Deep Learning II: Momentum & Adaptive Step Size
|
|
|
- Eric Fowler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Deep Learning II: Momentum & Adaptive Step Size CS 760: Machine Learning Spring 2018 Mark Craven and David Page 1
2 Goals for the Lecture You should understand the following concepts: momentum Nesterov momentum adaptive step size AdaGrad RMSProp Adam Thanks Yujia Bao! 2
3 Background: Mini-batch gradient descent Procedure: Pick a mini-batch of examples from the data For each example: Forward propagation to get the output; Backward propagation to get the gradient; Update the weights using the average gradient. Common mini-batch size: 32, 64, 128. Note: Forward/Backward propagation can both be done simultaneously for many examples using matrix multiplication, and this is fast on GPUs!
4 Mini-batch gradient descent Recall the forward prop for a MLP: z "#$ = f "#$ W " z " + b " where f "#$ is the activation function for the (k + 1)st layer, W " i [j] is the weights from z " [j] to z "#$ [i] If we have n examples, we can define Z " = z " $ z " 3, B " = b " b " and express the forward prop as Z "#$ = f " W " Z " + B "
5 An example
6 Weight Update Methods Steepest Descent (Review) Momentum (Review) Nesterov Accelerated Gradient AdaGrad [Duchi et al., 2011] RMSprop [Tieleman & Hinton, 2012] Adam [Kingma & Ba, 2015] Element-wise adaptive learning rate
7 Steepest Descent Algorithm: Step 1. w (8#$) = w (8) η => (A) Very simple. Just one step. Poor convergence if the function surface is more steep in one dimension than in another. Let s see an example!
8 Steepest Descent Objective: L w = w $ C + 25w C C -50w C 2w $ Gradient: L = 2w $ 50w C Small over w $ direction, large over w C direction!
9 Steepest Descent Zigzag behavior! Move very slowly on the flat direction, oscillate on the steep direction.
10 Trick 7: Momentum Algorithm: Step 1.v (8#$) = μv (8) η => (A) Interpret v as velocity, 1 μ as friction. v stores the moving average of the gradients. Step 2. w (8#$) = w (8) + v (8#$) A ball rolling down from the surface of the loss function. Initialize v (J) to zero. Common settings for μ ranges between 0.5 to 0.99.
11 Trick 7: Momentum Accelerate convergence on the direction that the gradient keeps the same sign over the past few iterations. If μ is large, momentum will overshoot the target, but the overall convergence is still faster than steepest descent in practice. As μ goes smaller, momentum behaves more similar to steepest descent.
12
13 Nesterov Accelerated Gradient Momentum Nesterov Accelerated Gradient w (8#$) Negative gradient direction: η => (A) #LM (A) Speed direction: μv (8) Actual update Speed direction: μv (8) w (8#$) Actual update w (8) Negative gradient direction: η => (A) w (8)
14 An example Suppose w (8) is already optimal, but v (8) 0. Speed direction: μv (8) w (8) Momentum w (8#$) Actual update Negative gradient direction: 0 Nesterov Accelerated Gradient Speed direction: μv (8) w (8) w (8#$) Actual update Negative gradient direction: η => (A) #LM (A) Look ahead! The actual update is more reliable than Momentum.
15 Nesterov Accelerated Gradient Algorithm: Step 1.v (8#$) = μv (8) η => (A) #LM (A) Step 2.w (8#$) = w (8) + v (8#$) Nesterov Accelerated Gradient has better performance than momentum [Ilya et al., 2013].
16
17 Trick 8: Adaptive Learning Rate
18 Some Notes on our Notation in this Lecture For a scalar η and vector v, ηv is a vector Likewise P v is a vector, just as η $ v is a vector By between two vectors, we mean element-wise multiplication rather than dot product
19 AdaGrad (Adaptive Gradient) Algorithm: Step 1. G (8#$) = G (8) + => (A) C G is the sum of the square gradient. Step 2.w (8#$) = w (8) P W (AXY) #$J[\ =?? (A) Scale the learning rate by 1/ G and follow the negative gradient direction. Common setting for η is Different learning rate for each w (each w has its own G). Increase the learning rate on the flat direction. Decrease the learning rate on the steep direction.
20 AdaGrad (Adaptive Gradient) Consider the previous example: Gradient: L w = w $ C + 25w C C L = 2w $ 50w C Initial w (J) is 1, 1. η ( 2) w ($) = C + 10^_ η ( 50) 50 C + 10^_ Will follow the diagonal direction! η η
21
22 AdaGrad (Adaptive Gradient) Algorithm: Step 1. G (8#$) = G (8) + => (A) C Step 2. w (8#$) = w (8) P W (AXY) #$J[\ =?? (A) Why that slow? Learning rate goes down monotonically as t increases. Stop learning!!!
23 RMSProp (Root Mean Square Propagation) Algorithm: C =?? (A) G is a moving exponential average of the square gradient. Step 1. G (8#$) = γg (8) + 1 γ Step 2. w (8#$) = w (8) P W (AXY) #$J[\ =?? (A) Scale the learning rate by 1/ G and follow the negative gradient direction. Default settings: γ = 0.9, η =
24
25 Another example (saddle point) Now consider minimizing L w = w $ e + w C C The problem is unbounded and (0,0) is a saddle point. At 0.01, 1, we have L = How will these methods behave if we start at this point?
