4.1 Haar Wavelets. Haar Wavelet. The Haar Scaling Function
|
|
|
- Martha Roberts
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 4 Haar Wavelets Wavelets were first aplied in geophysics to analyze data from seismic surveys, which are used in oil and mineral exploration to get pictures of layering in subsurface roc In fact, geophysicssts rediscovered them; mathematicians had developed them to solve abstract problems some twenty years earlier but had not anticipated their applications in signal processing The ey to an accurate seismic survey is a proper analysis of each trace The Four transform is not a good tool here It can only provide frequency information (the oscillations that comprise the signal) It does not provide direct informaton about when an oscillation occurred Wavelets can eep trac of time and frequency information Haar Wavelet The Haar Scaling Function There are two functions that play a primary role in wavelet analysis, the scaling function and the wavelet These two functions generate a family of functions that can be used to brea up or reconstruct a signal To emphasize the marriage involved in building this family, is sometimes called the father wavelet and, the mother wavelet The simplest wavelet analysis is based on the Haar scaling function, whose graph is given in Figure 2
2 Figure 2 The graph of the Haar scaling function Definition The Haar scaling function is defined as, if x ( x), elsewhere The building blocs are translations and dilations (both in height and width) of this basic graph We wish to illustrate the basic ideas involved in such an analysis Consider the signal shown below Fig 3 oltage from a faulty meter
3 We may thin of this as a measurement of some physical quantity perhaps line voltage over a single cycle---as a function of time The two sharp spies in the graph might represent noise coming from a loose connection in the volt meter, and we want to filter out this undesirable noise The graph in Figure 4 shows one possible approximation to the signal using Haar building blocs The high frequency noise sows up as tall, then blocs The high frequency noise shows up as tall, thin bloc An algorithm that deletes the thin blocs will eliminate the noise and not disturb the rest of the signal Figure 4 Approximation of voltage signal in Fig 2 by Haar functions The building blocs generated by the Haar scaling function are particularly simple and illustrate the general ideas underling a multiresolution analysis, which we will discuss in detail The disadvantage of the Haar wavelets is that they are discontinuous and therefore do not approximate continuous signals very well The function ( x- ) has the same graph as but translated to the right by units (assuming is positive) Let be the space of all functions of the form Z a ( x ) a R where can range over any finite set of positive or negative integers Since ( x ) is discontinuous at x and x, an alternative description of is that it consists of all piecewise constant functions whose discontinuities are contained in the set of integers Since ranges over a finite set, each element of is zero outside a bounded set Such a function is said to have finite or compact support The graph of a typical element of is given in the following graph
4 Graph of typical element in Note that a function in may not have discontinuities at all the integers ( for example, if a a2, then the preceding sum is continuous at x 2 ) Example : Graph f ( x) 2 ( x) 3 ( x ) 3 ( x 2) ( x 3) Graph of (2 x)
5 Example 2: Graph of function f ( x) 4 (2 x) 2 (2x ) 2 (2x 2) (2x 3) Definition 2 Suppose is any nonnegative integer The space of step functions at level, denoted by, is defined to be the space spanned by the set over the real numbers {, (2 x ), (2 x), (2 x ), (2 x 2), } discontinuities are contained in the set is the space of piecewise constant functions of finite support whose {,,,,,, } A function in is a piecewise constant function with discontinuities contained in the set of integers Any function in is also contained in, which consists of piecewise constant functions whose discontinuities are contained in the set of half-integers,/ 2,,/ 2,,3/ 2, The same applies for 2 and so forth: This containment is strict For example, the function (2 x) does not belong to Question: Prove Basic Properties of the Haar Scaling Function Theorem (a) A function f( x ) belongs to f(2 x ) belongs to (b) A function f( x ) belongs to f(2 x) belongs to
6 Proof (a) if f( x ) belongs to, then f ( x) a ( x ) a R, so f (2 x) a(2 x ) a R, this means that f(2 x ) belongs to Z For (b), we can similarly prove Z /2 /2 Theorem 2 The set of functions 2 (2 x ), Z is an orthonormal basis of Question: Prove Theorem 2 The Haar Wavelet Having an orthonormal basis of is only half of the picture In order to solve our noise-filtering problem, we need to have a way of isolating the spies that belong to This is where the wavelet enters the picture but that are not members of The idea is to decompose as an orthogonal sum of and its complement Again, let start with and identify the orthogonal complement of in Since is generated by and its translates, it is reasonable to expect that the orthogonal complement of is generated by the translates of some function We need, and is orthogonal to Consider the following function Definition 3 The Haar wavelet is the function ( x) (2 x) (2x ) The graph of Haar wavelet is below Question: Prove, and is orthogonal to
7 We find out that any function f ( x) a (2 x ) Z is orthogonal to, that is, orthogonal to each ( x l), l Z if and only if a a, a a, 3 2 (prove the above result as an exercise) In this case, we have f ( x) a ( (2 x ) (2x )) a ( x ) () 2 2 Z Z In other words, a function in is orthogonal to if and only if it is of the form a ( x ) (relabeling a 2 by a ) Definition 4 Let U and be subspaces of W Then W is said to be the direct sum of U and, and we write W U if W U U and Let W be the space of all functions of the form a ( x ) a Z R where, again, we assume that only a finite number of the that W is the orthogonal complement of in Z a are nonzero What we have ust shown is W or, in other words, In a similar manner, the following more general result can be established Theorem 3 Let W be the space of functions of the form a (2 x ) a Z assume that only a finite number of the and a are nonzero (2) W Proof To show (), we have to prove two facts: R Each function in W is orthogonal to every function in 2 Any function in that is orthogonal to W is the orthogonal complement of must belong to W in
8 For the first requirement, suppose that g( x) a (2 x ) W and f, we need to show g, f g( y) f ( y) dy 2 L Z Since f, the function f (2 x) So g, f g( y) f ( y) dy 2 L 2 a (2 y ) f ( y) dx (let y 2 x) Z 2 a ( x ) f (2 x) dx (because is orthogonal to ) Z Thus, g is orthogonal to any f and thus we have proved the first one requirement The discussion leading to equation () established the second requirement when since we proved that any function in that is orthogonal to must be a linear combination of ( x ), Z The argument of general is very similar to the case when By successively decomposing, and so on, we have W W W 2 2 W W W W 2 2 So each f can be decomposed uniquely as a sum f w w w v 2 where ww,, and v Intuitively, w represents the spies of f of width / 2 l that can t be represented as linear combinations of spies of other widths When, we have the following: Theorem 4 The space L 2 ( R ) can be decomposed as an infinite orthogonal direct sum 2 L ( R) W W W2 In other words, each f L 2 ( R) can be written uniquely as
