Kinetics. Rate of change in response to thermodynamic forces
|
|
|
- Ashley Young
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Kinetics Rate of change in response to thermodynamic forces Deviation from local equilibrium continuous change T heat flow temperature changes µ atom flow composition changes Deviation from global equilibrium discontinuous change ΔG (ΔF) phase change (or other change of structure)
2 Flow of Heat J Q T 2 T 1 Box of unit length, unit cross-section area Let: T 2 > T 1 (one-dimensional gradient) J Q = heat flow/unit area unit time (J/m 2 s) Ignore internal sources of heat From the Second Law: J Q = k dt dx Fourier s law of heat conduction k = thermal conductivity
3 Evolution of Temperature J Q 23 J Q 12 T 3 T 2 T 1 Let: T 3 > T 2 >T 1 (one-dimensional gradient) Q/ t = heat added/unit time (J/m 2 s) The net heat added to the center cell is: Q t = J Q Q [ 23 J 12 ]da = djq dv = dx d dx k dt dx dv J Q 12 = J Q 23 + djq dx dx Q t = E t = C V T t = k C V 2 T x 2 T t dv
4 Heat Conduction in 3-Dimensions A temperature gradient produces a heat flux: T = ( T/ x)e x + ( T/ y)e y + ( T/ z)e z J Q = J Q x e x + JQ y e y + Jq z e z How many thermal conductivities? In the most general case, 9 For a cubic or isotropic material, only need 1 For a cubic or isotropic material J Q = k T T t = k 2 T
5 Mechanisms of Heat Conduction J = (1/2)nev J Q+ J Q- v Energy must be transported through the solid Electrons Lattice vibrations - phonons Light - photons (usually negligible) J Q = J Q+ - J Q- T + > T - J Q > 0 Conduction is by a gas of moving particles Particles move both to left and right (J Q = J Q + -J Q- ) Particle energy increases with T If T decreases with x, particles moving right have more energy Net flow of heat to the right (J Q > 0)
6 Heat Conduction by Particles Transport of thermal energy Particle reaches thermal equilibrium by collisions Particle travels <l> = mean free path between collisions Particle transfers energy across plane Energy crossing plane reflects equilibrium <l x > upstream
7 Mechanisms of Heat Conduction J Q+ J Q- J = (1/2)nev J Q = J Q+ - J Q- Particles achieve thermal equilibrium by collision with one another Particles that cross at x were in equilibrium at x =x- l x l x = mean free path v J Q + = 1 2 nev x = 1 2 E v(t)v x = 1 2 E v[t(x l x )]v x E v J Q + = 1 2 E v v x 1 2 C v v x [ T( x l x )] = E v E v l x dt dx T dt dt l dx x = E v C v l dx x
8 Mechanisms of Heat Conduction J Q+ J Q- J = (1/2)nev J Q = J Q+ - J Q- Total heat flux: v J Q + = 1 2 E vv x 1 2 C dt vv x l x dx dt J Q = J Q + J Q = C v v x l x = k dt dx dx k = C v v x l x In three dimensions: k = 1 3 C vv l = 1 3 C vv 2 τ ( l = vτ)
9 Conduction of Heat J Q 23 J Q 12 T 3 T 2 T 1 J Q = k dt dx T t = k C V 2 T x 2 Thermal conductivity by particles: k = 1 3 C vv l = 1 3 C vv 2 τ - v = mean particle velocity - <l> = mean free path between collisions - τ = mean time between collisions Particles include - electrons - phonons
10 Heat Conduction by Electrons J = (1/2)nev k = 1 3 C vv l = 1 3 C vv 2 τ v Motion of electrons = electrical conductivity (ρ = ρ 0 + AT) k = LσT = LT ρ Wiedemann-Franz Law LT k = ρ 0 L A low temperature high temperature
11 Heat Conduction by Phonons k Crystal k = 1 3 C vv l = 1 3 C vv 2 τ Glass T Œ Scattering of phonons in imperfect crystals due to phonon-defect collisions <l> is the mean spacing between defects Phonon thermal conductivity is low Polygranular solids Defective solids Glasses High Θ D materials only have high k when they are nearly perfect Defective diamond films are no particular good
12 Kinetics Rate of change in response to thermodynamic forces Deviation from local equilibrium continuous change T heat flow temperature changes µ atom flow composition changes Deviation from global equilibrium discontinuous change ΔG (ΔF) phase change (or other change of structure)
13 Atom Diffusion J B 12 c c c J B 23 g = g(t,p,c) g c T,P = µ (T,P,c) Mass flux in response to a gradient in chemical potential Assume constant T,P Flux of solute Evolution of composition J B = M d g = M dµ µ = M dc dx c dx c dx J B = nd dc dx c B t = J x = nd 2 c x 2 Fick s First Law Fick s Second Law
14 Diffusion J B 12 J B 23 J B = nd dc dx c c c The diffusivity (D) is the material property that governs diffusion Diffusion in solids requires Atoms jump from position to position Atom jumps result in net flux Diffusion mechanism depends on atom site Interstitial Substitutional
15 Jumps of Interstitial Atoms G ΔG m Atom motion Must overcome barrier ΔG m to move from site to site (~ 1eV) Attempts with vibrational frequency ν e ~ /sec Number of jumps per unit time ω = (# attempts/time)(probability of jump/attempt) = ν e exp ΔG m kt = ν exp Q (of the order of 10 5 /sec at room T) m kt x
16 Jumps of Substitutional Atoms For a substitutional atom to jump There must be a neighboring vacancy to permit the jump The atom must overcome its barrier and jump ω = [P(vacant site)][p(jump given vacant site)] = [c v ]ν exp Q m kt = exp Q v kt ν exp Q m kt = ν exp (Q v + Q m ) kt
17 Concentration-Driven Diffusion a J 12 J 21 c 1 c 2 J = J 12 J 21 = nd dc dx Diffusion by interchange of atoms on adjacent planes J 12 = N 1 ω x = nc 1 aω x J = J 12 J 21 = naω x (c 1 c 2 ) N 1 = atoms of type 1 per unit area n = atom sites per unit volume a = volume per unit area of plane ω x = jumps in the x-direction/time = 1 6 naω(c 1 c 2 ) = 1 6 na2 ω dc dx D = 1 6 a2 ω
18 Concentration-Driven Diffusion a J 12 J 21 c 1 c 2 J = J 12 J 21 = nd dc dx Diffusion by interchange of atoms on adjacent planes Random-walk diffusion Atoms do not jump preferentially in either direction Net flux because there are more atoms on plane 1 than on 2 Diffusivity governs random-walk diffusion D = 1 6 a2 ω = 1 6 a2 ν exp Q D kt D = D 0 exp Q D kt Q Q D = m Q V + Q m interstitial substitutional
19 Random-Walk Diffusion X Let an atom move by random steps of length a Its position at time t is X(t) X(t) = 0 X 2 (t) = X X = na 2 = ωa 2 t (X and -X are equally likely) x 2 = 1 3 X 2 = 1 3 ωa2 t = 2Dt x = x 2 1/ 2 = 2Dt
20 Application: Homogenization time c c x Solidification usually results in chemical heterogeneities Represent it with a sinusoid of wavelength, λ Composition should homogenize when applex > λ/2 The approximate time necessary is: t > t h = 1 2 λ = λ2 2D 2 8D t h = 1 λ 2 exp Q D 8D 0 kt Homogenization time - increases with λ 2 - decreases exponentially with T
21 Application: Service Life of a Microelectronic Device Si P Microelectronic devices have built-in heterogeneities Can function only as long as these doped regions survive To estimate the limit on service life. t s Let doped island have dimension, λ Device is dead when applex ~ λ/2, hence t s << t h = 1 2 λ = λ2 2D 2 8D t h = 1 λ 2 exp Q D 8D 0 kt Service life - decreases with miniaturization (λ 2 ) - decreases exponentially with T
22 Influence of Microstructure on Diffusivity Interstitial species Usually no effect from microstructure Stress may enhance diffusion Substitutional species Raising vacancy concentration increases D Quenching from high T Solutes Irradiation Defects provide short-circuit paths Grain boundary diffusion Dislocation core diffusion
