HOM calculations of new RF cavities for a super B-factory *
|
|
|
- James Knight
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SAC PUB 79 Octoe 4 HOM calculation of new RF cavitie fo a upe B-factoy * A. ovokhatki Stanfod inea Acceleato Cente, Stanfod Univeity, Stanfod, Califonia 9439 Atact High aveage HOM powe geneated y eam in a vacuum chame of electon-poiton collide can limit achievement of high cuent. It i of geat concen fo futue upe B-factoie of vey high luminoity, otained fom high eam cuent and hot unch length. We can minimize the HOM powe y chooing the ight RF cavity hape. Hee we peent eult of compute pectum analye of diffeent kind of cavitie, which ae aleady ued o can e ued in B-factoie. Talk peented at the Supe B Factoy Wokhop in Hawaii Honolulu, Hawaii, USA Januay 9 Januay, 4 * Wok uppoted y Depatment of Enegy contact DE AC 76SF55.
2 Supe B Factoy Wokhop in Hawaii. Januay 9-, 4, Honolulu HOM calculation of new RF cavitie fo a upe B-factoy A. ovokhatki SAC, Stanfod, CA 945, USA High aveage HOM powe geneated y eam in a vacuum chame of electon-poiton collide can limit achievement of high cuent. It i of geat concen fo futue upe B-factoie of vey high luminoity, otained fom high eam cuent and hot unch length. We can minimize the HOM powe y chooing the ight RF cavity hape of. Hee we peent eult of compute pectum analye of diffeent kind of cavitie, which ae aleady ued o can e ued in B-factoie.. ITRODUCTIO In ecent time, a tong inteet ha developed in exploing the paamete egime ove which electonpoiton factoie may ultimately poduce high 36 cm - ec - luminoity[-]. Electon and poiton eam aveage cuent of ten of ampee ae needed to achieve thi luminoity. Additionally unch length of eam mut e vey hot, of the ode of eveal millimete. To compenate enegy lo due to ynchoton adiation, RF powe of ten megawatt i needed. The aveaged powe of wake field geneated in a vacuum chame can each utantial value, a it cale quadatically with cuent and invee with unch length. A thi powe come fom the eam kinetic enegy it mut e compenated y additional RF powe. It i of geat concen fo futue upe B-factoie of vey high luminoity, otained fom high eam cuent and hot unch length. Main pat of wake field come fom RF cavitie. We can minimize thee field y chooing the ight cavity hape. Hee we peent eult of compute pectum analye of diffeent kind of cavitie, which ae aleady ued o can e ued in the toage ing of electon poiton factoie.. WAKE FIEDS I RF CAVITIES Inteaction of electomagnetic field of a chaged unch with a vacuum chame lead to excitation of additional field. We call thee field wake field. Thee ae two main ouce of wake field. They can e geneated due to finite conductivity and uface oughne of the mateial of a vacuum chame. In pinciple thi pat can e educed y chooing high conductivity mateial, high quality uface tooling o inceaing tanvee dimenion of vacuum chame. Anothe ouce i geometical dicontinuitie of vacuum chame. We can make a vey mooth vacuum chame, ut we can not avoid uing RF cavitie which ecome the main non homogeneity in the mooth ing. Beam geneate electomagnetic field in a cavity. Some pat of thee field tay in a cavity in the fom of the main RF mode and ome High Ode Mode (HOM. Thi HOM ae uually called HOM ellow cut-off fequency. In a time othe pat of the wake field leave a cavity and popagate in the vacuum chame. Thee field ae called HOM aove cut-off fequency. Vey high fequency pat of the wake field tavel togethe with unche fo vey long time. The powe of the excited main mode effectively detemine the powe which eam take out fom the cavity. The HOM powe i diipated in the wall of the cavity o vacuum chame and aoe a Joule loe. Fig. how a naphot of electic foce line of wake field, excited in the PEP-II empty cavity y a ingle unch. At thi moment a unch i coing the ight exit of the cavity. Figue : Wake field electic foce line (geen and lue line in the PEP-II cavity at the time when a hot unch i leaving the cavity. Bunch denity i peented y a ed line. Bunch length i.8 mm... Geen wake function and wake potential The powe of the wake field i natually the ame powe that eam loe. To calculate the eam powe loe we need to find electomagnetic field along the tajectoy of the eam. When we know electomagnetic field, then we can calculate the integal of electic longitudinal component along the unch tajectoy. Thi integal i called wake potential W ( τ : W( τ Ez( t, z z c( t τ dt Vaiale τ define time inteval etween paticle in a eam. Sometime we will alo ue ditance etween paticle cτ, a they tavel with a peed of light c. Wake field and wake potential can e calculated in the time domain y integating Maxwell equation. Wake potential of a point chage i a Geen functiong(τ
3 Supe B Factoy Wokhop in Hawaii. Januay 9-, 4, Honolulu which can e ued fo calculation of the field of unche of any chage line ditiution ρ( τ τ ρ( ω ρ( τexp( iωτ dτ W( τ ρ( τ G( τ τ dτ ρ( τ τ G( τ dτ Fo a ingle unch with the Gauian chage denity and m unch length σ and total chage Q the Becaue of the difficultie of Geen function calculation, Fouie tanfom i the wake potential of a hot unch i ued a an σ appoximation fo the Geen function. We ue code ( ω c ρω ( Qe OVO [3] which give the et eult [4] fo the wake field, geneated y a vey hot ulta elativitic Fequency pectum of the wake potential of 4 mm unch in an axially ymmetic, pefectly conducting, unch in the PEP-II cavity i hown in Fig. 3. Thi vacuum chame pipe. Wake potential of 4 mm unch in pectum i calculated fom the wake potential of 5 the PEP-II cavity i hown in Fig.. Bunch ha the mm length. Gauian chage ditiution. Figue : Wake potential of 4 mm unch in PEP-II cavity. Beam enegy lo k i calculated y k W( τ ρτ ( dτ Fo a ingle unch lo facto i uually nomalized to a unch chage and meaued in V/pC... ongitudinal impedance and fequency pectum of wake potential The Fouie tanfom of Geen function give longitudinal coupling impedance Z( ω Z( ω G( τexp( iωτ dτ The Fouie tanfom of the wake potential W( ω W( τexp( iωτ dτ ρτ ( τ G( τ dτ exp( iωτ dτ ρ( ω G( τ exp( iωτ dτ ρ( ω Z( ω give the poduct of impedance Z( ω and Fouie tanfom of unch chage denity ρ ( ω Figue 3: Real (lue line and imaginay (pink line pat of wake field potential of 4 mm unch in the PEP-II cavity. Dotted line how cut-off fequency. A can e een the pectum ha hap peak in low fequency ange and ha oad-and peak in high fequency ange. Thi ehavio eflect the fact that low fequency mode ae tapped y the cavity and ocillate in the cavity. In eality the width of thee mode ae detemined y the loaded quality facto of a cavity Q due to wall conductivity and coupling with a tanmiion line and HOM load. In ou calculation we aume pefect conductivity of the cavity wall, o the width of thee mode i detemined y the time inteval of the wake potential. In the high fequency ange the mode afte eveal ocillation leak out of the cavity and popagate in the eam pipe. In pinciple the pectum fom a continuum in high fequency ange; howeve tapped mode can e thee too. We can aume that the fequency which epaate diffeent pectum ehavio i the cut-off fequency..3. Cut-off fequency Cut-off fequency i the maximum fequency of a captued mode in a cavity. It i detemined y the ize of a eam pipe. Thee can e eveal cut-off fequencie fo TM and TE mode. We conide the cae of longitudinal electic field o TM mode. Fo a ound pipe of adiu a the minimum cut-off fequency i fo TM mode
4 f cut off [ GHz] Supe B Factoy Wokhop in Hawaii. Januay 9-, 4, Honolulu 3 c a ν π.474 a Fig. 4 alo how intinic impedance (R/Q of tapped [ m] In the fomula we ued the fit zeo of the Beel functionν.448. Cut-off fequency i hown y a dotted line in Fig. 3. mode y pink cicle, which i calculated ove tep K of lo integal accoding to the fomula R/ Q k ω.4. Fequency pectum of enegy lo The fequency pectum of enegy lo will give u infomation aout how much enegy a unch loe fo mode ellow o aove cut-off fequency. Uing invee Fouie tanfom we can peent lo facto k in the following fom k W ( ω ρ( ω π ρω ( Z( ω π o facto i a pue eal function ecaue of the popetie of impedance function, whoe eal pat i ymmetic with fequency and imaginay pat i antiymmetic. et u intoduce fequency lo integal K( ω a π ρ ( ω Re{ Z( ω} ω ( K( ω Re{ W( ω ρ( ω } π Index mean wake potential of a ingle unch. In thi definition total integation give lo facto: K ( k. Fequency lo integal fo the PEP-II cavity i hown in Fig. 4 y a ed line. Tapped mode make tep in lo integal. o facto fo 4 mm unch i.85 V/pC. In fequency inteval up to 6 GHz enegy lo achieve 75% of it value. Enegy lo aove cut-off fequency i.389 V/pC o 48%. Figue 4: Spectum, lo integal and intinic impedance fo the PEP-II cavity..5. Powe lo of a tain of unche Analytical eult peented in thi and following chapte ae in ageement with eult aleady achieved y othe autho [5]. Becaue of upepoition of electomagnetic field, the total field i a linea um of field of each chage. If we have a tain of equal unche paced in time yt, then wake potential fo the -th unch i um of wake potential of peviou unche W ( τ W ( mt + τ m The wake potential um fo a tain with unch pacing equal to RF wavelength i hown in Fig. 5. Figue 5: Wake potential fo a tain of unche, paced y RF wavelength. It can e een that wake field i gowing with nume of unche, taking the hape of the main RF cavity mode with ome high fequency ocillation. We can ue equation ( to deive fomula fo the eam powe lo. Enegy lo of the th unche i Powe lo π Fo equal k ρ ( ω Re{ Z( ω} π P + can e defined a P + T ρ ( ω ρ ( ω T k k Re{ Z( ω} unche line chage denity i ρ ( t ρ ( t mt m
