Electromagnetism. Electromagnetic Waves : Topics. University of Twente Department Applied Physics. First-year course on
|
|
|
- Prudence Holland
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Universit of Twente Department Applied Phsics First-ear course on lectromagnetism lectromagnetic Waves : Topics F.F.M. de Mul 1
2 Presentations: lectromagnetism: Histor lectromagnetism: lectr. topics lectromagnetism: Magn. topics lectromagnetism: Waves topics Capacitor filling (complete) Capacitor filling (partial) Divergence Theorem -field of a thin long charged wire -field of a charged disk -field of a dipole -field of a line of dipoles -field of a charged sphere -field of a polaried object -field: field energ lectromagnetism: integrations lectromagnetism: integration elements Gauss Law for a clindrical charge Gauss Law for a charged plane Laplace s and Poisson s Law B-field of a thin long wire carring a current B-field of a conducting charged sphere B-field of a homogeneousl charged sphere
3 lectromagnetic Waves Contents: 1. Gauss and Farada s Laws for (D)-field. Gauss and Mawell s Laws for B (H)-field 3. Mawell s quations and The Wave quation 4. Harmonic olution of the Wave quation 5. Plane waves 1) orientation of field vectors ) comple wave vector 3) B - correspondence 6. The Ponting Vector and Intensit 3
4 1. Gauss and Farada s Laws for Gauss Law : V dv 1 1 d dv div. dv div V Div = micro-flu per unit of volume V d B c V ind Farada s Law : d rot Bd db c n dl rot d Rot = micro-circulation per unit of area 4
5 . Gauss and Mawell s Laws for B B V dv Gauss Law : Bd div B V divb. dv Mawell s Fi for Ampere s Law : j L L rot rot Bdl jd B j H j f dd d d d 5
6 3. Mawell s quations and Wave quation In vacuum ( = and j = ): db B db d... ( H) d ( B)... d D ( ) d } H j f dd d This is a 3-Dimensional Wave quation General form: A 1 A... v = velocit: v t A v 1 v = m/s = light velocit 6
7 4. Harmonic olution of thewave quation d ma have 3 components: Choose X-ais // = = ( Polariation direction = X-ais). Question: Does a plane-wave epression for satisf the wave equation? = ep{i (t-k)} : Propagation = amplitude + polariation vector; +Z-ais = direction of propagation NB. has a similar form for all -values!! (like rolling sea waves) 7
8 4. Harmonic olution of the Wave quation: Plane Waves d ma have 3 components: Choose X-ais // = = (Polariation direction = X-ais). Does a plane-wave epression for satisf the wave equation? = ep{i (t-k)} : = amplitude + polariation vector; +Z-ais = direction of propagation Propagation Insertion into wave equation: t k = =( /c ) k = / c = / k = wave number ; = wavelength 8 (in 3D-case: k = wave vector )
9 5. Plane waves (1): orientation of fields uppose: // -ais;.. propagation // +-ais: k // e.. = ep i (t-k).. = = Question: what is direction of B? H Propagation Remember: div A A A A A In div and rot: onl /, due to: ep i (ωt-k)! (1) div = () div B = -ik e. = -ik e.h =,D e H,B e 9
10 5. Plane waves (1): orientation of fields uppose: // -ais;.. propagation // +-ais: k // e.. = ep i (t-k).. = = div =,D e div H = H,B e What is mutual direction of,d and H,B? In div and rot: onl /, due to: ep i (ωt-k)! Remember: rot X X H e X Propagation e X e X (3) rot = - db/ -ik e = -ih,d H,B (4) rot H = j f + dd/ j f = -ik e H = +i,d H,B 1
11 5. Plane waves (1): orientation of fields uppose: // -ais;.. propagation // +-ais: k // e.. = ep i (t-k) Propagation H (1) div = () div B = (3) rot = - db/ (4) rot H = j f + dd/ j f = Consequences: (1)+(): and H e (3)+(4): H If chosen // -ais, then H,B // -ais H,B also harmonic: B = B ep i (t-k) 11
12 5. Plane waves (): comple wave vector uppose: // -ais;.. propagation // +-ais: k // e.. = ep i (t-k) Propagation (3) -ik e = -ih (4) -ik e H = +i H ik e H ik e ( ke ) i ( i ). and with: e e = - ik =(+i). k comple: k = k Re + ik Im ik ( i ). ep (-ik) = ep (-ik Re ). ep (k Im ) } harmonic } k Im < : absorption > : amplification ( laser ) 1
13 5. Plane waves (3): B- correspondence uppose: // -ais; B // -ais;.. propagation // +-ais: k // e.. = ep i (t-k).. B = B ep i (t-k) Farada: rot = - db/ e e e t. e B. e. e Y - components are B onl Propagation t B k B Result : B k : cb Mawell (for j=): rot H = dd/: similar result Mawell equations are (partl) redundant. 13
14 { { 6. The Ponting vector and Intensit Definition (for free space) : = H Direction of : // k k H = (H) = H() - (H) = 1 B = H(-dB/) - (j f +dd/) j f t t Integrate over wave volume V (with surface A) and appl Divergence Theorem A da v ( ) Outflu of energ [J/s] = [W] dv 1 d v B { Loss of lectromagnetic field energ [J/s] dv v ( j f ) dv Joule heating losses [J/s] = energ outflu per m = Intensit [W/m ] 14
15 Universit of Twente Department Applied Phsics First-ear course on lectromagnetism The end lectromagnetic Waves : Topics F.F.M. de Mul 15
I.3.5 Ringing. Ringing=Unwanted oscillations of voltage and/or current
 I.3.5 Ringing Ringing=Unwanted oscillations of voltage and/or current Ringing is caused b multiple reflections. The original wave is reflected at the load, this reflection then gets reflected back at the
I.3.5 Ringing Ringing=Unwanted oscillations of voltage and/or current Ringing is caused b multiple reflections. The original wave is reflected at the load, this reflection then gets reflected back at the
( ) ( ) ( ), ( 0 ), ( 0)
 . (a Find the eigenvalues and eigenfunctions of problem: (b The differential equation ( ( ( =, - =, =. (8% - - = has one basis solution =. Show that the other basis solution on the interval - < < is =
. (a Find the eigenvalues and eigenfunctions of problem: (b The differential equation ( ( ( =, - =, =. (8% - - = has one basis solution =. Show that the other basis solution on the interval - < < is =
roth t dive = 0 (4.2.3) divh = 0 (4.2.4) Chapter 4 Waves in Unbounded Medium Electromagnetic Sources 4.2 Uniform plane waves in free space
 Chapter 4 Waves in Unbounded Medium 4. lectromagnetic Sources 4. Uniform plane waves in free space Mawell s equation in free space is given b: H rot = (4..) roth = (4..) div = (4..3) divh = (4..4) which
Chapter 4 Waves in Unbounded Medium 4. lectromagnetic Sources 4. Uniform plane waves in free space Mawell s equation in free space is given b: H rot = (4..) roth = (4..) div = (4..3) divh = (4..4) which
9/28/2009. t kz H a x. in free space. find the value(s) of k such that E satisfies both of Maxwell s curl equations.
