Kinetic lattice Monte Carlo simulations of diffusion processes in Si and SiGe alloys
|
|
|
- Melvin Fisher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Kinetic lattice Monte Carlo simulations of diffusion processes in Si and SiGe alloys, Scott Dunham Department of Electrical Engineering
2 Multiscale Modeling Hierarchy Configuration energies and transition rates. Induced strains, binding/migration energies. Calibration/testing of empirical potentials Configuration energies and transition rates Behavior during regrowth, atomistic vs. global stress
3 KLMC Flow Chart Start Initialize rates k ij Generate r 1, select transition Perform transition Generate r 2, advance time by Update rates k ij t=-ln(r 2 )/k tot Conditions Satisfied? No Yes Terminate
4 Building the rate catalogue Task: find migration barriers for all allowed transitions at each step Surrounding conditions modify migration barriers Presence of other defects (binding energy) Presence of strain (additional strain energy) Solution: Store an unbiased energy barrier E m0 Calculate change of barriers due to change of formation energies of initial and final states. Assume transition state scales linearly with initial and final state E m = E m (ΔE fi ΔE in ) Unbiased Modified Δ in Dunham et al., J. Appl. Phys. 78, 2362 (1995) in (Δ in + Δ fi )/2 fi Δ fi
5 Outline Interstitial-mediated self-diffusion in Si Vacancy mediated inter-diffusion in SiGe
6 Silicon Self Diffusion Mediated by point defects (V, I) V I One of the few directly measurable point defect properties. Quantified by diffusion of an isotropic tracer (T) D T = f I D I C I f I, f V : correlation factors C s + f V D V C V Point defects perform uncorrelated random walks. Tracer atoms perform correlated random walks. C s
7 Correlation of Self Diffusion Tracer atoms perform correlated random walk The previous direction affects the direction of the next step V A tracer, once exchanges with a V, has a higher probability of reexchange with the V. I A tracer, once kicks an atom out, has a higher probability of being kicked back. Correlation of interstitial diffusion (f I ) via indirect process depends on mechanism/hopping network
8 Methodology Interstitial self diffusion on diamond lattice: KLMC: Simulates diffusion of various hopping mechanisms on different lattice networks, find f I by: f I = Δr2 /N tracer Δr 2 /N interstitial N: number of steps Δr 2 : square displacement A B C A B C Compaan et al., Trans. Faraday Soc Interstitial self diffusion in silicon DFT: Find dominant hopping mechanisms KLMC: Simulates diffusion in Si and find f I.
9 Kick-out Mechanism Tetrahedral network: Hexagonal network: I tet I tet f I = ± c.f [Compaan et. al.] I hex I hex f I = ±0.0001
10 Stable-split Mechanism Assuming the split configuration is stable Tetrahedral network: Hexagonal network: I tet I sp I tet f = ± I hex I sp I hex f = ±0.0001
11 DFT: Migration Events I sp I h I sp I t I t I sp I sp I h I h
12 KLMC Simulations Dominant mechanisms: The direct (uncorrelated) mechanism: I h I h via I t. Forward barrier:0.17 ev, reverse barrier: 0.17 ev. The indirect mechanism: I sp I h. Forward barrier:0.34 ev, reverse barrier: 0.25 ev. Probability to follow the direct path (P d ) depends on the barriers and temperature. Ω d exp ( E d m kt ) P d = Ω d exp E d m kt +Ω iexp ( E i m kt ) Effective correlation factor is temperature dependent P i (indirect) I sp P d (direct) I h I h
13 Correlation of Si Self Diffusion Effective correlation factor as a function of the probability of the direct mechanism. f at C calculated to be Experimental value is 0.6 [Voronkov et. al. 2005] Possible sources of inaccuracy: Uncertainties of DFT predicted barriers Neglect of entropy difference
14 Outline Interstitial-mediated self-diffusion in Si Vacancy mediated inter-diffusion in SiGe
15 Simulational perspective SiGe Inter-diffusion dominated by vacancy mechanism Si Ge V V + Si Si + V V + Ge Ge + V Change of formation energies due to Ge-V binding energy (DFT: 0.31 ev) Strain energy (determined by induced strains of defects) Energy barrier scales as: E m = E m (ΔE f fi ΔE f in ) Si V Unbiased Modified Δ in 0.34eV Ge V 0.17eV Unbiased barrier E m 0 (DFT) in (Δ in + Δ fi )/2 fi Δ fi
16 Determining Strain Energy Hooke s Law Strain energy C e 1 2 e E Strain dependence T E E0 xd C xd 2 1 ai a0 Dei x a e e e e e 0 stress strain x : defect concentration 1 C11 C12 C13 e1 C C C e e C C C 3 Induced strain (De) and elastic stiffness tensor (C) can be extracted from DFT calculations for different strain conditions
17 Simulation Set-up Simulation set-ups are chosen to mimic experimental conditions (Si layers on relaxed Si 1-x Ge x layers, 920 º C). Simulation results scaled to the condition of equilibrium vacancy concentration Experimental profile [Xia et al] Simulation domain [Blue: Ge, Yellow: Si]
18 Extracting interdiffusivity Ge affects inter-diffusivity via Stress effect: strain energy compensation of Ge and V Alloy effect: Ge-V binding lowers V formation energy. Interdiffusivity increases exponentially with Ge content D x Ge ~exp(bx Ge ) Extracting B from KLMC B alloy 5.8 alloy B stress 7.6 B total 13.4 B total (Expt*) 8.1 * [Xia et al] alloy + stress Sources of error: Inaccurate parameters for diffusion and formation energies Small lateral dimension that results in large fluctuations Insufficient sampling of Monte Carlo simulations
19 Conclusion KLMC combined with DFT calculations for Self diffusion in Si Interdiffusion in SiGe Future Research More accurate ways to calculate migration barriers based on local environment Fully implement strain effect
20 Acknowledgements Special thanks to Scott T. Dunham (Advisor) EMSL, PNNL Financial support
ATOMISTIC MODELING OF BORON ACTIVATION AND DIFFUSION IN STRAINED SIGE
 ATOMISTIC MODELING OF BORON ACTIVATION AND DIFFUSION IN STRAINED SIGE Scott T. Dunham,, Jakyoung Song, and Chihak Ahn Dept. of Electrical Engineering, Dept. of Physics University of Washington, Box 35500,
ATOMISTIC MODELING OF BORON ACTIVATION AND DIFFUSION IN STRAINED SIGE Scott T. Dunham,, Jakyoung Song, and Chihak Ahn Dept. of Electrical Engineering, Dept. of Physics University of Washington, Box 35500,
Models for Stress and Impurity Effects on Diffusion and Activation in Nanoscale CMOS
 Models for Stress and Impurity Effects on Diffusion and Activation in Nanoscale CMOS SRC e-workshop October 31, 2006 Scott Dunham Professor, Electrical Engineering, Univ. of Washington Talk Outline Nanoscale
Models for Stress and Impurity Effects on Diffusion and Activation in Nanoscale CMOS SRC e-workshop October 31, 2006 Scott Dunham Professor, Electrical Engineering, Univ. of Washington Talk Outline Nanoscale
Atomistic simulations of point defect diffusion in Si and SiGe
 Atomistic simulations of point defect diffusion in Si and SiGe P. Pochet, D. Caliste, K. Rushchanskii, F. Lançon & T. Deutsch CEA UJF INAC Institute for Nanoscience and Cryogenics Partially founded by
Atomistic simulations of point defect diffusion in Si and SiGe P. Pochet, D. Caliste, K. Rushchanskii, F. Lançon & T. Deutsch CEA UJF INAC Institute for Nanoscience and Cryogenics Partially founded by
Calculations of effect of anisotropic stress/strain on dopant diffusion in silicon under equilibrium and nonequilibrium conditions
 Calculations of effect of anisotropic stress/strain on dopant diffusion in silicon under equilibrium and nonequilibrium conditions Scott T. Dunham a Department of Electrical Engineering, University of
Calculations of effect of anisotropic stress/strain on dopant diffusion in silicon under equilibrium and nonequilibrium conditions Scott T. Dunham a Department of Electrical Engineering, University of
Kinetic Monte Carlo: from transition probabilities to transition rates
 Kinetic Monte Carlo: from transition probabilities to transition rates With MD we can only reproduce the dynamics of the system for 100 ns. Slow thermallyactivated processes, such as diffusion, cannot
Kinetic Monte Carlo: from transition probabilities to transition rates With MD we can only reproduce the dynamics of the system for 100 ns. Slow thermallyactivated processes, such as diffusion, cannot
Kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC)
 Kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC) Molecular Dynamics (MD): high-frequency motion dictate the time-step (e.g., vibrations). Time step is short: pico-seconds. Direct Monte Carlo (MC): stochastic (non-deterministic)
Kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC) Molecular Dynamics (MD): high-frequency motion dictate the time-step (e.g., vibrations). Time step is short: pico-seconds. Direct Monte Carlo (MC): stochastic (non-deterministic)
Diffusion in multicomponent solids. Anton Van der Ven Department of Materials Science and Engineering University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI
 Diffusion in multicomponent solids nton Van der Ven Department of Materials Science and Engineering University of Michigan nn rbor, MI Coarse graining time Diffusion in a crystal Two levels of time coarse
Diffusion in multicomponent solids nton Van der Ven Department of Materials Science and Engineering University of Michigan nn rbor, MI Coarse graining time Diffusion in a crystal Two levels of time coarse
6.730 Physics for Solid State Applications
 6.730 Physics for Solid State Applications Lecture 8: Lattice Waves in 1D Monatomic Crystals Outline Overview of Lattice Vibrations so far Models for Vibrations in Discrete 1-D Lattice Example of Nearest
6.730 Physics for Solid State Applications Lecture 8: Lattice Waves in 1D Monatomic Crystals Outline Overview of Lattice Vibrations so far Models for Vibrations in Discrete 1-D Lattice Example of Nearest
Reconstruction and intermixing in thin Ge layers on Si 001
 Reconstruction and intermixing in thin Ge layers on Si 001 L. Nurminen, 1 F. Tavazza, 2 D. P. Landau, 1,2 A. Kuronen, 1 and K. Kaski 1 1 Laboratory of Computational Engineering, Helsinki University of
Reconstruction and intermixing in thin Ge layers on Si 001 L. Nurminen, 1 F. Tavazza, 2 D. P. Landau, 1,2 A. Kuronen, 1 and K. Kaski 1 1 Laboratory of Computational Engineering, Helsinki University of
MODELING DEFECT MEDIATED DOPANT DIFFUSION IN SILICON. by Brian T. Puchala
 MODELING DEFECT MEDIATED DOPANT DIFFUSION IN SILICON by Brian T. Puchala A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (Materials Science and
MODELING DEFECT MEDIATED DOPANT DIFFUSION IN SILICON by Brian T. Puchala A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (Materials Science and
Lecture contents. Stress and strain Deformation potential. NNSE 618 Lecture #23
 1 Lecture contents Stress and strain Deformation potential Few concepts from linear elasticity theory : Stress and Strain 6 independent components 2 Stress = force/area ( 3x3 symmetric tensor! ) ij ji
1 Lecture contents Stress and strain Deformation potential Few concepts from linear elasticity theory : Stress and Strain 6 independent components 2 Stress = force/area ( 3x3 symmetric tensor! ) ij ji
3.320 Lecture 23 (5/3/05)
 3.320 Lecture 23 (5/3/05) Faster, faster,faster Bigger, Bigger, Bigger Accelerated Molecular Dynamics Kinetic Monte Carlo Inhomogeneous Spatial Coarse Graining 5/3/05 3.320 Atomistic Modeling of Materials
3.320 Lecture 23 (5/3/05) Faster, faster,faster Bigger, Bigger, Bigger Accelerated Molecular Dynamics Kinetic Monte Carlo Inhomogeneous Spatial Coarse Graining 5/3/05 3.320 Atomistic Modeling of Materials
ATOMIC-SCALE THEORY OF RADIATION-INDUCED PHENOMENA
 ATOMIC-SCALE THEORY OF RADIATION-INDUCED PHENOMENA OVERVIEW OF THE LAST FIVE YEARS AND NEW RESULTS Sokrates T. Pantelides Department of Physics and Astronomy, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN The theory
ATOMIC-SCALE THEORY OF RADIATION-INDUCED PHENOMENA OVERVIEW OF THE LAST FIVE YEARS AND NEW RESULTS Sokrates T. Pantelides Department of Physics and Astronomy, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN The theory
Theoretical Studies of Self-Diffusion and Dopant Clustering in Semiconductors
 phys. stat. sol. (b) 233, No., 24 30 (2002) Theoretical Studies of Self-Diffusion and Dopant Clustering in Semiconductors B. P. Uberuaga )(a), G. Henkelman (b), H. Jónsson (b, c), S. T. Dunham (d), W.
phys. stat. sol. (b) 233, No., 24 30 (2002) Theoretical Studies of Self-Diffusion and Dopant Clustering in Semiconductors B. P. Uberuaga )(a), G. Henkelman (b), H. Jónsson (b, c), S. T. Dunham (d), W.
Lecture 1: Atomic Diffusion
 Part IB Materials Science & Metallurgy H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia Course A, Metals and Alloys Lecture 1: Atomic Diffusion Mass transport in a gas or liquid generally involves the flow of fluid (e.g. convection
Part IB Materials Science & Metallurgy H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia Course A, Metals and Alloys Lecture 1: Atomic Diffusion Mass transport in a gas or liquid generally involves the flow of fluid (e.g. convection
THREE-DIMENSIONAL SIMULATION OF THERMAL OXIDATION AND THE INFLUENCE OF STRESS
 THREE-DIMENSIONAL SIMULATION OF THERMAL OXIDATION AND THE INFLUENCE OF STRESS Christian Hollauer, Hajdin Ceric, and Siegfried Selberherr Institute for Microelectronics, Technical University Vienna Gußhausstraße
THREE-DIMENSIONAL SIMULATION OF THERMAL OXIDATION AND THE INFLUENCE OF STRESS Christian Hollauer, Hajdin Ceric, and Siegfried Selberherr Institute for Microelectronics, Technical University Vienna Gußhausstraße
Kinetics. Rate of change in response to thermodynamic forces
 Kinetics Rate of change in response to thermodynamic forces Deviation from local equilibrium continuous change T heat flow temperature changes µ atom flow composition changes Deviation from global equilibrium
Kinetics Rate of change in response to thermodynamic forces Deviation from local equilibrium continuous change T heat flow temperature changes µ atom flow composition changes Deviation from global equilibrium
Theoretical Studies of Self-Diffusion and Dopant Clustering in Semiconductors
 phys. stat. sol. (b) zzz, No. z, zzz zzz (2002) Theoretical Studies of Self-Diffusion and Dopant Clustering in Semiconductors B.P. Uberuaga )(a), G. Henkelman (b), H. Jónsson (b) (c), S.T. Dunham (d),
phys. stat. sol. (b) zzz, No. z, zzz zzz (2002) Theoretical Studies of Self-Diffusion and Dopant Clustering in Semiconductors B.P. Uberuaga )(a), G. Henkelman (b), H. Jónsson (b) (c), S.T. Dunham (d),
EFFECTS OF STOICHIOMETRY ON POINT DEFECTS AND IMPURITIES IN GALLIUM NITRIDE
 EFFECTS OF STOICHIOMETRY ON POINT DEFECTS AND IMPURITIES IN GALLIUM NITRIDE C. G. VAN DE WALLE AND J. E. NORTHRUP Palo Alto Research Center, 3333 Coyote Hill Road, Palo Alto, CA 930, USA E-mail: vandewalle@parc.com
EFFECTS OF STOICHIOMETRY ON POINT DEFECTS AND IMPURITIES IN GALLIUM NITRIDE C. G. VAN DE WALLE AND J. E. NORTHRUP Palo Alto Research Center, 3333 Coyote Hill Road, Palo Alto, CA 930, USA E-mail: vandewalle@parc.com
Diffusion mechanisms in Cu grain boundaries
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 62, NUMBER 6 Diffusion mechanisms in Cu grain boundaries 1 AUGUST 2000-II Mads R. So rensen Theoretical Division, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico 87545 Yuri
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 62, NUMBER 6 Diffusion mechanisms in Cu grain boundaries 1 AUGUST 2000-II Mads R. So rensen Theoretical Division, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico 87545 Yuri
Atomistic simulations on the mobility of di- and tri-interstitials in Si
 Atomistic simulations on the mobility of di- and tri-interstitials in Si related publications (since 2001): Posselt, M., Gao, F., Zwicker, D., Atomistic study of the migration of di- and tri-interstitials
Atomistic simulations on the mobility of di- and tri-interstitials in Si related publications (since 2001): Posselt, M., Gao, F., Zwicker, D., Atomistic study of the migration of di- and tri-interstitials
6. Computational Design of Energy-related Materials
 6. Computational Design of Energy-related Materials Contents 6.1 Atomistic Simulation Methods for Energy Materials 6.2 ab initio design of photovoltaic materials 6.3 Solid Ion Conductors for Fuel Cells
6. Computational Design of Energy-related Materials Contents 6.1 Atomistic Simulation Methods for Energy Materials 6.2 ab initio design of photovoltaic materials 6.3 Solid Ion Conductors for Fuel Cells
Kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC) Kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC)
 Kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC) Molecular Dynamics (MD): high-frequency motion dictate the time-step (e.g., vibrations). Time step is short: pico-seconds. Direct Monte Carlo (MC): stochastic (non-deterministic)
Kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC) Molecular Dynamics (MD): high-frequency motion dictate the time-step (e.g., vibrations). Time step is short: pico-seconds. Direct Monte Carlo (MC): stochastic (non-deterministic)
Diffusion in Dilute Alloys
 Chapter 3 Diffusion in Dilute Alloys Our discussion of the atomistic mechanisms for diffusion has been confined to the situations where the diffusing species is chemically identical to the host atom. We
Chapter 3 Diffusion in Dilute Alloys Our discussion of the atomistic mechanisms for diffusion has been confined to the situations where the diffusing species is chemically identical to the host atom. We
QUASI-EQUILIBRIUM MONTE-CARLO: OFF-LATTICE KINETIC MONTE CARLO SIMULATION OF HETEROEPITAXY WITHOUT SADDLE POINTS
 QUASI-EQUILIBRIUM MONTE-CARLO: OFF-LATTICE KINETIC MONTE CARLO SIMULATION OF HETEROEPITAXY WITHOUT SADDLE POINTS Henry A. Boateng University of Michigan, Ann Arbor Joint work with Tim Schulze and Peter
QUASI-EQUILIBRIUM MONTE-CARLO: OFF-LATTICE KINETIC MONTE CARLO SIMULATION OF HETEROEPITAXY WITHOUT SADDLE POINTS Henry A. Boateng University of Michigan, Ann Arbor Joint work with Tim Schulze and Peter
Ab initio Berechungen für Datenbanken
 J Ab initio Berechungen für Datenbanken Jörg Neugebauer University of Paderborn Lehrstuhl Computational Materials Science Computational Materials Science Group CMS Group Scaling Problem in Modeling length
J Ab initio Berechungen für Datenbanken Jörg Neugebauer University of Paderborn Lehrstuhl Computational Materials Science Computational Materials Science Group CMS Group Scaling Problem in Modeling length
Diffusion in Extrinsic Silicon and Silicon Germanium
 1 Diffusion in Extrinsic Silicon and Silicon Germanium SFR Workshop & Review November 14, 2002 Hughes Silvestri, Ian Sharp, Hartmut Bracht, and Eugene Haller Berkeley, CA 2002 GOAL: Diffusion measurements
1 Diffusion in Extrinsic Silicon and Silicon Germanium SFR Workshop & Review November 14, 2002 Hughes Silvestri, Ian Sharp, Hartmut Bracht, and Eugene Haller Berkeley, CA 2002 GOAL: Diffusion measurements
Supporting information for. Direct imaging of kinetic pathways of atomic diffusion in. monolayer molybdenum disulfide
 Supporting information for Direct imaging of kinetic pathways of atomic diffusion in monolayer molybdenum disulfide Jinhua Hong,, Yuhao Pan,, Zhixin Hu, Danhui Lv, Chuanhong Jin, *, Wei Ji, *, Jun Yuan,,*,
Supporting information for Direct imaging of kinetic pathways of atomic diffusion in monolayer molybdenum disulfide Jinhua Hong,, Yuhao Pan,, Zhixin Hu, Danhui Lv, Chuanhong Jin, *, Wei Ji, *, Jun Yuan,,*,
Electronic Structure Theory for Periodic Systems: The Concepts. Christian Ratsch
 Electronic Structure Theory for Periodic Systems: The Concepts Christian Ratsch Institute for Pure and Applied Mathematics and Department of Mathematics, UCLA Motivation There are 10 20 atoms in 1 mm 3
Electronic Structure Theory for Periodic Systems: The Concepts Christian Ratsch Institute for Pure and Applied Mathematics and Department of Mathematics, UCLA Motivation There are 10 20 atoms in 1 mm 3
Dopant and Self-Diffusion in Semiconductors: A Tutorial
 Dopant and Self-Diffusion in Semiconductors: A Tutorial Eugene Haller and Hughes Silvestri MS&E, UCB and LBNL FLCC Tutorial 1/26/04 1 FLCC Outline Motivation Background Fick s Laws Diffusion Mechanisms
Dopant and Self-Diffusion in Semiconductors: A Tutorial Eugene Haller and Hughes Silvestri MS&E, UCB and LBNL FLCC Tutorial 1/26/04 1 FLCC Outline Motivation Background Fick s Laws Diffusion Mechanisms
Thermally Activated Processes
 General Description of Activated Process: 1 Diffusion: 2 Diffusion: Temperature Plays a significant role in diffusion Temperature is not the driving force. Remember: DRIVING FORCE GRADIENT of a FIELD VARIALE
General Description of Activated Process: 1 Diffusion: 2 Diffusion: Temperature Plays a significant role in diffusion Temperature is not the driving force. Remember: DRIVING FORCE GRADIENT of a FIELD VARIALE
3.091 Introduction to Solid State Chemistry. Lecture Notes No. 5a ELASTIC BEHAVIOR OF SOLIDS
 3.091 Introduction to Solid State Chemistry Lecture Notes No. 5a ELASTIC BEHAVIOR OF SOLIDS 1. INTRODUCTION Crystals are held together by interatomic or intermolecular bonds. The bonds can be covalent,
3.091 Introduction to Solid State Chemistry Lecture Notes No. 5a ELASTIC BEHAVIOR OF SOLIDS 1. INTRODUCTION Crystals are held together by interatomic or intermolecular bonds. The bonds can be covalent,
Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Fusion Materials: Challenges and Opportunities (Recent Developments)
 Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Fusion Materials: Challenges and Opportunities (Recent Developments) Fei Gao gaofeium@umich.edu Limitations of MD Time scales Length scales (PBC help a lot) Accuracy of
Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Fusion Materials: Challenges and Opportunities (Recent Developments) Fei Gao gaofeium@umich.edu Limitations of MD Time scales Length scales (PBC help a lot) Accuracy of
STRUCTURAL AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF AMORPHOUS SILICON: AB-INITIO AND CLASSICAL MOLECULAR DYNAMICS STUDY
 STRUCTURAL AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF AMORPHOUS SILICON: AB-INITIO AND CLASSICAL MOLECULAR DYNAMICS STUDY S. Hara, T. Kumagai, S. Izumi and S. Sakai Department of mechanical engineering, University of
STRUCTURAL AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF AMORPHOUS SILICON: AB-INITIO AND CLASSICAL MOLECULAR DYNAMICS STUDY S. Hara, T. Kumagai, S. Izumi and S. Sakai Department of mechanical engineering, University of
Quantum Monte Carlo Calculations of Point Defects in Alumina
 Quantum Monte Carlo Calculations of Nicholas Hine Condensed Matter Theory Group Imperial College London Sunday 22nd July 2007 Dramatis Personae Collaborators Matthew Foulkes Mike Finnis Kilian Frensch
Quantum Monte Carlo Calculations of Nicholas Hine Condensed Matter Theory Group Imperial College London Sunday 22nd July 2007 Dramatis Personae Collaborators Matthew Foulkes Mike Finnis Kilian Frensch
EFFECT OF PRESSURE ON BORON DIFFUSION IN SILICON Yuechao Zhao 1, Michael J. Aziz 1, Salman Mitha 2, and David Schiferl 3
 EFFECT OF PRESSURE ON BORON DIFFUSION IN SILICON Yuechao Zhao 1, Michael J. Aziz 1, Salman Mitha 2, and David Schiferl 3 1 Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA
EFFECT OF PRESSURE ON BORON DIFFUSION IN SILICON Yuechao Zhao 1, Michael J. Aziz 1, Salman Mitha 2, and David Schiferl 3 1 Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA
Christian Ratsch, UCLA
 Strain Dependence of Microscopic Parameters and its Effects on Ordering during Epitaxial Growth Christian Ratsch, UCLA Institute for Pure and Applied Mathematics, and Department of Mathematics Collaborators:
Strain Dependence of Microscopic Parameters and its Effects on Ordering during Epitaxial Growth Christian Ratsch, UCLA Institute for Pure and Applied Mathematics, and Department of Mathematics Collaborators:
Defects and diffusion in metal oxides: Challenges for first-principles modelling
 Defects and diffusion in metal oxides: Challenges for first-principles modelling Karsten Albe, FG Materialmodellierung, TU Darmstadt Johan Pohl, Peter Agoston, Paul Erhart, Manuel Diehm FUNDING: ICTP Workshop
Defects and diffusion in metal oxides: Challenges for first-principles modelling Karsten Albe, FG Materialmodellierung, TU Darmstadt Johan Pohl, Peter Agoston, Paul Erhart, Manuel Diehm FUNDING: ICTP Workshop
NITROGEN CONTAINING ULTRA THIN SiO 2 FILMS ON Si OBTAINED BY ION IMPLANTATION
 NITROGEN CONTAINING ULTRA THIN SiO 2 FILMS ON Si OBTAINED BY ION IMPLANTATION Sashka Petrova Alexandrova 1, Evgenia Petrova Valcheva 2, Rumen Georgiev Kobilarov 1 1 Department of Applied Physics, Technical
NITROGEN CONTAINING ULTRA THIN SiO 2 FILMS ON Si OBTAINED BY ION IMPLANTATION Sashka Petrova Alexandrova 1, Evgenia Petrova Valcheva 2, Rumen Georgiev Kobilarov 1 1 Department of Applied Physics, Technical
André Schleife Department of Materials Science and Engineering
 André Schleife Department of Materials Science and Engineering Yesterday you (should have) learned this: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/e/ea/ Simple_Harmonic_Motion_Orbit.gif 1. deterministic
André Schleife Department of Materials Science and Engineering Yesterday you (should have) learned this: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/e/ea/ Simple_Harmonic_Motion_Orbit.gif 1. deterministic
Motivation. Confined acoustics phonons. Modification of phonon lifetimes Antisymmetric Bulk. Symmetric. 10 nm
 Motivation Confined acoustics phonons Modification of phonon lifetimes 0 0 Symmetric Antisymmetric Bulk 0 nm A. Balandin et al, PRB 58(998) 544 Effect of native oxide on dispersion relation Heat transport
Motivation Confined acoustics phonons Modification of phonon lifetimes 0 0 Symmetric Antisymmetric Bulk 0 nm A. Balandin et al, PRB 58(998) 544 Effect of native oxide on dispersion relation Heat transport
Introduction To Materials Science FOR ENGINEERS, Ch. 5. Diffusion. MSE 201 Callister Chapter 5
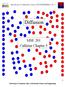 Diffusion MSE 201 Callister Chapter 5 1 Goals: Diffusion - how do atoms move through solids? Fundamental concepts and language Diffusion mechanisms Vacancy diffusion Interstitial diffusion Impurities Diffusion
Diffusion MSE 201 Callister Chapter 5 1 Goals: Diffusion - how do atoms move through solids? Fundamental concepts and language Diffusion mechanisms Vacancy diffusion Interstitial diffusion Impurities Diffusion
COMPARISON OF PROCESS OF DIFFUSION OF INTERSTITIAL OXYGEN ATOMS AND INTERSTITIAL HYDROGEN MOLECULES IN SILICON AND
 COMPARISON OF PROCESS OF DIFFUSION OF INTERSTITIAL OXYGEN ATOMS AND INTERSTITIAL HYDROGEN MOLECULES IN SILICON AND GERMANIUM CRYSTALS: QUANTUMCHEMICAL SIMULATION Vasilii Gusakov Joint Institute of Solid
COMPARISON OF PROCESS OF DIFFUSION OF INTERSTITIAL OXYGEN ATOMS AND INTERSTITIAL HYDROGEN MOLECULES IN SILICON AND GERMANIUM CRYSTALS: QUANTUMCHEMICAL SIMULATION Vasilii Gusakov Joint Institute of Solid
First-principles calculations of self-interstitial defect structures and diffusion paths in silicon
 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 11 (1999) 10437 10450. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(99)06618-7 First-principles calculations of self-interstitial defect structures and diffusion paths in silicon R J Needs
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 11 (1999) 10437 10450. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(99)06618-7 First-principles calculations of self-interstitial defect structures and diffusion paths in silicon R J Needs
SaifulIslam. Chemistry, Surrey April, Protons & Dopants. in Oxide Materials
 Protons & Dopants Chemistry, Surrey in Oxide Materials Outline Background & Methods Proton conductors: AZrO 3 ; ACeO 3 perovskite-type Proton transport Dopant sites Proton-dopant interactions Non-stoichiometry
Protons & Dopants Chemistry, Surrey in Oxide Materials Outline Background & Methods Proton conductors: AZrO 3 ; ACeO 3 perovskite-type Proton transport Dopant sites Proton-dopant interactions Non-stoichiometry
Kinetic Monte Carlo Simulation of Two-dimensional Semiconductor Quantum Dots Growth
 Kinetic Monte Carlo Simulation of Two-dimensional Semiconductor Quantum Dots Growth by Ernie Pan Richard Zhu Melissa Sun Peter Chung Computer Modeling and Simulation Group The University of Akron Outline
Kinetic Monte Carlo Simulation of Two-dimensional Semiconductor Quantum Dots Growth by Ernie Pan Richard Zhu Melissa Sun Peter Chung Computer Modeling and Simulation Group The University of Akron Outline
Simulations of Li ion diffusion in the electrolyte material Li 3 PO 4
 Simulations of Li ion diffusion in the electrolyte material Li 3 PO 4 a, b N. A. W. Holzwarth Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, NC, USA Motivation Calculational methods Diffusion in crystalline material
Simulations of Li ion diffusion in the electrolyte material Li 3 PO 4 a, b N. A. W. Holzwarth Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, NC, USA Motivation Calculational methods Diffusion in crystalline material
Modèle de liaisons fortes au 4ème moment pour traiter l ordre-désordre dans les alliages
 Modèle de liaisons fortes au 4ème moment pour traiter l ordre-désordre dans les alliages Jan Los, Christine Mottet, Guy Tréglia CINaM, Marseille Christine Goyhenex IPCMS, Strasbourg Outline Context Tight
Modèle de liaisons fortes au 4ème moment pour traiter l ordre-désordre dans les alliages Jan Los, Christine Mottet, Guy Tréglia CINaM, Marseille Christine Goyhenex IPCMS, Strasbourg Outline Context Tight
Basic 8 Micro-Nano Materials Science. and engineering
 Basic 8 Micro-Nano Materials Science and Analysis Atomistic simulations in materials science and engineering Assistant Prof. Y. Kinoshita and Prof. N. Ohno Dept. of Comp. Sci. Eng. and Dept. of Mech. Sci.
Basic 8 Micro-Nano Materials Science and Analysis Atomistic simulations in materials science and engineering Assistant Prof. Y. Kinoshita and Prof. N. Ohno Dept. of Comp. Sci. Eng. and Dept. of Mech. Sci.
Semiconductor physics I. The Crystal Structure of Solids
 Lecture 3 Semiconductor physics I The Crystal Structure of Solids 1 Semiconductor materials Types of solids Space lattices Atomic Bonding Imperfection and doping in SOLIDS 2 Semiconductor Semiconductors
Lecture 3 Semiconductor physics I The Crystal Structure of Solids 1 Semiconductor materials Types of solids Space lattices Atomic Bonding Imperfection and doping in SOLIDS 2 Semiconductor Semiconductors
Molecular Dynamics and Accelerated Molecular Dynamics
 Molecular Dynamics and Accelerated Molecular Dynamics Arthur F. Voter Theoretical Division National Laboratory Lecture 3 Tutorial Lecture Series Institute for Pure and Applied Mathematics (IPAM) UCLA September
Molecular Dynamics and Accelerated Molecular Dynamics Arthur F. Voter Theoretical Division National Laboratory Lecture 3 Tutorial Lecture Series Institute for Pure and Applied Mathematics (IPAM) UCLA September
Structure and dynamics of the diarsenic complex in crystalline silicon
 Structure and dynamics of the diarsenic complex in crystalline silicon Scott A. Harrison, Thomas F. Edgar, and Gyeong S. Hwang* Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Texas, Austin, Texas 78713,
Structure and dynamics of the diarsenic complex in crystalline silicon Scott A. Harrison, Thomas F. Edgar, and Gyeong S. Hwang* Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Texas, Austin, Texas 78713,
DFT modeling of novel materials for hydrogen storage
 DFT modeling of novel materials for hydrogen storage Tejs Vegge 1, J Voss 1,2, Q Shi 1, HS Jacobsen 1, JS Hummelshøj 1,2, AS Pedersen 1, JK Nørskov 2 1 Materials Research Department, Risø National Laboratory,
DFT modeling of novel materials for hydrogen storage Tejs Vegge 1, J Voss 1,2, Q Shi 1, HS Jacobsen 1, JS Hummelshøj 1,2, AS Pedersen 1, JK Nørskov 2 1 Materials Research Department, Risø National Laboratory,
Interaction of ion beams with matter
 Interaction of ion beams with matter Introduction Nuclear and electronic energy loss Radiation damage process Displacements by nuclear stopping Defects by electronic energy loss Defect-free irradiation
Interaction of ion beams with matter Introduction Nuclear and electronic energy loss Radiation damage process Displacements by nuclear stopping Defects by electronic energy loss Defect-free irradiation
Examples of Defects in Solids from ESPRESSO
 Examples of Defects in Solids from ESPRESSO Alessandra Satta SLACS-INFMCNR Sardinian LAboratory for Computational Materials Science Hands-on Tutorial on the Quantum-ESPRESSO Package Cagliari, September
Examples of Defects in Solids from ESPRESSO Alessandra Satta SLACS-INFMCNR Sardinian LAboratory for Computational Materials Science Hands-on Tutorial on the Quantum-ESPRESSO Package Cagliari, September
Comparisons of DFT-MD, TB- MD and classical MD calculations of radiation damage and plasmawallinteractions
 CMS Comparisons of DFT-MD, TB- MD and classical MD calculations of radiation damage and plasmawallinteractions Kai Nordlund Department of Physics and Helsinki Institute of Physics University of Helsinki,
CMS Comparisons of DFT-MD, TB- MD and classical MD calculations of radiation damage and plasmawallinteractions Kai Nordlund Department of Physics and Helsinki Institute of Physics University of Helsinki,
Van der Waals DFT Study of the Energetics of Alkali Metal Intercalation in Graphite
 1 Van der Waals DFT Study of the Energetics of Alkali Metal Intercalation in Graphite Zhaohui Wang, Sverre M. Selbacħ and Tor Grande Department of Material Science and Engineering Trondheim, Nov. 29, 2013
1 Van der Waals DFT Study of the Energetics of Alkali Metal Intercalation in Graphite Zhaohui Wang, Sverre M. Selbacħ and Tor Grande Department of Material Science and Engineering Trondheim, Nov. 29, 2013
First-Passage Kinetic Monte Carlo Algorithm for Complex Reaction-Diffusion Systems
 First-Passage Kinetic Monte Carlo Algorithm for Complex Reaction-Diffusion Systems Aleksandar Donev 1 Lawrence Postdoctoral Fellow Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory In collaboration with: Vasily V.
First-Passage Kinetic Monte Carlo Algorithm for Complex Reaction-Diffusion Systems Aleksandar Donev 1 Lawrence Postdoctoral Fellow Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory In collaboration with: Vasily V.
Kinetic Monte Carlo modelling of semiconductor growth
 Kinetic Monte Carlo modelling of semiconductor growth Peter Kratzer Faculty of Physics, University Duisburg-Essen, Germany Time and length scales morphology Ga As 2D islands surface reconstruction Methods
Kinetic Monte Carlo modelling of semiconductor growth Peter Kratzer Faculty of Physics, University Duisburg-Essen, Germany Time and length scales morphology Ga As 2D islands surface reconstruction Methods
Potentials, periodicity
 Potentials, periodicity Lecture 2 1/23/18 1 Survey responses 2 Topic requests DFT (10), Molecular dynamics (7), Monte Carlo (5) Machine Learning (4), High-throughput, Databases (4) NEB, phonons, Non-equilibrium
Potentials, periodicity Lecture 2 1/23/18 1 Survey responses 2 Topic requests DFT (10), Molecular dynamics (7), Monte Carlo (5) Machine Learning (4), High-throughput, Databases (4) NEB, phonons, Non-equilibrium
Charge equilibration
 Charge equilibration Taylor expansion of energy of atom A @E E A (Q) =E A0 + Q A + 1 @Q A 0 2 Q2 A @ 2 E @Q 2 A 0 +... The corresponding energy of cation/anion and neutral atom E A (+1) = E A0 + @E @Q
Charge equilibration Taylor expansion of energy of atom A @E E A (Q) =E A0 + Q A + 1 @Q A 0 2 Q2 A @ 2 E @Q 2 A 0 +... The corresponding energy of cation/anion and neutral atom E A (+1) = E A0 + @E @Q
Molybdenum Sulfide based electronics. Gotthard Seifert Physikalische Chemie,Technische Universität Dresden, Germany
 start Molybdenum Sulfide based electronics Gotthard Seifert Physikalische Chemie,Technische Universität Dresden, Germany Early studies 1960-ies R. Fivaz, E. Mooser Mobility of Charge Carriers in semiconducting
start Molybdenum Sulfide based electronics Gotthard Seifert Physikalische Chemie,Technische Universität Dresden, Germany Early studies 1960-ies R. Fivaz, E. Mooser Mobility of Charge Carriers in semiconducting
Modelling across different time and length scales
 18/1/007 Course MP5 Lecture 1 18/1/007 Modelling across different time and length scales An introduction to multiscale modelling and mesoscale methods Dr James Elliott 0.1 Introduction 6 lectures by JAE,
18/1/007 Course MP5 Lecture 1 18/1/007 Modelling across different time and length scales An introduction to multiscale modelling and mesoscale methods Dr James Elliott 0.1 Introduction 6 lectures by JAE,
Off-Lattice KMC Simulation of Quantum Dot Formation
 Off-Lattice KMC Simulation of Quantum Dot Formation T. P. Schulze University of Tennessee Peter Smereka & Henry Boateng University of Michigan Research supported by NSF-DMS-0854920 Heteroepitaxy and Quantum
Off-Lattice KMC Simulation of Quantum Dot Formation T. P. Schulze University of Tennessee Peter Smereka & Henry Boateng University of Michigan Research supported by NSF-DMS-0854920 Heteroepitaxy and Quantum
Second harmonic generation in silicon waveguides strained by silicon nitride
 Second harmonic generation in silicon waveguides strained by silicon nitride M. Cazzanelli, 1 F. Bianco, 1 E. Borga, 1 G. Pucker, 2 M. Ghulinyan, 2 E. Degoli, 3 E. Luppi, 4,7 V. Véniard, 4 S. Ossicini,
Second harmonic generation in silicon waveguides strained by silicon nitride M. Cazzanelli, 1 F. Bianco, 1 E. Borga, 1 G. Pucker, 2 M. Ghulinyan, 2 E. Degoli, 3 E. Luppi, 4,7 V. Véniard, 4 S. Ossicini,
Modeling Transport in Heusler-based Spin Devices
 Modeling Transport in Heusler-based Spin Devices Gautam Shine (Stanford) S. Manipatruni, A. Chaudhry, D. E. Nikonov, I. A. Young (Intel) Electronic Structure Extended Hückel theory Application to Heusler
Modeling Transport in Heusler-based Spin Devices Gautam Shine (Stanford) S. Manipatruni, A. Chaudhry, D. E. Nikonov, I. A. Young (Intel) Electronic Structure Extended Hückel theory Application to Heusler
Multi-Scale Modeling from First Principles
 m mm Multi-Scale Modeling from First Principles μm nm m mm μm nm space space Predictive modeling and simulations must address all time and Continuum Equations, densityfunctional space scales Rate Equations
m mm Multi-Scale Modeling from First Principles μm nm m mm μm nm space space Predictive modeling and simulations must address all time and Continuum Equations, densityfunctional space scales Rate Equations
Extrinsic Point Defects: Impurities
 Extrinsic Point Defects: Impurities Substitutional and interstitial impurities Sol solutions, solubility limit Entropy of ing, eal solution model Enthalpy of ing, quasi-chemical model Ideal and regular
Extrinsic Point Defects: Impurities Substitutional and interstitial impurities Sol solutions, solubility limit Entropy of ing, eal solution model Enthalpy of ing, quasi-chemical model Ideal and regular
ALMA: All-scale predictive design of heat management material structures
 ALMA: All-scale predictive design of heat management material structures Version Date: 2015.11.13. Last updated 2015.12.02 Purpose of this document: Definition of a data organisation that is applicable
ALMA: All-scale predictive design of heat management material structures Version Date: 2015.11.13. Last updated 2015.12.02 Purpose of this document: Definition of a data organisation that is applicable
Modeling and computational studies of surface shape dynamics of ultrathin single-crystal films with anisotropic surface energy, part I
 Modeling and computational studies of surface shape dynamics of ultrathin single-crystal films with anisotropic surface energy, part I Mikhail Khenner Department of Mathematics, Western Kentucky University
Modeling and computational studies of surface shape dynamics of ultrathin single-crystal films with anisotropic surface energy, part I Mikhail Khenner Department of Mathematics, Western Kentucky University
Available online at Physics Procedia 15 (2011) Stability and Rupture of Alloyed Atomic Terraces on Epitaxial Interfaces
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 15 (2011) 64 70 Stability and Rupture of Alloyed Atomic Terraces on Epitaxial Interfaces Michail Michailov Rostislaw Kaischew Institute of Physical
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 15 (2011) 64 70 Stability and Rupture of Alloyed Atomic Terraces on Epitaxial Interfaces Michail Michailov Rostislaw Kaischew Institute of Physical
High Temperature High Pressure Properties of Silica From Quantum Monte Carlo
 High Temperature High Pressure Properties of Silica From Quantum Monte Carlo K.P. Driver, R.E. Cohen, Z. Wu, B. Militzer, P. Lopez Rios, M. Towler, R. Needs, and J.W. Wilkins Funding: NSF, DOE; Computation:
High Temperature High Pressure Properties of Silica From Quantum Monte Carlo K.P. Driver, R.E. Cohen, Z. Wu, B. Militzer, P. Lopez Rios, M. Towler, R. Needs, and J.W. Wilkins Funding: NSF, DOE; Computation:
Morphological evolution of single-crystal ultrathin solid films
 Western Kentucky University From the SelectedWorks of Mikhail Khenner March 29, 2010 Morphological evolution of single-crystal ultrathin solid films Mikhail Khenner, Western Kentucky University Available
Western Kentucky University From the SelectedWorks of Mikhail Khenner March 29, 2010 Morphological evolution of single-crystal ultrathin solid films Mikhail Khenner, Western Kentucky University Available
LECTURE 11: Monte Carlo Methods III
 1 LECTURE 11: Monte Carlo Methods III December 3, 2012 In this last chapter, we discuss non-equilibrium Monte Carlo methods. We concentrate on lattice systems and discuss ways of simulating phenomena such
1 LECTURE 11: Monte Carlo Methods III December 3, 2012 In this last chapter, we discuss non-equilibrium Monte Carlo methods. We concentrate on lattice systems and discuss ways of simulating phenomena such
Quantum Monte Carlo Benchmarks Density Functionals: Si Defects
 Quantum Monte Carlo Benchmarks Density Functionals: Si Defects K P Driver, W D Parker, R G Hennig, J W Wilkins (OSU) C J Umrigar (Cornell), R Martin, E Batista, B Uberuaga (LANL), J Heyd, G Scuseria (Rice)
Quantum Monte Carlo Benchmarks Density Functionals: Si Defects K P Driver, W D Parker, R G Hennig, J W Wilkins (OSU) C J Umrigar (Cornell), R Martin, E Batista, B Uberuaga (LANL), J Heyd, G Scuseria (Rice)
A Zero Field Monte Carlo Algorithm Accounting for the Pauli Exclusion Principle
 A Zero Field Monte Carlo Algorithm Accounting for the Pauli Exclusion Principle Sergey Smirnov, Hans Kosina, Mihail Nedjalkov, and Siegfried Selberherr Institute for Microelectronics, TU-Vienna, Gusshausstrasse
A Zero Field Monte Carlo Algorithm Accounting for the Pauli Exclusion Principle Sergey Smirnov, Hans Kosina, Mihail Nedjalkov, and Siegfried Selberherr Institute for Microelectronics, TU-Vienna, Gusshausstrasse
Modified Maxwell-Garnett equation for the effective transport coefficients in inhomogeneous media
 J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 3 (998) 7227 7234. Printed in the UK PII: S0305-4470(98)93976-2 Modified Maxwell-Garnett equation for the effective transport coefficients in inhomogeneous media Juris Robert Kalnin
J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 3 (998) 7227 7234. Printed in the UK PII: S0305-4470(98)93976-2 Modified Maxwell-Garnett equation for the effective transport coefficients in inhomogeneous media Juris Robert Kalnin
Atomistic Front-End Process Modeling
 Atomistic Front-End Process Modeling A Powerful Tool for Deep-Submicron Device Fabrication SISPAD 2001, Athens Martin Jaraiz University of Valladolid, Spain Thanks to: P. Castrillo (U. Valladolid) R. Pinacho
Atomistic Front-End Process Modeling A Powerful Tool for Deep-Submicron Device Fabrication SISPAD 2001, Athens Martin Jaraiz University of Valladolid, Spain Thanks to: P. Castrillo (U. Valladolid) R. Pinacho
2007 Summer College on Plasma Physics
 SMR/1856-10 2007 Summer College on Plasma Physics 30 July - 24 August, 2007 Dielectric relaxation and ac universality in materials with disordered structure. J. Juul Rasmussen Risø National Laboratory
SMR/1856-10 2007 Summer College on Plasma Physics 30 July - 24 August, 2007 Dielectric relaxation and ac universality in materials with disordered structure. J. Juul Rasmussen Risø National Laboratory
Lecture 1 Modeling and simulation for the growth of thin films
 Lecture 1 Modeling and simulation for the growth of thin films Russel Caflisch Mathematics Department Materials Science and Engineering Department UCLA & IPAM www.math.ucla.edu/~material 1 Outline Epitaxial
Lecture 1 Modeling and simulation for the growth of thin films Russel Caflisch Mathematics Department Materials Science and Engineering Department UCLA & IPAM www.math.ucla.edu/~material 1 Outline Epitaxial
Feature-level Compensation & Control. Process Integration September 15, A UC Discovery Project
 Feature-level Compensation & Control Process Integration September 15, 2005 A UC Discovery Project Current Milestones Si/Ge-on-insulator and Strained Si-on-insulator Substrate Engineering (M28 YII.13)
Feature-level Compensation & Control Process Integration September 15, 2005 A UC Discovery Project Current Milestones Si/Ge-on-insulator and Strained Si-on-insulator Substrate Engineering (M28 YII.13)
Kinetic Monte Carlo. Heiko Rieger. Theoretical Physics Saarland University Saarbrücken, Germany
 Kinetic Monte Carlo Heiko Rieger Theoretical Physics Saarland University Saarbrücken, Germany DPG school on Efficient Algorithms in Computational Physics, 10.-14.9.2012, Bad Honnef Intro Kinetic Monte
Kinetic Monte Carlo Heiko Rieger Theoretical Physics Saarland University Saarbrücken, Germany DPG school on Efficient Algorithms in Computational Physics, 10.-14.9.2012, Bad Honnef Intro Kinetic Monte
CME 300 Properties of Materials. ANSWERS: Homework 9 November 26, As atoms approach each other in the solid state the quantized energy states:
 CME 300 Properties of Materials ANSWERS: Homework 9 November 26, 2011 As atoms approach each other in the solid state the quantized energy states: are split. This splitting is associated with the wave
CME 300 Properties of Materials ANSWERS: Homework 9 November 26, 2011 As atoms approach each other in the solid state the quantized energy states: are split. This splitting is associated with the wave
First-principles based design of Pt- and Pd-based catalysts for benzene hydrogenation
 1 1 First-principles based design of Pt- and Pd-based catalysts for benzene hydrogenation Maarten K. Sabbe, Gonzalo Canduela, Marie- Françoise Reyniers, Guy B. Marin Introduction: benzene hydrogenation
1 1 First-principles based design of Pt- and Pd-based catalysts for benzene hydrogenation Maarten K. Sabbe, Gonzalo Canduela, Marie- Françoise Reyniers, Guy B. Marin Introduction: benzene hydrogenation
Defects, Diffusion, Deformation and Thermal Conductivity in the Lower Mantle and D
 Defects, Diffusion, Deformation and Thermal Conductivity in the Lower Mantle and D John Brodholt UCL Thanks to: Michael Ammann, Simon Hunt, James Wookey, Kai Wang, Andrew Walker and David Dobson College
Defects, Diffusion, Deformation and Thermal Conductivity in the Lower Mantle and D John Brodholt UCL Thanks to: Michael Ammann, Simon Hunt, James Wookey, Kai Wang, Andrew Walker and David Dobson College
Improved model of nonaffine strain measure
 Improved model of nonaffine strain measure S. T. Milner a) ExxonMobil Research & Engineering, Route 22 East, Annandale, New Jersey 08801 (Received 27 December 2000; final revision received 3 April 2001)
Improved model of nonaffine strain measure S. T. Milner a) ExxonMobil Research & Engineering, Route 22 East, Annandale, New Jersey 08801 (Received 27 December 2000; final revision received 3 April 2001)
Available online at ScienceDirect. Physics Procedia 71 (2015 ) 30 34
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 71 (2015 ) 30 34 18th Conference on Plasma-Surface Interactions, PSI 2015, 5-6 February 2015, Moscow, Russian Federation and the
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 71 (2015 ) 30 34 18th Conference on Plasma-Surface Interactions, PSI 2015, 5-6 February 2015, Moscow, Russian Federation and the
Joint ICTP-IAEA Workshop on Physics of Radiation Effect and its Simulation for Non-Metallic Condensed Matter.
 2359-3 Joint ICTP-IAEA Workshop on Physics of Radiation Effect and its Simulation for Non-Metallic Condensed Matter 13-24 August 2012 Electrically active defects in semiconductors induced by radiation
2359-3 Joint ICTP-IAEA Workshop on Physics of Radiation Effect and its Simulation for Non-Metallic Condensed Matter 13-24 August 2012 Electrically active defects in semiconductors induced by radiation
Multi-Ensemble Markov Models and TRAM. Fabian Paul 21-Feb-2018
 Multi-Ensemble Markov Models and TRAM Fabian Paul 21-Feb-2018 Outline Free energies Simulation types Boltzmann reweighting Umbrella sampling multi-temperature simulation accelerated MD Analysis methods
Multi-Ensemble Markov Models and TRAM Fabian Paul 21-Feb-2018 Outline Free energies Simulation types Boltzmann reweighting Umbrella sampling multi-temperature simulation accelerated MD Analysis methods
An energy relaxation time model for device simulation
 Solid-State Electronics 43 (1999) 1791±1795 An energy relaxation time model for device simulation B. Gonzalez a, *, V. Palankovski b, H. Kosina b, A. Hernandez a, S. Selberherr b a University Institute
Solid-State Electronics 43 (1999) 1791±1795 An energy relaxation time model for device simulation B. Gonzalez a, *, V. Palankovski b, H. Kosina b, A. Hernandez a, S. Selberherr b a University Institute
Chapter 2. Rubber Elasticity:
 Chapter. Rubber Elasticity: The mechanical behavior of a rubber band, at first glance, might appear to be Hookean in that strain is close to 100% recoverable. However, the stress strain curve for a rubber
Chapter. Rubber Elasticity: The mechanical behavior of a rubber band, at first glance, might appear to be Hookean in that strain is close to 100% recoverable. However, the stress strain curve for a rubber
First principles computer simulations of Li 10 GeP 2 S 12 and related lithium superionic conductors*
 First principles computer simulations of Li 10 GeP 2 S 12 and related lithium superionic conductors* N. A. W. Holzwarth Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, NC, USA, 27109 Motivation and background information
First principles computer simulations of Li 10 GeP 2 S 12 and related lithium superionic conductors* N. A. W. Holzwarth Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, NC, USA, 27109 Motivation and background information
Luminescence Process
 Luminescence Process The absorption and the emission are related to each other and they are described by two terms which are complex conjugate of each other in the interaction Hamiltonian (H er ). In an
Luminescence Process The absorption and the emission are related to each other and they are described by two terms which are complex conjugate of each other in the interaction Hamiltonian (H er ). In an
Introduction to Seismology Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 1.510 Introduction to Seismology Spring 008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 1.510 Introduction to
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 1.510 Introduction to Seismology Spring 008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 1.510 Introduction to
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS. EQUATIONS AND THEOREMS
 1 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS. EQUATIONS AND THEOREMS Version 2011-01-14 Stress tensor Definition of traction vector (1) Cauchy theorem (2) Equilibrium (3) Invariants (4) (5) (6) or, written in terms of principal
1 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS. EQUATIONS AND THEOREMS Version 2011-01-14 Stress tensor Definition of traction vector (1) Cauchy theorem (2) Equilibrium (3) Invariants (4) (5) (6) or, written in terms of principal
Thermal transport from first-principles DFT calculations. Keivan Esfarjani MIT. Department of Mechanical Engineering. 5/23/2012 Phonon UWM 1
 Thermal transport from first-principles DFT calculations Keivan Esfarjani Department of Mechanical Engineering MIT 5/23/2012 Phonon School @ UWM 1 Classical MD simulations use an empirical potential fitted
Thermal transport from first-principles DFT calculations Keivan Esfarjani Department of Mechanical Engineering MIT 5/23/2012 Phonon School @ UWM 1 Classical MD simulations use an empirical potential fitted
Lecture 9. Strained-Si Technology I: Device Physics
 Strain Analysis in Daily Life Lecture 9 Strained-Si Technology I: Device Physics Background Planar MOSFETs FinFETs Reading: Y. Sun, S. Thompson, T. Nishida, Strain Effects in Semiconductors, Springer,
Strain Analysis in Daily Life Lecture 9 Strained-Si Technology I: Device Physics Background Planar MOSFETs FinFETs Reading: Y. Sun, S. Thompson, T. Nishida, Strain Effects in Semiconductors, Springer,
MatSci 331 Homework 4 Molecular Dynamics and Monte Carlo: Stress, heat capacity, quantum nuclear effects, and simulated annealing
 MatSci 331 Homework 4 Molecular Dynamics and Monte Carlo: Stress, heat capacity, quantum nuclear effects, and simulated annealing Due Thursday Feb. 21 at 5pm in Durand 110. Evan Reed In this homework,
MatSci 331 Homework 4 Molecular Dynamics and Monte Carlo: Stress, heat capacity, quantum nuclear effects, and simulated annealing Due Thursday Feb. 21 at 5pm in Durand 110. Evan Reed In this homework,
--- DiHusion in Diamond 1. V. A. FRATZKE 2 and W. J. LEIVO Research Foundation and Physics Department, Oklahoma State University, Stillwater
 PHYSICAL SCIENCES 125 DiHusion in Diamond 1 V. A. FRATZKE 2 and W. J. LEIVO Research Foundation and Physics Department, Oklahoma State University, Stillwater INTRODUCTION With the development of semiconducting
PHYSICAL SCIENCES 125 DiHusion in Diamond 1 V. A. FRATZKE 2 and W. J. LEIVO Research Foundation and Physics Department, Oklahoma State University, Stillwater INTRODUCTION With the development of semiconducting
Surface Physics Surface Diffusion. Assistant: Dr. Enrico Gnecco NCCR Nanoscale Science
 Surface Physics 008 8. Surface Diffusion Assistant: Dr. Enrico Gnecco NCCR Nanoscale Science Random-Walk Motion Thermal motion of an adatom on an ideal crystal surface: - Thermal excitation the adatom
Surface Physics 008 8. Surface Diffusion Assistant: Dr. Enrico Gnecco NCCR Nanoscale Science Random-Walk Motion Thermal motion of an adatom on an ideal crystal surface: - Thermal excitation the adatom