5 Supe B Factoy Wokhop in Hawaii. Januay 9-, 4, Honolulu 4 It Fouie tanfom i.7. Powe lo aove cut-off fequency ρ( ω ρ( ω exp( imωt m The pectum hee i a moe o le mooth function of fequency and we can change the eie peentation exp( iωt ρ( ω ack to the integal exp( iωt Then powe lo i P ρ ( ωm Re{ Z( ωm} m T in ωt ( + ρ( ω P Re{ Z( ω} ρ( ωm Re{ Z( ωm} ωt in πt πt ωcut off Finally, the eam powe lo aove cut-off fequency Fo a long tain of unche, left function unde integal take the fom goe to an infinite um of δ -function P Ieam T ( k K( ωcut off Ieam Rlo in ωt ( + et u call lim δ ( ω ωm ωt Rlo T ( k K ( ωcut off π in T m a lo impedance. π ω m m T and powe i P ( ( Re{ ( } m Z d T m δ ω ω ρ ω ω ω Afte integation we get well-known eult P ( Re{ Z ( } m m m T ρ ω ω We can analyze thi fomula fo fequency egion elow cut-off fequency and aove..6. Powe lo elow cut-off fequency Fo tapped mode impedance can e decied a y naow-and eonance of fequencyω, loaded quality facto Q ω and intinic impedance ω Z R / Q ω ω Q Z( ω Z ω ω ω + iq then powe lo fo the eam cuent Z I Q ω Q eam i T 3. CAVIES FOR SUPER B-FACTORY Fo upe B-factoy we need cavitie with vey mall lo impedance. We can ty to change the hape of exiting cavitie o the RF fequency too, in ode to deceae impedance. Seveal hape of a cavity ae peented elow. 3.. PEP-II type cavitie The hape of the PEP-II cavity i hown in Fig.. Fit modification can e lage apetue of the eam pipe fo the ame RF fequency. The hape of a cavity with a doule ize eam pipe i hown in Fig. 6 and it pectum i hown in Fig. 7. Figue 6: PEP cavity with doule eam pipe. ( ω m c eam ( m ω ω ω ( m ω Thee i only one HOM mode elow cut-off fequency. + Q Thi mode can e effectively damped y an appopiate ω load. The lo impedance i two time malle than PEP- Q y II cavity, R / Q of the main mode i alo le, ut only P I e σ ω ω The way to diminih powe lo i to deceae applying HOM load and pope detuning of tapped mode. y 35%.
6 Supe B Factoy Wokhop in Hawaii. Januay 9-, 4, Honolulu 5 Figue 7: Spectum of a cavity peented in Fig.6. Anothe poiility i to inceae RF fequency two time keeping the ame eam pipe ize. The hape of uch a cavity and it pectum i hown in Fig.8 and Fig.9. Figue : Optimized hape of the cavity. 3.. Single-mode cavity If we have only one mode (main elow cut-off and thi mode i an acceleating mode with intinic impedance R/Q then powe lo i ω R P Ieam T ( k (4 Q Supeconducting cavitie of Conell CESR-III and KEKB ae ingle-mode cavitie. Cavity hape and wake field of a hot unch in the CESR-III type cavity [8-9] i hown in Fig.. Figue 8: 95 MHz cavity. Figue : Electic foce line of a hot unch in CESR- III type cavity. Figue 9: Spectum of a cavity which i hown in Fig.8. o impedance of thi cavity i 3.4 time malle than impedance of PEP-II cavity fo a unch of.8mm length. R/Q of the cavity i 66 Ohm. Optimization of the cavity hape (Fig. impove R/Q a little. Thi cavity ha R/Q78 Ohm and 8% le lo impedance. Figue : Wake potential of 4 mm unch in the Conell CESR-III-type cavity.
7 Supe B Factoy Wokhop in Hawaii. Januay 9-, 4, Honolulu 6 Wake potential of a unch of 4 mm length i hown in Fig.. o integal and intinic impendence fo thi cavity ae hown in Fig. 3. Figue 3: Spectum, lo integal and intinic impedance fo Conell CESR III type cavity. Bunch length i 4 mm. KEKB cavity ha a little it diffeent hape []. o integal fo thi cavity i hown in Fig. 4. In thi example the unch length i.8 mm. Figue 6: Spectum fo the KEKB upeconductive cavity with tape. Bunch length i.8 mm. One moe example of a ingle-mode cavity and it pectum ae hown in Fig7 and Fig.8. Thi cavity ha R/Q3 Ohm and the mallet lo impedance of Ohm fo.8 mm unch. Figue 7: Single-mode cavity. Figue 4: Spectum, lo integal and intinic impedance fo KEKB type cavity. Bunch length i.8 mm. Cavitie with lage eam pipe uually have tape. Unfotunately, thee tape change wake potential damatically. Fig. 5 how pictue of electic foce line of wake field jut at the moment when unch i in the ight tape. Spectum fo thi cae i hown in Fig. 6 Figue 8: Spectum of a ingle-mode cavity. Bunch length i.8 mm. Figue 5: Electic foce line of the wake field in KEKB upeconductive cavity. At thi moment unch i in the cone of the ight tape. An additional advantage of the ingle mode cavity ytem which ha an automatically low R/Q, i that it i tonge againt the coupled-unch intaility [8]: it need le fequency detuning f I R/ Q inφ f V RF c
8 Supe B Factoy Wokhop in Hawaii. Januay 9-, 4, Honolulu 7 whee V the voltage pe cavity and φ the ynchonou phae. Alo a HOM damping ytem i le complicated fo a ingle mode cavity. Futue plan include moe numeical tudie of the polem, finding optimum hape of the cavity Shot unche Fo hot unche the lo facto can e etimated y the following expeion [6] : Zc g k π a σ whee g i the ize of cavity gap, a i the adiu of the eam pipe, Z π i impedance of fee pace. o facto goe up with deceaing unch length and ecome the main paamete fo the powe lo d g P Ieam T k Ieam Z π a σ Whee we intoduced he d T a the ditanced etween unche Minimum powe lo The minimum ditance etween unche i the RF wavelength. The adiu of the eam pipe i limited λ RF y the main mode and can not e moe than λ RF /. The cavity gap i appoximately half of the wave length, o the minimum powe lo i detemined y the atio of the RF wavelength and unch length λrf P Ieam Z π σ The coeponding minimum lo impedance i λrf Rlo Z π σ Thi minimum impedance i hown in Fig. 9 togethe with calculated impedance fo diffeent cavitie. It i inteeting to note that ingle-mode cavity (PEP-II SC, peented in Fig. 7 ha malle lo impedance, ut thi i ecaue of malle gap ize ( g << λ RF / of the cavity. 4. COCUSIOS High aveage cuent, hot unch length eam needed fo Supe B-factoie can give ie to lage amount of HOM powe, a high a hunded of kw pe cavity. Thi powe mut e damped y the wate cooled aoe. Mot of the powe lot y the eam i in mode elow GHz fo mm unche. Beam in a ingle mode cavity excite le HOM powe. A ingle mode cavity need to e a upeconducting cavity, a it ha mall intinic impedance R/Q. Paamete of all peented cavitie ae compiled in the Tale. Figue 9: Minimum lo impedance (lue line and lo impedance of diffeent cavitie. c ACKOWEDGEMETS The autho wih to thank John Seeman, Michael Sullivan and Stephen Weathey fo the inteet and fuitful dicuion. Wok uppoted y Depatment of Enegy contact DE-AC3-76SF55. REFERECES [] J. Seeman et al., Deign tudie fo a 36 upe factoy, Poceeding of the PAC 3, Potland, p.3 (3. [] K. Ohmi et al., Recent development in deign fo e+e- collide, Poceeding of the PAC 3, Potland, p.345 (3. [3] A. ovokhatki, to e pulihed ometime [4] O. Meincke, A.Wagne, B.Zotte ew Wake Filed and Bunch engthening Code, S-ote-97-7 (AP, CER, Switzeland (997. [5]. Meminga et al., Specifying HOM-powe extaction efficiency in a high aveage cuent, hot unch length SRF envionment, Poceeding of the XX Intenational inac Confeence, Monteey, p.86 (. [6 A. ovokhatki On the etimation of the wake potential fo the ulta elativitic chage in an acceleating tuctue, Pepint IP 88-39, Intitute of uclea Phyic, ovoiik (988. [7] B.Zotte and S.Kheifet Impedance and Wake in High-Enegy Paticle Acceleato, Wold Scientific, Singapoe, 998. [8] A.Chao, M.Tigne, Hand ook of Acceleato Phyic and Engineeing, Wold Scientific, p.537 (998. [9] S. Belometnykh, On the BB Cyomodule o Facto Calculation, Conell note SRF , Ithaca (999. [] KEKB B-factoy deign epot, KEK Repot 95-7 (995.