23 Adding Vacancies Increases D ln(d) t D eq D = c v ν exp Q m kt Quench from high T Rapid cooling freezes in high c v D decreases as c v evolves to equilibrium Add solutes that promote vacancies High-valence solutes in ionic solids Mg ++ increases vacancy content in Na + Cl - Ionic conductivity increases with c Mg Large solutes in metals Interstitials in metals Processes that introduce vacancies directly Irradiation Plastic deformation
24 Grain Boundary Diffusion ln(d) D 0 D 0 B -Q decreasing D grain size 1/kT -Q B d D = D 0 exp Q D kt = D 0 exp (Q m + Q V ) kt δ D GB D 0 exp Q m d kt Grain boundaries have high defect densities Effectively, vacancies are already present Q D ~ Q m Grain boundaries have low cross-section Effective width = δ Areal fraction of cross-section: δ A GB A = Kδd d 2 δ d δ D GB 0 D 0 d
collisions of electrons. In semiconductor, in certain temperature ranges the conductivity increases rapidly by increasing temperature
 1.9. Temperature Dependence of Semiconductor Conductivity Such dependence is one most important in semiconductor. In metals, Conductivity decreases by increasing temperature due to greater frequency of
1.9. Temperature Dependence of Semiconductor Conductivity Such dependence is one most important in semiconductor. In metals, Conductivity decreases by increasing temperature due to greater frequency of
Introduction To Materials Science FOR ENGINEERS, Ch. 5. Diffusion. MSE 201 Callister Chapter 5
 Diffusion MSE 201 Callister Chapter 5 1 Goals: Diffusion - how do atoms move through solids? Fundamental concepts and language Diffusion mechanisms Vacancy diffusion Interstitial diffusion Impurities Diffusion
Diffusion MSE 201 Callister Chapter 5 1 Goals: Diffusion - how do atoms move through solids? Fundamental concepts and language Diffusion mechanisms Vacancy diffusion Interstitial diffusion Impurities Diffusion
Lecture 15: Optoelectronic devices: Introduction
 Lecture 15: Optoelectronic devices: Introduction Contents 1 Optical absorption 1 1.1 Absorption coefficient....................... 2 2 Optical recombination 5 3 Recombination and carrier lifetime 6 3.1
Lecture 15: Optoelectronic devices: Introduction Contents 1 Optical absorption 1 1.1 Absorption coefficient....................... 2 2 Optical recombination 5 3 Recombination and carrier lifetime 6 3.1
Theory of Electromigration
 Theory of Electromigration Electromigration is the transport of material in a conductor under the influence of an applied electric field. All conductors are susceptible to electromigration, therefore it
Theory of Electromigration Electromigration is the transport of material in a conductor under the influence of an applied electric field. All conductors are susceptible to electromigration, therefore it
DIFFUSION IN SOLIDS. IE-114 Materials Science and General Chemistry Lecture-5
 DIFFUSION IN SOLIDS IE-114 Materials Science and General Chemistry Lecture-5 Diffusion The mechanism by which matter is transported through matter. It is related to internal atomic movement. Atomic movement;
DIFFUSION IN SOLIDS IE-114 Materials Science and General Chemistry Lecture-5 Diffusion The mechanism by which matter is transported through matter. It is related to internal atomic movement. Atomic movement;
Module 16. Diffusion in solids II. Lecture 16. Diffusion in solids II
 Module 16 Diffusion in solids II Lecture 16 Diffusion in solids II 1 NPTEL Phase II : IIT Kharagpur : Prof. R. N. Ghosh, Dept of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Keywords: Micro mechanisms of diffusion,
Module 16 Diffusion in solids II Lecture 16 Diffusion in solids II 1 NPTEL Phase II : IIT Kharagpur : Prof. R. N. Ghosh, Dept of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Keywords: Micro mechanisms of diffusion,
Diffusion. Diffusion = the spontaneous intermingling of the particles of two or more substances as a result of random thermal motion
 Diffusion Diffusion = the spontaneous intermingling of the particles of two or more substances as a result of random thermal motion Fick s First Law Γ ΔN AΔt Γ = flux ΔN = number of particles crossing
Diffusion Diffusion = the spontaneous intermingling of the particles of two or more substances as a result of random thermal motion Fick s First Law Γ ΔN AΔt Γ = flux ΔN = number of particles crossing
Steady-state diffusion is diffusion in which the concentration of the diffusing atoms at
 Chapter 7 What is steady state diffusion? Steady-state diffusion is diffusion in which the concentration of the diffusing atoms at any point, x, and hence the concentration gradient at x, in the solid,
Chapter 7 What is steady state diffusion? Steady-state diffusion is diffusion in which the concentration of the diffusing atoms at any point, x, and hence the concentration gradient at x, in the solid,
Carriers Concentration and Current in Semiconductors
 Carriers Concentration and Current in Semiconductors Carrier Transport Two driving forces for carrier transport: electric field and spatial variation of the carrier concentration. Both driving forces lead
Carriers Concentration and Current in Semiconductors Carrier Transport Two driving forces for carrier transport: electric field and spatial variation of the carrier concentration. Both driving forces lead
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000. Dr.Coates
 Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 18: Electrical Properties Dr.Coates 18.2 Ohm s Law V = IR where R is the resistance of the material, V is the voltage and I is the current. l R A
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 18: Electrical Properties Dr.Coates 18.2 Ohm s Law V = IR where R is the resistance of the material, V is the voltage and I is the current. l R A
Lecture 1: Atomic Diffusion
 Part IB Materials Science & Metallurgy H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia Course A, Metals and Alloys Lecture 1: Atomic Diffusion Mass transport in a gas or liquid generally involves the flow of fluid (e.g. convection
Part IB Materials Science & Metallurgy H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia Course A, Metals and Alloys Lecture 1: Atomic Diffusion Mass transport in a gas or liquid generally involves the flow of fluid (e.g. convection
Semiconductor Device Physics
 1 Semiconductor Device Physics Lecture 3 http://zitompul.wordpress.com 2 0 1 3 Semiconductor Device Physics 2 Three primary types of carrier action occur inside a semiconductor: Drift: charged particle
1 Semiconductor Device Physics Lecture 3 http://zitompul.wordpress.com 2 0 1 3 Semiconductor Device Physics 2 Three primary types of carrier action occur inside a semiconductor: Drift: charged particle
Lecture 3 Semiconductor Physics (II) Carrier Transport
 Lecture 3 Semiconductor Physics (II) Carrier Transport Thermal Motion Carrier Drift Carrier Diffusion Outline Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini; Chapter 2, Sect. 2.4-2.6 6.012 Spring 2009 Lecture 3 1
Lecture 3 Semiconductor Physics (II) Carrier Transport Thermal Motion Carrier Drift Carrier Diffusion Outline Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini; Chapter 2, Sect. 2.4-2.6 6.012 Spring 2009 Lecture 3 1
CHAPTER 4 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS
 4-1 CHAPTER 4 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Vacancies and Self-Interstitials 4.1 In order to compute the fraction of atom sites that are vacant in copper at 1357 K, we must employ Equation
4-1 CHAPTER 4 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Vacancies and Self-Interstitials 4.1 In order to compute the fraction of atom sites that are vacant in copper at 1357 K, we must employ Equation
Appendix 4. Appendix 4A Heat Capacity of Ideal Gases
 Appendix 4 W-143 Appendix 4A Heat Capacity of Ideal Gases We can determine the heat capacity from the energy content of materials as a function of temperature. The simplest material to model is an ideal
Appendix 4 W-143 Appendix 4A Heat Capacity of Ideal Gases We can determine the heat capacity from the energy content of materials as a function of temperature. The simplest material to model is an ideal
Investigations of the effects of 7 TeV proton beams on LHC collimator materials and other materials to be used in the LHC
 Russian Research Center Kurchatov Institute Investigations of the effects of 7 ev proton beams on LHC collimator materials and other materials to be used in the LHC A.I.Ryazanov Aims of Investigations:
Russian Research Center Kurchatov Institute Investigations of the effects of 7 ev proton beams on LHC collimator materials and other materials to be used in the LHC A.I.Ryazanov Aims of Investigations:
2. Point Defects. R. Krause-Rehberg
 R. Krause-Rehberg 2. Point Defects (F-center in acl) 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Classification 2.3 otation 2.4 Examples 2.5 Peculiarities in Semiconductors 2.6 Determination of Structure and Concentration 2.7
R. Krause-Rehberg 2. Point Defects (F-center in acl) 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Classification 2.3 otation 2.4 Examples 2.5 Peculiarities in Semiconductors 2.6 Determination of Structure and Concentration 2.7
Electrical Transport. Ref. Ihn Ch. 10 YC, Ch 5; BW, Chs 4 & 8
 Electrical Transport Ref. Ihn Ch. 10 YC, Ch 5; BW, Chs 4 & 8 Electrical Transport The study of the transport of electrons & holes (in semiconductors) under various conditions. A broad & somewhat specialized
Electrical Transport Ref. Ihn Ch. 10 YC, Ch 5; BW, Chs 4 & 8 Electrical Transport The study of the transport of electrons & holes (in semiconductors) under various conditions. A broad & somewhat specialized
7. FREE ELECTRON THEORY.
 7. FREE ELECTRON THEORY. Aim: To introduce the free electron model for the physical properties of metals. It is the simplest theory for these materials, but still gives a very good description of many
7. FREE ELECTRON THEORY. Aim: To introduce the free electron model for the physical properties of metals. It is the simplest theory for these materials, but still gives a very good description of many
ISSUES TO ADDRESS...
 Chapter 12: Electrical Properties School of Mechanical Engineering Choi, Hae-Jin Materials Science - Prof. Choi, Hae-Jin Chapter 12-1 ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How are electrical conductance and resistance
Chapter 12: Electrical Properties School of Mechanical Engineering Choi, Hae-Jin Materials Science - Prof. Choi, Hae-Jin Chapter 12-1 ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How are electrical conductance and resistance
Lecture 11 - Phonons II - Thermal Prop. Continued
 Phonons II - hermal Properties - Continued (Kittel Ch. 5) Low High Outline Anharmonicity Crucial for hermal expansion other changes with pressure temperature Gruneisen Constant hermal Heat ransport Phonon
Phonons II - hermal Properties - Continued (Kittel Ch. 5) Low High Outline Anharmonicity Crucial for hermal expansion other changes with pressure temperature Gruneisen Constant hermal Heat ransport Phonon
Lecture 7: Extrinsic semiconductors - Fermi level
 Lecture 7: Extrinsic semiconductors - Fermi level Contents 1 Dopant materials 1 2 E F in extrinsic semiconductors 5 3 Temperature dependence of carrier concentration 6 3.1 Low temperature regime (T < T
Lecture 7: Extrinsic semiconductors - Fermi level Contents 1 Dopant materials 1 2 E F in extrinsic semiconductors 5 3 Temperature dependence of carrier concentration 6 3.1 Low temperature regime (T < T
Materials and Devices in Electrical Engineering
 Examination WS 02/03 Materials and Devices in Electrical Engineering Monday 17 th of March, 9:00 11:00, International Department, SR. 203 Notice 1. It is allowed to use any kind of aids (books, scripts,
Examination WS 02/03 Materials and Devices in Electrical Engineering Monday 17 th of March, 9:00 11:00, International Department, SR. 203 Notice 1. It is allowed to use any kind of aids (books, scripts,
Session 5: Solid State Physics. Charge Mobility Drift Diffusion Recombination-Generation
 Session 5: Solid State Physics Charge Mobility Drift Diffusion Recombination-Generation 1 Outline A B C D E F G H I J 2 Mobile Charge Carriers in Semiconductors Three primary types of carrier action occur
Session 5: Solid State Physics Charge Mobility Drift Diffusion Recombination-Generation 1 Outline A B C D E F G H I J 2 Mobile Charge Carriers in Semiconductors Three primary types of carrier action occur
Materials for Civil and Construction Engineers CHAPTER 2. Nature of Materials
 Materials for Civil and Construction Engineers CHAPTER 2 Nature of Materials Bonds 1. Primary Bond: forms when atoms interchange or share electrons in order to fill the outer (valence) shells like noble
Materials for Civil and Construction Engineers CHAPTER 2 Nature of Materials Bonds 1. Primary Bond: forms when atoms interchange or share electrons in order to fill the outer (valence) shells like noble
Diffusion in Dilute Alloys
 Chapter 3 Diffusion in Dilute Alloys Our discussion of the atomistic mechanisms for diffusion has been confined to the situations where the diffusing species is chemically identical to the host atom. We
Chapter 3 Diffusion in Dilute Alloys Our discussion of the atomistic mechanisms for diffusion has been confined to the situations where the diffusing species is chemically identical to the host atom. We
Non equilibrium thermodynamics: foundations, scope, and extension to the meso scale. Miguel Rubi
 Non equilibrium thermodynamics: foundations, scope, and extension to the meso scale Miguel Rubi References S.R. de Groot and P. Mazur, Non equilibrium Thermodynamics, Dover, New York, 1984 J.M. Vilar and
Non equilibrium thermodynamics: foundations, scope, and extension to the meso scale Miguel Rubi References S.R. de Groot and P. Mazur, Non equilibrium Thermodynamics, Dover, New York, 1984 J.M. Vilar and
Electrical Resistance
 Electrical Resistance I + V _ W Material with resistivity ρ t L Resistance R V I = L ρ Wt (Unit: ohms) where ρ is the electrical resistivity 1 Adding parts/billion to parts/thousand of dopants to pure
Electrical Resistance I + V _ W Material with resistivity ρ t L Resistance R V I = L ρ Wt (Unit: ohms) where ρ is the electrical resistivity 1 Adding parts/billion to parts/thousand of dopants to pure
Topics to discuss...
 MME 467: Ceramics for Advanced Applications Lecture 18 Defects in Ceramics 2 Ref: Barsoum, Fundamentals of Ceramics, Ch6, McGraw-Hill, 2000 Prof. A. K. M. B. Rashid Department of MME, BUET, Dhaka Topics
MME 467: Ceramics for Advanced Applications Lecture 18 Defects in Ceramics 2 Ref: Barsoum, Fundamentals of Ceramics, Ch6, McGraw-Hill, 2000 Prof. A. K. M. B. Rashid Department of MME, BUET, Dhaka Topics
Physics of disordered materials. Gunnar A. Niklasson Solid State Physics Department of Engineering Sciences Uppsala University
 Physics of disordered materials Gunnar A. Niklasson Solid State Physics Department of Engineering Sciences Uppsala University Course plan Familiarity with the basic description of disordered structures
Physics of disordered materials Gunnar A. Niklasson Solid State Physics Department of Engineering Sciences Uppsala University Course plan Familiarity with the basic description of disordered structures
The Electromagnetic Properties of Materials
 The lectromagnetic Properties of Materials lectrical conduction Metals Semiconductors Insulators (dielectrics) Superconductors Magnetic materials Ferromagnetic materials Others Photonic Materials (optical)
The lectromagnetic Properties of Materials lectrical conduction Metals Semiconductors Insulators (dielectrics) Superconductors Magnetic materials Ferromagnetic materials Others Photonic Materials (optical)
3.225 Electrical,Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Materials
 3.5 Electrical,Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Materials Professor Eugene Fitzgerald Purpose: connect atoms and structure to properties Semi-historical context What was understood first from the micro
3.5 Electrical,Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Materials Professor Eugene Fitzgerald Purpose: connect atoms and structure to properties Semi-historical context What was understood first from the micro
MSE 360 Exam 1 Spring Points Total
 MSE 360 Exam 1 Spring 011 105 Points otal Name(print) ID number No notes, books, or information stored in calculator memories may be used. he NCSU academic integrity policies apply to this exam. As such,
MSE 360 Exam 1 Spring 011 105 Points otal Name(print) ID number No notes, books, or information stored in calculator memories may be used. he NCSU academic integrity policies apply to this exam. As such,
Summary: Thermodynamic Potentials and Conditions of Equilibrium
 Summary: Thermodynamic Potentials and Conditions of Equilibrium Isolated system: E, V, {N} controlled Entropy, S(E,V{N}) = maximum Thermal contact: T, V, {N} controlled Helmholtz free energy, F(T,V,{N})
Summary: Thermodynamic Potentials and Conditions of Equilibrium Isolated system: E, V, {N} controlled Entropy, S(E,V{N}) = maximum Thermal contact: T, V, {N} controlled Helmholtz free energy, F(T,V,{N})
The photovoltaic effect occurs in semiconductors where there are distinct valence and
 How a Photovoltaic Cell Works The photovoltaic effect occurs in semiconductors where there are distinct valence and conduction bands. (There are energies at which electrons can not exist within the solid)
How a Photovoltaic Cell Works The photovoltaic effect occurs in semiconductors where there are distinct valence and conduction bands. (There are energies at which electrons can not exist within the solid)
Chapter 4: Bonding in Solids and Electronic Properties. Free electron theory
 Chapter 4: Bonding in Solids and Electronic Properties Free electron theory Consider free electrons in a metal an electron gas. regards a metal as a box in which electrons are free to move. assumes nuclei
Chapter 4: Bonding in Solids and Electronic Properties Free electron theory Consider free electrons in a metal an electron gas. regards a metal as a box in which electrons are free to move. assumes nuclei
Mat E 272 Lecture 25: Electrical properties of materials
 Mat E 272 Lecture 25: Electrical properties of materials December 6, 2001 Introduction: Calcium and copper are both metals; Ca has a valence of +2 (2 electrons per atom) while Cu has a valence of +1 (1
Mat E 272 Lecture 25: Electrical properties of materials December 6, 2001 Introduction: Calcium and copper are both metals; Ca has a valence of +2 (2 electrons per atom) while Cu has a valence of +1 (1
Chapter 5. Carrier Transport Phenomena
 Chapter 5 Carrier Transport Phenomena 1 We now study the effect of external fields (electric field, magnetic field) on semiconducting material 2 Objective Discuss drift and diffusion current densities
Chapter 5 Carrier Transport Phenomena 1 We now study the effect of external fields (electric field, magnetic field) on semiconducting material 2 Objective Discuss drift and diffusion current densities
Semiconductor physics I. The Crystal Structure of Solids
 Lecture 3 Semiconductor physics I The Crystal Structure of Solids 1 Semiconductor materials Types of solids Space lattices Atomic Bonding Imperfection and doping in SOLIDS 2 Semiconductor Semiconductors
Lecture 3 Semiconductor physics I The Crystal Structure of Solids 1 Semiconductor materials Types of solids Space lattices Atomic Bonding Imperfection and doping in SOLIDS 2 Semiconductor Semiconductors
Carrier transport: Drift and Diffusion
 . Carrier transport: Drift and INEL 5209 - Solid State Devices - Spring 2012 Manuel Toledo April 10, 2012 Manuel Toledo Transport 1/ 32 Outline...1 Drift Drift current Mobility Resistivity Resistance Hall
. Carrier transport: Drift and INEL 5209 - Solid State Devices - Spring 2012 Manuel Toledo April 10, 2012 Manuel Toledo Transport 1/ 32 Outline...1 Drift Drift current Mobility Resistivity Resistance Hall
Heterogeneous vortex dynamics in high temperature superconductors
 Heterogeneous vortex dynamics in high temperature superconductors Feng YANG Laboratoire des Solides Irradiés, Ecole Polytechnique, 91128 Palaiseau, France. June 18, 2009/PhD thesis defense Outline 1 Introduction
Heterogeneous vortex dynamics in high temperature superconductors Feng YANG Laboratoire des Solides Irradiés, Ecole Polytechnique, 91128 Palaiseau, France. June 18, 2009/PhD thesis defense Outline 1 Introduction
Chapter Two. Energy Bands and Effective Mass
 Chapter Two Energy Bands and Effective Mass Energy Bands Formation At Low Temperature At Room Temperature Valence Band Insulators Metals Effective Mass Energy-Momentum Diagrams Direct and Indirect Semiconduction
Chapter Two Energy Bands and Effective Mass Energy Bands Formation At Low Temperature At Room Temperature Valence Band Insulators Metals Effective Mass Energy-Momentum Diagrams Direct and Indirect Semiconduction
Introduction into Positron Annihilation
 Introduction into Positron Annihilation Introduction (How to get positrons? What is special about positron annihilation?) The methods of positron annihilation (positron lifetime, Doppler broadening, ACAR...)
Introduction into Positron Annihilation Introduction (How to get positrons? What is special about positron annihilation?) The methods of positron annihilation (positron lifetime, Doppler broadening, ACAR...)
Equilibria in Materials
 009 fall Advanced Physical Metallurgy Phase Equilibria in Materials 10. 13. 009 Eun Soo Park Office: 33-316 Telephone: 880-71 Email: espark@snu.ac.kr Office hours: by an appointment 1 Contents for previous
009 fall Advanced Physical Metallurgy Phase Equilibria in Materials 10. 13. 009 Eun Soo Park Office: 33-316 Telephone: 880-71 Email: espark@snu.ac.kr Office hours: by an appointment 1 Contents for previous
Electrons, Holes, and Defect ionization
 Electrons, Holes, and Defect ionization The process of forming intrinsic electron-hole pairs is excitation a cross the band gap ( formation energy ). intrinsic electronic reaction : null e + h When electrons
Electrons, Holes, and Defect ionization The process of forming intrinsic electron-hole pairs is excitation a cross the band gap ( formation energy ). intrinsic electronic reaction : null e + h When electrons
SEMICONDUCTOR PHYSICS REVIEW BONDS,
 SEMICONDUCTOR PHYSICS REVIEW BONDS, BANDS, EFFECTIVE MASS, DRIFT, DIFFUSION, GENERATION, RECOMBINATION February 3, 2011 The University of Toledo, Department of Physics and Astronomy SSARE, PVIC Principles
SEMICONDUCTOR PHYSICS REVIEW BONDS, BANDS, EFFECTIVE MASS, DRIFT, DIFFUSION, GENERATION, RECOMBINATION February 3, 2011 The University of Toledo, Department of Physics and Astronomy SSARE, PVIC Principles
Lecture 2 Electrons and Holes in Semiconductors
 EE 471: Transport Phenomena in Solid State Devices Spring 2018 Lecture 2 Electrons and Holes in Semiconductors Bryan Ackland Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Stevens Institute of Technology
EE 471: Transport Phenomena in Solid State Devices Spring 2018 Lecture 2 Electrons and Holes in Semiconductors Bryan Ackland Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Stevens Institute of Technology
Unit III Free Electron Theory Engineering Physics
 . Introduction The electron theory of metals aims to explain the structure and properties of solids through their electronic structure. The electron theory is applicable to all solids i.e., both metals
. Introduction The electron theory of metals aims to explain the structure and properties of solids through their electronic structure. The electron theory is applicable to all solids i.e., both metals
Oxide growth model. Known as the Deal-Grove or linear-parabolic model
 Oxide growth model Known as the Deal-Grove or linear-parabolic model Important elements of the model: Gas molecules (oxygen or water) are incident on the surface of the wafer. Molecules diffuse through
Oxide growth model Known as the Deal-Grove or linear-parabolic model Important elements of the model: Gas molecules (oxygen or water) are incident on the surface of the wafer. Molecules diffuse through
Electrons & Phonons. Thermal Resistance, Electrical Resistance P = I 2 R T = P R TH V = I R. R = f( T)
 lectrons & Phonons Ohm s & Fourier s Laws Mobility & Thermal Conductivity Heat Capacity Wiedemann-Franz Relationship Size ffects and Breadown of Classical Laws 1 Thermal Resistance, lectrical Resistance
lectrons & Phonons Ohm s & Fourier s Laws Mobility & Thermal Conductivity Heat Capacity Wiedemann-Franz Relationship Size ffects and Breadown of Classical Laws 1 Thermal Resistance, lectrical Resistance
Non-Continuum Energy Transfer: Phonons
 Non-Continuum Energy Transfer: Phonons D. B. Go Slide 1 The Crystal Lattice The crystal lattice is the organization of atoms and/or molecules in a solid simple cubic body-centered cubic hexagonal a NaCl
Non-Continuum Energy Transfer: Phonons D. B. Go Slide 1 The Crystal Lattice The crystal lattice is the organization of atoms and/or molecules in a solid simple cubic body-centered cubic hexagonal a NaCl
Chapter 1 Overview of Semiconductor Materials and Physics
 Chapter 1 Overview of Semiconductor Materials and Physics Professor Paul K. Chu Conductivity / Resistivity of Insulators, Semiconductors, and Conductors Semiconductor Elements Period II III IV V VI 2 B
Chapter 1 Overview of Semiconductor Materials and Physics Professor Paul K. Chu Conductivity / Resistivity of Insulators, Semiconductors, and Conductors Semiconductor Elements Period II III IV V VI 2 B
Lecture 8. Equations of State, Equilibrium and Einstein Relationships and Generation/Recombination
 Lecture 8 Equations of State, Equilibrium and Einstein Relationships and Generation/Recombination Reading: (Cont d) Notes and Anderson 2 sections 3.4-3.11 Energy Equilibrium Concept Consider a non-uniformly
Lecture 8 Equations of State, Equilibrium and Einstein Relationships and Generation/Recombination Reading: (Cont d) Notes and Anderson 2 sections 3.4-3.11 Energy Equilibrium Concept Consider a non-uniformly
EMA5001 Lecture 2 Interstitial Diffusion & Fick s 1 st Law. Prof. Zhe Cheng Mechanical & Materials Engineering Florida International University
 EMA500 Lecture Interstitial Diffusion & Fick s st Law Prof. Zhe Cheng Mechanical & Materials Engineering Florida International University Substitutional Diffusion Different possibilities Exchange Mechanis
EMA500 Lecture Interstitial Diffusion & Fick s st Law Prof. Zhe Cheng Mechanical & Materials Engineering Florida International University Substitutional Diffusion Different possibilities Exchange Mechanis
Stress Evolution during Film Growth: CTC! Stress Evolution during Film Growth: CTC!
 When Vapor Deforms Metal: Thermodynamics of Deposition Flux Dependent Intrinsic Film Stress M.J. Rost Kamerlingh Onnes Laboratory, Leiden University (NL) Rost@physics.leidenuniv.nl www.physics.leidenuniv.nl/rost
When Vapor Deforms Metal: Thermodynamics of Deposition Flux Dependent Intrinsic Film Stress M.J. Rost Kamerlingh Onnes Laboratory, Leiden University (NL) Rost@physics.leidenuniv.nl www.physics.leidenuniv.nl/rost
Dopant Diffusion. (1) Predeposition dopant gas. (2) Drive-in Turn off dopant gas. dose control. Doped Si region
 Dopant Diffusion (1) Predeposition dopant gas dose control SiO Si SiO Doped Si region () Drive-in Turn off dopant gas or seal surface with oxide profile control (junction depth; concentration) SiO SiO
Dopant Diffusion (1) Predeposition dopant gas dose control SiO Si SiO Doped Si region () Drive-in Turn off dopant gas or seal surface with oxide profile control (junction depth; concentration) SiO SiO
Lecture 16. Equilibrium and Chemical Potential. Free Energy and Chemical Potential Simple defects in solids Intrinsic semiconductors
 Lecture 16 Equilibrium and Chemical Potential Free Energy and Chemical Potential Simple defects in solids Intrinsic semiconductors Reference for this Lecture: Elements Ch 11 Reference for Lecture 12: Elements
Lecture 16 Equilibrium and Chemical Potential Free Energy and Chemical Potential Simple defects in solids Intrinsic semiconductors Reference for this Lecture: Elements Ch 11 Reference for Lecture 12: Elements
Motion and Recombination of Electrons and Holes
 Chater Motion and Recombination of Electrons and Holes OBJECTIVES. Understand how the electrons and holes resond to an electric field (drift).. Understand how the electrons and holes resond to a gradient
Chater Motion and Recombination of Electrons and Holes OBJECTIVES. Understand how the electrons and holes resond to an electric field (drift).. Understand how the electrons and holes resond to a gradient
6.2 Governing Equations for Natural Convection
 6. Governing Equations for Natural Convection 6..1 Generalized Governing Equations The governing equations for natural convection are special cases of the generalized governing equations that were discussed
6. Governing Equations for Natural Convection 6..1 Generalized Governing Equations The governing equations for natural convection are special cases of the generalized governing equations that were discussed
Kinetic Monte Carlo: from transition probabilities to transition rates
 Kinetic Monte Carlo: from transition probabilities to transition rates With MD we can only reproduce the dynamics of the system for 100 ns. Slow thermallyactivated processes, such as diffusion, cannot
Kinetic Monte Carlo: from transition probabilities to transition rates With MD we can only reproduce the dynamics of the system for 100 ns. Slow thermallyactivated processes, such as diffusion, cannot
3.1 Introduction to Semiconductors. Y. Baghzouz ECE Department UNLV
 3.1 Introduction to Semiconductors Y. Baghzouz ECE Department UNLV Introduction In this lecture, we will cover the basic aspects of semiconductor materials, and the physical mechanisms which are at the
3.1 Introduction to Semiconductors Y. Baghzouz ECE Department UNLV Introduction In this lecture, we will cover the basic aspects of semiconductor materials, and the physical mechanisms which are at the
Diffusion in Solid State
 (Diffusion in Solid State): - Diffusion in Solid State Diffusion Mechanism It is known that at high temperature, the Amplitude of vibrations of atoms leads to expansion, while keeping the (Frequency of
(Diffusion in Solid State): - Diffusion in Solid State Diffusion Mechanism It is known that at high temperature, the Amplitude of vibrations of atoms leads to expansion, while keeping the (Frequency of
Lecture 1. OUTLINE Basic Semiconductor Physics. Reading: Chapter 2.1. Semiconductors Intrinsic (undoped) silicon Doping Carrier concentrations
 Lecture 1 OUTLINE Basic Semiconductor Physics Semiconductors Intrinsic (undoped) silicon Doping Carrier concentrations Reading: Chapter 2.1 EE105 Fall 2007 Lecture 1, Slide 1 What is a Semiconductor? Low
Lecture 1 OUTLINE Basic Semiconductor Physics Semiconductors Intrinsic (undoped) silicon Doping Carrier concentrations Reading: Chapter 2.1 EE105 Fall 2007 Lecture 1, Slide 1 What is a Semiconductor? Low
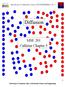
Precipitation. Size! Shape! Size distribution! Agglomeration!
 Precipitation Size! Shape! Size distribution! Agglomeration! Precipitation Four major questions: 1. Why do molecules/ions precipitate? 2. What determines the size? 3. What determines the size distribution?
Precipitation Size! Shape! Size distribution! Agglomeration! Precipitation Four major questions: 1. Why do molecules/ions precipitate? 2. What determines the size? 3. What determines the size distribution?
CME 300 Properties of Materials. ANSWERS: Homework 9 November 26, As atoms approach each other in the solid state the quantized energy states:
 CME 300 Properties of Materials ANSWERS: Homework 9 November 26, 2011 As atoms approach each other in the solid state the quantized energy states: are split. This splitting is associated with the wave
CME 300 Properties of Materials ANSWERS: Homework 9 November 26, 2011 As atoms approach each other in the solid state the quantized energy states: are split. This splitting is associated with the wave
Uniform excitation: applied field and optical generation. Non-uniform doping/excitation: diffusion, continuity
 6.012 - Electronic Devices and Circuits Lecture 2 - Uniform Excitation; Non-uniform conditions Announcements Review Carrier concentrations in TE given the doping level What happens above and below room
6.012 - Electronic Devices and Circuits Lecture 2 - Uniform Excitation; Non-uniform conditions Announcements Review Carrier concentrations in TE given the doping level What happens above and below room
Direct and Indirect Semiconductor
 Direct and Indirect Semiconductor Allowed values of energy can be plotted vs. the propagation constant, k. Since the periodicity of most lattices is different in various direction, the E-k diagram must
Direct and Indirect Semiconductor Allowed values of energy can be plotted vs. the propagation constant, k. Since the periodicity of most lattices is different in various direction, the E-k diagram must
Chapter 3 Properties of Nanostructures
 Chapter 3 Properties of Nanostructures In Chapter 2, the reduction of the extent of a solid in one or more dimensions was shown to lead to a dramatic alteration of the overall behavior of the solids. Generally,
Chapter 3 Properties of Nanostructures In Chapter 2, the reduction of the extent of a solid in one or more dimensions was shown to lead to a dramatic alteration of the overall behavior of the solids. Generally,
Thermally Activated Processes
 General Description of Activated Process: 1 Diffusion: 2 Diffusion: Temperature Plays a significant role in diffusion Temperature is not the driving force. Remember: DRIVING FORCE GRADIENT of a FIELD VARIALE
General Description of Activated Process: 1 Diffusion: 2 Diffusion: Temperature Plays a significant role in diffusion Temperature is not the driving force. Remember: DRIVING FORCE GRADIENT of a FIELD VARIALE
Structure and Dynamics : An Atomic View of Materials
 Structure and Dynamics : An Atomic View of Materials MARTIN T. DOVE Department ofearth Sciences University of Cambridge OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Observations 1 1.1.1 Microscopic
Structure and Dynamics : An Atomic View of Materials MARTIN T. DOVE Department ofearth Sciences University of Cambridge OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Observations 1 1.1.1 Microscopic
High Temperature Materials. By Docent. N. Menad. Luleå University of Technology ( Sweden )
 Course KGP003 Ch. 12 High Temperature Materials By Docent. N. Menad Dept. of Chemical Engineering and Geosciences Div. Of process metallurgy Luleå University of Technology ( Sweden ) Ceramic materials
Course KGP003 Ch. 12 High Temperature Materials By Docent. N. Menad Dept. of Chemical Engineering and Geosciences Div. Of process metallurgy Luleå University of Technology ( Sweden ) Ceramic materials
Solutions for Homework 4
 Solutions for Homework 4 October 6, 2006 1 Kittel 3.8 - Young s modulus and Poison ratio As shown in the figure stretching a cubic crystal in the x direction with a stress Xx causes a strain e xx = δl/l
Solutions for Homework 4 October 6, 2006 1 Kittel 3.8 - Young s modulus and Poison ratio As shown in the figure stretching a cubic crystal in the x direction with a stress Xx causes a strain e xx = δl/l
EE301 Electronics I , Fall
 EE301 Electronics I 2018-2019, Fall 1. Introduction to Microelectronics (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Introduction, Historical Background, Basic Consepts 2. Rewiev of Semiconductors (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Semiconductor materials
EE301 Electronics I 2018-2019, Fall 1. Introduction to Microelectronics (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Introduction, Historical Background, Basic Consepts 2. Rewiev of Semiconductors (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Semiconductor materials
Atoms, electrons and Solids
 Atoms, electrons and Solids Shell model of an atom negative electron orbiting a positive nucleus QM tells that to minimize total energy the electrons fill up shells. Each orbit in a shell has a specific
Atoms, electrons and Solids Shell model of an atom negative electron orbiting a positive nucleus QM tells that to minimize total energy the electrons fill up shells. Each orbit in a shell has a specific
Introduction Critical state models Pinning regimes Kinds of pinning sites HTS Results on YBCO Conclusions. Flux pinning.
 Department of Physics and Astronomy 14.6.2011 Contents Introduction Critical state models Pinning regimes Kinds of pinning sites HTS Results on YBCO Type II superconductors and vortices Type I ξ < λ S/N
Department of Physics and Astronomy 14.6.2011 Contents Introduction Critical state models Pinning regimes Kinds of pinning sites HTS Results on YBCO Type II superconductors and vortices Type I ξ < λ S/N
3.320 Lecture 23 (5/3/05)
 3.320 Lecture 23 (5/3/05) Faster, faster,faster Bigger, Bigger, Bigger Accelerated Molecular Dynamics Kinetic Monte Carlo Inhomogeneous Spatial Coarse Graining 5/3/05 3.320 Atomistic Modeling of Materials
3.320 Lecture 23 (5/3/05) Faster, faster,faster Bigger, Bigger, Bigger Accelerated Molecular Dynamics Kinetic Monte Carlo Inhomogeneous Spatial Coarse Graining 5/3/05 3.320 Atomistic Modeling of Materials
ELEMENTARY BAND THEORY
 ELEMENTARY BAND THEORY PHYSICIST Solid state band Valence band, VB Conduction band, CB Fermi energy, E F Bloch orbital, delocalized n-doping p-doping Band gap, E g Direct band gap Indirect band gap Phonon
ELEMENTARY BAND THEORY PHYSICIST Solid state band Valence band, VB Conduction band, CB Fermi energy, E F Bloch orbital, delocalized n-doping p-doping Band gap, E g Direct band gap Indirect band gap Phonon
Kinetic lattice Monte Carlo simulations of diffusion processes in Si and SiGe alloys
 Kinetic lattice Monte Carlo simulations of diffusion processes in Si and SiGe alloys, Scott Dunham Department of Electrical Engineering Multiscale Modeling Hierarchy Configuration energies and transition
Kinetic lattice Monte Carlo simulations of diffusion processes in Si and SiGe alloys, Scott Dunham Department of Electrical Engineering Multiscale Modeling Hierarchy Configuration energies and transition
PHYS208 P-N Junction. Olav Torheim. May 30, 2007
 1 PHYS208 P-N Junction Olav Torheim May 30, 2007 1 Intrinsic semiconductors The lower end of the conduction band is a parabola, just like in the quadratic free electron case (E = h2 k 2 2m ). The density
1 PHYS208 P-N Junction Olav Torheim May 30, 2007 1 Intrinsic semiconductors The lower end of the conduction band is a parabola, just like in the quadratic free electron case (E = h2 k 2 2m ). The density
Defect Ch em Ch istry 1
 Defect Chemistry 1 What is a defect? Fundamental definition Any deviation from the perfect crystal lattice is a defect! Macroscopic defects like porosities and cracks have an overall negative influence
Defect Chemistry 1 What is a defect? Fundamental definition Any deviation from the perfect crystal lattice is a defect! Macroscopic defects like porosities and cracks have an overall negative influence
In an electric field R and magnetic field B, the force on an electron (charge e) is given by:
 Lecture 17 Electric conduction Electrons motion in magnetic field Electrons thermal conductivity Brief review In solid state physics, we do not think about electrons zipping around randomly in real space.
Lecture 17 Electric conduction Electrons motion in magnetic field Electrons thermal conductivity Brief review In solid state physics, we do not think about electrons zipping around randomly in real space.
Diffusion - The Heat Equation
 Chapter 6 Diffusion - The Heat Equation 6.1 Goal Understand how to model a simple diffusion process and apply it to derive the heat equation in one dimension. We begin with the fundamental conservation
Chapter 6 Diffusion - The Heat Equation 6.1 Goal Understand how to model a simple diffusion process and apply it to derive the heat equation in one dimension. We begin with the fundamental conservation
12/10/09. Chapter 18: Electrical Properties. View of an Integrated Circuit. Electrical Conduction ISSUES TO ADDRESS...
 Chapter 18: Electrical Properties ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How are electrical conductance and resistance characterized? What are the physical phenomena that distinguish? For metals, how is affected by and
Chapter 18: Electrical Properties ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How are electrical conductance and resistance characterized? What are the physical phenomena that distinguish? For metals, how is affected by and
ESE 372 / Spring 2013 / Lecture 5 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor
 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor V G V G 1 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor We will need to understand how this current flows through Si What is electric current? 2 Back
Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor V G V G 1 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor We will need to understand how this current flows through Si What is electric current? 2 Back
VIII. Phase Transformations. Lecture 38: Nucleation and Spinodal Decomposition
 VIII. Phase Transformations Lecture 38: Nucleation and Spinodal Decomposition MIT Student In this lecture we will study the onset of phase transformation for phases that differ only in their equilibrium
VIII. Phase Transformations Lecture 38: Nucleation and Spinodal Decomposition MIT Student In this lecture we will study the onset of phase transformation for phases that differ only in their equilibrium
Supplement: Statistical Physics
 Supplement: Statistical Physics Fitting in a Box. Counting momentum states with momentum q and de Broglie wavelength λ = h q = 2π h q In a discrete volume L 3 there is a discrete set of states that satisfy
Supplement: Statistical Physics Fitting in a Box. Counting momentum states with momentum q and de Broglie wavelength λ = h q = 2π h q In a discrete volume L 3 there is a discrete set of states that satisfy
Electrical conduction in solids
 Equations of motion Electrical conduction in solids Electrical conduction is the movement of electrically charged particles through a conductor or semiconductor, which constitutes an electric current.
Equations of motion Electrical conduction in solids Electrical conduction is the movement of electrically charged particles through a conductor or semiconductor, which constitutes an electric current.
Introduction into defect studies. in ceramic materials(iii) Structure, Defects and Defect Chemistry. Z. Wang. January 18, 2002
 Introduction into defect studies in ceramic materials(iii) Structure, Defects and Defect Chemistry Z. Wang January 18, 2002 1. Mass, Charge and Site Balance The Schottky reactions for NaCl and MgO, respectively,
Introduction into defect studies in ceramic materials(iii) Structure, Defects and Defect Chemistry Z. Wang January 18, 2002 1. Mass, Charge and Site Balance The Schottky reactions for NaCl and MgO, respectively,
Course overview. Me: Dr Luke Wilson. The course: Physics and applications of semiconductors. Office: E17 open door policy
 Course overview Me: Dr Luke Wilson Office: E17 open door policy email: luke.wilson@sheffield.ac.uk The course: Physics and applications of semiconductors 10 lectures aim is to allow time for at least one
Course overview Me: Dr Luke Wilson Office: E17 open door policy email: luke.wilson@sheffield.ac.uk The course: Physics and applications of semiconductors 10 lectures aim is to allow time for at least one
Condensed Matter Physics Prof. G. Rangarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Condensed Matter Physics Prof. G. Rangarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 10 The Free Electron Theory of Metals - Electrical Conductivity (Refer Slide Time: 00:20)
Condensed Matter Physics Prof. G. Rangarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 10 The Free Electron Theory of Metals - Electrical Conductivity (Refer Slide Time: 00:20)
LEC E T C U T R U E R E 17 -Photodetectors
 LECTURE 17 -Photodetectors Topics to be covered Photodetectors PIN photodiode Avalanche Photodiode Photodetectors Principle of the p-n junction Photodiode A generic photodiode. Photodetectors Principle
LECTURE 17 -Photodetectors Topics to be covered Photodetectors PIN photodiode Avalanche Photodiode Photodetectors Principle of the p-n junction Photodiode A generic photodiode. Photodetectors Principle
J. Price, 1,2 Y. Q. An, 1 M. C. Downer 1 1 The university of Texas at Austin, Department of Physics, Austin, TX
 Understanding process-dependent oxygen vacancies in thin HfO 2 /SiO 2 stacked-films on Si (100) via competing electron-hole injection dynamic contributions to second harmonic generation. J. Price, 1,2
Understanding process-dependent oxygen vacancies in thin HfO 2 /SiO 2 stacked-films on Si (100) via competing electron-hole injection dynamic contributions to second harmonic generation. J. Price, 1,2
Introductory Nanotechnology ~ Basic Condensed Matter Physics ~
 Introductory Nanotechnology ~ Basic Condensed Matter Physics ~ Atsufumi Hirohata Department of Electronics Go into Nano-Scale Lateral Size [m] 10-3 10-6 Micron-scale Sub-Micron-scale Nano-scale Human hair
Introductory Nanotechnology ~ Basic Condensed Matter Physics ~ Atsufumi Hirohata Department of Electronics Go into Nano-Scale Lateral Size [m] 10-3 10-6 Micron-scale Sub-Micron-scale Nano-scale Human hair
MIT Amorphous Materials
 MIT 3.071 Amorphous Materials 10: Electrical and Transport Properties Juejun (JJ) Hu 1 After-class reading list Fundamentals of Inorganic Glasses Ch. 14, Ch. 16 Introduction to Glass Science and Technology
MIT 3.071 Amorphous Materials 10: Electrical and Transport Properties Juejun (JJ) Hu 1 After-class reading list Fundamentals of Inorganic Glasses Ch. 14, Ch. 16 Introduction to Glass Science and Technology
14. Energy transport.
 Phys780: Plasma Physics Lecture 14. Energy transport. 1 14. Energy transport. Chapman-Enskog theory. ([8], p.51-75) We derive macroscopic properties of plasma by calculating moments of the kinetic equation
Phys780: Plasma Physics Lecture 14. Energy transport. 1 14. Energy transport. Chapman-Enskog theory. ([8], p.51-75) We derive macroscopic properties of plasma by calculating moments of the kinetic equation
Advanced Heat and Mass Transfer by Amir Faghri, Yuwen Zhang, and John R. Howell
 Heat Transfer Heat transfer rate by conduction is related to the temperature gradient by Fourier s law. For the one-dimensional heat transfer problem in Fig. 1.8, in which temperature varies in the y-
Heat Transfer Heat transfer rate by conduction is related to the temperature gradient by Fourier s law. For the one-dimensional heat transfer problem in Fig. 1.8, in which temperature varies in the y-
1.3 Molecular Level Presentation
 1.3.1 Introduction A molecule is the smallest chemical unit of a substance that is capable of stable, independent existence. Not all substances are composed of molecules. Some substances are composed of
1.3.1 Introduction A molecule is the smallest chemical unit of a substance that is capable of stable, independent existence. Not all substances are composed of molecules. Some substances are composed of
EFFECTS OF STOICHIOMETRY ON POINT DEFECTS AND IMPURITIES IN GALLIUM NITRIDE
 EFFECTS OF STOICHIOMETRY ON POINT DEFECTS AND IMPURITIES IN GALLIUM NITRIDE C. G. VAN DE WALLE AND J. E. NORTHRUP Palo Alto Research Center, 3333 Coyote Hill Road, Palo Alto, CA 930, USA E-mail: vandewalle@parc.com
EFFECTS OF STOICHIOMETRY ON POINT DEFECTS AND IMPURITIES IN GALLIUM NITRIDE C. G. VAN DE WALLE AND J. E. NORTHRUP Palo Alto Research Center, 3333 Coyote Hill Road, Palo Alto, CA 930, USA E-mail: vandewalle@parc.com
Introduction to Semiconductor Physics. Prof.P. Ravindran, Department of Physics, Central University of Tamil Nadu, India
 Introduction to Semiconductor Physics 1 Prof.P. Ravindran, Department of Physics, Central University of Tamil Nadu, India http://folk.uio.no/ravi/cmp2013 Review of Semiconductor Physics Semiconductor fundamentals
Introduction to Semiconductor Physics 1 Prof.P. Ravindran, Department of Physics, Central University of Tamil Nadu, India http://folk.uio.no/ravi/cmp2013 Review of Semiconductor Physics Semiconductor fundamentals
water adding dye partial mixing homogenization time
 iffusion iffusion is a process of mass transport that involves the movement of one atomic species into another. It occurs by ranom atomic jumps from one position to another an takes place in the gaseous,
iffusion iffusion is a process of mass transport that involves the movement of one atomic species into another. It occurs by ranom atomic jumps from one position to another an takes place in the gaseous,
