ME357 Problem Set The wheel is a thin homogeneous disk that rolls without slip. sin. The wall moves with a specified motion x t. sin..
|
|
|
- Marjorie Brooks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ME357 Proble Set 3 Derive the equation(s) of otion for the systes shown using Newton s Method. For ultiple degree of freedo systes put you answer in atri for. Unless otherwise speified the degrees of freedo are easured fro the syste s equilibriu position. Unless otherwise stated all otion is sall.. The wheel is a thin hoogeneous dis that rolls without slip. The wall oves with a speified otion t X t sin. w w w sin.. The base oves with a speified otion t X t b b b w t R b t 3 bx bsin bt wx w os wt X wsin wt
2 . a. The wheel is a thin unifor dis of ass 3 that rolls without slip. b. The pulley is a thin unifor dis of ass.. What effet does the inlined plane have? Where would it have an effet? Equilibriu 3 3 A R B Equilibriu R ( )
3 3. a. First assue large displaeents for. b. Linearize your result fro a. for sall displaeents. Assue the two rigid lins of length L are assless. The ass is onstrained to ove vertially. The syste is shown in its equilibriu position. a a L L h a. h h ( ) 4 a a a h a a a h b. 4 0 a 0
4 4. Bar OB is rigid and assless. a o A B l a l a l 0
5 5. a. Bar AD with ass 3 and EI with ass 4 are rigid, unifor and pinned at A and I. b. Bar CF is rigid and assless.. Deterine the equation of otion in ters of. A L B L C L D E L L G L L H I F
6 6. a. Bars AC and DG an be onsidered as thin rigid unifor bars with asses and 3 respetively. b. Bar BE is assless and rigid. Deterine the equilibriu position of the two bars as easured fro the horizontal. d. Deterine the equation of otion in ters of as easured fro the horizontal. What does this assue? A L B L C D L L F L G E a. b. eq 3 g 34 l
7 7. a. Bars AC and DF an be onsidered as thin rigid unifor bars with asses and respetively. b. Bar CE is assless and rigid.. Deterine the equation of otion in ters of. A L B C L D 3L E L L F 6 8 L
8 8. a. Bars AD and EG an be onsidered as thin rigid unifor bars with asses 3 and 4 respetively. b. Bar BE is assless and rigid.. Deterine the equation of otion in ters of. A L B L L C D E L F L G
9 9. The pendulu is a rigid thin unifor bar. a. Deterine the equation of otion if the base is fied yb t 0 b. Deterine the equation if y t Y t () sin. Where does the vertial otion enter the b b b equation? What does it ae gravity/stiffness ter behave lie? yb t X a. g 3 0 l b. g Y b 3 b sinbt 0 l l
10 0. The wheel is onstruted of unifor thin diss. The inner dis has a radius R and a ass. and is fied to the outer dis. The outer dis is a rigid unifor dis with radius R and ass. Assue the wheel rolls without slip. Use as the degree of freedo. R R
11 . Deterine the equation of otion in ters of. Assue the wheel rolls without slip. The two asses are onstrained to ove only vertially and the pulleys are assless. The wheel has a ass of and a ass oent of inertia about its enter of ass of 4R. Cord EDCA is elasti and is odeled as a spring/daper. Cords BI and FG are inetensible. D C B H I E R O F A R G
12 . The drive wheel is a thin unifor dis of radius R and ass The driven dis is radius R and ass. Both roll without slip. Bar AB is rigid and assless. Deterine the equation of otion in ters of. Ft R R R A B : F () t 8 4
13 3. Deterine the equation of otion in ters of. Assue sall otion. The pendulu is pinned to the dis whih rotates with a onstant angular veloity.. The rod is rigid and assless and the ass at its tip is a point ass. O R L g R R os L L L t sin t
14 4. The thin hoogeneous dis is pinned at O and is driven by a otor that produes a torque, Mt. A point ass of is pinned to it with assless bar of length L. Deterine the equations of otion in ters of and. O R Mt L
15 5. Deterine the equations of otion in ters of and. Assue sall angles and that the wheel rolls without slip. The ass of the thin hoogeneous large dis of radius R is. The ass of the thin hoogeneous inner dis of radius R is. The rod of length R is assless and rigid. The two pulleys are assless. R O R Mt P R Ft g M t R 0 3 4r F t R R R R r R gr RF t
16 6. Deterine the equations of otion for the syste shown in ters of and assuing sall otion. The blo the dis is sitting on oves with a presribed otion b t. The wall the botto spring is attahed to oves with a presribed otion w t. The load Pt is always direted along the pendulu rod. Both diss of radius R and R are unifor and hoogenous with asses and respetively. The wheel rolls without slip. R P R O b t R w t Pt 9 g P R R P R R R R 0 0 R R gr g P 4 b b w R b R Rb Rb R 8 4 w
17 7. Repeat Prob if the wheel slips. Use and as your degrees of freedo. Assue a oeffiient of frition between the wheel and base of. g sign ( b) 0 R ( ) g sign b b w
18 8. a. Deterine the equations of otion for Eaple 9 of the notes for large. b. Redue your results to the equations of otion for sall. a. losl sin P sin F ( t) l gsin0 l 0 P() t F() t b. l l gl 0
19 9. Coplete Eaple 8 of the notes. M(t ) R 4 M(t ) 3 4 R
20 0. Deterine the equations of otion in ters of and. The pulley is assless. The inner hoogeneous thin dis of radius R has a ass. The outer dis of radius R has ass. The wheel rolls without slip. The pendulu is oposed of a assless rod and a point ass. R R O P l R I R l 3 R R R R R 0 R l l R 0 0 R R R R g l R R R R 0 R l 0 R l gl
21 . Deterine the equations of otion in ters of,, 3. All s ' are easured fro the equilibriu position. Masses and slide on a fritionless surfae. The thin hoogeneous dis has a preload on it suh that there is no slip, between it and the blo 3. The dis is driven by a torque Tt. There is a visous interfae between 3 and and 3 and. Assue the blos do not ollide or and that 3 stays in ontat with and. R T T sin t 0 f fritionless T o sinrt R
22 . The syste below odels a tightly strethed spring of length L and ass. The string is strethed with a tension T. Assue the otion is sall suh that the tension reains onstant along the string. Deterine the equations of otion in ters of the oordinates,,. By observing the pattern write the equations of otion for 5 asses. 3 L 4 L 4 L 4 L T T L L 0 T T T L L L T T L L
(Newton s 2 nd Law for linear motion)
 PHYSICS 3 Final Exaination ( Deeber Tie liit 3 hours Answer all 6 questions You and an assistant are holding the (opposite ends of a long plank when oops! the butterfingered assistant drops his end If
PHYSICS 3 Final Exaination ( Deeber Tie liit 3 hours Answer all 6 questions You and an assistant are holding the (opposite ends of a long plank when oops! the butterfingered assistant drops his end If
NAME NUMBER SEC. PHYCS 101 SUMMER 2001/2002 FINAL EXAME:24/8/2002. PART(I) 25% PART(II) 15% PART(III)/Lab 8% ( ) 2 Q2 Q3 Total 40%
 NAME NUMER SEC. PHYCS 101 SUMMER 2001/2002 FINAL EXAME:24/8/2002 PART(I) 25% PART(II) 15% PART(III)/Lab 8% ( ) 2.5 Q1 ( ) 2 Q2 Q3 Total 40% Use the followings: Magnitude of acceleration due to gravity
NAME NUMER SEC. PHYCS 101 SUMMER 2001/2002 FINAL EXAME:24/8/2002 PART(I) 25% PART(II) 15% PART(III)/Lab 8% ( ) 2.5 Q1 ( ) 2 Q2 Q3 Total 40% Use the followings: Magnitude of acceleration due to gravity
CHAPTER 3 PROBLEMS. δ = where A is the cross-sectional area, and E is the modulus of elasticity.
