2 Reading: Measurement section 1 Description and Measurement Before You Read Weight, height, and length are common measurements. List at least five things you can measure. What You
Name Block Pre-Lab 0.2 Reading: Measurement section 1 Description and Measurement Before You Read Weight, height, and length are common measurements. List at least five things you can measure. What You
Accelerated Chemistry Study Guide What is Chemistry? (Chapter 1)
 Accelerated Chemistry Study Guide What is Chemistry? (Chapter 1) Conversion factor Density Uncertainty Significant digits/figures Precision Accuracy Percent error September 2017 Page 1 of 32 Scientific
Accelerated Chemistry Study Guide What is Chemistry? (Chapter 1) Conversion factor Density Uncertainty Significant digits/figures Precision Accuracy Percent error September 2017 Page 1 of 32 Scientific
Chapter 2: Measurements and Problem Solving
 C h 2 : M e a s u r e m e n t s a n d P r o b l e m S o l v i n g P a g e 1 Chapter 2: Measurements and Problem Solving Read Chapter 2, work problems. Look over the lab assignments before the lab. Keep
C h 2 : M e a s u r e m e n t s a n d P r o b l e m S o l v i n g P a g e 1 Chapter 2: Measurements and Problem Solving Read Chapter 2, work problems. Look over the lab assignments before the lab. Keep
Countries that haven t adopted the Metric system yet
 Measurements Countries that haven t adopted the Metric system yet Customary Metric (Base Unit) International System (SI) Equivalents Length Mass inch, foot, yard, mile ounce, pound, ton Meter (m) Meter
Measurements Countries that haven t adopted the Metric system yet Customary Metric (Base Unit) International System (SI) Equivalents Length Mass inch, foot, yard, mile ounce, pound, ton Meter (m) Meter
Chemistry Unit 1 Primary reference: Chemistry: Matter and Change [Glencoe, 2017]
![Chemistry Unit 1 Primary reference: Chemistry: Matter and Change [Glencoe, 2017] Chemistry Unit 1 Primary reference: Chemistry: Matter and Change [Glencoe, 2017]](/thumbs/78/77085139.jpg) Scientific Investigation 1.1 SOL 1a, 1b,1c, 1e, 1g Chemistry Unit 1 Primary reference: Chemistry: Matter and Change [Glencoe, 2017] Topic Essential Knowledge Study Support Use chemicals and equipment safely.
Scientific Investigation 1.1 SOL 1a, 1b,1c, 1e, 1g Chemistry Unit 1 Primary reference: Chemistry: Matter and Change [Glencoe, 2017] Topic Essential Knowledge Study Support Use chemicals and equipment safely.
Math Skills Needed For Chemistry
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 1 Chemistry in Our Lives What is Chemistry? Chemistry is the study of composition, structure, properties, and reactions of matter. happens all around you every day. Antacid
Lecture Presentation Chapter 1 Chemistry in Our Lives What is Chemistry? Chemistry is the study of composition, structure, properties, and reactions of matter. happens all around you every day. Antacid
Everyday Conversion: Money
 Everyday Conversion: Money Everyday Measurement: Water Everyday Measurement: Water Everyday Accuracy: Weighing Scales The need to measure correctly and convert! Some Interesting Quantities Length Volume
Everyday Conversion: Money Everyday Measurement: Water Everyday Measurement: Water Everyday Accuracy: Weighing Scales The need to measure correctly and convert! Some Interesting Quantities Length Volume
Chapter 3 Scientific Measurement
 Chapter 3 Scientific Measurement Measurements We make measurements every day: buying products, sports activities, and cooking Qualitative measurements are words, such as heavy or hot Quantitative measurements
Chapter 3 Scientific Measurement Measurements We make measurements every day: buying products, sports activities, and cooking Qualitative measurements are words, such as heavy or hot Quantitative measurements
Welcome to Chemistry 121
 General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Fourth Edition Karen Timberlake Welcome to Chemistry 121 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Fourth Edition Karen Timberlake
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Fourth Edition Karen Timberlake Welcome to Chemistry 121 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Fourth Edition Karen Timberlake
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES
 SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
SCIENTIFIC MEASUREMENT. Ch 2 Chemistry is a lot of math!