26
27 Adam (Adaptive Moment Estimation) Algorithm [Simplified Version]: Step 1. m (8#$) = β $ m (8) + 1 β $ => (A) m is the exponential moving average of the gradients (similar as the speed in the momentum method); C =?? (A) v is the exponential moving average of the square gradients. Step 2. v (8#$) = β C v (8) + (1 β C ) Step 3. w (8#$) = w (8) P m(8#$) M AXY #$J[i Default settings: β $ = 0.9, β C = 0.999, η =
28 Adam (Adaptive Moment Estimation) Algorithm [Complete Version]: Step 1.m (8#$) = β $ m (8) + 1 β $ => (A) Step 2. v (8#$) = β C v (8) + (1 β C ) C =?? (A) Step 3. mj (8#$) = $ $^k Y A m (8#$) Step 4. vl (8#$) = $ $^k m A v (8#$) Bias Correction (since we set m (J), v (J) to 0) Step 5. w (8#$) = w (8) P Ml (AXY) #$J [i mj (8#$)
29
30
31 Adam (Adaptive Moment Estimation) Image credit: Kingma & Ba, 2015 Network configurations: Input layer: 28x28 2 hidden layers (1000 ReLUs each) Output: 10 SoftMax Cross-entropy loss. In practice, Adam is the default choice to use. [Fei- Fei Li, Andrej Karpathy, Justin Johnson]
Day 3 Lecture 3. Optimizing deep networks
 Day 3 Lecture 3 Optimizing deep networks Convex optimization A function is convex if for all α [0,1]: f(x) Tangent line Examples Quadratics 2-norms Properties Local minimum is global minimum x Gradient
Day 3 Lecture 3 Optimizing deep networks Convex optimization A function is convex if for all α [0,1]: f(x) Tangent line Examples Quadratics 2-norms Properties Local minimum is global minimum x Gradient
Optimization for Training I. First-Order Methods Training algorithm
 Optimization for Training I First-Order Methods Training algorithm 2 OPTIMIZATION METHODS Topics: Types of optimization methods. Practical optimization methods breakdown into two categories: 1. First-order
Optimization for Training I First-Order Methods Training algorithm 2 OPTIMIZATION METHODS Topics: Types of optimization methods. Practical optimization methods breakdown into two categories: 1. First-order
Non-Linearity. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence. Non-Linear Separators. Non-Linear Separators. Deep Learning I
 Non-Linearity CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Deep Learning I Instructors: Pieter Abbeel & Anca Dragan --- University of California, Berkeley [These slides were created by Dan Klein, Pieter Abbeel, Anca
Non-Linearity CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Deep Learning I Instructors: Pieter Abbeel & Anca Dragan --- University of California, Berkeley [These slides were created by Dan Klein, Pieter Abbeel, Anca
CSCI 1951-G Optimization Methods in Finance Part 12: Variants of Gradient Descent
 CSCI 1951-G Optimization Methods in Finance Part 12: Variants of Gradient Descent April 27, 2018 1 / 32 Outline 1) Moment and Nesterov s accelerated gradient descent 2) AdaGrad and RMSProp 4) Adam 5) Stochastic
CSCI 1951-G Optimization Methods in Finance Part 12: Variants of Gradient Descent April 27, 2018 1 / 32 Outline 1) Moment and Nesterov s accelerated gradient descent 2) AdaGrad and RMSProp 4) Adam 5) Stochastic
Machine Learning CS 4900/5900. Lecture 03. Razvan C. Bunescu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 Machine Learning CS 4900/5900 Razvan C. Bunescu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science bunescu@ohio.edu Machine Learning is Optimization Parametric ML involves minimizing an objective function
Machine Learning CS 4900/5900 Razvan C. Bunescu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science bunescu@ohio.edu Machine Learning is Optimization Parametric ML involves minimizing an objective function
Deep Neural Networks (3) Computational Graphs, Learning Algorithms, Initialisation
 Deep Neural Networks (3) Computational Graphs, Learning Algorithms, Initialisation Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 5 16 October 2018 MLP Lecture 5 / 16 October 2018 Deep Neural Networks
Deep Neural Networks (3) Computational Graphs, Learning Algorithms, Initialisation Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 5 16 October 2018 MLP Lecture 5 / 16 October 2018 Deep Neural Networks
Overview of gradient descent optimization algorithms. HYUNG IL KOO Based on
 Overview of gradient descent optimization algorithms HYUNG IL KOO Based on http://sebastianruder.com/optimizing-gradient-descent/ Problem Statement Machine Learning Optimization Problem Training samples:
Overview of gradient descent optimization algorithms HYUNG IL KOO Based on http://sebastianruder.com/optimizing-gradient-descent/ Problem Statement Machine Learning Optimization Problem Training samples:
Tutorial on: Optimization I. (from a deep learning perspective) Jimmy Ba
 Tutorial on: Optimization I (from a deep learning perspective) Jimmy Ba Outline Random search v.s. gradient descent Finding better search directions Design white-box optimization methods to improve computation
Tutorial on: Optimization I (from a deep learning perspective) Jimmy Ba Outline Random search v.s. gradient descent Finding better search directions Design white-box optimization methods to improve computation
CS260: Machine Learning Algorithms
 CS260: Machine Learning Algorithms Lecture 4: Stochastic Gradient Descent Cho-Jui Hsieh UCLA Jan 16, 2019 Large-scale Problems Machine learning: usually minimizing the training loss min w { 1 N min w {
CS260: Machine Learning Algorithms Lecture 4: Stochastic Gradient Descent Cho-Jui Hsieh UCLA Jan 16, 2019 Large-scale Problems Machine learning: usually minimizing the training loss min w { 1 N min w {
Deep Feedforward Networks
 Deep Feedforward Networks Liu Yang March 30, 2017 Liu Yang Short title March 30, 2017 1 / 24 Overview 1 Background A general introduction Example 2 Gradient based learning Cost functions Output Units 3
Deep Feedforward Networks Liu Yang March 30, 2017 Liu Yang Short title March 30, 2017 1 / 24 Overview 1 Background A general introduction Example 2 Gradient based learning Cost functions Output Units 3
Need for Deep Networks Perceptron. Can only model linear functions. Kernel Machines. Non-linearity provided by kernels
 Need for Deep Networks Perceptron Can only model linear functions Kernel Machines Non-linearity provided by kernels Need to design appropriate kernels (possibly selecting from a set, i.e. kernel learning)
Need for Deep Networks Perceptron Can only model linear functions Kernel Machines Non-linearity provided by kernels Need to design appropriate kernels (possibly selecting from a set, i.e. kernel learning)
CSC 578 Neural Networks and Deep Learning
 CSC 578 Neural Networks and Deep Learning Fall 2018/19 3. Improving Neural Networks (Some figures adapted from NNDL book) 1 Various Approaches to Improve Neural Networks 1. Cost functions Quadratic Cross