 CHPTER 3 PROLEMS d SPRING-MSS-DMPER PPLICTIONS Proble 3.1 The buoy shown in figure P3.1 has a irular ross-setion with diaeter d and has length L. Most of the weight of the buoy, w, is onentrated in the
CHPTER 3 PROLEMS d SPRING-MSS-DMPER PPLICTIONS Proble 3.1 The buoy shown in figure P3.1 has a irular ross-setion with diaeter d and has length L. Most of the weight of the buoy, w, is onentrated in the
Lecture 4 Normal Modes
 Lecture 4 Noral Modes Coupled driven oscillators Double pendulu The daped driven pendulu = g/l +k y+fcost y = y gy/l k y d dt + d dt + g + k l k k d dt + d dt + g + k l y = F 0 Re eit y =Re X Y eit CF
Lecture 4 Noral Modes Coupled driven oscillators Double pendulu The daped driven pendulu = g/l +k y+fcost y = y gy/l k y d dt + d dt + g + k l k k d dt + d dt + g + k l y = F 0 Re eit y =Re X Y eit CF
Modeling of vibration systems
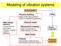 Modeling of vibration systes Atual syste Mae design deision Choose physial paraeters, hange or augent syste if neessary Physial odeling Mae siple approiations based on engineering judgeent Physial odel
Modeling of vibration systes Atual syste Mae design deision Choose physial paraeters, hange or augent syste if neessary Physial odeling Mae siple approiations based on engineering judgeent Physial odel
Physics 140 D100 Midterm Exam 2 Solutions 2017 Nov 10
 There are 10 ultiple choice questions. Select the correct answer for each one and ark it on the bubble for on the cover sheet. Each question has only one correct answer. (2 arks each) 1. An inertial reference
There are 10 ultiple choice questions. Select the correct answer for each one and ark it on the bubble for on the cover sheet. Each question has only one correct answer. (2 arks each) 1. An inertial reference
Tutorial Exercises: Incorporating constraints
 Tutorial Exercises: Incorporating constraints 1. A siple pendulu of length l ass is suspended fro a pivot of ass M that is free to slide on a frictionless wire frae in the shape of a parabola y = ax. The
Tutorial Exercises: Incorporating constraints 1. A siple pendulu of length l ass is suspended fro a pivot of ass M that is free to slide on a frictionless wire frae in the shape of a parabola y = ax. The
Unit 14 Harmonic Motion. Your Comments
 Today s Concepts: Periodic Motion Siple - Mass on spring Daped Forced Resonance Siple - Pendulu Unit 1, Slide 1 Your Coents Please go through the three equations for siple haronic otion and phase angle
Today s Concepts: Periodic Motion Siple - Mass on spring Daped Forced Resonance Siple - Pendulu Unit 1, Slide 1 Your Coents Please go through the three equations for siple haronic otion and phase angle
Problem Set 14: Oscillations AP Physics C Supplementary Problems
 Proble Set 14: Oscillations AP Physics C Suppleentary Probles 1 An oscillator consists of a bloc of ass 050 g connected to a spring When set into oscillation with aplitude 35 c, it is observed to repeat
Proble Set 14: Oscillations AP Physics C Suppleentary Probles 1 An oscillator consists of a bloc of ass 050 g connected to a spring When set into oscillation with aplitude 35 c, it is observed to repeat
Simple Harmonic Motion
 Siple Haronic Motion Physics Enhanceent Prograe for Gifted Students The Hong Kong Acadey for Gifted Education and Departent of Physics, HKBU Departent of Physics Siple haronic otion In echanical physics,
Siple Haronic Motion Physics Enhanceent Prograe for Gifted Students The Hong Kong Acadey for Gifted Education and Departent of Physics, HKBU Departent of Physics Siple haronic otion In echanical physics,
PHYS 1443 Section 003 Lecture #22
 PHYS 443 Section 003 Lecture # Monda, Nov. 4, 003. Siple Bloc-Spring Sste. Energ of the Siple Haronic Oscillator 3. Pendulu Siple Pendulu Phsical Pendulu orsion Pendulu 4. Siple Haronic Motion and Unifor
PHYS 443 Section 003 Lecture # Monda, Nov. 4, 003. Siple Bloc-Spring Sste. Energ of the Siple Haronic Oscillator 3. Pendulu Siple Pendulu Phsical Pendulu orsion Pendulu 4. Siple Haronic Motion and Unifor
Simple Harmonic Motion
 Reading: Chapter 15 Siple Haronic Motion Siple Haronic Motion Frequency f Period T T 1. f Siple haronic otion x ( t) x cos( t ). Aplitude x Phase Angular frequency Since the otion returns to its initial
Reading: Chapter 15 Siple Haronic Motion Siple Haronic Motion Frequency f Period T T 1. f Siple haronic otion x ( t) x cos( t ). Aplitude x Phase Angular frequency Since the otion returns to its initial
Lecture #8-3 Oscillations, Simple Harmonic Motion
 Lecture #8-3 Oscillations Siple Haronic Motion So far we have considered two basic types of otion: translation and rotation. But these are not the only two types of otion we can observe in every day life.
Lecture #8-3 Oscillations Siple Haronic Motion So far we have considered two basic types of otion: translation and rotation. But these are not the only two types of otion we can observe in every day life.
2009 Academic Challenge
 009 Acadeic Challenge PHYSICS TEST - REGIONAL This Test Consists of 5 Questions Physics Test Production Tea Len Stor, Eastern Illinois University Author/Tea Leader Doug Brandt, Eastern Illinois University
009 Acadeic Challenge PHYSICS TEST - REGIONAL This Test Consists of 5 Questions Physics Test Production Tea Len Stor, Eastern Illinois University Author/Tea Leader Doug Brandt, Eastern Illinois University
9. h = R. 10. h = 3 R
 Version PREVIEW Torque Chap. 8 sizeore (13756) 1 This print-out should have 3 questions. ultiple-choice questions ay continue on the next colun or page find all choices before answering. Note in the dropped
Version PREVIEW Torque Chap. 8 sizeore (13756) 1 This print-out should have 3 questions. ultiple-choice questions ay continue on the next colun or page find all choices before answering. Note in the dropped
1 (40) Gravitational Systems Two heavy spherical (radius 0.05R) objects are located at fixed positions along
 (40) Gravitational Systes Two heavy spherical (radius 0.05) objects are located at fixed positions along 2M 2M 0 an axis in space. The first ass is centered at r = 0 and has a ass of 2M. The second ass
(40) Gravitational Systes Two heavy spherical (radius 0.05) objects are located at fixed positions along 2M 2M 0 an axis in space. The first ass is centered at r = 0 and has a ass of 2M. The second ass
For a situation involving gravity near earth s surface, a = g = jg. Show. that for that case v 2 = v 0 2 g(y y 0 ).