 9//9 3- E3.1 For E E cos 6 1 tkz a in free space,, J=, find the value(s) of k such that E satisfies both of Mawell s curl equations. Noting that E E (z,t)a,we have from B E, t 3-1 a a a z B E t z E B E
9//9 3- E3.1 For E E cos 6 1 tkz a in free space,, J=, find the value(s) of k such that E satisfies both of Mawell s curl equations. Noting that E E (z,t)a,we have from B E, t 3-1 a a a z B E t z E B E
Ying-Ying Tran 2016 May 10 Review
 MATH 920 Final review Ying-Ying Tran 206 Ma 0 Review hapter 3: Vector geometr vectors dot products cross products planes quadratic surfaces clindrical and spherical coordinates hapter 4: alculus of vector-valued
MATH 920 Final review Ying-Ying Tran 206 Ma 0 Review hapter 3: Vector geometr vectors dot products cross products planes quadratic surfaces clindrical and spherical coordinates hapter 4: alculus of vector-valued
Physics of Tsunamis. This is an article from my home page: Ole Witt-Hansen 2011 (2016)
 Phsics of Tsunamis This is an article from m home page: www.olewitthansen.dk Ole Witt-Hansen 11 (16) Contents 1. Constructing a differential equation for the Tsunami wave...1. The velocit of propagation
Phsics of Tsunamis This is an article from m home page: www.olewitthansen.dk Ole Witt-Hansen 11 (16) Contents 1. Constructing a differential equation for the Tsunami wave...1. The velocit of propagation
Charge and current elements
 Charge and current elements for 1-, 2- and 3-dimensional integration Frits F.M. de Mul Presentations: Electromagnetism: History Electromagnetism: Electr. topics Electromagnetism: Magn. topics Electromagnetism:
Charge and current elements for 1-, 2- and 3-dimensional integration Frits F.M. de Mul Presentations: Electromagnetism: History Electromagnetism: Electr. topics Electromagnetism: Magn. topics Electromagnetism:
Physics 2135 Exam 3 April 19, 2016
 Exam Total / 200 hsics 2135 Exam 3 April 19, 2016 rinted Name: Rec. Sec. Letter: Five multiple choice questions, 8 points each. Choose the best or most nearl correct answer. 1. Two long, straight parallel
Exam Total / 200 hsics 2135 Exam 3 April 19, 2016 rinted Name: Rec. Sec. Letter: Five multiple choice questions, 8 points each. Choose the best or most nearl correct answer. 1. Two long, straight parallel
1300 (W/m 2 ) (V/cm) = 275 (V/m) (A/cm) = (A/m). E = 990 (V/m), H = 2.63 (A/m).
 Homework #4 P8-16 There is a continuing discuss on radiation hazards to human health The following calculations will provide a rough comparison a) The US standard for personal safet in a microwe environment
Homework #4 P8-16 There is a continuing discuss on radiation hazards to human health The following calculations will provide a rough comparison a) The US standard for personal safet in a microwe environment
Pretty electromagnetic waves: a rainbow over the Potala Palace, Lhasa, Tibet; photo by Galen Rowell. 27 November 2012 Physics 122, Fall
 Today in Physics 122: the Maxwell equations Ampère s law is broken, and Maxwell fixes it. Gauss s law for magnetic fields. The Maxwell equations. The Maxwell equations in vacuum lead to a wave equation.
Today in Physics 122: the Maxwell equations Ampère s law is broken, and Maxwell fixes it. Gauss s law for magnetic fields. The Maxwell equations. The Maxwell equations in vacuum lead to a wave equation.
Electromagnetism Physics 15b
 Electromagnetism Physics 15b Lecture #18 Maxwell s Equations Electromagnetic Waves Purcell 9.1 9.4 What We Did Last Time Impedance of R,, and L Z R = V R = R Z I = V = 1 Z R I iω L = V L = iωl I L Generally
Electromagnetism Physics 15b Lecture #18 Maxwell s Equations Electromagnetic Waves Purcell 9.1 9.4 What We Did Last Time Impedance of R,, and L Z R = V R = R Z I = V = 1 Z R I iω L = V L = iωl I L Generally
Pan Pearl River Delta Physics Olympiad 2005
 1 Jan. 29, 25 Morning Session (9 am 12 pm) Q1 (5 Two identical worms of length L are ling on a smooth and horizontal surface. The mass of the worms is evenl distributed along their bod length. The starting
1 Jan. 29, 25 Morning Session (9 am 12 pm) Q1 (5 Two identical worms of length L are ling on a smooth and horizontal surface. The mass of the worms is evenl distributed along their bod length. The starting
Theory of Optical Waveguide
 Theor of Optical Waveguide Class: Integrated Photonic Devices Time: Fri. 8:am ~ :am. Classroom: 資電 6 Lecturer: Prof. 李明昌 (Ming-Chang Lee Reflection and Refraction at an Interface (TE n kˆi H i E i θ θ
Theor of Optical Waveguide Class: Integrated Photonic Devices Time: Fri. 8:am ~ :am. Classroom: 資電 6 Lecturer: Prof. 李明昌 (Ming-Chang Lee Reflection and Refraction at an Interface (TE n kˆi H i E i θ θ
PY3107 Experimental Physics II
 PY317 Eperimental Phsics II Magnetic fields and the Hall effect M.P. Vaughan and F. Peters Related Eperiments Magnetic Lab Using a Hall-effect magnetic field sensor Overview Ampere s Law The solenoid Lorentz
PY317 Eperimental Phsics II Magnetic fields and the Hall effect M.P. Vaughan and F. Peters Related Eperiments Magnetic Lab Using a Hall-effect magnetic field sensor Overview Ampere s Law The solenoid Lorentz
Complex Wave Parameters Visualization of EM Waves Complex Wave Parameters for Special Cases
 Course Instructor Dr. Ramond C. Rumpf Office: A 337 Phone: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utep.edu EE 4347 Applied Electromagnetics Topic 3d Waves in Loss Dielectrics Loss Dielectrics These notes ma contain
Course Instructor Dr. Ramond C. Rumpf Office: A 337 Phone: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utep.edu EE 4347 Applied Electromagnetics Topic 3d Waves in Loss Dielectrics Loss Dielectrics These notes ma contain
Course no. 4. The Theory of Electromagnetic Field
 Cose no. 4 The Theory of Electromagnetic Field Technical University of Cluj-Napoca http://www.et.utcluj.ro/cs_electromagnetics2006_ac.htm http://www.et.utcluj.ro/~lcret March 19-2009 Chapter 3 Magnetostatics
Cose no. 4 The Theory of Electromagnetic Field Technical University of Cluj-Napoca http://www.et.utcluj.ro/cs_electromagnetics2006_ac.htm http://www.et.utcluj.ro/~lcret March 19-2009 Chapter 3 Magnetostatics
Polarized optical wave in optical fiber communication system
 IOSR Journal of Applied Phsics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 9, Issue 5 Ver. IV (Sep. - Oct. 2017), PP 09-14 www.iosrjournals.org Polarized optical wave in optical fiber communication sstem Dinesh
IOSR Journal of Applied Phsics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 9, Issue 5 Ver. IV (Sep. - Oct. 2017), PP 09-14 www.iosrjournals.org Polarized optical wave in optical fiber communication sstem Dinesh
Separation of Variables in Cartesian Coordinates
 Lecture 9 Separation of Variables in Cartesian Coordinates Phs 3750 Overview and Motivation: Toda we begin a more in-depth loo at the 3D wave euation. We introduce a techniue for finding solutions to partial
Lecture 9 Separation of Variables in Cartesian Coordinates Phs 3750 Overview and Motivation: Toda we begin a more in-depth loo at the 3D wave euation. We introduce a techniue for finding solutions to partial
Maxwell s equations. Kyoto. James Clerk Maxwell. Physics 122. James Clerk Maxwell ( ) Unification of electrical and magnetic interactions
 Maxwell s equations Physics /5/ Lecture XXIV Kyoto /5/ Lecture XXIV James Clerk Maxwell James Clerk Maxwell (83 879) Unification of electrical and magnetic interactions /5/ Lecture XXIV 3 Φ = da = Q ε
Maxwell s equations Physics /5/ Lecture XXIV Kyoto /5/ Lecture XXIV James Clerk Maxwell James Clerk Maxwell (83 879) Unification of electrical and magnetic interactions /5/ Lecture XXIV 3 Φ = da = Q ε
Electromagnetism. Christopher R Prior. ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory
 lectromagnetism Christopher R Prior Fellow and Tutor in Mathematics Trinity College, Oxford ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory Contents Review of Maxwell s equations and Lorentz Force
lectromagnetism Christopher R Prior Fellow and Tutor in Mathematics Trinity College, Oxford ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory Contents Review of Maxwell s equations and Lorentz Force
MTHE 227 Problem Set 10 Solutions. (1 y2 +z 2., 0, 0), y 2 + z 2 < 4 0, Otherwise.