CSC 578 Neural Networks and Deep Learning Fall 2018/19 3. Improving Neural Networks (Some figures adapted from NNDL book) 1 Various Approaches to Improve Neural Networks 1. Cost functions Quadratic Cross
Machine Learning for Large-Scale Data Analysis and Decision Making A. Neural Networks Week #6
 Machine Learning for Large-Scale Data Analysis and Decision Making 80-629-17A Neural Networks Week #6 Today Neural Networks A. Modeling B. Fitting C. Deep neural networks Today s material is (adapted)
Machine Learning for Large-Scale Data Analysis and Decision Making 80-629-17A Neural Networks Week #6 Today Neural Networks A. Modeling B. Fitting C. Deep neural networks Today s material is (adapted)
Deep Learning & Artificial Intelligence WS 2018/2019
 Deep Learning & Artificial Intelligence WS 2018/2019 Linear Regression Model Model Error Function: Squared Error Has no special meaning except it makes gradients look nicer Prediction Ground truth / target
Deep Learning & Artificial Intelligence WS 2018/2019 Linear Regression Model Model Error Function: Squared Error Has no special meaning except it makes gradients look nicer Prediction Ground truth / target
Need for Deep Networks Perceptron. Can only model linear functions. Kernel Machines. Non-linearity provided by kernels
 Need for Deep Networks Perceptron Can only model linear functions Kernel Machines Non-linearity provided by kernels Need to design appropriate kernels (possibly selecting from a set, i.e. kernel learning)
Need for Deep Networks Perceptron Can only model linear functions Kernel Machines Non-linearity provided by kernels Need to design appropriate kernels (possibly selecting from a set, i.e. kernel learning)
Large-scale Stochastic Optimization
 Large-scale Stochastic Optimization 11-741/641/441 (Spring 2016) Hanxiao Liu hanxiaol@cs.cmu.edu March 24, 2016 1 / 22 Outline 1. Gradient Descent (GD) 2. Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) Formulation
Large-scale Stochastic Optimization 11-741/641/441 (Spring 2016) Hanxiao Liu hanxiaol@cs.cmu.edu March 24, 2016 1 / 22 Outline 1. Gradient Descent (GD) 2. Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) Formulation
ECE521 lecture 4: 19 January Optimization, MLE, regularization
 ECE521 lecture 4: 19 January 2017 Optimization, MLE, regularization First four lectures Lectures 1 and 2: Intro to ML Probability review Types of loss functions and algorithms Lecture 3: KNN Convexity
ECE521 lecture 4: 19 January 2017 Optimization, MLE, regularization First four lectures Lectures 1 and 2: Intro to ML Probability review Types of loss functions and algorithms Lecture 3: KNN Convexity
Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization
 Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization Diederik P. Kingma, Jimmy Ba Presented by Content Background Supervised ML theory and the importance of optimum finding Gradient descent and its variants Limitations
Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization Diederik P. Kingma, Jimmy Ba Presented by Content Background Supervised ML theory and the importance of optimum finding Gradient descent and its variants Limitations
What Do Neural Networks Do? MLP Lecture 3 Multi-layer networks 1
 What Do Neural Networks Do? MLP Lecture 3 Multi-layer networks 1 Multi-layer networks Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 3 7 October 2015 MLP Lecture 3 Multi-layer networks 2 What Do Single
What Do Neural Networks Do? MLP Lecture 3 Multi-layer networks 1 Multi-layer networks Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 3 7 October 2015 MLP Lecture 3 Multi-layer networks 2 What Do Single
Deep Learning Lecture 2
 Fall 2016 Machine Learning CMPSCI 689 Deep Learning Lecture 2 Sridhar Mahadevan Autonomous Learning Lab UMass Amherst COLLEGE Outline of lecture New type of units Convolutional units, Rectified linear
Fall 2016 Machine Learning CMPSCI 689 Deep Learning Lecture 2 Sridhar Mahadevan Autonomous Learning Lab UMass Amherst COLLEGE Outline of lecture New type of units Convolutional units, Rectified linear
Neural Networks: Optimization & Regularization
 Neural Networks: Optimization & Regularization Shan-Hung Wu shwu@cs.nthu.edu.tw Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Machine Learning Shan-Hung Wu (CS, NTHU) NN Opt & Reg
Neural Networks: Optimization & Regularization Shan-Hung Wu shwu@cs.nthu.edu.tw Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Machine Learning Shan-Hung Wu (CS, NTHU) NN Opt & Reg
4. Multilayer Perceptrons
 4. Multilayer Perceptrons This is a supervised error-correction learning algorithm. 1 4.1 Introduction A multilayer feedforward network consists of an input layer, one or more hidden layers, and an output
4. Multilayer Perceptrons This is a supervised error-correction learning algorithm. 1 4.1 Introduction A multilayer feedforward network consists of an input layer, one or more hidden layers, and an output
Statistical Machine Learning (BE4M33SSU) Lecture 5: Artificial Neural Networks
 Statistical Machine Learning (BE4M33SSU) Lecture 5: Artificial Neural Networks Jan Drchal Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering Department of Computer Science Topics covered
Statistical Machine Learning (BE4M33SSU) Lecture 5: Artificial Neural Networks Jan Drchal Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering Department of Computer Science Topics covered
Advanced Training Techniques. Prajit Ramachandran
 Advanced Training Techniques Prajit Ramachandran Outline Optimization Regularization Initialization Optimization Optimization Outline Gradient Descent Momentum RMSProp Adam Distributed SGD Gradient Noise
Advanced Training Techniques Prajit Ramachandran Outline Optimization Regularization Initialization Optimization Optimization Outline Gradient Descent Momentum RMSProp Adam Distributed SGD Gradient Noise
CS60010: Deep Learning
 CS60010: Deep Learning Sudeshna Sarkar Spring 2018 16 Jan 2018 FFN Goal: Approximate some unknown ideal function f : X! Y Ideal classifier: y = f*(x) with x and category y Feedforward Network: Define parametric
CS60010: Deep Learning Sudeshna Sarkar Spring 2018 16 Jan 2018 FFN Goal: Approximate some unknown ideal function f : X! Y Ideal classifier: y = f*(x) with x and category y Feedforward Network: Define parametric
Understanding Neural Networks : Part I
 TensorFlow Workshop 2018 Understanding Neural Networks Part I : Artificial Neurons and Network Optimization Nick Winovich Department of Mathematics Purdue University July 2018 Outline 1 Neural Networks
TensorFlow Workshop 2018 Understanding Neural Networks Part I : Artificial Neurons and Network Optimization Nick Winovich Department of Mathematics Purdue University July 2018 Outline 1 Neural Networks