 SCIENTIFIC MEASUREMENT Ch 2 Chemistry is a lot of math! WARM UP 1.Name 3 tools used for measurement. 2.What is a unit? 3.Give an example of a unit. 4.Why are units important. CH 2 SCIENTIFIC MEASUREMENT
SCIENTIFIC MEASUREMENT Ch 2 Chemistry is a lot of math! WARM UP 1.Name 3 tools used for measurement. 2.What is a unit? 3.Give an example of a unit. 4.Why are units important. CH 2 SCIENTIFIC MEASUREMENT
Law vs. Theory. Steps in the Scientific Method. Outcomes Over the Long-Term. Measuring Matter in Two Ways
 Law vs. Theory A law summarizes what happens A theory (model) is an attempt to explain why it happens. Unit 2: (Chapter 5) Measurements and Calculations Cartoon courtesy of NearingZero.net Steps in the
Law vs. Theory A law summarizes what happens A theory (model) is an attempt to explain why it happens. Unit 2: (Chapter 5) Measurements and Calculations Cartoon courtesy of NearingZero.net Steps in the
Measurements and Calculations. Chapter 2
 Measurements and Calculations Chapter 2 Scientific Method Section 2-1 The Scientific Method The scientific method is a logical approach to solving problems by observing and collecting data, formulating
Measurements and Calculations Chapter 2 Scientific Method Section 2-1 The Scientific Method The scientific method is a logical approach to solving problems by observing and collecting data, formulating
Math 6, Unit 9 Notes: Measurement and Geometry
 Math 6, Unit 9 Notes: Measurement and Geometry Customary and Metric Units of Measure Objective: (6.3)The student will estimate corresponding units of measure between customary and metric systems for temperature,
Math 6, Unit 9 Notes: Measurement and Geometry Customary and Metric Units of Measure Objective: (6.3)The student will estimate corresponding units of measure between customary and metric systems for temperature,
CHAPTER 2 Data Analysis
 CHAPTER 2 Data Analysis 2.1 Units of Measurement The standard of measurement used in science are those of the metric system. All the units are based on 10 or multiples of 10. SI Units: The International
CHAPTER 2 Data Analysis 2.1 Units of Measurement The standard of measurement used in science are those of the metric system. All the units are based on 10 or multiples of 10. SI Units: The International
Chemistry Basic Science Concepts. Observations: are recorded using the senses. Examples: the paper is white; the air is cold; the drink is sweet.
 Note Packet # 1 1 Chemistry: the study of matter. Chemistry Basic Science Concepts Matter: anything that has mass and occupies space. Observations: are recorded using the senses. Examples: the paper is
Note Packet # 1 1 Chemistry: the study of matter. Chemistry Basic Science Concepts Matter: anything that has mass and occupies space. Observations: are recorded using the senses. Examples: the paper is
Chapter 5 Measurements and Calculations Objectives
 Objectives 1. To show how very large or very small numbers can be expressed in scientific notation 2. To learn the English, metric, and SI systems of measurement 3. To use the metric system to measure
Objectives 1. To show how very large or very small numbers can be expressed in scientific notation 2. To learn the English, metric, and SI systems of measurement 3. To use the metric system to measure
Chapter 2: Standards for Measurement. 2.1 Scientific Notation
 Chapter 2: Standards for Measurement 2.1 Scientific Notation A measurement (quantitative observation) consists of two parts: o Numerical value which gives magnitude, and o Unit which gives the scale used
Chapter 2: Standards for Measurement 2.1 Scientific Notation A measurement (quantitative observation) consists of two parts: o Numerical value which gives magnitude, and o Unit which gives the scale used
Section 5.1 Scientific Notation and Units Objectives
 Objectives 1. To show how very large or very small numbers can be expressed in scientific notation 2. To learn the English, metric, and SI systems of measurement 3. To use the metric system to measure
