An Introduction to Systems of Equations
|
|
|
- Henry Gabriel Parker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LESSON 17 An Introduction to Sstems of Equations LEARNING OBJECTIVES Toda I am: completing the Desmos activit Sstems of Two Linear Equations. So that I can: write and solve a sstem of two linear equations to explore the numerical and graphical meaning of solution. I ll know I have it when I can: write an equation of a line to describe Duke and Shirle s walk on a ramp. Opening Exercise 1. Go to student.desmos.com and tpe in our teacher s code: You ll be completing the activit, Sstems of Two Linear Equations. Complete the questions below as ou go through the activit.. On Screen 18, ou wrote two equations where the lines do not intersect. What is true about these two lines?. Write a new sstems of equations where the lines will not meet. alekleks/shutterstock.com 4. In general, what can we sa about lines that don t meet? What must be true about them? 47
2 48 Module Solving Equations and Sstems of Equations. For each set of lines below, determine which ones will have a solution and which will not. A. x 18 B. x C. x 8 D. x 18 x 0 x 0 x 0 x 0 one solution Nosolution No solution One solution Mental Math In man of these problems, the solution can be determined b thinking about the relationship between the s. Often ou can use mental math to determine the solution. Tr it out in Exercises 6 and Write a sstem of equations where the sum of two s is and the difference is 6. Can ou determine the solution without graphing? Explain our reasoning. X 19 X 8 X Write a sstem of equations where the sum of the two s is and the difference is. Can ou determine the solution without graphing? Explain our reasoning. Xt X Continuous and Discrete Data Points Discrete data points can be numeric like the of dogs but it can also be categorical like colors or gender. Continuous data are not restricted to defined separate values, but can take on ANY value over a continuous range. Think about which tpe of data points are given in Exercises 8 and Richard thinks of two s. The onl clue he gives is The sum of two s is. What are the s Richard could be thinking of? A. Create an equation using two variables to represent this situation. Be sure to explain the meaning of each variable. m B. List at least six solutions to the equation ou created in Part A. X b lo t X1 C. Create a graph that represents the solution set to the equation. continuous data 8,, 7, C 1,11 C 1, O 49.
3 9. Gia had songs in a plalist composed of songs from her two favorite artists, Beoncé and Jennifer Lopez. How man songs did she have b each one in the plalist? A. Create an equation using two variables to represent this situation. Be sure to explain the meaning of each variable. B. List at least three solutions to the equation ou created in Part A. C. Create a graph that represents the solution set to the equation. Unit 4 Sstems of Equations and Inequalities 49 Lesson 17 An Introduction to Sstems of Equations ofbeonce's JStone/Shutterstock.com; Andrea Raffin/Shutterstock.com Xt O of ILO's x io discrete data 7, 9,1 6,4,0. Compare our solutions to Exercises 8 and 9. How are the alike? How are the different? As the stand, Exercises 8 and 9 are not sstems of equations, since there is onl one equation for each. 11. For Exercise 8, graph an additional clue from Richard, The difference of m two s is 6. Use the graph to determine Richard s two s. X 6 to X 6 1. Gia sas that the difference in the of songs is 6. Use the graph in Exercise 9 to find the of Beoncé songs and the of Jennifer Lopez songs Gia has on her plalist.
4 440 Module Solving Equations and Sstems of Equations Throughout this unit, ou ll be writing sstems of equations or inequalities with different real-world problems. s look at a stor of two people walking along a ramp. Duke starts at the base of a ramp and walks up it at a constant rate. His elevation increases b!. ever second. Just as Duke starts walking up the ramp, Shirle starts at the top of the same!. high ramp and begins walking down the ramp at a constant rate. Her elevation decreases!. ever second. Q Wang/Shutterstock.com Understanding the Problem 1. Fill in the chart below to help ou understand how quickl Duke and Shirle move and where the start. Duke s Path Time in Elevation Shirle s Path Time in Elevation Seconds in Feet 0 X X Seconds in Feet I m b Elevation in Feet 6 The Stor of Duke and Shirle , Time in Seconds
5 Unit 4 Sstems of Equations and Inequalities 441 Lesson 17 An Introduction to Sstems of Equations 14. Use the extra row in each table to write an expression that describes the elevation pattern. 1. Use the grid to graph the data for Duke and Shirle. Be sure to add a legend to help the reader understand our graph. Writing an Equation of a Line The equation of a line can be in the form mx b, where m represents the slope of the line and b represents the -intercept. 16. Determine the slope of Duke s line and Shirle s line. Wh is one of the slopes negative? Duke s slope: Shirle s slope: 17. What is the -intercept for each line? Duke s -intercept: O Shirle s -intercept: 18. Write the equation of Duke s line and Shirle s line. Duke s line: Shirle s line: X 19. Where do the two lines intersect? This is the point of intersection. What time Sec,1 do Duke and Shirle pass each other? Dist I 0. How could ou use the equations to find the point of intersection? The equations ou wrote in Exercise 18 are in slope-intercept form or mx b. Set equal X Point-slope is another ver useful form of a linear equation. For point-slope we need an point on the line, not just the -intercept, and the slope of the line. The general form looks like 1 m(x x 1 ) where (x 1, 1 ) is an point on the line and m is the slope of the line. 1. A. Use the points when the time is seconds and the slopes from Exercise 16 with the pointslope equation to get equations for Duke and Shirle. D,9 m mm S,19 m 9 x 9 9 B. How do these equations compare to the ones ou wrote in Exercise 18? Same c a 9 X
6 44 Module Solving Equations and Sstems of Equations Lesson Summar A sstem of equations is a set of equations that describe a situation. Example: Two s have a sum of 1 and a difference of 4. What are those two s? Define our variables. Use the information in the problem to write two equations. x the first the second x 1 x 4 In later lessons, ou ll solve sstems of equations using graphing, substitution and a new method, elimination. Linear Equations: If ou know the slope and -intercept, ou can use the equation mx b to write an equation for the line. If ou have the slope and an point on line ou can use the point-slope equation, 1 m(x x 1 ) where (x 1, 1 ) is an point on the line and m is the slope of the line. Example 1: The slope of a line is and the -intercept is. An equation of this line is. Example : The slope of a line is ½ and the point (, 4) is on the line. The equation of this line is. Point of Intersection: The point of intersection is an ordered pair that is a solution to both equations. On a graph, this is where the two graphs cross each other. Example: Determine the point of intersection for the graph at the right. Point of intersection:
7 Unit 4 Sstems of Equations and Inequalities 44 Lesson 17 An Introduction to Sstems of Equations NAME: PERIOD: DATE: Homework Problem Set Write a sstem of equations for Problems 1 and. Be sure to define our variables. Then create a table and a graph of each problem and find a solution. 1. The difference of two s is and their sum is 1. What are the two s?. The difference of two s is and the sum is 4. What are the two s? Sstem of Equations: Sstem of Equations: 1st nd Sum of s 1st nd Difference of s 1st nd Sum of s 1st nd Difference of s Solution: Solution:
8 444 Module Solving Equations and Sstems of Equations Write a sstem of equations for Problems and 4. Be sure to define our variables. You do NOT need to solve these problems.. Jack and his sister, Malonie, are 4 ears apart in age. The sum of their ages is 8. What are their ages? 4. Two of Julie s textbooks are a total of $6. The difference in price between the two books is $9. What is the cost of each book? Sstem of Equations: Sstem of Equations: pixelheadphoto digitalskillet/shutterstock.com Vetal/Shutterstock.com
9 Unit 4 Sstems of Equations and Inequalities 44 Lesson 17 An Introduction to Sstems of Equations Spiral REVIEW Determining Slope and -intercept from Graphs Find the slope and -intercept of each line.. slope -intercept 6. slope -intercept 7. slope -intercept 8. slope -intercept 9. slope -intercept. slope -intercept 11. slope -intercept 1. slope -intercept 1. slope -intercept
10 446 Module Solving Equations and Sstems of Equations Spiral REVIEW Solving Equations Solve each equation (8 7) 1. (6b 8) 4 6b Spiral REVIEW Graphing Lines 16. Match each equation with its graph. Explain our reasoning. A. x 6 B. x 1 C. x 4 D. x 6 E. x x - - x x - - x - - x
An Introduction to Systems of Equations
 LESSON 17 An Introduction to Sstems of Equations LEARNING OBJECTIVES Toda I am: completing the Desmos activit Sstems of Two Linear Equations. So that I can: write and solve a sstem of two linear equations
LESSON 17 An Introduction to Sstems of Equations LEARNING OBJECTIVES Toda I am: completing the Desmos activit Sstems of Two Linear Equations. So that I can: write and solve a sstem of two linear equations
Comparing linear and exponential growth
 Januar 16, 2009 Comparing Linear and Exponential Growth page 1 Comparing linear and exponential growth How does exponential growth, which we ve been studing this week, compare to linear growth, which we
Januar 16, 2009 Comparing Linear and Exponential Growth page 1 Comparing linear and exponential growth How does exponential growth, which we ve been studing this week, compare to linear growth, which we
12.1 Systems of Linear equations: Substitution and Elimination
 . Sstems of Linear equations: Substitution and Elimination Sstems of two linear equations in two variables A sstem of equations is a collection of two or more equations. A solution of a sstem in two variables
. Sstems of Linear equations: Substitution and Elimination Sstems of two linear equations in two variables A sstem of equations is a collection of two or more equations. A solution of a sstem in two variables
Ch 3 Alg 2 Note Sheet.doc 3.1 Graphing Systems of Equations
 Ch 3 Alg Note Sheet.doc 3.1 Graphing Sstems of Equations Sstems of Linear Equations A sstem of equations is a set of two or more equations that use the same variables. If the graph of each equation =.4
Ch 3 Alg Note Sheet.doc 3.1 Graphing Sstems of Equations Sstems of Linear Equations A sstem of equations is a set of two or more equations that use the same variables. If the graph of each equation =.4
Pre-AP Algebra 2 Lesson 1-1 Basics of Functions
 Lesson 1-1 Basics of Functions Objectives: The students will be able to represent functions verball, numericall, smbolicall, and graphicall. The students will be able to determine if a relation is a function
Lesson 1-1 Basics of Functions Objectives: The students will be able to represent functions verball, numericall, smbolicall, and graphicall. The students will be able to determine if a relation is a function
Systems of Linear Equations with the System Solver
 Systems of Linear Equations with the System Solver In these activities, you explore the steps involved in solving systems of linear equations. You ll make observations about the effects of those operations
Systems of Linear Equations with the System Solver In these activities, you explore the steps involved in solving systems of linear equations. You ll make observations about the effects of those operations
7.1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing
 7.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Objectives: Learn how to solve a sstem of linear equations b graphing Learn how to model a real-life situation using a sstem of linear equations With an equation, an
7.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Objectives: Learn how to solve a sstem of linear equations b graphing Learn how to model a real-life situation using a sstem of linear equations With an equation, an
10.2 Graphing Exponential Functions
 Name Class Date 10. Graphing Eponential Functions Essential Question: How do ou graph an eponential function of the form f () = ab? Resource Locker Eplore Eploring Graphs of Eponential Functions Eponential
Name Class Date 10. Graphing Eponential Functions Essential Question: How do ou graph an eponential function of the form f () = ab? Resource Locker Eplore Eploring Graphs of Eponential Functions Eponential
LESSON 4.3 GRAPHING INEQUALITIES
 LESSON.3 GRAPHING INEQUALITIES LESSON.3 GRAPHING INEQUALITIES 9 OVERVIEW Here s what ou ll learn in this lesson: Linear Inequalities a. Ordered pairs as solutions of linear inequalities b. Graphing linear
LESSON.3 GRAPHING INEQUALITIES LESSON.3 GRAPHING INEQUALITIES 9 OVERVIEW Here s what ou ll learn in this lesson: Linear Inequalities a. Ordered pairs as solutions of linear inequalities b. Graphing linear
Systems of Linear and Quadratic Equations. Check Skills You ll Need. y x. Solve by Graphing. Solve the following system by graphing.
 NY- Learning Standards for Mathematics A.A. Solve a sstem of one linear and one quadratic equation in two variables, where onl factoring is required. A.G.9 Solve sstems of linear and quadratic equations
NY- Learning Standards for Mathematics A.A. Solve a sstem of one linear and one quadratic equation in two variables, where onl factoring is required. A.G.9 Solve sstems of linear and quadratic equations
2. Bunny Slope:, Medium Trail: 4. 58; The starting height of the trail is 58 meters ; The length of the trail is 1450 meters.
 ...7 Start Thinking! For use before Lesson.7 Sample answer: If ou need to write the equation of a line given the slope and a point on the line, ou can find the -intercept (either graphicall or algebraicall).
...7 Start Thinking! For use before Lesson.7 Sample answer: If ou need to write the equation of a line given the slope and a point on the line, ou can find the -intercept (either graphicall or algebraicall).
