A new model for surface roughness evolution in the Chemical Mechanical Polishing (CMP) process
|
|
|
- Josephine Douglas
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A new model for surface roughness evolution in the Chemical Mechanical Polishing (CMP) process G. Savio, R. Meneghello, G. Concheri DAUR - Laboratory of Design Methods and Tools in Industrial Engineering - University of Padua - Italy Abstract Surface polishing is a typical example of a machining process based on mixed chemical-mechanical phenomena, as pointed out in the recent literature on the polishing process (CPM - Chemical Mechanical Polishing). In this work, a model is proposed for the assessment of surface roughness evolution in the polishing process of glass moulds, used in the manufacturing of ophthalmic lenses, in order to identify the influence of the operating parameters on the material removal rate (MRR). In this model the evolution of surface roughness during the polishing process is based on Reye hypothesis. According to such hypothesis, the removed material in a specific time interval is proportional to the friction work: the removed material per unit area can be computed by aduately integrating the bearing ratio curve (Abbott-Firestone) of the surface; the friction work per unit area is proportional, according to the dynamic friction coefficient, to the integral of the product of pressure and velocity in the time interval. A similar result can be also obtained adopting other wear models, e.g. the Preston or Archard approaches. The model validation was performed on ground glass flat samples polished with increasing values of MRR. Pressure and velocity distributions on the sample surface were established according to the polishing machine operating parameters by means of the Hertz theory; the surface roughness of the sample was mapped using an atomic force microscope (AFM). The developed model shows a satisfactory estimate of surface roughness evolution during the polishing process and confirms the experimental results found in literature.
2 NOMENCLATURE CMP = Chemical Mechanical Process MRR = Material Removal Rate V = volume of removed material A = area t = polishing time h = volume of removed material per unit area z = ordinate of profile/surface coordinate system const = a generic constant in a model p = pressure v = relative sliding velocity between tool and workpiece w= angular velocity of wheel spindle (tool) v tr = tangential component of the angular velocity of the tool v av = feed rate = radial tool deformation p a = feed step E = modulus of elasticity of the workpiece E = modulus of elasticity of the tool E = uivalent modulus of elasticity E = ( / E + E ) R = curvature radius of workpiece surface R = curvature radius of tool surface R = / R + R / R = uivalent curvature radius ( ) R ac = contact area radius R ac = R / /t k = Reye s constant k p = Preston s constant k w = wear coefficient k s = proposed model constant µ = friction coefficient z = height of the surface from the mean plane Sa = arithmetic mean deviation of the surface Sa = MN Sq = root mean square deviation of the surface Svv = highest depth Svv = MIN z( x i, y )) ( j Sq = N M j= i= MN N z( x i, y j ) M j= i= z ( x i, y j ) St = highest peak from the highest depth St = MAX ( z x, y )) + MIN( z( x, y )) Introduction ( i j i j The glass polishing process is a typical polishing wear phenomenon in which the polishing pad (a polyurethane layer superimposed to a rubber bulk) and the abrasive slurry (a suspension of cerium oxide in water) perform the removing action on the glass workpiece. The involved mechanisms are both mechanical
3 and chemical (CMP). The mechanical action is based on the physical interaction between the abrasive particles and the glass surface; the chemical mechanism concerns the chemical reactions between abrasive slurry and glass. The study of factors influencing the CMP led to the proposal of various hypotheses and models: however the basic material removal mechanisms in CMP are not yet well understood []. The first fundamental study on glass polishing was made by Preston []. Brown et al. [3] proposed a model where the Hertz theory was applied to the interaction between the abrasive particles in suspension, assumed as spherical, and the polished workpiece surface. Cook [4] suggested a detailed mechanical-chemical model for the polishing process, taking into consideration the following phenomena: (a) the rate of molecular dissolution and water diffusion into the glass surface, (b) the subsuent glass dissolution under the load imposed by the polishing particles, (c) the adsorption rate of dissolution products onto the surface of the polishing grain, (d) the rate of silica re-deposition onto the glass surface, and (e) the aqueous corrosion rate between particles. Yu et al. [5] proposed a CMP model that includes the effects of the polishing pad roughness and the dynamic interaction between pad and wafer surface. Runnels et al. [] employed a feature-scale erosion model to estimate the stresses induced by the flowing slurry and the polishing rate on the feature surfaces. Venkatesh et al. [6] [7] highlighted the influence of temperature and the effects, both separate and combined, of mechanical and chemical actions. C. Wang et al. [8] proposed a model that more closely describes the relationships between polishing parameters and MRR, based on the hypothesis that the probability of contact between polishing pad and the polished surface be proportional to the slurry fluid film thickness. L. Wang et al. [9] pointed out the influence of the cerium oxide concentration on the removed material volume. In previous studies, the geometric characterization of the surface of glass ground surfaces [] was given and the evolution of the surface texture at different steps of the polishing process was compared with the increase of geometry deformation of surface in terms of curvature [], even if no models were proposed to describe such phenomena. In this paper, a model based on the analysis of the Abbott-Firestone curve is proposed in order to estimate the evolution of surface texture during the polishing process. In order to apply the proposed model the local distributions of pressure and velocity between the tool and the workpiece were evaluated by the Hertz theory []. The model was validated in the polishing process of glass moulds for ophthalmic lenses. Background. Surface roughness characterization In the present work the characterization of surface roughness conforms to ISO 487 standard [3] and Stout 3D areal parameters [4]; in addition, two 3D parameters are defined (see Nomenclature).
4 The bearing ratio curve of a profile (Abbott-Firestone curve) is defined as the curve representing the material ratio of the profile as a function of level (figure ); this curve can be interpreted as the cumulative probability function of the ordinate values z of the profile. The Abbott-Firestone curve and the roughness parameters defined by the ISO 487 standard can be extended from D to the 3D analysis of the surface texture. In the following, the considered surface roughness parameters are Sa, Sq, Svv and St, extracted from primary surface being filtered with a second order polynomial fitting of the surface. Alternatively such parameters can be estimated by using the Abbott-Firestone curve. In 3D surface texture analysis, the material volume per unit of area, relevant to a specific height z*, is given by the area comprised between the Abbott-Firestone curve and the horizontal line through z* (hatched area in figure ). z [µ m] z* Material ratio Figure : Abbott-Firestone curve and volume material per unit area relevant to height z*.. Reye, Preston and Archard hypotheses As previously discussed, in the literature many hypotheses are presented, stating the relationship between the volume of removed material and physical parameters, such as velocity and pressure, involved in polishing and wear processes. The analytical definition of the removed material volume brings together the proposed models (Reye, Preston and Archard): dh = const p v dt () The energetic approach by Reye (86) [5], relevant to the study of wear, assumes that the volume of material removed by wear per unit time is proportional to the work carried out by the friction force.
5 Preston (97) [], on the basis of experimental data, shows that the rate of glass polishing is proportional to the rate at which the work of friction is done on each unit area of the glass surface. The wear hypothesis attributed to Archard (953) [6-7] is based on the assumption that the ratio, named wear rate, between the volume of removed material per unit time and the sliding length is proportional to the ratio between normal load and surface hardness. According to these hypotheses, the constant in () assumes respectively the values µ/t k, k p and k w /H. In any case, from the three hypotheses described it can be derived that in a wear or polishing process, the volume of removed material is proportional to the product of pressure, velocity and time. 3 Polishing operation: kinematics and pressure distribution The polishing machine used in glass mould manufacturing is uipped with a workpiece spindle and a wheel spindle. The first spindle moves along x and z axes; the second one rotates at angular velocity w and translates along axis y. Moving over the mould surface, the tool follows a meandering path: firstly it travels along the y axis at a constant feed rate v av ; when the tool completes its run in y direction, the lens is moved of a constant feed step p a in x direction. When the tool is pushed against the mould surface the radial deformation is induced, producing a pressure distribution on the contact surface that can be estimated according to the Hertz theory [], disregarding the friction contribution. The assumption of a frictionless process is based on the presence of the cerium oxide (CeO ) suspension in water which acts as a lubricant during machining. According to these hypotheses, the resulting pressure distribution is ellipsoidal-like and may be expressed as: 8 E p( x, y ) = Rac ( x + y ) () 9 π R Y-axis wheel spindle spherical polishing tool glass mould workpiece spindle X-axis Z-axis Figure : Functional scheme of the polishing machine
6 Given the pressure distribution law, the feed rate (y-direction), the feed step (xdirection), the angular velocity of the tool and the tool deformation, it is possible to determine the pressure plot on a specific point of the glass mould surface as a function of time, as depicted in figure 3. Pressure [Mpa] Time [s] Figure 3: Pressure distribution in a point of glass mould surface. 4 The surface roughness evolution model 4. Relationship between material removal rate and roughness From uation (), and considering that the removed material volume per unit area can be expressed as dv/a, the following uation holds: dv A = const p v dt (3) Introducing in uation (3) the pressure distribution and speed, as presented in the previous paragraph, and integrating it, the (3) becomes: V A. 5 6 vtr = ks E R (4) 7 vav pa From uation (4), once experimentally determined the k s constant, it is possible to estimate the volume of removed material per unit area, relevant to specific values of the polishing process parameters. The volume of removed material per unit area can be related to the Abbott- Firestone curve assuming that the semi-polished surface, approximates the original ground surface from which the volume of material above a given height z has been removed (see fig. 4). Correspondingly, it can be assumed that the volume of removed material per unit area is uivalent to the area included between the Abbott-Firestone curve of the ground surface and the horizontal straight line at height z (hatched area in figure ). By eliminating the hatched area in figure, a new Abbott-Firestone curve is obtained which approximates the actual Abbott-Firestone curve of the semi-polished surface and that can be used to extract the 3D surface roughness parameters.
7 Figure 4: AFM plots of a ground and a semi-polished surface of glass moulds Finally, it is possible to determine a one-to-one relationship between the removed material volume per unit area and the value of the 3D roughness parameters for a given step of the polishing process, relevant to a defined set of operating parameters. 4. The uivalent elastic modulus E In order to assess the elastic modulus of the tool, a compression test was executed. By applying the Hertz theory [], the elastic modulus is expressed as a function of the applied load, the tool deformation,.5, and the uivalent curvature radius of the workpiece-tool system, R.5 : 3 F 3 m E = = (5) R 4 R where m represents the angular coefficient of the linear fitting relevant to the experimental curve F(.5 ). The testing apparatus was set with the purpose of obtaining an infinitely rigid, plane measuring support for the tool: therefore E =E and R =R. 5 The experimental campaign The experimental verification of the model was done by polishing a set of glass (Schott K5) ground plane samples []. The polishing parameters are shown in table. Table: Machining parameters p a [mm] v tr [m/s] v av [m/s] [mm]
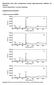
8 Each sample was measured before and after polishing, to estimate 3D surface roughness parameters and the Abbott-Firestone curve, by mean of an AFM Explorer Topometrix, over a µm µm area. 6 Results 6. Estimate of E The elastic modulus of the tool was experimentally assessed as described in paragraph 4.. In figure 5, the experimental curve F(.5 ) is given: it is evident the expected linear trend which confirms the linear elastic behaviour of the composite tool in the range of permissible deformations during polishing. The value of the angular coefficient of the linear fitting is m=94.7 N/mm.5. From uation (5), with a tool curvature radius R = R = 34.9 mm, an elastic modulus E = E = MPa is calculated. F [N] [mm.5 ] Figure 5. Results of the compression test (F vs.5 ). 6. Estimate of k s and validation of the model From the 3D measurement of the surface roughness of each ground sample, both the initial Abbott-Firestone curve and the 3D roughness parameters (Sa, Sq, Svv, St) are acquired; moreover, by analysing the Abbott-Firestone curve, as described in paragraph 4., the minimum, mean and maximum curves of the roughness parameters as a function of the volume of removed material per unit area are theoretically derived (figure 6). From the measurements of the semipolished samples the actual values of Sa, Sq, Svv and St are determinated. By adopting these values of Sa, Sq, Svv and St, the relevant actual volume of removed material is assessed. In such a way a relationship between the machining parameters and the actual volume of removed material is established. From uation (4) the estimate of a mean value of k s of.47-3 Pa -, in accordance to the abovementioned references in the literature [6], can be derived (figure 7). In figure 6, the comparison between the mean values of the effective roughness parameters and the theoretical values predicted by the model as a function of the volume of removed material per unit of area is presented.
9 .8.6 µm.4 Sa theoretical Sa measured 5 4 µm 3 Svv theoretical Svv measured V/A [µm 3 /µm ] Figure 6. Experimental versus predicted values of roughness parameters as a function of removed material per unit of area V/A [µm 3 /µm ] V/A [µm3/µm] 4 3 Sa Sq Svv St.E+ 5.E+.E+3.5E+3 av. 5 6 v tr E R 7 v p a [Pa µm] Figure 7. Determination of the constant k s. 7 Conclusions In this paper a model is presented integrating two different components: the first one, based on the Reye theory, defines the volume of removed material during the ground glass polishing process as a function of the machining parameters; the second one, starting from the Abbott-Firestone curves, defines the evolution of surface texture as a function of the removed material volume. Integrating the two components, a one-to-one correspondence between polishing parameters and surface texture parameters can be established. The integrated model is able to predict the surface texture as a function of the machining parameters within the statistical uncertainty typical in roughness measurements and gives an estimate of the Preston coefficient consistent with the values of previous works. Acknowledgements The authors are grateful to IODA srl for the technical and economical support given to the present study.
10 References [] J.Y. Lai: Mechanics mechanical and modeling of the chemical mechanical polishing process, Massachusetts institute of technology,. [] F.W. Preston: The theory and design of plate glass polishing machines, Journal of the Society of Glass Technology, Vol., 97, pp [3] N.J. Brown, P.C. Baker, R.T. Maney: Optical Polishing of Metals, Proc. SPIE, 98, Vol. 36, pp [4] L.M. Cook: Chemical Processes in Glass Polishing, J. Non-Crystalline Solids, 99, Vol., pp [5] T. K. Yu, C.C. Yu, M. Orlowski: A Statistical Polishing Pad Model for Chemical-Mechanical Polishing, Proc. IEEE, 993, pp [6] V.C. Venkatesh, S. Izman, S.C. Mahadevan: Electro-chemical mechanical polishing OF COPPER and chemical mechanical polishing of glass, Journal of materials processing technology, 4, Vol. 49, pp [7] V.C. Venkatesh, I. Inasaki, H.K. Toenshof, T. Nakagawa, I.D. Marinescu: Observation on polishing and ultraprecision machining of semiconductor substrate materials, Annals of the CIRP, 995, Vol. 44/, pp [8] C.-C. Wang, S.-C. Lin, H. Hochen: A material removal model for polishing glass ceramic and aluminum magnesium storage disks, International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture,, Vol. 4, pp [9] L. Wang, K. Zhang, Z. Song, S. Feng: Ceria concentration effect on chemical mechanical polishing of optical glass, Applied surface science, 7, Vol. 53 pp [] R. Meneghello, G. Concheri, G. Savio, D. Comelli: Surface and geometry error modeling in brittle mode grinding of ophthalmic lenses moulds, International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 6, Vol. 46, pp [] R. Meneghello, G. Concheri, G. Savio: Curvature error estimation in ground and polished surface of glass mould, Proc. of the Congreso Internacional conjunto XV ADM- XVII Ingegraf, Siviglia (Spagna), June -3, 5 [] H. Hertz: Gesammelte Werke, Leipzig, 895, Vol., pp [3] ISO 487:997, Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)-Surface Texture: Profile Method-Terms, Definitions and Surface Texture Parameters, 997. [4] K. J. Stout, P. J. Sullivan: The developing methods for the characterization of roughness in 3D, 993, Phase II report EC contract 3374///7/9/. [5] T. Reye: Zur Theorie der Zapfenreibung, Der Civilingenineur, 86, Vol. 4, pp [6] J.F. Archard: Contact and Rubbing of flat surfaces, J. of Applied Physics, 953, Vol. 4, pp [7] J.F. Archard, W. Hirst: The wears of metals under unlubricated conditions, Proc. of the Royal Society, 956, Vol. 36, pp
Analytical solution for polish-rate decay in chemical mechanical polishing
 J Eng Math DOI 10.1007/s10665-010-9369-9 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Analytical solution for polish-rate decay in chemical mechanical polishing Hong Shi Terry A. Ring Received: 17 August 2009 / Accepted: 15 March
J Eng Math DOI 10.1007/s10665-010-9369-9 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Analytical solution for polish-rate decay in chemical mechanical polishing Hong Shi Terry A. Ring Received: 17 August 2009 / Accepted: 15 March
A CONTACT-MECHANICS BASED MODEL FOR DISHING AND EROSION IN
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 671 001 Materials Research Society A CONTACT-MECHANICS BASED MODEL FOR DISHING AND EROSION IN CHEMICAL-MECHANICAL POLISHING Joost J. Vlassak Division of Engineering and
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 671 001 Materials Research Society A CONTACT-MECHANICS BASED MODEL FOR DISHING AND EROSION IN CHEMICAL-MECHANICAL POLISHING Joost J. Vlassak Division of Engineering and
Chemical Mechanical Planarization
 Mechanics of Contact and Lubrication, MTM G230 Department of Mechanical & Industrial Enineering Northeastern University Spring 2006 Chemical Mechanical Planarization George Calota Northeastern University
Mechanics of Contact and Lubrication, MTM G230 Department of Mechanical & Industrial Enineering Northeastern University Spring 2006 Chemical Mechanical Planarization George Calota Northeastern University
Analysis of contact deformation between a coated flat plate and a sphere and its practical application
 Computer Methods and Experimental Measurements for Surface Effects and Contact Mechanics VII 307 Analysis of contact deformation between a coated flat plate and a sphere and its practical application T.
