Journal of Theoretics
|
|
|
- Esther Thomas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Theoretics THE MISSED PHYSICS OF SOURCE-FREE MAGNETIC FIELD Author: Bibhas R. De P. O. Box 21141, Castro Valley, CA ABSTRACT Maxwell s equations are shown to have a second consequence beyond the electromagnetic (EM) wave: the source-free static magnetic field structure of finite extent in empty space. This has possible relevance to many current research areas such as field theory and plasma theory. When the result of the present paper is combined with a previous result (that a static magnetic field constitutes a mass), this relevance extends to a number of other fields: particle theory; string theory; dark matter; unified field theory; the ultimate nature of mass and matter; gravitation; cosmology etc. Additionally, the source-free structure may have implications for future technology. KEYWORDS: magnetostatic field, field theory, plasma theory, particle theory, string theory, unified field theory, dark matter, gravitation, cosmology, future technology. INTRODUCTION Maxwell s equations have two distinct solutions in empty space: the static solution, or the source-free static magnetic field structure of finite extent; and the dynamic solution, or the electromagnetic (EM) wave. To date, and for more than century, any attempts to construct the first solution have been forbidden. This paper presents that solution. The deduction is on the same solid footing as that of the EM wave requiring no assumptions or approximations. A source-free magnetic field structure is considered forbidden by certain theorems in conjunction with the uniqueness theorem (Cf. [1], Ch. 1; [2], Ch. 1). It is shown below that these considerations do not fully encompass the issue of source-free fields. Specifically, this theorem excludes a priori field structures (or a class of solutions) corresponding to sources at infinity. 2 It is shown below that in excluding such structures, useful information may have been discarded. THE INFINITE STRUCTURE o In cylindrical coordinates with no -dependence, the Maxwell s equations.b = 0 and xb for the magnetic field b can be expressed as: 2 b z / r 2 + ( b z / r)/r = - 2 b z / z 2 (1) 2 b r / r 2 + ( b r / r)/r - b r /r 2 = - 2 b r / z 2 (2) for which an exact solution o can be found in terms of the Bessel functions Jo and J1:
2 Clearly, this may be seen as a structure with (unspecified) sources at infinity. THE TRUNCATION STRUCTURE 1 One can devise a method of exploring this structure further, instead of discarding it. By taking o with the minus sign (of the exponent) in the upper half space and with the plus sign in the lower half space, a truncation structure 1 is found: with s = z / z a shorthand notation, and an arbitrary, positive real quantity. At the z = 0 plane - the boundary plane - the field b z1 is continuous, but b r1 flips sign. Thus the act of truncation generates a sheet current (with the permeability of free space.): THE STRUCTURE 2 WITH SOURCE I As a separately standing problem, the exact solution for the field structure 2 generated by a prescribed source current I can be calculated in terms of the potential A 2 = A 2 a, and is found to be: 1 Here k 2 = 4rR/(R 2 + r 2 + z 2 + 2rR), and K(k) and E(k) are the complete elliptical integrals of the First and the Second kind. 3 Since I has a delta-function behavior and since the above solution is exact at every point in space for which z 0, it follows that b r2 (r, z 0) = b r1 (r, z = 0), and that therefore b z2 (r, z 0) is a finite quantity. This can also be verified by numerical computations,
3 integrating around the pole at (z = 0, R = r). Thus: The structures 1 created outside the scope of the uniqueness theorem - and 2 created within the uniqueness theorem are now shown to be unequal. INEQUALITY OF 1 AND 2 The potential A 1 for 1 is found from b r1 = - A 1 / z: This can be rewritten in the following ad hoc form by invoking, for the upper half space, a mathematically provable identity: 3, ( ), ( ), (6.1.9): Since for for all values of R, but F 2 (R) remains unchanged, it follows that the two potential distributions are generally not equal. However, the inequality of the vector potentials does not necessarily prove the inequality of the field structures. To establish the latter inequality, one may readily verify that for r = 0, both potentials are zero regardless of. Thus, traveling from the axis outward, the two potentials are first in agreement, then begin to disagree. Therefore the same comment applies to the two field structures. THE SOURCE-FREE STRUCTURE: = 1 ~ 2 A superposition of 1 and 2 causes I to vanish identically, leaving a source-free solution :
4 with b z (r, z = 0) finite and continuous through the z = 0 plane, and b r (r, z = 0) = 0. No singularities or discontinuities remain across this plane (Cf. Eqs. (14) and (15). It should be noted that the structures 1 and 2 were only mathematical steps used in arriving at, and have no physical significance. The standard argument invoked to preempt any discussion of source-free structures may now be revisited. Let the magnetic fields in Eqs. (21)-(23) derive from a scalar potential. Then consider Green s first identity: The left-hand side is zero in a source-free volume. Consider then the surface integral for the upper half space: On the z = 0 plane, can be taken to be 0 since here b r = 0. In absence of any sources at infinity, the surface term should go to zero there as well. Thus the integral of the positive term ( ) 2 is zero, meaning that is a constant over all space, so that the magnetic field is zero everywhere. However, depending on the field structure being examined, there are three possible outcomes relative to the surface integral as it is expanded to infinite distances: (a) It approaches zero (the above case), (b) It approaches infinity (unphysical case), or (c) It remains constant. The last case would allow the source-free structure, and the constant would be reflective of the finite energy of the structure. With the help of results developed earlier, it has been shown that the energy in a static magnetic field far away from its source can be drawn down without prior communication with the source. 4-7 A conceptual process of creation of the source-free structure by removing a source of magnetic field from a location, without removing the field "energy," would accordingly present no theoretical difficulties. Thus the structure would not contravene any conservation principles. REMARKS The study of magnetized and magnetically confined plasmas requires a full understanding of the basic nature of magnetic field. The present paper suggests that this understanding may not yet be complete. Instabilities in plasmas cause the magnetic field to assume new structures, including force-free structures. Such structures may further transition to the source-free structure. It has been suggested recently that magnetic field in empty space constitutes a mass. 8 This suggestion, when combined with the present result, defines an entity in empty space made entirely of magnetostatic field and having a mass. In the limit of the smallest size, is then essentially a point particle. Whether a point particle or a macroscopic structure, such an entity would have implications for the current studies in gravitation, cosmology, unified field theory, the ultimate nature of mass and matter, particle theory, string theory, dark matter, etc. Additionally, if the structure can be created in the laboratory, it would have implications for future technology. REFERENCES [1] Jackson, J.D. Classical Electrodynamics. New York: Wiley, [2] Panofsky, W. K. H., and M. Phillips. Classical Electricity and Magnetism. Reading, Mass.: Addison-Wesley, [3] Abramowitz, M., and I. A. Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions. New York: Dover, [4] De, B.R. J. Phys. A 26 (1994): [5] De, B. R. Phys. Fluids 22.1 (1979): 189. [6.] De, B. R., in Plasma and the Universe. Ed. Falthammar, C. G. et al.