Lesson 14: An Introduction to Domain and Range
 Exploratory Activity 1. Watch the Coin Counting video. What questions do you have? 2. What is the least amount of pennies that could be in the machine? Explain your thinking. 3. A. Make a guess about the
Exploratory Activity 1. Watch the Coin Counting video. What questions do you have? 2. What is the least amount of pennies that could be in the machine? Explain your thinking. 3. A. Make a guess about the
Graphical Solutions of Linear Systems
 Graphical Solutions of Linear Systems Consistent System (At least one solution) Inconsistent System (No Solution) Independent (One solution) Dependent (Infinite many solutions) Parallel Lines Equations
Graphical Solutions of Linear Systems Consistent System (At least one solution) Inconsistent System (No Solution) Independent (One solution) Dependent (Infinite many solutions) Parallel Lines Equations
7.5 Solve Special Types of
 75 Solve Special Tpes of Linear Sstems Goal p Identif the number of of a linear sstem Your Notes VOCABULARY Inconsistent sstem Consistent dependent sstem Eample A linear sstem with no Show that the linear
75 Solve Special Tpes of Linear Sstems Goal p Identif the number of of a linear sstem Your Notes VOCABULARY Inconsistent sstem Consistent dependent sstem Eample A linear sstem with no Show that the linear
Can a system of linear equations have no solution? Can a system of linear equations have many solutions?
 5. Solving Special Sstems of Linear Equations Can a sstem of linear equations have no solution? Can a sstem of linear equations have man solutions? ACTIVITY: Writing a Sstem of Linear Equations Work with
5. Solving Special Sstems of Linear Equations Can a sstem of linear equations have no solution? Can a sstem of linear equations have man solutions? ACTIVITY: Writing a Sstem of Linear Equations Work with
Unit 12 Study Notes 1 Systems of Equations
 You should learn to: Unit Stud Notes Sstems of Equations. Solve sstems of equations b substitution.. Solve sstems of equations b graphing (calculator). 3. Solve sstems of equations b elimination. 4. Solve
You should learn to: Unit Stud Notes Sstems of Equations. Solve sstems of equations b substitution.. Solve sstems of equations b graphing (calculator). 3. Solve sstems of equations b elimination. 4. Solve
3-1. Solving Systems Using Tables and Graphs. Concept Summary. Graphical Solutions of Linear Systems VOCABULARY TEKS FOCUS ESSENTIAL UNDERSTANDING
 3- Solving Sstems Using Tables and Graphs TEKS FOCUS VOCABULARY Foundational to TEKS (3)(A) Formulate sstems of equations, including sstems consisting of three linear equations in three variables and sstems
3- Solving Sstems Using Tables and Graphs TEKS FOCUS VOCABULARY Foundational to TEKS (3)(A) Formulate sstems of equations, including sstems consisting of three linear equations in three variables and sstems
Absolute Value Inequalities
 LESSON 16 Absolute Value Inequalities LEARNING OBJECTIVES Today I am: reviewing solving and graphing inequalities. So that I can: determine the steps to solve absolute value inequalities. I ll know I have
LESSON 16 Absolute Value Inequalities LEARNING OBJECTIVES Today I am: reviewing solving and graphing inequalities. So that I can: determine the steps to solve absolute value inequalities. I ll know I have
( 7, 3) means x = 7 and y = 3. ( 7, 3) works in both equations so. Section 5 1: Solving a System of Linear Equations by Graphing
 Section 5 : Solving a Sstem of Linear Equations b Graphing What is a sstem of Linear Equations? A sstem of linear equations is a list of two or more linear equations that each represents the graph of a
Section 5 : Solving a Sstem of Linear Equations b Graphing What is a sstem of Linear Equations? A sstem of linear equations is a list of two or more linear equations that each represents the graph of a
Solving Systems of Linear and Quadratic Equations
 9.5 Solving Systems of Linear and Quadratic Equations How can you solve a system of two equations when one is linear and the other is quadratic? ACTIVITY: Solving a System of Equations Work with a partner.
9.5 Solving Systems of Linear and Quadratic Equations How can you solve a system of two equations when one is linear and the other is quadratic? ACTIVITY: Solving a System of Equations Work with a partner.
Chapter 6: Systems of Equations and Inequalities
 Chapter 6: Sstems of Equations and Inequalities 6-1: Solving Sstems b Graphing Objectives: Identif solutions of sstems of linear equation in two variables. Solve sstems of linear equation in two variables
Chapter 6: Sstems of Equations and Inequalities 6-1: Solving Sstems b Graphing Objectives: Identif solutions of sstems of linear equation in two variables. Solve sstems of linear equation in two variables
a. Do you think the function is linear or non-linear? Explain using what you know about powers of variables.
 8.5.8 Lesson Date: Graphs of Non-Linear Functions Student Objectives I can examine the average rate of change for non-linear functions and learn that they do not have a constant rate of change. I can determine
8.5.8 Lesson Date: Graphs of Non-Linear Functions Student Objectives I can examine the average rate of change for non-linear functions and learn that they do not have a constant rate of change. I can determine
Fair Game Review. Chapter 2. and y = 5. Evaluate the expression when x = xy 2. 4x. Evaluate the expression when a = 9 and b = 4.
 Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Evaluate the epression when = and =.... 0 +. 8( ) Evaluate the epression when a = 9 and b =.. ab. a ( b + ) 7. b b 7 8. 7b + ( ab ) 9. You go to the movies with five
Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Evaluate the epression when = and =.... 0 +. 8( ) Evaluate the epression when a = 9 and b =.. ab. a ( b + ) 7. b b 7 8. 7b + ( ab ) 9. You go to the movies with five
LESSON #12 - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
MATH GRADE 8 UNIT 4 LINEAR RELATIONSHIPS ANSWERS FOR EXERCISES. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 51
 MATH GRADE 8 UNIT LINEAR RELATIONSHIPS FOR EXERCISES Copright Pearson Education, Inc. Grade 8 Unit : Linear Relationships LESSON : MODELING RUNNING SPEEDS 8.EE.. A Runner A 8.EE.. D sec 8.EE.. D. m/sec
MATH GRADE 8 UNIT LINEAR RELATIONSHIPS FOR EXERCISES Copright Pearson Education, Inc. Grade 8 Unit : Linear Relationships LESSON : MODELING RUNNING SPEEDS 8.EE.. A Runner A 8.EE.. D sec 8.EE.. D. m/sec
Systems of Linear Equations
 Sstems of Linear Equations Monetar Sstems Overload Lesson 3-1 Learning Targets: Use graphing, substitution, and elimination to solve sstems of linear equations in two variables. Formulate sstems of linear
Sstems of Linear Equations Monetar Sstems Overload Lesson 3-1 Learning Targets: Use graphing, substitution, and elimination to solve sstems of linear equations in two variables. Formulate sstems of linear
STAAR Category 2 Grade 7 Mathematics TEKS 7.7A. Student Activity 1. Complete the table below to show the slope and y-intercept of each equation.
