Lecture 2:Matter. Wave Interferometry
|
|
|
- Kory Reed
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture :Matter Wave Interferometry Matter wave interferometry: as old as Quantum Mechanics Neutron diffraction and electron diffraction are standard investigation tools in solid state physics Cold atoms: new possibilities h λ DB = T 1μ K Mv = λ 1μm Rapid advances in precision measurements DB
2 Interferometry Beam splitter LASER DETECTOR Beam recombiner Change of optical path, Length, pressure, temperature, Atom interferometry Change of phase of interference pattern Atomic source Beam splitters, mirrors Detectors
3 Matter wave diffraction Huygens-Fresnel principle Monokinetic beam of particles described by ψ (,) rt Δ E m ψ = ψ Analogy with Δ + k = me Δ ψ + k ψ = 0 with k = E E 0 for electric field E(,) rt of light beam with λ = π k with T = D/ v k = mv 0 0 ik( X + Y ) im( X + Y ) ψ ( X, Y, D) = ψ0 exp = ψ0 exp D T
4 Neutron Diffraction from a slit Experiment with slow neutrons: λ = 1.96 nm v0 = 06 m/ s ILL Grenoble Neutrons produced at km/s slowed in successive steps to T=0K Detection by nuclear reaction with 100% efficiency producing alpha particles Slit width: 93 microns
5 Atom holography Generalization to arbitrary image patterns Principle of a transmission hologram We start from the momentum distribution I( X, Y) that we want to produce on the screen. Its amplitude is axy (, ) = IXY (, ) and is the amplitude diffracted in direction with k, k k = kx / f, k = ky / f x y a( X, Y ) = Fourier Transform of t( x, y) the transmission function of the diffracting hologram x y
6 Tokyo experiment i( kxx+ kyy) ak ( x, ky) = e txydxdy (, ) By inverse Fourier transform we deduce the required t(x,y) But! In general t(x,y) is complex! In fact, we can only code real values and only 0 or 1 (block or transmit!) Solution: code: This gives two images: I( XY, ) andi( X, Y) txy (, ) + t( xy, )/ M. Morinaga et al. PRL, 77, 80 (1996) One also adds a constant t 0 to the function to be coded Such that t0 + t( x, y) + t ( x, y)/ is a positive number between 0 and The transmission 0 or 1 of each pixel is then obtained by comparing tx ( i, yi) to η where is a constant t max η t max
7 Matter wave diffraction by periodic structures Material grating Laser standing wave 100% transmission Standing wave MIT P. Gould et al. PRL 56,87 (1986)
8 Thin phase grating approximation Standing wave Period:λ / k = π / λ Simple treatment: 1D along z, quasi monochromatic wave packet: mean momentum p 0, Δpz k pz pz U0 U0 Hamiltonian H = + U0 sin kz = + cos kz m m pz U0 U0 ikz ikz = + ( e + e ) m 4 iht / ψ ( T) = e ψ(0 with ψ(0 = p 0 First we neglect motion along z during T n=+ iut ( 0 / )cos( kz) n UT 0 inkz ψ ( T) = e p0 = ( i) Jn e p0 n= n=+ n UT 0 = () i Jn p0 n k n= UT 0 Intensity of diffracted peaks prop. to J n
9 3D case and validity of thin grating approx. w 3D motion T = v p p n k Validity: m m x 0 ( 0 + c ) TUE 0 R / 1 U Introducing the classical oscillation period in potential well Validity: 0 where n c is a typical diff. order n U0 T / ω = UE 0 R / ω T 1 If condition is violated: thick grating and Bragg diffraction c w Bragg diffraction
10 Energy conservation and Bragg regime Stationary problem: total energy is conserved For small momenta along z, and n c ~1 p 0 k The kinetic energy along z changes by p ( p ± k) Δ Ez = m m z z It must be compensated by a change of kinetic energy along x E Δ E R z = ΔE x How does a standing wave along z changes the kinetic energy along x? Finite transit time: standing wave (diameter w ) has angular divergence This enables momentum changes along x of and of kinetic energy As long as h T E Otherwise, for long times, choose R p x kθ x ± x x h/ w ( p h/ w) p p h h Δ Ex = = m m mw T z θ = λ / w total energy can be conserved and exchanged between x and z p = k Diffraction leads to pz = + k momentum along z is conserved. This is the Bragg regime. Rabi oscillation between the two states with pulsation U / 0 Adjustable beamsplitter
11 MIT, Konstanz Stanford,Vienna Yale,Toulouse, Paris, Hannover Three grating Interferometers Beam with Velocity v 0 x Phase shift calculated on classical path (See below) φ( k ) = k ( x) dx k ( x) dx 0 1 Γ1 Γ where k 0 = me / and kx ( ) = me ( Vx ( )/ xb V E 0 ( ) 1 tb For k V x and stationary: δϕ ( k0) = ( ) dx= V t dt xa E v ta 0 Example: Na beam with v 0 =1000m/s High precision measurement of x b -x a =0.1m, V= ev, δφ = 1 rad electric polarizability, A- B effect, index of refraction for matter waves,
12 Path integral formalism r, t r, t A particle travels from to with a probability amplitude given by: a a b b / b b a a Γ 3 b tb K b tb a ta ψ a ta d ra is K( r, t ; r, t ) = e Γ ψ ( r, ) = ( r, ; r, ) ( r, ) t b S = Γ L((),),) r t r t dt t a The sum is over all paths Γ connecting r, t r, t Remarkable result: For a Lagrangien which is linear or quadratic in position and momentum we have: isclass. K( r, t ; r, t ) = F( t, t ) e / b b a a b a b F( t, t ) b b a S class. is the action calculated along the path Γ where is independent of initial and final positions r a a a to r b, and where is the action evaluated on the classical path connecting to r, t Examples Particle in gravity field Particle in harmonic trap Particle in rotating frame L = mr / mgz L= mr / mω r / L= mr / + mr.( Ω r) + m( Ω r) / r t a a b b
13 Young slit experiment with free falling atoms F. Shimizu et al., Phys. Rev A, 46 R17 (199) rt v a, a 0 a H rt b, b T = v + gh + v 0 0 g ( rb, tb) cos ( mxba/ T) ψ δ x = a=6 μm, H= 0.85 m Fringe period b π T ma
14 Atom interferometers, Spectroscopy,, and Clocks Atoms have internal states Two level atom: g, e Laser resonant on g e transition Neglect spontaneous emission Use long lived upper states Mg, Ca, Sr, or Raman Transition between hyperfine ground states in alkalis for instance Effective two-level system e +k 1 -k g g 1
15 Optical clocks Mach-Zehnder interferometer with light beams π π π e, p+ k Atom beam g, p g, p t 0 t 1 t Laser beams Time δφ = φ ( t ) φ ( t ) + φ ( t ) Sensitive to rotation and accelerations: gyrometers and gravimeters
16 M. Kasevich and S. Chu, PRL 67, 1991 δφ = k at = k gt = k gt a Cold atom gravimeter eff eff L λ Tcycle = δφ 4πT τ L min noise min 1/ δφnoise = 0.01 rad, T = 0.4s a = 9 10 / 1 m s at s Detection of tides effects at ~10-7 g
17 Sagnac interferometer Interferometer area: A Rotation with angular speed Ω around z Path length increase (decrease) for counter clockwise (clockwise) δ l = ΩRT Travel time from A to B: Phase difference T = π R/ v δφ = kδl = kω RT = kω π R / v= kωa/ v Photons: v = c k = ω / c δφ photons = ΩAω / c Matter: k = mv/ δφ = ΩAm / matter Ratio of sensitivity: δφ δφ matter photons = mc 100GeV 10 ω 1eV 11
18 Stanford Gyroscope T. Gustavson, P. Bouyer and M. Kasevich PRL 78, 046, 1997 δω Current sensitivity 610 rad s Hz / Measurement of Earth rotation rate : 43 μrad/s
19 Optical clocks Ramsey-Bordé interferometer π π π π C. Bordé, Phys. Lett. A,140 (1989) Atom beam g, p g, p e, p- k T T with t 1 t t 3 P cos T( ω ω + δ) + φ t 4 ( ) e L 0 L δ = k /m and L Time φ = φ φ + φ φ 1 4 3
20 Recoil doublet in optical clocks U. Sterr et al., atom interferometry, P. Berman ed D D Cold atoms frequency standards Calcium: PTB, NIST T increases Lasers locked to Ca with fractional instability of at 1 s and at 000 s Accuracy: ~10-14
21 h/m and fine structure constant α Recoil splitting is: Δ f = hν / m c recoil atom Measuring Δ f recoil is a measure of h/ matom R h R h m m atom p = = c me c m atom m p me α All other quantities can be measured at 10-9 or better thus a photon recoil measurement at 10-9 can give α at 10-9 Cesium atom interferometry: α at Wicht et al. Phys. Scripta (00) Bloch oscillations of Rb atoms : α at Cladé et al., PRL 96, (006) g- of electrons with QED calculations: α at : Gabrielse et al, PRL, 97, (006)
22 Cold atoms and precision measurements Interferometers and clocks T : interaction time with ELM field Slow atoms: T large; atomic fountain or microgravity of space Interferometers on chips Clocks: gain prop. to T L Inertial sensors: Accelerometers: gain as T Sagnac gyroscopes : gain as L T Current sensitivity: Acceleration: δg/g= in 1min Rotation: Ω= rad s -1 in 1 s
23 Summary Atom interferometry has entered into high precision measurement phase Fine structure constant and h/m Towards a redefinition of the kilogram based on atomic masses Earth rotation, g, g gradients, inertial base (GOM, CASI) G: Magia (Firenze) Tests of Newton law at short distances Test of Equivalence principle Prospects for ultra-high sensitivity inertial sensors in space with long interrogation times: HYPER Quantum gases sources and atom lasers with atom chips (ICE, Quantus) See several talks at the workshop for most recent developments
24 Further reading Atom Interferometry ed. Paul Berman, Academic Press, 1997 Atoms quanta and relativity, special Issue of J Phys B: Atomic, Molecular and Optical physics, IoP (005) ed., T. Haensch, H. Schmidt-Boecking and H. Walther C. Bordé, metrologia, 39, 435 (00) C. Cohen-Tannoudji, lectures at Collège de France J. Dalibard, DEA lectures on cold atoms
Atom interferometry. Quantum metrology and fundamental constants. Laboratoire de physique des lasers, CNRS-Université Paris Nord
 Diffraction Interferometry Conclusion Laboratoire de physique des lasers, CNRS-Université Paris Nord Quantum metrology and fundamental constants Diffraction Interferometry Conclusion Introduction Why using
Diffraction Interferometry Conclusion Laboratoire de physique des lasers, CNRS-Université Paris Nord Quantum metrology and fundamental constants Diffraction Interferometry Conclusion Introduction Why using
Atom Interferometry I. F. Pereira Dos Santos
 Atom Interferometry I F. Pereira Dos Santos SYRTE SYRTE is one of the 4 Departments of Paris Obs. SYRTE research activities : - Time and Frequency Metrology (LNE-SYRTE) - Fundamental Astronomy - History
Atom Interferometry I F. Pereira Dos Santos SYRTE SYRTE is one of the 4 Departments of Paris Obs. SYRTE research activities : - Time and Frequency Metrology (LNE-SYRTE) - Fundamental Astronomy - History
Atomic Quantum Sensors and Fundamental Tests
 Atomic Quantum Sensors and Fundamental Tests C. Salomon Laboratoire Kastler Brossel, Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris ESA- ESTEC-FPRAT, January 21th, 2010 Fundamental Questions 1) Missing mass in the Universe
Atomic Quantum Sensors and Fundamental Tests C. Salomon Laboratoire Kastler Brossel, Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris ESA- ESTEC-FPRAT, January 21th, 2010 Fundamental Questions 1) Missing mass in the Universe
SYRTE - IACI. AtoM Interferometry dual Gravi- GradiOmeter AMIGGO. from capability demonstrations in laboratory to space missions
 SYRTE - IACI AtoM Interferometry dual Gravi- GradiOmeter AMIGGO from capability demonstrations in laboratory to space missions A. Trimeche, R. Caldani, M. Langlois, S. Merlet, C. Garrido Alzar and F. Pereira
SYRTE - IACI AtoM Interferometry dual Gravi- GradiOmeter AMIGGO from capability demonstrations in laboratory to space missions A. Trimeche, R. Caldani, M. Langlois, S. Merlet, C. Garrido Alzar and F. Pereira
Shau-Yu Lan 藍劭宇. University of California, Berkeley Department of Physics
 Atom Interferometry Experiments for Precision Measurement of Fundamental Physics Shau-Yu Lan 藍劭宇 University of California, Berkeley Department of Physics Contents Principle of Light-Pulse Atom Interferometer
Atom Interferometry Experiments for Precision Measurement of Fundamental Physics Shau-Yu Lan 藍劭宇 University of California, Berkeley Department of Physics Contents Principle of Light-Pulse Atom Interferometer
Gravitational tests using simultaneous atom interferometers
 Gravitational tests using simultaneous atom interferometers Gabriele Rosi Quantum gases, fundamental interactions and cosmology conference 5-7 October 017, Pisa Outline Introduction to atom interferometry
Gravitational tests using simultaneous atom interferometers Gabriele Rosi Quantum gases, fundamental interactions and cosmology conference 5-7 October 017, Pisa Outline Introduction to atom interferometry
Sensitivity limits of atom interferometry gravity gradiometers and strainmeters. Fiodor Sorrentino INFN Genova
 Sensitivity limits of atom interferometry gravity gradiometers and strainmeters Fiodor Sorrentino INFN Genova 1 Outline AI sensors, state of the art performance Main noise sources Potential improvements
Sensitivity limits of atom interferometry gravity gradiometers and strainmeters Fiodor Sorrentino INFN Genova 1 Outline AI sensors, state of the art performance Main noise sources Potential improvements
State of the art cold atom gyroscope without dead times
 State of the art cold atom gyroscope without dead times Remi Geiger SYRTE, Observatoire de Paris GDR IQFA Telecom Paris November 18 th, 2016 I. Dutta, D. Savoie, B. Fang, B. Venon, C. L. Garrido Alzar,
State of the art cold atom gyroscope without dead times Remi Geiger SYRTE, Observatoire de Paris GDR IQFA Telecom Paris November 18 th, 2016 I. Dutta, D. Savoie, B. Fang, B. Venon, C. L. Garrido Alzar,
Bloch oscillations of ultracold-atoms and Determination of the fine structure constant
 Bloch oscillations of ultracold-atoms and Determination of the fine structure constant Pierre Cladé P. Cladé Bloch oscillations and atom interferometry Sept., 2013 1 / 28 Outlook Bloch oscillations of
Bloch oscillations of ultracold-atoms and Determination of the fine structure constant Pierre Cladé P. Cladé Bloch oscillations and atom interferometry Sept., 2013 1 / 28 Outlook Bloch oscillations of
Atom interferometry in microgravity: the ICE project
 Atom interferometry in microgravity: the ICE project (4) G. Stern 1,2, R. Geiger 1, V. Ménoret 1,B. Battelier 1, R. Charrière 3, N. Zahzam 3, Y. Bidel 3, L. Mondin 4, F. Pereira 2, A. Bresson 3, A. Landragin
Atom interferometry in microgravity: the ICE project (4) G. Stern 1,2, R. Geiger 1, V. Ménoret 1,B. Battelier 1, R. Charrière 3, N. Zahzam 3, Y. Bidel 3, L. Mondin 4, F. Pereira 2, A. Bresson 3, A. Landragin
Towards compact transportable atom-interferometric inertial sensors
 Towards compact transportable atom-interferometric inertial sensors G. Stern (SYRTE/LCFIO) Increasing the interrogation time T is often the limiting parameter for the sensitivity. Different solutions:
Towards compact transportable atom-interferometric inertial sensors G. Stern (SYRTE/LCFIO) Increasing the interrogation time T is often the limiting parameter for the sensitivity. Different solutions:
Large Momentum Beamsplitter using Bloch Oscillations
 Large Momentum Beamsplitter using Bloch Oscillations Pierre Cladé, Saïda Guellati-Khélifa, François Nez, and François Biraben Laboratoire Kastler Brossel, UPMC, Ecole Normale Supérieure, CNRS, 4 place
Large Momentum Beamsplitter using Bloch Oscillations Pierre Cladé, Saïda Guellati-Khélifa, François Nez, and François Biraben Laboratoire Kastler Brossel, UPMC, Ecole Normale Supérieure, CNRS, 4 place
Atom Interferometry. Abstract
 Atom Interferometry Shohini Ghose Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, New Mexico 87131 (January 25, 2000) Abstract Atom interferometers are of interest because of
Atom Interferometry Shohini Ghose Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, New Mexico 87131 (January 25, 2000) Abstract Atom interferometers are of interest because of
Precision atom interferometry in a 10 meter tower
 Precision atom interferometry in a 10 meter tower Leibniz Universität Hannover RTG 1729, Lecture 1 Jason Hogan Stanford University January 23, 2014 Cold Atom Inertial Sensors Cold atom sensors: Laser cooling;
Precision atom interferometry in a 10 meter tower Leibniz Universität Hannover RTG 1729, Lecture 1 Jason Hogan Stanford University January 23, 2014 Cold Atom Inertial Sensors Cold atom sensors: Laser cooling;
Laser cooling and trapping
 Laser cooling and trapping William D. Phillips wdp@umd.edu Physics 623 14 April 2016 Why Cool and Trap Atoms? Original motivation and most practical current application: ATOMIC CLOCKS Current scientific
Laser cooling and trapping William D. Phillips wdp@umd.edu Physics 623 14 April 2016 Why Cool and Trap Atoms? Original motivation and most practical current application: ATOMIC CLOCKS Current scientific
Precision Interferometry with a Bose-Einstein Condensate. Cass Sackett. Research Talk 17 October 2008
 Precision Interferometry with a Bose-Einstein Condensate Cass Sackett Research Talk 17 October 2008 Outline Atom interferometry Bose condensates Our interferometer One application What is atom interferometry?
Precision Interferometry with a Bose-Einstein Condensate Cass Sackett Research Talk 17 October 2008 Outline Atom interferometry Bose condensates Our interferometer One application What is atom interferometry?
Exact phase shifts for atom interferometry
 Physics Letters A 306 003 77 84 wwwelseviercom/locate/pla Exact phase shifts for atom interferometry Ch Antoine a,, ChJ Bordé a,b, a Equipe de Relativité Gravitation et Astrophysique, LERMA, CNRS-Observatoire
Physics Letters A 306 003 77 84 wwwelseviercom/locate/pla Exact phase shifts for atom interferometry Ch Antoine a,, ChJ Bordé a,b, a Equipe de Relativité Gravitation et Astrophysique, LERMA, CNRS-Observatoire
arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 25 May 2017
![arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 25 May 2017 arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 25 May 2017](/thumbs/86/94468928.jpg) Prepared for submission to JINST arxiv:1705.09376v1 [physics.ins-det] 25 May 2017 Atom Interferometry for Dark Contents of the Vacuum Searches O. Burrow, a,1 A. Carroll, a S. Chattopadhyay, b,c,2 J. Coleman,
Prepared for submission to JINST arxiv:1705.09376v1 [physics.ins-det] 25 May 2017 Atom Interferometry for Dark Contents of the Vacuum Searches O. Burrow, a,1 A. Carroll, a S. Chattopadhyay, b,c,2 J. Coleman,
Atom Quantum Sensors on ground and in space
 Atom Quantum Sensors on ground and in space Ernst M. Rasel AG Wolfgang Ertmer Quantum Sensors Division Institut für Quantenoptik Leibniz Universität Hannover IQ - Quantum Sensors Inertial Quantum Probes
Atom Quantum Sensors on ground and in space Ernst M. Rasel AG Wolfgang Ertmer Quantum Sensors Division Institut für Quantenoptik Leibniz Universität Hannover IQ - Quantum Sensors Inertial Quantum Probes
New Searches for Subgravitational Forces
 New Searches for Subgravitational Forces Jay Wacker SLAC University of California, Davis November 26, 2007 with Peter Graham Mark Kasevich 1 New Era in Fundamental Physics Energy Frontier LHC Nature of
New Searches for Subgravitational Forces Jay Wacker SLAC University of California, Davis November 26, 2007 with Peter Graham Mark Kasevich 1 New Era in Fundamental Physics Energy Frontier LHC Nature of
ATOM INTERFEROMETERS WITH BEC A theoretical analysis based on mean-field approximation CHIEN-NAN LIU FU-JEN CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY TAIPEI, TAIWAN
 1 ATOM INTERFEROMETERS WITH BEC A theoretical analysis based on mean-field approximation CHIEN-NAN LIU FU-JEN CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY TAIPEI, TAIWAN Collaborators 2 Prof. Shinichi Watanabe G. Gopi Krishna
1 ATOM INTERFEROMETERS WITH BEC A theoretical analysis based on mean-field approximation CHIEN-NAN LIU FU-JEN CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY TAIPEI, TAIWAN Collaborators 2 Prof. Shinichi Watanabe G. Gopi Krishna
Strongly correlated systems in atomic and condensed matter physics. Lecture notes for Physics 284 by Eugene Demler Harvard University
 Strongly correlated systems in atomic and condensed matter physics Lecture notes for Physics 284 by Eugene Demler Harvard University September 18, 2014 2 Chapter 5 Atoms in optical lattices Optical lattices
Strongly correlated systems in atomic and condensed matter physics Lecture notes for Physics 284 by Eugene Demler Harvard University September 18, 2014 2 Chapter 5 Atoms in optical lattices Optical lattices
Cold Atom Clocks on Earth and in Space Fundamental Tests and Applications. C. Salomon Laboratoire Kastler Brossel, Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris
 Cold Atom Clocks on Earth and in Space Fundamental Tests and Applications C. Salomon Laboratoire Kastler Brossel, Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris http://www.lkb.ens.fr/recherche/atfroids/welcome Varenna
Cold Atom Clocks on Earth and in Space Fundamental Tests and Applications C. Salomon Laboratoire Kastler Brossel, Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris http://www.lkb.ens.fr/recherche/atfroids/welcome Varenna
Cold atom gyroscope with 1 nrad.s -1 rotation stability
 Cold atom gyroscope with 1 nrad.s -1 rotation stability D. Savoie, I. Dutta, B. Fang, B. Venon, N. Miélec, R. Sapam, C. Garrido Alzar, R. Geiger and A. Landragin LNE-SYRTE, Observatoire de Paris IACI team
Cold atom gyroscope with 1 nrad.s -1 rotation stability D. Savoie, I. Dutta, B. Fang, B. Venon, N. Miélec, R. Sapam, C. Garrido Alzar, R. Geiger and A. Landragin LNE-SYRTE, Observatoire de Paris IACI team
Advanced accelerometer/gradiometer concepts based on atom interferometry
 Advanced accelerometer/gradiometer concepts based on atom interferometry Malte Schmidt, Alexander Senger, Matthias Hauth, Sebastian Grede, Christian Freier, Achim Peters Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
Advanced accelerometer/gradiometer concepts based on atom interferometry Malte Schmidt, Alexander Senger, Matthias Hauth, Sebastian Grede, Christian Freier, Achim Peters Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course. Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C