9 Supe B Factoy Wokhop in Hawaii. Januay 9-, 4, Honolulu 8 Tale : Cavitie paamete HOM Powe o in the Supe B-factoy Cavity f36khz h349 Cavity Fequency Pipe R/Q Bunch Total Aove Beam Bunch Wake HOM type adiu length o cut-off cuent chage Voltage Powe [MHz] [mm] [Ohm] [mm] [V/pC] [V/pC] [A] [nc] [kv] [kw] PEP-II CESR-III PEP-II CESR-III KEKB-SC with tape 75 KEKB-SC-T no tape PEP-II-age PEP-II CESR-III KEKB-SC-T PEP-II-age PEP-II-age ew PEP-II ew PEP-II PEP-Ellip PEP-SC
Chapter 19 Webassign Help Problems
 Chapte 9 Webaign Help Poblem 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Poblem 4: The pictue fo thi poblem i a bit mileading. They eally jut give you the pictue fo Pat b. So let fix that. Hee i the pictue fo Pat (a): Pat (a) imply
Chapte 9 Webaign Help Poblem 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Poblem 4: The pictue fo thi poblem i a bit mileading. They eally jut give you the pictue fo Pat b. So let fix that. Hee i the pictue fo Pat (a): Pat (a) imply
TRAVELING WAVES. Chapter Simple Wave Motion. Waves in which the disturbance is parallel to the direction of propagation are called the
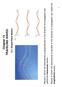 Chapte 15 RAVELING WAVES 15.1 Simple Wave Motion Wave in which the ditubance i pependicula to the diection of popagation ae called the tanvee wave. Wave in which the ditubance i paallel to the diection
Chapte 15 RAVELING WAVES 15.1 Simple Wave Motion Wave in which the ditubance i pependicula to the diection of popagation ae called the tanvee wave. Wave in which the ditubance i paallel to the diection
Simulation of Spatially Correlated Large-Scale Parameters and Obtaining Model Parameters from Measurements
 Simulation of Spatially Coelated Lage-Scale Paamete and Obtaining Model Paamete fom PER ZETTERBERG Stockholm Septembe 8 TRITA EE 8:49 Simulation of Spatially Coelated Lage-Scale Paamete and Obtaining Model
Simulation of Spatially Coelated Lage-Scale Paamete and Obtaining Model Paamete fom PER ZETTERBERG Stockholm Septembe 8 TRITA EE 8:49 Simulation of Spatially Coelated Lage-Scale Paamete and Obtaining Model
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University. ECE 303: Electromagnetic Fields and Waves. Fall 2007
 School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 303: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 007 Homewok 8 Due on Oct. 19, 007 by 5:00 PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes.
School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 303: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 007 Homewok 8 Due on Oct. 19, 007 by 5:00 PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes.
ASTR 3740 Relativity & Cosmology Spring Answers to Problem Set 4.
 ASTR 3740 Relativity & Comology Sping 019. Anwe to Poblem Set 4. 1. Tajectoie of paticle in the Schwazchild geomety The equation of motion fo a maive paticle feely falling in the Schwazchild geomety ae
ASTR 3740 Relativity & Comology Sping 019. Anwe to Poblem Set 4. 1. Tajectoie of paticle in the Schwazchild geomety The equation of motion fo a maive paticle feely falling in the Schwazchild geomety ae
RIGID-ROTOR VLASOV EQUILIBRIUM FOR AN INTENSE CHARGED-PARTICLE BEAM PROPAGATING THROUGH A PERIODIC SOLENOIDAL MAGNETIC FIELD
 RIGID-ROTOR VLASOV EQUILIBRIUM FOR AN INTENSE CHARGED-PARTICLE BEAM PROPAGATING THROUGH A PERIODIC SOLENOIDAL MAGNETIC FIELD Chiping Chen and Renato Pakte Plama Science and Fuion Cente Maachuett Intitute
RIGID-ROTOR VLASOV EQUILIBRIUM FOR AN INTENSE CHARGED-PARTICLE BEAM PROPAGATING THROUGH A PERIODIC SOLENOIDAL MAGNETIC FIELD Chiping Chen and Renato Pakte Plama Science and Fuion Cente Maachuett Intitute
Static Electric Fields. Coulomb s Law Ε = 4πε. Gauss s Law. Electric Potential. Electrical Properties of Materials. Dielectrics. Capacitance E.
 Coulomb Law Ε Gau Law Electic Potential E Electical Popetie of Mateial Conducto J σe ielectic Capacitance Rˆ V q 4πε R ρ v 2 Static Electic Field εe E.1 Intoduction Example: Electic field due to a chage
Coulomb Law Ε Gau Law Electic Potential E Electical Popetie of Mateial Conducto J σe ielectic Capacitance Rˆ V q 4πε R ρ v 2 Static Electic Field εe E.1 Intoduction Example: Electic field due to a chage
11) A thin, uniform rod of mass M is supported by two vertical strings, as shown below.
 Fall 2007 Qualifie Pat II 12 minute questions 11) A thin, unifom od of mass M is suppoted by two vetical stings, as shown below. Find the tension in the emaining sting immediately afte one of the stings
Fall 2007 Qualifie Pat II 12 minute questions 11) A thin, unifom od of mass M is suppoted by two vetical stings, as shown below. Find the tension in the emaining sting immediately afte one of the stings
A new force Magnetic force. Today. Force Fields: A disturbance of space. The correspondence of a loop of current and magnet.
 Today A new foce Magnetic foce Announcements HW#6 and HW#7 ae both due Wednesday Mach 18th. Thanks to my being WAY behind schedule, you 2nd exam will be a take-home exam! Stay tuned fo details Even if
Today A new foce Magnetic foce Announcements HW#6 and HW#7 ae both due Wednesday Mach 18th. Thanks to my being WAY behind schedule, you 2nd exam will be a take-home exam! Stay tuned fo details Even if
Gravity. David Barwacz 7778 Thornapple Bayou SE, Grand Rapids, MI David Barwacz 12/03/2003
 avity David Bawacz 7778 Thonapple Bayou, and Rapid, MI 495 David Bawacz /3/3 http://membe.titon.net/daveb Uing the concept dicued in the peceding pape ( http://membe.titon.net/daveb ), I will now deive
avity David Bawacz 7778 Thonapple Bayou, and Rapid, MI 495 David Bawacz /3/3 http://membe.titon.net/daveb Uing the concept dicued in the peceding pape ( http://membe.titon.net/daveb ), I will now deive
LECTURE 14. m 1 m 2 b) Based on the second law of Newton Figure 1 similarly F21 m2 c) Based on the third law of Newton F 12
 CTU 4 ] NWTON W O GVITY -The gavity law i foulated fo two point paticle with ae and at a ditance between the. Hee ae the fou tep that bing to univeal law of gavitation dicoveed by NWTON. a Baed on expeiental
CTU 4 ] NWTON W O GVITY -The gavity law i foulated fo two point paticle with ae and at a ditance between the. Hee ae the fou tep that bing to univeal law of gavitation dicoveed by NWTON. a Baed on expeiental
Theory. Single Soil Layer. ProShake User s Manual
 PoShake Ue Manual Theoy PoShake ue a fequency domain appoach to olve the gound epone poblem. In imple tem, the input motion i epeented a the um of a eie of ine wave of diffeent amplitude, fequencie, and
PoShake Ue Manual Theoy PoShake ue a fequency domain appoach to olve the gound epone poblem. In imple tem, the input motion i epeented a the um of a eie of ine wave of diffeent amplitude, fequencie, and
Impulse and Momentum
 Impule and Momentum 1. A ca poee 20,000 unit of momentum. What would be the ca' new momentum if... A. it elocity wee doubled. B. it elocity wee tipled. C. it ma wee doubled (by adding moe paenge and a
Impule and Momentum 1. A ca poee 20,000 unit of momentum. What would be the ca' new momentum if... A. it elocity wee doubled. B. it elocity wee tipled. C. it ma wee doubled (by adding moe paenge and a
Rotational Kinetic Energy
 Add Impotant Rotational Kinetic Enegy Page: 353 NGSS Standad: N/A Rotational Kinetic Enegy MA Cuiculum Famewok (006):.1,.,.3 AP Phyic 1 Leaning Objective: N/A, but olling poblem have appeaed on peviou
Add Impotant Rotational Kinetic Enegy Page: 353 NGSS Standad: N/A Rotational Kinetic Enegy MA Cuiculum Famewok (006):.1,.,.3 AP Phyic 1 Leaning Objective: N/A, but olling poblem have appeaed on peviou
Introduction to Accelerator Physics
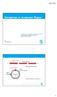 Intoduction to Acceleato Physics Pat 3 Pedo Casto / Acceleato Physics Goup (MPY) Intoduction to Acceleato Physics DSY, 5th July 017 acceleating devices vacuum chambe injecto acceleating device staight
Intoduction to Acceleato Physics Pat 3 Pedo Casto / Acceleato Physics Goup (MPY) Intoduction to Acceleato Physics DSY, 5th July 017 acceleating devices vacuum chambe injecto acceleating device staight
On a proper definition of spin current
 On a pope definition of pin cuent Qian Niu Univeity of Texa at Autin P. Zhang, Shi, Xiao, and Niu (cond-mat 0503505) P. Zhang and Niu (cond-mat/0406436) Culce, Sinova, Sintyn, Jungwith, MacDonald, and
On a pope definition of pin cuent Qian Niu Univeity of Texa at Autin P. Zhang, Shi, Xiao, and Niu (cond-mat 0503505) P. Zhang and Niu (cond-mat/0406436) Culce, Sinova, Sintyn, Jungwith, MacDonald, and
Lecture No. 6 (Waves) The Doppler Effect
 Lectue No. 6 (Wave) The Dopple Eect 1) A ound ouce i moving at 80 m/ towad a tationay litene that i tanding in till ai. (a) Find the wavelength o the ound in the egion between the ouce and the litene.