 Reading: Energy 1, 2. Key concepts: Scalar products, work, kinetic energy, work-energy theore; potential energy, total energy, conservation of echanical energy, equilibriu and turning points. 1.! In 1-D
Reading: Energy 1, 2. Key concepts: Scalar products, work, kinetic energy, work-energy theore; potential energy, total energy, conservation of echanical energy, equilibriu and turning points. 1.! In 1-D
which proves the motion is simple harmonic. Now A = a 2 + b 2 = =
 Worked out Exaples. The potential energy function for the force between two atos in a diatoic olecules can be expressed as follows: a U(x) = b x / x6 where a and b are positive constants and x is the distance
Worked out Exaples. The potential energy function for the force between two atos in a diatoic olecules can be expressed as follows: a U(x) = b x / x6 where a and b are positive constants and x is the distance
Physics 4A Winter 2016 Final Exam
 Physics 4A Winter 016 Final Exa Nae: Mar, 016 Please show your work! Answers are not coplete without clear reasoning. When asked for an expression, you ust give your answer in ters of the variables given
Physics 4A Winter 016 Final Exa Nae: Mar, 016 Please show your work! Answers are not coplete without clear reasoning. When asked for an expression, you ust give your answer in ters of the variables given
Department of Physics Preliminary Exam January 3 6, 2006
 Departent of Physics Preliinary Exa January 3 6, 2006 Day 1: Classical Mechanics Tuesday, January 3, 2006 9:00 a.. 12:00 p.. Instructions: 1. Write the answer to each question on a separate sheet of paper.
Departent of Physics Preliinary Exa January 3 6, 2006 Day 1: Classical Mechanics Tuesday, January 3, 2006 9:00 a.. 12:00 p.. Instructions: 1. Write the answer to each question on a separate sheet of paper.
PH 221-1D Spring Oscillations. Lectures Chapter 15 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 9 th edition)
 PH 1-1D Spring 013 Oscillations Lectures 35-37 Chapter 15 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundaentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 15 Oscillations In this chapter we will cover the following topics: Displaceent,
PH 1-1D Spring 013 Oscillations Lectures 35-37 Chapter 15 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundaentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 15 Oscillations In this chapter we will cover the following topics: Displaceent,
Axis. Axis. Axis. Solid cylinder (or disk) about. Hoop about. Annular cylinder (or ring) about central axis. central axis.
 Instructor(s): Acosta, inzler PHYSICS DEPATMENT PHY 048, Spring 04 Final Exa March 4, 04 Nae (print, last first): Signature: On y honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this exaination.
Instructor(s): Acosta, inzler PHYSICS DEPATMENT PHY 048, Spring 04 Final Exa March 4, 04 Nae (print, last first): Signature: On y honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this exaination.
Physics 120 Final Examination
 Physics 120 Final Exaination 12 August, 1998 Nae Tie: 3 hours Signature Calculator and one forula sheet allowed Student nuber Show coplete solutions to questions 3 to 8. This exaination has 8 questions.
Physics 120 Final Exaination 12 August, 1998 Nae Tie: 3 hours Signature Calculator and one forula sheet allowed Student nuber Show coplete solutions to questions 3 to 8. This exaination has 8 questions.
+ 1 2 mv 2. Since no forces act on the system in the x-direction, linear momentum in x-direction is conserved: (2) 0 = mv A2. + Rω 2.
 ME 74 Spring 018 Final Exaination Proble 1 Given: hoogeneous dis of ass and outer radius R is able to roll without slipping on the curved upper surface of a cart. art (of ass ) is able to ove along a sooth,
ME 74 Spring 018 Final Exaination Proble 1 Given: hoogeneous dis of ass and outer radius R is able to roll without slipping on the curved upper surface of a cart. art (of ass ) is able to ove along a sooth,
A body of unknown mass is attached to an ideal spring with force constant 123 N/m. It is found to vibrate with a frequency of
 Chapter 14 [ Edit ] Overview Suary View Diagnostics View Print View with Answers Chapter 14 Due: 11:59p on Sunday, Noveber 27, 2016 To understand how points are awarded, read the Grading Policy for this
Chapter 14 [ Edit ] Overview Suary View Diagnostics View Print View with Answers Chapter 14 Due: 11:59p on Sunday, Noveber 27, 2016 To understand how points are awarded, read the Grading Policy for this
ROTATIONAL MOTION FROM TRANSLATIONAL MOTION
 ROTATIONAL MOTION FROM TRANSLATIONAL MOTION Velocity Acceleration 1-D otion 3-D otion Linear oentu TO We have shown that, the translational otion of a acroscopic object is equivalent to the translational
ROTATIONAL MOTION FROM TRANSLATIONAL MOTION Velocity Acceleration 1-D otion 3-D otion Linear oentu TO We have shown that, the translational otion of a acroscopic object is equivalent to the translational
Physics 41 HW Set 1 Chapter 15 Serway 7 th Edition
 Physics HW Set Chapter 5 Serway 7 th Edition Conceptual Questions:, 3, 5,, 6, 9 Q53 You can take φ = π, or equally well, φ = π At t= 0, the particle is at its turning point on the negative side of equilibriu,
Physics HW Set Chapter 5 Serway 7 th Edition Conceptual Questions:, 3, 5,, 6, 9 Q53 You can take φ = π, or equally well, φ = π At t= 0, the particle is at its turning point on the negative side of equilibriu,
EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations. Final Examination Tuesday May 15, 2011
 EN40: ynaics and Vibrations Final Exaination Tuesday May 15, 011 School of Engineering rown University NME: General Instructions No collaboration of any ind is peritted on this exaination. You ay use double
EN40: ynaics and Vibrations Final Exaination Tuesday May 15, 011 School of Engineering rown University NME: General Instructions No collaboration of any ind is peritted on this exaination. You ay use double
Modern Control Systems (ECEG-4601) Instructor: Andinet Negash. Chapter 1 Lecture 3: State Space, II
 Modern Control Systes (ECEG-46) Instructor: Andinet Negash Chapter Lecture 3: State Space, II Eaples Eaple 5: control o liquid levels: in cheical plants, it is oten necessary to aintain the levels o liquids.
Modern Control Systes (ECEG-46) Instructor: Andinet Negash Chapter Lecture 3: State Space, II Eaples Eaple 5: control o liquid levels: in cheical plants, it is oten necessary to aintain the levels o liquids.
8.1 Force Laws Hooke s Law
 8.1 Force Laws There are forces that don't change appreciably fro one instant to another, which we refer to as constant in tie, and forces that don't change appreciably fro one point to another, which
8.1 Force Laws There are forces that don't change appreciably fro one instant to another, which we refer to as constant in tie, and forces that don't change appreciably fro one point to another, which
27 Oscillations: Introduction, Mass on a Spring
 Chapter 7 Oscillations: Introduction, Mass on a Spring 7 Oscillations: Introduction, Mass on a Spring If a siple haronic oscillation proble does not involve the tie, you should probably be using conservation
Chapter 7 Oscillations: Introduction, Mass on a Spring 7 Oscillations: Introduction, Mass on a Spring If a siple haronic oscillation proble does not involve the tie, you should probably be using conservation
ma x = -bv x + F rod.
 Notes on Dynaical Systes Dynaics is the study of change. The priary ingredients of a dynaical syste are its state and its rule of change (also soeties called the dynaic). Dynaical systes can be continuous
Notes on Dynaical Systes Dynaics is the study of change. The priary ingredients of a dynaical syste are its state and its rule of change (also soeties called the dynaic). Dynaical systes can be continuous
m A 1 m mgd k m v ( C) AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Oscillations
 P Physics Multiple Choice Practice Oscillations. ass, attached to a horizontal assless spring with spring constant, is set into siple haronic otion. Its axiu displaceent fro its equilibriu position is.
P Physics Multiple Choice Practice Oscillations. ass, attached to a horizontal assless spring with spring constant, is set into siple haronic otion. Its axiu displaceent fro its equilibriu position is.
NB1140: Physics 1A - Classical mechanics and Thermodynamics Problem set 2 - Forces and energy Week 2: November 2016
 NB1140: Physics 1A - Classical echanics and Therodynaics Proble set 2 - Forces and energy Week 2: 21-25 Noveber 2016 Proble 1. Why force is transitted uniforly through a assless string, a assless spring,
NB1140: Physics 1A - Classical echanics and Therodynaics Proble set 2 - Forces and energy Week 2: 21-25 Noveber 2016 Proble 1. Why force is transitted uniforly through a assless string, a assless spring,
Periodic Motion is everywhere
 Lecture 19 Goals: Chapter 14 Interrelate the physics and atheatics of oscillations. Draw and interpret oscillatory graphs. Learn the concepts of phase and phase constant. Understand and use energy conservation
Lecture 19 Goals: Chapter 14 Interrelate the physics and atheatics of oscillations. Draw and interpret oscillatory graphs. Learn the concepts of phase and phase constant. Understand and use energy conservation
EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations. Midterm Examination Tuesday March
 EN4: Dynaics and Vibrations Midter Exaination Tuesday March 8 16 School of Engineering Brown University NAME: General Instructions No collaboration of any kind is peritted on this exaination. You ay bring
EN4: Dynaics and Vibrations Midter Exaination Tuesday March 8 16 School of Engineering Brown University NAME: General Instructions No collaboration of any kind is peritted on this exaination. You ay bring
PHYSICS 2210 Fall Exam 4 Review 12/02/2015
 PHYSICS 10 Fall 015 Exa 4 Review 1/0/015 (yf09-049) A thin, light wire is wrapped around the ri of a unifor disk of radius R=0.80, as shown. The disk rotates without friction about a stationary horizontal
PHYSICS 10 Fall 015 Exa 4 Review 1/0/015 (yf09-049) A thin, light wire is wrapped around the ri of a unifor disk of radius R=0.80, as shown. The disk rotates without friction about a stationary horizontal
5/09/06 PHYSICS 213 Exam #1 NAME FEYNMAN Please write down your name also on the back side of the last page
 5/09/06 PHYSICS 13 Exa #1 NAME FEYNMAN Please write down your nae also on the back side of the last page 1 he figure shows a horizontal planks of length =50 c, and ass M= 1 Kg, pivoted at one end. he planks
5/09/06 PHYSICS 13 Exa #1 NAME FEYNMAN Please write down your nae also on the back side of the last page 1 he figure shows a horizontal planks of length =50 c, and ass M= 1 Kg, pivoted at one end. he planks
Question 1. [14 Marks]
![Question 1. [14 Marks] Question 1. [14 Marks]](/thumbs/88/116022373.jpg) 6 Question 1. [14 Marks] R r T! A string is attached to the dru (radius r) of a spool (radius R) as shown in side and end views here. (A spool is device for storing string, thread etc.) A tension T is
6 Question 1. [14 Marks] R r T! A string is attached to the dru (radius r) of a spool (radius R) as shown in side and end views here. (A spool is device for storing string, thread etc.) A tension T is
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 00 The Graw-Hill Copanies, n. All rights reserved. Third E CHAPTER Pure ECHANCS OF ATERALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Bending Leture Notes: J. Walt Oler Teas Teh Universit
00 The Graw-Hill Copanies, n. All rights reserved. Third E CHAPTER Pure ECHANCS OF ATERALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Bending Leture Notes: J. Walt Oler Teas Teh Universit
Systems of Masses. 1. Ignoring friction, calculate the acceleration of the system below and the tension in the rope. and (4.0)(9.80) 39.
 Systes of Masses. Ignoring friction, calculate the acceleration of the syste below and the tension in the rope. Drawing individual free body diagras we get 4.0kg 7.0kg g 9.80 / s a?? g and g (4.0)(9.80)
Systes of Masses. Ignoring friction, calculate the acceleration of the syste below and the tension in the rope. Drawing individual free body diagras we get 4.0kg 7.0kg g 9.80 / s a?? g and g (4.0)(9.80)
CE573 Structural Dynamics [Fall 2008]
![CE573 Structural Dynamics [Fall 2008] CE573 Structural Dynamics [Fall 2008]](/thumbs/84/89476445.jpg) CE573 Structural Dynaics [Fall 2008] 1) A rigid vehicle weighing 2000 lb, oving horizontally at a velocity of 12 ft/sec, is stopped by a barrier consisting of wire ropes stretched between two rigid anchors
CE573 Structural Dynaics [Fall 2008] 1) A rigid vehicle weighing 2000 lb, oving horizontally at a velocity of 12 ft/sec, is stopped by a barrier consisting of wire ropes stretched between two rigid anchors
TUTORIAL 1 SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 TUTORIAL 1 SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Instructor: Kazui Tolich About tutorials 2 Tutorials are conceptual exercises that should be worked on in groups. Each slide will consist of a series of questions that
TUTORIAL 1 SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Instructor: Kazui Tolich About tutorials 2 Tutorials are conceptual exercises that should be worked on in groups. Each slide will consist of a series of questions that
P235 Midterm Examination Prof. Cline
 P235 Mier Exaination Prof. Cline THIS IS A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION. Do all parts of all four questions. Show all steps to get full credit. 7:00-10.00p, 30 October 2009 1:(20pts) Consider a rocket fired
P235 Mier Exaination Prof. Cline THIS IS A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION. Do all parts of all four questions. Show all steps to get full credit. 7:00-10.00p, 30 October 2009 1:(20pts) Consider a rocket fired
Chapter 2: Introduction to Damping in Free and Forced Vibrations
 Chapter 2: Introduction to Daping in Free and Forced Vibrations This chapter ainly deals with the effect of daping in two conditions like free and forced excitation of echanical systes. Daping plays an
Chapter 2: Introduction to Daping in Free and Forced Vibrations This chapter ainly deals with the effect of daping in two conditions like free and forced excitation of echanical systes. Daping plays an
Physics 201 Lecture 29
 Phsics 1 ecture 9 Goals ecture 9 v Describe oscillator otion in a siple pendulu v Describe oscillator otion with torques v Introduce daping in SHM v Discuss resonance v Final Ea Details l Sunda, Ma 13th
Phsics 1 ecture 9 Goals ecture 9 v Describe oscillator otion in a siple pendulu v Describe oscillator otion with torques v Introduce daping in SHM v Discuss resonance v Final Ea Details l Sunda, Ma 13th
Chap. 10: Rotational Motion
 Chap. 10: Rotational Motion I. Rotational Kinematics II. Rotational Dynamics - Newton s Law for Rotation III. Angular Momentum Conservation (Chap. 10) 1 Newton s Laws for Rotation n e t I 3 rd part [N
Chap. 10: Rotational Motion I. Rotational Kinematics II. Rotational Dynamics - Newton s Law for Rotation III. Angular Momentum Conservation (Chap. 10) 1 Newton s Laws for Rotation n e t I 3 rd part [N
Shear Force and Bending Moment
 Shear Fore and Bending oent Shear Fore: is the algebrai su of the vertial fores ating to the left or right of a ut setion along the span of the bea Bending oent: is the algebrai su of the oent of the fores
Shear Fore and Bending oent Shear Fore: is the algebrai su of the vertial fores ating to the left or right of a ut setion along the span of the bea Bending oent: is the algebrai su of the oent of the fores
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 05: FRICTION, INCLINES, SYSTEMS.
 !! www.clutchprep.co INTRO TO FRICTION Friction happens when two surfaces are in contact f = μ =. KINETIC FRICTION (v 0 *): STATIC FRICTION (v 0 *): - Happens when ANY object slides/skids/slips. * = Point
!! www.clutchprep.co INTRO TO FRICTION Friction happens when two surfaces are in contact f = μ =. KINETIC FRICTION (v 0 *): STATIC FRICTION (v 0 *): - Happens when ANY object slides/skids/slips. * = Point
Physics 207 Lecture 18. Physics 207, Lecture 18, Nov. 3 Goals: Chapter 14
 Physics 07, Lecture 18, Nov. 3 Goals: Chapter 14 Interrelate the physics and atheatics of oscillations. Draw and interpret oscillatory graphs. Learn the concepts of phase and phase constant. Understand
Physics 07, Lecture 18, Nov. 3 Goals: Chapter 14 Interrelate the physics and atheatics of oscillations. Draw and interpret oscillatory graphs. Learn the concepts of phase and phase constant. Understand
fiziks Institute for NET/JRF, GATE, IIT JAM, JEST, TIFR and GRE in PHYSICAL SCIENCES CLASSICAL MECHANICS SOLUTIONS
 fizis CLASSICAL MECHANICS SOLUTIONS GATE- Q. For the set of all Lorentz transforations with eloities along the x-axis onsider the two stateents gien below: P: If L is a Lorentz transforation then, L -
fizis CLASSICAL MECHANICS SOLUTIONS GATE- Q. For the set of all Lorentz transforations with eloities along the x-axis onsider the two stateents gien below: P: If L is a Lorentz transforation then, L -
CHAPTER 15: Vibratory Motion
 CHAPTER 15: Vibratory Motion courtesy of Richard White courtesy of Richard White 2.) 1.) Two glaring observations can be ade fro the graphic on the previous slide: 1.) The PROJECTION of a point on a circle
CHAPTER 15: Vibratory Motion courtesy of Richard White courtesy of Richard White 2.) 1.) Two glaring observations can be ade fro the graphic on the previous slide: 1.) The PROJECTION of a point on a circle
PY241 Solutions Set 9 (Dated: November 7, 2002)
 PY241 Solutions Set 9 (Dated: Noveber 7, 2002) 9-9 At what displaceent of an object undergoing siple haronic otion is the agnitude greatest for the... (a) velocity? The velocity is greatest at x = 0, the
PY241 Solutions Set 9 (Dated: Noveber 7, 2002) 9-9 At what displaceent of an object undergoing siple haronic otion is the agnitude greatest for the... (a) velocity? The velocity is greatest at x = 0, the
FW Phys 130 G:\130 lecture\130 tests\formulas final03.docx page 1 of 7
 FW Phys 13 G:\13 leture\13 tests\forulas final3.dox page 1 of 7 dr dr r x y z ur ru (1.1) dt dt All onseratie fores derie fro a potential funtion U(x,y,z) (1.) U U U F gradu U,, x y z 1 MG 1 dr MG E K
FW Phys 13 G:\13 leture\13 tests\forulas final3.dox page 1 of 7 dr dr r x y z ur ru (1.1) dt dt All onseratie fores derie fro a potential funtion U(x,y,z) (1.) U U U F gradu U,, x y z 1 MG 1 dr MG E K
Chapter 4 FORCES AND NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION PREVIEW QUICK REFERENCE. Important Terms
 Chapter 4 FORCES AND NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION PREVIEW Dynaics is the study o the causes o otion, in particular, orces. A orce is a push or a pull. We arrange our knowledge o orces into three laws orulated
Chapter 4 FORCES AND NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION PREVIEW Dynaics is the study o the causes o otion, in particular, orces. A orce is a push or a pull. We arrange our knowledge o orces into three laws orulated
XI PHYSICS M. AFFAN KHAN LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K. https://promotephysics.wordpress.com
 XI PHYSICS M. AFFAN KHAN LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K affan_414@live.co https://prootephysics.wordpress.co [MOTION] CHAPTER NO. 3 In this chapter we are going to discuss otion in one diension in which we
XI PHYSICS M. AFFAN KHAN LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K affan_414@live.co https://prootephysics.wordpress.co [MOTION] CHAPTER NO. 3 In this chapter we are going to discuss otion in one diension in which we
EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations. Final Examination Monday May : 2pm-5pm
 EN40: Dynaics and Vibrations Final Exaination Monday May 13 013: p-5p School of Engineering Brown University NAME: General Instructions No collaboration of any kind is peritted on this exaination. You
EN40: Dynaics and Vibrations Final Exaination Monday May 13 013: p-5p School of Engineering Brown University NAME: General Instructions No collaboration of any kind is peritted on this exaination. You
Oscillations: Review (Chapter 12)
 Oscillations: Review (Chapter 1) Oscillations: otions that are periodic in tie (i.e. repetitive) o Swinging object (pendulu) o Vibrating object (spring, guitar string, etc.) o Part of ediu (i.e. string,
Oscillations: Review (Chapter 1) Oscillations: otions that are periodic in tie (i.e. repetitive) o Swinging object (pendulu) o Vibrating object (spring, guitar string, etc.) o Part of ediu (i.e. string,
Physics 207: Lecture 26. Announcements. Make-up labs are this week Final hwk assigned this week, final quiz next week.
 Torque due to gravit Rotation Recap Phsics 07: ecture 6 Announceents Make-up labs are this week Final hwk assigned this week, final quiz net week Toda s Agenda Statics Car on a Hill Static Equilibriu Equations
Torque due to gravit Rotation Recap Phsics 07: ecture 6 Announceents Make-up labs are this week Final hwk assigned this week, final quiz net week Toda s Agenda Statics Car on a Hill Static Equilibriu Equations
Part IA Paper 1: Mechanical Engineering MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS Examples paper 3
 ENGINEERING Part IA Paper 1: Mechanical Engineering MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS Exaples paper 3 IRST YEAR Straightforward questions are ared with a Tripos standard questions are ared *. Systes with two or ore
ENGINEERING Part IA Paper 1: Mechanical Engineering MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS Exaples paper 3 IRST YEAR Straightforward questions are ared with a Tripos standard questions are ared *. Systes with two or ore
) = slugs/ft 3. ) = lb ft/s. ) = ft/s
 1. Make use of Tables 1. in the text book (See the last page in this assignent) to express the following quantities in SI units: (a) 10. in./in, (b) 4.81 slugs, (c).0 lb, (d) 7.1 ft/s, (e) 0.04 lb s/ft.
1. Make use of Tables 1. in the text book (See the last page in this assignent) to express the following quantities in SI units: (a) 10. in./in, (b) 4.81 slugs, (c).0 lb, (d) 7.1 ft/s, (e) 0.04 lb s/ft.
Physics 2210 Fall smartphysics 20 Conservation of Angular Momentum 21 Simple Harmonic Motion 11/23/2015
 Physics 2210 Fall 2015 sartphysics 20 Conservation of Angular Moentu 21 Siple Haronic Motion 11/23/2015 Exa 4: sartphysics units 14-20 Midter Exa 2: Day: Fri Dec. 04, 2015 Tie: regular class tie Section
Physics 2210 Fall 2015 sartphysics 20 Conservation of Angular Moentu 21 Siple Haronic Motion 11/23/2015 Exa 4: sartphysics units 14-20 Midter Exa 2: Day: Fri Dec. 04, 2015 Tie: regular class tie Section
Physics 139B Solutions to Homework Set 3 Fall 2009
 Physics 139B Solutions to Hoework Set 3 Fall 009 1. Consider a particle of ass attached to a rigid assless rod of fixed length R whose other end is fixed at the origin. The rod is free to rotate about
Physics 139B Solutions to Hoework Set 3 Fall 009 1. Consider a particle of ass attached to a rigid assless rod of fixed length R whose other end is fixed at the origin. The rod is free to rotate about
Chapter 11 Simple Harmonic Motion
 Chapter 11 Siple Haronic Motion "We are to adit no ore causes of natural things than such as are both true and sufficient to explain their appearances." Isaac Newton 11.1 Introduction to Periodic Motion
Chapter 11 Siple Haronic Motion "We are to adit no ore causes of natural things than such as are both true and sufficient to explain their appearances." Isaac Newton 11.1 Introduction to Periodic Motion
PHYS 154 Practice Final Test Spring 2018
 The actual test contains 10 ultiple choice questions and 2 probles. However, for extra exercise and enjoyent, this practice test includes18 questions and 4 probles. Questions: N.. ake sure that you justify
The actual test contains 10 ultiple choice questions and 2 probles. However, for extra exercise and enjoyent, this practice test includes18 questions and 4 probles. Questions: N.. ake sure that you justify
Intro Wb3303 Kineto-statics and Dynamics
 Wb333 Kineto-statis and Dynais 8 ineto-statis and Dynais...8. 8. Introdution...8. 8. Virtual wor and equilibriu equations (statis)...8.3 8.. General priniple...8.3 8.. Driving fores...8.5 8..3 Support
Wb333 Kineto-statis and Dynais 8 ineto-statis and Dynais...8. 8. Introdution...8. 8. Virtual wor and equilibriu equations (statis)...8.3 8.. General priniple...8.3 8.. Driving fores...8.5 8..3 Support
Work and kinetic Energy
 Work and kinetic Energy Problem 66. M=4.5kg r = 0.05m I = 0.003kgm 2 Q: What is the velocity of mass m after it dropped a distance h? (No friction) h m=0.6kg mg Work and kinetic Energy Problem 66. M=4.5kg
Work and kinetic Energy Problem 66. M=4.5kg r = 0.05m I = 0.003kgm 2 Q: What is the velocity of mass m after it dropped a distance h? (No friction) h m=0.6kg mg Work and kinetic Energy Problem 66. M=4.5kg
Monitoring and system identification of suspension bridges: An alternative approach
 Monitoring and syste identification of suspension bridges: An alternative approach Erdal Şafak Boğaziçi University, Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Reseach Institute, Istanbul, Turkey Abstract This
Monitoring and syste identification of suspension bridges: An alternative approach Erdal Şafak Boğaziçi University, Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Reseach Institute, Istanbul, Turkey Abstract This
UDC DAMAGE DIAGNOSTICS IN A VERTICAL BAR ON THE ELASTIC SUSPENDER WITH CONCENTRATED MASS
 1 UDC 534113 DAAGE DIAGNOSTICS IN A VERTICAL BAR ON THE ELASTIC SUSPENDER WITH CONCENTRATED ASS A Ilgamov, BZ Sultanov, AN Tazhitdinov, AG Khakimov Institute of ehanis, Ufa Branh RAS, Ufa, Russia Using
1 UDC 534113 DAAGE DIAGNOSTICS IN A VERTICAL BAR ON THE ELASTIC SUSPENDER WITH CONCENTRATED ASS A Ilgamov, BZ Sultanov, AN Tazhitdinov, AG Khakimov Institute of ehanis, Ufa Branh RAS, Ufa, Russia Using
FOUNDATION STUDIES EXAMINATIONS January 2016
 1 FOUNDATION STUDIES EXAMINATIONS January 2016 PHYSICS Seester 2 Exa July Fast Track Tie allowed 2 hours for writing 10 inutes for reading This paper consists of 4 questions printed on 11 pages. PLEASE
1 FOUNDATION STUDIES EXAMINATIONS January 2016 PHYSICS Seester 2 Exa July Fast Track Tie allowed 2 hours for writing 10 inutes for reading This paper consists of 4 questions printed on 11 pages. PLEASE
3. In the figure below, the coefficient of friction between the center mass and the surface is
 Physics 04A Exa October 9, 05 Short-answer probles: Do any seven probles in your exa book. Start each proble on a new page and and clearly indicate the proble nuber for each. If you attept ore than seven
Physics 04A Exa October 9, 05 Short-answer probles: Do any seven probles in your exa book. Start each proble on a new page and and clearly indicate the proble nuber for each. If you attept ore than seven
L 2. AP Physics Free Response Practice Oscillations ANSWERS 1975B7. (a) F T2. (b) F NET(Y) = 0
 AP Physics Free Response Practice Oscillations ANSWERS 1975B7. (a) 60 F 1 F g (b) F NE(Y) = 0 F1 F1 = g / cos(60) = g (c) When the string is cut it swings fro top to botto, siilar to the diagra for 1974B1
AP Physics Free Response Practice Oscillations ANSWERS 1975B7. (a) 60 F 1 F g (b) F NE(Y) = 0 F1 F1 = g / cos(60) = g (c) When the string is cut it swings fro top to botto, siilar to the diagra for 1974B1
Strength of Materials
 Strength of Materials Session Pure Bending 04 Leture note : Praudianto, M.Eng. g{ V ä Ä tçw ÄtÇÇ Çz XÇz ÇÜ Çz Xwâvtà ÉÇ WÑtÜàÅÇà g{ V ä Ä tçw ÄtÇÇ Çz XÇz ÇÜ Çz Xwâvtà ÉÇ WÑtÜàÅÇà Pure Bending: Prisati
Strength of Materials Session Pure Bending 04 Leture note : Praudianto, M.Eng. g{ V ä Ä tçw ÄtÇÇ Çz XÇz ÇÜ Çz Xwâvtà ÉÇ WÑtÜàÅÇà g{ V ä Ä tçw ÄtÇÇ Çz XÇz ÇÜ Çz Xwâvtà ÉÇ WÑtÜàÅÇà Pure Bending: Prisati
Assignment 2. Tyler Shendruk October 8, Hamilton s Principle - Lagrangian and Hamiltonian dynamics.
