NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y. S. No. Ans. S. No. Ans. S. No. Ans.
|
|
|
- Tabitha Erika McCoy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y C o o n P r a c t i c e T e s t XII STD BATCHES [CF] Date: ANSWER PHYSICS CHEMISTRY MATHS S. No. Ans. S. No. Ans. S. No. Ans.. (A). (C) 6. (A). (B). (D) 6. (B). (C). (B) 6. (C) 4. (D) 4. (B) 64. (B) 5. (C) 5. (A) 65. (C) 6. (A) 6. (C) 66. (A) 7. (B) 7. (C) 67. (D) 8. (A) 8. (B) 68. (A) 9. (D) 9. (C) 69. (A) 0. (C) 40. (B) 70. (B). (B) 4. (A) 7. (C). (B) 4. (D) 7. (A). (C) 4. (C) 7. (D) 4. (A) 44. (B) 74. (A) 5. (C) 45. (B) 75. (D) 6. (C) 46. (B) 76. (A) 7. (A) 47. (D) 77. (B) 8. (B) 48. (B) 78. (A) 9. (A) 49. (C) 79. (A) 0. (C) 50. (B) 80. (B). (D) 5. (B) 8. (C). (D) 5. (C) 8. (C). (B) 5. (D) 8. (D) 4. (C) 54. (C) 84. (D) 5. (A) 55. (A) 85. (A) 6. (B) 56. (C) 86. (A) 7. (B) 57. (A) 87. (D) 8. (B) 58. (B) 88. (B) 9. (A) 59. (A) 89. (B) 0. (B) 60. (A) 90. (C) NARAYANA IIT/PMT ACADEMY ()
2 (Hint & Solution) PART A : PHYSICS. Here, Radius, r = 0 c = 0 0 Nuber of turns, N = 00 Current, I = A Area of the coil, A r Magnetic oent of the coil, M NIA NI r.4 A. Magnetic oent of the current loop M IA I a kˆ A. We know that force on a carrying wire placed a agnetic field, is given by F I l B Given that I A, l 0.5iˆ B iˆ 4 ˆj T and F 0.5iˆ iˆ 4 ˆj iˆ ˆj kˆ kn ˆ 4 0 Therefore, agnitude of force is N and its direction is along positive z-ais. v 5. As, r, Bq r q 4 Hence, p : r q p p 6. The agnetic field in between because of each will be in opposite direction in between 0 i ˆ 0 i B j ˆj d ˆj 0i d at d, Bin between 0 for d, Bin between ˆj for d, Bin between ˆj towards, net agnetic field will add up and direction will be ĵ towards ', net agnetic field will add up and direction will be ĵ NARAYANA IIT/PMT ACADEMY ()
3 8. Using F qv B, the force on the charge in the region a a ust be in the direction iˆ ˆ, j that is, in +Z-direction, which is vertically upward. And in the region a a, the force on the charge will be in Z-direction, which is vertically downward. For a a, path will be concave upwards. For a a, path will be concave downward Moreover, there ust not be any kind in the path at = a. 9. Conductor A attracts conductor C towards A Force towards A 0 IIl r N Again force towards B N 0. (C) 7 Resultant force towards B N N I I L d L I L F 0 d Where L is the overlapping length. Two long parallel conductor carrying currents in the sae direction attract each other.. or v qvbsin 90 r qbr v T r v qb. Magnetic field will not apply any force on the electron. Electric field will apply a force on the electron in the opposite direction to the otion. Also fro Lorentz equation, F e E v B ee F ee a ee vt v0 t Thus, velocity decreases. NARAYANA IIT/PMT ACADEMY ()
4 . (C) When a +ve charge of velocity v enters a unifor field of B acting in Z-direction k ˆ, the charge akes a circular trajectory. v qvb R 4. The agnetic field due to circular coil, 0i 0i B ; B r r As both the coils are perpendicular to each other, hence B is to B. 5. F B B B 0 qvb (directed radially outward) v N g sin qvb R v or N g sin qvb R Hence, at gr Na g qb gr R g qb gr Wb / 6. and 0II F l d 0 I I F ' l d F F. 7. Since, F is perpendicular to v, therefore work done per second W F v Fv cos i l B ; where r r (l being the length of the wire) 0 B i l Now, when the sae wire is bent into a circular loop of n turns n r ' l l r ' n n0i 0i Now, B ' n n B r ' l v r r v q 4 qb r v q NARAYANA IIT/PMT ACADEMY (4)
5 . Radius of the circular path of a charged particle in a agnetic field is given by: v K r Bq Bq ( kinetic energy, For the sae value of K and B, r q p d rp : rd : a : : q q q p d K v ) 4 : : : : or r rp rd e e e. Considering the aperian loop (shown by dotted line), no current is enclosed by this loop. Therefore, the agnetic field will be zero inside the tube because according to Apere s law, B. dl 0 current enclosed by aperian loop. 6. Magnetic induction at the centre of a circular loop of radius R carrying current I is 0 I 0I B 4 R R RB I Area of the loop, 0 A R RB Magnetic oent of the loop, M IA R 7. vr = l..(i) M = NIA (ii) BR Electric field can deviate the path of particle as shown in fig, when it is along negative Y- ais. This is not any option. The given path can be possible only if electric force iparts velocity along X-ais and agnetic force is along negative Y-ais. This is possible only in option (B). In this case F ae qv B qaiˆ qviˆ ckˆ aj ˆ qaiˆ qvcj ˆ. 0. If r is ore than l then the particle enters region V III where r (in region II) qb qbr i.e., V qbl in region III () is correct and () is wrong qbl Clearly path length in region II will be aiu when V () is correct Tie T, which is independent of V so tie spent in region II is sae for any velocity qb V as long as particle coes back to region I. NARAYANA IIT/PMT ACADEMY (5)
6 PART B : CHEMISTRY. Glycerol + oalic acid 0C HCH C. + NaH dil.hcl H/H CH CCl CH CNa CH CH CH CN (X) (Y) (Z) Acetonitrile. The order of increasing boiling point aong the acid derivatives is CH CCl < CHC CH < (CH C) < CH CNH. Absence of Higher Etensive Hydrogen olecular ass interolecular Bonding and ore surface area hydrogen bonding 4. The rate deterining step for esterification is the addition of alcohol. The rate deterining step involves change of hybridization of carbonyl carbon fro sp² to sp³ and consequently steric retardation increases as the size of alcohol increases and hence the rate of esterification decreases. +CHC 5. H CCH ne H group on acylation bring about a change in H olecular ass = 4, Molecular ass of C4H0 =4+0+ 6=06 Actual increases in olecular ass = 84 Nuber of H groups = 84/4 =. 7. Acetic acid is soluble in cold water while benzoic acid is not. 8. Larger the nuber of electron releasing alkyl groups at carbon, less the susceptibility of the acid to the nucleophilic attack of alcohol. Thus the order of esterification is I > II > III. 9. CH = C CCH CH CH Q= C = C H H H /H + CH CH CCH CH = C + H /H CHCH H Tautoetrises CH CH C = C Acetone and propanal can be distinguished by Fehling solution H H CH C CH Acetone H Tautoetrises CH CH CH Propanal 40. NH is stronger electron releasing than CH group. Therefore broination will take place at p-position w.r.t NH group. 4. Epect (A) other do not provide iodofor test 4. The electron- Releasing CH group facilitates the release of hydride ion. 44. Fehling s reagent. Tollen s reagent and Schiff s reagent react with acetaldehyde only. Grignard s reagent reacts with both acetaldehyde and acetone. 45. It is an eaple of nucleophilic addition. NARAYANA IIT/PMT ACADEMY (6)
7 46. Since the copound A reduces Fehling solution is ust be an aldelyde. CCl CH (A) chloral chloral could be obtained by the action of Cl on ethyl alcohol. ( ) Cl () C H H +Cl CH CH CCl CH CCl CH 5 HCl (A) (B) 47. C6H5CH H C CH CN NaH+Ca (A) H CHCCl Anhyd.AlCl (B) C CH H C CH H CH HCN (C) (D) 48. H AlCl CH C Cl HCl CH H C C H CH (trans diol) C CH C CH C CH + Mg.Hg/THF 49. This is perkin s reaction 50. CH CH CH although has no hydrogen ato, will not give aldol condensation. Cl Cnc.KH CH + HCH Cl CH H HCK 5. In Cannizzaro reaction of aroatic aldehyde and HCH. It is always foraldehyde which is oidized. H H H Δ 5. CH C + CH C CH C CH H H CH C CH CH CH CH C CH C CH Mesityl oide CH 54. C H C CH 6 5 H C H CH CH 6 5 Cl NaH(aq) Cl C 6 H 5 C CH H H H C H C CH + NaH/,H 6 5 Internal Cannizzaro NARAYANA IIT/PMT ACADEMY (7)
8 55. Cl Cl C CH although has no hydrogen ato, still it does not give Cannizzaro reaction. Cl This is because with H, it gives halofor reaction. 56. Benzaldehyde has not Hydrogen 57. (A) CH CH H C CH CH CH 60. (A) Cl CN CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH + KCN H/H PART C : MATHEMATICS 6. dy y y 0 d y dy y y d y Curves are orthogonal 0 6. f ' / / / [0,]] / / f ' 0 f is decreasing on [0, ]. Greatest value of f is f 0 6. f ' 0, R. f f ' 64. Signs of f ' Miniu occurs at = f ' 6 8a a 65. f ' 0 a, a f " 8a f " 6a 0 and f " a 6a 0 p a, q a p q a a a 0 0, a a Let ' f a b c a b f c d f 0 df a b 6 0 By Roll s theore, at least one root of f =0 lies in (0, ) ' 67. y² = 8 (i) Differentiating w.r.t t dy d y 8 dt dt dy d y. 8 dt dt 9 y NARAYANA IIT/PMT ACADEMY (8)
9 Fro equation (i) is 9 9, a cos, ya sin dy a cos d a sin Equation of noral at point a cos, a sin is 9 Required point 8 sin y a sin a cos cos y cos a sin It is clear that noral passes through fied point (a, 0) 69. y 5 5 dy 5 d dy d,0 dy d,0 Product of slopes tangents is angle between Increasing in, Let f4 f ' 0 Increasing in, 7. V 4 0 r,0 r 5 dv 50. dt 4 r dr 50 dt dr dt 8 (where r = 5) 7. Any point on ellipse is P, y a cos bsin Area of rectangle = 4ab cos sin absin Maiu area = ab. b a cos b sin a 70. Let f f Increasing in Let, 4 f f ' Not increasing in, Let / ( ) 6 f f By LMVT f 6 f f ',,6 6 f 6 f And f ' 6 f 6 f dy d a cos cos sin a sin sin cos dy sin d cos Equation of noral is y a sin cos cos a cos cos sin cos y sin a Distance fro origin = a (constant NARAYANA IIT/PMT ACADEMY (9)
10 cos Slope of noral = tan sin Angle ade with ais is 75. f ' 76. Signs of f ' f ' changes sign as crosses. f has inia at =. f f f ' c, c loge 0 c c log e log e f ' cos sin sin cos Graph of y p q cuts -ais at three distinct pints dy p 0 d Maiu at p, inia at 79. Condition for shortest distance is slope of tangent to = y² ust be sae as slope of line y = + y, y 4,, y 0 4 p Shortest distance = p a b c p ' 4 and ' 0 0 c 0 p ' 4 a b D 9a b 0 9a b 0( p ' = 0 has only one root = 0) P P a 0 p has only one change of sign. = 0 ' is a point of inia. P a b d P 0 d P a b d, 0, 0 P P P P P P P is not iniu but P() is aiu 4 8. y 8 y ' y (, ) is point of contact thus y = is tangent 8. f li f k li f k f has a local iniu at = - f f f k k k Possible value of k is NARAYANA IIT/PMT ACADEMY (0)
11 8. e e AM GM e e f 0 so stateent - is correct As f() is continuous and / belongs to range 0, or f, f c for soe C. Hence correction option is (d) 84. dy dy y 6y 0 d d dy y d y ] Slope of noral at (, ) = - y Equation of noral y Solving we get point as (, ) and, So in forth quadrant 85. f is constant is [, 5] 86. V 4500 r dv dr 7 7 dt dt r r r 9 dr dt 9 f ' b a 0 b a 0; 4b a 0 a b ; b 4 a f 89. ' 6 so f() is increasing have distinct roots. equation cannot f ' 4 sin cos 4 cos sin sin 4 for increasing sin f ' 0 e 0 f ' 0 NARAYANA IIT/PMT ACADEMY ()
12 TPIC/SUB TPIC Q. NS. PHYSICS Magnetic oent,, 6, 7, 5 Force a current carrying a wire, 9, 6 Apere law 4, Motion of charge in agnetic field 5, 8,,,, 5, 7, 9,,, 4, 8, 0 Biot-Savart law 6, 4, 8, 9 Magnetic force on a oving charge 7, 0, Magnetic force of a current carrying wire 0 CHEMISTRY Foration of Acid,, 57, 47, 46 Esterification 4, 8 Variation of B.P. rder of hydrolysis 58 Cannizzaro 4, 5, 55, 54, 5 HVZ Reaction 60 Aldol 5, 50, 56 Miscellaneous 5, 6, 7, 9, 40, 4, Perkin Reaction 49 Pinacol Pincacolone 48 Nucleophilic addition 44, 45 MATHEMATICS Maia-Minia 6, 64, 65, 7, 75, 79, 8, 87 Increasing-Decreaseing 6, 70, 7, 89, 90 Tangent Noral 6, 68, 69, 74, 8, 84 Rolle s Theore 66, 76, 78, 80, 88 Mean Value 67, 7, 7, 8, 85 NARAYANA IIT/PMT ACADEMY ()
CHAPTER 21 MAGNETIC FORCES AND MAGNETIC FIELDS
 CHAPTER 21 MAGNETIC FORCES AND MAGNETIC FIELDS PROBLEMS 5. SSM REASONING According to Equation 21.1, the agnitude of the agnetic force on a oving charge is F q 0 vb sinθ. Since the agnetic field points
CHAPTER 21 MAGNETIC FORCES AND MAGNETIC FIELDS PROBLEMS 5. SSM REASONING According to Equation 21.1, the agnitude of the agnetic force on a oving charge is F q 0 vb sinθ. Since the agnetic field points
XII-S (NEW) - Paper-I
 XII-S (NEW) / CPT /9/08/6 NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y CPT T EST 5 XII-S (NEW) - Paper-I (JEE ADVANCE MDEL 03-P) ANSWER KEY PHYSICS CHEMISTRY MATHEMATICS Q.N. KEY Q.N. KEY Q.N. KEY. (A) (B) 4 (B).
XII-S (NEW) / CPT /9/08/6 NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y CPT T EST 5 XII-S (NEW) - Paper-I (JEE ADVANCE MDEL 03-P) ANSWER KEY PHYSICS CHEMISTRY MATHEMATICS Q.N. KEY Q.N. KEY Q.N. KEY. (A) (B) 4 (B).
Important Formulae & Basic concepts. Unit 3: CHAPTER 4 - MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT AND MAGNETISM CHAPTER 5 MAGNETISM AND MATTER
 Iportant Forulae & Basic concepts Unit 3: CHAPTER 4 - MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT AND MAGNETISM CHAPTER 5 MAGNETISM AND MATTER S. No. Forula Description 1. Magnetic field induction at a point due to current
Iportant Forulae & Basic concepts Unit 3: CHAPTER 4 - MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT AND MAGNETISM CHAPTER 5 MAGNETISM AND MATTER S. No. Forula Description 1. Magnetic field induction at a point due to current
Pearson Physics Level 30 Unit VI Forces and Fields: Chapter 12 Solutions
 Concept Check (top) Pearson Physics Level 30 Unit VI Forces and Fields: Chapter 12 Solutions Student Book page 583 Concept Check (botto) The north-seeking needle of a copass is attracted to what is called
Concept Check (top) Pearson Physics Level 30 Unit VI Forces and Fields: Chapter 12 Solutions Student Book page 583 Concept Check (botto) The north-seeking needle of a copass is attracted to what is called
(1) I have completed at least 50% of the reading and study-guide assignments associated with the lecture, as indicated on the course schedule.
 iclicker Quiz (1) I have completed at least 50% of the reading and study-guide assignments associated with the lecture, as indicated on the course schedule. a) True b) False Hint: pay attention to how
iclicker Quiz (1) I have completed at least 50% of the reading and study-guide assignments associated with the lecture, as indicated on the course schedule. a) True b) False Hint: pay attention to how
ALDEHYDE, KETONES,& CARBOXYLIC ACID. a) 2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanenitrile
 ALDEHYDE, KETNES,& CARBXYLIC ACID 1) C H 3 CH dil.h 2 S 4 HgS 4 A HCN H 2 /Ni B The IUPAC name of B is 2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanenitrile b) 2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanoic acid 2-hydroxypropanoic acid d) 1-amino-2-methylpropanol-2
ALDEHYDE, KETNES,& CARBXYLIC ACID 1) C H 3 CH dil.h 2 S 4 HgS 4 A HCN H 2 /Ni B The IUPAC name of B is 2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanenitrile b) 2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanoic acid 2-hydroxypropanoic acid d) 1-amino-2-methylpropanol-2
3) Between aldehyde and ketones which one is confirmed using Tollen s reagent.
 UNIT ALDEHYDES KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS ) What are aldehydes? Aldehydes are the organic compounds containing carbonyl group,linked with one hydrogen and one alkyl /aryl group. ) What are carboxylic
UNIT ALDEHYDES KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS ) What are aldehydes? Aldehydes are the organic compounds containing carbonyl group,linked with one hydrogen and one alkyl /aryl group. ) What are carboxylic
SECTION A. 1. Which is general formula of aldehyde and ketone? (c) CnHnO
 SEM 4 SLE UNIT 5 SECTION A 1. Which is general formula of aldehyde and ketone? (a) CnH2n+1O (b) CnH2nO (c) CnHnO (d) CnH2n+2O Ans: (b) CnH2nO 2. Propanal and propan- 2- one are which type of isomers? (a)
SEM 4 SLE UNIT 5 SECTION A 1. Which is general formula of aldehyde and ketone? (a) CnH2n+1O (b) CnH2nO (c) CnHnO (d) CnH2n+2O Ans: (b) CnH2nO 2. Propanal and propan- 2- one are which type of isomers? (a)
Part A Here, the velocity is at an angle of 45 degrees to the x-axis toward the z-axis. The velocity is then given in component form as.
 Electrodynaics Chapter Andrew Robertson 32.30 Here we are given a proton oving in a agnetic eld ~ B 0:5^{ T at a speed of v :0 0 7 /s in the directions given in the gures. Part A Here, the velocity is
Electrodynaics Chapter Andrew Robertson 32.30 Here we are given a proton oving in a agnetic eld ~ B 0:5^{ T at a speed of v :0 0 7 /s in the directions given in the gures. Part A Here, the velocity is
Physics 8.02 Exam Two Equation Sheet Spring 2004
 Physics 8.0 Exam Two Equation Sheet Spring 004 closed surface EdA Q inside da points from inside o to outside I dsrˆ db 4o r rˆ points from source to observer V moving from a to b E ds 0 V b V a b E ds
Physics 8.0 Exam Two Equation Sheet Spring 004 closed surface EdA Q inside da points from inside o to outside I dsrˆ db 4o r rˆ points from source to observer V moving from a to b E ds 0 V b V a b E ds
( ) 1.5. Solution: r = mv qb ( 3.2!10 "19 C ) 2.4
 Section 8.4: Motion of Charged Particles in Magnetic Fields Tutorial 1 Practice, page 401 1. Given: q 3.2 10 19 C; 6.7 10 27 kg; B 2.4 T; v 1.5 10 7 /s Analysis: r v Solution: r v 6.7!10 "27 # kg ) 1.5!10
Section 8.4: Motion of Charged Particles in Magnetic Fields Tutorial 1 Practice, page 401 1. Given: q 3.2 10 19 C; 6.7 10 27 kg; B 2.4 T; v 1.5 10 7 /s Analysis: r v Solution: r v 6.7!10 "27 # kg ) 1.5!10
Q1. A wave travelling along a string is described by
 Coordinator: Saleem Rao Wednesday, May 24, 2017 Page: 1 Q1. A wave travelling along a string is described by y( x, t) = 0.00327 sin(72.1x 2.72t) In which all numerical constants are in SI units. Find the
Coordinator: Saleem Rao Wednesday, May 24, 2017 Page: 1 Q1. A wave travelling along a string is described by y( x, t) = 0.00327 sin(72.1x 2.72t) In which all numerical constants are in SI units. Find the
CHAPTER 27 HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS
 CHAPTER 7 HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS 7.1. IDENTIFY and SET UP: Apply Eq.(7.) to calculate F. Use the cross products of unit vectors from Section 1.10. EXECUTE: v 4.1910 4 m/siˆ 3.8510 4 m/s ˆj (a) B 1.40 Tˆ i
CHAPTER 7 HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS 7.1. IDENTIFY and SET UP: Apply Eq.(7.) to calculate F. Use the cross products of unit vectors from Section 1.10. EXECUTE: v 4.1910 4 m/siˆ 3.8510 4 m/s ˆj (a) B 1.40 Tˆ i
Magnetism. Permanent magnets Earth s magnetic field Magnetic force Motion of charged particles in magnetic fields
 Magnetism Permanent magnets Earth s magnetic field Magnetic force Motion of charged particles in magnetic fields Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Magnetism Permanent magnets Earth s magnetic field Magnetic force Motion of charged particles in magnetic fields Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
 Unit - 12 ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS 1. Indicate the electrophilic and nucleophilic centres in acetaldehyde. 2. Write the IUPAC names of the following organic compounds : 122 XII Chemistry
Unit - 12 ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS 1. Indicate the electrophilic and nucleophilic centres in acetaldehyde. 2. Write the IUPAC names of the following organic compounds : 122 XII Chemistry
Chapter 29 Solutions
 Chapter 29 Solutions 29.1 (a) up out of the page, since the charge is negative. (c) no deflection (d) into the page 29.2 At the equator, the Earth's agnetic field is horizontally north. Because an electron
Chapter 29 Solutions 29.1 (a) up out of the page, since the charge is negative. (c) no deflection (d) into the page 29.2 At the equator, the Earth's agnetic field is horizontally north. Because an electron
NARAYANA. C o m m o n P r a c t i c e T e s t 9 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Date: PHYSICS CHEMISTRY MATHEMATICS 16. (D) 31. (A) 46. (D) 61.
![NARAYANA. C o m m o n P r a c t i c e T e s t 9 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Date: PHYSICS CHEMISTRY MATHEMATICS 16. (D) 31. (A) 46. (D) 61. NARAYANA. C o m m o n P r a c t i c e T e s t 9 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Date: PHYSICS CHEMISTRY MATHEMATICS 16. (D) 31. (A) 46. (D) 61.](/thumbs/77/74538831.jpg) NAAYANA I I T / N E E T A C A D E M Y. (C). (B). (A). (D) 5. (B) 6. (D) 7. (B) 8. (B) 9. (B) 0. (D). (D). (C). (B). (D) 5. (C). (C) C o m m o n P r a c t i c e T e s t 9 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Date: 9.06.7
NAAYANA I I T / N E E T A C A D E M Y. (C). (B). (A). (D) 5. (B) 6. (D) 7. (B) 8. (B) 9. (B) 0. (D). (D). (C). (B). (D) 5. (C). (C) C o m m o n P r a c t i c e T e s t 9 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Date: 9.06.7
NARAYANA IIT ACADEMY INDIA DPT FOR OUTGOING IIT TOPPERS
 Date: 1-04-16 http://narayanadwarka.blogspot.in NARAYANA IIT ACADEMY INDIA DPT FR UTGING IIT TPPERS PHYSICS SECTIN 1 (TTAL MARKS 0) (Single correct Answer Type) This section contains 10 multiple choice
Date: 1-04-16 http://narayanadwarka.blogspot.in NARAYANA IIT ACADEMY INDIA DPT FR UTGING IIT TPPERS PHYSICS SECTIN 1 (TTAL MARKS 0) (Single correct Answer Type) This section contains 10 multiple choice
Alkyl phenyl ketones are usually named by adding the acyl group as prefix to phenone.
 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones Aldehydes: Often called by their common names instead of IUPAC names. Ketones: Derived by naming two alkyl or aryl groups bonded
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones Aldehydes: Often called by their common names instead of IUPAC names. Ketones: Derived by naming two alkyl or aryl groups bonded
NARAYANA XII STD BATCHES [CF] (Hint & Solution) PART A : PHYSICS. When then material is removed, the force between them becomes
![NARAYANA XII STD BATCHES [CF] (Hint & Solution) PART A : PHYSICS. When then material is removed, the force between them becomes NARAYANA XII STD BATCHES [CF] (Hint & Solution) PART A : PHYSICS. When then material is removed, the force between them becomes](/thumbs/83/88533061.jpg) NARAYANA I I T / N E E T A C A D E M Y Co m mo n Pr act i ce Te st Date: 6.04.7 XII STD BATCHES [CF] ANSWER.. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 0... 3. 4. 5. PHYSICS 6. 7. 8. 9. 0... 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 30. 3. 3.
NARAYANA I I T / N E E T A C A D E M Y Co m mo n Pr act i ce Te st Date: 6.04.7 XII STD BATCHES [CF] ANSWER.. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 0... 3. 4. 5. PHYSICS 6. 7. 8. 9. 0... 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 30. 3. 3.
ALDEH. I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
 Unit 12 ALDEHYDE ALDEH YDES, KETONE KET ONES AND CARBOX C ARBOXYLIC ACIDS I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Addition of water to alkynes occurs in acidic medium and in the presence of Hg 2+ ions
Unit 12 ALDEHYDE ALDEH YDES, KETONE KET ONES AND CARBOX C ARBOXYLIC ACIDS I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Addition of water to alkynes occurs in acidic medium and in the presence of Hg 2+ ions
IIT-JEE 2010 (Code-8) Answer Keys (Paper I)
 (ode-8) Answer Keys (Paper I) heistry. A. D. A 4. D 5. B 6. 7. 8. B 9. A,. A,B. B,,D.,D. B,D 4. B 5. D 6. 7. B 8. 9.. 4... 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 5 Matheatics 9. B. A. A.. 4. D 5. D 6. B 7. B 8. B, 9.,D 4. A 4.
(ode-8) Answer Keys (Paper I) heistry. A. D. A 4. D 5. B 6. 7. 8. B 9. A,. A,B. B,,D.,D. B,D 4. B 5. D 6. 7. B 8. 9.. 4... 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 5 Matheatics 9. B. A. A.. 4. D 5. D 6. B 7. B 8. B, 9.,D 4. A 4.
Class XII - Chemistry Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acid Chapter-wise Problems
 Class XII - Chemistry Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acid Chapter-wise Problems I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Addition of water to alkynes occurs in acidic medium and in the presence of Hg
Class XII - Chemistry Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acid Chapter-wise Problems I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Addition of water to alkynes occurs in acidic medium and in the presence of Hg
PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY & MATHEMATICS. Time Allotted: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 210
 FIITJEE PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY & MATHEMATICS CPT - 1 CDE: PAPER - 1 Time Allotted: Hours Maximum Marks: 10 Please read the instructions carefully. You are allotted 5 minutes specifically for this purpose.
FIITJEE PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY & MATHEMATICS CPT - 1 CDE: PAPER - 1 Time Allotted: Hours Maximum Marks: 10 Please read the instructions carefully. You are allotted 5 minutes specifically for this purpose.
72. (30.2) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires.
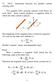 7. (3.) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires. Two parallel wires carrying currents exert forces on each other. Each current produces a agnetic field in which the other current is placed.
7. (3.) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires. Two parallel wires carrying currents exert forces on each other. Each current produces a agnetic field in which the other current is placed.
NARAYANA. Co m m o n Pr act ice T e st 3 Date: XII STD BATCHES [CF] (Hint & Solution) PART A : PHYSICS
![NARAYANA. Co m m o n Pr act ice T e st 3 Date: XII STD BATCHES [CF] (Hint & Solution) PART A : PHYSICS NARAYANA. Co m m o n Pr act ice T e st 3 Date: XII STD BATCHES [CF] (Hint & Solution) PART A : PHYSICS](/thumbs/86/93679485.jpg) NARAYANA I I T / N E E T A C A D E M Y Co m m o n Pr act ice T e st Date: 0.04.7 XII STD BATCHES [CF] ANSWER PHYSICS... 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 0.... 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 0.... 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 0. CHEMISTRY...
NARAYANA I I T / N E E T A C A D E M Y Co m m o n Pr act ice T e st Date: 0.04.7 XII STD BATCHES [CF] ANSWER PHYSICS... 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 0.... 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 0.... 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 0. CHEMISTRY...
Chemistry Questions ans Answers BASED ON HIGH ORDER THINKING SKILL (HOTS) UNIT- 12 ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBXYLIC ACID
 Chemistry Questions ans Answers BASED N IG RDER TINKING SKILL (TS) UNIT- 12 ALDEYDES, KETNES AND CARBXYLIC ACID 1 MARK QUESTINS Q. 1. Name the reaction and the reagent used for the conversion of acid chlorides
Chemistry Questions ans Answers BASED N IG RDER TINKING SKILL (TS) UNIT- 12 ALDEYDES, KETNES AND CARBXYLIC ACID 1 MARK QUESTINS Q. 1. Name the reaction and the reagent used for the conversion of acid chlorides
PHYS Fields and Waves
 PHYS 41 - Fields and Waves Consider a charge moving in a magnetic field B field into plane F=ma acceleration change of direction of velocity Take F as centripetal force: 0 F qvb cos90 qvb F Centripetal
PHYS 41 - Fields and Waves Consider a charge moving in a magnetic field B field into plane F=ma acceleration change of direction of velocity Take F as centripetal force: 0 F qvb cos90 qvb F Centripetal
16 - MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENTS Page 1 ( Answers at the end of all questions )
 16 - MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENTS Page 1 1 ) One conducting U tue can slide inside another as shown in the figure, aintaining electrical contacts etween the tues. The agnetic field B is perpendicular to
16 - MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENTS Page 1 1 ) One conducting U tue can slide inside another as shown in the figure, aintaining electrical contacts etween the tues. The agnetic field B is perpendicular to
Magnets. Domain = small magnetized region of a magnetic material. all the atoms are grouped together and aligned
 Magnetic Fields Magnets Domain = small magnetized region of a magnetic material all the atoms are grouped together and aligned Magnets Ferromagnetic materials domains can be forced to line up by applying
Magnetic Fields Magnets Domain = small magnetized region of a magnetic material all the atoms are grouped together and aligned Magnets Ferromagnetic materials domains can be forced to line up by applying
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids
 Teacher Orientation Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids contains following topics: Nomenclature Preparation Properties Student Orientation Preparation and Properties Of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic
Teacher Orientation Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids contains following topics: Nomenclature Preparation Properties Student Orientation Preparation and Properties Of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic
Class XII- Physics - Assignment Topic: - Magnetic Effect of Current
 LJPS Gurgaon 1. An electron beam projected along +X axis, experiences a force due to a magnetic field along +Y axis. What is the direction of the magnetic field? Class XII- Physics - Assignment Topic:
LJPS Gurgaon 1. An electron beam projected along +X axis, experiences a force due to a magnetic field along +Y axis. What is the direction of the magnetic field? Class XII- Physics - Assignment Topic:
Chapter VI: Motion in the 2-D Plane
 Chapter VI: Motion in the -D Plane Now that we have developed and refined our vector calculus concepts, we can ove on to specific application of otion in the plane. In this regard, we will deal with: projectile
Chapter VI: Motion in the -D Plane Now that we have developed and refined our vector calculus concepts, we can ove on to specific application of otion in the plane. In this regard, we will deal with: projectile
1 (40) Gravitational Systems Two heavy spherical (radius 0.05R) objects are located at fixed positions along
 (40) Gravitational Systes Two heavy spherical (radius 0.05) objects are located at fixed positions along 2M 2M 0 an axis in space. The first ass is centered at r = 0 and has a ass of 2M. The second ass
(40) Gravitational Systes Two heavy spherical (radius 0.05) objects are located at fixed positions along 2M 2M 0 an axis in space. The first ass is centered at r = 0 and has a ass of 2M. The second ass
Chapter 27 Sources of Magnetic Field
 Chapter 27 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents). Ampere s Law
Chapter 27 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents). Ampere s Law
Year 12 Physics Holiday Work
 Year 1 Physics Holiday Work 1. Coplete questions 1-8 in the Fields assessent booklet and questions 1-3 In the Further Mechanics assessent booklet (repeated below in case you have lost the booklet).. Revise
Year 1 Physics Holiday Work 1. Coplete questions 1-8 in the Fields assessent booklet and questions 1-3 In the Further Mechanics assessent booklet (repeated below in case you have lost the booklet).. Revise
Magnetic Force Acting on a Current- Carrying Conductor IL B
 Magnetic Force Acting on a Current- Carrying Conductor A segment of a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field. The magnetic force exerted on each charge making up the current is qvd and the net force
Magnetic Force Acting on a Current- Carrying Conductor A segment of a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field. The magnetic force exerted on each charge making up the current is qvd and the net force
Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones
 Aldehydes and Ketones Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Common aldehydes H H Methanl (formaldehyde) H3C H CH3CH2 ethanl (acetaldehyde) H propanal (propionaldehyde) CH3CH2CH2 butanal (n-butyraldehyde)
Aldehydes and Ketones Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Common aldehydes H H Methanl (formaldehyde) H3C H CH3CH2 ethanl (acetaldehyde) H propanal (propionaldehyde) CH3CH2CH2 butanal (n-butyraldehyde)
Today s lecture: Motion in a Uniform Magnetic Field continued Force on a Current Carrying Conductor Introduction to the Biot-Savart Law
 PHYSICS 1B Today s lecture: Motion in a Uniform Magnetic Field continued Force on a Current Carrying Conductor Introduction to the Biot-Savart Law Electricity & Magnetism A Charged Particle in a Magnetic
PHYSICS 1B Today s lecture: Motion in a Uniform Magnetic Field continued Force on a Current Carrying Conductor Introduction to the Biot-Savart Law Electricity & Magnetism A Charged Particle in a Magnetic
Lecture 28. PHYC 161 Fall 2016
 Lecture 28 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 CPS 27-1 At which point is the magnitude of the magnetic field the largest? A. B. C. D E. Yes, back to flux, which means back to surface integrals. Magnetic Flux We can define
Lecture 28 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 CPS 27-1 At which point is the magnitude of the magnetic field the largest? A. B. C. D E. Yes, back to flux, which means back to surface integrals. Magnetic Flux We can define
The Claisen Condensation
 Lecture 22 The Claisen Condensation CH 3 CCH 2 CH 3 CH 2 CCH 2 CH 3 April 10, 2018 Hydrolysis of Amides Hydrolysis of amides is irreversible. In acid solution the amine product is protonated to give an
Lecture 22 The Claisen Condensation CH 3 CCH 2 CH 3 CH 2 CCH 2 CH 3 April 10, 2018 Hydrolysis of Amides Hydrolysis of amides is irreversible. In acid solution the amine product is protonated to give an
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles شیمی آلی 2
 Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition The
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition The
ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS. Points to Remember
 193 UNIT 12 ALDEHYDES, KETNES AND CARBXYLIC ACIDS Points to Remember 1. Aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and their derivatives are commonly called as carbonyl compounds. 2. In Rosemund s reduction,
193 UNIT 12 ALDEHYDES, KETNES AND CARBXYLIC ACIDS Points to Remember 1. Aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and their derivatives are commonly called as carbonyl compounds. 2. In Rosemund s reduction,
14.1 Aldehydes and Ketones Copyright 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 14 Aldehydes, Ketones, and Chiral Molecules 14.1 Aldehydes and Ketones Copyright 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings Carbonyl Group in Aldehydes A carbonyl group and
Chapter 14 Aldehydes, Ketones, and Chiral Molecules 14.1 Aldehydes and Ketones Copyright 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings Carbonyl Group in Aldehydes A carbonyl group and
Ch 19 Aldehydes and Ketones
 Ch 19 Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes (RCHO), with the exception of formaldehyde (H 2 CO), are compounds with both an H and an organic group attached to a carbonyl. Ketones (R 2 CO) are compounds with
Ch 19 Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes (RCHO), with the exception of formaldehyde (H 2 CO), are compounds with both an H and an organic group attached to a carbonyl. Ketones (R 2 CO) are compounds with
ALL INDIA TEST SERIES
 AITS-FT-V-PCM(S)-JEE(Main)/4 Fro Classroo/Integrated School Progras 7 in Top, in Top, 54 in Top, 6 in Top 5 All India Ranks & 4 Students fro Classroo /Integrated School Progras & 7 Students fro All Progras
AITS-FT-V-PCM(S)-JEE(Main)/4 Fro Classroo/Integrated School Progras 7 in Top, in Top, 54 in Top, 6 in Top 5 All India Ranks & 4 Students fro Classroo /Integrated School Progras & 7 Students fro All Progras
Handout 8: Sources of magnetic field. Magnetic field of moving charge
 1 Handout 8: Sources of magnetic field Magnetic field of moving charge Moving charge creates magnetic field around it. In Fig. 1, charge q is moving at constant velocity v. The magnetic field at point
1 Handout 8: Sources of magnetic field Magnetic field of moving charge Moving charge creates magnetic field around it. In Fig. 1, charge q is moving at constant velocity v. The magnetic field at point
1. What is the major organic product obtained from the following sequence of reactions?
 CH320 N N_HW1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. Carefully record your answers on the Scantron
CH320 N N_HW1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. Carefully record your answers on the Scantron
SECTION-A (NEXT FOURTY FIVE QUESTIONS: SINGLE CHOICE ONLY ONE CORRECT ANSWER) (c) (c.) (c.) (b.) Dimerization of benzoic acid
 th Mains 7 th Aug Chemistry Paper Solution Subject-EMISTRY Part : SECTIN-A (NEXT FURTY FIVE QUESTINS: SINGLE ICE NLY NE CRRECT ANSWER) Q Q A compound formed by elements A and B crystallizes in cubic structure
th Mains 7 th Aug Chemistry Paper Solution Subject-EMISTRY Part : SECTIN-A (NEXT FURTY FIVE QUESTINS: SINGLE ICE NLY NE CRRECT ANSWER) Q Q A compound formed by elements A and B crystallizes in cubic structure
Chapter 4: Magnetic Field
 Chapter 4: Magnetic Field 4.1 Magnetic Field 4.1.1 Define magnetic field Magnetic field is defined as the region around a magnet where a magnetic force can be experienced. Magnetic field has two poles,
Chapter 4: Magnetic Field 4.1 Magnetic Field 4.1.1 Define magnetic field Magnetic field is defined as the region around a magnet where a magnetic force can be experienced. Magnetic field has two poles,
week 8 The Magnetic Field
 week 8 The Magnetic Field General Principles General Principles Applications Start with magnetic forces on moving charges and currents A positive charge enters a uniform magnetic field as shown. What is
week 8 The Magnetic Field General Principles General Principles Applications Start with magnetic forces on moving charges and currents A positive charge enters a uniform magnetic field as shown. What is
Physics 201 Lecture 29
 Phsics 1 ecture 9 Goals ecture 9 v Describe oscillator otion in a siple pendulu v Describe oscillator otion with torques v Introduce daping in SHM v Discuss resonance v Final Ea Details l Sunda, Ma 13th
Phsics 1 ecture 9 Goals ecture 9 v Describe oscillator otion in a siple pendulu v Describe oscillator otion with torques v Introduce daping in SHM v Discuss resonance v Final Ea Details l Sunda, Ma 13th
SOLUTIONS SECTION I: CHEMISTRY
 P. CH CH CH CH H CH CH CH CH SLUTINS SECTIN I: CHEMISTRY S N NaH yellow I. CH CH CH CH C CH CH CH C Na CHI H H. H Ea 4..9 = loga.r769 Ea. = loga.r667 Ea = 4.7 4 cal mol - CH CH Cl H C CN H C CH 5. Cl h
P. CH CH CH CH H CH CH CH CH SLUTINS SECTIN I: CHEMISTRY S N NaH yellow I. CH CH CH CH C CH CH CH C Na CHI H H. H Ea 4..9 = loga.r769 Ea. = loga.r667 Ea = 4.7 4 cal mol - CH CH Cl H C CN H C CH 5. Cl h
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Spring 2013 Exam 3 Equation Sheet. closed fixed path. ! = I ind.
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.0 Spring 013 Exam 3 Equation Sheet Force Law: F q = q( E ext + v q B ext ) Force on Current Carrying Wire: F = Id s " B # wire ext Magnetic
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.0 Spring 013 Exam 3 Equation Sheet Force Law: F q = q( E ext + v q B ext ) Force on Current Carrying Wire: F = Id s " B # wire ext Magnetic
Physics 169. Luis anchordoqui. Kitt Peak National Observatory. Monday, March 13, 17
 Physics 169 Kitt Peak National Observatory Luis anchordoqui 1 6.1 Magnetic Field Stationary charges experienced an electric force in an electric field Moving charges experienced a magnetic force in a magnetic
Physics 169 Kitt Peak National Observatory Luis anchordoqui 1 6.1 Magnetic Field Stationary charges experienced an electric force in an electric field Moving charges experienced a magnetic force in a magnetic
CHAPTER 10 VECTORS POINTS TO REMEMBER
 For more important questions visit : www4onocom CHAPTER 10 VECTORS POINTS TO REMEMBER A quantity that has magnitude as well as direction is called a vector It is denoted by a directed line segment Two
For more important questions visit : www4onocom CHAPTER 10 VECTORS POINTS TO REMEMBER A quantity that has magnitude as well as direction is called a vector It is denoted by a directed line segment Two
1. Answer the following questions.
 (06) Physics Nationality No. (Please print full nae, underlining faily nae) Marks Nae Before you start, fill in the necessary details (nationality, exaination nuber, nae etc.) in the box at the top of
(06) Physics Nationality No. (Please print full nae, underlining faily nae) Marks Nae Before you start, fill in the necessary details (nationality, exaination nuber, nae etc.) in the box at the top of
XII-IC (C/F) : 11/12/ (i) m As per question, pulley to be considered as a circular disc. Angular acceleration of the pulley is
 CDE REVISIN NARAYANA I I T / N E E T A C A D E M Y REVISIN TEST - 0 XII-IC (C/F) : //07..... 6. 7. 8. 9. 0........ PHYSICS 6. 7. 8. 9. 0...... 6. 7. 8. 9. 0...... 6. 7. 8. 9. 0...... CHEMISTRY 6. 7. 8.
CDE REVISIN NARAYANA I I T / N E E T A C A D E M Y REVISIN TEST - 0 XII-IC (C/F) : //07..... 6. 7. 8. 9. 0........ PHYSICS 6. 7. 8. 9. 0...... 6. 7. 8. 9. 0...... 6. 7. 8. 9. 0...... CHEMISTRY 6. 7. 8.
Physics 202, Lecture 11
 Physics 202, Lecture 11 Today s Topics Magnetic Fields and Forces (Ch. 27) Magnetic materials Magnetic forces on moving point charges Magnetic forces on currents, current loops Motion of charge in uniform
Physics 202, Lecture 11 Today s Topics Magnetic Fields and Forces (Ch. 27) Magnetic materials Magnetic forces on moving point charges Magnetic forces on currents, current loops Motion of charge in uniform
Oscillations: Review (Chapter 12)
 Oscillations: Review (Chapter 1) Oscillations: otions that are periodic in tie (i.e. repetitive) o Swinging object (pendulu) o Vibrating object (spring, guitar string, etc.) o Part of ediu (i.e. string,
Oscillations: Review (Chapter 1) Oscillations: otions that are periodic in tie (i.e. repetitive) o Swinging object (pendulu) o Vibrating object (spring, guitar string, etc.) o Part of ediu (i.e. string,
SRI LANKAN PHYSICS OLYMPIAD MULTIPLE CHOICE TEST 30 QUESTIONS ONE HOUR AND 15 MINUTES
 SRI LANKAN PHYSICS OLYMPIAD - 5 MULTIPLE CHOICE TEST QUESTIONS ONE HOUR AND 5 MINUTES INSTRUCTIONS This test contains ultiple choice questions. Your answer to each question ust be arked on the answer sheet
SRI LANKAN PHYSICS OLYMPIAD - 5 MULTIPLE CHOICE TEST QUESTIONS ONE HOUR AND 5 MINUTES INSTRUCTIONS This test contains ultiple choice questions. Your answer to each question ust be arked on the answer sheet
(a) zero. B 2 l 2. (c) (b)
 1. Two identical co-axial circular loops carry equal currents circulating in the same direction: (a) The current in each coil decrease as the coils approach each other. (b) The current in each coil increase
1. Two identical co-axial circular loops carry equal currents circulating in the same direction: (a) The current in each coil decrease as the coils approach each other. (b) The current in each coil increase
FIITJEE PET I (REG_2 ND YEAR)
 FIITJEE PET I (REG_ ND YEAR) MAINS_SET A DATE: 09.06.018 Time: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 360 INSTRUCTINS: Instructions to the Candidates 1. This Test Booklet consists of 90 questions. Use Blue/Black ball
FIITJEE PET I (REG_ ND YEAR) MAINS_SET A DATE: 09.06.018 Time: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 360 INSTRUCTINS: Instructions to the Candidates 1. This Test Booklet consists of 90 questions. Use Blue/Black ball
NAME NUMBER SEC. PHYCS 101 SUMMER 2001/2002 FINAL EXAME:24/8/2002. PART(I) 25% PART(II) 15% PART(III)/Lab 8% ( ) 2 Q2 Q3 Total 40%
 NAME NUMER SEC. PHYCS 101 SUMMER 2001/2002 FINAL EXAME:24/8/2002 PART(I) 25% PART(II) 15% PART(III)/Lab 8% ( ) 2.5 Q1 ( ) 2 Q2 Q3 Total 40% Use the followings: Magnitude of acceleration due to gravity
NAME NUMER SEC. PHYCS 101 SUMMER 2001/2002 FINAL EXAME:24/8/2002 PART(I) 25% PART(II) 15% PART(III)/Lab 8% ( ) 2.5 Q1 ( ) 2 Q2 Q3 Total 40% Use the followings: Magnitude of acceleration due to gravity
Lecture 13. Magnetic Field, Magnetic Forces on Moving Charges.
 Lecture 13. Magnetic Field, Magnetic Forces on Moving Charges. What are magnetic forces? Forces between magnets Forces between magnets and magnetizable materials Forces between magnets and moving charges
Lecture 13. Magnetic Field, Magnetic Forces on Moving Charges. What are magnetic forces? Forces between magnets Forces between magnets and magnetizable materials Forces between magnets and moving charges
Magnetostatics III. P.Ravindran, PHY041: Electricity & Magnetism 1 January 2013: Magntostatics
 Magnetostatics III Magnetization All magnetic phenomena are due to motion of the electric charges present in that material. A piece of magnetic material on an atomic scale have tiny currents due to electrons
Magnetostatics III Magnetization All magnetic phenomena are due to motion of the electric charges present in that material. A piece of magnetic material on an atomic scale have tiny currents due to electrons
Name. Department of Chemistry SUNY/Oneonta. Chem Organic Chemistry II Examination #3 - March 31, 2003
 INSTRUTINS Name Department of hemistry SUNY/neonta hem 322 - rganic hemistry II Examination #3 - March 31, 2003 This examination has two parts. Part I is in multiple choice format and the answers should
INSTRUTINS Name Department of hemistry SUNY/neonta hem 322 - rganic hemistry II Examination #3 - March 31, 2003 This examination has two parts. Part I is in multiple choice format and the answers should
PHYS 1443 Section 003 Lecture #22
 PHYS 443 Section 003 Lecture # Monda, Nov. 4, 003. Siple Bloc-Spring Sste. Energ of the Siple Haronic Oscillator 3. Pendulu Siple Pendulu Phsical Pendulu orsion Pendulu 4. Siple Haronic Motion and Unifor
PHYS 443 Section 003 Lecture # Monda, Nov. 4, 003. Siple Bloc-Spring Sste. Energ of the Siple Haronic Oscillator 3. Pendulu Siple Pendulu Phsical Pendulu orsion Pendulu 4. Siple Haronic Motion and Unifor
Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy
 By Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College of Science, King Saud University http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/melnewehy Aldehydes and Ketones 1 Structure of Aldehydes and Ketones - Aldehydes and ketones
By Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College of Science, King Saud University http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/melnewehy Aldehydes and Ketones 1 Structure of Aldehydes and Ketones - Aldehydes and ketones
Homework (lecture 11): 3, 5, 9, 13, 21, 25, 29, 31, 40, 45, 49, 51, 57, 62
 Homework (lecture ): 3, 5, 9, 3,, 5, 9, 3, 4, 45, 49, 5, 57, 6 3. An electron that has velocity: moves through the uniform magnetic field (a) Find the force on the electron. (b) Repeat your calculation
Homework (lecture ): 3, 5, 9, 3,, 5, 9, 3, 4, 45, 49, 5, 57, 6 3. An electron that has velocity: moves through the uniform magnetic field (a) Find the force on the electron. (b) Repeat your calculation
Carbonyl Group in Aldehydes and Ketones
 Lecture 4: Aldehydes, Ketones, and Chiral Molecules 14.1 Aldehydes and Ketones Carbonyl Group in Aldehydes and Ketones A carbonyl group (C=) In an aldehyde is attached to at least one atom. In a ketone
Lecture 4: Aldehydes, Ketones, and Chiral Molecules 14.1 Aldehydes and Ketones Carbonyl Group in Aldehydes and Ketones A carbonyl group (C=) In an aldehyde is attached to at least one atom. In a ketone
Lecture 24 Two Germans and an Englishman
 Lecture 24 Two Germans and an Englishman Robert Robinson 1886-1975 Nobel Laureate 1947 April 17, 2018 tto Paul Hermann Diels 1876-1954 Nobel Laureates 1950 Kurt Alder 1902-1958 Exam III Tomorrow Wed April
Lecture 24 Two Germans and an Englishman Robert Robinson 1886-1975 Nobel Laureate 1947 April 17, 2018 tto Paul Hermann Diels 1876-1954 Nobel Laureates 1950 Kurt Alder 1902-1958 Exam III Tomorrow Wed April
1-1 Magnetism. q ν B.(1) = q ( ) (2)
 1-1 Magnetism Magnets exert forces on each other just like charges. You can draw magnetic field lines just like you drew electric field lines. Magnetic north and south pole s behavior is not unlike electric
1-1 Magnetism Magnets exert forces on each other just like charges. You can draw magnetic field lines just like you drew electric field lines. Magnetic north and south pole s behavior is not unlike electric
N_HW1 N_HW1. 1. What is the purpose of the H 2 O in this sequence?
 N_HW1 N_HW1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. 1. What is the purpose of the H 2 O in this
N_HW1 N_HW1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. 1. What is the purpose of the H 2 O in this
CHEMISTRY 51. An S N 2 reaction at an asymmetric carbon of a compound always gives
 CHEMISTRY 51. An S N reaction at an asymmetric carbon of a compound always gives an enantiomer of the substrate a product with opposite optical rotation a mixture of diastereoisomers (d) a single stereoisomer
CHEMISTRY 51. An S N reaction at an asymmetric carbon of a compound always gives an enantiomer of the substrate a product with opposite optical rotation a mixture of diastereoisomers (d) a single stereoisomer
Alcohol, Phenols & Ethers
 Alcohol, Phenols & Ethers 1) Conc. H 2 S 4 Heated with excess of C 2 H 5 at 140 o c to form CH 2 b) CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 d) CH 2 = CH 2 2) In the following series of chemical reactions identify Z C 3 H
Alcohol, Phenols & Ethers 1) Conc. H 2 S 4 Heated with excess of C 2 H 5 at 140 o c to form CH 2 b) CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 d) CH 2 = CH 2 2) In the following series of chemical reactions identify Z C 3 H
Rao IIT Academy/ ISC - Board 2018_Std XII_Mathematics_QP + Solutions JEE MEDICAL-UG BOARDS KVPY NTSE OLYMPIADS. XII - ISC Board
 Rao IIT Academy/ ISC - Board 8_Std XII_Mathematics_QP + Solutions JEE MEDICAL-UG BOARDS KVPY NTSE OLYMPIADS XII - ISC Board MATHEMATICS - QP + SOLUTIONS Date: 6..8 Ma. Marks : Question SECTION - A (8 Marks)
Rao IIT Academy/ ISC - Board 8_Std XII_Mathematics_QP + Solutions JEE MEDICAL-UG BOARDS KVPY NTSE OLYMPIADS XII - ISC Board MATHEMATICS - QP + SOLUTIONS Date: 6..8 Ma. Marks : Question SECTION - A (8 Marks)
Vikasana CET Oxygen containing organic compounds-ii. Phenol Aldehydes & Ketones Carboxylic Acids
 Vikasana CET-2013 Oxygen containing organic compounds-ii Phenol Aldehydes & Ketones Carboxylic Acids 1 PHENOL 2 Cumene process does not involve 1) Oxidation 2) Alkylation 3) Molecular rearrangement 4)
Vikasana CET-2013 Oxygen containing organic compounds-ii Phenol Aldehydes & Ketones Carboxylic Acids 1 PHENOL 2 Cumene process does not involve 1) Oxidation 2) Alkylation 3) Molecular rearrangement 4)
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II 3. CARBONYL COMPOUNDS PREVIOUS EAMCET BITS.
 1 RGANIC EMISTRY II. CARBNYL CMPUNDS PREVIUS EAMCET BITS Cl Cl 1. What are the X and Y in the following reaction sequence : X Y (009 E) 1) 5, ), ), CCl 4) 5Cl, CCl Reaction. Cl HCl X Cl CCl. HCl Y. The
1 RGANIC EMISTRY II. CARBNYL CMPUNDS PREVIUS EAMCET BITS Cl Cl 1. What are the X and Y in the following reaction sequence : X Y (009 E) 1) 5, ), ), CCl 4) 5Cl, CCl Reaction. Cl HCl X Cl CCl. HCl Y. The
Chapter 23 Aldehydes and Ketones
 Chapter 23 Aldehydes and Ketones Ketones are common solvents for quickdrying paints. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris Hein, Scott Pattison, and Susan
Chapter 23 Aldehydes and Ketones Ketones are common solvents for quickdrying paints. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris Hein, Scott Pattison, and Susan
Magnetic Fields & Forces
 Magnetic Fields & Forces Oersted discovered that an electric current will produce a magnetic field around conductor only a moving charge creates a magnetic field the magnetic field is circular around the
Magnetic Fields & Forces Oersted discovered that an electric current will produce a magnetic field around conductor only a moving charge creates a magnetic field the magnetic field is circular around the
Q5 We know that a mass at the end of a spring when displaced will perform simple m harmonic oscillations with a period given by T = 2!
 Chapter 4.1 Q1 n oscillation is any otion in which the displaceent of a particle fro a fixed point keeps changing direction and there is a periodicity in the otion i.e. the otion repeats in soe way. In
Chapter 4.1 Q1 n oscillation is any otion in which the displaceent of a particle fro a fixed point keeps changing direction and there is a periodicity in the otion i.e. the otion repeats in soe way. In
Chapter 9 FARADAY'S LAW Recommended Problems:
 Chapter 9 FARADAY'S LAW Recommended Problems: 5,7,9,10,11,13,15,17,20,21,28,29,31,32,33,34,49,50,52,58,63,64. Faraday's Law of Induction We learned that e. current produces magnetic field. Now we want
Chapter 9 FARADAY'S LAW Recommended Problems: 5,7,9,10,11,13,15,17,20,21,28,29,31,32,33,34,49,50,52,58,63,64. Faraday's Law of Induction We learned that e. current produces magnetic field. Now we want
Motion of Charges in Uniform E
 Motion of Charges in Unifor E and Fields Assue an ionized gas is acted upon by a unifor (but possibly tie-dependent) electric field E, and a unifor, steady agnetic field. These fields are assued to be
Motion of Charges in Unifor E and Fields Assue an ionized gas is acted upon by a unifor (but possibly tie-dependent) electric field E, and a unifor, steady agnetic field. These fields are assued to be
Set of sure shot questions of Magnetic effect of Current for class XII CBSE Board Exam Reg.
 Set of sure shot questions of Magnetic effect of Current for class XII CBSE Board Exam. 2016- Reg. 1 Two Parallel Conducting wires carrying current in the same direction attract each other.why? I 1 A B
Set of sure shot questions of Magnetic effect of Current for class XII CBSE Board Exam. 2016- Reg. 1 Two Parallel Conducting wires carrying current in the same direction attract each other.why? I 1 A B
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch16_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which type of compound does not contain a carbonyl group? ketone B) aldehyde C) amine D)
Ch16_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which type of compound does not contain a carbonyl group? ketone B) aldehyde C) amine D)
(A) 10 (B) 10 (C) 140 (D) 140 (E) 70 7.Calculate the ionization energy, in kj/mol, of a mole of hydrogen atoms in the ground state.
 80 1.The term that describes the following series Ne, F -, 2-, and N 3- is (A) Isotopic (C) isobar anionic 2.Which oxide of chlorine is unstable? (B) isoelectronic allotropic (A) Cl 2 (B) Cl 2 3 (C) Cl
80 1.The term that describes the following series Ne, F -, 2-, and N 3- is (A) Isotopic (C) isobar anionic 2.Which oxide of chlorine is unstable? (B) isoelectronic allotropic (A) Cl 2 (B) Cl 2 3 (C) Cl
3.8 Aldehydes and ketones
 3.8 Aldehydes and ketones Introduction: p's to p's Like the alkenes, the carbonyl group consists of a s bond and a p bond between the carbon and oxygen: Oxygen is more electronegative than carbon meaning
3.8 Aldehydes and ketones Introduction: p's to p's Like the alkenes, the carbonyl group consists of a s bond and a p bond between the carbon and oxygen: Oxygen is more electronegative than carbon meaning
PH 222-2C Fall Magnetic Field. Lecture 13. Chapter 28 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition)
 PH 222-2C Fall 2012 Magnetic Field Lecture 13 Chapter 28 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 28 Magnetic Fields In this chapter we will cover the following topics:
PH 222-2C Fall 2012 Magnetic Field Lecture 13 Chapter 28 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 28 Magnetic Fields In this chapter we will cover the following topics:
INTRODUCTION MAGNETIC FIELD OF A MOVING POINT CHARGE. Introduction. Magnetic field due to a moving point charge. Units.
 Chapter 9 THE MAGNETC FELD ntroduction Magnetic field due to a moving point charge Units Biot-Savart Law Gauss s Law for magnetism Ampère s Law Maxwell s equations for statics Summary NTRODUCTON Last lecture
Chapter 9 THE MAGNETC FELD ntroduction Magnetic field due to a moving point charge Units Biot-Savart Law Gauss s Law for magnetism Ampère s Law Maxwell s equations for statics Summary NTRODUCTON Last lecture
CH 320/328 N Summer II 2018
 CH 320/328 N Summer II 2018 HW 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. (5 pts each) 1. Which
CH 320/328 N Summer II 2018 HW 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. (5 pts each) 1. Which
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT AND MAGNETISM
 UNIT III MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT AND MAGNETISM Weightage 8 Marks Concept of magnetic field and Oersted s experiment Biot-savart law and its application to current carrying circular loop. Ampere s law
UNIT III MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT AND MAGNETISM Weightage 8 Marks Concept of magnetic field and Oersted s experiment Biot-savart law and its application to current carrying circular loop. Ampere s law
Narayana IIT Academy
 INDI Sec: LT-IIT-SPRK Jee-dvanced Date: -3-8 Time: 3. 4_P MODEL Ma.Marks:8 KEY SHEET RPT-4 PHYSICS,B,C,D,B,C,D 3 B,C 4,C,D 5,B,C 6,B,C,D 7,B,C,D 8,B,C,D 9,B,C,D,B,D 6 4 3 5 4 4 5 3 6 3 7 6 8 4 9 5 8 CHEMISTRY,C,D,C
INDI Sec: LT-IIT-SPRK Jee-dvanced Date: -3-8 Time: 3. 4_P MODEL Ma.Marks:8 KEY SHEET RPT-4 PHYSICS,B,C,D,B,C,D 3 B,C 4,C,D 5,B,C 6,B,C,D 7,B,C,D 8,B,C,D 9,B,C,D,B,D 6 4 3 5 4 4 5 3 6 3 7 6 8 4 9 5 8 CHEMISTRY,C,D,C
2. An aldehyde can be obtained by the dehydrogenation of an alcohol. The catalyst used in the reaction is
 Class: 12 Subject: Chemistry Topic: Organic Chemistry of O compounds No. of Questions: 20 Duration: 60 Min Maximum Marks: 60 1. Rectified spirit is converted to absolute alcohol taking advantage of the
Class: 12 Subject: Chemistry Topic: Organic Chemistry of O compounds No. of Questions: 20 Duration: 60 Min Maximum Marks: 60 1. Rectified spirit is converted to absolute alcohol taking advantage of the
Magnetic Fields Due to Currents
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 29 Magnetic Fields Due to Currents Calculating the magnetic field Forces between currents Ampere s law Solenoids 1. Two long straight wires penetrate the plane of
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 29 Magnetic Fields Due to Currents Calculating the magnetic field Forces between currents Ampere s law Solenoids 1. Two long straight wires penetrate the plane of
Sources of Magnetic Field
 Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 28 To determine the
Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 28 To determine the
 1. Write the relation for the force acting on a charge carrier q moving with velocity through a magnetic field in vector notation. Using this relation, deduce the conditions under which this force will
1. Write the relation for the force acting on a charge carrier q moving with velocity through a magnetic field in vector notation. Using this relation, deduce the conditions under which this force will
Test Date: 30th September, 2018 (Sunday) Venue: Lajpat Rai Bhawan, Sector 15-B, Chandigarh
 Test Date: 0th September, 2018 (Sunday) Venue: Lajpat Rai Bhawan, Sector 15-B, handigarh Syllabus Physics hemistry Biology 1. Electrostatics 2. apacitors. urrent Electricity 4. Magnetic effects 5. Magnetism
Test Date: 0th September, 2018 (Sunday) Venue: Lajpat Rai Bhawan, Sector 15-B, handigarh Syllabus Physics hemistry Biology 1. Electrostatics 2. apacitors. urrent Electricity 4. Magnetic effects 5. Magnetism
Physical Properties. Alcohols can be: CH CH 2 OH CH 2 CH 3 C OH CH 3. Secondary alcohol. Primary alcohol. Tertiary alcohol
 Chapter 10: Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols 100 Physical Properties Alcohols can be: CH 3 CH 3 CH CH 2 OH * Primary alcohol CH 3 OH CH * CH 2 CH 3 Secondary alcohol CH 3 CH 3 * C OH CH 3 Tertiary alcohol
Chapter 10: Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols 100 Physical Properties Alcohols can be: CH 3 CH 3 CH CH 2 OH * Primary alcohol CH 3 OH CH * CH 2 CH 3 Secondary alcohol CH 3 CH 3 * C OH CH 3 Tertiary alcohol
8.1 Force Laws Hooke s Law
 8.1 Force Laws There are forces that don't change appreciably fro one instant to another, which we refer to as constant in tie, and forces that don't change appreciably fro one point to another, which
8.1 Force Laws There are forces that don't change appreciably fro one instant to another, which we refer to as constant in tie, and forces that don't change appreciably fro one point to another, which