 MTHE 7 Problem Set Solutions. (a) Sketch the cross-section of the (hollow) clinder + = in the -plane, as well as the vector field in this cross-section. ( +,, ), + < F(,, ) =, Otherwise. This is a simple
MTHE 7 Problem Set Solutions. (a) Sketch the cross-section of the (hollow) clinder + = in the -plane, as well as the vector field in this cross-section. ( +,, ), + < F(,, ) =, Otherwise. This is a simple
The equations so far... Gauss Law for E Fields. Gauss Law for B Fields. B da. inside. d dt. n C 3/28/2018
 The equations so far... Gauss Law for E Fields E da S n 1 Q inside Gauss Law for B Fields B da S n C Faraday s Law d E dl dt S B da n Ampere s Law B dl I C 3/8/18 1 Ampere s Law B dl I inside _ path No
The equations so far... Gauss Law for E Fields E da S n 1 Q inside Gauss Law for B Fields B da S n C Faraday s Law d E dl dt S B da n Ampere s Law B dl I C 3/8/18 1 Ampere s Law B dl I inside _ path No
ELE 3310 Tutorial 10. Maxwell s Equations & Plane Waves
 ELE 3310 Tutorial 10 Mawell s Equations & Plane Waves Mawell s Equations Differential Form Integral Form Faraday s law Ampere s law Gauss s law No isolated magnetic charge E H D B B D J + ρ 0 C C E r dl
ELE 3310 Tutorial 10 Mawell s Equations & Plane Waves Mawell s Equations Differential Form Integral Form Faraday s law Ampere s law Gauss s law No isolated magnetic charge E H D B B D J + ρ 0 C C E r dl
Intermission on Page 343
 Intermission on Page 343 Together with the force law, All of our cards are now on the table, and in a sense my job is done. In the first seven chapters we assembled electrodynamics piece by piece, and
Intermission on Page 343 Together with the force law, All of our cards are now on the table, and in a sense my job is done. In the first seven chapters we assembled electrodynamics piece by piece, and
Fundamentals of Applied Electromagnetics. Chapter 2 - Vector Analysis
 Fundamentals of pplied Electromagnetics Chapter - Vector nalsis Chapter Objectives Operations of vector algebra Dot product of two vectors Differential functions in vector calculus Divergence of a vector
Fundamentals of pplied Electromagnetics Chapter - Vector nalsis Chapter Objectives Operations of vector algebra Dot product of two vectors Differential functions in vector calculus Divergence of a vector
Vector Calculus. Vector Fields. Reading Trim Vector Fields. Assignment web page assignment #9. Chapter 14 will examine a vector field.
 Vector alculus Vector Fields Reading Trim 14.1 Vector Fields Assignment web page assignment #9 hapter 14 will eamine a vector field. For eample, if we eamine the temperature conditions in a room, for ever
Vector alculus Vector Fields Reading Trim 14.1 Vector Fields Assignment web page assignment #9 hapter 14 will eamine a vector field. For eample, if we eamine the temperature conditions in a room, for ever
Yell if you have any questions
 Class 36: Outline Hour 1: Concept Review / Overview PRS Questions Possible Exam Questions Hour : Sample Exam Yell if you have any questions P36-1 Before Starting All of your grades should now be posted
Class 36: Outline Hour 1: Concept Review / Overview PRS Questions Possible Exam Questions Hour : Sample Exam Yell if you have any questions P36-1 Before Starting All of your grades should now be posted
6.976 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 2 Transmission Lines
 6.976 High Speed Communication Circuits and Sstems Lecture 2 Transmission Lines Michael Perrott Massachusetts Institute of Technolog Copright 2003 b Michael H. Perrott Mawell s Equations General form:
6.976 High Speed Communication Circuits and Sstems Lecture 2 Transmission Lines Michael Perrott Massachusetts Institute of Technolog Copright 2003 b Michael H. Perrott Mawell s Equations General form:
ECE 222b Applied Electromagnetics Notes Set 4b
 ECE b Applied Electromagnetics Notes Set 4b Instructor: Prof. Vitali Lomain Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Universit of California, San Diego 1 Uniform Waveguide (1) Wave propagation
ECE b Applied Electromagnetics Notes Set 4b Instructor: Prof. Vitali Lomain Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Universit of California, San Diego 1 Uniform Waveguide (1) Wave propagation
Lecture 04. Curl and Divergence
 Lecture 04 Curl and Divergence UCF Curl of Vector Field (1) F c d l F C Curl (or rotor) of a vector field a n curlf F d l lim c s s 0 F s a n C a n : normal direction of s follow right-hand rule UCF Curl
Lecture 04 Curl and Divergence UCF Curl of Vector Field (1) F c d l F C Curl (or rotor) of a vector field a n curlf F d l lim c s s 0 F s a n C a n : normal direction of s follow right-hand rule UCF Curl
Regn. No. South Delhi : 28-A/11, Jia Sarai, Near-IIT Hauz Khas, New Delhi-16, Ph : ,
 . Section-A contains Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ). Each question has 4 choices,, and, for its answer, out of which ONLY ONE is correct. From Q. to Q. carries Marks and Q. to Q. carries Marks each..
. Section-A contains Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ). Each question has 4 choices,, and, for its answer, out of which ONLY ONE is correct. From Q. to Q. carries Marks and Q. to Q. carries Marks each..
Traveling Waves: Energy Transport
 Traveling Waves: Energ Transport wave is a traveling disturbance that transports energ but not matter. Intensit: I P power rea Intensit I power per unit area (measured in Watts/m 2 ) Intensit is proportional
Traveling Waves: Energ Transport wave is a traveling disturbance that transports energ but not matter. Intensit: I P power rea Intensit I power per unit area (measured in Watts/m 2 ) Intensit is proportional
PHYSICS PART II SECTION- I. Straight objective Type
 PHYSICS PAT II SECTION- I Straight objective Tpe This section contains 9 multiple choice questions numbered to 1. Each question has choices,, (C) and, out of which ONLY ONE is correct.. A parallel plate
PHYSICS PAT II SECTION- I Straight objective Tpe This section contains 9 multiple choice questions numbered to 1. Each question has choices,, (C) and, out of which ONLY ONE is correct.. A parallel plate
ELECTROMAGNETISM. Second Edition. I. S. Grant W. R. Phillips. John Wiley & Sons. Department of Physics University of Manchester
 ELECTROMAGNETISM Second Edition I. S. Grant W. R. Phillips Department of Physics University of Manchester John Wiley & Sons CHICHESTER NEW YORK BRISBANE TORONTO SINGAPORE Flow diagram inside front cover
ELECTROMAGNETISM Second Edition I. S. Grant W. R. Phillips Department of Physics University of Manchester John Wiley & Sons CHICHESTER NEW YORK BRISBANE TORONTO SINGAPORE Flow diagram inside front cover
Electrical and optical properties of materials
 Electrical and optical properties of materials John JL Morton Part 4: Mawell s Equations We have already used Mawell s equations for electromagnetism, and in many ways they are simply a reformulation (or
Electrical and optical properties of materials John JL Morton Part 4: Mawell s Equations We have already used Mawell s equations for electromagnetism, and in many ways they are simply a reformulation (or
Basics of Electromagnetics Maxwell s Equations (Part - I)
 Basics of Electromagnetics Maxwell s Equations (Part - I) Soln. 1. C A. dl = C. d S [GATE 1994: 1 Mark] A. dl = A. da using Stoke s Theorem = S A. ds 2. The electric field strength at distant point, P,
Basics of Electromagnetics Maxwell s Equations (Part - I) Soln. 1. C A. dl = C. d S [GATE 1994: 1 Mark] A. dl = A. da using Stoke s Theorem = S A. ds 2. The electric field strength at distant point, P,
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY
 DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY SIRUVACHUR-621113 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS DEPARTMENT 2 MARK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS SUBJECT CODE: EE 6302 SUBJECT NAME: ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY SIRUVACHUR-621113 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS DEPARTMENT 2 MARK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS SUBJECT CODE: EE 6302 SUBJECT NAME: ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY
Introduction to Electromagnetic Theory
 Introduction to Electromagnetic Theory Lecture topics Laws of magnetism and electricity Meaning of Maxwell s equations Solution of Maxwell s equations Electromagnetic radiation: wave model James Clerk
Introduction to Electromagnetic Theory Lecture topics Laws of magnetism and electricity Meaning of Maxwell s equations Solution of Maxwell s equations Electromagnetic radiation: wave model James Clerk
GUIDED WAVES IN A RECTANGULAR WAVE GUIDE
 GUIDED WAVES IN A RECTANGULAR WAVE GUIDE Consider waves propagating along Oz but with restrictions in the and/or directions. The wave is now no longer necessaril transverse. The wave equation can be written
GUIDED WAVES IN A RECTANGULAR WAVE GUIDE Consider waves propagating along Oz but with restrictions in the and/or directions. The wave is now no longer necessaril transverse. The wave equation can be written
5.3.3 The general solution for plane waves incident on a layered halfspace. The general solution to the Helmholz equation in rectangular coordinates
 5.3.3 The general solution for plane waves incident on a laered halfspace The general solution to the elmhol equation in rectangular coordinates The vector propagation constant Vector relationships between
5.3.3 The general solution for plane waves incident on a laered halfspace The general solution to the elmhol equation in rectangular coordinates The vector propagation constant Vector relationships between
Two-Dimensional Analysis of the Power Transfer between Crossed Laser Beams
 Two-Dimensional Analsis of the Power Transfer between Crossed Laser Beams The indirect-drive approach to inertial confinement fusion involves laser beams that cross as the enter the hohlraum. Ionacoustic
Two-Dimensional Analsis of the Power Transfer between Crossed Laser Beams The indirect-drive approach to inertial confinement fusion involves laser beams that cross as the enter the hohlraum. Ionacoustic
Lecture 6: Maxwell s Equations, Boundary Conditions.
 Whites, EE 382 Lecture 6 Page 1 of 7 Lecture 6: Maxwell s Equations, Boundar Conditions. In the last four lectures, we have been investigating the behavior of dnamic (i.e., time varing) electric and magnetic
Whites, EE 382 Lecture 6 Page 1 of 7 Lecture 6: Maxwell s Equations, Boundar Conditions. In the last four lectures, we have been investigating the behavior of dnamic (i.e., time varing) electric and magnetic
Electric Motor and Dynamo the Hall effect
 Electric Motor and Dynamo the Hall effect Frits F.M. de Mul Motor and Dynamo; Hall effect 1 Presentations: Electromagnetism: History Electromagnetism: Electr. topics Electromagnetism: Magn. topics Electromagnetism:
Electric Motor and Dynamo the Hall effect Frits F.M. de Mul Motor and Dynamo; Hall effect 1 Presentations: Electromagnetism: History Electromagnetism: Electr. topics Electromagnetism: Magn. topics Electromagnetism:
The Basic (Physical) Problem: Experiments. Internal Gravity Waves and Hyperbolic Boundary-Value Problems. Internal Gravity Waves. Governing Equations
 The Basic (Phsical) Problem: Eperiments Internal Gravit Waves and Hperbolic Boundar-Value Problems P. A. Martin Colorado chool of Mines Collaborator: tefan Llewelln mith, UC an Diego D. E. Mowbra & B..
The Basic (Phsical) Problem: Eperiments Internal Gravit Waves and Hperbolic Boundar-Value Problems P. A. Martin Colorado chool of Mines Collaborator: tefan Llewelln mith, UC an Diego D. E. Mowbra & B..
NST1A: Mathematics II (Course A) End of Course Summary, Lent 2011
 General notes Proofs NT1A: Mathematics II (Course A) End of Course ummar, Lent 011 tuart Dalziel (011) s.dalziel@damtp.cam.ac.uk This course is not about proofs, but rather about using different techniques.
General notes Proofs NT1A: Mathematics II (Course A) End of Course ummar, Lent 011 tuart Dalziel (011) s.dalziel@damtp.cam.ac.uk This course is not about proofs, but rather about using different techniques.
Physics 1502: Lecture 25 Today s Agenda
 Physics 1502: Lecture 25 Today s Agenda Announcements: Midterm 2: NOT Nov. 6 Following week Homework 07: due Friday net week AC current esonances Electromagnetic Waves Mawell s Equations - evised Energy
Physics 1502: Lecture 25 Today s Agenda Announcements: Midterm 2: NOT Nov. 6 Following week Homework 07: due Friday net week AC current esonances Electromagnetic Waves Mawell s Equations - evised Energy
r r 1 r r 1 2 = q 1 p = qd and it points from the negative charge to the positive charge.
 MP204, Important Equations page 1 Below is a list of important equations that we meet in our study of Electromagnetism in the MP204 module. For your exam, you are expected to understand all of these, and
MP204, Important Equations page 1 Below is a list of important equations that we meet in our study of Electromagnetism in the MP204 module. For your exam, you are expected to understand all of these, and
Magnetostatics Surface Current Density. Magnetostatics Surface Current Density
 Magnetostatics Surface Current Density A sheet current, K (A/m ) is considered to flow in an infinitesimally thin layer. Method 1: The surface charge problem can be treated as a sheet consisting of a continuous
Magnetostatics Surface Current Density A sheet current, K (A/m ) is considered to flow in an infinitesimally thin layer. Method 1: The surface charge problem can be treated as a sheet consisting of a continuous
CHAPTER 1 MEASUREMENTS AND VECTORS
 CHPTER 1 MESUREMENTS ND VECTORS 1 CHPTER 1 MESUREMENTS ND VECTORS 1.1 UNITS ND STNDRDS n phsical quantit must have, besides its numerical value, a standard unit. It will be meaningless to sa that the distance
CHPTER 1 MESUREMENTS ND VECTORS 1 CHPTER 1 MESUREMENTS ND VECTORS 1.1 UNITS ND STNDRDS n phsical quantit must have, besides its numerical value, a standard unit. It will be meaningless to sa that the distance
Assignment , 7.1, 7.2, 7.5, 7.11, 7.12, 7.15, TIR and FTIR
 LC45-summer, 1 1. 1.1, 7.1, 7., 7.5, 7.11, 7.1, 7.15, 7.1 1.1. TIR and FTIR a) B considering the electric field component in medium B in Figure 1. (b), eplain how ou can adjust the amount of transmitted
LC45-summer, 1 1. 1.1, 7.1, 7., 7.5, 7.11, 7.1, 7.15, 7.1 1.1. TIR and FTIR a) B considering the electric field component in medium B in Figure 1. (b), eplain how ou can adjust the amount of transmitted
Currents (1) Line charge λ (C/m) with velocity v : in time t, This constitutes a current I = λv (vector). Magnetic force on a segment of length dl is
 Magnetostatics 1. Currents 2. Relativistic origin of magnetic field 3. Biot-Savart law 4. Magnetic force between currents 5. Applications of Biot-Savart law 6. Ampere s law in differential form 7. Magnetic
Magnetostatics 1. Currents 2. Relativistic origin of magnetic field 3. Biot-Savart law 4. Magnetic force between currents 5. Applications of Biot-Savart law 6. Ampere s law in differential form 7. Magnetic
Exam 2 Solutions. Applying the junction rule: i 1 Applying the loop rule to the left loop (LL), right loop (RL), and the full loop (FL) gives:
 PHY61 Eam Solutions 1. [8 points] In the circuit shown, the resistance R 1 = 1Ω. The batter voltages are identical: ε1 = ε = ε3 = 1 V. What is the current (in amps) flowing through the middle branch from
PHY61 Eam Solutions 1. [8 points] In the circuit shown, the resistance R 1 = 1Ω. The batter voltages are identical: ε1 = ε = ε3 = 1 V. What is the current (in amps) flowing through the middle branch from
Maxwell s equations and EM waves. From previous Lecture Time dependent fields and Faraday s Law
 Maxwell s equations and EM waves This Lecture More on Motional EMF and Faraday s law Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves From previous Lecture Time dependent fields and Faraday s Law 1 Radar
Maxwell s equations and EM waves This Lecture More on Motional EMF and Faraday s law Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves From previous Lecture Time dependent fields and Faraday s Law 1 Radar
General Review. LECTURE 16 Faraday s Law of Induction
 Electrostatics General Review Motion of q in eternal E-field E-field generated b Sq i Magnetostatics Motion of q and I in eternal B-field B-field generated b I Electrodnamics Time dependent B-field generates
Electrostatics General Review Motion of q in eternal E-field E-field generated b Sq i Magnetostatics Motion of q and I in eternal B-field B-field generated b I Electrodnamics Time dependent B-field generates
Electrical Boundary Conditions. Electric Field Boundary Conditions: Magnetic Field Boundary Conditions: K=J s
 Electrical Boundar Condition Electric Field Boundar Condition: a n i a unit vector noral to the interface fro region to region 3 4 Magnetic Field Boundar Condition: K=J K=J 5 6 Dielectric- dielectric boundar
Electrical Boundar Condition Electric Field Boundar Condition: a n i a unit vector noral to the interface fro region to region 3 4 Magnetic Field Boundar Condition: K=J K=J 5 6 Dielectric- dielectric boundar
Time-Varying Systems; Maxwell s Equations
 Time-Varying Systems; Maxwell s Equations 1. Faraday s law in differential form 2. Scalar and vector potentials; the Lorenz condition 3. Ampere s law with displacement current 4. Maxwell s equations 5.
Time-Varying Systems; Maxwell s Equations 1. Faraday s law in differential form 2. Scalar and vector potentials; the Lorenz condition 3. Ampere s law with displacement current 4. Maxwell s equations 5.
Electromagnetic Field Theory Chapter 9: Time-varying EM Fields
 Electromagnetic Field Theory Chapter 9: Time-varying EM Fields Faraday s law of induction We have learned that a constant current induces magnetic field and a constant charge (or a voltage) makes an electric
Electromagnetic Field Theory Chapter 9: Time-varying EM Fields Faraday s law of induction We have learned that a constant current induces magnetic field and a constant charge (or a voltage) makes an electric
One-Dimensional Wave Propagation (without distortion or attenuation)
 Phsics 306: Waves Lecture 1 1//008 Phsics 306 Spring, 008 Waves and Optics Sllabus To get a good grade: Stud hard Come to class Email: satapal@phsics.gmu.edu Surve of waves One-Dimensional Wave Propagation
Phsics 306: Waves Lecture 1 1//008 Phsics 306 Spring, 008 Waves and Optics Sllabus To get a good grade: Stud hard Come to class Email: satapal@phsics.gmu.edu Surve of waves One-Dimensional Wave Propagation
Physics 2135 Exam 1 September 20, 2016
 Eam Total / 200 Phsics 2135 Eam 1 September 20, 2016 Printed Name: Rec. Sec. Letter: Five multiple choice questions, 8 points each. Choose the best or most nearl correct answer. 1. Two positive charges
Eam Total / 200 Phsics 2135 Eam 1 September 20, 2016 Printed Name: Rec. Sec. Letter: Five multiple choice questions, 8 points each. Choose the best or most nearl correct answer. 1. Two positive charges
PHYS 1444 Section 003 Lecture #23
 PHYS 1444 Section 3 Lecture #3 Monday, Nov. 8, 5 EM Waves from Maxwell s Equations Speed of EM Waves Light as EM Wave Electromagnetic Spectrum Energy in EM Waves Energy Transport The epilogue Today s homework
PHYS 1444 Section 3 Lecture #3 Monday, Nov. 8, 5 EM Waves from Maxwell s Equations Speed of EM Waves Light as EM Wave Electromagnetic Spectrum Energy in EM Waves Energy Transport The epilogue Today s homework
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c
 Wave Phenomena Phsics 15c Lecture 13 Multi-Dimensional Waves (H&L Chapter 7) Term Paper Topics! Have ou found a topic for the paper?! 2/3 of the class have, or have scheduled a meeting with me! If ou haven
Wave Phenomena Phsics 15c Lecture 13 Multi-Dimensional Waves (H&L Chapter 7) Term Paper Topics! Have ou found a topic for the paper?! 2/3 of the class have, or have scheduled a meeting with me! If ou haven
Fundamental Constants
 Fundamental Constants Atomic Mass Unit u 1.660 540 2 10 10 27 kg 931.434 32 28 MeV c 2 Avogadro s number N A 6.022 136 7 36 10 23 (g mol) 1 Bohr magneton μ B 9.274 015 4(31) 10-24 J/T Bohr radius a 0 0.529
Fundamental Constants Atomic Mass Unit u 1.660 540 2 10 10 27 kg 931.434 32 28 MeV c 2 Avogadro s number N A 6.022 136 7 36 10 23 (g mol) 1 Bohr magneton μ B 9.274 015 4(31) 10-24 J/T Bohr radius a 0 0.529
Course Updates. 2) This week: Electromagnetic Waves +
 Course Updates http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~varner/phys272-spr1/physics272.html Reminders: 1) Assignment #11 due Wednesday 2) This week: Electromagnetic Waves + 3) In the home stretch [review schedule]
Course Updates http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~varner/phys272-spr1/physics272.html Reminders: 1) Assignment #11 due Wednesday 2) This week: Electromagnetic Waves + 3) In the home stretch [review schedule]
1 Fundamentals of laser energy absorption
 1 Fundamentals of laser energy absorption 1.1 Classical electromagnetic-theory concepts 1.1.1 Electric and magnetic properties of materials Electric and magnetic fields can exert forces directly on atoms
1 Fundamentals of laser energy absorption 1.1 Classical electromagnetic-theory concepts 1.1.1 Electric and magnetic properties of materials Electric and magnetic fields can exert forces directly on atoms
VEKTORANALYS. GAUSS s THEOREM and STOKES s THEOREM. Kursvecka 3. Kapitel 6-7 Sidor 51-82
 VEKTORANAY Kursvecka 3 GAU s THEOREM and TOKE s THEOREM Kaptel 6-7 dor 51-82 TARGET PROBEM EECTRIC FIED MAGNETIC FIED N + Magnetc monopoles do not est n nature. How can we epress ths nformaton for E and
VEKTORANAY Kursvecka 3 GAU s THEOREM and TOKE s THEOREM Kaptel 6-7 dor 51-82 TARGET PROBEM EECTRIC FIED MAGNETIC FIED N + Magnetc monopoles do not est n nature. How can we epress ths nformaton for E and
F dr y 2. F r t r t dt. a sin t a sin t a cos t a cos t a 2 cos 2 t a 2 sin 2 t. P dx Q dy yy. x C. follows that F is a conservative vector field.
 6 CHAPTER 6 VECTOR CALCULU We now easil compute this last integral using the parametriation given b rt a cos t i a sin t j, t. Thus C F dr C F dr Frt rt dt a sin ta sin t a cos ta cos t a cos t a sin t
6 CHAPTER 6 VECTOR CALCULU We now easil compute this last integral using the parametriation given b rt a cos t i a sin t j, t. Thus C F dr C F dr Frt rt dt a sin ta sin t a cos ta cos t a cos t a sin t
Principles of Mobile Communications
 Communication Networks 1 Principles of Mobile Communications University Duisburg-Essen WS 2003/2004 Page 1 N e v e r s t o p t h i n k i n g. Wave Propagation Single- and Multipath Propagation Overview:
Communication Networks 1 Principles of Mobile Communications University Duisburg-Essen WS 2003/2004 Page 1 N e v e r s t o p t h i n k i n g. Wave Propagation Single- and Multipath Propagation Overview:
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c
 Wave Phenomena Phsics 15c Lecture 13 Multi-Dimensional Waves (H&L Chapter 7) Term Paper Topics! Have ou found a topic for the paper?! 2/3 of the class have, or have scheduled a meeting with me! If ou haven
Wave Phenomena Phsics 15c Lecture 13 Multi-Dimensional Waves (H&L Chapter 7) Term Paper Topics! Have ou found a topic for the paper?! 2/3 of the class have, or have scheduled a meeting with me! If ou haven
Physics Electricity and Magnetism Lecture 09 - Charges & Currents in Magnetic Fields Y&F Chapter 27, Sec. 1-8
 Phsics 121 - Electricit and Magnetism Lecture 09 - Charges & Currents in Magnetic Fields Y&F Chapter 27, Sec. 1-8 What Produces Magnetic Field? Properties of Magnetic ersus Electric Fields Force on a Charge
Phsics 121 - Electricit and Magnetism Lecture 09 - Charges & Currents in Magnetic Fields Y&F Chapter 27, Sec. 1-8 What Produces Magnetic Field? Properties of Magnetic ersus Electric Fields Force on a Charge
EM Waves. From previous Lecture. This Lecture More on EM waves EM spectrum Polarization. Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves
 EM Waves This Lecture More on EM waves EM spectrum Polarization From previous Lecture Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves 1 Reminders on waves Traveling waves on a string along x obey the
EM Waves This Lecture More on EM waves EM spectrum Polarization From previous Lecture Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves 1 Reminders on waves Traveling waves on a string along x obey the
Methods of plasma description Particle motion in external fields
 Methods of plasma description (suggested reading D.R. Nicholson, chap., Chen chap., 8.4) Charged particle motion in eternal electromagnetic (elmg) fields Charged particle motion in self-consistent elmg
Methods of plasma description (suggested reading D.R. Nicholson, chap., Chen chap., 8.4) Charged particle motion in eternal electromagnetic (elmg) fields Charged particle motion in self-consistent elmg
y=1/4 x x=4y y=x 3 x=y 1/3 Example: 3.1 (1/2, 1/8) (1/2, 1/8) Find the area in the positive quadrant bounded by y = 1 x and y = x3
 Eample: 3.1 Find the area in the positive quadrant bounded b 1 and 3 4 First find the points of intersection of the two curves: clearl the curves intersect at (, ) and at 1 4 3 1, 1 8 Select a strip at
Eample: 3.1 Find the area in the positive quadrant bounded b 1 and 3 4 First find the points of intersection of the two curves: clearl the curves intersect at (, ) and at 1 4 3 1, 1 8 Select a strip at
Department of Physics IIT Kanpur, Semester II,
 Department of Phsics IIT Kanpur, Semester II, 7-8 PHYA: Phsics II Solutions # Instructors: AKJ & SC Solution.: (a) At the top of the hill, the gradient of the height function should be ero, that is, h(,
Department of Phsics IIT Kanpur, Semester II, 7-8 PHYA: Phsics II Solutions # Instructors: AKJ & SC Solution.: (a) At the top of the hill, the gradient of the height function should be ero, that is, h(,
ET-105(A) : PHYSICS. Show that only an infinitesimal rotation can be regarded as a vector.
 No. of Printed Pages : 7 ET-105(A) B.Tech. Civil (Construction Management) / B.Tech. Civil (Water Resources Engineering) / BTCLEVI / BTMEVI / BTELVI / BTECVI / BTCSVI Term-End Examination June, 2017 ET-105(A)
No. of Printed Pages : 7 ET-105(A) B.Tech. Civil (Construction Management) / B.Tech. Civil (Water Resources Engineering) / BTCLEVI / BTMEVI / BTELVI / BTECVI / BTCSVI Term-End Examination June, 2017 ET-105(A)
Electromagnetic Theory: PHAS3201, Winter Maxwell s Equations and EM Waves
 Electromagnetic Theory: PHA3201, Winter 2008 5. Maxwell s Equations and EM Waves 1 Displacement Current We already have most of the pieces that we require for a full statement of Maxwell s Equations; however,
Electromagnetic Theory: PHA3201, Winter 2008 5. Maxwell s Equations and EM Waves 1 Displacement Current We already have most of the pieces that we require for a full statement of Maxwell s Equations; however,
Chapter 29: Maxwell s Equation and EM Waves. Slide 29-1
 Chapter 29: Maxwell s Equation and EM Waves Slide 29-1 Equations of electromagnetism: a review We ve now seen the four fundamental equations of electromagnetism, here listed together for the first time.
Chapter 29: Maxwell s Equation and EM Waves Slide 29-1 Equations of electromagnetism: a review We ve now seen the four fundamental equations of electromagnetism, here listed together for the first time.
Accelerator Physics Statistical and Beam-Beam Effects. G. A. Krafft Old Dominion University Jefferson Lab Lecture 14
 Accelerator Phsics Statistical and Beam-Beam Effects G. A. Krafft Old Dominion Universit Jefferson Lab Lecture 4 Graduate Accelerator Phsics Fall 7 Waterbag Distribution Lemons and Thode were first to
Accelerator Phsics Statistical and Beam-Beam Effects G. A. Krafft Old Dominion Universit Jefferson Lab Lecture 4 Graduate Accelerator Phsics Fall 7 Waterbag Distribution Lemons and Thode were first to
Principles of Physics II
 Principles of Physics II J. M. Veal, Ph. D. version 18.05.4 Contents 1 Fluid Mechanics 3 1.1 Fluid pressure............................ 3 1. Buoyancy.............................. 3 1.3 Fluid flow..............................
Principles of Physics II J. M. Veal, Ph. D. version 18.05.4 Contents 1 Fluid Mechanics 3 1.1 Fluid pressure............................ 3 1. Buoyancy.............................. 3 1.3 Fluid flow..............................
Introduction to Electromagnetism
 Introduction to Electromagnetism Electric Field Lines If a charge feels an electrostatic force (Coulombic Force), it is said to be in an electric field. We like to represent electric fields with lines.
Introduction to Electromagnetism Electric Field Lines If a charge feels an electrostatic force (Coulombic Force), it is said to be in an electric field. We like to represent electric fields with lines.
Light-induced spiral mass transport in azo-polymer films under vortex-beam illumination Supplementary Information
 Light-induced spiral mass transport in azo-polymer films under vorte-beam illumination Supplementary Information Antonio Ambrosio a),1, Lorenzo Marrucci 1, Fabio Borbone, Antonio Roviello and Pasqualino
Light-induced spiral mass transport in azo-polymer films under vorte-beam illumination Supplementary Information Antonio Ambrosio a),1, Lorenzo Marrucci 1, Fabio Borbone, Antonio Roviello and Pasqualino
VEKTORANALYS GAUSS THEOREM STOKES THEOREM. and. Kursvecka 3. Kapitel 6 7 Sidor 51 82
 VEKTORANAY Kursvecka 3 GAU THEOREM and TOKE THEOREM Kaptel 6 7 dor 51 82 TARGET PROBEM Do magnetc monopoles est? EECTRIC FIED MAGNETIC FIED N +? 1 TARGET PROBEM et s consder some EECTRIC CHARGE 2 - + +
VEKTORANAY Kursvecka 3 GAU THEOREM and TOKE THEOREM Kaptel 6 7 dor 51 82 TARGET PROBEM Do magnetc monopoles est? EECTRIC FIED MAGNETIC FIED N +? 1 TARGET PROBEM et s consder some EECTRIC CHARGE 2 - + +
Multivariable Calculus Lecture #13 Notes. in each piece. Then the mass mk. 0 σ = σ = σ
 Multivariable Calculus Lecture #1 Notes In this lecture, we ll loo at parameterization of surfaces in R and integration on a parameterized surface Applications will include surface area, mass of a surface
Multivariable Calculus Lecture #1 Notes In this lecture, we ll loo at parameterization of surfaces in R and integration on a parameterized surface Applications will include surface area, mass of a surface
D = 2(2) 3 2 = 4 9 = 5 < 0
 1. (7 points) Let f(, ) = +3 + +. Find and classif each critical point of f as a local minimum, a local maimum, or a saddle point. Solution: f = + 3 f = 3 + + 1 f = f = 3 f = Both f = and f = onl at (
1. (7 points) Let f(, ) = +3 + +. Find and classif each critical point of f as a local minimum, a local maimum, or a saddle point. Solution: f = + 3 f = 3 + + 1 f = f = 3 f = Both f = and f = onl at (
Chapter 16 Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 6 Mechanical Waves A wave is a disturbance that travels, or propagates, without the transport of matter. Examples: sound/ultrasonic wave, EM waves, and earthquake wave. Mechanical waves, such as
Chapter 6 Mechanical Waves A wave is a disturbance that travels, or propagates, without the transport of matter. Examples: sound/ultrasonic wave, EM waves, and earthquake wave. Mechanical waves, such as
EMF Notes 11; Maxwell s Equations. MAXWELL S EQUATIONS Maxwell s four equations
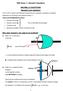 MAXWELL S EQUATONS Maxwell s four equations n the 870 s, James Clerk Maxwell showed that four equations constitute a complete description of the electric and magnetic fields, or THE ELECTROMAGNETC FELD
MAXWELL S EQUATONS Maxwell s four equations n the 870 s, James Clerk Maxwell showed that four equations constitute a complete description of the electric and magnetic fields, or THE ELECTROMAGNETC FELD
Dielectric metasurfaces for complete control of phase and polarization with subwavelength spatial resolution and high transmission
 DOI:.38/NNANO.25.86 Dielectric metasurfaces for complete control of phase and polarization with subwavelength spatial resolution and high transmission Amir Arbabi, Yu Horie, Mahmood Bagheri, and Andrei
DOI:.38/NNANO.25.86 Dielectric metasurfaces for complete control of phase and polarization with subwavelength spatial resolution and high transmission Amir Arbabi, Yu Horie, Mahmood Bagheri, and Andrei
Along with C1 the magnetic field is also observed at location C 2 though no current is threading through this loop.
 Displacement current British physicist James C. Maxwell gave final shape to all phenomenon connecting electricity and magnetism. He noticed an inconsistency in Ampere s Law connecting Electric current
Displacement current British physicist James C. Maxwell gave final shape to all phenomenon connecting electricity and magnetism. He noticed an inconsistency in Ampere s Law connecting Electric current
Problems set # 2 Physics 169 February 11, 2015
 Prof. Anchordoqui Problems set # 2 Phsics 169 Februar 11, 2015 1. Figure 1 shows the electric field lines for two point charges separated b a small distance. (i) Determine the ratio q 1 /q 2. (ii) What
Prof. Anchordoqui Problems set # 2 Phsics 169 Februar 11, 2015 1. Figure 1 shows the electric field lines for two point charges separated b a small distance. (i) Determine the ratio q 1 /q 2. (ii) What
Measurement and Control of a Photon's Spatial Wavefunction
 Measurement and Control of a Photon's Spatial Wavefunction Cod Lear The College of Wooster, Januar 2011 Institute of perimental Phsics Optics Division Universit of Warsaw Poland brief histor of light and
Measurement and Control of a Photon's Spatial Wavefunction Cod Lear The College of Wooster, Januar 2011 Institute of perimental Phsics Optics Division Universit of Warsaw Poland brief histor of light and
Electromagnetic Theory PHYS 402. Electrodynamics. Ohm s law Electromotive Force Electromagnetic Induction Maxwell s Equations
 Electromagnetic Theory PHYS 4 Electrodynamics Ohm s law Electromotive Force Electromagnetic Induction Maxwell s Equations 1 7.1.1 Ohms Law For the EM force Usually v is small so J = J = σ Current density
Electromagnetic Theory PHYS 4 Electrodynamics Ohm s law Electromotive Force Electromagnetic Induction Maxwell s Equations 1 7.1.1 Ohms Law For the EM force Usually v is small so J = J = σ Current density
Section 0.4 Inverse functions and logarithms
 Section 0.4 Inverse functions and logarithms (5/3/07) Overview: Some applications require not onl a function that converts a numer into a numer, ut also its inverse, which converts ack into. In this section
Section 0.4 Inverse functions and logarithms (5/3/07) Overview: Some applications require not onl a function that converts a numer into a numer, ut also its inverse, which converts ack into. In this section
1. Electrostatics Electric charge
 1 1. Electrostatics Petrović Branko Email: bpshalom@yahoo.co.uk Electrostatics is branch of electromagnetism that deals with electric phenomena not associated with electric charge in motion. Fundamental
1 1. Electrostatics Petrović Branko Email: bpshalom@yahoo.co.uk Electrostatics is branch of electromagnetism that deals with electric phenomena not associated with electric charge in motion. Fundamental
CHAPTER 2. COULOMB S LAW AND ELECTRONIC FIELD INTENSITY. 2.3 Field Due to a Continuous Volume Charge Distribution
 CONTENTS CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ANALYSIS 1. Scalars and Vectors 2. Vector Algebra 3. The Cartesian Coordinate System 4. Vector Cartesian Coordinate System 5. The Vector Field 6. The Dot Product 7. The Cross
CONTENTS CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ANALYSIS 1. Scalars and Vectors 2. Vector Algebra 3. The Cartesian Coordinate System 4. Vector Cartesian Coordinate System 5. The Vector Field 6. The Dot Product 7. The Cross
Electromagnetic Theory (Hecht Ch. 3)
 Phys 531 Lecture 2 30 August 2005 Electromagnetic Theory (Hecht Ch. 3) Last time, talked about waves in general wave equation: 2 ψ(r, t) = 1 v 2 2 ψ t 2 ψ = amplitude of disturbance of medium For light,
Phys 531 Lecture 2 30 August 2005 Electromagnetic Theory (Hecht Ch. 3) Last time, talked about waves in general wave equation: 2 ψ(r, t) = 1 v 2 2 ψ t 2 ψ = amplitude of disturbance of medium For light,
Maxwell s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves
 Phsics 36: Waves Lecure 3 /9/8 Maxwell s quaions and lecromagneic Waves Four Laws of lecromagneism. Gauss Law qenc all da ρdv Inegral From From he vecor ideni da dv Therefore, we ma wrie Gauss Law as ρ
Phsics 36: Waves Lecure 3 /9/8 Maxwell s quaions and lecromagneic Waves Four Laws of lecromagneism. Gauss Law qenc all da ρdv Inegral From From he vecor ideni da dv Therefore, we ma wrie Gauss Law as ρ
Worked Examples Set 2
 Worked Examples Set 2 Q.1. Application of Maxwell s eqns. [Griffiths Problem 7.42] In a perfect conductor the conductivity σ is infinite, so from Ohm s law J = σe, E = 0. Any net charge must be on the
Worked Examples Set 2 Q.1. Application of Maxwell s eqns. [Griffiths Problem 7.42] In a perfect conductor the conductivity σ is infinite, so from Ohm s law J = σe, E = 0. Any net charge must be on the
ENGI 4430 Gauss & Stokes Theorems; Potentials Page 10.01
 ENGI 443 Gauss & tokes heorems; Potentials Page.. Gauss Divergence heorem Let be a piecewise-smooth closed surface enclosing a volume in vector field. hen the net flux of F out of is F d F d, N 3 and let
ENGI 443 Gauss & tokes heorems; Potentials Page.. Gauss Divergence heorem Let be a piecewise-smooth closed surface enclosing a volume in vector field. hen the net flux of F out of is F d F d, N 3 and let
Physics 2102 Gabriela González. Marathon review of the course: 15 weeks in ~60 minutes!
 Physics 2102 Gabriela González Marathon review of the course: 15 weeks in ~60 minutes! Fields: electric & magnetic electric and magnetic forces on electric charges potential energy, electric potential,
Physics 2102 Gabriela González Marathon review of the course: 15 weeks in ~60 minutes! Fields: electric & magnetic electric and magnetic forces on electric charges potential energy, electric potential,
DIGITAL CORRELATION OF FIRST ORDER SPACE TIME IN A FLUCTUATING MEDIUM
 DIGITAL CORRELATION OF FIRST ORDER SPACE TIME IN A FLUCTUATING MEDIUM Budi Santoso Center For Partnership in Nuclear Technolog, National Nuclear Energ Agenc (BATAN) Puspiptek, Serpong ABSTRACT DIGITAL
DIGITAL CORRELATION OF FIRST ORDER SPACE TIME IN A FLUCTUATING MEDIUM Budi Santoso Center For Partnership in Nuclear Technolog, National Nuclear Energ Agenc (BATAN) Puspiptek, Serpong ABSTRACT DIGITAL
6.642, Continuum Electromechanics Prof. Markus Zahn Lecture 1: Review of Maxwell s Equations
 6.64, Continuum Electromechanics Prof. Markus Zahn Lecture 1: Review of Mawell s Equations I. Mawell s Equations in Integral Form in Free pace 1. Faraay s Law C E i s = - µ H a t i Circulation of E Magnetic
6.64, Continuum Electromechanics Prof. Markus Zahn Lecture 1: Review of Mawell s Equations I. Mawell s Equations in Integral Form in Free pace 1. Faraay s Law C E i s = - µ H a t i Circulation of E Magnetic