9 f v w where v and w W The infinite sum should be thought of as a limit of finite sums In other words, N lim N f v w where the limit is taen in the sense of 2 L The proof is beyond the scope of this course The approximation by step functions
Let p 2 ( t), (2 t k), we have the scaling relation,
 Multiresolution Analysis and Daubechies N Wavelet We have discussed decomposing a signal into its Haar wavelet components of varying frequencies. The Haar wavelet scheme relied on two functions: the Haar
Multiresolution Analysis and Daubechies N Wavelet We have discussed decomposing a signal into its Haar wavelet components of varying frequencies. The Haar wavelet scheme relied on two functions: the Haar
Piecewise constant approximation and the Haar Wavelet
 Chapter Piecewise constant approximation and the Haar Wavelet (Group - Sandeep Mullur 4339 and Shanmuganathan Raman 433). Introduction Piecewise constant approximation principle forms the basis for the
Chapter Piecewise constant approximation and the Haar Wavelet (Group - Sandeep Mullur 4339 and Shanmuganathan Raman 433). Introduction Piecewise constant approximation principle forms the basis for the
Introduction to Discrete-Time Wavelet Transform
 Introduction to Discrete-Time Wavelet Transform Selin Aviyente Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Michigan State University February 9, 2010 Definition of a Wavelet A wave is usually defined
Introduction to Discrete-Time Wavelet Transform Selin Aviyente Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Michigan State University February 9, 2010 Definition of a Wavelet A wave is usually defined
Wavelets Marialuce Graziadei
 Wavelets Marialuce Graziadei 1. A brief summary 2. Vanishing moments 3. 2D-wavelets 4. Compression 5. De-noising 1 1. A brief summary φ(t): scaling function. For φ the 2-scale relation hold φ(t) = p k
Wavelets Marialuce Graziadei 1. A brief summary 2. Vanishing moments 3. 2D-wavelets 4. Compression 5. De-noising 1 1. A brief summary φ(t): scaling function. For φ the 2-scale relation hold φ(t) = p k
Lecture 2: Haar Multiresolution analysis
 WAVELES AND MULIRAE DIGIAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Lecture 2: Haar Multiresolution analysis Prof.V. M. Gadre, EE, II Bombay 1 Introduction HAAR was a mathematician, who has given an idea that any continuous
WAVELES AND MULIRAE DIGIAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Lecture 2: Haar Multiresolution analysis Prof.V. M. Gadre, EE, II Bombay 1 Introduction HAAR was a mathematician, who has given an idea that any continuous
Module 4 MULTI- RESOLUTION ANALYSIS. Version 2 ECE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 4 MULTI- RESOLUTION ANALYSIS Lesson Theory of Wavelets Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the students should be able to:. Explain the space-frequency localization problem in sinusoidal
Module 4 MULTI- RESOLUTION ANALYSIS Lesson Theory of Wavelets Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the students should be able to:. Explain the space-frequency localization problem in sinusoidal
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Wavelets and Multiresolution Processing () Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr University of Ioannina - Department of Computer Science 2 Contents Image pyramids Subband coding
Digital Image Processing Wavelets and Multiresolution Processing () Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr University of Ioannina - Department of Computer Science 2 Contents Image pyramids Subband coding
Lecture 3: Haar MRA (Multi Resolution Analysis)
 U U U WAVELETS AND MULTIRATE DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Lecture 3: Haar MRA (Multi Resolution Analysis) Prof.V.M.Gadre, EE, IIT Bombay 1 Introduction The underlying principle of wavelets is to capture incremental
U U U WAVELETS AND MULTIRATE DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Lecture 3: Haar MRA (Multi Resolution Analysis) Prof.V.M.Gadre, EE, IIT Bombay 1 Introduction The underlying principle of wavelets is to capture incremental
Course and Wavelets and Filter Banks
 Course 8.327 and.30 Wavelets and Filter Banks Multiresolution Analysis (MRA): Requirements for MRA; Nested Spaces and Complementary Spaces; Scaling Functions and Wavelets Scaling Functions and Wavelets
Course 8.327 and.30 Wavelets and Filter Banks Multiresolution Analysis (MRA): Requirements for MRA; Nested Spaces and Complementary Spaces; Scaling Functions and Wavelets Scaling Functions and Wavelets
Chapter 7 Wavelets and Multiresolution Processing
 Chapter 7 Wavelets and Multiresolution Processing Background Multiresolution Expansions Wavelet Transforms in One Dimension Wavelet Transforms in Two Dimensions Image Pyramids Subband Coding The Haar
Chapter 7 Wavelets and Multiresolution Processing Background Multiresolution Expansions Wavelet Transforms in One Dimension Wavelet Transforms in Two Dimensions Image Pyramids Subband Coding The Haar
Multiresolution Analysis
 Multiresolution Analysis DS-GA 1013 / MATH-GA 2824 Optimization-based Data Analysis http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/obda_fall17/index.html Carlos Fernandez-Granda Frames Short-time Fourier transform
Multiresolution Analysis DS-GA 1013 / MATH-GA 2824 Optimization-based Data Analysis http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/obda_fall17/index.html Carlos Fernandez-Granda Frames Short-time Fourier transform
Lecture Notes 5: Multiresolution Analysis
 Optimization-based data analysis Fall 2017 Lecture Notes 5: Multiresolution Analysis 1 Frames A frame is a generalization of an orthonormal basis. The inner products between the vectors in a frame and
Optimization-based data analysis Fall 2017 Lecture Notes 5: Multiresolution Analysis 1 Frames A frame is a generalization of an orthonormal basis. The inner products between the vectors in a frame and
1 Introduction to Wavelet Analysis
 Jim Lambers ENERGY 281 Spring Quarter 2007-08 Lecture 9 Notes 1 Introduction to Wavelet Analysis Wavelets were developed in the 80 s and 90 s as an alternative to Fourier analysis of signals. Some of the
Jim Lambers ENERGY 281 Spring Quarter 2007-08 Lecture 9 Notes 1 Introduction to Wavelet Analysis Wavelets were developed in the 80 s and 90 s as an alternative to Fourier analysis of signals. Some of the
(Refer Slide Time: 0:18)
 Foundations of Wavelets, Filter Banks and Time Frequency Analysis. Professor Vikram M. Gadre. Department Of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology Bombay. Week-1. Lecture -2.3 L2 Norm of
Foundations of Wavelets, Filter Banks and Time Frequency Analysis. Professor Vikram M. Gadre. Department Of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology Bombay. Week-1. Lecture -2.3 L2 Norm of