Objectives 1. To show how very large or very small numbers can be expressed in scientific notation 2. To learn the English, metric, and SI systems of measurement 3. To use the metric system to measure
Chem 140 Section C Instructor: Ken Marr. Chem 140 Section A Instructor: Ken Marr. Chem 140 Section E Instructor: Ken Marr. Day 1 Activities CHEMISTRY
 Chem 140 Section A Instructor: Ken Marr Weekly Schedule Lecture 9-10, MWF in STB-2 Lab 8-10, Tu in STB-2 8-10, Th in STB-5 Chem 140 Section C Instructor: Ken Marr Weekly Schedule Lecture 10 11, MWF in
Chem 140 Section A Instructor: Ken Marr Weekly Schedule Lecture 9-10, MWF in STB-2 Lab 8-10, Tu in STB-2 8-10, Th in STB-5 Chem 140 Section C Instructor: Ken Marr Weekly Schedule Lecture 10 11, MWF in
CHEM 1305: Introductory Chemistry
 CHEM 1305: Introductory Chemistry Basic Science Skills From Chapter 1, PSS and 2 Textbook Introductory Chemistry: Concepts and Critical Thinking Seventh Edition by Charles H. Corwin Measurements In chemistry,
CHEM 1305: Introductory Chemistry Basic Science Skills From Chapter 1, PSS and 2 Textbook Introductory Chemistry: Concepts and Critical Thinking Seventh Edition by Charles H. Corwin Measurements In chemistry,
Chapter COURSE NAME: CHEMISTRY 101 COURSE CODE:
 Chapter 1 COURSE NAME: CHEMISTRY 101 COURSE CODE: 402101-4 Chapter 1 2 International System of Units (SI) Science problem solving requires both: Metric system English system 3 4 Volume SI derived unit
Chapter 1 COURSE NAME: CHEMISTRY 101 COURSE CODE: 402101-4 Chapter 1 2 International System of Units (SI) Science problem solving requires both: Metric system English system 3 4 Volume SI derived unit
INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking Seventh Edition by Charles H. Corwin
 Lecture INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking Seventh Edition by Charles H. Corwin The Metric System by Christopher G. Hamaker Illinois State University Basic Units and Symbols The English
Lecture INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking Seventh Edition by Charles H. Corwin The Metric System by Christopher G. Hamaker Illinois State University Basic Units and Symbols The English
Introduction to Chemistry
 Introduction to Chemistry Regents Chemistry: Unit 1 Essential Questions: What is chemistry? How do we know a study is valid? What are the most accurate and precise ways to work with numbers? 1 (I) What
Introduction to Chemistry Regents Chemistry: Unit 1 Essential Questions: What is chemistry? How do we know a study is valid? What are the most accurate and precise ways to work with numbers? 1 (I) What
Welcome to General Chemistry I
 Welcome to General Chemistry I Chemistry Chemistry is a branch of science that studies the composition and properties of matter and the changes it undergoes H 2 O http://theresilientearth.com/?q=content/climate-models-blown-away-water-vapor
Welcome to General Chemistry I Chemistry Chemistry is a branch of science that studies the composition and properties of matter and the changes it undergoes H 2 O http://theresilientearth.com/?q=content/climate-models-blown-away-water-vapor
Chapter 2. Preview. Objectives Scientific Method Observing and Collecting Data Formulating Hypotheses Testing Hypotheses Theorizing Scientific Method
 Preview Objectives Scientific Method Observing and Collecting Data Formulating Hypotheses Testing Hypotheses Theorizing Scientific Method Section 1 Scientific Method Objectives Describe the purpose of
Preview Objectives Scientific Method Observing and Collecting Data Formulating Hypotheses Testing Hypotheses Theorizing Scientific Method Section 1 Scientific Method Objectives Describe the purpose of
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 1. Chemistry in Our Lives. Karen C. Timberlake
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 1 Chemistry in Our Lives What is Chemistry? Chemistry is the study of composition, structure, properties, and reactions of matter. happens all around you every day. Antacid