 STAAR Categor Grade Mathematics TEKS.A Student Activit Work with our partner to answer the following questions. Problem : Complete the table below to show the slope and -intercept of each equation. Equation
STAAR Categor Grade Mathematics TEKS.A Student Activit Work with our partner to answer the following questions. Problem : Complete the table below to show the slope and -intercept of each equation. Equation
Chapter 9 BUILD YOUR VOCABULARY
 C H A P T E R 9 BUILD YUR VCABULARY Chapter 9 This is an alphabetical list of new vocabular terms ou will learn in Chapter 9. As ou complete the stud notes for the chapter, ou will see Build Your Vocabular
C H A P T E R 9 BUILD YUR VCABULARY Chapter 9 This is an alphabetical list of new vocabular terms ou will learn in Chapter 9. As ou complete the stud notes for the chapter, ou will see Build Your Vocabular
Math 1010 Lesson 1-4 (Textbook 1.7 and 1.8) Different equations of Lines
 Math 00 Lesson -4 (Textbook.7 and.8) Different equations of Lines. slope intercept form = mx + b. standard form Ax + B = C m x x 3. point slope form ( ) Which one we use depends on what information is
Math 00 Lesson -4 (Textbook.7 and.8) Different equations of Lines. slope intercept form = mx + b. standard form Ax + B = C m x x 3. point slope form ( ) Which one we use depends on what information is
CONSUMER CHOICES Madison is thinking about leasing a car for. Example 1 Solve the system of equations by graphing.
 2-1 BJECTIVES Solve sstems of equations graphicall. Solve sstems of equations algebraicall. Solving Sstems of Equations in Two Variables CNSUMER CHICES Madison is thinking about leasing a car for two ears.
2-1 BJECTIVES Solve sstems of equations graphicall. Solve sstems of equations algebraicall. Solving Sstems of Equations in Two Variables CNSUMER CHICES Madison is thinking about leasing a car for two ears.
Graphing to Solve Systems of Equations
 LESSN 19 Graphing to Solve Systems of Equations LEARNING BJECTIVES Today I am: writing systems of equations. So that I can: model real-life situations. I ll know I have it when I can: determine which system
LESSN 19 Graphing to Solve Systems of Equations LEARNING BJECTIVES Today I am: writing systems of equations. So that I can: model real-life situations. I ll know I have it when I can: determine which system
LESSON #11 - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
4 The Cartesian Coordinate System- Pictures of Equations
 The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem Graphs of Equations in Two Variables -intercepts and -intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the Pthagorean
The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem Graphs of Equations in Two Variables -intercepts and -intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the Pthagorean
Systems of Linear Equations Monetary Systems Overload
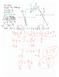 Sstems of Linear Equations SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Shared Reading, Close Reading, Interactive Word Wall Have ou ever noticed that when an item is popular and man people want to bu it, the price
Sstems of Linear Equations SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Shared Reading, Close Reading, Interactive Word Wall Have ou ever noticed that when an item is popular and man people want to bu it, the price
11.1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing
 Name Class Date 11.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Essential Question: How can ou find the solution of a sstem of linear equations b graphing? Resource Locker Eplore Tpes of Sstems of Linear Equations
Name Class Date 11.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Essential Question: How can ou find the solution of a sstem of linear equations b graphing? Resource Locker Eplore Tpes of Sstems of Linear Equations
MODELING WITH FUNCTIONS
 MATH HIGH SCHOOL MODELING WITH FUNCTIONS Copright 05 b Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. Printed in the United States of America. This publication is protected b copright,
MATH HIGH SCHOOL MODELING WITH FUNCTIONS Copright 05 b Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. Printed in the United States of America. This publication is protected b copright,
Fair Game Review. Chapter = How many calculators are sold when the profit is $425? Solve the equation. Check your solution.
 Name Date Chapter 4 Fair Game Review Solve the equation. Check our solution.. 8 3 = 3 2. 4a + a = 2 3. 9 = 4( 3k 4) 7k 4. ( m) 2 5 6 2 = 8 5. 5 t + 8t = 3 6. 3 5h 2 h + 4 = 0 2 7. The profit P (in dollars)
Name Date Chapter 4 Fair Game Review Solve the equation. Check our solution.. 8 3 = 3 2. 4a + a = 2 3. 9 = 4( 3k 4) 7k 4. ( m) 2 5 6 2 = 8 5. 5 t + 8t = 3 6. 3 5h 2 h + 4 = 0 2 7. The profit P (in dollars)
20.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors
 Name Class Date 20.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors Essential Question: How are -intercepts of a quadratic function and its linear factors related? Resource Locker Eplore Connecting Factors and
Name Class Date 20.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors Essential Question: How are -intercepts of a quadratic function and its linear factors related? Resource Locker Eplore Connecting Factors and
Essential Question How can you solve a system of linear equations? $15 per night. Cost, C (in dollars) $75 per Number of. Revenue, R (in dollars)
 5.1 Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing Essential Question How can ou solve a sstem of linear equations? Writing a Sstem of Linear Equations Work with a partner. Your famil opens a bed-and-breakfast.
5.1 Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing Essential Question How can ou solve a sstem of linear equations? Writing a Sstem of Linear Equations Work with a partner. Your famil opens a bed-and-breakfast.
Learning Target #1: I am learning to compare tables, equations, and graphs to model and solve linear & nonlinear situations.
 8 th Grade Honors Name: Chapter 2 Examples of Rigor Learning Target #: I am learning to compare tables, equations, and graphs to model and solve linear & nonlinear situations. Success Criteria I know I
8 th Grade Honors Name: Chapter 2 Examples of Rigor Learning Target #: I am learning to compare tables, equations, and graphs to model and solve linear & nonlinear situations. Success Criteria I know I
Fair Game Review. Chapter 5. feet and the length is 2x feet. Find the. perimeter of the garden. 24x 5 3. Name Date. Simplify the expression. 6.
 Name Date Chapter 5 Fair Game Review Simplif the expression. 1. 2x + 5 x 2. 4 + 2d 4d 3. 7 8 + 6 3 4. 5 + 4z 3 + 3z 5. 4( s + 2) + s 1 6. ( ) 24x 5 3 7. The width of a garden is ( 4x 1) perimeter of the
Name Date Chapter 5 Fair Game Review Simplif the expression. 1. 2x + 5 x 2. 4 + 2d 4d 3. 7 8 + 6 3 4. 5 + 4z 3 + 3z 5. 4( s + 2) + s 1 6. ( ) 24x 5 3 7. The width of a garden is ( 4x 1) perimeter of the
Math098 Practice Final Test
 Math098 Practice Final Test Find an equation of the line that contains the points listed in the table. 1) 0-6 1-2 -4 3-3 4-2 Find an equation of the line. 2) 10-10 - 10 - -10 Solve. 3) 2 = 3 + 4 Find the
Math098 Practice Final Test Find an equation of the line that contains the points listed in the table. 1) 0-6 1-2 -4 3-3 4-2 Find an equation of the line. 2) 10-10 - 10 - -10 Solve. 3) 2 = 3 + 4 Find the
14.1 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables
 86 Chapter 1 Sstems of Equations and Matrices 1.1 Sstems of Linear Equations in Two Variables Use the method of substitution to solve sstems of equations in two variables. Use the method of elimination
86 Chapter 1 Sstems of Equations and Matrices 1.1 Sstems of Linear Equations in Two Variables Use the method of substitution to solve sstems of equations in two variables. Use the method of elimination
Fair Game Review. Chapter 9. Find the square root(s) ± Find the side length of the square. 7. Simplify Simplify 63.