Eve: A Gradient Based Optimization Method with Locally and Globally Adaptive Learning Rates
 Eve: A Gradient Based Optimization Method with Locally and Globally Adaptive Learning Rates Hiroaki Hayashi 1,* Jayanth Koushik 1,* Graham Neubig 1 arxiv:1611.01505v3 [cs.lg] 11 Jun 2018 Abstract Adaptive
Eve: A Gradient Based Optimization Method with Locally and Globally Adaptive Learning Rates Hiroaki Hayashi 1,* Jayanth Koushik 1,* Graham Neubig 1 arxiv:1611.01505v3 [cs.lg] 11 Jun 2018 Abstract Adaptive
arxiv: v1 [cs.lg] 16 Jun 2017
![arxiv: v1 [cs.lg] 16 Jun 2017 arxiv: v1 [cs.lg] 16 Jun 2017](/thumbs/81/83659469.jpg) L 2 Regularization versus Batch and Weight Normalization arxiv:1706.05350v1 [cs.lg] 16 Jun 2017 Twan van Laarhoven Institute for Computer Science Radboud University Postbus 9010, 6500GL Nijmegen, The Netherlands
L 2 Regularization versus Batch and Weight Normalization arxiv:1706.05350v1 [cs.lg] 16 Jun 2017 Twan van Laarhoven Institute for Computer Science Radboud University Postbus 9010, 6500GL Nijmegen, The Netherlands
Classification goals: Make 1 guess about the label (Top-1 error) Make 5 guesses about the label (Top-5 error) No Bounding Box
 ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever, Geoffrey E. Hinton Motivation Classification goals: Make 1 guess about the label (Top-1 error) Make 5 guesses
ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever, Geoffrey E. Hinton Motivation Classification goals: Make 1 guess about the label (Top-1 error) Make 5 guesses
Data Mining & Machine Learning
 Data Mining & Machine Learning CS57300 Purdue University March 1, 2018 1 Recap of Last Class (Model Search) Forward and Backward passes 2 Feedforward Neural Networks Neural Networks: Architectures 2-layer
Data Mining & Machine Learning CS57300 Purdue University March 1, 2018 1 Recap of Last Class (Model Search) Forward and Backward passes 2 Feedforward Neural Networks Neural Networks: Architectures 2-layer
ECS289: Scalable Machine Learning
 ECS289: Scalable Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Sept 29, 2016 Outline Convex vs Nonconvex Functions Coordinate Descent Gradient Descent Newton s method Stochastic Gradient Descent Numerical Optimization
ECS289: Scalable Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Sept 29, 2016 Outline Convex vs Nonconvex Functions Coordinate Descent Gradient Descent Newton s method Stochastic Gradient Descent Numerical Optimization
Rapid Introduction to Machine Learning/ Deep Learning
 Rapid Introduction to Machine Learning/ Deep Learning Hyeong In Choi Seoul National University 1/59 Lecture 4a Feedforward neural network October 30, 2015 2/59 Table of contents 1 1. Objectives of Lecture
Rapid Introduction to Machine Learning/ Deep Learning Hyeong In Choi Seoul National University 1/59 Lecture 4a Feedforward neural network October 30, 2015 2/59 Table of contents 1 1. Objectives of Lecture
Lecture 35: Optimization and Neural Nets
 Lecture 35: Optimization and Neural Nets CS 4670/5670 Sean Bell DeepDream [Google, Inceptionism: Going Deeper into Neural Networks, blog 2015] Aside: CNN vs ConvNet Note: There are many papers that use
Lecture 35: Optimization and Neural Nets CS 4670/5670 Sean Bell DeepDream [Google, Inceptionism: Going Deeper into Neural Networks, blog 2015] Aside: CNN vs ConvNet Note: There are many papers that use
CS 343: Artificial Intelligence
 CS 343: Artificial Intelligence Deep Learning Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides based on those of Dan Klein, Pieter Abbeel, Anca Dragan for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley.
CS 343: Artificial Intelligence Deep Learning Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides based on those of Dan Klein, Pieter Abbeel, Anca Dragan for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley.
Support Vector Machines: Training with Stochastic Gradient Descent. Machine Learning Fall 2017
 Support Vector Machines: Training with Stochastic Gradient Descent Machine Learning Fall 2017 1 Support vector machines Training by maximizing margin The SVM objective Solving the SVM optimization problem
Support Vector Machines: Training with Stochastic Gradient Descent Machine Learning Fall 2017 1 Support vector machines Training by maximizing margin The SVM objective Solving the SVM optimization problem
Deep Neural Networks (1) Hidden layers; Back-propagation
 Deep Neural Networs (1) Hidden layers; Bac-propagation Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 3 4 October 2017 / 9 October 2017 MLP Lecture 3 Deep Neural Networs (1) 1 Recap: Softmax single
Deep Neural Networs (1) Hidden layers; Bac-propagation Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 3 4 October 2017 / 9 October 2017 MLP Lecture 3 Deep Neural Networs (1) 1 Recap: Softmax single
<Special Topics in VLSI> Learning for Deep Neural Networks (Back-propagation)
 Learning for Deep Neural Networks (Back-propagation) Outline Summary of Previous Standford Lecture Universal Approximation Theorem Inference vs Training Gradient Descent Back-Propagation
Learning for Deep Neural Networks (Back-propagation) Outline Summary of Previous Standford Lecture Universal Approximation Theorem Inference vs Training Gradient Descent Back-Propagation
Neural Networks. David Rosenberg. July 26, New York University. David Rosenberg (New York University) DS-GA 1003 July 26, / 35
 Neural Networks David Rosenberg New York University July 26, 2017 David Rosenberg (New York University) DS-GA 1003 July 26, 2017 1 / 35 Neural Networks Overview Objectives What are neural networks? How
Neural Networks David Rosenberg New York University July 26, 2017 David Rosenberg (New York University) DS-GA 1003 July 26, 2017 1 / 35 Neural Networks Overview Objectives What are neural networks? How
Optimization for neural networks
 0 - : Optimization for neural networks Prof. J.C. Kao, UCLA Optimization for neural networks We previously introduced the principle of gradient descent. Now we will discuss specific modifications we make
0 - : Optimization for neural networks Prof. J.C. Kao, UCLA Optimization for neural networks We previously introduced the principle of gradient descent. Now we will discuss specific modifications we make
Neural Networks. Lecture 2. Rob Fergus
 Neural Networks Lecture 2 Rob Fergus Overview Individual neuron Non-linearities (RELU, tanh, sigmoid) Single layer model Multiple layer models Theoretical discussion: representational power Examples shown
Neural Networks Lecture 2 Rob Fergus Overview Individual neuron Non-linearities (RELU, tanh, sigmoid) Single layer model Multiple layer models Theoretical discussion: representational power Examples shown
Lecture 10. Neural networks and optimization. Machine Learning and Data Mining November Nando de Freitas UBC. Nonlinear Supervised Learning
