Modern Methods of Data Analysis - SS 2009
|
|
|
- Frederica Phillips
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Modern Methods of Data Analysis Lecture X (2.6.09) Contents: Frequentist vs. Bayesian approach Confidence Level
2 Re: Bayes' Theorem (1) Conditional ( bedingte ) probability
3 Examples: Rare Disease (1) Probability of disease A: P(A) = P(not A) = Test for disease: P(+ A) = 0.98 P(- A) = 0.02 P(+ not A) = 0.03 P(- not A) = 0.97 Do you need to be worried if you get + as test result? What is the posteriori probability P(A +)?
4 Example: Rare Disease (2) The posterior probability is only 3.2%, due to the tiny prior probability and the non negligible misidentification rate.
5 Bayesian' Theorem with pdfs x1,... x10, measurements distributed accordingly to Gaussian with known σ, however mean a not known. Apriori pdf (probability) Normalization (does not depend on a): Frequentist approach: a is a fixed value, has no pdf, only work with L(a) Bayesian approach: Treat a as a random variable, work with f(a x)! This becomes very important for CL calculation.
6 Bayesian Interpretation of All available information about a is contained in f(a x). Possible interpretations are... best estimate Maxize probability error interval, in which the (true) parameter value is located with probability p center interval
7 Example: Coin Throwing N times a coin, obtaining H times head: Bayesian approach has proper description for parameter bounds.
8 Re: Unphysical Result in normal Likelihood Likelihood often sum of two or more components (signal + background) e.g. toy MC with 6 signal & 60 background events Although negative number of # signal unphysical, need to use them, when combining with other experiments otherwise bias.
9 Example Coin: Bayesian Likelihood Uniform distribution is mathematical identical to normal (Frequentist) Likelihood Seite 16
10 Example Coin: Bayesian Likelihood Seite 17
11 Example Coin: Bayesian Likelihood Use two different priors asuming almost unbiased coin: Gaussian distribution around 0.5 asuming very biased coin, don't exclude any other unlikely but possible hypothesis probability not zero in the center!
12 Example Coin: Bayesian Likelihood Seite 18
13 Example Coin: Bayesian Likelihood Seite 19 For large N prior has no impact anymore. Be careful to not exclude unlikely but possible results with prior!
14 Confidence Level So far got a set of recipes to derive an estimate for parameters of our model. A result is however useless without any statement how much it can be trusted. -> Confidence Level (CL) We warn the reader that there is no universal convention for the term confidence level - The Review of Particle Properties - When I use a word, it means just what I choose it to mean - neither more nor less. - Lewis Carroll ( Alice ) -
15 Example: Packets of Cereals Suppose cereal packets are produced according to Gaussian distribution of mean 520g and standard deviation 10g. 68% of the packets will weight more than 510 and less than 530g. Challenged by a consumer group we say, the real weight is between 510 and 530 g. This statement is true in 68% of the cases. Common values: Bild Seite % 90.0% 95.0% 95.4% 99.0% : : : : : 1σ 1.64σ 1.96σ 2σ 2.58σ Only true for 1-dim Gaussian!
16 Double Sided Confidence Level A CL is one number but defines two numbers a minimum and a maximum value => additional information needed The symmetric interval: limits are equidistant from the mean: The shortest interval: is minimal The central interval (usually the best one to use): (for symmetric distributions, the three definitions are equivalent)
17 Single Sided Confidence Level upper limit lower limit Be careful with wording: Upper limit of a 95% central confidence interval and the upper 95% limit are not the same. The former has 97.5% of the probability content below it and 2.5% above; the latter has 95% below and 5% above. Note: to give this intervals you assume that the pdf P(x) is given!
18 Confidence Intervals in Estimation Suppose we want to know parameter X. And have estimate from data. The measurement resolution is σ. Now need to turn knowledge of and σ into statement about confidence level about the true value X. Naïve answer: X lies in with 68% confidence and in with 95% confidence is dynamite. This means you interprete L(a) as a pdf of a, wich is not true! This contains hidden assumption of underlying (prior) distribution!
19 Example: Impossible Probability The weight of an empty dish is measured as 25.30±0.14g. A sample of powder is placed on the dish, and the combined weight measured as 25.50±0.14g. By subtraction and combination of errors, the weight of the powder is determined to be 0.2±0.2g. naïve approach to CL: There is a 16% chance of the weight being smaller 1σ and 16% being larger than 1σ compared to the measured value. It is nonsense to say, probability for negative mass is 16%!
20 How to determine CL range (I): L(x; A) is the probability density distribution to measure x, if A is the true value. For every value A we can compute the 90% central CL. For a given A, the probability to find a measurement result x outside this range is 10%. A A+ A- For true A smaller than A-, the chance to observe a value x is smaller 5%. For true A larger than A+, the chance to observe a value x is smaller 5%. Not say, the chance that true A is in [A-,A+] is 90%! (Frequentist: A is a parameter, it's value is fixed!)
21 How to determine CL range (II): E.g. Poission statistik: measure n=9 Naively (Gaussian approximation): 9±1.65* 9 = 9±4.9 True limits:
22 Confidence Level For Gaussian x is required to lie some number of standard deviations (in this case 1.64) above A-. This is the same as saying that A- must lie the same number of σ below the measured x, which can be written in the form (assume σ independ of x):
23 Confidence Level for Gaussian Lines are parallel (slope 45 ). This is only true for Gaussian distributions and no physical bounderies for A! A A A+ A+ A- A- Most of the time CL are given for searches for rare events... small rates not Gaussian.
24 Measurement of Constraint Quantity Measurement of the mass of a particle with mass 0.1g (clear physical boundary, m > 0) σ = 0.2: x ± 0.4 correspond to 95.4% Measurement of 0.5: Measurement of 0.3:... Measurement of -0.3: Measurement of -0.5: 95.4% CL: [0.1,0.9] 95.4% CL: [-0.1,0.7] => [0.0,0.7] 95.4% CL: [-0.7,0.1] => [0.0,0.1] 95.4% CL: [-0.9,-0.1] =>??? Extreme case is clear nonsense! At the moment physical boundary is touched, intervals don't correspond anymore to 95% CL.
25 Bayesian Approach Add restriction to physical boundaries to prior Renormalize probability in allowed range to 1. Distribution is now non-symmetric, so there is now a choice between symmetric, smallest & central interval. Prior is uniform for A in [0, ]
26 Example: measured mass: -0.5 ± 0.2, what is the 90% confidence single sided upper limit? P(A > x+2.5σ) = (see Table); P(A > x+3.24σ) = (see Table); including physical boundaries renormalization P(A>x+3.24*0.2)/P(A>0) = / < 10%; A+ = Bayesian approach only way to get meaningful conclusion from unphysical results Be aware: if you would use -A² or 1/A the resulting limits would be incompatible. The assumption of complete ignorance (flat distribution within physical allowed range) means different things when applied to different forms of the same basic variable.