Lectue No. 6 (Wave) The Dopple Eect 1) A ound ouce i moving at 80 m/ towad a tationay litene that i tanding in till ai. (a) Find the wavelength o the ound in the egion between the ouce and the litene.
Solutions Practice Test PHYS 211 Exam 2
 Solution Pactice Tet PHYS 11 Exam 1A We can plit thi poblem up into two pat, each one dealing with a epaate axi. Fo both the x- and y- axe, we have two foce (one given, one unknown) and we get the following
Solution Pactice Tet PHYS 11 Exam 1A We can plit thi poblem up into two pat, each one dealing with a epaate axi. Fo both the x- and y- axe, we have two foce (one given, one unknown) and we get the following
Precision Spectrophotometry
 Peciion Spectophotomety Pupoe The pinciple of peciion pectophotomety ae illutated in thi expeiment by the detemination of chomium (III). ppaatu Spectophotomete (B&L Spec 20 D) Cuvette (minimum 2) Pipet:
Peciion Spectophotomety Pupoe The pinciple of peciion pectophotomety ae illutated in thi expeiment by the detemination of chomium (III). ppaatu Spectophotomete (B&L Spec 20 D) Cuvette (minimum 2) Pipet:
σ = neμ = v D = E H, the Hall Field B Z E Y = ee y Determining n and μ: The Hall Effect V x, E x I, J x E y B z F = qe + qv B F y
 Detemining n and μ: The Hall Effect V x, E x + + + + + + + + + + + --------- E y I, J x F = qe + qv B F y = ev D B z F y = ee y B z In steady state, E Y = v D B Z = E H, the Hall Field Since v D =-J x
Detemining n and μ: The Hall Effect V x, E x + + + + + + + + + + + --------- E y I, J x F = qe + qv B F y = ev D B z F y = ee y B z In steady state, E Y = v D B Z = E H, the Hall Field Since v D =-J x
one primary direction in which heat transfers (generally the smallest dimension) simple model good representation for solving engineering problems
 CHAPTER 3: One-Dimenional Steady-State Conduction one pimay diection in which heat tanfe (geneally the mallet dimenion) imple model good epeentation fo olving engineeing poblem 3. Plane Wall 3.. hot fluid
CHAPTER 3: One-Dimenional Steady-State Conduction one pimay diection in which heat tanfe (geneally the mallet dimenion) imple model good epeentation fo olving engineeing poblem 3. Plane Wall 3.. hot fluid
Boise State University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE470 Electric Machines
 Boie State Univeity Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing ECE470 Electic Machine Deivation of the Pe-Phae Steady-State Equivalent Cicuit of a hee-phae Induction Machine Nomenclatue θ: oto haft
Boie State Univeity Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing ECE470 Electic Machine Deivation of the Pe-Phae Steady-State Equivalent Cicuit of a hee-phae Induction Machine Nomenclatue θ: oto haft
Lecture 2 Date:
 Lectue 2 Date: 5.1.217 Definition of Some TL Paametes Examples of Tansmission Lines Tansmission Lines (contd.) Fo a lossless tansmission line the second ode diffeential equation fo phasos ae: LC 2 d I
Lectue 2 Date: 5.1.217 Definition of Some TL Paametes Examples of Tansmission Lines Tansmission Lines (contd.) Fo a lossless tansmission line the second ode diffeential equation fo phasos ae: LC 2 d I
HW #5 Hints. Today. HW #5 Hints. HW #5 Hints. Announcements:
 Today HW #5 Hints Announcements: HW and Exta cedit #3 due 2/25 HW hints + Recap the 2nd law of themodynamics Electic and Magnetic Foces and thei unification the Foce Field concept -1-1) The speed at D
Today HW #5 Hints Announcements: HW and Exta cedit #3 due 2/25 HW hints + Recap the 2nd law of themodynamics Electic and Magnetic Foces and thei unification the Foce Field concept -1-1) The speed at D
Analytical calculation of the power dissipated in the LHC liner. Stefano De Santis - LBNL and Andrea Mostacci - CERN
 Analytical calculation of the powe dissipated in the LHC line Stefano De Santis - LBNL and Andea Mostacci - CERN Contents What is the Modified Bethe s Diffaction Theoy? Some inteesting consequences of
Analytical calculation of the powe dissipated in the LHC line Stefano De Santis - LBNL and Andea Mostacci - CERN Contents What is the Modified Bethe s Diffaction Theoy? Some inteesting consequences of
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics. Electricity & Magnetism Qualifying Examination
 E&M poblems Univesity of Illinois at Chicago Depatment of Physics Electicity & Magnetism Qualifying Examination Januay 3, 6 9. am : pm Full cedit can be achieved fom completely coect answes to 4 questions.
E&M poblems Univesity of Illinois at Chicago Depatment of Physics Electicity & Magnetism Qualifying Examination Januay 3, 6 9. am : pm Full cedit can be achieved fom completely coect answes to 4 questions.
3. Electromagnetic Waves II
 Lectue 3 - Electomagnetic Waves II 9 3. Electomagnetic Waves II Last time, we discussed the following. 1. The popagation of an EM wave though a macoscopic media: We discussed how the wave inteacts with
Lectue 3 - Electomagnetic Waves II 9 3. Electomagnetic Waves II Last time, we discussed the following. 1. The popagation of an EM wave though a macoscopic media: We discussed how the wave inteacts with
Then the number of elements of S of weight n is exactly the number of compositions of n into k parts.