 Lecture 0 Neural networks and optimization Machine Learning and Data Mining November 2009 UBC Gradient Searching for a good solution can be interpreted as looking for a minimum of some error (loss) function
Lecture 0 Neural networks and optimization Machine Learning and Data Mining November 2009 UBC Gradient Searching for a good solution can be interpreted as looking for a minimum of some error (loss) function
Reading Group on Deep Learning Session 1
 Reading Group on Deep Learning Session 1 Stephane Lathuiliere & Pablo Mesejo 2 June 2016 1/31 Contents Introduction to Artificial Neural Networks to understand, and to be able to efficiently use, the popular
Reading Group on Deep Learning Session 1 Stephane Lathuiliere & Pablo Mesejo 2 June 2016 1/31 Contents Introduction to Artificial Neural Networks to understand, and to be able to efficiently use, the popular
Lecture 6 Optimization for Deep Neural Networks
 Lecture 6 Optimization for Deep Neural Networks CMSC 35246: Deep Learning Shubhendu Trivedi & Risi Kondor University of Chicago April 12, 2017 Things we will look at today Stochastic Gradient Descent Things
Lecture 6 Optimization for Deep Neural Networks CMSC 35246: Deep Learning Shubhendu Trivedi & Risi Kondor University of Chicago April 12, 2017 Things we will look at today Stochastic Gradient Descent Things
DeepLearning on FPGAs
 DeepLearning on FPGAs Introduction to Deep Learning Sebastian Buschäger Technische Universität Dortmund - Fakultät Informatik - Lehrstuhl 8 October 21, 2017 1 Recap Computer Science Approach Technical
DeepLearning on FPGAs Introduction to Deep Learning Sebastian Buschäger Technische Universität Dortmund - Fakultät Informatik - Lehrstuhl 8 October 21, 2017 1 Recap Computer Science Approach Technical
Introduction to Neural Networks
 CUONG TUAN NGUYEN SEIJI HOTTA MASAKI NAKAGAWA Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Copyright by Nguyen, Hotta and Nakagawa 1 Pattern classification Which category of an input? Example: Character
CUONG TUAN NGUYEN SEIJI HOTTA MASAKI NAKAGAWA Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Copyright by Nguyen, Hotta and Nakagawa 1 Pattern classification Which category of an input? Example: Character
y(x n, w) t n 2. (1)
 Network training: Training a neural network involves determining the weight parameter vector w that minimizes a cost function. Given a training set comprising a set of input vector {x n }, n = 1,...N,
Network training: Training a neural network involves determining the weight parameter vector w that minimizes a cost function. Given a training set comprising a set of input vector {x n }, n = 1,...N,
Stochastic Gradient Descent
 Stochastic Gradient Descent Weihang Chen, Xingchen Chen, Jinxiu Liang, Cheng Xu, Zehao Chen and Donglin He March 26, 2017 Outline What is Stochastic Gradient Descent Comparison between BGD and SGD Analysis
Stochastic Gradient Descent Weihang Chen, Xingchen Chen, Jinxiu Liang, Cheng Xu, Zehao Chen and Donglin He March 26, 2017 Outline What is Stochastic Gradient Descent Comparison between BGD and SGD Analysis
CSC321 Lecture 15: Exploding and Vanishing Gradients
 CSC321 Lecture 15: Exploding and Vanishing Gradients Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 15: Exploding and Vanishing Gradients 1 / 23 Overview Yesterday, we saw how to compute the gradient descent
CSC321 Lecture 15: Exploding and Vanishing Gradients Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 15: Exploding and Vanishing Gradients 1 / 23 Overview Yesterday, we saw how to compute the gradient descent
More on Neural Networks
 More on Neural Networks Yujia Yan Fall 2018 Outline Linear Regression y = Wx + b (1) Linear Regression y = Wx + b (1) Polynomial Regression y = Wφ(x) + b (2) where φ(x) gives the polynomial basis, e.g.,
More on Neural Networks Yujia Yan Fall 2018 Outline Linear Regression y = Wx + b (1) Linear Regression y = Wx + b (1) Polynomial Regression y = Wφ(x) + b (2) where φ(x) gives the polynomial basis, e.g.,
Normalization Techniques
 Normalization Techniques Devansh Arpit Normalization Techniques 1 / 39 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 2 Motivation 3 Batch Normalization 4 Normalization Propagation 5 Weight Normalization 6 Layer Normalization
Normalization Techniques Devansh Arpit Normalization Techniques 1 / 39 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 2 Motivation 3 Batch Normalization 4 Normalization Propagation 5 Weight Normalization 6 Layer Normalization
Speaker Representation and Verification Part II. by Vasileios Vasilakakis
 Speaker Representation and Verification Part II by Vasileios Vasilakakis Outline -Approaches of Neural Networks in Speaker/Speech Recognition -Feed-Forward Neural Networks -Training with Back-propagation
Speaker Representation and Verification Part II by Vasileios Vasilakakis Outline -Approaches of Neural Networks in Speaker/Speech Recognition -Feed-Forward Neural Networks -Training with Back-propagation
Tips for Deep Learning
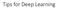 Tips for Deep Learning Recipe of Deep Learning Step : define a set of function Step : goodness of function Step 3: pick the best function NO Overfitting! NO YES Good Results on Testing Data? YES Good Results
Tips for Deep Learning Recipe of Deep Learning Step : define a set of function Step : goodness of function Step 3: pick the best function NO Overfitting! NO YES Good Results on Testing Data? YES Good Results
Neural Networks. Lecture 6. Rob Fergus
 Neural Networks Lecture 6 Rob Fergus Overview Individual neuron Non-linearities (RELU, tanh, sigmoid) Single layer model Multiple layer models Theoretical discussion: representational power Examples shown
Neural Networks Lecture 6 Rob Fergus Overview Individual neuron Non-linearities (RELU, tanh, sigmoid) Single layer model Multiple layer models Theoretical discussion: representational power Examples shown
Machine Learning: Chenhao Tan University of Colorado Boulder LECTURE 16
 Machine Learning: Chenhao Tan University of Colorado Boulder LECTURE 16 Slides adapted from Jordan Boyd-Graber, Justin Johnson, Andrej Karpathy, Chris Ketelsen, Fei-Fei Li, Mike Mozer, Michael Nielson
Machine Learning: Chenhao Tan University of Colorado Boulder LECTURE 16 Slides adapted from Jordan Boyd-Graber, Justin Johnson, Andrej Karpathy, Chris Ketelsen, Fei-Fei Li, Mike Mozer, Michael Nielson
ECE521 Lecture 7/8. Logistic Regression
 ECE521 Lecture 7/8 Logistic Regression Outline Logistic regression (Continue) A single neuron Learning neural networks Multi-class classification 2 Logistic regression The output of a logistic regression