A Tutorial on Wavelets and their Applications. Martin J. Mohlenkamp
 A Tutorial on Wavelets and their Applications Martin J. Mohlenkamp University of Colorado at Boulder Department of Applied Mathematics mjm@colorado.edu This tutorial is designed for people with little
A Tutorial on Wavelets and their Applications Martin J. Mohlenkamp University of Colorado at Boulder Department of Applied Mathematics mjm@colorado.edu This tutorial is designed for people with little
Wavelets. Introduction and Applications for Economic Time Series. Dag Björnberg. U.U.D.M. Project Report 2017:20
 U.U.D.M. Project Report 2017:20 Wavelets Introduction and Applications for Economic Time Series Dag Björnberg Examensarbete i matematik, 15 hp Handledare: Rolf Larsson Examinator: Jörgen Östensson Juni
U.U.D.M. Project Report 2017:20 Wavelets Introduction and Applications for Economic Time Series Dag Björnberg Examensarbete i matematik, 15 hp Handledare: Rolf Larsson Examinator: Jörgen Östensson Juni
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Wavelets and Multiresolution Processing (Wavelet Transforms) Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr University of Ioannina - Department of Computer Science 2 Contents Image pyramids
Digital Image Processing Wavelets and Multiresolution Processing (Wavelet Transforms) Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr University of Ioannina - Department of Computer Science 2 Contents Image pyramids
Wavelets and Multiresolution Processing. Thinh Nguyen
 Wavelets and Multiresolution Processing Thinh Nguyen Multiresolution Analysis (MRA) A scaling function is used to create a series of approximations of a function or image, each differing by a factor of
Wavelets and Multiresolution Processing Thinh Nguyen Multiresolution Analysis (MRA) A scaling function is used to create a series of approximations of a function or image, each differing by a factor of
MLISP: Machine Learning in Signal Processing Spring Lecture 8-9 May 4-7
 MLISP: Machine Learning in Signal Processing Spring 2018 Prof. Veniamin Morgenshtern Lecture 8-9 May 4-7 Scribe: Mohamed Solomon Agenda 1. Wavelets: beyond smoothness 2. A problem with Fourier transform
MLISP: Machine Learning in Signal Processing Spring 2018 Prof. Veniamin Morgenshtern Lecture 8-9 May 4-7 Scribe: Mohamed Solomon Agenda 1. Wavelets: beyond smoothness 2. A problem with Fourier transform
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing, 2nd ed. Digital Image Processing Chapter 7 Wavelets and Multiresolution Processing Dr. Kai Shuang Department of Electronic Engineering China University of Petroleum shuangkai@cup.edu.cn
Digital Image Processing, 2nd ed. Digital Image Processing Chapter 7 Wavelets and Multiresolution Processing Dr. Kai Shuang Department of Electronic Engineering China University of Petroleum shuangkai@cup.edu.cn
An Introduction to Wavelets and some Applications
 An Introduction to Wavelets and some Applications Milan, May 2003 Anestis Antoniadis Laboratoire IMAG-LMC University Joseph Fourier Grenoble, France An Introduction to Wavelets and some Applications p.1/54
An Introduction to Wavelets and some Applications Milan, May 2003 Anestis Antoniadis Laboratoire IMAG-LMC University Joseph Fourier Grenoble, France An Introduction to Wavelets and some Applications p.1/54
Multiresolution image processing
 Multiresolution image processing Laplacian pyramids Some applications of Laplacian pyramids Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) Wavelet theory Wavelet image compression Bernd Girod: EE368 Digital Image Processing
Multiresolution image processing Laplacian pyramids Some applications of Laplacian pyramids Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) Wavelet theory Wavelet image compression Bernd Girod: EE368 Digital Image Processing
Development and Applications of Wavelets in Signal Processing
 Development and Applications of Wavelets in Signal Processing Mathematics 097: Senior Conference Paper Published May 014 David Nahmias dnahmias1@gmailcom Abstract Wavelets have many powerful applications
Development and Applications of Wavelets in Signal Processing Mathematics 097: Senior Conference Paper Published May 014 David Nahmias dnahmias1@gmailcom Abstract Wavelets have many powerful applications
Decomposition of Riesz frames and wavelets into a finite union of linearly independent sets
 Decomposition of Riesz frames and wavelets into a finite union of linearly independent sets Ole Christensen, Alexander M. Lindner Abstract We characterize Riesz frames and prove that every Riesz frame
Decomposition of Riesz frames and wavelets into a finite union of linearly independent sets Ole Christensen, Alexander M. Lindner Abstract We characterize Riesz frames and prove that every Riesz frame
Haar wavelets. Set. 1 0 t < 1 0 otherwise. It is clear that {φ 0 (t n), n Z} is an orthobasis for V 0.
 Haar wavelets The Haar wavelet basis for L (R) breaks down a signal by looking at the difference between piecewise constant approximations at different scales. It is the simplest example of a wavelet transform,
Haar wavelets The Haar wavelet basis for L (R) breaks down a signal by looking at the difference between piecewise constant approximations at different scales. It is the simplest example of a wavelet transform,
Mathematical Methods for Computer Science
 Mathematical Methods for Computer Science Computer Laboratory Computer Science Tripos, Part IB Michaelmas Term 2016/17 Professor J. Daugman Exercise problems Fourier and related methods 15 JJ Thomson Avenue
Mathematical Methods for Computer Science Computer Laboratory Computer Science Tripos, Part IB Michaelmas Term 2016/17 Professor J. Daugman Exercise problems Fourier and related methods 15 JJ Thomson Avenue
Lecture 1. 1, 0 x < 1 2 1, 2. x < 1, 0, elsewhere. 1
 0 - - -3 Lecture Introductory mathematical ideas The term wavelet, meaning literally little wave, originated in the early 980s in its French version ondelette in the work of Morlet and some French seismologists.
0 - - -3 Lecture Introductory mathematical ideas The term wavelet, meaning literally little wave, originated in the early 980s in its French version ondelette in the work of Morlet and some French seismologists.
From Fourier to Wavelets in 60 Slides
 From Fourier to Wavelets in 60 Slides Bernhard G. Bodmann Math Department, UH September 20, 2008 B. G. Bodmann (UH Math) From Fourier to Wavelets in 60 Slides September 20, 2008 1 / 62 Outline 1 From Fourier
From Fourier to Wavelets in 60 Slides Bernhard G. Bodmann Math Department, UH September 20, 2008 B. G. Bodmann (UH Math) From Fourier to Wavelets in 60 Slides September 20, 2008 1 / 62 Outline 1 From Fourier
Discrete Wavelet Transform
 Discrete Wavelet Transform [11] Kartik Mehra July 2017 Math 190s Duke University "1 Introduction Wavelets break signals up and then analyse them separately with a resolution that is matched with scale.
Discrete Wavelet Transform [11] Kartik Mehra July 2017 Math 190s Duke University "1 Introduction Wavelets break signals up and then analyse them separately with a resolution that is matched with scale.