 2752 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C2: LASER SCIENCE AND QUANTUM INFORMATION PROCESSING TRINITY TERM 2013 Friday,
2752 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C2: LASER SCIENCE AND QUANTUM INFORMATION PROCESSING TRINITY TERM 2013 Friday,
Phys 531 Lecture 27 6 December 2005
 Phys 531 Lecture 27 6 December 2005 Final Review Last time: introduction to quantum field theory Like QM, but field is quantum variable rather than x, p for particle Understand photons, noise, weird quantum
Phys 531 Lecture 27 6 December 2005 Final Review Last time: introduction to quantum field theory Like QM, but field is quantum variable rather than x, p for particle Understand photons, noise, weird quantum
Atom interferometry applications in gravimetry
 Prof. Achim Peters, Ph.D. Atom interferometry applications in gravimetry and some thoughts on current sensitivity limitations and concepts for future improvements International Workshop on Gravitational
Prof. Achim Peters, Ph.D. Atom interferometry applications in gravimetry and some thoughts on current sensitivity limitations and concepts for future improvements International Workshop on Gravitational
Experimental AMO eets meets M odel Model Building: Part I (Precision Atom Interferometry)
 Experimental AMO meets Model Building: Part I (Precision Atom Interferometry) Interference of Rb atoms Chiow, et. al, PRL, 2011 Young s double slit with atoms Young s 2 slit with Helium atoms Interference
Experimental AMO meets Model Building: Part I (Precision Atom Interferometry) Interference of Rb atoms Chiow, et. al, PRL, 2011 Young s double slit with atoms Young s 2 slit with Helium atoms Interference
Looking For Dark Energy On Earth: A New Experiment Using Atom Interferometry That Galileo Would Understand
 Looking For Dark Energy On Earth: A New Experiment Using Atom Interferometry That Galileo Would Understand Martin Perl Kavli Institute For Particle Astrophysics And Cosmology SLAC Linear Accelerator Laboratory
Looking For Dark Energy On Earth: A New Experiment Using Atom Interferometry That Galileo Would Understand Martin Perl Kavli Institute For Particle Astrophysics And Cosmology SLAC Linear Accelerator Laboratory
Fundamental Physics with Atomic Interferometry
 Fundamental Physics with Atomic Interferometry Peter Graham Stanford with Savas Dimopoulos Jason Hogan Mark Kasevich Surjeet Rajendran PRL 98 (2007) PRD 78 (2008) PRD 78 (2008) PLB 678 (2009) arxiv:1009.2702
Fundamental Physics with Atomic Interferometry Peter Graham Stanford with Savas Dimopoulos Jason Hogan Mark Kasevich Surjeet Rajendran PRL 98 (2007) PRD 78 (2008) PRD 78 (2008) PLB 678 (2009) arxiv:1009.2702
Construction of an absolute gravimeter using atom interferometry with cold 87. Rb atoms
 Construction of an absolute gravimeter using atom interferometry with cold 87 Rb atoms Patrick Cheinet Julien Le Gouët Kasper Therkildsen Franck Pereira Dos Santos Arnaud Landragin David Holleville André
Construction of an absolute gravimeter using atom interferometry with cold 87 Rb atoms Patrick Cheinet Julien Le Gouët Kasper Therkildsen Franck Pereira Dos Santos Arnaud Landragin David Holleville André
9 Atomic Coherence in Three-Level Atoms
 9 Atomic Coherence in Three-Level Atoms 9.1 Coherent trapping - dark states In multi-level systems coherent superpositions between different states (atomic coherence) may lead to dramatic changes of light
9 Atomic Coherence in Three-Level Atoms 9.1 Coherent trapping - dark states In multi-level systems coherent superpositions between different states (atomic coherence) may lead to dramatic changes of light
Homework 3. 1 Coherent Control [22 pts.] 1.1 State vector vs Bloch vector [8 pts.]
![Homework 3. 1 Coherent Control [22 pts.] 1.1 State vector vs Bloch vector [8 pts.] Homework 3. 1 Coherent Control [22 pts.] 1.1 State vector vs Bloch vector [8 pts.]](/thumbs/95/125325883.jpg) Homework 3 Contact: jangi@ethz.ch Due date: December 5, 2014 Nano Optics, Fall Semester 2014 Photonics Laboratory, ETH Zürich www.photonics.ethz.ch 1 Coherent Control [22 pts.] In the first part of this
Homework 3 Contact: jangi@ethz.ch Due date: December 5, 2014 Nano Optics, Fall Semester 2014 Photonics Laboratory, ETH Zürich www.photonics.ethz.ch 1 Coherent Control [22 pts.] In the first part of this
Interference. Reminder: Exam 2 and Review quiz, more details on the course website
 Chapter 9 Interference Phys 322 Lecture 25 Reminder: Exam 2 and Review quiz, more details on the course website Interferometers Wavefront-splitting interferometers Amplitude-splitting interferometers ed
Chapter 9 Interference Phys 322 Lecture 25 Reminder: Exam 2 and Review quiz, more details on the course website Interferometers Wavefront-splitting interferometers Amplitude-splitting interferometers ed
Does an atom interferometer test the gravitational redshift at the Compton frequency?
 Does an atom interferometer test the gravitational redshift at the Compton frequency? Peter Wolf, 1 Luc Blanchet, 2 Christian J. Bordé, 1 Serge Reynaud, 3 Christophe Salomon, 4 and Claude Cohen-Tannoudji
Does an atom interferometer test the gravitational redshift at the Compton frequency? Peter Wolf, 1 Luc Blanchet, 2 Christian J. Bordé, 1 Serge Reynaud, 3 Christophe Salomon, 4 and Claude Cohen-Tannoudji
Hybrid Atom-Optical Interferometry for Gravitational Wave Detection and Geophysics
 Hybrid Atom-Optical Interferometry for Gravitational Wave Detection and Geophysics Remi Geiger, SYRTE for the MIGA consortium EGAS 46, July 3rd 2014, Lille, France http://syrte.obspm.fr/tfc/capteurs_inertiels
Hybrid Atom-Optical Interferometry for Gravitational Wave Detection and Geophysics Remi Geiger, SYRTE for the MIGA consortium EGAS 46, July 3rd 2014, Lille, France http://syrte.obspm.fr/tfc/capteurs_inertiels
 Fundamental of Spectroscopy for Optical Remote Sensing Xinzhao Chu I 10 3.4. Principle of Uncertainty Indeterminacy 0. Expression of Heisenberg s Principle of Uncertainty It is worth to point out that
Fundamental of Spectroscopy for Optical Remote Sensing Xinzhao Chu I 10 3.4. Principle of Uncertainty Indeterminacy 0. Expression of Heisenberg s Principle of Uncertainty It is worth to point out that
Quantum optics of many-body systems
 Quantum optics of many-body systems Igor Mekhov Université Paris-Saclay (SPEC CEA) University of Oxford, St. Petersburg State University Lecture 2 Previous lecture 1 Classical optics light waves material
Quantum optics of many-body systems Igor Mekhov Université Paris-Saclay (SPEC CEA) University of Oxford, St. Petersburg State University Lecture 2 Previous lecture 1 Classical optics light waves material
arxiv: v2 [gr-qc] 6 Jan 2009
![arxiv: v2 [gr-qc] 6 Jan 2009 arxiv: v2 [gr-qc] 6 Jan 2009](/thumbs/79/79554103.jpg) An Atomic Gravitational Wave Interferometric Sensor (AGIS) arxiv:0806.15v [gr-qc] 6 Jan 009 Savas Dimopoulos, 1, Peter W. Graham,, Jason M. Hogan, 1, Mark A. Kasevich, 1, and Surjeet Rajendran,1, 1 Department
An Atomic Gravitational Wave Interferometric Sensor (AGIS) arxiv:0806.15v [gr-qc] 6 Jan 009 Savas Dimopoulos, 1, Peter W. Graham,, Jason M. Hogan, 1, Mark A. Kasevich, 1, and Surjeet Rajendran,1, 1 Department
A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth.
 Waves_P2 [152 marks] A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth. The beam is incident normally on a double slit. The distance between the slits
Waves_P2 [152 marks] A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth. The beam is incident normally on a double slit. The distance between the slits
FOUNDATIONAL EXPERIMENTS IN QUANTUM MECHANICS
 FOUNDATIONAL EXPERIMENTS IN QUANTUM MECHANICS Matter Optics and Shelving Effect Bassano Vacchini DIPARTIMENTO DI FISICA - UNIVERSITÀ DI MILANO ISTITUZIONI DI FISICA TEORICA 30 MAGGIO 2003 FOUNDATIONAL
FOUNDATIONAL EXPERIMENTS IN QUANTUM MECHANICS Matter Optics and Shelving Effect Bassano Vacchini DIPARTIMENTO DI FISICA - UNIVERSITÀ DI MILANO ISTITUZIONI DI FISICA TEORICA 30 MAGGIO 2003 FOUNDATIONAL
PS210 - Optical Techniques. Section VI
 PS210 - Optical Techniques Section VI Section I Light as Waves, Rays and Photons Section II Geometrical Optics & Optical Instrumentation Section III Periodic and Non-Periodic (Aperiodic) Waves Section
PS210 - Optical Techniques Section VI Section I Light as Waves, Rays and Photons Section II Geometrical Optics & Optical Instrumentation Section III Periodic and Non-Periodic (Aperiodic) Waves Section
Some Topics in Optics
 Some Topics in Optics The HeNe LASER The index of refraction and dispersion Interference The Michelson Interferometer Diffraction Wavemeter Fabry-Pérot Etalon and Interferometer The Helium Neon LASER A
Some Topics in Optics The HeNe LASER The index of refraction and dispersion Interference The Michelson Interferometer Diffraction Wavemeter Fabry-Pérot Etalon and Interferometer The Helium Neon LASER A
Optical Lattices. Chapter Polarization
 Chapter Optical Lattices Abstract In this chapter we give details of the atomic physics that underlies the Bose- Hubbard model used to describe ultracold atoms in optical lattices. We show how the AC-Stark
Chapter Optical Lattices Abstract In this chapter we give details of the atomic physics that underlies the Bose- Hubbard model used to describe ultracold atoms in optical lattices. We show how the AC-Stark
Lecture 9: Introduction to Diffraction of Light
 Lecture 9: Introduction to Diffraction of Light Lecture aims to explain: 1. Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications 2. Interference of two one dimensional electromagnetic waves 3. Typical
Lecture 9: Introduction to Diffraction of Light Lecture aims to explain: 1. Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications 2. Interference of two one dimensional electromagnetic waves 3. Typical
Spectroscopic Instruments
 Spectroscopic Instruments 95 Spectroscopic Instruments by division of amplitude Mach-Zehnder (division of amplitude) Michelson Fringe localisation LIGO Fabry-Perot (FPI) Multi-layer coatings 96 Mach-Zehnder
Spectroscopic Instruments 95 Spectroscopic Instruments by division of amplitude Mach-Zehnder (division of amplitude) Michelson Fringe localisation LIGO Fabry-Perot (FPI) Multi-layer coatings 96 Mach-Zehnder
Atom-Based Test of the Equivalence Principle
 Space Sci Rev (2009) 148: 225 232 DOI 10.1007/s11214-009-9566-x Atom-Based Test of the Equivalence Principle Sebastian Fray Martin Weitz Received: 3 April 2009 / Accepted: 7 July 2009 / Published online:
Space Sci Rev (2009) 148: 225 232 DOI 10.1007/s11214-009-9566-x Atom-Based Test of the Equivalence Principle Sebastian Fray Martin Weitz Received: 3 April 2009 / Accepted: 7 July 2009 / Published online:
Christian J. Bordé. Bruxelles, mai 2018
 A consistent Fondations unified théoriques framework for de the la new métrologie International et du système System d unités of Units de (SI): base: de la géométrie Matter-wave et des optics nombres Christian
A consistent Fondations unified théoriques framework for de the la new métrologie International et du système System d unités of Units de (SI): base: de la géométrie Matter-wave et des optics nombres Christian
cond-mat/ v2 16 Aug 1999
 Mach-Zehnder Bragg interferometer for a Bose-Einstein Condensate Yoshio Torii,* Yoichi Suzuki, Mikio Kozuma and Takahiro Kuga Institute of Physics, University of Tokyo, 3-8-1 Komaba, Meguro-ku, Tokyo 153-8902,
Mach-Zehnder Bragg interferometer for a Bose-Einstein Condensate Yoshio Torii,* Yoichi Suzuki, Mikio Kozuma and Takahiro Kuga Institute of Physics, University of Tokyo, 3-8-1 Komaba, Meguro-ku, Tokyo 153-8902,
NanoKelvin Quantum Engineering
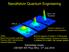 NanoKelvin Quantum Engineering Few x 10 5 Yb atoms 250mm 400 nk 250 nk < 200 nk Control of atomic c.m. position and momentum. Today: Bose-Fermi double superfluid Precision BEC interferometry Ultracold
NanoKelvin Quantum Engineering Few x 10 5 Yb atoms 250mm 400 nk 250 nk < 200 nk Control of atomic c.m. position and momentum. Today: Bose-Fermi double superfluid Precision BEC interferometry Ultracold
Absolute gravity measurements with a cold atom gravimeter
 Absolute gravity measurements with a cold atom gravimeter Anne Louchet-Chauvet, Sébastien Merlet, Quentin Bodart, Tristan Farah, Arnaud Landragin, Franck Pereira Dos Santos LNE-SYRTE Observatoire de Paris
Absolute gravity measurements with a cold atom gravimeter Anne Louchet-Chauvet, Sébastien Merlet, Quentin Bodart, Tristan Farah, Arnaud Landragin, Franck Pereira Dos Santos LNE-SYRTE Observatoire de Paris
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS6012W1 SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATION 2012/13 Coherent Light, Coherent Matter Duration: 120 MINS Answer all questions in Section A and only two questions in Section B. Section A carries
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS6012W1 SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATION 2012/13 Coherent Light, Coherent Matter Duration: 120 MINS Answer all questions in Section A and only two questions in Section B. Section A carries
Testing General Relativity with Atom Interferometry
 Testing General lativity with Atom Interferometry Savas Dimopoulos with Peter Graham Jason Hogan Mark Kasevich Testing Large Distance GR Cosmological Constant Problem suggests Our understanding of GR is
Testing General lativity with Atom Interferometry Savas Dimopoulos with Peter Graham Jason Hogan Mark Kasevich Testing Large Distance GR Cosmological Constant Problem suggests Our understanding of GR is
Supported by NIST, the Packard Foundation, the NSF, ARO. Penn State
 Measuring the electron edm using Cs and Rb atoms in optical lattices (and other experiments) Fang Fang Osama Kassis Xiao Li Dr. Karl Nelson Trevor Wenger Josh Albert Dr. Toshiya Kinoshita DSW Penn State
Measuring the electron edm using Cs and Rb atoms in optical lattices (and other experiments) Fang Fang Osama Kassis Xiao Li Dr. Karl Nelson Trevor Wenger Josh Albert Dr. Toshiya Kinoshita DSW Penn State
EE485 Introduction to Photonics
 Pattern formed by fluorescence of quantum dots EE485 Introduction to Photonics Photon and Laser Basics 1. Photon properties 2. Laser basics 3. Characteristics of laser beams Reading: Pedrotti 3, Sec. 1.2,
Pattern formed by fluorescence of quantum dots EE485 Introduction to Photonics Photon and Laser Basics 1. Photon properties 2. Laser basics 3. Characteristics of laser beams Reading: Pedrotti 3, Sec. 1.2,
Lecture 11: Introduction to diffraction of light
 Lecture 11: Introduction to diffraction of light Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications Diffraction in everyday life Diffraction in applications Spectroscopy: physics, chemistry, medicine,
Lecture 11: Introduction to diffraction of light Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications Diffraction in everyday life Diffraction in applications Spectroscopy: physics, chemistry, medicine,
High-Resolution. Transmission. Electron Microscopy
 Part 4 High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy 186 Significance high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM): resolve object details smaller than 1nm (10 9 m) image the interior of
Part 4 High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy 186 Significance high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM): resolve object details smaller than 1nm (10 9 m) image the interior of
MATH4104: Quantum nonlinear dynamics. Lecture Two. Review of quantum theory.
 MATH4104: Quantum nonlinear dynamics. Lecture Two. Review of quantum theory. G J Milburn The University of Queensland S2, 2009 Two quantum principles. THE QUANTUM PRINCIPLE I. The physical universe is
MATH4104: Quantum nonlinear dynamics. Lecture Two. Review of quantum theory. G J Milburn The University of Queensland S2, 2009 Two quantum principles. THE QUANTUM PRINCIPLE I. The physical universe is
arxiv: v1 [physics.atom-ph] 26 Feb 2014
![arxiv: v1 [physics.atom-ph] 26 Feb 2014 arxiv: v1 [physics.atom-ph] 26 Feb 2014](/thumbs/93/112536193.jpg) Analysis of Atom-Interferometer Clocks Steven Peil and Christopher R. Ekstrom United States Naval Observatory, Washington, DC 20392 arxiv:1402.6621v1 [physics.atom-ph] 26 Feb 2014 (Dated: September 4,
Analysis of Atom-Interferometer Clocks Steven Peil and Christopher R. Ekstrom United States Naval Observatory, Washington, DC 20392 arxiv:1402.6621v1 [physics.atom-ph] 26 Feb 2014 (Dated: September 4,
Ultracold atoms and molecules
 Advanced Experimental Techniques Ultracold atoms and molecules Steven Knoop s.knoop@vu.nl VU, June 014 1 Ultracold atoms laser cooling evaporative cooling BEC Bose-Einstein condensation atom trap: magnetic
Advanced Experimental Techniques Ultracold atoms and molecules Steven Knoop s.knoop@vu.nl VU, June 014 1 Ultracold atoms laser cooling evaporative cooling BEC Bose-Einstein condensation atom trap: magnetic
Atomic Physics (Phys 551) Final Exam Solutions
 Atomic Physics (Phys 551) Final Exam Solutions Problem 1. For a Rydberg atom in n = 50, l = 49 state estimate within an order of magnitude the numerical value of a) Decay lifetime A = 1 τ = 4αω3 3c D (1)
Atomic Physics (Phys 551) Final Exam Solutions Problem 1. For a Rydberg atom in n = 50, l = 49 state estimate within an order of magnitude the numerical value of a) Decay lifetime A = 1 τ = 4αω3 3c D (1)
Forca-G: A trapped atom interferometer for the measurement of short range forces
 Forca-G: A trapped atom interferometer for the measurement of short range forces Bruno Pelle, Quentin Beaufils, Gunnar Tackmann, Xiaolong Wang, Adèle Hilico and Franck Pereira dos Santos Sophie Pelisson,
Forca-G: A trapped atom interferometer for the measurement of short range forces Bruno Pelle, Quentin Beaufils, Gunnar Tackmann, Xiaolong Wang, Adèle Hilico and Franck Pereira dos Santos Sophie Pelisson,
Where are the Fringes? (in a real system) Div. of Amplitude - Wedged Plates. Fringe Localisation Double Slit. Fringe Localisation Grating
 Where are the Fringes? (in a real system) Fringe Localisation Double Slit spatial modulation transverse fringes? everywhere or well localised? affected by source properties: coherence, extension Plane
Where are the Fringes? (in a real system) Fringe Localisation Double Slit spatial modulation transverse fringes? everywhere or well localised? affected by source properties: coherence, extension Plane
Fourier Approach to Wave Propagation
 Phys 531 Lecture 15 13 October 005 Fourier Approach to Wave Propagation Last time, reviewed Fourier transform Write any function of space/time = sum of harmonic functions e i(k r ωt) Actual waves: harmonic
Phys 531 Lecture 15 13 October 005 Fourier Approach to Wave Propagation Last time, reviewed Fourier transform Write any function of space/time = sum of harmonic functions e i(k r ωt) Actual waves: harmonic
Name :. Roll No. :... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B. Tech (New)/SEM-1/PH-101/ PHYSICS-I
 Name :. Roll No. :..... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B. Tech (New)/SEM-1/PH-101/2011-12 2011 PHYSICS-I Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates
Name :. Roll No. :..... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B. Tech (New)/SEM-1/PH-101/2011-12 2011 PHYSICS-I Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates
The sensitivity of atom interferometers to gravitational waves
 The sensitivity of atom interferometers to gravitational waves The Galileo Galilei Institute for Theoretical Physics Arcetri, Florence February 24, 2009 Pacôme DELVA ESA DG-PI Advanced Concepts Team Gravitational
The sensitivity of atom interferometers to gravitational waves The Galileo Galilei Institute for Theoretical Physics Arcetri, Florence February 24, 2009 Pacôme DELVA ESA DG-PI Advanced Concepts Team Gravitational
KEELE UNIVERSITY PHYSICS/ASTROPHYSICS MODULE PHY OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES PRACTICE EXAM
 KEELE UNIVERSITY PHYSICS/ASTROPHYSICS MODULE PHY-10012 OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES PRACTICE EXAM Candidates should attempt ALL of PARTS A and B, and TWO questions from PART C. PARTS A and B should be answered
KEELE UNIVERSITY PHYSICS/ASTROPHYSICS MODULE PHY-10012 OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES PRACTICE EXAM Candidates should attempt ALL of PARTS A and B, and TWO questions from PART C. PARTS A and B should be answered
Questions from April 2003 Physics Final Exam
 Questions from April 003 Physics 111.6 Final Exam A1. Which one of the following statements concerning scalars and vectors is FALSE? (A) A vector quantity deals with magnitude and direction. (B) The direction
Questions from April 003 Physics 111.6 Final Exam A1. Which one of the following statements concerning scalars and vectors is FALSE? (A) A vector quantity deals with magnitude and direction. (B) The direction
8 Quantized Interaction of Light and Matter
 8 Quantized Interaction of Light and Matter 8.1 Dressed States Before we start with a fully quantized description of matter and light we would like to discuss the evolution of a two-level atom interacting
8 Quantized Interaction of Light and Matter 8.1 Dressed States Before we start with a fully quantized description of matter and light we would like to discuss the evolution of a two-level atom interacting
Determining the Fine Structure Constant with Bose-Einstein Condensate Interferometry
 Determining the Fine Structure Constant with Bose-Einstein Condensate Interferometry Eric Cooper, Dan Gochnauer, Ben Plotkin-Swing, Katie McAlpine, Subhadeep Gupta August 16, 2017 S Outline S Introduction
Determining the Fine Structure Constant with Bose-Einstein Condensate Interferometry Eric Cooper, Dan Gochnauer, Ben Plotkin-Swing, Katie McAlpine, Subhadeep Gupta August 16, 2017 S Outline S Introduction
6. Interference of BECs
 6. Interference of BECs Josephson effects Weak link: tunnel junction between two traps. Josephson oscillation An initial imbalance between the population of the double well potential leads to periodic
6. Interference of BECs Josephson effects Weak link: tunnel junction between two traps. Josephson oscillation An initial imbalance between the population of the double well potential leads to periodic
Electricity & Optics
 Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 26 Chapter 33 sec. 1-4 Fall 2017 Semester Professor Koltick Interference of Light Interference phenomena are a consequence of the wave-like nature of light Electric
Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 26 Chapter 33 sec. 1-4 Fall 2017 Semester Professor Koltick Interference of Light Interference phenomena are a consequence of the wave-like nature of light Electric
LONG-LIVED QUANTUM MEMORY USING NUCLEAR SPINS
 LONG-LIVED QUANTUM MEMORY USING NUCLEAR SPINS Laboratoire Kastler Brossel A. Sinatra, G. Reinaudi, F. Laloë (ENS, Paris) A. Dantan, E. Giacobino, M. Pinard (UPMC, Paris) NUCLEAR SPINS HAVE LONG RELAXATION
LONG-LIVED QUANTUM MEMORY USING NUCLEAR SPINS Laboratoire Kastler Brossel A. Sinatra, G. Reinaudi, F. Laloë (ENS, Paris) A. Dantan, E. Giacobino, M. Pinard (UPMC, Paris) NUCLEAR SPINS HAVE LONG RELAXATION
Nonequilibrium dynamics of interacting systems of cold atoms
 Nonequilibrium dynamics of interacting systems of cold atoms Eugene Demler Harvard University Collaborators: Ehud Altman, Anton Burkov, Robert Cherng, Adilet Imambekov, Vladimir Gritsev, Mikhail Lukin,
Nonequilibrium dynamics of interacting systems of cold atoms Eugene Demler Harvard University Collaborators: Ehud Altman, Anton Burkov, Robert Cherng, Adilet Imambekov, Vladimir Gritsev, Mikhail Lukin,
A preliminary measurement of the fine structure constant based on atom interferometry
 A preliminary measurement of the fine structure constant based on atom interferometry Andreas Wicht, Joel M. Hensley, Edina Sarajlic and Steven Chu Physics Department, Stanford University, Stanford, CA
A preliminary measurement of the fine structure constant based on atom interferometry Andreas Wicht, Joel M. Hensley, Edina Sarajlic and Steven Chu Physics Department, Stanford University, Stanford, CA
FIG. 16: A Mach Zehnder interferometer consists of two symmetric beam splitters BS1 and BS2
 Lecture 11: Application: The Mach Zehnder interferometer Coherent-state input Squeezed-state input Mach-Zehnder interferometer with coherent-state input: Now we apply our knowledge about quantum-state
Lecture 11: Application: The Mach Zehnder interferometer Coherent-state input Squeezed-state input Mach-Zehnder interferometer with coherent-state input: Now we apply our knowledge about quantum-state
Wave nature of particles
 Wave nature of particles We have thus far developed a model of atomic structure based on the particle nature of matter: Atoms have a dense nucleus of positive charge with electrons orbiting the nucleus
Wave nature of particles We have thus far developed a model of atomic structure based on the particle nature of matter: Atoms have a dense nucleus of positive charge with electrons orbiting the nucleus
Neutron interferometry. Hofer Joachim
 20.01.2011 Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Foundations of neutron optics...................................... 2 1.2 Fundamental techniques......................................... 2 1.2.1 Superposition
20.01.2011 Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Foundations of neutron optics...................................... 2 1.2 Fundamental techniques......................................... 2 1.2.1 Superposition
Hong-Ou-Mandel effect with matter waves
 Hong-Ou-Mandel effect with matter waves R. Lopes, A. Imanaliev, A. Aspect, M. Cheneau, DB, C. I. Westbrook Laboratoire Charles Fabry, Institut d Optique, CNRS, Univ Paris-Sud Progresses in quantum information
Hong-Ou-Mandel effect with matter waves R. Lopes, A. Imanaliev, A. Aspect, M. Cheneau, DB, C. I. Westbrook Laboratoire Charles Fabry, Institut d Optique, CNRS, Univ Paris-Sud Progresses in quantum information
Feedback control of atomic coherent spin states
 Feedback control of atomic coherent spin states Andrea Bertoldi Institut d Optique, France RG Colloquium Hannover 13/12/2012 Feedback control h(t) Constant flow is required to keep time P = r H2O g h(t)
Feedback control of atomic coherent spin states Andrea Bertoldi Institut d Optique, France RG Colloquium Hannover 13/12/2012 Feedback control h(t) Constant flow is required to keep time P = r H2O g h(t)
Non-linear Optics II (Modulators & Harmonic Generation)
 Non-linear Optics II (Modulators & Harmonic Generation) P.E.G. Baird MT2011 Electro-optic modulation of light An electro-optic crystal is essentially a variable phase plate and as such can be used either
Non-linear Optics II (Modulators & Harmonic Generation) P.E.G. Baird MT2011 Electro-optic modulation of light An electro-optic crystal is essentially a variable phase plate and as such can be used either
Coherence. Tsuneaki Miyahara, Japan Women s Univ.
 Coherence Tsuneaki Miyahara, Japan Women s Univ. 1) Description of light in the phase space First-order spatial coherence: Experiments First order temporal coherence Description of light in the 6-dimensional
Coherence Tsuneaki Miyahara, Japan Women s Univ. 1) Description of light in the phase space First-order spatial coherence: Experiments First order temporal coherence Description of light in the 6-dimensional
Progress on Atom Interferometer (AI) in BUAA
 Progress on Atom Interferometer (AI) in BUAA Group of Prof. FANG Jiancheng Beihang University ZHANG Yuchi, Hu Zhaohui, QI Lu, WANG Tongyu, WANG Tao 01.09.2011 7 th UK-China Workshop on Space Science and
Progress on Atom Interferometer (AI) in BUAA Group of Prof. FANG Jiancheng Beihang University ZHANG Yuchi, Hu Zhaohui, QI Lu, WANG Tongyu, WANG Tao 01.09.2011 7 th UK-China Workshop on Space Science and
Atomic Motion in a Laser Standing Wave
 Atomic Motion in a Laser Standing Wave J. DaJjbard, C. Salomon, A. Aspect, H. MetcaJf( *), A. Heidmann, and C. Cohen- Tannoudji Laboratoire de Spectroscopie Hertzienne de l'ens et Collège de France, 24
Atomic Motion in a Laser Standing Wave J. DaJjbard, C. Salomon, A. Aspect, H. MetcaJf( *), A. Heidmann, and C. Cohen- Tannoudji Laboratoire de Spectroscopie Hertzienne de l'ens et Collège de France, 24
Interferometry with atomicand molecular matter waves
 Interferometry with atomicand molecular matter waves Håkon Bjørgen Thesis submitted for the degree of Master of Science Department of Physics University of Oslo May 2010 Abstract The thesis is twofold.
Interferometry with atomicand molecular matter waves Håkon Bjørgen Thesis submitted for the degree of Master of Science Department of Physics University of Oslo May 2010 Abstract The thesis is twofold.
Atomic clocks. Clocks
 Atomic clocks Clocks 1 Ingredients for a clock 1. Need a system with periodic behavior: it cycles occur at constant frequency 2. Count the cycles to produce time interval 3. Agree on the origin of time
Atomic clocks Clocks 1 Ingredients for a clock 1. Need a system with periodic behavior: it cycles occur at constant frequency 2. Count the cycles to produce time interval 3. Agree on the origin of time
Travaux en gravimétrie au SYRTE
 Travaux en gravimétrie au SYRTE F. Pereira Dos Santos LNE-SYRTE (OP, LNE, UPMC, CNRS) https://syrte.obspm.fr/spip/science/iaci/ CNFGG, 1er Février 2017 1 Outline 1. Principle of Atom Interferometry 2.
Travaux en gravimétrie au SYRTE F. Pereira Dos Santos LNE-SYRTE (OP, LNE, UPMC, CNRS) https://syrte.obspm.fr/spip/science/iaci/ CNFGG, 1er Février 2017 1 Outline 1. Principle of Atom Interferometry 2.
Quantum Gases. Subhadeep Gupta. UW REU Seminar, 11 July 2011
 Quantum Gases Subhadeep Gupta UW REU Seminar, 11 July 2011 Ultracold Atoms, Mixtures, and Molecules Subhadeep Gupta UW REU Seminar, 11 July 2011 Ultracold Atoms High sensitivity (large signal to noise,
Quantum Gases Subhadeep Gupta UW REU Seminar, 11 July 2011 Ultracold Atoms, Mixtures, and Molecules Subhadeep Gupta UW REU Seminar, 11 July 2011 Ultracold Atoms High sensitivity (large signal to noise,
Atom Interferometric Gravity Wave Detectors. Mark Kasevich Dept. of Physics and Applied Physics Stanford University, Stanford CA
 Atom Interferometric Gravity Wave Detectors Mark Kasevich Dept. of Physics and Applied Physics Stanford University, Stanford CA Outline Basic concepts Current instrumentation AGIS detectors Space-based/LEO
Atom Interferometric Gravity Wave Detectors Mark Kasevich Dept. of Physics and Applied Physics Stanford University, Stanford CA Outline Basic concepts Current instrumentation AGIS detectors Space-based/LEO
Phys 622 Problems Chapter 5
 1 Phys 622 Problems Chapter 5 Problem 1 The correct basis set of perturbation theory Consider the relativistic correction to the electron-nucleus interaction H LS = α L S, also known as the spin-orbit
1 Phys 622 Problems Chapter 5 Problem 1 The correct basis set of perturbation theory Consider the relativistic correction to the electron-nucleus interaction H LS = α L S, also known as the spin-orbit
Ion traps. Trapping of charged particles in electromagnetic. Laser cooling, sympathetic cooling, optical clocks
 Ion traps Trapping of charged particles in electromagnetic fields Dynamics of trapped ions Applications to nuclear physics and QED The Paul trap Laser cooling, sympathetic cooling, optical clocks Coulomb
Ion traps Trapping of charged particles in electromagnetic fields Dynamics of trapped ions Applications to nuclear physics and QED The Paul trap Laser cooling, sympathetic cooling, optical clocks Coulomb
Dept. of Physics, MIT Manipal 1
 Chapter 1: Optics 1. In the phenomenon of interference, there is A Annihilation of light energy B Addition of energy C Redistribution energy D Creation of energy 2. Interference fringes are obtained using
Chapter 1: Optics 1. In the phenomenon of interference, there is A Annihilation of light energy B Addition of energy C Redistribution energy D Creation of energy 2. Interference fringes are obtained using
Coherent states, beam splitters and photons
 Coherent states, beam splitters and photons S.J. van Enk 1. Each mode of the electromagnetic (radiation) field with frequency ω is described mathematically by a 1D harmonic oscillator with frequency ω.
Coherent states, beam splitters and photons S.J. van Enk 1. Each mode of the electromagnetic (radiation) field with frequency ω is described mathematically by a 1D harmonic oscillator with frequency ω.
Diffraction Gratings, Atomic Spectra. Prof. Shawhan (substituting for Prof. Hall) November 14, 2016
 Diffraction Gratings, Atomic Spectra Prof. Shawhan (substituting for Prof. Hall) November 14, 2016 1 Increase number of slits: 2 Visual Comparisons 3 4 8 2 Diffraction Grating Note: despite the name, this
Diffraction Gratings, Atomic Spectra Prof. Shawhan (substituting for Prof. Hall) November 14, 2016 1 Increase number of slits: 2 Visual Comparisons 3 4 8 2 Diffraction Grating Note: despite the name, this
Compensation of gravity gradients and rotations in precision atom interferometry
 Compensation of gravity gradients and rotations in precision atom interferometry Albert Roura partly based on Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 160401 (2017) Vienna, 11 April 2018 Motivation Tests of universality
Compensation of gravity gradients and rotations in precision atom interferometry Albert Roura partly based on Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 160401 (2017) Vienna, 11 April 2018 Motivation Tests of universality
Multipath Interferometer on an AtomChip. Francesco Saverio Cataliotti
 Multipath Interferometer on an AtomChip Francesco Saverio Cataliotti Outlook Bose-Einstein condensates on a microchip Atom Interferometry Multipath Interferometry on an AtomChip Results and Conclusions
Multipath Interferometer on an AtomChip Francesco Saverio Cataliotti Outlook Bose-Einstein condensates on a microchip Atom Interferometry Multipath Interferometry on an AtomChip Results and Conclusions
Modulation of atomic de Broglie waves using Bragg diffraction
 Quantum Semiclass. Opt. 8 (1996) 497 509. Printed in the UK Modulation of atomic de Broglie waves using Bragg diffraction Stefan Bernet, Markus Oberthaler, Roland Abfalterer, Jörg Schmiedmayer and Anton
Quantum Semiclass. Opt. 8 (1996) 497 509. Printed in the UK Modulation of atomic de Broglie waves using Bragg diffraction Stefan Bernet, Markus Oberthaler, Roland Abfalterer, Jörg Schmiedmayer and Anton
Prospects for atom interferometry
 Contemporary Physics, 2001, volume 42, number 2, pages 77± 95 Prospects for atom interferometry R. M. GODUN, M. B. D ARCY, G. S. SUMMY and K. BURNETT Atom interferometers were rst realized ten years ago,
Contemporary Physics, 2001, volume 42, number 2, pages 77± 95 Prospects for atom interferometry R. M. GODUN, M. B. D ARCY, G. S. SUMMY and K. BURNETT Atom interferometers were rst realized ten years ago,
Optics, Optoelectronics and Photonics
 Optics, Optoelectronics and Photonics Engineering Principles and Applications Alan Billings Emeritus Professor, University of Western Australia New York London Toronto Sydney Tokyo Singapore v Contents
Optics, Optoelectronics and Photonics Engineering Principles and Applications Alan Billings Emeritus Professor, University of Western Australia New York London Toronto Sydney Tokyo Singapore v Contents