Computer Methods and Experimental Measurements for Surface Effects and Contact Mechanics VII 307 Analysis of contact deformation between a coated flat plate and a sphere and its practical application T.
Normal Force and Drag Force in Magnetorheological Finishing
 Normal Force and Drag Force in Magnetorheological Finishing C. Miao, S. N. Shafrir, J. C. Lambropoulos, and S. D. Jacobs University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics Optical Manufacturing and
Normal Force and Drag Force in Magnetorheological Finishing C. Miao, S. N. Shafrir, J. C. Lambropoulos, and S. D. Jacobs University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics Optical Manufacturing and
Table of Content. Mechanical Removing Techniques. Ultrasonic Machining (USM) Sputtering and Focused Ion Beam Milling (FIB)
 Table of Content Mechanical Removing Techniques Ultrasonic Machining (USM) Sputtering and Focused Ion Beam Milling (FIB) Ultrasonic Machining In ultrasonic machining (USM), also called ultrasonic grinding,
Table of Content Mechanical Removing Techniques Ultrasonic Machining (USM) Sputtering and Focused Ion Beam Milling (FIB) Ultrasonic Machining In ultrasonic machining (USM), also called ultrasonic grinding,
Performance Enhancement of Grinding Processes Mutual Interaction between the Material Removal Process and the Machine Tool
 CONTRIBUTION Performance Enhancement of Grinding Processes Mutual Interaction between the Material Removal Process and the Machine Tool Professor Ichiro INASAKI Institute of Science and Technology Research
CONTRIBUTION Performance Enhancement of Grinding Processes Mutual Interaction between the Material Removal Process and the Machine Tool Professor Ichiro INASAKI Institute of Science and Technology Research
A Mechanical Model for Erosion in Copper Chemical-Mechanical Polishing
 A Mechanical Model for Erosion in Copper Chemical-Mechanical Polishing Kyungyoon Noh, Nannaji Saka and Jung-Hoon Chun Laboratory for Manufacturing and Productivity Massachusetts Institute of Technology
A Mechanical Model for Erosion in Copper Chemical-Mechanical Polishing Kyungyoon Noh, Nannaji Saka and Jung-Hoon Chun Laboratory for Manufacturing and Productivity Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Modeling and Estimation of Grinding Forces for Mono Layer cbn Grinding Wheel
 Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 46, P-ISSN 2347-5161 14 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Modeling
Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 46, P-ISSN 2347-5161 14 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Modeling
FE contact and thermal simulation of an alumina-steel dry sliding friction pair
 Computer Methods and Experimental Measurements for Surface Effects and Contact Mechanics VII 35 FE contact and thermal simulation of an alumina-steel dry sliding friction pair Z. Lestyán 1, K. Váradi 1
Computer Methods and Experimental Measurements for Surface Effects and Contact Mechanics VII 35 FE contact and thermal simulation of an alumina-steel dry sliding friction pair Z. Lestyán 1, K. Váradi 1
A Finite Element Study of Elastic-Plastic Hemispherical Contact Behavior against a Rigid Flat under Varying Modulus of Elasticity and Sphere Radius
 Engineering, 2010, 2, 205-211 doi:10.4236/eng.2010.24030 Published Online April 2010 (http://www. SciRP.org/journal/eng) 205 A Finite Element Study of Elastic-Plastic Hemispherical Contact Behavior against
Engineering, 2010, 2, 205-211 doi:10.4236/eng.2010.24030 Published Online April 2010 (http://www. SciRP.org/journal/eng) 205 A Finite Element Study of Elastic-Plastic Hemispherical Contact Behavior against
The Mechanics of CMP and Post-CMP Cleaning
 The Mechanics of CMP and Post-CMP Cleaning Sinan Müftü Ahmed Busnaina George Adams Department of Mechanical, Industrial and Manuf. Engineering Northeastern University Boston, MA 02115 Introduction Objective
The Mechanics of CMP and Post-CMP Cleaning Sinan Müftü Ahmed Busnaina George Adams Department of Mechanical, Industrial and Manuf. Engineering Northeastern University Boston, MA 02115 Introduction Objective
A FINITE ELEMENT STUDY OF ELASTIC-PLASTIC HEMISPHERICAL CONTACT BEHAVIOR AGAINST A RIGID FLAT UNDER VARYING MODULUS OF ELASTICITY AND SPHERE RADIUS
 Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering 2009 (ICME2009) 26-28 December 2009, Dhaka, Bangladesh ICME09- A FINITE ELEMENT STUDY OF ELASTIC-PLASTIC HEMISPHERICAL CONTACT BEHAVIOR
Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering 2009 (ICME2009) 26-28 December 2009, Dhaka, Bangladesh ICME09- A FINITE ELEMENT STUDY OF ELASTIC-PLASTIC HEMISPHERICAL CONTACT BEHAVIOR
UNLOADING OF AN ELASTIC-PLASTIC LOADED SPHERICAL CONTACT
 2004 AIMETA International Tribology Conference, September 14-17, 2004, Rome, Italy UNLOADING OF AN ELASTIC-PLASTIC LOADED SPHERICAL CONTACT Yuri KLIGERMAN( ), Yuri Kadin( ), Izhak ETSION( ) Faculty of
2004 AIMETA International Tribology Conference, September 14-17, 2004, Rome, Italy UNLOADING OF AN ELASTIC-PLASTIC LOADED SPHERICAL CONTACT Yuri KLIGERMAN( ), Yuri Kadin( ), Izhak ETSION( ) Faculty of
Supplementary Material
 Mangili et al. Supplementary Material 2 A. Evaluation of substrate Young modulus from AFM measurements 3 4 5 6 7 8 Using the experimental correlations between force and deformation from AFM measurements,
Mangili et al. Supplementary Material 2 A. Evaluation of substrate Young modulus from AFM measurements 3 4 5 6 7 8 Using the experimental correlations between force and deformation from AFM measurements,
CONTACT MODEL FOR A ROUGH SURFACE
 23 Paper presented at Bucharest, Romania CONTACT MODEL FOR A ROUGH SURFACE Sorin CĂNĂNĂU Polytechnic University of Bucharest, Dep. of Machine Elements & Tribology, ROMANIA s_cananau@yahoo.com ABSTRACT
23 Paper presented at Bucharest, Romania CONTACT MODEL FOR A ROUGH SURFACE Sorin CĂNĂNĂU Polytechnic University of Bucharest, Dep. of Machine Elements & Tribology, ROMANIA s_cananau@yahoo.com ABSTRACT
EFFECT OF STRAIN HARDENING ON ELASTIC-PLASTIC CONTACT BEHAVIOUR OF A SPHERE AGAINST A RIGID FLAT A FINITE ELEMENT STUDY
 Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering 2009 (ICME2009) 26-28 December 2009, Dhaka, Bangladesh ICME09- EFFECT OF STRAIN HARDENING ON ELASTIC-PLASTIC CONTACT BEHAVIOUR OF A
Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering 2009 (ICME2009) 26-28 December 2009, Dhaka, Bangladesh ICME09- EFFECT OF STRAIN HARDENING ON ELASTIC-PLASTIC CONTACT BEHAVIOUR OF A
Normal contact and friction of rubber with model randomly rough surfaces
 Normal contact and friction of rubber with model randomly rough surfaces S. Yashima 1-2, C. Fretigny 1 and A. Chateauminois 1 1. Soft Matter Science and Engineering Laboratory - SIMM Ecole Supérieure de
Normal contact and friction of rubber with model randomly rough surfaces S. Yashima 1-2, C. Fretigny 1 and A. Chateauminois 1 1. Soft Matter Science and Engineering Laboratory - SIMM Ecole Supérieure de
VIBRATION MODELING IN CMP. M Brij Bhushan IIT Madras
 1 VIBRATION MODELING IN CMP Jul-14-2010 M Brij Bhushan IIT Madras Outline 2 Introduction Model description Implementation details Experimentation details Verification of simulation output with experimental
1 VIBRATION MODELING IN CMP Jul-14-2010 M Brij Bhushan IIT Madras Outline 2 Introduction Model description Implementation details Experimentation details Verification of simulation output with experimental
Experimental Investigation of Fully Plastic Contact of a Sphere Against a Hard Flat
 J. Jamari e-mail: j.jamari@ctw.utwente.nl D. J. Schipper University of Twente, Surface Technology and Tribology, Faculty of Engineering Technology, Drienerloolaan 5, Postbus 17, 7500 AE, Enschede, The
J. Jamari e-mail: j.jamari@ctw.utwente.nl D. J. Schipper University of Twente, Surface Technology and Tribology, Faculty of Engineering Technology, Drienerloolaan 5, Postbus 17, 7500 AE, Enschede, The
On The Temperature and Residual Stress Field During Grinding
 On The Temperature and Residual Stress Field During Grinding S. M. H-Gangaraj, G. H. Farrahi and H. Ghadbeigi Abstract Grinding is widely used for manufacturing of components that require fine surface
On The Temperature and Residual Stress Field During Grinding S. M. H-Gangaraj, G. H. Farrahi and H. Ghadbeigi Abstract Grinding is widely used for manufacturing of components that require fine surface
TE 75R RESEARCH RUBBER FRICTION TEST MACHINE
 TE 75R RESEARCH RUBBER FRICTION TEST MACHINE Background: The Research Rubber Friction Test Machine offers the ability to investigate fully the frictional behaviour of rubbery materials both in dry and
TE 75R RESEARCH RUBBER FRICTION TEST MACHINE Background: The Research Rubber Friction Test Machine offers the ability to investigate fully the frictional behaviour of rubbery materials both in dry and
Step 1: Mathematical Modeling
 083 Mechanical Vibrations Lesson Vibration Analysis Procedure The analysis of a vibrating system usually involves four steps: mathematical modeling derivation of the governing uations solution of the uations
083 Mechanical Vibrations Lesson Vibration Analysis Procedure The analysis of a vibrating system usually involves four steps: mathematical modeling derivation of the governing uations solution of the uations
Transactions on Engineering Sciences vol 14, 1997 WIT Press, ISSN
 On the Computation of Elastic Elastic Rolling Contact using Adaptive Finite Element Techniques B. Zastrau^, U. Nackenhorst*,J. Jarewski^ ^Institute of Mechanics and Informatics, Technical University Dresden,
On the Computation of Elastic Elastic Rolling Contact using Adaptive Finite Element Techniques B. Zastrau^, U. Nackenhorst*,J. Jarewski^ ^Institute of Mechanics and Informatics, Technical University Dresden,
SURFACE ROUGHNESS EVALUATION IN TURNING BASED ON ABBOTT FIRESTONE CURVE
 SURFACE ROUGHNESS EVAUATION IN TURNING BASED ON ABBOTT FIRESTONE CURVE Adriana Carmen Cîrstoiu Materials, Equipments, Installations and Robots Department, VAAHIA University of Târgovişte, România, e-mail:
SURFACE ROUGHNESS EVAUATION IN TURNING BASED ON ABBOTT FIRESTONE CURVE Adriana Carmen Cîrstoiu Materials, Equipments, Installations and Robots Department, VAAHIA University of Târgovişte, România, e-mail:
A Study on the Process of Granite Belt Grinding
 Key Engineering Materials Online: 2003-04-15 ISSN: 1662-9795, Vols. 238-239, pp 111-116 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/kem.238-239.111 2003 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland A Study on the Process of
Key Engineering Materials Online: 2003-04-15 ISSN: 1662-9795, Vols. 238-239, pp 111-116 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/kem.238-239.111 2003 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland A Study on the Process of
PARTICLE ADHESION AND REMOVAL IN POST-CMP APPLICATIONS
 PARTICLE ADHESION AND REMOVAL IN POST-CMP APPLICATIONS George Adams, Ahmed A. Busnaina and Sinan Muftu the oratory Mechanical, Industrial, and Manufacturing Eng. Department Northeastern University, Boston,
PARTICLE ADHESION AND REMOVAL IN POST-CMP APPLICATIONS George Adams, Ahmed A. Busnaina and Sinan Muftu the oratory Mechanical, Industrial, and Manufacturing Eng. Department Northeastern University, Boston,
I-SUP 2008 April Evaluating self-lubricating materials for large scale bearings functioning under seawater conditions
 I-SUP 2008 April 23 2008 Evaluating self-lubricating materials for large scale bearings functioning under seawater conditions Van Autrève S., Ost W., Van Wittenberghe J. and De Baets P. 1 Application Civil
I-SUP 2008 April 23 2008 Evaluating self-lubricating materials for large scale bearings functioning under seawater conditions Van Autrève S., Ost W., Van Wittenberghe J. and De Baets P. 1 Application Civil
Lubrication and Journal Bearings
 UNIVERSITY OF HAIL College of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering Chapter 12 Lubrication and Journal Bearings Text Book : Mechanical Engineering Design, 9th Edition Dr. Badreddine AYADI 2016
UNIVERSITY OF HAIL College of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering Chapter 12 Lubrication and Journal Bearings Text Book : Mechanical Engineering Design, 9th Edition Dr. Badreddine AYADI 2016
INFLUENCE OF NORMAL FORCE AND HUMIDITY ON FRICTION AND WEAR OF UNLUBRICATED STEEL/ STEEL COUPLES
 INFLUENCE OF NORMAL FORCE AND HUMIDITY ON FRICTION AND WEAR OF UNLUBRICATED STEEL/ STEEL COUPLES D. KLAFFKE Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing (BAM), Lab. VIII.2, Unter den Eichen 87,
INFLUENCE OF NORMAL FORCE AND HUMIDITY ON FRICTION AND WEAR OF UNLUBRICATED STEEL/ STEEL COUPLES D. KLAFFKE Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing (BAM), Lab. VIII.2, Unter den Eichen 87,
Conception mécanique et usinage MECA Hydrodynamic plain bearings
 Conception mécanique et usinage MECA0444-1 Hydrodynamic plain bearings Pr. Jean-Luc BOZET Dr. Christophe SERVAIS Année académique 2016-2017 1 Tribology Tribology comes from the greek word tribein, which
Conception mécanique et usinage MECA0444-1 Hydrodynamic plain bearings Pr. Jean-Luc BOZET Dr. Christophe SERVAIS Année académique 2016-2017 1 Tribology Tribology comes from the greek word tribein, which
Modeling and control of material removal and defectivity in chemical mechanical planarization
 Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 2009 Modeling and control of material removal and defectivity in chemical mechanical planarization Pavan Kumar Karra Iowa State University Follow this
Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 2009 Modeling and control of material removal and defectivity in chemical mechanical planarization Pavan Kumar Karra Iowa State University Follow this
Micro/nano and precision manufacturing technologies and applications
 The 4th China-American Frontiers of Engineering Symposium Micro/nano and precision manufacturing technologies and applications Dazhi Wang School of Mechanical Engineering Dalian University of Technology
The 4th China-American Frontiers of Engineering Symposium Micro/nano and precision manufacturing technologies and applications Dazhi Wang School of Mechanical Engineering Dalian University of Technology
Lecture #2: Split Hopkinson Bar Systems
 Lecture #2: Split Hopkinson Bar Systems by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling of Materials in Manufacturing 2015 1 1 1 Uniaxial Compression
Lecture #2: Split Hopkinson Bar Systems by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling of Materials in Manufacturing 2015 1 1 1 Uniaxial Compression
Effect of kinematics and abrasive particle dynamics on material removal rate uniformity during polishing
 Effect of kinematics and abrasive particle dynamics on material removal rate uniformity during polishing Armin Saeedi Vahdat 1,2 and S V Babu 2 1 Dept. of Mechanical and Aeronautical Engineering 2 Center
Effect of kinematics and abrasive particle dynamics on material removal rate uniformity during polishing Armin Saeedi Vahdat 1,2 and S V Babu 2 1 Dept. of Mechanical and Aeronautical Engineering 2 Center
Figure 43. Some common mechanical systems involving contact.
 33 Demonstration: experimental surface measurement ADE PhaseShift Whitelight Interferometer Surface measurement Surface characterization - Probability density function - Statistical analyses - Autocorrelation
33 Demonstration: experimental surface measurement ADE PhaseShift Whitelight Interferometer Surface measurement Surface characterization - Probability density function - Statistical analyses - Autocorrelation
STRESS, STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS
 VELAMMAL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, MADURAI 625009 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING CE8301 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS I -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
VELAMMAL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, MADURAI 625009 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING CE8301 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS I -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
New Representation of Bearings in LS-DYNA
 13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Aerospace New Representation of Bearings in LS-DYNA Kelly S. Carney Samuel A. Howard NASA Glenn Research Center, Cleveland, OH 44135 Brad A. Miller
13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Aerospace New Representation of Bearings in LS-DYNA Kelly S. Carney Samuel A. Howard NASA Glenn Research Center, Cleveland, OH 44135 Brad A. Miller
Lecture 6 Friction. Friction Phenomena Types of Friction
 Lecture 6 Friction Tangential forces generated between contacting surfaces are called friction forces and occur to some degree in the interaction between all real surfaces. whenever a tendency exists for
Lecture 6 Friction Tangential forces generated between contacting surfaces are called friction forces and occur to some degree in the interaction between all real surfaces. whenever a tendency exists for
Slide 1 Raymond Jin, Adcon Lab, Inc.
 Volume Production Proven Advanced Nanometer Slurries for CMP Applications, Capable of Recycling and Extendable to Larger Si Wafer Sizes and Future IC Technology Nodes Raymond R. Jin, X. L. Song, S. M.
Volume Production Proven Advanced Nanometer Slurries for CMP Applications, Capable of Recycling and Extendable to Larger Si Wafer Sizes and Future IC Technology Nodes Raymond R. Jin, X. L. Song, S. M.
The plastic behaviour of silicon subjected to micro-indentation
 JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE 31 (1996) 5671-5676 The plastic behaviour of silicon subjected to micro-indentation L. ZHANG, M. MAHDI Centre for Advanced Materials Technology, Department of Mechanical and
JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE 31 (1996) 5671-5676 The plastic behaviour of silicon subjected to micro-indentation L. ZHANG, M. MAHDI Centre for Advanced Materials Technology, Department of Mechanical and
9-11 April 2008 Measurement of Large Forces and Deflections in Microstructures
 9-11 April 28 Measurement of Large Forces and Deflections in Microstructures Kai Axel Hals 1, Einar Halvorsen, and Xuyuan Chen Institute for Microsystem Technology, Vestfold University College, P.O. Box
9-11 April 28 Measurement of Large Forces and Deflections in Microstructures Kai Axel Hals 1, Einar Halvorsen, and Xuyuan Chen Institute for Microsystem Technology, Vestfold University College, P.O. Box
Benchmarkingfiniteelement simulation of rigid indenters in elastomers S.J. Jerrams, N. Reece-Pinchin
 Benchmarkingfiniteelement simulation of rigid indenters in elastomers S.J. Jerrams, N. Reece-Pinchin Abstract Verifications of finite element techniques applied to elastomers are difficult to achieve since
Benchmarkingfiniteelement simulation of rigid indenters in elastomers S.J. Jerrams, N. Reece-Pinchin Abstract Verifications of finite element techniques applied to elastomers are difficult to achieve since
Outline. Advances in STAR-CCM+ DEM models for simulating deformation, breakage, and flow of solids
 Advances in STAR-CCM+ DEM models for simulating deformation, breakage, and flow of solids Oleh Baran Outline Overview of DEM in STAR-CCM+ Recent DEM capabilities Parallel Bonds in STAR-CCM+ Constant Rate
Advances in STAR-CCM+ DEM models for simulating deformation, breakage, and flow of solids Oleh Baran Outline Overview of DEM in STAR-CCM+ Recent DEM capabilities Parallel Bonds in STAR-CCM+ Constant Rate
Cutting with geometrically undefined cutting edges
 Cutting with geometrically undefined cutting edges Simulation Techniques in Manufacturing Technology Lecture 10 Laboratory for Machine Tools and Production Engineering Chair of Manufacturing Technology
Cutting with geometrically undefined cutting edges Simulation Techniques in Manufacturing Technology Lecture 10 Laboratory for Machine Tools and Production Engineering Chair of Manufacturing Technology
International Workshop on Extreme Optics and Sensors
 International Workshop on Extreme Optics and Sensors ---------- 1 Multi-axis utting Shin-ya MORIT Materials Fabrication Laboratory, the Institute of Physical and hemical Research (RIKEN), 2-1 Hirosawa,
International Workshop on Extreme Optics and Sensors ---------- 1 Multi-axis utting Shin-ya MORIT Materials Fabrication Laboratory, the Institute of Physical and hemical Research (RIKEN), 2-1 Hirosawa,
Notes on Rubber Friction
 Notes on Rubber Friction 2011 A G Plint Laws of Friction: In dry sliding between a given pair of materials under steady conditions, the coefficient of friction may be almost constant. This is the basis
Notes on Rubber Friction 2011 A G Plint Laws of Friction: In dry sliding between a given pair of materials under steady conditions, the coefficient of friction may be almost constant. This is the basis
Influential Factors on Adhesion between Wheel and Rail under Wet Conditions
 Influential Factors on Adhesion between Wheel and Rail under Wet Conditions H. Chen, M. Ishida, 2 T. Nakahara Railway Technical Research Institute, Tokyo, Japan ; Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo,
Influential Factors on Adhesion between Wheel and Rail under Wet Conditions H. Chen, M. Ishida, 2 T. Nakahara Railway Technical Research Institute, Tokyo, Japan ; Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo,
Fundamental Tribological and Removal Rate Studies of Inter-Layer Dielectric Chemical Mechanical Planarization
 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Vol. 42 (2003) pp. 637 6379 Part, No. 0, October 2003 #2003 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Fundamental Tribological and Removal Rate Studies of Inter-Layer Dielectric Chemical
Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Vol. 42 (2003) pp. 637 6379 Part, No. 0, October 2003 #2003 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Fundamental Tribological and Removal Rate Studies of Inter-Layer Dielectric Chemical
The Effect of Coefficient of Restitution for Two Collision Models
 The Effect of Coefficient of Restitution for Two Collision Models ALACI STELIAN 1, FILOTE CONSTANTIN 2, CIORNEI FLORINA-CARMEN 1 1 Mechanics and Technologies Department 2 The Computers, Electronics and
The Effect of Coefficient of Restitution for Two Collision Models ALACI STELIAN 1, FILOTE CONSTANTIN 2, CIORNEI FLORINA-CARMEN 1 1 Mechanics and Technologies Department 2 The Computers, Electronics and
Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics
 1896 1920 1987 2006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA235) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & Civil Engineering First Assignment The first
