VKR Classes TIME BOUND TESTS 1-10 Target JEE ADVANCED For Class XII VKR Classes, C , Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
|
|
|
- Samuel Carson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VKR Classes TIME BOUND TESTS - Target JEE ADVANCED For Class XII VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
2 Comprehension Type Paragraph for Question Nos. to Let a + b y + c z + d = and a + b y + c z + d = be two planes, where d, d >. Then origin O lies in acute angle if a a + b b + c c < and origin lies in obtuse angle if a a + b b + c c >. Further point (, y, z ) and origin both lie either in acute angle or in obtuse angle, if (a + b y + c z + d ) (a + b y + c z + d ) >. One of (, y, z ) and origin lie in acute angle and the other in obtuse angle, if (a + b y + c z + d ) (a + b y + c z + d ) <.. Given the planes + y 4z + 7 = and y + z 5 =, if a point P is (,, ), then (A) O and P both lie in acute angle between the planes (B) O and P both lie in obtuse angle (C) O lies in acute angle, P lies in obtuse angle (D) O lies in obtuse angle, P lies in acute angle.. Given the planes + y z + 5 = and + y + z + =. If a point P is (,, ), then (A) O and P both lie in acute angle between the planes (B) O and P both lie in obtuse angle (C) O lies in acute angle, P lies in obtuse angle (D) O lies in obtuse angle, P lies in acute angle.. Given the planes + y z + = and y + z + 7 =. If a point P is (,, ), then (A) O and P both lie in acute angle between the planes (B) O and P both lie in obtuse angle (C) O lies in acute angle, P lies in obtuse angle (D) O lies in obtuse angle, P lies in acute angle. 4. If Paragraph for Question Nos. 4 to 6 Consider a triangle ABC, where, y, z are the length of perpendicular drawn from the vertices of the triangle to the opposite sides a, b, c respectively let the letters R, r, s, denote the circumradius, inradius semiperimeter and area of the triangle respectively. b cy az = c a b PRACTICE TEST- a b c, then the value of k is k (A) R (B) s (C) R (D) R 5. If cot A + cot B + cot C = k y z, then the value of k is (A) R (B) rr (C) (D) a + b + c 6. The value of (A) r R c sin B b sin C (B) R s + a sin C csin A y + b sin A a sin B is equal to z (C) (D) 6 Match the Column : 7. Column-I Column-I VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
3 (A) The equation of tangent of the ellipse which cuts off (P) equal intercepts on aes is y = a where a equal to (B) The normal y = m am am to the parabola y = 4a (Q) subtends a right angle at the verte if m equals to (C) The equation of the common tangent to parabola y = 4 (R) 8 and = 4y is + y + k =, then k is equal to (D) An equation of common tangent to parabola y = 8 and (S) 4 the hyperbola y = is 4 y + k =, then k is equal to 8. Column-I Column-I (A) In a ABC, let C =, r = inradius (P) a + b + c R = circumradius then (r + R) (B) It, m, n are perpendicular drawn from the vertices (Q) a b of triangle ABC teo sides a, b and c respectibvely then b cm an R ab bc ca c a b (C) In a ABC, R(b sin C + c sin B) equals (R) a + b (D) In a right angle triangle ABC, C =, then (S) abc 4R sin A B. sub ( A B) Single Choice Question : 9. The number of integral solutions of where, and,, 4 are is (A) 55 (B) 75 (C) 495 (C) 79. Tthe value of (A) equals! 4! 5! 7! 6 (B) (7!) 6. 7 (C) (7!) 7 (D) (7!) 6. 7 (7!). If a i + b i + c i =, i =,, and a i a j + b i b j + c i c j =, i j, i, j =,, then the value of is (A) (B) (C) (D). If s, s, s... s n are the sums of infinite geometric series whose first terms are,, 5,...(n - ) and a b c a b c a b c VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
4 whose common ratios are (A) 5, (B) 6,... 5 n respectively, then lim n s ss (C) s s s... s s 4 n ns n (D) =. If k is a factor of the determinant (n) (n) C C (n4) (n4) C C (n7) (n7) (A) 4 (B) (C) (D) 6 C C, then the maimum value of k is 4. Let S r = r + r + r. Then D = S S S S S S S S S 4 is equal to (A) ( ) ( ) ( ) (B) {( ) ( ) ( )} (C) ( + ) ( + ) ( + ) (D) One or More than One Correct : 5. The value of ( ) r n r C is equal to n r (r ) Cr (A) n if n is even (B) n if n is odd (C) n if n is even (D) (n )(n ) 6. If cos = + and cos = y + y, then which of the following is/are possible y (A) cos( ) (B) y m y n + n m y = cos (m + n) (C) m n y y n m = cos (m + n) (D) y + y y = cos ( + ) 7. If + i = ( + i) n ( i) n, n, n N, then (A) = if both n and n are even (B) = if both n and n are odd (C) = if both one of n and n is odd (D) + i is an even number provided n n 8. A variable plane passes through a fied point (a, b, c) and meets the coordinates aes in A, B, C. The locus of the point comon to the planes through A, B, C parallel to the coordinats planes is (A) ayz + bz + cy = yz (B) ayz + bz + cy = yz a b c (C) (D) a + by + cz = y z VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
5 Single Choice Question : 6. ( ) d = PRACTICE TEST- (A) (B) /6 (C) /8 (D) /6. If f( + f(y)) = f() + y, y R and f() =, then f ( ) d is equal to (A) (B) (C) f () d (D) f () d. let g() = e f() and f( + ) = + f(), then X = g' N g' g N g is equal to (N natural number) (A) X = (C) X =... (B) X =... N 7 N (D) none of these 4. In a circle with centre O, OA, OB are radii AOB = 9º. A semi-circle (S ) is constructed using segment AB as its diameter non-overlapping with OAB. The ratio of the area of S outside given circle to the area of OAB is equal to (A) / (B) /4 (C) (D) none of these 5. If f() is a continuous function in [, ] such that f() = f() = then the value of / ( f () f"()) sin. cos d is equal to (A) (B) (C) (D) none of these 6. Let f(), [, ) be a non-negative continuous function. If f () cos f() sin then the value of f() is equal to (A) (B) (C) (D) none of these One or more than one correct 7. If f (sin ) > R then which of the following are always correct for g() = f (sin ) (A) g is monotonically strictly increasing R (B) g is monotonically strictly increasing n,n ni (C) g is monotonically strictly decreasing n,(n ) ni (D) g is monotonically strictly decreasing, VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
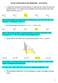
6 8. If y = f() has finite slope everywhere is an invertible function, then (A) y = f() and y = f () cannot intersect orthogonally on line y = (B) y = f() and y = f () may have points of intersection not on line y = (C) If f() then b a (D) b a f (b) b f () d f () d (a b) a f () d + f () d = b f(b) a f(a), Given that f () > R f (a) n 9. T n = rn r n r n n, S n = rn r n r n, then n {,,...} (A) T n > ln (B) Sn < ln (C) Tn < ln (D) Sn > ln. A line = k intersects the graph of y = log 5 and the graph of y = log 5 ( + 4). The distance between the points of intersection is.5. Given that k = a + b where a, b N then (A) a =, b = 4 (B) a =, b = 5 (C) a + b = 6 (D) a = b = Comprehension Type Paragraph for Question Nos. to (,) (-,) (,) In the given figure graph of (-,) (,) (,) y = p() = 4 + a + b + c + d is given. The product of all imaginary roots of p() = (A) (B) (C) / (D) none of these. If p() + k = has 4 distinct real roots,,, then [] + [] + [] + [], (where [.] denotes greatest integer function) is euqal to (A) (B) (C) (D). The minimum number of real roots of equation (p ()) + p() p () = are (A) (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 Paragraph for Question Nos. 4 to 6 Given f is a twice differentiable function R and f (). If f() + f () = h () f () where h() > R, f() =, f () = 4 and F() = (f()) + (f ()) then 4. F() is monotonically strictly decreasing function in (A) ( 5, 5) (B) ( 4, 4) (C) (, ) (D) (, ) 5. If F() M (, ) then least possible value of such M is (A) 4 (B) 9 (C) 6 (D) 5 6. The number of points of etrema for F() is/are (A) (B) (C) (D) infinite VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
7 Match the Column 7. f() = 9 a then Column-I Column-II (A) For a = 8, f() = has (P) eactly 4 distinct real roots (B) For a =, f() = has (Q) eactly distinct real roots (C) For a =, f() = has (R) eactly distinct real roots (D) For a =, f() = has (S) eactly one distinct real roots 8. Column-I Column-II (A) f() = tan tan tan on tan (B) f() = (sin ) on, (C) f() = on, (D) f() = sin + cos on,, (P) greatest value of f = (Q) least value of f = (R) maimum value of f = (S) minimum value of f = VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
8 PRACTICE TEST- Single Choice Question :. A circle C is drawn having any pint P on -ais as its centre and passing through the centre of the circle(c) + y =. A common tangent to C and C intersects the circles at Q and R respectively. Then, Q(, y) always satisfies (A) = (B) + y = (C) y = (D) None of these. If y = cot + cot 8 + cot , then tan y is (A) (B) (C) 4 (D) None of these. The minimum distance between the circle + y = 9 and the curve + y + 6y = is (A) (B) (C) (D) 4. The medians AA and BB of triangle ABC intersect at right angle. If BC =, AC = 4, then AB is (A) 5 (B) 5 (C) (D) None of these One or more tan one correct : 5. If 5a + 6b 4ab c =, then the family of straight line a + by + c = is current at 5 (A), 4 5 (B),4 5 (C), 4 VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No (D),4 6. Let f be a differential function such that f() = f( ) R and g() = f( + ) then (A) g() is an odd function (B) g() is an even function (C) graph of f() is symmetrical w.r.t. line = (D) f () = 7. A sequence is defined as a = a = and a n = a n + + a n n then (A) (C) a n a n a n a a = n n n a n a n a a n n (B) a n a n n = = (D) {a n } is an increasing sequence a 8. f : R + R + be a differentiable function such that f = then (A) f () f '() f ''() = (f '()) f () (B) f() = f (), R + also a R + and f()=f ()= (C) f() = (D) f() = Match the Column : 9. Let A = {,, 5, 7} and B = {, 4, 6, 8} and f : A B, then number of functions f possible or Column - I Column - II (A) i + f(i) <, i = {,,, 4} (P) 8 (B) f(i) >, i = {,,, 4} (Q) 4 (C) i f(i) 6, i {,,, 4} (R) (D) f(i) (i + ), i = {,,, 4} (S) 8 (T) 9 8
9 . Let a, b, c and d are four real numbers satisfying the system of equations a + b = 8, ab + c + d =, ad + bc = 8 and cd =. Now match the following Column - I Column - II (A) a + b + c + d = (P) 5 (B) ab + cd = (Q) 6 (C) ac + bd = (R) 7 (D) ab = (S) 8 (T) 6 Integral Answer Type. Let E(N) denotes the sum of the even digits of n. For eample E(568) = = 4. Find E() E() E()... E() n, if n is odd. Let f : I I is defined as follows f(n) = n, if n is even suppose k is odd and f(f(f(k))) = 7 then find the sum of digits of k.. Find the value of lim e /. 4. Let f : A B be an onto function where A = {,,, 4}, B = {, y, z} also f() =. Let M be total such functions then find the value of M. r(r!) 5. Let n r r(r!) sin d = a ((n + b)! c!), where a, b, c N. Find the value of a + b + c. 6. Let P, Q, R be any three points on the ellipse y. Find the maimum area of PQR Let f : R + R + be a differentiable function satisfying f(y) = f () y + f (y), y R + also f()=,f ()=. If M be the greatest value of f() then find the value of [M + e]. (where [.] denotes the greatest integer function). 8. Circle ( ) + (y ) = touches X and Y ais at A and B respectively. A line y = m intersects this circle at P and Q. If area of PQB is maimum then find the value of greatest integer function). m. (where [.] denotes the VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
10 PRACTICE TEST-4 Single Choice Question :. The figure shown is the union of a circle and two semi-circles of diameter a and b all of whose centres are collinear. Then the ratio of the area of the shaded region to that of the unshaded region is a b (A) ab a (B) b (C) a b (D) b a. The value of [, ] such that tangent at (, y) on the curve y = + bounds maimum area with lines =, y =, = is (A) (B). If I = ( sin 5cos) (A) cos( sin d, then I equals (C) + tan + c (B) 5cos) (C) ( sin 5 cos ) sin c 4. Let g() =, R + then ln( ) sin ( sin (D) none of these (D) + cot + c 5cos) (A) a < g() < (B) < g() < (C) < g() < (D) none of these One or more than one correct : 5. If,, such that (sin + sin ) + lim n (sin ) (sin ) (A) a = 6 n 6. The value of lim n n then n r (B) = r n r n r r r is equal to sin = and (sin + sin ) sin (C) = (D) = (A) 4/ (B) (C) 8/ (D) 5/ 7. Let the numbers a, b, c, d are in AP, then a bc (A) abc, a c, a c, a b, are in HP d (B) a (bc + cd + bd), b (ac + ad + cd), c (ab + bd + ad), d (ac + ab + bc) are in AP (C) bcd, acd, abd, abc are in HP (D) None of the above sin = and = sin VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
11 8. The coordinats of the point(s) on the line + y = 5, which is/are equidistant from the lines = y is/are (A) (5, ) (B) (, 5) (C) ( 5, ) (D) (, 5) Paragraph for Question nos. 9 to ABC is an isosceles with AB = AC = 5 and BC = 6. Let P be a point inside the triangle ABC such that the distance from P to the base BC equals the geometric mean of the distances to the sides AB and AC. 9. The locus is the point P is (A) a semi circle (B) a minor arc of a circle (C) a major arc of a circle (D) a complete circle. The minimum distance of the point A from the locus of the point is (A) 5/ (B) / (C) (D) None of these. If the tangent to the locus at B and C intersect at point P, then the area of the triangle PBC is (A) (B) (C) 4 (D) 8 Paragraph for Question Nos. to 4 Let P be a point in the plane of ABC, such that at the triangles PAB, PBC, PCA all have the same perimeter and the same area.. If P lies inside the ABC, the ABC (A) must be equilateral (B) may not be equilateral (C) must be right angled (D) None of these. If P lies outside the ABC, the ABC (A) must be equilateral (C) must be right angled (B) may not be equilateral (D) None of these 4. If P lies outside the ABC, then the equilateral formed by A, B, C and P is necessarily (A) rectangle (B) square (C) rhombus (D) None of these 5. Match the following Column-I Column-II (A) The minimum value of ab if roots of the equation (P) 4 a + b = are positive, is (B) The number of divisors of the form + 6, ( N) of the (Q) number 5 are (C) The number of equadrilateral formed in an octagon having two (R) adjacent sides common with the polygon are (D) The number of solution of the equation [cos ] = tan, where (S) 8 [.] denotes GIF, [, 6] are 6. Column-I Column-II (A) Vector along a bisector of the angle between the vectors (P) 4î 9ĵkˆ î ĵ kˆ and y î 4ĵ (B) Vector orthogonal to the vectors î ĵ kˆ and y î kˆ (Q) î ĵ 5kˆ (C) vector coplanar with the vectors î ĵ and y î 5ĵ 6kˆ (R) î 5ĵ kˆ (D) vector v such that v, î ĵ 7kˆ, î ĵ kˆ are linearly independent (S) 7î ĵ 5kˆ VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