ECE521 Lecture 7/8 Logistic Regression Outline Logistic regression (Continue) A single neuron Learning neural networks Multi-class classification 2 Logistic regression The output of a logistic regression
Neural Network Tutorial & Application in Nuclear Physics. Weiguang Jiang ( 蒋炜光 ) UTK / ORNL
 Neural Network Tutorial & Application in Nuclear Physics Weiguang Jiang ( 蒋炜光 ) UTK / ORNL Machine Learning Logistic Regression Gaussian Processes Neural Network Support vector machine Random Forest Genetic
Neural Network Tutorial & Application in Nuclear Physics Weiguang Jiang ( 蒋炜光 ) UTK / ORNL Machine Learning Logistic Regression Gaussian Processes Neural Network Support vector machine Random Forest Genetic
Deep Neural Networks (1) Hidden layers; Back-propagation
 Deep Neural Networs (1) Hidden layers; Bac-propagation Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 3 2 October 2018 http://www.inf.ed.ac.u/teaching/courses/mlp/ MLP Lecture 3 / 2 October 2018 Deep
Deep Neural Networs (1) Hidden layers; Bac-propagation Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 3 2 October 2018 http://www.inf.ed.ac.u/teaching/courses/mlp/ MLP Lecture 3 / 2 October 2018 Deep
Neural Networks (Part 1) Goals for the lecture
 Neural Networks (Part ) Mark Craven and David Page Computer Sciences 760 Spring 208 www.biostat.wisc.edu/~craven/cs760/ Some of the slides in these lectures have been adapted/borrowed from materials developed
Neural Networks (Part ) Mark Craven and David Page Computer Sciences 760 Spring 208 www.biostat.wisc.edu/~craven/cs760/ Some of the slides in these lectures have been adapted/borrowed from materials developed
Deep Feedforward Networks. Seung-Hoon Na Chonbuk National University
 Deep Feedforward Networks Seung-Hoon Na Chonbuk National University Neural Network: Types Feedforward neural networks (FNN) = Deep feedforward networks = multilayer perceptrons (MLP) No feedback connections
Deep Feedforward Networks Seung-Hoon Na Chonbuk National University Neural Network: Types Feedforward neural networks (FNN) = Deep feedforward networks = multilayer perceptrons (MLP) No feedback connections
Accelerating Stochastic Optimization
 Accelerating Stochastic Optimization Shai Shalev-Shwartz School of CS and Engineering, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem and Mobileye Master Class at Tel-Aviv, Tel-Aviv University, November 2014 Shalev-Shwartz
Accelerating Stochastic Optimization Shai Shalev-Shwartz School of CS and Engineering, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem and Mobileye Master Class at Tel-Aviv, Tel-Aviv University, November 2014 Shalev-Shwartz
TTIC 31230, Fundamentals of Deep Learning David McAllester, Winter Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) The Classical Convergence Thoerem
 TTIC 31230, Fundamentals of Deep Learning David McAllester, Winter 2018 Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) The Classical Convergence Thoerem RMSProp, Momentum and Adam Scaling Learnng Rates with Batch Size
TTIC 31230, Fundamentals of Deep Learning David McAllester, Winter 2018 Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) The Classical Convergence Thoerem RMSProp, Momentum and Adam Scaling Learnng Rates with Batch Size
Statistical Machine Learning II Spring 2017, Learning Theory, Lecture 4
 Statistical Machine Learning II Spring 07, Learning Theory, Lecture 4 Jean Honorio jhonorio@purdue.edu Deterministic Optimization For brevity, everywhere differentiable functions will be called smooth.
Statistical Machine Learning II Spring 07, Learning Theory, Lecture 4 Jean Honorio jhonorio@purdue.edu Deterministic Optimization For brevity, everywhere differentiable functions will be called smooth.
Based on the original slides of Hung-yi Lee
 Based on the original slides of Hung-yi Lee New Activation Function Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) σ z a a = z Reason: 1. Fast to compute 2. Biological reason a = 0 [Xavier Glorot, AISTATS 11] [Andrew L.
Based on the original slides of Hung-yi Lee New Activation Function Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) σ z a a = z Reason: 1. Fast to compute 2. Biological reason a = 0 [Xavier Glorot, AISTATS 11] [Andrew L.
ECS171: Machine Learning
 ECS171: Machine Learning Lecture 4: Optimization (LFD 3.3, SGD) Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Jan 22, 2018 Gradient descent Optimization Goal: find the minimizer of a function min f (w) w For now we assume f
ECS171: Machine Learning Lecture 4: Optimization (LFD 3.3, SGD) Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Jan 22, 2018 Gradient descent Optimization Goal: find the minimizer of a function min f (w) w For now we assume f
Neural Networks and Deep Learning
 Neural Networks and Deep Learning Professor Ameet Talwalkar November 12, 2015 Professor Ameet Talwalkar Neural Networks and Deep Learning November 12, 2015 1 / 16 Outline 1 Review of last lecture AdaBoost
Neural Networks and Deep Learning Professor Ameet Talwalkar November 12, 2015 Professor Ameet Talwalkar Neural Networks and Deep Learning November 12, 2015 1 / 16 Outline 1 Review of last lecture AdaBoost
Deep Learning Lab Course 2017 (Deep Learning Practical)
 Deep Learning Lab Course 207 (Deep Learning Practical) Labs: (Computer Vision) Thomas Brox, (Robotics) Wolfram Burgard, (Machine Learning) Frank Hutter, (Neurorobotics) Joschka Boedecker University of
Deep Learning Lab Course 207 (Deep Learning Practical) Labs: (Computer Vision) Thomas Brox, (Robotics) Wolfram Burgard, (Machine Learning) Frank Hutter, (Neurorobotics) Joschka Boedecker University of
Simple Techniques for Improving SGD. CS6787 Lecture 2 Fall 2017
 Simple Techniques for Improving SGD CS6787 Lecture 2 Fall 2017 Step Sizes and Convergence Where we left off Stochastic gradient descent x t+1 = x t rf(x t ; yĩt ) Much faster per iteration than gradient
Simple Techniques for Improving SGD CS6787 Lecture 2 Fall 2017 Step Sizes and Convergence Where we left off Stochastic gradient descent x t+1 = x t rf(x t ; yĩt ) Much faster per iteration than gradient
CS 6501: Deep Learning for Computer Graphics. Basics of Neural Networks. Connelly Barnes
 CS 6501: Deep Learning for Computer Graphics Basics of Neural Networks Connelly Barnes Overview Simple neural networks Perceptron Feedforward neural networks Multilayer perceptron and properties Autoencoders
CS 6501: Deep Learning for Computer Graphics Basics of Neural Networks Connelly Barnes Overview Simple neural networks Perceptron Feedforward neural networks Multilayer perceptron and properties Autoencoders
IMPROVING STOCHASTIC GRADIENT DESCENT
 IMPROVING STOCHASTIC GRADIENT DESCENT WITH FEEDBACK Jayanth Koushik & Hiroaki Hayashi Language Technologies Institute Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213, USA {jkoushik,hiroakih}@cs.cmu.edu