5 Dordrecht-Holland: Kluwer Academic Publishers, [7] De, B. R. J. Phys. A 27 (1994): L431 [8] De, B. R. Astrophys. Space Sci. 25 (1996): 239. Journal Home Page mail@journaloftheoretics.com Journal of Theoretics, Inc (Note: all submissions become the property of the Journal)
THE PHOTON DEMYSTIFIED
 The photon demystified by Bibhas De THE PHOTON DEMYSTIFIED (wwwchasedesignscom) by Bibhas De (wwwbibhasdecom) Posted 26 October 2009 THE-FOUNDATION-IS-THE-FRONTIER-SERIES Essays on Twenty-first Century
The photon demystified by Bibhas De THE PHOTON DEMYSTIFIED (wwwchasedesignscom) by Bibhas De (wwwbibhasdecom) Posted 26 October 2009 THE-FOUNDATION-IS-THE-FRONTIER-SERIES Essays on Twenty-first Century
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.class-ph] 10 Nov 2006
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.class-ph] 10 Nov 2006 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.class-ph] 10 Nov 2006](/thumbs/89/99434850.jpg) Derivation of magnetic Coulomb s law for thin, semi-infinite solenoids Masao Kitano Department of Electronic Science and Engineering, Kyoto University, Katsura, Kyoto 615-8510, Japan and CREST, Japan Science
Derivation of magnetic Coulomb s law for thin, semi-infinite solenoids Masao Kitano Department of Electronic Science and Engineering, Kyoto University, Katsura, Kyoto 615-8510, Japan and CREST, Japan Science
ROTATIONAL STABILITY OF A CHARGED DIELEC- TRIC RIGID BODY IN A UNIFORM MAGNETIC FIELD
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 11, 103 11, 009 ROTATIONAL STABILITY OF A CHARGED DIELEC- TRIC RIGID BODY IN A UNIFORM MAGNETIC FIELD G.-Q. Zhou Department of Physics Wuhan University
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 11, 103 11, 009 ROTATIONAL STABILITY OF A CHARGED DIELEC- TRIC RIGID BODY IN A UNIFORM MAGNETIC FIELD G.-Q. Zhou Department of Physics Wuhan University
SOURCE-FREE MAGNETIC STRUCTURES. Bibhas R. De P. O. Box Castro Valley, California 94546, USA
 SOURCE-FREE MAGNETIC STRUCTURES Bibhas R. De P. O. Box 21141 Castro Valley, California 94546, USA Email: BibhasDe@aol.com Abstract A seminal discovery shaping science and technology thus far is that of
SOURCE-FREE MAGNETIC STRUCTURES Bibhas R. De P. O. Box 21141 Castro Valley, California 94546, USA Email: BibhasDe@aol.com Abstract A seminal discovery shaping science and technology thus far is that of
Mathematical Constraint on Functions with Continuous Second Partial Derivatives
 1 Mathematical Constraint on Functions with Continuous Second Partial Derivatives J.D. Franson Physics Department, University of Maryland, Baltimore County, Baltimore, MD 15 Abstract A new integral identity
1 Mathematical Constraint on Functions with Continuous Second Partial Derivatives J.D. Franson Physics Department, University of Maryland, Baltimore County, Baltimore, MD 15 Abstract A new integral identity
Chapter Three: Propagation of light waves
 Chapter Three Propagation of Light Waves CHAPTER OUTLINE 3.1 Maxwell s Equations 3.2 Physical Significance of Maxwell s Equations 3.3 Properties of Electromagnetic Waves 3.4 Constitutive Relations 3.5
Chapter Three Propagation of Light Waves CHAPTER OUTLINE 3.1 Maxwell s Equations 3.2 Physical Significance of Maxwell s Equations 3.3 Properties of Electromagnetic Waves 3.4 Constitutive Relations 3.5
The Helmholtz Decomposition and the Coulomb Gauge
 The Helmholtz Decomposition and the Coulomb Gauge 1 Problem Kirk T. McDonald Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 (April 17, 2008; updated February 7, 2015 Helmholtz showed
The Helmholtz Decomposition and the Coulomb Gauge 1 Problem Kirk T. McDonald Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 (April 17, 2008; updated February 7, 2015 Helmholtz showed
Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts
 NE 2 Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts Important Laws in Electromagnetics Coulomb s Law (1785) Gauss s Law (1839) Ampere s Law (1827) Ohm s Law (1827) Kirchhoff s Law (1845) Biot-Savart Law (1820) Faradays
NE 2 Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts Important Laws in Electromagnetics Coulomb s Law (1785) Gauss s Law (1839) Ampere s Law (1827) Ohm s Law (1827) Kirchhoff s Law (1845) Biot-Savart Law (1820) Faradays
1 Fundamentals. 1.1 Overview. 1.2 Units: Physics 704 Spring 2018
 Physics 704 Spring 2018 1 Fundamentals 1.1 Overview The objective of this course is: to determine and fields in various physical systems and the forces and/or torques resulting from them. The domain of
Physics 704 Spring 2018 1 Fundamentals 1.1 Overview The objective of this course is: to determine and fields in various physical systems and the forces and/or torques resulting from them. The domain of
On the evolutionary form of the constraints in electrodynamics
 On the evolutionary form of the constraints in electrodynamics István Rácz,1,2 arxiv:1811.06873v1 [gr-qc] 12 Nov 2018 1 Faculty of Physics, University of Warsaw, Ludwika Pasteura 5, 02-093 Warsaw, Poland
On the evolutionary form of the constraints in electrodynamics István Rácz,1,2 arxiv:1811.06873v1 [gr-qc] 12 Nov 2018 1 Faculty of Physics, University of Warsaw, Ludwika Pasteura 5, 02-093 Warsaw, Poland
Comment about Didactical formulation of the
 Comment about Didactical formulation of the Ampère law Hendrik van Hees Institute for Theoretical Physics, Goethe University Frankfurt, Max-von-Laue-Str. 1, D-60438 Frankfurt, Germany Frankfurt Institute
Comment about Didactical formulation of the Ampère law Hendrik van Hees Institute for Theoretical Physics, Goethe University Frankfurt, Max-von-Laue-Str. 1, D-60438 Frankfurt, Germany Frankfurt Institute
The Weber Force. Introduction
 The Weber Force Eamon McAlea Contact@forbinsystems.com December 7th 2010 Abstract: In this paper It will be shown how the Weber Force law emerges as an averaged effect between two electrically neutral
The Weber Force Eamon McAlea Contact@forbinsystems.com December 7th 2010 Abstract: In this paper It will be shown how the Weber Force law emerges as an averaged effect between two electrically neutral
Energy Conservation and Poynting Theorem in Electromagnetics: A Conceptual Perspective
 Energy Conservation and Poynting Theorem in Electromagnetics: A Conceptual Perspective Krishnasamy T. Selvan Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering SSN College of Engineering, Kalavakkam,
Energy Conservation and Poynting Theorem in Electromagnetics: A Conceptual Perspective Krishnasamy T. Selvan Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering SSN College of Engineering, Kalavakkam,
Advanced Study, 9 Adela Court, Mulgrave, Victoria 3170, Australia
 ON OLBERS PARADOX Vu B Ho Advanced Study, 9 Adela Court, Mulgrave, Victoria 3170, Australia Email: vubho@bigpond.net.au Abstract: In this work we discuss a possibility to resolve Olbers paradox that states
ON OLBERS PARADOX Vu B Ho Advanced Study, 9 Adela Court, Mulgrave, Victoria 3170, Australia Email: vubho@bigpond.net.au Abstract: In this work we discuss a possibility to resolve Olbers paradox that states
RELATIVISTIC TRANSFORMATION OF MAGNETIC DIPOLE MOMENT
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 47, 63 78, 013 RELATIVISTIC TRANSFORMATION OF MAGNETIC DIPOLE MOMENT Alexander Kholmetskii 1, *, Oleg Missevitch, and Tolga Yarman 3, 4 1 Belarus State University,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 47, 63 78, 013 RELATIVISTIC TRANSFORMATION OF MAGNETIC DIPOLE MOMENT Alexander Kholmetskii 1, *, Oleg Missevitch, and Tolga Yarman 3, 4 1 Belarus State University,
Unit-1 Electrostatics-1
 1. Describe about Co-ordinate Systems. Co-ordinate Systems Unit-1 Electrostatics-1 In order to describe the spatial variations of the quantities, we require using appropriate coordinate system. A point
1. Describe about Co-ordinate Systems. Co-ordinate Systems Unit-1 Electrostatics-1 In order to describe the spatial variations of the quantities, we require using appropriate coordinate system. A point
Magnetostatics relation to gravity with experiment that rejects Biot-Savart Law
 Magnetostatics relation to gravity with experiment that rejects Biot-Savart Law J.C. Hodge 1 1 Retired, 477 Mincey Rd., Franklin, NC, 28734 Abstract Relating the concept of gravity to electromagnetics
Magnetostatics relation to gravity with experiment that rejects Biot-Savart Law J.C. Hodge 1 1 Retired, 477 Mincey Rd., Franklin, NC, 28734 Abstract Relating the concept of gravity to electromagnetics
Quantum Mechanics without Complex Numbers: A Simple Model for the Electron Wavefunction Including Spin. Alan M. Kadin* Princeton Junction, NJ
 Quantum Mechanics without Complex Numbers: A Simple Model for the Electron Wavefunction Including Spin Alan M. Kadin* Princeton Junction, NJ February 22, 2005 Abstract: A simple real-space model for the
Quantum Mechanics without Complex Numbers: A Simple Model for the Electron Wavefunction Including Spin Alan M. Kadin* Princeton Junction, NJ February 22, 2005 Abstract: A simple real-space model for the
APPLICATION OF THE MAGNETIC FIELD INTEGRAL EQUATION TO DIFFRACTION AND REFLECTION BY A CONDUCTING SHEET
 In: International Journal of Theoretical Physics, Group Theory... ISSN: 1525-4674 Volume 14, Issue 3 pp. 1 12 2011 Nova Science Publishers, Inc. APPLICATION OF THE MAGNETIC FIELD INTEGRAL EQUATION TO DIFFRACTION
In: International Journal of Theoretical Physics, Group Theory... ISSN: 1525-4674 Volume 14, Issue 3 pp. 1 12 2011 Nova Science Publishers, Inc. APPLICATION OF THE MAGNETIC FIELD INTEGRAL EQUATION TO DIFFRACTION
Accepted Manuscript. Magnetic Field Expulsion from an Infinite Cylindrical Superconductor. Miguel C.N. Fiolhais, Hanno Essén
 Accepted Manuscript Magnetic Field Expulsion from an Infinite Cylindrical Superconductor Miguel C.N. Fiolhais, Hanno Essén PII: S091-45341300454-1 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.physc.013.11.006 Reference:
Accepted Manuscript Magnetic Field Expulsion from an Infinite Cylindrical Superconductor Miguel C.N. Fiolhais, Hanno Essén PII: S091-45341300454-1 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.physc.013.11.006 Reference:
Green s Function for Problems with Layers
 Chapter 9 Green s Function for Problems with Layers 9. Continuity conditions The medium comprises two or more straight or curved layers. The properties of the medium are constant within each layer; they
Chapter 9 Green s Function for Problems with Layers 9. Continuity conditions The medium comprises two or more straight or curved layers. The properties of the medium are constant within each layer; they
Mathematical Tripos, Part IB : Electromagnetism
 Mathematical Tripos, Part IB : Electromagnetism Proof of the result G = m B Refer to Sec. 3.7, Force and couples, and supply the proof that the couple exerted by a uniform magnetic field B on a plane current
Mathematical Tripos, Part IB : Electromagnetism Proof of the result G = m B Refer to Sec. 3.7, Force and couples, and supply the proof that the couple exerted by a uniform magnetic field B on a plane current
Electromagnetic energy and momentum
 Electromagnetic energy and momentum Conservation of energy: the Poynting vector In previous chapters of Jackson we have seen that the energy density of the electric eq. 4.89 in Jackson and magnetic eq.
Electromagnetic energy and momentum Conservation of energy: the Poynting vector In previous chapters of Jackson we have seen that the energy density of the electric eq. 4.89 in Jackson and magnetic eq.
ECE Antisymmetry Laws in the Natural Sciences and Engineering
 Chapter 10 ECE Antisymmetry Laws in the Natural Sciences and Engineering by M. W. Evans 1, H. Eckardt 2, D. W. Lindstrom 3, S. Crothers 4, G. J. Evans 5 Alpha Institute for Advanced Study (AIAS) (www.aias.us,
Chapter 10 ECE Antisymmetry Laws in the Natural Sciences and Engineering by M. W. Evans 1, H. Eckardt 2, D. W. Lindstrom 3, S. Crothers 4, G. J. Evans 5 Alpha Institute for Advanced Study (AIAS) (www.aias.us,
Charge, geometry, and effective mass
 Gerald E. Marsh Argonne National Laboratory (Ret) 5433 East View Park Chicago, IL 60615 E-mail: geraldemarsh63@yahoo.com Abstract. Charge, like mass in Newtonian mechanics, is an irreducible element of
Gerald E. Marsh Argonne National Laboratory (Ret) 5433 East View Park Chicago, IL 60615 E-mail: geraldemarsh63@yahoo.com Abstract. Charge, like mass in Newtonian mechanics, is an irreducible element of
ECE Theory of gravity induced polarization changes
 Chapter 13 ECE Theory of gravity induced polarization changes (Paper 67) by Myron W. Evans Alpha Institute for Advanced Study (AIAS). (emyrone@aol.com, www.aias.us, www.atomicprecision.com) Abstract Gravity
Chapter 13 ECE Theory of gravity induced polarization changes (Paper 67) by Myron W. Evans Alpha Institute for Advanced Study (AIAS). (emyrone@aol.com, www.aias.us, www.atomicprecision.com) Abstract Gravity
Magnetostatics. Lecture 23: Electromagnetic Theory. Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay
 Magnetostatics Lecture 23: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay Magnetostatics Up until now, we have been discussing electrostatics, which deals with physics
Magnetostatics Lecture 23: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay Magnetostatics Up until now, we have been discussing electrostatics, which deals with physics
2 Formulation. = arg = 2 (1)
 Acoustic di raction by an impedance wedge Aladin H. Kamel (alaahassan.kamel@yahoo.com) PO Box 433 Heliopolis Center 11757, Cairo, Egypt Abstract. We consider the boundary-value problem for the Helmholtz
Acoustic di raction by an impedance wedge Aladin H. Kamel (alaahassan.kamel@yahoo.com) PO Box 433 Heliopolis Center 11757, Cairo, Egypt Abstract. We consider the boundary-value problem for the Helmholtz
Physical intuition and time-dependent generalizations of the Coulomb and Biot-Savart laws
 Physical intuition time-dependent generalizations of the Coulomb Biot-Savart laws arxiv:physics/0508047v1 [physics.ed-ph] 8 Aug 2005 Nivaldo A. Lemos Departamento de Física Universidade Federal Fluminense
Physical intuition time-dependent generalizations of the Coulomb Biot-Savart laws arxiv:physics/0508047v1 [physics.ed-ph] 8 Aug 2005 Nivaldo A. Lemos Departamento de Física Universidade Federal Fluminense
Chapter 17 & 18. Electric Field and Electric Potential
 Chapter 17 & 18 Electric Field and Electric Potential Electric Field Maxwell developed an approach to discussing fields An electric field is said to exist in the region of space around a charged object
Chapter 17 & 18 Electric Field and Electric Potential Electric Field Maxwell developed an approach to discussing fields An electric field is said to exist in the region of space around a charged object
AN EXAMPLE OF SYSTEM WHICH CAN BE USED TO EXPLICITLY SHOW THE SYMMETRY BETWEEN THE ELECTRIC AND MAGNETIC FIELDS. Arief Hermanto
 P - 17 AN EXAMPLE OF SYSTEM WHICH CAN BE USED TO EXPLICITLY SHOW THE SYMMETRY BETWEEN THE ELECTRIC AND MAGNETIC FIELDS Arief Hermanto Physics Department, Gadjah Mada University Abstract Electric and magnetic
P - 17 AN EXAMPLE OF SYSTEM WHICH CAN BE USED TO EXPLICITLY SHOW THE SYMMETRY BETWEEN THE ELECTRIC AND MAGNETIC FIELDS Arief Hermanto Physics Department, Gadjah Mada University Abstract Electric and magnetic
Eddy Current Testing using the Bode 100
 Page 1 of 12 using the Bode 100 Lukas Heinzle Abstract: (ET) is a commonly used technique surface inspections of conducting materials. An eddy current sensor, namely a probe coil that produces an alternating
Page 1 of 12 using the Bode 100 Lukas Heinzle Abstract: (ET) is a commonly used technique surface inspections of conducting materials. An eddy current sensor, namely a probe coil that produces an alternating
Maxwell's Equations and Conservation Laws
 Maxwell's Equations and Conservation Laws 1 Reading: Jackson 6.1 through 6.4, 6.7 Ampère's Law, since identically. Although for magnetostatics, generally Maxwell suggested: Use Gauss's Law to rewrite continuity
Maxwell's Equations and Conservation Laws 1 Reading: Jackson 6.1 through 6.4, 6.7 Ampère's Law, since identically. Although for magnetostatics, generally Maxwell suggested: Use Gauss's Law to rewrite continuity
Development of fundamental dynamics from differential geometry
 Development of fundamental dynamics from differential geometry by M. W. Evans, Civil List Scientist, Alpha Institute for Advanced Study. (www.aias.us). Abstract The fundamental quantities of classical
Development of fundamental dynamics from differential geometry by M. W. Evans, Civil List Scientist, Alpha Institute for Advanced Study. (www.aias.us). Abstract The fundamental quantities of classical
Maxwell s displacement current revisited
 Eur. J. Phys. 20 (1999) 495 499. Printed in the UK PII: S0143-0807(99)06956-1 Maxwell s displacement current revisited J D Jackson University of California, Berkeley, and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory,
Eur. J. Phys. 20 (1999) 495 499. Printed in the UK PII: S0143-0807(99)06956-1 Maxwell s displacement current revisited J D Jackson University of California, Berkeley, and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory,
On Maxwell s discovery of electromagnetic waves and the gauge condition. P. T. Leung
 On Maxwell s discovery of electromagnetic waves and the gauge condition P. T. Leung Department of Physics, Portland State University, P. O. Box 751, Portland, OR 9707-0751 Abstract The original theoretical
On Maxwell s discovery of electromagnetic waves and the gauge condition P. T. Leung Department of Physics, Portland State University, P. O. Box 751, Portland, OR 9707-0751 Abstract The original theoretical
Spin Connection Resonance in Magnetic Motors
 4 Spin Connection Resonance in Magnetic Motors by Myron W. Evans, Alpha Institute for Advanced Study, Civil List Scientist. (emyrone@aol.com and www.aias.us) and H. Eckardt, Alpha Institute for Advanced
4 Spin Connection Resonance in Magnetic Motors by Myron W. Evans, Alpha Institute for Advanced Study, Civil List Scientist. (emyrone@aol.com and www.aias.us) and H. Eckardt, Alpha Institute for Advanced
arxiv: v1 [physics.class-ph] 17 Mar 2011
![arxiv: v1 [physics.class-ph] 17 Mar 2011 arxiv: v1 [physics.class-ph] 17 Mar 2011](/thumbs/94/119145307.jpg) A formal interpretation of the displacement current and the instantaneous formulation of Maxwell s equations José A. Heras arxiv:113.3529v1 [physics.class-ph] 17 Mar 211 Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana
A formal interpretation of the displacement current and the instantaneous formulation of Maxwell s equations José A. Heras arxiv:113.3529v1 [physics.class-ph] 17 Mar 211 Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana
- - as having contributions from the material or circuit and from the interaction of the circuit
 CONSERVATION OF ANTISYMMETRY IN ECE2 ELECTROSTATICS AND MAGNETOSTA TICS. by M. W. Evans and H. Eckardt Civil List and AlAS I UPITEC (www.aias.us. W\Vw.upitec.org. \vww.et3m.net. www.archive.org, www.webarchive.org.uk)
CONSERVATION OF ANTISYMMETRY IN ECE2 ELECTROSTATICS AND MAGNETOSTA TICS. by M. W. Evans and H. Eckardt Civil List and AlAS I UPITEC (www.aias.us. W\Vw.upitec.org. \vww.et3m.net. www.archive.org, www.webarchive.org.uk)
Spin connection resonance in gravitational general relativity
 Chapter 10 Spin connection resonance in gravitational general relativity Abstract (Paper 64) by Myron W. Evans Alpha Institute for Advanced Study (AIAS). (emyrone@aol.com, www.aias.us, www.atomicprecision.com)
Chapter 10 Spin connection resonance in gravitational general relativity Abstract (Paper 64) by Myron W. Evans Alpha Institute for Advanced Study (AIAS). (emyrone@aol.com, www.aias.us, www.atomicprecision.com)
FLUX OF VECTOR FIELD INTRODUCTION
 Chapter 3 GAUSS LAW ntroduction Flux of vector field Solid angle Gauss s Law Symmetry Spherical symmetry Cylindrical symmetry Plane symmetry Superposition of symmetric geometries Motion of point charges
Chapter 3 GAUSS LAW ntroduction Flux of vector field Solid angle Gauss s Law Symmetry Spherical symmetry Cylindrical symmetry Plane symmetry Superposition of symmetric geometries Motion of point charges
COMPUTATIONAL METHODS AND ALGORITHMS Vol. II- Solution of Electromagnetism Theory Problems - V.V. Denisenko
 SOLUTION OF ELECTROMAGNETISM THEORY PROBLEMS V.V. Institute of Computational Modeling SB RAS, Krasnoyarsk, Russia Keywords: Electric field, magnetic field, mathematical modeling, Maxwell equations, electrostatics,
SOLUTION OF ELECTROMAGNETISM THEORY PROBLEMS V.V. Institute of Computational Modeling SB RAS, Krasnoyarsk, Russia Keywords: Electric field, magnetic field, mathematical modeling, Maxwell equations, electrostatics,
Electromagnetic fields and waves
 Electromagnetic fields and waves Maxwell s rainbow Outline Maxwell s equations Plane waves Pulses and group velocity Polarization of light Transmission and reflection at an interface Macroscopic Maxwell
Electromagnetic fields and waves Maxwell s rainbow Outline Maxwell s equations Plane waves Pulses and group velocity Polarization of light Transmission and reflection at an interface Macroscopic Maxwell
Electricity and Magnetism PHYS-242: ( Monday, Wednesday, Rutherford 115)
 Electricity and Magnetism PHYS-242: (1135-1225 Monday, Wednesday, Rutherford 115) Instructor: Shaun Lovejoy, Rutherford Physics, rm. 213, local 6537, email: lovejoy@physics.mcgill.ca Teaching assistants:
Electricity and Magnetism PHYS-242: (1135-1225 Monday, Wednesday, Rutherford 115) Instructor: Shaun Lovejoy, Rutherford Physics, rm. 213, local 6537, email: lovejoy@physics.mcgill.ca Teaching assistants:
Unit-Jacobian Coordinate Transformations: The Superior Consequence of the Little-Known Einstein-Schwarzschild Coordinate Condition
 Unit-Jacobian Coordinate Transformations: The Superior Consequence of the Little-Known Einstein-Schwarzschild Coordinate Condition Steven Kenneth Kauffmann Abstract Because the Einstein equation can t
Unit-Jacobian Coordinate Transformations: The Superior Consequence of the Little-Known Einstein-Schwarzschild Coordinate Condition Steven Kenneth Kauffmann Abstract Because the Einstein equation can t
Is the Energy Balance Paradox Solved?
 1 Is the Energy Balance Paradox Solved? Amos Harpaz(1) and Noam Soker(2) 1. Institute of Theoretical Physics, Technion, Haifa, ISRAEL 2. Department of Physics, Oranim, Tivon 36006, ISRAEL phr89ah@tx.technion.ac.il
1 Is the Energy Balance Paradox Solved? Amos Harpaz(1) and Noam Soker(2) 1. Institute of Theoretical Physics, Technion, Haifa, ISRAEL 2. Department of Physics, Oranim, Tivon 36006, ISRAEL phr89ah@tx.technion.ac.il
PHY752, Fall 2016, Assigned Problems
 PHY752, Fall 26, Assigned Problems For clarification or to point out a typo (or worse! please send email to curtright@miami.edu [] Find the URL for the course webpage and email it to curtright@miami.edu
PHY752, Fall 26, Assigned Problems For clarification or to point out a typo (or worse! please send email to curtright@miami.edu [] Find the URL for the course webpage and email it to curtright@miami.edu
Biot-Savart-like law in electrostatics. Abstract
 Biot-Savart-like law in electrostatics Mário H. Oliveira and José A.Miranda Laboratório de Física Teórica e Computacional, Departamento de Física, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Recife, PE 50670-901
Biot-Savart-like law in electrostatics Mário H. Oliveira and José A.Miranda Laboratório de Física Teórica e Computacional, Departamento de Física, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Recife, PE 50670-901
9 Wave solution of Maxwells equations.
 9 Wave solution of Maxwells equations. Contents 9.1 Wave solution: Plane waves 9.2 Scalar Spherical waves 9.3 Cylindrical waves 9.4 Momentum and energy of the electromagnetic field Keywords: Plane, cylindrical
9 Wave solution of Maxwells equations. Contents 9.1 Wave solution: Plane waves 9.2 Scalar Spherical waves 9.3 Cylindrical waves 9.4 Momentum and energy of the electromagnetic field Keywords: Plane, cylindrical
Umm Al-Qura University Dr. Abdulsalam Ali. Physics 101. Lecture 1. Lecturer: Dr. Abdulsalam Ali Soud
 Physics 101 Lecture 1 Lecturer: Dr. Abdulsalam Ali Soud Course Text Book Course Text Book Physics 4 th By James S. Walker COURSE SYLLABUS Week No. 1 2 3 4 Contents Introduction to Physics 1- Unit of Length,
Physics 101 Lecture 1 Lecturer: Dr. Abdulsalam Ali Soud Course Text Book Course Text Book Physics 4 th By James S. Walker COURSE SYLLABUS Week No. 1 2 3 4 Contents Introduction to Physics 1- Unit of Length,
Electricity and Magnetism PHYS-340:
 Electricity and Magnetism PHYS-340: 2013 (2:35-3:25 Monday, Wednesday, Friday, Rutherford 114) http://www.physics.mcgill.ca/~gang/phys340/phys340.home.htm Instructor: Shaun Lovejoy, Rutherford Physics,
Electricity and Magnetism PHYS-340: 2013 (2:35-3:25 Monday, Wednesday, Friday, Rutherford 114) http://www.physics.mcgill.ca/~gang/phys340/phys340.home.htm Instructor: Shaun Lovejoy, Rutherford Physics,
Green s Tensors for the Electromagnetic Field in Cylindrical Coordinates
 Chapter 25 Green s Tensors for the Electromagnetic Field in Cylindrical Coordinates The solutions of the vector Helmholtz equation in three dimensions can be expressed by a complete set of vector fields
Chapter 25 Green s Tensors for the Electromagnetic Field in Cylindrical Coordinates The solutions of the vector Helmholtz equation in three dimensions can be expressed by a complete set of vector fields
Electromagnetic Stress and Momentum in the Combined-Field Formalism
 Physics Notes Note 0 11 March 009 Electromagnetic Stress and Momentum in the Combined-Field Formalism Carl E. Baum University of New Mexico Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Albuquerque
Physics Notes Note 0 11 March 009 Electromagnetic Stress and Momentum in the Combined-Field Formalism Carl E. Baum University of New Mexico Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Albuquerque
arxiv: v1 [physics.class-ph] 28 Dec 2008
![arxiv: v1 [physics.class-ph] 28 Dec 2008 arxiv: v1 [physics.class-ph] 28 Dec 2008](/thumbs/77/76689828.jpg) Can Maxwell s equations be obtained from the continuity equation? José A. Heras arxiv:0812.4785v1 [physics.class-ph] 28 Dec 2008 Departamento de Física y Matemáticas, Universidad Iberoamericana, Prolongación
Can Maxwell s equations be obtained from the continuity equation? José A. Heras arxiv:0812.4785v1 [physics.class-ph] 28 Dec 2008 Departamento de Física y Matemáticas, Universidad Iberoamericana, Prolongación
Electromagnetic momentum of a point electric dipole in a uniform magnetic field
 Electromagnetic momentum of a point electric dipole in a uniform magnetic field arxiv:physics/7216v1 [physics.class-ph] 2 Feb 27 Andre Gsponer Independent Scientific Research Institute Oxford, OX4 4YS,
Electromagnetic momentum of a point electric dipole in a uniform magnetic field arxiv:physics/7216v1 [physics.class-ph] 2 Feb 27 Andre Gsponer Independent Scientific Research Institute Oxford, OX4 4YS,
Introduction. Chapter Presentation of Macroscopic Electrodynamics. 1.1 What is Electrodynamics?
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 What is Electrodynamics? Electrodynamics as a theory deals with electric charges which move in space and with electromagnetic fields that are produced by the charges and again
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 What is Electrodynamics? Electrodynamics as a theory deals with electric charges which move in space and with electromagnetic fields that are produced by the charges and again
SOLAR MHD Lecture 2 Plan
 SOLAR MHD Lecture Plan Magnetostatic Equilibrium ü Structure of Magnetic Flux Tubes ü Force-free fields Waves in a homogenous magnetized medium ü Linearized wave equation ü Alfvén wave ü Magnetoacoustic
SOLAR MHD Lecture Plan Magnetostatic Equilibrium ü Structure of Magnetic Flux Tubes ü Force-free fields Waves in a homogenous magnetized medium ü Linearized wave equation ü Alfvén wave ü Magnetoacoustic
Recapitulation: Questions on Chaps. 1 and 2 #A
 Recapitulation: Questions on Chaps. 1 and 2 #A Chapter 1. Introduction What is the importance of plasma physics? How are plasmas confined in the laboratory and in nature? Why are plasmas important in astrophysics?
Recapitulation: Questions on Chaps. 1 and 2 #A Chapter 1. Introduction What is the importance of plasma physics? How are plasmas confined in the laboratory and in nature? Why are plasmas important in astrophysics?
CHAPTER 8 CONSERVATION LAWS
 CHAPTER 8 CONSERVATION LAWS Outlines 1. Charge and Energy 2. The Poynting s Theorem 3. Momentum 4. Angular Momentum 2 Conservation of charge and energy The net amount of charges in a volume V is given
CHAPTER 8 CONSERVATION LAWS Outlines 1. Charge and Energy 2. The Poynting s Theorem 3. Momentum 4. Angular Momentum 2 Conservation of charge and energy The net amount of charges in a volume V is given
The Conservation of Matter in General Relativity
 Commun. math. Phys. 18, 301 306 (1970) by Springer-Verlag 1970 The Conservation of Matter in General Relativity STEPHEN HAWKING Institute of Theoretical Astronomy, Cambridge, England Received June 1, 1970
Commun. math. Phys. 18, 301 306 (1970) by Springer-Verlag 1970 The Conservation of Matter in General Relativity STEPHEN HAWKING Institute of Theoretical Astronomy, Cambridge, England Received June 1, 1970
Vector Green s Functions for Electrodynamics Applications
 ENZCon 2016 Vector Green s Functions for Electrodynamics Applications Malcolm Morrison, Colin Fox Electronics Group University of Otago Email: morma584@student.otago.ac.nz Abstract The use of scalar Green
ENZCon 2016 Vector Green s Functions for Electrodynamics Applications Malcolm Morrison, Colin Fox Electronics Group University of Otago Email: morma584@student.otago.ac.nz Abstract The use of scalar Green
arxiv: v1 [physics.plasm-ph] 3 Apr 2011
![arxiv: v1 [physics.plasm-ph] 3 Apr 2011 arxiv: v1 [physics.plasm-ph] 3 Apr 2011](/thumbs/91/106515569.jpg) A comparison of Vlasov with drift kinetic and gyrokinetic theories arxiv:1104.0427v1 [physics.plasm-ph] 3 Apr 2011 H. Tasso 1, G. N. Throumoulopoulos 2 1 Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, Euratom Association,
A comparison of Vlasov with drift kinetic and gyrokinetic theories arxiv:1104.0427v1 [physics.plasm-ph] 3 Apr 2011 H. Tasso 1, G. N. Throumoulopoulos 2 1 Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, Euratom Association,
INTRODUCTION ELECTRODYNAMICS BEFORE MAXWELL MAXWELL S DISPLACEMENT CURRENT. Introduction Z B S. E l = Electrodynamics before Maxwell
 Chapter 14 MAXWELL S EQUATONS ntroduction Electrodynamics before Maxwell Maxwell s displacement current Maxwell s equations: General Maxwell s equations in vacuum The mathematics of waves Summary NTRODUCTON
Chapter 14 MAXWELL S EQUATONS ntroduction Electrodynamics before Maxwell Maxwell s displacement current Maxwell s equations: General Maxwell s equations in vacuum The mathematics of waves Summary NTRODUCTON
APPLICATION OF SOMMERFELD - WATSON TRANSFORMATION TO AN ELECTROSTATICS PROBLEM*
 SLAC -PUB-533 December 19 68 (MISC) APPLICATION OF SOMMERFELD - WATSON TRANSFORMATION TO AN ELECTROSTATICS PROBLEM* Jon Pumplin Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Stanford University, Stanford, California
SLAC -PUB-533 December 19 68 (MISC) APPLICATION OF SOMMERFELD - WATSON TRANSFORMATION TO AN ELECTROSTATICS PROBLEM* Jon Pumplin Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Stanford University, Stanford, California
Intermission Page 343, Griffith
 Intermission Page 343, Griffith Chapter 8. Conservation Laws (Page 346, Griffith) Lecture : Electromagnetic Power Flow Flow of Electromagnetic Power Electromagnetic waves transport throughout space the
Intermission Page 343, Griffith Chapter 8. Conservation Laws (Page 346, Griffith) Lecture : Electromagnetic Power Flow Flow of Electromagnetic Power Electromagnetic waves transport throughout space the
International Journal of Applied and Universal Research ISSN No: Volume III, Issue II, Mar-Apr Available online at:
 BIANCHI TYPE III ELECTRO MAGNETIZED COSMOLOGICAL MODEL WITH NAMBU STRINGS IN GENERAL THEORY OF RELATIVITY R.K.Dubey 1, Anil Saini 2, Neelam Yadav 3 1 Department of Mathematics, Govt. SKN PG College Mauganj
BIANCHI TYPE III ELECTRO MAGNETIZED COSMOLOGICAL MODEL WITH NAMBU STRINGS IN GENERAL THEORY OF RELATIVITY R.K.Dubey 1, Anil Saini 2, Neelam Yadav 3 1 Department of Mathematics, Govt. SKN PG College Mauganj
Electromagnetic waves in free space
 Waveguide notes 018 Electromagnetic waves in free space We start with Maxwell s equations for an LIH medum in the case that the source terms are both zero. = =0 =0 = = Take the curl of Faraday s law, then
Waveguide notes 018 Electromagnetic waves in free space We start with Maxwell s equations for an LIH medum in the case that the source terms are both zero. = =0 =0 = = Take the curl of Faraday s law, then
CLASSICAL ELECTRICITY
 CLASSICAL ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM by WOLFGANG K. H. PANOFSKY Stanford University and MELBA PHILLIPS Washington University SECOND EDITION ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo
CLASSICAL ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM by WOLFGANG K. H. PANOFSKY Stanford University and MELBA PHILLIPS Washington University SECOND EDITION ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo
On the paper Role of potentials in the Aharonov-Bohm effect. A. M. Stewart
 On the paper Role of potentials in the Aharonov-Bohm effect A. M. Stewart Emeritus Faculty, The Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia. http://www.anu.edu.au/emeritus/members/pages/a_stewart/
On the paper Role of potentials in the Aharonov-Bohm effect A. M. Stewart Emeritus Faculty, The Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia. http://www.anu.edu.au/emeritus/members/pages/a_stewart/
Advanced Study, 9 Adela Court, Mulgrave, Victoria 3170, Australia
 A CLASSIFICATION OF QUANTUM PARTICLES Vu B Ho Advanced Study, 9 Adela Court, Mulgrave, Victoria 3170, Australia Email: vubho@bigpond.net.au Abstract: In this work, by summarising our recent works on the
A CLASSIFICATION OF QUANTUM PARTICLES Vu B Ho Advanced Study, 9 Adela Court, Mulgrave, Victoria 3170, Australia Email: vubho@bigpond.net.au Abstract: In this work, by summarising our recent works on the
Classical electromagnetism - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 Page 1 of 6 Classical electromagnetism From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia (Redirected from Classical electrodynamics) Classical electromagnetism (or classical electrodynamics) is a branch of theoretical
Page 1 of 6 Classical electromagnetism From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia (Redirected from Classical electrodynamics) Classical electromagnetism (or classical electrodynamics) is a branch of theoretical
Ultimate Thickness to Bandwidth Ratio of Radar Absorbers
 1230 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 48, NO. 8, AUGUST 2000 Ultimate Thickness to Bandwidth Ratio of Radar Absorbers Konstantin N. Rozanov Abstract Analytic properties of the reflection
1230 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 48, NO. 8, AUGUST 2000 Ultimate Thickness to Bandwidth Ratio of Radar Absorbers Konstantin N. Rozanov Abstract Analytic properties of the reflection
Vector boson character of the static electric field
 Chapter 12 Vector boson character of the static electric field (Paper 66) by Myron W. Evans Alpha Institute for Advanced Study (AIAS). (emyrone@aol.com, www.aias.us, www.atomicprecision.com) Abstract The
Chapter 12 Vector boson character of the static electric field (Paper 66) by Myron W. Evans Alpha Institute for Advanced Study (AIAS). (emyrone@aol.com, www.aias.us, www.atomicprecision.com) Abstract The
University of Warwick institutional repository:
 University of Warwick institutional repository: http://go.warwick.ac.uk/wrap This paper is made available online in accordance with publisher policies. Please scroll down to view the document itself. Please
University of Warwick institutional repository: http://go.warwick.ac.uk/wrap This paper is made available online in accordance with publisher policies. Please scroll down to view the document itself. Please
Uniqueness theorems, Separation of variables for Poisson's equation
 NPTEL Syllabus Electrodynamics - Web course COURSE OUTLINE The course is a one semester advanced course on Electrodynamics at the M.Sc. Level. It will start by revising the behaviour of electric and magnetic
NPTEL Syllabus Electrodynamics - Web course COURSE OUTLINE The course is a one semester advanced course on Electrodynamics at the M.Sc. Level. It will start by revising the behaviour of electric and magnetic
Elektrodynamiikan sovellutuksia Applications of electrodynamics. Ari Viljanen
 Elektrodynamiikan sovellutuksia Applications of electrodynamics Ari Viljanen 2005 2 Lecturer: Ari Viljanen (Finnish Meteorological Institute, Space Research Unit, ari.viljanen@fmi.fi, tel. 1929 4668).
Elektrodynamiikan sovellutuksia Applications of electrodynamics Ari Viljanen 2005 2 Lecturer: Ari Viljanen (Finnish Meteorological Institute, Space Research Unit, ari.viljanen@fmi.fi, tel. 1929 4668).
Gravity s Hidden Inverse Relationship With Electromagnetism: A Possible Path to Solving the Hierarchy Problem
 Gravity s Hidden Inverse Relationship With Electromagnetism: A Possible Path to Solving the Hierarchy Problem About the Author: Lamont Williams is a science writer in the Washington, DC, area. He is author
Gravity s Hidden Inverse Relationship With Electromagnetism: A Possible Path to Solving the Hierarchy Problem About the Author: Lamont Williams is a science writer in the Washington, DC, area. He is author
EM concept map. Field laws. No monopoles. Gauss s law. Conservation laws. equations (In vacuum) Ampere s law. radiation. Faraday s law.
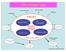 EM concept map radiation Conservation laws Special relativity EM waves Field laws Gauss s law No monopoles electrostatics Faraday s law Conservation Maxwell s laws equations (In vacuum) Ampere s law magnetostatics
EM concept map radiation Conservation laws Special relativity EM waves Field laws Gauss s law No monopoles electrostatics Faraday s law Conservation Maxwell s laws equations (In vacuum) Ampere s law magnetostatics
Green dyadic for the Proca fields
 Green dyadic for the Proca fields Paul Dragulin P. T. Leung ( 梁培德 * Department of Physics, Portl State University, P. O. Box 75, Portl, Oregon 97207-075, USA Received 4 March 2008; published 4 August 2008
Green dyadic for the Proca fields Paul Dragulin P. T. Leung ( 梁培德 * Department of Physics, Portl State University, P. O. Box 75, Portl, Oregon 97207-075, USA Received 4 March 2008; published 4 August 2008
The closed-form resolution of integrals is one of the
 Construction of Generalized Integral Formulas By Means of Laplace Transformations Adam C. Buss, Department of Physics, Indiana University - Northwest Faculty Mentor: Dr. Axel Schulze-Halberg ABSTRACT We
Construction of Generalized Integral Formulas By Means of Laplace Transformations Adam C. Buss, Department of Physics, Indiana University - Northwest Faculty Mentor: Dr. Axel Schulze-Halberg ABSTRACT We
Causality in Classical Physics
 GENERAL ARTICLE Causality in Classical Physics Asrarul Haque Classical physics encompasses the study of physical phenomena which range from local (a point) to nonlocal (a region) in space and/or time.
GENERAL ARTICLE Causality in Classical Physics Asrarul Haque Classical physics encompasses the study of physical phenomena which range from local (a point) to nonlocal (a region) in space and/or time.
The Pole Condition: A Padé Approximation of the Dirichlet to Neumann Operator
 The Pole Condition: A Padé Approximation of the Dirichlet to Neumann Operator Martin J. Gander and Achim Schädle Mathematics Section, University of Geneva, CH-, Geneva, Switzerland, Martin.gander@unige.ch
The Pole Condition: A Padé Approximation of the Dirichlet to Neumann Operator Martin J. Gander and Achim Schädle Mathematics Section, University of Geneva, CH-, Geneva, Switzerland, Martin.gander@unige.ch
Physics 505 Fall Homework Assignment #9 Solutions
 Physics 55 Fall 25 Textbook problems: Ch. 5: 5.2, 5.22, 5.26 Ch. 6: 6.1 Homework Assignment #9 olutions 5.2 a) tarting from the force equation (5.12) and the fact that a magnetization M inside a volume
Physics 55 Fall 25 Textbook problems: Ch. 5: 5.2, 5.22, 5.26 Ch. 6: 6.1 Homework Assignment #9 olutions 5.2 a) tarting from the force equation (5.12) and the fact that a magnetization M inside a volume
Matrix Transformation and Solutions of Wave Equation of Free Electromagnetic Field
 Matrix Transformation and Solutions of Wave Equation of Free Electromagnetic Field Xianzhao Zhong Meteorological College of Yunnan Province, Kunming, 6508, China Abstract In this paper, the generalized
Matrix Transformation and Solutions of Wave Equation of Free Electromagnetic Field Xianzhao Zhong Meteorological College of Yunnan Province, Kunming, 6508, China Abstract In this paper, the generalized
PHY102 Electricity Topic 3 (Lectures 4 & 5) Gauss s Law
 PHY1 Electricity Topic 3 (Lectures 4 & 5) Gauss s Law In this topic, we will cover: 1) Electric Flux ) Gauss s Law, relating flux to enclosed charge 3) Electric Fields and Conductors revisited Reading
PHY1 Electricity Topic 3 (Lectures 4 & 5) Gauss s Law In this topic, we will cover: 1) Electric Flux ) Gauss s Law, relating flux to enclosed charge 3) Electric Fields and Conductors revisited Reading
Lecture 3: Gaussian Elimination, continued. Lecture 3: Gaussian Elimination, continued
 Definition The process of solving a system of linear equations by converting the system to an augmented matrix is called Gaussian Elimination. The general strategy is as follows: Convert the system of
Definition The process of solving a system of linear equations by converting the system to an augmented matrix is called Gaussian Elimination. The general strategy is as follows: Convert the system of
What is spin? André Gsponer Independent Scientific Research Institute Box 30, CH-1211 Geneva-12, Switzerland
 What is spin? arxiv:physics/030807v3 [physics.class-ph] 0 Sep 003 André Gsponer Independent Scientific Research Institute Box 30, CH- Geneva-, Switzerland e-mail: isri@vtx.ch ISRI-03-0.3 February, 008
What is spin? arxiv:physics/030807v3 [physics.class-ph] 0 Sep 003 André Gsponer Independent Scientific Research Institute Box 30, CH- Geneva-, Switzerland e-mail: isri@vtx.ch ISRI-03-0.3 February, 008
Chapter 8. Conservation Laws. 8.3 Magnetic Forces Do No Work
 Chapter 8. Conservation Laws 8.3 Magnetic Forces Do No Work 8.2 Momentum of EM fields 8.2.1 Newton's Third Law in Electrodynamics Consider two charges, q 1 and q 2, moving with speeds v 1 and v 2 magnetic
Chapter 8. Conservation Laws 8.3 Magnetic Forces Do No Work 8.2 Momentum of EM fields 8.2.1 Newton's Third Law in Electrodynamics Consider two charges, q 1 and q 2, moving with speeds v 1 and v 2 magnetic
CHAPTER 4 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES IN CYLINDRICAL SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 4 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES IN CYLINDRICAL SYSTEMS The vector Helmholtz equations satisfied by the phasor) electric and magnetic fields are where. In low-loss media and for a high frequency, i.e.,
CHAPTER 4 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES IN CYLINDRICAL SYSTEMS The vector Helmholtz equations satisfied by the phasor) electric and magnetic fields are where. In low-loss media and for a high frequency, i.e.,
Shallow Water Gravity Waves: A Note on the Particle Orbits
 Journal of Oceanography Vol. 5, pp. 353 to 357. 1996 Shallow Water Gravity Waves: A Note on the Particle Orbits KERN E. KENYON 463 North Lane, Del Mar, CA 9014-4134, U.S.A. (Received 4 July 1995; in revised
Journal of Oceanography Vol. 5, pp. 353 to 357. 1996 Shallow Water Gravity Waves: A Note on the Particle Orbits KERN E. KENYON 463 North Lane, Del Mar, CA 9014-4134, U.S.A. (Received 4 July 1995; in revised
Solutions for the electric potential and field distribution in cylindrical core-shell nanoparticles using the image charge method
 Solutions for the electric potential and field distribution in cylindrical core-shell nanoparticles using the image charge method Nader Daneshfar, and Nasrin Moradbeigi Citation: AIP Advances 5, 1714 (15);
Solutions for the electric potential and field distribution in cylindrical core-shell nanoparticles using the image charge method Nader Daneshfar, and Nasrin Moradbeigi Citation: AIP Advances 5, 1714 (15);
Bounded Infinite Sequences/Functions : Orders of Infinity
 Bounded Infinite Sequences/Functions : Orders of Infinity by Garimella Ramamurthy Report No: IIIT/TR/2009/247 Centre for Security, Theory and Algorithms International Institute of Information Technology
Bounded Infinite Sequences/Functions : Orders of Infinity by Garimella Ramamurthy Report No: IIIT/TR/2009/247 Centre for Security, Theory and Algorithms International Institute of Information Technology
Maxwell s equations for electrostatics
 Maxwell s equations for electrostatics October 6, 5 The differential form of Gauss s law Starting from the integral form of Gauss s law, we treat the charge as a continuous distribution, ρ x. Then, letting
Maxwell s equations for electrostatics October 6, 5 The differential form of Gauss s law Starting from the integral form of Gauss s law, we treat the charge as a continuous distribution, ρ x. Then, letting
DISCRETE SCALE RELATIVITY
 DISCRETE SCALE RELATIVITY Robert L. Oldershaw Amherst College Amherst, MA 01002 USA rloldershaw@amherst.edu ABSTRACT: The possibility that global discrete dilation invariance is a fundamental symmetry
DISCRETE SCALE RELATIVITY Robert L. Oldershaw Amherst College Amherst, MA 01002 USA rloldershaw@amherst.edu ABSTRACT: The possibility that global discrete dilation invariance is a fundamental symmetry
Application of the ECE Lemma to the fermion and electromagnetic fields
 Chapter 8 Application of the ECE Lemma to the fermion and electromagnetic fields Abstract (Paper 62) by Myron W. Evans Alpha Institute for Advanced Study (AIAS). (emyrone@aol.com, www.aias.us, www.atomicprecision.com)
Chapter 8 Application of the ECE Lemma to the fermion and electromagnetic fields Abstract (Paper 62) by Myron W. Evans Alpha Institute for Advanced Study (AIAS). (emyrone@aol.com, www.aias.us, www.atomicprecision.com)
Transactions on Modelling and Simulation vol 18, 1997 WIT Press, ISSN X
 Implicit scheme time domain BEM transient electromagnetic fields analysis of H. Kawaguchi, M. Isoda and T. Honma Division of Systems and Info. Engineering, Faculty ofengineering, Hokkaido University, Kita
Implicit scheme time domain BEM transient electromagnetic fields analysis of H. Kawaguchi, M. Isoda and T. Honma Division of Systems and Info. Engineering, Faculty ofengineering, Hokkaido University, Kita
7/'D-A PROPERTIES OF A MAGr4EIIC DIPOLE(U MATERIALS RESEAR0H 1/1 LAB! ASCOT VALE (AUS IALIA) PJ RYAN JU 7? M L-TM-52 I 7,7CLASSIFIED FIG 29/3
 7/'D-A186 129 PROPERTIES OF A MAGr4EIIC DIPOLE(U MATERIALS RESEAR0H 1/1 LAB! ASCOT VALE (AUS IALIA) PJ RYAN JU 7? M L-TM-52 I 7,7CLASSIFIED FIG 29/3 NL 132 MICRCCp RLJQIOUION LS T i AR MRL-TN-521 AR-005-156
7/'D-A186 129 PROPERTIES OF A MAGr4EIIC DIPOLE(U MATERIALS RESEAR0H 1/1 LAB! ASCOT VALE (AUS IALIA) PJ RYAN JU 7? M L-TM-52 I 7,7CLASSIFIED FIG 29/3 NL 132 MICRCCp RLJQIOUION LS T i AR MRL-TN-521 AR-005-156
Logical difficulty from combining counterfactuals in the GHZ-Bell theorems
 Logical difficulty from combining counterfactuals in the GHZ-Bell theorems ABSTRACT Louis Sica 1,2 1 Chapman University, Orange, CA & Burtonsville, MD, USA 2 Inspire Institute Inc., Alexandria, VA, USA
Logical difficulty from combining counterfactuals in the GHZ-Bell theorems ABSTRACT Louis Sica 1,2 1 Chapman University, Orange, CA & Burtonsville, MD, USA 2 Inspire Institute Inc., Alexandria, VA, USA
4 Electrodynamics and Relativity
 4 Electrodynamics and Relativity The first time I experienced beauty in physics was when I learned how Einstein s special relativity is hidden in the equations of Maxwell s theory of electricity and magnetism.
4 Electrodynamics and Relativity The first time I experienced beauty in physics was when I learned how Einstein s special relativity is hidden in the equations of Maxwell s theory of electricity and magnetism.
PHYS 532 Lecture 8 Page GAUGE TRANSFORMATIONS E =!" #A B =! " A (6.7) #(! A) = $/% o A A + Λ (6.12) Φ Φ!"
 PHYS 532 Lecture 8 Page 1 6.3 GAUGE TRANSFORMATIONS Results for scalar and vector potentials: E =!" #A #t (6.9) Inhomogeneous Maxwell equations in terms of A, Φ B =! " A (6.7)! 2 " + #(! A) #t = $/% o
PHYS 532 Lecture 8 Page 1 6.3 GAUGE TRANSFORMATIONS Results for scalar and vector potentials: E =!" #A #t (6.9) Inhomogeneous Maxwell equations in terms of A, Φ B =! " A (6.7)! 2 " + #(! A) #t = $/% o