12 PRACTICE TEST-5 Single Choice Question :. If a, b, c are non-zero, then the system of equatin (p + a) + py + pz =, p + (p + b) y + pz = and p + py + (p + c) z = has a non-trivials solution if (A) p a b c (B) p a b c (C) p (D) p + a + b + c = a b c. If the system of equations 9 + y =, and 5y = has positive solutions for and y, then 45 (A), (9, ) (B) (, ) 45 (C), 9 (D) None of these. If z + + i and z i, then the minimum possibnle value of z z is 7 (A) 5 (B) 6 49 (C) 6 (D) 4. The area of the region defined z 4 and z + z is (A) 5 (B) 8 (C) 45 4 (D) 4 5. Origin is an interior point of an ellipse whose foci correspond to the comple number z and z. Then the eccentricity of ellipse is (A) < z z z z (B) < z z ( z z ) (C) > z z z z (D) z z ( z z ) AB 6. If A(z ) B(z ) C(z ) are the vertices of ABC in which BAC = and = 4 AC, then z = (A) z + i (z + z ) (B) z i (z z ) (C) z + i (z z ) (D) z + i (z z ) One or mor than one correct : 7. Let f() = (a + b) cos + (c + d) sin and f () = sin, f() =, R. Then (A) a = (B) b = (C) c = (D) d = 8. f() = [] and g() =, I where [.] denotes the greatest integer function. Then, I (A) gof is continuous for all (B) gof is not continuous for all (C) fog is continuous everywhere (D) fog is not continuous everywhere VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
13 9. In the set R of real number the function f : R R is defined such that f() f(y) ( y), y R. Then f() is (A) strictly increasing (B) strictly decreasing (C) neither increasing nor decreasing (D) a constant function. If A and B are events such that P(A B) 4 and 8 P( A B) 8, then (A) P(A) + P(B) (B) P(A).P(B) 8 8 (C) P(A) + P(B) 8 7 (D) P(A) P(B) >. Match the following Column-I Column-II (A) In a ABC, (a + b + c) (b + c a) = bc, (P) where I, then greatest value of is (B) In a ABC, tan A + tan B + tan C = 9. (Q) 9() / If tan A + tan B + tan C = k, then least value of k satisfying is (C) In a triangle ABC, then line joining the circumcentre (R) to the incentre is parallel to BC, then value of cos B + cos C is (D) If in a ABC, a = 5, b = 4 and cos (A B) =, (S) 6 then the third side c is equal to. [.] represents greatest integer function is parts (A), (B) and (C) Column-I Column-II (A) If f() = sin and then [a] = lim f( 4 ) = a lim f(), (P) (B) If f() = tan g() where g() = and (Q) lim h f (a h) f (a) h a =, where < a < then find f 6h) f lim 6h h = (C) If cos (4 ) = a + b cos for < < then [a + b + ] =, (R) 4 (D) If f() = cos (4 ) and lim f () = and (S) lim f () = b, then a + b + = VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
14 Comprehension (Q. to Q.5) y z Let L be the line whose equation are = =. Let P represent the point (,, ). L meets the plane p given by the equation + y + z = at A. Produce PA to B such that PA = AB. Let C be the image of B in. Let D be a point on the plane such that ABCD is a parallelogram. Let L be the projection of L on.. Coordinates of C are (A) 7,, (B) 5,, 7 (C),, 7 (D),, 4. Equation of L is (A) 7 = y = z (B) 7 = y = z (C) 7 = y = z (D) 7 = y = z 5. Equation of line CD is y (A) = = y z (C) Comprehension (Q.6 to Q.8) z 7 (B) y = y (D) = = y 7 z 7 It is given that A = (tan ) + (cot ) where > and B = (cos t) + (sin t) where t,, and sin + cos = for and tan + cot = for all R. 6. The interval in which A lies is (A) 7, (B), 8 (C), 4 (D) None of these 7. The maimum value of B is (A) 8 (B) 6 (C) 4 (D) None of these 8. If least value of A is and maimum value of B is then cot cot = (A) 8 (B) 8 (C) 7 8 (D) 7 8 VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
15 PRACTICE TEST-6 Comprehension (Q. to Q.) Let f() = log {} [] g() = log {} {} h() = log {} {} Where [.] {.} denotes the greatest integer function and fractional part function.. For (, 5) the f() is not defined at how many points (A) 5 (B) 4 (C) (D). If A = { : domain of f()} and B = { : domain of g()} then (, 5), A B will be (A) (, ) (B) (, ) (C) (, ) (D) None of these. Domain of h() is (A) R (B) {I} (C) R {I} (D) R + {I} I denotes integers Comprehension (Q.4 to Q.6) Let z be a comple number lying on a circle z = a and b = b + ib (any comple number), lying on the circle then 4. Tthe equation of tangent at point b is (A) zb zb a (B) zb zb a (C) zb zb a (D) zb zb 4a 5. The equation of straight line parallel to the tangent and passing through centre of circle is (A) zb zb (B) zb zb (C) zb zb (D) zb zb 6. The equation of line passing through the centre of the circle making an angle 4 with the normal at b are ib ib ib ib (A) z = ± z (B) z = ± z (C) z = ± z (D) z = ± a a a 4a Match the Column : 7. Column-I Column-II (A)... (P) is a prime 9 times (B) n (n + ) (n.....) (Q) is not a prime (C) 4n + 4 (n ) , n N (R) is a perfect square integer (D) n times (S) is a perfect square of odd integer (n )times 8. Column-I Column-II (A) If the roots of the equation a + a + a = (P) (, ] are real and less than, then a is (B) Let f() = ( + b ) + b + and let m(b) the (Q), minimum value of f(). as varies, then m(b) is (C) If a, b, c R and equation p + q + r = has two (R) < real roots and such that < and >, then + p q + p r is z (D) The set of values of a for which bot the roots of the (S) < equation + (a ) + a = are positive is VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
16 Integer Answer Type 9. In a class tournament where the participants were to play one game with another, two class players fell ill, having played games each. If the total number of games played is 84, then the number of participants at the beginning is.. A pack of playing cards was found to contain only 5 cards. If the first cards which are eamined are all black. If P is the probability that the missed one is red. Then the value of P is.. If =. ( ) +. ( ) +.4 (4 ) +... upto 5 terms, then the value of 5 is.. The value of satisfying the equation log (log ) + log / (log / y) = ; y = 9 is.. The numbers of five digits that can be made with the digits,, each of which can be used at most thrice in a number, is. 4. Let, y, z be three positive real numbers such that + y + z = then the maimum value of the epression ( ) ( y) ( z) is. 5. Anubhav and Shivendra decided to meet on New Year s day eve at a place in Cannaught Place between 7 pm and 8 pm. The first one to arrive waits for 5 minutes and then leave. Assuming that each is independently equally likely to arrive at any time during the hour (between 7 pm and 8 pm). The probability that they meet, is n m. Find (n m). VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
17 PRACTICE TEST-7 One or more than one correct :. If the equation c + b a = has no real roots and a < (A) ac < (B) a < (C) c b b c then > a (D) c b 8 > a. If z = + i, then z n + n z n + 4n, n N may be equal to (A) n (B) (C). n (D) None of these. The number of ways in which we can choose distinct integers from to such that difference between them is at most is (A) C 9 C (B) C 98 9 C 88 (C) C 9 C 88 (D) None of these 4. Let n be a positive integer with f(n) =! +! +! n! and P(), Q() be polynomials in such that f(n + ) = P(n) f(n + ) + Q(n) f(n) for all n. Then (A) P() = + (B) Q() = (C) P() = (D) Q() = + 5. If A, B, C and D are four points with positive vectors î, ĵ, kˆ and î + ĵ + kˆ respectively, then D is the (A) Orthocentre of ABC (B) Circumcentre of ABC (C) Centroid of ABC (D) Incentre of ABC 6. If the first and the (n ) th terms of an A.P., a G.P. and an H.P. are equal whereas their n th terms are a, b, c respectivey, then (A) a = b = c (B) a b c (C) a + c = b (D) ac = b 7. Let f() is a quadratic epression with positive integral coefficients such that for every a, b R, >, f () d >. Let g(t) = f (t) f(t) and g() =, then (A) 6 such quadratics are possible (B) f() = has either no real root or distinct roots (C) Minimum value of f() is 6 (D) Maimum value of f() is Comprehension Type : Comprehension (Q.8 to Q.) Three distinct vertices are chosen at random from the vertices of a given regular of (n + ) sides. Let all such choices are equally likely and the probability that the centre of the given polygon lies in the interior of the triangle determined by these three chosen random points is The number of diagonals of the polygon is equal to (A) 4 (B) 8 (C) (D) 7 9. The number of points of intersection of the diagonals lying eactly inside the polygon is equal to (A) 7 (B) 5 (C) 6 (D) 96. Three vertices of the polygon are chosen at random. The probability that these vertices from an isosceles triangle is (A) / (B) /7 (C) /8 (D) None of these VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
18 Comprehension (Q. to Q.) We have to choose players for cricket team from 8 batsmen, 6 bowlers, 4 allrounders and wicketkeepers, in the following conditions.. The number of selections when at most allrounder and wicket keeper will play (A) 4 C. 4 C + C. 4 C + 4 C. C. 4 C C (B) 4 C. 5 C + 5 C (C) 4 C. 5 C + 5 C (D) None of these. Number of selections when particular batsman don t want to play, if a particular bowler will play (A) 7 C + 9 C (B) 7 C + 9 C + 7 C (C) 7 C + C (D) 9 C + 9 C. Number of selections when a particular batsman and a particular wicketkeeper don t want to play together (A) 8 C (B) 9 C + 8 C (C) 9 C + 9 C (D) None of these Match the Column : 4. Column-I Column-II (A) f(z) is a comple valued function f(z) = (a + ib) z where (P) 5 a, b R and a + ib =. It has the property that f(z) is always equidistant from and z, then a b = (B) The number of all positive integers n = a b (a, b ) (Q) such that n 6 does not divide 6 n is (C) A is the region of the comple plan {z : z/4 and 4/ z (R) 6 have real and imaginary part in (, )}, then [p] (where p is the area of the region A and [.] denotes the greatest integer function) is (D) If + 4y + z = 5, where, y, z R, then minimum (S) 5 value of 6( + y + z ) is 5. Let a, b, c are the three vectors such that a b c = and angle between a and b is /, b and c is / and a and c is /. Column-I (A) If a, b, c represents adjacent edges of parallelopiped then its volume is (B) If a, b, c represents adjacent edges of parallelopiped Column-II (P) (Q) then its height is (C) If a, b, c represents adjacent edges of tetrahedron (R) 4 then its volume is (D) If a, b, c represents adjacent edges of tetrahedron then its height is (S) VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
19 PRACTICE TEST-8 Comprehension Type : Comprehension (Q. to Q.) One the ground n stones are place in a straight line. Let (r, i) denotes the distance (in mts) between the r th stone and the i th stone in a row. A basket is placed at a distance of 5 mts before the st stone. A person starts from the backet and picks up a stone, comes back to basket and put the stone into abasket and then goes for the nd stone and so on.. If d(r, r + ) = 4, where r N, if the person had traveled a total of 65 mts. Then (A) He has collected stones in basket (B) He has collected stones in basket (C) He has collected stones in basket (D) He has collected stones in basket. If d(r, r + ) = r +, where r N, if the person need to travel 96 mts. to pick up and i th stone and put in basket then i is (A) (B) (C) (D). Let d(r, ) =, where r N and r. The person collects in total in stones in basket then (r )r (A) i = 8, if he travelled mts. in total (B) i = 9, if he travelled 5 4 mts. in total (C) i =, if he travelled 9 mts. in total (D) i =, if he travelled 9 5 mts. in total Comprehension (Q.4 to Q.6) Tangents drawn to the parabola y = 8 at the points P(t ) and Q(t ) intersects at a point T and normals at P and Q intersects at a point R such that t and t are the roots of equation t + at + = ; a >. 4. Locus of R is (A) y = 4 (B) y = 4 (C) y = (D) = 8 5. Locus of circumcentre of PTQ is (A) y = (B) y = + (C) y = (D) y = ( ) 6. The point on the curve given by locus in part() which is at a minimum distinct from the line y = + 9 (A) (6, ) (B), 4 (C), (D) (, ) VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
