Assignment linearalgebrahw1 due 10/15/2012 at 02:32pm EDT
|
|
|
- Steven Atkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 mustafa zeki Assignment linearalgebrahw1 due 10/15/2012 at 02:32pm EDT math (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra24SingularValues- /ur la 24 7.pg -1 7 Let A = A singular value decomposition of A is as follows: A = Find the least-squares solution of the linear system -1 A b, where b = x1 =, x2 =. 2. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra3Matrices/ur la 3 33.pg Find a non-zero, two-by-two matrix such that: = \(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}cc} \mbox } &\mbox } \cr \mbox } &\mbox } \cr 3. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra3Matrices/ur Ch1 3 4.pg 5x + 7y 8z = 3 3x + 8y 5z = 3 4x + 1y 5z = 7 Write the above system of equations in matrix form: x y = z \(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}ccc} \mbox5} &\mbox7} &\mbox-8} \cr \mbox3} &\mbox8} &\mbox-5} \cr \mbox4} &\mbox1} &\mbox-5} \cr \(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox3} \cr \mbox-3} \cr \mbox7} \cr (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra3Matrices/ur la 3 25.pg x 5 If A =, determine the values of x and y for which y -6 A 2 = A., (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra3Matrices/ur la 3 15.pg Find a and b such that = a 3 +b a = b = (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra3Matrices/ur la 3 34.pg Find a non-zero, two-by-two matrix such that: 0 0 A 2 = A = 0 0 \(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}cc} \mbox1} &\mbox1} \cr \mbox-1} &\mbox-1} \cr 7. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 16.pg Solve the system x +y= 6 5x 3y= 6 11x 5y= (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 12.pg Determine the value of k for which the system has no solutions. k = x +y+5z= 1 x +2y 3z= 1 6x+13y+kz= 9
2 6 9. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 3.pg Solve the system using substitution x 3y= x 8y= (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 4.pg Solve the system using substitution 8x+5y= 43 7x+4y= (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 5.pg Solve the system using elimination z = 2x+3y+5z= 35 3x+2y 4z= 19 6x 5y+2z= (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 17.pg Solve the system x 1 = x 2 = x 3 = x 4 = 7 x 1 +2x 3 +2x 4 = 26 x 2 4x 3 3x 4 = 38 2x 1 3x 2 +18x 3 +13x 4 = 180 x 2 +4x 3 +7x 4 = (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 15.pg Solve the system x 1 x 2 = x 3 x 1 x 2 +3x 3 = 6 4x 1 3x 2 +5x 3 = 3 3x 1 +12x 3 = 45 + s. \(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox15} \cr \mbox21} \cr \mbox0} \cr,\(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox4} \cr \mbox7} \cr \mbox1} \cr 14. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 14.pg Solve the system x1 +x 2 +4x 3 = 8 x 1 x 2 = x 3 + 3x 1 +2x 2 3x 3 = 6 s. \(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox10} \cr \mbox-18} \cr \mbox0} \cr,\(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox11} \cr \mbox-15} \cr \mbox1} \cr 15. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 4b.pg Solve the system using matrices (row operations) x+5y= 69 7x 5y= 51 2
3 16. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 6.pg For each system, determine whether it has a unique solution (in this case, find the solution), infinitely many solutions, or no solutions. 1. 2x+3y= x+9y= 59 A. Unique solution: 59, 20 B. No solutions C. Unique solution: 0, 0 D. Infinitely many solutions E. Unique solution: 20, 59 F. None of the above 2x+2y=10 6x+6y=30 A. Unique solution: 0, 0 B. Infinitely many solutions C. Unique solution: 10, 30 D. No solutions E. Unique solution: 5, 0 F. None of the above 9x+7y=0 6x+3y=0 A. Unique solution: 2, 3 B. No solutions C. Unique solution: 3, 9 D. Infinitely many solutions E. Unique solution: 0, 0 F. None of the above 5x+4y= 0 6x 7y=11 A. No solutions B. Unique solution: 4, 5 C. Unique solution: 5, 4 D. Unique solution: 0, 0 E. Infinitely many solutions F. None of the above B B E B (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 4a.pg Solve the system using elimination 2x 7y= x+8y= (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 1.pg Perform one step of row reduction, in order to calculate the values for x and y by back substitution. Then calculate the values for x and for y. Also calculate the determinant of the original matrix. You can let webwork do much of the calculation for you if you want (e.g. enter 45-(56/76)(-3) instead of calculating the value out). You can also use the preview feature in order to make sure that you have used the correct syntax in entering the answer. Note since the determinant is unchanged by row reduction it will be easier to calculate the determinant of the row reduced matrix x 10-8 y 2 20 x y 0 det = -2 = 4 = (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 21.pg x 1 x 2 The dot product of two vectors. x n and y 1 y 2. y n in R n is defined by x x 1 y 1 + x 2 y x n y n. The vectors x and y are called perpendicular if x 0. Then any vector in R 3 perpendicular to -2-2 can be written -3 in the form s + t. \(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox-2} \cr
4 \mbox2} \cr \mbox0} \cr,\(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox-3} \cr \mbox0} \cr \mbox2} \cr 20. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 4c.pg Solve the system by using Cramer s Rule. 4x+7y= 11 7x+2y= (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 22.pg The reduced row-echelon forms of the augmented matrices of four systems are given below. How many solutions does each system have? A. Infinitely many solutions B. No solutions C. Unique solution D. None of the above A. Unique solution B. No solutions C. Infinitely many solutions D. None of the above A. Infinitely many solutions B. No solutions C. Unique solution D. None of the above A. No solutions B. Infinitely many solutions C. Unique solution D. None of the above B C A C (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 23.pg Write the system 2y 3z= 2 7x x 4y 6z= 9 in matrix form x y z = 23. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 20.pg Solve the system x 1 4x 2 +2x 3 4x 5 +5x 6 =4 x 4 5x 5 +5x 6 =5 x 1 4x 2 6x 5 9x 6 =4 x 1 x 2 x 3 x 4 x 5 x 6 + = u. + s + \(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox4} \cr \mbox0} \cr \mbox0} \cr \mbox-5} \cr \mbox0} \cr \mbox0} \cr,\(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox4} \cr \mbox1} \cr \mbox0} \cr \mbox0} \cr \mbox0} \cr \mbox0} \cr t
5 ,\(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox6} \cr \mbox0} \cr \mbox-1} \cr \mbox-5} \cr \mbox1} \cr \mbox0} \cr x y =,\(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} z \mbox9} \cr \mbox0} \cr \mbox-7} \cr \mbox5} \cr \mbox0} \cr \mbox1} \cr 24. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 7.pg Write the augmented matrix of the system x +3z=3 8x 2y z=4 47x (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 5a.pg Solve the system using matrices (row operations) z = -5 2x 4y+5z= 13 3x+2y+4z= 10 2x 3y 2z= (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 10.pg Solve the equation 8x + 7y + 5z = s + t. \(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox1.25} \cr \mbox0} \cr \mbox0} \cr,\(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox0.875} \cr \mbox1} \cr \mbox0} \cr,\(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox0.625} \cr \mbox0} \cr \mbox1} \cr 27. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 19.pg Solve the system x 1 x 2 x 3 = x 4 4x 1 5x 2 +2x 3 +4x 4 = 0 x 1 +x 2 +3x 3 +3x 4 = 2 3x 1 4x 2 +5x 3 +7x 4 = 2 3x 1 3x 2 9x 3 9x 4 = 6 + s + t. \(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox-10} \cr \mbox-8} \cr \mbox0} \cr \mbox0} \cr,\(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox17} \cr \mbox14} \cr \mbox1} \cr \mbox0} \cr,\(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox19} \cr \mbox16} \cr \mbox0} \cr \mbox1} \cr 28. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 9.pg Determine the value of h such that the matrix is the augmented matrix of a linear system with infinitely many solutions h 2 6
6 h = (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 11.pg Solve the system (a*-6-5*b)/1 (4*b-a*-5)/1 4x+5y=a 5x 6y=b 30. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 13.pg Solve the system 2x1 +x 2 = 3 6x 1 3x 2 = 9 = + s. x1 x 2 \(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox1.5} \cr \mbox0} \cr matrix.,\(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox-0.5} \cr \mbox1} \cr 31. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 8.pg Determine the value of h such that the matrix is the augmented matrix of a consistent linear system. h = h 8 \(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox5} \cr \mbox-3} \cr \mbox-2} \cr \mbox0} \cr,\(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox-1} \cr \mbox1} \cr \mbox-1} \cr \mbox1} \cr 33. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 2.pg Perform one step of row reduction, in order to calculate the values for x and y by back substitution. Then calculate the values for x and for y. Also calculate the determinant of the original matrix. You can let webwork do much of the calculation for you if you want (e.g. enter 45-(56/76)(-3) instead of calculating the value out). You can also use the preview feature in order to make sure that you have used the correct syntax in entering the answer. This problem has rather difficult complex calculations. Note since the determinant is unchanged by row reduction it will be easier to calculate the determinant of the row reduced 1+2i -2-4i x -2+2i 4-2i y 1+2i -2-4i 0 det = i -4+2i -1+3i +2i -4+2i -1-7i = 4-2i x y = -1-7i 32. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 18.pg Solve the system x 1 +x 2 = 2 x 2 +x 3 = 5 x 3 +x 4 = 2 x 1 +x 4 = 5 x 1 x 2 x 3 = x 4 + s (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra2SystemsApplications- /ur la 2 2.pg Find the quadratic polynomial whose graph goes through the points ( 2,6), (0,4), and (2,18). f (x) = x 2 + x+
7 35. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra2SystemsApplications- /ur la 2 7.pg Consider a two-commodity market. When the unit prices of the products are P 1 and P 2, the quantities demanded, D 1 and D 2, and the quantities supplied, S 1 and S 2, are given by D 1 = 55 3P 1 + P 2 D 2 = 163+ P 1 3P 2 S 1 = 28+2P 1 S 2 = 22 +2P 2 (a) What is the relationship between the two commodities? Do they compete, as do Volvos and BMWs, or do they complement one another, as do shirts and ties? (type in compete or complement ) (b) Find the equilibrium prices (i.e. the prices for which supply equals demand), for both products. P 1 = P 2 = compete (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra2SystemsApplications- /ur la 2 6.pg In a grid of wires, the temperature at exterior mesh poins is maintained at constant values as shown in the figure. When the grid is in thermal equilibrium, the temperature at each interior mesh point is the average of the temperatures at the four adjacent points. For instance, T 1 = T 2 + T Find the temperatures T 1, T 2, T 3, T 4, when the grid is in thermal equilibrium. T 3 = T 4 = (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra2SystemsApplications- /ur la 2 1.pg Tonya and Steve are sister and brother. Tonya has twice as many brothers as sisters, and Steve has as many brothers as sisters. How many girls and boys are there in this family? Answer: girls and boys. 38. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra2SystemsApplications- /ur la 2 8.pg A dietitian is planning a meal that supplies certain quantities of vitamin C, calcium, and magnesium. Three foods will be used, their quantities measured in milligrams. The nutrients supplied by one unit of each food and the dietary requirements are given in the table below. Nutrient Food 1 Food 2 Food 3 Total Required (mg) Vitamin C Calcium Magnesium Write the augmented matrix for this problem. What quantity (in units) of Food 1 is necesary to meet the dietary requirements? T 1 = T 2 = 7 What quantity (in units) of Food 2 is necesary to meet the dietary requirements? What quantity (in units) of Food 3 is necesary to meet the dietary requirements?
8 (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra2SystemsApplications- /ur la 2 5.pg Consider the chemical reaction an 2 H 4 + bn 2 O 4 cn 2 + dh 2 O, where a, b, c, and d are unknown positive integers. The reaction mush be balanced; that is, the number of atoms of each element must be the same before and after the reaction. For example, because the number of oxygen atoms must remain the same, 4b = d. While there are many possible choices for a, b, c, and d that balance the reaction, it is customary to use the smallest possible integers. Balance this reaction. a = b = c = d = 40. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra2SystemsApplications- /ur la 2 3.pg Find the polynomial of degree 4 whose graph goes through the points ( 2, 54), ( 1, 3), (0,2), (2, 6), and (3, 139). f (x) = x 4 + x 3 + x 2 + x (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra2SystemsApplications- /ur la 2 4.pg Find the cubic polynomial f (x) such that f (1) = 3, f (1) = 6, f (1) = 16, and f (1) = 12. f (x) = x 3 + x 2 + x (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setAlgebra34Matrices/sw7 4 5.pg Given the matrices B =, C =, find 3B + 2C. Write 3B + 2C as a11 a 3B + 2C = 12 a 13. a 21 a 22 a 23 Input your answer below: a 11 = a 12 = a 13 = a 21 = a 22 = a 23 = (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setAlgebra34Matrices/sw7 4 1.pg Given the matrices B =, C =, find B +C. Write B +C as a11 a B +C = 12 a 13. a 21 a 22 a 23 Input your answer below: a 11 = a 12 = a 13 = a 21 = a 22 = a 23 = (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setAlgebra34Matrices/scalarmult3.pg If A = and B = Then 2A + B = and A T = 8
9 (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setAlgebra34Matrices/sw7 4 3.pg Given the matrices B =, C =, find C B. Write C B as a11 a C B = 12 a 13. a 21 a 22 a 23 Input your answer below: a 11 = a 12 = a 13 = a 21 = a 22 = a 23 = (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setAlgebra34Matrices/scalarmult3a.pg If A = and B = Then 2A 2B = and 4A T = (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra20LeastSquares- /ur la 20 4.pg Find the least-squares solution x of the system x = (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra20LeastSquares- /ur la 20 7.pg Fit a trigonometric function of the form f (t) = c 0 + c 1 sin(t) + c 2 cos(t) to the data points (0, 2), ( π 2,5), (π, 12), ( 3π 2, 7), using least squares. c 0 =, c 1 =, c 2 = (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra20LeastSquares- /ur la 20 6.pg Fit a quadratic function of the form f (t) = c 0 + c 1 t + c 2 t 2 to the data points (0, 7), (1, 13), (2, 11), (3, 21), using least squares. c 0 =, c 1 =, c 2 =
10 50. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra20LeastSquares- /ur la 20 3.pg Find the least-squares solution x of the system x =. 51. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra20LeastSquares- /ur la 20 9.pg The table below lists the height h (in cm), the age a (in years), the gender g (1= Male, 0= Female ), and the weight w (in kg) of some college students. Height Age Gender Weight We wish to fit a linear function of the form w(t) = c 0 + c 1 h + c 2 a + c 3 g which predicts the weight from the rest of the data. Find the best approximation of this function, using least squares. c 0 =, c 1 =, c 2 =, c 3 = (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra20LeastSquares- /ur la 20 8.pg Let S(t) be the number of daylight hours on the tth day of the year in Manley Hot Springs. We are given the following data for S(t): Day t S(t) January March May July We wish to fit a trigonometric function of the form ( ) ( ) 2π 2π f (t) = a + bsin 365 t + ccos 365 t to these data. Find the best approximation of this form, using least squares. a =, 10 b =, c = (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra20LeastSquares- /ur la pg During the summer months Terry makes and sells necklaces on the beach. Terry notices that if he lowers the price, he can sell more necklaces, and if he raises the price than he sells fewer necklaces. The table below shows how the number n of necklaces sold in one day depends on the price p (in dollars). Price Number of necklaces sold (a) Find a linear function of the form n = c 0 + c 1 p that best fits these data, using least squares. c 0 =, c 1 =. (b) Find the revenue (number of items sold times the price of each item) as a function of price p. R =. (c) If the material for each necklace costs Terry 5 dollars, find the profit (revenue minus cost of the material) as a function of price p. P =. (d) Finally, find the price that will maximize the profit. p = *p *p*p *(p - 5) *p*(p-5) (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra20LeastSquares- /ur la 20 5.pg Fit a linear function of the form f (t) = c 0 +c 1 t to the data points ( 9,60), (0,0), (9, 66), using least squares. c 0 =, c 1 =. -7
11 55. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra20LeastSquares- /ur la 20 2.pg Find the least-squares solution x of the system x = (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra20LeastSquares- /ur la 20 1.pg Find the least-squares solution x of the system x = (1 pt) Library/maCalcDB/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 3.pg Solve the system using substitution x 4y= x 14y=4 58. (1 pt) Library/maCalcDB/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 4.pg Solve the system using substitution 4x+3y= 42 9x+5y= (1 pt) Library/maCalcDB/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 5.pg Solve the system using elimination z = 2x 2y 5z= 21 5x 2y 2z= 26 5x 3y+4z= (1 pt) Library/maCalcDB/setLinearAlgebra1Systems- /ur la 1 4a.pg Solve the system using elimination 8x+5y= x 4y= (1 pt) Library/maCalcDB/setLinearAlgebra1Systems/ur la 1 7.pg Write the augmented matrix of the system x 69y +9z=63 18y 6z= 0 91x +93z= (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem2.pg Determine whether the following system has no solution, an infinite number of solutions or a unique solution.? 1. 10x + 10y 25z = 0 6x 6y + 15z = 0? 2. 10x + 10y 25z = 0 6x 6y + 15z = 1? 3. 3x 4y + 3z = 1 3x + 3y + 7z = 7 Infinite Solutions No Solution Infinite Solutions
12 63. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem18.pg Determine all values of h and k for which the system 9x + 5 h 6x + k 7 has no solution. k = h (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem4.pg Give a geometric description of the following system of equations? 1.? 2.? 3. 2x + 4y 6z = 12 3x 6y + 9z = 18 2x + 4y 6z = 12 x + 5y 9z = 1 2x + 4y 6z = 12 3x 6y + 9z = 16 Two planes that are the same Two planes intersecting in a line Two parallel planes 65. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem7.pg Solve the system. x 4 1 2x (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem15.pg Solve the system: 4x 3 a 3x 2 b (a*-2--3*b)/1 (4*b-a*3)/ (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem1.pg Determine whether the following system has no solution, an infinite number of solutions or a unique solution. 5x +5 3? 1. 4x x x +5 3? 2. 4x x x +20 5? 3. 8x x Unique Solution No Solution Infinite Solutions 68. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem19.pg The system 6x 30y 35z = 0 8x + 39y + 46z = 0 5x + 25y + 30z = 0 has the solution,, z =. 69. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem14.pg Solve the system using elimination z = x 2y+3z= 5 3x+2y+4z= 18 6x 5y+4z= (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem13.pg Determine the value of k for which the system has no solutions. k = x +y+5z= 2 x +2y 3z= 2 5x+12y+kz=11
13 1 71. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem8.pg The system 3 x 15 y z = 4 9 x + 44 y z = 1 5x has the solution,, z = (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem16.pg Determine whether the following systems have no solution, an infinite number of solutions or a unique solution.? 1.? 2.? 3. 5x x x x x x x x x Unique Solution No Solution Infinite Solutions 73. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem3.pg Give a geometric description of the following systems of equations? 1.? 2.? 3. x x x x 8 4 8x x 12 6 x x x Three non-parallel lines with no common intersection Three identical lines Three lines intersecting at a single point 74. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem11.pg Give a geometric description of the following systems of equations.? 1.? 2.? 3. 2x x x x x 5 8 4x Two parallel lines Two lines that are the same Two lines intersecting in a point 75. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem12.pg x 2y + 9z = 3 x 7y + 9z = 13 3x 11y + 27z = k In order for the above system of equations to be a consistent system, then k must be equal to (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem5.pg Determine whether the following system has no solution, an infinite number of solutions or a unique solution.? 1.? 2.? 3. 3x x 3 1 6x x x x Unique Solution Infinite Solutions No Solution 77. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem9.pg The system 5x x has the solution:, 13