CHAPTER VIII HILBERT SPACES
 CHAPTER VIII HILBERT SPACES DEFINITION Let X and Y be two complex vector spaces. A map T : X Y is called a conjugate-linear transformation if it is a reallinear transformation from X into Y, and if T (λx)
CHAPTER VIII HILBERT SPACES DEFINITION Let X and Y be two complex vector spaces. A map T : X Y is called a conjugate-linear transformation if it is a reallinear transformation from X into Y, and if T (λx)
Vectors in Function Spaces
 Jim Lambers MAT 66 Spring Semester 15-16 Lecture 18 Notes These notes correspond to Section 6.3 in the text. Vectors in Function Spaces We begin with some necessary terminology. A vector space V, also
Jim Lambers MAT 66 Spring Semester 15-16 Lecture 18 Notes These notes correspond to Section 6.3 in the text. Vectors in Function Spaces We begin with some necessary terminology. A vector space V, also
Defining the Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT)
 Defining the Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) can formulate DWT via elegant pyramid algorithm defines W for non-haar wavelets (consistent with Haar) computes W = WX using O(N) multiplications brute force
Defining the Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) can formulate DWT via elegant pyramid algorithm defines W for non-haar wavelets (consistent with Haar) computes W = WX using O(N) multiplications brute force
Lecture 7 Multiresolution Analysis
 David Walnut Department of Mathematical Sciences George Mason University Fairfax, VA USA Chapman Lectures, Chapman University, Orange, CA Outline Definition of MRA in one dimension Finding the wavelet
David Walnut Department of Mathematical Sciences George Mason University Fairfax, VA USA Chapman Lectures, Chapman University, Orange, CA Outline Definition of MRA in one dimension Finding the wavelet
Lecture 15: Time and Frequency Joint Perspective
 WAVELETS AND MULTIRATE DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Lecture 15: Time and Frequency Joint Perspective Prof.V.M.Gadre, EE, IIT Bombay Introduction In lecture 14, we studied steps required to design conjugate
WAVELETS AND MULTIRATE DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Lecture 15: Time and Frequency Joint Perspective Prof.V.M.Gadre, EE, IIT Bombay Introduction In lecture 14, we studied steps required to design conjugate
ACM 126a Solutions for Homework Set 4
 ACM 26a Solutions for Homewor Set 4 Laurent Demanet March 2, 25 Problem. Problem 7.7 page 36 We need to recall a few standard facts about Fourier series. Convolution: Subsampling (see p. 26): Zero insertion
ACM 26a Solutions for Homewor Set 4 Laurent Demanet March 2, 25 Problem. Problem 7.7 page 36 We need to recall a few standard facts about Fourier series. Convolution: Subsampling (see p. 26): Zero insertion
V. SUBSPACES AND ORTHOGONAL PROJECTION
 V. SUBSPACES AND ORTHOGONAL PROJECTION In this chapter we will discuss the concept of subspace of Hilbert space, introduce a series of subspaces related to Haar wavelet, explore the orthogonal projection
V. SUBSPACES AND ORTHOGONAL PROJECTION In this chapter we will discuss the concept of subspace of Hilbert space, introduce a series of subspaces related to Haar wavelet, explore the orthogonal projection
Wavelets and multiresolution representations. Time meets frequency
 Wavelets and multiresolution representations Time meets frequency Time-Frequency resolution Depends on the time-frequency spread of the wavelet atoms Assuming that ψ is centred in t=0 Signal domain + t
Wavelets and multiresolution representations Time meets frequency Time-Frequency resolution Depends on the time-frequency spread of the wavelet atoms Assuming that ψ is centred in t=0 Signal domain + t
Sparse linear models
 Sparse linear models Optimization-Based Data Analysis http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/obda_spring16 Carlos Fernandez-Granda 2/22/2016 Introduction Linear transforms Frequency representation Short-time
Sparse linear models Optimization-Based Data Analysis http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/obda_spring16 Carlos Fernandez-Granda 2/22/2016 Introduction Linear transforms Frequency representation Short-time
Lecture 27. Wavelets and multiresolution analysis (cont d) Analysis and synthesis algorithms for wavelet expansions
 Lecture 7 Wavelets and multiresolution analysis (cont d) Analysis and synthesis algorithms for wavelet expansions We now return to the general case of square-integrable functions supported on the entire
Lecture 7 Wavelets and multiresolution analysis (cont d) Analysis and synthesis algorithms for wavelet expansions We now return to the general case of square-integrable functions supported on the entire
Wavelets For Computer Graphics
 {f g} := f(x) g(x) dx A collection of linearly independent functions Ψ j spanning W j are called wavelets. i J(x) := 6 x +2 x + x + x Ψ j (x) := Ψ j (2 j x i) i =,..., 2 j Res. Avge. Detail Coef 4 [9 7
{f g} := f(x) g(x) dx A collection of linearly independent functions Ψ j spanning W j are called wavelets. i J(x) := 6 x +2 x + x + x Ψ j (x) := Ψ j (2 j x i) i =,..., 2 j Res. Avge. Detail Coef 4 [9 7
DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 10 November 23, Linear models
 DS-GA 2 Lecture notes November 23, 2 Linear functions Linear models A linear model encodes the assumption that two quantities are linearly related. Mathematically, this is characterized using linear functions.
DS-GA 2 Lecture notes November 23, 2 Linear functions Linear models A linear model encodes the assumption that two quantities are linearly related. Mathematically, this is characterized using linear functions.
chapter 12 MORE MATRIX ALGEBRA 12.1 Systems of Linear Equations GOALS
 chapter MORE MATRIX ALGEBRA GOALS In Chapter we studied matrix operations and the algebra of sets and logic. We also made note of the strong resemblance of matrix algebra to elementary algebra. The reader
chapter MORE MATRIX ALGEBRA GOALS In Chapter we studied matrix operations and the algebra of sets and logic. We also made note of the strong resemblance of matrix algebra to elementary algebra. The reader
Chapter 7 Wavelets and Multiresolution Processing. Subband coding Quadrature mirror filtering Pyramid image processing
 Chapter 7 Wavelets and Multiresolution Processing Wavelet transform vs Fourier transform Basis functions are small waves called wavelet with different frequency and limited duration Multiresolution theory:
Chapter 7 Wavelets and Multiresolution Processing Wavelet transform vs Fourier transform Basis functions are small waves called wavelet with different frequency and limited duration Multiresolution theory:
Assignment #09 - Solution Manual
 Assignment #09 - Solution Manual 1. Choose the correct statements about representation of a continuous signal using Haar wavelets. 1.5 points The signal is approximated using sin and cos functions. The
Assignment #09 - Solution Manual 1. Choose the correct statements about representation of a continuous signal using Haar wavelets. 1.5 points The signal is approximated using sin and cos functions. The
1.5 Approximate Identities
 38 1 The Fourier Transform on L 1 (R) which are dense subspaces of L p (R). On these domains, P : D P L p (R) and M : D M L p (R). Show, however, that P and M are unbounded even when restricted to these
38 1 The Fourier Transform on L 1 (R) which are dense subspaces of L p (R). On these domains, P : D P L p (R) and M : D M L p (R). Show, however, that P and M are unbounded even when restricted to these
An Introduction to Wavelets
 1 An Introduction to Wavelets Advanced Linear Algebra (Linear Algebra II) Heng-Yu Lin May 27 2013 2 Abstract With the prosperity of the Digital Age, information is nowadays increasingly, if not exclusively,
1 An Introduction to Wavelets Advanced Linear Algebra (Linear Algebra II) Heng-Yu Lin May 27 2013 2 Abstract With the prosperity of the Digital Age, information is nowadays increasingly, if not exclusively,
A Wavelet-Based Technique for Identifying, Labeling, and Tracking of Ocean Eddies
 MARCH 2002 LUO AND JAMESON 381 A Wavelet-Based Technique for Identifying, Labeling, and Tracking of Ocean Eddies JINGJIA LUO Department of Earth and Planetary Physics, Graduate School of Science, University
MARCH 2002 LUO AND JAMESON 381 A Wavelet-Based Technique for Identifying, Labeling, and Tracking of Ocean Eddies JINGJIA LUO Department of Earth and Planetary Physics, Graduate School of Science, University
Computationally Efficient Optimization of Linear Time Invariant Systems using Haar wavelet
 Computationally Efficient Optimization of Linear Time Invariant Systems using Haar wavelet Abhinav Jain 1, Monika Mittal 2 1 Department of Electrical Engg., National Institute of Technology, Kurukshetra,
Computationally Efficient Optimization of Linear Time Invariant Systems using Haar wavelet Abhinav Jain 1, Monika Mittal 2 1 Department of Electrical Engg., National Institute of Technology, Kurukshetra,
MATH The Derivative as a Function - Section 3.2. The derivative of f is the function. f x h f x. f x lim
 MATH 90 - The Derivative as a Function - Section 3.2 The derivative of f is the function f x lim h 0 f x h f x h for all x for which the limit exists. The notation f x is read "f prime of x". Note that
MATH 90 - The Derivative as a Function - Section 3.2 The derivative of f is the function f x lim h 0 f x h f x h for all x for which the limit exists. The notation f x is read "f prime of x". Note that
MATH 426, TOPOLOGY. p 1.
 MATH 426, TOPOLOGY THE p-norms In this document we assume an extended real line, where is an element greater than all real numbers; the interval notation [1, ] will be used to mean [1, ) { }. 1. THE p
MATH 426, TOPOLOGY THE p-norms In this document we assume an extended real line, where is an element greater than all real numbers; the interval notation [1, ] will be used to mean [1, ) { }. 1. THE p
Orthogonal Complements
 Orthogonal Complements Definition Let W be a subspace of R n. If a vector z is orthogonal to every vector in W, then z is said to be orthogonal to W. The set of all such vectors z is called the orthogonal
Orthogonal Complements Definition Let W be a subspace of R n. If a vector z is orthogonal to every vector in W, then z is said to be orthogonal to W. The set of all such vectors z is called the orthogonal
We have to prove now that (3.38) defines an orthonormal wavelet. It belongs to W 0 by Lemma and (3.55) with j = 1. We can write any f W 1 as
 88 CHAPTER 3. WAVELETS AND APPLICATIONS We have to prove now that (3.38) defines an orthonormal wavelet. It belongs to W 0 by Lemma 3..7 and (3.55) with j =. We can write any f W as (3.58) f(ξ) = p(2ξ)ν(2ξ)
88 CHAPTER 3. WAVELETS AND APPLICATIONS We have to prove now that (3.38) defines an orthonormal wavelet. It belongs to W 0 by Lemma 3..7 and (3.55) with j =. We can write any f W as (3.58) f(ξ) = p(2ξ)ν(2ξ)
REAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES: 1.4 OUTER MEASURE
 REAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES: 1.4 OUTER MEASURE CHRISTOPHER HEIL 1.4.1 Introduction We will expand on Section 1.4 of Folland s text, which covers abstract outer measures also called exterior measures).
REAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES: 1.4 OUTER MEASURE CHRISTOPHER HEIL 1.4.1 Introduction We will expand on Section 1.4 of Folland s text, which covers abstract outer measures also called exterior measures).
2.4 Hilbert Spaces. Outline
 2.4 Hilbert Spaces Tom Lewis Spring Semester 2017 Outline Hilbert spaces L 2 ([a, b]) Orthogonality Approximations Definition A Hilbert space is an inner product space which is complete in the norm defined
2.4 Hilbert Spaces Tom Lewis Spring Semester 2017 Outline Hilbert spaces L 2 ([a, b]) Orthogonality Approximations Definition A Hilbert space is an inner product space which is complete in the norm defined
Last Update: April 7, 201 0
 M ath E S W inter Last Update: April 7, Introduction to Partial Differential Equations Disclaimer: his lecture note tries to provide an alternative approach to the material in Sections.. 5 in the textbook.
M ath E S W inter Last Update: April 7, Introduction to Partial Differential Equations Disclaimer: his lecture note tries to provide an alternative approach to the material in Sections.. 5 in the textbook.
Introduction to Real Analysis Alternative Chapter 1
 Christopher Heil Introduction to Real Analysis Alternative Chapter 1 A Primer on Norms and Banach Spaces Last Updated: March 10, 2018 c 2018 by Christopher Heil Chapter 1 A Primer on Norms and Banach Spaces
Christopher Heil Introduction to Real Analysis Alternative Chapter 1 A Primer on Norms and Banach Spaces Last Updated: March 10, 2018 c 2018 by Christopher Heil Chapter 1 A Primer on Norms and Banach Spaces
August 23, 2017 Let us measure everything that is measurable, and make measurable everything that is not yet so. Galileo Galilei. 1.
 August 23, 2017 Let us measure everything that is measurable, and make measurable everything that is not yet so. Galileo Galilei 1. Vector spaces 1.1. Notations. x S denotes the fact that the element x
August 23, 2017 Let us measure everything that is measurable, and make measurable everything that is not yet so. Galileo Galilei 1. Vector spaces 1.1. Notations. x S denotes the fact that the element x
Lecture 16: Multiresolution Image Analysis
 Lecture 16: Multiresolution Image Analysis Harvey Rhody Chester F. Carlson Center for Imaging Science Rochester Institute of Technology rhody@cis.rit.edu November 9, 2004 Abstract Multiresolution analysis
Lecture 16: Multiresolution Image Analysis Harvey Rhody Chester F. Carlson Center for Imaging Science Rochester Institute of Technology rhody@cis.rit.edu November 9, 2004 Abstract Multiresolution analysis
Vector spaces. DS-GA 1013 / MATH-GA 2824 Optimization-based Data Analysis.
