Numerical Solutions in 5D Standing Wave Braneworld
|
|
|
- Thomasina Rodgers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Numerical Solutions in 5D Standing Wave Braneworld Merab Gogberashvili 1,2, Otari Sakhelashvili 1, and Giorgi Tukhashvili 1 arxiv: v1 [hep-th] 22 Apr I. Javakhishvili Tbilisi State University, 3 Chavchavadze Avenue, Tbilisi 0179, Georgia 2 E. Andronikashvili Institute of Physics, 6 Tamarashvili Street, Tbilisi 0177, Georgia August 27, 2018 Abstract Within the 5D standing wave braneworld model numerical solutions of the equations for matter fields with various spins are found. It is shown that corresponding action integrals are factorizable and convergent over the extra coordinate, i.e. 4D fields are localized on the brane. We find that only left massless fermions are localized on the brane, while the right fermions are localized in the bulk. We demonstrate also quantization of Kaluza-Klein excited modes in our model. PACS numbers: h, w, d Keywords: Brane; Standing waves; Zero modes 1 Introduction Braneworld models with large extra dimensions [1 4] have attracted wide attention owing to their success in solving some open questions in modern physics [5 8]. To realize the braneworld idea one should find a mechanism of localization, however, there are some difficulties in this matter within standard brane approaches [9,10]. It is especially economical to consider models with a pure gravitational localization mechanism, since gravity has universal couplings with all matter fields. In this paper we consider one such scenario within the standing waves braneworld [11,12] and explicitly show existence of the universal gravitational trapping of all kinds of matter fields on the brane. Main differences of the model with the most brane scenarios are that our metric ansatz is time-dependent and contains increasing warp factor. gogber@gmail.com otosaxel@gmail.com gtukhashvili10@gmail.com 1
2 The standing waves braneworld is formed by the background solution [11,12]: ds 2 = e 2a r dt 2 e u dx 2 e u dy 2 e 2u dz 2) dr 2, 1) of the coupled Einstein and massless ghost scalar field equations. In 1) r denotes the extra space-like coordinate, a > 0 is a curvature scalar we choice increasing warp factor), the determinant, g = e 4a r, 2) is u-independent and the oscillatory function ut,r) has the form: ut,r) = sinωt)zr), Zr) = Ce 2a r Y 2 ω a e a r ). 3) Here ω denotes the oscillation frequency, C is an integration constant and Y 2 r) is the secondorder Bessel function of the second kind. The solution 1) describes the brane located at the node of the standing bulk wave 3). In this paper we consider the case with one node, i.e. the function Y 2 r) in 3) has a single zero at the position of the brane, r = 0. This is accomplished by the assumption: ω ) a In the equations of the matter fields, the oscillatory function 3) enters via exponentials. We suppose that the frequency ω of standing waves is much larger than the frequencies associated with the energies of particles on the brane and in these equations we can perform the time averaging of oscillating exponents. Non-vanishing averages are expressed by the formula [13 15]: e u = I 0 Z), 5) where I 0 r) is the modified Bessel function. The brane at the node of the standing wave the point where Zr) and ut, r) vanish) can be considered as a 4D island, where the matter particles are assumed to be bound. Indeed the system of 5D geodesic equations of motion for a classical particle or a photon) reduces to [13]: 1 2 e 2a r ) 2 dr +a1 V 2 ) r = ǫ, 6) dt where V is the velocity along the brane and the constant ǫ corresponds to the energy of the particle per unit mass for massive particles 0 < ǫ = E/m < 1 and for photons ǫ = 1). From 6) it is clear that the motion towards the extra dimension r is possible when ǫ a1 V 2 ) r 0. 7) The term a1 V 2 ) r plays the role of the trapping gravitational potential and there exists maximal distance in the bulk r max ǫ/a. In the standard brane approach with decreasing warp factor a < 0) localization was achieved due to the fact that the extra space actually is 2
3 finite [3,4]. In our case, the increasing of the brane warp factor, e 2a r, creates the potential well that confines particles. Let us now consider the localization problem of quantum fields with various spin using the brane solution 1) [13 16]. To have localized fields on a brane coupling constants appearing after integration of their Lagrangians over the extra coordinate, r, must be non-vanishing and finite. Using numerical solutions we shall demonstrate existence of normalizable zero modes of various fields on the brane within the model. 2 Localization of bosons In this section, using numerical solutions, it is shown localization of massless modes of the spin-0, spin-1 and spin-2 particles on the brane. At first let us consider 5D massless scalar field. We assume that for the case ω E E is the typical energy of scalar particles on the brane) variables can be separated [13 15], Φ x A) = φx ν )ςr), 8) Capital Latin letters numerate 5D coordinates, while Greek ones are used for 4D indices. Then the action integral for scalar fields can be split in two parts: S Φ = 1 2 d 5 x g g MN M Φ N Φ = 1 2 [ d 4 x α φ α φ dre 2a r ς 2 φ 2 dre 4a r ς 2 ], 9) where prime denotes the derivative with respect to extra coordinate r. We are looking for zero mode solution on the brane, φ e ipνxν, and assume that energy-momentum along the brane, p ν, obeys the dispersion relation: E 2 p 2 x p 2 y p 2 z = 0. 10) Than the 5D Klein-Gordon equation after time averaging reduces to [13 15]: e 4a r ς ) e 2a r P 2 r)ς = 0, 11) where P 2 r) = e u 1 ) p 2 x +p2 y) + e 2u 1 ) p 2 z. 12) Close to the brane the function P 2 r), which describes oscillatory properties of standing waves, and the extra dimension part of wave function ςr), behave as: P 2 r) r 2, r 0 So for the equation 11) we use the boundary conditions: ςr) r 0 e 4a r. 13) ς0) = 1, ς 0) = 4a. 14) 3
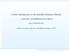
4 r) Figure 1: Scalar zero mode s profile in the bulk. Figure 1 shows the numerical solution of the equation 11) for these boundary conditions for the following values of the parameters: a = 1, ω = 3.38 a, p = 0.01 a. 15) We see that ςr), which governs of probability of scalar particles to reach the bulk, falls off from the brane to zero. The integrals over r in the action 9) are convergent if integrand functions decrease stronger than 1/r. Figure 2 displays the products of r on these integrand functions. We see that they decrease, i.e. the integrals over r in the action 9) are convergent, hence 4D scalar fields are localized on the brane. Recall that the action of scalar fields 9) due to the determinant 2) contains increasing exponential factor a > 0). This is the reason why in the original brane models [3, 4] the scalar field zero modes with the constant extra dimension parts can be localized on the brane only in the case of decreasing warp factor i.e. a < 0). In our model the extra part of wave function 13) is not constant, moreover, from Figure 1 it is clear that it strongly decreases and according to Figure 2 the integrals over r in the action 9) are convergent. It is known that the transverse traceless graviton modes obey the equations similar to the massless scalar fields in a curved background. Accordingly, the condition of localization of spin-2 graviton field is equivalent to that of scalar field considered above [13,14]. In the case of 5D Abelian vector fields the generalization to the case of non-abelian gauge fields is straightforward) we are looking for the solution of field equations in the form [13,14,16]: A α x A ) = e 2a r g αβ A β x ν )vr), A r x A ) = 0. 16) Than the 5D action of vector fields can be written as: S A = 1 d 5 x g g MN g PR F MP F NR = 4 4
5 r r e 2 a r 2 r r e 4 a r Figure 2: Convergence of integrand functions in S Φ 9). = 1 4 d 4 x [F αβ F αβ drv 2 2A α A α dre 2a r v 2 ]. 17) We require the existence of 4D vector zero mode on the brane, A µ x ν ) ε µ e ipνxν, 18) where p ν obey dispersion relation 10). Then 5D Maxwell equations after time averaging yields the single equation for vr): e 2a r v ) P 2 r)v = 0, 19) where P 2 r) is done by 12). Close to the brane, vr) r 0 e 2a r, and we set the boundary conditions: v0) = 1, v 0) = 2a. 20) From Figure 3 we see that the solution of the equation 19) for these boundary conditions, or the probability of photon to leave the brane, falls off in the bulk down to zero. As for the case of scalar field the integrals over r in the vector functions action 17) are convergent if integrand functions decrease stronger than 1/r. From the Figure 4 we see that the products of r with integrand functions decrease, i.e. the integral over r in 17) is convergent and 4D photon is localized on the brane. In 5D brane models the implementation of pure gravitational trapping mechanism of vector field particles remains the most problematic [9,10]. The reason is that in the vector action 17) the extra dimension parts of the determinant 2) and two metric tensors with upper indices cancel each other. Because of this in the original brane models the vector field zero modes with the constant extra dimension part) cannot be localized on the brane for any sign of a. In our model the extra dimension part of vector field vr) is rapidly decreasing function Fig. 3) and the integral over r in 17) is convergent. 5