IMPROVING STOCHASTIC GRADIENT DESCENT WITH FEEDBACK Jayanth Koushik & Hiroaki Hayashi Language Technologies Institute Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213, USA {jkoushik,hiroakih}@cs.cmu.edu
Based on the original slides of Hung-yi Lee
 Based on the original slides of Hung-yi Lee Google Trends Deep learning obtains many exciting results. Can contribute to new Smart Services in the Context of the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT Services
Based on the original slides of Hung-yi Lee Google Trends Deep learning obtains many exciting results. Can contribute to new Smart Services in the Context of the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT Services
Neural networks COMS 4771
 Neural networks COMS 4771 1. Logistic regression Logistic regression Suppose X = R d and Y = {0, 1}. A logistic regression model is a statistical model where the conditional probability function has a
Neural networks COMS 4771 1. Logistic regression Logistic regression Suppose X = R d and Y = {0, 1}. A logistic regression model is a statistical model where the conditional probability function has a
Comparison of Modern Stochastic Optimization Algorithms
 Comparison of Modern Stochastic Optimization Algorithms George Papamakarios December 214 Abstract Gradient-based optimization methods are popular in machine learning applications. In large-scale problems,
Comparison of Modern Stochastic Optimization Algorithms George Papamakarios December 214 Abstract Gradient-based optimization methods are popular in machine learning applications. In large-scale problems,
Normalization Techniques in Training of Deep Neural Networks
 Normalization Techniques in Training of Deep Neural Networks Lei Huang ( 黄雷 ) State Key Laboratory of Software Development Environment, Beihang University Mail:huanglei@nlsde.buaa.edu.cn August 17 th,
Normalization Techniques in Training of Deep Neural Networks Lei Huang ( 黄雷 ) State Key Laboratory of Software Development Environment, Beihang University Mail:huanglei@nlsde.buaa.edu.cn August 17 th,
Artificial Neuron (Perceptron)
 9/6/208 Gradient Descent (GD) Hantao Zhang Deep Learning with Python Reading: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/gradient_descent Artificial Neuron (Perceptron) = w T = w 0 0 + + w 2 2 + + w d d where
9/6/208 Gradient Descent (GD) Hantao Zhang Deep Learning with Python Reading: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/gradient_descent Artificial Neuron (Perceptron) = w T = w 0 0 + + w 2 2 + + w d d where
Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
 Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) nojunk@snu.ac.kr http://mipal.snu.ac.kr Department of Transdisciplinary Studies Seoul National University, Korea Jan. 2016 Many slides are from Fei-Fei
Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) nojunk@snu.ac.kr http://mipal.snu.ac.kr Department of Transdisciplinary Studies Seoul National University, Korea Jan. 2016 Many slides are from Fei-Fei
Adaptive Gradient Methods AdaGrad / Adam
 Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities Adaptive Gradient Methods AdaGrad / Adam Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Sham Kakade 1 The Problem with GD (and SGD)
Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities Adaptive Gradient Methods AdaGrad / Adam Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Sham Kakade 1 The Problem with GD (and SGD)
Machine Learning Basics III
 Machine Learning Basics III Benjamin Roth CIS LMU München Benjamin Roth (CIS LMU München) Machine Learning Basics III 1 / 62 Outline 1 Classification Logistic Regression 2 Gradient Based Optimization Gradient
Machine Learning Basics III Benjamin Roth CIS LMU München Benjamin Roth (CIS LMU München) Machine Learning Basics III 1 / 62 Outline 1 Classification Logistic Regression 2 Gradient Based Optimization Gradient
Neural Networks Learning the network: Backprop , Fall 2018 Lecture 4
 Neural Networks Learning the network: Backprop 11-785, Fall 2018 Lecture 4 1 Recap: The MLP can represent any function The MLP can be constructed to represent anything But how do we construct it? 2 Recap:
Neural Networks Learning the network: Backprop 11-785, Fall 2018 Lecture 4 1 Recap: The MLP can represent any function The MLP can be constructed to represent anything But how do we construct it? 2 Recap:
CSC321 Lecture 8: Optimization
 CSC321 Lecture 8: Optimization Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 8: Optimization 1 / 26 Overview We ve talked a lot about how to compute gradients. What do we actually do with them? Today s lecture:
CSC321 Lecture 8: Optimization Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 8: Optimization 1 / 26 Overview We ve talked a lot about how to compute gradients. What do we actually do with them? Today s lecture:
Neural Network Training
 Neural Network Training Sargur Srihari Topics in Network Training 0. Neural network parameters Probabilistic problem formulation Specifying the activation and error functions for Regression Binary classification
Neural Network Training Sargur Srihari Topics in Network Training 0. Neural network parameters Probabilistic problem formulation Specifying the activation and error functions for Regression Binary classification
ECS289: Scalable Machine Learning
 ECS289: Scalable Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Nov 2, 2016 Outline SGD-typed algorithms for Deep Learning Parallel SGD for deep learning Perceptron Prediction value for a training data: prediction
ECS289: Scalable Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Nov 2, 2016 Outline SGD-typed algorithms for Deep Learning Parallel SGD for deep learning Perceptron Prediction value for a training data: prediction
Multi-layer Neural Networks
 Multi-layer Neural Networks Steve Renals Informatics 2B Learning and Data Lecture 13 8 March 2011 Informatics 2B: Learning and Data Lecture 13 Multi-layer Neural Networks 1 Overview Multi-layer neural
Multi-layer Neural Networks Steve Renals Informatics 2B Learning and Data Lecture 13 8 March 2011 Informatics 2B: Learning and Data Lecture 13 Multi-layer Neural Networks 1 Overview Multi-layer neural
Machine Learning Basics
 Security and Fairness of Deep Learning Machine Learning Basics Anupam Datta CMU Spring 2019 Image Classification Image Classification Image classification pipeline Input: A training set of N images, each
Security and Fairness of Deep Learning Machine Learning Basics Anupam Datta CMU Spring 2019 Image Classification Image Classification Image classification pipeline Input: A training set of N images, each
Mark Gales October y (x) x 1. x 2 y (x) Inputs. Outputs. x d. y (x) Second Output layer layer. layer.