27 Poisson Confidence Intervals Poisson distribution (for low rates): Assume we have measured n events: or or Note: If # observed events: 0; no lower limit can be placed. Poisson values are listed in tables
28 Exercise: Measurement with n=4 events. Give upper and lower 90% CL for # of expected events.assuming Poisson statistic, and physical boundary n 0 Compare to 90% CL obtained for assuming Gaussian prior without physical boundary. Compare to 90% CL obtained for assuming Gaussian prior with physical boundary (# expected events 0).
29 Confidence Region for Several Variables Consider for the moment being far away from any physical boundary - nσ region/surface defined as: Note: ± 1.96σ (ΔΧ² = 1.96²) does not correspond to 95% CL! To do: check Χ²-probability P(ndf=2, Χ²>5.99) < 5% (look at table) ΔΧ² = 5.99 or Δln(L) = 5.99/2 contour correspond to 95% CL
30 Student's t-distribution How to quote CL if there are add. uncertainties on σ? unbiased estimate if μ known: else: normalized Gaussian distribution t is distributed according to Student's distribution (slightly broader than Gaussian, slightly larger CL regions) Bild Student's distribution Seite 136
31 Exercise: A test of 20 students shows an average IQ of 128 with an of 15. What is the 90% central confidence limit on the IQ of all students? What is the 90% CL if same mean and spread is measured with 5 students only. The usual metal content of a certain ore is 5.6%. Samples of ore from a possible mining site are assayed and have metal contents of 6,7,9, and 8%. The average content is better than usual, but is this 95% significant? A ML fit gives you the result (a,b) with following Δln(L) ellipse. Is the indicated point (a1,b1) in the 95/98% CL region?
Modern Methods of Data Analysis - WS 07/08
 Modern Methods of Data Analysis Lecture VII (26.11.07) Contents: Maximum Likelihood (II) Exercise: Quality of Estimators Assume hight of students is Gaussian distributed. You measure the size of N students.
Modern Methods of Data Analysis Lecture VII (26.11.07) Contents: Maximum Likelihood (II) Exercise: Quality of Estimators Assume hight of students is Gaussian distributed. You measure the size of N students.
E. Santovetti lesson 4 Maximum likelihood Interval estimation
 E. Santovetti lesson 4 Maximum likelihood Interval estimation 1 Extended Maximum Likelihood Sometimes the number of total events measurements of the experiment n is not fixed, but, for example, is a Poisson
E. Santovetti lesson 4 Maximum likelihood Interval estimation 1 Extended Maximum Likelihood Sometimes the number of total events measurements of the experiment n is not fixed, but, for example, is a Poisson
Lecture 5. G. Cowan Lectures on Statistical Data Analysis Lecture 5 page 1
 Lecture 5 1 Probability (90 min.) Definition, Bayes theorem, probability densities and their properties, catalogue of pdfs, Monte Carlo 2 Statistical tests (90 min.) general concepts, test statistics,
Lecture 5 1 Probability (90 min.) Definition, Bayes theorem, probability densities and their properties, catalogue of pdfs, Monte Carlo 2 Statistical tests (90 min.) general concepts, test statistics,
Modern Methods of Data Analysis - WS 07/08
 Modern Methods of Data Analysis Lecture VIc (19.11.07) Contents: Maximum Likelihood Fit Maximum Likelihood (I) Assume N measurements of a random variable Assume them to be independent and distributed according
Modern Methods of Data Analysis Lecture VIc (19.11.07) Contents: Maximum Likelihood Fit Maximum Likelihood (I) Assume N measurements of a random variable Assume them to be independent and distributed according
Lecture 3. G. Cowan. Lecture 3 page 1. Lectures on Statistical Data Analysis
 Lecture 3 1 Probability (90 min.) Definition, Bayes theorem, probability densities and their properties, catalogue of pdfs, Monte Carlo 2 Statistical tests (90 min.) general concepts, test statistics,
Lecture 3 1 Probability (90 min.) Definition, Bayes theorem, probability densities and their properties, catalogue of pdfs, Monte Carlo 2 Statistical tests (90 min.) general concepts, test statistics,
Statistics of Small Signals
 Statistics of Small Signals Gary Feldman Harvard University NEPPSR August 17, 2005 Statistics of Small Signals In 1998, Bob Cousins and I were working on the NOMAD neutrino oscillation experiment and we
Statistics of Small Signals Gary Feldman Harvard University NEPPSR August 17, 2005 Statistics of Small Signals In 1998, Bob Cousins and I were working on the NOMAD neutrino oscillation experiment and we
Physics 403. Segev BenZvi. Credible Intervals, Confidence Intervals, and Limits. Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Rochester
 Physics 403 Credible Intervals, Confidence Intervals, and Limits Segev BenZvi Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Rochester Table of Contents 1 Summarizing Parameters with a Range Bayesian
Physics 403 Credible Intervals, Confidence Intervals, and Limits Segev BenZvi Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Rochester Table of Contents 1 Summarizing Parameters with a Range Bayesian
Physics 509: Bootstrap and Robust Parameter Estimation
 Physics 509: Bootstrap and Robust Parameter Estimation Scott Oser Lecture #20 Physics 509 1 Nonparametric parameter estimation Question: what error estimate should you assign to the slope and intercept
Physics 509: Bootstrap and Robust Parameter Estimation Scott Oser Lecture #20 Physics 509 1 Nonparametric parameter estimation Question: what error estimate should you assign to the slope and intercept
Statistical Methods for Astronomy
 Statistical Methods for Astronomy If your experiment needs statistics, you ought to have done a better experiment. -Ernest Rutherford Lecture 1 Lecture 2 Why do we need statistics? Definitions Statistical
Statistical Methods for Astronomy If your experiment needs statistics, you ought to have done a better experiment. -Ernest Rutherford Lecture 1 Lecture 2 Why do we need statistics? Definitions Statistical
Bayesian Models in Machine Learning
 Bayesian Models in Machine Learning Lukáš Burget Escuela de Ciencias Informáticas 2017 Buenos Aires, July 24-29 2017 Frequentist vs. Bayesian Frequentist point of view: Probability is the frequency of
Bayesian Models in Machine Learning Lukáš Burget Escuela de Ciencias Informáticas 2017 Buenos Aires, July 24-29 2017 Frequentist vs. Bayesian Frequentist point of view: Probability is the frequency of
Statistical Methods for Astronomy
 Statistical Methods for Astronomy Probability (Lecture 1) Statistics (Lecture 2) Why do we need statistics? Useful Statistics Definitions Error Analysis Probability distributions Error Propagation Binomial
Statistical Methods for Astronomy Probability (Lecture 1) Statistics (Lecture 2) Why do we need statistics? Useful Statistics Definitions Error Analysis Probability distributions Error Propagation Binomial
Statistical Data Analysis Stat 3: p-values, parameter estimation
 Statistical Data Analysis Stat 3: p-values, parameter estimation London Postgraduate Lectures on Particle Physics; University of London MSci course PH4515 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway,
Statistical Data Analysis Stat 3: p-values, parameter estimation London Postgraduate Lectures on Particle Physics; University of London MSci course PH4515 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway,
Journeys of an Accidental Statistician
 Journeys of an Accidental Statistician A partially anecdotal account of A Unified Approach to the Classical Statistical Analysis of Small Signals, GJF and Robert D. Cousins, Phys. Rev. D 57, 3873 (1998)
Journeys of an Accidental Statistician A partially anecdotal account of A Unified Approach to the Classical Statistical Analysis of Small Signals, GJF and Robert D. Cousins, Phys. Rev. D 57, 3873 (1998)
Parameter estimation Conditional risk
 Parameter estimation Conditional risk Formalizing the problem Specify random variables we care about e.g., Commute Time e.g., Heights of buildings in a city We might then pick a particular distribution
Parameter estimation Conditional risk Formalizing the problem Specify random variables we care about e.g., Commute Time e.g., Heights of buildings in a city We might then pick a particular distribution
Statistical Methods for Astronomy
 Statistical Methods for Astronomy Probability (Lecture 1) Statistics (Lecture 2) Why do we need statistics? Useful Statistics Definitions Error Analysis Probability distributions Error Propagation Binomial
Statistical Methods for Astronomy Probability (Lecture 1) Statistics (Lecture 2) Why do we need statistics? Useful Statistics Definitions Error Analysis Probability distributions Error Propagation Binomial
Statistical Methods in Particle Physics
 Statistical Methods in Particle Physics Lecture 11 January 7, 2013 Silvia Masciocchi, GSI Darmstadt s.masciocchi@gsi.de Winter Semester 2012 / 13 Outline How to communicate the statistical uncertainty
Statistical Methods in Particle Physics Lecture 11 January 7, 2013 Silvia Masciocchi, GSI Darmstadt s.masciocchi@gsi.de Winter Semester 2012 / 13 Outline How to communicate the statistical uncertainty
Systematic uncertainties in statistical data analysis for particle physics. DESY Seminar Hamburg, 31 March, 2009
 Systematic uncertainties in statistical data analysis for particle physics DESY Seminar Hamburg, 31 March, 2009 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway, University of London g.cowan@rhul.ac.uk www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan
Systematic uncertainties in statistical data analysis for particle physics DESY Seminar Hamburg, 31 March, 2009 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway, University of London g.cowan@rhul.ac.uk www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan
Statistics and Data Analysis
 Statistics and Data Analysis The Crash Course Physics 226, Fall 2013 "There are three kinds of lies: lies, damned lies, and statistics. Mark Twain, allegedly after Benjamin Disraeli Statistics and Data
Statistics and Data Analysis The Crash Course Physics 226, Fall 2013 "There are three kinds of lies: lies, damned lies, and statistics. Mark Twain, allegedly after Benjamin Disraeli Statistics and Data
Statistics. Lent Term 2015 Prof. Mark Thomson. 2: The Gaussian Limit
 Statistics Lent Term 2015 Prof. Mark Thomson Lecture 2 : The Gaussian Limit Prof. M.A. Thomson Lent Term 2015 29 Lecture Lecture Lecture Lecture 1: Back to basics Introduction, Probability distribution
Statistics Lent Term 2015 Prof. Mark Thomson Lecture 2 : The Gaussian Limit Prof. M.A. Thomson Lent Term 2015 29 Lecture Lecture Lecture Lecture 1: Back to basics Introduction, Probability distribution
Statistics for the LHC Lecture 1: Introduction
 Statistics for the LHC Lecture 1: Introduction Academic Training Lectures CERN, 14 17 June, 2010 indico.cern.ch/conferencedisplay.py?confid=77830 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway, University
Statistics for the LHC Lecture 1: Introduction Academic Training Lectures CERN, 14 17 June, 2010 indico.cern.ch/conferencedisplay.py?confid=77830 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway, University
Parametric Models. Dr. Shuang LIANG. School of Software Engineering TongJi University Fall, 2012
 Parametric Models Dr. Shuang LIANG School of Software Engineering TongJi University Fall, 2012 Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood Estimation Bayesian Density Estimation Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood
Parametric Models Dr. Shuang LIANG School of Software Engineering TongJi University Fall, 2012 Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood Estimation Bayesian Density Estimation Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood
AST 418/518 Instrumentation and Statistics
 AST 418/518 Instrumentation and Statistics Class Website: http://ircamera.as.arizona.edu/astr_518 Class Texts: Practical Statistics for Astronomers, J.V. Wall, and C.R. Jenkins Measuring the Universe,
AST 418/518 Instrumentation and Statistics Class Website: http://ircamera.as.arizona.edu/astr_518 Class Texts: Practical Statistics for Astronomers, J.V. Wall, and C.R. Jenkins Measuring the Universe,
Brandon C. Kelly (Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics)
 Brandon C. Kelly (Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics) Probability quantifies randomness and uncertainty How do I estimate the normalization and logarithmic slope of a X ray continuum, assuming
Brandon C. Kelly (Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics) Probability quantifies randomness and uncertainty How do I estimate the normalization and logarithmic slope of a X ray continuum, assuming
Statistics notes. A clear statistical framework formulates the logic of what we are doing and why. It allows us to make precise statements.
 Statistics notes Introductory comments These notes provide a summary or cheat sheet covering some basic statistical recipes and methods. These will be discussed in more detail in the lectures! What is
Statistics notes Introductory comments These notes provide a summary or cheat sheet covering some basic statistical recipes and methods. These will be discussed in more detail in the lectures! What is
Statistics for Data Analysis. Niklaus Berger. PSI Practical Course Physics Institute, University of Heidelberg
 Statistics for Data Analysis PSI Practical Course 2014 Niklaus Berger Physics Institute, University of Heidelberg Overview You are going to perform a data analysis: Compare measured distributions to theoretical
Statistics for Data Analysis PSI Practical Course 2014 Niklaus Berger Physics Institute, University of Heidelberg Overview You are going to perform a data analysis: Compare measured distributions to theoretical
Frequentist Statistics and Hypothesis Testing Spring
 Frequentist Statistics and Hypothesis Testing 18.05 Spring 2018 http://xkcd.com/539/ Agenda Introduction to the frequentist way of life. What is a statistic? NHST ingredients; rejection regions Simple
Frequentist Statistics and Hypothesis Testing 18.05 Spring 2018 http://xkcd.com/539/ Agenda Introduction to the frequentist way of life. What is a statistic? NHST ingredients; rejection regions Simple
Chapter 3: Maximum-Likelihood & Bayesian Parameter Estimation (part 1)
 HW 1 due today Parameter Estimation Biometrics CSE 190 Lecture 7 Today s lecture was on the blackboard. These slides are an alternative presentation of the material. CSE190, Winter10 CSE190, Winter10 Chapter
HW 1 due today Parameter Estimation Biometrics CSE 190 Lecture 7 Today s lecture was on the blackboard. These slides are an alternative presentation of the material. CSE190, Winter10 CSE190, Winter10 Chapter
Statistical Methods for Discovery and Limits in HEP Experiments Day 3: Exclusion Limits
 Statistical Methods for Discovery and Limits in HEP Experiments Day 3: Exclusion Limits www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan/stat_freiburg.html Vorlesungen des GK Physik an Hadron-Beschleunigern, Freiburg, 27-29 June,
Statistical Methods for Discovery and Limits in HEP Experiments Day 3: Exclusion Limits www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan/stat_freiburg.html Vorlesungen des GK Physik an Hadron-Beschleunigern, Freiburg, 27-29 June,
Primer on statistics:
 Primer on statistics: MLE, Confidence Intervals, and Hypothesis Testing ryan.reece@gmail.com http://rreece.github.io/ Insight Data Science - AI Fellows Workshop Feb 16, 018 Outline 1. Maximum likelihood
Primer on statistics: MLE, Confidence Intervals, and Hypothesis Testing ryan.reece@gmail.com http://rreece.github.io/ Insight Data Science - AI Fellows Workshop Feb 16, 018 Outline 1. Maximum likelihood
Stat 535 C - Statistical Computing & Monte Carlo Methods. Arnaud Doucet.
 Stat 535 C - Statistical Computing & Monte Carlo Methods Arnaud Doucet Email: arnaud@cs.ubc.ca 1 CS students: don t forget to re-register in CS-535D. Even if you just audit this course, please do register.
Stat 535 C - Statistical Computing & Monte Carlo Methods Arnaud Doucet Email: arnaud@cs.ubc.ca 1 CS students: don t forget to re-register in CS-535D. Even if you just audit this course, please do register.
Statistical Models with Uncertain Error Parameters (G. Cowan, arxiv: )
 Statistical Models with Uncertain Error Parameters (G. Cowan, arxiv:1809.05778) Workshop on Advanced Statistics for Physics Discovery aspd.stat.unipd.it Department of Statistical Sciences, University of
Statistical Models with Uncertain Error Parameters (G. Cowan, arxiv:1809.05778) Workshop on Advanced Statistics for Physics Discovery aspd.stat.unipd.it Department of Statistical Sciences, University of
ECE295, Data Assimila0on and Inverse Problems, Spring 2015
 ECE295, Data Assimila0on and Inverse Problems, Spring 2015 1 April, Intro; Linear discrete Inverse problems (Aster Ch 1 and 2) Slides 8 April, SVD (Aster ch 2 and 3) Slides 15 April, RegularizaFon (ch
ECE295, Data Assimila0on and Inverse Problems, Spring 2015 1 April, Intro; Linear discrete Inverse problems (Aster Ch 1 and 2) Slides 8 April, SVD (Aster ch 2 and 3) Slides 15 April, RegularizaFon (ch
Advanced Statistical Methods. Lecture 6
 Advanced Statistical Methods Lecture 6 Convergence distribution of M.-H. MCMC We denote the PDF estimated by the MCMC as. It has the property Convergence distribution After some time, the distribution
Advanced Statistical Methods Lecture 6 Convergence distribution of M.-H. MCMC We denote the PDF estimated by the MCMC as. It has the property Convergence distribution After some time, the distribution
Statistical Methods in Particle Physics Lecture 1: Bayesian methods
 Statistical Methods in Particle Physics Lecture 1: Bayesian methods SUSSP65 St Andrews 16 29 August 2009 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway, University of London g.cowan@rhul.ac.uk www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan
Statistical Methods in Particle Physics Lecture 1: Bayesian methods SUSSP65 St Andrews 16 29 August 2009 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway, University of London g.cowan@rhul.ac.uk www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan
Strong Lens Modeling (II): Statistical Methods
 Strong Lens Modeling (II): Statistical Methods Chuck Keeton Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey Probability theory multiple random variables, a and b joint distribution p(a, b) conditional distribution
Strong Lens Modeling (II): Statistical Methods Chuck Keeton Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey Probability theory multiple random variables, a and b joint distribution p(a, b) conditional distribution
Statistical Methods in Particle Physics. Lecture 2
 Statistical Methods in Particle Physics Lecture 2 October 17, 2011 Silvia Masciocchi, GSI Darmstadt s.masciocchi@gsi.de Winter Semester 2011 / 12 Outline Probability Definition and interpretation Kolmogorov's
Statistical Methods in Particle Physics Lecture 2 October 17, 2011 Silvia Masciocchi, GSI Darmstadt s.masciocchi@gsi.de Winter Semester 2011 / 12 Outline Probability Definition and interpretation Kolmogorov's
Statistical Distribution Assumptions of General Linear Models
 Statistical Distribution Assumptions of General Linear Models Applied Multilevel Models for Cross Sectional Data Lecture 4 ICPSR Summer Workshop University of Colorado Boulder Lecture 4: Statistical Distributions
Statistical Distribution Assumptions of General Linear Models Applied Multilevel Models for Cross Sectional Data Lecture 4 ICPSR Summer Workshop University of Colorado Boulder Lecture 4: Statistical Distributions
Statistical Methods for Particle Physics Lecture 1: parameter estimation, statistical tests
 Statistical Methods for Particle Physics Lecture 1: parameter estimation, statistical tests http://benasque.org/2018tae/cgi-bin/talks/allprint.pl TAE 2018 Benasque, Spain 3-15 Sept 2018 Glen Cowan Physics
Statistical Methods for Particle Physics Lecture 1: parameter estimation, statistical tests http://benasque.org/2018tae/cgi-bin/talks/allprint.pl TAE 2018 Benasque, Spain 3-15 Sept 2018 Glen Cowan Physics
Parameter Estimation and Fitting to Data
 Parameter Estimation and Fitting to Data Parameter estimation Maximum likelihood Least squares Goodness-of-fit Examples Elton S. Smith, Jefferson Lab 1 Parameter estimation Properties of estimators 3 An
Parameter Estimation and Fitting to Data Parameter estimation Maximum likelihood Least squares Goodness-of-fit Examples Elton S. Smith, Jefferson Lab 1 Parameter estimation Properties of estimators 3 An
Bayesian Inference. STA 121: Regression Analysis Artin Armagan
 Bayesian Inference STA 121: Regression Analysis Artin Armagan Bayes Rule...s! Reverend Thomas Bayes Posterior Prior p(θ y) = p(y θ)p(θ)/p(y) Likelihood - Sampling Distribution Normalizing Constant: p(y
Bayesian Inference STA 121: Regression Analysis Artin Armagan Bayes Rule...s! Reverend Thomas Bayes Posterior Prior p(θ y) = p(y θ)p(θ)/p(y) Likelihood - Sampling Distribution Normalizing Constant: p(y
arxiv:hep-ex/ v1 2 Jun 2000
 MPI H - V7-000 May 3, 000 Averaging Measurements with Hidden Correlations and Asymmetric Errors Michael Schmelling / MPI for Nuclear Physics Postfach 03980, D-6909 Heidelberg arxiv:hep-ex/0006004v Jun
MPI H - V7-000 May 3, 000 Averaging Measurements with Hidden Correlations and Asymmetric Errors Michael Schmelling / MPI for Nuclear Physics Postfach 03980, D-6909 Heidelberg arxiv:hep-ex/0006004v Jun
Physics 509: Propagating Systematic Uncertainties. Scott Oser Lecture #12
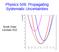 Physics 509: Propagating Systematic Uncertainties Scott Oser Lecture #1 1 Additive offset model Suppose we take N measurements from a distribution, and wish to estimate the true mean of the underlying
Physics 509: Propagating Systematic Uncertainties Scott Oser Lecture #1 1 Additive offset model Suppose we take N measurements from a distribution, and wish to estimate the true mean of the underlying
Introduction: MLE, MAP, Bayesian reasoning (28/8/13)
 STA561: Probabilistic machine learning Introduction: MLE, MAP, Bayesian reasoning (28/8/13) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribes: K. Ulrich, J. Subramanian, N. Raval, J. O Hollaren 1 Classifiers In this
STA561: Probabilistic machine learning Introduction: MLE, MAP, Bayesian reasoning (28/8/13) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribes: K. Ulrich, J. Subramanian, N. Raval, J. O Hollaren 1 Classifiers In this
Lecture 1: Probability Fundamentals
 Lecture 1: Probability Fundamentals IB Paper 7: Probability and Statistics Carl Edward Rasmussen Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge January 22nd, 2008 Rasmussen (CUED) Lecture 1: Probability
Lecture 1: Probability Fundamentals IB Paper 7: Probability and Statistics Carl Edward Rasmussen Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge January 22nd, 2008 Rasmussen (CUED) Lecture 1: Probability
Probability and Estimation. Alan Moses
 Probability and Estimation Alan Moses Random variables and probability A random variable is like a variable in algebra (e.g., y=e x ), but where at least part of the variability is taken to be stochastic.
Probability and Estimation Alan Moses Random variables and probability A random variable is like a variable in algebra (e.g., y=e x ), but where at least part of the variability is taken to be stochastic.
Machine Learning 4771
 Machine Learning 4771 Instructor: Tony Jebara Topic 11 Maximum Likelihood as Bayesian Inference Maximum A Posteriori Bayesian Gaussian Estimation Why Maximum Likelihood? So far, assumed max (log) likelihood
Machine Learning 4771 Instructor: Tony Jebara Topic 11 Maximum Likelihood as Bayesian Inference Maximum A Posteriori Bayesian Gaussian Estimation Why Maximum Likelihood? So far, assumed max (log) likelihood
COS513: FOUNDATIONS OF PROBABILISTIC MODELS LECTURE 10
 COS53: FOUNDATIONS OF PROBABILISTIC MODELS LECTURE 0 MELISSA CARROLL, LINJIE LUO. BIAS-VARIANCE TRADE-OFF (CONTINUED FROM LAST LECTURE) If V = (X n, Y n )} are observed data, the linear regression problem
COS53: FOUNDATIONS OF PROBABILISTIC MODELS LECTURE 0 MELISSA CARROLL, LINJIE LUO. BIAS-VARIANCE TRADE-OFF (CONTINUED FROM LAST LECTURE) If V = (X n, Y n )} are observed data, the linear regression problem
Computational Biology Lecture #3: Probability and Statistics. Bud Mishra Professor of Computer Science, Mathematics, & Cell Biology Sept
 Computational Biology Lecture #3: Probability and Statistics Bud Mishra Professor of Computer Science, Mathematics, & Cell Biology Sept 26 2005 L2-1 Basic Probabilities L2-2 1 Random Variables L2-3 Examples
Computational Biology Lecture #3: Probability and Statistics Bud Mishra Professor of Computer Science, Mathematics, & Cell Biology Sept 26 2005 L2-1 Basic Probabilities L2-2 1 Random Variables L2-3 Examples
Parameter estimation and forecasting. Cristiano Porciani AIfA, Uni-Bonn
 Parameter estimation and forecasting Cristiano Porciani AIfA, Uni-Bonn Questions? C. Porciani Estimation & forecasting 2 Temperature fluctuations Variance at multipole l (angle ~180o/l) C. Porciani Estimation
Parameter estimation and forecasting Cristiano Porciani AIfA, Uni-Bonn Questions? C. Porciani Estimation & forecasting 2 Temperature fluctuations Variance at multipole l (angle ~180o/l) C. Porciani Estimation
arxiv: v1 [physics.data-an] 2 Mar 2011
![arxiv: v1 [physics.data-an] 2 Mar 2011 arxiv: v1 [physics.data-an] 2 Mar 2011](/thumbs/74/70548665.jpg) Incorporating Nuisance Parameters in Likelihoods for Multisource Spectra J. S. Conway University of California, Davis, USA arxiv:1103.0354v1 [physics.data-an] Mar 011 1 Overview Abstract We describe here
Incorporating Nuisance Parameters in Likelihoods for Multisource Spectra J. S. Conway University of California, Davis, USA arxiv:1103.0354v1 [physics.data-an] Mar 011 1 Overview Abstract We describe here
Machine Learning. Bayes Basics. Marc Toussaint U Stuttgart. Bayes, probabilities, Bayes theorem & examples
 Machine Learning Bayes Basics Bayes, probabilities, Bayes theorem & examples Marc Toussaint U Stuttgart So far: Basic regression & classification methods: Features + Loss + Regularization & CV All kinds
Machine Learning Bayes Basics Bayes, probabilities, Bayes theorem & examples Marc Toussaint U Stuttgart So far: Basic regression & classification methods: Features + Loss + Regularization & CV All kinds
Statistics: Learning models from data
 DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 5 October 19, 2015 Statistics: Learning models from data Learning models from data that are assumed to be generated probabilistically from a certain unknown distribution is a crucial
DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 5 October 19, 2015 Statistics: Learning models from data Learning models from data that are assumed to be generated probabilistically from a certain unknown distribution is a crucial
Today. Statistical Learning. Coin Flip. Coin Flip. Experiment 1: Heads. Experiment 1: Heads. Which coin will I use? Which coin will I use?
 Today Statistical Learning Parameter Estimation: Maximum Likelihood (ML) Maximum A Posteriori (MAP) Bayesian Continuous case Learning Parameters for a Bayesian Network Naive Bayes Maximum Likelihood estimates
Today Statistical Learning Parameter Estimation: Maximum Likelihood (ML) Maximum A Posteriori (MAP) Bayesian Continuous case Learning Parameters for a Bayesian Network Naive Bayes Maximum Likelihood estimates
Estimation of reliability parameters from Experimental data (Parte 2) Prof. Enrico Zio
 Estimation of reliability parameters from Experimental data (Parte 2) This lecture Life test (t 1,t 2,...,t n ) Estimate θ of f T t θ For example: λ of f T (t)= λe - λt Classical approach (frequentist
Estimation of reliability parameters from Experimental data (Parte 2) This lecture Life test (t 1,t 2,...,t n ) Estimate θ of f T t θ For example: λ of f T (t)= λe - λt Classical approach (frequentist
Statistics. Lecture 4 August 9, 2000 Frank Porter Caltech. 1. The Fundamentals; Point Estimation. 2. Maximum Likelihood, Least Squares and All That
 Statistics Lecture 4 August 9, 2000 Frank Porter Caltech The plan for these lectures: 1. The Fundamentals; Point Estimation 2. Maximum Likelihood, Least Squares and All That 3. What is a Confidence Interval?
Statistics Lecture 4 August 9, 2000 Frank Porter Caltech The plan for these lectures: 1. The Fundamentals; Point Estimation 2. Maximum Likelihood, Least Squares and All That 3. What is a Confidence Interval?
A Brief Review of Probability, Bayesian Statistics, and Information Theory
 A Brief Review of Probability, Bayesian Statistics, and Information Theory Brendan Frey Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto frey@psi.toronto.edu http://www.psi.toronto.edu A system
A Brief Review of Probability, Bayesian Statistics, and Information Theory Brendan Frey Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto frey@psi.toronto.edu http://www.psi.toronto.edu A system
Physics 509: Error Propagation, and the Meaning of Error Bars. Scott Oser Lecture #10
 Physics 509: Error Propagation, and the Meaning of Error Bars Scott Oser Lecture #10 1 What is an error bar? Someone hands you a plot like this. What do the error bars indicate? Answer: you can never be
Physics 509: Error Propagation, and the Meaning of Error Bars Scott Oser Lecture #10 1 What is an error bar? Someone hands you a plot like this. What do the error bars indicate? Answer: you can never be
Universität Potsdam Institut für Informatik Lehrstuhl Maschinelles Lernen. Bayesian Learning. Tobias Scheffer, Niels Landwehr
 Universität Potsdam Institut für Informatik Lehrstuhl Maschinelles Lernen Bayesian Learning Tobias Scheffer, Niels Landwehr Remember: Normal Distribution Distribution over x. Density function with parameters
Universität Potsdam Institut für Informatik Lehrstuhl Maschinelles Lernen Bayesian Learning Tobias Scheffer, Niels Landwehr Remember: Normal Distribution Distribution over x. Density function with parameters
PHYS 6710: Nuclear and Particle Physics II
 Data Analysis Content (~7 Classes) Uncertainties and errors Random variables, expectation value, (co)variance Distributions and samples Binomial, Poisson, and Normal Distribution Student's t-distribution
Data Analysis Content (~7 Classes) Uncertainties and errors Random variables, expectation value, (co)variance Distributions and samples Binomial, Poisson, and Normal Distribution Student's t-distribution
Natural Hazards and Disaster. Lab 1: Risk Concept Risk Probability Questions
 Natural Hazards and Disaster Lab 1: Risk Concept Risk Questions Risk Definition: Risk is the potential for consequences where something of value is at stake and where the outcome is uncertain Measuring
Natural Hazards and Disaster Lab 1: Risk Concept Risk Questions Risk Definition: Risk is the potential for consequences where something of value is at stake and where the outcome is uncertain Measuring
Bayesian Inference. Introduction
 Bayesian Inference Introduction The frequentist approach to inference holds that probabilities are intrinsicially tied (unsurprisingly) to frequencies. This interpretation is actually quite natural. What,
Bayesian Inference Introduction The frequentist approach to inference holds that probabilities are intrinsicially tied (unsurprisingly) to frequencies. This interpretation is actually quite natural. What,
STAT 499/962 Topics in Statistics Bayesian Inference and Decision Theory Jan 2018, Handout 01
 STAT 499/962 Topics in Statistics Bayesian Inference and Decision Theory Jan 2018, Handout 01 Nasser Sadeghkhani a.sadeghkhani@queensu.ca There are two main schools to statistical inference: 1-frequentist
STAT 499/962 Topics in Statistics Bayesian Inference and Decision Theory Jan 2018, Handout 01 Nasser Sadeghkhani a.sadeghkhani@queensu.ca There are two main schools to statistical inference: 1-frequentist
Chapter 5. Bayesian Statistics
 Chapter 5. Bayesian Statistics Principles of Bayesian Statistics Anything unknown is given a probability distribution, representing degrees of belief [subjective probability]. Degrees of belief [subjective
Chapter 5. Bayesian Statistics Principles of Bayesian Statistics Anything unknown is given a probability distribution, representing degrees of belief [subjective probability]. Degrees of belief [subjective
MS&E 226: Small Data
 MS&E 226: Small Data Lecture 12: Frequentist properties of estimators (v4) Ramesh Johari ramesh.johari@stanford.edu 1 / 39 Frequentist inference 2 / 39 Thinking like a frequentist Suppose that for some
MS&E 226: Small Data Lecture 12: Frequentist properties of estimators (v4) Ramesh Johari ramesh.johari@stanford.edu 1 / 39 Frequentist inference 2 / 39 Thinking like a frequentist Suppose that for some
Hypothesis Testing - Frequentist
 Frequentist Hypothesis Testing - Frequentist Compare two hypotheses to see which one better explains the data. Or, alternatively, what is the best way to separate events into two classes, those originating
Frequentist Hypothesis Testing - Frequentist Compare two hypotheses to see which one better explains the data. Or, alternatively, what is the best way to separate events into two classes, those originating
9/12/17. Types of learning. Modeling data. Supervised learning: Classification. Supervised learning: Regression. Unsupervised learning: Clustering
 Types of learning Modeling data Supervised: we know input and targets Goal is to learn a model that, given input data, accurately predicts target data Unsupervised: we know the input only and want to make
Types of learning Modeling data Supervised: we know input and targets Goal is to learn a model that, given input data, accurately predicts target data Unsupervised: we know the input only and want to make
Bayes Formula. MATH 107: Finite Mathematics University of Louisville. March 26, 2014
 Bayes Formula MATH 07: Finite Mathematics University of Louisville March 26, 204 Test Accuracy Conditional reversal 2 / 5 A motivating question A rare disease occurs in out of every 0,000 people. A test
Bayes Formula MATH 07: Finite Mathematics University of Louisville March 26, 204 Test Accuracy Conditional reversal 2 / 5 A motivating question A rare disease occurs in out of every 0,000 people. A test
Topics in Statistical Data Analysis for HEP Lecture 1: Bayesian Methods CERN-JINR European School of High Energy Physics Bautzen, June 2009
 Topics in Statistical Data Analysis for HEP Lecture 1: Bayesian Methods CERN-JINR European School of High Energy Physics Bautzen, 14 27 June 2009 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway, University
Topics in Statistical Data Analysis for HEP Lecture 1: Bayesian Methods CERN-JINR European School of High Energy Physics Bautzen, 14 27 June 2009 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway, University
Statistical techniques for data analysis in Cosmology
 Statistical techniques for data analysis in Cosmology arxiv:0712.3028; arxiv:0911.3105 Numerical recipes (the bible ) Licia Verde ICREA & ICC UB-IEEC http://icc.ub.edu/~liciaverde outline Lecture 1: Introduction
Statistical techniques for data analysis in Cosmology arxiv:0712.3028; arxiv:0911.3105 Numerical recipes (the bible ) Licia Verde ICREA & ICC UB-IEEC http://icc.ub.edu/~liciaverde outline Lecture 1: Introduction
Some slides from Carlos Guestrin, Luke Zettlemoyer & K Gajos 2
 Logistics CSE 446: Point Estimation Winter 2012 PS2 out shortly Dan Weld Some slides from Carlos Guestrin, Luke Zettlemoyer & K Gajos 2 Last Time Random variables, distributions Marginal, joint & conditional
Logistics CSE 446: Point Estimation Winter 2012 PS2 out shortly Dan Weld Some slides from Carlos Guestrin, Luke Zettlemoyer & K Gajos 2 Last Time Random variables, distributions Marginal, joint & conditional
Classical and Bayesian inference
 Classical and Bayesian inference AMS 132 Claudia Wehrhahn (UCSC) Classical and Bayesian inference January 8 1 / 11 The Prior Distribution Definition Suppose that one has a statistical model with parameter
Classical and Bayesian inference AMS 132 Claudia Wehrhahn (UCSC) Classical and Bayesian inference January 8 1 / 11 The Prior Distribution Definition Suppose that one has a statistical model with parameter
Probabilistic Machine Learning
 Probabilistic Machine Learning Bayesian Nets, MCMC, and more Marek Petrik 4/18/2017 Based on: P. Murphy, K. (2012). Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective. Chapter 10. Conditional Independence Independent
Probabilistic Machine Learning Bayesian Nets, MCMC, and more Marek Petrik 4/18/2017 Based on: P. Murphy, K. (2012). Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective. Chapter 10. Conditional Independence Independent
Data Mining Chapter 4: Data Analysis and Uncertainty Fall 2011 Ming Li Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University
 Data Mining Chapter 4: Data Analysis and Uncertainty Fall 2011 Ming Li Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University Why uncertainty? Why should data mining care about uncertainty? We
Data Mining Chapter 4: Data Analysis and Uncertainty Fall 2011 Ming Li Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University Why uncertainty? Why should data mining care about uncertainty? We
Introductory Statistics Course Part II
 Introductory Statistics Course Part II https://indico.cern.ch/event/735431/ PHYSTAT ν CERN 22-25 January 2019 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway, University of London g.cowan@rhul.ac.uk www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan
Introductory Statistics Course Part II https://indico.cern.ch/event/735431/ PHYSTAT ν CERN 22-25 January 2019 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway, University of London g.cowan@rhul.ac.uk www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan
SYDE 372 Introduction to Pattern Recognition. Probability Measures for Classification: Part I
 SYDE 372 Introduction to Pattern Recognition Probability Measures for Classification: Part I Alexander Wong Department of Systems Design Engineering University of Waterloo Outline 1 2 3 4 Why use probability
SYDE 372 Introduction to Pattern Recognition Probability Measures for Classification: Part I Alexander Wong Department of Systems Design Engineering University of Waterloo Outline 1 2 3 4 Why use probability
Lecture 5: Bayes pt. 1
 Lecture 5: Bayes pt. 1 D. Jason Koskinen koskinen@nbi.ku.dk Photo by Howard Jackman University of Copenhagen Advanced Methods in Applied Statistics Feb - Apr 2016 Niels Bohr Institute 2 Bayes Probabilities
Lecture 5: Bayes pt. 1 D. Jason Koskinen koskinen@nbi.ku.dk Photo by Howard Jackman University of Copenhagen Advanced Methods in Applied Statistics Feb - Apr 2016 Niels Bohr Institute 2 Bayes Probabilities
Bayesian Learning (II)
 Universität Potsdam Institut für Informatik Lehrstuhl Maschinelles Lernen Bayesian Learning (II) Niels Landwehr Overview Probabilities, expected values, variance Basic concepts of Bayesian learning MAP
Universität Potsdam Institut für Informatik Lehrstuhl Maschinelles Lernen Bayesian Learning (II) Niels Landwehr Overview Probabilities, expected values, variance Basic concepts of Bayesian learning MAP
2. A Basic Statistical Toolbox
 . A Basic Statistical Toolbo Statistics is a mathematical science pertaining to the collection, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. Wikipedia definition Mathematical statistics: concerned
. A Basic Statistical Toolbo Statistics is a mathematical science pertaining to the collection, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. Wikipedia definition Mathematical statistics: concerned
Statistical Methods for Particle Physics (I)
 Statistical Methods for Particle Physics (I) https://agenda.infn.it/conferencedisplay.py?confid=14407 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway, University of London g.cowan@rhul.ac.uk www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan
Statistical Methods for Particle Physics (I) https://agenda.infn.it/conferencedisplay.py?confid=14407 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway, University of London g.cowan@rhul.ac.uk www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan
Advanced Herd Management Probabilities and distributions
 Advanced Herd Management Probabilities and distributions Anders Ringgaard Kristensen Slide 1 Outline Probabilities Conditional probabilities Bayes theorem Distributions Discrete Continuous Distribution
Advanced Herd Management Probabilities and distributions Anders Ringgaard Kristensen Slide 1 Outline Probabilities Conditional probabilities Bayes theorem Distributions Discrete Continuous Distribution
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining
 CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining MLE and MAP Original version of these slides by Mark Schmidt, with modifications by Mike Gelbart. 1 Admin Assignment 4: Due tonight. Assignment 5: Will be released
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining MLE and MAP Original version of these slides by Mark Schmidt, with modifications by Mike Gelbart. 1 Admin Assignment 4: Due tonight. Assignment 5: Will be released
Accouncements. You should turn in a PDF and a python file(s) Figure for problem 9 should be in the PDF
 Accouncements You should turn in a PDF and a python file(s) Figure for problem 9 should be in the PDF Please do not zip these files and submit (unless there are >5 files) 1 Bayesian Methods Machine Learning
Accouncements You should turn in a PDF and a python file(s) Figure for problem 9 should be in the PDF Please do not zip these files and submit (unless there are >5 files) 1 Bayesian Methods Machine Learning
Algorithmisches Lernen/Machine Learning
 Algorithmisches Lernen/Machine Learning Part 1: Stefan Wermter Introduction Connectionist Learning (e.g. Neural Networks) Decision-Trees, Genetic Algorithms Part 2: Norman Hendrich Support-Vector Machines
Algorithmisches Lernen/Machine Learning Part 1: Stefan Wermter Introduction Connectionist Learning (e.g. Neural Networks) Decision-Trees, Genetic Algorithms Part 2: Norman Hendrich Support-Vector Machines
Bayesian data analysis using JASP
 Bayesian data analysis using JASP Dani Navarro compcogscisydney.com/jasp-tute.html Part 1: Theory Philosophy of probability Introducing Bayes rule Bayesian reasoning A simple example Bayesian hypothesis
Bayesian data analysis using JASP Dani Navarro compcogscisydney.com/jasp-tute.html Part 1: Theory Philosophy of probability Introducing Bayes rule Bayesian reasoning A simple example Bayesian hypothesis
Statistical Data Analysis Stat 5: More on nuisance parameters, Bayesian methods
 Statistical Data Analysis Stat 5: More on nuisance parameters, Bayesian methods London Postgraduate Lectures on Particle Physics; University of London MSci course PH4515 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal
Statistical Data Analysis Stat 5: More on nuisance parameters, Bayesian methods London Postgraduate Lectures on Particle Physics; University of London MSci course PH4515 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal
Statistics for Particle Physics. Kyle Cranmer. New York University. Kyle Cranmer (NYU) CERN Academic Training, Feb 2-5, 2009
 Statistics for Particle Physics Kyle Cranmer New York University 91 Remaining Lectures Lecture 3:! Compound hypotheses, nuisance parameters, & similar tests! The Neyman-Construction (illustrated)! Inverted
Statistics for Particle Physics Kyle Cranmer New York University 91 Remaining Lectures Lecture 3:! Compound hypotheses, nuisance parameters, & similar tests! The Neyman-Construction (illustrated)! Inverted
Ways to make neural networks generalize better
 Ways to make neural networks generalize better Seminar in Deep Learning University of Tartu 04 / 10 / 2014 Pihel Saatmann Topics Overview of ways to improve generalization Limiting the size of the weights
Ways to make neural networks generalize better Seminar in Deep Learning University of Tartu 04 / 10 / 2014 Pihel Saatmann Topics Overview of ways to improve generalization Limiting the size of the weights
Stat260: Bayesian Modeling and Inference Lecture Date: February 10th, Jeffreys priors. exp 1 ) p 2
 Stat260: Bayesian Modeling and Inference Lecture Date: February 10th, 2010 Jeffreys priors Lecturer: Michael I. Jordan Scribe: Timothy Hunter 1 Priors for the multivariate Gaussian Consider a multivariate
Stat260: Bayesian Modeling and Inference Lecture Date: February 10th, 2010 Jeffreys priors Lecturer: Michael I. Jordan Scribe: Timothy Hunter 1 Priors for the multivariate Gaussian Consider a multivariate
(1) Introduction to Bayesian statistics
 Spring, 2018 A motivating example Student 1 will write down a number and then flip a coin If the flip is heads, they will honestly tell student 2 if the number is even or odd If the flip is tails, they
Spring, 2018 A motivating example Student 1 will write down a number and then flip a coin If the flip is heads, they will honestly tell student 2 if the number is even or odd If the flip is tails, they
A Bayesian Approach to Phylogenetics
 A Bayesian Approach to Phylogenetics Niklas Wahlberg Based largely on slides by Paul Lewis (www.eeb.uconn.edu) An Introduction to Bayesian Phylogenetics Bayesian inference in general Markov chain Monte
A Bayesian Approach to Phylogenetics Niklas Wahlberg Based largely on slides by Paul Lewis (www.eeb.uconn.edu) An Introduction to Bayesian Phylogenetics Bayesian inference in general Markov chain Monte
STAT 425: Introduction to Bayesian Analysis
 STAT 425: Introduction to Bayesian Analysis Marina Vannucci Rice University, USA Fall 2017 Marina Vannucci (Rice University, USA) Bayesian Analysis (Part 1) Fall 2017 1 / 10 Lecture 7: Prior Types Subjective
STAT 425: Introduction to Bayesian Analysis Marina Vannucci Rice University, USA Fall 2017 Marina Vannucci (Rice University, USA) Bayesian Analysis (Part 1) Fall 2017 1 / 10 Lecture 7: Prior Types Subjective
Parametric Techniques Lecture 3
 Parametric Techniques Lecture 3 Jason Corso SUNY at Buffalo 22 January 2009 J. Corso (SUNY at Buffalo) Parametric Techniques Lecture 3 22 January 2009 1 / 39 Introduction In Lecture 2, we learned how to
Parametric Techniques Lecture 3 Jason Corso SUNY at Buffalo 22 January 2009 J. Corso (SUNY at Buffalo) Parametric Techniques Lecture 3 22 January 2009 1 / 39 Introduction In Lecture 2, we learned how to
Part 4: Multi-parameter and normal models
 Part 4: Multi-parameter and normal models 1 The normal model Perhaps the most useful (or utilized) probability model for data analysis is the normal distribution There are several reasons for this, e.g.,
Part 4: Multi-parameter and normal models 1 The normal model Perhaps the most useful (or utilized) probability model for data analysis is the normal distribution There are several reasons for this, e.g.,
CLASS NOTES Models, Algorithms and Data: Introduction to computing 2018
 CLASS NOTES Models, Algorithms and Data: Introduction to computing 208 Petros Koumoutsakos, Jens Honore Walther (Last update: June, 208) IMPORTANT DISCLAIMERS. REFERENCES: Much of the material (ideas,
CLASS NOTES Models, Algorithms and Data: Introduction to computing 208 Petros Koumoutsakos, Jens Honore Walther (Last update: June, 208) IMPORTANT DISCLAIMERS. REFERENCES: Much of the material (ideas,
Use of the likelihood principle in physics. Statistics II
 Use of the likelihood principle in physics Statistics II 1 2 3 + Bayesians vs Frequentists 4 Why ML does work? hypothesis observation 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ) 12 13 14 15 16 Fit of Histograms corresponds This
Use of the likelihood principle in physics Statistics II 1 2 3 + Bayesians vs Frequentists 4 Why ML does work? hypothesis observation 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ) 12 13 14 15 16 Fit of Histograms corresponds This
Bayesian Methods: Naïve Bayes
 Bayesian Methods: aïve Bayes icholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas based on the slides of Vibhav Gogate Last Time Parameter learning Learning the parameter of a simple coin flipping model Prior
Bayesian Methods: aïve Bayes icholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas based on the slides of Vibhav Gogate Last Time Parameter learning Learning the parameter of a simple coin flipping model Prior
University of Cambridge Engineering Part IIB Module 4F10: Statistical Pattern Processing Handout 2: Multivariate Gaussians
 University of Cambridge Engineering Part IIB Module 4F: Statistical Pattern Processing Handout 2: Multivariate Gaussians.2.5..5 8 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 Mark Gales mjfg@eng.cam.ac.uk Michaelmas 2 2 Engineering
University of Cambridge Engineering Part IIB Module 4F: Statistical Pattern Processing Handout 2: Multivariate Gaussians.2.5..5 8 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 Mark Gales mjfg@eng.cam.ac.uk Michaelmas 2 2 Engineering
Confidence intervals fundamental issues
 Confidence intervals fundamental issues Null Hypothesis testing P-values Classical or frequentist confidence intervals Issues that arise in interpretation of fit result Bayesian statistics and intervals
Confidence intervals fundamental issues Null Hypothesis testing P-values Classical or frequentist confidence intervals Issues that arise in interpretation of fit result Bayesian statistics and intervals
2.830J / 6.780J / ESD.63J Control of Manufacturing Processes (SMA 6303) Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.830J / 6.780J / ESD.63J Control of Processes (SMA 6303) Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.830J / 6.780J / ESD.63J Control of Processes (SMA 6303) Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Reading for Lecture 6 Release v10
 Reading for Lecture 6 Release v10 Christopher Lee October 11, 2011 Contents 1 The Basics ii 1.1 What is a Hypothesis Test?........................................ ii Example..................................................
Reading for Lecture 6 Release v10 Christopher Lee October 11, 2011 Contents 1 The Basics ii 1.1 What is a Hypothesis Test?........................................ ii Example..................................................