Lecture Presentation Chapter 1 Chemistry in Our Lives What is Chemistry? Chemistry is the study of composition, structure, properties, and reactions of matter. happens all around you every day. Antacid
Measurement Chapter 1.6-7
 Unit 1 Essential Skills Measurement Chapter 1.6-7 The Unit 1 Test will cover material from the following Chapters and Sections: 1.all 2.5-8 3.all 2 Two types of Data: When we make observations of matter,
Unit 1 Essential Skills Measurement Chapter 1.6-7 The Unit 1 Test will cover material from the following Chapters and Sections: 1.all 2.5-8 3.all 2 Two types of Data: When we make observations of matter,
6.5 Metric U.S. Customary Measurement Conversions
 6. Metric U.S. Customary Measurement Conversions Since most of the world uses the metric system of measurement, we often need to know how to convert back and forth between U.S. Customary measurements and
6. Metric U.S. Customary Measurement Conversions Since most of the world uses the metric system of measurement, we often need to know how to convert back and forth between U.S. Customary measurements and
GraspIT Questions AQA GCSE Physics Space physics
 A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
Full file at
 Chapter Two Multiple Choice 1. Which SI prefix means 1000? A. Milli B. Centi C. Deci D. Kilo Answer: D; Difficulty: easy; Reference: Section 2.5 2. The number, 14.74999, when rounded to three digits is
Chapter Two Multiple Choice 1. Which SI prefix means 1000? A. Milli B. Centi C. Deci D. Kilo Answer: D; Difficulty: easy; Reference: Section 2.5 2. The number, 14.74999, when rounded to three digits is
Chapter 2: Measurements & Calculations
 Chapter 2: Measurements & Calculations LA-PRIVATE:sg:sg.02_Measurements_and_Calculations.docx (9/1/14) Chemistry Measurements & Calculations p.1 TABLE OF CONTENTS I. SCIENTIFIC METHOD... 2 II. METRIC UNITS
Chapter 2: Measurements & Calculations LA-PRIVATE:sg:sg.02_Measurements_and_Calculations.docx (9/1/14) Chemistry Measurements & Calculations p.1 TABLE OF CONTENTS I. SCIENTIFIC METHOD... 2 II. METRIC UNITS
History of the Universe Unit Tracking Sheet
 Name Period Mrs. Coates Earth Science History of the Universe Unit Tracking Sheet Learning Target Question Example Date Target was Taught in Class The Big Bang Theory explains how the universe formed The
Name Period Mrs. Coates Earth Science History of the Universe Unit Tracking Sheet Learning Target Question Example Date Target was Taught in Class The Big Bang Theory explains how the universe formed The
MindTrap. Read the question. Think about the question. Please Do not yell out the answer
 Metric System Read the question Think about the question MindTrap Please Do not yell out the answer Dee Septor, the famous magician, filled an ordinary glass to the top. Holding the glass above his head
Metric System Read the question Think about the question MindTrap Please Do not yell out the answer Dee Septor, the famous magician, filled an ordinary glass to the top. Holding the glass above his head
Notes: Unit 1: Math and Measurement
 Name: Regents Chemistry: Notes: Unit 1: Math and Measurement www.chempride.weebly.com Key Ideas Major Understandings: o Chemistry is the study of matter: Matter takes up space and has mass. (K- 4, 3.1a)
Name: Regents Chemistry: Notes: Unit 1: Math and Measurement www.chempride.weebly.com Key Ideas Major Understandings: o Chemistry is the study of matter: Matter takes up space and has mass. (K- 4, 3.1a)
Notes: Unit 1: Math and Measurement
 Name: Regents Chemistry: Notes: Unit 1: Math and Measurement www.chempride.weebly.com Key Ideas Major Understandings: o Chemistry is the study of matter: Matter takes up space and has mass. (K- 4, 3.1a)
Name: Regents Chemistry: Notes: Unit 1: Math and Measurement www.chempride.weebly.com Key Ideas Major Understandings: o Chemistry is the study of matter: Matter takes up space and has mass. (K- 4, 3.1a)
Note: at no time will we be measuring the weight of any substance in this class, only its mass.