6 Υr) Figure 3: Vector zero mode s profile in the bulk. 3 Localization of fermions Now we investigate the localization problem for massless fermions [13,14]. For Minkowskian 4 4 gamma matrices we use the Weyl basis, ) ) 0 I 0 σ γ t =, γ I 0 i i I 0 = σ i, γ 0 5 = iγ t γ x γ y γ z = 0 I ), 21) and 5D gamma matrices Υ A = h Ā A ΥĀ, where h Ā A = e a r,e a r u/2,e a r u/2,e a r +u,1). The inverse fünfbein for the metric 1), we choice as: Υ ν = h ν µ γµ, Υ r = iγ 5. 22) Non-vanishing components of the spin-connection in the background 1), which enter covariant derivatives defined as: after time averaging are given by: D A = A Ω B C A Υ BΥ C, 23) Ω ν r µ = a sgnr) h ν µ. 24) For the wavefunction of the bulk fermion field we use the chiral decomposition: Ψx ν,r) = ψ L x ν )λr)+ψ R x ν )ρr), 25) where λr) and ρr) are the extra dimension factors of the left and right fermion wavefunctions respectively. 6
7 Υ 2 r r Υ 2 r r e 2 a r Figure 4: Convergence of integrand functions in the vector field action 17). Then the 5D Dirac action for massless fermions can be written as: S Ψ = d 5 x g ΨiΥ M D M Ψ+H.c. ) = = d 4 x {ψ L iγ µ µ ψ L dre 3a r λ 2 +ψ R iγ µ µ ψ R dre 3a r ρ ) } +ψ R ψ L dre 4a r ρ[λ +2a sgnr)λ] ψ L ψ R dre 4a r λ[ρ +2a sgnr)ρ]. We assume that 4D left and right Dirac spinors γ 5 ψ R/L = ±ψ R/L ) are solutions of the free 4D massless Dirac equations: ) R ψ R x ν ) = e ipνxν, 0 ) 0 ψ L x ν ) = e ipνxν, 27) L where p ν satisfy the dispersion relation 10) and the constant 2-spinors L and R obey: pt +σ i p i ) L = pt σ i p i ) R = 0. 28) Derived from 26) 5D Dirac equation, after time averaging, takes the form: ie a r [ γ t t + e u/2 γ x x +γ y y )+ e u γ z z ] Ψ γ 5 [2a sgnr)+ r ]Ψ = 0. 29) Using the expressions 27) and 28) it can be rewritten as the system: e a r [2a sgnr)+ r ] σ i ) ) P i r) ρr)r σ i P i r) e a r = 0. 30) [2a sgnr)+ r ] λr)l 7
8 Here we have introduced the functions P i r): P x r) = e u/2 1 ) p x = [I 0 Z/2) 1]p x, P y r) = e u/2 1 ) p y = [I 0 Z/2) 1]p y, P z r) = e u 1)p z = [I 0 Z) 1]p z, 31) where Zr) is defined in 3) Λr) Ρr) Figure 5: Profiles of the left and right fermion wavefunctions in the bulk. To find boundary conditions for the system 30) note that from the last two terms of 26) we see that the action is even under the Z 2 orbifold symmetry if λr) is an even function of r and ρr) is odd or vice versa) with respect to the transformation r r. We require, λ k r) = λ k r), ρ k r) = ρ k r), 32) what can be accomplished if we impose that the bulk fermion wavefunction is even under five-dimensional parity [17,18]: γ 5 Ψx α, r) = Ψx α,r). 33) Then from the symmetry of the problem with respect to the transformation r r we get the following important boundary conditions: ρ0) = 0, λ0) = 1. 34) Solutions of the Dirac equations 30) with the boundary conditions 34) are displayed on the Figure 5. We see that in our model the extra dimension part of the left spinor wave function λr) has maximum on the brane and decreases in the bulk. While, as a consequence of 34), 8
9 in our setup the right fermionic modes are absent on the brane and ρr) has maximum in the bulk outside the brane. Integrals over r in the spinor field action 26) are convergent if integrand functions decrease stronger than 1/r. This feature for 26) is demonstrated on the Figure 6. So in our model left massless fermions are localized on the brane and right fermions are localized in the bulk. Ρr)[Λ r)+2asignr) Λr)] e 4 a r Ρ 2 r r e 3 a r Λr) [Ρ r)+2a signr) Ρr)] e 4 a r Λ 2 r r e 3 a r Figure 6: Convergence of bulk integrals in S Ψ 26). 4 Massive modes In this section we want to estimate masses of Kaluza-Klein excitations. For simplicity let us consider the case of 5D scalar particles. For a massive mode the dispersion relation 10) takes the form: E 2 p 2 x p2 y p2 z = m2, 35) where m denotes the mass of lightest KK mode on the brane. Then the equation for scalar particles 11) transforms to: e 4a r ς ) e 2a r [ P 2 r) m 2] ς = 0. 36) It is more convenient to put 36) into the form of an analogue non-relativistic quantum mechanical problem by making the change: ςr) = e 2a r ψr). 37) For ψr) we find: ψ +e 2a r [ m 2 Vr) ] ψ = 0, 38) 9
10 where the function, Vr) = 4ae 2a r δr)+4a 2 e 2a r +P 2 r), 39) is the analog of non-relativistic potential. Because this potential contains Dirac delta function, it becomes infinitely large at the point r = 0. This means that if we interpret ψr) as a wave function, it must vanish at the point r = 0. Profile of the Vr) is shown on the Figure Vr) Figure 7: The effective bulk potential 39). To show existence of mass gap between zero and massive modes we approximate Vr) by the rectangular potential and study quantum mechanical problem in potential well with the parameters: { 4a 2 0 < r L) Vr) = + r > L). 40) Here L is the width of the rectangular effective potential Vr), which can be estimated from 39). Inside of the potential well the equation 38) obtains the form: Thus in the first region, if the solution can be written in the form: ψ 1 +e 2a r [ m 2 4a 2] ψ 1 = 0. 41) m 2 > 4a 2, 42) ψ 1 r) = C 1 J 0 e a r β ) +C 2 Y 0 e a r β ), 0 r L) 43) where C 1, C 2 and J 0, Y 0 are integration constants and Bessel functions, respectively, and we have introduced the parameter: β = 1 a m2 4a 2. 44) 10
11 In the second region, where the potential is infinitely large, we have: ψ 2 r) = 0. r > L) 45) The boundary and continuity conditions at the point of junction: ψ 1 0) = 0, ψ 1 L) = ψ 2 L), ψ 1 L) = ψ 2 L), 46) as usual, lead to the quantization of the mass: J 0 β) J 0 e al β) = Y 0β) Y 0 e al β), 47) which can be satisfied if β = 1 a m2 4a 2 = 0. 48) So we find that in our model Kaluza-Klein excitations have discreet spectrum and the mass of the lightest KK massive mode is of order of the curvature scalar, m 2a. 49) This miens that KK states are very heavy since a correspond to the energy scale characterizing the brane as a topological defect in higher-dimensional space-time. 5 Conclusions In this letter within the 5D standing wave braneworld model we numerically find profiles of massless matter field wave-functions in the bulk. Using numerical solution in action integrals we have demonstrated the existences of gravitational localization of all kinds of matter fields on the brane. For the case of fermions we found that, while left ones are localized on the brane, the right massless fermions are absent on the brane, they are localized in the bulk. We have also estimated masses of KK modes and found that, as in the standard single brane models, they are very heavy - of order of the energy scale associated with the brane. Acknowledgments This research was supported by the grant of Shota Rustaveli National Science Foundation #DI/8/6 100/12. References [1] N. Arkani-Hamed, S. Dimopoulos and G. Dvali, Phys. Lett. B ) 263 [hep-ph/ ]. [2] I. Antoniadis, N. Arkani-Hamed, S. Dimopoulos and G. Dvali, Phys. Lett. B ) 257 [hep-ph/ ]. 11
12 [3] M. Gogberashvili, Int. J. Mod. Phys. D ) 1635 [hep-ph/ ]; Mod. Phys. Lett. A ) 2025 [hep-ph/ ]. [4] L. Randall and R. Sundrum, Phys. Rev. Lett ) 3370 [hep-ph/ ]; Phys. Rev. Lett ) 4690 [hep-th/ ]. [5] V.A. Rubakov, Phys. Usp ) 871 Usp. Fiz. Nauk ) 913). [6] D. Langlois, Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl ) 181 [hep-th/ ]. [7] P.D. Mannheim, Brane-localized Gravity World Scientific, Singapore 2005). [8] R. Maartens and K. Koyama, Living Rev. Rel ) 5 [ [hep-th]]. [9] B. Bajc and G. Gabadadze, Phys. Lett. B ) 282 [hep-th/ ]. [10] I. Oda, Phys. Rev. D ) [hep-th/ ]. [11] M. Gogberashvili and D. Singleton, Mod. Phys. Lett. A ) 2131 [ [hepth]]. [12] M. Gogberashvili, A. Herrera-Aguilar and D. Malagón-Morejón, Class. Quantum Grav ) [ [hep-th]]. [13] M. Gogberashvili, JHEP ) 056 [ [hep-th]]. [14] M. Gogberashvili, P. Midodashvili and L. Midodashvili, Int. J. Mod. Phys. D ) [ [hep-th]]. [15] M. Gogberashvili, P. Midodashvili and L. Midodashvili, Phys. Lett. B ) 276 [ [hep-th]]. [16] M. Gogberashvili, P. Midodashvili and L. Midodashvili, Phys. Lett. B ) 276 [ [hep-th]]. [17] Y. Grossman and M. Neubert, Phys. Lett. B ) 361 [hep-ph/ ] [18] S. Chang, J. Hisano, H. Nakano, N. Okada and M. Yamaguchi, Phys. Rev. D ) [hep-ph/ ]. 12
LOCALIZATION OF FIELDS ON A BRANE IN SIX DIMENSIONS.
 LOCALIZATION OF FIELDS ON A BRANE IN SIX DIMENSIONS Merab Gogberashvili a and Paul Midodashvili b a Andronikashvili Institute of Physics, 6 Tamarashvili Str., Tbilisi 3877, Georgia E-mail: gogber@hotmail.com
LOCALIZATION OF FIELDS ON A BRANE IN SIX DIMENSIONS Merab Gogberashvili a and Paul Midodashvili b a Andronikashvili Institute of Physics, 6 Tamarashvili Str., Tbilisi 3877, Georgia E-mail: gogber@hotmail.com
Brane Gravity from Bulk Vector Field
 Brane Gravity from Bulk Vector Field Merab Gogberashvili Andronikashvili Institute of Physics, 6 Tamarashvili Str., Tbilisi 380077, Georgia E-mail: gogber@hotmail.com September 7, 00 Abstract It is shown
Brane Gravity from Bulk Vector Field Merab Gogberashvili Andronikashvili Institute of Physics, 6 Tamarashvili Str., Tbilisi 380077, Georgia E-mail: gogber@hotmail.com September 7, 00 Abstract It is shown
arxiv: v2 [hep-th] 18 May 2016
![arxiv: v2 [hep-th] 18 May 2016 arxiv: v2 [hep-th] 18 May 2016](/thumbs/76/73119871.jpg) International Journal of Modern Physics D c World Scientific Publishing Company arxiv:160.00607v [hep-th] 18 May 016 Standing Waves Braneworlds Merab Gogberashvili Javakhishvili Tbilisi State University,
International Journal of Modern Physics D c World Scientific Publishing Company arxiv:160.00607v [hep-th] 18 May 016 Standing Waves Braneworlds Merab Gogberashvili Javakhishvili Tbilisi State University,
Braneworlds: gravity & cosmology. David Langlois APC & IAP, Paris
 Braneworlds: gravity & cosmology David Langlois APC & IAP, Paris Outline Introduction Extra dimensions and gravity Large (flat) extra dimensions Warped extra dimensions Homogeneous brane cosmology Brane
Braneworlds: gravity & cosmology David Langlois APC & IAP, Paris Outline Introduction Extra dimensions and gravity Large (flat) extra dimensions Warped extra dimensions Homogeneous brane cosmology Brane
Thick Brane World. Seyen Kouwn Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute Korea
 Thick Brane World Seyen Kouwn Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute Korea Introduction - Multidimensional theory 1 Why are the physically observed dimensions of our Universe = 3 + 1 (space + time)?
Thick Brane World Seyen Kouwn Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute Korea Introduction - Multidimensional theory 1 Why are the physically observed dimensions of our Universe = 3 + 1 (space + time)?
Non-SUSY BSM: Lecture 1/2
 Non-SUSY BSM: Lecture 1/2 Generalities Benasque September 26, 2013 Mariano Quirós ICREA/IFAE Mariano Quirós (ICREA/IFAE) Non-SUSY BSM: Lecture 1/2 1 / 31 Introduction Introduction There are a number of
Non-SUSY BSM: Lecture 1/2 Generalities Benasque September 26, 2013 Mariano Quirós ICREA/IFAE Mariano Quirós (ICREA/IFAE) Non-SUSY BSM: Lecture 1/2 1 / 31 Introduction Introduction There are a number of
arxiv:hep-th/ v1 28 Apr 2002
 Vector field localization and negative tension branes Massimo Giovannini Institute of Theoretical Physics, University of Lausanne BSP-1015 Dorigny, Lausanne, Switzerland arxiv:hep-th/0204235v1 28 Apr 2002
Vector field localization and negative tension branes Massimo Giovannini Institute of Theoretical Physics, University of Lausanne BSP-1015 Dorigny, Lausanne, Switzerland arxiv:hep-th/0204235v1 28 Apr 2002
1. Introduction. [Arkani-Hamed, Dimopoulos, Dvali]
![1. Introduction. [Arkani-Hamed, Dimopoulos, Dvali] 1. Introduction. [Arkani-Hamed, Dimopoulos, Dvali]](/thumbs/93/111202940.jpg) 2014 Ï Ò (í «) Ò Ò Ù Åǽ À 20145 7 Content 1. Introduction and Motivation 2. f(r)-brane model and solutions 3. Localization of gravity on f(r)-brane 4. Gravity resonances on f(r)-brane 5. Corrections to
2014 Ï Ò (í «) Ò Ò Ù Åǽ À 20145 7 Content 1. Introduction and Motivation 2. f(r)-brane model and solutions 3. Localization of gravity on f(r)-brane 4. Gravity resonances on f(r)-brane 5. Corrections to
Life with More Than 4: Extra Dimensions
 Life with More Than 4: Extra Dimensions Andrew Larkoski 4/15/09 Andrew Larkoski SASS 5 Outline A Simple Example: The 2D Infinite Square Well Describing Arbitrary Dimensional Spacetime Motivations for Extra
Life with More Than 4: Extra Dimensions Andrew Larkoski 4/15/09 Andrew Larkoski SASS 5 Outline A Simple Example: The 2D Infinite Square Well Describing Arbitrary Dimensional Spacetime Motivations for Extra
Braneworld in f(r) gravity and critical gravity
 Braneworld in f(r) gravity and critical gravity Yu-Xiao Liu Institute of Theoretical Physics, Lanzhou University ICTS, USTC, Hefei 2011.12.13 Content Introduction and motivation f(r) thick brane f(r) thick
Braneworld in f(r) gravity and critical gravity Yu-Xiao Liu Institute of Theoretical Physics, Lanzhou University ICTS, USTC, Hefei 2011.12.13 Content Introduction and motivation f(r) thick brane f(r) thick
Dynamical Domain Wall and Localization
 Dynamical Domain Wall and Localization Shin ichi Nojiri Department of Physics & Kobayashi-Maskawa Institute for the Origin of Particles and the Universe (KMI), Nagoya Univ. Typeset by FoilTEX 1 Based on
Dynamical Domain Wall and Localization Shin ichi Nojiri Department of Physics & Kobayashi-Maskawa Institute for the Origin of Particles and the Universe (KMI), Nagoya Univ. Typeset by FoilTEX 1 Based on
Large Extra Dimensions and the Hierarchy Problem
 Large Extra Dimensions and the Hierarchy Problem The Hierarchy Problem - At Planck energies (M P L 10 19 GeV ) all four forces have the same strength. -At the Electroweak scale (M EW 1T ev ) the four forces
Large Extra Dimensions and the Hierarchy Problem The Hierarchy Problem - At Planck energies (M P L 10 19 GeV ) all four forces have the same strength. -At the Electroweak scale (M EW 1T ev ) the four forces
arxiv:hep-ph/ v1 31 Jan 2003
 UT-03-05 Warped QCD without the Strong CP Problem arxiv:hep-ph/0301273v1 31 Jan 2003 Akito Fukunaga and Izawa K.-I. Department of Physics, University of Tokyo, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan Abstract QCD in a five-dimensional
UT-03-05 Warped QCD without the Strong CP Problem arxiv:hep-ph/0301273v1 31 Jan 2003 Akito Fukunaga and Izawa K.-I. Department of Physics, University of Tokyo, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan Abstract QCD in a five-dimensional
Time-Like Extra Dimension and Cosmological Constant in Brane Models. Tianjun Li
 UPR-901-T Time-Like Extra Dimension and Cosmological Constant in Brane Models Tianjun Li Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104-6396 U. S. A. Abstract We
UPR-901-T Time-Like Extra Dimension and Cosmological Constant in Brane Models Tianjun Li Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104-6396 U. S. A. Abstract We
Introduction to (Large) Extra Dimensions
 SLAC Dark Matter & Exotic Physics WG p. 1/39 Introduction to (Large) Extra Dimensions A. Lionetto Department of Physics & INFN Roma Tor Vergata SLAC Dark Matter & Exotic Physics WG p. 2/39 Outline Introduction
SLAC Dark Matter & Exotic Physics WG p. 1/39 Introduction to (Large) Extra Dimensions A. Lionetto Department of Physics & INFN Roma Tor Vergata SLAC Dark Matter & Exotic Physics WG p. 2/39 Outline Introduction
Gravity in the Braneworld and
 Gravity in the Braneworld and the AdS/CFT Correspondence Takahiro TANAKA Department of Physics, Kyoto University, Kyoto 606-8502, Japan October 18, 2004 Abstract We discuss gravitational interaction realized
Gravity in the Braneworld and the AdS/CFT Correspondence Takahiro TANAKA Department of Physics, Kyoto University, Kyoto 606-8502, Japan October 18, 2004 Abstract We discuss gravitational interaction realized
Gravitational perturbations on branes
 º ( Ò Ò ) Ò ± 2015.4.9 Content 1. Introduction and Motivation 2. Braneworld solutions in various gravities 2.1 General relativity 2.2 Scalar-tensor gravity 2.3 f(r) gravity 3. Gravitational perturbation
º ( Ò Ò ) Ò ± 2015.4.9 Content 1. Introduction and Motivation 2. Braneworld solutions in various gravities 2.1 General relativity 2.2 Scalar-tensor gravity 2.3 f(r) gravity 3. Gravitational perturbation
BEYOND THE SM (II) Kaustubh Agashe (University of Maryland)
 BEYOND THE SM (II) Kaustubh Agashe (University of Maryland) ierarchy problems (from lecture 1) Planck-weak hierarchy problem Flavor (hierarchy) puzzle...extra dimensions can address both... Extra dimensions:
BEYOND THE SM (II) Kaustubh Agashe (University of Maryland) ierarchy problems (from lecture 1) Planck-weak hierarchy problem Flavor (hierarchy) puzzle...extra dimensions can address both... Extra dimensions:
3.3 Lagrangian and symmetries for a spin- 1 2 field
 3.3 Lagrangian and symmetries for a spin- 1 2 field The Lagrangian for the free spin- 1 2 field is The corresponding Hamiltonian density is L = ψ(i/ µ m)ψ. (3.31) H = ψ( γ p + m)ψ. (3.32) The Lagrangian
3.3 Lagrangian and symmetries for a spin- 1 2 field The Lagrangian for the free spin- 1 2 field is The corresponding Hamiltonian density is L = ψ(i/ µ m)ψ. (3.31) H = ψ( γ p + m)ψ. (3.32) The Lagrangian
Neutron Stars in the Braneworld
 Neutron Stars in the Braneworld Mike Georg Bernhardt Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg Zentrum für Astronomie, Landessternwarte 24 April 29 Outline Introduction Why bother with Extra Dimensions? Braneworlds
Neutron Stars in the Braneworld Mike Georg Bernhardt Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg Zentrum für Astronomie, Landessternwarte 24 April 29 Outline Introduction Why bother with Extra Dimensions? Braneworlds
Gauge field localization on brane worlds
 Gauge field localization on brane worlds Rommel Guerrero and R. Omar Rodriguez Universidad Centroccidental Lisandro Alvarado - Venezuela Miami 2013 R. Guerrero UCLA) Gauge field localization December 2013
Gauge field localization on brane worlds Rommel Guerrero and R. Omar Rodriguez Universidad Centroccidental Lisandro Alvarado - Venezuela Miami 2013 R. Guerrero UCLA) Gauge field localization December 2013
arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 23 Nov 2017
![arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 23 Nov 2017 arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 23 Nov 2017](/thumbs/73/68798748.jpg) Regular string-like braneworlds J. E. G. Silva, 1, W. H. P. Brandão,, R. V. Maluf,, and C. A. S. Almeida, 1 Universidade Federal do Cariri (UFCA, Av. Tenente Raimundo Rocha, Cidade Universitária, Juazeiro
Regular string-like braneworlds J. E. G. Silva, 1, W. H. P. Brandão,, R. V. Maluf,, and C. A. S. Almeida, 1 Universidade Federal do Cariri (UFCA, Av. Tenente Raimundo Rocha, Cidade Universitária, Juazeiro
Attempts at relativistic QM
 Attempts at relativistic QM based on S-1 A proper description of particle physics should incorporate both quantum mechanics and special relativity. However historically combining quantum mechanics and
Attempts at relativistic QM based on S-1 A proper description of particle physics should incorporate both quantum mechanics and special relativity. However historically combining quantum mechanics and
The Randall-Sundrum model
 The Randall-Sundrum model Aleksandr Chatrchyan & Björn Jüliger After a brief non-technical introduction to the Hierarchy problem, we first discuss the old five-dimensional Kaluza-Klein model, its tower
The Randall-Sundrum model Aleksandr Chatrchyan & Björn Jüliger After a brief non-technical introduction to the Hierarchy problem, we first discuss the old five-dimensional Kaluza-Klein model, its tower
Warp Duality in Braneworlds
 Warp Duality in Braneworlds Andrew B. McGowan September 14, 2007 Abstract In recent years there have emerged numerous models of spacetime that include extra dimensions. In particular there have been a
Warp Duality in Braneworlds Andrew B. McGowan September 14, 2007 Abstract In recent years there have emerged numerous models of spacetime that include extra dimensions. In particular there have been a
Supersymmetric Randall-Sundrum Scenario
 CIT-USC/00-015 Supersymmetric Randall-Sundrum Scenario arxiv:hep-th/000117v May 000 Richard Altendorfer, Jonathan Bagger Department of Physics and Astronomy The Johns Hopkins University 400 North Charles
CIT-USC/00-015 Supersymmetric Randall-Sundrum Scenario arxiv:hep-th/000117v May 000 Richard Altendorfer, Jonathan Bagger Department of Physics and Astronomy The Johns Hopkins University 400 North Charles
Aether compactification
 PHYSICAL REVIEW D 78, 044047 (2008) Aether compactification Sean M. Carroll 1 and Heywood Tam 1 1 California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California 91125, USA (Received 8 April 2008; published 29
PHYSICAL REVIEW D 78, 044047 (2008) Aether compactification Sean M. Carroll 1 and Heywood Tam 1 1 California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California 91125, USA (Received 8 April 2008; published 29
Klein-Gordon Equation for a Particle in Brane Model
 Global Journal of Science Frontier Research Physics and Space Science Volume 13 Issue 8 Version 1.0 Year Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc.
Global Journal of Science Frontier Research Physics and Space Science Volume 13 Issue 8 Version 1.0 Year Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc.
Quantum Fields in Curved Spacetime
 Quantum Fields in Curved Spacetime Lecture 3 Finn Larsen Michigan Center for Theoretical Physics Yerevan, August 22, 2016. Recap AdS 3 is an instructive application of quantum fields in curved space. The
Quantum Fields in Curved Spacetime Lecture 3 Finn Larsen Michigan Center for Theoretical Physics Yerevan, August 22, 2016. Recap AdS 3 is an instructive application of quantum fields in curved space. The
...and the extradimensions quest
 A brief introduction to the Randall-Sundrum Models...and the extradimensions quest Bruno BERTRAND Center for particle physics and phenomenology (CP3) CP3 Seminar : Randall-Sundrum models - Bruno BERTRAND
A brief introduction to the Randall-Sundrum Models...and the extradimensions quest Bruno BERTRAND Center for particle physics and phenomenology (CP3) CP3 Seminar : Randall-Sundrum models - Bruno BERTRAND
Localization of Kaluza-Klein gauge fields on a brane. Abstract
 Localization of Kaluza-Klein gauge fields on a brane. Andrey Neronov Theoretische Physik, Universität Munchen, 80333, Munich, Germany March 5, 2001) Abstract In phenomenological models with extra dimensions
Localization of Kaluza-Klein gauge fields on a brane. Andrey Neronov Theoretische Physik, Universität Munchen, 80333, Munich, Germany March 5, 2001) Abstract In phenomenological models with extra dimensions
Brane-World Cosmology and Inflation
 ICGC04, 2004/1/5-10 Brane-World Cosmology and Inflation Extra dimension G µν = κ T µν? Misao Sasaki YITP, Kyoto University 1. Introduction Braneworld domain wall (n 1)-brane = singular (time-like) hypersurface
ICGC04, 2004/1/5-10 Brane-World Cosmology and Inflation Extra dimension G µν = κ T µν? Misao Sasaki YITP, Kyoto University 1. Introduction Braneworld domain wall (n 1)-brane = singular (time-like) hypersurface
4D Gravity on a Brane in 5D Minkowski Space
 NYU-TH/00/04/0 April 25, 2000 4D Gravity on a Brane in 5D Minkowski Space Gia Dvali, Gregory Gabadadze, Massimo Porrati Department of Physics, New York University, New York, NY 0003 Abstract We suggest
NYU-TH/00/04/0 April 25, 2000 4D Gravity on a Brane in 5D Minkowski Space Gia Dvali, Gregory Gabadadze, Massimo Porrati Department of Physics, New York University, New York, NY 0003 Abstract We suggest
Inter-brane distance stabilization by bulk Higgs field in RS model
 EPJ Web of Conferences 58, 0500 07 QFTHEP 07 DOI: 0.05/epjconf/07580500 Inter-brane distance stabilization by bulk Higgs field in RS model Vadim Egorov,, and Igor Volobuev, Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear
EPJ Web of Conferences 58, 0500 07 QFTHEP 07 DOI: 0.05/epjconf/07580500 Inter-brane distance stabilization by bulk Higgs field in RS model Vadim Egorov,, and Igor Volobuev, Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear
An exotic class of Kaluza Klein models
 An exotic class of Kaluza Klein models arxiv:hep-th/9910093v1 1 Oct 1999 Matt Visser Physics Department, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA 90080-0484, USA 1 September 1985; L A TEX-ed
An exotic class of Kaluza Klein models arxiv:hep-th/9910093v1 1 Oct 1999 Matt Visser Physics Department, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA 90080-0484, USA 1 September 1985; L A TEX-ed
Elementary/Composite Mixing in Randall-Sundrum Models
 Elementary/Composite Mixing in Randall-Sundrum Models Brian Batell University of Minnesota with Tony Gherghetta - arxiv:0706.0890 - arxiv:0710.1838 Cornell 1/30/08 5D Warped Dimension = 4D Strong Dynamics
Elementary/Composite Mixing in Randall-Sundrum Models Brian Batell University of Minnesota with Tony Gherghetta - arxiv:0706.0890 - arxiv:0710.1838 Cornell 1/30/08 5D Warped Dimension = 4D Strong Dynamics
Trapped in an infinite extra dimension
 Trapped in an infinite extra dimension Damien George Nikhef theory group Nikhef Jamboree 15 16 th December 2009 Amsterdam Extra dimensions D.P. George Trapped in an infinite extra dimension 2/11 Beyond
Trapped in an infinite extra dimension Damien George Nikhef theory group Nikhef Jamboree 15 16 th December 2009 Amsterdam Extra dimensions D.P. George Trapped in an infinite extra dimension 2/11 Beyond
Lecture 9: RR-sector and D-branes
 Lecture 9: RR-sector and D-branes José D. Edelstein University of Santiago de Compostela STRING THEORY Santiago de Compostela, March 6, 2013 José D. Edelstein (USC) Lecture 9: RR-sector and D-branes 6-mar-2013
Lecture 9: RR-sector and D-branes José D. Edelstein University of Santiago de Compostela STRING THEORY Santiago de Compostela, March 6, 2013 José D. Edelstein (USC) Lecture 9: RR-sector and D-branes 6-mar-2013
arxiv:hep-ph/ v1 1 Feb 2005
 Vector Goldstone Boson and Lorentz Invariance arxiv:hep-ph/050011v1 1 Feb 005 Ling-Fong Li Department of Physics, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA 1513 January 5, 018 Abstract Spontanous symmetry
Vector Goldstone Boson and Lorentz Invariance arxiv:hep-ph/050011v1 1 Feb 005 Ling-Fong Li Department of Physics, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA 1513 January 5, 018 Abstract Spontanous symmetry
Does a Randall-Sundrum scenario create the illusion of a torsion-free universe?
 hep-th/0204242 Does a Randall-Sundrum scenario create the illusion of a torsion-free universe? Biswarup Mukhopadhyaya 1, Somasri Sen 2 Harish-Chandra Research Institute, Chhatnag Road, Jhusi, Allahabad
hep-th/0204242 Does a Randall-Sundrum scenario create the illusion of a torsion-free universe? Biswarup Mukhopadhyaya 1, Somasri Sen 2 Harish-Chandra Research Institute, Chhatnag Road, Jhusi, Allahabad
Lecture 4 - Dirac Spinors
 Lecture 4 - Dirac Spinors Schrödinger & Klein-Gordon Equations Dirac Equation Gamma & Pauli spin matrices Solutions of Dirac Equation Fermion & Antifermion states Left and Right-handedness Non-Relativistic
Lecture 4 - Dirac Spinors Schrödinger & Klein-Gordon Equations Dirac Equation Gamma & Pauli spin matrices Solutions of Dirac Equation Fermion & Antifermion states Left and Right-handedness Non-Relativistic
arxiv:quant-ph/ v1 16 Jun 2005
 Black-body radiation in extra dimensions Haavard Alnes, Finn Ravndal 2 and Ingunn Kathrine Wehus 3 Institute of Physics, University of Oslo, N-036 Oslo, Norway. arxiv:quant-ph/05063 v 6 Jun 2005 Abstract
Black-body radiation in extra dimensions Haavard Alnes, Finn Ravndal 2 and Ingunn Kathrine Wehus 3 Institute of Physics, University of Oslo, N-036 Oslo, Norway. arxiv:quant-ph/05063 v 6 Jun 2005 Abstract
Warped and compact extra dimensions: 5D branes in 6D models
 Physics Letters B 545 (2002) 389 402 www.elsevier.com/locate/npe Warped and compact extra dimensions: 5D branes in 6D models Tuomas Multamäki, Iiro Vilja Department of Physics, University of Turku, FIN-20014,
Physics Letters B 545 (2002) 389 402 www.elsevier.com/locate/npe Warped and compact extra dimensions: 5D branes in 6D models Tuomas Multamäki, Iiro Vilja Department of Physics, University of Turku, FIN-20014,
arxiv:gr-qc/ v1 4 Jun 2003
 Wormhole solutions in the Randall-Sundrum scenario M. La Camera Department of Physics and INFN - University of Genoa Via Dodecaneso 33, 16146 Genova, Italy Abstract In the simplest form of the Randall-Sundrum
Wormhole solutions in the Randall-Sundrum scenario M. La Camera Department of Physics and INFN - University of Genoa Via Dodecaneso 33, 16146 Genova, Italy Abstract In the simplest form of the Randall-Sundrum
Physics Beyond the Standard Model. Marina Cobal Fisica Sperimentale Nucleare e Sub-Nucleare
 Physics Beyond the Standard Model Marina Cobal Fisica Sperimentale Nucleare e Sub-Nucleare Increasingly General Theories Grand Unified Theories of electroweak and strong interactions Supersymmetry
Physics Beyond the Standard Model Marina Cobal Fisica Sperimentale Nucleare e Sub-Nucleare Increasingly General Theories Grand Unified Theories of electroweak and strong interactions Supersymmetry
Extra Dimensional Signatures at CLIC
 Extra Dimensional Signatures at CLIC Thomas G. Rizzo SLAC A brief overview is presented of the signatures for several different models with extra dimensions at CLIC, an e + e linear collider with a center
Extra Dimensional Signatures at CLIC Thomas G. Rizzo SLAC A brief overview is presented of the signatures for several different models with extra dimensions at CLIC, an e + e linear collider with a center
D. f(r) gravity. φ = 1 + f R (R). (48)
 5 D. f(r) gravity f(r) gravity is the first modified gravity model proposed as an alternative explanation for the accelerated expansion of the Universe [9]. We write the gravitational action as S = d 4
5 D. f(r) gravity f(r) gravity is the first modified gravity model proposed as an alternative explanation for the accelerated expansion of the Universe [9]. We write the gravitational action as S = d 4
arxiv: v1 [hep-th] 3 Feb 2016
![arxiv: v1 [hep-th] 3 Feb 2016 arxiv: v1 [hep-th] 3 Feb 2016](/thumbs/76/73492002.jpg) Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Thermodynamics of Asymptotically Flat Black Holes in Lovelock Background N. Abbasvandi M. J. Soleimani Shahidan Radiman W.A.T. Wan Abdullah G. Gopir
Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Thermodynamics of Asymptotically Flat Black Holes in Lovelock Background N. Abbasvandi M. J. Soleimani Shahidan Radiman W.A.T. Wan Abdullah G. Gopir
Dynamically generated embeddings of spacetime
 arxiv:gr-qc/0503103v2 18 Oct 2005 Dynamically generated embeddings of spacetime F. Dahia 1 and C. Romero 2 1 Departamento de Física, UFCG, Campina Grande-PB, Brazil, 58109-970. 2 Departamento de Física,
arxiv:gr-qc/0503103v2 18 Oct 2005 Dynamically generated embeddings of spacetime F. Dahia 1 and C. Romero 2 1 Departamento de Física, UFCG, Campina Grande-PB, Brazil, 58109-970. 2 Departamento de Física,
Domain Wall Brane in Eddington Inspired Born-Infeld Gravity
 2012cüWâfÔn»Æï? Domain Wall Brane in Eddington Inspired Born-Infeld Gravity µ4œ Ç =²ŒÆnØÔnïÄ Email: yangke09@lzu.edu.cn I# Ÿ 2012.05.10 Outline Introduction to Brane World Introduction to Eddington Inspired
2012cüWâfÔn»Æï? Domain Wall Brane in Eddington Inspired Born-Infeld Gravity µ4œ Ç =²ŒÆnØÔnïÄ Email: yangke09@lzu.edu.cn I# Ÿ 2012.05.10 Outline Introduction to Brane World Introduction to Eddington Inspired
Eternally accelerating spacelike br Title cosmologies. Journal Modern Physics Letters A, 21(40): 2
 Eternally accelerating spacelike br Title cosmologies Author(s) Mochizuki, R Alternative Journal Modern Physics Letters A, 21(40): 2 RL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/46 Electronic version of an article pu
Eternally accelerating spacelike br Title cosmologies Author(s) Mochizuki, R Alternative Journal Modern Physics Letters A, 21(40): 2 RL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/46 Electronic version of an article pu
arxiv:hep-th/ v1 8 Jun 1999
 hep-th/9906064 MIT-CTP-2874 PUPT-1867 BUHEP-99-13 An Alternative to Compactification arxiv:hep-th/9906064v1 8 Jun 1999 Lisa Randall Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08543,
hep-th/9906064 MIT-CTP-2874 PUPT-1867 BUHEP-99-13 An Alternative to Compactification arxiv:hep-th/9906064v1 8 Jun 1999 Lisa Randall Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08543,
Chiral fermions, orbifolds, scalars and fat branes
 #HUTP-00/A09 7/00 Chiral fermions, orbifolds, scalars and fat branes arxiv:hep-ph/0007350v 1 Aug 000 Howard Georgi, Aaron K. Grant, Girma Hailu Lyman Laboratory of Physics Harvard University Cambridge,
#HUTP-00/A09 7/00 Chiral fermions, orbifolds, scalars and fat branes arxiv:hep-ph/0007350v 1 Aug 000 Howard Georgi, Aaron K. Grant, Girma Hailu Lyman Laboratory of Physics Harvard University Cambridge,
q form field and Hodge duality on brane
 Lanzhou University (=²ŒÆ) With C.E. Fu, H. Guo and S.L. Zhang [PRD 93 (206) 064007] 4th International Workshop on Dark Matter, Dark Energy and Matter-Antimatter Asymmetry December 29-3, 206, December 3,
Lanzhou University (=²ŒÆ) With C.E. Fu, H. Guo and S.L. Zhang [PRD 93 (206) 064007] 4th International Workshop on Dark Matter, Dark Energy and Matter-Antimatter Asymmetry December 29-3, 206, December 3,
Classical-quantum Correspondence and Wave Packet Solutions of the Dirac Equation in a Curved Spacetime
 Classical-quantum Correspondence and Wave Packet Solutions of the Dirac Equation in a Curved Spacetime Mayeul Arminjon 1,2 and Frank Reifler 3 1 CNRS (Section of Theoretical Physics) 2 Lab. Soils, Solids,
Classical-quantum Correspondence and Wave Packet Solutions of the Dirac Equation in a Curved Spacetime Mayeul Arminjon 1,2 and Frank Reifler 3 1 CNRS (Section of Theoretical Physics) 2 Lab. Soils, Solids,
arxiv:hep-th/ v1 29 Nov 2001
 Scalar fluctuations in dilatonic brane worlds February 1, 2008 Valerio Bozza arxiv:hep-th/0111268v1 29 Nov 2001 Dipartimento di Fisica E.R. Caianiello, Università di Salerno Via S. Allende, 84081 Baronissi
Scalar fluctuations in dilatonic brane worlds February 1, 2008 Valerio Bozza arxiv:hep-th/0111268v1 29 Nov 2001 Dipartimento di Fisica E.R. Caianiello, Università di Salerno Via S. Allende, 84081 Baronissi
Lecture 4 - Relativistic wave equations. Relativistic wave equations must satisfy several general postulates. These are;
 Lecture 4 - Relativistic wave equations Postulates Relativistic wave equations must satisfy several general postulates. These are;. The equation is developed for a field amplitude function, ψ 2. The normal
Lecture 4 - Relativistic wave equations Postulates Relativistic wave equations must satisfy several general postulates. These are;. The equation is developed for a field amplitude function, ψ 2. The normal
Brane world scenarios
 PRAMANA cfl Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 60, No. 2 journal of February 2003 physics pp. 183 188 Brane world scenarios DILEEP P JATKAR Harish-Chandra Research Institute, Chhatnag Road, Jhusi, Allahabad
PRAMANA cfl Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 60, No. 2 journal of February 2003 physics pp. 183 188 Brane world scenarios DILEEP P JATKAR Harish-Chandra Research Institute, Chhatnag Road, Jhusi, Allahabad
Final Exam: Sat. Dec. 18, 2:45-4:45 pm, 1300 Sterling Exam is cumulative, covering all material. From last time
 Final Exam: Sat. Dec. 18, 2:45-4:45 pm, 1300 Sterling Exam is cumulative, covering all material From last time Quantum field theory is a relativistic quantum theory of fields and interactions. Fermions
Final Exam: Sat. Dec. 18, 2:45-4:45 pm, 1300 Sterling Exam is cumulative, covering all material From last time Quantum field theory is a relativistic quantum theory of fields and interactions. Fermions
arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 12 Jun 2013
![arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 12 Jun 2013 arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 12 Jun 2013](/thumbs/86/94727409.jpg) Cosmological solutions for a two-branes system in a vacuum bulk Juan L. Pérez, Miguel A. García-Aspeitia, L. Arturo Ureña-López and Rubén Cordero. Departamento de Física, DCI, Campus León, Universidad
Cosmological solutions for a two-branes system in a vacuum bulk Juan L. Pérez, Miguel A. García-Aspeitia, L. Arturo Ureña-López and Rubén Cordero. Departamento de Física, DCI, Campus León, Universidad
Week 3: Renormalizable lagrangians and the Standard model lagrangian 1 Reading material from the books
 Week 3: Renormalizable lagrangians and the Standard model lagrangian 1 Reading material from the books Burgess-Moore, Chapter Weiberg, Chapter 5 Donoghue, Golowich, Holstein Chapter 1, 1 Free field Lagrangians
Week 3: Renormalizable lagrangians and the Standard model lagrangian 1 Reading material from the books Burgess-Moore, Chapter Weiberg, Chapter 5 Donoghue, Golowich, Holstein Chapter 1, 1 Free field Lagrangians
Lecture 10. The Dirac equation. WS2010/11: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics
 Lecture 10 The Dirac equation WS2010/11: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics The Dirac equation The Dirac equation is a relativistic quantum mechanical wave equation formulated by British physicist
Lecture 10 The Dirac equation WS2010/11: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics The Dirac equation The Dirac equation is a relativistic quantum mechanical wave equation formulated by British physicist
arxiv:hep-th/ v2 29 Nov 2002
 Preferred Frame in Brane World Merab GOGBERASHVILI Andronikashvili Institute of Physics 6 Tamarashvili Str., Tbilisi 380077, Georgia (E-mail: gogber@hotmail.com) arxiv:hep-th/0207042v2 29 Nov 2002 Abstract
Preferred Frame in Brane World Merab GOGBERASHVILI Andronikashvili Institute of Physics 6 Tamarashvili Str., Tbilisi 380077, Georgia (E-mail: gogber@hotmail.com) arxiv:hep-th/0207042v2 29 Nov 2002 Abstract
NTNU Trondheim, Institutt for fysikk
 NTNU Trondheim, Institutt for fysikk Examination for FY3464 Quantum Field Theory I Contact: Michael Kachelrieß, tel. 998971 Allowed tools: mathematical tables 1. Spin zero. Consider a real, scalar field
NTNU Trondheim, Institutt for fysikk Examination for FY3464 Quantum Field Theory I Contact: Michael Kachelrieß, tel. 998971 Allowed tools: mathematical tables 1. Spin zero. Consider a real, scalar field
Graviton contributions to the graviton self-energy at one loop order during inflation
 Graviton contributions to the graviton self-energy at one loop order during inflation PEDRO J. MORA DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA PASI2012 1. Description of my thesis problem. i. Graviton
Graviton contributions to the graviton self-energy at one loop order during inflation PEDRO J. MORA DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA PASI2012 1. Description of my thesis problem. i. Graviton
Quantization of scalar fields
 Quantization of scalar fields March 8, 06 We have introduced several distinct types of fields, with actions that give their field equations. These include scalar fields, S α ϕ α ϕ m ϕ d 4 x and complex
Quantization of scalar fields March 8, 06 We have introduced several distinct types of fields, with actions that give their field equations. These include scalar fields, S α ϕ α ϕ m ϕ d 4 x and complex
Searching for Extra Space Dimensions at the LHC. M.A.Parker Cavendish Laboratory Cambridge
 Searching for Extra Space Dimensions at the LHC M.A.Parker Cavendish Laboratory Cambridge I shall use ATLAS to illustrate LHC physics, because it is the experiment I know best. Both general purpose detectors
Searching for Extra Space Dimensions at the LHC M.A.Parker Cavendish Laboratory Cambridge I shall use ATLAS to illustrate LHC physics, because it is the experiment I know best. Both general purpose detectors
Maxwell s equations. electric field charge density. current density
 Maxwell s equations based on S-54 Our next task is to find a quantum field theory description of spin-1 particles, e.g. photons. Classical electrodynamics is governed by Maxwell s equations: electric field
Maxwell s equations based on S-54 Our next task is to find a quantum field theory description of spin-1 particles, e.g. photons. Classical electrodynamics is governed by Maxwell s equations: electric field
Relativistic Quantum Mechanics
 Physics 342 Lecture 34 Relativistic Quantum Mechanics Lecture 34 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Wednesday, April 30th, 2008 We know that the Schrödinger equation logically replaces Newton s second law
Physics 342 Lecture 34 Relativistic Quantum Mechanics Lecture 34 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Wednesday, April 30th, 2008 We know that the Schrödinger equation logically replaces Newton s second law
A Note On The Chern-Simons And Kodama Wavefunctions
 hep-th/0306083 arxiv:gr-qc/0306083v2 19 Jun 2003 A Note On The Chern-Simons And Kodama Wavefunctions Edward Witten Institute For Advanced Study, Princeton NJ 08540 USA Yang-Mills theory in four dimensions
hep-th/0306083 arxiv:gr-qc/0306083v2 19 Jun 2003 A Note On The Chern-Simons And Kodama Wavefunctions Edward Witten Institute For Advanced Study, Princeton NJ 08540 USA Yang-Mills theory in four dimensions
INTRODUCTION TO EXTRA DIMENSIONS
 INTRODUCTION TO EXTRA DIMENSIONS MARIANO QUIROS, ICREA/IFAE MORIOND 2006 INTRODUCTION TO EXTRA DIMENSIONS p.1/36 OUTLINE Introduction Where do extra dimensions come from? Strings and Branes Experimental
INTRODUCTION TO EXTRA DIMENSIONS MARIANO QUIROS, ICREA/IFAE MORIOND 2006 INTRODUCTION TO EXTRA DIMENSIONS p.1/36 OUTLINE Introduction Where do extra dimensions come from? Strings and Branes Experimental
Solutions to gauge hierarchy problem. SS 10, Uli Haisch
 Solutions to gauge hierarchy problem SS 10, Uli Haisch 1 Quantum instability of Higgs mass So far we considered only at RGE of Higgs quartic coupling (dimensionless parameter). Higgs mass has a totally
Solutions to gauge hierarchy problem SS 10, Uli Haisch 1 Quantum instability of Higgs mass So far we considered only at RGE of Higgs quartic coupling (dimensionless parameter). Higgs mass has a totally
Quantum Field Theory
 Quantum Field Theory PHYS-P 621 Radovan Dermisek, Indiana University Notes based on: M. Srednicki, Quantum Field Theory 1 Attempts at relativistic QM based on S-1 A proper description of particle physics
Quantum Field Theory PHYS-P 621 Radovan Dermisek, Indiana University Notes based on: M. Srednicki, Quantum Field Theory 1 Attempts at relativistic QM based on S-1 A proper description of particle physics
Quantum Field Theory
 Quantum Field Theory PHYS-P 621 Radovan Dermisek, Indiana University Notes based on: M. Srednicki, Quantum Field Theory 1 Attempts at relativistic QM based on S-1 A proper description of particle physics
Quantum Field Theory PHYS-P 621 Radovan Dermisek, Indiana University Notes based on: M. Srednicki, Quantum Field Theory 1 Attempts at relativistic QM based on S-1 A proper description of particle physics
Modelling an extra dimension with domain-wall branes
 Modelling an extra dimension with domain-wall branes Damien George Nikhef theory seminar 5 th November 2009 Overview Physics beyond the standard model: extra dimensions. Brane domain wall (topological
Modelling an extra dimension with domain-wall branes Damien George Nikhef theory seminar 5 th November 2009 Overview Physics beyond the standard model: extra dimensions. Brane domain wall (topological
arxiv:hep-th/ v2 21 Apr 2005
 Why do we live in 3+1 dimensions? R. Durrer a M. Kunz a M. Sakellariadou a,b arxiv:hep-th/0501163v2 21 Apr 2005 a Department of Theoretical Physics, University of Geneva, 24 quai Ernest Ansermet, CH-1211
Why do we live in 3+1 dimensions? R. Durrer a M. Kunz a M. Sakellariadou a,b arxiv:hep-th/0501163v2 21 Apr 2005 a Department of Theoretical Physics, University of Geneva, 24 quai Ernest Ansermet, CH-1211
arxiv: v1 [hep-th] 1 Oct 2008
![arxiv: v1 [hep-th] 1 Oct 2008 arxiv: v1 [hep-th] 1 Oct 2008](/thumbs/89/100527607.jpg) Cascading Gravity and Degravitation Claudia de Rham Dept. of Physics & Astronomy, McMaster University, Hamilton ON, Canada Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics, Waterloo, ON, Canada arxiv:0810.069v1
Cascading Gravity and Degravitation Claudia de Rham Dept. of Physics & Astronomy, McMaster University, Hamilton ON, Canada Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics, Waterloo, ON, Canada arxiv:0810.069v1
Quantum Field Theory
 Quantum Field Theory PHYS-P 621 Radovan Dermisek, Indiana University Notes based on: M. Srednicki, Quantum Field Theory 1 Attempts at relativistic QM based on S-1 A proper description of particle physics
Quantum Field Theory PHYS-P 621 Radovan Dermisek, Indiana University Notes based on: M. Srednicki, Quantum Field Theory 1 Attempts at relativistic QM based on S-1 A proper description of particle physics
STABILIZING EXTRA DIMENSIONS
 STABILIZING EXTRA DIMENSIONS Gero von Gersdorff (École Polytechnique) Warsaw, October 19th 2009 Collaboration with J.A.Cabrer and M.Quirós OUTLINE Features of Warped Extra Dimensions Stabilizing Models
STABILIZING EXTRA DIMENSIONS Gero von Gersdorff (École Polytechnique) Warsaw, October 19th 2009 Collaboration with J.A.Cabrer and M.Quirós OUTLINE Features of Warped Extra Dimensions Stabilizing Models
AdS spacetimes and Kaluza-Klein consistency. Oscar Varela
 AdS spacetimes and Kaluza-Klein consistency Oscar Varela based on work with Jerome Gauntlett and Eoin Ó Colgáin hep-th/0611219, 0707.2315, 0711.xxxx CALTECH 16 November 2007 Outline 1 Consistent KK reductions
AdS spacetimes and Kaluza-Klein consistency Oscar Varela based on work with Jerome Gauntlett and Eoin Ó Colgáin hep-th/0611219, 0707.2315, 0711.xxxx CALTECH 16 November 2007 Outline 1 Consistent KK reductions
Massive Spinors and ds/cft Correspondence
 Massive Spinors and ds/cft Correspondence Farhang Loran arxiv:hep-th/00135v3 16 Jun 00 Department of Physics, Isfahan University of Technology IUT) Isfahan, Iran, Institute for Studies in Theoretical Physics
Massive Spinors and ds/cft Correspondence Farhang Loran arxiv:hep-th/00135v3 16 Jun 00 Department of Physics, Isfahan University of Technology IUT) Isfahan, Iran, Institute for Studies in Theoretical Physics
BRANE COSMOLOGY and Randall-Sundrum model
 BRANE COSMOLOGY and Randall-Sundrum model M. J. Guzmán June 16, 2009 Standard Model of Cosmology CMB and large-scale structure observations provide us a high-precision estimation of the cosmological parameters:
BRANE COSMOLOGY and Randall-Sundrum model M. J. Guzmán June 16, 2009 Standard Model of Cosmology CMB and large-scale structure observations provide us a high-precision estimation of the cosmological parameters:
International Journal of Theoretical Physics, October 2015, Volume 54, Issue 10, pp ABSTRACT
 1 meson-nucleon coupling constant from the soft-wall AdS/QCD model Narmin Huseynova a,b1 and Shahin Mamedov a a Institute for Physical Problems, Baku State University, Z.Khalilov 3, Baku, AZ-1148, Azerbaijan
1 meson-nucleon coupling constant from the soft-wall AdS/QCD model Narmin Huseynova a,b1 and Shahin Mamedov a a Institute for Physical Problems, Baku State University, Z.Khalilov 3, Baku, AZ-1148, Azerbaijan
be stationary under variations in A, we obtain Maxwell s equations in the form ν J ν = 0. (7.5)
 Chapter 7 A Synopsis of QED We will here sketch the outlines of quantum electrodynamics, the theory of electrons and photons, and indicate how a calculation of an important physical quantity can be carried
Chapter 7 A Synopsis of QED We will here sketch the outlines of quantum electrodynamics, the theory of electrons and photons, and indicate how a calculation of an important physical quantity can be carried
Generalized N = 1 orientifold compactifications
 Generalized N = 1 orientifold compactifications Thomas W. Grimm University of Wisconsin, Madison based on: [hep-th/0602241] Iman Benmachiche, TWG [hep-th/0507153] TWG Madison, Wisconsin, November 2006
Generalized N = 1 orientifold compactifications Thomas W. Grimm University of Wisconsin, Madison based on: [hep-th/0602241] Iman Benmachiche, TWG [hep-th/0507153] TWG Madison, Wisconsin, November 2006
Coordinate/Field Duality in Gauge Theories: Emergence of Matrix Coordinates
 Coordinate/Field Duality in Gauge Theories: Emergence of Matrix Coordinates Amir H. Fatollahi Department of Physics, Alzahra University, P. O. Box 19938, Tehran 91167, Iran fath@alzahra.ac.ir Abstract
Coordinate/Field Duality in Gauge Theories: Emergence of Matrix Coordinates Amir H. Fatollahi Department of Physics, Alzahra University, P. O. Box 19938, Tehran 91167, Iran fath@alzahra.ac.ir Abstract
arxiv: v2 [gr-qc] 7 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v2 [gr-qc] 7 Jan 2019 arxiv: v2 [gr-qc] 7 Jan 2019](/thumbs/88/115362000.jpg) Classical Double Copy: Kerr-Schild-Kundt metrics from Yang-Mills Theory arxiv:1810.03411v2 [gr-qc] 7 Jan 2019 Metin Gürses 1, and Bayram Tekin 2, 1 Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Sciences Bilkent
Classical Double Copy: Kerr-Schild-Kundt metrics from Yang-Mills Theory arxiv:1810.03411v2 [gr-qc] 7 Jan 2019 Metin Gürses 1, and Bayram Tekin 2, 1 Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Sciences Bilkent
e θ 1 4 [σ 1,σ 2 ] = e i θ 2 σ 3
![e θ 1 4 [σ 1,σ 2 ] = e i θ 2 σ 3 e θ 1 4 [σ 1,σ 2 ] = e i θ 2 σ 3](/thumbs/75/72742606.jpg) Fermions Consider the string world sheet. We have bosons X µ (σ,τ) on this world sheet. We will now also put ψ µ (σ,τ) on the world sheet. These fermions are spin objects on the worldsheet. In higher dimensions,
Fermions Consider the string world sheet. We have bosons X µ (σ,τ) on this world sheet. We will now also put ψ µ (σ,τ) on the world sheet. These fermions are spin objects on the worldsheet. In higher dimensions,
MSci EXAMINATION. Date: XX th May, Time: 14:30-17:00
 MSci EXAMINATION PHY-415 (MSci 4242 Relativistic Waves and Quantum Fields Time Allowed: 2 hours 30 minutes Date: XX th May, 2010 Time: 14:30-17:00 Instructions: Answer THREE QUESTIONS only. Each question
MSci EXAMINATION PHY-415 (MSci 4242 Relativistic Waves and Quantum Fields Time Allowed: 2 hours 30 minutes Date: XX th May, 2010 Time: 14:30-17:00 Instructions: Answer THREE QUESTIONS only. Each question
Complex entangled states of quantum matter, not adiabatically connected to independent particle states. Compressible quantum matter
 Complex entangled states of quantum matter, not adiabatically connected to independent particle states Gapped quantum matter Z2 Spin liquids, quantum Hall states Conformal quantum matter Graphene, ultracold
Complex entangled states of quantum matter, not adiabatically connected to independent particle states Gapped quantum matter Z2 Spin liquids, quantum Hall states Conformal quantum matter Graphene, ultracold
Higher-Spin Fermionic Gauge Fields & Their Electromagnetic Coupling
 Higher-Spin Fermionic Gauge Fields & Their Electromagnetic Coupling Rakibur Rahman Université Libre de Bruxelles, Belgium April 18, 2012 ESI Workshop on Higher Spin Gravity Erwin Schrödinger Institute,
Higher-Spin Fermionic Gauge Fields & Their Electromagnetic Coupling Rakibur Rahman Université Libre de Bruxelles, Belgium April 18, 2012 ESI Workshop on Higher Spin Gravity Erwin Schrödinger Institute,
The dynamical Casimir effect in braneworlds. DURRER, Ruth, RUSER, Marcus. Abstract
 Article The dynamical Casimir effect in braneworlds DURRER, Ruth, RUSER, Marcus Abstract In braneworld cosmology the expanding Universe is realized as a brane moving through a warped higher-dimensional
Article The dynamical Casimir effect in braneworlds DURRER, Ruth, RUSER, Marcus Abstract In braneworld cosmology the expanding Universe is realized as a brane moving through a warped higher-dimensional
Warped Models in String Theory
 Warped Models in String Theory SISSA/ISAS Trieste (Italy) Rutgers 14 November 2006 (Work in collaboration with B.S.Acharya and F.Benini) Appearing soon Introduction 5D Models 5D warped models in a slice
Warped Models in String Theory SISSA/ISAS Trieste (Italy) Rutgers 14 November 2006 (Work in collaboration with B.S.Acharya and F.Benini) Appearing soon Introduction 5D Models 5D warped models in a slice
arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 22 Jul 2015
![arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 22 Jul 2015 arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 22 Jul 2015](/thumbs/72/66365292.jpg) Spinor Field with Polynomial Nonlinearity in LRS Bianchi type-i spacetime Bijan Saha arxiv:1507.06236v1 [gr-qc] 22 Jul 2015 Laboratory of Information Technologies Joint Institute for Nuclear Research 141980
Spinor Field with Polynomial Nonlinearity in LRS Bianchi type-i spacetime Bijan Saha arxiv:1507.06236v1 [gr-qc] 22 Jul 2015 Laboratory of Information Technologies Joint Institute for Nuclear Research 141980
Yet Another Alternative to Compactification by Heterotic Five-branes
 The University of Tokyo, Hongo: October 26, 2009 Yet Another Alternative to Compactification by Heterotic Five-branes arxiv: 0905.285 [hep-th] Tetsuji KIMURA (KEK) Shun ya Mizoguchi (KEK, SOKENDAI) Introduction
The University of Tokyo, Hongo: October 26, 2009 Yet Another Alternative to Compactification by Heterotic Five-branes arxiv: 0905.285 [hep-th] Tetsuji KIMURA (KEK) Shun ya Mizoguchi (KEK, SOKENDAI) Introduction
Beyond the standard model? From last time. What does the SM say? Grand Unified Theories. Unifications: now and the future
 From last time Quantum field theory is a relativistic quantum theory of fields and interactions. Fermions make up matter, and bosons mediate the forces by particle exchange. Lots of particles, lots of
From last time Quantum field theory is a relativistic quantum theory of fields and interactions. Fermions make up matter, and bosons mediate the forces by particle exchange. Lots of particles, lots of
7 Quantized Free Dirac Fields
 7 Quantized Free Dirac Fields 7.1 The Dirac Equation and Quantum Field Theory The Dirac equation is a relativistic wave equation which describes the quantum dynamics of spinors. We will see in this section
7 Quantized Free Dirac Fields 7.1 The Dirac Equation and Quantum Field Theory The Dirac equation is a relativistic wave equation which describes the quantum dynamics of spinors. We will see in this section
arxiv:hep-th/ v1 31 Jan 2006
 hep-th/61228 arxiv:hep-th/61228v1 31 Jan 26 BTZ Black Hole with Chern-Simons and Higher Derivative Terms Bindusar Sahoo and Ashoke Sen Harish-Chandra Research Institute Chhatnag Road, Jhusi, Allahabad
hep-th/61228 arxiv:hep-th/61228v1 31 Jan 26 BTZ Black Hole with Chern-Simons and Higher Derivative Terms Bindusar Sahoo and Ashoke Sen Harish-Chandra Research Institute Chhatnag Road, Jhusi, Allahabad
Extra-dimensional models on the lattice and the Layer Phase. Petros Dimopoulos
 Extra-dimensional models on the lattice and the Layer Phase Petros Dimopoulos Frascati, 7/6/008 OUTLINE Introductory hints on the extra dimensional theories Models with extra dimension on the lattice;
Extra-dimensional models on the lattice and the Layer Phase Petros Dimopoulos Frascati, 7/6/008 OUTLINE Introductory hints on the extra dimensional theories Models with extra dimension on the lattice;
SISSA entrance examination (2007)
 SISSA Entrance Examination Theory of Elementary Particles Trieste, 18 July 2007 Four problems are given. You are expected to solve completely two of them. Please, do not try to solve more than two problems;
SISSA Entrance Examination Theory of Elementary Particles Trieste, 18 July 2007 Four problems are given. You are expected to solve completely two of them. Please, do not try to solve more than two problems;