20 Match the Column : 7. Column-I Column-II (A) The triangle PQR is inscribed in the circie (P) /4 + y = 69. If Q and R have coordinates (5, ) and (, 5) respectively find QPR (B) What is the angle between the line joining (Q) / origin to the point of intersection of the line 4 + y = 4 with circle ( ) + (y 4) = 5 (C) Two parallel tangents drawn to given circle (R) are cut by a third tangent. The angle subtended by the third tangent at the centre is (D) For a circle if a chord is drawn along the point (S) /6 of contact of tangents drawn from a point P. If the chord subtends an angle / then find the angle at P. 8. Column-I Column-II (A) Point (4, ) is reflected about y = and then transformed (P) through distance units along positive direction of -ais. it also rotates through an angle about the origin in counter (B) clockwise direction. If its final position is 7, then tan is. 8 y Tangent to ellipse = at ( cos, 8 sin ) (Q) (, /). The value of tan such that sum of intercepts on aes made by this tangent is minimum is (C) If the line + 6 y = touches the hyperbola (R) y = 4. Then slope of line joining origin and point of contact is (D) Tangent at P on the circle + y y = meets a (S) straight line at point Q on y-ais where length PQ = 5. Then, length OQ =?, (where O is the origin) Integer Answer Type : 9. Let P(, ), Q(, ) and R(, ) be the centroid, orthocentre and circumcentre of a scelene triangle having its vertices on the curve y =, then + + is equal to. ( 4). If the equation of the curve on reflection of the ellipse 6 is 6 + 9y + k 6y + k =, then k + k is. + ( ) 9 = about the line y =. The base AB of a triangle is and height h of C from AB is less than or equal to /. The maimum value of the 4 times the product of the altitudes of the triangle is.. In a triangle ABC, c a, c b and a + b = Rc, (Notations have their usual meaning). The value of the angle C is /k, then k is VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
21 PRACTICE TEST-9 Single Choice Quesion :. Equation of the image of the line + y = sin (a 6 + ) + cos (a 4 + ) tan (a + ), a R about -ais is given by (A) y = (B) y = (C) y = (D) y = 4. If f() = (A) sin cos then value of f(º). f(4º) equals cos (B) (C) 4 4 (D) /. cos sin ( cos)( sin ) d equals (A) cos (B) cos () (C) cos () (D) cos ( ) 4. The roots of the equation + = are u, v, and w. The value of (tan u + tan v + tan w) equals (A) (B) tan () (C) (D) tan ( ) log(log8(log4 )) 5. If the equation log (log (log (log ))) = has a solution for when c < y < b, y a, where b is as 5 4 y large as possible and c is as small as possible, then the value of (a + b + c) is equal to (A) 8 (B) 9 (C) (D) 6. If the equation + 4y + 7y y + t = where t is a parameter has eactly one real solution of the form (, y). Then the sum of ( + y) is equal to (A) (B) 5 (C) 5 (D) Comprehension (Q.7 to Q.9) 6 4 Consider a rational function f() = and a quadratic function 4 g() = ( + m) ( + m) ( + m) where m is a parameter. 7. Which one of the following statement does not hold good for the rational function f()? (A) It is a continuous function (B) It has only one asymptote (C) It has eactly one maima and one minima (D) f() is monotonic in (, ) 8. If cot (cot f()) = k, has eactly two distinct real solutions then the integral value of k can be (A) (B) (C) (D) 5 9. If the range of the function f() lies between the roots of g() = fthenthe number of integral values of m equals (A) 7 (B) 8 (C) 9 (D) VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
22 One or more than one correct :. For the function f() = ( + b + c) e and g() = ( + b + c) e ( + b). Which of the following holds good? (A) if f() > for all real g() > (B) if f() > for all real g() > (C) if g() > for all real f() > (D) if g() > for all real f() >. For any odd integer n, if the value of the sum n (n ) + (n ) ( ) n ( ) equals 8 then n can not be (A) 5 (B) 7 (C) 9 (D). Which of the following equations have no real real solutions? (A) = (B) log.5 (cos sgn(e )) = (C) 4 sin + = (D) tan = tan 6 Match the Column :. Column-I Column-II (A) k for f : R R is defined as f() = (P) k for (B) If Lim (C) If Lim If f() is injective then k can be equal to (Q) 5 f () 9 = then Lim f(), is (R) k 5 8 does not eist then k can be (S) 6. Column-I Column-II (A) If both roots of f() = are confined in (, ) then (P), 5 (B) Eactly one root of f() = lies in (, ) (Q) (C) Both roots of f() = are greater than (R), 7 (D) One root of f() = is greater than and other root is (S), 7, f() = is less than (R),, 7 Subjective : 5. Polynomial P() contains only terms of odd degree. When P() is divided by ( ), the remainder is 6. If P() is divided by ( 9) then remainder is 9(). Find the value of g(). 6. If the sum of the roots of the equation cos = 7 cos in the interval [, 4] is k, k R. Find k. VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
23 PRACTICE TEST- Single Choice Quesion :. Let P() = a + a + a a, where a = and a i R i =,, 4,...,.. Then lim P() has the value equal to (A) (B) / 4 sec e sin d equals cos (C) (D) 55 (A) e (B) e (C) e (D) e e. Let A(, ), B(,, ), C(,, ) are the vetives of ABC. If R and r denote the circumradius and inradius of ABC, then the value of (R + r ) is equal to (A) 5/6 (B) /6 (C) / (D) / 4. Most general value of c for which the equation (cos cos( c)) d = cos( c) d holds c / ( / ) c good, are given by (A) n + ( ) n / (B) n + ( ) n /6 (C) n + ( ) n / (D) n + ( ) n /6 5. If sin (sin + cos ) = cos (cos sin ), then the greatest possible value of sin, is (A) (B) (C) Minimum distance between the curve f() = e and g() = n is (A) (B) (D) 4 (C) (D) ( ) 7. Number of terms common to the two sequences 7,, 5,..., 47 and 6,, 6,..., 466 isd (A) 9 (B) (C) (D) 8. Two loaded dice each have the property that or 4 is three times as likely to appear as,, 5 or 6 on each roll. /when two such dice are rolled, the probability of obtaininga total of 7, is (A) /8 (B) /7 (C) 7/5 (D) 7/5 9. If â, bˆ and ĉ are three unit vectors inclined to each other at an angle, then the maimum value of is (A) (B) (C) 5 (D) 6. If,,,... n be a zero s of the polynomial P() = n + +, where i j i & j =,,,... (n ). The value of Q() = ( ) ( ) ( 4 )... ( n ), is (A) n (n ) n (B) n C n (C) (n n ) + (D) zero VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
24 . A variable line cos + y sin = p where p is a constant, mets the and y ais at A and B respectively. The locus of a point R whch divide the line segment AB etrenally in the ratio : is given by (A) 9 4y = p (B) 4 9y = p (C) 9 + 4y = p (D) 4 + 9y = p. For, the smalest value of the function f() = 4 8, is 6( ) 5 (A) (B) (C) (D) 6. How many numbers from ro are divisible by 6 but not byu 4? (A) 8 (B) (C) 6 (D) 4 4. Lim n... 4 equals n (A) /8 (B) / (C) /4 (D) /8 5. In ABC, angle A is º, BC + CA = and AB + BC =, then the length of the side BC, equals (A) (B) 5 (C) 7 (D) 9 6. A line passes through the point A(î ĵ kˆ ) and is parallel to the vector V (î ĵ kˆ ). The shortest distance from the origin, of the line is (A) (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 7. Equation of a straight line which passes through the point of intersection of the lines 4y + 6 = and + y + and has equal intercepts on the coordinates aes, is (A) y + = (B) + y + = (C) + y + = (D) no such line can be found out 8. If f be a continuous function on [, ], differentiable in (, ) such that f() =, then their eists some c (, ) such that (A) c f (c) f(c) = (B) f (c) + cf(c) = (C) f (c) cf(c) = (D) cf (c) + f(c) = 9. If f() = ( ) cos and g is the inverse function of f, then g () is equal to (A) (B) (C) (D) Comprehension (Q. to Q.) Consider a polynomial y = P() of the least degree passing through A(, ) and whose graph has two points of infletion B(, ) and C with abscissa at which the curve is inclined to the positive ais of abscissas at an angle of sec. k. If P () d =, k N then k equals 5 (A) 7 (B) 4 (C) (D) 4. The value of P( ) equals (A) (B) (C) (D). The area of ABC equals (A) / (B) /4 (C) /8 (D) / VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
25 One or more than one correct :. The function f() = tan tan is (A) both many one and even function (B) lim f() equals (C) periodic function (D) lim f() does not eists / 4. If a and b are any two unit vectors, then possible integer(s) in the range of (A) (B) (C) 4 (D) 5 a b + a b is 5. Consider a real valued continuous function f such that f() = sin + (sin tf (t)) dt. If M and m are maimum and minimum value of the function f, then M (A) = (B) M m = + (C) M + m = 4( + ) (D) Mm = ( + ) m / / 6. If and sin = sin sin, then possible values of tan, is (A) 4/ (B) (C) /4 (D) 4/ (k) 7. Let I = good? / (A) I = sin d sin cos k sin d sin cos /4, (k N) and J = d sin cos ' (B) I = 4 4J (C) I = 4 J (D) I = J then which of the following hold(s) 8. Which of the following hold(s) good for the function f() = /? I The function has an etremum point at = II The function has a critical numberat = III The graph is concave down at every point in (, ) (A) Statement I (B) Statement II (C) Statement III (D) I, II and III are true 9. If p, q, r are positive rational numbers such that p > q > r and the quadratic equation (p + q r) + (q + r p) + (r + p q) = has a root in (, ) then which of the following statement hold(s) good? (A) Equation p + q + r = (B) Both roots of the given quadratic equation are rational (C) Equation p + q + r = has real and distinct roots r p (D) < q. Number of real values of satisfying the equation + + = 8 is not equal to (A) Number of real solutions of the equation ( + ) = 4 + 9, such that the quantity n (5 ) is a real number log5 5 log (B) The value of the epression log 5 log 5 5 when simplified (C) Number of real solutions of the equation, n + = (D) The value of m if a line of gradient m passes through the points (m, 9) and (7, m) 5 5 VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
26 PRACTICE TEST- Single Choice Quesion : Let f() be a differentiable function and satisfy f() =, f () = and f () = f(). The range of the function f() is (A) (, ) (B) (, ) (C) [, ) (D) (, ]. The value of the function when = n is 9 (A) 4 (B) (C) (D) 6. The area enclosed by y = f() in the nd quadrant is (A) + n 5 (B) + n5 (C) 5 (D) Assertion & Reason : 4. Statement- : If f() is differentiable in [, ] such that f() = f() =, then for any R, there eists c such that f (c) = f(c), < c <. Statement- : If g() is differentiable in [, ] where g() = g(), then there eists c such that g (c) =, < c <. (A) Statement- is true, Statement- is true and Statement- is correct eplanation for Statement- (B) Statement- is true, Statement- is true and Statement- is NOT correct eplanation for Statement (C) Statement- is true, Statement- is false (D) Statement- is false, Statement- is true. 5. Statement- : If f() is differentiable in [, ] such that f() = f() =, then for any R, there eists c such that f (c) = f(c), < c <. Statement- : If g() is differentiable in [, ] where g() = g(), then there eists c such that g (c) =, < c <. (A) Statement- is true, Statement- is true and Statement- is correct eplanation for Statement- (B) Statement- is true, Statement- is true and Statement- is NOT correct eplanation for Statement (C) Statement- is true, Statement- is false (D) Statement- is false, Statement- is true. 6. Statement- : Let u, v, w satisfy the equations uvw = 6, uv + vw = 5, u + v + w = where u > v > w, then the set of value(s) of a for which the points P(u, w) and Q(v, a ) lies onthe same side ofthe line 4 y + 5 = are given by (, ). Statement- : If two points M(, y ) and N(, y ) lies on the same side of the line a + by + c =, then (a + by + c) (a + by + c) >. (A) Statement- is true, Statement- is true and Statement- is correct eplanation for Statement- (B) Statement- is true, Statement- is true and Statement- is NOT correct eplanation for Statement (C) Statement- is true, Statement- is false (D) Statement- is false, Statement- is true. VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
27 7. Consider a curve C : y = cos ( ) and a straight line L = p 4y + p =. Statement- : The set of values of p for which the line L intersects the curve at three distinct points is [, 4] Statement- : The line L is always passing through point of inflection of the curve C. (A) Statement- is true, Statement- is true and Statement- is correct eplanation for Statement- (B) Statement- is true, Statement- is true and Statement- is NOT correct eplanation for Statement (C) Statement- is true, Statement- is false (D) Statement- is false, Statement- is true. Mathc the Column : 8. Column-I Column-II (A) Possible integral value(s) of m for which the equation (P) z + ( + i) z z (m + i) = has at least one real root is (B) The value of the definite integral 5 / 4 / 4 cos sin ( / 4) e d equals (Q) (C) Let a, a, a,..., A ARE IN G.P. with a = 5 and a i 65 (R) i Then the value of i equals a i (D) If cos = cos cos where, (, ) (S) 4 then the value of tan tan equals (T) 5 9. Column-I Column-II (A) Let f() (sin g() cos g()) +, where is constant of (P) y = integration is the primitive of sin (n). If a = lim f() and b = g(e 5 ) + g(e ) 6, then point (a, b) lies on the curve (B) If the equation sin ( + + ) + cos ( + ) = has (Q) y = + (C) eactly two solution for [a, b), then point (a, b) lies on the curve n i Let f(n) =. If a = f() and b = f(), then point (R) y = i j k (a, b) lies on the curve j (D) If a and b are real numbers and + is a root of the (S) y = equation b + a =, then point (a, b) lies on the curve (T) y = 4 VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
28 Subjective :. Given f () + g () + h () 9 and U() = f() + 4g() + h(). where f(), g() and h() are continuous R. If maimum vaue of U() is N, then find N. P(). Let P() be a polynomial of degree 5 having etremum at =. and Lim = 4. If M and m are the maimum and minimum value of the function y = P () on the set A = {{ + 6 5} then find M m.. Let f() be a non-constant thrice differentiable function defined on (, ) such that f() = f(6 ) and f () = = f () = f (5). Determine the minimum number of zeroes of g() = (f ()) + (f () f ()) in the interval [, 6].. Let f() = + + /4. Find the value of f (f ())d 4 / In ABC, a point P is chosen on side so that CQ + QB = :. Segment number of the lowest terms as b a, then find (a + b). AB so that AP : PB = : 4 and a point Q is chosen on the side BC CP and MC AQ intersect at M. If the ratio is epressed as a rational PC 5. Let two parallel lines L and L with positive slope are tangent to the circle C : + y 6y +64=. If L is also tangent to the circle C : + y + y = and equation of L is a a by+c a a = where a, b, c N, then find the value of (a + b + c). VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
29 PRACTICE TEST- Single Choice Quesion :. The range of k for which the inequality k cos k cos + (, ), is (A) k > (B) k > 4 (C) k 4 (D) k 5. If [] and {} denotes the greatest integer function less than or equal to and fractional part function respectivey, then the number of real, satisfying the equation ( ) [] = {}, is (A) (B) (C) (D) infinite. Let f() = dt t and g() be the inverse of f(), then which one of the following holds good? (A) g = g (B) G = g (C) g = g (D) g = g 4. If g() = t e dt then the value of t e dt equals (A) g( ) g() (B) g( ) + g() (C) g( ) (D) g( ) g() 5. Let g() = a + b, where a < and g is defined from [, ] onto [, ] then the value of cos (cos ( sin + cos ) + sin ( cos sin )) is equal to (A) g() (B) g() (C) g() (D) g() + g() 6. Let A be the set of all skew symmetric matrices whose entries are either, or. If there are eatcly three s three s and three ( ) s, the the number of such matrices, is (A) (B) 6 (C) 8 (D) 9 Comprehension (Q.7 to Q.) Consider two curves y = f() passing through (, ) and the curve g() = f (t) dt passing through (, /). The tangent drawn to both curves at the points with equal abscissas intersect on the -ais. 7. The value of f () equals (A) (B) / (C) (D) 8. The value of g equals (A) e (B) e/ (C) e (D) 9. Lim f () equals (A) (B) (C) (D) 4. The area bounded by the -ais, the tangent and normal to the curve y = f() at the point where it cuts the y-ais, is (A) /4 (B) (C) 5/4 / One or more than one correct :. If the epression ( + ir) is of the form of s( + i) for some real s where r is also real and i =, then the value of r can be (A) cot 8 (B) sec (C) tan 5 (D) tan VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
30 . Consider a real valued continuous function f() defined on the interval [a, b]. Which of the following statements does not hold(s) good? (A) If f() on [a, b] then b a f () d b f () d a (B) If f() is increasing on [a, b]l, then f () is increasing on [a, b] (C) If f() is increasing on [a, b]l, then () on (a, b) (D) If f() attains a minimum at = c where a < c < b, then f (c) =. If a, b, c R + then Lim n (A) ln a b b(b ) if a b a(a ) (C) non eistent if a = b n n k (k an)(k bn) is equal to (B) ln a b (D) if a = b a( a) a(b ) if a b b(a ) Match the Column : 4. Column-I Column-II (A) The 5 th and 8 th terms of a geometric sequence of real numbers are 7! and 8! (P) respectively. If the sum of first n terms of the G.P. is 5, then n equals (B) If (, ) and y (, ), then the number of distinct ordered pairs (, y) (Q) satisfying the equation 9 cos + sec y 6 cos 4 sec y + 5 =, is (C) Let f() = a + b + c (where a and a, b, c R) (R) and (a + c) < b, then the number of distinct values of in (, ) (S) 4 satisfying the equation f() = will be 5. In a ABC, BC =, CA = + and C = 6º. Feet of the perpendicular from A, B and C on the Subjective : opposite sides BC, CA and AB are D, E and F respectively and are concurrent at P. Now match the entries of column-i with respective entries of column-ii. Column-I Column-II (A) Radius of the circle circumscribing the DEF, is (P) ( 6 )/4 (B) Area of the DEF, is (Q) (C) Radius of the circle inscribed in the DEF, is (R) 4 (S) ( 6 + )/4 6. If f() = + t ( t) f(t) dt, then the value of the definite integral f () d can be epressed in the form of rational as p/q (where p and q are coprime). Find (p + q) 7. There is a point (p, q) on the graph of f() = and a point (r, s) on the graph of g() = 8/, where p > and r >. If the line through (p, q) and (r, s) is also tangent to both the curves at these pointys respectively, then find the vlaue of (p + r) VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
31 PRACTICE TEST- Single Choice Quesion :. If r, s and non zero roots of a + a + a = (a, a, a R and a ), then the equality a +a + a =a holds r s (A) for all values of, a (B) only when = (C) only when = r or = s (D) only when = r or = s, a. If y = (A) a a sin a tan where a (, ) (, ) then y a a cos (B) a (C) a (D) a equals. For,, the value of definite integral ln( tan tan ) d is equal to ln (A) on (sec ) (B) on (cosec ) (C) (D) ln sec Comprehension (Q.4 to Q.6) Consider f() = be a polynomial function and,,, are the roots of the equation f() =, where < < <. Let sum of two roots of the equation f() = vanishes. 4. The value of the epression is (A) 6 (B) 5 (C) (D) 6 5. d is (A) 8n (B) 6n (C) 6n 4 4 ( ) 4 ( ) 6 ( ) + ( ) + 6 ( ) + 6 ( ) 6 ( ) 6 ( ) + C + C + C (D) 8n 4 ( ) 6 ( ) + 6 ( ) + C d is (A) n (B) n (C) n (D) n VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
32 Comprehension (Q.7 to Q.9) c a, b, c are the sides of ABC satisfying log + log a log b = log. a Also the quadratic equation a( ) + b + c ( + ) = has two equal roots. 7. a, b, c are in (A) A.P. (B) G.P. (C) H.P. (D) None 8. Measure of angle C is (A) º (B) 45º (C) 6º (D) 9º 9. The value of (sin A + sin B + sin C) is equal to (A) 5/ (B) /5 (C) 8/ (D) Assertion & Reason :. Statement- : Only one straight line can be drawn passing through the origin, at equal distances from the points A(, ) and B(4, ) Statement- : Only one straight line can be drawn passing through two given points. (A) Statement- is true, Statement- is true and Statement- is correct eplanation for Statement- (B) Statement- is true, Statement- is true and Statement- is NOT correct eplanation for Statement (C) Statement- is true, Statement- is false (D) Statement- is false, Statement- is true.. Statement- : If the circles + y + 4y + 4 = and + y + 4 y + c = intersect such that the common chod is longest, then c = 4. Statement- : If two circles intersect, the common chord is longest if it is a diameter of the smaller circle. (A) Statement- is true, Statement- is true and Statement- is correct eplanation for Statement- (B) Statement- is true, Statement- is true and Statement- is NOT correct eplanation for Statement (C) Statement- is true, Statement- is false (D) Statement- is false, Statement- is true.. Consider two functions f() = sin and g() = f() Statement- : The function h() = f() is not differentiable in [, ] Statement- : f() is differentiable and g() is not differentiable in [, ] (A) Statement- is true, Statement- is true and Statement- is correct eplanation for Statement- (B) Statement- is true, Statement- is true and Statement- is NOT correct eplanation for Statement (C) Statement- is true, Statement- is false (D) Statement- is false, Statement- is true. One or more than one correct :. Let f() = sgn(are cot ) + tan [], where [] is the greatest integer function less than or equal to. Then which of the following alternatives is/are true? (A) f() is many one but not even function (B) f() is periodic function (C) f() is bounded function (D) Graph of f() remains above -ais d 4. Let I n = n (n =,,,... ) and Lim I n n = I (say), then which of the following statement(s) is/are correct? (Given : e =.788) (A) I > I (B) I < I (C) I + I + I > (D) I + I > VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
33 5. The possible radius of a circle whose centre is at the origin and which touches the circle + y 6 8y + =. (A) (B) (C) 5 (D) 7 Match the Column : 6. Column-I Column-II (A) The value of the definite integral 4 ( ) d equals (P) ln (B) If f() =, then f () = for equals (Q) (C) The cosine of the angle of intersection of curves f() = n and g() =, is (R) (D) If H is the number of horizontal tangents and V is the number of vertical (S) tangents to the curve y y + =, then the value of (H + V) equals (T) e Subjective : 7. If the variable line 4y + k = lies between the circles + y y + = and + y 6 y + 6 = without intersecting or touching either circle, then the range of k is (a, b) where a, b I. Find the value of (b a). n 4 r 8. Let (r )(r ) r n n 5n = + + A B C + f (n) D where f(n) is the ratio of two linear polynomials such that Find the value of (A + B + C + D). (A, B, C, D N) Lim f(n) = n n / 4 9. If ln(cot ) 9 ((sin ) (cos) 9 find the value of (a + b + c). ) b a ln a. (sin ) 8 d = c (where a, b, c are in their lowest form) then VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
34 PRACTICE TEST-4 Comprehension (Q. to Q.) Consider,f g and h be three real valued function defined on R. Let f() = sin + cosa, g() = cos + sin and h() = f () + g (). The length of a longest interval in which the function y = h() is increasing, is (A) /8 (B) /4 (C) /6 (D) /. General solution of the equation h() = 4, is (A) (4n + ) (B) (8n + ) 8 8 where n I (C) (n + ) 4 (D) (7n + ) 4. Number of point(s) where the graph of the two function, yh = f() and y = g() intersects in [, ], is (A) (B) (C) 4 (D) 5 Single Choice Question : 4. Let a line through origin is tangent to the curve y = The slope of the line is (A) (B) 8 (C) (D) 6 5. An ellipse has semi major ais of length and semi minor ais of length. The distance between its foci is (A) (B) (C) (D) 6. The domain of definition of f() = log ( ) ( 7 + 9) is (A) R (B) R {} (C) R {, } (D) R {} 7. A coin that comes up head with probability p > and tails with probability p > independently on each fdlip, is flipped eight times. Suppose the probability of three heads and five tails is equal to of 5 the probability of five heads and three tails. Let p = n m, where m and n are relative prime positive integers The value of (m + n) equals (A) 9 (B) (C) (D) 5 8. The value of the integral I = 4 sin( ) 4 sin( ) 4 sin( ) d is (A) / (B) (C) (D) 9. Let f, g and h are differentiable function such that g() = f() and h() = f() are both strictly increasing functions, then the function F() = f() (A) Strictly increasing R (B) Strictly decreasing R is (C) Strictly decreasing on, and strictly increasing on, (D) Strictly increasing on, and strictly decreasing on, VKR Classes, C-9-4, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
VKR Classes TIME BOUND TESTS 1-7 Target JEE ADVANCED For Class XI VKR Classes, C , Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
 VKR Classes TIME BOUND TESTS -7 Target JEE ADVANCED For Class XI VKR Classes, C-9-0, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No. 9890605 Single Choice Question : PRACTICE TEST-. The smallest integer greater than log +
VKR Classes TIME BOUND TESTS -7 Target JEE ADVANCED For Class XI VKR Classes, C-9-0, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No. 9890605 Single Choice Question : PRACTICE TEST-. The smallest integer greater than log +
(D) (A) Q.3 To which of the following circles, the line y x + 3 = 0 is normal at the point ? 2 (A) 2
 CIRCLE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. The line x y + = 0 is tangent to the circle at the point (, 5) and the centre of the circles lies on x y = 4. The radius of the circle is (A) 3 5 (B) 5 3 (C) 5 (D) 5
CIRCLE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. The line x y + = 0 is tangent to the circle at the point (, 5) and the centre of the circles lies on x y = 4. The radius of the circle is (A) 3 5 (B) 5 3 (C) 5 (D) 5
Q.2 A, B and C are points in the xy plane such that A(1, 2) ; B (5, 6) and AC = 3BC. Then. (C) 1 1 or
 STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. A variable rectangle PQRS has its sides parallel to fied directions. Q and S lie respectivel on the lines = a, = a and P lies on the ais. Then the locus of R
STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. A variable rectangle PQRS has its sides parallel to fied directions. Q and S lie respectivel on the lines = a, = a and P lies on the ais. Then the locus of R
QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE
 QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; 4x + y + 4 = 0 and x + αy + β = 0, where α + β =, are concurrent then α =,
QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; 4x + y + 4 = 0 and x + αy + β = 0, where α + β =, are concurrent then α =,
1 (C) 1 e. Q.3 The angle between the tangent lines to the graph of the function f (x) = ( 2t 5)dt at the points where (C) (A) 0 (B) 1/2 (C) 1 (D) 3
 [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. Point 'A' lies on the curve y e and has the coordinate (, ) where > 0. Point B has the coordinates (, 0). If 'O' is the origin then the maimum area of the triangle AOB is (A)
[STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. Point 'A' lies on the curve y e and has the coordinate (, ) where > 0. Point B has the coordinates (, 0). If 'O' is the origin then the maimum area of the triangle AOB is (A)
FILL THE ANSWER HERE
 HOM ASSIGNMNT # 0 STRAIGHT OBJCTIV TYP. If A, B & C are matrices of order such that A =, B = 9, C =, then (AC) is equal to - (A) 8 6. The length of the sub-tangent to the curve y = (A) 8 0 0 8 ( ) 5 5
HOM ASSIGNMNT # 0 STRAIGHT OBJCTIV TYP. If A, B & C are matrices of order such that A =, B = 9, C =, then (AC) is equal to - (A) 8 6. The length of the sub-tangent to the curve y = (A) 8 0 0 8 ( ) 5 5
TARGET : JEE 2013 SCORE. JEE (Advanced) Home Assignment # 03. Kota Chandigarh Ahmedabad
 TARGT : J 01 SCOR J (Advanced) Home Assignment # 0 Kota Chandigarh Ahmedabad J-Mathematics HOM ASSIGNMNT # 0 STRAIGHT OBJCTIV TYP 1. If x + y = 0 is a tangent at the vertex of a parabola and x + y 7 =
TARGT : J 01 SCOR J (Advanced) Home Assignment # 0 Kota Chandigarh Ahmedabad J-Mathematics HOM ASSIGNMNT # 0 STRAIGHT OBJCTIV TYP 1. If x + y = 0 is a tangent at the vertex of a parabola and x + y 7 =
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS SUBJECT : MATHEMATICS Duration : Two Hours Maximum Marks : 100. [ Q. 1 to 60 carry one mark each ] A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D.
![MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS SUBJECT : MATHEMATICS Duration : Two Hours Maximum Marks : 100. [ Q. 1 to 60 carry one mark each ] A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS SUBJECT : MATHEMATICS Duration : Two Hours Maximum Marks : 100. [ Q. 1 to 60 carry one mark each ] A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D.](/thumbs/95/125385791.jpg) M 68 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS SUBJECT : MATHEMATICS Duration : Two Hours Maimum Marks : [ Q. to 6 carry one mark each ]. If sin sin sin y z, then the value of 9 y 9 z 9 9 y 9 z 9 A. B. C. D. is equal
M 68 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS SUBJECT : MATHEMATICS Duration : Two Hours Maimum Marks : [ Q. to 6 carry one mark each ]. If sin sin sin y z, then the value of 9 y 9 z 9 9 y 9 z 9 A. B. C. D. is equal
Q.1 If a, b, c are distinct positive real in H.P., then the value of the expression, (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4. (A) 2 (B) 5/2 (C) 3 (D) none of these
 Q. If a, b, c are distinct positive real in H.P., then the value of the expression, b a b c + is equal to b a b c () (C) (D) 4 Q. In a triangle BC, (b + c) = a bc where is the circumradius of the triangle.
Q. If a, b, c are distinct positive real in H.P., then the value of the expression, b a b c + is equal to b a b c () (C) (D) 4 Q. In a triangle BC, (b + c) = a bc where is the circumradius of the triangle.
Objective Mathematics
 . A tangent to the ellipse is intersected by a b the tangents at the etremities of the major ais at 'P' and 'Q' circle on PQ as diameter always passes through : (a) one fied point two fied points (c) four
. A tangent to the ellipse is intersected by a b the tangents at the etremities of the major ais at 'P' and 'Q' circle on PQ as diameter always passes through : (a) one fied point two fied points (c) four
QUESTION BANK ON. CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola)
 QUESTION BANK ON CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola) Question bank on Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. Two mutually perpendicular tangents
QUESTION BANK ON CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola) Question bank on Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. Two mutually perpendicular tangents
I K J are two points on the graph given by y = 2 sin x + cos 2x. Prove that there exists
 LEVEL I. A circular metal plate epands under heating so that its radius increase by %. Find the approimate increase in the area of the plate, if the radius of the plate before heating is 0cm.. The length
LEVEL I. A circular metal plate epands under heating so that its radius increase by %. Find the approimate increase in the area of the plate, if the radius of the plate before heating is 0cm.. The length
PREPARED BY: ER. VINEET LOOMBA (B.TECH. IIT ROORKEE) 60 Best JEE Main and Advanced Level Problems (IIT-JEE). Prepared by IITians.
 www. Class XI TARGET : JEE Main/Adv PREPARED BY: ER. VINEET LOOMBA (B.TECH. IIT ROORKEE) ALP ADVANCED LEVEL PROBLEMS Straight Lines 60 Best JEE Main and Advanced Level Problems (IIT-JEE). Prepared b IITians.
www. Class XI TARGET : JEE Main/Adv PREPARED BY: ER. VINEET LOOMBA (B.TECH. IIT ROORKEE) ALP ADVANCED LEVEL PROBLEMS Straight Lines 60 Best JEE Main and Advanced Level Problems (IIT-JEE). Prepared b IITians.
HEAT-3 APPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES BY ABHIJIT KUMAR JHA MAX-MARKS-(112(3)+20(5)=436)
 HEAT- APPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES BY ABHIJIT KUMAR JHA TIME-(HRS) Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) MAX-MARKS-(()+0(5)=6) Q. Suppose & are the point of maimum and the point of minimum
HEAT- APPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES BY ABHIJIT KUMAR JHA TIME-(HRS) Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) MAX-MARKS-(()+0(5)=6) Q. Suppose & are the point of maimum and the point of minimum
= 0 1 (3 4 ) 1 (4 4) + 1 (4 3) = = + 1 = 0 = 1 = ± 1 ]
![= 0 1 (3 4 ) 1 (4 4) + 1 (4 3) = = + 1 = 0 = 1 = ± 1 ] = 0 1 (3 4 ) 1 (4 4) + 1 (4 3) = = + 1 = 0 = 1 = ± 1 ]](/thumbs/74/71228184.jpg) STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; x + y + = 0 and x + y + = 0, where + =, are concurrent then (A) =, = (B) =, = ± (C) =, = ± (D*) = ±, = [Sol. Lines are x + y + = 0
STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; x + y + = 0 and x + y + = 0, where + =, are concurrent then (A) =, = (B) =, = ± (C) =, = ± (D*) = ±, = [Sol. Lines are x + y + = 0
l (D) 36 (C) 9 x + a sin at which the tangent is parallel to x-axis lie on
 Dpp- to MATHEMATICS Dail Practice Problems Target IIT JEE 00 CLASS : XIII (VXYZ) DPP. NO.- to DPP- Q. If on a given base, a triangle be described such that the sum of the tangents of the base angles is
Dpp- to MATHEMATICS Dail Practice Problems Target IIT JEE 00 CLASS : XIII (VXYZ) DPP. NO.- to DPP- Q. If on a given base, a triangle be described such that the sum of the tangents of the base angles is
So, eqn. to the bisector containing (-1, 4) is = x + 27y = 0
 Q.No. The bisector of the acute angle between the lines x - 4y + 7 = 0 and x + 5y - = 0, is: Option x + y - 9 = 0 Option x + 77y - 0 = 0 Option x - y + 9 = 0 Correct Answer L : x - 4y + 7 = 0 L :-x- 5y
Q.No. The bisector of the acute angle between the lines x - 4y + 7 = 0 and x + 5y - = 0, is: Option x + y - 9 = 0 Option x + 77y - 0 = 0 Option x - y + 9 = 0 Correct Answer L : x - 4y + 7 = 0 L :-x- 5y
WBJEEM Answer Keys by Aakash Institute, Kolkata Centre MATHEMATICS
 WBJEEM - 05 Answer Keys by, Kolkata Centre MATHEMATICS Q.No. μ β γ δ 0 B A A D 0 B A C A 0 B C A * 04 C B B C 05 D D B A 06 A A B C 07 A * C A 08 D C D A 09 C C A * 0 C B D D B C A A D A A B A C A B 4
WBJEEM - 05 Answer Keys by, Kolkata Centre MATHEMATICS Q.No. μ β γ δ 0 B A A D 0 B A C A 0 B C A * 04 C B B C 05 D D B A 06 A A B C 07 A * C A 08 D C D A 09 C C A * 0 C B D D B C A A D A A B A C A B 4
1 is equal to. 1 (B) a. (C) a (B) (D) 4. (C) P lies inside both C & E (D) P lies inside C but outside E. (B) 1 (D) 1
 Single Correct Q. Two mutuall perpendicular tangents of the parabola = a meet the ais in P and P. If S is the focus of the parabola then l a (SP ) is equal to (SP ) l (B) a (C) a Q. ABCD and EFGC are squares
Single Correct Q. Two mutuall perpendicular tangents of the parabola = a meet the ais in P and P. If S is the focus of the parabola then l a (SP ) is equal to (SP ) l (B) a (C) a Q. ABCD and EFGC are squares
DEEPAWALI ASSIGNMENT CLASS 11 FOR TARGET IIT JEE 2012 SOLUTION
 DEEPAWALI ASSIGNMENT CLASS FOR TARGET IIT JEE 0 SOLUTION IMAGE OF SHRI GANESH LAXMI SARASWATI Director & H.O.D. IITJEE Mathematics SUHAG R. KARIYA (S.R.K. Sir) DOWNLOAD FREE STUDY PACKAGE, TEST SERIES
DEEPAWALI ASSIGNMENT CLASS FOR TARGET IIT JEE 0 SOLUTION IMAGE OF SHRI GANESH LAXMI SARASWATI Director & H.O.D. IITJEE Mathematics SUHAG R. KARIYA (S.R.K. Sir) DOWNLOAD FREE STUDY PACKAGE, TEST SERIES
POINT. Preface. The concept of Point is very important for the study of coordinate
 POINT Preface The concept of Point is ver important for the stud of coordinate geometr. This chapter deals with various forms of representing a Point and several associated properties. The concept of coordinates
POINT Preface The concept of Point is ver important for the stud of coordinate geometr. This chapter deals with various forms of representing a Point and several associated properties. The concept of coordinates
MATHEMATICS. r Statement I Statement II p q ~p ~q ~p q q p ~(p ~q) F F T T F F T F T T F T T F T F F T T T F T T F F F T T
 MATHEMATICS Directions : Questions number to 5 are Assertion-Reason type questions. Each of these questions contains two statements : Statement- (Assertion) and Statement- (Reason). Each of these questions
MATHEMATICS Directions : Questions number to 5 are Assertion-Reason type questions. Each of these questions contains two statements : Statement- (Assertion) and Statement- (Reason). Each of these questions
Objective Mathematics
 . In BC, if angles, B, C are in geometric seq- uence with common ratio, then is : b c a (a) (c) 0 (d) 6. If the angles of a triangle are in the ratio 4 : :, then the ratio of the longest side to the perimeter
. In BC, if angles, B, C are in geometric seq- uence with common ratio, then is : b c a (a) (c) 0 (d) 6. If the angles of a triangle are in the ratio 4 : :, then the ratio of the longest side to the perimeter
2016 SEC 4 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS CW & HW
 FEB EXAM 06 SEC 4 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS CW & HW Find the values of k for which the line y 6 is a tangent to the curve k 7 y. Find also the coordinates of the point at which this tangent touches the curve.
FEB EXAM 06 SEC 4 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS CW & HW Find the values of k for which the line y 6 is a tangent to the curve k 7 y. Find also the coordinates of the point at which this tangent touches the curve.
IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR INTERMEDIATE PUBLIC EXAMINATIONS IN MATHS-IB
 ` KUKATPALLY CENTRE IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR INTERMEDIATE PUBLIC EXAMINATIONS IN MATHS-IB 017-18 FIITJEE KUKATPALLY CENTRE: # -97, Plot No1, Opp Patel Kunta Huda Park, Vijaynagar Colony, Hyderabad - 500
` KUKATPALLY CENTRE IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR INTERMEDIATE PUBLIC EXAMINATIONS IN MATHS-IB 017-18 FIITJEE KUKATPALLY CENTRE: # -97, Plot No1, Opp Patel Kunta Huda Park, Vijaynagar Colony, Hyderabad - 500
MockTime.com. NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1.
 346 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. Let A = { 1, 2, 5, 8}, B = {0, 1, 3, 6, 7} and R be the relation is one less than from A to B, then how many elements will R contain? 2 3 5 9 7. 1 only 2 only 1 and
346 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. Let A = { 1, 2, 5, 8}, B = {0, 1, 3, 6, 7} and R be the relation is one less than from A to B, then how many elements will R contain? 2 3 5 9 7. 1 only 2 only 1 and
JEE-ADVANCED MATHEMATICS. Paper-1. SECTION 1: (One or More Options Correct Type)
 JEE-ADVANCED MATHEMATICS Paper- SECTION : (One or More Options Correct Type) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONE OR
JEE-ADVANCED MATHEMATICS Paper- SECTION : (One or More Options Correct Type) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONE OR
Time : 3 hours 02 - Mathematics - July 2006 Marks : 100 Pg - 1 Instructions : S E CT I O N - A
 Time : 3 hours 0 Mathematics July 006 Marks : 00 Pg Instructions :. Answer all questions.. Write your answers according to the instructions given below with the questions. 3. Begin each section on a new
Time : 3 hours 0 Mathematics July 006 Marks : 00 Pg Instructions :. Answer all questions.. Write your answers according to the instructions given below with the questions. 3. Begin each section on a new
Chapter (Circle) * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in
 Chapter - 10 (Circle) Key Concept * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in a plane. * Concentric circle - Circle having same centre called concentric circle.
Chapter - 10 (Circle) Key Concept * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in a plane. * Concentric circle - Circle having same centre called concentric circle.
MockTime.com. (a) 36 (b) 33 (c) 20 (d) 6
 185 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. Which of the following statements is not correct for the relation R defined by arb if and only if b lives within one kilometer from a? R is reflexive R is symmetric
185 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. Which of the following statements is not correct for the relation R defined by arb if and only if b lives within one kilometer from a? R is reflexive R is symmetric
( 1 ) Show that P ( a, b + c ), Q ( b, c + a ) and R ( c, a + b ) are collinear.
 Problems 01 - POINT Page 1 ( 1 ) Show that P ( a, b + c ), Q ( b, c + a ) and R ( c, a + b ) are collinear. ( ) Prove that the two lines joining the mid-points of the pairs of opposite sides and the line
Problems 01 - POINT Page 1 ( 1 ) Show that P ( a, b + c ), Q ( b, c + a ) and R ( c, a + b ) are collinear. ( ) Prove that the two lines joining the mid-points of the pairs of opposite sides and the line
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 MCN COMPLEX NUMBER C The complex number Complex number is denoted by ie = a + ib, where a is called as real part of (denoted by Re and b is called as imaginary part of (denoted by Im Here i =, also i =,
MCN COMPLEX NUMBER C The complex number Complex number is denoted by ie = a + ib, where a is called as real part of (denoted by Re and b is called as imaginary part of (denoted by Im Here i =, also i =,
63487 [Q. Booklet Number]
![63487 [Q. Booklet Number] 63487 [Q. Booklet Number]](/thumbs/88/114675139.jpg) WBJEE - 0 (Answers & Hints) 687 [Q. Booklet Number] Regd. Office : Aakash Tower, Plot No., Sector-, Dwarka, New Delhi-0075 Ph. : 0-7656 Fa : 0-767 ANSWERS & HINTS for WBJEE - 0 by & Aakash IIT-JEE MULTIPLE
WBJEE - 0 (Answers & Hints) 687 [Q. Booklet Number] Regd. Office : Aakash Tower, Plot No., Sector-, Dwarka, New Delhi-0075 Ph. : 0-7656 Fa : 0-767 ANSWERS & HINTS for WBJEE - 0 by & Aakash IIT-JEE MULTIPLE
MockTime.com. (b) 9/2 (c) 18 (d) 27
 212 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. Let X be any non-empty set containing n elements. Then what is the number of relations on X? 2 n 2 2n 2 2n n 2 2. Only 1 2 and 3 1 and 2 1 and 3 3. Consider the following
212 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. Let X be any non-empty set containing n elements. Then what is the number of relations on X? 2 n 2 2n 2 2n n 2 2. Only 1 2 and 3 1 and 2 1 and 3 3. Consider the following
MATH TOURNAMENT 2012 PROBLEMS SOLUTIONS
 MATH TOURNAMENT 0 PROBLEMS SOLUTIONS. Consider the eperiment of throwing two 6 sided fair dice, where, the faces are numbered from to 6. What is the probability of the event that the sum of the values
MATH TOURNAMENT 0 PROBLEMS SOLUTIONS. Consider the eperiment of throwing two 6 sided fair dice, where, the faces are numbered from to 6. What is the probability of the event that the sum of the values
Topic 2 [312 marks] The rectangle ABCD is inscribed in a circle. Sides [AD] and [AB] have lengths
![Topic 2 [312 marks] The rectangle ABCD is inscribed in a circle. Sides [AD] and [AB] have lengths Topic 2 [312 marks] The rectangle ABCD is inscribed in a circle. Sides [AD] and [AB] have lengths](/thumbs/86/93150791.jpg) Topic 2 [312 marks] 1 The rectangle ABCD is inscribed in a circle Sides [AD] and [AB] have lengths [12 marks] 3 cm and (\9\) cm respectively E is a point on side [AB] such that AE is 3 cm Side [DE] is
Topic 2 [312 marks] 1 The rectangle ABCD is inscribed in a circle Sides [AD] and [AB] have lengths [12 marks] 3 cm and (\9\) cm respectively E is a point on side [AB] such that AE is 3 cm Side [DE] is
 oo ks. co m w w w.s ur ab For Order : orders@surabooks.com Ph: 960075757 / 84000 http://www.trbtnpsc.com/07/08/th-eam-model-question-papers-download.html Model Question Papers Based on Scheme of Eamination
oo ks. co m w w w.s ur ab For Order : orders@surabooks.com Ph: 960075757 / 84000 http://www.trbtnpsc.com/07/08/th-eam-model-question-papers-download.html Model Question Papers Based on Scheme of Eamination
FIITJEE SOLUTION TO AIEEE-2005 MATHEMATICS
 FIITJEE SOLUTION TO AIEEE-5 MATHEMATICS. If A A + I =, then the inverse of A is () A + I () A () A I () I A. () Given A A + I = A A A A + A I = A (Multiplying A on both sides) A - I + A - = or A = I A..
FIITJEE SOLUTION TO AIEEE-5 MATHEMATICS. If A A + I =, then the inverse of A is () A + I () A () A I () I A. () Given A A + I = A A A A + A I = A (Multiplying A on both sides) A - I + A - = or A = I A..
(c) n (d) n 2. (a) (b) (c) (d) (a) Null set (b) {P} (c) {P, Q, R} (d) {Q, R} (a) 2k (b) 7 (c) 2 (d) K (a) 1 (b) 3 (c) 3xyz (d) 27xyz
 318 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. (1001)2 (101)2 (110)2 (100)2 2. z 1/z 2z z/2 3. The multiplication of the number (10101)2 by (1101)2 yields which one of the following? (100011001)2 (100010001)2 (110010011)2
318 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. (1001)2 (101)2 (110)2 (100)2 2. z 1/z 2z z/2 3. The multiplication of the number (10101)2 by (1101)2 yields which one of the following? (100011001)2 (100010001)2 (110010011)2
Mathematics. Single Correct Questions
 Mathematics Single Correct Questions +4 1.00 1. If and then 2. The number of solutions of, in the interval is : 3. If then equals : 4. A plane bisects the line segment joining the points and at right angles.
Mathematics Single Correct Questions +4 1.00 1. If and then 2. The number of solutions of, in the interval is : 3. If then equals : 4. A plane bisects the line segment joining the points and at right angles.
1. SETS AND FUNCTIONS
 . SETS AND FUNCTIONS. For two sets A and B, A, B A if and only if B A A B A! B A + B z. If A B, then A + B is B A\ B A B\ A. For any two sets Pand Q, P + Q is " x : x! P or x! Q, " x : x! P and x b Q,
. SETS AND FUNCTIONS. For two sets A and B, A, B A if and only if B A A B A! B A + B z. If A B, then A + B is B A\ B A B\ A. For any two sets Pand Q, P + Q is " x : x! P or x! Q, " x : x! P and x b Q,
DISCUSSION CLASS OF DAX IS ON 22ND MARCH, TIME : 9-12 BRING ALL YOUR DOUBTS [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE]
![DISCUSSION CLASS OF DAX IS ON 22ND MARCH, TIME : 9-12 BRING ALL YOUR DOUBTS [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] DISCUSSION CLASS OF DAX IS ON 22ND MARCH, TIME : 9-12 BRING ALL YOUR DOUBTS [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE]](/thumbs/90/102188445.jpg) DISCUSSION CLASS OF DAX IS ON ND MARCH, TIME : 9- BRING ALL YOUR DOUBTS [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. Let y = cos x (cos x cos x). Then y is (A) 0 only when x 0 (B) 0 for all real x (C) 0 for all real x
DISCUSSION CLASS OF DAX IS ON ND MARCH, TIME : 9- BRING ALL YOUR DOUBTS [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. Let y = cos x (cos x cos x). Then y is (A) 0 only when x 0 (B) 0 for all real x (C) 0 for all real x
MATHEMATICS. metres (D) metres (C)
 MATHEMATICS. If is the root of the equation + k = 0, then what is the value of k? 9. Two striaght lines y = 0 and 6y 6 = 0 never intersect intersect at a single point intersect at infinite number of points
MATHEMATICS. If is the root of the equation + k = 0, then what is the value of k? 9. Two striaght lines y = 0 and 6y 6 = 0 never intersect intersect at a single point intersect at infinite number of points
1. Let g(x) and h(x) be polynomials with real coefficients such that
 1. Let g(x) and h(x) be polynomials with real coefficients such that g(x)(x 2 3x + 2) = h(x)(x 2 + 3x + 2) and f(x) = g(x)h(x) + (x 4 5x 2 + 4). Prove that f(x) has at least four real roots. 2. Let M be
1. Let g(x) and h(x) be polynomials with real coefficients such that g(x)(x 2 3x + 2) = h(x)(x 2 + 3x + 2) and f(x) = g(x)h(x) + (x 4 5x 2 + 4). Prove that f(x) has at least four real roots. 2. Let M be
Objective Mathematics
 Chapter No - ( Area Bounded by Curves ). Normal at (, ) is given by : y y. f ( ) or f ( ). Area d ()() 7 Square units. Area (8)() 6 dy. ( ) d y c or f ( ) c f () c f ( ) As shown in figure, point P is
Chapter No - ( Area Bounded by Curves ). Normal at (, ) is given by : y y. f ( ) or f ( ). Area d ()() 7 Square units. Area (8)() 6 dy. ( ) d y c or f ( ) c f () c f ( ) As shown in figure, point P is
CLASS XII MATHEMATICS. Weightage (Marks) (i) Relations and Functions 10. Type of Questions Weightage of Number of Total Marks each question questions
 CLASS XII MATHEMATICS Units Weightage (Marks) (i) Relations and Functions 0 (ii) Algebra (Matrices and Determinants) (iii) Calculus 44 (iv) Vector and Three dimensional Geometry 7 (v) Linear Programming
CLASS XII MATHEMATICS Units Weightage (Marks) (i) Relations and Functions 0 (ii) Algebra (Matrices and Determinants) (iii) Calculus 44 (iv) Vector and Three dimensional Geometry 7 (v) Linear Programming
FREE Download Study Package from website: &
 Q.4 Using LMVT prove that : (a) tan > in 0,, (b) sin < for > 0 Q.5 Prove that if f is differentiable on [a, b] and if f (a) = f (b) = 0 then for any real there is an (a, b) such that f () + f ' () = 0.
Q.4 Using LMVT prove that : (a) tan > in 0,, (b) sin < for > 0 Q.5 Prove that if f is differentiable on [a, b] and if f (a) = f (b) = 0 then for any real there is an (a, b) such that f () + f ' () = 0.
6 CHAPTER. Triangles. A plane figure bounded by three line segments is called a triangle.
 6 CHAPTER We are Starting from a Point but want to Make it a Circle of Infinite Radius A plane figure bounded by three line segments is called a triangle We denote a triangle by the symbol In fig ABC has
6 CHAPTER We are Starting from a Point but want to Make it a Circle of Infinite Radius A plane figure bounded by three line segments is called a triangle We denote a triangle by the symbol In fig ABC has
Math Bank - 6. What is the area of the triangle on the Argand diagram formed by the complex number z, -iz, z iz? (a) z 2 (b) 2 z 2
 Math Bank - 6 Q.) Suppose A represents the symbol, B represents the symbol 0, C represents the symbol, D represents the symbol 0 and so on. If we divide INDIA by AGRA, then which one of the following is
Math Bank - 6 Q.) Suppose A represents the symbol, B represents the symbol 0, C represents the symbol, D represents the symbol 0 and so on. If we divide INDIA by AGRA, then which one of the following is
1. Matrices and Determinants
 Important Questions 1. Matrices and Determinants Ex.1.1 (2) x 3x y Find the values of x, y, z if 2x + z 3y w = 0 7 3 2a Ex 1.1 (3) 2x 3x y If 2x + z 3y w = 3 2 find x, y, z, w 4 7 Ex 1.1 (13) 3 7 3 2 Find
Important Questions 1. Matrices and Determinants Ex.1.1 (2) x 3x y Find the values of x, y, z if 2x + z 3y w = 0 7 3 2a Ex 1.1 (3) 2x 3x y If 2x + z 3y w = 3 2 find x, y, z, w 4 7 Ex 1.1 (13) 3 7 3 2 Find
KEAM (ENGINEERING) ANSWER KEY 2018
 MTHEMTIS KEM KEY 08 PGE: M.O: Kunnumpuram, yurveda ollege Jn., Trivandrum-, (: 047-57040, 47040 E-mail: info@zephyrentrance.in, Website: www.zephyrentrance.in KOHI KOLLM RNHES Puthussery uilding, Kaloor
MTHEMTIS KEM KEY 08 PGE: M.O: Kunnumpuram, yurveda ollege Jn., Trivandrum-, (: 047-57040, 47040 E-mail: info@zephyrentrance.in, Website: www.zephyrentrance.in KOHI KOLLM RNHES Puthussery uilding, Kaloor
(iii) For each question in Section III, you will be awarded 4 Marks if you darken only the bubble corresponding to the
 FIITJEE Solutions to IIT - JEE 8 (Paper, Code 4) Time: hours M. Marks: 4 Note: (i) The question paper consists of parts (Part I : Mathematics, Part II : Physics, Part III : Chemistry). Each part has 4
FIITJEE Solutions to IIT - JEE 8 (Paper, Code 4) Time: hours M. Marks: 4 Note: (i) The question paper consists of parts (Part I : Mathematics, Part II : Physics, Part III : Chemistry). Each part has 4
MockTime.com. (b) (c) (d)
 373 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. If A, B and C are any three arbitrary events then which one of the following expressions shows that both A and B occur but not C? 2. Which one of the following is an
373 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. If A, B and C are any three arbitrary events then which one of the following expressions shows that both A and B occur but not C? 2. Which one of the following is an
LLT Education Services
 8. The length of a tangent from a point A at distance 5 cm from the centre of the circle is 4 cm. Find the radius of the circle. (a) 4 cm (b) 3 cm (c) 6 cm (d) 5 cm 9. From a point P, 10 cm away from the
8. The length of a tangent from a point A at distance 5 cm from the centre of the circle is 4 cm. Find the radius of the circle. (a) 4 cm (b) 3 cm (c) 6 cm (d) 5 cm 9. From a point P, 10 cm away from the
02. If (x, y) is equidistant from (a + b, b a) and (a b, a + b), then (A) x + y = 0 (B) bx ay = 0 (C) ax by = 0 (D) bx + ay = 0 (E) ax + by =
 0. π/ sin d 0 sin + cos (A) 0 (B) π (C) 3 π / (D) π / (E) π /4 0. If (, y) is equidistant from (a + b, b a) and (a b, a + b), then (A) + y = 0 (B) b ay = 0 (C) a by = 0 (D) b + ay = 0 (E) a + by = 0 03.
0. π/ sin d 0 sin + cos (A) 0 (B) π (C) 3 π / (D) π / (E) π /4 0. If (, y) is equidistant from (a + b, b a) and (a b, a + b), then (A) + y = 0 (B) b ay = 0 (C) a by = 0 (D) b + ay = 0 (E) a + by = 0 03.
CHMMC 2015 Individual Round Problems
 CHMMC 05 Individual Round Problems November, 05 Problem 0.. The following number is the product of the divisors of n. What is n? 6 3 3 Solution.. In general, the product of the divisors of n is n # of
CHMMC 05 Individual Round Problems November, 05 Problem 0.. The following number is the product of the divisors of n. What is n? 6 3 3 Solution.. In general, the product of the divisors of n is n # of
CHAPTER-1. SETS. Q.4 Write down the proper subsets of { a, b, Q.5 Write down the power set of { 5,6,7 }? Verify the following result :
 CHAPTER-. SETS Q. Write the following sets in roster form (i) A = { : is an integer and 5 5 } (ii) B = { : is a natural number and < < 4} (iii) C= { : is a two- digit natural number such that sum of digit
CHAPTER-. SETS Q. Write the following sets in roster form (i) A = { : is an integer and 5 5 } (ii) B = { : is a natural number and < < 4} (iii) C= { : is a two- digit natural number such that sum of digit
IIT JEE Maths Paper 2
 IIT JEE - 009 Maths Paper A. Question paper format: 1. The question paper consists of 4 sections.. Section I contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has 4 choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) for
IIT JEE - 009 Maths Paper A. Question paper format: 1. The question paper consists of 4 sections.. Section I contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has 4 choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) for
Lesson-3 TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS AND IDENTITIES
 Lesson- TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS AND IDENTITIES Angle in trigonometry In trigonometry, the measure of an angle is the amount of rotation from B the direction of one ray of the angle to the other ray. Angle
Lesson- TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS AND IDENTITIES Angle in trigonometry In trigonometry, the measure of an angle is the amount of rotation from B the direction of one ray of the angle to the other ray. Angle
PAPER ¼isij½- 1. SECTION-1 (Maximum Marks : 24)
 JEE (Advanced) (ADVANCED) 06 08 PAPER ¼isij½- -05-06 DATE: 0-05-08 This question paper has three (0) parts: PART-I: Physics, PART-II: Chemistry and PART-III: Mathematics. Each part has total of eighteen
JEE (Advanced) (ADVANCED) 06 08 PAPER ¼isij½- -05-06 DATE: 0-05-08 This question paper has three (0) parts: PART-I: Physics, PART-II: Chemistry and PART-III: Mathematics. Each part has total of eighteen
1 / 23
 CBSE-XII-017 EXAMINATION CBSE-X-008 EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Series: RLH/ Paper & Solution Code: 30//1 Time: 3 Hrs. Max. Marks: 80 General Instuctions : (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question
CBSE-XII-017 EXAMINATION CBSE-X-008 EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Series: RLH/ Paper & Solution Code: 30//1 Time: 3 Hrs. Max. Marks: 80 General Instuctions : (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question
Practice Set for IIT JEE. Paper I
 Objective Questions I [Only one correct option] Practice Set for IIT JEE Paper I Q 1. The number of lines in the xy-plane, Whose distance from (-1, 2) is 2 and from (2, 6) is 3, is a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. None
Objective Questions I [Only one correct option] Practice Set for IIT JEE Paper I Q 1. The number of lines in the xy-plane, Whose distance from (-1, 2) is 2 and from (2, 6) is 3, is a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. None
SURA's Guides for 3rd to 12th Std for all Subjects in TM & EM Available. MARCH Public Exam Question Paper with Answers MATHEMATICS
 SURA's Guides for rd to 1th Std for all Subjects in TM & EM Available 10 th STD. MARCH - 017 Public Exam Question Paper with Answers MATHEMATICS [Time Allowed : ½ Hrs.] [Maximum Marks : 100] SECTION -
SURA's Guides for rd to 1th Std for all Subjects in TM & EM Available 10 th STD. MARCH - 017 Public Exam Question Paper with Answers MATHEMATICS [Time Allowed : ½ Hrs.] [Maximum Marks : 100] SECTION -
Math 2414 Activity 1 (Due by end of class Jan. 26) Precalculus Problems: 3,0 and are tangent to the parabola axis. Find the other line.
 Math Activity (Due by end of class Jan. 6) Precalculus Problems: 3, and are tangent to the parabola ais. Find the other line.. One of the two lines that pass through y is the - {Hint: For a line through
Math Activity (Due by end of class Jan. 6) Precalculus Problems: 3, and are tangent to the parabola ais. Find the other line.. One of the two lines that pass through y is the - {Hint: For a line through
CAREER POINT PRE FOUNDATION DIVISON CLASS-9. IMO Stage-II Exam MATHEMATICS Date :
 CAREER POINT PRE FOUNDATION DIVISON IMO Stage-II Exam.-07 CLASS-9 MATHEMATICS Date : -0-07 Q. In the given figure, PQR is a right angled triangle, right angled at Q. If QRST is a square on side QR and
CAREER POINT PRE FOUNDATION DIVISON IMO Stage-II Exam.-07 CLASS-9 MATHEMATICS Date : -0-07 Q. In the given figure, PQR is a right angled triangle, right angled at Q. If QRST is a square on side QR and
[STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q.4 The expression cot 9 + cot 27 + cot 63 + cot 81 is equal to (A) 16 (B) 64 (C) 80 (D) none of these
![[STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q.4 The expression cot 9 + cot 27 + cot 63 + cot 81 is equal to (A) 16 (B) 64 (C) 80 (D) none of these [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q.4 The expression cot 9 + cot 27 + cot 63 + cot 81 is equal to (A) 16 (B) 64 (C) 80 (D) none of these](/thumbs/84/89289186.jpg) Q. Given a + a + cosec [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] F HG ( a x) I K J = 0 then, which of the following holds good? (A) a = ; x I a = ; x I a R ; x a, x are finite but not possible to find Q. The minimum value
Q. Given a + a + cosec [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] F HG ( a x) I K J = 0 then, which of the following holds good? (A) a = ; x I a = ; x I a R ; x a, x are finite but not possible to find Q. The minimum value
11 th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Questions, Answers, and Hints
 view.php3 (JPEG Image, 840x888 pixels) - Scaled (71%) https://mail.ateneo.net/horde/imp/view.php3?mailbox=inbox&inde... 1 of 1 11/5/2008 5:02 PM 11 th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Questions, Answers,
view.php3 (JPEG Image, 840x888 pixels) - Scaled (71%) https://mail.ateneo.net/horde/imp/view.php3?mailbox=inbox&inde... 1 of 1 11/5/2008 5:02 PM 11 th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Questions, Answers,
Part (1) Second : Trigonometry. Tan
 Part (1) Second : Trigonometry (1) Complete the following table : The angle Ratio 42 12 \ Sin 0.3214 Cas 0.5321 Tan 2.0625 (2) Complete the following : 1) 46 36 \ 24 \\ =. In degrees. 2) 44.125 = in degrees,
Part (1) Second : Trigonometry (1) Complete the following table : The angle Ratio 42 12 \ Sin 0.3214 Cas 0.5321 Tan 2.0625 (2) Complete the following : 1) 46 36 \ 24 \\ =. In degrees. 2) 44.125 = in degrees,
CDS-I 2019 Elementary Mathematics (Set-C)
 1 CDS-I 019 Elementary Mathematics (Set-C) Direction: Consider the following for the next three (03) items : A cube is inscribed in a sphere. A right circular cylinder is within the cube touching all the
1 CDS-I 019 Elementary Mathematics (Set-C) Direction: Consider the following for the next three (03) items : A cube is inscribed in a sphere. A right circular cylinder is within the cube touching all the
3. Total number of functions from the set A to set B is n. 4. Total number of one-one functions from the set A to set B is n Pm
 ASSIGNMENT CLASS XII RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS Important Formulas If A and B are finite sets containing m and n elements, then Total number of relations from the set A to set B is mn Total number of relations
ASSIGNMENT CLASS XII RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS Important Formulas If A and B are finite sets containing m and n elements, then Total number of relations from the set A to set B is mn Total number of relations
Secondary School Mathematics & Science Competition. Mathematics. Date: 1 st May, 2013
 Secondary School Mathematics & Science Competition Mathematics Date: 1 st May, 01 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes 1. Write your Name (both in English and Chinese), Name of School, Form, Date, Se, Language,
Secondary School Mathematics & Science Competition Mathematics Date: 1 st May, 01 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes 1. Write your Name (both in English and Chinese), Name of School, Form, Date, Se, Language,
PRMO _ (SOLUTIONS) [ 1 ]
![PRMO _ (SOLUTIONS) [ 1 ] PRMO _ (SOLUTIONS) [ 1 ]](/thumbs/91/105094923.jpg) PRMO 07-8_0-08-07 (SOLUTIONS) [ ] PRMO 07-8 : QUESTIONS & SOLUTIONS. How many positive integers less than 000 have the property that the sum of the digits of each such number is divisible by 7 and the
PRMO 07-8_0-08-07 (SOLUTIONS) [ ] PRMO 07-8 : QUESTIONS & SOLUTIONS. How many positive integers less than 000 have the property that the sum of the digits of each such number is divisible by 7 and the
Question 1 ( 1.0 marks) places of decimals? Solution: Now, on dividing by 2, we obtain =
 Question 1 ( 1.0 marks) The decimal expansion of the rational number places of decimals? will terminate after how many The given expression i.e., can be rewritten as Now, on dividing 0.043 by 2, we obtain
Question 1 ( 1.0 marks) The decimal expansion of the rational number places of decimals? will terminate after how many The given expression i.e., can be rewritten as Now, on dividing 0.043 by 2, we obtain
1 / 23
 CBSE-XII-07 EXAMINATION CBSE-X-009 EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Series: HRL Paper & Solution Code: 0/ Time: Hrs. Max. Marks: 80 General Instuctions : (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper
CBSE-XII-07 EXAMINATION CBSE-X-009 EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Series: HRL Paper & Solution Code: 0/ Time: Hrs. Max. Marks: 80 General Instuctions : (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper
COORDINATE GEOMETRY BASIC CONCEPTS AND FORMULAE. To find the length of a line segment joining two points A(x 1, y 1 ) and B(x 2, y 2 ), use
 COORDINATE GEOMETRY BASIC CONCEPTS AND FORMULAE I. Length of a Line Segment: The distance between two points A ( x1, 1 ) B ( x, ) is given b A B = ( x x1) ( 1) To find the length of a line segment joining
COORDINATE GEOMETRY BASIC CONCEPTS AND FORMULAE I. Length of a Line Segment: The distance between two points A ( x1, 1 ) B ( x, ) is given b A B = ( x x1) ( 1) To find the length of a line segment joining
EXERCISE - 01 CHECK YOUR GRASP
 J-Mathematics XRCIS - 0 CHCK YOUR GRASP SLCT TH CORRCT ALTRNATIV (ONLY ON CORRCT ANSWR). If ABCDF is a regular hexagon and if AB AC AD A AF AD, then is - (A) 0 (B) (C) (D). If a b is along the angle bisector
J-Mathematics XRCIS - 0 CHCK YOUR GRASP SLCT TH CORRCT ALTRNATIV (ONLY ON CORRCT ANSWR). If ABCDF is a regular hexagon and if AB AC AD A AF AD, then is - (A) 0 (B) (C) (D). If a b is along the angle bisector
e x for x 0. Find the coordinates of the point of inflexion and justify that it is a point of inflexion. (Total 7 marks)
 Chapter 0 Application of differential calculus 014 GDC required 1. Consider the curve with equation f () = e for 0. Find the coordinates of the point of infleion and justify that it is a point of infleion.
Chapter 0 Application of differential calculus 014 GDC required 1. Consider the curve with equation f () = e for 0. Find the coordinates of the point of infleion and justify that it is a point of infleion.
y mx 25m 25 4 circle. Then the perpendicular distance of tangent from the centre (0, 0) is the radius. Since tangent
 Mathematics. The sides AB, BC and CA of ABC have, 4 and 5 interior points respectively on them as shown in the figure. The number of triangles that can be formed using these interior points is () 80 ()
Mathematics. The sides AB, BC and CA of ABC have, 4 and 5 interior points respectively on them as shown in the figure. The number of triangles that can be formed using these interior points is () 80 ()
TARGET QUARTERLY MATHS MATERIAL
 Adyar Adambakkam Pallavaram Pammal Chromepet Now also at SELAIYUR TARGET QUARTERLY MATHS MATERIAL Achievement through HARDWORK Improvement through INNOVATION Target Centum Practising Package +2 GENERAL
Adyar Adambakkam Pallavaram Pammal Chromepet Now also at SELAIYUR TARGET QUARTERLY MATHS MATERIAL Achievement through HARDWORK Improvement through INNOVATION Target Centum Practising Package +2 GENERAL
2. In ABC, the measure of angle B is twice the measure of angle A. Angle C measures three times the measure of angle A. If AC = 26, find AB.
 2009 FGCU Mathematics Competition. Geometry Individual Test 1. You want to prove that the perpendicular bisector of the base of an isosceles triangle is also the angle bisector of the vertex. Which postulate/theorem
2009 FGCU Mathematics Competition. Geometry Individual Test 1. You want to prove that the perpendicular bisector of the base of an isosceles triangle is also the angle bisector of the vertex. Which postulate/theorem
DIRECTORATE OF EDUCATION GOVT. OF NCT OF DELHI
 456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890 456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890 QUESTION BANK 456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890
456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890 456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890 QUESTION BANK 456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD SCHEME OF VALUATION. Subject : MATHEMATICS Subject Code : 35
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH APRIL 0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject : MATHEMATICS Subject Code : 5 PART A Write the prime
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH APRIL 0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject : MATHEMATICS Subject Code : 5 PART A Write the prime
Prerna Tower, Road No 2, Contractors Area, Bistupur, Jamshedpur , Tel (0657) , PART III MATHEMATICS
 R Prerna Tower, Road No, Contractors Area, Bistupur, Jamshedpur 8300, Tel (0657)89, www.prernaclasses.com Jee Advance 03 Mathematics Paper I PART III MATHEMATICS SECTION : (Only One Option Correct Type)
R Prerna Tower, Road No, Contractors Area, Bistupur, Jamshedpur 8300, Tel (0657)89, www.prernaclasses.com Jee Advance 03 Mathematics Paper I PART III MATHEMATICS SECTION : (Only One Option Correct Type)
KEAM (ENGINEERING) ANSWER KEY 2017
 MTHMTICS KM KY 07 PG: KM (NGINRING) KY 07 PPR II MTHMTICS QUSTIONS & S. p q r p q r + is equal to () q p () q + p (C) q () p () 0 5 0. Let = 0 5 5 () 0 and () 0 = 0. If + 5 C = 0, then C is 0 5 5 5 5 0
MTHMTICS KM KY 07 PG: KM (NGINRING) KY 07 PPR II MTHMTICS QUSTIONS & S. p q r p q r + is equal to () q p () q + p (C) q () p () 0 5 0. Let = 0 5 5 () 0 and () 0 = 0. If + 5 C = 0, then C is 0 5 5 5 5 0
WBJEE Answer Keys by Aakash Institute, Kolkata Centre
 WBJEE - 08 Answer Keys by, Kolkata Centre MATHEMATICS Q.No. 0 A B C D 0 C D A B 0 B D A C 04 C B A B 05 C A C C 06 A C D C 07 B A C C 08 B *C,D C A 09 C D D B 0 D A C D B A B C C D A B B A A C 4 C C B
WBJEE - 08 Answer Keys by, Kolkata Centre MATHEMATICS Q.No. 0 A B C D 0 C D A B 0 B D A C 04 C B A B 05 C A C C 06 A C D C 07 B A C C 08 B *C,D C A 09 C D D B 0 D A C D B A B C C D A B B A A C 4 C C B
1 / 24
 CBSE-XII-017 EXAMINATION CBSE-X-01 EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Paper & Solution Time: 3 Hrs. Max. Marks: 90 General Instuctions : 1. All questions are compulsory.. The question paper consists of 34 questions
CBSE-XII-017 EXAMINATION CBSE-X-01 EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Paper & Solution Time: 3 Hrs. Max. Marks: 90 General Instuctions : 1. All questions are compulsory.. The question paper consists of 34 questions
PRACTICE TEST 1 Math Level IC
 SOLID VOLUME OTHER REFERENCE DATA Right circular cone L = cl V = volume L = lateral area r = radius c = circumference of base h = height l = slant height Sphere S = 4 r 2 V = volume r = radius S = surface
SOLID VOLUME OTHER REFERENCE DATA Right circular cone L = cl V = volume L = lateral area r = radius c = circumference of base h = height l = slant height Sphere S = 4 r 2 V = volume r = radius S = surface
Pre RMO Exam Paper Solution:
 Paper Solution:. How many positive integers less than 000 have the property that the sum of the digits of each such number is divisible by 7 and the number itself is divisible by 3? Sum of Digits Drivable
Paper Solution:. How many positive integers less than 000 have the property that the sum of the digits of each such number is divisible by 7 and the number itself is divisible by 3? Sum of Digits Drivable
X- MATHS IMPORTANT FORMULAS SELF EVALUVATION 1. SETS AND FUNCTIONS. 1. Commutative property i ii. 2. Associative property i ii
 X- MATHS IMPORTANT FORMULAS SELF EVALUVATION 1. SETS AND FUNCTIONS 1. Commutative property i ii 2. Associative property i ii 3. Distributive property i ii 4. De Morgan s laws i ii i ii 5. Cardinality of
X- MATHS IMPORTANT FORMULAS SELF EVALUVATION 1. SETS AND FUNCTIONS 1. Commutative property i ii 2. Associative property i ii 3. Distributive property i ii 4. De Morgan s laws i ii i ii 5. Cardinality of
Board Answer Paper: MARCH 2014
 Board Answer Paper: MARCH 04 and Statistics SECTION I Q.. (A) Select and write the correct answer from the given alternatives in each of the following: i. (C) Let l 0, m 3, n be the direction cosines of
Board Answer Paper: MARCH 04 and Statistics SECTION I Q.. (A) Select and write the correct answer from the given alternatives in each of the following: i. (C) Let l 0, m 3, n be the direction cosines of
SOLVED SUBJECTIVE EXAMPLES
 Example 1 : SOLVED SUBJECTIVE EXAMPLES Find the locus of the points of intersection of the tangents to the circle x = r cos, y = r sin at points whose parametric angles differ by /3. All such points P
Example 1 : SOLVED SUBJECTIVE EXAMPLES Find the locus of the points of intersection of the tangents to the circle x = r cos, y = r sin at points whose parametric angles differ by /3. All such points P
Test Codes : MIA (Objective Type) and MIB (Short Answer Type) 2007
 Test Codes : MIA (Objective Type) and MIB (Short Answer Type) 007 Questions will be set on the following and related topics. Algebra: Sets, operations on sets. Prime numbers, factorisation of integers
Test Codes : MIA (Objective Type) and MIB (Short Answer Type) 007 Questions will be set on the following and related topics. Algebra: Sets, operations on sets. Prime numbers, factorisation of integers
INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICAL OLYMPIADS. Hojoo Lee, Version 1.0. Contents 1. Problems 1 2. Answers and Hints References
 INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICAL OLYMPIADS 1990 2002 Hojoo Lee, Version 1.0 Contents 1. Problems 1 2. Answers and Hints 15 3. References 16 1. Problems 021 Let n be a positive integer. Let T be the set of points
INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICAL OLYMPIADS 1990 2002 Hojoo Lee, Version 1.0 Contents 1. Problems 1 2. Answers and Hints 15 3. References 16 1. Problems 021 Let n be a positive integer. Let T be the set of points
CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW
 NAME CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW Slope of a non vertical line: rise y y y m run Point Slope Equation: y y m( ) The slope is m and a point on your line is, ). ( y Slope-Intercept Equation: y m b slope=
NAME CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW Slope of a non vertical line: rise y y y m run Point Slope Equation: y y m( ) The slope is m and a point on your line is, ). ( y Slope-Intercept Equation: y m b slope=
Calgary Math Circles: Triangles, Concurrency and Quadrilaterals 1
 Calgary Math Circles: Triangles, Concurrency and Quadrilaterals 1 1 Triangles: Basics This section will cover all the basic properties you need to know about triangles and the important points of a triangle.
Calgary Math Circles: Triangles, Concurrency and Quadrilaterals 1 1 Triangles: Basics This section will cover all the basic properties you need to know about triangles and the important points of a triangle.
It is known that the length of the tangents drawn from an external point to a circle is equal.
 CBSE -MATHS-SET 1-2014 Q1. The first three terms of an AP are 3y-1, 3y+5 and 5y+1, respectively. We need to find the value of y. We know that if a, b and c are in AP, then: b a = c b 2b = a + c 2 (3y+5)
CBSE -MATHS-SET 1-2014 Q1. The first three terms of an AP are 3y-1, 3y+5 and 5y+1, respectively. We need to find the value of y. We know that if a, b and c are in AP, then: b a = c b 2b = a + c 2 (3y+5)
SYSTEM OF CIRCLES OBJECTIVES (a) Touch each other internally (b) Touch each other externally
 SYSTEM OF CIRCLES OBJECTIVES. A circle passes through (0, 0) and (, 0) and touches the circle x + y = 9, then the centre of circle is (a) (c) 3,, (b) (d) 3,, ±. The equation of the circle having its centre
SYSTEM OF CIRCLES OBJECTIVES. A circle passes through (0, 0) and (, 0) and touches the circle x + y = 9, then the centre of circle is (a) (c) 3,, (b) (d) 3,, ±. The equation of the circle having its centre
0609ge. Geometry Regents Exam AB DE, A D, and B E.
 0609ge 1 Juliann plans on drawing ABC, where the measure of A can range from 50 to 60 and the measure of B can range from 90 to 100. Given these conditions, what is the correct range of measures possible
0609ge 1 Juliann plans on drawing ABC, where the measure of A can range from 50 to 60 and the measure of B can range from 90 to 100. Given these conditions, what is the correct range of measures possible
DO NOT OPEN THIS TEST BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE ASKED TO DO SO
 DO NOT OPEN THIS TEST BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE ASKED TO DO SO T.B.C. : P-AQNA-L-ZNGU Serial No.- TEST BOOKLET MATHEMATICS Test Booklet Series Time Allowed : Two Hours and Thirty Minutes Maximum Marks : 00
DO NOT OPEN THIS TEST BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE ASKED TO DO SO T.B.C. : P-AQNA-L-ZNGU Serial No.- TEST BOOKLET MATHEMATICS Test Booklet Series Time Allowed : Two Hours and Thirty Minutes Maximum Marks : 00
0611ge. Geometry Regents Exam Line segment AB is shown in the diagram below.
 0611ge 1 Line segment AB is shown in the diagram below. In the diagram below, A B C is a transformation of ABC, and A B C is a transformation of A B C. Which two sets of construction marks, labeled I,
0611ge 1 Line segment AB is shown in the diagram below. In the diagram below, A B C is a transformation of ABC, and A B C is a transformation of A B C. Which two sets of construction marks, labeled I,
