STIFFNESS EVALUATION OF THE COMPOSITE LAMINATES WITH WAVY PLIES AND THEIR STABILITY ANALYSIS
|
|
|
- Tracey Sharp
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE 9 TH ITERATIOA COFERECE O COMPOITE MATERIA TIFFE EVAUATIO OF THE COMPOITE AMIATE WITH WAVY PIE AD THEIR TABIITY AAYI H. Dalir *, J. E. Brunel, F. Dervault, A. andry Department of Composites Development, Bombardier Aerospace, Montreal, Canada * Corresponding author (hamid.dalir@aero.bombardier.com) Keyords: ply aviness, avy laminate, elastic properties, compression and shear buckling Introduction Creation of the ply aviness during different composite fabrication processes is a critical issue for the analysis of the composite structures. It is a source of geometrical non-uniformity hich makes the composite analysis and modeling complicated and computation-intensive. For simplicity, hen analyzing laminated composites, idealized lamina ith perfectly straight fibers is often assumed. Hoever, the aviness usually produces different mechanical properties for such laminates [-8]. Ply aviness could be either the outcome of the local deformation of the fibers, or be caused by the residual stresses accumulated during the curing process. It usually happens through the thickness of the composite parts and can be often revealed by their destructive inspection. everal researchers have introduced different theories, micro-mechanical finite element methods (M-FEM) and eperimental techniques to investigate the elastic behavior of composite laminates having ply aviness. in et al. [9] developed a formulation to predict the compressive failure of the composite laminates ith avy fibers and a nonlinear matri. Wisnom et al. [0] discussed the effect of the misalignment angle beteen the fibers and the loading ais and shoed that small misalignment angles have a very strong effect on compressive strength. Camponeschi et al. [] designed an interface measurement technique using an optical microscope equipped ith an -z indeing table to measure aviness at the mid-plane of the laminate and then analyzed and established a theoretical relationship beteen fiber aviness and reduction of compressive strength. o et al. [] developed a model to predict the compressive strength of composite laminates using a combined analytical and semi-empirical approach. In the tension case, Rai et al. [] and Chan et al. [4] investigated the effect of fiber aviness on stiffness of composites by a numerical method. Bogetti et al. [5,6], developed an analytical model for evaluating the stiffness reduction of a laminate having aviness. Hoever, no eplicit analytical formulation as obtained in their model. Garnich et al. [7], developed an incremental scheme to predict the general stress-strain response for a curved fiber composite lamina. Chun et al. [8], evaluated the influence of in-plane aviness on the structural response and its sensitivity on a composite beam. Ray et al. [9] and Reddy et al. [0] developed finite element micromechanical models for stiffness of composite plates having aviness. The main objective of this paper is to present eplicit formulas to evaluate the influence of the out-of-plane fiber aviness on the stiffness of the composite panels. tability sensitivities due to the variation of fiber aviness ould also be assessed by determination of their effects on the critical buckling loads of the composite laminates under compression and shear. Our proposed approach to the problem of aviness is to calculate the equivalent homogenized properties of the composite laminate under consideration, and subsequently use these properties for structural analysis. Results of the developed method are compared ith those of M-FEM of Garnich et al. [7]. et, the effects of the ply aviness on the buckling behavior of the composite laminates under compression and pure shear are investigated ith to different Finite Element Model (FEM) approaches hich ould be presented in details in the folloing section. Finally, the results are compared ith those of analytical solutions. Effective Mechanical Properties. Analytical Formulation The cross section of a monolithic laminate ith local ply aviness has been shon in Fig.. To obtain the reduced stiffness values, the average strain values over the length of the laminate should be calculated.
2 PREDICTIO OF THE EATIC PROPERTIE FOR COMPOITE TAPE AMIATE WITH WAVY PIE Fig.. aminate configuration ith ply aviness The stress-strain relation in XZ coordinate system is defined as [], and y y y y () are the strain and stress tensors, respectively, and is the compliance matri hich is defined as, here 6 6 () () Here, cos, sin and is the angle beteen the fiber and direction X throughout the laminate and 0 E E ij 0 (4) E E 0 0 G here E, E,, and G are the stiffness properties of the lamina, i, j,,6. o if e assume the fiber aviness as a sinusoidal function that its amplitude is reducing linearly from h ma to zero at the etreme plies, e can assume the out-of-plane fiber aviness as: and z hma sin t (5) l z h t l ma tan cos l (6) hma and l are the maimum aviness height and length over all the laminate plies. t is the laminate thickness. Therefore the equivalent values for the compliance matri could be ritten as: t eqij ij ddz (7) t t 0 and the equivalent major Young s modulus ould be obtained as: E here l is the aviness fraction and i i i t t i i i i t t i i i t i t i (8) (9) and i t are the total number of laminate plies and thickness of the i th ply respectively; and
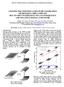
3 z i h ma l t. All other effective laminate properties could be obtained in the similar manner.. Evaluation of the aminate tiffness To validate the formulations obtained in the previous section, the stiffness results are compared ith those of finite element micromechanics modeling done by Garnich et al. [7]. In their study, the aviness as assumed to be sinusoidal. Based on the volume percentage of each constituent, the avelength and the amplitude of the aved fibers, the unit cell geometry as defined (see Fig. ). This unit cell as divided into heahedral finite elements as shon in Fig.. In order to determine the stiffness parameters, stress analysis of the avy unit cell as carried out for several independent load cases. Here e consider the same fiber and matri properties of a graphite/epoy system as ere employed by Garnich et al. [7]. The fiber is assumed to have transversely isotropic elastic properties of E 07.5 GPa, E 5 GPa, E G G 95 GPa, G 9. GPa, 0.4 and The polymer matri is assumed to have isotropic elastic properties of E 4.5 GPa and 0.4. For 40, 50, 60, and 70% of fiber volume fractions ( V ), the predicted equivalent major V f Young s modulus is shon in Fig. 4. As it can be seen the modulus values obtained from Eq. (8) are in close agreement ith those of comple M-FEM results of Garnich et al. [7]. Fig.. A avy fiber unit cell volume [7] Fig.. M-FEM discretization of part of the unit cell [7] E (GPa) Fig. 4. Major modulus ( E ) as a function of aviness Buckling of Composite Panels ith Wavy Plies. Compression Case.. Analytical Formulation In this section, e consider a rectangular composite plate having a region ith avy plies (see Fig. 5). We are specifically interested to see if it is a valid assumption to consider the effects of the ply aviness on the buckling analysis by applying the equivalent homogenized properties of the composite laminate under consideration. The plate is assumed to be simply-supported on all of its four edges. The out-of-plane displacement, y of the plate is assumed to be in the form of V f / V M m ny, Amn sin sin (0) m n y a ma / l Micromechanical FEM Analytical solution here m and n are odd numbers, and A mn are
4 PREDICTIO OF THE EATIC PROPERTIE FOR COMPOITE TAPE AMIATE WITH WAVY PIE Carrying out the integrations, and setting the derivative of ith respect to A mn equal to zero, leads to the generalized eigenvalue problem: A B () here the eigenvalue is the buckling load hen lbf in contains the constants Amn is applied; the eigenvector of Eq. (0), and the matrices A and B contain stiffness and geometry information of the problem. Therefore, in case of a square plate, the main critical buckling load is given as crit D D D D (4) Fig. 5. aminate ith aviness under pure compression unknon coefficients to be determined. Assuming that the layup is symmetric and balanced ith D6 D6 0, the buckling load can be determined by minimizing the total potential energy of the plate: 0 0 D 4D d dy y y D D 0 0 d dy () here is the applied compressive load per unit idth, and i,, 6, are the bending D ij stiffnesses at any location in the plate. The coupling terms D6 and D6 could be incorporated ith appropriate changes in Eq. (0) at a slight increase in compleity by introducing an anisotropy factor []. The unknons Amn are determined by minimizing the total energy 0 A mn () To compensate for the effects of transverse shear hich could become important hen analyzing thick laminate plates, one can rite [] crit G t (5) crit here G y and t are the shear modulus and thickness of the laminate plate, respectively. Eq. (5) is only applicable to balanced and symmetric laminates. To account for the anisotropy of the laminate plate here the coupling terms D6 and D6 could not be neglected, an anisotropy factor ould be considered as [] * crit 0. D D 6 D y D.. Finite Element Modeling 6 crit (6) Based on the formulation introduced in section., a macro as prepared using Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) enabling the users to calculate the equivalent homogenized properties of the composite laminate having avy plies (see Fig. 6). The users ill have to insert the geometry of the aviness, stiffness properties of the idealized lamina ith perfectly straight fibers along ith the laminates layup as the input. The output of the program ould be the averaged equivalent homogenized mechanical properties of the avy