14 78. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem10.pg Give a geometric description of the following system of equations.? 1.? 2.? 3. 2x x x x x x Two lines intersecting in a point Two parallel lines Two lines that are the same 79. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem6.pg Give a geometric description of the following systems of equations x + 4y + 16z = 1? 4. x 3y 12z = 2 4x + 16y + 60z = 6 Infinite Solutions Infinite Solutions No Solution Unique Solution 81. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ SolutionSetsLinearSystems- /problem7.pg Let A = Describe all solutions of A 0. x 2 +x 4 +x 6? 1.? 2.? 3.? 4. x + 3y + 8z = 5 4x 11y 26z = 4 3x + 9y + 21z = 5 7x + 7y + 5z = 1 4x 3y + z = 3 15x 13y 3z = 12 7x + 7y + 5z = 1 4x 3y + z = 3 15x 13y 3z = 7 8x + 10y 4z = 4 20x 25y + 10z = x + 35 y 14 z = 14 Three planes intersecting at a point Three planes with no common intersection Three planes intersecting in a line Three identical planes 80. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem17.pg Determine whether the following system has no solution, an infinite number of solutions or a unique solution.? 1.? 2.? 3. 3 x + y + 5 z = 3 3x 5y + 4z = 3 9x 15y 17z = 21 6x 15y + 3z = 6 8x + 20y 4z = 8 12x + 30y 6z = 12 3 x + y + 5 z = 3 3x 5y + 4z = 3 9x 15y 17z = a multiple of ( -3, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 ) a multiple of ( -6, 0, 4, 1, 0, 0 ) a multiple of ( 11, 0, -4, 0, 1, 1 ) 82. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ SolutionSetsLinearSystems- /problem1.pg Find a set of vectors u, v in R 4 that spans the solution set of the equations: u = x y w = 0 3x + 2y + z + 3w = 0, v =. \(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox-1} \cr \mbox-6} \cr \mbox0} \cr \mbox5} \cr,\(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox-1} \cr \mbox-1} \cr \mbox5} \cr \mbox0} \cr 83. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ SolutionSetsLinearSystems- /problem8.pg Suppose the solution set of a certain system of equations can be described as x 1 = 1 + 5t, x 2 = 2 + 4t, x 3 = 6 + 4t, where t is a free variable. Use vectors to describe this set as a line in R 4.
15 +t (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ SolutionSetsLinearSystems- /problem9.pg Given A = find one nontrivial solution of A 0 by inspection (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ SolutionSetsLinearSystems- /problem6.pg Let A = Describe all solutions of A 0. x 2 +x 3 +x 4 a multiple of ( -3, 1, 0, 0 ) a multiple of ( -4, 0, 1, 0 ) a multiple of ( 1, 0, 0, 1 ) 86. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ RowReduction/problem4.pg 88. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ RowReduction/problem8.pg For the following system to be consistent, 6x + 5y 3z = 5 7x 8y + k z = 3 34x + 37y 23z = 18 we must have, k (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ RowReduction/problem3.pg Determine all values of h and k for which the system 5x + 5y 7z = 3 4x + 7y 7z = 2 31x + 13y + hz = k has no solution. k h = (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ RowReduction/problem11.pg Let k,h be unknown constants and consider the linear system: 4x + 5y 5z = 4 5x + 8y + 2z = 6 6x 21y + hz = k This system has a unique solution whenever h. If h is the (correct) value entered above, then the above system will be consistent for how many value(s) of k? A. no values B. a unique value C. infinitely many values 6x x 35 k For the above system of equations to be consistent, k must equal (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ RowReduction/problem7.pg If the following system 4x x + k 22 is consistent, then k B 91. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ RowReduction/problem12.pg Let k,h be unknown constants and consider the linear system: x + 3 h 8x + k 10 This system has a unique solution whenever k. If k is the (correct) value entered above, then the above system will be consistent for how many value(s) of h? A. no values B. infinitely many values
16 C. a unique value 4 C 92. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ RowReduction/problem5.pg Suppose that the following 12x x 14 k 20 x is a consistent system. Then k = (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ RowReduction/problem9.pg If the following system is consistent, 4x k x then k (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ RowReduction/problem10.pg If the following system has infinitely many solutions, 6x + 5y 7z = 7 5x 7y + 2z = 9 8x + 29y + hz = k then k =, h = (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ RowReduction/problem6.pg If there are an infinite number of solution to the system 7x + 9 h 8x + k 1 then k =, h = (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ MatrixEquations/problem2.pg Perform one step of row reduction, in order to calculate the values for x and y by back substitution. Then calculate the values for x and for y. Also calculate the determinant of the original matrix. You can let webwork do much of the calculation for you if you want (e.g. enter 45-(56/76)(-3) instead of calculating the value out). You can also use the preview feature in order to 16 make sure that you have used the correct syntax in entering the answer. Note since the determinant is unchanged by row reduction it will be easier to calculate the determinant of the row reduced matrix. 1-3 x 4 3 y = -1 x y 0 det = = - 4*-3/ *1/1 (1/1) - (-3/1)* (1*-1-4*1)/(1*3 - -3*4) *3 - -3*4 97. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ MatrixEquations/problem4.pg Let A = and ? 1. What does Ax mean? Linear combination of the columns of A 98. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ MatrixEquations/problem11.pg To see if b = 3 16 is a linear combination of the vectors 6 a 1 = 4 3 and a 2 = one can solve the matrix equation A c where the columns of A are v 1 = and v 2 = 1 and c = \(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox4} \cr \mbox3} \cr \mbox3} \cr,\(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox6} \cr \mbox10} \cr \mbox-6} \cr \(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox3} \cr \mbox16} \cr \mbox6} \cr.
17 99. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ MatrixEquations/problem12.pg 5 To see if b = is a linear combination of the vectors a 1 = and a -1 2 = 7 one can solve the matrix equation A c where the columns of A are v 1 = and v 2 = and c =. \(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox2} \cr \mbox-1} \cr,\(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox10} \cr \mbox7} \cr \(\displaystyle\left.\beginarray}c} \mbox5} \cr \mbox-5} \cr 100. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ MatrixEquations/problem10.pg -1 Let A be a 3x2 matrix. Suppose we know that u = and -4 1 v = satisfy the equations Au = a and Av = b. Find a solution x to A 4a + 2b (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ Dets CramersRule Misc- /problem2.pg 102. (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ Dets CramersRule Misc- /problem1.pg Solve the system using Cramer s Rule. 5x 2 2 6x 1 det = (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ MatrixInverse/problem17.pg For each section, find the matrix X solving the given equation a. X = X = b. X = X = c. X = X = d. X = X = e X = f X = X = X = Solve the system using Cramer s Rule. 2x + 6y + 25z = 4 9x 23y 97z = 5 6x + 18y + 78z = 5 det = z = g X = X =
18 (1 pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ VectorEquations/problem2.pg Write a vector equation x+ y+ z = that is equivalent to the system of equations: 7x + y 3z = 9 3x + 9y + 7z = 9 2x 3y 4z = Generated by c WeBWorK, Mathematical Association of America 18
Assignment linearalgebrahw1 due 10/15/2012 at 02:32pm EDT
 mustafa zeki Assignment linearalgebrahw1 due 10/15/2012 at 02:32pm EDT math201 1 (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra24SingularValues- /ur la 24 7pg -1 7 Let A 1-7 -7-1 7 1 A singular value decomposition
mustafa zeki Assignment linearalgebrahw1 due 10/15/2012 at 02:32pm EDT math201 1 (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setLinearAlgebra24SingularValues- /ur la 24 7pg -1 7 Let A 1-7 -7-1 7 1 A singular value decomposition
Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables. Break Even. Example. 240x x This is when total cost equals total revenue.
 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables 1 Break Even This is when total cost equals total revenue C(x) = R(x) A company breaks even when the profit is zero P(x) = R(x) C(x) = 0 2 R x 565x C x 6000
Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables 1 Break Even This is when total cost equals total revenue C(x) = R(x) A company breaks even when the profit is zero P(x) = R(x) C(x) = 0 2 R x 565x C x 6000
This file is /conf/snippets/setheader.pg you can use it as a model for creating files which introduce each problem set.
 Ivan Ivanov WeBWorK assignment number hw is due : 9/7/ at :am EDT The (* replace with url for the course home page *) for the course contains the syllabus, grading policy and other information linalg This
Ivan Ivanov WeBWorK assignment number hw is due : 9/7/ at :am EDT The (* replace with url for the course home page *) for the course contains the syllabus, grading policy and other information linalg This
Math Studio College Algebra
 Math 100 - Studio College Algebra Rekha Natarajan Kansas State University November 19, 2014 Systems of Equations Systems of Equations A system of equations consists of Systems of Equations A system of
Math 100 - Studio College Algebra Rekha Natarajan Kansas State University November 19, 2014 Systems of Equations Systems of Equations A system of equations consists of Systems of Equations A system of
ft-uiowa-math2550 Assignment OptionalFinalExamReviewMultChoiceMEDIUMlengthForm due 12/31/2014 at 10:36pm CST
 me me ft-uiowa-math255 Assignment OptionalFinalExamReviewMultChoiceMEDIUMlengthForm due 2/3/2 at :3pm CST. ( pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem3.pg Give a geometric description of the following
me me ft-uiowa-math255 Assignment OptionalFinalExamReviewMultChoiceMEDIUMlengthForm due 2/3/2 at :3pm CST. ( pt) Library/TCNJ/TCNJ LinearSystems/problem3.pg Give a geometric description of the following
SECTION 5.1: Polynomials
 1 SECTION 5.1: Polynomials Functions Definitions: Function, Independent Variable, Dependent Variable, Domain, and Range A function is a rule that assigns to each input value x exactly output value y =
1 SECTION 5.1: Polynomials Functions Definitions: Function, Independent Variable, Dependent Variable, Domain, and Range A function is a rule that assigns to each input value x exactly output value y =
Math 141:512. Practice Exam 1 (extra credit) Due: February 6, 2019
 Math 141:512 Due: February 6, 2019 Practice Exam 1 (extra credit) This is an open book, extra credit practice exam which covers the material that Exam 1 will cover (Sections 1.3, 1.4, 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4,
Math 141:512 Due: February 6, 2019 Practice Exam 1 (extra credit) This is an open book, extra credit practice exam which covers the material that Exam 1 will cover (Sections 1.3, 1.4, 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4,
Algebra 1 Practice Test
 Part 1: Directions: For questions 1-20, circle the correct answer on your answer sheet. 1. Solve for x: 2(x+ 7) 3(2x-4) = -18 A. x = 5 B. x = 11 C. x = -11 D. x = -5 2. Which system of equations is represented
Part 1: Directions: For questions 1-20, circle the correct answer on your answer sheet. 1. Solve for x: 2(x+ 7) 3(2x-4) = -18 A. x = 5 B. x = 11 C. x = -11 D. x = -5 2. Which system of equations is represented
You solved systems of equations algebraically and represented data using matrices. (Lessons 0-5 and 0-6)
 You solved systems of equations algebraically and represented data using matrices. (Lessons 0-5 and 0-6) Solve systems of linear equations using matrices and Gaussian elimination. Solve systems of linear
You solved systems of equations algebraically and represented data using matrices. (Lessons 0-5 and 0-6) Solve systems of linear equations using matrices and Gaussian elimination. Solve systems of linear
Quadratic function and equations Quadratic function/equations, supply, demand, market equilibrium
 Exercises 8 Quadratic function and equations Quadratic function/equations, supply, demand, market equilibrium Objectives - know and understand the relation between a quadratic function and a quadratic
Exercises 8 Quadratic function and equations Quadratic function/equations, supply, demand, market equilibrium Objectives - know and understand the relation between a quadratic function and a quadratic
WeBWorK demonstration assignment
 WeBWorK demonstration assignment The main purpose of this WeBWorK set is to familiarize yourself with WeBWorK. Here are some hints on how to use WeBWorK effectively: After first logging into WeBWorK change
WeBWorK demonstration assignment The main purpose of this WeBWorK set is to familiarize yourself with WeBWorK. Here are some hints on how to use WeBWorK effectively: After first logging into WeBWorK change
MTH Linear Algebra. Study Guide. Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education
 MTH 3 Linear Algebra Study Guide Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education June 3, ii Contents Table of Contents iii Matrix Algebra. Real Life
MTH 3 Linear Algebra Study Guide Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education June 3, ii Contents Table of Contents iii Matrix Algebra. Real Life
Chapter 7 Linear Systems
 Chapter 7 Linear Systems Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables Multivariable Linear Systems Vocabulary Systems of equations Substitution
Chapter 7 Linear Systems Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables Multivariable Linear Systems Vocabulary Systems of equations Substitution
Assignment busshw1 due 10/15/2012 at 01:04pm EDT
 Administrator Assignment busshw1 due 10/15/2012 at 01:04pm EDT math111 1. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setVectors0Introduction/ur vc 0 2.pg If the distance from the town of Bree to Weathertop is 6 miles on
Administrator Assignment busshw1 due 10/15/2012 at 01:04pm EDT math111 1. (1 pt) Library/Rochester/setVectors0Introduction/ur vc 0 2.pg If the distance from the town of Bree to Weathertop is 6 miles on
1. Let m 1 and n 1 be two natural numbers such that m > n. Which of the following is/are true?
 . Let m and n be two natural numbers such that m > n. Which of the following is/are true? (i) A linear system of m equations in n variables is always consistent. (ii) A linear system of n equations in
. Let m and n be two natural numbers such that m > n. Which of the following is/are true? (i) A linear system of m equations in n variables is always consistent. (ii) A linear system of n equations in
MHCA Math Summer Packet 2015
 Directions: MHCA Math Summer Packet 2015 For students entering PreCalculus Honors You are to complete all the problems assigned in this packet by Friday, September 4 th. If you don t turn in your summer
Directions: MHCA Math Summer Packet 2015 For students entering PreCalculus Honors You are to complete all the problems assigned in this packet by Friday, September 4 th. If you don t turn in your summer
3. Replace any row by the sum of that row and a constant multiple of any other row.
 Section. Solution of Linear Systems by Gauss-Jordan Method A matrix is an ordered rectangular array of numbers, letters, symbols or algebraic expressions. A matrix with m rows and n columns has size or
Section. Solution of Linear Systems by Gauss-Jordan Method A matrix is an ordered rectangular array of numbers, letters, symbols or algebraic expressions. A matrix with m rows and n columns has size or
The Method of Substitution. Linear and Nonlinear Systems of Equations. The Method of Substitution. The Method of Substitution. Example 2.
 The Method of Substitution Linear and Nonlinear Systems of Equations Precalculus 7.1 Here is an example of a system of two equations in two unknowns. Equation 1 x + y = 5 Equation 3x y = 4 A solution of
The Method of Substitution Linear and Nonlinear Systems of Equations Precalculus 7.1 Here is an example of a system of two equations in two unknowns. Equation 1 x + y = 5 Equation 3x y = 4 A solution of
Chapter 1: Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices
 : Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Multiple Choice Questions. Which of the following equations is linear? (A) x + 3x 3 + 4x 4 3 = 5 (B) 3x x + x 3 = 5 (C) 5x + 5 x x 3 = x + cos (x ) + 4x 3 = 7.
: Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Multiple Choice Questions. Which of the following equations is linear? (A) x + 3x 3 + 4x 4 3 = 5 (B) 3x x + x 3 = 5 (C) 5x + 5 x x 3 = x + cos (x ) + 4x 3 = 7.
Section 1.1 System of Linear Equations. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 211: Linear Algebra
 Section 1.1 System of Linear Equations College of Science MATHS 211: Linear Algebra (University of Bahrain) Linear System 1 / 33 Goals:. 1 Define system of linear equations and their solutions. 2 To represent
Section 1.1 System of Linear Equations College of Science MATHS 211: Linear Algebra (University of Bahrain) Linear System 1 / 33 Goals:. 1 Define system of linear equations and their solutions. 2 To represent
MATH 3321 Sample Questions for Exam 3. 3y y, C = Perform the indicated operations, if possible: (a) AC (b) AB (c) B + AC (d) CBA
 MATH 33 Sample Questions for Exam 3. Find x and y so that x 4 3 5x 3y + y = 5 5. x = 3/7, y = 49/7. Let A = 3 4, B = 3 5, C = 3 Perform the indicated operations, if possible: a AC b AB c B + AC d CBA AB
MATH 33 Sample Questions for Exam 3. Find x and y so that x 4 3 5x 3y + y = 5 5. x = 3/7, y = 49/7. Let A = 3 4, B = 3 5, C = 3 Perform the indicated operations, if possible: a AC b AB c B + AC d CBA AB
Chapter Practice Test Name: Period: Date:
 Name: Period: Date: 1. Draw the graph of the following system: 3 x+ 5 y+ 13 = 0 29 x 11 y 7 = 0 3 13 y = x 3x+ 5y+ 13= 0 5 5 29x 11y 7 = 0 29 7 y = x 11 11 Practice Test Page 1 2. Determine the ordered
Name: Period: Date: 1. Draw the graph of the following system: 3 x+ 5 y+ 13 = 0 29 x 11 y 7 = 0 3 13 y = x 3x+ 5y+ 13= 0 5 5 29x 11y 7 = 0 29 7 y = x 11 11 Practice Test Page 1 2. Determine the ordered
Lecture 6: Sections 2.2 and 2.3 Polynomial Functions, Quadratic Models
 L6-1 Lecture 6: Sections 2.2 and 2.3 Polynomial Functions, Quadratic Models Polynomial Functions Def. A polynomial function of degree n is a function of the form f(x) = a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 +... + a 1
L6-1 Lecture 6: Sections 2.2 and 2.3 Polynomial Functions, Quadratic Models Polynomial Functions Def. A polynomial function of degree n is a function of the form f(x) = a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 +... + a 1
The value of a problem is not so much coming up with the answer as in the ideas and attempted ideas it forces on the would be solver I.N.
 Math 410 Homework Problems In the following pages you will find all of the homework problems for the semester. Homework should be written out neatly and stapled and turned in at the beginning of class
Math 410 Homework Problems In the following pages you will find all of the homework problems for the semester. Homework should be written out neatly and stapled and turned in at the beginning of class
Math 234 March 6 I. Determine if the demand is elastic, inelastic, or of unit elasticity at the indicated price p.
 Math 234 March 6 I. Determine if the demand is elastic, inelastic, or of unit elasticity at the indicated price p. 1. D(p) = 1.3p + 10; p = 4 2. D(p) = 1.5p + 25; p = 12 3. D(p) = 2p + 40; p = 10 4. D(p)
Math 234 March 6 I. Determine if the demand is elastic, inelastic, or of unit elasticity at the indicated price p. 1. D(p) = 1.3p + 10; p = 4 2. D(p) = 1.5p + 25; p = 12 3. D(p) = 2p + 40; p = 10 4. D(p)
Chapter 14: Basics of Functions
 Math 91 Final Exam Study Guide Name Chapter 14: Basics of Functions Find the domain and range. 1) {(5,1), (5,-4), (6,7), (3,4), (-9,-6)} Find the indicated function value. 2) Find f(3) when f(x) = x2 +
Math 91 Final Exam Study Guide Name Chapter 14: Basics of Functions Find the domain and range. 1) {(5,1), (5,-4), (6,7), (3,4), (-9,-6)} Find the indicated function value. 2) Find f(3) when f(x) = x2 +
5.1 - Polynomials. Ex: Let k(x) = x 2 +2x+1. Find (and completely simplify) the following: (a) k(1) (b) k( 2) (c) k(a)
 c Kathryn Bollinger, March 15, 2017 1 5.1 - Polynomials Def: A function is a rule (process) that assigns to each element in the domain (the set of independent variables, x) ONE AND ONLY ONE element in
c Kathryn Bollinger, March 15, 2017 1 5.1 - Polynomials Def: A function is a rule (process) that assigns to each element in the domain (the set of independent variables, x) ONE AND ONLY ONE element in
Linear Algebra: Lecture Notes. Dr Rachel Quinlan School of Mathematics, Statistics and Applied Mathematics NUI Galway
 Linear Algebra: Lecture Notes Dr Rachel Quinlan School of Mathematics, Statistics and Applied Mathematics NUI Galway November 6, 23 Contents Systems of Linear Equations 2 Introduction 2 2 Elementary Row
Linear Algebra: Lecture Notes Dr Rachel Quinlan School of Mathematics, Statistics and Applied Mathematics NUI Galway November 6, 23 Contents Systems of Linear Equations 2 Introduction 2 2 Elementary Row
ft-uiowa-math2550 Assignment Hw1fall14 due 09/03/2014 at 10:56pm CDT 3. (1 pt) Library/WHFreeman/Holt linear algebra/chaps 1-4- /holt
 me me Assignment Hw1fall14 due 09/03/2014 at 10:56pm CDT ft-uiowa-math2550 1. (1 pt) Library/WHFreeman/Holt linear algebra/chaps 1-4- /holt 01 02 007.pg 2 3 1 1 0 0 0 5 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 in echelon form, reduced
me me Assignment Hw1fall14 due 09/03/2014 at 10:56pm CDT ft-uiowa-math2550 1. (1 pt) Library/WHFreeman/Holt linear algebra/chaps 1-4- /holt 01 02 007.pg 2 3 1 1 0 0 0 5 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 in echelon form, reduced
MTH 2032 Semester II
 MTH 232 Semester II 2-2 Linear Algebra Reference Notes Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education December 28, 2 ii Contents Table of Contents
MTH 232 Semester II 2-2 Linear Algebra Reference Notes Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education December 28, 2 ii Contents Table of Contents
Math 301 Test I. M. Randall Holmes. September 8, 2008
 Math 0 Test I M. Randall Holmes September 8, 008 This exam will begin at 9:40 am and end at 0:5 am. You may use your writing instrument, a calculator, and your test paper; books, notes and neighbors to
Math 0 Test I M. Randall Holmes September 8, 008 This exam will begin at 9:40 am and end at 0:5 am. You may use your writing instrument, a calculator, and your test paper; books, notes and neighbors to
7.1 Solving Systems of Equations
 Date: Precalculus Notes: Unit 7 Systems of Equations and Matrices 7.1 Solving Systems of Equations Syllabus Objectives: 8.1 The student will solve a given system of equations or system of inequalities.
Date: Precalculus Notes: Unit 7 Systems of Equations and Matrices 7.1 Solving Systems of Equations Syllabus Objectives: 8.1 The student will solve a given system of equations or system of inequalities.
Chapter 7 Linear Systems and Matrices
 Chapter 7 Linear Systems and Matrices Overview: 7.1 Solving Systems of Equations 7.2 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables 7.3 Multivariable Linear Systems 7.1 Solving Systems of Equations What
Chapter 7 Linear Systems and Matrices Overview: 7.1 Solving Systems of Equations 7.2 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables 7.3 Multivariable Linear Systems 7.1 Solving Systems of Equations What
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 10: Linear independence. Wronskian.
 MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 10: Linear independence. Wronskian. Spanning set Let S be a subset of a vector space V. Definition. The span of the set S is the smallest subspace W V that contains S. If
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 10: Linear independence. Wronskian. Spanning set Let S be a subset of a vector space V. Definition. The span of the set S is the smallest subspace W V that contains S. If
Lecture 2 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices, Continued
 Lecture 2 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices, Continued Math 19620 Outline of Lecture Algorithm for putting a matrix in row reduced echelon form - i.e. Gauss-Jordan Elimination Number of Solutions
Lecture 2 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices, Continued Math 19620 Outline of Lecture Algorithm for putting a matrix in row reduced echelon form - i.e. Gauss-Jordan Elimination Number of Solutions
Algebra 1 Practice Test. Algebra 1. Practice Test. Copyright Karin Hutchinson, All rights reserved.
 Algebra 1 Practice Test Copyright Karin Hutchinson, 2011. All rights reserved. Please respect the time, effort, and careful planning spent to prepare these materials. The distribution of this e-book via
Algebra 1 Practice Test Copyright Karin Hutchinson, 2011. All rights reserved. Please respect the time, effort, and careful planning spent to prepare these materials. The distribution of this e-book via
System of Linear Equations. Slide for MA1203 Business Mathematics II Week 1 & 2
 System of Linear Equations Slide for MA1203 Business Mathematics II Week 1 & 2 Function A manufacturer would like to know how his company s profit is related to its production level. How does one quantity
System of Linear Equations Slide for MA1203 Business Mathematics II Week 1 & 2 Function A manufacturer would like to know how his company s profit is related to its production level. How does one quantity
Algebra 2 Notes Systems of Equations and Inequalities Unit 03c. System of Equations in Three Variables
 System of Equations in Three Variables Big Idea A system of equations in three variables consists of multiple planes graphed on the same coordinate plane. The solutions to these systems consists of a single
System of Equations in Three Variables Big Idea A system of equations in three variables consists of multiple planes graphed on the same coordinate plane. The solutions to these systems consists of a single
Exam A. Exam 3. (e) Two critical points; one is a local maximum, the other a local minimum.
 1.(6 pts) The function f(x) = x 3 2x 2 has: Exam A Exam 3 (a) Two critical points; one is a local minimum, the other is neither a local maximum nor a local minimum. (b) Two critical points; one is a local
1.(6 pts) The function f(x) = x 3 2x 2 has: Exam A Exam 3 (a) Two critical points; one is a local minimum, the other is neither a local maximum nor a local minimum. (b) Two critical points; one is a local
Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations
 What is a linear equation? Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations We are now going to discuss solving systems of two or more linear equations with two variables. Recall that solving an equation
What is a linear equation? Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations We are now going to discuss solving systems of two or more linear equations with two variables. Recall that solving an equation
Lecture Notes in Mathematics. Arkansas Tech University Department of Mathematics. The Basics of Linear Algebra
 Lecture Notes in Mathematics Arkansas Tech University Department of Mathematics The Basics of Linear Algebra Marcel B. Finan c All Rights Reserved Last Updated November 30, 2015 2 Preface Linear algebra
Lecture Notes in Mathematics Arkansas Tech University Department of Mathematics The Basics of Linear Algebra Marcel B. Finan c All Rights Reserved Last Updated November 30, 2015 2 Preface Linear algebra
Problem #1. The following matrices are augmented matrices of linear systems. How many solutions has each system? Motivate your answer.
 Exam #4 covers the material about systems of linear equations and matrices (CH. 4.1-4.4, PART II); systems of linear inequalities in two variables (geometric approach) and linear programming (CH.5.1-5.2,
Exam #4 covers the material about systems of linear equations and matrices (CH. 4.1-4.4, PART II); systems of linear inequalities in two variables (geometric approach) and linear programming (CH.5.1-5.2,
Chapter 4. Systems of Linear Equations; Matrices. Opening Example. Section 1 Review: Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables
 Chapter 4 Systems of Linear Equations; Matrices Section 1 Review: Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables Opening Example A restaurant serves two types of fish dinners- small for $5.99 and large for
Chapter 4 Systems of Linear Equations; Matrices Section 1 Review: Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables Opening Example A restaurant serves two types of fish dinners- small for $5.99 and large for
ID: ID: ID: of 39 1/18/ :43 AM. Student: Date: Instructor: Alfredo Alvarez Course: 2017 Spring Math 1314
 1 of 39 1/18/017 10:43 AM Student: Date: Instructor: Alfredo Alvarez Course: 017 Spring Math 1314 Assignment: Practice Final 1. Graph the equation. y= x 3 ID: 1.1-11. Perform the multiplication and write
1 of 39 1/18/017 10:43 AM Student: Date: Instructor: Alfredo Alvarez Course: 017 Spring Math 1314 Assignment: Practice Final 1. Graph the equation. y= x 3 ID: 1.1-11. Perform the multiplication and write
Linear Algebra Practice Problems
 Math 7, Professor Ramras Linear Algebra Practice Problems () Consider the following system of linear equations in the variables x, y, and z, in which the constants a and b are real numbers. x y + z = a
Math 7, Professor Ramras Linear Algebra Practice Problems () Consider the following system of linear equations in the variables x, y, and z, in which the constants a and b are real numbers. x y + z = a
5x 2 = 10. x 1 + 7(2) = 4. x 1 3x 2 = 4. 3x 1 + 9x 2 = 8
 1 To solve the system x 1 + x 2 = 4 2x 1 9x 2 = 2 we find an (easier to solve) equivalent system as follows: Replace equation 2 with (2 times equation 1 + equation 2): x 1 + x 2 = 4 Solve equation 2 for
1 To solve the system x 1 + x 2 = 4 2x 1 9x 2 = 2 we find an (easier to solve) equivalent system as follows: Replace equation 2 with (2 times equation 1 + equation 2): x 1 + x 2 = 4 Solve equation 2 for
Section 4.1 Solving Systems of Linear Inequalities
 Section 4.1 Solving Systems of Linear Inequalities Question 1 How do you graph a linear inequality? Question 2 How do you graph a system of linear inequalities? Question 1 How do you graph a linear inequality?
Section 4.1 Solving Systems of Linear Inequalities Question 1 How do you graph a linear inequality? Question 2 How do you graph a system of linear inequalities? Question 1 How do you graph a linear inequality?
BARUCH COLLEGE MATH 2207 FALL 2007 MANUAL FOR THE UNIFORM FINAL EXAMINATION. No calculator will be allowed on this part.
 BARUCH COLLEGE MATH 07 FALL 007 MANUAL FOR THE UNIFORM FINAL EXAMINATION The final eamination for Math 07 will consist of two parts. Part I: Part II: This part will consist of 5 questions. No calculator
BARUCH COLLEGE MATH 07 FALL 007 MANUAL FOR THE UNIFORM FINAL EXAMINATION The final eamination for Math 07 will consist of two parts. Part I: Part II: This part will consist of 5 questions. No calculator
An equation is a statement that states that two expressions are equal. For example:
 Section 0.1: Linear Equations Solving linear equation in one variable: An equation is a statement that states that two expressions are equal. For example: (1) 513 (2) 16 (3) 4252 (4) 64153 To solve the
Section 0.1: Linear Equations Solving linear equation in one variable: An equation is a statement that states that two expressions are equal. For example: (1) 513 (2) 16 (3) 4252 (4) 64153 To solve the
ALGEBRA II WITH TRIGONOMETRY EXAM
 First Round : March 7, 00 Second Round: April, 00 at The University of Alabama ALGEBRA II WITH TRIGONOMETRY EXAM Construction of this test directed by Congxiao Liu, Alabama A&M University and Alzaki Fadl
First Round : March 7, 00 Second Round: April, 00 at The University of Alabama ALGEBRA II WITH TRIGONOMETRY EXAM Construction of this test directed by Congxiao Liu, Alabama A&M University and Alzaki Fadl
Linear Algebra Homework and Study Guide
 Linear Algebra Homework and Study Guide Phil R. Smith, Ph.D. February 28, 20 Homework Problem Sets Organized by Learning Outcomes Test I: Systems of Linear Equations; Matrices Lesson. Give examples of
Linear Algebra Homework and Study Guide Phil R. Smith, Ph.D. February 28, 20 Homework Problem Sets Organized by Learning Outcomes Test I: Systems of Linear Equations; Matrices Lesson. Give examples of
Example 7.3.1: For what values of k does the following system of linear equations have no solution, a unique solution, or infinitely many solutions?
 Example 7.2.2: Instructions Screen Shot First enter the augmented matrix, here into m1. Note: To remove a variable used for a matrix or other calculation use Ω Delvar (variable name). Then use the command
Example 7.2.2: Instructions Screen Shot First enter the augmented matrix, here into m1. Note: To remove a variable used for a matrix or other calculation use Ω Delvar (variable name). Then use the command
LESSON 13.1 NONLINEAR EQUATIONS
 LESSON. NONLINEAR EQUATIONS LESSON. NONLINEAR EQUATIONS 58 OVERVIEW Here's what you'll learn in this lesson: Solving Equations a. Solving polynomial equations by factoring b. Solving quadratic type equations
LESSON. NONLINEAR EQUATIONS LESSON. NONLINEAR EQUATIONS 58 OVERVIEW Here's what you'll learn in this lesson: Solving Equations a. Solving polynomial equations by factoring b. Solving quadratic type equations
4 6 Quarter. During which of the following periods is the increase in the number of students with part-time jobs largest?
 1 of 1 9/22/2016 7:59 PM Math: Question 1 Number of students 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 Number of Students with Part-Time Jobs 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 Quarter During which of the following periods is the increase
1 of 1 9/22/2016 7:59 PM Math: Question 1 Number of students 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 Number of Students with Part-Time Jobs 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 Quarter During which of the following periods is the increase
3 6 x a. 12 b. 63 c. 27 d. 0. 6, find
 Advanced Algebra Topics COMPASS Review revised Summer 0 You will be allowed to use a calculator on the COMPASS test Acceptable calculators are basic calculators, scientific calculators, and approved models
Advanced Algebra Topics COMPASS Review revised Summer 0 You will be allowed to use a calculator on the COMPASS test Acceptable calculators are basic calculators, scientific calculators, and approved models
Review for Final Review
 Topics Review for Final Review 1. Functions and equations and graphing: linear, absolute value, quadratic, polynomials, rational (first 1/3 of semester) 2. Simple Interest, compounded interest, and continuously
Topics Review for Final Review 1. Functions and equations and graphing: linear, absolute value, quadratic, polynomials, rational (first 1/3 of semester) 2. Simple Interest, compounded interest, and continuously
3. Find the slope of the tangent line to the curve given by 3x y e x+y = 1 + ln x at (1, 1).
 1. Find the derivative of each of the following: (a) f(x) = 3 2x 1 (b) f(x) = log 4 (x 2 x) 2. Find the slope of the tangent line to f(x) = ln 2 ln x at x = e. 3. Find the slope of the tangent line to
1. Find the derivative of each of the following: (a) f(x) = 3 2x 1 (b) f(x) = log 4 (x 2 x) 2. Find the slope of the tangent line to f(x) = ln 2 ln x at x = e. 3. Find the slope of the tangent line to
6-1 Study Guide and Intervention Multivariable Linear Systems and Row Operations
 6-1 Study Guide and Intervention Multivariable Linear Systems and Row Operations Gaussian Elimination You can solve a system of linear equations using matrices. Solving a system by transforming it into
6-1 Study Guide and Intervention Multivariable Linear Systems and Row Operations Gaussian Elimination You can solve a system of linear equations using matrices. Solving a system by transforming it into
MATH 2070 Test 3 (Sections , , & )
 Multiple Choice: Use a #2 pencil and completely fill in each bubble on your scantron to indicate the answer to each question. Each question has one correct answer. If you indicate more than one answer,
Multiple Choice: Use a #2 pencil and completely fill in each bubble on your scantron to indicate the answer to each question. Each question has one correct answer. If you indicate more than one answer,
College Algebra. Chapter 6. Mary Stangler Center for Academic Success
 College Algebra Chapter 6 Note: This review is composed of questions similar to those in the chapter review at the end of chapter 6. This review is meant to highlight basic concepts from chapter 6. It
College Algebra Chapter 6 Note: This review is composed of questions similar to those in the chapter review at the end of chapter 6. This review is meant to highlight basic concepts from chapter 6. It
On a separate sheet of paper, answer the following questions by showing ALL of your work.
 Final Exam Review Cummulative Math 20-1 Ch.1 Sequence and Series Final Exam Review On a separate sheet of paper, answer the following questions by showing ALL of your work. 1. The common difference in
Final Exam Review Cummulative Math 20-1 Ch.1 Sequence and Series Final Exam Review On a separate sheet of paper, answer the following questions by showing ALL of your work. 1. The common difference in
UNC Charlotte Super Competition Level 3 Test March 4, 2019 Test with Solutions for Sponsors
 . Find the minimum value of the function f (x) x 2 + (A) 6 (B) 3 6 (C) 4 Solution. We have f (x) x 2 + + x 2 + (D) 3 4, which is equivalent to x 0. x 2 + (E) x 2 +, x R. x 2 + 2 (x 2 + ) 2. How many solutions
. Find the minimum value of the function f (x) x 2 + (A) 6 (B) 3 6 (C) 4 Solution. We have f (x) x 2 + + x 2 + (D) 3 4, which is equivalent to x 0. x 2 + (E) x 2 +, x R. x 2 + 2 (x 2 + ) 2. How many solutions
Vector Spaces 4.4 Spanning and Independence
 Vector Spaces 4.4 and Independence Summer 2017 Goals Discuss two important basic concepts: Define linear combination of vectors. Define Span(S) of a set S of vectors. Define linear Independence of a set
Vector Spaces 4.4 and Independence Summer 2017 Goals Discuss two important basic concepts: Define linear combination of vectors. Define Span(S) of a set S of vectors. Define linear Independence of a set
Math 118, Fall 2014 Final Exam
 Math 8, Fall 4 Final Exam True or false Please circle your choice; no explanation is necessary True There is a linear transformation T such that T e ) = e and T e ) = e Solution Since T is linear, if T
Math 8, Fall 4 Final Exam True or false Please circle your choice; no explanation is necessary True There is a linear transformation T such that T e ) = e and T e ) = e Solution Since T is linear, if T
Solving Systems of Linear Equations. Classification by Number of Solutions
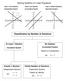 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Case 1: One Solution Case : No Solution Case 3: Infinite Solutions Independent System Inconsistent System Dependent System x = 4 y = Classification by Number of Solutions
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Case 1: One Solution Case : No Solution Case 3: Infinite Solutions Independent System Inconsistent System Dependent System x = 4 y = Classification by Number of Solutions
NEW ENGLAND COMMON ASSESSMENT PROGRAM
 NEW ENGLAND COMMON ASSESSMENT PROGRAM Released Items 2010 Grade 11 Mathematics Mathematics Items with this symbol were selected from Session One no calculators or other mathematics tools allowed. 140029.004
NEW ENGLAND COMMON ASSESSMENT PROGRAM Released Items 2010 Grade 11 Mathematics Mathematics Items with this symbol were selected from Session One no calculators or other mathematics tools allowed. 140029.004
Student study guide for the MAT 151 Spring 2016 final examination
 Student study guide for the MAT 151 Spring 016 final examination Use the problems in this study guide to help you prepare for the problems on the final. The problems below are similar to the ones on the
Student study guide for the MAT 151 Spring 016 final examination Use the problems in this study guide to help you prepare for the problems on the final. The problems below are similar to the ones on the
Math 51, Homework-2. Section numbers are from the course textbook.
 SSEA Summer 2017 Math 51, Homework-2 Section numbers are from the course textbook. 1. Write the parametric equation of the plane that contains the following point and line: 1 1 1 3 2, 4 2 + t 3 0 t R.
SSEA Summer 2017 Math 51, Homework-2 Section numbers are from the course textbook. 1. Write the parametric equation of the plane that contains the following point and line: 1 1 1 3 2, 4 2 + t 3 0 t R.
C. Finding roots of trinomials: 1st Example: x 2 5x = 14 x 2 5x 14 = 0 (x 7)(x + 2) = 0 Answer: x = 7 or x = -2
 AP Calculus Students: Welcome to AP Calculus. Class begins in approimately - months. In this packet, you will find numerous topics that were covered in your Algebra and Pre-Calculus courses. These are
AP Calculus Students: Welcome to AP Calculus. Class begins in approimately - months. In this packet, you will find numerous topics that were covered in your Algebra and Pre-Calculus courses. These are
Math Week in Review #7
 Math 166 Fall 2008 c Heather Ramsey Page 1 Math 166 - Week in Review #7 Section 4.3 - Gauss Elimination for Systems of Linear Equations When a system of linear equations has only two variables, each equation
Math 166 Fall 2008 c Heather Ramsey Page 1 Math 166 - Week in Review #7 Section 4.3 - Gauss Elimination for Systems of Linear Equations When a system of linear equations has only two variables, each equation
Conceptual Questions for Review
 Conceptual Questions for Review Chapter 1 1.1 Which vectors are linear combinations of v = (3, 1) and w = (4, 3)? 1.2 Compare the dot product of v = (3, 1) and w = (4, 3) to the product of their lengths.
Conceptual Questions for Review Chapter 1 1.1 Which vectors are linear combinations of v = (3, 1) and w = (4, 3)? 1.2 Compare the dot product of v = (3, 1) and w = (4, 3) to the product of their lengths.
(c) n (d) n 2. (a) (b) (c) (d) (a) Null set (b) {P} (c) {P, Q, R} (d) {Q, R} (a) 2k (b) 7 (c) 2 (d) K (a) 1 (b) 3 (c) 3xyz (d) 27xyz
 318 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. (1001)2 (101)2 (110)2 (100)2 2. z 1/z 2z z/2 3. The multiplication of the number (10101)2 by (1101)2 yields which one of the following? (100011001)2 (100010001)2 (110010011)2
318 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. (1001)2 (101)2 (110)2 (100)2 2. z 1/z 2z z/2 3. The multiplication of the number (10101)2 by (1101)2 yields which one of the following? (100011001)2 (100010001)2 (110010011)2
Math 205B Exam 02 page 1 03/19/2010 Name /7 4/7 1/ /7 1/7 5/ /7 1/7 2/
 Math 205B Exam 02 page 1 03/19/2010 Name 3 8 14 1 1. Let A = 1 1 1 3 2 0 4 1 ; then [ A I 4 ] is row-equivalent to 1 2 0 2 Let R = rref(a). 1A. Find a basis for Col(A). 1 0 2 0 0 2/7 4/7 1/7 0 1 1 0 0
Math 205B Exam 02 page 1 03/19/2010 Name 3 8 14 1 1. Let A = 1 1 1 3 2 0 4 1 ; then [ A I 4 ] is row-equivalent to 1 2 0 2 Let R = rref(a). 1A. Find a basis for Col(A). 1 0 2 0 0 2/7 4/7 1/7 0 1 1 0 0
ELEMENTARY MATHEMATICS FOR ECONOMICS
 ELEMENTARY MATHEMATICS FOR ECONOMICS Catering the need of Second year B.A./B.Sc. Students of Economics (Major) Third Semester of Guwahati and other Indian Universities. 2nd Semester R.C. Joshi M.A., M.Phil.
ELEMENTARY MATHEMATICS FOR ECONOMICS Catering the need of Second year B.A./B.Sc. Students of Economics (Major) Third Semester of Guwahati and other Indian Universities. 2nd Semester R.C. Joshi M.A., M.Phil.
The Quadratic Formula. ax 2 bx c 0 where a 0. Deriving the Quadratic Formula. Isolate the constant on the right side of the equation.
 SECTION 11.2 11.2 The Quadratic Formula 11.2 OBJECTIVES 1. Solve quadratic equations by using the quadratic formula 2. Determine the nature of the solutions of a quadratic equation by using the discriminant
SECTION 11.2 11.2 The Quadratic Formula 11.2 OBJECTIVES 1. Solve quadratic equations by using the quadratic formula 2. Determine the nature of the solutions of a quadratic equation by using the discriminant
Practice Questions for Math 131 Exam # 1
 Practice Questions for Math 131 Exam # 1 1) A company produces a product for which the variable cost per unit is $3.50 and fixed cost 1) is $20,000 per year. Next year, the company wants the total cost
Practice Questions for Math 131 Exam # 1 1) A company produces a product for which the variable cost per unit is $3.50 and fixed cost 1) is $20,000 per year. Next year, the company wants the total cost
Page Points Score Total: 100
 Math 1130 Spring 2019 Sample Exam 1c 1/31/19 Name (Print): Username.#: Lecturer: Rec. Instructor: Rec. Time: This exam contains 8 pages (including this cover page) and 7 problems. Check to see if any pages
Math 1130 Spring 2019 Sample Exam 1c 1/31/19 Name (Print): Username.#: Lecturer: Rec. Instructor: Rec. Time: This exam contains 8 pages (including this cover page) and 7 problems. Check to see if any pages
LINEAR SYSTEMS AND MATRICES
 CHAPTER 3 LINEAR SYSTEMS AND MATRICES SECTION 3. INTRODUCTION TO LINEAR SYSTEMS This initial section takes account of the fact that some students remember only hazily the method of elimination for and
CHAPTER 3 LINEAR SYSTEMS AND MATRICES SECTION 3. INTRODUCTION TO LINEAR SYSTEMS This initial section takes account of the fact that some students remember only hazily the method of elimination for and
Midterm 1 Review. Written by Victoria Kala SH 6432u Office Hours: R 12:30 1:30 pm Last updated 10/10/2015
 Midterm 1 Review Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu SH 6432u Office Hours: R 12:30 1:30 pm Last updated 10/10/2015 Summary This Midterm Review contains notes on sections 1.1 1.5 and 1.7 in your
Midterm 1 Review Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu SH 6432u Office Hours: R 12:30 1:30 pm Last updated 10/10/2015 Summary This Midterm Review contains notes on sections 1.1 1.5 and 1.7 in your
Math E-21b Spring 2018 Homework #1 Problems due in class on Thurs, Feb 1 or online by Sat, Feb 3, 11:59pm EST: Section 1.1:
 Math E-b Spring 08 Homework # Problems due in class on Thurs, Feb or online by Sat, Feb 3, :59pm EST: Section.: x y =. Find all solutions of the linear system. Represent your solutions graphically, as
Math E-b Spring 08 Homework # Problems due in class on Thurs, Feb or online by Sat, Feb 3, :59pm EST: Section.: x y =. Find all solutions of the linear system. Represent your solutions graphically, as
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MAC 1105 Module Test 3 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Give the coordinates of the point of intersection of the linear equations.
MAC 1105 Module Test 3 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Give the coordinates of the point of intersection of the linear equations.
Math Practice Problems for Test 1
 Math 290 - Practice Problems for Test UNSUBSTANTIATED ANSWERS MAY NOT RECEIVE CREDIT. 5 3 4. Show that w is in the span of v 5 and v 2 2 by writing w as a linear 6 6 6 combination of v and v 2. 2. Find
Math 290 - Practice Problems for Test UNSUBSTANTIATED ANSWERS MAY NOT RECEIVE CREDIT. 5 3 4. Show that w is in the span of v 5 and v 2 2 by writing w as a linear 6 6 6 combination of v and v 2. 2. Find
Math 3013 Problem Set 4
 (e) W = {x, 3x, 4x 3, 5x 4 x i R} in R 4 Math 33 Problem Set 4 Problems from.6 (pgs. 99- of text):,3,5,7,9,,7,9,,35,37,38. (Problems,3,4,7,9 in text). Determine whether the indicated subset is a subspace
(e) W = {x, 3x, 4x 3, 5x 4 x i R} in R 4 Math 33 Problem Set 4 Problems from.6 (pgs. 99- of text):,3,5,7,9,,7,9,,35,37,38. (Problems,3,4,7,9 in text). Determine whether the indicated subset is a subspace
8.4. Systems of Equations in Three Variables. Identifying Solutions 2/20/2018. Example. Identifying Solutions. Solving Systems in Three Variables
 8.4 Systems of Equations in Three Variables Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison- Wesley Identifying Solutions Solving Systems in Three Variables Dependency, Inconsistency,
8.4 Systems of Equations in Three Variables Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison- Wesley Identifying Solutions Solving Systems in Three Variables Dependency, Inconsistency,
H-Pre-Calculus Targets Chapter I can write quadratic functions in standard form and use the results to sketch graphs of the function.
 H-Pre-Calculus Targets Chapter Section. Sketch and analyze graphs of quadratic functions.. I can write quadratic functions in standard form and use the results to sketch graphs of the function. Identify
H-Pre-Calculus Targets Chapter Section. Sketch and analyze graphs of quadratic functions.. I can write quadratic functions in standard form and use the results to sketch graphs of the function. Identify
Mini Lecture 3.1 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables
 Mini Lecture. Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables. Determine whether an ordered pair is a solution of a system of linear equations. 2. Solve systems of equations by graphing.. Solve systems of
Mini Lecture. Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables. Determine whether an ordered pair is a solution of a system of linear equations. 2. Solve systems of equations by graphing.. Solve systems of
Date: Pd: Unit 4. GSE H Analytic Geometry EOC Review Name: Units Rewrite ( 12 3) 2 in simplest form. 2. Simplify
 GSE H Analytic Geometry EOC Review Name: Units 4 7 Date: Pd: Unit 4 1. Rewrite ( 12 3) 2 in simplest form. 2. Simplify 18 25 3. Which expression is equivalent to 32 8? a) 2 2 27 4. Which expression is
GSE H Analytic Geometry EOC Review Name: Units 4 7 Date: Pd: Unit 4 1. Rewrite ( 12 3) 2 in simplest form. 2. Simplify 18 25 3. Which expression is equivalent to 32 8? a) 2 2 27 4. Which expression is
ANALYTICAL MATHEMATICS FOR APPLICATIONS 2018 LECTURE NOTES 3
 ANALYTICAL MATHEMATICS FOR APPLICATIONS 2018 LECTURE NOTES 3 ISSUED 24 FEBRUARY 2018 1 Gaussian elimination Let A be an (m n)-matrix Consider the following row operations on A (1) Swap the positions any
ANALYTICAL MATHEMATICS FOR APPLICATIONS 2018 LECTURE NOTES 3 ISSUED 24 FEBRUARY 2018 1 Gaussian elimination Let A be an (m n)-matrix Consider the following row operations on A (1) Swap the positions any
LINEAR ALGEBRA KNOWLEDGE SURVEY
 LINEAR ALGEBRA KNOWLEDGE SURVEY Instructions: This is a Knowledge Survey. For this assignment, I am only interested in your level of confidence about your ability to do the tasks on the following pages.
LINEAR ALGEBRA KNOWLEDGE SURVEY Instructions: This is a Knowledge Survey. For this assignment, I am only interested in your level of confidence about your ability to do the tasks on the following pages.
Graphing Systems of Linear Equations
 Graphing Systems of Linear Equations Groups of equations, called systems, serve as a model for a wide variety of applications in science and business. In these notes, we will be concerned only with groups
Graphing Systems of Linear Equations Groups of equations, called systems, serve as a model for a wide variety of applications in science and business. In these notes, we will be concerned only with groups
Math Practice Final - solutions
 Math 151 - Practice Final - solutions 2 1-2 -1 0 1 2 3 Problem 1 Indicate the following from looking at the graph of f(x) above. All answers are small integers, ±, or DNE for does not exist. a) lim x 1
Math 151 - Practice Final - solutions 2 1-2 -1 0 1 2 3 Problem 1 Indicate the following from looking at the graph of f(x) above. All answers are small integers, ±, or DNE for does not exist. a) lim x 1
UNLV University of Nevada, Las Vegas
 UNLV University of Nevada, Las Vegas The Department of Mathematical Sciences Information Regarding Math 14 Final Exam Revised 8.8.016 While all material covered in the syllabus is essential for success
UNLV University of Nevada, Las Vegas The Department of Mathematical Sciences Information Regarding Math 14 Final Exam Revised 8.8.016 While all material covered in the syllabus is essential for success
x 1 2x 2 +x 3 = 0 2x 2 8x 3 = 8 4x 1 +5x 2 +9x 3 = 9
 Sec 2.1 Row Operations and Gaussian Elimination Consider a system of linear equations x 1 2x 2 +x 3 = 0 2x 2 8x 3 = 8 4x 1 +5x 2 +9x 3 = 9 The coefficient matrix of the system is The augmented matrix of
Sec 2.1 Row Operations and Gaussian Elimination Consider a system of linear equations x 1 2x 2 +x 3 = 0 2x 2 8x 3 = 8 4x 1 +5x 2 +9x 3 = 9 The coefficient matrix of the system is The augmented matrix of
2.1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
 .1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions A term is a number or the product of a number and variables raised to powers. The numerical coefficient of a term is the numerical factor. The numerical coefficient
.1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions A term is a number or the product of a number and variables raised to powers. The numerical coefficient of a term is the numerical factor. The numerical coefficient
SLCSE Math 1050, Spring, 2013 Lesson 1, Monday, January 7, 2013: Quadratic Functions
 SLCSE Math 1050, Spring, 2013 Lesson 1, Monday, January 7, 2013: Quadratic Functions Note: The activities are to be done and discussed in class. Homework, due at 4 pm Monday, Jan 14, 2013 consists of all
SLCSE Math 1050, Spring, 2013 Lesson 1, Monday, January 7, 2013: Quadratic Functions Note: The activities are to be done and discussed in class. Homework, due at 4 pm Monday, Jan 14, 2013 consists of all
MA 1B PRACTICAL - HOMEWORK SET 3 SOLUTIONS. Solution. (d) We have matrix form Ax = b and vector equation 4
 MA B PRACTICAL - HOMEWORK SET SOLUTIONS (Reading) ( pts)[ch, Problem (d), (e)] Solution (d) We have matrix form Ax = b and vector equation 4 i= x iv i = b, where v i is the ith column of A, and 4 A = 8
MA B PRACTICAL - HOMEWORK SET SOLUTIONS (Reading) ( pts)[ch, Problem (d), (e)] Solution (d) We have matrix form Ax = b and vector equation 4 i= x iv i = b, where v i is the ith column of A, and 4 A = 8
1.1 Introduction to Linear Systems and Row Reduction
 .. INTRODUTION TO LINEAR SYSTEMS AND ROW REDUTION. Introduction to Linear Systems and Row Reduction MATH 9 FALL 98 PRELIM # 9FA8PQ.tex.. Solve the following systems of linear equations. If there is no
.. INTRODUTION TO LINEAR SYSTEMS AND ROW REDUTION. Introduction to Linear Systems and Row Reduction MATH 9 FALL 98 PRELIM # 9FA8PQ.tex.. Solve the following systems of linear equations. If there is no
Linear Systems. Math A Bianca Santoro. September 23, 2016
 Linear Systems Math A4600 - Bianca Santoro September 3, 06 Goal: Understand how to solve Ax = b. Toy Model: Let s study the following system There are two nice ways of thinking about this system: x + y
Linear Systems Math A4600 - Bianca Santoro September 3, 06 Goal: Understand how to solve Ax = b. Toy Model: Let s study the following system There are two nice ways of thinking about this system: x + y
EOC FSA Practice Test
 Name: EOC FSA Practice Test Algebra 2 Calculator Portion Compiled by the Broward County Public Schools Office of Instruction and Intervention Mathematics, Science, & Gifted Department FSA Mathematics Reference
Name: EOC FSA Practice Test Algebra 2 Calculator Portion Compiled by the Broward County Public Schools Office of Instruction and Intervention Mathematics, Science, & Gifted Department FSA Mathematics Reference
Algebra & Trig. I. For example, the system. x y 2 z. may be represented by the augmented matrix
 Algebra & Trig. I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
Algebra & Trig. I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
