HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS MATH 1910 Sections 6.1, 6.2, 6.3 Fall 2016
|
|
|
- Hilary Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS MATH 191 Sections.1,.,. Fall 1 Problem.1.19 Find the area of the shaded region. SOLUTION. The equation of the line passing through ( π, is given by y 1() = π, and the equation of the line passing through ( π, 1 ) is given by y () = The area of the region to the left of = π is π (y 1 () y ()) d = π ( π π π ) d = ( π = π π π 4π = ( 1)π. 48 And the area of the region to the right of = π is π/ π/ (cos ) d = (sin π 4π ) π/ π/ 4π ) = 8 8 π. 1 π Thus, the total area of the region is ( 1)π π 1 = ( )π. 4 Problem Find the area of the region lying to the right of = y + 4y and to the left of = y + 8. SOLUTION. To figure out where the two curves intersect, we set y + 4y = y + 8. This yields = y + y = (y 5)(y + ), so the curves intersect at y = 5 and y =. Thus, the area of the region is given by 5 ((y + 8) (y + 4y )) dy = 5 ( y y + ) dy = ( 1 y 1 y + y) 5 =
2 Problem.1.48 Sketch the region enclosed by the curves and compute its area as an integral along the - or y-ais: y = sin, y =, π 9π SOLUTION. To compute the area enclosed by the curves, first we need to find where the two curves intersect, in the given interval. So we set = sin ; and since is nonzero on the interval [π, 9π ], this equation becomes = sin. Since = sin θ has solutions θ = nπ for integers n, setting θ = shows that sin has solutions = n π for integers n. The only such solutions in [π, 9π ] are = π, 4π, 9π Now, we need to see which curve is above the other for the intervals [π, 4π ] and [4π, 9π ], respectively. To do this, we choose a point in the interior of each interval, and check if sin or equal to, or less than or equal to, : We choose 9 4 π in [π, 4π ]. Then sin 9 4 π 9 4 π = sin( π ) π = 1 π is greater than Since these curves are continuous, and do not intersect in (π, 4π ), we know that sin for all in [π, 4π ] So the curve y = sin is below the curve y = on the interval [π, 4π ]. Similar work will show that the curve y = is below the curve y = sin on the interval [4π, 9π ] (for eample, you can plug in = 5π 4 ). Thus, the area A enclosed by the two curves is given by 4π A = ( sin 9π ) d + ( sin ) d 4π π To evaluate this integral, choose u = = 1/. Then du = 1 1/ d = 1 d, so the integral becomes 1 4π A = π ( sin π ) d = 4π π = cos u cos u = = 8 sin 9π d + π π π π π sin u du + sin u du π.1.48
3 Problem.1. Find the line y = m that divides the area under the curve y = (1 ) over [, 1] into two regions of equal area. SOLUTION. First note that the area under the curve y = (1 ) is 1 (1 ) d = 1 ( ) d = ( 1 1 ) 1 = 1 1 = 1. Now, the curves y = m and y = (1 ) intersect when m = (1 ): at = or at = 1 m. [Note that if m > 1, then we d have an intersection at a negative value. In the contet of our problem, this is nonsense: the line with a such a slope passes above the curve y = (1 ) on the interval [, 1], and therefore cannot divide the region into two parts. So a valid solution requires that m 1.] So the area A of the region enclosed by the curves y = m and y = (1 ) is given by A = 1 m ((1 ) m) d = 1 m ((1 m) ) d = (1 m) 1 1 m = 1 (1 m) Setting A = 1 1 = 1 1, we get 1 (1 m) = 1 1, which requires m = 1 ( 1 )1/. Problem Find the volume of liquid needed to fill a sphere of radius R to height h. SOLUTION. The horizontal cross section of the sphere at a height y above the sphere s lowest point is a circle. Its radius is r(y) = R (R y), by the Pythagorean theorem. So the area A(y) of such a cross section at height y is given by A(y) = π(r(y)) = π(r (R y) ). To find the volume V of the region, we integrate these cross sectional areas for heights y ranging from to h: that is, V = h π((r (R y) )) dy = π h (Ry y ) dy = π(ry y ) h = π(rh h ). Problem....5 A plane inclined at an angle of 45 degrees passes through a diameter of the base of a cylinder of radius r. Find the volume of the region within the cylinder and below the plane.
4 SOLUTION. Place the origin at the center of the base of the cylinder, with the -ais running perpendicularly to the diameter defined by the plane intersecting the cylinder. The point = r should lie directly below the highest point of the intersection of the plane and cylinder, as we ve defined things here. Now, for each in [, r], the vertical cross section taken perpendicular to the -ais is a rectangle of base r and height. Thus, the volume V of the region is V r r d Choose u = r. Then du = d, so our integral becomes V r r d = u 1/ du = r u/ = r r. Problem..1.. The solid S in Figure 5 is the intersection of two cylinders of radius r whose aes are perpendicular. (a) The horizontal cross section of each cylinder at distance y from the central ais is a rectangular strip. Find the strip s width. (b) Find the area of the horizontal cross section of S at distance y. (c) Find the volume of S as a function of r. SOLUTION. (a) Since our strip is a distance y above the central ais, and the radius of our cylinder is r, the Pythagorean theorem tells us that the width of the strip is r y. (b) The horizontal cross section of S at distance y from the central ais is the intersection of the two rectangular strips at distance y from the central ais, from each cylinder. Since each strip has width r y, and the two rectangular strips intersect at right angles, this horizontal cross section is a square of width r y. Thus, the area of the horizontal cross section of S at distance y is ( r y ) = 4(r y ). (c) Since y ranges from r to r, the volume V of S is given by V = r r 4(r y ) dy = 4(r y 1 y ) r r = 1 r. Problem
5 Let v(r) be the velocity of blood in an arterial capillary of radius R = m. Use Poiseuille s Law (Eample ) with k = 1 /(meter-seconds) to determine the velocity at the center of the capillary, and the flow rate (use correct units). SOLUTION. Poiseuille s Law states that v(r) = k(r r ), but with R and r measured in cm and k measured in 1/(centimeter-seconds). So R = m = cm = 4 1 cm, and k = 1 /(m-s) = 1 /(1cm-s) = 1 4 /(cm-s). Now, the velocity at the center of the capillary is v() = kr = 1 4 (4 1 ) = 1 1 cm/s =.1m/s. The flow rate Q is given by Q = π R rv(r) dr = π R rk(r r ) dr = kπ( R r r4 4 ) R in cm /s. = πk R4 4 = π(14 )(4 1 1 ) = 1.8π 1, This is the same as 1.8π 1 1 m /s...8 Problem..5 An object with zero initial velocity accelerates at a constant rate of 1m/s. Find the average velocity during the first 15 s. SOLUTION. An acceleration a(t) = 1 gives v(t) = 1t + c for some constant c and zero initial velocity implies c =. Thus the average velocity is given by t dt = 1 15 t = 75m/s. Problem..58 What is the average area of the circles whose radii vary from to R? SOLUTION. The average area is 1 R R πr dr = π R r R = 1 πr. Problem..1 Consider the functions y =, y = +. (a) Sketch the region enclosed by the curves. (b) Describe the cross section perpendicular to the ais located at. (c) Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating the region about the ais
6 SOLUTION. (a) Setting = + yields = = ( )( + 1) The two curves therefore intersect at = 1 and =. The region enclosed by the two curves is shown in the figure below. (b) When the region is rotated about the ais, each cross section is a washer with outer radius R = + and inner radius r =. (c) The volume of the solid of revolution is ( π ( + ) ( ) ) d = π ( )d 1 1 ( 4 = π ) = 188π Problem.. Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating the region enclosed by = sin(y) and = about the y-ais over the interval y π SOLUTION. Graphing the region yields the following:
7 Then rotating about the y-ais gives disks of radius sin(y), so the volume is: π πr dy = π π sin(y)dy = π( cos(y)) π = π.. Problem..5 The torus is obtained by rotating the circle ( a) + y = b around the y-ais (assume that a > b). Show that it has volume π ab SOLUTION. The image of the torus is as follows: Rotating the region enclosed by the circle ( a) + y = b about the Y ais produces a torus whose cross sections are washers with outer radius R = a + b y and inner radius r = a b y. The volume of the torus is then b ( ( π a + ) b y (a ) ) b y dy = 4aπ b b b b y dy. Now, the remaining definite integral is one-half the area of a circle of radius B; therefore, the volume of the torus is 4aπ. 1 πb = π ab..5 Problem..59 A bead is formed by removing a cylinder of radius r from the center of a sphere of radius R. Find the volume of the bead with r = 1 and R =. 7
8 SOLUTION. The equation of the outer circle is + y = = 4 and the inner cylinder intersects the sphere when y = ±. Eachcross section of the bead is a washer with outer radius 4 y and inner radius 1, so the volume is given by ( ( ) π 4 y 1 ) dy = π ( y )dy = 4π..59 8
Volume: The Disk Method. Using the integral to find volume.
 Volume: The Disk Method Using the integral to find volume. If a region in a plane is revolved about a line, the resulting solid is a solid of revolution and the line is called the axis of revolution. y
Volume: The Disk Method Using the integral to find volume. If a region in a plane is revolved about a line, the resulting solid is a solid of revolution and the line is called the axis of revolution. y
Technique 1: Volumes by Slicing
 Finding Volumes of Solids We have used integrals to find the areas of regions under curves; it may not seem obvious at first, but we can actually use similar methods to find volumes of certain types of
Finding Volumes of Solids We have used integrals to find the areas of regions under curves; it may not seem obvious at first, but we can actually use similar methods to find volumes of certain types of
HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS MATH 1910 Sections 6.4, 6.5, 7.1 Fall 2016
 HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS MATH 9 Sections 6.4, 6.5, 7. Fall 6 Problem 6.4. Sketch the region enclosed by x = 4 y +, x = 4y, and y =. Use the Shell Method to calculate the volume of rotation about the x-axis SOLUTION.
HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS MATH 9 Sections 6.4, 6.5, 7. Fall 6 Problem 6.4. Sketch the region enclosed by x = 4 y +, x = 4y, and y =. Use the Shell Method to calculate the volume of rotation about the x-axis SOLUTION.
Math 20C Homework 2 Partial Solutions
 Math 2C Homework 2 Partial Solutions Problem 1 (12.4.14). Calculate (j k) (j + k). Solution. The basic properties of the cross product are found in Theorem 2 of Section 12.4. From these properties, we
Math 2C Homework 2 Partial Solutions Problem 1 (12.4.14). Calculate (j k) (j + k). Solution. The basic properties of the cross product are found in Theorem 2 of Section 12.4. From these properties, we
Math 75B Practice Midterm III Solutions Chapter 6 (Stewart) Multiple Choice. Circle the letter of the best answer.
 Math 75B Practice Midterm III Solutions Chapter 6 Stewart) English system formulas: Metric system formulas: ft. = in. F = m a 58 ft. = mi. g = 9.8 m/s 6 oz. = lb. cm = m Weight of water: ω = 6.5 lb./ft.
Math 75B Practice Midterm III Solutions Chapter 6 Stewart) English system formulas: Metric system formulas: ft. = in. F = m a 58 ft. = mi. g = 9.8 m/s 6 oz. = lb. cm = m Weight of water: ω = 6.5 lb./ft.
PDF Created with deskpdf PDF Writer - Trial ::
 y 3 5 Graph of f ' x 76. The graph of f ', the derivative f, is shown above for x 5. n what intervals is f increasing? (A) [, ] only (B) [, 3] (C) [3, 5] only (D) [0,.5] and [3, 5] (E) [, ], [, ], and
y 3 5 Graph of f ' x 76. The graph of f ', the derivative f, is shown above for x 5. n what intervals is f increasing? (A) [, ] only (B) [, 3] (C) [3, 5] only (D) [0,.5] and [3, 5] (E) [, ], [, ], and
1985 AP Calculus AB: Section I
 985 AP Calculus AB: Section I 9 Minutes No Calculator Notes: () In this eamination, ln denotes the natural logarithm of (that is, logarithm to the base e). () Unless otherwise specified, the domain of
985 AP Calculus AB: Section I 9 Minutes No Calculator Notes: () In this eamination, ln denotes the natural logarithm of (that is, logarithm to the base e). () Unless otherwise specified, the domain of
Integrals. D. DeTurck. January 1, University of Pennsylvania. D. DeTurck Math A: Integrals 1 / 61
 Integrals D. DeTurck University of Pennsylvania January 1, 2018 D. DeTurck Math 104 002 2018A: Integrals 1 / 61 Integrals Start with dx this means a little bit of x or a little change in x If we add up
Integrals D. DeTurck University of Pennsylvania January 1, 2018 D. DeTurck Math 104 002 2018A: Integrals 1 / 61 Integrals Start with dx this means a little bit of x or a little change in x If we add up
Solutions to Homework 1
 Solutions to Homework 1 1. Let f(x) = x 2, a = 1, b = 2, and let x = a = 1, x 1 = 1.1, x 2 = 1.2, x 3 = 1.4, x 4 = b = 2. Let P = (x,..., x 4 ), so that P is a partition of the interval [1, 2]. List the
Solutions to Homework 1 1. Let f(x) = x 2, a = 1, b = 2, and let x = a = 1, x 1 = 1.1, x 2 = 1.2, x 3 = 1.4, x 4 = b = 2. Let P = (x,..., x 4 ), so that P is a partition of the interval [1, 2]. List the
LESSON 14: VOLUME OF SOLIDS OF REVOLUTION SEPTEMBER 27, 2017
 LESSON 4: VOLUME OF SOLIDS OF REVOLUTION SEPTEMBER 27, 27 We continue to expand our understanding of solids of revolution. The key takeaway from today s lesson is that finding the volume of a solid of
LESSON 4: VOLUME OF SOLIDS OF REVOLUTION SEPTEMBER 27, 27 We continue to expand our understanding of solids of revolution. The key takeaway from today s lesson is that finding the volume of a solid of
The region enclosed by the curve of f and the x-axis is rotated 360 about the x-axis. Find the volume of the solid formed.
 Section A ln. Let g() =, for > 0. ln Use the quotient rule to show that g ( ). 3 (b) The graph of g has a maimum point at A. Find the -coordinate of A. (Total 7 marks) 6. Let h() =. Find h (0). cos 3.
Section A ln. Let g() =, for > 0. ln Use the quotient rule to show that g ( ). 3 (b) The graph of g has a maimum point at A. Find the -coordinate of A. (Total 7 marks) 6. Let h() =. Find h (0). cos 3.
Math 259 Winter Solutions to Homework # We will substitute for x and y in the linear equation and then solve for r. x + y = 9.
 Math 59 Winter 9 Solutions to Homework Problems from Pages 5-5 (Section 9.) 18. We will substitute for x and y in the linear equation and then solve for r. x + y = 9 r cos(θ) + r sin(θ) = 9 r (cos(θ) +
Math 59 Winter 9 Solutions to Homework Problems from Pages 5-5 (Section 9.) 18. We will substitute for x and y in the linear equation and then solve for r. x + y = 9 r cos(θ) + r sin(θ) = 9 r (cos(θ) +
Volume of Solid of Known Cross-Sections
 Volume of Solid of Known Cross-Sections Problem: To find the volume of a given solid S. What do we know about the solid? Suppose we are told what the cross-sections perpendicular to some axis are. Figure:
Volume of Solid of Known Cross-Sections Problem: To find the volume of a given solid S. What do we know about the solid? Suppose we are told what the cross-sections perpendicular to some axis are. Figure:
Green s Theorem. MATH 311, Calculus III. J. Robert Buchanan. Fall Department of Mathematics. J. Robert Buchanan Green s Theorem
 Green s Theorem MATH 311, alculus III J. obert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Main Idea Main idea: the line integral around a positively oriented, simple closed curve is related to a double
Green s Theorem MATH 311, alculus III J. obert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Main Idea Main idea: the line integral around a positively oriented, simple closed curve is related to a double
x+1 e 2t dt. h(x) := Find the equation of the tangent line to y = h(x) at x = 0.
 Math Sample final problems Here are some problems that appeared on past Math exams. Note that you will be given a table of Z-scores for the standard normal distribution on the test. Don t forget to have
Math Sample final problems Here are some problems that appeared on past Math exams. Note that you will be given a table of Z-scores for the standard normal distribution on the test. Don t forget to have
Tuesday, September 29, Page 453. Problem 5
 Tuesday, September 9, 15 Page 5 Problem 5 Problem. Set up and evaluate the integral that gives the volume of the solid formed by revolving the region bounded by y = x, y = x 5 about the x-axis. Solution.
Tuesday, September 9, 15 Page 5 Problem 5 Problem. Set up and evaluate the integral that gives the volume of the solid formed by revolving the region bounded by y = x, y = x 5 about the x-axis. Solution.
Math 140 Final Sample A Solutions. Tyrone Crisp
 Math 4 Final Sample A Solutions Tyrone Crisp (B) Direct substitution gives, so the limit is infinite. When is close to, but greater than,, the numerator is negative while the denominator is positive. So
Math 4 Final Sample A Solutions Tyrone Crisp (B) Direct substitution gives, so the limit is infinite. When is close to, but greater than,, the numerator is negative while the denominator is positive. So
Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral
 Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral Section 6.1 More on Area a. Representative Rectangle b. Vertical Separation c. Example d. Integration with Respect to y e. Example Section 6.2 Volume by Parallel
Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral Section 6.1 More on Area a. Representative Rectangle b. Vertical Separation c. Example d. Integration with Respect to y e. Example Section 6.2 Volume by Parallel
MATH 32A: MIDTERM 1 REVIEW. 1. Vectors. v v = 1 22
 MATH 3A: MIDTERM 1 REVIEW JOE HUGHES 1. Let v = 3,, 3. a. Find e v. Solution: v = 9 + 4 + 9 =, so 1. Vectors e v = 1 v v = 1 3,, 3 b. Find the vectors parallel to v which lie on the sphere of radius two
MATH 3A: MIDTERM 1 REVIEW JOE HUGHES 1. Let v = 3,, 3. a. Find e v. Solution: v = 9 + 4 + 9 =, so 1. Vectors e v = 1 v v = 1 3,, 3 b. Find the vectors parallel to v which lie on the sphere of radius two
2) ( 8 points) The point 1/4 of the way from (1, 3, 1) and (7, 9, 9) is
 MATH 6 FALL 6 FIRST EXAM SEPTEMBER 8, 6 SOLUTIONS ) ( points) The center and the radius of the sphere given by x + y + z = x + 3y are A) Center (, 3/, ) and radius 3/ B) Center (, 3/, ) and radius 3/ C)
MATH 6 FALL 6 FIRST EXAM SEPTEMBER 8, 6 SOLUTIONS ) ( points) The center and the radius of the sphere given by x + y + z = x + 3y are A) Center (, 3/, ) and radius 3/ B) Center (, 3/, ) and radius 3/ C)
Volumes of Solids of Revolution. We revolve this curve about the x-axis and create a solid of revolution.
 Volumes of Solids of Revolution Consider the function ( ) from a = to b = 9. 5 6 7 8 9 We revolve this curve about the x-axis and create a solid of revolution. - 5 6 7 8 9 - - - We want to find the volume
Volumes of Solids of Revolution Consider the function ( ) from a = to b = 9. 5 6 7 8 9 We revolve this curve about the x-axis and create a solid of revolution. - 5 6 7 8 9 - - - We want to find the volume
f x and the x axis on an interval from x a and
 Unit 6: Chapter 8 Areas and Volumes & Density Functions Part 1: Areas To find the area bounded by a function bwe use the integral: f d b a b 0 f d f d. a b a f and the ais on an interval from a and. This
Unit 6: Chapter 8 Areas and Volumes & Density Functions Part 1: Areas To find the area bounded by a function bwe use the integral: f d b a b 0 f d f d. a b a f and the ais on an interval from a and. This
MCB4UW Handout 7.6. Comparison of the Disk/Washer and Shell Methods. V f x g x. V f y g y
 MCBUW Handout 7.6 Comparison of the Disk/Washer and Shell Methods Method Ais of Formula Notes aout the Revolution Representative Rectangle a Disk Method -ais V f d -ais a V g d Washer Method -ais a V f
MCBUW Handout 7.6 Comparison of the Disk/Washer and Shell Methods Method Ais of Formula Notes aout the Revolution Representative Rectangle a Disk Method -ais V f d -ais a V g d Washer Method -ais a V f
and y c from x 0 to x 1
 Math 44 Activity 9 (Due by end of class August 6). Find the value of c, c, that minimizes the volume of the solid generated by revolving the region between the graphs of y 4 and y c from to about the line
Math 44 Activity 9 (Due by end of class August 6). Find the value of c, c, that minimizes the volume of the solid generated by revolving the region between the graphs of y 4 and y c from to about the line
is the intuition: the derivative tells us the change in output y (from f(b)) in response to a change of input x at x = b.
 Uses of differentials to estimate errors. Recall the derivative notation df d is the intuition: the derivative tells us the change in output y (from f(b)) in response to a change of input at = b. Eamples.
Uses of differentials to estimate errors. Recall the derivative notation df d is the intuition: the derivative tells us the change in output y (from f(b)) in response to a change of input at = b. Eamples.
14.1. Multiple Integration. Iterated Integrals and Area in the Plane. Iterated Integrals. Iterated Integrals. MAC2313 Calculus III - Chapter 14
 14 Multiple Integration 14.1 Iterated Integrals and Area in the Plane Objectives Evaluate an iterated integral. Use an iterated integral to find the area of a plane region. Copyright Cengage Learning.
14 Multiple Integration 14.1 Iterated Integrals and Area in the Plane Objectives Evaluate an iterated integral. Use an iterated integral to find the area of a plane region. Copyright Cengage Learning.
Review sheet Final Exam Math 140 Calculus I Fall 2015 UMass Boston
 Review sheet Final Eam Math Calculus I Fall 5 UMass Boston The eam is closed tetbook NO CALCULATORS OR ELECTRONIC DEVICES ARE ALLOWED DURING THE EXAM The final eam will contain problems of types similar
Review sheet Final Eam Math Calculus I Fall 5 UMass Boston The eam is closed tetbook NO CALCULATORS OR ELECTRONIC DEVICES ARE ALLOWED DURING THE EXAM The final eam will contain problems of types similar
MATH141: Calculus II Exam #1 review 6/8/2017 Page 1
 MATH: Calculus II Eam # review /8/7 Page No review sheet can cover everything that is potentially fair game for an eam, but I tried to hit on all of the topics with these questions, as well as show you
MATH: Calculus II Eam # review /8/7 Page No review sheet can cover everything that is potentially fair game for an eam, but I tried to hit on all of the topics with these questions, as well as show you
Multiple Choice. Circle the best answer. No work needed. No partial credit available. is continuous.
 Multiple Choice. Circle the best answer. No work needed. No partial credit available. + +. Evaluate lim + (a (b (c (d 0 (e None of the above.. Evaluate lim (a (b (c (d 0 (e + + None of the above.. Find
Multiple Choice. Circle the best answer. No work needed. No partial credit available. + +. Evaluate lim + (a (b (c (d 0 (e None of the above.. Evaluate lim (a (b (c (d 0 (e + + None of the above.. Find
For the intersections: cos x = 0 or sin x = 1 2
 Chapter 6 Set-up examples The purpose of this document is to demonstrate the work that will be required if you are asked to set-up integrals on an exam and/or quiz.. Areas () Set up, do not evaluate, any
Chapter 6 Set-up examples The purpose of this document is to demonstrate the work that will be required if you are asked to set-up integrals on an exam and/or quiz.. Areas () Set up, do not evaluate, any
Review Problems for the Final
 Review Problems for the Final Math -3 5 7 These problems are provided to help you study. The presence of a problem on this handout does not imply that there will be a similar problem on the test. And the
Review Problems for the Final Math -3 5 7 These problems are provided to help you study. The presence of a problem on this handout does not imply that there will be a similar problem on the test. And the
Calculus II Practice Test 1 Problems: , 6.5, Page 1 of 10
 Calculus II Practice Test Problems: 6.-6.3, 6.5, 7.-7.3 Page of This is in no way an inclusive set of problems there can be other types of problems on the actual test. To prepare for the test: review homework,
Calculus II Practice Test Problems: 6.-6.3, 6.5, 7.-7.3 Page of This is in no way an inclusive set of problems there can be other types of problems on the actual test. To prepare for the test: review homework,
Math 11 Fall 2018 Practice Final Exam
 Math 11 Fall 218 Practice Final Exam Disclaimer: This practice exam should give you an idea of the sort of questions we may ask on the actual exam. Since the practice exam (like the real exam) is not long
Math 11 Fall 218 Practice Final Exam Disclaimer: This practice exam should give you an idea of the sort of questions we may ask on the actual exam. Since the practice exam (like the real exam) is not long
Examples. 1. (Solution) (a) Suppose f is an increasing function, and let A(x) = x
 Math 31A Final Exam Practice Problems Austin Christian December 1, 15 Here are some practice problems for the final. You ll notice that these problems all come from material since the last exam. You are,
Math 31A Final Exam Practice Problems Austin Christian December 1, 15 Here are some practice problems for the final. You ll notice that these problems all come from material since the last exam. You are,
AP Calculus (BC) Summer Assignment (169 points)
 AP Calculus (BC) Summer Assignment (69 points) This packet is a review of some Precalculus topics and some Calculus topics. It is to be done NEATLY and on a SEPARATE sheet of paper. Use your discretion
AP Calculus (BC) Summer Assignment (69 points) This packet is a review of some Precalculus topics and some Calculus topics. It is to be done NEATLY and on a SEPARATE sheet of paper. Use your discretion
Answers for Ch. 6 Review: Applications of the Integral
 Answers for Ch. 6 Review: Applications of the Integral. The formula for the average value of a function, which you must have stored in your magical mathematical brain, is b b a f d. a d / / 8 6 6 ( 8 )
Answers for Ch. 6 Review: Applications of the Integral. The formula for the average value of a function, which you must have stored in your magical mathematical brain, is b b a f d. a d / / 8 6 6 ( 8 )
Applications of the Definite Integral
 Department of Mathematics, Computer Science, and Statistics loomsburg University loomsburg, Pennsylvania 17815 pplications of the Definite Integral Summary The new dvanced Placement Course Description
Department of Mathematics, Computer Science, and Statistics loomsburg University loomsburg, Pennsylvania 17815 pplications of the Definite Integral Summary The new dvanced Placement Course Description
ENGI 4430 Multiple Integration Cartesian Double Integrals Page 3-01
 ENGI 4430 Multiple Integration Cartesian Double Integrals Page 3-01 3. Multiple Integration This chapter provides only a very brief introduction to the major topic of multiple integration. Uses of multiple
ENGI 4430 Multiple Integration Cartesian Double Integrals Page 3-01 3. Multiple Integration This chapter provides only a very brief introduction to the major topic of multiple integration. Uses of multiple
ANOTHER FIVE QUESTIONS:
 No peaking!!!!! See if you can do the following: f 5 tan 6 sin 7 cos 8 sin 9 cos 5 e e ln ln @ @ Epress sin Power Series Epansion: d as a Power Series: Estimate sin Estimate MACLAURIN SERIES ANOTHER FIVE
No peaking!!!!! See if you can do the following: f 5 tan 6 sin 7 cos 8 sin 9 cos 5 e e ln ln @ @ Epress sin Power Series Epansion: d as a Power Series: Estimate sin Estimate MACLAURIN SERIES ANOTHER FIVE
1993 AP Calculus AB: Section I
 99 AP Calculus AB: Section I 90 Minutes Scientific Calculator Notes: () The eact numerical value of the correct answer does not always appear among the choices given. When this happens, select from among
99 AP Calculus AB: Section I 90 Minutes Scientific Calculator Notes: () The eact numerical value of the correct answer does not always appear among the choices given. When this happens, select from among
Sample Questions to the Final Exam in Math 1111 Chapter 2 Section 2.1: Basics of Functions and Their Graphs
 Sample Questions to the Final Eam in Math 1111 Chapter Section.1: Basics of Functions and Their Graphs 1. Find the range of the function: y 16. a.[-4,4] b.(, 4],[4, ) c.[0, ) d.(, ) e.. Find the domain
Sample Questions to the Final Eam in Math 1111 Chapter Section.1: Basics of Functions and Their Graphs 1. Find the range of the function: y 16. a.[-4,4] b.(, 4],[4, ) c.[0, ) d.(, ) e.. Find the domain
2.1 The Rectangular Coordinate System
 . The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem In this section ou will learn to: plot points in a rectangular coordinate sstem understand basic functions of the graphing calculator graph equations b generating a table
. The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem In this section ou will learn to: plot points in a rectangular coordinate sstem understand basic functions of the graphing calculator graph equations b generating a table
Solutionbank C2 Edexcel Modular Mathematics for AS and A-Level
 Heinemann Solutionbank: Core Maths C Page of Solutionbank C Eercise A, Question Find the values of for which f() is an increasing function, given that f() equals: (a) + 8 + (b) (c) 5 8 (d) 5 + 6 (e) +
Heinemann Solutionbank: Core Maths C Page of Solutionbank C Eercise A, Question Find the values of for which f() is an increasing function, given that f() equals: (a) + 8 + (b) (c) 5 8 (d) 5 + 6 (e) +
Questions Q1. The function f is defined by. (a) Show that (5) The function g is defined by. (b) Differentiate g(x) to show that g '(x) = (3)
 Questions Q1. The function f is defined by (a) Show that The function g is defined by (b) Differentiate g(x) to show that g '(x) = (c) Find the exact values of x for which g '(x) = 1 (Total 12 marks) Q2.
Questions Q1. The function f is defined by (a) Show that The function g is defined by (b) Differentiate g(x) to show that g '(x) = (c) Find the exact values of x for which g '(x) = 1 (Total 12 marks) Q2.
Math 2414 Activity 1 (Due by end of class July 23) Precalculus Problems: 3,0 and are tangent to the parabola axis. Find the other line.
 Math 44 Activity (Due by end of class July 3) Precalculus Problems: 3, and are tangent to the parabola ais. Find the other line.. One of the two lines that pass through y is the - {Hint: For a line through
Math 44 Activity (Due by end of class July 3) Precalculus Problems: 3, and are tangent to the parabola ais. Find the other line.. One of the two lines that pass through y is the - {Hint: For a line through
MATH 18.01, FALL PROBLEM SET # 6 SOLUTIONS
 MATH 181, FALL 17 - PROBLEM SET # 6 SOLUTIONS Part II (5 points) 1 (Thurs, Oct 6; Second Fundamental Theorem; + + + + + = 16 points) Let sinc(x) denote the sinc function { 1 if x =, sinc(x) = sin x if
MATH 181, FALL 17 - PROBLEM SET # 6 SOLUTIONS Part II (5 points) 1 (Thurs, Oct 6; Second Fundamental Theorem; + + + + + = 16 points) Let sinc(x) denote the sinc function { 1 if x =, sinc(x) = sin x if
4.4: Optimization. Problem 2 Find the radius of a cylindrical container with a volume of 2π m 3 that minimizes the surface area.
 4.4: Optimization Problem 1 Suppose you want to maximize a continuous function on a closed interval, but you find that it only has one local extremum on the interval which happens to be a local minimum.
4.4: Optimization Problem 1 Suppose you want to maximize a continuous function on a closed interval, but you find that it only has one local extremum on the interval which happens to be a local minimum.
Add Math (4047) Paper 2
 1. Solve the simultaneous equations 5 and 1. [5]. (i) Sketch the graph of, showing the coordinates of the points where our graph meets the coordinate aes. [] Solve the equation 10, giving our answer correct
1. Solve the simultaneous equations 5 and 1. [5]. (i) Sketch the graph of, showing the coordinates of the points where our graph meets the coordinate aes. [] Solve the equation 10, giving our answer correct
Math 461 Homework 8. Paul Hacking. November 27, 2018
 Math 461 Homework 8 Paul Hacking November 27, 2018 (1) Let S 2 = {(x, y, z) x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = 1} R 3 be the sphere with center the origin and radius 1. Let N = (0, 0, 1) S 2 be the north pole. Let F :
Math 461 Homework 8 Paul Hacking November 27, 2018 (1) Let S 2 = {(x, y, z) x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = 1} R 3 be the sphere with center the origin and radius 1. Let N = (0, 0, 1) S 2 be the north pole. Let F :
There are some trigonometric identities given on the last page.
 MA 114 Calculus II Fall 2015 Exam 4 December 15, 2015 Name: Section: Last 4 digits of student ID #: No books or notes may be used. Turn off all your electronic devices and do not wear ear-plugs during
MA 114 Calculus II Fall 2015 Exam 4 December 15, 2015 Name: Section: Last 4 digits of student ID #: No books or notes may be used. Turn off all your electronic devices and do not wear ear-plugs during
Math 461 Homework 8 Paul Hacking November 27, 2018
 (1) Let Math 461 Homework 8 Paul Hacking November 27, 2018 S 2 = {(x, y, z) x 2 +y 2 +z 2 = 1} R 3 be the sphere with center the origin and radius 1. Let N = (0, 0, 1) S 2 be the north pole. Let F : S
(1) Let Math 461 Homework 8 Paul Hacking November 27, 2018 S 2 = {(x, y, z) x 2 +y 2 +z 2 = 1} R 3 be the sphere with center the origin and radius 1. Let N = (0, 0, 1) S 2 be the north pole. Let F : S
BE SURE TO READ THE DIRECTIONS PAGE & MAKE YOUR NOTECARDS FIRST!! Part I: Unlimited and Continuous! (21 points)
 BE SURE TO READ THE DIRECTIONS PAGE & MAKE YOUR NOTECARDS FIRST!! Part I: United and Continuous! ( points) For #- below, find the its, if they eist.(#- are pt each) ) 7 ) 9 9 ) 5 ) 8 For #5-7, eplain why
BE SURE TO READ THE DIRECTIONS PAGE & MAKE YOUR NOTECARDS FIRST!! Part I: United and Continuous! ( points) For #- below, find the its, if they eist.(#- are pt each) ) 7 ) 9 9 ) 5 ) 8 For #5-7, eplain why
ENGI Multiple Integration Page 8-01
 ENGI 345 8. Multiple Integration Page 8-01 8. Multiple Integration This chapter provides only a very brief introduction to the major topic of multiple integration. Uses of multiple integration include
ENGI 345 8. Multiple Integration Page 8-01 8. Multiple Integration This chapter provides only a very brief introduction to the major topic of multiple integration. Uses of multiple integration include
MATH Final Review
 MATH 1592 - Final Review 1 Chapter 7 1.1 Main Topics 1. Integration techniques: Fitting integrands to basic rules on page 485. Integration by parts, Theorem 7.1 on page 488. Guidelines for trigonometric
MATH 1592 - Final Review 1 Chapter 7 1.1 Main Topics 1. Integration techniques: Fitting integrands to basic rules on page 485. Integration by parts, Theorem 7.1 on page 488. Guidelines for trigonometric
AP Physics C. Gauss s Law. Free Response Problems
 AP Physics Gauss s Law Free Response Problems 1. A flat sheet of glass of area 0.4 m 2 is placed in a uniform electric field E = 500 N/. The normal line to the sheet makes an angle θ = 60 ẘith the electric
AP Physics Gauss s Law Free Response Problems 1. A flat sheet of glass of area 0.4 m 2 is placed in a uniform electric field E = 500 N/. The normal line to the sheet makes an angle θ = 60 ẘith the electric
Unit #13 - Integration to Find Areas and Volumes, Volumes of Revolution
 Unit #1 - Integration to Find Areas and Volumes, Volumes of Revolution Some problems and solutions selected or adapted from Hughes-Hallett Calculus. Areas In Questions #1-8, find the area of one strip
Unit #1 - Integration to Find Areas and Volumes, Volumes of Revolution Some problems and solutions selected or adapted from Hughes-Hallett Calculus. Areas In Questions #1-8, find the area of one strip
Solutions th AMC 12 A (E) Since $20 is 2000 cents, she pays (0.0145)(2000) = 29 cents per hour in local taxes.
 Solutions 2004 55 th AMC 12 A 2 1. (E) Since $20 is 2000 cents, she pays (0.0145)(2000) = 29 cents per hour in local taxes. 2. (C) The 8 unanswered problems are worth (2.5)(8) = 20 points, so Charlyn must
Solutions 2004 55 th AMC 12 A 2 1. (E) Since $20 is 2000 cents, she pays (0.0145)(2000) = 29 cents per hour in local taxes. 2. (C) The 8 unanswered problems are worth (2.5)(8) = 20 points, so Charlyn must
C4 "International A-level" (150 minute) papers: June 2014 and Specimen 1. C4 INTERNATIONAL A LEVEL PAPER JUNE 2014
 C4 "International A-level" (150 minute) papers: June 2014 and Specimen 1. C4 INTERNATIONAL A LEVEL PAPER JUNE 2014 1. f(x) = 2x 3 + x 10 (a) Show that the equation f(x) = 0 has a root in the interval [1.5,
C4 "International A-level" (150 minute) papers: June 2014 and Specimen 1. C4 INTERNATIONAL A LEVEL PAPER JUNE 2014 1. f(x) = 2x 3 + x 10 (a) Show that the equation f(x) = 0 has a root in the interval [1.5,
Graphing Review Part 1: Circles, Ellipses and Lines
 Graphing Review Part : Circles, Ellipses and Lines Definition The graph of an equation is the set of ordered pairs, (, y), that satisfy the equation We can represent the graph of a function by sketching
Graphing Review Part : Circles, Ellipses and Lines Definition The graph of an equation is the set of ordered pairs, (, y), that satisfy the equation We can represent the graph of a function by sketching
Math 147 Exam II Practice Problems
 Math 147 Exam II Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture, all homework problems, all lab
Math 147 Exam II Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture, all homework problems, all lab
3 Applications of Derivatives Instantaneous Rates of Change Optimization Related Rates... 13
 Contents Limits Derivatives 3. Difference Quotients......................................... 3. Average Rate of Change...................................... 4.3 Derivative Rules...........................................
Contents Limits Derivatives 3. Difference Quotients......................................... 3. Average Rate of Change...................................... 4.3 Derivative Rules...........................................
5.5 Volumes: Tubes. The Tube Method. = (2π [radius]) (height) ( x k ) = (2πc k ) f (c k ) x k. 5.5 volumes: tubes 435
![5.5 Volumes: Tubes. The Tube Method. = (2π [radius]) (height) ( x k ) = (2πc k ) f (c k ) x k. 5.5 volumes: tubes 435 5.5 Volumes: Tubes. The Tube Method. = (2π [radius]) (height) ( x k ) = (2πc k ) f (c k ) x k. 5.5 volumes: tubes 435](/thumbs/78/77255700.jpg) 5.5 volumes: tubes 45 5.5 Volumes: Tubes In Section 5., we devised the disk method to find the volume swept out when a region is revolved about a line. To find the volume swept out when revolving a region
5.5 volumes: tubes 45 5.5 Volumes: Tubes In Section 5., we devised the disk method to find the volume swept out when a region is revolved about a line. To find the volume swept out when revolving a region
Math 107. Rumbos Fall Solutions to Review Problems for Exam 3
 Math 17. umbos Fall 29 1 Solutions to eview Problems for Eam 3 1. Consider a wheel of radius a which is rolling on the ais in the plane. Suppose that the center of the wheel moves in the positive direction
Math 17. umbos Fall 29 1 Solutions to eview Problems for Eam 3 1. Consider a wheel of radius a which is rolling on the ais in the plane. Suppose that the center of the wheel moves in the positive direction
5 Find an equation of the circle in which AB is a diameter in each case. a A (1, 2) B (3, 2) b A ( 7, 2) B (1, 8) c A (1, 1) B (4, 0)
 C2 CRDINATE GEMETRY Worksheet A 1 Write down an equation of the circle with the given centre and radius in each case. a centre (0, 0) radius 5 b centre (1, 3) radius 2 c centre (4, 6) radius 1 1 d centre
C2 CRDINATE GEMETRY Worksheet A 1 Write down an equation of the circle with the given centre and radius in each case. a centre (0, 0) radius 5 b centre (1, 3) radius 2 c centre (4, 6) radius 1 1 d centre
MATH 162. Midterm 2 ANSWERS November 18, 2005
 MATH 62 Midterm 2 ANSWERS November 8, 2005. (0 points) Does the following integral converge or diverge? To get full credit, you must justify your answer. 3x 2 x 3 + 4x 2 + 2x + 4 dx You may not be able
MATH 62 Midterm 2 ANSWERS November 8, 2005. (0 points) Does the following integral converge or diverge? To get full credit, you must justify your answer. 3x 2 x 3 + 4x 2 + 2x + 4 dx You may not be able
Practice Final Solutions
 Practice Final Solutions Math 1, Fall 17 Problem 1. Find a parameterization for the given curve, including bounds on the parameter t. Part a) The ellipse in R whose major axis has endpoints, ) and 6, )
Practice Final Solutions Math 1, Fall 17 Problem 1. Find a parameterization for the given curve, including bounds on the parameter t. Part a) The ellipse in R whose major axis has endpoints, ) and 6, )
Math 2414 Activity 1 (Due by end of class Jan. 26) Precalculus Problems: 3,0 and are tangent to the parabola axis. Find the other line.
 Math Activity (Due by end of class Jan. 6) Precalculus Problems: 3, and are tangent to the parabola ais. Find the other line.. One of the two lines that pass through y is the - {Hint: For a line through
Math Activity (Due by end of class Jan. 6) Precalculus Problems: 3, and are tangent to the parabola ais. Find the other line.. One of the two lines that pass through y is the - {Hint: For a line through
Math 233. Practice Problems Chapter 15. i j k
 Math 233. Practice Problems hapter 15 1. ompute the curl and divergence of the vector field F given by F (4 cos(x 2 ) 2y)i + (4 sin(y 2 ) + 6x)j + (6x 2 y 6x + 4e 3z )k olution: The curl of F is computed
Math 233. Practice Problems hapter 15 1. ompute the curl and divergence of the vector field F given by F (4 cos(x 2 ) 2y)i + (4 sin(y 2 ) + 6x)j + (6x 2 y 6x + 4e 3z )k olution: The curl of F is computed
SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #2, Math 253
 SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #, Math 5. Find the equation of a sphere if one of its diameters has end points (, 0, 5) and (5, 4, 7). The length of the diameter is (5 ) + ( 4 0) + (7 5) = =, so the
SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #, Math 5. Find the equation of a sphere if one of its diameters has end points (, 0, 5) and (5, 4, 7). The length of the diameter is (5 ) + ( 4 0) + (7 5) = =, so the
Solutions to old Exam 3 problems
 Solutions to old Exam 3 problems Hi students! I am putting this version of my review for the Final exam review here on the web site, place and time to be announced. Enjoy!! Best, Bill Meeks PS. There are
Solutions to old Exam 3 problems Hi students! I am putting this version of my review for the Final exam review here on the web site, place and time to be announced. Enjoy!! Best, Bill Meeks PS. There are
Math 005A Prerequisite Material Answer Key
 Math 005A Prerequisite Material Answer Key 1. a) P = 4s (definition of perimeter and square) b) P = l + w (definition of perimeter and rectangle) c) P = a + b + c (definition of perimeter and triangle)
Math 005A Prerequisite Material Answer Key 1. a) P = 4s (definition of perimeter and square) b) P = l + w (definition of perimeter and rectangle) c) P = a + b + c (definition of perimeter and triangle)
MATH 1207 R02 FINAL SOLUTION
 MATH 7 R FINAL SOLUTION SPRING 6 - MOON Write your answer neatly and show steps. Except calculators, any electronic devices including laptops and cell phones are not allowed. () Let f(x) = x cos x. (a)
MATH 7 R FINAL SOLUTION SPRING 6 - MOON Write your answer neatly and show steps. Except calculators, any electronic devices including laptops and cell phones are not allowed. () Let f(x) = x cos x. (a)
Chapter 6 Overview: Applications of Derivatives
 Chapter 6 Overview: Applications of Derivatives There are two main contets for derivatives: graphing and motion. In this chapter, we will consider the graphical applications of the derivative. Much of
Chapter 6 Overview: Applications of Derivatives There are two main contets for derivatives: graphing and motion. In this chapter, we will consider the graphical applications of the derivative. Much of
Mathematics Extension 2
 0 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION Mathematics Etension General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time hours Write using black or blue pen Black pen is preferred Board-approved calculators
0 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION Mathematics Etension General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time hours Write using black or blue pen Black pen is preferred Board-approved calculators
10550 PRACTICE FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS. x 2 4. x 2 x 2 5x +6 = lim x +2. x 2 x 3 = 4 1 = 4.
 55 PRACTICE FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS. First notice that x 2 4 x 2x + 2 x 2 5x +6 x 2x. This function is undefined at x 2. Since, in the it as x 2, we only care about what happens near x 2 an for x less than
55 PRACTICE FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS. First notice that x 2 4 x 2x + 2 x 2 5x +6 x 2x. This function is undefined at x 2. Since, in the it as x 2, we only care about what happens near x 2 an for x less than
General Definition of Torque, final. Lever Arm. General Definition of Torque 7/29/2010. Units of Chapter 10
 Units of Chapter 10 Determining Moments of Inertia Rotational Kinetic Energy Rotational Plus Translational Motion; Rolling Why Does a Rolling Sphere Slow Down? General Definition of Torque, final Taking
Units of Chapter 10 Determining Moments of Inertia Rotational Kinetic Energy Rotational Plus Translational Motion; Rolling Why Does a Rolling Sphere Slow Down? General Definition of Torque, final Taking
MATHEMATICS 317 December 2010 Final Exam Solutions
 MATHEMATI 317 December 1 Final Eam olutions 1. Let r(t) = ( 3 cos t, 3 sin t, 4t ) be the position vector of a particle as a function of time t. (a) Find the velocity of the particle as a function of time
MATHEMATI 317 December 1 Final Eam olutions 1. Let r(t) = ( 3 cos t, 3 sin t, 4t ) be the position vector of a particle as a function of time t. (a) Find the velocity of the particle as a function of time
AP Calculus BC Chapter 4 AP Exam Problems A) 4 B) 2 C) 1 D) 0 E) 2 A) 9 B) 12 C) 14 D) 21 E) 40
 Extreme Values in an Interval AP Calculus BC 1. The absolute maximum value of x = f ( x) x x 1 on the closed interval, 4 occurs at A) 4 B) C) 1 D) 0 E). The maximum acceleration attained on the interval
Extreme Values in an Interval AP Calculus BC 1. The absolute maximum value of x = f ( x) x x 1 on the closed interval, 4 occurs at A) 4 B) C) 1 D) 0 E). The maximum acceleration attained on the interval
Sample Final Questions: Solutions Math 21B, Winter y ( y 1)(1 + y)) = A y + B
 Sample Final Questions: Solutions Math 2B, Winter 23. Evaluate the following integrals: tan a) y y dy; b) x dx; c) 3 x 2 + x dx. a) We use partial fractions: y y 3 = y y ) + y)) = A y + B y + C y +. Putting
Sample Final Questions: Solutions Math 2B, Winter 23. Evaluate the following integrals: tan a) y y dy; b) x dx; c) 3 x 2 + x dx. a) We use partial fractions: y y 3 = y y ) + y)) = A y + B y + C y +. Putting
Math 2250 Final Exam Practice Problem Solutions. f(x) = ln x x. 1 x. lim. lim. x x = lim. = lim 2
 Math 5 Final Eam Practice Problem Solutions. What are the domain and range of the function f() = ln? Answer: is only defined for, and ln is only defined for >. Hence, the domain of the function is >. Notice
Math 5 Final Eam Practice Problem Solutions. What are the domain and range of the function f() = ln? Answer: is only defined for, and ln is only defined for >. Hence, the domain of the function is >. Notice
Chapter 9 Overview: Parametric and Polar Coordinates
 Chapter 9 Overview: Parametric and Polar Coordinates As we saw briefly last year, there are axis systems other than the Cartesian System for graphing (vector coordinates, polar coordinates, rectangular
Chapter 9 Overview: Parametric and Polar Coordinates As we saw briefly last year, there are axis systems other than the Cartesian System for graphing (vector coordinates, polar coordinates, rectangular
Math 8 Honors Coordinate Geometry part 1 Unit Updated July 29, 2016
 Reviewing the basics The number line A number line is a visual representation of all real numbers. Each of the images below are examples of number lines. The top left one includes only positive whole numbers,
Reviewing the basics The number line A number line is a visual representation of all real numbers. Each of the images below are examples of number lines. The top left one includes only positive whole numbers,
CHAPTER 72 AREAS UNDER AND BETWEEN CURVES
 CHAPTER 7 AREAS UNDER AND BETWEEN CURVES EXERCISE 8 Page 77. Show by integration that the area of the triangle formed by the line y, the ordinates and and the -ais is 6 square units. A sketch of y is shown
CHAPTER 7 AREAS UNDER AND BETWEEN CURVES EXERCISE 8 Page 77. Show by integration that the area of the triangle formed by the line y, the ordinates and and the -ais is 6 square units. A sketch of y is shown
Mth Review Problems for Test 2 Stewart 8e Chapter 3. For Test #2 study these problems, the examples in your notes, and the homework.
 For Test # study these problems, the examples in your notes, and the homework. Derivative Rules D [u n ] = nu n 1 du D [ln u] = du u D [log b u] = du u ln b D [e u ] = e u du D [a u ] = a u ln a du D [sin
For Test # study these problems, the examples in your notes, and the homework. Derivative Rules D [u n ] = nu n 1 du D [ln u] = du u D [log b u] = du u ln b D [e u ] = e u du D [a u ] = a u ln a du D [sin
THE NCUK INTERNATIONAL FOUNDATION YEAR (IFY) Further Mathematics
 IFYFM00 Further Maths THE NCUK INTERNATIONAL FOUNDATION YEAR (IFY) Further Mathematics Examination Session Summer 009 Time Allowed hours 0 minutes (Including 0 minutes reading time) INSTRUCTIONS TO STUDENTS
IFYFM00 Further Maths THE NCUK INTERNATIONAL FOUNDATION YEAR (IFY) Further Mathematics Examination Session Summer 009 Time Allowed hours 0 minutes (Including 0 minutes reading time) INSTRUCTIONS TO STUDENTS
DIFFERENTIATION RULES
 3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES Before starting this section, you might need to review the trigonometric functions. DIFFERENTIATION RULES In particular, it is important to remember that,
3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES Before starting this section, you might need to review the trigonometric functions. DIFFERENTIATION RULES In particular, it is important to remember that,
Math 132 Information for Test 2
 Math 13 Information for Test Test will cover material from Sections 5.6, 5.7, 5.8, 6.1, 6., 6.3, 7.1, 7., and 7.3. The use of graphing calculators will not be allowed on the test. Some practice questions
Math 13 Information for Test Test will cover material from Sections 5.6, 5.7, 5.8, 6.1, 6., 6.3, 7.1, 7., and 7.3. The use of graphing calculators will not be allowed on the test. Some practice questions
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER INTEGRATION APPLICATIONS 13 (Second moments of a volume (A)) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 13.13 INTEGRATION APPLICATIONS 13 (Second moments of a volume (A)) by A.J.Hobson 13.13.1 Introduction 13.13. The second moment of a volume of revolution about the y-axis 13.13.3
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 13.13 INTEGRATION APPLICATIONS 13 (Second moments of a volume (A)) by A.J.Hobson 13.13.1 Introduction 13.13. The second moment of a volume of revolution about the y-axis 13.13.3
Practice Midterm Exam 1. Instructions. You have 60 minutes. No calculators allowed. Show all your work in order to receive full credit.
 MATH202X-F01/UX1 Spring 2015 Practice Midterm Exam 1 Name: Answer Key Instructions You have 60 minutes No calculators allowed Show all your work in order to receive full credit 1 Consider the points P
MATH202X-F01/UX1 Spring 2015 Practice Midterm Exam 1 Name: Answer Key Instructions You have 60 minutes No calculators allowed Show all your work in order to receive full credit 1 Consider the points P
1 + f 2 x + f 2 y dy dx, where f(x, y) = 2 + 3x + 4y, is
 1. The value of the double integral (a) 15 26 (b) 15 8 (c) 75 (d) 105 26 5 4 0 1 1 + f 2 x + f 2 y dy dx, where f(x, y) = 2 + 3x + 4y, is 2. What is the value of the double integral interchange the order
1. The value of the double integral (a) 15 26 (b) 15 8 (c) 75 (d) 105 26 5 4 0 1 1 + f 2 x + f 2 y dy dx, where f(x, y) = 2 + 3x + 4y, is 2. What is the value of the double integral interchange the order
AP Calculus AB 2nd Semester Homework List
 AP Calculus AB 2nd Semester Homework List Date Assigned: 1/4 DUE Date: 1/6 Title: Typsetting Basic L A TEX and Sigma Notation Write the homework out on paper. Then type the homework on L A TEX. Use this
AP Calculus AB 2nd Semester Homework List Date Assigned: 1/4 DUE Date: 1/6 Title: Typsetting Basic L A TEX and Sigma Notation Write the homework out on paper. Then type the homework on L A TEX. Use this
Chapter 3: Derivatives and Graphing
 Chapter 3: Derivatives and Graphing 127 Chapter 3 Overview: Derivatives and Graphs There are two main contexts for derivatives: graphing and motion. In this chapter, we will consider the graphical applications
Chapter 3: Derivatives and Graphing 127 Chapter 3 Overview: Derivatives and Graphs There are two main contexts for derivatives: graphing and motion. In this chapter, we will consider the graphical applications
Math 1 packet for Coordinate Geometry part 1. Reviewing the basics. The coordinate plane
 Math 1 packet for Coordinate Geometry part 1 Reviewing the basics The coordinate plane The coordinate plane (also called the Cartesian plane named after French mathematician Rene Descartes, who formalized
Math 1 packet for Coordinate Geometry part 1 Reviewing the basics The coordinate plane The coordinate plane (also called the Cartesian plane named after French mathematician Rene Descartes, who formalized
MA 114 Worksheet # 1: Improper Integrals
 MA 4 Worksheet # : Improper Integrals. For each of the following, determine if the integral is proper or improper. If it is improper, explain why. Do not evaluate any of the integrals. (c) 2 0 2 2 x x
MA 4 Worksheet # : Improper Integrals. For each of the following, determine if the integral is proper or improper. If it is improper, explain why. Do not evaluate any of the integrals. (c) 2 0 2 2 x x
Answer Key. ( 1) n (2x+3) n. n n=1. (2x+3) n. = lim. < 1 or 2x+3 < 4. ( 1) ( 1) 2n n
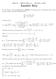 Math Midterm Eam #3 December, 3 Answer Key. [5 Points] Find the Interval and Radius of Convergence for the following power series. Analyze carefully and with full justification. Use Ratio Test. L lim a
Math Midterm Eam #3 December, 3 Answer Key. [5 Points] Find the Interval and Radius of Convergence for the following power series. Analyze carefully and with full justification. Use Ratio Test. L lim a
Chapter 8: Radical Functions
 Chapter 8: Radical Functions Chapter 8 Overview: Types and Traits of Radical Functions Vocabulary:. Radical (Irrational) Function an epression whose general equation contains a root of a variable and possibly
Chapter 8: Radical Functions Chapter 8 Overview: Types and Traits of Radical Functions Vocabulary:. Radical (Irrational) Function an epression whose general equation contains a root of a variable and possibly
Final practice, Math 31A - Lec 1, Fall 2013 Name and student ID: Question Points Score Total: 90
 Final practice, Math 31A - Lec 1, Fall 13 Name and student ID: Question Points Score 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 6 1 7 1 8 1 9 1 Total: 9 1. a) 4 points) Find all points x at which the function fx) x 4x + 3 + x
Final practice, Math 31A - Lec 1, Fall 13 Name and student ID: Question Points Score 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 6 1 7 1 8 1 9 1 Total: 9 1. a) 4 points) Find all points x at which the function fx) x 4x + 3 + x
MATH 32 FALL 2012 FINAL EXAM - PRACTICE EXAM SOLUTIONS
 MATH 3 FALL 0 FINAL EXAM - PRACTICE EXAM SOLUTIONS () You cut a slice from a circular pizza (centered at the origin) with radius 6 along radii at angles 4 and 3 with the positive horizontal axis. (a) (3
MATH 3 FALL 0 FINAL EXAM - PRACTICE EXAM SOLUTIONS () You cut a slice from a circular pizza (centered at the origin) with radius 6 along radii at angles 4 and 3 with the positive horizontal axis. (a) (3
Find the rectangular coordinates for each of the following polar coordinates:
 WORKSHEET 13.1 1. Plot the following: 7 3 A. 6, B. 3, 6 4 5 8 D. 6, 3 C., 11 2 E. 5, F. 4, 6 3 Find the rectangular coordinates for each of the following polar coordinates: 5 2 2. 4, 3. 8, 6 3 Given the
WORKSHEET 13.1 1. Plot the following: 7 3 A. 6, B. 3, 6 4 5 8 D. 6, 3 C., 11 2 E. 5, F. 4, 6 3 Find the rectangular coordinates for each of the following polar coordinates: 5 2 2. 4, 3. 8, 6 3 Given the
Math 2250 Final Exam Practice Problem Solutions. f(x) = ln x x. 1 x. lim. lim. x x = lim. = lim 2
 Math 5 Final Eam Practice Problem Solutions. What are the domain and range of the function f() = ln? Answer: is only defined for, and ln is only defined for >. Hence, the domain of the function is >. Notice
Math 5 Final Eam Practice Problem Solutions. What are the domain and range of the function f() = ln? Answer: is only defined for, and ln is only defined for >. Hence, the domain of the function is >. Notice