 Measurement 1. Handout: Condensed notes for Measurement Unit 2. Film: Measurement of Flouride Video Clip 3. Homework: Read article on the loss of the Mars Orbiter 4. Units/Scientific Notation 1. Scientific
Measurement 1. Handout: Condensed notes for Measurement Unit 2. Film: Measurement of Flouride Video Clip 3. Homework: Read article on the loss of the Mars Orbiter 4. Units/Scientific Notation 1. Scientific
Chapter 3 Scientific Measurement
 Chapter 3 Scientific Measurement Measurements 2 types: Qualitative measurements (words) Heavy, hot, or long Quantitative measurements (# s) & depend on: 1) Reliability of measuring instrument 2) Care w/
Chapter 3 Scientific Measurement Measurements 2 types: Qualitative measurements (words) Heavy, hot, or long Quantitative measurements (# s) & depend on: 1) Reliability of measuring instrument 2) Care w/
2.1 Units of Measurement. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 2 Measurements 2.1 Units of Measurement 1 Measurement You make a measurement every time you measure your height read your watch take your temperature weigh a cantaloupe 2 Measurement in Chemistry
Chapter 2 Measurements 2.1 Units of Measurement 1 Measurement You make a measurement every time you measure your height read your watch take your temperature weigh a cantaloupe 2 Measurement in Chemistry
The behavior and changes of matter and the related energy changes. Matter and processes of living organisms
 Unit One Review Name Period Date Areas of Chemistry and Scientific Method Chemistry is the study of matter and the changes that it undergoes. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Mass is
Unit One Review Name Period Date Areas of Chemistry and Scientific Method Chemistry is the study of matter and the changes that it undergoes. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Mass is
Contents Decimals Averages Percentages Metric Units Scientific Notation Dimensional Analysis
 This year in APES you will hear the two words most dreaded by high school students NO CALCULATORS! That s right, you cannot use a calculator on the AP Environmental Science exam. Since the regular tests
This year in APES you will hear the two words most dreaded by high school students NO CALCULATORS! That s right, you cannot use a calculator on the AP Environmental Science exam. Since the regular tests
Required Items. ACTIVE PARTICIPATION in class and lab. Use of iclicker
 Welcome to Chem103 Required Items Textbook: Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change, Martin S. Silberberg, 5 th Edition, McGraw-Hill, 2009 iclicker Scientific calculator ACTIVE PARTICIPATION
Welcome to Chem103 Required Items Textbook: Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change, Martin S. Silberberg, 5 th Edition, McGraw-Hill, 2009 iclicker Scientific calculator ACTIVE PARTICIPATION
Honors Chemistry Chapter 2 Problem Handout Solve the following on separate sheets of paper. Where appropriate, show all work. 1. Convert each of the
 Honors Chemistry Chapter 2 Problem Handout Solve the following on separate sheets of paper. Where appropriate, show all work. 1. Convert each of the following quantities to the required unit. a. 12.75
Honors Chemistry Chapter 2 Problem Handout Solve the following on separate sheets of paper. Where appropriate, show all work. 1. Convert each of the following quantities to the required unit. a. 12.75
Chapter 2. Measurements and Calculations
 Chapter 2 Measurements and Calculations Section 2.1 Scientific Notation Measurement Quantitative observation. Has 2 parts number and unit. Number tells comparison. Unit tells scale. If something HAS a
Chapter 2 Measurements and Calculations Section 2.1 Scientific Notation Measurement Quantitative observation. Has 2 parts number and unit. Number tells comparison. Unit tells scale. If something HAS a
BRCC CHM 101 Class Notes Chapter 1 Page 1 of 7
 BRCC CHM 101 Class Notes Chapter 1 Page 1 of 7 Chemistry - the study of matter, its behavior and interactions. matter - anything that takes up space and has mass mass - the substance which makes up the
BRCC CHM 101 Class Notes Chapter 1 Page 1 of 7 Chemistry - the study of matter, its behavior and interactions. matter - anything that takes up space and has mass mass - the substance which makes up the
Chapter 1 (Part 2) Measurements in Chemistry 1.6 Physical Quantities
 Chapter 1 (Part 2) Measurements in Chemistry 1.6 Physical Quantities This is a property that can by physically measured. It consists of a number and a unit of measure. (e.g. ) Units Units are very important.
Chapter 1 (Part 2) Measurements in Chemistry 1.6 Physical Quantities This is a property that can by physically measured. It consists of a number and a unit of measure. (e.g. ) Units Units are very important.
Chapter 12 Review. 2) About 90% of the star's total life is spent on the main sequence. 2)
 Chapter 12 Review TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) As a main-sequence star, the Sun's hydrogen supply should last about 10 billion years from the zero-age
Chapter 12 Review TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) As a main-sequence star, the Sun's hydrogen supply should last about 10 billion years from the zero-age
Chapter 1 (Part 2) Measurements in Chemistry
 Chapter 1 (Part 2) Measurements in Chemistry 1.7 Physical Quantities English Units Those of us who were raised in the US are very accustomed to these. Elsewhere in the world, these are very confusing.
Chapter 1 (Part 2) Measurements in Chemistry 1.7 Physical Quantities English Units Those of us who were raised in the US are very accustomed to these. Elsewhere in the world, these are very confusing.
The sun, an engine of nuclear energy
 The sun, an engine of nuclear energy By Big History Project, adapted by Newsela staff on 08.22.17 Word Count 905 Level 980L This image shows a view of all that remains of the oldest documented example
The sun, an engine of nuclear energy By Big History Project, adapted by Newsela staff on 08.22.17 Word Count 905 Level 980L This image shows a view of all that remains of the oldest documented example
Chapter 3 - Measurements
 Chapter 3 - Measurements You ll learn it in the summer, If not, it ll be a bummer. You ll need to know conversions, For units, Euro version. Metrics are powers of ten, And you might cry when, You re forced
Chapter 3 - Measurements You ll learn it in the summer, If not, it ll be a bummer. You ll need to know conversions, For units, Euro version. Metrics are powers of ten, And you might cry when, You re forced
In chemistry we use metric units (called SI units after the French term for Systeme internationale.
 Metric system / SI units: In chemistry we use metric units (called SI units after the French term for Systeme internationale. SI units: The SI units we ll be primarily concerned with are shown here: Base
Metric system / SI units: In chemistry we use metric units (called SI units after the French term for Systeme internationale. SI units: The SI units we ll be primarily concerned with are shown here: Base
AP Environmental Science Math Prep
 AP Environmental Science Math Prep Courtesy of Kara House, Franklin Central High School, Indiana This year in APES you will hear the two words most dreaded by high school students NO CALCULATORS! That
AP Environmental Science Math Prep Courtesy of Kara House, Franklin Central High School, Indiana This year in APES you will hear the two words most dreaded by high school students NO CALCULATORS! That
Chemistry in Our Lives. Chemistry and Chemicals
 Chemistry in Our Lives Chemistry and Chemicals What is chemistry? Chemistry is the study of substances in terms of Composition Structure Properties Reactions What a material it made of How the elementary
Chemistry in Our Lives Chemistry and Chemicals What is chemistry? Chemistry is the study of substances in terms of Composition Structure Properties Reactions What a material it made of How the elementary
Accuracy of Measurement: how close your measured value is to the actual measurement
 Standard: an exact quantity that people use to make measurements Good Example: a meter stick (everyone one knows the length of a meter) Bad Example: Ms. Pluchino s foot (everyone does not know how big
Standard: an exact quantity that people use to make measurements Good Example: a meter stick (everyone one knows the length of a meter) Bad Example: Ms. Pluchino s foot (everyone does not know how big
Introduction. The Scientific Method and Measurement
 Introduction The Scientific Method and Measurement Defining How We Look At The Universe Observation: seeing an event or process in nature we wish to explain Hypothesis: a tentative explanation based on
Introduction The Scientific Method and Measurement Defining How We Look At The Universe Observation: seeing an event or process in nature we wish to explain Hypothesis: a tentative explanation based on
