Example Let VœÖÐBßCÑ À b-, CœB - ( see the example above). Explain why
|
|
|
- Roger Floyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Definition If V is a relation from E to F, then a) the domain of V œ dom ÐVÑ œ Ö+ E À b, F such that Ð+ß,Ñ V b) the range of V œ ran( VÑ œ Ö, F À b+ E such that Ð+ß,Ñ V " c) the inverse relation of V œ V œ ÖÐ,ß +Ñ À Ð+ß,Ñ V. " " V is a relation from F to E (because V F E.) # Example Let VœÖÐBßCÑ À b-, CœB - ( see the example above). Explain why domðvñ œ ran ÐVÑ œ Þ " # In this case, V œ ÖÐCß BÑ À b-, C œ B - Þ Since (1,4) V and " " " " Ð"ß "Ñ V, we have Ð%ß "Ñ V and Ð"ß "Ñ V. We can write %V " and "V "Þ Of course, these particular relations V and V " are usually called by their more familiar " names Ÿ and, so we write " Ÿ % and % " rather than "V% and %V "Þ Every subset of œ # is a relation on, so there are infinitely many possible relations on. For example, V œ ÖÐ1ß #Ñß Ð/ß È# Ñß Ð"ß (Ñ Þ For this V, dom ÐVÑ œ Ö1ß /ß " and ran ÐVÑ œ Ö#ß È# ß (, so we can write 1V#ß /V È # ß and "V(. But this particular relation V is of no interest to anybody, so it has never been given a familiar name (unlike the relation Vœ Ÿ). Most of the infinitely many possible relations on are uninteresting. Exercise Define the familiar relations and as sets (avoiding, of course, the use of and in the definitions). Example Let E œ Ö ÖB ß gß $ and F œ ÖCß Ög ß Dß A and V œ Ö ÐÖB ß CÑß Ðgß CÑß ÐÖB ß Ög Ñ E F. V is a relation from E to F. We can write, for example: ÖB VC and $VC Î. dom ÐVÑ œ Ö ÖB ß g E (but dom ÐVÑ Á E) ran ÐVÑ œ ÖCß Ög F (but ran ÐVÑ Á F) V œ Ö ÐCß ÖB Ñß ÐCß gñß ÐÖg ß ÖB Ñ, so, for example, CV gþ Example Suppose 7ß 8 = and that E has 7 elements and F has 8 elements. Then 78 E F has 78 elements (ordered pairs), and a set with 78 elements has # subsets. 78 Therefore there are exactly # different relations from Eto F.
2 Example If V œ ÖÐ7ß 8Ñ À Ðb5 Ñ 8 œ 57. V is a relation on that has a more common name: lœöð7ß8ñ ÀÐb5 Ñ8œ57 We write 7l8 iff Ð7ß 8Ñ lþ For example, we write #l% because Ð#ß %Ñ lþ Note: This set is the relation on. The divides relation on is defined by a different set ÖÐ7ß8Ñ À Ð b5 Ñ8œ57. But it's customary to use the same symbol, l, for this relation. Context usually tells us whether l refers to the division relation in or the division relation in. We do the same thing with other relation symbols for example, Ÿ ( on ) was defined above as a certain set. We use the same symbol, Ÿ for the corresponding relation in, say, =. Example We can define a relation 0 on by # 0 œ ÖÐBß CÑ À C œ B. The plot of this set of points in is a familiar parabola: the graph of the function CœB #. This suggests that functions can perhaps be thought of as special kinds of relations ( we will give a careful definition of function later ). # Dom Ð0Ñ œ RanÐ0Ñ œ Ò!ß _Ñ Ð#ß %Ñ 0 and Ð #ß %Ñ 0ß so we write #0% and #0%Þ However in this situation, it's more customary to use function notation and write %œ0ð#ñand %œ0ð #ÑÞ Both " " Ð%ß#Ñ 0 and Ð%ß #Ñ 0 Þ (When we have defined functions, it will turn out that although this particular perfectly good relation, it is not a function.) 0 " is a Can you guess what additional property or properties a relation should have to be called a function? We can also introduce the more general idea of composition of relations here, although composition of relations is mostly used when the relations are actually functions. Definition Suppose V is a relation from E to F and that W is a relation from F to CÞ We define the composition relation W Vfrom Eto G by W V œ ÖÐ+ß -Ñ À b, F such that Ð+ß,Ñ V and Ð,ß -Ñ W.
3 Examples 1. Suppose E œ Ö"ß #ß $ ß F œ Ö#ß $ß %ß & ß G œ Ö+ß,ß - and let V œ ÖÐ"ß $Ñß Ð"ß %Ñß Ð#ß &Ñ ß W œ ÖÐ$ß +Ñß Ð$ß,Ñß Ð&ß +Ñß Ð&ß,Ñ Then W V œ ÖÐ"ß +Ñß Ð"ß,Ñß Ð#ß +Ñß Ð#ß,Ñ (a subset of E G). dom ÐW VÑ œ Ö"ß #, a subset of E (and in this case, Á E) ran ÐW VÑ œ Ö+ß,, a subset of G (and in this case, Á G). #. Define relations V and W on by V œ ÖÐBß CÑ À B and C œ sin B and WœÖÐBßCÑÀB, B! and CœÈB. We could also write these as V œ ÖÐBß sin BÑ À B and W œ ÖÐBß È B Ñ À B, B!. Then W VœÖÐBßÈ sin B ÑÀB and sin B! and V W œ Ö ÐBß sin ÐÈ B Ñ Ñ À B and B! Þ Usually, V WÁW VÞ Most of the relations that exist on a set are not very interesting or useful. Relations become more interesting when then have some special additional properties. Definition Let V be a relation on a set E (that is, V E E). V is called a) reflexive iff a+ Eß +V+ b) symmetric iff a+ E a, E Ð+V, Ê,V+Ñ c) transitive iff a+ E a, E a- E Ð +V,,V-Ñ Ê +Vd) antisymmetric iff a+ E a, E Ð+V,,V+Ñ Ê Ð+ œ,ñ
4 Example Check that each Yes or No in the table is correct. Ÿ l (on ) (on ) (on ) (on c(a) Reflexive Symmetric Transitive Antisymmetric Y N Y Y N N Y Y Y N Y N Y N Y Y Comments about a couple of the table entries might be helpful. The divides relation l on is antisymmetric, but not on. Why is an antisymmetric relation on? Consider the negation of the definition: V is not antisymmetric means µ Ð a+ a, Ð+V,,V+Ñ Ê Ð+ œ,ñ Ñ b+ b, µ Ð+V,,V+Ñ Ê Ð+ œ,ñ Ñ b+ b, Ð +V,,V+ Ð+ Á,Ñ Ñ which is equivalent to which is equivalent to For to be not antisymmetric there would have to exist real numbers +ß, such that Ð+,Ñ and Ð, +Ñ and Ð+ Á,Ñ. This is impossible. Definition A relation Von a set E is called an equivalence relation iff V is reflexive, symmetric, and transitive. Symbols like,, and µ are often used to denote equivalence relations. None of the relations listed in the table above is an equivalence relation. In everyday language, when we say that two things are equivalent, the meaning is not that they are necessarily the same thing, but that for certain purposes they can be treated as if they were the same. For example, we might say that brothers and sisters are equivalent under Missouri inheritance law. Of course that is not to say there is no difference between brothers and sisters, but rather that for purposes of inheritance law, they can't be distinguished from each other: gender doesn't matter. In mathematics, an equivalence relation has roughly the same purpose. For example, the trig function sine can't distinguish between Band B # 1 À since sin B œ sin ÐB # 1Ñ, the two numbers are equivalent for the purpose of computing values of the sine function. Example Let _ œö6à 6is a straight line in the BC-plane whose equation has the form C œ %B, For two points TßU in the plane, #, define T U iff b6 _ such that TU, are both on the line 6
5 If we use coordinates and write TœÐBßCÑ, UœÐDßAÑ, then the relation can be written as # # œ ÖÐ ÐBß CÑß ÐDß AÑ Ñ À ÞÞÞ. What is the condition...? Check that is an equivalence relation on #. For a particular point T in the plane, describe the points that are in the set ÒTÓœÖU # À T U? ( This set is called the equivalence class of T Þ)
Relations. Relations occur all the time in mathematics. For example, there are many relations between # and % À
 Relations Relations occur all the time in mathematics. For example, there are many relations between and % À Ÿ% % Á% l% Ÿ,, Á ß and l are examples of relations which might or might not hold between two
Relations Relations occur all the time in mathematics. For example, there are many relations between and % À Ÿ% % Á% l% Ÿ,, Á ß and l are examples of relations which might or might not hold between two
PART I. Multiple choice. 1. Find the slope of the line shown here. 2. Find the slope of the line with equation $ÐB CÑœ(B &.