 University of Cambridge Engineering Part IIB & EIST Part II Paper I0: Advanced Pattern Processing Handouts 4 & 5: Multi-Layer Perceptron: Introduction and Training x y (x) Inputs x 2 y (x) 2 Outputs x
University of Cambridge Engineering Part IIB & EIST Part II Paper I0: Advanced Pattern Processing Handouts 4 & 5: Multi-Layer Perceptron: Introduction and Training x y (x) Inputs x 2 y (x) 2 Outputs x
Deep Learning (CNNs)
 10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Deep Learning (CNNs) Deep Learning Readings: Murphy 28 Bishop - - HTF - - Mitchell
10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Deep Learning (CNNs) Deep Learning Readings: Murphy 28 Bishop - - HTF - - Mitchell
Tips for Deep Learning
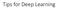 Tips for Deep Learning Recipe of Deep Learning Step : define a set of function Step : goodness of function Step 3: pick the best function NO Overfitting! NO YES Good Results on Testing Data? YES Good Results
Tips for Deep Learning Recipe of Deep Learning Step : define a set of function Step : goodness of function Step 3: pick the best function NO Overfitting! NO YES Good Results on Testing Data? YES Good Results
CPSC 540: Machine Learning
 CPSC 540: Machine Learning First-Order Methods, L1-Regularization, Coordinate Descent Winter 2016 Some images from this lecture are taken from Google Image Search. Admin Room: We ll count final numbers
CPSC 540: Machine Learning First-Order Methods, L1-Regularization, Coordinate Descent Winter 2016 Some images from this lecture are taken from Google Image Search. Admin Room: We ll count final numbers
Machine Learning Lecture 14
 Machine Learning Lecture 14 Tricks of the Trade 07.12.2017 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Course Outline Fundamentals Bayes Decision Theory Probability
Machine Learning Lecture 14 Tricks of the Trade 07.12.2017 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Course Outline Fundamentals Bayes Decision Theory Probability
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing
 STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Lecture 8: Optimization Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis May 9, 2017 Optimization Numerical Optimization Numerical Optimization: min X f (X ) Can be applied
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Lecture 8: Optimization Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis May 9, 2017 Optimization Numerical Optimization Numerical Optimization: min X f (X ) Can be applied
Serious limitations of (single-layer) perceptrons: Cannot learn non-linearly separable tasks. Cannot approximate (learn) non-linear functions
 BACK-PROPAGATION NETWORKS Serious limitations of (single-layer) perceptrons: Cannot learn non-linearly separable tasks Cannot approximate (learn) non-linear functions Difficult (if not impossible) to design
BACK-PROPAGATION NETWORKS Serious limitations of (single-layer) perceptrons: Cannot learn non-linearly separable tasks Cannot approximate (learn) non-linear functions Difficult (if not impossible) to design
Adaptive Gradient Methods AdaGrad / Adam. Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Sham Kakade
 Adaptive Gradient Methods AdaGrad / Adam Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Sham Kakade 1 Announcements: HW3 posted Dual coordinate ascent (some review of SGD and random
Adaptive Gradient Methods AdaGrad / Adam Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Sham Kakade 1 Announcements: HW3 posted Dual coordinate ascent (some review of SGD and random
Gradient Descent. Sargur Srihari
 Gradient Descent Sargur srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Topics Simple Gradient Descent/Ascent Difficulties with Simple Gradient Descent Line Search Brent s Method Conjugate Gradient Descent Weight vectors
Gradient Descent Sargur srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Topics Simple Gradient Descent/Ascent Difficulties with Simple Gradient Descent Line Search Brent s Method Conjugate Gradient Descent Weight vectors
Multilayer Neural Networks. (sometimes called Multilayer Perceptrons or MLPs)
 Multilayer Neural Networks (sometimes called Multilayer Perceptrons or MLPs) Linear separability Hyperplane In 2D: w x + w 2 x 2 + w 0 = 0 Feature x 2 = w w 2 x w 0 w 2 Feature 2 A perceptron can separate
Multilayer Neural Networks (sometimes called Multilayer Perceptrons or MLPs) Linear separability Hyperplane In 2D: w x + w 2 x 2 + w 0 = 0 Feature x 2 = w w 2 x w 0 w 2 Feature 2 A perceptron can separate
(Feed-Forward) Neural Networks Dr. Hajira Jabeen, Prof. Jens Lehmann
 (Feed-Forward) Neural Networks 2016-12-06 Dr. Hajira Jabeen, Prof. Jens Lehmann Outline In the previous lectures we have learned about tensors and factorization methods. RESCAL is a bilinear model for
(Feed-Forward) Neural Networks 2016-12-06 Dr. Hajira Jabeen, Prof. Jens Lehmann Outline In the previous lectures we have learned about tensors and factorization methods. RESCAL is a bilinear model for
Lasso: Algorithms and Extensions
 ELE 538B: Sparsity, Structure and Inference Lasso: Algorithms and Extensions Yuxin Chen Princeton University, Spring 2017 Outline Proximal operators Proximal gradient methods for lasso and its extensions
ELE 538B: Sparsity, Structure and Inference Lasso: Algorithms and Extensions Yuxin Chen Princeton University, Spring 2017 Outline Proximal operators Proximal gradient methods for lasso and its extensions
Nostalgic Adam: Weighing more of the past gradients when designing the adaptive learning rate
 Nostalgic Adam: Weighing more of the past gradients when designing the adaptive learning rate Haiwen Huang School of Mathematical Sciences Peking University, Beijing, 100871 smshhw@pku.edu.cn Chang Wang
Nostalgic Adam: Weighing more of the past gradients when designing the adaptive learning rate Haiwen Huang School of Mathematical Sciences Peking University, Beijing, 100871 smshhw@pku.edu.cn Chang Wang
Computational statistics
 Computational statistics Lecture 3: Neural networks Thierry Denœux 5 March, 2016 Neural networks A class of learning methods that was developed separately in different fields statistics and artificial
Computational statistics Lecture 3: Neural networks Thierry Denœux 5 March, 2016 Neural networks A class of learning methods that was developed separately in different fields statistics and artificial
Multilayer Neural Networks. (sometimes called Multilayer Perceptrons or MLPs)
 Multilayer Neural Networks (sometimes called Multilayer Perceptrons or MLPs) Linear separability Hyperplane In 2D: w 1 x 1 + w 2 x 2 + w 0 = 0 Feature 1 x 2 = w 1 w 2 x 1 w 0 w 2 Feature 2 A perceptron
Multilayer Neural Networks (sometimes called Multilayer Perceptrons or MLPs) Linear separability Hyperplane In 2D: w 1 x 1 + w 2 x 2 + w 0 = 0 Feature 1 x 2 = w 1 w 2 x 1 w 0 w 2 Feature 2 A perceptron
Lecture 4: Perceptrons and Multilayer Perceptrons
 Lecture 4: Perceptrons and Multilayer Perceptrons Cognitive Systems II - Machine Learning SS 2005 Part I: Basic Approaches of Concept Learning Perceptrons, Artificial Neuronal Networks Lecture 4: Perceptrons
Lecture 4: Perceptrons and Multilayer Perceptrons Cognitive Systems II - Machine Learning SS 2005 Part I: Basic Approaches of Concept Learning Perceptrons, Artificial Neuronal Networks Lecture 4: Perceptrons
CSC321 Lecture 7: Optimization
 CSC321 Lecture 7: Optimization Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 7: Optimization 1 / 25 Overview We ve talked a lot about how to compute gradients. What do we actually do with them? Today s lecture:
CSC321 Lecture 7: Optimization Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 7: Optimization 1 / 25 Overview We ve talked a lot about how to compute gradients. What do we actually do with them? Today s lecture:
