Linear Functions (I)
|
|
|
- Alan Nash
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 4. MAPPING BY ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS There are many practical situations where we try to simplify a problem by transforming it. We investigate how various regions in the plane are transformed by elementary analytic functions. You may find the following website helpful: Linear Functions (I) 1. w = f(z) = z + c (c = (c 1, c 2 ) C) this is a translation through c. Each z = (x, y) maps to w = (x + c 1, y + c 2 ). 2. Let b = b cis θ be a complex constant and let w = f(z) = bz. If z = r cis φ, then w = r. b. cis(θ + φ). That is, each point (r, θ) maps to ( b.r, θ + φ). Thus we have a rotation about O through φ and an enlargement through b.
2 Linear Functions (II) The general linear function is the mapping w = f(z) = bz + c. This is the rotation and enlargement (2), followed by the translation (1) previously discussed. That is, Example z bz bz + c. Consider the transformation w = iz + (i + 1). This maps square A to square B in the figure below. Notice that S is an invariant point of this transformation. Geometrically, we have: rotation translation = rotation.
3 The Function f (z) = z 2 (I) Let w = f(z) = z 2. Then if z = r cis θ and w = ρ cis φ, we have ρ cis φ = r 2 cis 2θ and (r, θ) (ρ, φ) = (r 2, 2θ ). Example The first quadrant of the complex plane maps to the top half-plane under this mapping, since the angle range 0 θ π / 2 maps to the range 0 φ π. We note that in general, the mapping w = f (z) = z 2 will not be 1 1. For example, the points ± z both map to the same w.
4 The Function f (z) = z 2 (II) Let us now write w = f(z) = z 2 in cartesian coordinates. Setting w = u + iv, z = x + iy,we obtain u + iv = (x 2 y 2 ) + 2xyi. That is,(x, y) (x 2 y 2, 2xy). So z-points on the hyperbola x 2 y 2 = k map to points on the straight line u = k. Similarly z-points on the hyperbola 2xy = k map to points on the straight line v = k. y O k = 2 k = 1 k = 0 k = -1 k = -2 x k' = 2 k' = 1 k' = 0 k' = -1 k' = -2-2 v O u
5 Quiz Under the mapping w = iz + 2 the point 1 + i is left invariant. (a) True ; (b) False. 2. Under w = iz + 2, (2, 0) is a vertex of the image of the square 0 x, y 1. (a) True ; (b) False. 3. The mapping w = z 2 with domain {z z = r cis θ, π / 4 < θ < 0} is 1 1. (a) True ; (b) False. 4. The mapping w = z 2 maps the second quadrant π / θ 2 π to a halfplane. (a) True ; (b) False. 1. True. Substitute 1 + i. 2. True. The given square is rotated about O through π / 2 and translated 2 in the x-direction. 3. True. The image region π / 2 < θ < 0 does not overlap itself. 4. True. The image is π θ 2π. x
6 The Function f (z) = 1 / z The mapping w = f ( z ) = 1 / z (equivalently z = 1 / w ) sets up a 1 1 correspondence between points in the z- and w - planes excluding z = 0, w = 0. In polar coordinates, w = 1 / z becomes ρ cis φ = 1 r cis ( θ). This transformation is the product of two simpler transformations: z = r cis θ z = 1 r cis θ and z = 1 r cis θ w = z inversion in the unit circle followed by reflection in the x-axis. Notes 1. Under inversion, the points on remain invariant. 2. Under w = 1 / z, (and under inversion), the centre of remains invariant; lines through O map to lines through O; the interior of the exterior of ; (in fact, all circles centred at O map to circles centred at O ).
7 Mapping Circles and Lines under f (z) = 1 / z (I) Question What is the effect of f ( z ) = 1 / z on more general lines and circles? Expressing w = f ( z ) = 1 / z in terms of cartesian coordinates, we obtain Thus and inversely w = u + iv = 1 = x iy x + iy x 2 + y 2 x 2 + y 2 u = x, v = y x 2 + y 2 x 2 + y 2 x = u, y = v. u 2 + v 2 u 2 + v 2 To catch a lion in the Sahara Desert, place a spherical cage in the desert, enter it, and lock it. Now perform an inversion with respect to the cage. The lion is then in the interior of the cage, and we are outside. H. Pétard
8 Mapping Circles and Lines under f (z) = 1 / z (II) Now consider the equation a(x 2 + y 2 ) + bx + cy + d = 0 (a, b, c, d R). (*) If a 0, this is the equation of a circle; if a = 0, the equation of a straight line. Substituting for x, y in terms of u, v we get d ( u 2 + v 2 ) + bu cv + a = 0 ( ) Points (u, v) satisfying ( ) correspond to points (x, y ) satisfying (*). Hence we have the four cases: (a) a 0, d 0. Circle not through O circle not through O. (b) a 0, d = 0. Circle through O straight line not through O. (c) a = 0, d 0. Straight line not through O circle through O. (d) a = 0, d = 0. Straight line through O straight line through O.
9 Example of a Mapping under f ( z ) = 1 / z What is the image under w = f(z) = 1 / z of the line x = c? The line x = c maps to the set of points satisfying u u 2 + v 2 = c, that is, u 2 + v 2 u c = 0, or (u 1 2 c)2 + v 2 = ( 1 2 c)2. This is the circle with centre ( 1 2c, 0), passing through the origin O. The half plane x > c maps to the interior of the disc. y v O c x O 1 2c u
10 QUIZ Under the mapping w = 1 / z the image of 3 + 2i is 2. Under w = 1 / z, the circle z 1 = 1 maps to 3. Under w = 1 / z, the halfplane y > 1 maps to 4. Under w = 1 / z, any circle centred at O maps to itself. (a) True ; (b) False. 1. The image is i. 2. The given circle passes through O. It maps to the straight line x = The interior of the circle with diamter OP where P(0,1). 4. Only true for the circle of radius 1. x
11 Bilinear Transformations Let T be the transformation w = az + b, (ad bc 0, a, b, c, d C ). cz + d This is called a bilinear transformation as it can be rewritten as cwz + dw az b = 0 an equation which is linear in each of its variables, z and w. Solving for w transformation: in terms of z, we see that the inverse of T is another bilinear T 1 : z = dw + b. cw a Notes 1. The singular points for T, T 1 are z = d / c,w = a / c respectively. As each mapping has just one singular point, we write z = d / c w =, w = a / c z =. 2. The set of bilinear transformations forms a group.
12 Understanding the Bilinear Transformation In the formula for a bilinear transformation, if c 0, we can write w = az + b = a(z + d / c ) + (b ad / c ) = a + (b ad / c ) cz + d c(z + d / c ) c cz + d Setting z = cz + d, w = z = 1 / z we obtain a + (bc ad ) z. (*) c c If c = 0, we get an expression of type (*) immediately. It follows that any bilinear transformation can be obtained as the composition of linear transformations and the mapping f (z) = 1 / z, all of which map lines and circles to lines and circles. Hence any bilinear transformation maps the set of lines and circles to itself.
13 Images under a Bilinear Transformation The following reult will be useful. Theorem 4.1 There exists a unique bilinear transformation which maps three given distinct points z 1, z 2, z 3 onto three distinct points w 1, w 2, w 3 respectively. Proof The algebraic expression for the bilinear transformation can be written as cwz + dw az b = 0. This is an equation in four unknowns a, b, c, d. Hence the three ratios a : b : c : d of these numbers are determined by substituting three pairs of corresponding values of z i, w i (1 i 3). In practice, this means that in general if we allocate image points to three points in the z-plane, then the bilinear transformation will be completely determined. Conversely, if we want to find the image of a circle (say) under a given bilinear transformation, then it is sufficient to find the images of three points on the circle.
14 Bilinear Transformation: Example Let a C be constant with Im a > 0. Find the image of the upper half plane (y 0) under the bilinear transformation w = z a. z a We first consider the boundary. For z on the x-axis, we have z a = z a. Hence for such points, w = z a = 1. z a That is, the x-axis maps to the unit circle having centre O. Also, z = a (a point in the upper half plane) maps to w = 0 (a point interior to the unit circle). Observing that the mapping is continuous, we deduce that the image of the upper half plane is the interior of the disc. y O a a x v O 1 u
15 QUIZ The bilinear transformation which maps 0 1, 1 0, 1 maps i 2. The image of the x-axis under w = z i z + 1 is 3. The image of the y-axis under w = z i z + 1 is 4. A bilinear transformation mapping a circle to a circle must map the interior of one to the interior of the other. (a) True (b) False. 1. The image is i. 2. The line y = x + 1. Note that The circle centre i,passing through O. Thus 0 i, 1, i False. Consider z < 1 under w = 1 / z. x
16 The Transformation w = exp z As before, we set z = x + iy, w = ρ cis φ. Then w = exp z gives ρ = e x and φ = y. The line y = c maps onto the ray φ = c (excluding the end-point O) in a 1 1 fashion. Similarly, the line x = c maps onto the circle ρ = e c. However, here, an infinite number of points on the line map to each image point. Combining these results, we see that the rectangular region a x b, c y d is mapped to the region e a ρ e b, c φ d, bounded by portions of circles and rays. y d c O a b x v O u This mapping is 1 1 if d c < 2π. c d e a e b
17 Special Case of w = exp z As a particular case, under the exponential mapping, the strip 0 < y < π maps to the upper half plane ρ > 0, 0 < φ < π of the w-plane. y π v O x O u It is interesting to map the boundary points here. This mapping is useful in applications.
18 1. Under the mapping w = exp z, the image of the x-axis is unbounded. (a) True ; (b) False. 2. Under the mapping w = exp z, the image of the y-axis is unbounded. (a) True ; (b) False. 3. Under w = exp z, equally spaced lines parallel to the y-axis map to equally spaced concentric circles. (a) True ; (b) False. QUIZ True: x unbounded ρ = e x unbounded. 2. False: x = 0 ρ = 1, so bounded. 3. False: there is an exponential factor. 4. False: the opposite ray arises from y = c + (2k + 1)π. 4. Under w = exp z, the line y = c maps to a ray in the w-plane. Then the opposite ray arises from the line y = c. x (a) True ; (b) False.
Conformal Mapping, Möbius Transformations. Slides-13
 , Möbius Transformations Slides-13 Let γ : [a, b] C be a smooth curve in a domain D. Let f be a function defined at all points z on γ. Let C denotes the image of γ under the transformation w = f (z).
, Möbius Transformations Slides-13 Let γ : [a, b] C be a smooth curve in a domain D. Let f be a function defined at all points z on γ. Let C denotes the image of γ under the transformation w = f (z).
Möbius transformations and its applications
 Möbius transformation and its applications Every Möbius transformation is the composition of translations, dilations and the inversion. Proof. Let w = S(z) = az + b, ad bc 0 be a Möbius cz + d transformation.
Möbius transformation and its applications Every Möbius transformation is the composition of translations, dilations and the inversion. Proof. Let w = S(z) = az + b, ad bc 0 be a Möbius cz + d transformation.
CHAPTER 9. Conformal Mapping and Bilinear Transformation. Dr. Pulak Sahoo
 CHAPTER 9 Conformal Mapping and Bilinear Transformation BY Dr. Pulak Sahoo Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics University of Kalyani West Bengal, India E-mail : sahoopulak1@gmail.com 1 Module-4:
CHAPTER 9 Conformal Mapping and Bilinear Transformation BY Dr. Pulak Sahoo Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics University of Kalyani West Bengal, India E-mail : sahoopulak1@gmail.com 1 Module-4:
CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58
 CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58 We prove that a strong form of converse of the above statement also holds. Please note we could apply the Theorem 1.11.3 to prove the theorem. But we prefer to apply the
CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58 We prove that a strong form of converse of the above statement also holds. Please note we could apply the Theorem 1.11.3 to prove the theorem. But we prefer to apply the
26.2. Cauchy-Riemann Equations and Conformal Mapping. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Cauchy-Riemann Equations and Conformal Mapping 26.2 Introduction In this Section we consider two important features of complex functions. The Cauchy-Riemann equations provide a necessary and sufficient
Cauchy-Riemann Equations and Conformal Mapping 26.2 Introduction In this Section we consider two important features of complex functions. The Cauchy-Riemann equations provide a necessary and sufficient
5.3 The Upper Half Plane
 Remark. Combining Schwarz Lemma with the map g α, we can obtain some inequalities of analytic maps f : D D. For example, if z D and w = f(z) D, then the composition h := g w f g z satisfies the condition
Remark. Combining Schwarz Lemma with the map g α, we can obtain some inequalities of analytic maps f : D D. For example, if z D and w = f(z) D, then the composition h := g w f g z satisfies the condition
COMPLEX NUMBERS AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS
 Chapter 5 COMPLEX NUMBERS AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS 5. Overview We know that the square of a real number is always non-negative e.g. (4) 6 and ( 4) 6. Therefore, square root of 6 is ± 4. What about the square
Chapter 5 COMPLEX NUMBERS AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS 5. Overview We know that the square of a real number is always non-negative e.g. (4) 6 and ( 4) 6. Therefore, square root of 6 is ± 4. What about the square
Worked examples Conformal mappings and bilinear transformations
 Worked examples Conformal mappings and bilinear transformations Example 1 Suppose we wish to find a bilinear transformation which maps the circle z i = 1 to the circle w =. Since w/ = 1, the linear transformation
Worked examples Conformal mappings and bilinear transformations Example 1 Suppose we wish to find a bilinear transformation which maps the circle z i = 1 to the circle w =. Since w/ = 1, the linear transformation
NPTEL web course on Complex Analysis. A. Swaminathan I.I.T. Roorkee, India. and. V.K. Katiyar I.I.T. Roorkee, India
 NPTEL web course on Complex Analysis A. Swaminathan I.I.T. Roorkee, India and V.K. Katiyar I.I.T. Roorkee, India A.Swaminathan and V.K.Katiyar (NPTEL) Complex Analysis 1 / 36 Complex Analysis Module: 7:
NPTEL web course on Complex Analysis A. Swaminathan I.I.T. Roorkee, India and V.K. Katiyar I.I.T. Roorkee, India A.Swaminathan and V.K.Katiyar (NPTEL) Complex Analysis 1 / 36 Complex Analysis Module: 7:
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY MA205 Complex Analysis Autumn 2012
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY MA205 Complex Analysis Autumn 2012 September 5, 2012 Mapping Properties Lecture 13 We shall once again return to the study of general behaviour of holomorphic functions
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY MA205 Complex Analysis Autumn 2012 September 5, 2012 Mapping Properties Lecture 13 We shall once again return to the study of general behaviour of holomorphic functions
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 530) January 2019
 Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
Solutions to Exercises 6.1
 34 Chapter 6 Conformal Mappings Solutions to Exercises 6.. An analytic function fz is conformal where f z. If fz = z + e z, then f z =e z z + z. We have f z = z z += z =. Thus f is conformal at all z.
34 Chapter 6 Conformal Mappings Solutions to Exercises 6.. An analytic function fz is conformal where f z. If fz = z + e z, then f z =e z z + z. We have f z = z z += z =. Thus f is conformal at all z.
Section 5.8. (i) ( 3 + i)(14 2i) = ( 3)(14 2i) + i(14 2i) = {( 3)14 ( 3)(2i)} + i(14) i(2i) = ( i) + (14i + 2) = i.
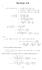 1. Section 5.8 (i) ( 3 + i)(14 i) ( 3)(14 i) + i(14 i) {( 3)14 ( 3)(i)} + i(14) i(i) ( 4 + 6i) + (14i + ) 40 + 0i. (ii) + 3i 1 4i ( + 3i)(1 + 4i) (1 4i)(1 + 4i) (( + 3i) + ( + 3i)(4i) 1 + 4 10 + 11i 10
1. Section 5.8 (i) ( 3 + i)(14 i) ( 3)(14 i) + i(14 i) {( 3)14 ( 3)(i)} + i(14) i(i) ( 4 + 6i) + (14i + ) 40 + 0i. (ii) + 3i 1 4i ( + 3i)(1 + 4i) (1 4i)(1 + 4i) (( + 3i) + ( + 3i)(4i) 1 + 4 10 + 11i 10
Conformal Mappings. Chapter Schwarz Lemma
 Chapter 5 Conformal Mappings In this chapter we study analytic isomorphisms. An analytic isomorphism is also called a conformal map. We say that f is an analytic isomorphism of U with V if f is an analytic
Chapter 5 Conformal Mappings In this chapter we study analytic isomorphisms. An analytic isomorphism is also called a conformal map. We say that f is an analytic isomorphism of U with V if f is an analytic
Conformal Mapping Lecture 20 Conformal Mapping
 Let γ : [a, b] C be a smooth curve in a domain D. Let f (z) be a function defined at all points z on γ. Let C denotes the image of γ under the transformation w = f (z). The parametric equation of C is
Let γ : [a, b] C be a smooth curve in a domain D. Let f (z) be a function defined at all points z on γ. Let C denotes the image of γ under the transformation w = f (z). The parametric equation of C is
COMPLEX NUMBERS
 COMPLEX NUMBERS 1. Any number of the form x+iy where x, y R and i -1 is called a Complex Number.. In the complex number x+iy, x is called the real part and y is called the imaginary part of the complex
COMPLEX NUMBERS 1. Any number of the form x+iy where x, y R and i -1 is called a Complex Number.. In the complex number x+iy, x is called the real part and y is called the imaginary part of the complex
Find the common ratio of the geometric sequence. (2) 1 + 2
 . Given that z z 2 = 2 i, z, find z in the form a + ib. (Total 4 marks) 2. A geometric sequence u, u 2, u 3,... has u = 27 and a sum to infinity of 8. 2 Find the common ratio of the geometric sequence.
. Given that z z 2 = 2 i, z, find z in the form a + ib. (Total 4 marks) 2. A geometric sequence u, u 2, u 3,... has u = 27 and a sum to infinity of 8. 2 Find the common ratio of the geometric sequence.
Conformal maps. Lent 2019 COMPLEX METHODS G. Taylor. A star means optional and not necessarily harder.
 Lent 29 COMPLEX METHODS G. Taylor A star means optional and not necessarily harder. Conformal maps. (i) Let f(z) = az + b, with ad bc. Where in C is f conformal? cz + d (ii) Let f(z) = z +. What are the
Lent 29 COMPLEX METHODS G. Taylor A star means optional and not necessarily harder. Conformal maps. (i) Let f(z) = az + b, with ad bc. Where in C is f conformal? cz + d (ii) Let f(z) = z +. What are the
Considering our result for the sum and product of analytic functions, this means that for (a 0, a 1,..., a N ) C N+1, the polynomial.
 Lecture 3 Usual complex functions MATH-GA 245.00 Complex Variables Polynomials. Construction f : z z is analytic on all of C since its real and imaginary parts satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann relations and
Lecture 3 Usual complex functions MATH-GA 245.00 Complex Variables Polynomials. Construction f : z z is analytic on all of C since its real and imaginary parts satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann relations and
ENGI 4430 Multiple Integration Cartesian Double Integrals Page 3-01
 ENGI 4430 Multiple Integration Cartesian Double Integrals Page 3-01 3. Multiple Integration This chapter provides only a very brief introduction to the major topic of multiple integration. Uses of multiple
ENGI 4430 Multiple Integration Cartesian Double Integrals Page 3-01 3. Multiple Integration This chapter provides only a very brief introduction to the major topic of multiple integration. Uses of multiple
Higher Geometry Problems
 Higher Geometry Problems (1) Look up Eucidean Geometry on Wikipedia, and write down the English translation given of each of the first four postulates of Euclid. Rewrite each postulate as a clear statement
Higher Geometry Problems (1) Look up Eucidean Geometry on Wikipedia, and write down the English translation given of each of the first four postulates of Euclid. Rewrite each postulate as a clear statement
ALGEBRAIC LONG DIVISION
 QUESTIONS: 2014; 2c 2013; 1c ALGEBRAIC LONG DIVISION x + n ax 3 + bx 2 + cx +d Used to find factors and remainders of functions for instance 2x 3 + 9x 2 + 8x + p This process is useful for finding factors
QUESTIONS: 2014; 2c 2013; 1c ALGEBRAIC LONG DIVISION x + n ax 3 + bx 2 + cx +d Used to find factors and remainders of functions for instance 2x 3 + 9x 2 + 8x + p This process is useful for finding factors
Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser
 Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser In preparation for the complex analysis prelim, I typed up solutions to some old exams. This document includes complete solutions to both exams in 23,
Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser In preparation for the complex analysis prelim, I typed up solutions to some old exams. This document includes complete solutions to both exams in 23,
The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and engineering.
 Lecture 16 Applications of Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 451.001 Complex Variables The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and
Lecture 16 Applications of Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 451.001 Complex Variables The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and
SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #2, Math 253
 SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #, Math 5. Find the equation of a sphere if one of its diameters has end points (, 0, 5) and (5, 4, 7). The length of the diameter is (5 ) + ( 4 0) + (7 5) = =, so the
SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #, Math 5. Find the equation of a sphere if one of its diameters has end points (, 0, 5) and (5, 4, 7). The length of the diameter is (5 ) + ( 4 0) + (7 5) = =, so the
, B = (b) Use induction to prove that, for all positive integers n, f(n) is divisible by 4. (a) Use differentiation to find f (x).
 Edexcel FP1 FP1 Practice Practice Papers A and B Papers A and B PRACTICE PAPER A 1. A = 2 1, B = 4 3 3 1, I = 4 2 1 0. 0 1 (a) Show that AB = ci, stating the value of the constant c. (b) Hence, or otherwise,
Edexcel FP1 FP1 Practice Practice Papers A and B Papers A and B PRACTICE PAPER A 1. A = 2 1, B = 4 3 3 1, I = 4 2 1 0. 0 1 (a) Show that AB = ci, stating the value of the constant c. (b) Hence, or otherwise,
CHAPTER 9. Conformal Mapping and Bilinear Transformation. Dr. Pulak Sahoo
 CHAPTER 9 Conformal Mapping and Bilinear Transformation BY Dr. Pulak Sahoo Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics University of Kalyani West Bengal, India E-mail : sahoopulak@gmail.com Module-3:
CHAPTER 9 Conformal Mapping and Bilinear Transformation BY Dr. Pulak Sahoo Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics University of Kalyani West Bengal, India E-mail : sahoopulak@gmail.com Module-3:
Department of Physics, Korea University
 Name: Department: Notice +2 ( 1) points per correct (incorrect) answer. No penalty for an unanswered question. Fill the blank ( ) with (8) if the statement is correct (incorrect).!!!: corrections to an
Name: Department: Notice +2 ( 1) points per correct (incorrect) answer. No penalty for an unanswered question. Fill the blank ( ) with (8) if the statement is correct (incorrect).!!!: corrections to an
or i 2 = -1 i 4 = 1 Example : ( i ),, 7 i and 0 are complex numbers. and Imaginary part of z = b or img z = b
 1 A- LEVEL MATHEMATICS P 3 Complex Numbers (NOTES) 1. Given a quadratic equation : x 2 + 1 = 0 or ( x 2 = -1 ) has no solution in the set of real numbers, as there does not exist any real number whose
1 A- LEVEL MATHEMATICS P 3 Complex Numbers (NOTES) 1. Given a quadratic equation : x 2 + 1 = 0 or ( x 2 = -1 ) has no solution in the set of real numbers, as there does not exist any real number whose
MAT389 Fall 2016, Problem Set 4
 MAT389 Fall 2016, Problem Set 4 Harmonic conjugates 4.1 Check that each of the functions u(x, y) below is harmonic at every (x, y) R 2, and find the unique harmonic conjugate, v(x, y), satisfying v(0,
MAT389 Fall 2016, Problem Set 4 Harmonic conjugates 4.1 Check that each of the functions u(x, y) below is harmonic at every (x, y) R 2, and find the unique harmonic conjugate, v(x, y), satisfying v(0,
Part II. Geometry and Groups. Year
 Part II Year 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2014 Paper 4, Section I 3F 49 Define the limit set Λ(G) of a Kleinian group G. Assuming that G has no finite orbit in H 3 S 2, and that Λ(G),
Part II Year 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2014 Paper 4, Section I 3F 49 Define the limit set Λ(G) of a Kleinian group G. Assuming that G has no finite orbit in H 3 S 2, and that Λ(G),
The Sphere OPTIONAL - I Vectors and three dimensional Geometry THE SPHERE
 36 THE SPHERE You must have played or seen students playing football, basketball or table tennis. Football, basketball, table tennis ball are all examples of geometrical figures which we call "spheres"
36 THE SPHERE You must have played or seen students playing football, basketball or table tennis. Football, basketball, table tennis ball are all examples of geometrical figures which we call "spheres"
ENGI Multiple Integration Page 8-01
 ENGI 345 8. Multiple Integration Page 8-01 8. Multiple Integration This chapter provides only a very brief introduction to the major topic of multiple integration. Uses of multiple integration include
ENGI 345 8. Multiple Integration Page 8-01 8. Multiple Integration This chapter provides only a very brief introduction to the major topic of multiple integration. Uses of multiple integration include
Problem 1: (3 points) Recall that the dot product of two vectors in R 3 is
 Linear Algebra, Spring 206 Homework 3 Name: Problem : (3 points) Recall that the dot product of two vectors in R 3 is a x b y = ax + by + cz, c z and this is essentially the same as the matrix multiplication
Linear Algebra, Spring 206 Homework 3 Name: Problem : (3 points) Recall that the dot product of two vectors in R 3 is a x b y = ax + by + cz, c z and this is essentially the same as the matrix multiplication
QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE
 QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; 4x + y + 4 = 0 and x + αy + β = 0, where α + β =, are concurrent then α =,
QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; 4x + y + 4 = 0 and x + αy + β = 0, where α + β =, are concurrent then α =,
Definition 1.1 Let a and b be numbers, a smaller than b. Then the set of all numbers between a and b :
 1 Week 1 Definition 1.1 Let a and b be numbers, a smaller than b. Then the set of all numbers between a and b : a and b included is denoted [a, b] a included, b excluded is denoted [a, b) a excluded, b
1 Week 1 Definition 1.1 Let a and b be numbers, a smaller than b. Then the set of all numbers between a and b : a and b included is denoted [a, b] a included, b excluded is denoted [a, b) a excluded, b
Higher Geometry Problems
 Higher Geometry Problems (1 Look up Eucidean Geometry on Wikipedia, and write down the English translation given of each of the first four postulates of Euclid. Rewrite each postulate as a clear statement
Higher Geometry Problems (1 Look up Eucidean Geometry on Wikipedia, and write down the English translation given of each of the first four postulates of Euclid. Rewrite each postulate as a clear statement
MAT1035 Analytic Geometry
 MAT1035 Analytic Geometry Lecture Notes R.A. Sabri Kaan Gürbüzer Dokuz Eylül University 2016 2 Contents 1 Review of Trigonometry 5 2 Polar Coordinates 7 3 Vectors in R n 9 3.1 Located Vectors..............................................
MAT1035 Analytic Geometry Lecture Notes R.A. Sabri Kaan Gürbüzer Dokuz Eylül University 2016 2 Contents 1 Review of Trigonometry 5 2 Polar Coordinates 7 3 Vectors in R n 9 3.1 Located Vectors..............................................
A2 HW Imaginary Numbers
 Name: A2 HW Imaginary Numbers Rewrite the following in terms of i and in simplest form: 1) 100 2) 289 3) 15 4) 4 81 5) 5 12 6) -8 72 Rewrite the following as a radical: 7) 12i 8) 20i Solve for x in simplest
Name: A2 HW Imaginary Numbers Rewrite the following in terms of i and in simplest form: 1) 100 2) 289 3) 15 4) 4 81 5) 5 12 6) -8 72 Rewrite the following as a radical: 7) 12i 8) 20i Solve for x in simplest
Rotation of Axes. By: OpenStaxCollege
 Rotation of Axes By: OpenStaxCollege As we have seen, conic sections are formed when a plane intersects two right circular cones aligned tip to tip and extending infinitely far in opposite directions,
Rotation of Axes By: OpenStaxCollege As we have seen, conic sections are formed when a plane intersects two right circular cones aligned tip to tip and extending infinitely far in opposite directions,
y mx 25m 25 4 circle. Then the perpendicular distance of tangent from the centre (0, 0) is the radius. Since tangent
 Mathematics. The sides AB, BC and CA of ABC have, 4 and 5 interior points respectively on them as shown in the figure. The number of triangles that can be formed using these interior points is () 80 ()
Mathematics. The sides AB, BC and CA of ABC have, 4 and 5 interior points respectively on them as shown in the figure. The number of triangles that can be formed using these interior points is () 80 ()
MATHS (O) NOTES. SUBJECT: Maths LEVEL: Ordinary Level TEACHER: Jean Kelly. The Institute of Education Topics Covered: Complex Numbers
 MATHS (O) NOTES The Institute of Education 07 SUBJECT: Maths LEVEL: Ordinary Level TEACHER: Jean Kelly Topics Covered: COMPLEX NUMBERS Strand 3(Unit ) Syllabus - Understanding the origin and need for complex
MATHS (O) NOTES The Institute of Education 07 SUBJECT: Maths LEVEL: Ordinary Level TEACHER: Jean Kelly Topics Covered: COMPLEX NUMBERS Strand 3(Unit ) Syllabus - Understanding the origin and need for complex
Lecture Notes Complex Analysis. Complex Variables and Applications 7th Edition Brown and Churchhill
 Lecture Notes omplex Analysis based on omplex Variables and Applications 7th Edition Brown and hurchhill Yvette Fajardo-Lim, Ph.D. Department of Mathematics De La Salle University - Manila 2 ontents THE
Lecture Notes omplex Analysis based on omplex Variables and Applications 7th Edition Brown and hurchhill Yvette Fajardo-Lim, Ph.D. Department of Mathematics De La Salle University - Manila 2 ontents THE
Lecture 14 Conformal Mapping. 1 Conformality. 1.1 Preservation of angle. 1.2 Length and area. MATH-GA Complex Variables
 Lecture 14 Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 2451.001 Complex Variables 1 Conformality 1.1 Preservation of angle The open mapping theorem tells us that an analytic function such that f (z 0 ) 0 maps a small neighborhood
Lecture 14 Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 2451.001 Complex Variables 1 Conformality 1.1 Preservation of angle The open mapping theorem tells us that an analytic function such that f (z 0 ) 0 maps a small neighborhood
(7) Suppose α, β, γ are nonzero complex numbers such that α = β = γ.
 January 22, 2011 COMPLEX ANALYSIS: PROBLEMS SHEET -1 M.THAMBAN NAIR (1) Show that C is a field under the addition and multiplication defined for complex numbers. (2) Show that the map f : R C defined by
January 22, 2011 COMPLEX ANALYSIS: PROBLEMS SHEET -1 M.THAMBAN NAIR (1) Show that C is a field under the addition and multiplication defined for complex numbers. (2) Show that the map f : R C defined by
Topic 1 Part 3 [483 marks]
![Topic 1 Part 3 [483 marks] Topic 1 Part 3 [483 marks]](/thumbs/89/97777750.jpg) Topic Part 3 [483 marks] The complex numbers z = i and z = 3 i are represented by the points A and B respectively on an Argand diagram Given that O is the origin, a Find AB, giving your answer in the form
Topic Part 3 [483 marks] The complex numbers z = i and z = 3 i are represented by the points A and B respectively on an Argand diagram Given that O is the origin, a Find AB, giving your answer in the form
18.02 Multivariable Calculus Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.02 Multivariable Calculus Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 3. Double Integrals 3A. Double
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.02 Multivariable Calculus Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 3. Double Integrals 3A. Double
Inversive Geometry. James Emery 6/11/ Inversion Through a Circle 1. 9 TheMöbius Transformation Peaucellier-Lipkin Linkage 6
 Inversive Geometry James Emery 6/11/2011 Contents 1 Inversion Through a Circle 1 2 TheMöbius Transformation 2 3 Circles Go To Circles 3 4 Inversive Linkage 5 5 Peaucellier-Lipkin Linkage 6 6 A Geometrical
Inversive Geometry James Emery 6/11/2011 Contents 1 Inversion Through a Circle 1 2 TheMöbius Transformation 2 3 Circles Go To Circles 3 4 Inversive Linkage 5 5 Peaucellier-Lipkin Linkage 6 6 A Geometrical
Aero III/IV Conformal Mapping
 Aero III/IV Conformal Mapping View complex function as a mapping Unlike a real function, a complex function w = f(z) cannot be represented by a curve. Instead it is useful to view it as a mapping. Write
Aero III/IV Conformal Mapping View complex function as a mapping Unlike a real function, a complex function w = f(z) cannot be represented by a curve. Instead it is useful to view it as a mapping. Write
OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 13.1
 OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 13.1 (37) If a bug walks on the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + 2x 2y 4z 3 = 0 how close and how far can it get from the origin? Solution: Complete
OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 13.1 (37) If a bug walks on the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + 2x 2y 4z 3 = 0 how close and how far can it get from the origin? Solution: Complete
Mathematics I. Exercises with solutions. 1 Linear Algebra. Vectors and Matrices Let , C = , B = A = Determine the following matrices:
 Mathematics I Exercises with solutions Linear Algebra Vectors and Matrices.. Let A = 5, B = Determine the following matrices: 4 5, C = a) A + B; b) A B; c) AB; d) BA; e) (AB)C; f) A(BC) Solution: 4 5 a)
Mathematics I Exercises with solutions Linear Algebra Vectors and Matrices.. Let A = 5, B = Determine the following matrices: 4 5, C = a) A + B; b) A B; c) AB; d) BA; e) (AB)C; f) A(BC) Solution: 4 5 a)
Möbius transformations
 Möbius transformations By convention we write a complex function of a complex variable as w=f(z) rather than y=f(x) and by convention the real and imaginary parts are written x, y, u, v z = x + iy w =
Möbius transformations By convention we write a complex function of a complex variable as w=f(z) rather than y=f(x) and by convention the real and imaginary parts are written x, y, u, v z = x + iy w =
III.3. Analytic Functions as Mapping, Möbius Transformations
 III.3. Analytic Functions as Mapping, Möbius Transformations 1 III.3. Analytic Functions as Mapping, Möbius Transformations Note. To graph y = f(x) where x,y R, we can simply plot points (x,y) in R 2 (that
III.3. Analytic Functions as Mapping, Möbius Transformations 1 III.3. Analytic Functions as Mapping, Möbius Transformations Note. To graph y = f(x) where x,y R, we can simply plot points (x,y) in R 2 (that
7.2 Conformal mappings
 7.2 Conformal mappings Let f be an analytic function. At points where f (z) 0 such a map has the remarkable property that it is conformal. This means that angle is preserved (in the sense that any 2 smooth
7.2 Conformal mappings Let f be an analytic function. At points where f (z) 0 such a map has the remarkable property that it is conformal. This means that angle is preserved (in the sense that any 2 smooth
Packing Congruent Bricks into a Cube
 Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 5 (2001), No. 1, 1 11. Packing Congruent Bricks into a Cube Ákos G. Horváth, István Prok Department of Geometry, Budapest University of Technology and Economics
Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 5 (2001), No. 1, 1 11. Packing Congruent Bricks into a Cube Ákos G. Horváth, István Prok Department of Geometry, Budapest University of Technology and Economics
Conic Sections and Polar Graphing Lab Part 1 - Circles
 MAC 1114 Name Conic Sections and Polar Graphing Lab Part 1 - Circles 1. What is the standard equation for a circle with center at the origin and a radius of k? 3. Consider the circle x + y = 9. a. What
MAC 1114 Name Conic Sections and Polar Graphing Lab Part 1 - Circles 1. What is the standard equation for a circle with center at the origin and a radius of k? 3. Consider the circle x + y = 9. a. What
MockTime.com. (b) (c) (d)
 373 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. If A, B and C are any three arbitrary events then which one of the following expressions shows that both A and B occur but not C? 2. Which one of the following is an
373 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. If A, B and C are any three arbitrary events then which one of the following expressions shows that both A and B occur but not C? 2. Which one of the following is an
MATH 311: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONFORMAL MAPPINGS LECTURE
 MATH 311: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONFORMAL MAPPINGS LECTURE 1. Introduction Let D denote the unit disk and let D denote its boundary circle. Consider a piecewise continuous function on the boundary circle, {
MATH 311: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONFORMAL MAPPINGS LECTURE 1. Introduction Let D denote the unit disk and let D denote its boundary circle. Consider a piecewise continuous function on the boundary circle, {
Hyperbolic Transformations
 C H A P T E R 17 Hyperbolic Transformations Though the text of your article on Crystal Symmetry and Its Generalizations is much too learned for a simple, selfmade pattern man like me, some of the text-illustrations
C H A P T E R 17 Hyperbolic Transformations Though the text of your article on Crystal Symmetry and Its Generalizations is much too learned for a simple, selfmade pattern man like me, some of the text-illustrations
Distance Formula in 3-D Given any two points P 1 (x 1, y 1, z 1 ) and P 2 (x 2, y 2, z 2 ) the distance between them is ( ) ( ) ( )
 Vectors and the Geometry of Space Vector Space The 3-D coordinate system (rectangular coordinates ) is the intersection of three perpendicular (orthogonal) lines called coordinate axis: x, y, and z. Their
Vectors and the Geometry of Space Vector Space The 3-D coordinate system (rectangular coordinates ) is the intersection of three perpendicular (orthogonal) lines called coordinate axis: x, y, and z. Their
Elementary maths for GMT
 Elementary maths for GMT Linear Algebra Part 1: Vectors, Representations Algebra and Linear Algebra Algebra: numbers and operations on numbers 2 + 3 = 5 3 7 = 21 Linear Algebra: tuples, triples... of numbers
Elementary maths for GMT Linear Algebra Part 1: Vectors, Representations Algebra and Linear Algebra Algebra: numbers and operations on numbers 2 + 3 = 5 3 7 = 21 Linear Algebra: tuples, triples... of numbers
4.3 Equations in 3-space
 4.3 Equations in 3-space istance can be used to define functions from a 3-space R 3 to the line R. Let P be a fixed point in the 3-space R 3 (say, with coordinates P (2, 5, 7)). Consider a function f :
4.3 Equations in 3-space istance can be used to define functions from a 3-space R 3 to the line R. Let P be a fixed point in the 3-space R 3 (say, with coordinates P (2, 5, 7)). Consider a function f :
Standard Form of Conics
 When we teach linear equations in Algebra1, we teach the simplest linear function (the mother function) as y = x. We then usually lead to the understanding of the effects of the slope and the y-intercept
When we teach linear equations in Algebra1, we teach the simplest linear function (the mother function) as y = x. We then usually lead to the understanding of the effects of the slope and the y-intercept
COMPLEX NUMBERS II L. MARIZZA A. BAILEY
 COMPLEX NUMBERS II L. MARIZZA A. BAILEY 1. Roots of Unity Previously, we learned that the product of z = z cis(θ), w = w cis(α) C is represented geometrically by the rotation of z by the angle α = arg
COMPLEX NUMBERS II L. MARIZZA A. BAILEY 1. Roots of Unity Previously, we learned that the product of z = z cis(θ), w = w cis(α) C is represented geometrically by the rotation of z by the angle α = arg
Complex Variables. Instructions Solve any eight of the following ten problems. Explain your reasoning in complete sentences to maximize credit.
 Instructions Solve any eight of the following ten problems. Explain your reasoning in complete sentences to maximize credit. 1. The TI-89 calculator says, reasonably enough, that x 1) 1/3 1 ) 3 = 8. lim
Instructions Solve any eight of the following ten problems. Explain your reasoning in complete sentences to maximize credit. 1. The TI-89 calculator says, reasonably enough, that x 1) 1/3 1 ) 3 = 8. lim
12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes
 12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes Equation of Lines Vector Equation of Lines Parametric Equation of Lines Symmetric Equation of Lines Relation Between Two Lines Equations of Planes Vector Equation of
12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes Equation of Lines Vector Equation of Lines Parametric Equation of Lines Symmetric Equation of Lines Relation Between Two Lines Equations of Planes Vector Equation of
Complex Analysis Math 185A, Winter 2010 Final: Solutions
 Complex Analysis Math 85A, Winter 200 Final: Solutions. [25 pts] The Jacobian of two real-valued functions u(x, y), v(x, y) of (x, y) is defined by the determinant (u, v) J = (x, y) = u x u y v x v y.
Complex Analysis Math 85A, Winter 200 Final: Solutions. [25 pts] The Jacobian of two real-valued functions u(x, y), v(x, y) of (x, y) is defined by the determinant (u, v) J = (x, y) = u x u y v x v y.
Spring 2018 CIS 610. Advanced Geometric Methods in Computer Science Jean Gallier Homework 3
 Spring 2018 CIS 610 Advanced Geometric Methods in Computer Science Jean Gallier Homework 3 March 20; Due April 5, 2018 Problem B1 (80). This problem is from Knapp, Lie Groups Beyond an Introduction, Introduction,
Spring 2018 CIS 610 Advanced Geometric Methods in Computer Science Jean Gallier Homework 3 March 20; Due April 5, 2018 Problem B1 (80). This problem is from Knapp, Lie Groups Beyond an Introduction, Introduction,
Precalculus Table of Contents Unit 1 : Algebra Review Lesson 1: (For worksheet #1) Factoring Review Factoring Using the Distributive Laws Factoring
 Unit 1 : Algebra Review Factoring Review Factoring Using the Distributive Laws Factoring Trinomials Factoring the Difference of Two Squares Factoring Perfect Square Trinomials Factoring the Sum and Difference
Unit 1 : Algebra Review Factoring Review Factoring Using the Distributive Laws Factoring Trinomials Factoring the Difference of Two Squares Factoring Perfect Square Trinomials Factoring the Sum and Difference
carries the circle w 1 onto the circle z R and sends w = 0 to z = a. The function u(s(w)) is harmonic in the unit circle w 1 and we obtain
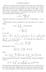 4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
MATRICES EXAM QUESTIONS
 MATRICES EXAM QUESTIONS (Part One) Question 1 (**) The matrices A, B and C are given below in terms of the scalar constants a, b, c and d, by 2 3 A =, 1 a b 1 B =, 2 4 1 c C =. d 4 Given that A + B = C,
MATRICES EXAM QUESTIONS (Part One) Question 1 (**) The matrices A, B and C are given below in terms of the scalar constants a, b, c and d, by 2 3 A =, 1 a b 1 B =, 2 4 1 c C =. d 4 Given that A + B = C,
MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter Midterm 1 Review Solutions
 MATH 55 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 11 Midterm 1 Review Solutions 11.1: #19 Particle starts at point ( 1,, traces out a semicircle in the counterclockwise direction, ending at the point (1,. 11.1:
MATH 55 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 11 Midterm 1 Review Solutions 11.1: #19 Particle starts at point ( 1,, traces out a semicircle in the counterclockwise direction, ending at the point (1,. 11.1:
DISCRIMINANT EXAM QUESTIONS
 DISCRIMINANT EXAM QUESTIONS Question 1 (**) Show by using the discriminant that the graph of the curve with equation y = x 4x + 10, does not cross the x axis. proof Question (**) Show that the quadratic
DISCRIMINANT EXAM QUESTIONS Question 1 (**) Show by using the discriminant that the graph of the curve with equation y = x 4x + 10, does not cross the x axis. proof Question (**) Show that the quadratic
Geometry in the Complex Plane
 Geometry in the Complex Plane Hongyi Chen UNC Awards Banquet 016 All Geometry is Algebra Many geometry problems can be solved using a purely algebraic approach - by placing the geometric diagram on a coordinate
Geometry in the Complex Plane Hongyi Chen UNC Awards Banquet 016 All Geometry is Algebra Many geometry problems can be solved using a purely algebraic approach - by placing the geometric diagram on a coordinate
(x 1, y 1 ) = (x 2, y 2 ) if and only if x 1 = x 2 and y 1 = y 2.
 1. Complex numbers A complex number z is defined as an ordered pair z = (x, y), where x and y are a pair of real numbers. In usual notation, we write z = x + iy, where i is a symbol. The operations of
1. Complex numbers A complex number z is defined as an ordered pair z = (x, y), where x and y are a pair of real numbers. In usual notation, we write z = x + iy, where i is a symbol. The operations of
SKILL BUILDER TEN. Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables. If x = 2 then y = = = 7 and (2, 7) is a solution.
 SKILL BUILDER TEN Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables A first degree equation is called a linear equation, since its graph is a straight line. In a linear equation, each term is a constant or
SKILL BUILDER TEN Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables A first degree equation is called a linear equation, since its graph is a straight line. In a linear equation, each term is a constant or
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 MCN COMPLEX NUMBER C The complex number Complex number is denoted by ie = a + ib, where a is called as real part of (denoted by Re and b is called as imaginary part of (denoted by Im Here i =, also i =,
MCN COMPLEX NUMBER C The complex number Complex number is denoted by ie = a + ib, where a is called as real part of (denoted by Re and b is called as imaginary part of (denoted by Im Here i =, also i =,
Class test: week 10, 75 minutes. (30%) Final exam: April/May exam period, 3 hours (70%).
 17-4-2013 12:55 c M. K. Warby MA3914 Complex variable methods and applications 0 1 MA3914 Complex variable methods and applications Lecture Notes by M.K. Warby in 2012/3 Department of Mathematical Sciences
17-4-2013 12:55 c M. K. Warby MA3914 Complex variable methods and applications 0 1 MA3914 Complex variable methods and applications Lecture Notes by M.K. Warby in 2012/3 Department of Mathematical Sciences
ECE-S Introduction to Digital Signal Processing Lecture 4 Part A The Z-Transform and LTI Systems
 ECE-S352-70 Introduction to Digital Signal Processing Lecture 4 Part A The Z-Transform and LTI Systems Transform techniques are an important tool in the analysis of signals and linear time invariant (LTI)
ECE-S352-70 Introduction to Digital Signal Processing Lecture 4 Part A The Z-Transform and LTI Systems Transform techniques are an important tool in the analysis of signals and linear time invariant (LTI)
MockTime.com. (b) 9/2 (c) 18 (d) 27
 212 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. Let X be any non-empty set containing n elements. Then what is the number of relations on X? 2 n 2 2n 2 2n n 2 2. Only 1 2 and 3 1 and 2 1 and 3 3. Consider the following
212 NDA Mathematics Practice Set 1. Let X be any non-empty set containing n elements. Then what is the number of relations on X? 2 n 2 2n 2 2n n 2 2. Only 1 2 and 3 1 and 2 1 and 3 3. Consider the following
Chapter 8: Polar Coordinates and Vectors
 Chapter 8: Polar Coordinates and Vectors 8.1 Polar Coordinates This is another way (in addition to the x-y system) of specifying the position of a point in the plane. We give the distance r of the point
Chapter 8: Polar Coordinates and Vectors 8.1 Polar Coordinates This is another way (in addition to the x-y system) of specifying the position of a point in the plane. We give the distance r of the point
Introduction to conic sections. Author: Eduard Ortega
 Introduction to conic sections Author: Eduard Ortega 1 Introduction A conic is a two-dimensional figure created by the intersection of a plane and a right circular cone. All conics can be written in terms
Introduction to conic sections Author: Eduard Ortega 1 Introduction A conic is a two-dimensional figure created by the intersection of a plane and a right circular cone. All conics can be written in terms
In Z: x + 3 = 2 3x = 2 x = 1 No solution In Q: 3x = 2 x 2 = 2. x = 2 No solution. In R: x 2 = 2 x = 0 x = ± 2 No solution Z Q.
 THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS MATH 1141 HIGHER MATHEMATICS 1A ALGEBRA. Section 1: - Complex Numbers. 1. The Number Systems. Let us begin by trying to solve various
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS MATH 1141 HIGHER MATHEMATICS 1A ALGEBRA. Section 1: - Complex Numbers. 1. The Number Systems. Let us begin by trying to solve various
P3.C8.COMPLEX NUMBERS
 Recall: Within the real number system, we can solve equation of the form and b 2 4ac 0. ax 2 + bx + c =0, where a, b, c R What is R? They are real numbers on the number line e.g: 2, 4, π, 3.167, 2 3 Therefore,
Recall: Within the real number system, we can solve equation of the form and b 2 4ac 0. ax 2 + bx + c =0, where a, b, c R What is R? They are real numbers on the number line e.g: 2, 4, π, 3.167, 2 3 Therefore,
z b k P k p k (z), (z a) f (n 1) (a) 2 (n 1)! (z a)n 1 +f n (z)(z a) n, where f n (z) = 1 C
 . Representations of Meromorphic Functions There are two natural ways to represent a rational function. One is to express it as a quotient of two polynomials, the other is to use partial fractions. The
. Representations of Meromorphic Functions There are two natural ways to represent a rational function. One is to express it as a quotient of two polynomials, the other is to use partial fractions. The
Complex Numbers. Introduction
 10 Assessment statements 1.5 Complex numbers: the number i 5 1 ; the term s real part, imaginary part, conjugate, modulus and argument. Cartesian form z 5 a 1 ib. Sums, products and quotients of complex
10 Assessment statements 1.5 Complex numbers: the number i 5 1 ; the term s real part, imaginary part, conjugate, modulus and argument. Cartesian form z 5 a 1 ib. Sums, products and quotients of complex
Further Pure Mathematics FP1
 Write your name here Surname Other names Centre Number Pearson Edexcel GCE Further Pure Mathematics FP1 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Friday 20 May 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes You must have: Mathematical
Write your name here Surname Other names Centre Number Pearson Edexcel GCE Further Pure Mathematics FP1 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Friday 20 May 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes You must have: Mathematical
Mathematics AQA Advanced Subsidiary GCE Core 1 (MPC1) January 2010
 Link to past paper on AQA website: http://store.aqa.org.uk/qual/gce/pdf/aqa-mpc1-w-qp-jan10.pdf These solutions are for your personal use only. DO NOT photocopy or pass on to third parties. If you are
Link to past paper on AQA website: http://store.aqa.org.uk/qual/gce/pdf/aqa-mpc1-w-qp-jan10.pdf These solutions are for your personal use only. DO NOT photocopy or pass on to third parties. If you are
Course Notes Math 275 Boise State University. Shari Ultman
 Course Notes Math 275 Boise State University Shari Ultman Fall 2017 Contents 1 Vectors 1 1.1 Introduction to 3-Space & Vectors.............. 3 1.2 Working With Vectors.................... 7 1.3 Introduction
Course Notes Math 275 Boise State University Shari Ultman Fall 2017 Contents 1 Vectors 1 1.1 Introduction to 3-Space & Vectors.............. 3 1.2 Working With Vectors.................... 7 1.3 Introduction
Solutions to Tutorial for Week 3
 The University of Sydney School of Mathematics and Statistics Solutions to Tutorial for Week 3 MATH9/93: Calculus of One Variable (Advanced) Semester, 08 Web Page: sydney.edu.au/science/maths/u/ug/jm/math9/
The University of Sydney School of Mathematics and Statistics Solutions to Tutorial for Week 3 MATH9/93: Calculus of One Variable (Advanced) Semester, 08 Web Page: sydney.edu.au/science/maths/u/ug/jm/math9/
Chapter 1: Precalculus Review
 : Precalculus Review Math 115 17 January 2018 Overview 1 Important Notation 2 Exponents 3 Polynomials 4 Rational Functions 5 Cartesian Coordinates 6 Lines Notation Intervals: Interval Notation (a, b) (a,
: Precalculus Review Math 115 17 January 2018 Overview 1 Important Notation 2 Exponents 3 Polynomials 4 Rational Functions 5 Cartesian Coordinates 6 Lines Notation Intervals: Interval Notation (a, b) (a,
AP PHYSICS SUMMER ASSIGNMENT
 AP PHYSICS SUMMER ASSIGNMENT There are two parts of the summer assignment, both parts mirror the course. The first part is problem solving, where there are 14 math problems that you are given to solve
AP PHYSICS SUMMER ASSIGNMENT There are two parts of the summer assignment, both parts mirror the course. The first part is problem solving, where there are 14 math problems that you are given to solve
MA 460 Supplement: Analytic geometry
 M 460 Supplement: nalytic geometry Donu rapura In the 1600 s Descartes introduced cartesian coordinates which changed the way we now do geometry. This also paved for subsequent developments such as calculus.
M 460 Supplement: nalytic geometry Donu rapura In the 1600 s Descartes introduced cartesian coordinates which changed the way we now do geometry. This also paved for subsequent developments such as calculus.
Practice Assessment Task SET 3
 PRACTICE ASSESSMENT TASK 3 655 Practice Assessment Task SET 3 Solve m - 5m + 6 $ 0 0 Find the locus of point P that moves so that it is equidistant from the points A^-3, h and B ^57, h 3 Write x = 4t,
PRACTICE ASSESSMENT TASK 3 655 Practice Assessment Task SET 3 Solve m - 5m + 6 $ 0 0 Find the locus of point P that moves so that it is equidistant from the points A^-3, h and B ^57, h 3 Write x = 4t,
13 Spherical geometry
 13 Spherical geometry Let ABC be a triangle in the Euclidean plane. From now on, we indicate the interior angles A = CAB, B = ABC, C = BCA at the vertices merely by A, B, C. The sides of length a = BC
13 Spherical geometry Let ABC be a triangle in the Euclidean plane. From now on, we indicate the interior angles A = CAB, B = ABC, C = BCA at the vertices merely by A, B, C. The sides of length a = BC
Candidates are expected to have available a calculator. Only division by (x + a) or (x a) will be required.
 Revision Checklist Unit C2: Core Mathematics 2 Unit description Algebra and functions; coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane; sequences and series; trigonometry; exponentials and logarithms; differentiation;
Revision Checklist Unit C2: Core Mathematics 2 Unit description Algebra and functions; coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane; sequences and series; trigonometry; exponentials and logarithms; differentiation;
EE2 Mathematics : Complex Variables
 EE Mathematics : omplex Variables J. D. Gibbon (Professor J. D Gibbon 1, Dept of Mathematics) j.d.gibbon@ic.ac.uk http://www.imperial.ac.uk/ jdg These notes are not identical word-for-word with my lectures
EE Mathematics : omplex Variables J. D. Gibbon (Professor J. D Gibbon 1, Dept of Mathematics) j.d.gibbon@ic.ac.uk http://www.imperial.ac.uk/ jdg These notes are not identical word-for-word with my lectures
TEST CODE: MIII (Objective type) 2010 SYLLABUS
 TEST CODE: MIII (Objective type) 200 SYLLABUS Algebra Permutations and combinations. Binomial theorem. Theory of equations. Inequalities. Complex numbers and De Moivre s theorem. Elementary set theory.
TEST CODE: MIII (Objective type) 200 SYLLABUS Algebra Permutations and combinations. Binomial theorem. Theory of equations. Inequalities. Complex numbers and De Moivre s theorem. Elementary set theory.
MATH Final Review
 MATH 1592 - Final Review 1 Chapter 7 1.1 Main Topics 1. Integration techniques: Fitting integrands to basic rules on page 485. Integration by parts, Theorem 7.1 on page 488. Guidelines for trigonometric
MATH 1592 - Final Review 1 Chapter 7 1.1 Main Topics 1. Integration techniques: Fitting integrands to basic rules on page 485. Integration by parts, Theorem 7.1 on page 488. Guidelines for trigonometric
1 Vectors and the Scalar Product
 1 Vectors and the Scalar Product 1.1 Vector Algebra vector in R n : an n-tuple of real numbers v = a 1, a 2,..., a n. For example, if n = 2 and a 1 = 1 and a 2 = 1, then w = 1, 1 is vector in R 2. Vectors
1 Vectors and the Scalar Product 1.1 Vector Algebra vector in R n : an n-tuple of real numbers v = a 1, a 2,..., a n. For example, if n = 2 and a 1 = 1 and a 2 = 1, then w = 1, 1 is vector in R 2. Vectors