1896 1920 1987 2006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA235) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & Civil Engineering First Assignment The first
Bifunctional hairy silica nanoparticles towards high-performance additives for lubricant Tianyi Sui, Baoyu Song*, Yu-ho Wen, Feng Zhang
 Bifunctional hairy silica nanoparticles towards high-performance additives for lubricant Tianyi Sui, Baoyu Song*, Yu-ho Wen, Feng Zhang Supplementary information 1. XPS survey spectra of BHSNs 5 4 O1s
Bifunctional hairy silica nanoparticles towards high-performance additives for lubricant Tianyi Sui, Baoyu Song*, Yu-ho Wen, Feng Zhang Supplementary information 1. XPS survey spectra of BHSNs 5 4 O1s
Supplementary Figures
 Fracture Strength (GPa) Supplementary Figures a b 10 R=0.88 mm 1 0.1 Gordon et al Zhu et al Tang et al im et al 5 7 6 4 This work 5 50 500 Si Nanowire Diameter (nm) Supplementary Figure 1: (a) TEM image
Fracture Strength (GPa) Supplementary Figures a b 10 R=0.88 mm 1 0.1 Gordon et al Zhu et al Tang et al im et al 5 7 6 4 This work 5 50 500 Si Nanowire Diameter (nm) Supplementary Figure 1: (a) TEM image
ROCK TRIBOLOGY USING TRIBOMETER
 ROCK TRIBOLOGY USING TRIBOMETER Prepared by Duanjie Li, PhD 6 Morgan, Ste156, Irvine CA 92618 P: 949.461.9292 F: 949.461.9232 nanovea.com Today's standard for tomorrow's materials. 2015 NANOVEA INTRO Rocks
ROCK TRIBOLOGY USING TRIBOMETER Prepared by Duanjie Li, PhD 6 Morgan, Ste156, Irvine CA 92618 P: 949.461.9292 F: 949.461.9232 nanovea.com Today's standard for tomorrow's materials. 2015 NANOVEA INTRO Rocks
12/8/2009. Prof. A.K.M.B. Rashid Department of MME BUET, Dhaka
 Prof. A.K.M.B. Rashid Department of MME BUET, Dhaka Introduction and classes of properties Case studies showing selection of the right material for the job Deformation of material under the action of a
Prof. A.K.M.B. Rashid Department of MME BUET, Dhaka Introduction and classes of properties Case studies showing selection of the right material for the job Deformation of material under the action of a
Multilayer contacts in electrical connectors: experimental results and modelling
 Computer Methods and Experimental Measurements VIII 89 Multilayer contacts in electrical connectors: experimental results and modelling F. Ossart 1, S. Noel 1, D. Alamarguy 1, S. Correia 2 & P. Gendre
Computer Methods and Experimental Measurements VIII 89 Multilayer contacts in electrical connectors: experimental results and modelling F. Ossart 1, S. Noel 1, D. Alamarguy 1, S. Correia 2 & P. Gendre
UNIT I SIMPLE STRESSES AND STRAINS
 Subject with Code : SM-1(15A01303) Year & Sem: II-B.Tech & I-Sem SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) UNIT I SIMPLE STRESSES
Subject with Code : SM-1(15A01303) Year & Sem: II-B.Tech & I-Sem SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) UNIT I SIMPLE STRESSES
A STUDY OF THE ACCURACY OF THE MICRO ELECTRICAL DISCHARGE MACHINING DRILLING PROCESS
 A STUDY OF TE ACCURACY OF TE MICRO ELECTRICAL DISCARGE MACINING DRILLING PROCESS D.T. Pham, S.S. Dimov, S. Bigot, A. Ivanov, and K. Popov Manufacturing Engineering Centre, School of Engineering, Cardiff
A STUDY OF TE ACCURACY OF TE MICRO ELECTRICAL DISCARGE MACINING DRILLING PROCESS D.T. Pham, S.S. Dimov, S. Bigot, A. Ivanov, and K. Popov Manufacturing Engineering Centre, School of Engineering, Cardiff
Physical Properties Testing Technical Bulletin
 Technical Bulletin MANUFACTURER Raven Lining Systems 13105 E. 61 st Street, Suite A Broken Arrow, OK 74012 (918) 615-0020 TENSILE TESTING OF PLASTICS ASTM D638, ISO 527 Tensile tests measure the force
Technical Bulletin MANUFACTURER Raven Lining Systems 13105 E. 61 st Street, Suite A Broken Arrow, OK 74012 (918) 615-0020 TENSILE TESTING OF PLASTICS ASTM D638, ISO 527 Tensile tests measure the force
Study on Erosion Mechanism of Magnetic-field-assisted Micro-EDM
 Study on Erosion Mechanism of Magnetic-field-assisted Micro-EDM Xuyang Chu a, Kai Zhu b, Yiru Zhang c and Chunmei Wang d Department of mechanical and electrical engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005,
Study on Erosion Mechanism of Magnetic-field-assisted Micro-EDM Xuyang Chu a, Kai Zhu b, Yiru Zhang c and Chunmei Wang d Department of mechanical and electrical engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005,
Influence of the working parameters at the plane grinding upon the surface roughness, upon...
 INFLUENCE OF THE WORKING PARAMETERS AT PLANE GRINDING UPON THE SURFACE ROUGHNESS, UPON THE GRINDING FORCES AND UPON THE WEAR ANGLE OF THE GRINDING WHEEL O.V. Pruteanu, Universitatea Tehnică Gh. Asachi
INFLUENCE OF THE WORKING PARAMETERS AT PLANE GRINDING UPON THE SURFACE ROUGHNESS, UPON THE GRINDING FORCES AND UPON THE WEAR ANGLE OF THE GRINDING WHEEL O.V. Pruteanu, Universitatea Tehnică Gh. Asachi
STICK SLIP EVALUATION
 3225 Mainway, Burlington, Ontario, L7M 1A6 Canada Tel: +1.905.335.1440 Fax: +1.905.335.4033 www.thordonbearings.com STICK SLIP EVALUATION Self-lubricated Bearing Material Assessment DATE: 18November2015
3225 Mainway, Burlington, Ontario, L7M 1A6 Canada Tel: +1.905.335.1440 Fax: +1.905.335.4033 www.thordonbearings.com STICK SLIP EVALUATION Self-lubricated Bearing Material Assessment DATE: 18November2015
Regular, low density cellular structures - rapid prototyping, numerical simulation, mechanical testing
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 823 2004 Materials Research Society W8.8.1 Regular, low density cellular structures - rapid prototyping, numerical simulation, mechanical testing J. Stampfl 1, M.M. Seyr
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 823 2004 Materials Research Society W8.8.1 Regular, low density cellular structures - rapid prototyping, numerical simulation, mechanical testing J. Stampfl 1, M.M. Seyr
Analysis of Wear Models for Advanced Coated Materials
 Dublin Institute of Technology ARROW@DIT Conference Papers School of Mechanical and Design Engineering 2009-01-01 Analysis of Wear Models for Advanced Coated Materials Simon Montgomery Dublin Institute
Dublin Institute of Technology ARROW@DIT Conference Papers School of Mechanical and Design Engineering 2009-01-01 Analysis of Wear Models for Advanced Coated Materials Simon Montgomery Dublin Institute
ROLLING FRICTION TORQUE IN MICROSYSTEMS
 Proceedings of VAREHD 15, Suceava, May 6-8, 010 170 ROLLING FRICTION TORQUE IN MICROSYSTEMS D. N. Olaru, C. Stamate, A. Dumitrascu, Gh. Prisacaru Department of Machine Elements and Mechatronics,Technical
Proceedings of VAREHD 15, Suceava, May 6-8, 010 170 ROLLING FRICTION TORQUE IN MICROSYSTEMS D. N. Olaru, C. Stamate, A. Dumitrascu, Gh. Prisacaru Department of Machine Elements and Mechatronics,Technical
SIMULATION FOR INSTABLE FLOATING OF HYDRODYNAMIC GUIDES DURING ACCELERATION AND AT CONSTANT VELOCITY 1. INTRODUCTION
 Journal of Machine Engineering, 08, Vol. 8, No., 5 5 ISSN 895-7595 (Print) ISSN 9-807 (Online) Received: December 07 / Accepted: 0 August 08 / Published online: 8 September 08 Yingying ZHANG * Volker WITTSTOCK
Journal of Machine Engineering, 08, Vol. 8, No., 5 5 ISSN 895-7595 (Print) ISSN 9-807 (Online) Received: December 07 / Accepted: 0 August 08 / Published online: 8 September 08 Yingying ZHANG * Volker WITTSTOCK
EFFECT OF FEED RATE ON THE GENERATION OF SURFACE ROUGHNESS IN TURNING
 EFFECT OF FEED RATE ON THE GENERATION OF SURFACE ROUGHNESS IN TURNING M.RAMALINGA REDDY 1 Professor,Department of Mechanical Engineering CMR College of Engineering & Technology Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh,
EFFECT OF FEED RATE ON THE GENERATION OF SURFACE ROUGHNESS IN TURNING M.RAMALINGA REDDY 1 Professor,Department of Mechanical Engineering CMR College of Engineering & Technology Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh,
A novel technique of friction and material property measurement by tip test in cold forging
 A novel technique of friction and material property measurement by tip test in cold forging Y T Im*, S H Kang, and J S Cheon Department of Mechanical Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and
A novel technique of friction and material property measurement by tip test in cold forging Y T Im*, S H Kang, and J S Cheon Department of Mechanical Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and
Determination of Young s modulus of glass by Cornu s apparatus
 Determination of Young s modulus of glass b Cornu s apparatus Objective To determine Young s modulus and Poisson s ratio of a glass plate using Cornu s method. Theoretical Background Young s modulus, also
Determination of Young s modulus of glass b Cornu s apparatus Objective To determine Young s modulus and Poisson s ratio of a glass plate using Cornu s method. Theoretical Background Young s modulus, also
AME COMPUTATIONAL MULTIBODY DYNAMICS. Friction and Contact-Impact
 1 Friction AME553 -- COMPUTATIONAL MULTIBODY DYNAMICS Friction and Contact-Impact Friction force may be imposed between contacting bodies to oppose their relative motion. Friction force can be a function
1 Friction AME553 -- COMPUTATIONAL MULTIBODY DYNAMICS Friction and Contact-Impact Friction force may be imposed between contacting bodies to oppose their relative motion. Friction force can be a function
Determining thermal noise limiting properties of thin films
 Determining thermal noise limiting properties of thin films Courtney Linn Institute for Gravitational Research University of Glasgow Summer 2011 Abstract In order to make thermally stable mirrors to be
Determining thermal noise limiting properties of thin films Courtney Linn Institute for Gravitational Research University of Glasgow Summer 2011 Abstract In order to make thermally stable mirrors to be
Experimental Investigation of the Performances of a WRS-BTU Seismic Isolator
 , July 3-5, 2013, London, U.K. Experimental Investigation of the Performances of a WRS-BTU Seismic Isolator R. Brancati, G. Di Massa, S. Pagano, E. Rocca and S. Strano Abstract This paper describes an
, July 3-5, 2013, London, U.K. Experimental Investigation of the Performances of a WRS-BTU Seismic Isolator R. Brancati, G. Di Massa, S. Pagano, E. Rocca and S. Strano Abstract This paper describes an
New Way Porous Gas Bearings as Seals. Bearings Seals
 New Way Porous Gas Bearings as Seals Bearings Seals 1 New Way Overview Founded January 1994. Aston, Pa. 15 miles south of Philadelphia 54 employees 35,000 sq ft facility, Environmentally Controlled Precision
New Way Porous Gas Bearings as Seals Bearings Seals 1 New Way Overview Founded January 1994. Aston, Pa. 15 miles south of Philadelphia 54 employees 35,000 sq ft facility, Environmentally Controlled Precision
Lecture 11 Friction Lubrication, and Wear
 Lecture 11 Friction, Lubrication and Wear Definitions Friction force between the interacting surfaces that resists or hinders their relative movement Static friction force to overcome to start movement
Lecture 11 Friction, Lubrication and Wear Definitions Friction force between the interacting surfaces that resists or hinders their relative movement Static friction force to overcome to start movement
Example-3. Title. Description. Cylindrical Hole in an Infinite Mohr-Coulomb Medium
 Example-3 Title Cylindrical Hole in an Infinite Mohr-Coulomb Medium Description The problem concerns the determination of stresses and displacements for the case of a cylindrical hole in an infinite elasto-plastic
Example-3 Title Cylindrical Hole in an Infinite Mohr-Coulomb Medium Description The problem concerns the determination of stresses and displacements for the case of a cylindrical hole in an infinite elasto-plastic
Design of a hydrostatic symmetric-pad bearing with the membrane-type restrictor
 Design of a hydrostatic symmetric-pad bearing with the membrane-type restrictor Professor: Shih-Chieh Lin Manufacturing and Production System Lab Dept. of Power Mechanical Engineering, National Tsing Hua
Design of a hydrostatic symmetric-pad bearing with the membrane-type restrictor Professor: Shih-Chieh Lin Manufacturing and Production System Lab Dept. of Power Mechanical Engineering, National Tsing Hua
Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017
 A Correlation of Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017 To the AP Physics C: Mechanics Course Descriptions AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which was not
A Correlation of Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017 To the AP Physics C: Mechanics Course Descriptions AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which was not
 Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 10 5 m 2 under a given load.
Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 10 5 m 2 under a given load.
PREFACE. performance of various bearings lubricated with non-newtonian fluids.
 PREFACE The present thesis deals with the theoretical study of lubrication characteristics of bearings with non-newtonian fluids. In these theoretical investigations of the problems, the Mathematical models
PREFACE The present thesis deals with the theoretical study of lubrication characteristics of bearings with non-newtonian fluids. In these theoretical investigations of the problems, the Mathematical models
Computational Modelling of the Surface Roughness Effects on the Thermal-elastohydrodynamic Lubrication Problem
 Proceedings of the International Conference on Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow Prague, Czech Republic, August 11-12, 2014 Paper No. 192 Computational Modelling of the Surface Roughness Effects on the Thermal-elastohydrodynamic
Proceedings of the International Conference on Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow Prague, Czech Republic, August 11-12, 2014 Paper No. 192 Computational Modelling of the Surface Roughness Effects on the Thermal-elastohydrodynamic
Basic Laboratory. Materials Science and Engineering. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
 Basic Laboratory Materials Science and Engineering Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) M108 Stand: 20.10.2015 Aim: Presentation of an application of the AFM for studying surface morphology. Inhalt 1.Introduction...
Basic Laboratory Materials Science and Engineering Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) M108 Stand: 20.10.2015 Aim: Presentation of an application of the AFM for studying surface morphology. Inhalt 1.Introduction...
FRICTION AND WEAR OF CARBON-CARBON COMPOSITE PART 2: TEMPERATURE AND STRESS FIELDS ANALYSIS
 FRICTION AND WEAR OF CARBON-CARBON COMPOSITE PART 2: TEMPERATURE AND STRESS FIELDS ANALYSIS Kia-Moh Teo and Khalid Lafdi NSF-University-Industry Center For Advanced Friction Studies, Southern Illinois
FRICTION AND WEAR OF CARBON-CARBON COMPOSITE PART 2: TEMPERATURE AND STRESS FIELDS ANALYSIS Kia-Moh Teo and Khalid Lafdi NSF-University-Industry Center For Advanced Friction Studies, Southern Illinois
Design of a fastener based on negative Poisson's ratio foam adapted from
 1 Design of a fastener based on negative Poisson's ratio foam adapted from Choi, J. B. and Lakes, R. S., "Design of a fastener based on negative Poisson's ratio foam", Cellular Polymers, 10, 205-212 (1991).
1 Design of a fastener based on negative Poisson's ratio foam adapted from Choi, J. B. and Lakes, R. S., "Design of a fastener based on negative Poisson's ratio foam", Cellular Polymers, 10, 205-212 (1991).
Chapter 11 Design of Low Friction Surfaces
 Chapter 11 Design of Low Friction Surfaces 1 Design of Low Friction Surfaces (no lubricant allowed) Consider the task of creating low friction surfaces for sliding applications. FR 1 = Support the normal
Chapter 11 Design of Low Friction Surfaces 1 Design of Low Friction Surfaces (no lubricant allowed) Consider the task of creating low friction surfaces for sliding applications. FR 1 = Support the normal
Agricultural Science 1B Principles & Processes in Agriculture. Mike Wheatland
 Agricultural Science 1B Principles & Processes in Agriculture Mike Wheatland (m.wheatland@physics.usyd.edu.au) Outline - Lectures weeks 9-12 Chapter 6: Balance in nature - description of energy balance
Agricultural Science 1B Principles & Processes in Agriculture Mike Wheatland (m.wheatland@physics.usyd.edu.au) Outline - Lectures weeks 9-12 Chapter 6: Balance in nature - description of energy balance
N = Shear stress / Shear strain
 UNIT - I 1. What is meant by factor of safety? [A/M-15] It is the ratio between ultimate stress to the working stress. Factor of safety = Ultimate stress Permissible stress 2. Define Resilience. [A/M-15]
UNIT - I 1. What is meant by factor of safety? [A/M-15] It is the ratio between ultimate stress to the working stress. Factor of safety = Ultimate stress Permissible stress 2. Define Resilience. [A/M-15]
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown.
 D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
For an imposed stress history consisting of a rapidly applied step-function jump in
 Problem 2 (20 points) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 0239 2.002 MECHANICS AND MATERIALS II SOLUTION for QUIZ NO. October 5, 2003 For
Problem 2 (20 points) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 0239 2.002 MECHANICS AND MATERIALS II SOLUTION for QUIZ NO. October 5, 2003 For
The Effect of Pad-asperity Curvature on Material Removal Rate in Chemical-mechanical Polishing
 The Effect of Pad-asperity Curvature on Material Removal Rate in Chemical-mechanical Polishing The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
The Effect of Pad-asperity Curvature on Material Removal Rate in Chemical-mechanical Polishing The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Progressive wave: a new multisource vibration technique to assist forming processes - kinematic study, simulation results and design proposition
 Progressive wave: a new multisource vibration technique to assist forming processes - kinematic stud, simulation results and design proposition A. Khan a, T. H. Nguen a, C. Giraud-Audine a, G. Abba b,
Progressive wave: a new multisource vibration technique to assist forming processes - kinematic stud, simulation results and design proposition A. Khan a, T. H. Nguen a, C. Giraud-Audine a, G. Abba b,
Class XI Physics. Ch. 9: Mechanical Properties of solids. NCERT Solutions
 Downloaded from Class XI Physics Ch. 9: Mechanical Properties of solids NCERT Solutions Page 242 Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount
Downloaded from Class XI Physics Ch. 9: Mechanical Properties of solids NCERT Solutions Page 242 Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount
Bolted Busbar Connections with Slotted Bolt Holes
 Bolted Busbar Connections with Slotted Bolt Holes RAINA TZENEVA 1, YANKO SLAVTCHEV 2 and VALERI MLADENOV 3 1 Department of Electrical Apparatus, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Technical University
Bolted Busbar Connections with Slotted Bolt Holes RAINA TZENEVA 1, YANKO SLAVTCHEV 2 and VALERI MLADENOV 3 1 Department of Electrical Apparatus, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Technical University
MECHANICS, MECHANISMS, AND MODELING OF THE CHEMICAL MECHANICAL POLISHING PROCESS
 MECHANICS, MECHANISMS, AND MODELING OF THE CHEMICAL MECHANICAL POLISHING PROCESS by Jiun-Yu Lai B.S., Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering National Taiwan University, 1993 S.M., Mechanical Engineering
MECHANICS, MECHANISMS, AND MODELING OF THE CHEMICAL MECHANICAL POLISHING PROCESS by Jiun-Yu Lai B.S., Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering National Taiwan University, 1993 S.M., Mechanical Engineering
INFLUENCE OF TOOL NOSE RADIUS ON THE CUTTING PERFORMANCE AND SURFACE FINISH DURING HARD TURNING WITH CBN CUTTING TOOLS 1.
 Journal of Machine Engineering, Vol. 17, No. 2, 2017 Received: 23 January 2017/ Accepted: 16 April 2017 / Published online: 12 June 2017 Wit GRZESIK 1* Krzysztof ZAK 1 Roman CHUDY 1 hardened steel, surface
Journal of Machine Engineering, Vol. 17, No. 2, 2017 Received: 23 January 2017/ Accepted: 16 April 2017 / Published online: 12 June 2017 Wit GRZESIK 1* Krzysztof ZAK 1 Roman CHUDY 1 hardened steel, surface
Bacillus spores as building blocks for stimuliresponsive materials and nanogenerators
 Bacillus spores as building blocks for stimuliresponsive materials and nanogenerators Xi Chen, L Mahadevan, Adam Driks & Ozgur Sahin 1- Estimation of energy densities from the AFM based measurements Supplementary
Bacillus spores as building blocks for stimuliresponsive materials and nanogenerators Xi Chen, L Mahadevan, Adam Driks & Ozgur Sahin 1- Estimation of energy densities from the AFM based measurements Supplementary
Sliding Bearings. Fig.(1) (a) Full-journal bearing and (b) partial-journal bearing
 Sliding Bearings The goal of a bearing is to provide relative positioning and rotational freedom while transmitting a load between two parts, commonly a shaft and its housing. The object of lubrication
Sliding Bearings The goal of a bearing is to provide relative positioning and rotational freedom while transmitting a load between two parts, commonly a shaft and its housing. The object of lubrication
MEASUREMENT OF THE FRICTION AND LUBRICITY PROPERTIES OF CONTACT LENSES
 Proceedings of ANTEC `95, Boston, MA, May 7-11, 1995. MEASUREMENT OF THE FRICTION AND LUBRICITY PROPERTIES OF CONTACT LENSES John A. Nairn, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA Tong-bi Jiang,
Proceedings of ANTEC `95, Boston, MA, May 7-11, 1995. MEASUREMENT OF THE FRICTION AND LUBRICITY PROPERTIES OF CONTACT LENSES John A. Nairn, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA Tong-bi Jiang,
Key words: Polymeric Composite Bearing, Clearance, FEM
 A study on the effect of the clearance on the contact stresses and kinematics of polymeric composite journal bearings under reciprocating sliding conditions Abstract The effect of the clearance on the
A study on the effect of the clearance on the contact stresses and kinematics of polymeric composite journal bearings under reciprocating sliding conditions Abstract The effect of the clearance on the
Study of electrostatic potential induced by friction
 Proc. ESA Annual Meeting on Electrostatics 2014 1 Study of electrostatic potential induced by friction Shiyu Hu, Yuanyue Zhang, Tianmin Shao* State Key Lab of Tribology, Tsinghua University shaotm@tsinghua.edu.cn
Proc. ESA Annual Meeting on Electrostatics 2014 1 Study of electrostatic potential induced by friction Shiyu Hu, Yuanyue Zhang, Tianmin Shao* State Key Lab of Tribology, Tsinghua University shaotm@tsinghua.edu.cn
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF A THREE-DIMENSIONAL DISC-PAD MODEL WITH AND WITHOUT THERMAL EFFECTS
 THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 2015, Vol. 19, No. 6, pp. 2195-2204 2195 NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF A THREE-DIMENSIONAL DISC-PAD MODEL WITH AND WITHOUT THERMAL EFFECTS by Ali BELHOCINE * Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 2015, Vol. 19, No. 6, pp. 2195-2204 2195 NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF A THREE-DIMENSIONAL DISC-PAD MODEL WITH AND WITHOUT THERMAL EFFECTS by Ali BELHOCINE * Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