 Vector spaces DS-GA 1013 / MATH-GA 2824 Optimization-based Data Analysis http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/obda_fall17/index.html Carlos Fernandez-Granda Vector space Consists of: A set V A scalar
Vector spaces DS-GA 1013 / MATH-GA 2824 Optimization-based Data Analysis http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/obda_fall17/index.html Carlos Fernandez-Granda Vector space Consists of: A set V A scalar
Scientific Computing: An Introductory Survey
 Scientific Computing: An Introductory Survey Chapter 12 Prof. Michael T. Heath Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Copyright c 2002. Reproduction permitted for noncommercial,
Scientific Computing: An Introductory Survey Chapter 12 Prof. Michael T. Heath Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Copyright c 2002. Reproduction permitted for noncommercial,
Continuity. MATH 161 Calculus I. J. Robert Buchanan. Fall Department of Mathematics
 Continuity MATH 161 Calculus I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2017 Intuitive Idea A process or an item can be described as continuous if it exists without interruption. The mathematical
Continuity MATH 161 Calculus I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2017 Intuitive Idea A process or an item can be described as continuous if it exists without interruption. The mathematical
Bell Ringer. 1. Make a table and sketch the graph of the piecewise function. f(x) =
 Bell Ringer 1. Make a table and sketch the graph of the piecewise function f(x) = Power and Radical Functions Learning Target: 1. I can graph and analyze power functions. 2. I can graph and analyze radical
Bell Ringer 1. Make a table and sketch the graph of the piecewise function f(x) = Power and Radical Functions Learning Target: 1. I can graph and analyze power functions. 2. I can graph and analyze radical
Wavelet Transform And Principal Component Analysis Based Feature Extraction
 Wavelet Transform And Principal Component Analysis Based Feature Extraction Keyun Tong June 3, 2010 As the amount of information grows rapidly and widely, feature extraction become an indispensable technique
Wavelet Transform And Principal Component Analysis Based Feature Extraction Keyun Tong June 3, 2010 As the amount of information grows rapidly and widely, feature extraction become an indispensable technique
COMPLEX PRINCIPAL COMPONENT SPECTRA EXTRACTION
 COMPLEX PRINCIPAL COMPONEN SPECRA EXRACION PROGRAM complex_pca_spectra Computing principal components o begin, click the Formation attributes tab in the AASPI-UIL window and select program complex_pca_spectra:
COMPLEX PRINCIPAL COMPONEN SPECRA EXRACION PROGRAM complex_pca_spectra Computing principal components o begin, click the Formation attributes tab in the AASPI-UIL window and select program complex_pca_spectra:
Math Linear Algebra
 Math 220 - Linear Algebra (Summer 208) Solutions to Homework #7 Exercise 6..20 (a) TRUE. u v v u = 0 is equivalent to u v = v u. The latter identity is true due to the commutative property of the inner
Math 220 - Linear Algebra (Summer 208) Solutions to Homework #7 Exercise 6..20 (a) TRUE. u v v u = 0 is equivalent to u v = v u. The latter identity is true due to the commutative property of the inner
Econ 2120: Section 2
 Econ 2120: Section 2 Part I - Linear Predictor Loose Ends Ashesh Rambachan Fall 2018 Outline Big Picture Matrix Version of the Linear Predictor and Least Squares Fit Linear Predictor Least Squares Omitted
Econ 2120: Section 2 Part I - Linear Predictor Loose Ends Ashesh Rambachan Fall 2018 Outline Big Picture Matrix Version of the Linear Predictor and Least Squares Fit Linear Predictor Least Squares Omitted
The New Graphic Description of the Haar Wavelet Transform
 he New Graphic Description of the Haar Wavelet ransform Piotr Porwik and Agnieszka Lisowska Institute of Informatics, Silesian University, ul.b dzi ska 39, 4-00 Sosnowiec, Poland porwik@us.edu.pl Institute
he New Graphic Description of the Haar Wavelet ransform Piotr Porwik and Agnieszka Lisowska Institute of Informatics, Silesian University, ul.b dzi ska 39, 4-00 Sosnowiec, Poland porwik@us.edu.pl Institute
Lecture Notes 1: Vector spaces
 Optimization-based data analysis Fall 2017 Lecture Notes 1: Vector spaces In this chapter we review certain basic concepts of linear algebra, highlighting their application to signal processing. 1 Vector
Optimization-based data analysis Fall 2017 Lecture Notes 1: Vector spaces In this chapter we review certain basic concepts of linear algebra, highlighting their application to signal processing. 1 Vector
Wavelets and Multiresolution Processing
 Wavelets and Multiresolution Processing Wavelets Fourier transform has it basis functions in sinusoids Wavelets based on small waves of varying frequency and limited duration In addition to frequency,
Wavelets and Multiresolution Processing Wavelets Fourier transform has it basis functions in sinusoids Wavelets based on small waves of varying frequency and limited duration In addition to frequency,
Lecture 1: Systems of linear equations and their solutions
 Lecture 1: Systems of linear equations and their solutions Course overview Topics to be covered this semester: Systems of linear equations and Gaussian elimination: Solving linear equations and applications
Lecture 1: Systems of linear equations and their solutions Course overview Topics to be covered this semester: Systems of linear equations and Gaussian elimination: Solving linear equations and applications
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.436J/15.085J Fall 2008 Lecture 8 10/1/2008 CONTINUOUS RANDOM VARIABLES
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.436J/15.085J Fall 2008 Lecture 8 10/1/2008 CONTINUOUS RANDOM VARIABLES Contents 1. Continuous random variables 2. Examples 3. Expected values 4. Joint distributions
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.436J/15.085J Fall 2008 Lecture 8 10/1/2008 CONTINUOUS RANDOM VARIABLES Contents 1. Continuous random variables 2. Examples 3. Expected values 4. Joint distributions
Wavelet analysis on financial time series. By Arlington Fonseca Lemus. Tutor Hugo Eduardo Ramirez Jaime
 Wavelet analysis on financial time series By Arlington Fonseca Lemus Tutor Hugo Eduardo Ramirez Jaime A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment for the degree of Master in Quantitative Finance Faculty
Wavelet analysis on financial time series By Arlington Fonseca Lemus Tutor Hugo Eduardo Ramirez Jaime A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment for the degree of Master in Quantitative Finance Faculty
6.4 BASIS AND DIMENSION (Review) DEF 1 Vectors v 1, v 2,, v k in a vector space V are said to form a basis for V if. (a) v 1,, v k span V and
 6.4 BASIS AND DIMENSION (Review) DEF 1 Vectors v 1, v 2,, v k in a vector space V are said to form a basis for V if (a) v 1,, v k span V and (b) v 1,, v k are linearly independent. HMHsueh 1 Natural Basis
6.4 BASIS AND DIMENSION (Review) DEF 1 Vectors v 1, v 2,, v k in a vector space V are said to form a basis for V if (a) v 1,, v k span V and (b) v 1,, v k are linearly independent. HMHsueh 1 Natural Basis
1 Functions and Graphs
 1 Functions and Graphs 1.1 Functions Cartesian Coordinate System A Cartesian or rectangular coordinate system is formed by the intersection of a horizontal real number line, usually called the x axis,
1 Functions and Graphs 1.1 Functions Cartesian Coordinate System A Cartesian or rectangular coordinate system is formed by the intersection of a horizontal real number line, usually called the x axis,
Module 7:Data Representation Lecture 35: Wavelets. The Lecture Contains: Wavelets. Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) Haar wavelets: Example
 The Lecture Contains: Wavelets Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) Haar wavelets: Example Haar wavelets: Theory Matrix form Haar wavelet matrices Dimensionality reduction using Haar wavelets file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture35/35_1.htm[6/14/2012
The Lecture Contains: Wavelets Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) Haar wavelets: Example Haar wavelets: Theory Matrix form Haar wavelet matrices Dimensionality reduction using Haar wavelets file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture35/35_1.htm[6/14/2012
Since G is a compact Lie group, we can apply Schur orthogonality to see that G χ π (g) 2 dg =
 Problem 1 Show that if π is an irreducible representation of a compact lie group G then π is also irreducible. Give an example of a G and π such that π = π, and another for which π π. Is this true for
Problem 1 Show that if π is an irreducible representation of a compact lie group G then π is also irreducible. Give an example of a G and π such that π = π, and another for which π π. Is this true for
The Application of Legendre Multiwavelet Functions in Image Compression
 Journal of Modern Applied Statistical Methods Volume 5 Issue 2 Article 3 --206 The Application of Legendre Multiwavelet Functions in Image Compression Elham Hashemizadeh Department of Mathematics, Karaj
Journal of Modern Applied Statistical Methods Volume 5 Issue 2 Article 3 --206 The Application of Legendre Multiwavelet Functions in Image Compression Elham Hashemizadeh Department of Mathematics, Karaj
Archive of past papers, solutions and homeworks for. MATH 224, Linear Algebra 2, Spring 2013, Laurence Barker
 Archive of past papers, solutions and homeworks for MATH 224, Linear Algebra 2, Spring 213, Laurence Barker version: 4 June 213 Source file: archfall99.tex page 2: Homeworks. page 3: Quizzes. page 4: Midterm
Archive of past papers, solutions and homeworks for MATH 224, Linear Algebra 2, Spring 213, Laurence Barker version: 4 June 213 Source file: archfall99.tex page 2: Homeworks. page 3: Quizzes. page 4: Midterm
Wavelets on hierarchical trees
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Fall 2016 Wavelets on hierarchical trees Lu Yu University of Iowa Copyright 2016 Lu Yu This dissertation is available at Iowa Research Online:
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Fall 2016 Wavelets on hierarchical trees Lu Yu University of Iowa Copyright 2016 Lu Yu This dissertation is available at Iowa Research Online:
96 CHAPTER 4. HILBERT SPACES. Spaces of square integrable functions. Take a Cauchy sequence f n in L 2 so that. f n f m 1 (b a) f n f m 2.
 96 CHAPTER 4. HILBERT SPACES 4.2 Hilbert Spaces Hilbert Space. An inner product space is called a Hilbert space if it is complete as a normed space. Examples. Spaces of sequences The space l 2 of square
96 CHAPTER 4. HILBERT SPACES 4.2 Hilbert Spaces Hilbert Space. An inner product space is called a Hilbert space if it is complete as a normed space. Examples. Spaces of sequences The space l 2 of square
Answer Key for Exam #2
 . Use elimination on an augmented matrix: Answer Key for Exam # 4 4 8 4 4 4 The fourth column has no pivot, so x 4 is a free variable. The corresponding system is x + x 4 =, x =, x x 4 = which we solve
. Use elimination on an augmented matrix: Answer Key for Exam # 4 4 8 4 4 4 The fourth column has no pivot, so x 4 is a free variable. The corresponding system is x + x 4 =, x =, x x 4 = which we solve
Some Background Material
 Chapter 1 Some Background Material In the first chapter, we present a quick review of elementary - but important - material as a way of dipping our toes in the water. This chapter also introduces important
Chapter 1 Some Background Material In the first chapter, we present a quick review of elementary - but important - material as a way of dipping our toes in the water. This chapter also introduces important
Chapter 10. Infinite Sequences and Series
 10.6 Alternating Series, Absolute and Conditional Convergence 1 Chapter 10. Infinite Sequences and Series 10.6 Alternating Series, Absolute and Conditional Convergence Note. The convergence tests investigated
10.6 Alternating Series, Absolute and Conditional Convergence 1 Chapter 10. Infinite Sequences and Series 10.6 Alternating Series, Absolute and Conditional Convergence Note. The convergence tests investigated
Errata Applied Analysis
 Errata Applied Analysis p. 9: line 2 from the bottom: 2 instead of 2. p. 10: Last sentence should read: The lim sup of a sequence whose terms are bounded from above is finite or, and the lim inf of a sequence
Errata Applied Analysis p. 9: line 2 from the bottom: 2 instead of 2. p. 10: Last sentence should read: The lim sup of a sequence whose terms are bounded from above is finite or, and the lim inf of a sequence
Chapter 2 The Group U(1) and its Representations
 Chapter 2 The Group U(1) and its Representations The simplest example of a Lie group is the group of rotations of the plane, with elements parametrized by a single number, the angle of rotation θ. It is
Chapter 2 The Group U(1) and its Representations The simplest example of a Lie group is the group of rotations of the plane, with elements parametrized by a single number, the angle of rotation θ. It is
Topic 2 Limits and Continuity c and d) Continuity Handout Notes Assigned Problems: Intro book pg 73, 1-3 and 6-8
 c&d. Continuity Handout. Page 1 of 5 Topic Limits and Continuity c and d) Continuity Handout Notes Assigned Problems: Intro book pg 73, 1-3 and 6-8 Recall Limits and Function Values: We have already studied
c&d. Continuity Handout. Page 1 of 5 Topic Limits and Continuity c and d) Continuity Handout Notes Assigned Problems: Intro book pg 73, 1-3 and 6-8 Recall Limits and Function Values: We have already studied
MAT2342 : Introduction to Applied Linear Algebra Mike Newman, fall Projections. introduction
 MAT4 : Introduction to Applied Linear Algebra Mike Newman fall 7 9. Projections introduction One reason to consider projections is to understand approximate solutions to linear systems. A common example
MAT4 : Introduction to Applied Linear Algebra Mike Newman fall 7 9. Projections introduction One reason to consider projections is to understand approximate solutions to linear systems. A common example
Section 2.1: The Derivative and the Tangent Line Problem Goals for this Section:
 Section 2.1: The Derivative and the Tangent Line Problem Goals for this Section: Find the slope of the tangent line to a curve at a point. Day 1 Use the limit definition to find the derivative of a function.
Section 2.1: The Derivative and the Tangent Line Problem Goals for this Section: Find the slope of the tangent line to a curve at a point. Day 1 Use the limit definition to find the derivative of a function.
9 Brownian Motion: Construction
 9 Brownian Motion: Construction 9.1 Definition and Heuristics The central limit theorem states that the standard Gaussian distribution arises as the weak limit of the rescaled partial sums S n / p n of
9 Brownian Motion: Construction 9.1 Definition and Heuristics The central limit theorem states that the standard Gaussian distribution arises as the weak limit of the rescaled partial sums S n / p n of
where the bar indicates complex conjugation. Note that this implies that, from Property 2, x,αy = α x,y, x,y X, α C.
 Lecture 4 Inner product spaces Of course, you are familiar with the idea of inner product spaces at least finite-dimensional ones. Let X be an abstract vector space with an inner product, denoted as,,
Lecture 4 Inner product spaces Of course, you are familiar with the idea of inner product spaces at least finite-dimensional ones. Let X be an abstract vector space with an inner product, denoted as,,
Continuous Random Variables
 MATH 38 Continuous Random Variables Dr. Neal, WKU Throughout, let Ω be a sample space with a defined probability measure P. Definition. A continuous random variable is a real-valued function X defined
MATH 38 Continuous Random Variables Dr. Neal, WKU Throughout, let Ω be a sample space with a defined probability measure P. Definition. A continuous random variable is a real-valued function X defined
INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES
 11 INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES Infinite sequences and series were introduced briefly in A Preview of Calculus in connection with Zeno s paradoxes and the decimal representation
11 INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES Infinite sequences and series were introduced briefly in A Preview of Calculus in connection with Zeno s paradoxes and the decimal representation
DAVID FERRONE. s k s k 2j = δ 0j. s k = 1
 FINITE BIORTHOGONAL TRANSFORMS AND MULTIRESOLUTION ANALYSES ON INTERVALS DAVID FERRONE 1. Introduction Wavelet theory over the entire real line is well understood and elegantly presented in various textboos
FINITE BIORTHOGONAL TRANSFORMS AND MULTIRESOLUTION ANALYSES ON INTERVALS DAVID FERRONE 1. Introduction Wavelet theory over the entire real line is well understood and elegantly presented in various textboos
GRE Math Subject Test #5 Solutions.
 GRE Math Subject Test #5 Solutions. 1. E (Calculus) Apply L Hôpital s Rule two times: cos(3x) 1 3 sin(3x) 9 cos(3x) lim x 0 = lim x 2 x 0 = lim 2x x 0 = 9. 2 2 2. C (Geometry) Note that a line segment
GRE Math Subject Test #5 Solutions. 1. E (Calculus) Apply L Hôpital s Rule two times: cos(3x) 1 3 sin(3x) 9 cos(3x) lim x 0 = lim x 2 x 0 = lim 2x x 0 = 9. 2 2 2. C (Geometry) Note that a line segment
March 27 Math 3260 sec. 56 Spring 2018
 March 27 Math 3260 sec. 56 Spring 2018 Section 4.6: Rank Definition: The row space, denoted Row A, of an m n matrix A is the subspace of R n spanned by the rows of A. We now have three vector spaces associated
March 27 Math 3260 sec. 56 Spring 2018 Section 4.6: Rank Definition: The row space, denoted Row A, of an m n matrix A is the subspace of R n spanned by the rows of A. We now have three vector spaces associated
Lectures notes. Rheology and Fluid Dynamics
 ÉC O L E P O L Y T E C H N IQ U E FÉ DÉR A L E D E L A U S A N N E Christophe Ancey Laboratoire hydraulique environnementale (LHE) École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne Écublens CH-05 Lausanne Lectures
ÉC O L E P O L Y T E C H N IQ U E FÉ DÉR A L E D E L A U S A N N E Christophe Ancey Laboratoire hydraulique environnementale (LHE) École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne Écublens CH-05 Lausanne Lectures
Linear Independence x
 Linear Independence A consistent system of linear equations with matrix equation Ax = b, where A is an m n matrix, has a solution set whose graph in R n is a linear object, that is, has one of only n +
Linear Independence A consistent system of linear equations with matrix equation Ax = b, where A is an m n matrix, has a solution set whose graph in R n is a linear object, that is, has one of only n +
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 20: The Gram-Schmidt process (continued). Eigenvalues and eigenvectors.
 MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 20: The Gram-Schmidt process (continued). Eigenvalues and eigenvectors. Orthogonal sets Let V be a vector space with an inner product. Definition. Nonzero vectors v 1,v
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 20: The Gram-Schmidt process (continued). Eigenvalues and eigenvectors. Orthogonal sets Let V be a vector space with an inner product. Definition. Nonzero vectors v 1,v
Chapter 3a Topics in differentiation. Problems in differentiation. Problems in differentiation. LC Abueg: mathematical economics
 Chapter 3a Topics in differentiation Lectures in Mathematical Economics L Cagandahan Abueg De La Salle University School of Economics Problems in differentiation Problems in differentiation Problem 1.
Chapter 3a Topics in differentiation Lectures in Mathematical Economics L Cagandahan Abueg De La Salle University School of Economics Problems in differentiation Problems in differentiation Problem 1.
Machine Learning: Basis and Wavelet 김화평 (CSE ) Medical Image computing lab 서진근교수연구실 Haar DWT in 2 levels
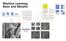 Machine Learning: Basis and Wavelet 32 157 146 204 + + + + + - + - 김화평 (CSE ) Medical Image computing lab 서진근교수연구실 7 22 38 191 17 83 188 211 71 167 194 207 135 46 40-17 18 42 20 44 31 7 13-32 + + - - +
Machine Learning: Basis and Wavelet 32 157 146 204 + + + + + - + - 김화평 (CSE ) Medical Image computing lab 서진근교수연구실 7 22 38 191 17 83 188 211 71 167 194 207 135 46 40-17 18 42 20 44 31 7 13-32 + + - - +
