Citation for published version (APA): Raschke, A. E. (1998). Collective nuclear flow and shadowing by spectator matter Groningen: s.n.
|
|
|
- Horatio Stanley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Groningen Collective nuclear flow and shadowing by spectator matter Raschke, Ansgar Egon IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document version below. Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Publication date: 1998 Link to publication in University of Groningen/UMCG research database Citation for published version (APA): Raschke, A. E. (1998). Collective nuclear flow and shadowing by spectator matter Groningen: s.n. Copyright Other than for strictly personal use, it is not permitted to download or to forward/distribute the text or part of it without the consent of the author(s) and/or copyright holder(s), unless the work is under an open content license (like Creative Commons). Take-down policy If you believe that this document breaches copyright please contact us providing details, and we will remove access to the work immediately and investigate your claim. Downloaded from the University of Groningen/UMCG research database (Pure): For technical reasons the number of authors shown on this cover page is limited to 10 maximum. Download date:
2 1. Collective Behaviour of Preface Particles In the nineteen-seventies a series of experiments at the Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory (LBL) opened a new eld of research into the reaction dynamics of heavyion collisions. The results of those investigations with close connection to the present thesis are charged-particle ow [Gus84a] and squeeze-out of charged particles [Gut89a]. In the early nineties experiments in the energy domain well above the kinematical limit for pion production were performed at the Gesellschaft fur Schwerionenforschung (GSI, Darmstadt). \Mesonic squeeze-out" was found by two independent experimental setups [Ven93, Bri93] at this laboratory. Model calculations of Bass et al. [Bas93c] indicate that rescattering and absorption on spectator matter are responsible for the depletion of the pion distributions in the reaction plane. From this nding it is interesting to look for similar eects for baryons. Therefore, this thesis investigates the connection between collective nuclear ow and shadowing eects by spectator matter. 1.1 Relativistic Heavy-Ion Reactions During the mid-seventies a rst series of experiments with relativistic heavy ions took place at the Berkeley accelerator complex. These made use of relativistic heavy-ion beams from the BevaLac which resulted from the coupling of the synchrotron Bevatron (from 1955) to the Super Heavy-Ion Linear Accelerator (SuperHILAC). By injecting a heavy-ion beam into the Bevatron nuclei could be accelerated to nearly the speed of light ( 0:95; 2 GeV/u). The experimental setups used were the Plastic Ball [Bad82, Gut89b] and the Streamer Chamber [Str83, San83, Bib83, Kea88, Jia92]. The aim of the early experiments with relativistic heavy-ions was mainly the study of the equation of state of nuclear matter (gure 1.1) [Gre89, Sto86, Sto86]. The equation of state expresses the internal energy of the system as a function of density. The total center-of-mass energy per baryon (E cm ) is divided into a thermal (E th ) and a compressional component(e c ). The function E C () is dened as the compressional energy at zero temperature and is commonly referred to as the nuclear Equation Of State (EOS). Whereas previously only the ground state of nuclear matter could be studied (= 0 = 1), with the upcoming relativistic 9
3 Relativistic Heavy-Ion Reactions Figure 1.1: The Equation of State (EOS) expresses the internal energy of nuclear matter as function of density. The ground state density 0 of nuclear matter corresponds to the minimum of the EOS. E th is the thermal excitation energy per baryon and E c is the compressional energy per baryon [Kam89]. heavy-ion accelerators the main challenge became the investigation of the EOS at higher densities and higher compressional energies of nuclear matter. In the mid-eighties the following important topics of relativistic heavy-ion physics were studied by LBL setups: thermalization [Gus84b], cluster production [Gut83] and collective ow [Gus84a], important for this thesis. In the beginning of the nineties several collaborations especially at the GSI investigated charged-particle emission in relativistic heavy-ion reactions [Abb93, Bri93, Bri96, Her93, Kie91, Met93, Mis94, Spe94]. In particular FOPI published several articles on studies of intermediate-mass fragments in Au + Au collisions mainly done at 150 GeV/u [Ala92, Kam93, Jeo94]. The most interesting \Composite-fragment ow" results of the Plastic Ball are recalled in section 1.3. An insight into these results is a prerequisite for the understanding of the forthcoming extended descriptions of collective behaviour of particles.
4 Chapter 1: Collective Behaviour of Particles Azimuthal Asymmetries in Pion Distributions The main motivation for the present study originates from the investigation of pion distributions at 1 GeV/u from the Au + Au reaction by Venema [Ven94] for the TAPS collaboration and by the Kaon-Spectrometer (KaoS) collaboration [Bri93]. KaoS published angular distributions for charged pions which show azimuthal asymmetries. The TAPS results on neutral pions, shown in gure 1.2, display an enhancement of neutral pions perpendicular to the reaction plane (azimuthal asymmetry). Expressions like reaction plane and azimuthal angle are explained in the following section. We rst deal with the motivation for the research on the collective behaviour of charged particles. The \squeeze-out"-like 0 distributions, shown in gure 1.2, imply an inuence of hadronic matter on these distributions. Various model calculations [Bas93c, Bau91, Gle88, Hah88a, Hah88b, Har94, Li91a, Li91b, Li91c, Li93] investigated pion spectra. Following reference [Bas93c] \mesonic squeeze-out" is caused by absorption and rescattering. The aim of the present thesis is to study the behaviour of charged particles 1 in the same reaction: will we observe the undisturbed collective ow of baryons in the azimuthal angular distributions, or will we be able to infer the inuence of cold nuclear matter? If observed, the latter would conrm the pion results of reference [Ven94]. 1.3 Dynamical Aspects of Heavy-Ion Collisions The experiments at the Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory revealed that relativistic heavy-ion collisions are strongly inuenced by collective behaviour of the interacting particles in the reaction volume. The reaction zone is primarily dened by the overlap volume of the colliding nuclei. An important geometrical parameter of the reaction mechanism is the impact-parameter vector which points from the center of the one nucleus to the other at closest approach for a linear trajectory. Moreover, this vector and the beam direction span a plane, the so-called reaction plane. Consequently, the centers of the nuclei are situated in the reaction plane. Figure 1.3 (1) illustrates the denition of the reaction plane. The term rapidity will rst be explained before discussing dynamical aspects of heavy-ion collisions in more detail. The rapidity of the particles in the labo- 1 If we talk in this thesis of \charged particles" we refer to charged baryonic particles and mainly not to charged mesons.
5 Dynamical Aspects of Heavy-Ion Collisions dn/d φ φ [ ] φ [ ] φ [ ] φ dn/d φ dn/d KVIHV032 φ dn/d φ [ ] φ dn/d φ [ ] Figure 1.2: Azimuthal angular () distributions with respect to the reaction plane of 0 mesons from Au + Au collisions at 1 GeV/u for increasing transverse momentum (from top left to bottom right) in equal bins of 200 MeV/c from 0 to 1000 MeV/c [Ven94]. ratory frame is dened as follows [Gut90] Y = 1 2 ln! 1+ k : (1:1) 1, k Here, k stands for the longitudinal (parallel to the beam axis) component of the particle velocity v=c. The Lorentz invariance of the rapidity is the advantage of this additive quantity. Midrapidity (y cm ) is the value for the rapidity of the center of mass of the reaction system. It corresponds to a value Y =0:677 at 1 GeV/u for a symmetric collision as used for the present study (Au + Au). For this type of collisions a scaling to midrapidity is convenient Y CM = Y, y cm : (1:2) Equation 1.2 denes the \center-of-mass rapidity". In this thesis mainly rapidity is used in terms of relative rapidity Y REL = Y CM y cm = Y, y cm y cm : (1:3)
6 Chapter 1: Collective Behaviour of Particles 13 Figure 1.3: Sketch of collective particle behaviour in heavy-ion collisions. 1) Projectile and target with impact parameter b 6= 0 spanning the reaction plane. 2) Squeeze-out of particles perpendicular to the reaction plane. 3) Charged-particle ow of the participants as well as bounce-o of the spectators in the reaction plane. The ow direction is given by the big arrows. The spectator remnants are directed into angles varying around the ow direction (bounce-o). [Gut91]. Midrapidity y cm results in the values Y CM = 0 and Y REL = 0. The target rapidity y T is found at Y =0,Y CM =,0:677 and Y REL =,1. Similarly we obtain the values for the projectile rapidity y P Y =1:354, Y CM =+0:677 and Y REL = +1. For symmetric collisions the advantage of the scaled (equation 1.2) and the relative (equation 1.3) rapidities is obvious. Dynamical aspects of heavy-ion collisions are classied by their orientation with respect to the reaction plane. Collective eects like transverse particle \ow" [Gus84a] in the reaction plane and \squeeze-out" [Gut89a] of nuclear matter perpendicular to this plane have been observed. These eects are depicted in gure 1.3 and are described in the following paragraphs. The charged-particle ow [Gus84a] as the rst sort of collective behaviour of
7 Dynamical Aspects of Heavy-Ion Collisions nuclear matter, discussed in the context of this thesis, is illustrated by the following scenario. In the initial stage of the heavy-ion collision the two nuclei can be represented by two independent fermi spheres (gure 1.3 (1)). The nuclei hit each other. As a consequence of the compression in the overlap volume of the colliding nuclei a high-density region develops. When the high-density region is built up the nucleons in the reaction zone get pushed sidewards by nucleon-nucleon collisions (kinetic pressure) and repulsion of the density-dependent potential. These nucleons ow away sidewards from the participant region under the so-called ow angle (gure 1.3 (3)). Therefore, this specic ow is also referred to as sideward ow. The ow angle gives information on the repulsive forces in the high-density zone of the reaction. Measurements of the ow angle were rst published by the Plastic Ball group [Gus84a]. The analysis of transverse-momentum ow done by Kampert [Kam86] is presented in gure 1.4. Here, the mean transverse momentum in the reaction plane as a function of rapidity describes the ow for Au + Au reactions at an incident beam energy of 200 MeV/u. This kind of measurement averages over all particles and is insensitive to the azimuthal-angle information. In gure 1.4 is shown the average ratio of momenta in the reaction plane divided by the momenta which are azimuthally averaged. Furthermore, it is worthwhile to note the fact of bending of the curve towards higher rapidity values, depicted in gure 1.4. This can be interpreted as an inuence of the spectator matter. The strength of the ow can be visualized by the azimuthal distributions of the particles emitted relative to the reaction plane, which is determined per event. The ow strength is depicted in gure 1.5 for the same reaction [Gut89b]. The steepness of the curves corresponds to the ow strength. The idea of studying ow by azimuthal distributions is adopted in this thesis for a more detailed analysis. The azimuthal distributions reveal more details of the collective behaviour of the particles than the data based on the mean transverse momenta. In gure 1.3 (2) another dynamical eect, the \bounce-o", as well as the ow of charged particles are sketched. The pictorial description of the heavy-ioncollision scenario will be evoked again to give a good insight into this phenomenon. After projectile and target nucleons hit each other, the participants (nucleons in the reaction zone) ow sidewards. The spectators, initially oriented next to the participating regions but outside the overlap- and therefore reaction-zone, suer a collective deection. The mean additional momentum the spectator fragments get is reected in the bounce-o angle, which is smaller than the ow angle. Both eects, the bounce-o of the spectators as well as the transverse ow of the participants are situated in the reaction plane. We nally discuss a head-on collision with the impact parameter b = 0. In that case the collective particle ow would appear as a radially symmetric disc around the beam axis. Hydrodynamic calculations showed this emission pattern [Sch74]. At b 6= 0 the symmetric disc gets divided into the known collective particle ow
8 Chapter 1: Collective Behaviour of Particles 15 Figure 1.4: Transverse-momentum ow observed by the Plastic Ball. The average fraction of the transverse momentum in the reaction plane is shown for dierent fragments as function of rapidity for Au + Au reactions at 200 MeV/u [Gut89b]. in the reaction plane (main contribution; gure 1.3 (3)) and perpendicular to the reaction plane the \squeeze-out" of particles [Gut89a] (as a remnant of the symmetric b = 0 disc; gure 1.3 (2)). This is the consequence of the asymmetry (b 6= 0) in the entrance channel. This description reects one of the possible scenarios for the interpretation of the squeeze-out eect of baryons. For pions one encounters a dierent situation [Bas93c] due to enhanced absorption on target and projectile spectator matter in the reaction plane. In contrast, the absorption is the smallest perpendicular to the reaction plane. Here, no spectator matter obstructs the pions. This allows \mesonic squeeze-out" perpendicular to the reaction plane as an additional particle-emission pattern. Charged-particle ow is analysed quantitatively by the azimuthal distribution of particles relative to the reaction plane. Squeeze-out of baryons, as well as of mesons, is shown by this type of spectra, too (for charged particles: gure 1.6) [Gut89b]. 1.4 Collective Motion and Shadowing The absorption of particles on target and projectile spectator matter in the reaction plane was mentioned before as a possible interpretation for the eect of \mesonic squeeze-out" observed in nuclear reactions. This idea of spectator mat-
9 Collective Motion and Shadowing Figure 1.5: Flow observed in azimuthal distributions of particles relative to the reaction plane (Au + Au, 200 MeV/u). On the left the ow is shown for peripheral events (MUL2) and on the right for semi-central events (MUL4). From top to bottom distributions are plotted for particles with charge Z = 1, 2, 3 and 6. The data are selected for two dierent rapidity intervals 0:32 <Y 0:42() and 0:52 <Y 0:62() [Gut89b]. ter which inuences particle distributions is now adopted for baryons. In this case either spectator matter or squeeze-out of particles is seen perpendicular to the beam axis, dependent on the azimuthal angle of observation. In other words: particles from inside the reaction volume are shadowed by particles from outside the overlapping zone of the colliding nuclei. The absence of spectator matter, and therefore shadowing, perpendicular to the reaction plane allows for observation of squeeze-out of baryons. In this thesis shadowing by spectator matter has for the rst time been studied in kinetic-energy spectra. For the quantitative extraction of the degree of shadowing more eort is needed in the development of microscopic dynamical models, which must include coalescence of nucleons to light nuclear fragments. A promising attempt in this direction was made by the diploma thesis of Lesny [Les95a, Les95b]. Here, coalescence stands for the mech-
10 Chapter 1: Collective Behaviour of Particles 17 Figure 1.6: Azimuthal distributions of baryons relative to the reaction plane. Left: backward-, center: mid- and right: forward-rapidity regions. The center plot shows the squeeze-out which manifest itself by a peak at stands for out of plane emission. The left and the right panel show the eect of ow. (Au + Au, 400 MeV/u) [Gut89b]. anism which allows to form composites out of nucleons, e.g., combination of a proton and a neutron to a deuteron. Coalescence is described in more detail in chapter 2. Figure 1.7 shows a spatial representation of participant shadowing by spectator matter. Also sketched are the top and various side views on the reaction plane with special attention to the shadowing eect. In gure 1.8 the transition from pure coordinate space (gure 1.7) to phase space is introduced by a representation of shadowing by spectator matter. The phase space is spanned by the rapidity of fragments and their momenta. As long as participants and spectators move with velocities of the same order (in gure 1.8: crossing of ow axis (participants) and bounce-o axis for spectators) interactions of particles from the reaction zone with fragments from the cold periphery become possible. This is valid before the nal state of the reaction is reached. Furthermore, in gure 1.8 the vector Q ~ is introduced. Q ~ is the sum of the transverse momenta of all particles. In chapter 4 the orientation of the reaction plane is measured by means of analyzing Q. ~
11 Collective Motion and Shadowing a) top SPECTATOR MATTER KVIHR496 REACTION PLANE BEAM AXIS b b) spatial d) front SPECTATOR MATTER REACTION PLANE REACTION PLANE BEAM AXIS b c) side BEAM AXIS SPECTATOR MATTER Figure 1.7: Sketch of shadowing by spectator matter. A) top view of the reaction plane and the nuclei; the spectator matter is indicated by hatched areas. B) spatial presentation. C) side view of the colliding nuclei and the reaction plane in impact-parameter direction. D) front view of the colliding nuclei and the reaction plane in beam direction.
12 Chapter 1: Collective Behaviour of Particles 19 SHADOWING BY SPECTATOR MATTER AZIMUTH 9 0 O 0 O REACTION PLANE KVIHR480 FLOW AXIS BOUNCE OFF BEAM AXIS Y Y T CM P Y RAPIDITY Figure 1.8: Sketch of shadowing by spectator matter in phase space. The hatched area in the overlapping zone of the ellipsoids of charged-particle ow and spectator-matter bounce-o represents the region where the shadowing happens. 1.5 The Instrument The investigation of collective behaviour of light charged particles makes exclusive measurements necessary. Impact-parameter selections and the analysis of sections of azimuthal angles are the main techniques used here. The detector system which was employed for the present charged-particle studies was designed to measure photons mainly for pion reconstruction by invariant-mass analysis. For the development of this detector in 1987 an international collaboration of nuclear physics research groups was founded. Physicists from GSI and the two German Universities of Gieen and Munster joined in the so-called \High-Energy-Photon Collaboration" to design and exploit the Two- Arm Photon Spectrometer (TAPS) 2 [Tap87]. The collaboration was joined at an early stage by the institute Grand Accelerateur National d'ions Lourds (GANIL at Caen) and the Kernfysisch Versneller Instituut (KVI at Groningen). In 1990 TAPS was nished in time to measure with the rst heavy-ion beams from the GSI heavy-ion synchrotron SIS 3. In addition to the investigation of photon and neutral-meson production in heavy-ion reactions in the 1 GeV/u energy domain, TAPS provides the possibility to measure charged particles and thus to yield important information on their rapidity distributions and transverse momenta at backward rapidity. 2 Later the name of the instrument was also used as collaboration name (see section D for the collaboration list at the time of the experiment). 3 SIS = Schwerionen Synchrotron.
13 Outline of this Thesis At GSI, nuclear physics in the energy regime of relativistic heavy-ion collisions (E=mc 2 1) uses the linac machine UNILAC as a pre-accelerator for the heavy-ion synchrotron SIS. UNILAC stands for UNIversal Linear ACcelerator. This accelerator has the capacity to accelerate nearly all existing elements up to energies of 18 MeV/u. The UNILAC-SIS combination can push these up to 2 GeV/u and accelerates projectiles up to the mass of uranium. Furthermore, the GSI facility oers some features which are necessary for a heavy-ion experiment if selective particle triggers are used. These features are a sucient high particle current density and a good energy resolution. 1.6 Outline of this Thesis After this introductory chapter the tools to handle the physics of this thesis are discussed in chapter 2. In this chapter various theoretical models needed for the interpretation of the experimental data are discussed. These include the Isospin Quantum Molecular Dynamics (IQMD) code [Har92, Har93], the Dubna- Cascade Model (DCM) [Gud78, Gud79, Ton83] and the Perpendicular Emitting Thermal Source parameter model (PETS) [Kug95]. A comprehensive review of the detectors, the setup and the experiment are the subjects of chapter 3. In particular emphasis is laid on the description of the two independently designed and operated detector systems TAPS and the Forward Wall of the FOur PI (FOPI 4 )-collaboration at GSI. For the rst time in July 1991 a Au beam of 1 GeV/u from the SIS accelerator was used for a combined experiment of TAPS with the Forward Wall. This thesis describes this experiment and discusses the related analysis. The joint setup of TAPS with the Forward Wall allows a selection of neutral meson [Ven94] and charged-particle spectra. The Forward Wall is used in this thesis for event characterization while it is possible with TAPS to identify the charged particles and to measure their energy spectra as a function of the azimuthal angle. In chapter 4 the conversion from the raw data to physical observables is described. This starts with the data calibration for both detector systems, TAPS and the Forward Wall. After that the data have to undergo necessary corrections. TAPS data are corrected for reaction losses and Forward Wall data for hit-acceptance ineciencies. Finally, the physically meaningful variables can be extracted. The important capability of the Forward Wall is the reaction-plane determination. The reaction plane is determined from the azimuthal asymmetry of the charged-particle distributions. For TAPS the charged-particle identication and isotope separation are discussed extensively. At the end of chapter 4 the 4 4: depicts the coverage of the whole 4 sphere in phase II of the project.
14 Chapter 1: Collective Behaviour of Particles 21 procedure to combine the two independently designed analysis program packages is given. In the thesis of Venema [Ven94] a more straight-forward method for the impact-parameter determination by means of information obtained from the Forward Wall is applied. In chapter 4 this method is compared to the one adopted here for the charged-particle analysis. The current reaction-plane analysis makes use of the full information of the Forward Wall. The collective behaviour of light charged particles in the reaction of Au + Au at 1 GeV/u is studied in this thesis. The photon and meson production mechanisms in the same reaction have been studied in earlier works [Sch93, Ven94, Ber94, Sch94, Ven93]. In chapter 5 the particle separation with TAPS is discussed. A good separation of particles is important for this work. Another important aspect is the phase-space coverage of the applied detector systems. The collective behaviour of charged particles is studied via charged-particle ow, ratios of charged-particle numbers and sideward energy ow. Azimuthal distributions of light charged particles from relativistic heavy-ion collisions have been determined. Collective behaviour of hydrogen and helium isotopes manifests itself as azimuthal anisotropy. From the magnitude of this anisotropy aow strength parameter is derived. The anisotropy is further studied by analyzing the ratios of the azimuthal distributions for dierent fragment isotopes. From these ratio distributions the mean charged-particle ratios are determined. Angular sections from the azimuthal distributions are chosen to investigate the behaviour of hydrogen isotopes. This analysis reveals the inuence of shadowing by spectator matter (chapters 5 and 6). In chapter 6 the interpretation of the experimental results is made by comparison to model calculations. The comparison of particle spectra, like kinetic energy, allows to judge whether the proper nucleon-nucleon dynamics and cross sections are implemented in microscopic model calculations. After that, ow strength parameters can be derived from azimuthal distributions of light charged-particle isotopes. The analysis of baryon distributions selected in or perpendicular to the reaction plane is sensitive to the collective particle-emission pattern known as \collective particle ow" (section 1.3). Restrictions on extraction of entropy from particle ratios [Dos85, Dos88] are discussed, based on these distributions. One of the main issues addressed in this thesis is the interpretation of sideward energy ow spectra due to shadowing by spectator matter. For that purpose the experimental data are compared to results of the model calculations introduced in chapter 2. The adoption of detector acceptance lters to the models is discussed in this context.
Citation for published version (APA): Martinus, G. H. (1998). Proton-proton bremsstrahlung in a relativistic covariant model s.n.
 University of Groningen Proton-proton bremsstrahlung in a relativistic covariant model Martinus, Gerard Henk IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
University of Groningen Proton-proton bremsstrahlung in a relativistic covariant model Martinus, Gerard Henk IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
University of Groningen. Extraction and transport of ion beams from an ECR ion source Saminathan, Suresh
 University of Groningen Extraction and transport of ion beams from an ECR ion source Saminathan, Suresh IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen Extraction and transport of ion beams from an ECR ion source Saminathan, Suresh IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen. Study of compression modes in 56Ni using an active target Bagchi, Soumya
 University of Groningen Study of compression modes in 56Ni using an active target Bagchi, Soumya IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Study of compression modes in 56Ni using an active target Bagchi, Soumya IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
Citation for published version (APA): Hoefman, M. (1999). A study of coherent bremsstrahlung and radiative capture s.n.
 University of Groningen A study of coherent bremsstrahlung and radiative capture Hoefman, Marieke IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen A study of coherent bremsstrahlung and radiative capture Hoefman, Marieke IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
AZIMUTHAL CORRELATION FUNCTIONS AS A PROBE FOR COLLECTIVE MOTION. A.Kravcakova, S.Vokal. and. the Kr Collaboration
 AZIMUTHAL CORRELATION FUNCTIONS AS A PROBE FOR COLLECTIVE MOTION A.Kravcakova, S.Vokal and the Kr Collaboration (Dubna, Kosice, Lund, Moscow, Tashkent, Varanasi) Faculty of Science, P.J. Safarik University,
AZIMUTHAL CORRELATION FUNCTIONS AS A PROBE FOR COLLECTIVE MOTION A.Kravcakova, S.Vokal and the Kr Collaboration (Dubna, Kosice, Lund, Moscow, Tashkent, Varanasi) Faculty of Science, P.J. Safarik University,
Dedicated Arrays: MEDEA GDR studies (E γ = MeV) Highly excited CN E*~ MeV, 4 T 8 MeV
 Dedicated Arrays: MEDEA GDR studies (E γ = 10-25 MeV) Highly excited CN E*~ 250-350 MeV, 4 T 8 MeV γ-ray spectrum intermediate energy region 10 MeV/A E beam 100 MeV/A - large variety of emitted particles
Dedicated Arrays: MEDEA GDR studies (E γ = 10-25 MeV) Highly excited CN E*~ 250-350 MeV, 4 T 8 MeV γ-ray spectrum intermediate energy region 10 MeV/A E beam 100 MeV/A - large variety of emitted particles
PoS(Bormio2012)013. K 0 production in pp and pnb reactions. Jia-Chii Berger-Chen
 Excellence Cluster Universe, Technische Universität München E-mail: jia-chii.chen@tum.de The kaon nucleus (KN) interaction in nuclear matter is predicted to be repulsive and dependent from the density.
Excellence Cluster Universe, Technische Universität München E-mail: jia-chii.chen@tum.de The kaon nucleus (KN) interaction in nuclear matter is predicted to be repulsive and dependent from the density.
Azimuthal anisotropy of the identified charged hadrons in Au+Au collisions at S NN. = GeV at RHIC
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Azimuthal anisotropy of the identified charged hadrons in Au+Au collisions at S NN = 39-200 GeV at RHIC To cite this article: S S Vdovkina 2017 J.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Azimuthal anisotropy of the identified charged hadrons in Au+Au collisions at S NN = 39-200 GeV at RHIC To cite this article: S S Vdovkina 2017 J.
Citation for published version (APA): van Pol, J. H. G. (1996). Dissipation mechanisms studied with nuclear bremsstrahlung Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Dissipation mechanisms studied with nuclear bremsstrahlung van Pol, Johannes Hubertus Gerardus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF)
University of Groningen Dissipation mechanisms studied with nuclear bremsstrahlung van Pol, Johannes Hubertus Gerardus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF)
Investigation of hadronic matter properties with heavy ion collisions Particle production and flow from SIS to FAIR. Yvonne Leifels GSI
 Investigation of hadronic matter properties with heavy ion collisions Particle production and flow from SIS to FAIR Yvonne Leifels GSI Investigation of compressed baryonic matter with heavy ion collisions
Investigation of hadronic matter properties with heavy ion collisions Particle production and flow from SIS to FAIR Yvonne Leifels GSI Investigation of compressed baryonic matter with heavy ion collisions
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008](/thumbs/82/87023836.jpg) Elie: an event generator for nuclear reactions Dominique Durand arxiv:0803.2159v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008 LPC Caen-ENSICAEN-Université de Caen-Basse-Normandie durand@lpccaen.in2p3.fr Abstract An event generator
Elie: an event generator for nuclear reactions Dominique Durand arxiv:0803.2159v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008 LPC Caen-ENSICAEN-Université de Caen-Basse-Normandie durand@lpccaen.in2p3.fr Abstract An event generator
University of Groningen. Hollow-atom probing of surfaces Limburg, Johannes
 University of Groningen Hollow-atom probing of surfaces Limburg, Johannes IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen Hollow-atom probing of surfaces Limburg, Johannes IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 23 Jul 2003
 K + - and K -production in heavy-ion collisions at SIS-energies arxiv:nucl-ex/3718v1 23 Jul 23 A. Förster for the KaoS-Collaboration: I. Böttcher d, A. Förster a, E. Grosse f,g, P. Koczoń b, B. Kohlmeyer
K + - and K -production in heavy-ion collisions at SIS-energies arxiv:nucl-ex/3718v1 23 Jul 23 A. Förster for the KaoS-Collaboration: I. Böttcher d, A. Förster a, E. Grosse f,g, P. Koczoń b, B. Kohlmeyer
Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions studied with INDRA Comparison with models
 EPJ Web of Conferences 31, 00007 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20123100007 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2012 Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions
EPJ Web of Conferences 31, 00007 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20123100007 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2012 Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions
University of Groningen. Laser Spectroscopy of Trapped Ra+ Ion Versolato, Oscar Oreste
 University of Groningen Laser Spectroscopy of Trapped Ra+ Ion Versolato, Oscar Oreste IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen Laser Spectroscopy of Trapped Ra+ Ion Versolato, Oscar Oreste IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
Citation for published version (APA): Wang, Y. (2018). Disc reflection in low-mass X-ray binaries. [Groningen]: Rijksuniversiteit Groningen.
![Citation for published version (APA): Wang, Y. (2018). Disc reflection in low-mass X-ray binaries. [Groningen]: Rijksuniversiteit Groningen. Citation for published version (APA): Wang, Y. (2018). Disc reflection in low-mass X-ray binaries. [Groningen]: Rijksuniversiteit Groningen.](/thumbs/95/126078116.jpg) University of Groningen Disc reflection in low-mass X-ray binaries Wang, Yanan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen Disc reflection in low-mass X-ray binaries Wang, Yanan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
Constraining the Equation of State of Asymmetric Nuclear Matter with Collective Flow Measurements
 Constraining the Equation of State of Asymmetric Nuclear Matter with Collective Flow Measurements Roy Lemmon STFC Daresbury Laboratory United Kingdom NuSYM11 Workshop, 19-21 June 2011, Smith College The
Constraining the Equation of State of Asymmetric Nuclear Matter with Collective Flow Measurements Roy Lemmon STFC Daresbury Laboratory United Kingdom NuSYM11 Workshop, 19-21 June 2011, Smith College The
Citation for published version (APA): Fathi, K. (2004). Dynamics and morphology in the inner regions of spiral galaxies Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Dynamics and morphology in the inner regions of spiral galaxies Fathi, Kambiz IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to
University of Groningen Dynamics and morphology in the inner regions of spiral galaxies Fathi, Kambiz IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to
Dynamical fragment production in central collisions Xe(50 A.MeV)+Sn
 Dynamical fragment production in central collisions Xe(5 A.MeV)+Sn Regina Nebauer + and Jörg Aichelin SUBATECH Université de Nantes, EMN, IN2P3/CNRS 4, Rue Alfred Kastler, 447 Nantes Cedex 3, France Universität
Dynamical fragment production in central collisions Xe(5 A.MeV)+Sn Regina Nebauer + and Jörg Aichelin SUBATECH Université de Nantes, EMN, IN2P3/CNRS 4, Rue Alfred Kastler, 447 Nantes Cedex 3, France Universität
VOL 18, #2 THE JOURNAL OF UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH IN PHYSICS 39
 VOL 18, #2 THE JOURNAL OF UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH IN PHYSICS 39 MODELING PION FLOW IN A 139 La + 139 La COLLISION Daniel Valente * Department of Physics and Engineering Hope College Holland, MI 49423 received
VOL 18, #2 THE JOURNAL OF UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH IN PHYSICS 39 MODELING PION FLOW IN A 139 La + 139 La COLLISION Daniel Valente * Department of Physics and Engineering Hope College Holland, MI 49423 received
Citation for published version (APA): Shen, C. (2006). Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs: Imaging and Localization. [S.l.]: s.n.
![Citation for published version (APA): Shen, C. (2006). Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs: Imaging and Localization. [S.l.]: s.n. Citation for published version (APA): Shen, C. (2006). Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs: Imaging and Localization. [S.l.]: s.n.](/thumbs/95/124821981.jpg) University of Groningen Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs Shen, Chuanjian IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
University of Groningen Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs Shen, Chuanjian IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
Citation for published version (APA): Shen, C. (2006). Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs: Imaging and Localization. [S.l.]: s.n.
![Citation for published version (APA): Shen, C. (2006). Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs: Imaging and Localization. [S.l.]: s.n. Citation for published version (APA): Shen, C. (2006). Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs: Imaging and Localization. [S.l.]: s.n.](/thumbs/95/124821987.jpg) University of Groningen Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs Shen, Chuanjian IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
University of Groningen Wave Propagation through Photonic Crystal Slabs Shen, Chuanjian IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
PoS(Baldin ISHEPP XXII)042
 Multifragmentation of nuclei by photons: new approaches and results Institute for Nuclear Research RAS Prospect 60-let Octabra, 7A, 117312 Moscow, Russia E-mail: vladimir@cpc.inr.ac.ru A review on multifragmentation
Multifragmentation of nuclei by photons: new approaches and results Institute for Nuclear Research RAS Prospect 60-let Octabra, 7A, 117312 Moscow, Russia E-mail: vladimir@cpc.inr.ac.ru A review on multifragmentation
The experiment at JINR: status and physics program
 The 3rd International Conference on Particle Physics and Astrophysics Volume 2018 Conference Paper The BM@N experiment at JINR: status and physics program D. Baranov, M. Kapishin, T. Mamontova, G. Pokatashkin,
The 3rd International Conference on Particle Physics and Astrophysics Volume 2018 Conference Paper The BM@N experiment at JINR: status and physics program D. Baranov, M. Kapishin, T. Mamontova, G. Pokatashkin,
Theory English (Official)
 Q3-1 Large Hadron Collider (10 points) Please read the general instructions in the separate envelope before you start this problem. In this task, the physics of the particle accelerator LHC (Large Hadron
Q3-1 Large Hadron Collider (10 points) Please read the general instructions in the separate envelope before you start this problem. In this task, the physics of the particle accelerator LHC (Large Hadron
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF NEUTRON FIELDS PRODUCED IN PROTON REACTIONS WITH HEAVY TARGETS. Nuclear Physics Institute AS CR, Rez Czech Republic
 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF NEUTRON FIELDS PRODUCED IN PROTON REACTIONS WITH HEAVY TARGETS A. Kugler, V. Wagner Nuclear Physics Institute AS CR, 25068 Rez Czech Republic I. Introduction One of important aspects
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF NEUTRON FIELDS PRODUCED IN PROTON REACTIONS WITH HEAVY TARGETS A. Kugler, V. Wagner Nuclear Physics Institute AS CR, 25068 Rez Czech Republic I. Introduction One of important aspects
Stars Nuclei Baryons Quarks. STRANGENESS IN NUCLEI UNIQUE OPPORTUNITIES at FAIR Josef Pochodzalla
 Stars Nuclei Baryons Quarks STRANGENESS IN NUCLEI UNIQUE OPPORTUNITIES at FAIR Josef Pochodzalla Facility for Antiproton and Ion Research GSI, Darmstadt heavy ion physics nuclear structure atomic and plasma
Stars Nuclei Baryons Quarks STRANGENESS IN NUCLEI UNIQUE OPPORTUNITIES at FAIR Josef Pochodzalla Facility for Antiproton and Ion Research GSI, Darmstadt heavy ion physics nuclear structure atomic and plasma
Reactions of neutron-rich Sn isotopes investigated at relativistic energies at R 3 B
 investigated at relativistic energies at R 3 B for the R 3 B collaboration Technische Universität Darmstadt E-mail: fa.schindler@gsi.de Reactions of neutron-rich Sn isotopes have been measured in inverse
investigated at relativistic energies at R 3 B for the R 3 B collaboration Technische Universität Darmstadt E-mail: fa.schindler@gsi.de Reactions of neutron-rich Sn isotopes have been measured in inverse
Compound and heavy-ion reactions
 Compound and heavy-ion reactions Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 23, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 24) March 23, 2011 1 / 32 Outline 1 Density of states in a
Compound and heavy-ion reactions Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 23, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 24) March 23, 2011 1 / 32 Outline 1 Density of states in a
Noncentral collisions
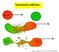 Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
PoS(BORMIO2010)052. Measurement of the Λ(1405) in proton proton reactions with HADES
 Measurement of the Λ(145) in proton proton reactions with HADES HADES Collaboration Email: johannes.siebenson@ph.tum.de We present an analysis of the Λ(145) resonance in p p reactions at a kinetic beam
Measurement of the Λ(145) in proton proton reactions with HADES HADES Collaboration Email: johannes.siebenson@ph.tum.de We present an analysis of the Λ(145) resonance in p p reactions at a kinetic beam
Physics with Exotic Nuclei
 Physics with Exotic Nuclei Hans-Jürgen Wollersheim NUclear STructure, Astrophysics and Reaction Outline Projectile Fragmentation A Route to Exotic Nuclei Fragmentation Cross Sections Nuclear Reaction Rates
Physics with Exotic Nuclei Hans-Jürgen Wollersheim NUclear STructure, Astrophysics and Reaction Outline Projectile Fragmentation A Route to Exotic Nuclei Fragmentation Cross Sections Nuclear Reaction Rates
The effect of the spectator charge on the charged pion spectra in peripheral ultrarelativistic heavy-ion collisions
 The effect of the spectator charge on the charged pion spectra in peripheral ultrarelativistic heavy-ion collisions Antoni Szczurek and Andrzej Rybicki INSTITUTE OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
The effect of the spectator charge on the charged pion spectra in peripheral ultrarelativistic heavy-ion collisions Antoni Szczurek and Andrzej Rybicki INSTITUTE OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Review of collective flow at RHIC and LHC
 Review of collective flow at RHIC and LHC Jaap Onderwaater 29 November 2012 J. Onderwaater (EMMI,GSI) Collective flow 29 November 2012 1 / 37 Heavy ion collision stages Outline Heavy ion collisions and
Review of collective flow at RHIC and LHC Jaap Onderwaater 29 November 2012 J. Onderwaater (EMMI,GSI) Collective flow 29 November 2012 1 / 37 Heavy ion collision stages Outline Heavy ion collisions and
Soft physics results from the PHENIX experiment
 Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2015, 03A104 (15 pages) DOI: 10.1093/ptep/ptu069 PHYSICS at PHENIX, 15 years of discoveries Soft physics results from the PHENIX experiment ShinIchi Esumi, Institute of Physics,
Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2015, 03A104 (15 pages) DOI: 10.1093/ptep/ptu069 PHYSICS at PHENIX, 15 years of discoveries Soft physics results from the PHENIX experiment ShinIchi Esumi, Institute of Physics,
Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department. Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas Abstract
 Subthreshold kaon production and the nuclear equation of state G. Q. Li and C. M. Ko Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas 77843 Abstract We reexamine
Subthreshold kaon production and the nuclear equation of state G. Q. Li and C. M. Ko Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas 77843 Abstract We reexamine
Theoretical simulation of nonlinear spectroscopy in the liquid phase La Cour Jansen, Thomas
 University of Groningen Theoretical simulation of nonlinear spectroscopy in the liquid phase La Cour Jansen, Thomas IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF)
University of Groningen Theoretical simulation of nonlinear spectroscopy in the liquid phase La Cour Jansen, Thomas IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF)
Particle flow and reaction plane reconstruction in the CBM experiment
 Particle flow and reaction plane reconstruction in the CBM experiment Nuclear Physics Institute, Czech Academy of Sciences, Řež, Czech Republic Czech Technical University in Prague, Faculty of Nuclear
Particle flow and reaction plane reconstruction in the CBM experiment Nuclear Physics Institute, Czech Academy of Sciences, Řež, Czech Republic Czech Technical University in Prague, Faculty of Nuclear
High Energy Frontier Recent Results from the LHC: Heavy Ions I
 High Energy Frontier Recent Results from the LHC: Heavy Ions I Ralf Averbeck ExtreMe Matter Institute EMMI and Research Division GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung Darmstadt, Germany Winter
High Energy Frontier Recent Results from the LHC: Heavy Ions I Ralf Averbeck ExtreMe Matter Institute EMMI and Research Division GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung Darmstadt, Germany Winter
A new approach to detect hypernuclei and isotopes in the QMD phase space distribution at relativistic energies
 A new approach to detect hypernuclei and isotopes in the QMD phase space distribution at relativistic energies A. Le Fèvre 1, J. Aichelin 2, Ch. Hartnack 2 and Y. Leifels 1 1 GSI Darmstadt, Germany 2 Subatech
A new approach to detect hypernuclei and isotopes in the QMD phase space distribution at relativistic energies A. Le Fèvre 1, J. Aichelin 2, Ch. Hartnack 2 and Y. Leifels 1 1 GSI Darmstadt, Germany 2 Subatech
System theory and system identification of compartmental systems Hof, Jacoba Marchiena van den
 University of Groningen System theory and system identification of compartmental systems Hof, Jacoba Marchiena van den IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF)
University of Groningen System theory and system identification of compartmental systems Hof, Jacoba Marchiena van den IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF)
Strange Hadron Production from STAR Fixed-Target Program
 Strange Hadron Production from STAR Fixed-Target Program (for the STAR Collaboration) Department of Engineering Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 84, China E-mail: musman_mughal@yahoo.com We report
Strange Hadron Production from STAR Fixed-Target Program (for the STAR Collaboration) Department of Engineering Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 84, China E-mail: musman_mughal@yahoo.com We report
The Yukawa Particle and the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle Revisited *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m42669 1 The Yukawa Particle and the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle Revisited * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
OpenStax-CNX module: m42669 1 The Yukawa Particle and the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle Revisited * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
Study of nuclear dynamics using IQMD model
 Study of nuclear dynamics using IQMD model Rajni Bansal Department of Physics, MCM DAV College for Women, Sector 36 A, Chandigarh -160 036, India. Abstract-We study the role of colliding geometry, incident
Study of nuclear dynamics using IQMD model Rajni Bansal Department of Physics, MCM DAV College for Women, Sector 36 A, Chandigarh -160 036, India. Abstract-We study the role of colliding geometry, incident
HADRONIZATION IN A NUCLEAR ENVIRONMENT. Nationaal Instituut voor Kernfysica en Hoge-Energiefysica, NIKHEF
 98 7 HADRONIZATION IN A NUCLEAR ENVIRONMENT J. J. VAN HUNEN (for the HERMES collaboration) Nationaal Instituut voor Kernfysica en Hoge-Energiefysica, NIKHEF Postbus 41882, 1009 DB Amsterdam, The Netherlands
98 7 HADRONIZATION IN A NUCLEAR ENVIRONMENT J. J. VAN HUNEN (for the HERMES collaboration) Nationaal Instituut voor Kernfysica en Hoge-Energiefysica, NIKHEF Postbus 41882, 1009 DB Amsterdam, The Netherlands
PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE ENERGIES
 EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
Validation of Geant4 Hadronic Physics Models at Intermediate Energies. Outline
 Models at Intermediate Energies Outline Motivation Models Data Used Validation Results Summary CHEP 2009 Prague, March 23-27, 2009 Sunanda Banerjee, Fermilab (on behalf of Geant4 Hadronic Group) Motivation
Models at Intermediate Energies Outline Motivation Models Data Used Validation Results Summary CHEP 2009 Prague, March 23-27, 2009 Sunanda Banerjee, Fermilab (on behalf of Geant4 Hadronic Group) Motivation
On the impact parameter dependence of the peak mass production
 On the impact parameter dependence of the peak mass production Sukhjit Kaur * SGGS College Sector-26 Chandigarh-160 019 INDIA sukhjitkaur.pu@gmail.com Abstract We study the effect of colliding geometry
On the impact parameter dependence of the peak mass production Sukhjit Kaur * SGGS College Sector-26 Chandigarh-160 019 INDIA sukhjitkaur.pu@gmail.com Abstract We study the effect of colliding geometry
The Development of Particle Physics. Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev E45, Tel.:
 The Development of Particle Physics Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev E45, Tel.: 0114 2224531 v.kudryavtsev@sheffield.ac.uk Discovery of the muon and the pion Energy losses of charged particles. This is an important
The Development of Particle Physics Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev E45, Tel.: 0114 2224531 v.kudryavtsev@sheffield.ac.uk Discovery of the muon and the pion Energy losses of charged particles. This is an important
Today, I will present the first of two lectures on neutron interactions.
 Today, I will present the first of two lectures on neutron interactions. I first need to acknowledge that these two lectures were based on lectures presented previously in Med Phys I by Dr Howell. 1 Before
Today, I will present the first of two lectures on neutron interactions. I first need to acknowledge that these two lectures were based on lectures presented previously in Med Phys I by Dr Howell. 1 Before
Cross Section of Exclusive π Electro-production from Neutron. Jixie Zhang (CLAS Collaboration) Old Dominion University Sep. 2009
 Cross Section of Exclusive π Electro-production from Neutron Jixie Zhang (CLAS Collaboration) Old Dominion University Sep. 2009 Exclusive π electro-production Detect e`, π and at least ONE of the two final
Cross Section of Exclusive π Electro-production from Neutron Jixie Zhang (CLAS Collaboration) Old Dominion University Sep. 2009 Exclusive π electro-production Detect e`, π and at least ONE of the two final
Anti-Nuclei in Relativistic Nuclear Collisions: Results and Expectations
 Makutsi-Symposium, Nov. 20 Anti-Nuclei in Relativistic Nuclear Collisions: Results and Expectations Reinhard Stock, Goethe University Frankfurt Content Nuclei and Anti-Nuclei in A+A collisions - - Early
Makutsi-Symposium, Nov. 20 Anti-Nuclei in Relativistic Nuclear Collisions: Results and Expectations Reinhard Stock, Goethe University Frankfurt Content Nuclei and Anti-Nuclei in A+A collisions - - Early
Overview of recent HERMES results
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Overview of recent HERMES results To cite this article: Hrachya Marukyan and 216 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 678 1238 View the article online for updates
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Overview of recent HERMES results To cite this article: Hrachya Marukyan and 216 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 678 1238 View the article online for updates
Elementary Particle Physics Glossary. Course organiser: Dr Marcella Bona February 9, 2016
 Elementary Particle Physics Glossary Course organiser: Dr Marcella Bona February 9, 2016 1 Contents 1 Terms A-C 5 1.1 Accelerator.............................. 5 1.2 Annihilation..............................
Elementary Particle Physics Glossary Course organiser: Dr Marcella Bona February 9, 2016 1 Contents 1 Terms A-C 5 1.1 Accelerator.............................. 5 1.2 Annihilation..............................
Lecture 3. lecture slides are at:
 Lecture 3 lecture slides are at: http://www.physics.smu.edu/ryszard/5380fa16/ Proton mass m p = 938.28 MeV/c 2 Electron mass m e = 0.511 MeV/c 2 Neutron mass m n = 939.56 MeV/c 2 Helium nucleus α: 2 protons+2
Lecture 3 lecture slides are at: http://www.physics.smu.edu/ryszard/5380fa16/ Proton mass m p = 938.28 MeV/c 2 Electron mass m e = 0.511 MeV/c 2 Neutron mass m n = 939.56 MeV/c 2 Helium nucleus α: 2 protons+2
Citation for published version (APA): Hoekstra, S. (2005). Atom Trap Trace Analysis of Calcium Isotopes s.n.
 University of Groningen Atom Trap Trace Analysis of Calcium Isotopes Hoekstra, Steven IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen Atom Trap Trace Analysis of Calcium Isotopes Hoekstra, Steven IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
Citation for published version (APA): Kooistra, F. B. (2007). Fullerenes for organic electronics [Groningen]: s.n.
![Citation for published version (APA): Kooistra, F. B. (2007). Fullerenes for organic electronics [Groningen]: s.n. Citation for published version (APA): Kooistra, F. B. (2007). Fullerenes for organic electronics [Groningen]: s.n.](/thumbs/86/93829092.jpg) University of Groningen Fullerenes for organic electronics Kooistra, Floris Berend IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen Fullerenes for organic electronics Kooistra, Floris Berend IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
Lecture 3. lecture slides are at:
 Lecture 3 lecture slides are at: http://www.physics.smu.edu/ryszard/5380fa17/ Proton mass m p = 938.28 MeV/c 2 Electron mass m e = 0.511 MeV/c 2 Neutron mass m n = 939.56 MeV/c 2 Helium nucleus α: 2 protons+2
Lecture 3 lecture slides are at: http://www.physics.smu.edu/ryszard/5380fa17/ Proton mass m p = 938.28 MeV/c 2 Electron mass m e = 0.511 MeV/c 2 Neutron mass m n = 939.56 MeV/c 2 Helium nucleus α: 2 protons+2
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 9 May 1996
 Phys. Rev. C (Aug., 1996) in press. p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions Bao-An Li, C.M. Ko and G.Q. Li Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department, arxiv:nucl-th/9605014v1
Phys. Rev. C (Aug., 1996) in press. p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions Bao-An Li, C.M. Ko and G.Q. Li Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department, arxiv:nucl-th/9605014v1
Can a Hexapole magnet of an ECR Ion Source be too strong? Drentje, A. G.; Barzangy, F.; Kremers, Herman; Meyer, D.; Mulder, J.; Sijbring, J.
 University of Groningen Can a Hexapole magnet of an ECR Ion Source be too strong? Drentje, A. G.; Barzangy, F.; Kremers, Herman; Meyer, D.; Mulder, J.; Sijbring, J. Published in: Default journal IMPORTANT
University of Groningen Can a Hexapole magnet of an ECR Ion Source be too strong? Drentje, A. G.; Barzangy, F.; Kremers, Herman; Meyer, D.; Mulder, J.; Sijbring, J. Published in: Default journal IMPORTANT
p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions
 Phys. Rev. C (Aug., 1996) in press. p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions Bao-An Li, C.M. Ko and G.Q. Li Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department, Texas A&M University,
Phys. Rev. C (Aug., 1996) in press. p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions Bao-An Li, C.M. Ko and G.Q. Li Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department, Texas A&M University,
& Λ Production in ALICE
 Journal of Physics: Conference eries OPEN ACCE Related content K & Λ Production in ALICE - trangeness production in ALICE Domenico Elia and the ALICE Collaboration o cite this article: Luke Hanratty and
Journal of Physics: Conference eries OPEN ACCE Related content K & Λ Production in ALICE - trangeness production in ALICE Domenico Elia and the ALICE Collaboration o cite this article: Luke Hanratty and
arxiv: v2 [nucl-th] 15 Jun 2017
![arxiv: v2 [nucl-th] 15 Jun 2017 arxiv: v2 [nucl-th] 15 Jun 2017](/thumbs/74/70981616.jpg) Kinetic freeze-out temperatures in central and peripheral collisions: Which one is larger? Hai-Ling Lao, Fu-Hu Liu, Bao-Chun Li, Mai-Ying Duan Institute of heoretical Physics, Shanxi University, aiyuan,
Kinetic freeze-out temperatures in central and peripheral collisions: Which one is larger? Hai-Ling Lao, Fu-Hu Liu, Bao-Chun Li, Mai-Ying Duan Institute of heoretical Physics, Shanxi University, aiyuan,
67. W.M. Snow et al. (M. Sarsour), NSR collaboration, Parity violating neutron spin rotation in He-4 and H., Nuovo Cim. C035N04, (2012).
 68. A. Adare et al. (M. Sarsour), PHENIX collaboration, J/ψ suppression at forward rapidity in Au + Au collisions at s NN =39 and 62.4 GeV, Phys. Rev. C 86, 064901 (2012). 67. W.M. Snow et al. (M. Sarsour),
68. A. Adare et al. (M. Sarsour), PHENIX collaboration, J/ψ suppression at forward rapidity in Au + Au collisions at s NN =39 and 62.4 GeV, Phys. Rev. C 86, 064901 (2012). 67. W.M. Snow et al. (M. Sarsour),
University of Groningen. Water in protoplanetary disks Antonellini, Stefano
 University of Groningen Water in protoplanetary disks Antonellini, Stefano IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen Water in protoplanetary disks Antonellini, Stefano IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
Neutron Interactions Part I. Rebecca M. Howell, Ph.D. Radiation Physics Y2.5321
 Neutron Interactions Part I Rebecca M. Howell, Ph.D. Radiation Physics rhowell@mdanderson.org Y2.5321 Why do we as Medical Physicists care about neutrons? Neutrons in Radiation Therapy Neutron Therapy
Neutron Interactions Part I Rebecca M. Howell, Ph.D. Radiation Physics rhowell@mdanderson.org Y2.5321 Why do we as Medical Physicists care about neutrons? Neutrons in Radiation Therapy Neutron Therapy
Energy scan with Be+Be collisions: cross-section, centrality determination, pion spectra and mean multiplicities
 : crosssection, centrality determination, pion spectra and mean multiplicities for the NA/SHINE collaboration Institute of Physics, University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland Email: emil.aleksander.kaptur@cern.ch
: crosssection, centrality determination, pion spectra and mean multiplicities for the NA/SHINE collaboration Institute of Physics, University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland Email: emil.aleksander.kaptur@cern.ch
Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup
 Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup Dominic Rossi for the LAND collaboration GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH D 64291 Darmstadt, Germany
Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup Dominic Rossi for the LAND collaboration GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH D 64291 Darmstadt, Germany
ISOSPIN RESOLVED DOUBLE PION PRODUCTION AT CELSIUS
 Vol. 29 (1998) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA B No 11 ISOSPIN RESOLVED DOUBLE PION PRODUCTION AT CELSIUS M. Andersson a, Chr. Bargholtz a, E. Fumero a, K. Fransson a L. Holmberg a, K. Lindh a, L. Mårtensson a,
Vol. 29 (1998) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA B No 11 ISOSPIN RESOLVED DOUBLE PION PRODUCTION AT CELSIUS M. Andersson a, Chr. Bargholtz a, E. Fumero a, K. Fransson a L. Holmberg a, K. Lindh a, L. Mårtensson a,
arxiv: v1 [hep-ex] 18 May 2015
![arxiv: v1 [hep-ex] 18 May 2015 arxiv: v1 [hep-ex] 18 May 2015](/thumbs/94/118739665.jpg) ALICE summary of light flavour results at intermediate and high p arxiv:55.477v [hep-ex] 8 May 5 uva Richert, on behalf of the ALICE collaboration Lund University, Department of Physics, Div. of Particle
ALICE summary of light flavour results at intermediate and high p arxiv:55.477v [hep-ex] 8 May 5 uva Richert, on behalf of the ALICE collaboration Lund University, Department of Physics, Div. of Particle
New results related to QGP-like effects in small systems with ALICE
 New results related to QGP-like effects in small systems with ALICE for the ALICE collaboration Lund University E-mail: vytautas.vislavicius@cern. Results on the production of π ±, K ±, p( p), Λ( Λ), Ξ
New results related to QGP-like effects in small systems with ALICE for the ALICE collaboration Lund University E-mail: vytautas.vislavicius@cern. Results on the production of π ±, K ±, p( p), Λ( Λ), Ξ
Tracking at the LAND/R B setup on 17
 3 Tracking at the LAND/R B setup on 17 the example of Ne(γ,2p)15O R. Plag*, J. Marganiec 21. Januar 2011 Dedicated to the students of LAND/R3B Outline rp process and motivation coulomb dissociation as
3 Tracking at the LAND/R B setup on 17 the example of Ne(γ,2p)15O R. Plag*, J. Marganiec 21. Januar 2011 Dedicated to the students of LAND/R3B Outline rp process and motivation coulomb dissociation as
University of Groningen. Statistical inference via fiducial methods Salomé, Diemer
 University of Groningen Statistical inference via fiducial methods Salomé, Diemer IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen Statistical inference via fiducial methods Salomé, Diemer IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
Strangeness Production at SIS: Au+Au at 1.23A GeV with HADES & Microscopic Description by Transport Models
 Strangeness Production at SIS: Au+Au at 1.23A GeV with HADES & Microscopic Description by Transport Models Timo Scheib Goethe Universität Frankfurt am Main // Outline HADES at SIS Strangeness Production
Strangeness Production at SIS: Au+Au at 1.23A GeV with HADES & Microscopic Description by Transport Models Timo Scheib Goethe Universität Frankfurt am Main // Outline HADES at SIS Strangeness Production
Minicourse on Experimental techniques at the NSCL Fragment Separators
 Minicourse on Experimental techniques at the NSCL Fragment Separators Thomas Baumann National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan State University e-mail: baumann@nscl.msu.edu August 2, 2001
Minicourse on Experimental techniques at the NSCL Fragment Separators Thomas Baumann National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory Michigan State University e-mail: baumann@nscl.msu.edu August 2, 2001
Physics 9e/Cutnell. correlated to the. College Board AP Physics 2 Course Objectives
 correlated to the College Board AP Physics 2 Course Objectives Big Idea 1: Objects and systems have properties such as mass and charge. Systems may have internal structure. Enduring Understanding 1.A:
correlated to the College Board AP Physics 2 Course Objectives Big Idea 1: Objects and systems have properties such as mass and charge. Systems may have internal structure. Enduring Understanding 1.A:
Impact of the in-medium conservation of energy on the π /π + multiplicity ratio
 Impact of the in-medium conservation of energy on the π /π + multiplicity ratio M.D. Cozma IFIN-HH, Reactorului 30, 077125 Mǎgurele-Bucharest, Romania Abstract An upgraded version of the isospin dependent
Impact of the in-medium conservation of energy on the π /π + multiplicity ratio M.D. Cozma IFIN-HH, Reactorului 30, 077125 Mǎgurele-Bucharest, Romania Abstract An upgraded version of the isospin dependent
Lecture 12: Hydrodynamics in heavy ion collisions. Elliptic flow Last lecture we learned:
 Lecture 12: Hydrodynamics in heavy ion collisions. Elliptic flow Last lecture we learned: Particle spectral shapes in thermal model ( static medium) are exponential in m T with common slope for all particles.
Lecture 12: Hydrodynamics in heavy ion collisions. Elliptic flow Last lecture we learned: Particle spectral shapes in thermal model ( static medium) are exponential in m T with common slope for all particles.
University of Groningen. Morphological design of Discrete-Time Cellular Neural Networks Brugge, Mark Harm ter
 University of Groningen Morphological design of Discrete-Time Cellular Neural Networks Brugge, Mark Harm ter IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
University of Groningen Morphological design of Discrete-Time Cellular Neural Networks Brugge, Mark Harm ter IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 1 Dec 2007
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 1 Dec 2007 arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 1 Dec 2007](/thumbs/74/69624022.jpg) Multiplicity and angular distribution of particles emitted in relativistic nuclear-nuclear interactions M. K. Suleymanov1, 2, E. U. Khan 1, A Kravchakova 3, Mahnaz Q. Haseeb 1,S. M. Saleem 1, Y. H. Huseynaliyev
Multiplicity and angular distribution of particles emitted in relativistic nuclear-nuclear interactions M. K. Suleymanov1, 2, E. U. Khan 1, A Kravchakova 3, Mahnaz Q. Haseeb 1,S. M. Saleem 1, Y. H. Huseynaliyev
FLOW STUDIES IN NUCLEUS-NUCLEUS COLLISIONS AT FAIR-GSI AVAILABLE ENERGIES
 (c) 2017 Rom. Rep. Phys. (for accepted papers only) FLOW STUDIES IN NUCLEUS-NUCLEUS COLLISIONS AT FAIR-GSI AVAILABLE ENERGIES O. RISTEA 1, C. RISTEA 1,2,a, A. JIPA 1, T. PETRUSE 1, T. ESANU 3, M. CALIN
(c) 2017 Rom. Rep. Phys. (for accepted papers only) FLOW STUDIES IN NUCLEUS-NUCLEUS COLLISIONS AT FAIR-GSI AVAILABLE ENERGIES O. RISTEA 1, C. RISTEA 1,2,a, A. JIPA 1, T. PETRUSE 1, T. ESANU 3, M. CALIN
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title SEARCH FOR FLOW IN THE REACTION Ar + Pb Permalink https:escholarship.orgucitem85s8b502 Author Renfordt, R.E. Publication
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title SEARCH FOR FLOW IN THE REACTION Ar + Pb Permalink https:escholarship.orgucitem85s8b502 Author Renfordt, R.E. Publication
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 University of Groningen Direct observation of the spin-dependent Peltier effect Flipse, J.; Bakker, F. L.; Slachter, A.; Dejene, F. K.; van Wees, Bart Published in: Nature Nanotechnology DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2012.2
University of Groningen Direct observation of the spin-dependent Peltier effect Flipse, J.; Bakker, F. L.; Slachter, A.; Dejene, F. K.; van Wees, Bart Published in: Nature Nanotechnology DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2012.2
Results on heavy ion collisions at LHCb
 Results on heavy ion collisions at LHCb Marcin Kucharczyk on behalf of LHCb collaboration HNI Krakow 28th Rencontres de Blois 29.05-03.06 2016 Outline LHCb - general purpose forward experiment Physics
Results on heavy ion collisions at LHCb Marcin Kucharczyk on behalf of LHCb collaboration HNI Krakow 28th Rencontres de Blois 29.05-03.06 2016 Outline LHCb - general purpose forward experiment Physics
PoS(Baldin ISHEPP XXII)072
 Cumulative protons in hadron-nucleus and nucleus-nucleus interactions E-mail: yuldashev@jinr.ru E.Kh. Bazarov S.L. Lutpullaev K. Olimov E-mail: olimov@uzsci.net V.I. Petrov New experimental data on the
Cumulative protons in hadron-nucleus and nucleus-nucleus interactions E-mail: yuldashev@jinr.ru E.Kh. Bazarov S.L. Lutpullaev K. Olimov E-mail: olimov@uzsci.net V.I. Petrov New experimental data on the
Proton induced reactions in search for kaonic nuclear clusters
 Proton induced reactions in search for kaonic nuclear clusters K. Suzuki a,l.fabbietti a,p.kienle a,b, N. Herrmann c, T. Yamazaki d and J. Zmeskal b a Physik Department, TU München, Germany b Stefan Meyer
Proton induced reactions in search for kaonic nuclear clusters K. Suzuki a,l.fabbietti a,p.kienle a,b, N. Herrmann c, T. Yamazaki d and J. Zmeskal b a Physik Department, TU München, Germany b Stefan Meyer
What is Spallation???
 What is Spallation??? Definition found in Nuclear Physics Academic press: projectile (p, n, π,...) target Spallation---a type of nuclear reaction in which the high-energy level of incident particles causes
What is Spallation??? Definition found in Nuclear Physics Academic press: projectile (p, n, π,...) target Spallation---a type of nuclear reaction in which the high-energy level of incident particles causes
Monte Carlo Non-Linear Flow modes studies with AMPT
 Monte Carlo Non-Linear Flow modes studies with AMP Daniel Noel Supervised by: Naghmeh Mohammadi 2 July - 31 August 218 1 Introduction Heavy-ion collisions at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) generate such
Monte Carlo Non-Linear Flow modes studies with AMP Daniel Noel Supervised by: Naghmeh Mohammadi 2 July - 31 August 218 1 Introduction Heavy-ion collisions at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) generate such
University of Groningen. Event-based simulation of quantum phenomena Zhao, Shuang
 University of Groningen Event-based simulation of quantum phenomena Zhao, Shuang IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen Event-based simulation of quantum phenomena Zhao, Shuang IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
ESSENTIAL QUANTUM PHYSICS PETER LANDSHOFF. University of Cambridge ALLEN METHERELL. University of Central Florida GARETH REES. University of Cambridge
 ESSENTIAL QUANTUM PHYSICS PETER LANDSHOFF University of Cambridge ALLEN METHERELL University of Central Florida GARETH REES University of Cambridge CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Constants of quantum physics
ESSENTIAL QUANTUM PHYSICS PETER LANDSHOFF University of Cambridge ALLEN METHERELL University of Central Florida GARETH REES University of Cambridge CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Constants of quantum physics
Exciting baryon resonances in isobar charge-exchange reactions
 IL NUOVO CIMENTO 39 C (2016) 401 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i2016-16401-0 Colloquia: IWM-EC 2016 Exciting baryon resonances in isobar charge-exchange reactions J. Benlliure( 1 ),J.L.Rodriguez-Sanchez( 1 ),J.Vargas(
IL NUOVO CIMENTO 39 C (2016) 401 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i2016-16401-0 Colloquia: IWM-EC 2016 Exciting baryon resonances in isobar charge-exchange reactions J. Benlliure( 1 ),J.L.Rodriguez-Sanchez( 1 ),J.Vargas(
Citation for published version (APA): Mollema, A. K. (2008). Laser cooling, trapping and spectroscopy of calcium isotopes s.n.
 University of Groningen Laser cooling, trapping and spectroscopy of calcium isotopes Mollema, Albert Kornelis IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
University of Groningen Laser cooling, trapping and spectroscopy of calcium isotopes Mollema, Albert Kornelis IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
Citation for published version (APA): Raimond, J. J. (1934). The coefficient of differential galactic absorption Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen The coefficient of differential galactic absorption Raimond, Jean Jacques IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen The coefficient of differential galactic absorption Raimond, Jean Jacques IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
Small Collision Systems at RHIC
 EPJ Web of Conferences 7, (8) SQM 7 https://doi.org/.5/epjconf/87 Small Collision Systems at RHIC Norbert Novitzky, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, NY 79, USA
EPJ Web of Conferences 7, (8) SQM 7 https://doi.org/.5/epjconf/87 Small Collision Systems at RHIC Norbert Novitzky, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, NY 79, USA
Citation for published version (APA): Andogah, G. (2010). Geographically constrained information retrieval Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Geographically constrained information retrieval Andogah, Geoffrey IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Geographically constrained information retrieval Andogah, Geoffrey IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
Physics of heavy multiply-charged ions: Studies on the borderile of atomic and nuclear physics
 Physics of heavy multiply-charged ions: Studies on the borderile of atomic and nuclear physics Andrey Surzhykov Technische Universität Braunschweig Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB) Lecture 1
Physics of heavy multiply-charged ions: Studies on the borderile of atomic and nuclear physics Andrey Surzhykov Technische Universität Braunschweig Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB) Lecture 1
Citation for published version (APA): Sok, R. M. (1994). Permeation of small molecules across a polymer membrane: a computer simulation study s.n.
 University of Groningen Permeation of small molecules across a polymer membrane Sok, Robert Martin IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Permeation of small molecules across a polymer membrane Sok, Robert Martin IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
Impact parameter dependence of elliptical flow at intermediate energy
 Impact parameter dependence of elliptical flow at intermediate energy Dissertation submitted for partial fulfillment of requirement for The award of the degree of Masters of Science In PHYSICS Submitted
Impact parameter dependence of elliptical flow at intermediate energy Dissertation submitted for partial fulfillment of requirement for The award of the degree of Masters of Science In PHYSICS Submitted
The balance function in azimuthal angle is a measure of the transverse flow
 Physics Letters B 609 (2005) 247 251 www.elsevier.com/locate/physletb The balance function in azimuthal angle is a measure of the transverse flow Piotr Bożek The H. Niewodniczański Institute of Nuclear
Physics Letters B 609 (2005) 247 251 www.elsevier.com/locate/physletb The balance function in azimuthal angle is a measure of the transverse flow Piotr Bożek The H. Niewodniczański Institute of Nuclear
Centrality Dependence of Rapidity Spectra of Negative Pions in 12 C+ 12 C and
 Centrality Dependence of Rapidity Spectra of Negative Pions in 12 C+ 12 C and 12 C+ 181 Ta Collisions at 4.2 GeV/c per Nucleon* Kh. K. Olimov 1),2) **, Sayyed A. Hadi 3) 1) *** and Mahnaz Q. Haseeb Abstract
Centrality Dependence of Rapidity Spectra of Negative Pions in 12 C+ 12 C and 12 C+ 181 Ta Collisions at 4.2 GeV/c per Nucleon* Kh. K. Olimov 1),2) **, Sayyed A. Hadi 3) 1) *** and Mahnaz Q. Haseeb Abstract