 Geneating Function In a geneal combinatoial poblem, we have a univee S of object, and we want to count the numbe of object with a cetain popety. Fo example, if S i the et of all gaph, we might want to
Geneating Function In a geneal combinatoial poblem, we have a univee S of object, and we want to count the numbe of object with a cetain popety. Fo example, if S i the et of all gaph, we might want to
Flux. Area Vector. Flux of Electric Field. Gauss s Law
 Gauss s Law Flux Flux in Physics is used to two distinct ways. The fist meaning is the ate of flow, such as the amount of wate flowing in a ive, i.e. volume pe unit aea pe unit time. O, fo light, it is
Gauss s Law Flux Flux in Physics is used to two distinct ways. The fist meaning is the ate of flow, such as the amount of wate flowing in a ive, i.e. volume pe unit aea pe unit time. O, fo light, it is
Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapte 32 Electomagnetic Waves PowePoint Lectues fo Univesity Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roge A. Feedman Lectues by James Pazun Modified P. Lam 8_11_2008 Topics fo Chapte 32 Maxwell s equations
Chapte 32 Electomagnetic Waves PowePoint Lectues fo Univesity Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roge A. Feedman Lectues by James Pazun Modified P. Lam 8_11_2008 Topics fo Chapte 32 Maxwell s equations
Non-Linear Dynamics Homework Solutions Week 2
 Non-Linea Dynamics Homewok Solutions Week Chis Small Mach, 7 Please email me at smach9@evegeen.edu with any questions o concens eguading these solutions. Fo the ececises fom section., we sketch all qualitatively
Non-Linea Dynamics Homewok Solutions Week Chis Small Mach, 7 Please email me at smach9@evegeen.edu with any questions o concens eguading these solutions. Fo the ececises fom section., we sketch all qualitatively
Module 9: Electromagnetic Waves-I Lecture 9: Electromagnetic Waves-I
 Module 9: Electomagnetic Waves-I Lectue 9: Electomagnetic Waves-I What is light, paticle o wave? Much of ou daily expeience with light, paticulaly the fact that light ays move in staight lines tells us
Module 9: Electomagnetic Waves-I Lectue 9: Electomagnetic Waves-I What is light, paticle o wave? Much of ou daily expeience with light, paticulaly the fact that light ays move in staight lines tells us
LECTURE 22. Collective effects in multi-particle beams: Parasitic Losses. Longitudinal impedances in accelerators (continued)
 LECTURE Collective effect in multi-particle beam: Longitudinal impedance in accelerator Tranvere impedance in accelerator Paraitic Loe /7/0 USPAS Lecture Longitudinal impedance in accelerator (continued)
LECTURE Collective effect in multi-particle beam: Longitudinal impedance in accelerator Tranvere impedance in accelerator Paraitic Loe /7/0 USPAS Lecture Longitudinal impedance in accelerator (continued)
EFFECTS OF FRINGING FIELDS ON SINGLE PARTICLE DYNAMICS. M. Bassetti and C. Biscari INFN-LNF, CP 13, Frascati (RM), Italy
 Fascati Physics Seies Vol. X (998), pp. 47-54 4 th Advanced ICFA Beam Dynamics Wokshop, Fascati, Oct. -5, 997 EFFECTS OF FRININ FIELDS ON SINLE PARTICLE DYNAMICS M. Bassetti and C. Biscai INFN-LNF, CP
Fascati Physics Seies Vol. X (998), pp. 47-54 4 th Advanced ICFA Beam Dynamics Wokshop, Fascati, Oct. -5, 997 EFFECTS OF FRININ FIELDS ON SINLE PARTICLE DYNAMICS M. Bassetti and C. Biscai INFN-LNF, CP
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University. ECE 303: Electromagnetic Fields and Waves. Fall 2007
 School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 33: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 7 Homewok 6 Due on Oct. 5, 7 by 5: PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes. ii) Review
School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 33: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 7 Homewok 6 Due on Oct. 5, 7 by 5: PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes. ii) Review
Eddy Currents in Permanent Magnets of a Multi-pole Direct Drive Motor
 Acta Technica Jauineni Vol. 6. No. 1. 2013 Eddy Cuent in Pemanent Magnet of a Multi-pole Diect Dive Moto G. Gotovac 1, G. Lampic 1, D. Miljavec 2 Elaphe Ltd. 1, Univeity of Ljubljana, Faculty of Electical
Acta Technica Jauineni Vol. 6. No. 1. 2013 Eddy Cuent in Pemanent Magnet of a Multi-pole Diect Dive Moto G. Gotovac 1, G. Lampic 1, D. Miljavec 2 Elaphe Ltd. 1, Univeity of Ljubljana, Faculty of Electical
Chapter 8 Sampling. Contents. Dr. Norrarat Wattanamongkhol. Lecturer. Department of Electrical Engineering, Engineering Faculty, sampling
 Content Chate 8 Samling Lectue D Noaat Wattanamongkhol Samling Theoem Samling of Continuou-Time Signal 3 Poceing Continuou-Time Signal 4 Samling of Dicete-Time Signal 5 Multi-ate Samling Deatment of Electical
Content Chate 8 Samling Lectue D Noaat Wattanamongkhol Samling Theoem Samling of Continuou-Time Signal 3 Poceing Continuou-Time Signal 4 Samling of Dicete-Time Signal 5 Multi-ate Samling Deatment of Electical
Force between two parallel current wires and Newton s. third law
 Foce between two paallel cuent wies and Newton s thid law Yannan Yang (Shanghai Jinjuan Infomation Science and Technology Co., Ltd.) Abstact: In this pape, the essence of the inteaction between two paallel
Foce between two paallel cuent wies and Newton s thid law Yannan Yang (Shanghai Jinjuan Infomation Science and Technology Co., Ltd.) Abstact: In this pape, the essence of the inteaction between two paallel
Transverse Wakefield in a Dielectric Tube with Frequency Dependent Dielectric Constant
 ARDB-378 Bob Siemann & Alex Chao /4/5 Page of 8 Tansvese Wakefield in a Dielectic Tube with Fequency Dependent Dielectic Constant This note is a continuation of ARDB-368 that is now extended to the tansvese
ARDB-378 Bob Siemann & Alex Chao /4/5 Page of 8 Tansvese Wakefield in a Dielectic Tube with Fequency Dependent Dielectic Constant This note is a continuation of ARDB-368 that is now extended to the tansvese
Algebra-based Physics II
 lgebabased Physics II Chapte 19 Electic potential enegy & The Electic potential Why enegy is stoed in an electic field? How to descibe an field fom enegetic point of view? Class Website: Natual way of
lgebabased Physics II Chapte 19 Electic potential enegy & The Electic potential Why enegy is stoed in an electic field? How to descibe an field fom enegetic point of view? Class Website: Natual way of
Estimation and Confidence Intervals: Additional Topics
 Chapte 8 Etimation and Confidence Inteval: Additional Topic Thi chapte imply follow the method in Chapte 7 fo foming confidence inteval The text i a bit dioganized hee o hopefully we can implify Etimation:
Chapte 8 Etimation and Confidence Inteval: Additional Topic Thi chapte imply follow the method in Chapte 7 fo foming confidence inteval The text i a bit dioganized hee o hopefully we can implify Etimation:
FI 2201 Electromagnetism
 FI Electomagnetim Aleande A. Ikanda, Ph.D. Phyic of Magnetim and Photonic Reeach Goup ecto Analyi CURILINEAR COORDINAES, DIRAC DELA FUNCION AND HEORY OF ECOR FIELDS Cuvilinea Coodinate Sytem Cateian coodinate:
FI Electomagnetim Aleande A. Ikanda, Ph.D. Phyic of Magnetim and Photonic Reeach Goup ecto Analyi CURILINEAR COORDINAES, DIRAC DELA FUNCION AND HEORY OF ECOR FIELDS Cuvilinea Coodinate Sytem Cateian coodinate:
Chapter Introduction to Finite Element Methods
 Chapte 1.4 Intoduction to Finite Element Methods Afte eading this chapte, you should e ale to: 1. Undestand the asics of finite element methods using a one-dimensional polem. In the last fifty yeas, the
Chapte 1.4 Intoduction to Finite Element Methods Afte eading this chapte, you should e ale to: 1. Undestand the asics of finite element methods using a one-dimensional polem. In the last fifty yeas, the
High precision computer simulation of cyclotrons KARAMYSHEVA T., AMIRKHANOV I. MALININ V., POPOV D.
 High pecision compute simulation of cyclotons KARAMYSHEVA T., AMIRKHANOV I. MALININ V., POPOV D. Abstact Effective and accuate compute simulations ae highly impotant in acceleatos design and poduction.
High pecision compute simulation of cyclotons KARAMYSHEVA T., AMIRKHANOV I. MALININ V., POPOV D. Abstact Effective and accuate compute simulations ae highly impotant in acceleatos design and poduction.
PY208 Matter & Interactions Final Exam S2005
 PY Matte & Inteactions Final Exam S2005 Name (pint) Please cicle you lectue section below: 003 (Ramakishnan 11:20 AM) 004 (Clake 1:30 PM) 005 (Chabay 2:35 PM) When you tun in the test, including the fomula
PY Matte & Inteactions Final Exam S2005 Name (pint) Please cicle you lectue section below: 003 (Ramakishnan 11:20 AM) 004 (Clake 1:30 PM) 005 (Chabay 2:35 PM) When you tun in the test, including the fomula
RE 7.a. RE 7.b Energy Dissipation & Resonance RE 7.c EP7, HW7: Ch 7 Pr s 31, 32, 45, 62 & CP
 Wed. Lab Fi. Mon. Tue. 7.-.4 Macocopic Enegy Quiz 6 4pm, hee Math & Phy Reeach L6 Wok and Enegy 7.5-.9 Enegy Tanfe RE 7.a RE 7.b 7.0-. Enegy Diipation & Reonance RE 7.c EP7, HW7: Ch 7 P 3, 3, 45, 6 & CP
Wed. Lab Fi. Mon. Tue. 7.-.4 Macocopic Enegy Quiz 6 4pm, hee Math & Phy Reeach L6 Wok and Enegy 7.5-.9 Enegy Tanfe RE 7.a RE 7.b 7.0-. Enegy Diipation & Reonance RE 7.c EP7, HW7: Ch 7 P 3, 3, 45, 6 & CP
Honors Classical Physics I
 Hono Claical Phyic I PHY141 Lectue 9 Newton Law of Gavity Pleae et you Clicke Channel to 1 9/15/014 Lectue 9 1 Newton Law of Gavity Gavitational attaction i the foce that act between object that have a
Hono Claical Phyic I PHY141 Lectue 9 Newton Law of Gavity Pleae et you Clicke Channel to 1 9/15/014 Lectue 9 1 Newton Law of Gavity Gavitational attaction i the foce that act between object that have a
Chapter 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements
 Chapte 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements Decembe 1, 215 1 Supplement 2.1: Centipetal Acceleation This supplement expands on a topic addessed on page 19 of the textbook. Ou task hee is to calculate
Chapte 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements Decembe 1, 215 1 Supplement 2.1: Centipetal Acceleation This supplement expands on a topic addessed on page 19 of the textbook. Ou task hee is to calculate
ECE 6340 Intermediate EM Waves. Fall Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE. Notes 4
 ECE 6340 Intemediate EM Waves Fall 016 Pof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE Notes 4 1 Debye Model This model explains molecula effects. y We conside an electic field applied in the x diection. Molecule:
ECE 6340 Intemediate EM Waves Fall 016 Pof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE Notes 4 1 Debye Model This model explains molecula effects. y We conside an electic field applied in the x diection. Molecule:
Development of Model Reduction using Stability Equation and Cauer Continued Fraction Method
 Intenational Jounal of Electical and Compute Engineeing. ISSN 0974-90 Volume 5, Numbe (03), pp. -7 Intenational Reeach Publication Houe http://www.iphoue.com Development of Model Reduction uing Stability
Intenational Jounal of Electical and Compute Engineeing. ISSN 0974-90 Volume 5, Numbe (03), pp. -7 Intenational Reeach Publication Houe http://www.iphoue.com Development of Model Reduction uing Stability
3. Perturbation of Kerr BH
 3. Petubation of Ke BH hoizon at Δ = 0 ( = ± ) Unfotunately, it i technically fomidable to deal with the metic petubation of Ke BH becaue of coupling between and θ Nevethele, thee exit a fomalim (Newman-Penoe
3. Petubation of Ke BH hoizon at Δ = 0 ( = ± ) Unfotunately, it i technically fomidable to deal with the metic petubation of Ke BH becaue of coupling between and θ Nevethele, thee exit a fomalim (Newman-Penoe
Perhaps the greatest success of his theory of gravity was to successfully explain the motion of the heavens planets, moons, &tc.
 AP Phyic Gavity Si Iaac Newton i cedited with the dicovey of gavity. Now, of coue we know that he didn t eally dicove the thing let face it, people knew about gavity fo a long a thee have been people.
AP Phyic Gavity Si Iaac Newton i cedited with the dicovey of gavity. Now, of coue we know that he didn t eally dicove the thing let face it, people knew about gavity fo a long a thee have been people.
Absorbance of Iron Nanoparticles Dispersed in the Ethylene Glycol and n-propanol
 Amenian Jounal of Phyic, 2016, vol. 9, iue 3, pp. 211-219 Abobance of Ion Nanopaticle Dipeed in the Ethylene Glycol and n-popanol R. Khodad Depatment of Phyic, College of Science, Yaouj Univeity, Ian E-mail:
Amenian Jounal of Phyic, 2016, vol. 9, iue 3, pp. 211-219 Abobance of Ion Nanopaticle Dipeed in the Ethylene Glycol and n-popanol R. Khodad Depatment of Phyic, College of Science, Yaouj Univeity, Ian E-mail:
The geometric construction of Ewald sphere and Bragg condition:
 The geometic constuction of Ewald sphee and Bagg condition: The constuction of Ewald sphee must be done such that the Bagg condition is satisfied. This can be done as follows: i) Daw a wave vecto k in
The geometic constuction of Ewald sphee and Bagg condition: The constuction of Ewald sphee must be done such that the Bagg condition is satisfied. This can be done as follows: i) Daw a wave vecto k in
V V The circumflex (^) tells us this is a unit vector
 Vecto Vecto have Diection and Magnitude Mike ailey mjb@c.oegontate.edu Magnitude: V V V V x y z vecto.pptx Vecto Can lo e Defined a the oitional Diffeence etween Two oint 3 Unit Vecto have a Magnitude
Vecto Vecto have Diection and Magnitude Mike ailey mjb@c.oegontate.edu Magnitude: V V V V x y z vecto.pptx Vecto Can lo e Defined a the oitional Diffeence etween Two oint 3 Unit Vecto have a Magnitude
Waves and Polarization in General
 Waves and Polaization in Geneal Wave means a distubance in a medium that tavels. Fo light, the medium is the electomagnetic field, which can exist in vacuum. The tavel pat defines a diection. The distubance
Waves and Polaization in Geneal Wave means a distubance in a medium that tavels. Fo light, the medium is the electomagnetic field, which can exist in vacuum. The tavel pat defines a diection. The distubance
Ch 30 - Sources of Magnetic Field! The Biot-Savart Law! = k m. r 2. Example 1! Example 2!
 Ch 30 - Souces of Magnetic Field 1.) Example 1 Detemine the magnitude and diection of the magnetic field at the point O in the diagam. (Cuent flows fom top to bottom, adius of cuvatue.) Fo staight segments,
Ch 30 - Souces of Magnetic Field 1.) Example 1 Detemine the magnitude and diection of the magnetic field at the point O in the diagam. (Cuent flows fom top to bottom, adius of cuvatue.) Fo staight segments,
The evolution of the phase space density of particle beams in external fields
 The evolution of the phase space density of paticle beams in extenal fields E.G.Bessonov Lebedev Phys. Inst. RAS, Moscow, Russia, COOL 09 Wokshop on Beam Cooling and Related Topics August 31 Septembe 4,
The evolution of the phase space density of paticle beams in extenal fields E.G.Bessonov Lebedev Phys. Inst. RAS, Moscow, Russia, COOL 09 Wokshop on Beam Cooling and Related Topics August 31 Septembe 4,
Faraday s Law. Faraday s Law. Faraday s Experiments. Faraday s Experiments. Magnetic Flux. Chapter 31. Law of Induction (emf( emf) Faraday s Law
 Faaday s Law Faaday s Epeiments Chapte 3 Law of nduction (emf( emf) Faaday s Law Magnetic Flu Lenz s Law Geneatos nduced Electic fields Michael Faaday discoeed induction in 83 Moing the magnet induces
Faaday s Law Faaday s Epeiments Chapte 3 Law of nduction (emf( emf) Faaday s Law Magnetic Flu Lenz s Law Geneatos nduced Electic fields Michael Faaday discoeed induction in 83 Moing the magnet induces
ECE 3318 Applied Electricity and Magnetism. Spring Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. Of ECE. Notes 20 Dielectrics
 ECE 3318 Applied Electicity and Magnetism Sping 218 Pof. David R. Jackson Dept. Of ECE Notes 2 Dielectics 1 Dielectics Single H 2 O molecule: H H Wate ε= εε O 2 Dielectics (cont.) H H Wate ε= εε O Vecto
ECE 3318 Applied Electicity and Magnetism Sping 218 Pof. David R. Jackson Dept. Of ECE Notes 2 Dielectics 1 Dielectics Single H 2 O molecule: H H Wate ε= εε O 2 Dielectics (cont.) H H Wate ε= εε O Vecto
Fall 2004/05 Solutions to Assignment 5: The Stationary Phase Method Provided by Mustafa Sabri Kilic. I(x) = e ixt e it5 /5 dt (1) Z J(λ) =
 8.35 Fall 24/5 Solution to Aignment 5: The Stationay Phae Method Povided by Mutafa Sabi Kilic. Find the leading tem fo each of the integal below fo λ >>. (a) R eiλt3 dt (b) R e iλt2 dt (c) R eiλ co t dt
8.35 Fall 24/5 Solution to Aignment 5: The Stationay Phae Method Povided by Mutafa Sabi Kilic. Find the leading tem fo each of the integal below fo λ >>. (a) R eiλt3 dt (b) R e iλt2 dt (c) R eiλ co t dt
Current, Resistance and
 Cuent, Resistance and Electomotive Foce Chapte 25 Octobe 2, 2012 Octobe 2, 2012 Physics 208 1 Leaning Goals The meaning of electic cuent, and how chages move in a conducto. What is meant by esistivity
Cuent, Resistance and Electomotive Foce Chapte 25 Octobe 2, 2012 Octobe 2, 2012 Physics 208 1 Leaning Goals The meaning of electic cuent, and how chages move in a conducto. What is meant by esistivity
How can you find the dimensions of a square or a circle when you are given its area? When you multiply a number by itself, you square the number.
 7. Finding Squae Root How can you find the dimenion of a quae o a cicle when you ae given it aea? When you multiply a numbe by itelf, you quae the numbe. Symbol fo quaing i the exponent. = = 6 quaed i
7. Finding Squae Root How can you find the dimenion of a quae o a cicle when you ae given it aea? When you multiply a numbe by itelf, you quae the numbe. Symbol fo quaing i the exponent. = = 6 quaed i
Chapter 3 Optical Systems with Annular Pupils
 Chapte 3 Optical Systems with Annula Pupils 3 INTRODUCTION In this chapte, we discuss the imaging popeties of a system with an annula pupil in a manne simila to those fo a system with a cicula pupil The
Chapte 3 Optical Systems with Annula Pupils 3 INTRODUCTION In this chapte, we discuss the imaging popeties of a system with an annula pupil in a manne simila to those fo a system with a cicula pupil The
Lecture Principles of scattering and main concepts.
 Lectue 15. Light catteing and aboption by atmopheic paticuate. Pat 1: Pincipe of catteing. Main concept: eementay wave, poaization, Stoke matix, and catteing phae function. Rayeigh catteing. Objective:
Lectue 15. Light catteing and aboption by atmopheic paticuate. Pat 1: Pincipe of catteing. Main concept: eementay wave, poaization, Stoke matix, and catteing phae function. Rayeigh catteing. Objective:
Homework 7 Solutions
 Homewok 7 olutions Phys 4 Octobe 3, 208. Let s talk about a space monkey. As the space monkey is oiginally obiting in a cicula obit and is massive, its tajectoy satisfies m mon 2 G m mon + L 2 2m mon 2
Homewok 7 olutions Phys 4 Octobe 3, 208. Let s talk about a space monkey. As the space monkey is oiginally obiting in a cicula obit and is massive, its tajectoy satisfies m mon 2 G m mon + L 2 2m mon 2
SPH4U Magnetism Test Name: Solutions
 SPH4U Magneti et Nae: Solution QUESION 1 [4 Mak] hi and the following two quetion petain to the diaga below howing two cuent-caying wie. wo cuent ae flowing in the ae diection (out of the page) a hown.
SPH4U Magneti et Nae: Solution QUESION 1 [4 Mak] hi and the following two quetion petain to the diaga below howing two cuent-caying wie. wo cuent ae flowing in the ae diection (out of the page) a hown.
Force & Motion: Newton s Laws
 oce & otion: Newton Law ( t Law) If no net foce act on a body then the body velocity cannot change. Zeo net foce implie zeo acceleation. The ma of an object detemine how difficult it i to change the object
oce & otion: Newton Law ( t Law) If no net foce act on a body then the body velocity cannot change. Zeo net foce implie zeo acceleation. The ma of an object detemine how difficult it i to change the object
Problem 1. Part b. Part a. Wayne Witzke ProblemSet #1 PHY 361. Calculate x, the expected value of x, defined by
 Poblem Pat a The nomal distibution Gaussian distibution o bell cuve has the fom f Ce µ Calculate the nomalization facto C by equiing the distibution to be nomalized f Substituting in f, defined above,
Poblem Pat a The nomal distibution Gaussian distibution o bell cuve has the fom f Ce µ Calculate the nomalization facto C by equiing the distibution to be nomalized f Substituting in f, defined above,
EM Boundary Value Problems
 EM Bounday Value Poblems 10/ 9 11/ By Ilekta chistidi & Lee, Seung-Hyun A. Geneal Desciption : Maxwell Equations & Loentz Foce We want to find the equations of motion of chaged paticles. The way to do
EM Bounday Value Poblems 10/ 9 11/ By Ilekta chistidi & Lee, Seung-Hyun A. Geneal Desciption : Maxwell Equations & Loentz Foce We want to find the equations of motion of chaged paticles. The way to do
Theorem 2: Proof: Note 1: Proof: Note 2:
 A New 3-Dimenional Polynomial Intepolation Method: An Algoithmic Appoach Amitava Chattejee* and Rupak Bhattachayya** A new 3-dimenional intepolation method i intoduced in thi pape. Coeponding to the method
A New 3-Dimenional Polynomial Intepolation Method: An Algoithmic Appoach Amitava Chattejee* and Rupak Bhattachayya** A new 3-dimenional intepolation method i intoduced in thi pape. Coeponding to the method
LC transfer of energy between the driving source and the circuit will be a maximum.
 The Q of oscillatos efeences: L.. Fotney Pinciples of Electonics: Analog and Digital, Hacout Bace Jovanovich 987, Chapte (AC Cicuits) H. J. Pain The Physics of Vibations and Waves, 5 th edition, Wiley
The Q of oscillatos efeences: L.. Fotney Pinciples of Electonics: Analog and Digital, Hacout Bace Jovanovich 987, Chapte (AC Cicuits) H. J. Pain The Physics of Vibations and Waves, 5 th edition, Wiley
Magnetic Fields Due to Currents
 PH -C Fall 1 Magnetic Fields Due to Cuents Lectue 14 Chapte 9 (Halliday/esnick/Walke, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapte 9 Magnetic Fields Due to Cuents In this chapte we will exploe the elationship
PH -C Fall 1 Magnetic Fields Due to Cuents Lectue 14 Chapte 9 (Halliday/esnick/Walke, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapte 9 Magnetic Fields Due to Cuents In this chapte we will exploe the elationship
The physics of induction stoves
 The physics of uction stoves This is an aticle fom my home page: www.olewitthansen.dk Contents 1. What is an uction stove...1. Including self-uctance...4 3. The contibution fom the magnetic moments...6
The physics of uction stoves This is an aticle fom my home page: www.olewitthansen.dk Contents 1. What is an uction stove...1. Including self-uctance...4 3. The contibution fom the magnetic moments...6
Appendix B The Relativistic Transformation of Forces
 Appendix B The Relativistic Tansfomation of oces B. The ou-foce We intoduced the idea of foces in Chapte 3 whee we saw that the change in the fou-momentum pe unit time is given by the expession d d w x
Appendix B The Relativistic Tansfomation of oces B. The ou-foce We intoduced the idea of foces in Chapte 3 whee we saw that the change in the fou-momentum pe unit time is given by the expession d d w x
( ) [ ] [ ] [ ] δf φ = F φ+δφ F. xdx.
![( ) [ ] [ ] [ ] δf φ = F φ+δφ F. xdx. ( ) [ ] [ ] [ ] δf φ = F φ+δφ F. xdx.](/thumbs/90/103689049.jpg) 9. LAGRANGIAN OF THE ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD In the pevious section the Lagangian and Hamiltonian of an ensemble of point paticles was developed. This appoach is based on a qt. This discete fomulation can
9. LAGRANGIAN OF THE ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD In the pevious section the Lagangian and Hamiltonian of an ensemble of point paticles was developed. This appoach is based on a qt. This discete fomulation can
AE 423 Space Technology I Chapter 2 Satellite Dynamics
 AE 43 Space Technology I Chapte Satellite Dynamic.1 Intoduction In thi chapte we eview ome dynamic elevant to atellite dynamic and we etablih ome of the baic popetie of atellite dynamic.. Dynamic of a
AE 43 Space Technology I Chapte Satellite Dynamic.1 Intoduction In thi chapte we eview ome dynamic elevant to atellite dynamic and we etablih ome of the baic popetie of atellite dynamic.. Dynamic of a
2 x 8 2 x 2 SKILLS Determine whether the given value is a solution of the. equation. (a) x 2 (b) x 4. (a) x 2 (b) x 4 (a) x 4 (b) x 8
 5 CHAPTER Fundamentals When solving equations that involve absolute values, we usually take cases. EXAMPLE An Absolute Value Equation Solve the equation 0 x 5 0 3. SOLUTION By the definition of absolute
5 CHAPTER Fundamentals When solving equations that involve absolute values, we usually take cases. EXAMPLE An Absolute Value Equation Solve the equation 0 x 5 0 3. SOLUTION By the definition of absolute
EQUATIONS OF MOTION LUCA GUIDO MOLINARI
 EQUATIONS OF MOTION LUCA GUIDO MOLINARI 1. Equation of motion of destuction opeatos Conside a system of bosons o femions descibed by a Hamiltonian H = H 1 + H 2, whee H 1 and H 2 ae espectively the one
EQUATIONS OF MOTION LUCA GUIDO MOLINARI 1. Equation of motion of destuction opeatos Conside a system of bosons o femions descibed by a Hamiltonian H = H 1 + H 2, whee H 1 and H 2 ae espectively the one
γ from B D(Kπ)K and B D(KX)K, X=3π or ππ 0
 fom and X, X= o 0 Jim Libby, Andew Powell and Guy Wilkinon Univeity of Oxfod 8th Januay 007 Gamma meeting 1 Outline The AS technique to meaue Uing o 0 : intoducing the coheence facto Meauing the coheence
fom and X, X= o 0 Jim Libby, Andew Powell and Guy Wilkinon Univeity of Oxfod 8th Januay 007 Gamma meeting 1 Outline The AS technique to meaue Uing o 0 : intoducing the coheence facto Meauing the coheence
MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION
 MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION It was found when a magnet suspended fom its cente, it tends to line itself up in a noth-south diection (the compass needle). The noth end is called the Noth Pole (N-pole),
MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION It was found when a magnet suspended fom its cente, it tends to line itself up in a noth-south diection (the compass needle). The noth end is called the Noth Pole (N-pole),
MAGNETIC FIELD AROUND TWO SEPARATED MAGNETIZING COILS
 The 8 th Intenational Confeence of the Slovenian Society fo Non-Destuctive Testing»pplication of Contempoay Non-Destuctive Testing in Engineeing«Septembe 1-3, 5, Potoož, Slovenia, pp. 17-1 MGNETIC FIELD
The 8 th Intenational Confeence of the Slovenian Society fo Non-Destuctive Testing»pplication of Contempoay Non-Destuctive Testing in Engineeing«Septembe 1-3, 5, Potoož, Slovenia, pp. 17-1 MGNETIC FIELD
Roof Support 1. Stand-Up Time (RMR):
 Roof Suppot 1 Enty Design is a complex polem. 1. One can use a Roof Classification System. o one can use Beam Fomulas Stand-Up Time (RMR): Maximum Unsuppoted Span (Q): Accoding to the Q system, the maximum
Roof Suppot 1 Enty Design is a complex polem. 1. One can use a Roof Classification System. o one can use Beam Fomulas Stand-Up Time (RMR): Maximum Unsuppoted Span (Q): Accoding to the Q system, the maximum
Supplemental Materials. Advanced Thermoelectrics Governed by Single Parabolic Band Model:
 Electonic Supplementay Mateial (ESI) fo Phyical Chemity Chemical Phyic. Thi jounal i The Royal Society of Chemity 04 Supplemental Mateial Advanced Themoelectic Govened by Single Paabolic and Model: Mg
Electonic Supplementay Mateial (ESI) fo Phyical Chemity Chemical Phyic. Thi jounal i The Royal Society of Chemity 04 Supplemental Mateial Advanced Themoelectic Govened by Single Paabolic and Model: Mg
2.5 The Quarter-Wave Transformer
 /3/5 _5 The Quate Wave Tansfome /.5 The Quate-Wave Tansfome Reading Assignment: pp. 73-76 By now you ve noticed that a quate-wave length of tansmission line ( λ 4, β π ) appeas often in micowave engineeing
/3/5 _5 The Quate Wave Tansfome /.5 The Quate-Wave Tansfome Reading Assignment: pp. 73-76 By now you ve noticed that a quate-wave length of tansmission line ( λ 4, β π ) appeas often in micowave engineeing
Ultrafast effects in 3D Metamaterials
 Ultafast effects in 3D Metamateials Nkoni Katte,2 and Philip G.Evans 3 Electical Engineeing Wilbefoce Univesity, 2 Sensos Laboatoy Wight State Univesity and 3 Oak idge National Laboatoy *Coesponding autho:
Ultafast effects in 3D Metamateials Nkoni Katte,2 and Philip G.Evans 3 Electical Engineeing Wilbefoce Univesity, 2 Sensos Laboatoy Wight State Univesity and 3 Oak idge National Laboatoy *Coesponding autho:
Midterm Exam #2, Part A
 Physics 151 Mach 17, 2006 Midtem Exam #2, Pat A Roste No.: Scoe: Exam time limit: 50 minutes. You may use calculatos and both sides of ONE sheet of notes, handwitten only. Closed book; no collaboation.
Physics 151 Mach 17, 2006 Midtem Exam #2, Pat A Roste No.: Scoe: Exam time limit: 50 minutes. You may use calculatos and both sides of ONE sheet of notes, handwitten only. Closed book; no collaboation.
Rotational Motion. Lecture 6. Chapter 4. Physics I. Course website:
 Lectue 6 Chapte 4 Physics I Rotational Motion Couse website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andiy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Today we ae going to discuss: Chapte 4: Unifom Cicula Motion: Section 4.4 Nonunifom Cicula
Lectue 6 Chapte 4 Physics I Rotational Motion Couse website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andiy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Today we ae going to discuss: Chapte 4: Unifom Cicula Motion: Section 4.4 Nonunifom Cicula
On the Comparison of Stability Analysis with Phase Portrait for a Discrete Prey-Predator System
 Intenational Jounal of Applied Engineeing Reseach ISSN 0973-4562 Volume 12, Nume 24 (2017) pp. 15273-15277 Reseach India Pulications. http://www.ipulication.com On the Compaison of Staility Analysis with
Intenational Jounal of Applied Engineeing Reseach ISSN 0973-4562 Volume 12, Nume 24 (2017) pp. 15273-15277 Reseach India Pulications. http://www.ipulication.com On the Compaison of Staility Analysis with
Fields and Waves I Spring 2005 Homework 4. Due 8 March 2005
 Homewok 4 Due 8 Mach 005. Inceasing the Beakdown Voltage: This fist question is a mini design poject. You fist step is to find a commecial cable (coaxial o two wie line) fo which you have the following
Homewok 4 Due 8 Mach 005. Inceasing the Beakdown Voltage: This fist question is a mini design poject. You fist step is to find a commecial cable (coaxial o two wie line) fo which you have the following
Experiment I Voltage Variation and Control
 ELE303 Electicity Netwoks Expeiment I oltage aiation and ontol Objective To demonstate that the voltage diffeence between the sending end of a tansmission line and the load o eceiving end depends mainly
ELE303 Electicity Netwoks Expeiment I oltage aiation and ontol Objective To demonstate that the voltage diffeence between the sending end of a tansmission line and the load o eceiving end depends mainly
( n x ( ) Last Time Exam 3 results. Question. 3-D particle in box: summary. Modified Bohr model. 3-D Hydrogen atom. r n. = n 2 a o
 Last Time Exam 3 esults Quantum tunneling 3-dimensional wave functions Deceasing paticle size Quantum dots paticle in box) This week s honos lectue: Pof. ad histian, Positon Emission Tomogaphy Tue. Dec.
Last Time Exam 3 esults Quantum tunneling 3-dimensional wave functions Deceasing paticle size Quantum dots paticle in box) This week s honos lectue: Pof. ad histian, Positon Emission Tomogaphy Tue. Dec.
AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism 2001 Scoring Guidelines
 AP Physics C: Electicity and Magnetism 1 Scoing Guidelines The mateials included in these files ae intended fo non-commecial use by AP teaches fo couse and exam pepaation; pemission fo any othe use must
AP Physics C: Electicity and Magnetism 1 Scoing Guidelines The mateials included in these files ae intended fo non-commecial use by AP teaches fo couse and exam pepaation; pemission fo any othe use must
Physics NYB problem set 5 solution
 Physics NY poblem set 5 solutions 1 Physics NY poblem set 5 solution Hello eveybody, this is ED. Hi ED! ED is useful fo dawing the ight hand ule when you don t know how to daw. When you have a coss poduct
Physics NY poblem set 5 solutions 1 Physics NY poblem set 5 solution Hello eveybody, this is ED. Hi ED! ED is useful fo dawing the ight hand ule when you don t know how to daw. When you have a coss poduct
Inference for A One Way Factorial Experiment. By Ed Stanek and Elaine Puleo
 Infeence fo A One Way Factoial Expeiment By Ed Stanek and Elaine Puleo. Intoduction We develop etimating equation fo Facto Level mean in a completely andomized one way factoial expeiment. Thi development
Infeence fo A One Way Factoial Expeiment By Ed Stanek and Elaine Puleo. Intoduction We develop etimating equation fo Facto Level mean in a completely andomized one way factoial expeiment. Thi development
Magnetic Field. Conference 6. Physics 102 General Physics II
 Physics 102 Confeence 6 Magnetic Field Confeence 6 Physics 102 Geneal Physics II Monday, Mach 3d, 2014 6.1 Quiz Poblem 6.1 Think about the magnetic field associated with an infinite, cuent caying wie.
Physics 102 Confeence 6 Magnetic Field Confeence 6 Physics 102 Geneal Physics II Monday, Mach 3d, 2014 6.1 Quiz Poblem 6.1 Think about the magnetic field associated with an infinite, cuent caying wie.
Detailed solution of IES 2014 (ECE) Conventional Paper II. solve I 0 and use same formula again. Saturation region
 etailed olution of IS 4 (C) Conventional Pape II qv qv Sol. (a) IC I e Ie K K 4 I =.7 Fo I C = m olve I and ue ame fomula again K IC V ln 5ln 4 q I.7 =.8576 Volt Sol. (b) VGS VS Vupply 5V N MOS channel,
etailed olution of IS 4 (C) Conventional Pape II qv qv Sol. (a) IC I e Ie K K 4 I =.7 Fo I C = m olve I and ue ame fomula again K IC V ln 5ln 4 q I.7 =.8576 Volt Sol. (b) VGS VS Vupply 5V N MOS channel,
Chapter 6. NEWTON S 2nd LAW AND UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION
 Chapte 6 NEWTON S nd LAW AND UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION Phyic 1 1 3 4 ting Quetion: A ball attached to the end of a ting i whiled in a hoizontal plane. At the point indicated, the ting beak. Looking down
Chapte 6 NEWTON S nd LAW AND UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION Phyic 1 1 3 4 ting Quetion: A ball attached to the end of a ting i whiled in a hoizontal plane. At the point indicated, the ting beak. Looking down
1 2 U CV. K dq I dt J nqv d J V IR P VI
 o 5 o T C T F 9 T K T o C 7.5 L L T V VT Q mct nct Q F V ml F V dq A H k TH TC dt L pv nt Kt nt CV ideal monatomic gas 5 CV ideal diatomic gas w/o vibation V W pdv V U Q W W Q e Q Q e Canot H C T T S C
o 5 o T C T F 9 T K T o C 7.5 L L T V VT Q mct nct Q F V ml F V dq A H k TH TC dt L pv nt Kt nt CV ideal monatomic gas 5 CV ideal diatomic gas w/o vibation V W pdv V U Q W W Q e Q Q e Canot H C T T S C
Adiabatic evolution of the constants of motion in resonance (I)
 Adiabatic evolution of the constants of motion in esonance (I) BH Gavitational 重 力力波 waves Takahio Tanaka (YITP, Kyoto univesity) R. Fujita, S. Isoyama, H. Nakano, N. Sago PTEP 013 (013) 6, 063E01 e-pint:
Adiabatic evolution of the constants of motion in esonance (I) BH Gavitational 重 力力波 waves Takahio Tanaka (YITP, Kyoto univesity) R. Fujita, S. Isoyama, H. Nakano, N. Sago PTEP 013 (013) 6, 063E01 e-pint:
