Fundamentals of Turbulence
|
|
|
- Daisy Hutchinson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fundamentals of Turbulence Stanislav Boldyrev (University of Wisconsin - Madison) Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical Plasmas
2 What is turbulence? No exact definition. Loosely, random motion of fluid where many nonlinearly interacting modes are involved. Plasma in astrophysical systems is typically turbulent and magnetized: magnetic dynamo action density structures in the Interstellar Medium star formation, scintillation of radio sources cosmic ray acceleration and scattering heat conduction in galaxy clusters transport in fusion devices solar corona/solar wind heating etc. 2
3 Hydrodynamics equations Navier Stokes Equation: pressure viscosity driving force Incompressible hydrodynamics does not have linear waves. Velocity fluctuations are referred to as eddies 3
4 Hydrodynamics equations Navier Stokes Equation: pressure viscosity driving force If L 0 is the typical velocity scale, V 0 is the typical velocity, then = Reynolds number A flow is turbulent when Re À 1 4
5 Hydrodynamics equations Navier Stokes Equation: pressure viscosity driving force When the viscous and force terms are absent, the equation is scale invariant: this scaling transform does not change the equation, for any h 5
6 Scale invariance and correlation functions Velocity is not universal since it depends on the reference frame. Consider velocity difference Scale invariance means that For example, the second-order structure function has the form 6
7 Structure function and spectrum of turbulence Fourier transform of velocity field: Energy spectrum: E k v k 2 4πk 2 3D volume element Energy spectrum is a Fourier transform of the second-order structure function. The rule is: If the structure function scales as: then the energy spectrum scales as: Need to find h! 7
8 Energy conservation Energy: Assume that velocity field vanishes at infinity or has periodic boundary conditions 0 (by parts) Nonlinear interaction does not change energy. Redistributes energy over Fourier harmonics. viscous energy dissipation at small scale energy supply at large scales 8
9 Kolmogorov phenomenology When energy is supplied at large scales, it gets redistributed over fluctuations of different scales, and removed at small scales due to viscosity. In a steady state, rate of energy supply = rate of energy transfer = rate of energy dissipation: x Inertial interval Forcing scale or outer scale Viscous scale or inner scale 9
10 Locality of turbulence Navier-Stokes equation is invariant under the Galilean transform: MIT opencourseware Consider eddies at scale r. Much larger eddies, whose velocity is more uniform, do not affect the dynamics at scale r. Neither do much smaller eddies, which are weaker and provide incoherent disturbances. 10
11 Kolmogorov spectrum 1. Rate of energy transfer. Velocity difference should depend on and. By dimensional analysis: A.N. Kolmogorov ( ) 2. Energy density Time of energy transfer Rate of energy transfer Kolmogorov spectrum of turbulence 11
12 Kolmogorov theory An exact relation for scales, where is the scale where energy is supplied to the system. and, additionally,, where is the scale where energy is removed from the system by viscosity: Kolmogorov 4/5 law The range of scales,, is called the inertial interval. Homogeneous and isotropic turbulence in the inertial interval obeys the Kolmogorov 4/5 law. This is the exact law. It explains in what sense the phenomenological relation must be understood. 12
13 Kolmogorov spectrum: numerical simulations Hydrodynamic turbulence is universal. Has same spectrum (close to -5/3) independent of large-scale driving and small-scale dissipation Gotoh
14 Turbulence of a conducting fluid always gets magnetized and turns into MHD turbulence t v + (v r)v = -rp + (r B) B + v + f t B = r (v B) + B Kinematic dynamo Re=VL/ R m =VL/ - Reynolds number - magnetic Reynolds number B V 1 B V 2
15 Magnetic turbulence in nature energy spectra Solar wind [Goldstein, Roberts, Matthaeus (1995)] ISM [Armstrong, Rickett, Spangler (1995)] 15
16 Magnetic turbulence in numerical simulations structures Neutral fluid, B=0 MHD, B 0 Filaments Ishihara et al (2007) Ribbons stretched along B Biskamp & Muller (2000) 16
17 Nature of Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) turbulence HD turbulence: interaction of eddies MHD turbulence: interaction of wave packets moving with Alfven velocities V A v L B 0 V A 17
18 Guide field in MHD turbulence V A B 0 B 0 V A B 0 imposed by external sources B 0 created by large-scale eddies 18
19 Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) turbulence Separate the uniform magnetic field: And introduce the Elsasser variables Then the equations take a symmetric form: With the Alfven velocity The uniform magnetic field cannot be removed by a Galilean transform! 19
20 Alfvenic turbulence Ideal system conserves the Elsasser energies z - z + V z + A z- V A After interaction, shape of each packet changes, but energy does not. E + ~ E - : balanced case. E + À E - : imbalanced case 20
21 Strong MHD turbulence: collision of eddies 21
22 Strong MHD turbulence: collision of eddies 22
23 Iroshnikov-Kraichnan spectrum during one collision: R..S.Iroshnikov ( ) R. H. Kraichnan ( ) number of collisions required to deform packet considerably: λ λ Constant energy flux: MHD spectrum is isotropic [Iroshnikov (1963); Kraichnan (1965)] 23
24 MHD turbulence is locally anisotropic W.-C. Muller et al (2005) 24
25 Goldreich-Sridhar spectrum Anisotropy of eddies P. Goldreich S.Sridhar Critical Balance B Energy spectrum: E GS (k? ) / k? -5/3 [Goldreich & Sridhar 1995] 25
26 Goldreich-Sridhar theory: critical balance B Causality GS Critical balance Correlation time of fluctuations, or eddy turnover time 26
27 Strong collision of eddies 27
28 Strong collision of eddies 28
29 Spectrum of strong MHD turbulence: balanced case up to Computational resources: DoE 2010 INCITE, Machine: Intrepid, IBM BG/P at Argonne Leadership Computing Facility Perez et al, Phys Rev X (2012) 29
30 Conclusions of Part I We have reviewed phenomenological description of hydrodynamic and MHD turbulence Astrophysical turbulence is typically magnetic ---See Part II for MDH turbulence 30
Magnetohydrodynamic Turbulence: solar wind and numerical simulations
 Magnetohydrodynamic Turbulence: solar wind and numerical simulations Stanislav Boldyrev (UW-Madison) Jean Carlos Perez (U. New Hampshire) Fausto Cattaneo (U. Chicago) Joanne Mason (U. Exeter, UK) Vladimir
Magnetohydrodynamic Turbulence: solar wind and numerical simulations Stanislav Boldyrev (UW-Madison) Jean Carlos Perez (U. New Hampshire) Fausto Cattaneo (U. Chicago) Joanne Mason (U. Exeter, UK) Vladimir
Magnetohydrodynamic Turbulence
 Magnetohydrodynamic Turbulence Stanislav Boldyrev (UW-Madison) Jean Carlos Perez (U. New Hampshire), Fausto Cattaneo (U. Chicago), Joanne Mason (U. Exeter, UK) Vladimir Zhdankin (UW-Madison) Konstantinos
Magnetohydrodynamic Turbulence Stanislav Boldyrev (UW-Madison) Jean Carlos Perez (U. New Hampshire), Fausto Cattaneo (U. Chicago), Joanne Mason (U. Exeter, UK) Vladimir Zhdankin (UW-Madison) Konstantinos
TURBULENCE IN FLUIDS AND SPACE PLASMAS. Amitava Bhattacharjee Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory, Princeton University
 TURBULENCE IN FLUIDS AND SPACE PLASMAS Amitava Bhattacharjee Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory, Princeton University What is Turbulence? Webster s 1913 Dictionary: The quality or state of being turbulent;
TURBULENCE IN FLUIDS AND SPACE PLASMAS Amitava Bhattacharjee Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory, Princeton University What is Turbulence? Webster s 1913 Dictionary: The quality or state of being turbulent;
Alfvén wave turbulence: new results with applications to astrophysics. Sébastien GALTIER Université Paris-Sud & Institut Universitaire de France
 Alfvén wave turbulence: new results with applications to astrophysics Sébastien GALTIER Université Paris-Sud & Institut Universitaire de France 1 Recent co-workers : - Barbara Bigot (France/USA) - Ben
Alfvén wave turbulence: new results with applications to astrophysics Sébastien GALTIER Université Paris-Sud & Institut Universitaire de France 1 Recent co-workers : - Barbara Bigot (France/USA) - Ben
Natalia Tronko S.V.Nazarenko S. Galtier
 IPP Garching, ESF Exploratory Workshop Natalia Tronko University of York, York Plasma Institute In collaboration with S.V.Nazarenko University of Warwick S. Galtier University of Paris XI Outline Motivations:
IPP Garching, ESF Exploratory Workshop Natalia Tronko University of York, York Plasma Institute In collaboration with S.V.Nazarenko University of Warwick S. Galtier University of Paris XI Outline Motivations:
UNCONDITIONAL STABILITY OF A PARTITIONED IMEX METHOD FOR MAGNETOHYDRODYNAMIC FLOWS
 UNCONDITIONAL STABILITY OF A PARTITIONED IMEX METHOD FOR MAGNETOHYDRODYNAMIC FLOWS CATALIN TRENCHEA Key words. magnetohydrodynamics, partitioned methods, IMEX methods, stability, Elsässer variables. Abstract.
UNCONDITIONAL STABILITY OF A PARTITIONED IMEX METHOD FOR MAGNETOHYDRODYNAMIC FLOWS CATALIN TRENCHEA Key words. magnetohydrodynamics, partitioned methods, IMEX methods, stability, Elsässer variables. Abstract.
Incompressible MHD simulations
 Incompressible MHD simulations Felix Spanier 1 Lehrstuhl für Astronomie Universität Würzburg Simulation methods in astrophysics Felix Spanier (Uni Würzburg) Simulation methods in astrophysics 1 / 20 Outline
Incompressible MHD simulations Felix Spanier 1 Lehrstuhl für Astronomie Universität Würzburg Simulation methods in astrophysics Felix Spanier (Uni Würzburg) Simulation methods in astrophysics 1 / 20 Outline
Energy spectrum of isotropic magnetohydrodynamic turbulence in the Lagrangian renormalized approximation
 START: 19/Jul/2006, Warwick Turbulence Symposium Energy spectrum of isotropic magnetohydrodynamic turbulence in the Lagrangian renormalized approximation Kyo Yoshida (Univ. Tsukuba) In collaboration with:
START: 19/Jul/2006, Warwick Turbulence Symposium Energy spectrum of isotropic magnetohydrodynamic turbulence in the Lagrangian renormalized approximation Kyo Yoshida (Univ. Tsukuba) In collaboration with:
The Physics of Fluids and Plasmas
 The Physics of Fluids and Plasmas An Introduction for Astrophysicists ARNAB RAI CHOUDHURI CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface Acknowledgements xiii xvii Introduction 1 1. 3 1.1 Fluids and plasmas in the
The Physics of Fluids and Plasmas An Introduction for Astrophysicists ARNAB RAI CHOUDHURI CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface Acknowledgements xiii xvii Introduction 1 1. 3 1.1 Fluids and plasmas in the
1 TH/P8-43 Role of Impurity Cyclotron Damping in Ion Heating and RFP Turbulence
 1 Role of Impurity Cyclotron Damping in Ion Heating and RFP Turbulence P.W. Terry, V. Tangri, J.S. Sarff, G. Fiksel, A.F. Almagri, Y. Ren, and S.C. Prager Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison,
1 Role of Impurity Cyclotron Damping in Ion Heating and RFP Turbulence P.W. Terry, V. Tangri, J.S. Sarff, G. Fiksel, A.F. Almagri, Y. Ren, and S.C. Prager Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison,
Shell-to-shell energy transfer in magnetohydrodynamics. I. Steady state turbulence
 Shell-to-shell energy transfer in magnetohydrodynamics. I. Steady state turbulence Alexandros Alexakis,* Pablo D. Mininni, and Annick Pouquet National Center for Atmospheric Research, P.O. Box 3000, Boulder,
Shell-to-shell energy transfer in magnetohydrodynamics. I. Steady state turbulence Alexandros Alexakis,* Pablo D. Mininni, and Annick Pouquet National Center for Atmospheric Research, P.O. Box 3000, Boulder,
Solar Wind Turbulent Heating by Interstellar Pickup Protons: 2-Component Model
 Solar Wind Turbulent Heating by Interstellar Pickup Protons: 2-Component Model Philip A. Isenberg a, Sean Oughton b, Charles W. Smith a and William H. Matthaeus c a Inst. for Study of Earth, Oceans and
Solar Wind Turbulent Heating by Interstellar Pickup Protons: 2-Component Model Philip A. Isenberg a, Sean Oughton b, Charles W. Smith a and William H. Matthaeus c a Inst. for Study of Earth, Oceans and
Solar Wind Turbulence
 Solar Wind Turbulence Presentation to the Solar and Heliospheric Survey Panel W H Matthaeus Bartol Research Institute, University of Delaware 2 June 2001 Overview Context and SH Themes Scientific status
Solar Wind Turbulence Presentation to the Solar and Heliospheric Survey Panel W H Matthaeus Bartol Research Institute, University of Delaware 2 June 2001 Overview Context and SH Themes Scientific status
Turbulence and Reconnection
 Turbulence and Reconnection Jeff Tessein July 10, 2011 NASA turbulence study at Wallops Island, Virginia Outline Turbulence (length scales, Reynolds decomposition) Navier-Stokes Equation Turbulence Spectrum
Turbulence and Reconnection Jeff Tessein July 10, 2011 NASA turbulence study at Wallops Island, Virginia Outline Turbulence (length scales, Reynolds decomposition) Navier-Stokes Equation Turbulence Spectrum
Scaling relations in MHD and EMHD Turbulence
 Scaling relations in MHD and EMHD Turbulence Jungyeon Cho Chungnam National University, Korea Outline MHD Non-MHD E(k) MHD turb. small-scale turb. ~1/r i k Topic 1. Strong MHD Turbulence Alfven wave Suppose
Scaling relations in MHD and EMHD Turbulence Jungyeon Cho Chungnam National University, Korea Outline MHD Non-MHD E(k) MHD turb. small-scale turb. ~1/r i k Topic 1. Strong MHD Turbulence Alfven wave Suppose
36. TURBULENCE. Patriotism is the last refuge of a scoundrel. - Samuel Johnson
 36. TURBULENCE Patriotism is the last refuge of a scoundrel. - Samuel Johnson Suppose you set up an experiment in which you can control all the mean parameters. An example might be steady flow through
36. TURBULENCE Patriotism is the last refuge of a scoundrel. - Samuel Johnson Suppose you set up an experiment in which you can control all the mean parameters. An example might be steady flow through
Greg Hammett Imperial College, London & Princeton Plasma Physics Lab With major contributions from:
 Greg Hammett Imperial College, London & Princeton Plasma Physics Lab With major contributions from: Steve Cowley (Imperial College) Bill Dorland (Imperial College) Eliot Quataert (Berkeley) LMS Durham
Greg Hammett Imperial College, London & Princeton Plasma Physics Lab With major contributions from: Steve Cowley (Imperial College) Bill Dorland (Imperial College) Eliot Quataert (Berkeley) LMS Durham
Effect of current sheets on the power spectrum of the solar wind magnetic field using a cell model
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Advances in Space Research 49 (2012) 1327 1332 www.elsevier.com/locate/asr Effect of current sheets on the power spectrum of the solar wind magnetic field using
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Advances in Space Research 49 (2012) 1327 1332 www.elsevier.com/locate/asr Effect of current sheets on the power spectrum of the solar wind magnetic field using
Statistical studies of turbulent flows: self-similarity, intermittency, and structure visualization
 Statistical studies of turbulent flows: self-similarity, intermittency, and structure visualization P.D. Mininni Departamento de Física, FCEyN, UBA and CONICET, Argentina and National Center for Atmospheric
Statistical studies of turbulent flows: self-similarity, intermittency, and structure visualization P.D. Mininni Departamento de Física, FCEyN, UBA and CONICET, Argentina and National Center for Atmospheric
Fluctuation dynamo amplified by intermittent shear bursts
 by intermittent Thanks to my collaborators: A. Busse (U. Glasgow), W.-C. Müller (TU Berlin) Dynamics Days Europe 8-12 September 2014 Mini-symposium on Nonlinear Problems in Plasma Astrophysics Introduction
by intermittent Thanks to my collaborators: A. Busse (U. Glasgow), W.-C. Müller (TU Berlin) Dynamics Days Europe 8-12 September 2014 Mini-symposium on Nonlinear Problems in Plasma Astrophysics Introduction
Plasma Physics for Astrophysics
 - ' ' * ' Plasma Physics for Astrophysics RUSSELL M. KULSRUD PRINCETON UNIVERSITY E;RESS '. ' PRINCETON AND OXFORD,, ', V. List of Figures Foreword by John N. Bahcall Preface Chapter 1. Introduction 1
- ' ' * ' Plasma Physics for Astrophysics RUSSELL M. KULSRUD PRINCETON UNIVERSITY E;RESS '. ' PRINCETON AND OXFORD,, ', V. List of Figures Foreword by John N. Bahcall Preface Chapter 1. Introduction 1
Chapter 7. Basic Turbulence
 Chapter 7 Basic Turbulence The universe is a highly turbulent place, and we must understand turbulence if we want to understand a lot of what s going on. Interstellar turbulence causes the twinkling of
Chapter 7 Basic Turbulence The universe is a highly turbulent place, and we must understand turbulence if we want to understand a lot of what s going on. Interstellar turbulence causes the twinkling of
Introduction to Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD)
 Introduction to Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) Tony Arber University of Warwick 4th SOLARNET Summer School on Solar MHD and Reconnection Aim Derivation of MHD equations from conservation laws Quasi-neutrality
Introduction to Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) Tony Arber University of Warwick 4th SOLARNET Summer School on Solar MHD and Reconnection Aim Derivation of MHD equations from conservation laws Quasi-neutrality
MHD Turbulence: Nonlocal, Anisotropic, Nonuniversal?
 MHD Turbulence: Nonlocal, Anisotropic, Nonuniversal? Alexander A Schekochihin 1,2,3, Steven C Cowley 1,4, and Tarek A Yousef 3 1 Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College, London SW7 2BW, UK 2 King s College,
MHD Turbulence: Nonlocal, Anisotropic, Nonuniversal? Alexander A Schekochihin 1,2,3, Steven C Cowley 1,4, and Tarek A Yousef 3 1 Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College, London SW7 2BW, UK 2 King s College,
The Madison Dynamo Experiment: magnetic instabilities driven by sheared flow in a sphere. Cary Forest Department of Physics University of Wisconsin
 The Madison Dynamo Experiment: magnetic instabilities driven by sheared flow in a sphere Cary Forest Department of Physics University of Wisconsin February 28, 2001 Planets, stars and perhaps the galaxy
The Madison Dynamo Experiment: magnetic instabilities driven by sheared flow in a sphere Cary Forest Department of Physics University of Wisconsin February 28, 2001 Planets, stars and perhaps the galaxy
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 23 Oct 2001
 Kolmogorov Burgers Model for Star Forming Turbulence Stanislav Boldyrev 1 Institute for Theoretical Physics, Santa Barbara, CA 93106 arxiv:astro-ph/0108300v2 23 Oct 2001 ABSTRACT The process of star formation
Kolmogorov Burgers Model for Star Forming Turbulence Stanislav Boldyrev 1 Institute for Theoretical Physics, Santa Barbara, CA 93106 arxiv:astro-ph/0108300v2 23 Oct 2001 ABSTRACT The process of star formation
arxiv:physics/ v1 8 Sep 2005
 On the inverse cascade of magnetic helicity Alexandros Alexakis, Pablo Mininni, and Annick Pouquet National Center for Atmospheric Research (Dated: September 12, 2005) arxiv:physics/0509069 v1 8 Sep 2005
On the inverse cascade of magnetic helicity Alexandros Alexakis, Pablo Mininni, and Annick Pouquet National Center for Atmospheric Research (Dated: September 12, 2005) arxiv:physics/0509069 v1 8 Sep 2005
PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS. ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP. NOTES: (references therein)
 PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP NOTES:http://www.astro.iag.usp.br/~dalpino (references therein) ICTP-SAIFR, October 7-18, 2013 Contents What is plasma? Why plasmas in astrophysics?
PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP NOTES:http://www.astro.iag.usp.br/~dalpino (references therein) ICTP-SAIFR, October 7-18, 2013 Contents What is plasma? Why plasmas in astrophysics?
Physical Processes in Astrophysics
 Physical Processes in Astrophysics Huirong Yan Uni Potsdam & Desy Email: hyan@mail.desy.de 1 Reference Books: Plasma Physics for Astrophysics, Russell M. Kulsrud (2005) The Physics of Astrophysics, Frank
Physical Processes in Astrophysics Huirong Yan Uni Potsdam & Desy Email: hyan@mail.desy.de 1 Reference Books: Plasma Physics for Astrophysics, Russell M. Kulsrud (2005) The Physics of Astrophysics, Frank
Accretion Disks I. High Energy Astrophysics: Accretion Disks I 1/60
 Accretion Disks I References: Accretion Power in Astrophysics, J. Frank, A. King and D. Raine. High Energy Astrophysics, Vol. 2, M.S. Longair, Cambridge University Press Active Galactic Nuclei, J.H. Krolik,
Accretion Disks I References: Accretion Power in Astrophysics, J. Frank, A. King and D. Raine. High Energy Astrophysics, Vol. 2, M.S. Longair, Cambridge University Press Active Galactic Nuclei, J.H. Krolik,
The Effect of Magnetic Turbulence Energy Spectra and Pickup Ions on the Heating of the Solar Wind
 The Effect of Magnetic Turbulence Energy Spectra and Pickup Ions on the Heating of the Solar Wind C. S. Ng Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska Fairbanks A. Bhattacharjee, P. A. Isenberg, D. Munsi,
The Effect of Magnetic Turbulence Energy Spectra and Pickup Ions on the Heating of the Solar Wind C. S. Ng Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska Fairbanks A. Bhattacharjee, P. A. Isenberg, D. Munsi,
Cascade Phenomenology in Turbulence: Navier-Stokes and MHD
 Cascade Phenomenology in Turbulence: Navier-Stoes and MHD WeiHan Hsiao a a Department of Physics, The University of Chicago E-mail: weihanhsiao@uchicago.edu ABSTRACT: This is the note prepared for the
Cascade Phenomenology in Turbulence: Navier-Stoes and MHD WeiHan Hsiao a a Department of Physics, The University of Chicago E-mail: weihanhsiao@uchicago.edu ABSTRACT: This is the note prepared for the
Small-Scale Dynamo and the Magnetic Prandtl Number
 MRI Turbulence Workshop, IAS, Princeton, 17.06.08 Small-Scale Dynamo and the Magnetic Prandtl Number Alexander Schekochihin (Imperial College) with Steve Cowley (Culham & Imperial) Greg Hammett (Princeton)
MRI Turbulence Workshop, IAS, Princeton, 17.06.08 Small-Scale Dynamo and the Magnetic Prandtl Number Alexander Schekochihin (Imperial College) with Steve Cowley (Culham & Imperial) Greg Hammett (Princeton)
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 19 Mar 2010
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 19 Mar 2010 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 19 Mar 2010](/thumbs/93/112005337.jpg) DRAFT VERSION OCTOBER 29, 2018 Preprint typeset using LATEX style emulateapj v. 11/10/09 arxiv:1003.3697v1 [astro-ph.ga] 19 Mar 2010 VELOCITY FIELD OF COMPRESSIBLE MHD TURBULENCE: WAVELET DECOMPOSITION
DRAFT VERSION OCTOBER 29, 2018 Preprint typeset using LATEX style emulateapj v. 11/10/09 arxiv:1003.3697v1 [astro-ph.ga] 19 Mar 2010 VELOCITY FIELD OF COMPRESSIBLE MHD TURBULENCE: WAVELET DECOMPOSITION
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 15 Jul 2007
 Draft version September 27, 2018 Preprint typeset using L TEX style emulateapj v. 10/09/06 CORONL HETING, WEK MHD TURBULENCE ND SCLING LWS. F. Rappazzo 1,2, M. Velli 2,3, G. Einaudi 1 and R. B. Dahlburg
Draft version September 27, 2018 Preprint typeset using L TEX style emulateapj v. 10/09/06 CORONL HETING, WEK MHD TURBULENCE ND SCLING LWS. F. Rappazzo 1,2, M. Velli 2,3, G. Einaudi 1 and R. B. Dahlburg
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 5 Nov 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 5 Nov 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 5 Nov 2008](/thumbs/88/117210820.jpg) SSRv manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Properties and selected implications of magnetic turbulence for interstellar medium, Local Bubble and solar wind arxiv:0811.0826v1 [astro-ph] 5 Nov
SSRv manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Properties and selected implications of magnetic turbulence for interstellar medium, Local Bubble and solar wind arxiv:0811.0826v1 [astro-ph] 5 Nov
THE RIGA DYNAMO EXPERIMENTS
 THE RIGA DYNAMO EXPERIMENTS Frank Stefani, Thomas Gundrum, Gunter Gerbeth, Agris Gailitis, Olgerts Lielausis, and Ernests Platacis. Introduction Cosmic magnetic fields, including the magnetic fields of
THE RIGA DYNAMO EXPERIMENTS Frank Stefani, Thomas Gundrum, Gunter Gerbeth, Agris Gailitis, Olgerts Lielausis, and Ernests Platacis. Introduction Cosmic magnetic fields, including the magnetic fields of
Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields
 Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Ellen Zweibel zweibel@astro.wisc.edu Departments of Astronomy & Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison and Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical
Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Ellen Zweibel zweibel@astro.wisc.edu Departments of Astronomy & Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison and Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory and Astrophysical
THE INTERACTION OF TURBULENCE WITH THE HELIOSPHERIC SHOCK
 THE INTERACTION OF TURBULENCE WITH THE HELIOSPHERIC SHOCK G.P. Zank, I. Kryukov, N. Pogorelov, S. Borovikov, Dastgeer Shaikh, and X. Ao CSPAR, University of Alabama in Huntsville Heliospheric observations
THE INTERACTION OF TURBULENCE WITH THE HELIOSPHERIC SHOCK G.P. Zank, I. Kryukov, N. Pogorelov, S. Borovikov, Dastgeer Shaikh, and X. Ao CSPAR, University of Alabama in Huntsville Heliospheric observations
Evidence for Anisotropy and Intermittency in the Turbulent Interstellar Plasma
 Evidence for Anisotropy and Intermittency in the Turbulent Interstellar Plasma Bill Coles, University of California, San Diego 1. It had been thought that turbulence in the WIM was more or less isotropic.
Evidence for Anisotropy and Intermittency in the Turbulent Interstellar Plasma Bill Coles, University of California, San Diego 1. It had been thought that turbulence in the WIM was more or less isotropic.
Project Topic. Simulation of turbulent flow laden with finite-size particles using LBM. Leila Jahanshaloo
 Project Topic Simulation of turbulent flow laden with finite-size particles using LBM Leila Jahanshaloo Project Details Turbulent flow modeling Lattice Boltzmann Method All I know about my project Solid-liquid
Project Topic Simulation of turbulent flow laden with finite-size particles using LBM Leila Jahanshaloo Project Details Turbulent flow modeling Lattice Boltzmann Method All I know about my project Solid-liquid
MHD Modes of Solar Plasma Structures
 PX420 Solar MHD 2013-2014 MHD Modes of Solar Plasma Structures Centre for Fusion, Space & Astrophysics Wave and oscillatory processes in the solar corona: Possible relevance to coronal heating and solar
PX420 Solar MHD 2013-2014 MHD Modes of Solar Plasma Structures Centre for Fusion, Space & Astrophysics Wave and oscillatory processes in the solar corona: Possible relevance to coronal heating and solar
Growth of Magnetic Fields by Turbulent Motions and Characteristic Scales of MHD Turbulence
 Growth of Magnetic Fields by Turbulent Motions and Characteristic Scales of MHD Turbulence Jungyeon Cho Chungnam National University, Korea Cho, Vishniac, Beresnyak, Lazarian & Ryu 2009, ApJ Cho & Ryu,
Growth of Magnetic Fields by Turbulent Motions and Characteristic Scales of MHD Turbulence Jungyeon Cho Chungnam National University, Korea Cho, Vishniac, Beresnyak, Lazarian & Ryu 2009, ApJ Cho & Ryu,
Turbulence: Basic Physics and Engineering Modeling
 DEPARTMENT OF ENERGETICS Turbulence: Basic Physics and Engineering Modeling Numerical Heat Transfer Pietro Asinari, PhD Spring 2007, TOP UIC Program: The Master of Science Degree of the University of Illinois
DEPARTMENT OF ENERGETICS Turbulence: Basic Physics and Engineering Modeling Numerical Heat Transfer Pietro Asinari, PhD Spring 2007, TOP UIC Program: The Master of Science Degree of the University of Illinois
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 25 Jul 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 25 Jul 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 25 Jul 2016](/thumbs/90/101400394.jpg) Draft version September 9, 8 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5// THE DYNAMICAL GENERATION OF CURRENT SHEETS IN ASTROPHYSICAL PLASMA TURBULENCE Gregory G. Howes Department of Physics
Draft version September 9, 8 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5// THE DYNAMICAL GENERATION OF CURRENT SHEETS IN ASTROPHYSICAL PLASMA TURBULENCE Gregory G. Howes Department of Physics
Spacecraft observations of solar wind turbulence: an overview
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 47 (2005) B703 B717 PLASMA PHYSICS AND CONTROLLED FUSION doi:10.1088/0741-3335/47/12b/s52 Spacecraft observations of solar wind turbulence:
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 47 (2005) B703 B717 PLASMA PHYSICS AND CONTROLLED FUSION doi:10.1088/0741-3335/47/12b/s52 Spacecraft observations of solar wind turbulence:
Energy spectrum in the dissipation range of fluid turbulence
 J. Plasma Physics (1997), vol. 57, part 1, pp. 195 201 Copyright 1997 Cambridge University Press 195 Energy spectrum in the dissipation range of fluid turbulence D. O. MARTI NEZ,,, S. CHEN,, G. D. DOOLEN,
J. Plasma Physics (1997), vol. 57, part 1, pp. 195 201 Copyright 1997 Cambridge University Press 195 Energy spectrum in the dissipation range of fluid turbulence D. O. MARTI NEZ,,, S. CHEN,, G. D. DOOLEN,
6 VORTICITY DYNAMICS 41
 6 VORTICITY DYNAMICS 41 6 VORTICITY DYNAMICS As mentioned in the introduction, turbulence is rotational and characterized by large uctuations in vorticity. In this section we would like to identify some
6 VORTICITY DYNAMICS 41 6 VORTICITY DYNAMICS As mentioned in the introduction, turbulence is rotational and characterized by large uctuations in vorticity. In this section we would like to identify some
Coronal Heating Problem
 PHY 690C Project Report Coronal Heating Problem by Mani Chandra, Arnab Dhabal and Raziman T V (Y6233) (Y7081) (Y7355) Mentor: Dr. M.K. Verma 1 Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 The Coronal Heating Problem 4
PHY 690C Project Report Coronal Heating Problem by Mani Chandra, Arnab Dhabal and Raziman T V (Y6233) (Y7081) (Y7355) Mentor: Dr. M.K. Verma 1 Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 The Coronal Heating Problem 4
MHD turbulence in the solar corona and solar wind
 MHD turbulence in the solar corona and solar wind Pablo Dmitruk Departamento de Física, FCEN, Universidad de Buenos Aires Motivations The role of MHD turbulence in several phenomena in space and solar
MHD turbulence in the solar corona and solar wind Pablo Dmitruk Departamento de Física, FCEN, Universidad de Buenos Aires Motivations The role of MHD turbulence in several phenomena in space and solar
Intermittency of quasi-static magnetohydrodynamic turbulence: A wavelet viewpoint
 Intermittency of quasi-static magnetohydrodynamic turbulence: A wavelet viewpoint Naoya Okamoto 1, Katsunori Yoshimatsu 2, Kai Schneider 3 and Marie Farge 4 1 Center for Computational Science, Nagoya University,
Intermittency of quasi-static magnetohydrodynamic turbulence: A wavelet viewpoint Naoya Okamoto 1, Katsunori Yoshimatsu 2, Kai Schneider 3 and Marie Farge 4 1 Center for Computational Science, Nagoya University,
Theory and modelling of turbulent transport in astrophysical phenomena
 MHD 2017 Tokyo, 29 August 2017 Theory and modelling of turbulent transport in astrophysical phenomena Nobumitsu YOKOI Institute of Industrial Science (IIS), University of Tokyo In collaboration with Akira
MHD 2017 Tokyo, 29 August 2017 Theory and modelling of turbulent transport in astrophysical phenomena Nobumitsu YOKOI Institute of Industrial Science (IIS), University of Tokyo In collaboration with Akira
Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse
 Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse Miguel Àngel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz Universitat de València; Max-Planck-Institut
Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse Miguel Àngel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz Universitat de València; Max-Planck-Institut
Max Planck Institut für Plasmaphysik
 ASDEX Upgrade Max Planck Institut für Plasmaphysik 2D Fluid Turbulence Florian Merz Seminar on Turbulence, 08.09.05 2D turbulence? strictly speaking, there are no two-dimensional flows in nature approximately
ASDEX Upgrade Max Planck Institut für Plasmaphysik 2D Fluid Turbulence Florian Merz Seminar on Turbulence, 08.09.05 2D turbulence? strictly speaking, there are no two-dimensional flows in nature approximately
Cosmic Rays in CMSO. Ellen Zweibel University of Wisconsin-Madison Santa Fe, 2014
 Cosmic Rays in CMSO Ellen Zweibel University of Wisconsin-Madison Santa Fe, 2014 Galaxies are Pervaded by Magnetic Fields & Relativistic Particles Synchrotron radiation from M51 (MPIfR/NRAO) Galactic molecular
Cosmic Rays in CMSO Ellen Zweibel University of Wisconsin-Madison Santa Fe, 2014 Galaxies are Pervaded by Magnetic Fields & Relativistic Particles Synchrotron radiation from M51 (MPIfR/NRAO) Galactic molecular
School and Conference on Analytical and Computational Astrophysics November, Angular momentum transport in accretion disks
 2292-13 School and Conference on Analytical and Computational Astrophysics 14-25 November, 2011 Angular momentum transport in accretion disks Gianluigi Bodo Osservatorio Astronomico, Torino Italy Angular
2292-13 School and Conference on Analytical and Computational Astrophysics 14-25 November, 2011 Angular momentum transport in accretion disks Gianluigi Bodo Osservatorio Astronomico, Torino Italy Angular
Space Physics. An Introduction to Plasmas and Particles in the Heliosphere and Magnetospheres. May-Britt Kallenrode. Springer
 May-Britt Kallenrode Space Physics An Introduction to Plasmas and Particles in the Heliosphere and Magnetospheres With 170 Figures, 9 Tables, Numerous Exercises and Problems Springer Contents 1. Introduction
May-Britt Kallenrode Space Physics An Introduction to Plasmas and Particles in the Heliosphere and Magnetospheres With 170 Figures, 9 Tables, Numerous Exercises and Problems Springer Contents 1. Introduction
Direct numerical simulation of forced MHD turbulence at low magnetic Reynolds number
 J. Fluid Mech. (1998), vol. 358, pp. 99 333. Printed in the United Kingdom c 1998 Cambridge University Press 99 Direct numerical simulation of forced MHD turbulence at low magnetic Reynolds number By OLEG
J. Fluid Mech. (1998), vol. 358, pp. 99 333. Printed in the United Kingdom c 1998 Cambridge University Press 99 Direct numerical simulation of forced MHD turbulence at low magnetic Reynolds number By OLEG
Turbulence and Magnetic Field in High-β Plasma of Intracluster Medium
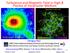 Turbulence and Magnetic Field in High-β Plasma of Intracluster Medium Coma cluster of galaxies Dongsu Ryu UNIST (Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) KASI (Korea Astronomy and Space
Turbulence and Magnetic Field in High-β Plasma of Intracluster Medium Coma cluster of galaxies Dongsu Ryu UNIST (Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) KASI (Korea Astronomy and Space
THEORETICAL RESEARCH ON SOLAR WIND TURBULENCE
 THEORETICAL RESEARCH ON SOLAR WIND TURBULENCE A White Paper Submitted to the NRC Decadal Survey of Solar and Space Physics Benjamin D. G. Chandran, Eliot Quataert, Jean Perez, Aveek Sarkar, Steve Cranmer,
THEORETICAL RESEARCH ON SOLAR WIND TURBULENCE A White Paper Submitted to the NRC Decadal Survey of Solar and Space Physics Benjamin D. G. Chandran, Eliot Quataert, Jean Perez, Aveek Sarkar, Steve Cranmer,
Reynolds-averaged turbulence model for magnetohydrodynamic dynamo in a rotating spherical shell
 PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 11, NUMBER 11 NOVEMBER 2004 Reynolds-averaged turbulence model for magnetohydrodynamic dynamo in a rotating spherical shell Fujihiro Hamba a) Institute of Industrial Science,
PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 11, NUMBER 11 NOVEMBER 2004 Reynolds-averaged turbulence model for magnetohydrodynamic dynamo in a rotating spherical shell Fujihiro Hamba a) Institute of Industrial Science,
Note the diverse scales of eddy motion and self-similar appearance at different lengthscales of the turbulence in this water jet. Only eddies of size
 L Note the diverse scales of eddy motion and self-similar appearance at different lengthscales of the turbulence in this water jet. Only eddies of size 0.01L or smaller are subject to substantial viscous
L Note the diverse scales of eddy motion and self-similar appearance at different lengthscales of the turbulence in this water jet. Only eddies of size 0.01L or smaller are subject to substantial viscous
MAGNETOHYDRODYNAMIC TURBULENCE
 MAGNETOHYDRODYNAMIC TURBULENCE This book presents an introduction to,and state-of-the-art account of, magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) turbulence,an active field both in general turbulence theory and in various
MAGNETOHYDRODYNAMIC TURBULENCE This book presents an introduction to,and state-of-the-art account of, magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) turbulence,an active field both in general turbulence theory and in various
Two Fluid Dynamo and Edge-Resonant m=0 Tearing Instability in Reversed Field Pinch
 1 Two Fluid Dynamo and Edge-Resonant m= Tearing Instability in Reversed Field Pinch V.V. Mirnov 1), C.C.Hegna 1), S.C. Prager 1), C.R.Sovinec 1), and H.Tian 1) 1) The University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison,
1 Two Fluid Dynamo and Edge-Resonant m= Tearing Instability in Reversed Field Pinch V.V. Mirnov 1), C.C.Hegna 1), S.C. Prager 1), C.R.Sovinec 1), and H.Tian 1) 1) The University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison,
Heating of Test Particles in Numerical Simulations of MHD Turbulence and the Solar Wind
 Heating of Test Particles in Numerical Simulations of MHD Turbulence and the Solar Wind Ian Parrish UC Berkeley Collaborators: Rémi Lehe (ENS), Eliot Quataert (UCB) Einstein Fellows Symposium October 27,
Heating of Test Particles in Numerical Simulations of MHD Turbulence and the Solar Wind Ian Parrish UC Berkeley Collaborators: Rémi Lehe (ENS), Eliot Quataert (UCB) Einstein Fellows Symposium October 27,
Turbulent Magnetic Helicity Transport and the Rapid Growth of Large Scale Magnetic Fields
 Turbulent Magnetic Helicity Transport and the Rapid Growth of Large Scale Magnetic Fields Jungyeon Cho Dmitry Shapovalov MWMF Madison, Wisconsin April 2012 The Large Scale Dynamo The accumulation of magnetic
Turbulent Magnetic Helicity Transport and the Rapid Growth of Large Scale Magnetic Fields Jungyeon Cho Dmitry Shapovalov MWMF Madison, Wisconsin April 2012 The Large Scale Dynamo The accumulation of magnetic
Special topic JPFR article Prospects of Research on Innovative Concepts in ITER Era contribution by M. Brown Section 5.2.2
 Special topic JPFR article Prospects of Research on Innovative Concepts in ITER Era contribution by M. Brown Section 5.2.2 5.2.2 Dynamo and Reconnection Research: Overview: Spheromaks undergo a relaxation
Special topic JPFR article Prospects of Research on Innovative Concepts in ITER Era contribution by M. Brown Section 5.2.2 5.2.2 Dynamo and Reconnection Research: Overview: Spheromaks undergo a relaxation
Dissipation Scales & Small Scale Structure
 Dissipation Scales & Small Scale Structure Ellen Zweibel zweibel@astro.wisc.edu Departments of Astronomy & Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison and Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory
Dissipation Scales & Small Scale Structure Ellen Zweibel zweibel@astro.wisc.edu Departments of Astronomy & Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison and Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory
Modulation of waves due to charge-exchange collisions in magnetized partially ionized space plasma. Abstract
 Modulation of waves due to charge-exchange collisions in magnetized partially ionized space plasma Dastgeer Shaikh and G. P. Zank 1 1 Department of Physics and Center for Space Plasma and Aeronomy Research,
Modulation of waves due to charge-exchange collisions in magnetized partially ionized space plasma Dastgeer Shaikh and G. P. Zank 1 1 Department of Physics and Center for Space Plasma and Aeronomy Research,
A simple subgrid-scale model for astrophysical turbulence
 CfCA User Meeting NAOJ, 29-30 November 2016 A simple subgrid-scale model for astrophysical turbulence Nobumitsu Yokoi Institute of Industrial Science (IIS), Univ. of Tokyo Collaborators Axel Brandenburg
CfCA User Meeting NAOJ, 29-30 November 2016 A simple subgrid-scale model for astrophysical turbulence Nobumitsu Yokoi Institute of Industrial Science (IIS), Univ. of Tokyo Collaborators Axel Brandenburg
Scope of this lecture ASTR 7500: Solar & Stellar Magnetism. Lecture 9 Tues 19 Feb Magnetic fields in the Universe. Geomagnetism.
 Scope of this lecture ASTR 7500: Solar & Stellar Magnetism Hale CGEG Solar & Space Physics Processes of magnetic field generation and destruction in turbulent plasma flows Introduction to general concepts
Scope of this lecture ASTR 7500: Solar & Stellar Magnetism Hale CGEG Solar & Space Physics Processes of magnetic field generation and destruction in turbulent plasma flows Introduction to general concepts
Turbulence. 2. Reynolds number is an indicator for turbulence in a fluid stream
 Turbulence injection of a water jet into a water tank Reynolds number EF$ 1. There is no clear definition and range of turbulence (multi-scale phenomena) 2. Reynolds number is an indicator for turbulence
Turbulence injection of a water jet into a water tank Reynolds number EF$ 1. There is no clear definition and range of turbulence (multi-scale phenomena) 2. Reynolds number is an indicator for turbulence
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 6 Feb 2013
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 6 Feb 2013 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 6 Feb 2013](/thumbs/79/79148193.jpg) Draft version February 7, 2013 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF CURRENT SHEETS IN THREE-DIMENSIONAL MAGNETOHYDRODYNAMIC TURBULENCE Vladimir Zhdankin Department
Draft version February 7, 2013 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF CURRENT SHEETS IN THREE-DIMENSIONAL MAGNETOHYDRODYNAMIC TURBULENCE Vladimir Zhdankin Department
Astrophysical Hydromagnetic Turbulence
 Space Sci Rev (2013) 178:163 200 DOI 10.1007/s11214-013-0009-3 Astrophysical Hydromagnetic Turbulence A. Brandenburg A. Lazarian Received: 1 March 2013 / Accepted: 21 July 2013 / Published online: 31 August
Space Sci Rev (2013) 178:163 200 DOI 10.1007/s11214-013-0009-3 Astrophysical Hydromagnetic Turbulence A. Brandenburg A. Lazarian Received: 1 March 2013 / Accepted: 21 July 2013 / Published online: 31 August
M.A. Aziz, M.A.K. Azad and M.S. Alam Sarker Department of Applied Mathematics, University of Rajshahi-6205, Bangladesh
 Research Journal of Mathematics Statistics 2(2): 56-68, 2010 ISSN: 2040-7505 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2009 Submitted Date: November 27, 2009 Accepted Date: December 21, 2010 Published Date: June
Research Journal of Mathematics Statistics 2(2): 56-68, 2010 ISSN: 2040-7505 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2009 Submitted Date: November 27, 2009 Accepted Date: December 21, 2010 Published Date: June
On Cosmic-Ray Production Efficiency at Realistic Supernova Remnant Shocks
 On Cosmic-Ray Production Efficiency at Realistic Supernova Remnant Shocks, 1 T. Inoue 2, Y. Ohira 1, R. Yamazaki 1, A. Bamba 1 and J. Vink 3 1 Department of Physics and Mathematics, Aoyama-Gakuin University,
On Cosmic-Ray Production Efficiency at Realistic Supernova Remnant Shocks, 1 T. Inoue 2, Y. Ohira 1, R. Yamazaki 1, A. Bamba 1 and J. Vink 3 1 Department of Physics and Mathematics, Aoyama-Gakuin University,
Magnetic Reconnection: explosions in space and astrophysical plasma. J. F. Drake University of Maryland
 Magnetic Reconnection: explosions in space and astrophysical plasma J. F. Drake University of Maryland Magnetic Energy Dissipation in the Universe The conversion of magnetic energy to heat and high speed
Magnetic Reconnection: explosions in space and astrophysical plasma J. F. Drake University of Maryland Magnetic Energy Dissipation in the Universe The conversion of magnetic energy to heat and high speed
Creation and destruction of magnetic fields
 HAO/NCAR July 30 2007 Magnetic fields in the Universe Earth Magnetic field present for 3.5 10 9 years, much longer than Ohmic decay time ( 10 4 years) Strong variability on shorter time scales (10 3 years)
HAO/NCAR July 30 2007 Magnetic fields in the Universe Earth Magnetic field present for 3.5 10 9 years, much longer than Ohmic decay time ( 10 4 years) Strong variability on shorter time scales (10 3 years)
Small-Scale Statistics and Structure of Turbulence in the Light of High Resolution Direct Numerical Simulation
 1 Small-Scale Statistics and Structure of Turbulence in the Light of High Resolution Direct Numerical Simulation Yukio Kaneda and Koji Morishita 1.1 Introduction Fully developed turbulence is a phenomenon
1 Small-Scale Statistics and Structure of Turbulence in the Light of High Resolution Direct Numerical Simulation Yukio Kaneda and Koji Morishita 1.1 Introduction Fully developed turbulence is a phenomenon
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 31 Oct 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 31 Oct 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 31 Oct 2012](/thumbs/73/68615484.jpg) Space Sci Rev manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Turbulence, Magnetic Reconnection in Turbulent Fluids and Energetic Particle Acceleration A. Lazarian L. Vlahos G. Kowal H. Yan A. Beresnyak
Space Sci Rev manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Turbulence, Magnetic Reconnection in Turbulent Fluids and Energetic Particle Acceleration A. Lazarian L. Vlahos G. Kowal H. Yan A. Beresnyak
Lecture 2. Turbulent Flow
 Lecture 2. Turbulent Flow Note the diverse scales of eddy motion and self-similar appearance at different lengthscales of this turbulent water jet. If L is the size of the largest eddies, only very small
Lecture 2. Turbulent Flow Note the diverse scales of eddy motion and self-similar appearance at different lengthscales of this turbulent water jet. If L is the size of the largest eddies, only very small
Turbulence Instability
 Turbulence Instability 1) All flows become unstable above a certain Reynolds number. 2) At low Reynolds numbers flows are laminar. 3) For high Reynolds numbers flows are turbulent. 4) The transition occurs
Turbulence Instability 1) All flows become unstable above a certain Reynolds number. 2) At low Reynolds numbers flows are laminar. 3) For high Reynolds numbers flows are turbulent. 4) The transition occurs
Vladimir Zhdankin, JILA/CU-Boulder US-Japan Magne>c Reconnec>on Workshop, 3/7/2016
 Vladimir Zhdankin, JILA/CU-Boulder US-Japan Magne>c Reconnec>on Workshop, 3/7/2016 Stanislav Boldyrev (UW-Madison), Dmitri Uzdensky (CU-Boulder), Steve Tobias (U-Leeds), Jean Carlos Perez (FIT) 1 I. Introduc>on:
Vladimir Zhdankin, JILA/CU-Boulder US-Japan Magne>c Reconnec>on Workshop, 3/7/2016 Stanislav Boldyrev (UW-Madison), Dmitri Uzdensky (CU-Boulder), Steve Tobias (U-Leeds), Jean Carlos Perez (FIT) 1 I. Introduc>on:
MHD turbulence in the solar corona and solar wind
 MHD turbulence in the solar corona and solar wind Pablo Dmitruk Departamento de Física, FCEN, Universidad de Buenos Aires Turbulence, magnetic reconnection, particle acceleration Understand the mechanisms
MHD turbulence in the solar corona and solar wind Pablo Dmitruk Departamento de Física, FCEN, Universidad de Buenos Aires Turbulence, magnetic reconnection, particle acceleration Understand the mechanisms
Nonequilibrium Dynamics in Astrophysics and Material Science YITP, Kyoto
 Nonequilibrium Dynamics in Astrophysics and Material Science 2011-11-02 @ YITP, Kyoto Multi-scale coherent structures and their role in the Richardson cascade of turbulence Susumu Goto (Okayama Univ.)
Nonequilibrium Dynamics in Astrophysics and Material Science 2011-11-02 @ YITP, Kyoto Multi-scale coherent structures and their role in the Richardson cascade of turbulence Susumu Goto (Okayama Univ.)
Macroscopic plasma description
 Macroscopic plasma description Macroscopic plasma theories are fluid theories at different levels single fluid (magnetohydrodynamics MHD) two-fluid (multifluid, separate equations for electron and ion
Macroscopic plasma description Macroscopic plasma theories are fluid theories at different levels single fluid (magnetohydrodynamics MHD) two-fluid (multifluid, separate equations for electron and ion
NONLINEAR MHD WAVES THE INTERESTING INFLUENCE OF FIREHOSE AND MIRROR IN ASTROPHYSICAL PLASMAS. Jono Squire (Caltech) UCLA April 2017
 NONLINEAR MHD WAVES THE INTERESTING INFLUENCE OF FIREHOSE AND MIRROR IN ASTROPHYSICAL PLASMAS Jono Squire (Caltech) UCLA April 2017 Along with: E. Quataert, A. Schekochihin, M. Kunz, S. Bale, C. Chen,
NONLINEAR MHD WAVES THE INTERESTING INFLUENCE OF FIREHOSE AND MIRROR IN ASTROPHYSICAL PLASMAS Jono Squire (Caltech) UCLA April 2017 Along with: E. Quataert, A. Schekochihin, M. Kunz, S. Bale, C. Chen,
A model of turbulence in magnetized plasmas: Implications for the dissipation range in the solar wind
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007ja012665, 2008 A model of turbulence in magnetized plasmas: Implications for the dissipation range in the solar wind G. G. Howes, 1 S. C. Cowley,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007ja012665, 2008 A model of turbulence in magnetized plasmas: Implications for the dissipation range in the solar wind G. G. Howes, 1 S. C. Cowley,
centrifugal acceleration, whose magnitude is r cos, is zero at the poles and maximum at the equator. This distribution of the centrifugal acceleration
 Lecture 10. Equations of Motion Centripetal Acceleration, Gravitation and Gravity The centripetal acceleration of a body located on the Earth's surface at a distance from the center is the force (per unit
Lecture 10. Equations of Motion Centripetal Acceleration, Gravitation and Gravity The centripetal acceleration of a body located on the Earth's surface at a distance from the center is the force (per unit
Electron magnetohydrodynamic turbulence
 PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 6, NUMBER 3 MARCH 1999 Electron magnetohydrodynamic turbulence D. Biskamp, E. Schwarz, and A. Zeiler Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, D-85748 Garching, Germany A. Celani
PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 6, NUMBER 3 MARCH 1999 Electron magnetohydrodynamic turbulence D. Biskamp, E. Schwarz, and A. Zeiler Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, D-85748 Garching, Germany A. Celani
Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields
 Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields Robi Banerjee University of Hamburg Collaborators: Dominik Schleicher (Göttingen), C. Federrath (Lyon, HD), Karsten Jedamzik (Montpellier), R. Klessen (Heidelberg),
Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields Robi Banerjee University of Hamburg Collaborators: Dominik Schleicher (Göttingen), C. Federrath (Lyon, HD), Karsten Jedamzik (Montpellier), R. Klessen (Heidelberg),
Preferential concentration of inertial particles in turbulent flows. Jérémie Bec CNRS, Observatoire de la Côte d Azur, Université de Nice
 Preferential concentration of inertial particles in turbulent flows Jérémie Bec CNRS, Observatoire de la Côte d Azur, Université de Nice EE250, Aussois, June 22, 2007 Particle laden flows Warm clouds Plankton
Preferential concentration of inertial particles in turbulent flows Jérémie Bec CNRS, Observatoire de la Côte d Azur, Université de Nice EE250, Aussois, June 22, 2007 Particle laden flows Warm clouds Plankton
DAMPING OF MAGNETOHYDRODYNAMIC TURBULENCE IN PARTIALLY IONIZED GAS AND THE OBSERVED DIFFERENCE OF VELOCITIES OF NEUTRALS AND IONS
 The Astrophysical Journal, 713:1376 1385, 2010 April 20 C 2010. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A. doi:10.1088/0004-637x/713/2/1376 DAMPING OF MAGNETOHYDRODYNAMIC
The Astrophysical Journal, 713:1376 1385, 2010 April 20 C 2010. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A. doi:10.1088/0004-637x/713/2/1376 DAMPING OF MAGNETOHYDRODYNAMIC
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 6 Jan 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 6 Jan 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 6 Jan 2012](/thumbs/93/111753454.jpg) arxiv:1201.1370v1 [astro-ph.sr] 6 Jan 2012 Contents 1. Wave turbulence in magnetohydrodynamics 1 1.1 Introduction............................... 1 1.2 Waves and turbulence in space plasmas...............
arxiv:1201.1370v1 [astro-ph.sr] 6 Jan 2012 Contents 1. Wave turbulence in magnetohydrodynamics 1 1.1 Introduction............................... 1 1.2 Waves and turbulence in space plasmas...............
Small scale solar wind turbulence: Recent observations and theoretical modeling
 Small scale solar wind turbulence: Recent observations and theoretical modeling F. Sahraoui 1,2 & M. Goldstein 1 1 NASA/GSFC, Greenbelt, USA 2 LPP, CNRS-Ecole Polytechnique, Vélizy, France Outline Motivations
Small scale solar wind turbulence: Recent observations and theoretical modeling F. Sahraoui 1,2 & M. Goldstein 1 1 NASA/GSFC, Greenbelt, USA 2 LPP, CNRS-Ecole Polytechnique, Vélizy, France Outline Motivations
Formation and Long Term Evolution of an Externally Driven Magnetic Island in Rotating Plasmas )
 Formation and Long Term Evolution of an Externally Driven Magnetic Island in Rotating Plasmas ) Yasutomo ISHII and Andrei SMOLYAKOV 1) Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Ibaraki 311-0102, Japan 1) University
Formation and Long Term Evolution of an Externally Driven Magnetic Island in Rotating Plasmas ) Yasutomo ISHII and Andrei SMOLYAKOV 1) Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Ibaraki 311-0102, Japan 1) University
the ICM Power Spectrum:
 the ICM Power Spectrum: probing the gas physics of galaxy clusters Massimo Gaspari Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Collaborators: E. Churazov, D. Nagai, E. Lau, I. Zhuravleva, R. Sunyaev Power Spectrum
the ICM Power Spectrum: probing the gas physics of galaxy clusters Massimo Gaspari Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Collaborators: E. Churazov, D. Nagai, E. Lau, I. Zhuravleva, R. Sunyaev Power Spectrum
Dimensionality influence on energy, enstrophy and passive scalar transport.
 Dimensionality influence on energy, enstrophy and passive scalar transport. M. Iovieno, L. Ducasse, S. Di Savino, L. Gallana, D. Tordella 1 The advection of a passive substance by a turbulent flow is important
Dimensionality influence on energy, enstrophy and passive scalar transport. M. Iovieno, L. Ducasse, S. Di Savino, L. Gallana, D. Tordella 1 The advection of a passive substance by a turbulent flow is important
Characteristics of Linearly-Forced Scalar Mixing in Homogeneous, Isotropic Turbulence
 Seventh International Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ICCFD7), Big Island, Hawaii, July 9-13, 2012 ICCFD7-1103 Characteristics of Linearly-Forced Scalar Mixing in Homogeneous, Isotropic Turbulence
Seventh International Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ICCFD7), Big Island, Hawaii, July 9-13, 2012 ICCFD7-1103 Characteristics of Linearly-Forced Scalar Mixing in Homogeneous, Isotropic Turbulence
Francesco Califano. Physics Department, University of Pisa. The role of the magnetic field in the interaction of the solar wind with a magnetosphere
 Francesco Califano Physics Department, University of Pisa The role of the magnetic field in the interaction of the solar wind with a magnetosphere Collaboration with M. Faganello & F. Pegoraro Vien na,
Francesco Califano Physics Department, University of Pisa The role of the magnetic field in the interaction of the solar wind with a magnetosphere Collaboration with M. Faganello & F. Pegoraro Vien na,