Name /100. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chap. 1 & 2 Study Sheet AccChemistry Name /100 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements about soda pop
Chap. 1 & 2 Study Sheet AccChemistry Name /100 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements about soda pop
Module 4 Conversion Factors
 Module 4 Conversion Factors Prerequisite Module 4 requires Lessons 1A and 1B (on exponential fundamentals) and 2A and 2B (on metric fundamentals). Lesson 2C and Module 3 will be helpful, but not essential,
Module 4 Conversion Factors Prerequisite Module 4 requires Lessons 1A and 1B (on exponential fundamentals) and 2A and 2B (on metric fundamentals). Lesson 2C and Module 3 will be helpful, but not essential,
The Metric System & Conversions
 Purpose of this lab: The purpose of this lab exercise is for you to become familiar with basic measurements in metric units (SI), English units, and conversions between the two systems. Assignment Objectives:
Purpose of this lab: The purpose of this lab exercise is for you to become familiar with basic measurements in metric units (SI), English units, and conversions between the two systems. Assignment Objectives:
1. Scientific Notation A shorthand method of displaying very (distance to. Express in Scientific Notation
 Unit 2: MEASUREMENT 1. Scientific Notation 2. Metric System 3. Accuracy and Precision 4. Measuring & Counting Significant Figures 5. Calculations with Significant Figures 6. Density 1. Scientific Notation
Unit 2: MEASUREMENT 1. Scientific Notation 2. Metric System 3. Accuracy and Precision 4. Measuring & Counting Significant Figures 5. Calculations with Significant Figures 6. Density 1. Scientific Notation
Chapter 2a. Measurements and Calculations
 Chapter 2a Measurements and Calculations Chapter 2 Table of Contents 2.1 Scientific Notation 2.2 Units 2.3 Measurements of Length, Volume, and Mass 2.4 Uncertainty in Measurement 2.5 Significant Figures
Chapter 2a Measurements and Calculations Chapter 2 Table of Contents 2.1 Scientific Notation 2.2 Units 2.3 Measurements of Length, Volume, and Mass 2.4 Uncertainty in Measurement 2.5 Significant Figures
The Nature of Science
 chapter 1 The Nature of Science section 2 Standards of Measurement Before You Read If someone asked you how wide your desk is, how would you measure it? Would you measure using inches, centimeters, feet,
chapter 1 The Nature of Science section 2 Standards of Measurement Before You Read If someone asked you how wide your desk is, how would you measure it? Would you measure using inches, centimeters, feet,
The Metric System and Measurement
 Introduction The Metric System and Measurement The metric system is the world standard for measurement. Not only is it used by scientists throughout the world, but most nations have adopted it as their
Introduction The Metric System and Measurement The metric system is the world standard for measurement. Not only is it used by scientists throughout the world, but most nations have adopted it as their
The Metric System, Measurements, and Scientific Inquiry (Chapter 23)
 GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: The Metric System, Measurements, and Scientific Inquiry (Chapter 23) For this assignment, you will require: a calculator & a metric ruler. Objectives:
GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: The Metric System, Measurements, and Scientific Inquiry (Chapter 23) For this assignment, you will require: a calculator & a metric ruler. Objectives:
Ch 1: Introduction: Matter and Measurement
 AP Chemistry: Introduction: Matter and Measurement Lecture Outline 1.1 The Study of Chemistry Chemistry study of properties of materials and changes that they undergo. Can be applied to all aspects of
AP Chemistry: Introduction: Matter and Measurement Lecture Outline 1.1 The Study of Chemistry Chemistry study of properties of materials and changes that they undergo. Can be applied to all aspects of
# x 10. Quiz 1next Monday, June 18 Names/symbols of common elements Two math problems from chapter 2
 Announcements Wednesday, June 13, 2012 Quiz 1next Monday, June 18 Names/symbols of common elements Two math problems from chapter 2 MasteringChemistry assignments (due at 11:59 pm): Ch 1-2a: this Fri,
Announcements Wednesday, June 13, 2012 Quiz 1next Monday, June 18 Names/symbols of common elements Two math problems from chapter 2 MasteringChemistry assignments (due at 11:59 pm): Ch 1-2a: this Fri,
Where did measurement come from? What were the earliest measures? (No need to take notes yet)
 Where did measurement come from? What were the earliest measures? (No need to take notes yet) The earliest weights - seeds and beans. Ancient measurement of length was based on the human body, foot, stride,
Where did measurement come from? What were the earliest measures? (No need to take notes yet) The earliest weights - seeds and beans. Ancient measurement of length was based on the human body, foot, stride,
1 The Life Cycle of a Star
 CHAPTER 1 The Life Cycle of a Star Describe the life cycle of various size stars. Rings of glowing gas encircling Supernova 1987A, about 179,000 light-years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud, one of the
CHAPTER 1 The Life Cycle of a Star Describe the life cycle of various size stars. Rings of glowing gas encircling Supernova 1987A, about 179,000 light-years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud, one of the
Scientific Notation: Standard to Scientific
 Scientific Notation: Standard to Scientific Do you know what 300,000,000 m/sec is the measure of? It s the speed of light. Do you recognize what 0.000 000 000 753 kilograms is the measure of? This is the
Scientific Notation: Standard to Scientific Do you know what 300,000,000 m/sec is the measure of? It s the speed of light. Do you recognize what 0.000 000 000 753 kilograms is the measure of? This is the
Bell Work: Pre AP 22-Aug Why is it important to be able to a document to somebody, give two reasons that are not school focused?
 Bell Work: Pre AP 22-Aug-2016 Why is it important to be able to email a document to somebody, give two reasons that are not school focused? Turn in 22-Aug-2016 1. So you think you can Google EQ: How can
Bell Work: Pre AP 22-Aug-2016 Why is it important to be able to email a document to somebody, give two reasons that are not school focused? Turn in 22-Aug-2016 1. So you think you can Google EQ: How can
Chapter 3 - Scientific measurement. Using and expressing measurements
 Chapter 3 - Scientific measurement Using and expressing measurements How far off was Usain Bolt from winning gold in the 100m last weekend? What is a measurement? How do scientists make reporting measurement
Chapter 3 - Scientific measurement Using and expressing measurements How far off was Usain Bolt from winning gold in the 100m last weekend? What is a measurement? How do scientists make reporting measurement
Chapter 2 Measurements & Calculations. Quantity: A thing that can be measured. ex. Length (6.3 ft), mass (35 kg), and time (7.2 s)
 Chapter 2 Measurements & Calculations Quantity: A thing that can be measured. ex. Length (6.3 ft), mass (35 kg), and time (7.2 s) Measurements can be expressed in a variety of units: Example: length(cm,
Chapter 2 Measurements & Calculations Quantity: A thing that can be measured. ex. Length (6.3 ft), mass (35 kg), and time (7.2 s) Measurements can be expressed in a variety of units: Example: length(cm,
LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR
 LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR First stage = Protostar PROTOSTAR Cloud of gas and dust many light-years across Gravity tries to pull the materials together Eventually, at the center of the ball of dust and gas,
LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR First stage = Protostar PROTOSTAR Cloud of gas and dust many light-years across Gravity tries to pull the materials together Eventually, at the center of the ball of dust and gas,
Part 1: Matter. Chapter 1: Matter, Measurements, and Calculations. Sections MATTER Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space.
 Part 1: Matter Chapter 1: Matter, Measurements, and Calculations Sections 1.1-1.4 1 2 MATTER Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. MASS Mass is a measurement of the amount of matter in an
Part 1: Matter Chapter 1: Matter, Measurements, and Calculations Sections 1.1-1.4 1 2 MATTER Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. MASS Mass is a measurement of the amount of matter in an