5 THE 9 TH ITERATIOA COFERECE O COMPOITE MATERIA Fig. 6. VBA program developed to obtain the equivalent homogenized properties of the laminates having avy plies lamina or laminates hich could be used for structural analysis of the composite structures having avy plies. Here e consider a 0 in 0 in square panel comprised of 88 plies [(±45 /0 ) /(±45 4 /0 ) ] of Carbon/Epoy tape laminate ith the lamina properties of E 9.0 msi, E.40 msi, E.9 msi, G msi, G 0.4 msi, G 0.7 msi, 0.7, 0.57 and Eight different FEM cases ere run, each ith different aviness lengths ( l ) of 0 (laminate having plies ith straight fibers), in, in, 4 in, 8 in, in, 6 in and 0 in. The maimum height of the aviness as considered to be 0.0 in. For the FEM, the astran softare (O 05) by MC as used. The model consisted of 600 fournoded quadrilateral elements ith 68 nodes. The geometry, loading, and typical results obtained from FEM are shon in Figs. 5 and 7. Fig. 7. Typical buckling results under compression To different approaches ere considered ith FEM. In the first called to-phase FEM approach, the panel as considered to be made of to different regions, regions at etremities having the properties of laminas ith straight fibers and the avy region
6 THE 9 TH ITERATIOA COFERECE O COMPOITE MATERIA Table. Comparison of different FEM and analytical approaches for the case of the pure compression l (in) : To-phase FEM (lbf/in) : One-phase FEM (lbf/in) : One-phase Analytical (lbf/in) Difference beteen & (%) Difference beteen & (%) / o One-phase Analytical One-phase FEM To-phase FEM l (in) Fig. 8. Compression buckling load reduction by aviness / o in the middle of the panel ith averaged reduced properties obtained from the VBA program by considering l (see Fig. 6). In the second approach called one-phase FEM, the equivalent homogenized properties of the composite laminate ith avy plies ere applied all over the panel. In this approach, in the VBA program as considered to be 0 in, and the average homogenized properties ere obtained for laminas ith different aviness length. The buckling loads predicted by the to FEM approaches have been compared in Table and Fig. 8 ith those obtained from Eq. 6. In all cases and ith the both FEM approaches used here, the FE-predicted buckling modes ere symmetric. The highest difference beteen the to FEM approaches as.5%. The FEM results ere successfully correlated to those obtained from Eq. (6) ith the maimum of 6.7% deviation (see Table ). Fig. 9 shos the reduction in the buckling load of the panel in compression as a function of aviness parameters ( l and h ma ). For eample, for l in and h ma 0.4 in, one can epect ~% reduction in the critical buckling load in compression Fig. 9. Effect of the aviness parameters on the critical compression buckling load of our 88-ply composite panel. hear Case.. Analytical Formulation For the case of shear, e considered the same rectangular composite plate as in section. having the same aviness characteristics (see Fig. 0). The plate as loaded by a shear load. Therefore the total potential energy of the plate (Eq. ) for the case of pure shear can be reritten as l (in) 0 0 D 0 0 D 4D y y h ma (0-4 in) D d dy y y d dy y (7)
7 Table. Comparison of different FEM and analytical approaches for the case of the pure shear l (in) : To-phase FEM (lbf/in) : One-phase FEM (lbf/in) : One-phase Analytical (lbf/in) Difference beteen & (%) Difference beteen & (%) a polynomial-based displacement function hich consists of a boundary polynomial specifying the geometric and kinematic boundary conditions, multiplied by a complete to-dimensional simple polynomial. This displacement function has been used successfully for the modeling of bilateral plate buckling problems [4,5], and can be ritten as M n n, ak y (8) m0 n0 y y y Fig. 0. aminate ith aviness under pure shear here M is the degree of a to-dimensional polynomial, a k is the arbitrary Ritz coefficient and k is determined as k n (9) Fig. shos the typical shear mode shape of the panel under shear loading. The edges of the plate are all simply supported. Therefore, the shear buckling load can be epressed as [6] ycrit k s 0. D D 5 (0) here k s is the shear buckling factor and for our specific layup, it as determined to be equal to.8. Fig.. Typical buckling results under pure shear The Rayleigh-Ritz method as used to determine the buckling load. This method is set out in Timoshenko and Gere s tet []. The out-of-plane, y of the plate as considered as displacement.. Finite Element Modeling For the FEM, the same models as those introduced in section.. ere used by astran softare. The nodes located on the edge lines ere loaded under pure shear. The comparison of the analytical Rayleigh-Ritz method ith the results of the to 7
8 PREDICTIO OF THE EATIC PROPERTIE FOR COMPOITE TAPE AMIATE WITH WAVY PIE y / yo y / yo Fig.. hear buckling load reduction by aviness l (in) h ma (0-4 in) Fig.. Effect of the aviness parameters on the critical shear buckling load of our 88-ply composite panel different FEM approaches hich ere introduces in section.., has been shon in Table and Fig.. As it can be seen, there is an ecellent agreement beteen the to FEM approaches (orst deviation is -.%). Fig. shos the reduction in the buckling load of the panel under pure shear as a function of aviness parameters ( l h ). 4 ummary and Conclusions One-phase Analytical One-phase FEM To-phase FEM l (in) and ma The eplicit forms of the stiffness for a laminate containing out-of-plane fiber aviness ere derived. The results ere in ecellent agreement ith those obtained from comple M-FEM of Garnich et al. [7]. The reduction of the lamina stiffness E as found to be %, 0%, 40% and 70% for plies having %, %, 5% and 0% aviness, respectively. These equivalent homogenized properties ere then used for the compression and shear stability analysis of the composite panels having fiber aviness. For a 0 in 0 in square panel comprised of 88 plies [(±45 /0 ) /(±45 4 /0 ) ] of Carbon/Epoy tape laminate having aviness parameters of 0. l and a ma l 0.075, it as found that the reduction of the stiffness ill lead to 8% and 7% decrease in the buckling load for the case of pure compression and pure shear, respectively. To different FE modeling approaches ere selected and their results ere compared ith those of closed form analytical formulations. It as also shon that the results are in close agreement ith each other ith the maimum deviation of 6.7% and 0.% for the case of pure compression and pure shear, respectively. We also found that for thick laminates, the effects of the local changes of the fiber volume fraction hich is caused by the aviness (i.e., changes on the local ply stiffness and the aviness geometry), don t have considerable effect on the compression and shear buckling loads (results not shon). Therefore, to find the effective stiffness of a laminate having ply aviness, one need to first measure the aviness parameters ( l and a ma l ) and then use the formulations introduced in section. (VBA tool shon in Fig. 6). Once the equivalent homogenized properties of the laminate having aviness ere determined, they can be used subsequently for the stability analysis using the analytical formulations introduced in section. Although the aviness is usually local, hoever, it ould be accurate enough if the homogenized stiffness values be applied all over the panel instead of considering the panel ith several regions ith or ithout aviness. 5 Acknoledgements The ork described in this paper as sponsored by Bombardier Aerospace. The authors ould like to acknoledge the technical support of Dr. aid Jazouli and Mr. Christian Faure from Core Engineering of Bombardier Aerospace. pecial thank goes to Prof. Daniel Therriault from Ecole Polytechnique de Montreal for his valuable comments and several discussions. The vies and conclusions contained in this article should not be interpreted as representing the official policies, either epressed or implied, of the Bombardier Aerospace.
9 References [] D.O. Adams and M.W. Hyer, Effects of ayer Waviness on the Compression Fatigue Performance of Thermoplastic Composite aminates. Fatigue, Vol. 6, pp 85-9, 994. [] H.M. Hsiao and I.M. Daniel, onlinear Elastic Behavior of Unidirectional Composites ith Fiber Waviness under Compressive oading. AME Journal of Engineering Materials and Technology, Vol. 8, pp , 996. [] T. tecenko and M.R. Piggott, Fiber Waviness and Other Mesostructures in Filament Wound Materials. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites, Vol. 6, pp , 997. [4] A.B. De Morais and A.T. Marques, A Micromechanical Model for the Prediction of the amina ongitudinal Compression trength of Composite aminates. Journal of Composite Materials, Vol., o. 4, pp 97-4, 997. [5] P.J. Joyce, D. Kugler and T.J. Moon, A Technique for Characterizing Process-Induced Fiber Waviness in Unidirectional Composite aminates - Using Optical Microscopy. Journal of Composite Materials, Vol., o. 7, pp , 997. [6] D.J. Bradley, D.O. Adams and H.E. Gascoigne, Interlaminar trains and Compressive trength Reductions due to ested ayer Waviness in Composite aminates. Journal of Reinforced Plastic and Composites, Vol. 7, o., pp 989-0, 998. [7] M.R. Wisnom and J.W. Atkinson, Fiber Waviness Generation and Measurement and Its Effect on Compressive trength. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites, Vol. 9, pp 96-0, 000. [8] H-J. Chun, J-Y. hin and I.M. Daniel, Effect of Material Geometric onlinearities on the Tensile and Compressive Behavior of Composite Materials ith Fiber Waviness. Composite cience and Technology, Vol. 6, pp 5-4, 00. [9] K. Y. in and X. J. Zhang, Effect of Fiber Waviness on the Compressive trength of aminated Composites. Proceedings of the nd International ymposium on Composite Materials and tructures, Beijing, China, August 99, pp 0-5, 99. [0] M.R. Wisnom, The Effect of Fiber Misalignment on the Compressive trength of Unidirectional Carbon Fiber/Epoy. Composites, Vol., o. 5, pp , 990. [] E.T. Camponeschi, amina Waviness evels in Thick Composites and Its Effect on Their Compression trength. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Composite Materials, Honolulu, Haaii, pp 0-E-, 0-E-, 99. [] K.H. o and E..M. Chim, Compressive trength of Unidirectional Composites. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites, Vol., pp , 99. [] H.G. Rai, C.W. Rogers and D.A. Crane, Mechanics of Curved Fiber Composites. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites, Vol., pp , 99. [4] W.. Chan and C.J. Chou, Effects of Delamination and Ply Fiber Waviness on Effective Aial and Bending tiffness. Proceedings of the nd International ymposium on Composite Materials and tructures, Beijing, China, August, 99. [5] T.A. Bogetti, J.W. Gillespie and M.A. amontia, Influence of Ply Waviness on the tiffness and trength and trength Reduction on Composite aminates. Journal of Thermoplastic Composite Materials, Vol. 5, pp 44-69, 99. [6] T.A. Bogetti, J.W. Gillespie and M.A. amontia, The Influence of Ply Waviness ith onlinear hear on the tiffness and trength Reduction of Composite aminates. Mechanics of Composite Materials, AMD-Vol. 59, pp. -67, 99. [7] M.R., Garnich, G. Karami. Finite Element Micromechanics for tiffness and trength of Wavy Fiber Composites. Journal of Composite Materials, Vol. 8, o. 4, pp 7-9, 004. [8] H-J. Chun, J-Y. hin and I.M. Daniel, Effect of Material Geometric onlinearities on the Tensile and Compressive Behavior of Composite Materials ith Fiber Waviness, Composite cience and Technology, Vol. 6, pp 5-4, 00. [9] H.G. Ray, C.W. Rogers and D.A. Crane, Mechanics of Curved Fiber Composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos., Vol., pp 55-5, 99. [0] J.. Reddy, Mechanics of aminated Composite Plates and hells Theory and Analysis, CRC Press C Boca Raton, pp 8-8, 004. [] I.M. Daniel and O. Ishai, Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials. Oford University Press, 994. [] J.F. Mandell, An Eperimental Investigation of the Buckling of Anisotropic Fiber Reinforced Plastic Plates. U Department of Commerce, 968 [].P. Timoshenko and J.M. Gere, Theory of Elastic tability. e York: McGra Hill, 96. [4] C.M. Wang and K.M. ie, Buckling of Triangular Plates Under Uniform Compression. Engineering tructures, Vol. 6, o., pp 4-50, 94. [5] K.M. ie and C.M. Wang, Elastic Buckling of Regular Polygonal Plates. Thin-Walled tructures, Vol., pp 60-67, 995. [6] P.. Bulson, The tability of Flat Plates. ondon: Chatto and Windus,
KINK BAND FORMATION OF FIBER REINFORCED POLYMER (FRP)
 KINK BAND FORMATION OF FIBER REINFORCED POLYMER (FRP) 1 University of Science & Technology Beijing, China, niukm@ustb.edu.cn 2 Tsinghua University, Department of Engineering Mechanics, Beijing, China,
KINK BAND FORMATION OF FIBER REINFORCED POLYMER (FRP) 1 University of Science & Technology Beijing, China, niukm@ustb.edu.cn 2 Tsinghua University, Department of Engineering Mechanics, Beijing, China,
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Mechanics of Composite Materials, Second Edition Autar K Kaw University of South Florida, Tampa, USA
 Mechanics of Composite Materials, Second Edition Autar K Kaw University of South Florida, Tampa, USA TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION TO COMPOSITE MATERIALS 1.1 Introduction... 1.2 Classification... 1.2.1
Mechanics of Composite Materials, Second Edition Autar K Kaw University of South Florida, Tampa, USA TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION TO COMPOSITE MATERIALS 1.1 Introduction... 1.2 Classification... 1.2.1
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF COMPOSITE MATERIALS
 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF COMPOSITE MATERIALS Ever J. Barbero Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering West Virginia University USA CRC Press Taylor &.Francis Group Boca Raton London New York
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF COMPOSITE MATERIALS Ever J. Barbero Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering West Virginia University USA CRC Press Taylor &.Francis Group Boca Raton London New York
PLY WAVINESS ON IN-PLANE STIFFNESS OF COMPOSITE LAMINATES
 PLY WAVINESS ON IN-PLANE STIFFNESS OF COMPOSITE LAMINATES Cimini Jr., Carlos A., and Tsai, Stephen W. 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Federal University of Minas Gerais Av. Antônio Carlos, 6627
PLY WAVINESS ON IN-PLANE STIFFNESS OF COMPOSITE LAMINATES Cimini Jr., Carlos A., and Tsai, Stephen W. 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Federal University of Minas Gerais Av. Antônio Carlos, 6627
QUESTION BANK Composite Materials
 QUESTION BANK Composite Materials 1. Define composite material. 2. What is the need for composite material? 3. Mention important characterits of composite material 4. Give examples for fiber material 5.
QUESTION BANK Composite Materials 1. Define composite material. 2. What is the need for composite material? 3. Mention important characterits of composite material 4. Give examples for fiber material 5.
Finite Element Instability Analysis of the Steel Joist of Continuous Composite Beams with Flexible Shear Connectors
 Journal of Solid Mechanics Vol. 9, No. (07) pp. 5-69 Finite Element Instability Analysis of the Steel Joist of Continuous Composite Beams ith Fleible Shear Connectors H. Bakhshi,*, H.R. Ronagh Engineering
Journal of Solid Mechanics Vol. 9, No. (07) pp. 5-69 Finite Element Instability Analysis of the Steel Joist of Continuous Composite Beams ith Fleible Shear Connectors H. Bakhshi,*, H.R. Ronagh Engineering
SANDWICH COMPOSITE BEAMS for STRUCTURAL APPLICATIONS
 SANDWICH COMPOSITE BEAMS for STRUCTURAL APPLICATIONS de Aguiar, José M., josemaguiar@gmail.com Faculdade de Tecnologia de São Paulo, FATEC-SP Centro Estadual de Educação Tecnológica Paula Souza. CEETEPS
SANDWICH COMPOSITE BEAMS for STRUCTURAL APPLICATIONS de Aguiar, José M., josemaguiar@gmail.com Faculdade de Tecnologia de São Paulo, FATEC-SP Centro Estadual de Educação Tecnológica Paula Souza. CEETEPS
Computational Analysis for Composites
 Computational Analysis for Composites Professor Johann Sienz and Dr. Tony Murmu Swansea University July, 011 The topics covered include: OUTLINE Overview of composites and their applications Micromechanics
Computational Analysis for Composites Professor Johann Sienz and Dr. Tony Murmu Swansea University July, 011 The topics covered include: OUTLINE Overview of composites and their applications Micromechanics
Hygrothermal stresses in laminates
 Hygrothermal stresses in laminates Changing environment conditions (temperature and moisture) have an important effect on the properties which are matrix dominated. Change in temperaturet and moisture
Hygrothermal stresses in laminates Changing environment conditions (temperature and moisture) have an important effect on the properties which are matrix dominated. Change in temperaturet and moisture
Multi Disciplinary Delamination Studies In Frp Composites Using 3d Finite Element Analysis Mohan Rentala
 Multi Disciplinary Delamination Studies In Frp Composites Using 3d Finite Element Analysis Mohan Rentala Abstract: FRP laminated composites have been extensively used in Aerospace and allied industries
Multi Disciplinary Delamination Studies In Frp Composites Using 3d Finite Element Analysis Mohan Rentala Abstract: FRP laminated composites have been extensively used in Aerospace and allied industries
A HIGHER-ORDER BEAM THEORY FOR COMPOSITE BOX BEAMS
 A HIGHER-ORDER BEAM THEORY FOR COMPOSITE BOX BEAMS A. Kroker, W. Becker TU Darmstadt, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Chair of Structural Mechanics Hochschulstr. 1, D-64289 Darmstadt, Germany kroker@mechanik.tu-darmstadt.de,
A HIGHER-ORDER BEAM THEORY FOR COMPOSITE BOX BEAMS A. Kroker, W. Becker TU Darmstadt, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Chair of Structural Mechanics Hochschulstr. 1, D-64289 Darmstadt, Germany kroker@mechanik.tu-darmstadt.de,
Bending of Simply Supported Isotropic and Composite Laminate Plates
 Bending of Simply Supported Isotropic and Composite Laminate Plates Ernesto Gutierrez-Miravete 1 Isotropic Plates Consider simply a supported rectangular plate of isotropic material (length a, width b,
Bending of Simply Supported Isotropic and Composite Laminate Plates Ernesto Gutierrez-Miravete 1 Isotropic Plates Consider simply a supported rectangular plate of isotropic material (length a, width b,
ISSN: ISO 9001:2008 Certified International Journal of Engineering Science and Innovative Technology (IJESIT) Volume 2, Issue 4, July 2013
 Delamination Studies in Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Composites K.Kantha Rao, Dr P. Shailesh, K. Vijay Kumar 1 Associate Professor, Narasimha Reddy Engineering College Hyderabad. 2 Professor, St. Peter s Engineering
Delamination Studies in Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Composites K.Kantha Rao, Dr P. Shailesh, K. Vijay Kumar 1 Associate Professor, Narasimha Reddy Engineering College Hyderabad. 2 Professor, St. Peter s Engineering
Passive Damping Characteristics of Carbon Epoxy Composite Plates
 Journal of Materials Science and Engineering A 6 (-) 35-4 doi:.765/6-63/6.-.5 D DAVID PUBLISHING Passive Damping Characteristics of Carbon Epoxy Composite Plates Dileep Kumar K * and V V Subba Rao Faculty
Journal of Materials Science and Engineering A 6 (-) 35-4 doi:.765/6-63/6.-.5 D DAVID PUBLISHING Passive Damping Characteristics of Carbon Epoxy Composite Plates Dileep Kumar K * and V V Subba Rao Faculty
Fracture Mechanics, Damage and Fatigue: Composites
 University of Liège Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering Fracture Mechanics, Damage and Fatigue: Composites Ludovic Noels Computational & Multiscale Mechanics of Materials CM3 http://www.ltas-cm3.ulg.ac.be/
University of Liège Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering Fracture Mechanics, Damage and Fatigue: Composites Ludovic Noels Computational & Multiscale Mechanics of Materials CM3 http://www.ltas-cm3.ulg.ac.be/
American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) Standards. Mechanical Testing of Composites and their Constituents
 Mechanical Testing of Composites and their Constituents American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) Standards Tests done to determine intrinsic material properties such as modulus and strength for
Mechanical Testing of Composites and their Constituents American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) Standards Tests done to determine intrinsic material properties such as modulus and strength for
Dynamic analysis of Composite Micro Air Vehicles
 Dynamic analysis of Composite Micro Air Vehicles Shishir Kr. Sahu Professor and Head, Civil Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, India E-mail: sksahu@nitrkl.ac.in ABSTRACT The present
Dynamic analysis of Composite Micro Air Vehicles Shishir Kr. Sahu Professor and Head, Civil Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, India E-mail: sksahu@nitrkl.ac.in ABSTRACT The present
Effect of Specimen Dimensions on Flexural Modulus in a 3-Point Bending Test
 Effect of Specimen Dimensions on Flexural Modulus in a 3-Point Bending Test M. Praveen Kumar 1 and V. Balakrishna Murthy 2* 1 Mechanical Engineering Department, P.V.P. Siddhartha Institute of Technology,
Effect of Specimen Dimensions on Flexural Modulus in a 3-Point Bending Test M. Praveen Kumar 1 and V. Balakrishna Murthy 2* 1 Mechanical Engineering Department, P.V.P. Siddhartha Institute of Technology,
Materials and Structures. Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur
 Introduction to Composite Materials and Structures Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture 34 Thermal Stresses in Plates Lecture Overview Introduction Mechanical and Thermal Strains
Introduction to Composite Materials and Structures Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture 34 Thermal Stresses in Plates Lecture Overview Introduction Mechanical and Thermal Strains
ME 7502 Lecture 2 Effective Properties of Particulate and Unidirectional Composites
 ME 75 Lecture Effective Properties of Particulate and Unidirectional Composites Concepts from Elasticit Theor Statistical Homogeneit, Representative Volume Element, Composite Material Effective Stress-
ME 75 Lecture Effective Properties of Particulate and Unidirectional Composites Concepts from Elasticit Theor Statistical Homogeneit, Representative Volume Element, Composite Material Effective Stress-
Materials and Structures. Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur
 Introduction to Composite Materials and Structures Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture 16 Behavior of Unidirectional Composites Lecture Overview Mt Material ilaxes in unidirectional
Introduction to Composite Materials and Structures Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture 16 Behavior of Unidirectional Composites Lecture Overview Mt Material ilaxes in unidirectional
MICROMECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF FRP COMPOSITES SUBJECTED TO LONGITUDINAL LOADING
 MICROMECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF FRP COMPOSITES SUBJECTED TO LONGITUDINAL LOADING N. Krishna Vihari 1, P. Phani Prasanthi 1, V. Bala Krishna Murthy 2* and A. Srihari Prasad 3 1 Mech. Engg. Dept., P. V. P. Siddhartha
MICROMECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF FRP COMPOSITES SUBJECTED TO LONGITUDINAL LOADING N. Krishna Vihari 1, P. Phani Prasanthi 1, V. Bala Krishna Murthy 2* and A. Srihari Prasad 3 1 Mech. Engg. Dept., P. V. P. Siddhartha
Multiscale Approach to Damage Analysis of Laminated Composite Structures
 Multiscale Approach to Damage Analysis of Laminated Composite Structures D. Ivančević and I. Smojver Department of Aeronautical Engineering, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture, University
Multiscale Approach to Damage Analysis of Laminated Composite Structures D. Ivančević and I. Smojver Department of Aeronautical Engineering, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture, University
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF APPLIED ENGINEERING RESEARCH, DINDIGUL Volume 2, No 1, 2011
 Interlaminar failure analysis of FRP cross ply laminate with elliptical cutout Venkateswara Rao.S 1, Sd. Abdul Kalam 1, Srilakshmi.S 1, Bala Krishna Murthy.V 2 1 Mechanical Engineering Department, P. V.
Interlaminar failure analysis of FRP cross ply laminate with elliptical cutout Venkateswara Rao.S 1, Sd. Abdul Kalam 1, Srilakshmi.S 1, Bala Krishna Murthy.V 2 1 Mechanical Engineering Department, P. V.
Effect of Thermal Stresses on the Failure Criteria of Fiber Composites
 Effect of Thermal Stresses on the Failure Criteria of Fiber Composites Martin Leong * Institute of Mechanical Engineering Aalborg University, Aalborg, Denmark Bhavani V. Sankar Department of Mechanical
Effect of Thermal Stresses on the Failure Criteria of Fiber Composites Martin Leong * Institute of Mechanical Engineering Aalborg University, Aalborg, Denmark Bhavani V. Sankar Department of Mechanical
Using MATLAB to Design and Analyse Composite Laminates
 Engineering, 2010, 2, 904-916 doi:10.4236/eng.2010.211114 Published Online November 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/eng). Using MATLAB to Design and Analyse Composite Laminates Abstract Avinash Ramsaroop,
Engineering, 2010, 2, 904-916 doi:10.4236/eng.2010.211114 Published Online November 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/eng). Using MATLAB to Design and Analyse Composite Laminates Abstract Avinash Ramsaroop,
Elastic parameters prediction under dynamic loading based on the. unit cell of composites considering end constraint effect
 Elastic parameters prediction under dynamic loading based on the unit cell of composites considering end constraint effect Wang Meng 1,, Fei Qingguo 1,, Zhang Peiwei 1, (1. Institute of Aerospace Machinery
Elastic parameters prediction under dynamic loading based on the unit cell of composites considering end constraint effect Wang Meng 1,, Fei Qingguo 1,, Zhang Peiwei 1, (1. Institute of Aerospace Machinery
Stress and Strain ( , 3.14) MAE 316 Strength of Mechanical Components NC State University Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
 (3.8-3.1, 3.14) MAE 316 Strength of Mechanical Components NC State Universit Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering 1 Introduction MAE 316 is a continuation of MAE 314 (solid mechanics) Review
(3.8-3.1, 3.14) MAE 316 Strength of Mechanical Components NC State Universit Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering 1 Introduction MAE 316 is a continuation of MAE 314 (solid mechanics) Review
Modeling of the Bending Stiffness of a Bimaterial Beam by the Approximation of One-Dimensional of Laminated Theory
 . Flores-Domínguez Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Applications RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS odeling of the Bending Stiffness of a Bimaterial Beam by the Approimation of One-Dimensional of Laminated
. Flores-Domínguez Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Applications RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS odeling of the Bending Stiffness of a Bimaterial Beam by the Approimation of One-Dimensional of Laminated
Prediction of Elastic Constants on 3D Four-directional Braided
 Prediction of Elastic Constants on 3D Four-directional Braided Composites Prediction of Elastic Constants on 3D Four-directional Braided Composites Liang Dao Zhou 1,2,* and Zhuo Zhuang 1 1 School of Aerospace,
Prediction of Elastic Constants on 3D Four-directional Braided Composites Prediction of Elastic Constants on 3D Four-directional Braided Composites Liang Dao Zhou 1,2,* and Zhuo Zhuang 1 1 School of Aerospace,
Unit 18 Other Issues In Buckling/Structural Instability
 Unit 18 Other Issues In Buckling/Structural Instability Readings: Rivello Timoshenko Jones 14.3, 14.5, 14.6, 14.7 (read these at least, others at your leisure ) Ch. 15, Ch. 16 Theory of Elastic Stability
Unit 18 Other Issues In Buckling/Structural Instability Readings: Rivello Timoshenko Jones 14.3, 14.5, 14.6, 14.7 (read these at least, others at your leisure ) Ch. 15, Ch. 16 Theory of Elastic Stability
DYNAMIC FAILURE ANALYSIS OF LAMINATED COMPOSITE PLATES
 Association of Metallurgical Engineers of Serbia AMES Scientific paper UDC:669.1-419:628.183=20 DYNAMIC FAILURE ANALYSIS OF LAMINATED COMPOSITE PLATES J. ESKANDARI JAM 1 and N. GARSHASBI NIA 2 1- Aerospace
Association of Metallurgical Engineers of Serbia AMES Scientific paper UDC:669.1-419:628.183=20 DYNAMIC FAILURE ANALYSIS OF LAMINATED COMPOSITE PLATES J. ESKANDARI JAM 1 and N. GARSHASBI NIA 2 1- Aerospace
Materials and Structures. Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur
 Introduction to Composite Materials and Structures Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture 15 Behavior of Unidirectional Composites Lecture Overview Mt Material ilaxes in unidirectional
Introduction to Composite Materials and Structures Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture 15 Behavior of Unidirectional Composites Lecture Overview Mt Material ilaxes in unidirectional
Module III - Macro-mechanics of Lamina. Lecture 23. Macro-Mechanics of Lamina
 Module III - Macro-mechanics of Lamina Lecture 23 Macro-Mechanics of Lamina For better understanding of the macromechanics of lamina, the knowledge of the material properties in essential. Therefore, the
Module III - Macro-mechanics of Lamina Lecture 23 Macro-Mechanics of Lamina For better understanding of the macromechanics of lamina, the knowledge of the material properties in essential. Therefore, the
Analysis of Thick Cantilever Beam Using New Hyperbolic Shear Deformation Theory
 International Journal of Research in Advent Technology, Vol.4, No.5, May 16 E-ISSN: 1-967 Analysis of Thick Cantilever Beam Using New Hyperbolic Shear Deformation Theory Mr. Mithun. K. Sawant 1, Dr. Ajay.
International Journal of Research in Advent Technology, Vol.4, No.5, May 16 E-ISSN: 1-967 Analysis of Thick Cantilever Beam Using New Hyperbolic Shear Deformation Theory Mr. Mithun. K. Sawant 1, Dr. Ajay.
Numerical Analysis of Delamination Behavior in Laminated Composite with Double Delaminations Embedded in Different Depth Positions
 Numerical Analysis of Delamination Behavior in Laminated Composite with Double Delaminations Embedded in Different Depth Positions Numerical Analysis of Delamination Behavior in Laminated Composite with
Numerical Analysis of Delamination Behavior in Laminated Composite with Double Delaminations Embedded in Different Depth Positions Numerical Analysis of Delamination Behavior in Laminated Composite with
Comparison of Ply-wise Stress-Strain results for graphite/epoxy laminated plate subjected to in-plane normal loads using CLT and ANSYS ACP PrepPost
 Comparison of Ply-wise Stress-Strain results for graphite/epoxy laminated plate subjected to in-plane normal loads using CLT and ANSYS ACP PrepPost 1 Mihir A. Mehta, 2 Satyen D. Ramani 1 PG Student, Department
Comparison of Ply-wise Stress-Strain results for graphite/epoxy laminated plate subjected to in-plane normal loads using CLT and ANSYS ACP PrepPost 1 Mihir A. Mehta, 2 Satyen D. Ramani 1 PG Student, Department
DRAPING SIMULATION. Recent achievements and future trends. Dr. Sylvain Bel LGCIE University Lyon 1
 DRAPING SIMULATION Recent achievements and future trends 1 Dr. Sylvain Bel LGCIE University Lyon 1 2 DRAPING SIMULATION Why? How? What? DRAPING SIMULATION WHY? Clamps Punch Fabric Die 1 2 Resin 3 4 Fig.
DRAPING SIMULATION Recent achievements and future trends 1 Dr. Sylvain Bel LGCIE University Lyon 1 2 DRAPING SIMULATION Why? How? What? DRAPING SIMULATION WHY? Clamps Punch Fabric Die 1 2 Resin 3 4 Fig.
Open-hole compressive strength prediction of CFRP composite laminates
 Open-hole compressive strength prediction of CFRP composite laminates O. İnal 1, A. Ataş 2,* 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Balikesir University, Balikesir, 10145, Turkey, inal@balikesir.edu.tr
Open-hole compressive strength prediction of CFRP composite laminates O. İnal 1, A. Ataş 2,* 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Balikesir University, Balikesir, 10145, Turkey, inal@balikesir.edu.tr
Finite element modelling of infinitely wide Angle-ply FRP. laminates
 www.ijaser.com 2012 by the authors Licensee IJASER- Under Creative Commons License 3.0 editorial@ijaser.com Research article ISSN 2277 9442 Finite element modelling of infinitely wide Angle-ply FRP laminates
www.ijaser.com 2012 by the authors Licensee IJASER- Under Creative Commons License 3.0 editorial@ijaser.com Research article ISSN 2277 9442 Finite element modelling of infinitely wide Angle-ply FRP laminates
Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis
 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Internal shear force V & bending moment M must ensure equilibrium Fig. 3 2 Sign Conventions for Bending and Shear Fig. 3 3
Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Internal shear force V & bending moment M must ensure equilibrium Fig. 3 2 Sign Conventions for Bending and Shear Fig. 3 3
Tensile behaviour of anti-symmetric CFRP composite
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 1 (211) 1865 187 ICM11 Tensile behaviour of anti-symmetric CFRP composite K. J. Wong a,b, *, X. J. Gong a, S. Aivazzadeh a, M. N. Tamin b
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 1 (211) 1865 187 ICM11 Tensile behaviour of anti-symmetric CFRP composite K. J. Wong a,b, *, X. J. Gong a, S. Aivazzadeh a, M. N. Tamin b
Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Coir Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites Using a Micromechanical Approach
 Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Coir Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites Using a Micromechanical Approach Sandhyarani Biswas Department of Mechanical Engineering, N.I.T Rourkela, INDIA Abstract: Now-a-days,
Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Coir Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites Using a Micromechanical Approach Sandhyarani Biswas Department of Mechanical Engineering, N.I.T Rourkela, INDIA Abstract: Now-a-days,
Passive Damping Characteristics of Carbon Epoxy Composite Plates
 Journal of aterials Science and Engineering A 6 (1-2) (2016) 35-42 doi: 10.17265/2161-6213/2016.1-2.005 D DAVID PUBLISHIG Passive Damping Characteristics of Carbon Epoxy Composite Plates Dileep Kumar K
Journal of aterials Science and Engineering A 6 (1-2) (2016) 35-42 doi: 10.17265/2161-6213/2016.1-2.005 D DAVID PUBLISHIG Passive Damping Characteristics of Carbon Epoxy Composite Plates Dileep Kumar K
STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF FIBER REINFORCED COMPOSITE MATERIALS CESAR AUGUSTO ROJAS. Presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School of
 STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF FIBER REINFORCED COMPOSITE MATERIALS by CESAR AUGUSTO ROJAS Presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School of The University of Teas at Arlington in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF FIBER REINFORCED COMPOSITE MATERIALS by CESAR AUGUSTO ROJAS Presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School of The University of Teas at Arlington in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
7.4 The Elementary Beam Theory
 7.4 The Elementary Beam Theory In this section, problems involving long and slender beams are addressed. s with pressure vessels, the geometry of the beam, and the specific type of loading which will be
7.4 The Elementary Beam Theory In this section, problems involving long and slender beams are addressed. s with pressure vessels, the geometry of the beam, and the specific type of loading which will be
A STRUCTURE DESIGN OF CFRP REAR PRESSURE BULKHEAD WITHOUT STIFFENERS
 Xi an, 2-25 th August 217 A STRUCTURE DESIGN OF CFRP REAR PRESSURE BULKHEAD WITHOUT STIFFENERS LI Zhongyang 1, LI Dong 2 Mailbox72-35, Yanliang District, Xian, China, Email: zhongyangli@live.com Keywords:
Xi an, 2-25 th August 217 A STRUCTURE DESIGN OF CFRP REAR PRESSURE BULKHEAD WITHOUT STIFFENERS LI Zhongyang 1, LI Dong 2 Mailbox72-35, Yanliang District, Xian, China, Email: zhongyangli@live.com Keywords:
A RESEARCH ON NONLINEAR STABILITY AND FAILURE OF THIN- WALLED COMPOSITE COLUMNS WITH OPEN CROSS-SECTION
 A RESEARCH ON NONLINEAR STABILITY AND FAILURE OF THIN- WALLED COMPOSITE COLUMNS WITH OPEN CROSS-SECTION H. Debski a*, J. Bienias b, P. Jakubczak b a Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Department of Machine
A RESEARCH ON NONLINEAR STABILITY AND FAILURE OF THIN- WALLED COMPOSITE COLUMNS WITH OPEN CROSS-SECTION H. Debski a*, J. Bienias b, P. Jakubczak b a Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Department of Machine
Calculation of Energy Release Rate in Mode I Delamination of Angle Ply Laminated Composites
 Copyright c 2007 ICCES ICCES, vol.1, no.2, pp.61-67, 2007 Calculation of Energy Release Rate in Mode I Delamination of Angle Ply Laminated Composites K. Gordnian 1, H. Hadavinia 1, G. Simpson 1 and A.
Copyright c 2007 ICCES ICCES, vol.1, no.2, pp.61-67, 2007 Calculation of Energy Release Rate in Mode I Delamination of Angle Ply Laminated Composites K. Gordnian 1, H. Hadavinia 1, G. Simpson 1 and A.
MODELING OF THE BEHAVIOR OF WOVEN LAMINATED COMPOSITES UNTIL RUPTURE
 MODELING OF THE BEHAVIOR OF WOVEN LAMINATED COMPOSITES UNTIL RUPTURE Jean Paul Charles, Christian Hochard,3, Pierre Antoine Aubourg,3 Eurocopter, 375 Marignane cedex, France Unimeca, 6 rue J. Curie, 3453
MODELING OF THE BEHAVIOR OF WOVEN LAMINATED COMPOSITES UNTIL RUPTURE Jean Paul Charles, Christian Hochard,3, Pierre Antoine Aubourg,3 Eurocopter, 375 Marignane cedex, France Unimeca, 6 rue J. Curie, 3453
9 Strength Theories of Lamina
 9 trength Theories of Lamina 9- TRENGTH O ORTHOTROPIC LAMINA or isotropic materials the simplest method to predict failure is to compare the applied stresses to the strengths or some other allowable stresses.
9 trength Theories of Lamina 9- TRENGTH O ORTHOTROPIC LAMINA or isotropic materials the simplest method to predict failure is to compare the applied stresses to the strengths or some other allowable stresses.
ON THE NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF COMPOSITE MATERIAL
 The 4th International Conference Advanced Composite Materials Engineering COMAT 8- October, Brasov, Romania O THE UMERICAL AALYSIS OF COMPOSITE MATERIAL D.D. icoara Transilvania University, City Brasov,
The 4th International Conference Advanced Composite Materials Engineering COMAT 8- October, Brasov, Romania O THE UMERICAL AALYSIS OF COMPOSITE MATERIAL D.D. icoara Transilvania University, City Brasov,
Dynamic Analysis of Laminated Composite Plate Structure with Square Cut-Out under Hygrothermal Load
 Dynamic Analysis of Laminated Composite Plate Structure with Square Cut-Out under Hygrothermal Load Arun Mukherjee 1, Dr. Sreyashi Das (nee Pal) 2 and Dr. A. Guha Niyogi 3 1 PG student, 2 Asst. Professor,
Dynamic Analysis of Laminated Composite Plate Structure with Square Cut-Out under Hygrothermal Load Arun Mukherjee 1, Dr. Sreyashi Das (nee Pal) 2 and Dr. A. Guha Niyogi 3 1 PG student, 2 Asst. Professor,
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Sample Problem 4.2
 Sample Problem 4. SOLUTON: Based on the cross section geometry, calculate the location of the section centroid and moment of inertia. ya ( + Y Ad ) A A cast-iron machine part is acted upon by a kn-m couple.
Sample Problem 4. SOLUTON: Based on the cross section geometry, calculate the location of the section centroid and moment of inertia. ya ( + Y Ad ) A A cast-iron machine part is acted upon by a kn-m couple.
FINITE ELEMENT AND EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF NOVEL CONCEPT OF 3D FIBRE CELL STRUCTURE
 FINITE ELEMENT AND EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF NOVEL CONCEPT OF 3D FIBRE CELL STRUCTURE M. Růžička, V. Kulíšek 2, J. Had, O. Prejzek Department of Mechanics, Biomechanics and Mechatronics, Faculty of Mechanical
FINITE ELEMENT AND EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF NOVEL CONCEPT OF 3D FIBRE CELL STRUCTURE M. Růžička, V. Kulíšek 2, J. Had, O. Prejzek Department of Mechanics, Biomechanics and Mechatronics, Faculty of Mechanical
VIBRATION AND DAMPING ANALYSIS OF FIBER REINFORCED COMPOSITE MATERIAL CONICAL SHELLS
 VIBRATION AND DAMPING ANALYSIS OF FIBER REINFORCED COMPOSITE MATERIAL CONICAL SHELLS Mechanical Engineering Department, Indian Institute of Technology, New Delhi 110 016, India (Received 22 January 1992,
VIBRATION AND DAMPING ANALYSIS OF FIBER REINFORCED COMPOSITE MATERIAL CONICAL SHELLS Mechanical Engineering Department, Indian Institute of Technology, New Delhi 110 016, India (Received 22 January 1992,
An efficient analytical model to evaluate the first two local buckling modes of finite cracked plate under tension
 278 An efficient analytical model to evaluate the first two local buckling modes of finite cracked plate under tension Abstract The analytical approach is presented for both symmetric and anti-symmetric
278 An efficient analytical model to evaluate the first two local buckling modes of finite cracked plate under tension Abstract The analytical approach is presented for both symmetric and anti-symmetric
Shear Strength of End Web Panels
 Paper 10 Shear Strength of End Web Panels Civil-Comp Press, 2012 Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Computational Structures Technology, B.H.V. Topping, (Editor), Civil-Comp Press,
Paper 10 Shear Strength of End Web Panels Civil-Comp Press, 2012 Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Computational Structures Technology, B.H.V. Topping, (Editor), Civil-Comp Press,
THE MUTUAL EFFECTS OF SHEAR AND TRANSVERSE DAMAGE IN POLYMERIC COMPOSITES
 THE 19 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS THE MUTUAL EFFECTS OF SHEAR AND TRANSVERSE DAMAGE IN POLYMERIC COMPOSITES L.V. Smith 1 *, M. Salavatian 1 1 School of Mechanical and Materials
THE 19 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS THE MUTUAL EFFECTS OF SHEAR AND TRANSVERSE DAMAGE IN POLYMERIC COMPOSITES L.V. Smith 1 *, M. Salavatian 1 1 School of Mechanical and Materials
REPORT. No.: D3.3 part 4. Axially loaded sandwich panels
 REPORT Axially loaded sandich panels Publisher: Saskia Käpplein Thomas isiek Karlsruher Institut für Technologie (KIT) Versuchsanstalt für Stahl, Holz und Steine Task: 3.4 Object: Design of axially loaded
REPORT Axially loaded sandich panels Publisher: Saskia Käpplein Thomas isiek Karlsruher Institut für Technologie (KIT) Versuchsanstalt für Stahl, Holz und Steine Task: 3.4 Object: Design of axially loaded
COMPRESSIVE BEHAVIOR OF IMPACT DAMAGED COMPOSITE LAMINATES
 16 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS COMPRESSIVE BEHAVIOR OF IMPACT DAMAGED COMPOSITE LAMINATES Hiroshi Suemasu*, Wataru Sasaki**, Yuuichiro Aoki***, Takashi Ishikawa**** *Department of
16 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS COMPRESSIVE BEHAVIOR OF IMPACT DAMAGED COMPOSITE LAMINATES Hiroshi Suemasu*, Wataru Sasaki**, Yuuichiro Aoki***, Takashi Ishikawa**** *Department of
Thermal buckling and post-buckling of laminated composite plates with. temperature dependent properties by an asymptotic numerical method
 hermal buckling and post-buckling of laminated composite plates with temperature dependent properties by an asymptotic numerical method F. Abdoun a,*, L. Azrar a,b, E.M. Daya c a LAMA, Higher School of
hermal buckling and post-buckling of laminated composite plates with temperature dependent properties by an asymptotic numerical method F. Abdoun a,*, L. Azrar a,b, E.M. Daya c a LAMA, Higher School of
Prediction of Micromechanical Behaviour of Elliptical Frp Composites
 Prediction of Micromechanical Behaviour of Elliptical Frp Composites Kiranmayee.Nerusu Dept. of Mechanical Engg. P. V. P. Siddhartha Institute of Technology, Vijayawada 520 007, A.P, India. P. Phani Prasanthi
Prediction of Micromechanical Behaviour of Elliptical Frp Composites Kiranmayee.Nerusu Dept. of Mechanical Engg. P. V. P. Siddhartha Institute of Technology, Vijayawada 520 007, A.P, India. P. Phani Prasanthi
Predicting Failure of Multiangle Composite Laminates
 Predicting Failure of Multiangle Composite Laminates Preliminary discussion (not in textbook): Micromechanics failure analyses vs Macromechanics failure analyses Fiber Architecture of Some Common Composite
Predicting Failure of Multiangle Composite Laminates Preliminary discussion (not in textbook): Micromechanics failure analyses vs Macromechanics failure analyses Fiber Architecture of Some Common Composite
Crash and Impact Simulation of Composite Structures by Using CAE Process Chain
 Crash and Impact Simulation of Composite Structures by Using CAE Process Chain Madhukar Chatiri 1, Thorsten Schütz 2, Anton Matzenmiller 3, Ulrich Stelzmann 1 1 CADFEM GmbH, Grafing/Munich, Germany, mchatiri@cadfem.de
Crash and Impact Simulation of Composite Structures by Using CAE Process Chain Madhukar Chatiri 1, Thorsten Schütz 2, Anton Matzenmiller 3, Ulrich Stelzmann 1 1 CADFEM GmbH, Grafing/Munich, Germany, mchatiri@cadfem.de
UNEXPECTED TWISTING CURVATURE GENERATION OF BISTABLE CFRP LAMINATE DUE TO THE UNCERTAINTY OF LAY-UP SEQUENCE AND NEGATIVE INITIAL CURVATURE
 THE 9 TH INTERNATIONA CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIAS UNEXPECTED TWISTING CURVATURE GENERATION OF BISTABE CFRP AMINATE DUE TO THE UNCERTAINTY OF AY-UP SEQUENCE AND NEGATIVE INITIA CURVATURE J. Ryu, J-G.
THE 9 TH INTERNATIONA CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIAS UNEXPECTED TWISTING CURVATURE GENERATION OF BISTABE CFRP AMINATE DUE TO THE UNCERTAINTY OF AY-UP SEQUENCE AND NEGATIVE INITIA CURVATURE J. Ryu, J-G.
Enhancing Prediction Accuracy In Sift Theory
 18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS Enhancing Prediction Accuracy In Sift Theory J. Wang 1 *, W. K. Chiu 1 Defence Science and Technology Organisation, Fishermans Bend, Australia, Department
18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS Enhancing Prediction Accuracy In Sift Theory J. Wang 1 *, W. K. Chiu 1 Defence Science and Technology Organisation, Fishermans Bend, Australia, Department
Modelling the nonlinear shear stress-strain response of glass fibrereinforced composites. Part II: Model development and finite element simulations
 Modelling the nonlinear shear stress-strain response of glass fibrereinforced composites. Part II: Model development and finite element simulations W. Van Paepegem *, I. De Baere and J. Degrieck Ghent
Modelling the nonlinear shear stress-strain response of glass fibrereinforced composites. Part II: Model development and finite element simulations W. Van Paepegem *, I. De Baere and J. Degrieck Ghent
five Mechanics of Materials 1 ARCHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: FORM, BEHAVIOR, AND DESIGN DR. ANNE NICHOLS SUMMER 2017 lecture
 ARCHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: FORM, BEHAVIOR, AND DESIGN DR. ANNE NICHOLS SUMMER 2017 lecture five mechanics www.carttalk.com of materials Mechanics of Materials 1 Mechanics of Materials MECHANICS MATERIALS
ARCHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: FORM, BEHAVIOR, AND DESIGN DR. ANNE NICHOLS SUMMER 2017 lecture five mechanics www.carttalk.com of materials Mechanics of Materials 1 Mechanics of Materials MECHANICS MATERIALS
Composite Structural Mechanics using MATLAB
 Session 2520 Composite Structural Mechanics using MATLAB Oscar Barton, Jr., Jacob B. Wallace United States Naval Academy Annapolis, Md 21402 Abstract In this paper MATLAB is adopted as the programming
Session 2520 Composite Structural Mechanics using MATLAB Oscar Barton, Jr., Jacob B. Wallace United States Naval Academy Annapolis, Md 21402 Abstract In this paper MATLAB is adopted as the programming
Shishir Kumar Sahu, Ph. D. Professor Civil Engineering Department National Institute of Technology, Rourkela Orissa, India
 Shishir Kumar Sahu, Ph. D. Professor Civil Engineering Department National Institute of Technology, Rourkela Orissa, India Introduction Review Of Literature Aim & Scope Of Present Investigation Finite
Shishir Kumar Sahu, Ph. D. Professor Civil Engineering Department National Institute of Technology, Rourkela Orissa, India Introduction Review Of Literature Aim & Scope Of Present Investigation Finite
MECHANICAL FAILURE OF A COMPOSITE HELICOPTER STRUCTURE UNDER STATIC LOADING
 MECHANICAL FAILURE OF A COMPOSITE HELICOPTER STRUCTURE UNDER STATIC LOADING Steven Roy, Larry Lessard Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, McGill University, Montreal, Québec, Canada ABSTRACT The design and
MECHANICAL FAILURE OF A COMPOSITE HELICOPTER STRUCTURE UNDER STATIC LOADING Steven Roy, Larry Lessard Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, McGill University, Montreal, Québec, Canada ABSTRACT The design and
Fracture Behaviour of FRP Cross-Ply Laminate With Embedded Delamination Subjected To Transverse Load
 Fracture Behaviour of FRP Cross-Ply Laminate With Embedded Delamination Subjected To Transverse Load Sriram Chintapalli 1, S.Srilakshmi 1 1 Dept. of Mech. Engg., P. V. P. Siddhartha Institute of Technology.
Fracture Behaviour of FRP Cross-Ply Laminate With Embedded Delamination Subjected To Transverse Load Sriram Chintapalli 1, S.Srilakshmi 1 1 Dept. of Mech. Engg., P. V. P. Siddhartha Institute of Technology.
MESH MODELING OF ANGLE-PLY LAMINATED COMPOSITE PLATES FOR DNS AND IPSAP
 16 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS MESH MODELING OF ANGLE-PLY LAMINATED COMPOSITE PLATES FOR DNS AND IPSAP Wanil Byun*, Seung Jo Kim*, Joris Wismans** *Seoul National University, Republic
16 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS MESH MODELING OF ANGLE-PLY LAMINATED COMPOSITE PLATES FOR DNS AND IPSAP Wanil Byun*, Seung Jo Kim*, Joris Wismans** *Seoul National University, Republic
Longitudinal buckling of slender pressurised tubes
 Fluid Structure Interaction VII 133 Longitudinal buckling of slender pressurised tubes S. Syngellakis Wesse Institute of Technology, UK Abstract This paper is concerned with Euler buckling of long slender
Fluid Structure Interaction VII 133 Longitudinal buckling of slender pressurised tubes S. Syngellakis Wesse Institute of Technology, UK Abstract This paper is concerned with Euler buckling of long slender
DESIGN OF LAMINATES FOR IN-PLANE LOADING
 DESIGN OF LAMINATES FOR IN-PLANOADING G. VERCHERY ISMANS 44 avenue F.A. Bartholdi, 72000 Le Mans, France Georges.Verchery@m4x.org SUMMARY This work relates to the design of laminated structures primarily
DESIGN OF LAMINATES FOR IN-PLANOADING G. VERCHERY ISMANS 44 avenue F.A. Bartholdi, 72000 Le Mans, France Georges.Verchery@m4x.org SUMMARY This work relates to the design of laminated structures primarily
Lecture 15 Strain and stress in beams
 Spring, 2019 ME 323 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 15 Strain and stress in beams Reading assignment: 6.1 6.2 News: Instructor: Prof. Marcial Gonzalez Last modified: 1/6/19 9:42:38 PM Beam theory (@ ME
Spring, 2019 ME 323 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 15 Strain and stress in beams Reading assignment: 6.1 6.2 News: Instructor: Prof. Marcial Gonzalez Last modified: 1/6/19 9:42:38 PM Beam theory (@ ME
COMPUTER AIDED DESIGN IN CASE OF THE LAMINATED COMPOSITE MATERIALS
 6 th International Conference Computational Mechanics and Virtual Engineering COMEC 15 15-16 October 15, Braşov, Romania COMPUER AIDED DESIGN IN CASE OF HE LAMINAED COMPOSIE MAERIALS Camelia Cerbu ransilvania
6 th International Conference Computational Mechanics and Virtual Engineering COMEC 15 15-16 October 15, Braşov, Romania COMPUER AIDED DESIGN IN CASE OF HE LAMINAED COMPOSIE MAERIALS Camelia Cerbu ransilvania
EE C245 ME C218 Introduction to MEMS Design
 EE C245 ME C218 Introduction to MEMS Design Fall 2007 Prof. Clark T.-C. Nguyen Dept. of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley Berkeley, CA 94720 Lecture 16: Energy
EE C245 ME C218 Introduction to MEMS Design Fall 2007 Prof. Clark T.-C. Nguyen Dept. of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley Berkeley, CA 94720 Lecture 16: Energy
HIGHER-ORDER THEORIES
 HIGHER-ORDER THEORIES THIRD-ORDER SHEAR DEFORMATION PLATE THEORY LAYERWISE LAMINATE THEORY J.N. Reddy 1 Third-Order Shear Deformation Plate Theory Assumed Displacement Field µ u(x y z t) u 0 (x y t) +
HIGHER-ORDER THEORIES THIRD-ORDER SHEAR DEFORMATION PLATE THEORY LAYERWISE LAMINATE THEORY J.N. Reddy 1 Third-Order Shear Deformation Plate Theory Assumed Displacement Field µ u(x y z t) u 0 (x y t) +
SKIN-STRINGER DEBONDING AND DELAMINATION ANALYSIS IN COMPOSITE STIFFENED SHELLS
 SKIN-STRINER DEBONDIN AND DELAMINATION ANALYSIS IN COMPOSITE STIFFENED SHELLS R. Rikards, K. Kalnins & O. Ozolinsh Institute of Materials and Structures, Riga Technical University, Riga 1658, Latvia ABSTRACT
SKIN-STRINER DEBONDIN AND DELAMINATION ANALYSIS IN COMPOSITE STIFFENED SHELLS R. Rikards, K. Kalnins & O. Ozolinsh Institute of Materials and Structures, Riga Technical University, Riga 1658, Latvia ABSTRACT
2.2 Relation Between Mathematical & Engineering Constants Isotropic Materials Orthotropic Materials
 Chapter : lastic Constitutive quations of a Laminate.0 Introduction quations of Motion Symmetric of Stresses Tensorial and ngineering Strains Symmetry of Constitutive quations. Three-Dimensional Constitutive
Chapter : lastic Constitutive quations of a Laminate.0 Introduction quations of Motion Symmetric of Stresses Tensorial and ngineering Strains Symmetry of Constitutive quations. Three-Dimensional Constitutive
International Institute of Welding A world of joining experience
 International Institute of Welding A orld of joining eperience XV- 105-06, XV-F-74-06 Special cases of the calculation of residual elding distortions J. Farkas K. Jármai University of Miskolc, Hungary
International Institute of Welding A orld of joining eperience XV- 105-06, XV-F-74-06 Special cases of the calculation of residual elding distortions J. Farkas K. Jármai University of Miskolc, Hungary
LAMINATION THEORY FOR THE STRENGTH OF FIBER COMPOSITE MATERIALS
 XXII. LAMINATION THEORY FOR THE STRENGTH OF FIBER COMPOSITE MATERIALS Introduction The lamination theory for the elastic stiffness of fiber composite materials is the backbone of the entire field, it holds
XXII. LAMINATION THEORY FOR THE STRENGTH OF FIBER COMPOSITE MATERIALS Introduction The lamination theory for the elastic stiffness of fiber composite materials is the backbone of the entire field, it holds
SIMULATION OF PROGRESSIVE FAILURE PREDICTION OF FILAMENT WOUND COMPOSITE TUBES SUBJECTED TO MULTIPLE LOADING WITH MEMBRANE-FLEXION COUPLING EFFECTS
 VOL. 5, NO. 4, APRIL 010 ISSN 1819-6608 006-010 Asian Research Publishing Network (ARPN). All rights reserved. SIMULATION OF PROGRESSIVE FAILURE PREDICTION OF FILAMENT WOUND COMPOSITE TUBES SUBJECTED TO
VOL. 5, NO. 4, APRIL 010 ISSN 1819-6608 006-010 Asian Research Publishing Network (ARPN). All rights reserved. SIMULATION OF PROGRESSIVE FAILURE PREDICTION OF FILAMENT WOUND COMPOSITE TUBES SUBJECTED TO
Flexure of Thick Cantilever Beam using Third Order Shear Deformation Theory
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 78-67X, p-issn: 78-8X, www.ijerd.com Volume 6, Issue 1 (April 13), PP. 9-14 Fleure of Thick Cantilever Beam using Third Order Shear
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 78-67X, p-issn: 78-8X, www.ijerd.com Volume 6, Issue 1 (April 13), PP. 9-14 Fleure of Thick Cantilever Beam using Third Order Shear
Composite Laminate Modeling
 omposite Laminate Modeling White Paper for Femap and NX Nastran Users Venkata Bheemreddy, Ph.D., Senior Staff Mechanical Engineer Adrian Jensen, PE, Senior Staff Mechanical Engineer WHAT THIS WHITE PAPER
omposite Laminate Modeling White Paper for Femap and NX Nastran Users Venkata Bheemreddy, Ph.D., Senior Staff Mechanical Engineer Adrian Jensen, PE, Senior Staff Mechanical Engineer WHAT THIS WHITE PAPER
Mechanical Behavior of Composite Tapered Lamina
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 10, Issue 8 (August 2014), PP.19-27 Mechanical Behavior of Composite Tapered Lamina
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 10, Issue 8 (August 2014), PP.19-27 Mechanical Behavior of Composite Tapered Lamina
IJSER 1. INTRODUCTION. M.Elhadary
 1591 A new failure criterion for GRP composite materials subjected to in-phase and out-of-phase biaxial fatigue loading under different stress ratios M.Elhadary Abstract this studying the fatigue behavior
1591 A new failure criterion for GRP composite materials subjected to in-phase and out-of-phase biaxial fatigue loading under different stress ratios M.Elhadary Abstract this studying the fatigue behavior
Strength Prediction Of Composite Laminate
 Strength Prediction Of Composite te Prof. Yogananda. A 1, Mr. R. Vijayakumar 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, East West Institute of Technology, Bangalore. Research Scholar,
Strength Prediction Of Composite te Prof. Yogananda. A 1, Mr. R. Vijayakumar 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, East West Institute of Technology, Bangalore. Research Scholar,
8 Properties of Lamina
 8 Properties of Lamina 8- ORTHOTROPIC LAMINA An orthotropic lamina is a sheet with unique and predictable properties and consists of an assemblage of fibers ling in the plane of the sheet and held in place
8 Properties of Lamina 8- ORTHOTROPIC LAMINA An orthotropic lamina is a sheet with unique and predictable properties and consists of an assemblage of fibers ling in the plane of the sheet and held in place
Composite Structures. Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur
 Mechanics of Laminated Composite Structures Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture 23 Analysis of an Orthotropic Ply Lecture Overview Introduction Engineering constants for an 2
Mechanics of Laminated Composite Structures Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture 23 Analysis of an Orthotropic Ply Lecture Overview Introduction Engineering constants for an 2
Buckling Behavior of 3D Randomly Oriented CNT Reinforced Nanocomposite Plate
 Buckling Behavior of 3D Randomly Oriented CNT Reinforced Nanocomposite Plate Outline Introduction Representative Volume Element (RVE) Periodic Boundary Conditions on RVE Homogenization Method Analytical
Buckling Behavior of 3D Randomly Oriented CNT Reinforced Nanocomposite Plate Outline Introduction Representative Volume Element (RVE) Periodic Boundary Conditions on RVE Homogenization Method Analytical
Determining the Residual Stresses of Circular Weld Bead with Eigenstrain BIE. as an Inverse Approach
 CCM014 8-30 th July, Cambridge, England Determining the Residual Stresses of Circular Weld Bead ith Eigenstrain BE as an nverse Approach H. Ma¹, Y.J. Tang, and C. Yan 3 1 College of Sciences, Shanghai
CCM014 8-30 th July, Cambridge, England Determining the Residual Stresses of Circular Weld Bead ith Eigenstrain BE as an nverse Approach H. Ma¹, Y.J. Tang, and C. Yan 3 1 College of Sciences, Shanghai
Micromechanical analysis of FRP hybrid composite lamina for in-plane transverse loading
 Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 15, October 2008, pp. 382-390 Micromechanical analysis of FRP hybrid composite lamina for in-plane transverse loading K Sivaji Babu a *, K Mohana
Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 15, October 2008, pp. 382-390 Micromechanical analysis of FRP hybrid composite lamina for in-plane transverse loading K Sivaji Babu a *, K Mohana
EE C245 ME C218 Introduction to MEMS Design Fall 2010
 EE C245 ME C218 Introduction to MEMS Design Fall 2010 Prof. Clark T.-C. Nguyen Dept. of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley Berkeley, CA 94720 Lecture EE C245:
EE C245 ME C218 Introduction to MEMS Design Fall 2010 Prof. Clark T.-C. Nguyen Dept. of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley Berkeley, CA 94720 Lecture EE C245:
CHEM-C2410: Materials Science from Microstructures to Properties Composites: basic principles
 CHEM-C2410: Materials Science from Microstructures to Properties Composites: basic principles Mark Hughes 14 th March 2017 Today s learning outcomes To understand the role of reinforcement, matrix and
CHEM-C2410: Materials Science from Microstructures to Properties Composites: basic principles Mark Hughes 14 th March 2017 Today s learning outcomes To understand the role of reinforcement, matrix and
Composites: Part A 40 (2009) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Composites: Part A
 Composites: Part A 40 (2009) 376 387 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Composites: Part A journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/compositesa A comprehensive explanation of compression strength
Composites: Part A 40 (2009) 376 387 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Composites: Part A journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/compositesa A comprehensive explanation of compression strength
Flexural Analysis of Deep Aluminum Beam
 Journal of Soft Computing in Civil Engineering -1 (018) 71-84 journal homepage: http://www.jsoftcivil.com/ Fleural Analysis of Deep Aluminum Beam P. Kapdis 1, U. Kalwane 1, U. Salunkhe 1 and A. Dahake
Journal of Soft Computing in Civil Engineering -1 (018) 71-84 journal homepage: http://www.jsoftcivil.com/ Fleural Analysis of Deep Aluminum Beam P. Kapdis 1, U. Kalwane 1, U. Salunkhe 1 and A. Dahake
FLEXURAL RESPONSE OF FIBER RENFORCED PLASTIC DECKS USING HIGHER-ORDER SHEAR DEFORMABLE PLATE THEORY
 Asia-Pacific Conference on FRP in Structures (APFIS 2007) S.T. Smith (ed) 2007 International Institute for FRP in Construction FLEXURAL RESPONSE OF FIBER RENFORCED PLASTIC DECKS USING HIGHER-ORDER SHEAR
Asia-Pacific Conference on FRP in Structures (APFIS 2007) S.T. Smith (ed) 2007 International Institute for FRP in Construction FLEXURAL RESPONSE OF FIBER RENFORCED PLASTIC DECKS USING HIGHER-ORDER SHEAR