 Name Date Chapter 9 Find the square root(s). Fair Game Review... 9. ±. Find the side length of the square.. s. s s Area = 9 ft s Area = 0. m 7. Simplif 0. 8. Simplif. 9. Simplif 08. 0. Simplif 88. Copright
Name Date Chapter 9 Find the square root(s). Fair Game Review... 9. ±. Find the side length of the square.. s. s s Area = 9 ft s Area = 0. m 7. Simplif 0. 8. Simplif. 9. Simplif 08. 0. Simplif 88. Copright
Today I am: reviewing solving and graphing inequalities. So that I can: determine the steps to solve absolute value inequalities.
 2tI o LESSON 16 Absolute Value Inequalities LEARNING OBJECTIVES Today I am: reviewing solving and graphing inequalities. So that I can: determine the steps to solve absolute value inequalities. I ll know
2tI o LESSON 16 Absolute Value Inequalities LEARNING OBJECTIVES Today I am: reviewing solving and graphing inequalities. So that I can: determine the steps to solve absolute value inequalities. I ll know
9.1.1 What else can I solve?
 CCA Ch 9: Solving Quadratics and Inequalities Name Team # 9.1.1 What else can I solve? Solving Quadratic Equations 9-1. USE THE ZERO PRODUCT PROPERTY TO SOLVE FOR X. a. 9 3 2 4 6 b. 0 3 5 2 3 c. 2 6 0
CCA Ch 9: Solving Quadratics and Inequalities Name Team # 9.1.1 What else can I solve? Solving Quadratic Equations 9-1. USE THE ZERO PRODUCT PROPERTY TO SOLVE FOR X. a. 9 3 2 4 6 b. 0 3 5 2 3 c. 2 6 0
Solve each system by substitution or elimination. Check your solutions. b.
 Algebra: 10.3.1: Intersect or Intercept? Name Solutions Block Date Bell Work: a. = 4 2 3 = 3 2 3(4 ) = 3 2 12 + 3 = 3 5 12 = 3 5 = 15 Solve each sstem b substitution or elimination. Check our solutions.
Algebra: 10.3.1: Intersect or Intercept? Name Solutions Block Date Bell Work: a. = 4 2 3 = 3 2 3(4 ) = 3 2 12 + 3 = 3 5 12 = 3 5 = 15 Solve each sstem b substitution or elimination. Check our solutions.
Graphs of Non-Linear Functions
 Classwork Exploratory Challenge 1. Plot a graphical representation of the distance of the ball down a ramp over time. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zinszqvhaok Discussion 2. Did everyone s graph have
Classwork Exploratory Challenge 1. Plot a graphical representation of the distance of the ball down a ramp over time. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zinszqvhaok Discussion 2. Did everyone s graph have
Name Date Class Period. pencil straightedge graph paper How can you relate slope, y-intercept, and an equation?
 Name Date Class Period Activit 8.5 Investigating Slope-Intercept Form MATERIALS QUESTION pencil straightedge graph paper How can ou relate slope, -intercept, and an equation? You can find the slope and
Name Date Class Period Activit 8.5 Investigating Slope-Intercept Form MATERIALS QUESTION pencil straightedge graph paper How can ou relate slope, -intercept, and an equation? You can find the slope and
Unit 3 NOTES Honors Common Core Math 2 1. Day 1: Properties of Exponents
 Unit NOTES Honors Common Core Math Da : Properties of Eponents Warm-Up: Before we begin toda s lesson, how much do ou remember about eponents? Use epanded form to write the rules for the eponents. OBJECTIVE
Unit NOTES Honors Common Core Math Da : Properties of Eponents Warm-Up: Before we begin toda s lesson, how much do ou remember about eponents? Use epanded form to write the rules for the eponents. OBJECTIVE
Linear Equations and Arithmetic Sequences
 CONDENSED LESSON.1 Linear Equations and Arithmetic Sequences In this lesson, ou Write eplicit formulas for arithmetic sequences Write linear equations in intercept form You learned about recursive formulas
CONDENSED LESSON.1 Linear Equations and Arithmetic Sequences In this lesson, ou Write eplicit formulas for arithmetic sequences Write linear equations in intercept form You learned about recursive formulas
Systems of Linear Equations
 Sstems of Linear Equations Monetar Sstems Overload Lesson 3-1 Learning Targets: Use graphing, substitution, and elimination to solve sstems of linear equations in two variables. Formulate sstems of linear
Sstems of Linear Equations Monetar Sstems Overload Lesson 3-1 Learning Targets: Use graphing, substitution, and elimination to solve sstems of linear equations in two variables. Formulate sstems of linear
Systems of Linear Inequalities
 . Sstems of Linear Inequalities sstem of linear inequalities? How can ou sketch the graph of a ACTIVITY: Graphing Linear Inequalities Work with a partner. Match the linear inequalit with its graph. + Inequalit
. Sstems of Linear Inequalities sstem of linear inequalities? How can ou sketch the graph of a ACTIVITY: Graphing Linear Inequalities Work with a partner. Match the linear inequalit with its graph. + Inequalit
7.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors
 Name Class Date 7.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors Essential Question: How are -intercepts of a quadratic function and its linear factors related? Resource Locker Eplore Connecting Factors and
Name Class Date 7.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors Essential Question: How are -intercepts of a quadratic function and its linear factors related? Resource Locker Eplore Connecting Factors and
Systems of Linear Equations: Solving by Graphing
 8.1 Sstems of Linear Equations: Solving b Graphing 8.1 OBJECTIVE 1. Find the solution(s) for a set of linear equations b graphing NOTE There is no other ordered pair that satisfies both equations. From
8.1 Sstems of Linear Equations: Solving b Graphing 8.1 OBJECTIVE 1. Find the solution(s) for a set of linear equations b graphing NOTE There is no other ordered pair that satisfies both equations. From
Domain, Range, and End Behavior
 Locker LESSON 1.1 Domain, Range, and End Behavior Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F-IF.5 Relate the domain of a function to its graph and, where applicable, to the quantitative relationship
Locker LESSON 1.1 Domain, Range, and End Behavior Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F-IF.5 Relate the domain of a function to its graph and, where applicable, to the quantitative relationship
You are looking at a textile fabric pattern. Please answer the following questions.
 Introductory Activity: You are looking at a textile fabric pattern. Please answer the following questions. 1.) What different patterns do you see inside the fabric? 2.) How are the shapes in the pattern
Introductory Activity: You are looking at a textile fabric pattern. Please answer the following questions. 1.) What different patterns do you see inside the fabric? 2.) How are the shapes in the pattern
10.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions
 COMMON CORE Locker LESSON 0. Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Name Class Date 0. Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Essential Question: What functions are the inverses of
COMMON CORE Locker LESSON 0. Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Name Class Date 0. Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Essential Question: What functions are the inverses of
UNIT 8: LINEAR FUNCTIONS WEEK 31: Student Packet
 Name Period Date UNIT 8: LINEAR FUNCTIONS WEEK 31: Student Packet 31.1 Introduction to Systems of Equations Use variables to write equations and systems of equations. Solve problems involving rate, distance,
Name Period Date UNIT 8: LINEAR FUNCTIONS WEEK 31: Student Packet 31.1 Introduction to Systems of Equations Use variables to write equations and systems of equations. Solve problems involving rate, distance,
CORE. Chapter 3: Interacting Linear Functions, Linear Systems. Algebra Assessments
 CORE Algebra Assessments Chapter 3: Interacting Linear Functions, Linear Systems 97 98 Bears Band Booster Club The Bears Band Booster Club has decided to sell calendars to the band members and their parents.
CORE Algebra Assessments Chapter 3: Interacting Linear Functions, Linear Systems 97 98 Bears Band Booster Club The Bears Band Booster Club has decided to sell calendars to the band members and their parents.
Solve each system by graphing. Check your solution. y =-3x x + y = 5 y =-7
 Practice Solving Sstems b Graphing Solve each sstem b graphing. Check our solution. 1. =- + 3 = - (1, ). = 1 - (, 1) =-3 + 5 3. = 3 + + = 1 (, 3). =-5 = - 7. = 3-5 3 - = 0 (1, 5) 5. -3 + = 5 =-7 (, 7).
Practice Solving Sstems b Graphing Solve each sstem b graphing. Check our solution. 1. =- + 3 = - (1, ). = 1 - (, 1) =-3 + 5 3. = 3 + + = 1 (, 3). =-5 = - 7. = 3-5 3 - = 0 (1, 5) 5. -3 + = 5 =-7 (, 7).
MATH GRADE 8 UNIT 4 LINEAR RELATIONSHIPS EXERCISES
 MATH GRADE 8 UNIT LINEAR RELATIONSHIPS Copright 01 Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliate(s). All Rights Reserved. Printed in the United States of America. This publication is protected b copright,
MATH GRADE 8 UNIT LINEAR RELATIONSHIPS Copright 01 Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliate(s). All Rights Reserved. Printed in the United States of America. This publication is protected b copright,
LESSON #42 - INVERSES OF FUNCTIONS AND FUNCTION NOTATION PART 2 COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 LESSON #4 - INVERSES OF FUNCTIONS AND FUNCTION NOTATION PART COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II You will recall from unit 1 that in order to find the inverse of a function, ou must switch and and solve for. Also,
LESSON #4 - INVERSES OF FUNCTIONS AND FUNCTION NOTATION PART COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II You will recall from unit 1 that in order to find the inverse of a function, ou must switch and and solve for. Also,
Solving Linear Quadratic Systems Algebraically Algebra 1
 Name: Solving Linear Quadratic Systems Algebraically Algebra 1 Date: In this lesson we will begin to work with solving linear-quadratic systems of equations. Recall that to x, y that satisfy all equations
Name: Solving Linear Quadratic Systems Algebraically Algebra 1 Date: In this lesson we will begin to work with solving linear-quadratic systems of equations. Recall that to x, y that satisfy all equations
Algebra II Notes Unit Five: Quadratic Functions. Syllabus Objectives: 5.1 The student will graph quadratic functions with and without technology.
 Sllabus Objectives:.1 The student will graph quadratic functions with and without technolog. Quadratic Function: a function that can be written in the form are real numbers Parabola: the U-shaped graph
Sllabus Objectives:.1 The student will graph quadratic functions with and without technolog. Quadratic Function: a function that can be written in the form are real numbers Parabola: the U-shaped graph
The slope, m, compares the change in y-values to the change in x-values. Use the points (2, 4) and (6, 6) to determine the slope.
 LESSON Relating Slope and -intercept to Linear Equations UNDERSTAND The slope of a line is the ratio of the line s vertical change, called the rise, to its horizontal change, called the run. You can find
LESSON Relating Slope and -intercept to Linear Equations UNDERSTAND The slope of a line is the ratio of the line s vertical change, called the rise, to its horizontal change, called the run. You can find
Chapter 5: Systems of Equations
 Chapter : Sstems of Equations Section.: Sstems in Two Variables... 0 Section. Eercises... 9 Section.: Sstems in Three Variables... Section. Eercises... Section.: Linear Inequalities... Section.: Eercises.
Chapter : Sstems of Equations Section.: Sstems in Two Variables... 0 Section. Eercises... 9 Section.: Sstems in Three Variables... Section. Eercises... Section.: Linear Inequalities... Section.: Eercises.
1. Radium has a half-life of 1600 years. How much radium will be left from a 1000-gram sample after 1600 years?
 The Radioactive Deca Eperiment ACTIVITY 7 Learning Targets: Given a verbal description of a function, make a table and a graph of the function. Graph a function and identif and interpret ke features of
The Radioactive Deca Eperiment ACTIVITY 7 Learning Targets: Given a verbal description of a function, make a table and a graph of the function. Graph a function and identif and interpret ke features of
2-3. Linear Regression and Correlation. Vocabulary
 Chapter 2 Lesson 2-3 Linear Regression and Correlation BIG IDEA The regression line is the line of best fi t to data. The correlation coeffi cient measures the strength and direction of a linear pattern
Chapter 2 Lesson 2-3 Linear Regression and Correlation BIG IDEA The regression line is the line of best fi t to data. The correlation coeffi cient measures the strength and direction of a linear pattern
Chapter Start Thinking! For use before Activity 6.1. For use before Activity Start Thinking! For use before Lesson
 . Enrichment and Etension. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b is an number ecept.. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. Check students work.. Puzzle PAY HIM Etension. Start Thinking! For use before
. Enrichment and Etension. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b is an number ecept.. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. Check students work.. Puzzle PAY HIM Etension. Start Thinking! For use before
Algebra II Notes Unit Six: Polynomials Syllabus Objectives: 6.2 The student will simplify polynomial expressions.