 Math 1301 - College Algebra Final Exam Review Sheet Version X This review, while fairly comprehensive, should not be the only material used to study for the final exam. It should not be considered a preview
Math 1301 - College Algebra Final Exam Review Sheet Version X This review, while fairly comprehensive, should not be the only material used to study for the final exam. It should not be considered a preview
Math 131 Exam 4 (Final Exam) F04M
 Math 3 Exam 4 (Final Exam) F04M3.4. Name ID Number The exam consists of 8 multiple choice questions (5 points each) and 0 true/false questions ( point each), for a total of 00 points. Mark the correct
Math 3 Exam 4 (Final Exam) F04M3.4. Name ID Number The exam consists of 8 multiple choice questions (5 points each) and 0 true/false questions ( point each), for a total of 00 points. Mark the correct
Dr. H. Joseph Straight SUNY Fredonia Smokin' Joe's Catalog of Groups: Direct Products and Semi-direct Products
 Dr. H. Joseph Straight SUNY Fredonia Smokin' Joe's Catalog of Groups: Direct Products and Semi-direct Products One of the fundamental problems in group theory is to catalog all the groups of some given
Dr. H. Joseph Straight SUNY Fredonia Smokin' Joe's Catalog of Groups: Direct Products and Semi-direct Products One of the fundamental problems in group theory is to catalog all the groups of some given
Math 1AA3/1ZB3 Sample Test 3, Version #1
 Math 1AA3/1ZB3 Sample Test 3, Version 1 Name: (Last Name) (First Name) Student Number: Tutorial Number: This test consists of 16 multiple choice questions worth 1 mark each (no part marks), and 1 question
Math 1AA3/1ZB3 Sample Test 3, Version 1 Name: (Last Name) (First Name) Student Number: Tutorial Number: This test consists of 16 multiple choice questions worth 1 mark each (no part marks), and 1 question
B œ c " " ã B œ c 8 8. such that substituting these values for the B 3 's will make all the equations true
 System of Linear Equations variables Ð unknowns Ñ B" ß B# ß ÞÞÞ ß B8 Æ Æ Æ + B + B ÞÞÞ + B œ, "" " "# # "8 8 " + B + B ÞÞÞ + B œ, #" " ## # #8 8 # ã + B + B ÞÞÞ + B œ, 3" " 3# # 38 8 3 ã + 7" B" + 7# B#
System of Linear Equations variables Ð unknowns Ñ B" ß B# ß ÞÞÞ ß B8 Æ Æ Æ + B + B ÞÞÞ + B œ, "" " "# # "8 8 " + B + B ÞÞÞ + B œ, #" " ## # #8 8 # ã + B + B ÞÞÞ + B œ, 3" " 3# # 38 8 3 ã + 7" B" + 7# B#
Definition Suppose M is a collection (set) of sets. M is called inductive if
 Definition Suppose M is a collection (set) of sets. M is called inductive if a) g M, and b) if B Mß then B MÞ Then we ask: are there any inductive sets? Informally, it certainly looks like there are. For
Definition Suppose M is a collection (set) of sets. M is called inductive if a) g M, and b) if B Mß then B MÞ Then we ask: are there any inductive sets? Informally, it certainly looks like there are. For
Cellular Automaton Growth on # : Theorems, Examples, and Problems
 Cellular Automaton Growth on : Theorems, Examples, and Problems (Excerpt from Advances in Applied Mathematics) Exactly 1 Solidification We will study the evolution starting from a single occupied cell
Cellular Automaton Growth on : Theorems, Examples, and Problems (Excerpt from Advances in Applied Mathematics) Exactly 1 Solidification We will study the evolution starting from a single occupied cell
Æ Å not every column in E is a pivot column (so EB œ! has at least one free variable) Æ Å E has linearly dependent columns
 ßÞÞÞß @ is linearly independent if B" @" B# @# ÞÞÞ B: @: œ! has only the trivial solution EB œ! has only the trivial solution Ðwhere E œ Ò@ @ ÞÞÞ@ ÓÑ every column in E is a pivot column E has linearly
ßÞÞÞß @ is linearly independent if B" @" B# @# ÞÞÞ B: @: œ! has only the trivial solution EB œ! has only the trivial solution Ðwhere E œ Ò@ @ ÞÞÞ@ ÓÑ every column in E is a pivot column E has linearly
8œ! This theorem is justified by repeating the process developed for a Taylor polynomial an infinite number of times.
 Taylor and Maclaurin Series We can use the same process we used to find a Taylor or Maclaurin polynomial to find a power series for a particular function as long as the function has infinitely many derivatives.
Taylor and Maclaurin Series We can use the same process we used to find a Taylor or Maclaurin polynomial to find a power series for a particular function as long as the function has infinitely many derivatives.
Inner Product Spaces
 Inner Product Spaces In 8 X, we defined an inner product? @? @?@ ÞÞÞ? 8@ 8. Another notation sometimes used is? @? ß@. The inner product in 8 has several important properties ( see Theorem, p. 33) that
Inner Product Spaces In 8 X, we defined an inner product? @? @?@ ÞÞÞ? 8@ 8. Another notation sometimes used is? @? ß@. The inner product in 8 has several important properties ( see Theorem, p. 33) that
The Rational Numbers
 The Rational Numbers Fields The system of integers that e formally defined is an improvement algebraically on the hole number system = (e can subtract in ) But still has some serious deficiencies: for
The Rational Numbers Fields The system of integers that e formally defined is an improvement algebraically on the hole number system = (e can subtract in ) But still has some serious deficiencies: for
e) D œ < f) D œ < b) A parametric equation for the line passing through Ð %, &,) ) and (#,(, %Ñ.
 Page 1 Calculus III : Bonus Problems: Set 1 Grade /42 Name Due at Exam 1 6/29/2018 1. (2 points) Give the equations for the following geometrical objects : a) A sphere of radius & centered at the point
Page 1 Calculus III : Bonus Problems: Set 1 Grade /42 Name Due at Exam 1 6/29/2018 1. (2 points) Give the equations for the following geometrical objects : a) A sphere of radius & centered at the point
: œ Ö: =? À =ß> real numbers. œ the previous plane with each point translated by : Ðfor example,! is translated to :)
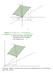 â SpanÖ?ß@ œ Ö =? > @ À =ß> real numbers : SpanÖ?ß@ œ Ö: =? > @ À =ß> real numbers œ the previous plane with each point translated by : Ðfor example, is translated to :) á In general: Adding a vector :
â SpanÖ?ß@ œ Ö =? > @ À =ß> real numbers : SpanÖ?ß@ œ Ö: =? > @ À =ß> real numbers œ the previous plane with each point translated by : Ðfor example, is translated to :) á In general: Adding a vector :
Proofs Involving Quantifiers. Proof Let B be an arbitrary member Proof Somehow show that there is a value
 Proofs Involving Quantifiers For a given universe Y : Theorem ÐaBÑ T ÐBÑ Theorem ÐbBÑ T ÐBÑ Proof Let B be an arbitrary member Proof Somehow show that there is a value of Y. Call it B œ +, say Þ ÐYou can
Proofs Involving Quantifiers For a given universe Y : Theorem ÐaBÑ T ÐBÑ Theorem ÐbBÑ T ÐBÑ Proof Let B be an arbitrary member Proof Somehow show that there is a value of Y. Call it B œ +, say Þ ÐYou can
Product Measures and Fubini's Theorem
 Product Measures and Fubini's Theorem 1. Product Measures Recall: Borel sets U in are generated by open sets. They are also generated by rectangles VœN " á N hich are products of intervals NÞ 3 Let V be
Product Measures and Fubini's Theorem 1. Product Measures Recall: Borel sets U in are generated by open sets. They are also generated by rectangles VœN " á N hich are products of intervals NÞ 3 Let V be
MATH 1301 (College Algebra) - Final Exam Review
 MATH 1301 (College Algebra) - Final Exam Review This review is comprehensive but should not be the only material used to study for the final exam. It should not be considered a preview of the final exam.
MATH 1301 (College Algebra) - Final Exam Review This review is comprehensive but should not be the only material used to study for the final exam. It should not be considered a preview of the final exam.
2. Let 0 be as in problem 1. Find the Fourier coefficient,&. (In other words, find the constant,& the Fourier series for 0.)
 Engineering Mathematics (ESE 317) Exam 4 April 23, 200 This exam contains seven multiple-choice problems worth two points each, 11 true-false problems worth one point each, and some free-response problems
Engineering Mathematics (ESE 317) Exam 4 April 23, 200 This exam contains seven multiple-choice problems worth two points each, 11 true-false problems worth one point each, and some free-response problems
solve EB œ,, we can row reduce the augmented matrix
 Motivation To PY Decomposition: Factoring E œ P Y solve EB œ,, we can row reduce the augmented matrix Ò + + ÞÞÞ+ ÞÞÞ + l, Ó µ ÞÞÞ µ Ò- - ÞÞÞ- ÞÞÞ-. Ó " # 3 8 " # 3 8 we get to Ò-" -# ÞÞÞ -3 ÞÞÞ-8Ó in an
Motivation To PY Decomposition: Factoring E œ P Y solve EB œ,, we can row reduce the augmented matrix Ò + + ÞÞÞ+ ÞÞÞ + l, Ó µ ÞÞÞ µ Ò- - ÞÞÞ- ÞÞÞ-. Ó " # 3 8 " # 3 8 we get to Ò-" -# ÞÞÞ -3 ÞÞÞ-8Ó in an
solve EB œ,, we can row reduce the augmented matrix
 PY Decomposition: Factoring E œ P Y Motivation To solve EB œ,, we can row reduce the augmented matrix Ò + + ÞÞÞ+ ÞÞÞ + l, Ó µ ÞÞÞ µ Ò- - ÞÞÞ- ÞÞÞ-. Ó " # 3 8 " # 3 8 When we get to Ò-" -# ÞÞÞ -3 ÞÞÞ-8Ó
PY Decomposition: Factoring E œ P Y Motivation To solve EB œ,, we can row reduce the augmented matrix Ò + + ÞÞÞ+ ÞÞÞ + l, Ó µ ÞÞÞ µ Ò- - ÞÞÞ- ÞÞÞ-. Ó " # 3 8 " # 3 8 When we get to Ò-" -# ÞÞÞ -3 ÞÞÞ-8Ó
Part I consists of 14 multiple choice questions (worth 5 points each) and 5 true/false question (worth 1 point each), for a total of 75 points.
 Math 131 Exam 1 Solutions Part I consists of 14 multiple choice questions (orth 5 points each) and 5 true/false question (orth 1 point each), for a total of 75 points. 1. The folloing table gives the number
Math 131 Exam 1 Solutions Part I consists of 14 multiple choice questions (orth 5 points each) and 5 true/false question (orth 1 point each), for a total of 75 points. 1. The folloing table gives the number
Digital Communications: An Overview of Fundamentals
 IMPERIAL COLLEGE of SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY and MEDICINE, DEPARTMENT of ELECTRICAL and ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING. COMPACT LECTURE NOTES on COMMUNICATION THEORY. Prof Athanassios Manikas, Spring 2001 Digital Communications:
IMPERIAL COLLEGE of SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY and MEDICINE, DEPARTMENT of ELECTRICAL and ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING. COMPACT LECTURE NOTES on COMMUNICATION THEORY. Prof Athanassios Manikas, Spring 2001 Digital Communications:
SVM example: cancer classification Support Vector Machines
 SVM example: cancer classification Support Vector Machines 1. Cancer genomics: TCGA The cancer genome atlas (TCGA) will provide high-quality cancer data for large scale analysis by many groups: SVM example:
SVM example: cancer classification Support Vector Machines 1. Cancer genomics: TCGA The cancer genome atlas (TCGA) will provide high-quality cancer data for large scale analysis by many groups: SVM example:
Probability basics. Probability and Measure Theory. Probability = mathematical analysis
 MA 751 Probability basics Probability and Measure Theory 1. Basics of probability 2 aspects of probability: Probability = mathematical analysis Probability = common sense Probability basics A set-up of
MA 751 Probability basics Probability and Measure Theory 1. Basics of probability 2 aspects of probability: Probability = mathematical analysis Probability = common sense Probability basics A set-up of
The Hahn-Banach and Radon-Nikodym Theorems
 The Hahn-Banach and Radon-Nikodym Theorems 1. Signed measures Definition 1. Given a set Hand a 5-field of sets Y, we define a set function. À Y Ä to be a signed measure if it has all the properties of
The Hahn-Banach and Radon-Nikodym Theorems 1. Signed measures Definition 1. Given a set Hand a 5-field of sets Y, we define a set function. À Y Ä to be a signed measure if it has all the properties of
Solving SVM: Quadratic Programming
 MA 751 Part 7 Solving SVM: Quadratic Programming 1. Quadratic programming (QP): Introducing Lagrange multipliers α 4 and. 4 (can be justified in QP for inequality as well as equality constraints) we define
MA 751 Part 7 Solving SVM: Quadratic Programming 1. Quadratic programming (QP): Introducing Lagrange multipliers α 4 and. 4 (can be justified in QP for inequality as well as equality constraints) we define
1. Classify each number. Choose all correct answers. b. È # : (i) natural number (ii) integer (iii) rational number (iv) real number
 Review for Placement Test To ypass Math 1301 College Algebra Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences University of Houston-Downtown Revised: Fall 2009 PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING CAREFULLY: 1. The
Review for Placement Test To ypass Math 1301 College Algebra Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences University of Houston-Downtown Revised: Fall 2009 PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING CAREFULLY: 1. The
EXCERPTS FROM ACTEX CALCULUS REVIEW MANUAL
 EXCERPTS FROM ACTEX CALCULUS REVIEW MANUAL Table of Contents Introductory Comments SECTION 6 - Differentiation PROLEM SET 6 TALE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTORY COMMENTS Section 1 Set Theory 1 Section 2 Intervals,
EXCERPTS FROM ACTEX CALCULUS REVIEW MANUAL Table of Contents Introductory Comments SECTION 6 - Differentiation PROLEM SET 6 TALE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTORY COMMENTS Section 1 Set Theory 1 Section 2 Intervals,
Suggestions - Problem Set (a) Show the discriminant condition (1) takes the form. ln ln, # # R R
 Suggetion - Problem Set 3 4.2 (a) Show the dicriminant condition (1) take the form x D Ð.. Ñ. D.. D. ln ln, a deired. We then replace the quantitie. 3ß D3 by their etimate to get the proper form for thi
Suggetion - Problem Set 3 4.2 (a) Show the dicriminant condition (1) take the form x D Ð.. Ñ. D.. D. ln ln, a deired. We then replace the quantitie. 3ß D3 by their etimate to get the proper form for thi
Here are proofs for some of the results about diagonalization that were presented without proof in class.
 Suppose E is an 8 8 matrix. In what follows, terms like eigenvectors, eigenvalues, and eigenspaces all refer to the matrix E. Here are proofs for some of the results about diagonalization that were presented
Suppose E is an 8 8 matrix. In what follows, terms like eigenvectors, eigenvalues, and eigenspaces all refer to the matrix E. Here are proofs for some of the results about diagonalization that were presented
Gene expression experiments. Infinite Dimensional Vector Spaces. 1. Motivation: Statistical machine learning and reproducing kernel Hilbert Spaces
 MA 751 Part 3 Gene expression experiments Infinite Dimensional Vector Spaces 1. Motivation: Statistical machine learning and reproducing kernel Hilbert Spaces Gene expression experiments Question: Gene
MA 751 Part 3 Gene expression experiments Infinite Dimensional Vector Spaces 1. Motivation: Statistical machine learning and reproducing kernel Hilbert Spaces Gene expression experiments Question: Gene
Equivalent Sets. It is intuitively clear that for finite sets E F iff Eand Fhave the same number of elementsþ
 Equivalent Sets Definition Let Eß F be sets. We say that E is equivalent to F iff there exists a bijection 0ÀEÄF. If Eis equivalent to F, we write E FÐor E For EµFor something similar: the notation varies
Equivalent Sets Definition Let Eß F be sets. We say that E is equivalent to F iff there exists a bijection 0ÀEÄF. If Eis equivalent to F, we write E FÐor E For EµFor something similar: the notation varies
Inner Product Spaces. Another notation sometimes used is X.?
 Inner Product Spaces X In 8 we have an inner product? @? @?@ ÞÞÞ? 8@ 8Þ Another notation sometimes used is X? ß@? @? @? @ ÞÞÞ? @ 8 8 The inner product in?@ ß in 8 has several essential properties ( see
Inner Product Spaces X In 8 we have an inner product? @? @?@ ÞÞÞ? 8@ 8Þ Another notation sometimes used is X? ß@? @? @? @ ÞÞÞ? @ 8 8 The inner product in?@ ß in 8 has several essential properties ( see
Implicit in the definition of orthogonal arrays is a projection propertyþ
 Projection properties Implicit in the definition of orthogonal arrays is a projection propertyþ factor screening effect ( factor) sparsity A design is said to be of projectivity : if in every subset of
Projection properties Implicit in the definition of orthogonal arrays is a projection propertyþ factor screening effect ( factor) sparsity A design is said to be of projectivity : if in every subset of
Engineering Mathematics (E35 317) Final Exam December 18, 2007
 Engineering Mathematics (E35 317) Final Exam December 18, 2007 This exam contains 18 multile-choice roblems orth to oints each, five short-anser roblems orth one oint each, and nine true-false roblems
Engineering Mathematics (E35 317) Final Exam December 18, 2007 This exam contains 18 multile-choice roblems orth to oints each, five short-anser roblems orth one oint each, and nine true-false roblems
Dr. Nestler - Math 2 - Ch 3: Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Dr. Nestler - Math 2 - Ch 3: Polynomial and Rational Functions 3.1 - Polynomial Functions We have studied linear functions and quadratic functions Defn. A monomial or power function is a function of the
Dr. Nestler - Math 2 - Ch 3: Polynomial and Rational Functions 3.1 - Polynomial Functions We have studied linear functions and quadratic functions Defn. A monomial or power function is a function of the
QUALIFYING EXAMINATION II IN MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS SATURDAY, MAY 9, Examiners: Drs. K. M. Ramachandran and G. S. Ladde
 QUALIFYING EXAMINATION II IN MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS SATURDAY, MAY 9, 2015 Examiners: Drs. K. M. Ramachandran and G. S. Ladde INSTRUCTIONS: a. The quality is more important than the quantity. b. Attempt
QUALIFYING EXAMINATION II IN MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS SATURDAY, MAY 9, 2015 Examiners: Drs. K. M. Ramachandran and G. S. Ladde INSTRUCTIONS: a. The quality is more important than the quantity. b. Attempt
Statistical machine learning and kernel methods. Primary references: John Shawe-Taylor and Nello Cristianini, Kernel Methods for Pattern Analysis
 Part 5 (MA 751) Statistical machine learning and kernel methods Primary references: John Shawe-Taylor and Nello Cristianini, Kernel Methods for Pattern Analysis Christopher Burges, A tutorial on support
Part 5 (MA 751) Statistical machine learning and kernel methods Primary references: John Shawe-Taylor and Nello Cristianini, Kernel Methods for Pattern Analysis Christopher Burges, A tutorial on support
TOTAL DIFFERENTIALS. In Section B-4, we observed that.c is a pretty good approximation for? C, which is the increment of
 TOTAL DIFFERENTIALS The differential was introduced in Section -4. Recall that the differential of a function œ0ðñis w. œ 0 ÐÑ.Þ Here. is the differential with respect to the independent variable and is
TOTAL DIFFERENTIALS The differential was introduced in Section -4. Recall that the differential of a function œ0ðñis w. œ 0 ÐÑ.Þ Here. is the differential with respect to the independent variable and is
Course Learning Objectives: Demonstrate an understanding of trigonometric functions and their applications.
 Right Triangle Trigonometry Video Lecture Section 8.1 Course Learning Objectives: Demonstrate an understanding of trigonometric functions and their applications. Weekly Learning Objectives: 1)Find the
Right Triangle Trigonometry Video Lecture Section 8.1 Course Learning Objectives: Demonstrate an understanding of trigonometric functions and their applications. Weekly Learning Objectives: 1)Find the
Example: A Markov Process
 Example: A Markov Process Divide the greater metro region into three parts: city such as St. Louis), suburbs to include such areas as Clayton, University City, Richmond Heights, Maplewood, Kirkwood,...)
Example: A Markov Process Divide the greater metro region into three parts: city such as St. Louis), suburbs to include such areas as Clayton, University City, Richmond Heights, Maplewood, Kirkwood,...)
LA PRISE DE CALAIS. çoys, çoys, har - dis. çoys, dis. tons, mantz, tons, Gas. c est. à ce. C est à ce. coup, c est à ce
 > ƒ? @ Z [ \ _ ' µ `. l 1 2 3 z Æ Ñ 6 = Ð l sl (~131 1606) rn % & +, l r s s, r 7 nr ss r r s s s, r s, r! " # $ s s ( ) r * s, / 0 s, r 4 r r 9;: < 10 r mnz, rz, r ns, 1 s ; j;k ns, q r s { } ~ l r mnz,
> ƒ? @ Z [ \ _ ' µ `. l 1 2 3 z Æ Ñ 6 = Ð l sl (~131 1606) rn % & +, l r s s, r 7 nr ss r r s s s, r s, r! " # $ s s ( ) r * s, / 0 s, r 4 r r 9;: < 10 r mnz, rz, r ns, 1 s ; j;k ns, q r s { } ~ l r mnz,
You may have a simple scientific calculator to assist with arithmetic, but no graphing calculators are allowed on this exam.
 Math 131 Exam 3 Solutions You may have a simple scientific calculator to assist ith arithmetic, but no graphing calculators are alloed on this exam. Part I consists of 14 multiple choice questions (orth
Math 131 Exam 3 Solutions You may have a simple scientific calculator to assist ith arithmetic, but no graphing calculators are alloed on this exam. Part I consists of 14 multiple choice questions (orth
Math 132, Spring 2003 Exam 2: Solutions
 Math 132, Spring 2003 Exam 2: Solutions No calculators with a CAS are allowed. e sure your calculator is set for radians, not degrees if you do any calculus computations with trig functions. Part I, Multiple
Math 132, Spring 2003 Exam 2: Solutions No calculators with a CAS are allowed. e sure your calculator is set for radians, not degrees if you do any calculus computations with trig functions. Part I, Multiple
Lesson 6.6 Radical Equations
 Lesson 6.6 Radical Equations Activity 1 Radical Equations 1. a. To solve a radical equation, we: (1) isolate the radical, then () square both sides. Be careful when squaring a binomial! For example, #
Lesson 6.6 Radical Equations Activity 1 Radical Equations 1. a. To solve a radical equation, we: (1) isolate the radical, then () square both sides. Be careful when squaring a binomial! For example, #
Notes on the Unique Extension Theorem. Recall that we were interested in defining a general measure of a size of a set on Ò!ß "Ó.
 1. More on measures: Notes on the Unique Extension Theorem Recall that we were interested in defining a general measure of a size of a set on Ò!ß "Ó. Defined this measure T. Defined TÐ ( +ß, ) Ñ œ, +Þ
1. More on measures: Notes on the Unique Extension Theorem Recall that we were interested in defining a general measure of a size of a set on Ò!ß "Ó. Defined this measure T. Defined TÐ ( +ß, ) Ñ œ, +Þ
Examples of non-orthogonal designs
 Examples of non-orthogonal designs Incomplete block designs > treatments,, blocks of size 5, 5 > The condition of proportional frequencies cannot be satisfied by the treatment and block factors. ¾ g Z
Examples of non-orthogonal designs Incomplete block designs > treatments,, blocks of size 5, 5 > The condition of proportional frequencies cannot be satisfied by the treatment and block factors. ¾ g Z
E.G., data mining, prediction. Function approximation problem: How >9 best estimate the function 0 from partial information (examples)
 Can Neural Network and Statistical Learning Theory be Formulated in terms of Continuous Complexity Theory? 1. Neural Networks and Statistical Learning Theory Many areas of mathematics, statistics, and
Can Neural Network and Statistical Learning Theory be Formulated in terms of Continuous Complexity Theory? 1. Neural Networks and Statistical Learning Theory Many areas of mathematics, statistics, and
SIMULATION - PROBLEM SET 1
 SIMULATION - PROBLEM SET 1 " if! Ÿ B Ÿ 1. The random variable X has probability density function 0ÐBÑ œ " $ if Ÿ B Ÿ.! otherwise Using the inverse transform method of simulation, find the random observation
SIMULATION - PROBLEM SET 1 " if! Ÿ B Ÿ 1. The random variable X has probability density function 0ÐBÑ œ " $ if Ÿ B Ÿ.! otherwise Using the inverse transform method of simulation, find the random observation
Math 131, Exam 2 Solutions, Fall 2010
 Math 131, Exam 2 Solutions, Fall 2010 Part I consists of 14 multiple choice questions (orth 5 points each) and 5 true/false questions (orth 1 point each), for a total of 75 points. Mark the correct anser
Math 131, Exam 2 Solutions, Fall 2010 Part I consists of 14 multiple choice questions (orth 5 points each) and 5 true/false questions (orth 1 point each), for a total of 75 points. Mark the correct anser
Systems of Equations 1. Systems of Linear Equations
 Lecture 1 Systems of Equations 1. Systems of Linear Equations [We will see examples of how linear equations arise here, and how they are solved:] Example 1: In a lab experiment, a researcher wants to provide
Lecture 1 Systems of Equations 1. Systems of Linear Equations [We will see examples of how linear equations arise here, and how they are solved:] Example 1: In a lab experiment, a researcher wants to provide
236 Chapter 4 Applications of Derivatives
 26 Chapter Applications of Derivatives Î$ &Î$ Î$ 5 Î$ 0 "Î$ 5( 2) $È 26. (a) g() œ ( 5) œ 5 Ê g () œ œ Ê critical points at œ 2 and œ 0 Ê g œ ± )(, increasing on ( _ß 2) and (!ß _), decreasing on ( 2 ß!)!
26 Chapter Applications of Derivatives Î$ &Î$ Î$ 5 Î$ 0 "Î$ 5( 2) $È 26. (a) g() œ ( 5) œ 5 Ê g () œ œ Ê critical points at œ 2 and œ 0 Ê g œ ± )(, increasing on ( _ß 2) and (!ß _), decreasing on ( 2 ß!)!
Ð"Ñ + Ð"Ñ, Ð"Ñ +, +, + +, +,,
 Handout #11 Confounding: Complete factorial experiments in incomplete blocks Blocking is one of the important principles in experimental design. In this handout we address the issue of designing complete
Handout #11 Confounding: Complete factorial experiments in incomplete blocks Blocking is one of the important principles in experimental design. In this handout we address the issue of designing complete
B-9= B.Bà B 68 B.Bß B/.Bß B=38 B.B >+8 ab b.bß ' 68aB b.bà
 8.1 Integration y Parts.@ a.? a Consider. a? a @ a œ? a @ a Þ....@ a..? a We can write this as? a œ a? a @ a@ a Þ... If we integrate oth sides, we otain.@ a a.?. œ a? a @ a..? a @ a. or...? a.@ œ? a @
8.1 Integration y Parts.@ a.? a Consider. a? a @ a œ? a @ a Þ....@ a..? a We can write this as? a œ a? a @ a@ a Þ... If we integrate oth sides, we otain.@ a a.?. œ a? a @ a..? a @ a. or...? a.@ œ? a @
T i t l e o f t h e w o r k : L a M a r e a Y o k o h a m a. A r t i s t : M a r i a n o P e n s o t t i ( P l a y w r i g h t, D i r e c t o r )
 v e r. E N G O u t l i n e T i t l e o f t h e w o r k : L a M a r e a Y o k o h a m a A r t i s t : M a r i a n o P e n s o t t i ( P l a y w r i g h t, D i r e c t o r ) C o n t e n t s : T h i s w o
v e r. E N G O u t l i n e T i t l e o f t h e w o r k : L a M a r e a Y o k o h a m a A r t i s t : M a r i a n o P e n s o t t i ( P l a y w r i g h t, D i r e c t o r ) C o n t e n t s : T h i s w o
Engineering Mathematics (E35 317) Exam 3 November 7, 2007
 Engineering Mathematics (E35 317) Exam 3 November 7, 2007 This exam contains four multile-choice roblems worth two oints each, twelve true-false roblems worth one oint each, and four free-resonse roblems
Engineering Mathematics (E35 317) Exam 3 November 7, 2007 This exam contains four multile-choice roblems worth two oints each, twelve true-false roblems worth one oint each, and four free-resonse roblems
Section 1.3 Functions and Their Graphs 19
 23. 0 1 2 24. 0 1 2 y 0 1 0 y 1 0 0 Section 1.3 Functions and Their Graphs 19 3, Ÿ 1, 0 25. y œ 26. y œ œ 2, 1 œ, 0 Ÿ " 27. (a) Line through a!ß! band a"ß " b: y œ Line through a"ß " band aß! b: y œ 2,
23. 0 1 2 24. 0 1 2 y 0 1 0 y 1 0 0 Section 1.3 Functions and Their Graphs 19 3, Ÿ 1, 0 25. y œ 26. y œ œ 2, 1 œ, 0 Ÿ " 27. (a) Line through a!ß! band a"ß " b: y œ Line through a"ß " band aß! b: y œ 2,
Introduction to Diagonalization
 Introduction to Diagonalization For a square matrix E, a process called diagonalization can sometimes give us more insight into how the transformation B ÈE B works. The insight has a strong geometric flavor,
Introduction to Diagonalization For a square matrix E, a process called diagonalization can sometimes give us more insight into how the transformation B ÈE B works. The insight has a strong geometric flavor,
Framework for functional tree simulation applied to 'golden delicious' apple trees
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Open Access Theses Theses and Dissertations Spring 2015 Framework for functional tree simulation applied to 'golden delicious' apple trees Marek Fiser Purdue University
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Open Access Theses Theses and Dissertations Spring 2015 Framework for functional tree simulation applied to 'golden delicious' apple trees Marek Fiser Purdue University
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS QUALIFYING EXAMINATION II IN MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS SATURDAY, SEPTEMBER 24, 2016
 DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS QUALIFYING EXAMINATION II IN MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS SATURDAY, SEPTEMBER 24, 2016 Examiners: Drs. K. M. Ramachandran and G. S. Ladde INSTRUCTIONS: a. The quality
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS QUALIFYING EXAMINATION II IN MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS SATURDAY, SEPTEMBER 24, 2016 Examiners: Drs. K. M. Ramachandran and G. S. Ladde INSTRUCTIONS: a. The quality
ACT455H1S - TEST 2 - MARCH 25, 2008
 ACT455H1S - TEST 2 - MARCH 25, 2008 Write name and student number on each page. Write your solution for each question in the space provided. For the multiple decrement questions, it is always assumed that
ACT455H1S - TEST 2 - MARCH 25, 2008 Write name and student number on each page. Write your solution for each question in the space provided. For the multiple decrement questions, it is always assumed that
ETIKA V PROFESII PSYCHOLÓGA
 P r a ž s k á v y s o k á š k o l a p s y c h o s o c i á l n í c h s t u d i í ETIKA V PROFESII PSYCHOLÓGA N a t á l i a S l o b o d n í k o v á v e d ú c i p r á c e : P h D r. M a r t i n S t r o u
P r a ž s k á v y s o k á š k o l a p s y c h o s o c i á l n í c h s t u d i í ETIKA V PROFESII PSYCHOLÓGA N a t á l i a S l o b o d n í k o v á v e d ú c i p r á c e : P h D r. M a r t i n S t r o u
Multiple Choice Questions
 Multiple Choice Questions There is no penalty for guessing. Three points per question, so a total of 48 points for this section.. What is the complete relationship between homogeneous linear systems of
Multiple Choice Questions There is no penalty for guessing. Three points per question, so a total of 48 points for this section.. What is the complete relationship between homogeneous linear systems of
STAT 2122 Homework # 3 Solutions Fall 2018 Instr. Sonin
 STAT 2122 Homeork Solutions Fall 2018 Instr. Sonin Due Friday, October 5 NAME (25 + 5 points) Sho all ork on problems! (4) 1. In the... Lotto, you may pick six different numbers from the set Ö"ß ß $ß ÞÞÞß
STAT 2122 Homeork Solutions Fall 2018 Instr. Sonin Due Friday, October 5 NAME (25 + 5 points) Sho all ork on problems! (4) 1. In the... Lotto, you may pick six different numbers from the set Ö"ß ß $ß ÞÞÞß
Constructive Decision Theory
 Constructive Decision Theory Joe Halpern Cornell University Joint work with Larry Blume and David Easley Economics Cornell Constructive Decision Theory p. 1/2 Savage s Approach Savage s approach to decision
Constructive Decision Theory Joe Halpern Cornell University Joint work with Larry Blume and David Easley Economics Cornell Constructive Decision Theory p. 1/2 Savage s Approach Savage s approach to decision
MAP METHODS FOR MACHINE LEARNING. Mark A. Kon, Boston University Leszek Plaskota, Warsaw University, Warsaw Andrzej Przybyszewski, McGill University
 MAP METHODS FOR MACHINE LEARNING Mark A. Kon, Boston University Leszek Plaskota, Warsaw University, Warsaw Andrzej Przybyszewski, McGill University Example: Control System 1. Paradigm: Machine learning
MAP METHODS FOR MACHINE LEARNING Mark A. Kon, Boston University Leszek Plaskota, Warsaw University, Warsaw Andrzej Przybyszewski, McGill University Example: Control System 1. Paradigm: Machine learning
 ! " # $! % & '! , ) ( + - (. ) ( ) * + / 0 1 2 3 0 / 4 5 / 6 0 ; 8 7 < = 7 > 8 7 8 9 : Œ Š ž P P h ˆ Š ˆ Œ ˆ Š ˆ Ž Ž Ý Ü Ý Ü Ý Ž Ý ê ç è ± ¹ ¼ ¹ ä ± ¹ w ç ¹ è ¼ è Œ ¹ ± ¹ è ¹ è ä ç w ¹ ã ¼ ¹ ä ¹ ¼ ¹ ±
! " # $! % & '! , ) ( + - (. ) ( ) * + / 0 1 2 3 0 / 4 5 / 6 0 ; 8 7 < = 7 > 8 7 8 9 : Œ Š ž P P h ˆ Š ˆ Œ ˆ Š ˆ Ž Ž Ý Ü Ý Ü Ý Ž Ý ê ç è ± ¹ ¼ ¹ ä ± ¹ w ç ¹ è ¼ è Œ ¹ ± ¹ è ¹ è ä ç w ¹ ã ¼ ¹ ä ¹ ¼ ¹ ±
Infinite Dimensional Vector Spaces. 1. Motivation: Statistical machine learning and reproducing kernel Hilbert Spaces
 MA 751 Part 3 Infinite Dimensional Vector Spaces 1. Motivation: Statistical machine learning and reproducing kernel Hilbert Spaces Microarray experiment: Question: Gene expression - when is the DNA in
MA 751 Part 3 Infinite Dimensional Vector Spaces 1. Motivation: Statistical machine learning and reproducing kernel Hilbert Spaces Microarray experiment: Question: Gene expression - when is the DNA in
Review of Elementary Probability Theory Math 495, Spring 2011
 Revie of Elementary Probability Theory Math 495, Spring 2011 0.1 Probability spaces 0.1.1 Definition. A probability space is a triple ( HT,,P) here ( 3Ñ H is a non-empty setà Ð33Ñ T is a collection of
Revie of Elementary Probability Theory Math 495, Spring 2011 0.1 Probability spaces 0.1.1 Definition. A probability space is a triple ( HT,,P) here ( 3Ñ H is a non-empty setà Ð33Ñ T is a collection of
Redoing the Foundations of Decision Theory
 Redoing the Foundations of Decision Theory Joe Halpern Cornell University Joint work with Larry Blume and David Easley Economics Cornell Redoing the Foundations of Decision Theory p. 1/21 Decision Making:
Redoing the Foundations of Decision Theory Joe Halpern Cornell University Joint work with Larry Blume and David Easley Economics Cornell Redoing the Foundations of Decision Theory p. 1/21 Decision Making:
1. To be a grandfather. Objects of our consideration are people; a person a is associated with a person b if a is a grandfather of b.
 20 [161016-1020 ] 3.3 Binary relations In mathematics, as in everyday situations, we often speak about a relationship between objects, which means an idea of two objects being related or associated one
20 [161016-1020 ] 3.3 Binary relations In mathematics, as in everyday situations, we often speak about a relationship between objects, which means an idea of two objects being related or associated one
Juan Juan Salon. EH National Bank. Sandwich Shop Nail Design. OSKA Beverly. Chase Bank. Marina Rinaldi. Orogold. Mariposa.
 ( ) X é X é Q Ó / 8 ( ) Q / ( ) ( ) : ( ) : 44-3-8999 433 4 z 78-19 941, #115 Z 385-194 77-51 76-51 74-7777, 75-5 47-55 74-8141 74-5115 78-3344 73-3 14 81-4 86-784 78-33 551-888 j 48-4 61-35 z/ zz / 138
( ) X é X é Q Ó / 8 ( ) Q / ( ) ( ) : ( ) : 44-3-8999 433 4 z 78-19 941, #115 Z 385-194 77-51 76-51 74-7777, 75-5 47-55 74-8141 74-5115 78-3344 73-3 14 81-4 86-784 78-33 551-888 j 48-4 61-35 z/ zz / 138
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION Preliminaries. Perturbation theory is the study of the effects of small disturbances in the mathematical model of a physical system. The model could be expressed as an algebraic
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION Preliminaries. Perturbation theory is the study of the effects of small disturbances in the mathematical model of a physical system. The model could be expressed as an algebraic
Vectors. Teaching Learning Point. Ç, where OP. l m n
 Vectors 9 Teaching Learning Point l A quantity that has magnitude as well as direction is called is called a vector. l A directed line segment represents a vector and is denoted y AB Å or a Æ. l Position
Vectors 9 Teaching Learning Point l A quantity that has magnitude as well as direction is called is called a vector. l A directed line segment represents a vector and is denoted y AB Å or a Æ. l Position
The Spotted Owls 5 " 5. = 5 " œ!þ")45 Ð'!% leave nest, 30% of those succeed) + 5 " œ!þ("= 5!Þ*%+ 5 ( adults live about 20 yrs)
 The Spotted Owls Be sure to read the example at the introduction to Chapter in the textbook. It gives more general background information for this example. The example leads to a dynamical system which
The Spotted Owls Be sure to read the example at the introduction to Chapter in the textbook. It gives more general background information for this example. The example leads to a dynamical system which
OC330C. Wiring Diagram. Recommended PKH- P35 / P50 GALH PKA- RP35 / RP50. Remarks (Drawing No.) No. Parts No. Parts Name Specifications
 G G " # $ % & " ' ( ) $ * " # $ % & " ( + ) $ * " # C % " ' ( ) $ * C " # C % " ( + ) $ * C D ; E @ F @ 9 = H I J ; @ = : @ A > B ; : K 9 L 9 M N O D K P D N O Q P D R S > T ; U V > = : W X Y J > E ; Z
G G " # $ % & " ' ( ) $ * " # $ % & " ( + ) $ * " # C % " ' ( ) $ * C " # C % " ( + ) $ * C D ; E @ F @ 9 = H I J ; @ = : @ A > B ; : K 9 L 9 M N O D K P D N O Q P D R S > T ; U V > = : W X Y J > E ; Z
Théorie Analytique des Probabilités
 Théorie Analytique des Probabilités Pierre Simon Laplace Book II 5 9. pp. 203 228 5. An urn being supposed to contain the number B of balls, e dra from it a part or the totality, and e ask the probability
Théorie Analytique des Probabilités Pierre Simon Laplace Book II 5 9. pp. 203 228 5. An urn being supposed to contain the number B of balls, e dra from it a part or the totality, and e ask the probability
Outline. 1. The Screening Philosophy 2. Robust Products/Processes 3. A Statistical Screening Procedure 4. Some Caveats 5.
 Screening to Identify Robust Products Based on Fractional Factorial Experiments Thomas J. Santner Ohio State University Guohua Pan Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp Outline 1. The Screening Philosophy 2. Robust
Screening to Identify Robust Products Based on Fractional Factorial Experiments Thomas J. Santner Ohio State University Guohua Pan Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp Outline 1. The Screening Philosophy 2. Robust
u x + u y = x u . u(x, 0) = e x2 The characteristics satisfy dx dt = 1, dy dt = 1
 Õ 83-25 Þ ÛÐ Þ Ð ÚÔÜØ Þ ÝÒ Þ Ô ÜÞØ ¹ 3 Ñ Ð ÜÞ u x + u y = x u u(x, 0) = e x2 ÝÒ Þ Ü ÞØ º½ dt =, dt = x = t + c, y = t + c 2 We can choose c to be zero without loss of generality Note that each characteristic
Õ 83-25 Þ ÛÐ Þ Ð ÚÔÜØ Þ ÝÒ Þ Ô ÜÞØ ¹ 3 Ñ Ð ÜÞ u x + u y = x u u(x, 0) = e x2 ÝÒ Þ Ü ÞØ º½ dt =, dt = x = t + c, y = t + c 2 We can choose c to be zero without loss of generality Note that each characteristic
MA 180 Lecture. Chapter 0. College Algebra and Calculus by Larson/Hodgkins. Fundamental Concepts of Algebra
 0.) Real Numbers: Order and Absolute Value Definitions: Set: is a collection of objections in mathematics Real Numbers: set of numbers used in arithmetic MA 80 Lecture Chapter 0 College Algebra and Calculus
0.) Real Numbers: Order and Absolute Value Definitions: Set: is a collection of objections in mathematics Real Numbers: set of numbers used in arithmetic MA 80 Lecture Chapter 0 College Algebra and Calculus
From Handout #1, the randomization model for a design with a simple block structure can be written as
 Hout 4 Strata Null ANOVA From Hout 1 the romization model for a design with a simple block structure can be written as C œ.1 \ X α % (4.1) w where α œðα á α > Ñ E ÐÑœ % 0 Z œcov ÐÑ % with cov( % 3 % 4
Hout 4 Strata Null ANOVA From Hout 1 the romization model for a design with a simple block structure can be written as C œ.1 \ X α % (4.1) w where α œðα á α > Ñ E ÐÑœ % 0 Z œcov ÐÑ % with cov( % 3 % 4
Stat 643 Problems. a) Show that V is a sub 5-algebra of T. b) Let \ be an integrable random variable. Find EÐ\lVÑÞ
 Stat 643 Problems 1. Let ( HT, ) be a measurable space. Suppose that., T and Uare 5-finite positive measures on this space with T Uand U...T.T.U a) Show that T. and œ a.s......u.....u.u Š.. b) Show that
Stat 643 Problems 1. Let ( HT, ) be a measurable space. Suppose that., T and Uare 5-finite positive measures on this space with T Uand U...T.T.U a) Show that T. and œ a.s......u.....u.u Š.. b) Show that
Appendix 4.1 Alternate Solution to the Infinite Square Well with Symmetric Boundary Conditions. V(x) I II III +L/2
 Appendix 4.1 Alternate Solution to the Infinite Square Well with Symmetric Boundary Conditions V(x) I II III -L/2 +L/2 x In this problem, a particle of mass 7 confined by a potential energy which has a
Appendix 4.1 Alternate Solution to the Infinite Square Well with Symmetric Boundary Conditions V(x) I II III -L/2 +L/2 x In this problem, a particle of mass 7 confined by a potential energy which has a
Math 308 Midterm Answers and Comments July 18, Part A. Short answer questions
 Math 308 Midterm Answers and Comments July 18, 2011 Part A. Short answer questions (1) Compute the determinant of the matrix a 3 3 1 1 2. 1 a 3 The determinant is 2a 2 12. Comments: Everyone seemed to
Math 308 Midterm Answers and Comments July 18, 2011 Part A. Short answer questions (1) Compute the determinant of the matrix a 3 3 1 1 2. 1 a 3 The determinant is 2a 2 12. Comments: Everyone seemed to
Math 1M03 (Version 1) Sample Exam
 Math 1M03 (Version 1) Sample Exam Name: (Last Name) (First Name) Student Number: Day Class Duration: 3 Hours Maximum Mark: 40 McMaster University Sample Final Examination This examination paper consists
Math 1M03 (Version 1) Sample Exam Name: (Last Name) (First Name) Student Number: Day Class Duration: 3 Hours Maximum Mark: 40 McMaster University Sample Final Examination This examination paper consists
Things You Should Know (But Likely Forgot)
 Things You Should Know (ut Likely Forgot), page 1 of ( Things You Should Know (ut Likely Forgot) Trigonometric identities: cos ) sin ) tan ) sec ) cosa ) cos ) sin ) cos ) sin ) sina ) cos ) sin ) ß cos
Things You Should Know (ut Likely Forgot), page 1 of ( Things You Should Know (ut Likely Forgot) Trigonometric identities: cos ) sin ) tan ) sec ) cosa ) cos ) sin ) cos ) sin ) sina ) cos ) sin ) ß cos
SIMULTANEOUS CONFIDENCE BANDS FOR THE PTH PERCENTILE AND THE MEAN LIFETIME IN EXPONENTIAL AND WEIBULL REGRESSION MODELS. Ping Sa and S.J.
 SIMULTANEOUS CONFIDENCE BANDS FOR THE PTH PERCENTILE AND THE MEAN LIFETIME IN EXPONENTIAL AND WEIBULL REGRESSION MODELS " # Ping Sa and S.J. Lee " Dept. of Mathematics and Statistics, U. of North Florida,
SIMULTANEOUS CONFIDENCE BANDS FOR THE PTH PERCENTILE AND THE MEAN LIFETIME IN EXPONENTIAL AND WEIBULL REGRESSION MODELS " # Ping Sa and S.J. Lee " Dept. of Mathematics and Statistics, U. of North Florida,
Engineering Mathematics (E35 317) Final Exam December 15, 2006
 Engineering Mathematics (E35 317) Final Exam December 15, 2006 This exam contains six free-resonse roblems orth 36 oints altogether, eight short-anser roblems orth one oint each, seven multile-choice roblems
Engineering Mathematics (E35 317) Final Exam December 15, 2006 This exam contains six free-resonse roblems orth 36 oints altogether, eight short-anser roblems orth one oint each, seven multile-choice roblems
The Leontief Open Economy Production Model
 The Leontief Open Economy Production Model We will look at the idea for Leontief's model of an open economy a term which we will explain below. It starts by looking very similar to an example of a closed
The Leontief Open Economy Production Model We will look at the idea for Leontief's model of an open economy a term which we will explain below. It starts by looking very similar to an example of a closed
Dr. Nestler - Math 11 - Some Definitions and Theorems from Calculus 1 and 2. lim
 Dr. Nestler - Math 11 - Some Definitions and Theorems from Calculus 1 and 2 Definition. A function 0 is continuous at a number + if lim 0ÐBÑ œ 0Ð+Ñ. Extreme Value Theorem. A continuous function on a closed
Dr. Nestler - Math 11 - Some Definitions and Theorems from Calculus 1 and 2 Definition. A function 0 is continuous at a number + if lim 0ÐBÑ œ 0Ð+Ñ. Extreme Value Theorem. A continuous function on a closed
OPERATIONAL BEHAVIOR OF THE MAP/G/1 QUEUE UNDER N-POLICY WITH A SINGLE VACATION AND SET-UP 1
 Journal of Applied Mathematics and Stochastic Analysis, 15:2 (2002), 15110 OPRATIONAL BHAVIOR OF TH MAP/G/1 QUU UNDR NPOLICY WITH A SINGL VACATION AND STUP 1 HO WOO L Sung Kyun Kwan University Department
Journal of Applied Mathematics and Stochastic Analysis, 15:2 (2002), 15110 OPRATIONAL BHAVIOR OF TH MAP/G/1 QUU UNDR NPOLICY WITH A SINGL VACATION AND STUP 1 HO WOO L Sung Kyun Kwan University Department
Examination paper for TFY4240 Electromagnetic theory
 Department of Physics Examination paper for TFY4240 Electromagnetic theory Academic contact during examination: Associate Professor John Ove Fjærestad Phone: 97 94 00 36 Examination date: 16 December 2015
Department of Physics Examination paper for TFY4240 Electromagnetic theory Academic contact during examination: Associate Professor John Ove Fjærestad Phone: 97 94 00 36 Examination date: 16 December 2015
An Example file... log.txt
 # ' ' Start of fie & %$ " 1 - : 5? ;., B - ( * * B - ( * * F I / 0. )- +, * ( ) 8 8 7 /. 6 )- +, 5 5 3 2( 7 7 +, 6 6 9( 3 5( ) 7-0 +, => - +< ( ) )- +, 7 / +, 5 9 (. 6 )- 0 * D>. C )- +, (A :, C 0 )- +,
# ' ' Start of fie & %$ " 1 - : 5? ;., B - ( * * B - ( * * F I / 0. )- +, * ( ) 8 8 7 /. 6 )- +, 5 5 3 2( 7 7 +, 6 6 9( 3 5( ) 7-0 +, => - +< ( ) )- +, 7 / +, 5 9 (. 6 )- 0 * D>. C )- +, (A :, C 0 )- +,
Elementary Properties of the Integers
 Elementary Properties of the Integers 1 1. Basis Representation Theorem (Thm 1-3) 2. Euclid s Division Lemma (Thm 2-1) 3. Greatest Common Divisor 4. Properties of Prime Numbers 5. Fundamental Theorem of
Elementary Properties of the Integers 1 1. Basis Representation Theorem (Thm 1-3) 2. Euclid s Division Lemma (Thm 2-1) 3. Greatest Common Divisor 4. Properties of Prime Numbers 5. Fundamental Theorem of
The Fourier series are applicable to periodic signals. They were discovered by the
 3.1 Fourier Series The Fourier series are applicable to periodic signals. They were discovered by the famous French mathematician Joseph Fourier in 1807. By using the Fourier series, a periodic signal
3.1 Fourier Series The Fourier series are applicable to periodic signals. They were discovered by the famous French mathematician Joseph Fourier in 1807. By using the Fourier series, a periodic signal
CHAPTER 1. Relations. 1. Relations and Their Properties. Discussion
 CHAPTER 1 Relations 1. Relations and Their Properties 1.1. Definition of a Relation. Definition 1.1.1. A binary relation from a set A to a set B is a subset R A B. If (a, b) R we say a is Related to b
CHAPTER 1 Relations 1. Relations and Their Properties 1.1. Definition of a Relation. Definition 1.1.1. A binary relation from a set A to a set B is a subset R A B. If (a, b) R we say a is Related to b
The Leontief Open Economy Production Model
 The Leontief Open Economy Production Model We will look at the idea for Leontief's model of an open economy a term which we will explain below. It starts by looking very similar to an example of a closed
The Leontief Open Economy Production Model We will look at the idea for Leontief's model of an open economy a term which we will explain below. It starts by looking very similar to an example of a closed
Chapter 10. Definition of the Derivative Velocity and Tangents
 Chapter 10 Definition of the Derivative 10.1 Velocity and Tangents 10.1 Notation. If E 1 (x, y) and E 2 (x, y) denote equations or inequalities in x and y, we will use the notation {E 1 (x, y)} = {(x,
Chapter 10 Definition of the Derivative 10.1 Velocity and Tangents 10.1 Notation. If E 1 (x, y) and E 2 (x, y) denote equations or inequalities in x and y, we will use the notation {E 1 (x, y)} = {(x,
Today. Binary relations establish a relationship between elements of two sets
 Today Relations Binary relations and properties Relationship to functions n-ary relations Definitions Binary relations establish a relationship between elements of two sets Definition: Let A and B be two
Today Relations Binary relations and properties Relationship to functions n-ary relations Definitions Binary relations establish a relationship between elements of two sets Definition: Let A and B be two
Topics in Logic, Set Theory and Computability
 Topics in Logic, Set Theory and Computability Homework Set #3 Due Friday 4/6 at 3pm (by email or in person at 08-3234) Exercises from Handouts 7-C-2 7-E-6 7-E-7(a) 8-A-4 8-A-9(a) 8-B-2 8-C-2(a,b,c) 8-D-4(a)
Topics in Logic, Set Theory and Computability Homework Set #3 Due Friday 4/6 at 3pm (by email or in person at 08-3234) Exercises from Handouts 7-C-2 7-E-6 7-E-7(a) 8-A-4 8-A-9(a) 8-B-2 8-C-2(a,b,c) 8-D-4(a)
