INTRODUCTION ELECTRODYNAMICS BEFORE MAXWELL MAXWELL S DISPLACEMENT CURRENT. Introduction Z B S. E l = Electrodynamics before Maxwell
|
|
|
- Rosalyn Wilson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 14 MAXWELL S EQUATONS ntroduction Electrodynamics before Maxwell Maxwell s displacement current Maxwell s equations: General Maxwell s equations in vacuum The mathematics of waves Summary NTRODUCTON The contributions of James Clerk Maxwell to science are remarkable, they are of comparable importance to those of Newton. Maxwell summarized the laws of electricity and magnetism, developed by Coulomb, Faraday, and Ampère, and expressed them in the following concise mathematical form in terms of flux and circulation, and most importantly added a missing term that is of crucial importance. The four Maxwell Equations summarize the fundamental laws that underlie all of electricity and magnetism. ELECTRODYNAMCS BEFORE MAXWELL Flux: Gauss s Law: Coulomb s Law implies that the electric flux out of a closed surface is: Φ = 1 E S = 0 The Biot Savart Law implies that the magnetic flux out of a closed surface is: Φ = B S =0 Although these two flux equations were derived only for statics, they also are obeyed for electrodynamics. Circulation: Faraday s Law implies that the circulation of the electric field is coupled to the rate of change of magnetic flux. E l = B S Ampère s law gives the circulation of the magnetic field: B dl = 0 j S Charge conservation is an important law of nature that must be obeyed by the laws of electrodynamics. Charge conservation implies that the net current flowing out of a closed surface must equal the rate of loss of charge from the enclosed volume. j S + =0 Maxwell realized that the above four equations for electrodynamics violate charge conservation. He showed that an additional term, called the displacement current,thatdependsontherateofchangeofelectric field, missing from Ampère s Law; is needed to satisfy charge conservation. This lecture will first discuss the need for the introduction of a new displacement current term to satisfy charge conservation. This will be followed by a summary of the fundamental Maxwell Equations. MAXWELL S DSPLACEMENT CURRENT Maxwell showed that Ampère s law could be generalized and made to satisfy charge conservation, by including an additional term to the current density called the displacement current density, j, where: j 0 E Addition of this displacement current density to the real current density j gives the Maxwell-Ampère law: B l = 0 j S+0 0 E S The second integral equals 0 R j S that is the Maxwell-Ampère includes the sum of the the real current density and the displacement current. 107
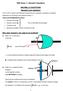
2 Figure 1 Evaluation of Ampère s Law when the closed loop C 0 A formal proof for the need of the displacement current term is as follows. Consider that the closed loop C, in figure 1, shrinks to zero, that is 0 then the surface integral becomes a closed surface. That is: =0 B l =0=0 j S E S Gauss law gives: 1 E S = 0 therefore, the time derivative of Gauss s law; E S = 1 0 nserting this into the above line integral for a closed loop C gives j S + =0 that is, the charge conservation relation is obtained. nclusion of the displacement current term leads to the second integral which is essential to this proof. Charging capacitor An understanding of Maxwell s displacement current density can be obtained by considering the case of a capacitor charging with current as illustrated in figure 2. The current in the wire produces a measurable magnetic field circling around the wire carrying the current. For surface S 1, bounded by the closed loop C, there is a real current passing inwards through this surface which is related to the non-zero circulation of B around the closed loop C given by Ampère s law. However, as shown in figure 2, surface S 2 which passes between the capacitor plates, has no real current flowing through its surface, and thus Ampère s law implies that there is 108 Figure 2 Two surfaces S 1 and S 2 bounded by the same curve C. The current passes through the surface S 1 but not S 2. However, there is a changing electric flux through S 2 no magnetic field around C. However, there remains a measurable magnetic field around the wire carrying the current. Clearly something is wrong with Ampère s Law. Maxwell s displacement current corrects this flaw in Ampère s Law, and satisfies charge conservation. nclusion of the displacement current does not change the integral of current though surface S 1 since the displacement current is zero for this surface because 0 R 1 E S =0 whereas the real current is. However, for 2, the real current density is zero but the displacement current is non-zero since the electric field between the capacitor plates in increasing. t is shown below that the net current through both 1 and 2 are the same if both the real and displacement currents are summed. ntegrating the displacement current over the surface S 2 gives: j E S = S Consider Gauss law for the closed surface defined by E S = 1 0 where 1 is used to reflect the fact that the righthand rule connecting C and 1 was taken such that 1 is taken pointing into the volume. The time derivative of this gives; E 1+ 2 S = 1 0 The left-hand integral has a zero contribution for surface 1 Thus the net displacement current is given by: 0 j S+ S = E S =
3 nserting this in the charge conservation relation j S + =0 and using the fact that the real current density is nonzero only for 1 and displacement current is non-zero only for 2 gives j S + j S =0 1 2 or j S = j S = 1 2 where the direction of the first integral has been reversed. That is, the total displacement current flowing through 2 equals the total real current flowing through 1 Thus the Maxwell-Ampère s law can be written: E B l = 0 j S S where the first integral equals 0 for surface S 1 and zero for surface S 2, while the second integral equals 0 for surface S 2 and is zero for surface S 1 That is, the circulation of B around the loop C is the same whether surface 1 or surface 2 are used. Thus Maxwell s corrected version of Ampères Law satisfies charge conservation, that is, the circulation of magnetic field is independent on whether a current is flowing or the electric flux is changing, that is whether surface S 1 or surface S 2 are used for the closed loop C. Addition of the displacement current implies that the circulation of the B field around a closed loop depends on both the current and the rate of change of electric flux through the loop. This is analogous to Faraday s Law which relates the circulation of the E field around a closed loop to the rate of change of the magnetic flux through the loop. The enormous significance of the displacement current will become more apparent after we summarize Maxwell s Equations. Maxwell s displacement current states that a changing electric flux through a closed curve induces a circulation of the magnetic field around that circuit. This is a direct analogy to Faraday s Law where a changing magnetic flux though a circuit induces a circulation of the electric field around the circuit. This analogy can be illustrated by considering the induced magnetic field between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor with circular plates, see figure 3. Consider a concentric circular path of radius in the plane of the radius circular capacitor plates. By symmetry using Maxwell-Ampère s law, plus the fact that the current density j between the plates is zero, gives B l = 0 j S E S Figure 3 Parallel-plate capacitor having circular plates of radius Current of charges the plates. Calculate the magnetic field around the concentric circular path of radius. 2 = Using Gauss s Law at the surface of the capacitor plates gives that Thesegivethat = = 0 2 = = This result is the same as for the magnetic field inside a cylindrical conductor of radius having a uniform current density However, this result was obtained by 2 calculating the induced magnetic field due to a changing flux of electric field. MAXWELL S EQUATONS: GENERAL Aftermuchhardworkwefinally have arrived at the basic laws of electromagnetism as first developed by Maxwell. These are derived from the experimental laws of Coulomb, Faraday and Ampère plus superposition. Maxwell expressed these laws in terms of the flux and circulation of the electric and magnetic vector fields, as well as adding the missing term, the displacement current. The most general form of the Maxwell s Equationsisgivenbelow. Maxwell Equations, General form. Flux Gauss s Law for electric field: Φ = 1 E S = 0 109
4 = 1 0 (Enclosed charge) Gauss s law for magnetism Φ = Circulation: Faraday s Law B S =0 F = ( E + v B) Maxwell used his four equations to predict that electromagnetic waves can occur and these will travel at a velocity in vacuum of = 1 0 He was astonished to discover that this equalled the measured ve- 0 locity of light convincing him that light was an electromagnetic wave. t was not until after Maxwell s death that Hertz demonstrated that electromagnetic waves are created via oscillating electric fields. E l = Ampère-Maxwell law: B dl = 0 B S ( E j + 0 ) S = 0 (Net real and displacement currents flowing through the loop) Remember that the total flux of the electric field out of a closed surface is independent of the size or shape of the Gaussian surface because the electric field for a point charge has a 1 dependence. Gauss s law 2 for the electric field gives the strength of the enclosed charge. The total flux for the magnetic field also is independent of the size and shape of the surface because it also has a 1 dependence. However, the net magnetic flux is always zero because the magnetic field 2 for an current element is tangential not radial. The fact that the net flux is zero is equivalent to the statement that magnetic monopoles do not exist. That is, north and south poles only occur in pairs in contrast to charge which comes in two flavors, positive or negative. The circulation of the electric field is a statement of Faraday s law of induction. Also it includes the fact that for statics, the circulation is zero implying that the electric field from a point charge is radial, not tangential. A consequence for statics is that the line integral R E l is path independent allowing the use of the concept of electric potential. The circulation of the magnetic field is a statement of the Ampère-Maxwell law. Remember to use a righthanded definition relating the line integral and the direction of the flux through the loop when using either of the circulation relations. The complete description of electromagnetism requires the four Maxwell equations plus the Lorentz force relation that defines the electric and magnetic fields. That is: MAXWELL S EQUATONS N VACUUM t helps to consider the special case of Maxwell s Equations in vacuum, that is, where current and charge densities are zero, j = =0 Then Maxwell s equations in vacuum simplify to the following. Maxwell Equations for Vacuum Flux Circulation E l = E S =0 B S =0 B dl = 0 0 B S E S Note the symmetry between these pairs of equations both for the flux and circulation. The right-hand side of the last equation comes from Maxwell s displacement current. The only non-symmetric aspects are the negative sign in Faraday s law, and the product of the constants, 0 0 This product equals the square of the velocity of light in vacuum, as will be shown next lecture. That is: 0 0 =
5 where the phase is fixed with respect to the waveform shape. tcancorrespondtomotionineitherdirection. General wave motion can be described by solutions of a wave equation. The wave equation can be written in terms of the spatial and temporal derivatives ofthewavefunctionψ() Consider the first partial derivatives of Ψ() =( ) =() Figure 4 Travelling wave, moving at velocity v in the direction, at times t=0 and t= 0 Thus the system of units used for the velocity of light is the only parameter in Maxwell s equations. Remember, that the velocity of light in vacuum is taken to be a fundamental constant. That is, the equations are independent of the system of units used in defining 0 and 0. The symmetry of the Maxwell equations and the direct inclusion of the velocity of light is related to the direct connection of the electric and magnetic fields predicted by Einstein s Theory of Relativity. Next lecture will use Maxwell s equations in vacuum to demonstrate that they lead to the prediction of electromagnetic radiation. The discussion of electromagnetic radiation requires a knowledge of wave motion which will be reviewed next. MATHEMATCS OF WAVES Consider a travelling wave in one dimension. f the wave is moving, then the wave function Ψ ( ) describing the shape of the wave, is a function of both and. The instantaneous amplitude of the wave Ψ ( ) could correspond to the transverse displacement of a wave on a string, the longitudinal amplitude of a wave on a spring, the pressure of a longitudinal soundwave,theelectricormagneticfields in an electromagnetic wave, a matter wave, etc. f the wave train maintains its shape as it moves, then one can describe thewavetrainbythefunction () where the coordinate is measured relative to the shape of the wave, that is, it is like a phase. Consider that ( =0) corresponds to the peak of the travelling pulse shown in figure 4. f the wave travels at velocity v in the direction, then the peak is at =0for =0 and is at = at time t. That is: the fixed point on the wave profile () moves in the following way = = + moving in +x direction moving in -x direction That is, any arbitrary shaped wave form travelling in either direction can be written as: Ψ() =( ) =() Ψ = Ψ = Ψ and Ψ = Ψ Factoring out Ψ = Ψ for the first derivatives gives Ψ = Ψ The sign in this equation is independent of the shape of the waveform but depends on the sign of the wave velocity making it not a generally useful formula. Consider the second derivatives and 2 Ψ 2 2 Ψ 2 Factoring out 2 Ψ 2 = 2 Ψ 2 = 2 Ψ 2 = 2 Ψ 2 =+2 2 Ψ 2 gives 2 Ψ 2 = Ψ 2 This wave equation in one dimension is independent of both the shape of the waveform and the sign of the velocity. There are an infinite number of possible shapes of waves travelling in one dimension, all of these must satisfy this one-dimensional wave equation. The converse is that any function that satisfies this one dimensional wave equation must be a wave in this one dimension. One example of a solution of this one-dimensional wave equations is the sinusoidal wave Ψ() = sin([ ]) = sin( ) where = Thewavenumber = 2 where is the wavelength of the wave, and angular frequency = 2. Note that this satisfies the above wave equation where the wave velocity equals = = The Wave Equation in three dimensions is 2 Ψ 2 Ψ Ψ Ψ 2 = 1 2 Ψ 2 2 There are an infinite number of possible solutions Ψ to this wave equation, any one of which corresponds to a wave motion with velocity v. 111
6 The Wave Equation is applicable to all forms of wave motion, both transverse and longitudinal. That is, it applies to waves on a string, siesmic waves, water waves, sound waves, electromagnetic waves, matter waves, etc. n the subsequent discussion of electromagnetic waves, the Maxwell Equations will be used to deduce a wave equation. The existence of a wave equation is equivalent to proving the existence of electromagnetic waves of any wave form, frequency or wavelength travelling with the velocity given by the wave equation. SUMMARY The Maxwell equations, which are the fundamental laws of electromagnetism, have been obtained. They play a crucial role in most branches of science and engineering. The Maxwell Equations apply to all manifestions of electromagnetism and they contain Einstein s Theory of Special Relativity. For example Maxwell s equations predict that the velocity of light is independent of motion of the frame of reference. Maxwell did not realize this important facet of his equations: it took Einstein to discover this crucial fact which he presented in his seminal 1905 paper entitled On the electrodynamics of moving bodies. Reading assignment: Giancoli, Chapter 32, Review the physics of waves, Giancoli, Chapter
INTRODUCTION MAGNETIC FIELD OF A MOVING POINT CHARGE. Introduction. Magnetic field due to a moving point charge. Units.
 Chapter 9 THE MAGNETC FELD ntroduction Magnetic field due to a moving point charge Units Biot-Savart Law Gauss s Law for magnetism Ampère s Law Maxwell s equations for statics Summary NTRODUCTON Last lecture
Chapter 9 THE MAGNETC FELD ntroduction Magnetic field due to a moving point charge Units Biot-Savart Law Gauss s Law for magnetism Ampère s Law Maxwell s equations for statics Summary NTRODUCTON Last lecture
Maxwell s equations and EM waves. From previous Lecture Time dependent fields and Faraday s Law
 Maxwell s equations and EM waves This Lecture More on Motional EMF and Faraday s law Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves From previous Lecture Time dependent fields and Faraday s Law 1 Radar
Maxwell s equations and EM waves This Lecture More on Motional EMF and Faraday s law Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves From previous Lecture Time dependent fields and Faraday s Law 1 Radar
PHYS 1444 Section 004 Lecture #22
 PHYS 1444 Section 004 Lecture #22 Monday, April 23, 2012 Dr. Extension of Ampere s Law Gauss Law of Magnetism Maxwell s Equations Production of Electromagnetic Waves Today s homework is #13, due 10pm,
PHYS 1444 Section 004 Lecture #22 Monday, April 23, 2012 Dr. Extension of Ampere s Law Gauss Law of Magnetism Maxwell s Equations Production of Electromagnetic Waves Today s homework is #13, due 10pm,
PES 1120 Spring 2014, Spendier Lecture 38/Page 1
 PES 1120 Spring 2014, Spendier Lecture 38/Page 1 Today: Start last chapter 32 - Maxwell s Equations James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879) Scottish mathematical physicist. He united all observations, experiments
PES 1120 Spring 2014, Spendier Lecture 38/Page 1 Today: Start last chapter 32 - Maxwell s Equations James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879) Scottish mathematical physicist. He united all observations, experiments
Discipline Course-I Semester-II
 Maxwell's equation: "Introduction of Displacement Current" Discipline Course-I Semester-II Paper No: Electricity and Magnetism Lesson: Maxwell's equation: "Introduction of Displacement Current" Lesson
Maxwell's equation: "Introduction of Displacement Current" Discipline Course-I Semester-II Paper No: Electricity and Magnetism Lesson: Maxwell's equation: "Introduction of Displacement Current" Lesson
EMF Notes 11; Maxwell s Equations. MAXWELL S EQUATIONS Maxwell s four equations
 MAXWELL S EQUATONS Maxwell s four equations n the 870 s, James Clerk Maxwell showed that four equations constitute a complete description of the electric and magnetic fields, or THE ELECTROMAGNETC FELD
MAXWELL S EQUATONS Maxwell s four equations n the 870 s, James Clerk Maxwell showed that four equations constitute a complete description of the electric and magnetic fields, or THE ELECTROMAGNETC FELD
Lecture 22 Chapter 31 Maxwell s equations
 Lecture 22 Chapter 31 Maxwell s equations Finally, I see the goal, the summit of this Everest Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 31: Section 31.2-4 Let s revisit Ampere s Law a straight wire with current
Lecture 22 Chapter 31 Maxwell s equations Finally, I see the goal, the summit of this Everest Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 31: Section 31.2-4 Let s revisit Ampere s Law a straight wire with current
Describe the forces and torques exerted on an electric dipole in a field.
 Learning Outcomes - PHYS 2015 Electric charges and forces: Describe the electrical nature of matter; Explain how an object can be charged; Distinguish between electrical conductors and insulators and the
Learning Outcomes - PHYS 2015 Electric charges and forces: Describe the electrical nature of matter; Explain how an object can be charged; Distinguish between electrical conductors and insulators and the
Chapter 8. Conservation Laws. 8.3 Magnetic Forces Do No Work
 Chapter 8. Conservation Laws 8.3 Magnetic Forces Do No Work 8.2 Momentum of EM fields 8.2.1 Newton's Third Law in Electrodynamics Consider two charges, q 1 and q 2, moving with speeds v 1 and v 2 magnetic
Chapter 8. Conservation Laws 8.3 Magnetic Forces Do No Work 8.2 Momentum of EM fields 8.2.1 Newton's Third Law in Electrodynamics Consider two charges, q 1 and q 2, moving with speeds v 1 and v 2 magnetic
Unit-1 Electrostatics-1
 1. Describe about Co-ordinate Systems. Co-ordinate Systems Unit-1 Electrostatics-1 In order to describe the spatial variations of the quantities, we require using appropriate coordinate system. A point
1. Describe about Co-ordinate Systems. Co-ordinate Systems Unit-1 Electrostatics-1 In order to describe the spatial variations of the quantities, we require using appropriate coordinate system. A point
Introduction to Electromagnetism
 Introduction to Electromagnetism Electric Field Lines If a charge feels an electrostatic force (Coulombic Force), it is said to be in an electric field. We like to represent electric fields with lines.
Introduction to Electromagnetism Electric Field Lines If a charge feels an electrostatic force (Coulombic Force), it is said to be in an electric field. We like to represent electric fields with lines.
E or B? It Depends on Your Perspective
 E or B? It Depends on Your Perspective Alec sees a moving charge, and he knows that this creates a magnetic field. From Brittney s perspective, the charge is at rest, so the magnetic field is zero. Is
E or B? It Depends on Your Perspective Alec sees a moving charge, and he knows that this creates a magnetic field. From Brittney s perspective, the charge is at rest, so the magnetic field is zero. Is
4. The last equation is Ampère's Law, which ultimately came from our derivation of the magnetic field from Coulomb's Law and special relativity.
 lectromagnetic Theory Prof Ruiz, UNC Asheville, doctorphys on YouTube Chapter G Notes Maxwell's quations: Integral Form G1 No Magnetic Monopoles Q da ε da dl dl µ I The equations at the left summarize
lectromagnetic Theory Prof Ruiz, UNC Asheville, doctorphys on YouTube Chapter G Notes Maxwell's quations: Integral Form G1 No Magnetic Monopoles Q da ε da dl dl µ I The equations at the left summarize
FLUX OF VECTOR FIELD INTRODUCTION
 Chapter 3 GAUSS LAW ntroduction Flux of vector field Solid angle Gauss s Law Symmetry Spherical symmetry Cylindrical symmetry Plane symmetry Superposition of symmetric geometries Motion of point charges
Chapter 3 GAUSS LAW ntroduction Flux of vector field Solid angle Gauss s Law Symmetry Spherical symmetry Cylindrical symmetry Plane symmetry Superposition of symmetric geometries Motion of point charges
Intermission Page 343, Griffith
 Intermission Page 343, Griffith Chapter 8. Conservation Laws (Page 346, Griffith) Lecture : Electromagnetic Power Flow Flow of Electromagnetic Power Electromagnetic waves transport throughout space the
Intermission Page 343, Griffith Chapter 8. Conservation Laws (Page 346, Griffith) Lecture : Electromagnetic Power Flow Flow of Electromagnetic Power Electromagnetic waves transport throughout space the
Introduction to Electromagnetic Theory
 Introduction to Electromagnetic Theory Lecture topics Laws of magnetism and electricity Meaning of Maxwell s equations Solution of Maxwell s equations Electromagnetic radiation: wave model James Clerk
Introduction to Electromagnetic Theory Lecture topics Laws of magnetism and electricity Meaning of Maxwell s equations Solution of Maxwell s equations Electromagnetic radiation: wave model James Clerk
where the last equality follows from the divergence theorem. Now since we did this for an arbitrary volume τ, it must hold locally:
 8 Electrodynamics Read: Boas Ch. 6, particularly sec. 10 and 11. 8.1 Maxwell equations Some of you may have seen Maxwell s equations on t-shirts or encountered them briefly in electromagnetism courses.
8 Electrodynamics Read: Boas Ch. 6, particularly sec. 10 and 11. 8.1 Maxwell equations Some of you may have seen Maxwell s equations on t-shirts or encountered them briefly in electromagnetism courses.
Lecture Sound Waves Review. Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org. Force on a Charge Moving in a Magnetic Field
 Lecture 1101 Sound Waves Review Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org Force on a Charge Moving in a Magnetic Field A charge moving in a magnetic field can have a magnetic force exerted by the B-field.
Lecture 1101 Sound Waves Review Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org Force on a Charge Moving in a Magnetic Field A charge moving in a magnetic field can have a magnetic force exerted by the B-field.
Chapter 5. Magnetostatics
 Chapter 5. Magnetostatics 5.1 The Lorentz Force Law 5.1.1 Magnetic Fields Consider the forces between charges in motion Attraction of parallel currents and Repulsion of antiparallel ones: How do you explain
Chapter 5. Magnetostatics 5.1 The Lorentz Force Law 5.1.1 Magnetic Fields Consider the forces between charges in motion Attraction of parallel currents and Repulsion of antiparallel ones: How do you explain
AP Physics C Electricity and Magnetism
 AP Physics C Electricity and Magnetism Course overview This is a calculus based course in physics. The course is the equivalent of an introductory engineering course in Physics. The main objective of the
AP Physics C Electricity and Magnetism Course overview This is a calculus based course in physics. The course is the equivalent of an introductory engineering course in Physics. The main objective of the
Electromagnetic Waves
 Lecture 20 Chapter 34 Physics II Electromagnetic Waves Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Let s finish climbing our EM mountain. Maxwell s equations Let s revisit
Lecture 20 Chapter 34 Physics II Electromagnetic Waves Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Let s finish climbing our EM mountain. Maxwell s equations Let s revisit
Electromagnetism. Christopher R Prior. ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory
 lectromagnetism Christopher R Prior Fellow and Tutor in Mathematics Trinity College, Oxford ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory Contents Review of Maxwell s equations and Lorentz Force
lectromagnetism Christopher R Prior Fellow and Tutor in Mathematics Trinity College, Oxford ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory Contents Review of Maxwell s equations and Lorentz Force
Physics For Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach 3 rd Edition, AP Edition, 2013 Knight
 For Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach 3 rd Edition, AP Edition, 2013 Knight To the Advanced Placement Topics for C *Advanced Placement, Advanced Placement Program, AP, and Pre-AP are registered
For Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach 3 rd Edition, AP Edition, 2013 Knight To the Advanced Placement Topics for C *Advanced Placement, Advanced Placement Program, AP, and Pre-AP are registered
CHAPTER 7 ELECTRODYNAMICS
 CHAPTER 7 ELECTRODYNAMICS Outlines 1. Electromotive Force 2. Electromagnetic Induction 3. Maxwell s Equations Michael Faraday James C. Maxwell 2 Summary of Electrostatics and Magnetostatics ρ/ε This semester,
CHAPTER 7 ELECTRODYNAMICS Outlines 1. Electromotive Force 2. Electromagnetic Induction 3. Maxwell s Equations Michael Faraday James C. Maxwell 2 Summary of Electrostatics and Magnetostatics ρ/ε This semester,
2426 Required Topics (May 4, 2012 draft) Halliday, FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS, 9e Required topics are in bold text. Optional topics are in normal text.
 2426 Required Topics (May 4, 2012 draft) Halliday, FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS, 9e Required topics are in bold text. Optional topics are in normal text. Chapter 21 Electric Charge 21-1 What Is Physics? 21-2
2426 Required Topics (May 4, 2012 draft) Halliday, FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS, 9e Required topics are in bold text. Optional topics are in normal text. Chapter 21 Electric Charge 21-1 What Is Physics? 21-2
Lecture Sound Waves EM Waves. Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org. The Doppler Effect 11/11/2014
 Lecture 1102 Sound Waves EM Waves Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org The Doppler Effect The Doppler effect (or Doppler shift) is the change in frequency (or wavelength) of a wave for an observer moving
Lecture 1102 Sound Waves EM Waves Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org The Doppler Effect The Doppler effect (or Doppler shift) is the change in frequency (or wavelength) of a wave for an observer moving
CHAPTER 8 CONSERVATION LAWS
 CHAPTER 8 CONSERVATION LAWS Outlines 1. Charge and Energy 2. The Poynting s Theorem 3. Momentum 4. Angular Momentum 2 Conservation of charge and energy The net amount of charges in a volume V is given
CHAPTER 8 CONSERVATION LAWS Outlines 1. Charge and Energy 2. The Poynting s Theorem 3. Momentum 4. Angular Momentum 2 Conservation of charge and energy The net amount of charges in a volume V is given
Maxwell s equations. Kyoto. James Clerk Maxwell. Physics 122. James Clerk Maxwell ( ) Unification of electrical and magnetic interactions
 Maxwell s equations Physics /5/ Lecture XXIV Kyoto /5/ Lecture XXIV James Clerk Maxwell James Clerk Maxwell (83 879) Unification of electrical and magnetic interactions /5/ Lecture XXIV 3 Φ = da = Q ε
Maxwell s equations Physics /5/ Lecture XXIV Kyoto /5/ Lecture XXIV James Clerk Maxwell James Clerk Maxwell (83 879) Unification of electrical and magnetic interactions /5/ Lecture XXIV 3 Φ = da = Q ε
AP Physics C Mechanics Objectives
 AP Physics C Mechanics Objectives I. KINEMATICS A. Motion in One Dimension 1. The relationships among position, velocity and acceleration a. Given a graph of position vs. time, identify or sketch a graph
AP Physics C Mechanics Objectives I. KINEMATICS A. Motion in One Dimension 1. The relationships among position, velocity and acceleration a. Given a graph of position vs. time, identify or sketch a graph
CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY NH-67, TRICHY MAIN ROAD, PULIYUR, C.F , KARUR DT.
 CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY NH-67, TRICHY MAIN ROAD, PULIYUR, C.F. 639 114, KARUR DT. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING COURSE MATERIAL Subject Name: Electromagnetic
CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY NH-67, TRICHY MAIN ROAD, PULIYUR, C.F. 639 114, KARUR DT. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING COURSE MATERIAL Subject Name: Electromagnetic
The Steady Magnetic Fields
 The Steady Magnetic Fields Prepared By Dr. Eng. Sherif Hekal Assistant Professor Electronics and Communications Engineering 1/8/017 1 Agenda Intended Learning Outcomes Why Study Magnetic Field Biot-Savart
The Steady Magnetic Fields Prepared By Dr. Eng. Sherif Hekal Assistant Professor Electronics and Communications Engineering 1/8/017 1 Agenda Intended Learning Outcomes Why Study Magnetic Field Biot-Savart
PH 1120 Term D, 2017
 PH 1120 Term D, 2017 Study Guide 4 / Objective 13 The Biot-Savart Law \ / a) Calculate the contribution made to the magnetic field at a \ / specified point by a current element, given the current, location,
PH 1120 Term D, 2017 Study Guide 4 / Objective 13 The Biot-Savart Law \ / a) Calculate the contribution made to the magnetic field at a \ / specified point by a current element, given the current, location,
Lecture 13 Notes, Electromagnetic Theory I Dr. Christopher S. Baird University of Massachusetts Lowell
 Lecture 13 Notes, Electromagnetic Theory I Dr. Christopher S. Baird University of Massachusetts Lowell 1. Static Equations and Faraday's Law - The two fundamental equations of electrostatics are shown
Lecture 13 Notes, Electromagnetic Theory I Dr. Christopher S. Baird University of Massachusetts Lowell 1. Static Equations and Faraday's Law - The two fundamental equations of electrostatics are shown
Electromagnetic Field Theory Chapter 9: Time-varying EM Fields
 Electromagnetic Field Theory Chapter 9: Time-varying EM Fields Faraday s law of induction We have learned that a constant current induces magnetic field and a constant charge (or a voltage) makes an electric
Electromagnetic Field Theory Chapter 9: Time-varying EM Fields Faraday s law of induction We have learned that a constant current induces magnetic field and a constant charge (or a voltage) makes an electric
Here are some internet links to instructional and necessary background materials:
 The general areas covered by the University Physics course are subdivided into major categories. For each category, answer the conceptual questions in the form of a short paragraph. Although fewer topics
The general areas covered by the University Physics course are subdivided into major categories. For each category, answer the conceptual questions in the form of a short paragraph. Although fewer topics
Lecture 36: WED 18 NOV CH32: Maxwell s Equations I
 Physics 2113 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 36: WED 18 NOV H32: Maxwell s Equations I James lerk Maxwell (1831-1879) Maxwell I: Gauss Law for E-Fields: charges produce electric fields, field lines start and
Physics 2113 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 36: WED 18 NOV H32: Maxwell s Equations I James lerk Maxwell (1831-1879) Maxwell I: Gauss Law for E-Fields: charges produce electric fields, field lines start and
Along with C1 the magnetic field is also observed at location C 2 though no current is threading through this loop.
 Displacement current British physicist James C. Maxwell gave final shape to all phenomenon connecting electricity and magnetism. He noticed an inconsistency in Ampere s Law connecting Electric current
Displacement current British physicist James C. Maxwell gave final shape to all phenomenon connecting electricity and magnetism. He noticed an inconsistency in Ampere s Law connecting Electric current
Slide 1 / 24. Electromagnetic Induction 2011 by Bryan Pflueger
 Slide 1 / 24 Electromagnetic Induction 2011 by Bryan Pflueger Slide 2 / 24 Induced Currents If we have a galvanometer attached to a coil of wire we can induce a current simply by changing the magnetic
Slide 1 / 24 Electromagnetic Induction 2011 by Bryan Pflueger Slide 2 / 24 Induced Currents If we have a galvanometer attached to a coil of wire we can induce a current simply by changing the magnetic
AP Physics C. Magnetism - Term 4
 AP Physics C Magnetism - Term 4 Interest Packet Term Introduction: AP Physics has been specifically designed to build on physics knowledge previously acquired for a more in depth understanding of the world
AP Physics C Magnetism - Term 4 Interest Packet Term Introduction: AP Physics has been specifically designed to build on physics knowledge previously acquired for a more in depth understanding of the world
TECHNO INDIA BATANAGAR
 TECHNO INDIA BATANAGAR ( DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING) QUESTION BANK- 2018 1.Vector Calculus Assistant Professor 9432183958.mukherjee@tib.edu.in 1. When the operator operates on
TECHNO INDIA BATANAGAR ( DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING) QUESTION BANK- 2018 1.Vector Calculus Assistant Professor 9432183958.mukherjee@tib.edu.in 1. When the operator operates on
INTRODUCTION. Introduction. Discrete charges: Electric dipole. Continuous charge distributions. Flux of a vector field
 Chapter 2 THE ELECTRC FELD ntroduction Discrete charges: Electric dipole Continuous charge distributions Flux of a vector field Flux of an electric field for a spherical Gaussian surface concentric to
Chapter 2 THE ELECTRC FELD ntroduction Discrete charges: Electric dipole Continuous charge distributions Flux of a vector field Flux of an electric field for a spherical Gaussian surface concentric to
The Steady Magnetic Field LECTURE 7
 The Steady Magnetic Field LECTURE 7 Learning Objectives Understand the Biot-Savart Law Understand the Ampere s Circuital Law Explain the Application of Ampere s Law Motivating the Magnetic Field Concept:
The Steady Magnetic Field LECTURE 7 Learning Objectives Understand the Biot-Savart Law Understand the Ampere s Circuital Law Explain the Application of Ampere s Law Motivating the Magnetic Field Concept:
Final Exam Concept Map
 Final Exam Concept Map Rule of thumb to study for any comprehensive final exam - start with what you know - look at the quiz problems. If you did not do well on the quizzes, you should certainly learn
Final Exam Concept Map Rule of thumb to study for any comprehensive final exam - start with what you know - look at the quiz problems. If you did not do well on the quizzes, you should certainly learn
ELECTRO MAGNETIC FIELDS
 SET - 1 1. a) State and explain Gauss law in differential form and also list the limitations of Guess law. b) A square sheet defined by -2 x 2m, -2 y 2m lies in the = -2m plane. The charge density on the
SET - 1 1. a) State and explain Gauss law in differential form and also list the limitations of Guess law. b) A square sheet defined by -2 x 2m, -2 y 2m lies in the = -2m plane. The charge density on the
Magnetostatics. Lecture 23: Electromagnetic Theory. Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay
 Magnetostatics Lecture 23: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay Magnetostatics Up until now, we have been discussing electrostatics, which deals with physics
Magnetostatics Lecture 23: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay Magnetostatics Up until now, we have been discussing electrostatics, which deals with physics
r r 1 r r 1 2 = q 1 p = qd and it points from the negative charge to the positive charge.
 MP204, Important Equations page 1 Below is a list of important equations that we meet in our study of Electromagnetism in the MP204 module. For your exam, you are expected to understand all of these, and
MP204, Important Equations page 1 Below is a list of important equations that we meet in our study of Electromagnetism in the MP204 module. For your exam, you are expected to understand all of these, and
Maxwell Equations: Electromagnetic Waves
 Maxwell Equations: Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s Equations contain the wave equation The velocity of electromagnetic waves: c = 2.99792458 x 10 8 m/s The relationship between E and B in an EM wave Energy
Maxwell Equations: Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s Equations contain the wave equation The velocity of electromagnetic waves: c = 2.99792458 x 10 8 m/s The relationship between E and B in an EM wave Energy
The Steady Magnetic Field
 The Steady Magnetic Field Prepared By Dr. Eng. Sherif Hekal Assistant Professor Electronics and Communications Engineering 1/13/016 1 Agenda Intended Learning Outcomes Why Study Magnetic Field Biot-Savart
The Steady Magnetic Field Prepared By Dr. Eng. Sherif Hekal Assistant Professor Electronics and Communications Engineering 1/13/016 1 Agenda Intended Learning Outcomes Why Study Magnetic Field Biot-Savart
1 Maxwell s Equations
 PHYS 280 Lecture problems outline Spring 2015 Electricity and Magnetism We previously hinted a links between electricity and magnetism, finding that one can induce electric fields by changing the flux
PHYS 280 Lecture problems outline Spring 2015 Electricity and Magnetism We previously hinted a links between electricity and magnetism, finding that one can induce electric fields by changing the flux
Physics 202, Lecture 13. Today s Topics. Magnetic Forces: Hall Effect (Ch. 27.8)
 Physics 202, Lecture 13 Today s Topics Magnetic Forces: Hall Effect (Ch. 27.8) Sources of the Magnetic Field (Ch. 28) B field of infinite wire Force between parallel wires Biot-Savart Law Examples: ring,
Physics 202, Lecture 13 Today s Topics Magnetic Forces: Hall Effect (Ch. 27.8) Sources of the Magnetic Field (Ch. 28) B field of infinite wire Force between parallel wires Biot-Savart Law Examples: ring,
March 11. Physics 272. Spring Prof. Philip von Doetinchem
 Physics 272 March 11 Spring 2014 http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~philipvd/pvd_14_spring_272_uhm.html Prof. Philip von Doetinchem philipvd@hawaii.edu Phys272 - Spring 14 - von Doetinchem - 32 Summary Magnetic
Physics 272 March 11 Spring 2014 http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~philipvd/pvd_14_spring_272_uhm.html Prof. Philip von Doetinchem philipvd@hawaii.edu Phys272 - Spring 14 - von Doetinchem - 32 Summary Magnetic
Magnetic Induction Faraday, Lenz, Mutual & Self Inductance Maxwell s Eqns, E-M waves. Reading Journals for Tuesday from table(s)
 PHYS 2015 -- Week 12 Magnetic Induction Faraday, Lenz, Mutual & Self Inductance Maxwell s Eqns, E-M waves Reading Journals for Tuesday from table(s) WebAssign due Friday night For exclusive use in PHYS
PHYS 2015 -- Week 12 Magnetic Induction Faraday, Lenz, Mutual & Self Inductance Maxwell s Eqns, E-M waves Reading Journals for Tuesday from table(s) WebAssign due Friday night For exclusive use in PHYS
Chapter Three: Propagation of light waves
 Chapter Three Propagation of Light Waves CHAPTER OUTLINE 3.1 Maxwell s Equations 3.2 Physical Significance of Maxwell s Equations 3.3 Properties of Electromagnetic Waves 3.4 Constitutive Relations 3.5
Chapter Three Propagation of Light Waves CHAPTER OUTLINE 3.1 Maxwell s Equations 3.2 Physical Significance of Maxwell s Equations 3.3 Properties of Electromagnetic Waves 3.4 Constitutive Relations 3.5
UNIT-I INTRODUCTION TO COORDINATE SYSTEMS AND VECTOR ALGEBRA
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : EMF(16EE214) Sem: II-B.Tech & II-Sem Course & Branch: B.Tech - EEE Year
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : EMF(16EE214) Sem: II-B.Tech & II-Sem Course & Branch: B.Tech - EEE Year
Lecture 35. PHYC 161 Fall 2016
 Lecture 35 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Induced electric fields A long, thin solenoid is encircled by a circular conducting loop. Electric field in the loop is what must drive the current. When the solenoid current
Lecture 35 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Induced electric fields A long, thin solenoid is encircled by a circular conducting loop. Electric field in the loop is what must drive the current. When the solenoid current
Mansfield Independent School District AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Year at a Glance
 Mansfield Independent School District AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Year at a Glance First Six-Weeks Second Six-Weeks Third Six-Weeks Lab safety Lab practices and ethical practices Math and Calculus
Mansfield Independent School District AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Year at a Glance First Six-Weeks Second Six-Weeks Third Six-Weeks Lab safety Lab practices and ethical practices Math and Calculus
ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD
 UNIT-III INTRODUCTION: In our study of static fields so far, we have observed that static electric fields are produced by electric charges, static magnetic fields are produced by charges in motion or by
UNIT-III INTRODUCTION: In our study of static fields so far, we have observed that static electric fields are produced by electric charges, static magnetic fields are produced by charges in motion or by
Haus, Hermann A., and James R. Melcher. Electromagnetic Fields and Energy. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, ISBN:
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu Haus, Hermann A., and James R. Melcher. Electromagnetic Fields and Energy. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1989. ISBN: 9780132490207. Please use the following
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu Haus, Hermann A., and James R. Melcher. Electromagnetic Fields and Energy. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1989. ISBN: 9780132490207. Please use the following
October 23. Physics 272. Fall Prof. Philip von Doetinchem
 Physics 272 October 23 Fall 2014 http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~philipvd/pvd_14_fall_272_uhm.html Prof. Philip von Doetinchem philipvd@hawaii.edu Phys272 - Fall 14 - von Doetinchem - 170 Motional electromotive
Physics 272 October 23 Fall 2014 http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~philipvd/pvd_14_fall_272_uhm.html Prof. Philip von Doetinchem philipvd@hawaii.edu Phys272 - Fall 14 - von Doetinchem - 170 Motional electromotive
UNIT-III Maxwell's equations (Time varying fields)
 UNIT-III Maxwell's equations (Time varying fields) Faraday s law, transformer emf &inconsistency of ampere s law Displacement current density Maxwell s equations in final form Maxwell s equations in word
UNIT-III Maxwell's equations (Time varying fields) Faraday s law, transformer emf &inconsistency of ampere s law Displacement current density Maxwell s equations in final form Maxwell s equations in word
CHAPTER 29: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
 CHAPTER 29: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION So far we have seen that electric charges are the source for both electric and magnetic fields. We have also seen that these fields can exert forces on other electric
CHAPTER 29: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION So far we have seen that electric charges are the source for both electric and magnetic fields. We have also seen that these fields can exert forces on other electric
Lecture 27: MON 26 OCT Magnetic Fields Due to Currents II
 Physics 212 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 27: MON 26 OCT Magnetic Fields Due to Currents II Jean-Baptiste Biot (1774-1862) Felix Savart (1791 1841) Electric Current: A Source of Magnetic Field Observation:
Physics 212 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 27: MON 26 OCT Magnetic Fields Due to Currents II Jean-Baptiste Biot (1774-1862) Felix Savart (1791 1841) Electric Current: A Source of Magnetic Field Observation:
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS Q-1. Light of uniform intensity shines perpendicularly on a totally absorbing surface, fully illuminating the surface. If the area of the surface is decreased,
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS Q-1. Light of uniform intensity shines perpendicularly on a totally absorbing surface, fully illuminating the surface. If the area of the surface is decreased,
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUB.NAME : ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS SUBJECT CODE : EC 2253 YEAR / SEMESTER : II / IV UNIT- I - STATIC ELECTRIC
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUB.NAME : ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS SUBJECT CODE : EC 2253 YEAR / SEMESTER : II / IV UNIT- I - STATIC ELECTRIC
Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts
 NE 2 Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts Important Laws in Electromagnetics Coulomb s Law (1785) Gauss s Law (1839) Ampere s Law (1827) Ohm s Law (1827) Kirchhoff s Law (1845) Biot-Savart Law (1820) Faradays
NE 2 Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts Important Laws in Electromagnetics Coulomb s Law (1785) Gauss s Law (1839) Ampere s Law (1827) Ohm s Law (1827) Kirchhoff s Law (1845) Biot-Savart Law (1820) Faradays
Module 3: Electromagnetism
 Module 3: Electromagnetism Lecture - Magnetic Field Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Electric current is the source of magnetic field. When a charged particle is placed in an electromagnetic
Module 3: Electromagnetism Lecture - Magnetic Field Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Electric current is the source of magnetic field. When a charged particle is placed in an electromagnetic
fiziks Institute for NET/JRF, GATE, IIT-JAM, JEST, TIFR and GRE in PHYSICAL SCIENCES
 Content-ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 1. Electrostatics (1-58) 1.1 Coulomb s Law and Superposition Principle 1.1.1 Electric field 1.2 Gauss s law 1.2.1 Field lines and Electric flux 1.2.2 Applications 1.3
Content-ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 1. Electrostatics (1-58) 1.1 Coulomb s Law and Superposition Principle 1.1.1 Electric field 1.2 Gauss s law 1.2.1 Field lines and Electric flux 1.2.2 Applications 1.3
Electromagnetic Theory Prof. D. K. Ghosh Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Electromagnetic Theory Prof. D. K. Ghosh Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module -4 Time Varying Lecture - 29 Faraday s Law and Inductance In the previous lecture, we had started
Electromagnetic Theory Prof. D. K. Ghosh Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module -4 Time Varying Lecture - 29 Faraday s Law and Inductance In the previous lecture, we had started
Chapter 27 Sources of Magnetic Field
 Chapter 27 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents). Ampere s Law
Chapter 27 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents). Ampere s Law
we can said that matter can be regarded as composed of three kinds of elementary particles; proton, neutron (no charge), and electron.
 Physics II we can said that matter can be regarded as composed of three kinds of elementary particles; proton, neutron (no charge), and electron. Particle Symbol Charge (e) Mass (kg) Proton P +1 1.67
Physics II we can said that matter can be regarded as composed of three kinds of elementary particles; proton, neutron (no charge), and electron. Particle Symbol Charge (e) Mass (kg) Proton P +1 1.67
Where k = 1. The electric field produced by a point charge is given by
 Ch 21 review: 1. Electric charge: Electric charge is a property of a matter. There are two kinds of charges, positive and negative. Charges of the same sign repel each other. Charges of opposite sign attract.
Ch 21 review: 1. Electric charge: Electric charge is a property of a matter. There are two kinds of charges, positive and negative. Charges of the same sign repel each other. Charges of opposite sign attract.
Calculus Relationships in AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism
 C: Electricity This chapter focuses on some of the quantitative skills that are important in your C: Mechanics course. These are not all of the skills that you will learn, practice, and apply during the
C: Electricity This chapter focuses on some of the quantitative skills that are important in your C: Mechanics course. These are not all of the skills that you will learn, practice, and apply during the
Electrodynamics Exam 3 and Final Exam Sample Exam Problems Dr. Colton, Fall 2016
 Electrodynamics Exam 3 and Final Exam Sample Exam Problems Dr. Colton, Fall 016 Multiple choice conceptual questions 1. An infinitely long, straight wire carrying current passes through the center of a
Electrodynamics Exam 3 and Final Exam Sample Exam Problems Dr. Colton, Fall 016 Multiple choice conceptual questions 1. An infinitely long, straight wire carrying current passes through the center of a
Chapter 30. Sources of the Magnetic Field Amperes and Biot-Savart Laws
 Chapter 30 Sources of the Magnetic Field Amperes and Biot-Savart Laws F B on a Charge Moving in a Magnetic Field Magnitude proportional to charge and speed of the particle Direction depends on the velocity
Chapter 30 Sources of the Magnetic Field Amperes and Biot-Savart Laws F B on a Charge Moving in a Magnetic Field Magnitude proportional to charge and speed of the particle Direction depends on the velocity
Magnetostatic Fields. Dr. Talal Skaik Islamic University of Gaza Palestine
 Magnetostatic Fields Dr. Talal Skaik Islamic University of Gaza Palestine 01 Introduction In chapters 4 to 6, static electric fields characterized by E or D (D=εE) were discussed. This chapter considers
Magnetostatic Fields Dr. Talal Skaik Islamic University of Gaza Palestine 01 Introduction In chapters 4 to 6, static electric fields characterized by E or D (D=εE) were discussed. This chapter considers
ECE 3209 Electromagnetic Fields Final Exam Example. University of Virginia Solutions
 ECE 3209 Electromagnetic Fields Final Exam Example University of Virginia Solutions (print name above) This exam is closed book and closed notes. Please perform all work on the exam sheets in a neat and
ECE 3209 Electromagnetic Fields Final Exam Example University of Virginia Solutions (print name above) This exam is closed book and closed notes. Please perform all work on the exam sheets in a neat and
Michael Faraday. Chapter 31. EMF Produced by a Changing Magnetic Field, 1. Induction. Faraday s Law
 Michael Faraday Chapter 31 Faraday s Law Great experimental physicist and chemist 1791 1867 Contributions to early electricity include: Invention of motor, generator, and transformer Electromagnetic induction
Michael Faraday Chapter 31 Faraday s Law Great experimental physicist and chemist 1791 1867 Contributions to early electricity include: Invention of motor, generator, and transformer Electromagnetic induction
Today in Physics 218: the Maxwell equations
 Today in Physics 218: the Maxwell equations Beyond magnetoquasistatics Displacement current, and Maxwell s repair of Ampère s Law The Maxwell equations Symmetry of the equations: magnetic monopoles? Rainbow
Today in Physics 218: the Maxwell equations Beyond magnetoquasistatics Displacement current, and Maxwell s repair of Ampère s Law The Maxwell equations Symmetry of the equations: magnetic monopoles? Rainbow
AP Physics C. Electricity - Term 3
 AP Physics C Electricity - Term 3 Interest Packet Term Introduction: AP Physics has been specifically designed to build on physics knowledge previously acquired for a more in depth understanding of the
AP Physics C Electricity - Term 3 Interest Packet Term Introduction: AP Physics has been specifically designed to build on physics knowledge previously acquired for a more in depth understanding of the
UNIT I ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS
 UNIT I ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS 1) Define electric potential and potential difference. 2) Name few applications of gauss law in electrostatics. 3) State point form of Ohm s Law. 4) State Divergence Theorem.
UNIT I ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS 1) Define electric potential and potential difference. 2) Name few applications of gauss law in electrostatics. 3) State point form of Ohm s Law. 4) State Divergence Theorem.
PHYSICS. Chapter 24 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 24 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 24 Gauss s Law IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about and apply Gauss s law. Slide 24-2 Chapter
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 24 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 24 Gauss s Law IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about and apply Gauss s law. Slide 24-2 Chapter
Last Homework. Reading: Chap. 33 and Chap. 33. Suggested exercises: 33.1, 33.3, 33.5, 33.7, 33.9, 33.11, 33.13, 33.15,
 Chapter 33. Electromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic induction is the scientific principle that underlies many modern technologies, from the generation of electricity to communications and data storage.
Chapter 33. Electromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic induction is the scientific principle that underlies many modern technologies, from the generation of electricity to communications and data storage.
cancel each other out. Thus, we only need to consider magnetic field produced by wire carrying current 2.
 PC1143 2011/2012 Exam Solutions Question 1 a) Assumption: shells are conductors. Notes: the system given is a capacitor. Make use of spherical symmetry. Energy density, =. in this case means electric field
PC1143 2011/2012 Exam Solutions Question 1 a) Assumption: shells are conductors. Notes: the system given is a capacitor. Make use of spherical symmetry. Energy density, =. in this case means electric field
Physics GRE: Electromagnetism. G. J. Loges 1. University of Rochester Dept. of Physics & Astronomy. xkcd.com/567/
 Physics GRE: Electromagnetism G. J. Loges University of Rochester Dept. of Physics & stronomy xkcd.com/567/ c Gregory Loges, 206 Contents Electrostatics 2 Magnetostatics 2 3 Method of Images 3 4 Lorentz
Physics GRE: Electromagnetism G. J. Loges University of Rochester Dept. of Physics & stronomy xkcd.com/567/ c Gregory Loges, 206 Contents Electrostatics 2 Magnetostatics 2 3 Method of Images 3 4 Lorentz
Motional Electromotive Force
 Motional Electromotive Force The charges inside the moving conductive rod feel the Lorentz force The charges drift toward the point a of the rod The accumulating excess charges at point a create an electric
Motional Electromotive Force The charges inside the moving conductive rod feel the Lorentz force The charges drift toward the point a of the rod The accumulating excess charges at point a create an electric
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY
 DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY SIRUVACHUR-621113 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS DEPARTMENT 2 MARK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS SUBJECT CODE: EE 6302 SUBJECT NAME: ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY SIRUVACHUR-621113 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS DEPARTMENT 2 MARK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS SUBJECT CODE: EE 6302 SUBJECT NAME: ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY
Chapter 29: Magnetic Fields Due to Currents. PHY2049: Chapter 29 1
 Chapter 29: Magnetic Fields Due to Currents PHY2049: Chapter 29 1 Law of Magnetism Unlike the law of static electricity, comes in two pieces Piece 1: Effect of B field on moving charge r r F = qv B (Chapt.
Chapter 29: Magnetic Fields Due to Currents PHY2049: Chapter 29 1 Law of Magnetism Unlike the law of static electricity, comes in two pieces Piece 1: Effect of B field on moving charge r r F = qv B (Chapt.
The ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD
 The ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD In the year 2003, it is still the case that the most important single scientific development for our world has been the understanding of the EM field. Although many played a role
The ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD In the year 2003, it is still the case that the most important single scientific development for our world has been the understanding of the EM field. Although many played a role
Lecture 33. PHYC 161 Fall 2016
 Lecture 33 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Faraday s law of induction When the magnetic flux through a single closed loop changes with time, there is an induced emf that can drive a current around the loop: Recall
Lecture 33 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Faraday s law of induction When the magnetic flux through a single closed loop changes with time, there is an induced emf that can drive a current around the loop: Recall
Worked Examples Set 2
 Worked Examples Set 2 Q.1. Application of Maxwell s eqns. [Griffiths Problem 7.42] In a perfect conductor the conductivity σ is infinite, so from Ohm s law J = σe, E = 0. Any net charge must be on the
Worked Examples Set 2 Q.1. Application of Maxwell s eqns. [Griffiths Problem 7.42] In a perfect conductor the conductivity σ is infinite, so from Ohm s law J = σe, E = 0. Any net charge must be on the
Inductors Maxwell s equations
 Lecture 19 Chapter 34 Physics II Inductors Maxwell s equations Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Inductors Inductors (solenoids) store potential energy in a form
Lecture 19 Chapter 34 Physics II Inductors Maxwell s equations Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Inductors Inductors (solenoids) store potential energy in a form
MARKING SCHEME SET 55/1/RU Q. No. Expected Answer / Value Points Marks Total Marks
 MARKING SCHEME SET 55//RU Q. No. Expected Answer / Value Points Marks Total Marks Set, Q Set2,Q5 Set,Q4 Section A Self inductance of the coil is numerically equal to magnetic flux linked with it when unit
MARKING SCHEME SET 55//RU Q. No. Expected Answer / Value Points Marks Total Marks Set, Q Set2,Q5 Set,Q4 Section A Self inductance of the coil is numerically equal to magnetic flux linked with it when unit
Maxwell s Equations & Hertz Waves
 Maxwell s Equations & Hertz Waves XI. Maxwell & Electromagnetic Waves A. Maxwell s Equations Dr. Bill Pezzaglia B. Hertz Waves & Poynting C. Polarization Updated: 3Aug5 A. Maxwell s Equations 3. Hints
Maxwell s Equations & Hertz Waves XI. Maxwell & Electromagnetic Waves A. Maxwell s Equations Dr. Bill Pezzaglia B. Hertz Waves & Poynting C. Polarization Updated: 3Aug5 A. Maxwell s Equations 3. Hints
Electromagnetic Field Theory (EMT) Lecture # 25
 Electromagnetic Field Theory (EMT) Lecture # 25 1) Transformer and Motional EMFs 2) Displacement Current 3) Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Waves & Applications Time Varying Fields Until now, we have
Electromagnetic Field Theory (EMT) Lecture # 25 1) Transformer and Motional EMFs 2) Displacement Current 3) Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Waves & Applications Time Varying Fields Until now, we have
Magnetic Fields Part 2: Sources of Magnetic Fields
 Magnetic Fields Part 2: Sources of Magnetic Fields Last modified: 08/01/2018 Contents Links What Causes a Magnetic Field? Moving Charges Right Hand Grip Rule Permanent Magnets Biot-Savart Law Magnetic
Magnetic Fields Part 2: Sources of Magnetic Fields Last modified: 08/01/2018 Contents Links What Causes a Magnetic Field? Moving Charges Right Hand Grip Rule Permanent Magnets Biot-Savart Law Magnetic
EECS 117. Lecture 17: Magnetic Forces/Torque, Faraday s Law. Prof. Niknejad. University of California, Berkeley
 University of California, Berkeley EECS 117 Lecture 17 p. 1/? EECS 117 Lecture 17: Magnetic Forces/Torque, Faraday s Law Prof. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley University of California, Berkeley
University of California, Berkeley EECS 117 Lecture 17 p. 1/? EECS 117 Lecture 17: Magnetic Forces/Torque, Faraday s Law Prof. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley University of California, Berkeley
Chapter 7. Electrodynamics
 Chapter 7. Electrodynamics 7.3 Maxwell's Equations 7.3.1 Electrodynamics Before Maxwell So far, in the electromagnetic theory But, there is a fatal inconsistency (Divergence of curl = 0) ( = 0 ) It s OK.
Chapter 7. Electrodynamics 7.3 Maxwell's Equations 7.3.1 Electrodynamics Before Maxwell So far, in the electromagnetic theory But, there is a fatal inconsistency (Divergence of curl = 0) ( = 0 ) It s OK.
Maxwell Equations Dr. Anurag Srivastava
 Maxwell Equations Dr. Anurag Srivastava Web address: http://tiiciiitm.com/profanurag Email: profanurag@gmail.com Visit me: Room-110, Block-E, IIITM Campus Syllabus Electrodynamics: Maxwell s equations:
Maxwell Equations Dr. Anurag Srivastava Web address: http://tiiciiitm.com/profanurag Email: profanurag@gmail.com Visit me: Room-110, Block-E, IIITM Campus Syllabus Electrodynamics: Maxwell s equations:
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES WHAT IS LIGHT?
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE MODULE 7 NATURE OF LIGHT ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES WHAT IS LIGHT? James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879), was a Scottish mathematician and theoretical physicist. He had an unquenchable curiosity
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE MODULE 7 NATURE OF LIGHT ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES WHAT IS LIGHT? James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879), was a Scottish mathematician and theoretical physicist. He had an unquenchable curiosity
UNIT-I Static Electric fields
 UNIT-I Static Electric fields In this chapter we will discuss on the followings: Coulomb's Law Electric Field & Electric Flux Density Gauss's Law with Application Electrostatic Potential, Equipotential
UNIT-I Static Electric fields In this chapter we will discuss on the followings: Coulomb's Law Electric Field & Electric Flux Density Gauss's Law with Application Electrostatic Potential, Equipotential