 Algebra II Notes Unit Si: Polnomials Sllabus Objectives: 6. The student will simplif polnomial epressions. Review: Properties of Eponents (Allow students to come up with these on their own.) Let a and
Algebra II Notes Unit Si: Polnomials Sllabus Objectives: 6. The student will simplif polnomial epressions. Review: Properties of Eponents (Allow students to come up with these on their own.) Let a and
Note: Two perpendicular lines form a system of the first type. (Nothing special about being )
 Math 100 Elementary Algebra Sec 7.1: Solving Linear Systems by Graphing Two or more equations [inequalities] in several variables that are considered simultaneously are called a system of equations [inequalities].
Math 100 Elementary Algebra Sec 7.1: Solving Linear Systems by Graphing Two or more equations [inequalities] in several variables that are considered simultaneously are called a system of equations [inequalities].
Unit 1 Lesson 6: Seeing Structure in Expressions
 Unit 1 Lesson 6: Seeing Structure in Expressions Objective: Students will be able to use inductive reasoning to try to solve problems that are puzzle like in nature. CCSS: A.SSE.1.b, A.SSE.2 Example Problems
Unit 1 Lesson 6: Seeing Structure in Expressions Objective: Students will be able to use inductive reasoning to try to solve problems that are puzzle like in nature. CCSS: A.SSE.1.b, A.SSE.2 Example Problems
9-1. The Function with Equation y = ax 2. Vocabulary. Graphing y = x 2. Lesson
 Chapter 9 Lesson 9-1 The Function with Equation = a BIG IDEA The graph of an quadratic function with equation = a, with a 0, is a parabola with verte at the origin. Vocabular parabola refl ection-smmetric
Chapter 9 Lesson 9-1 The Function with Equation = a BIG IDEA The graph of an quadratic function with equation = a, with a 0, is a parabola with verte at the origin. Vocabular parabola refl ection-smmetric
ACCELERATED MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 7 NON-PROPORTIONAL LINEAR RELATIONSHIPS TOPICS COVERED:
 ACCELERATED MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 7 NON-PROPORTIONAL LINEAR RELATIONSHIPS TOPICS COVERED: Representing Linear Non-Proportional Equations Slope & -Intercept Graphing Using Slope & -Intercept Proportional
ACCELERATED MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 7 NON-PROPORTIONAL LINEAR RELATIONSHIPS TOPICS COVERED: Representing Linear Non-Proportional Equations Slope & -Intercept Graphing Using Slope & -Intercept Proportional
Linear Programming. Maximize the function. P = Ax + By + C. subject to the constraints. a 1 x + b 1 y < c 1 a 2 x + b 2 y < c 2
 Linear Programming Man real world problems require the optimization of some function subject to a collection of constraints. Note: Think of optimizing as maimizing or minimizing for MATH1010. For eample,
Linear Programming Man real world problems require the optimization of some function subject to a collection of constraints. Note: Think of optimizing as maimizing or minimizing for MATH1010. For eample,
5.2 Solving Linear-Quadratic Systems
 Name Class Date 5. Solving Linear-Quadratic Sstems Essential Question: How can ou solve a sstem composed of a linear equation in two variables and a quadratic equation in two variables? Resource Locker
Name Class Date 5. Solving Linear-Quadratic Sstems Essential Question: How can ou solve a sstem composed of a linear equation in two variables and a quadratic equation in two variables? Resource Locker
1.7 Inverse Functions
 71_0107.qd 1/7/0 10: AM Page 17 Section 1.7 Inverse Functions 17 1.7 Inverse Functions Inverse Functions Recall from Section 1. that a function can be represented b a set of ordered pairs. For instance,
71_0107.qd 1/7/0 10: AM Page 17 Section 1.7 Inverse Functions 17 1.7 Inverse Functions Inverse Functions Recall from Section 1. that a function can be represented b a set of ordered pairs. For instance,
Lesson 12: Absolute Value Inequalities
 Warm-Up Exercise 1. Use the number lines below to graph each inequality. A. x < 4 B. x > 1 C. 2 + x < 5 Exploratory Exercise Next, we ll combine two ideas inequalities and absolute value. 2. For each inequality
Warm-Up Exercise 1. Use the number lines below to graph each inequality. A. x < 4 B. x > 1 C. 2 + x < 5 Exploratory Exercise Next, we ll combine two ideas inequalities and absolute value. 2. For each inequality
Write Quadratic Functions and Models
 4.0 A..B, A.6.B, A.6.C, A.8.A TEKS Write Quadratic Functions and Models Before You wrote linear functions and models. Now You will write quadratic functions and models. Wh? So ou can model the cross section
4.0 A..B, A.6.B, A.6.C, A.8.A TEKS Write Quadratic Functions and Models Before You wrote linear functions and models. Now You will write quadratic functions and models. Wh? So ou can model the cross section
Inequalities. CK12 Editor. Say Thanks to the Authors Click (No sign in required)
 Inequalities CK12 Editor Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org
Inequalities CK12 Editor Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org
MiSP Force and Gravity Worksheet #3, L3
 MiSP Force and Gravity Worksheet #3, L3 Name Date FORCE AND ACCELERATION Introduction Today you will view a video of a typical skydive. The skydiver had a skydiving altimeter mounted in a special box with
MiSP Force and Gravity Worksheet #3, L3 Name Date FORCE AND ACCELERATION Introduction Today you will view a video of a typical skydive. The skydiver had a skydiving altimeter mounted in a special box with
UNIT 5. SIMULTANEOUS EQUATIONS
 3º ESO. Definitions UNIT 5. SIMULTANEOUS EQUATIONS A linear equation with two unknowns is an equation with two unknowns having both of them degree one. Eamples. 3 + 5 and + 6 9. The standard form for these
3º ESO. Definitions UNIT 5. SIMULTANEOUS EQUATIONS A linear equation with two unknowns is an equation with two unknowns having both of them degree one. Eamples. 3 + 5 and + 6 9. The standard form for these
MATH GRADE 8 UNIT 7 FUNCTIONS ANSWERS FOR EXERCISES
 MATH GRADE 8 UNIT 7 FUNCTIONS FOR EXERCISES LESSON 2: WHAT A GRAPH CAN TELL YOU 1. A Increasing and nonlinear 2. D 4 to 3. a. x (input) 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 (output) 1 4 1 3 1 2 1 Not defined 1 1 2 1 3 1 4
MATH GRADE 8 UNIT 7 FUNCTIONS FOR EXERCISES LESSON 2: WHAT A GRAPH CAN TELL YOU 1. A Increasing and nonlinear 2. D 4 to 3. a. x (input) 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 (output) 1 4 1 3 1 2 1 Not defined 1 1 2 1 3 1 4
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions
 Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions Find these vocabular words in Lesson 5-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular quadratic function parabola verte
Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions Find these vocabular words in Lesson 5-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular quadratic function parabola verte
15.2 Graphing Logarithmic
 _ - - - - - - Locker LESSON 5. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes on the graphs of f () = b and f () = log b
_ - - - - - - Locker LESSON 5. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes on the graphs of f () = b and f () = log b
Solving Linear-Quadratic Systems
 36 LESSON Solving Linear-Quadratic Sstems UNDERSTAND A sstem of two or more equations can include linear and nonlinear equations. In a linear-quadratic sstem, there is one linear equation and one quadratic
36 LESSON Solving Linear-Quadratic Sstems UNDERSTAND A sstem of two or more equations can include linear and nonlinear equations. In a linear-quadratic sstem, there is one linear equation and one quadratic
t s time we revisit our friend, the equation of a line: y = mx + b
 CH PARALLEL AND PERPENDICULAR LINES Introduction I t s time we revisit our friend, the equation of a line: mx + b SLOPE -INTERCEPT To be precise, b is not the -intercept; b is the -coordinate of the -intercept.
CH PARALLEL AND PERPENDICULAR LINES Introduction I t s time we revisit our friend, the equation of a line: mx + b SLOPE -INTERCEPT To be precise, b is not the -intercept; b is the -coordinate of the -intercept.
Course 15 Numbers and Their Properties
 Course Numbers and Their Properties KEY Module: Objective: Rules for Eponents and Radicals To practice appling rules for eponents when the eponents are rational numbers Name: Date: Fill in the blanks.
Course Numbers and Their Properties KEY Module: Objective: Rules for Eponents and Radicals To practice appling rules for eponents when the eponents are rational numbers Name: Date: Fill in the blanks.
Understand Positive and Negative Numbers
 Lesson. Understand Positive and Negative Numbers Positive integers are to the right of on the number line. Negative integers are to the left of on the number line. Opposites are the same distance from,
Lesson. Understand Positive and Negative Numbers Positive integers are to the right of on the number line. Negative integers are to the left of on the number line. Opposites are the same distance from,
Math101, Sections 2 and 3, Spring 2008 Review Sheet for Exam #2:
 Math101, Sections 2 and 3, Spring 2008 Review Sheet for Exam #2: 03 17 08 3 All about lines 3.1 The Rectangular Coordinate System Know how to plot points in the rectangular coordinate system. Know the
Math101, Sections 2 and 3, Spring 2008 Review Sheet for Exam #2: 03 17 08 3 All about lines 3.1 The Rectangular Coordinate System Know how to plot points in the rectangular coordinate system. Know the
Name: Richard Montgomery High School Department of Mathematics. Summer Math Packet. for students entering. Algebra 2/Trig*
 Name: Richard Montgomer High School Department of Mathematics Summer Math Packet for students entering Algebra 2/Trig* For the following courses: AAF, Honors Algebra 2, Algebra 2 (Please go the RM website
Name: Richard Montgomer High School Department of Mathematics Summer Math Packet for students entering Algebra 2/Trig* For the following courses: AAF, Honors Algebra 2, Algebra 2 (Please go the RM website
Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Graphing
 . Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing How can ou solve a sstem of linear equations? ACTIVITY: Writing a Sstem of Linear Equations Work with a partner. Your famil starts a bed-and-breakfast. The
. Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing How can ou solve a sstem of linear equations? ACTIVITY: Writing a Sstem of Linear Equations Work with a partner. Your famil starts a bed-and-breakfast. The
Vocabulary. Fitting a Line to Data. Lesson 2-2 Linear Models
 Lesson 2-2 Linear Models BIG IDEA The sum of squared deviations is a statistic for determining which of two lines fi ts the data better. A linear function is a set of ordered pairs (, ) satisfing an equation
Lesson 2-2 Linear Models BIG IDEA The sum of squared deviations is a statistic for determining which of two lines fi ts the data better. A linear function is a set of ordered pairs (, ) satisfing an equation
Solving and Graphing Inequalities
 Solving and Graphing Inequalities Graphing Simple Inequalities: x > 3 When finding the solution for an equation we get one answer for x. (There is only one number that satisfies the equation.) For 3x 5
Solving and Graphing Inequalities Graphing Simple Inequalities: x > 3 When finding the solution for an equation we get one answer for x. (There is only one number that satisfies the equation.) For 3x 5
Linear Equations and Inequalities
 Unit 2 Linear Equations and Inequalities 9/26/2016 10/21/2016 Name: By the end of this unit, you will be able to Use rate of change to solve problems Find the slope of a line Model real-world data with
Unit 2 Linear Equations and Inequalities 9/26/2016 10/21/2016 Name: By the end of this unit, you will be able to Use rate of change to solve problems Find the slope of a line Model real-world data with
Algebra 2 CPA Summer Assignment 2018
 Algebra CPA Summer Assignment 018 This assignment is designed for ou to practice topics learned in Algebra 1 that will be relevant in the Algebra CPA curriculum. This review is especiall important as ou
Algebra CPA Summer Assignment 018 This assignment is designed for ou to practice topics learned in Algebra 1 that will be relevant in the Algebra CPA curriculum. This review is especiall important as ou
How can you write an equation of a line when you are given the slope and a point on the line? ACTIVITY: Writing Equations of Lines
 .7 Writing Equations in Point-Slope Form How can ou write an equation of a line when ou are given the slope and a point on the line? ACTIVITY: Writing Equations of Lines Work with a partner. Sketch the
.7 Writing Equations in Point-Slope Form How can ou write an equation of a line when ou are given the slope and a point on the line? ACTIVITY: Writing Equations of Lines Work with a partner. Sketch the
Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Graphing. ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you solve a system of equations by graphing? 8.9 Slope-intercept form
 ? LESSN. Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing ESSENTIAL QUESTIN How can ou solve a sstem of equations b graphing? Epressions, equations, and relationships.9 Identif and verif the values of and
? LESSN. Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing ESSENTIAL QUESTIN How can ou solve a sstem of equations b graphing? Epressions, equations, and relationships.9 Identif and verif the values of and
8.4. If we let x denote the number of gallons pumped, then the price y in dollars can $ $1.70 $ $1.70 $ $1.70 $ $1.
 8.4 An Introduction to Functions: Linear Functions, Applications, and Models We often describe one quantit in terms of another; for eample, the growth of a plant is related to the amount of light it receives,
8.4 An Introduction to Functions: Linear Functions, Applications, and Models We often describe one quantit in terms of another; for eample, the growth of a plant is related to the amount of light it receives,