 Assignent Tyler Shendruk October 8, 010 1 Marion and Thornton Chapter 7 Hailton s Principle - Lagrangian and Hailtonian dynaics. 1.1 Proble 7.9 y z x l θ α Figure 1: A disk rolling down an incline plane.
Assignent Tyler Shendruk October 8, 010 1 Marion and Thornton Chapter 7 Hailton s Principle - Lagrangian and Hailtonian dynaics. 1.1 Proble 7.9 y z x l θ α Figure 1: A disk rolling down an incline plane.
1 k. 1 m. m A. AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Work-Energy
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Wor-Energy 1. A ass attached to a horizontal assless spring with spring constant, is set into siple haronic otion. Its axiu displaceent fro its equilibriu position is
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Wor-Energy 1. A ass attached to a horizontal assless spring with spring constant, is set into siple haronic otion. Its axiu displaceent fro its equilibriu position is
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 006 The Graw-Hill Copanies, n. ll rights reserved. Fourth E CHTER ure ECHNCS OF TERLS Ferdinand. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Bending Leture Notes: J. Walt Oler Teas Teh Universit ECHNCS
006 The Graw-Hill Copanies, n. ll rights reserved. Fourth E CHTER ure ECHNCS OF TERLS Ferdinand. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Bending Leture Notes: J. Walt Oler Teas Teh Universit ECHNCS
Optimal sliding mode control of the pendubot
 International Researh Journal of Coputer Siene and Inforation Systes (IRJCSIS Vol. ( pp. 45-5, April, Available online http://www.interesjournals.org/irjcsis Copyright International Researh Journals Full
International Researh Journal of Coputer Siene and Inforation Systes (IRJCSIS Vol. ( pp. 45-5, April, Available online http://www.interesjournals.org/irjcsis Copyright International Researh Journals Full
1 MR SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 2013
 SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world
 Pearson Education Liited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Esse CM0 JE England and Associated Copanies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Liited 04 All rights
Pearson Education Liited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Esse CM0 JE England and Associated Copanies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Liited 04 All rights
TOPIC E: OSCILLATIONS SPRING 2018
 TOPIC E: OSCILLATIONS SPRING 018 1. Introduction 1.1 Overview 1. Degrees of freedo 1.3 Siple haronic otion. Undaped free oscillation.1 Generalised ass-spring syste: siple haronic otion. Natural frequency
TOPIC E: OSCILLATIONS SPRING 018 1. Introduction 1.1 Overview 1. Degrees of freedo 1.3 Siple haronic otion. Undaped free oscillation.1 Generalised ass-spring syste: siple haronic otion. Natural frequency
1. Which two values of temperature are equivalent to the nearest degree when measured on the Kelvin and on the
 . Whih two values of teperature are equivalent to the nearest degree when easured on the Kelvin and on the Celsius sales of teperature? Kelvin sale Celsius sale A. 40 33 B. 273 00 C. 33 40 D. 373 0 2.
. Whih two values of teperature are equivalent to the nearest degree when easured on the Kelvin and on the Celsius sales of teperature? Kelvin sale Celsius sale A. 40 33 B. 273 00 C. 33 40 D. 373 0 2.
Physics 4A Solutions to Chapter 15 Homework
 Physics 4A Solutions to Chapter 15 Hoework Chapter 15 Questions:, 8, 1 Exercises & Probles 6, 5, 31, 41, 59, 7, 73, 88, 90 Answers to Questions: Q 15- (a) toward -x (b) toward +x (c) between -x and 0 (d)
Physics 4A Solutions to Chapter 15 Hoework Chapter 15 Questions:, 8, 1 Exercises & Probles 6, 5, 31, 41, 59, 7, 73, 88, 90 Answers to Questions: Q 15- (a) toward -x (b) toward +x (c) between -x and 0 (d)
2.003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set 2 Solutions
 .003 Engineering Dynaics Proble Set Solutions This proble set is priarily eant to give the student practice in describing otion. This is the subject of kineatics. It is strongly recoended that you study
.003 Engineering Dynaics Proble Set Solutions This proble set is priarily eant to give the student practice in describing otion. This is the subject of kineatics. It is strongly recoended that you study
Particle Kinetics Homework
 Chapter 4: article Kinetics Hoework Chapter 4 article Kinetics Hoework Freefor c 2018 4-1 Chapter 4: article Kinetics Hoework 4-2 Freefor c 2018 Chapter 4: article Kinetics Hoework Hoework H.4. Given:
Chapter 4: article Kinetics Hoework Chapter 4 article Kinetics Hoework Freefor c 2018 4-1 Chapter 4: article Kinetics Hoework 4-2 Freefor c 2018 Chapter 4: article Kinetics Hoework Hoework H.4. Given:
F = 0. x o F = -k x o v = 0 F = 0. F = k x o v = 0 F = 0. x = 0 F = 0. F = -k x 1. PHYSICS 151 Notes for Online Lecture 2.4.
 PHYSICS 151 Notes for Online Lecture.4 Springs, Strings, Pulleys, and Connected Objects Hook s Law F = 0 F = -k x 1 x = 0 x = x 1 Let s start with a horizontal spring, resting on a frictionless table.
PHYSICS 151 Notes for Online Lecture.4 Springs, Strings, Pulleys, and Connected Objects Hook s Law F = 0 F = -k x 1 x = 0 x = x 1 Let s start with a horizontal spring, resting on a frictionless table.
PHY 140Y FOUNDATIONS OF PHYSICS Tutorial Questions #9 Solutions November 12/13
 PHY 4Y FOUNDAIONS OF PHYSICS - utorial Questions #9 Solutions Noveber /3 Conservation of Ener and Sprins. One end of a assless sprin is placed on a flat surface, with the other end pointin upward, as shown
PHY 4Y FOUNDAIONS OF PHYSICS - utorial Questions #9 Solutions Noveber /3 Conservation of Ener and Sprins. One end of a assless sprin is placed on a flat surface, with the other end pointin upward, as shown
The ballistic pendulum
 (ta initials) first nae (print) last nae (print) brock id (ab17cd) (lab date) Experient 4 The ballistic pendulu In this Experient you will learn how to deterine the speed of a projectile as well as the
(ta initials) first nae (print) last nae (print) brock id (ab17cd) (lab date) Experient 4 The ballistic pendulu In this Experient you will learn how to deterine the speed of a projectile as well as the
x(t) y(t) c c F(t) F(t) EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations Homework 6: Forced Vibrations Due Friday April 5, 2018
 EN40: Dynais and Vibrations Hoewor 6: Fored Vibrations Due Friday April 5, 2018 Shool of Engineering Brown University 1. The vibration isolation syste shown in the figure has =20g, = 19.8 N / = 1.259 Ns
EN40: Dynais and Vibrations Hoewor 6: Fored Vibrations Due Friday April 5, 2018 Shool of Engineering Brown University 1. The vibration isolation syste shown in the figure has =20g, = 19.8 N / = 1.259 Ns
CHECKLIST. r r. Newton s Second Law. natural frequency ω o (rad.s -1 ) (Eq ) a03/p1/waves/waves doc 9:19 AM 29/03/05 1
 PHYS12 Physics 1 FUNDAMENTALS Module 3 OSCILLATIONS & WAVES Text Physics by Hecht Chapter 1 OSCILLATIONS Sections: 1.5 1.6 Exaples: 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 CHECKLIST Haronic otion, periodic otion, siple haronic
PHYS12 Physics 1 FUNDAMENTALS Module 3 OSCILLATIONS & WAVES Text Physics by Hecht Chapter 1 OSCILLATIONS Sections: 1.5 1.6 Exaples: 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 CHECKLIST Haronic otion, periodic otion, siple haronic
Physics 4A Solutions to Chapter 10 Homework
 Physics 4A Solutions to Chapter 0 Homework Chapter 0 Questions: 4, 6, 8 Exercises & Problems 6, 3, 6, 4, 45, 5, 5, 7, 8 Answers to Questions: Q 0-4 (a) positive (b) zero (c) negative (d) negative Q 0-6
Physics 4A Solutions to Chapter 0 Homework Chapter 0 Questions: 4, 6, 8 Exercises & Problems 6, 3, 6, 4, 45, 5, 5, 7, 8 Answers to Questions: Q 0-4 (a) positive (b) zero (c) negative (d) negative Q 0-6
EFFECTIVE MODAL MASS & MODAL PARTICIPATION FACTORS Revision I
 EFFECTIVE MODA MASS & MODA PARTICIPATION FACTORS Revision I B To Irvine Eail: to@vibrationdata.co Deceber, 5 Introduction The effective odal ass provides a ethod for judging the significance of a vibration
EFFECTIVE MODA MASS & MODA PARTICIPATION FACTORS Revision I B To Irvine Eail: to@vibrationdata.co Deceber, 5 Introduction The effective odal ass provides a ethod for judging the significance of a vibration
MECHANICS of FLUIDS INSTRUCTOR'S SOLUTIONS MANUAL TO ACCOMPANY FOURTH EDITION. MERLE C. POTTER Michigan State University DAVID C.
 INSTRUCTOR'S SOLUTIONS MANUAL TO ACCOMPANY MECHANICS of FLUIDS FOURTH EDITION MERLE C. POTTER Michigan State University DAVID C. WIGGERT Michigan State University BASSEM RAMADAN Kettering University Contents
INSTRUCTOR'S SOLUTIONS MANUAL TO ACCOMPANY MECHANICS of FLUIDS FOURTH EDITION MERLE C. POTTER Michigan State University DAVID C. WIGGERT Michigan State University BASSEM RAMADAN Kettering University Contents
Q5 We know that a mass at the end of a spring when displaced will perform simple m harmonic oscillations with a period given by T = 2!
 Chapter 4.1 Q1 n oscillation is any otion in which the displaceent of a particle fro a fixed point keeps changing direction and there is a periodicity in the otion i.e. the otion repeats in soe way. In
Chapter 4.1 Q1 n oscillation is any otion in which the displaceent of a particle fro a fixed point keeps changing direction and there is a periodicity in the otion i.e. the otion repeats in soe way. In
(b) Frequency is simply the reciprocal of the period: f = 1/T = 2.0 Hz.
 Chapter 5. (a) During siple haronic otion, the speed is (oentarily) zero when the object is at a turning point (that is, when x = +x or x = x ). Consider that it starts at x = +x and we are told that t
Chapter 5. (a) During siple haronic otion, the speed is (oentarily) zero when the object is at a turning point (that is, when x = +x or x = x ). Consider that it starts at x = +x and we are told that t
acceleration of 2.4 m/s. (b) Now, we have two rubber bands (force 2F) pulling two glued objects (mass 2m). Using F ma, 2.0 furlongs x 2.0 s 2 4.
 5.. 5.6. Model: An object s acceleration is linearl proportional to the net force. Solve: (a) One rubber band produces a force F, two rubber bands produce a force F, and so on. Because F a and two rubber
5.. 5.6. Model: An object s acceleration is linearl proportional to the net force. Solve: (a) One rubber band produces a force F, two rubber bands produce a force F, and so on. Because F a and two rubber
Chapter 11: Vibration Isolation of the Source [Part I]
![Chapter 11: Vibration Isolation of the Source [Part I] Chapter 11: Vibration Isolation of the Source [Part I]](/thumbs/89/99791370.jpg) Chapter : Vibration Isolation of the Source [Part I] Eaple 3.4 Consider the achine arrangeent illustrated in figure 3.. An electric otor is elastically ounted, by way of identical isolators, to a - thick
Chapter : Vibration Isolation of the Source [Part I] Eaple 3.4 Consider the achine arrangeent illustrated in figure 3.. An electric otor is elastically ounted, by way of identical isolators, to a - thick
Chapter 10 Practice Test
 Chapter 10 Practice Test 1. At t = 0, a wheel rotating about a fixed axis at a constant angular acceleration of 0.40 rad/s 2 has an angular velocity of 1.5 rad/s and an angular position of 2.3 rad. What
Chapter 10 Practice Test 1. At t = 0, a wheel rotating about a fixed axis at a constant angular acceleration of 0.40 rad/s 2 has an angular velocity of 1.5 rad/s and an angular position of 2.3 rad. What
( ) ( ) 1. (a) The amplitude is half the range of the displacement, or x m = 1.0 mm.
 1. (a) The aplitude is half the range of the displaceent, or x = 1.0. (b) The axiu speed v is related to the aplitude x by v = ωx, where ω is the angular frequency. Since ω = πf, where f is the frequency,
1. (a) The aplitude is half the range of the displaceent, or x = 1.0. (b) The axiu speed v is related to the aplitude x by v = ωx, where ω is the angular frequency. Since ω = πf, where f is the frequency,
In the session you will be divided into groups and perform four separate experiments:
 Mechanics Lab (Civil Engineers) Nae (please print): Tutor (please print): Lab group: Date of lab: Experients In the session you will be divided into groups and perfor four separate experients: (1) air-track
Mechanics Lab (Civil Engineers) Nae (please print): Tutor (please print): Lab group: Date of lab: Experients In the session you will be divided into groups and perfor four separate experients: (1) air-track
Moment of inertia and torsional vibrations (Item No.: P )
 Moent of inertia and torsional vibrations (Ite No.: P2133100) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Education Level: University Topic: Mechanics Subtopic: Static Equilibriu and Elasticity Experient:
Moent of inertia and torsional vibrations (Ite No.: P2133100) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Education Level: University Topic: Mechanics Subtopic: Static Equilibriu and Elasticity Experient:
